Koji mold-origin phospholipase a2
a technology of phospholipase and koji mold, which is applied in the field of phospholipase a2, can solve the problem of about 1 billion yen cost and achieve the effect of higher homology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Production Method of Whole-Genome Shotgun Library
1. Preparation of Insert Side
[0058] (1) Obtaining of Chromosomal DNA
[0059] Spores of filamentous fungi, Aspergillus oryzae RIB-40 strain (ATCC 42149) were inoculated in a YPD culture medium (0.5% yeast extract, 1% peptone and 2% glucose) and cultured with shaking ovemight at 30° C. Thereafter, a genome DNA was extracted in accordance with a method by Iimura (Argric. Biol. Chem. 323-328, 51 (1987)). In order to exclude a mitochondrial DNA mixed in the genome DNA, purification by cesium chloride ultracentrifugation was carried out so as to obtain only a chromosomal DNA in accordance with the method by Watson et al. (Methods Enzymol. 57-75 118 (1986)).
[0060] (2) Fragmentation of Chromosomal DNA
[0061] The obtained pure chromosomal DNA was placed in a DNA fragmentation device HydroShear (TOMY SEIKO Co., Ltd.) so as to form the chromosomal DNA into fragments of about 1-2 kb.
[0062] (3) End Treatment of Fragmented DNA
[0063] The fragme...
example 2
Identification of Gene
[0068] Identification of gene from a genome DNA base sequence was conducted by the following technique. In the technique of identifying genes, with respect to the contig sequence of the genome DNA base sequence, the combination of a gene region prediction system GeneDecoder based on algorithm by Kiyoshi Asai et al. (Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 