Patents
Literature
33 results about "Blastema" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A blastema (Greek βλάστημα, "offspring") is a mass of cells capable of growth and regeneration into organs or body parts. Historically, blastemas were thought to be composed of undifferentiated pluripotent cells, but recent research indicates that in some organisms blastemas may retain memory of tissue origin. Blastemas are typically found in the early stages of an organism's development such as in embryos, and in the regeneration of tissues, organs and bone.
Method for cultivating and producing sporocarps of dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome
The invention relates to a method for cultivating and producing sporocarps of Dictyophora multicolor Berk. and Broome (1882), which is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out the tissue isolation on the fresh sporocarps of the wild dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome (1882), inoculating the fresh sporocarps of the wild dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome (1882) to integrated PDA slope culture medium or pine needle decoction culture medium, culturing until a slope is covered by mycelia to obtain a slope maternal strain, inoculating the slope maternal strain to wheat grain culture medium, culturing until the wheat grain culture medium is covered by mycelia, selecting strains with white, thick and thick mycelia as original strains, sowing the original strains in culture medium for producing layer by layer, covering the culture medium for producing by soil, culturing until the mycelia grow out of the surface of the soil covered on the culture medium for producing, forming a large number of rhizomorphs from the mycelia, expanding the tail ends of the rhizomorphs to form young blastemas and buds, continuing culturing until indusiums have the largest opening degree, and harvesting the fresh sporocarps of the dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome (1882). Due to the adoption of the method, the biological efficiency of the sporocarps of the dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome (1882) can be 1.5-2.5kg / m<2>. The sporocarps of the dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome (1882) can be used as medicinal raw materials or research materials.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Human embryonic stem cells and culturing methods thereof
Provided herein are human embryonic stem cells and their method of culturing. In one embodiment, the human embryonic stem cells are maintained in an environment containing an extracellular matrix isolated from feeder cells and a conditioned medium pre-conditioned by the feeder cells; the feeder cells are pre-inactivated by either gamma ray radiation or by mitomycin C treatment. The cultured human embryonic stem cells remain substantially undifferentiated and maintain their pluripotency to differentiate into three germ layer cells.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
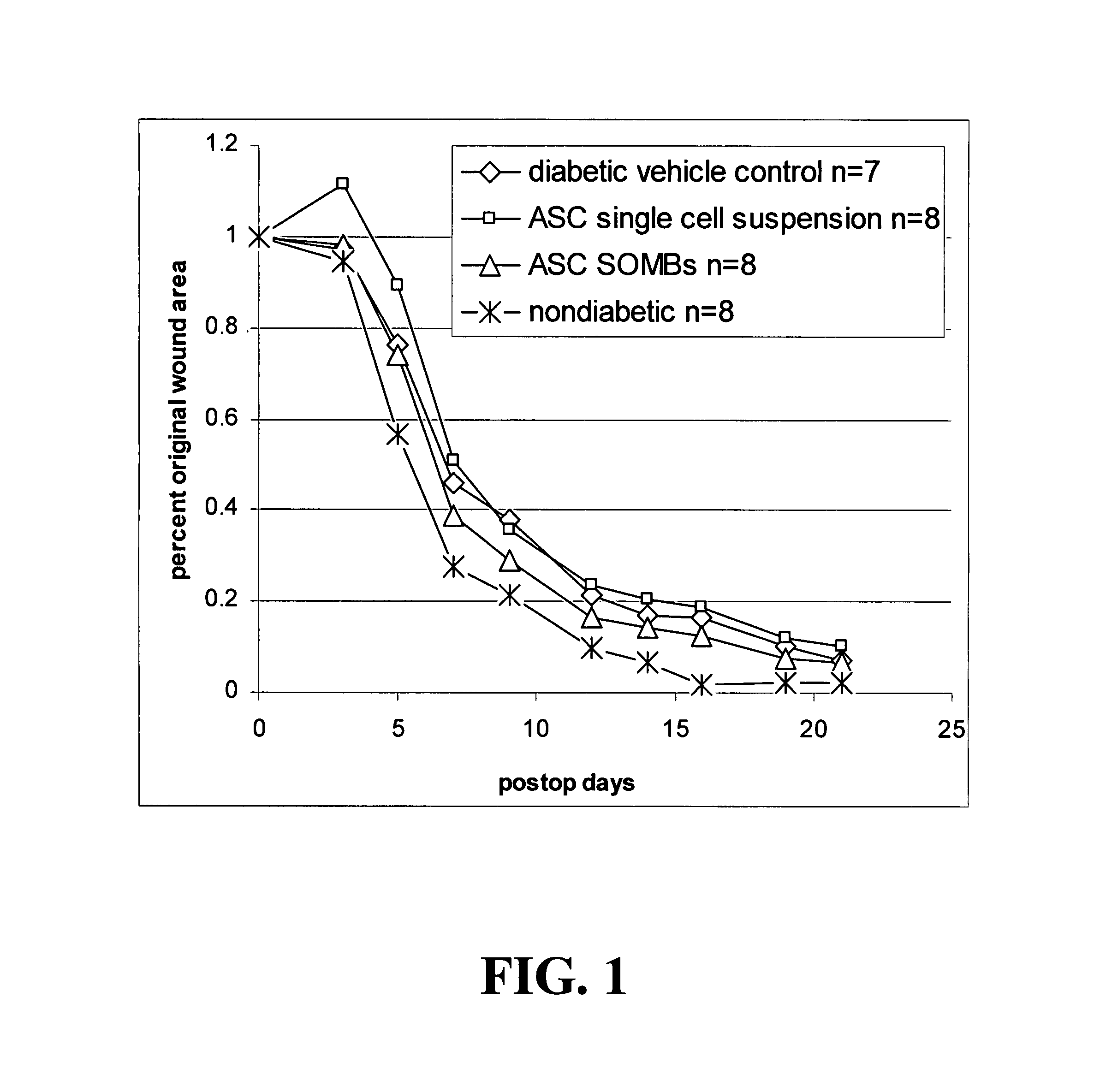
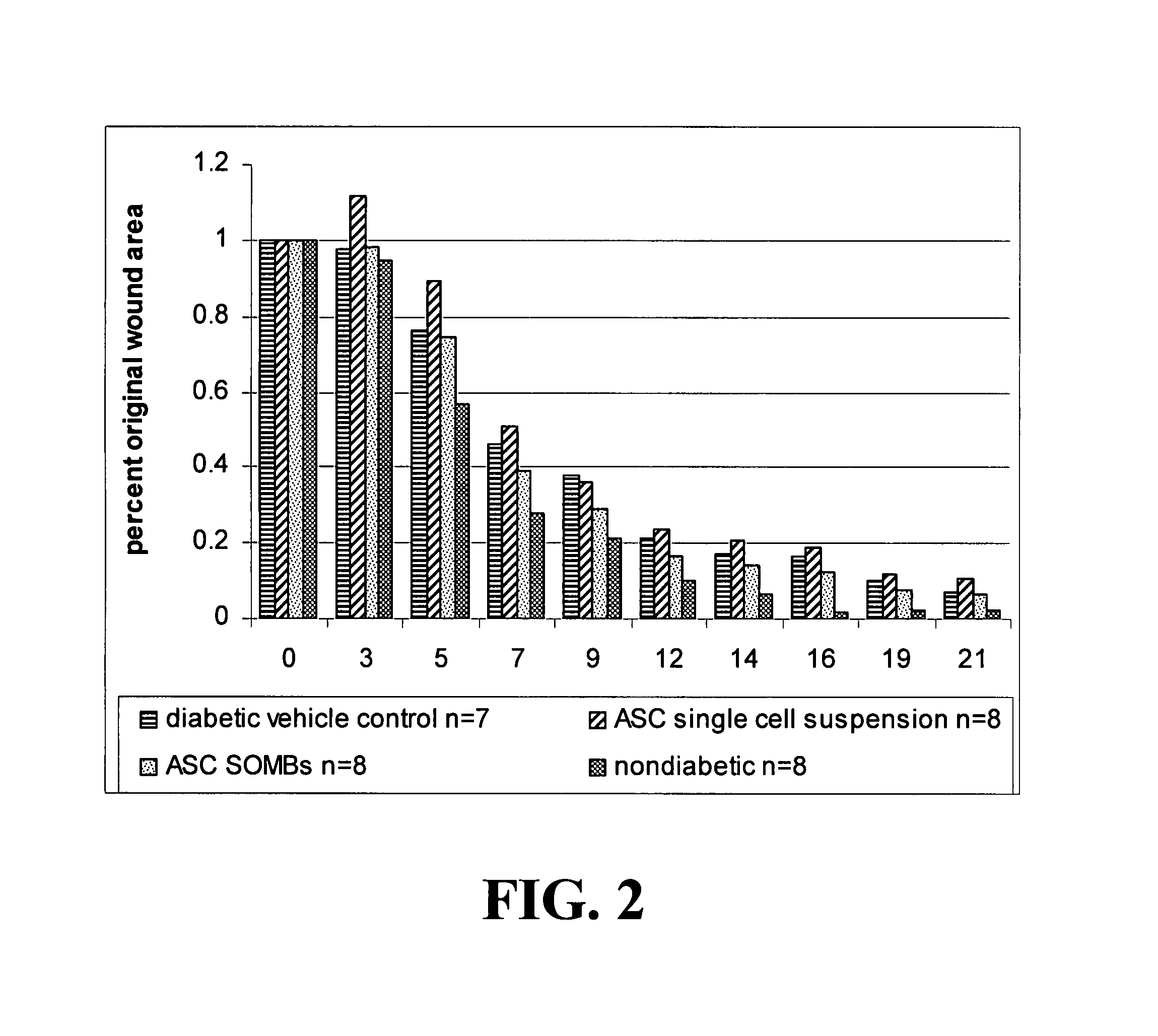
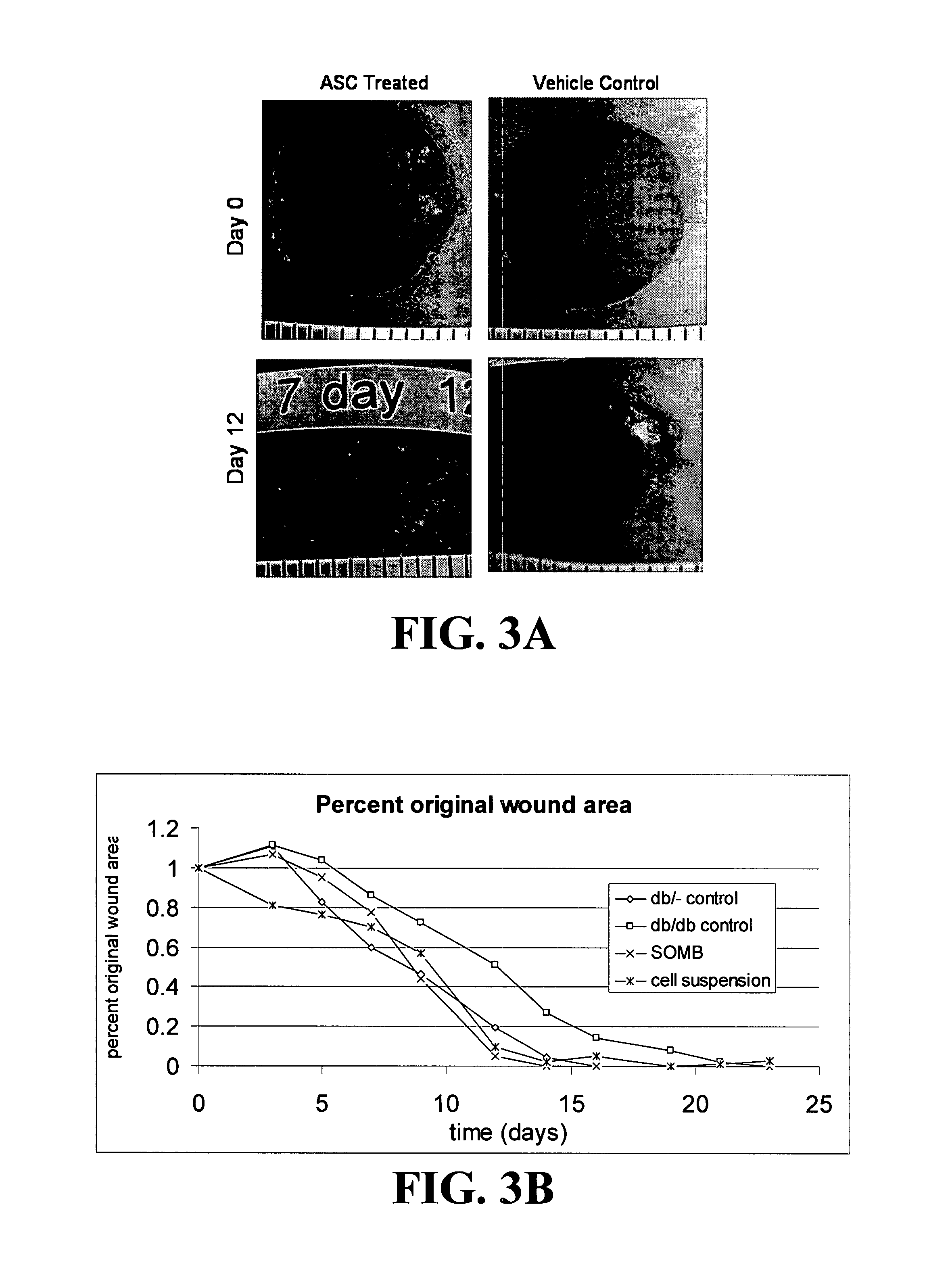
Methods and compositions useful for diabetic wound healing
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method for efficiently inducing generation of adventitious roots of Pinus densiflora tissue culture plantlets
ActiveCN101589690AQuality improvementLess callusPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsDiseaseSucrose
The invention discloses a method for efficiently inducing the generation of adventitious roots of Pinus densiflora tissue culture plantlets, which uses growing young Pinus densiflora tissue culture plantlets as explants, and adopts a 'two-step method', namely firstly, inducing the generation of adventitious root blastemas in a culture medium containing 1 / 2 to 1 / 4 of WPM, 0.1 to 0.2 mg / L NAA, 1.0 to 2.0 mg / L IBA and 0.5 to 1.5 percent sucrose, and secondly, transferring the explants into a culture medium containing 1 / 2 of the WPM, 0.5 to 1.0 g / L AC and 2.0 percent of the sucrose to promote the expression and the extension of the adventitious roots so as to finish the generation process of the adventitious roots. By adopting the method, the generation ratio of the adventitious roots of the Pinus densiflora tissue culture plantlets is high, the root system develops well and the transplant survival rate is high, thus the method lays a solid foundation for the mass production of Pinus densiflora tissue culture regeneration plants for resisting pine wood nematode diseases, and simultaneously has important reference value for the cultivation of other pine species tissue culture plantlets.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Luc-GFP marked high-transitivity human hepatoma cell line and application thereof in in situ hepatoma model
The invention discloses an Luc-GFP marked high-transitivity human hepatoma cell line. Hepatoma cells are taken as mother cells, a virus solution packaged with pCDH-CMV-Luc-EF1-GFP-Puro is transfectedthrough slow viruses, and then through puromycin screening, the high-transitivity human hepatoma cell line with stable GFP expression and luciferase activity is obtained. By using the Luc-GFP marked high-transitivity human hepatoma cell line, an in situ hepatoma model for a naked mouse is established through a cell suspension method and a tumor tissue block conversion method respectively, the tumor formation rate of the hepatoma model is 100% respectively, the rates of lung metastasis are 100% and 80% respectively, a foundation is laid for monitoring the growth of tumor in the level of livinganimals and evaluating the curative effect of hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis resistant medicine, and the cell line has greater application prospect.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Bacillus firmus for killing plant parasitic nematodes, and preparation method and application thereof