98, 228-239) and a gene region prediction system ALN based on algorithm (Bioinformatics 2000 16: 190-202) by Osamu Goto was used while considering the homology between sequence information on the previously obtained EST and the amino acid sequence database of the well-known protein. Furthermore, for predicting a tRNA gene, tRNA-scan was used.
“Extraction of BLAST Homologous Gene Candidate Region”
[0069] A region having a high homology to the amino acid sequence of the known protein was extracted from the contig sequence of the genome DNA base sequence. The homology of amino acid sequence can be determined by algorit...
example 3
Retrieving for Sequence Encoding Phospholipase A2
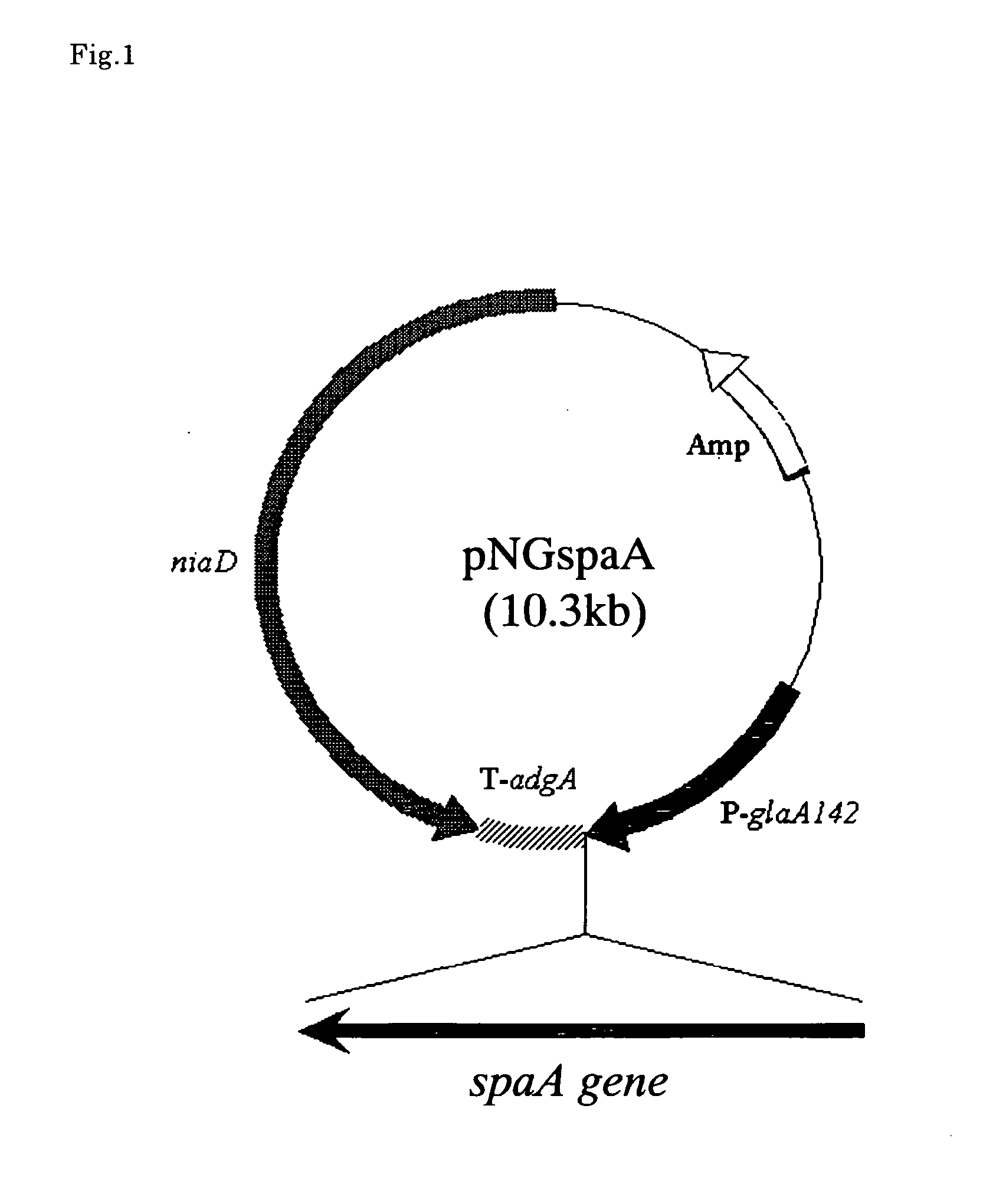
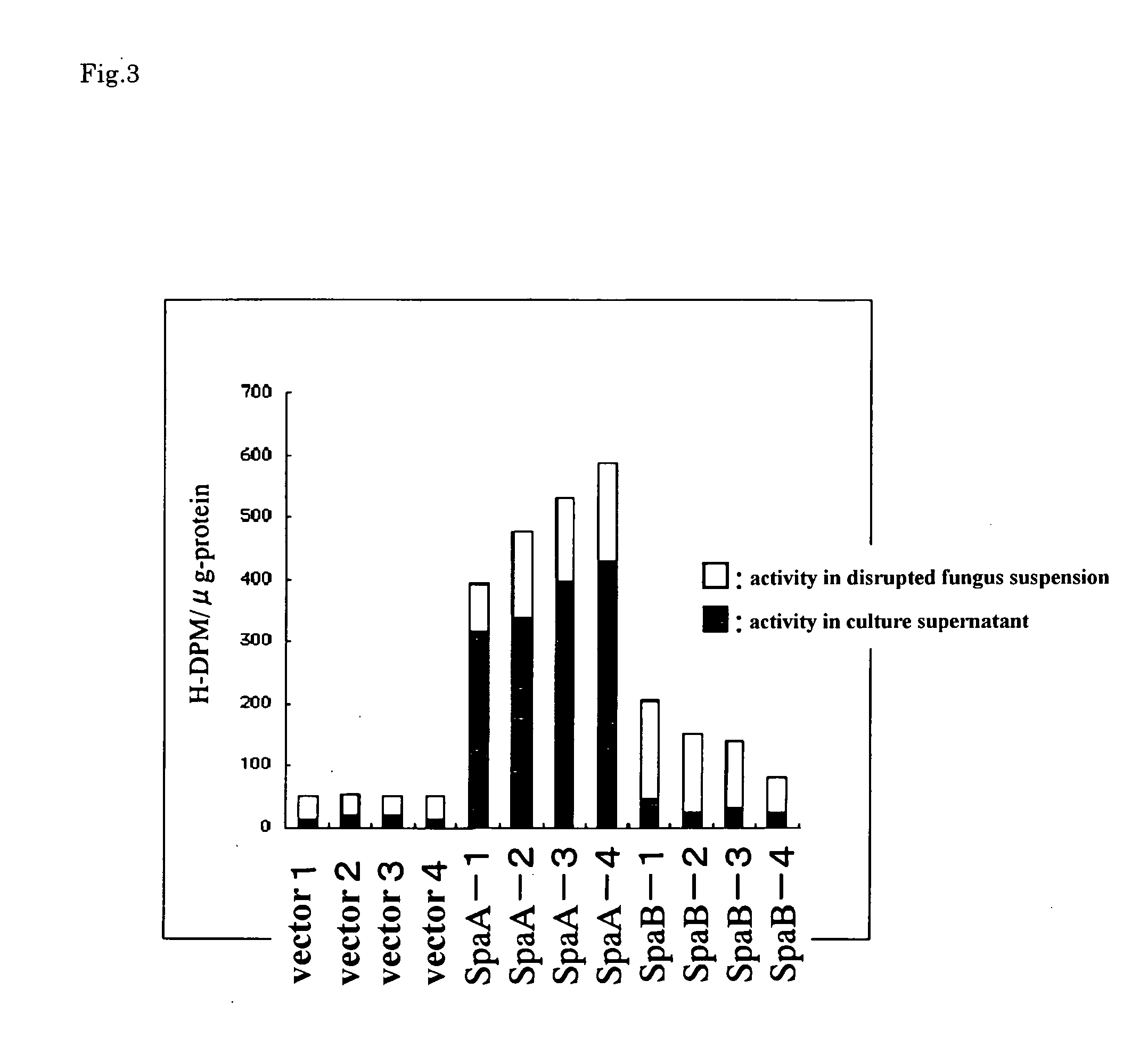
[0079] Based on DNA sequence of phospholipase A2 gene derived from filamentous fungi of Helicosporium sp., BLAST search (Standard protein-protein BLAST: blastp) provided by NCBI was carried out with respect to all DNA sequence of Aspergillus genome DNA. As a result, the present inventors succeeded in finding two regions having high homology to phospholipase A2 gene derived from filamentous fungi of Helicosporium sp. One of the found regions was a region that had been expected to be a sequence having certain functions in identifying the above-mentioned gene in which the function had not been estimated. Note here that a coding region of the gene (putative phospholipase A2-spaA coding region) is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3. Furthermore, an amino acid sequence encoded by the region is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1.