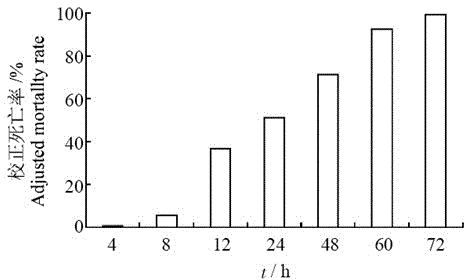
The invention relates to blastema firmus for killing plant parasitic nematodes, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The blastema firmus for killing the plant parasitic nematodes is a wild type strain of the blastema firmus YBf-10 which is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in June 14th, 2012, with a preservation number of CCTCCNO. M2012233. The invention also provides the preparation method and the application of blastema firmus for killing the plant parasitic nematodes. Metabolic product of the blastema firmus YBf-10 is prepared by the fermentation of the blastema firmus YBf-10 in a common bacteria culture medium, and can be applied to kill root-knot nematodes. A corrected mortality rate of 24 h is over 50% and the corrected mortality rate of 72 h can reach 100% when the metabolic product acts on second-stage larvas; and inhibited egg hatching rate of 48 h is over 80% when the metabolic product acts on the eggs of the root-knot nematodes.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for carrying out agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated banana genes by employing liquid co-culture system
The invention discloses a method for converting the meloidogynosis agrobacterium lead banana gene with the fluid co culture system, which comprises the following steps: stewing the banana ECS in the meloidogynosis agrobacterium and the black condition for a spell of time; proceeding with the co culture in the banana ECS liquid culture medium; transferring the banana ECS to the idiosome directly in order to induce and grow; culturing on the selective culture medium; transferring the mature resistant idiosome to the blastema germination culture medium; culturing in the light-black alternative condition until the idiosome is germinated; getting sprout; transferring the sprout to the basis screen selective culture medium; acquiring the whole conversion plant by culturing in the light-black alternative condition. The invention changes the co culture condition, which solves the brown problem of banana ECS in the co culture process, and shortens the cycle of converting the plant.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for isolating and identifying sperm cells of Buffalo testis
InactiveCN109182254ACertified pureGood identification effectCell dissociation methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle cell suspensionHyaluronidase
The invention belongs to the technical field of sperm cell treatment, and specifically relates to a method for isolating and identifying sperm cells of Buffalo testis, including the following steps: obtaining Buffalo testis, digest with collagenase IV, hyaluronidase and DNase I combined enzyme, sieving, filtering, and taking suspension cells after differential adherence; 2) taking the suspend cells for live cell stain; and 3) separating by flow cytometry. Beneficial effect: the technical scheme is an effective method for separating buffalo sperm cells, By digesting bovine testis tissue with two enzymes, so that a single cell suspension is obtain, the interference of somatic cells is removed by the method of continuous differential adherence, according to the fluorescence intensity of non-adherent cells stained by flow cytometry, the DNA content of cells is judged, and the interference of other non-target cells such as diploid spermatogonia and tetraploid primary meningoblasts is effectively digested and removed to achieve the successful sorting of a large number of haploid spermatozoa.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
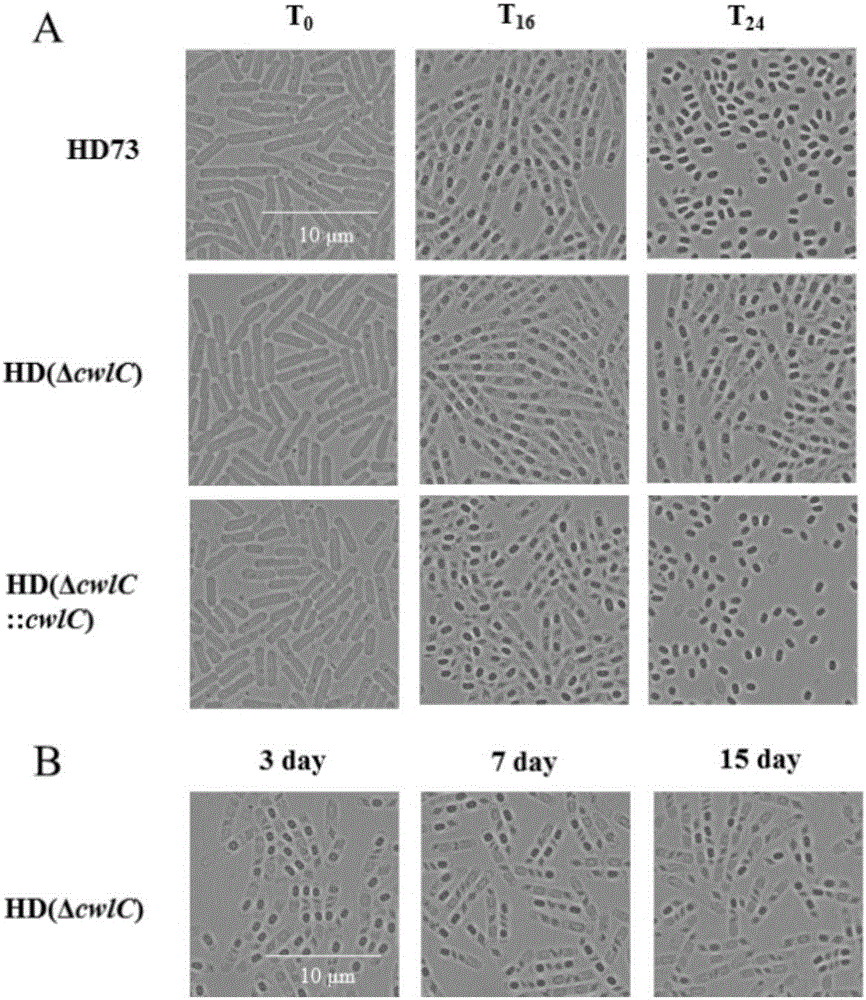
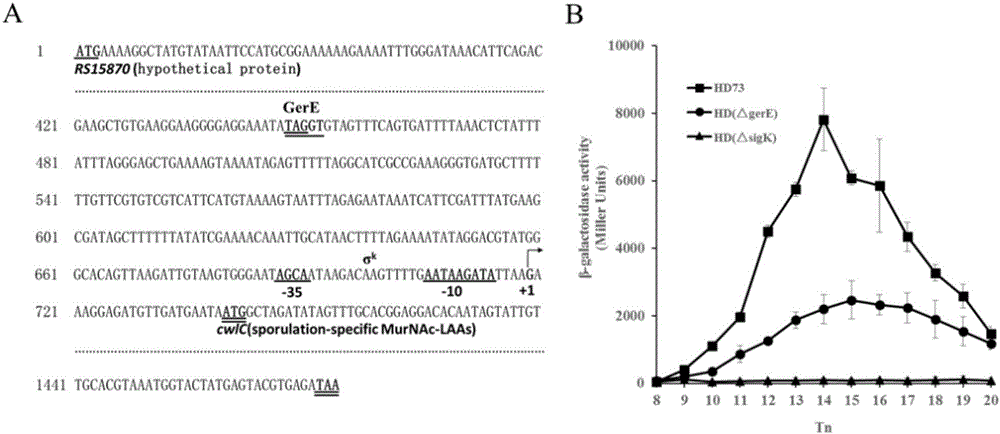
Application of hydrolytic enzyme CwlC in metrocyte lysis of bacillus
The invention relates to 'application of a hydrolytic enzyme CwlC in metrocyte lysis of bacillus'. The invention identifies a novel cwlC gene which joins in metrocyte lysis in B.thuringiensis, cwlC gene deletion can completely block metrocyte lysis, and the yield of spore formation and Cry1Ac protein are not affected. Meanwhile, a CwlC protein marked by a GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) can be tightly combined with cell walls. More importantly, walls of cells of B.thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus with activities in logarithmic phases can be hydrolyzed by CwlC. Tests show that CwlC is not only a key point of metrocyte lysis of B.thuringiensis in a spore period and has great significances in establishing B.thuringiensis engineering bacteria for efficient agricultural production, but also has great application prospects in biological medicines and food production.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for rapidly propagating potato minitubers by using potato minituber budlets
InactiveCN110226505ALow costImprove survival rateSeed and root treatmentCultivating equipmentsNutrient solutionHigh survival rate
The invention discloses a method for rapidly propagating potato minitubers by using potato minituber budlets. The method comprises specific steps as follows: germination acceleration of the potato minitubers: the potato minitubers are placed in a GA3 solution for soaking and then transferred into an illumination culture room at the constant temperature of 25 DEG C to send forth budlets; inductionrooting of budlets: the budlets are stripped from blastema of the potato minitubers and transferred into a nutrient solution until the budlets take root; substrate preparation: a substrate is preparedfrom vermiculite and perlite; transplantation of new seedlings: the new seedlings are cut in a seedbed, natural illumination is adopted, and water or a nutrient solution is sprayed according to nutrient conditions of plants after seedling recovery; the nutrient solution is sprayed according to the seedling condition 20 days after planting; the substrate is kept moist in the growing process of thenew seedlings; harvesting of minitubers: the minitubers can be harvested after the cutting seedlings grow for 35-40 days. The method has the advantages of short seedling culture time, high survival rate, high reproduction coefficient and low cost.