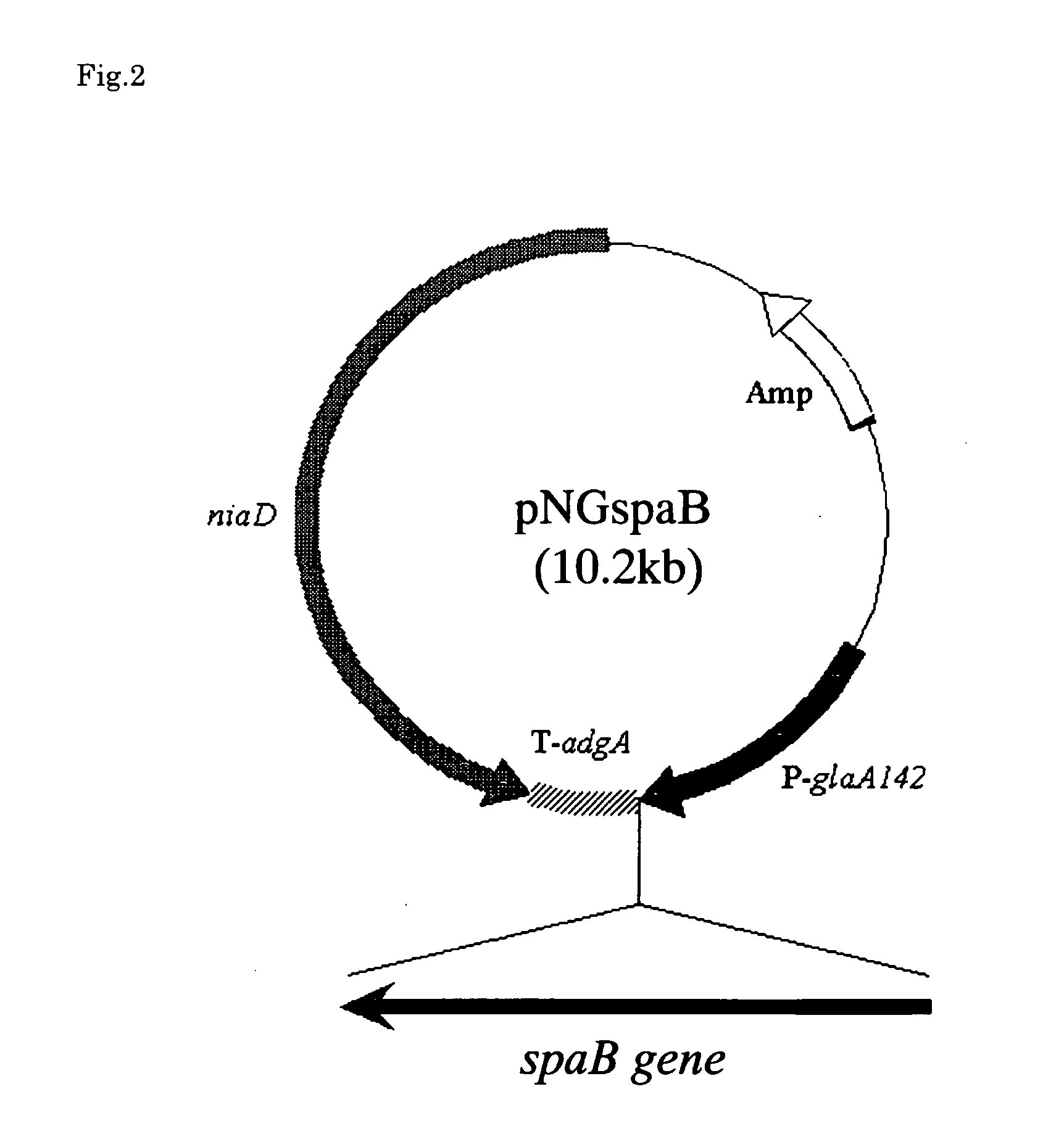
[0080] On the other hand, another region (sequence) was firstly expected to have a translation function and existed in the sequence whose ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com