Owner:XUZHOU INST OF AGRI SCI IN JIANGSU XUHUAI DISTRICT (JIANGSU XUZHOU SWEETPOTATO CENT)
Method for inducing regenerated plant from blastema part of Kaempferia rotunda rhizome
PendingCN107182783AImprove tissue culture reproduction efficiencyHigh reproductive coefficientPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsShoot apexShoot
The invention discloses a method for inducing and regenerating plants at the base of rhizome buds of Hainan notoginseng, and belongs to the technical field of plant inducing regeneration. In this method, after the pre-treatment of the rhizome buds of Hainan notoginseng, the leaves and shoot tips on the rhizome buds are cut off, and the base of the buds is left as explants; the sterilized explants are inoculated on the induction medium and cultivated until the explants Clustered buds are formed at the base; when the clustered buds at the base of the primary buds grow to 4-6 cm, cut off the buds, intercept the 1.0-1.5 cm of the base of the buds and inoculate them into the proliferation medium to induce clustered buds; then cut off the clustered buds and transfer them to the rooting medium Carry out rooting, when the height of the seedlings on the rooting medium is 5-8 cm, harden the seedlings under natural light in the greenhouse for 7-10 days, take out the seedlings, wash the root medium, and obtain transplanted seedlings after cultivation. The invention significantly improves the tissue culture propagation efficiency of Hainan notoginseng.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL HORTICULTURE RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for inducing doubling of pollen chromosome of Eucommia ulmoides
A method for reduplicating the pollen chromosomes of eucommia tree by inducing features that a high-temp reduplicating device of tree is used to heat the male flower buds of eucommia tree in the meiophase of pollen metrocytes at 45-47 deg.C for 2 hr to increase the 2n pollen percentage to 45-70%, especially in the diakinasis-metaphase I.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing composite biological fertilizer by combined solid fermentation of double bacterium
InactiveCN101585722BReproduce fastShorten the fermentation cycleOrganic fertilisersBiotechnologySucrose
The invention relates to a method for preparing a composite biological fertilizer from tremellose bacillus and gigantochromoblast, which comprises: culturing and growing secondary tremellose bacillus strain and secondary gigantochromoblast strain; then, (1) stirring the solid culture medium uniformly, and placing into a disinfected solid fermentation pool, wherein, the weight percentage of the components are: wheat bran 15-25%, straw 25-36%, fly ash 11-19%, bean cake powder 3-9%, CaCO3 0.3-0.9%, turf 7.5-14%, K2HPO4 0.1-0.6%, sucrose 1-5%, and fertilizer soil 9-15%; (2) inoculating the two secondary strains into the solid fermentation pool according to that: the inoculation amount is 20% of the total weight, while the amount of the secondary tremellose bacillus strain is twice of the secondary gigantochromoblast strain; (3) adding water into the solid fermentation pool to keep the humidity of the ferment material at 50%, sealing and controlling the temperature in the solid fermentation pool, and fermenting and growing for 48-54 hours to obtain the finished product. The invention adopts combined solid fermentation of double bacterium, accelerates the strain breeding speed, shortens the fermentation period, reduces production cost, and improves the blastema formation ratio of the product.
Owner:ANHUI JINNONG HUIMIN BIOTECH CO LTD
Quick selection method for strong-stem abelmoschus manilhot
InactiveCN105746108AThick diameterLarge quantity of gelatinPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGerminationRoot system
The invention provides a quick selection method for strong-stem abelmoschus manilhot. The quick selection method for the strong-stem abelmoschus manilhot is characterized by comprising the following steps: A, abelmoschus manilhot seed selecting; B, abelmoschus manilhot seed sterilizing treatment; C, abelmoschus manilhot seed soaking and germination accelerating; D, rooting and plantlet hardening cultivation; E, abelmoschus manilhot blastema rooting and growing; F, abelmoschus manilhot blastema foundation bed cultivating; G, abelmoschus manilhot transplanting. The quick selection method for the strong-stem abelmoschus manilhot has the beneficial effects: by adopting the quick selection method, the planted abelmoschus manilhot has a thick stem, the amount of extracted gel is large, the root system of each plant is developed, and the yield of the abelmoschus manilhot is improved.
Owner:枞阳县铜板洲中药材种植专业合作社
Method for quickly detecting fruiting performance of pleurotus nebrodensis
InactiveCN101824461AStrong identification and detection reliabilityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural sciencePleurotus nebrodensis
The invention discloses a method for quickly detecting the fruiting performance of pleurotus nebrodensis, which comprises the following steps of: inoculating pleurotus nebrodensis strains into the center of a solid culture medium, culturing for 7 to 10d at the temperature of 22 to 26 DEG C under a dark condition and culturing again for 3 to 5d after hyphae overgrow with a culture dish; then, freezing the culture dish at the temperature of 0 to 4 DEG C under a dark condition for 3 to 5d; and afterwards, putting the culture dish at the temperature of 8 to 12 DEG C under the illumination of 200 to 800Lux for carrying out recovering culture for 10 to 20d and selecting the strains which can form white blastemas with dense texture, i.e. the strains with better fruiting performance. The method has high identification and detection accuracy, short time and high efficiency, lowers the breeding or production cost and is suitable for the quick detection and identification of the fruiting performance of the pleurotus nebrodensis strains on a large scale.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Bacterial strain capable of producing phosphatidase C, and screening method thereof
ActiveCN103509736AAccurately determineOvercoming the Shortcomings of ScreeningBacteriaMicroorganism based processesYolkHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a bacterial strain capable of producing phosphatidase C, and a screening method thereof. The bacterial strain is Pseudomonas fluorescens P.f-9103, and preservation number is CCTCC No.M2013298. The bacterial strain is obtained by screening and separation from soil near oil workshops. Morphological characteristics are that: the shape of a bacterial colony is round, the surface of the colony is salient, the color is white, and the bacterial colony is nontransparent and yellows with the increasing of age; the colony is smooth, is relatively viscous and dense, and is easy to be stirred up, and the edge is smooth; the colony has a flagellum, is capable of moving, and produces no blastema; the bacterial strain is gram negative, the optimum growth temperature is 25 to 30 DEG C, and pH value is 7.0 to 7.6. The screening method comprises following steps: primary screening is performed on LB medium containing yolk; then phosphatide is taken as a substrate, and enzymatic reaction is performed; and reaction products are analyzed by HPLC so as to realize secondary screening. According to the method, natural phosphatide is taken as the substrate, so that problems caused by inactivity of phosphatidase C on phosphatide substrate analogue NPPC are avoided. Sources of primary screening raw material are abundant, operation is convenient, secondary screening is accurate and rapid, and the screening method is suitable for high throughput screening of the bacterial strain capable of producing phosphatidase C.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of hirsutella sinensis refined fermentation liquor as bacteriostatic agent of bat moth infection paecilomyces farinosus
The invention relates to the field of prevention and control of animal diseases, and in particular relates to application of hirsutella sinensis refined fermentation liquor as a bacteriostatic agent of bat moth infection paecilomyces farinosus, a paecilomyces farinosus bacteriostatic agent and a preparation method of the paecilomyces farinosus bacteriostatic agent. The bacteriostatic agent provided by the invention can be used for well inhibiting paecilomyces farinosus cultured in vitro and / or in vivo without causing any bad influence on bat moths. Although the bacteriostatic agent is applied continuously to infected moths, hirsutella sinensis in the moths can still live till the moths become stiff. Moreover, stiff moths can form a sporocarp blastema.
Owner:YICHANG SHANCHENGSHUIDU CORDYCEPS +1
Method of cutturing polyploid seed breedign using diploid/tetraploid oclimera abalone
InactiveCN100415085CSolve the problem of triploid breedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBiologyGonad
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for dwarfing potted Hainan pseudo-ginseng
InactiveCN108293824ABeautiful plant typeImprove viewing valueFlowers cultivationHorticulture methodsWater solublePaclobutrazol
The invention discloses a method for dwarfing potted Hainan pseudo-ginseng, and provides a cultivation method for dwarfing the potted Hainan pseudo-ginseng through multi-effect triazole. The method for dwarfing the potted Hainan pseudo-ginseng includes the steps that (1), acclimatization and transplanting are carried out; (2), orderly and consistent seedlings are screened and planted in pots; (3),500-1,000-fold water-soluble slow-release fertilizer is watered in Hainan pseudo-ginseng plants which are planted in the pots and survive, and stem bases are watered once every 7-10 days; (4), when the seedlings planted in the pots grow to 20-30 cm high, 100-500 mg / l of multi-effect triazole is used for watering the stem bases of the seedlings; (5), environment control is carried out. The methodis easy to operate, the plant heights of the potted Hainan pseudo-ginseng treated through the technical scheme are reduced by 46.6% to 65.6%, main blastema stems are thickened by 10.1% to 14.1%, and the lodging resistance is enhanced; the plants are totally compact, leaves are invisible green and lovely, plant types are attractive, the ornamental value is high, and the plants are suitable for being used as potted foliage plants.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL HORTICULTURE RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing composite biological fertilizer by combined solid fermentation of double bacterium
The invention relates to a method for preparing a composite biological fertilizer from tremellose bacillus and gigantochromoblast, which comprises: culturing and growing secondary tremellose bacillus strain and secondary gigantochromoblast strain; then, (1) stirring the solid culture medium uniformly, and placing into a disinfected solid fermentation pool, wherein, the weight percentage of the components are: wheat bran 15-25%, straw 25-36%, fly ash 11-19%, bean cake powder 3-9%, CaCO3 0.3-0.9%, turf 7.5-14%, K2HPO4 0.1-0.6%, sucrose 1-5%, and fertilizer soil 9-15%; (2) inoculating the two secondary strains into the solid fermentation pool according to that: the inoculation amount is 20% of the total weight, while the amount of the secondary tremellose bacillus strain is twice of the secondary gigantochromoblast strain; (3) adding water into the solid fermentation pool to keep the humidity of the ferment material at 50%, sealing and controlling the temperature in the solid fermentation pool, and fermenting and growing for 48-54 hours to obtain the finished product. The invention adopts combined solid fermentation of double bacterium, accelerates the strain breeding speed, shortens the fermentation period, reduces production cost, and improves the blastema formation ratio of the product.
Owner:ANHUI JINNONG HUIMIN BIOTECH CO LTD
Method of cutturing polyploid seed breedign using diploid/tetraploid oclimera abalone
InactiveCN1596627ASolve the problem of triploid breedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBiologyGonad
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for cultivating and producing sporocarps of dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome
The invention relates to a method for cultivating and producing sporocarps of Dictyophora multicolor Berk. and Broome (1882), which is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out the tissue isolation on the fresh sporocarps of the wild dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome (1882), inoculating the fresh sporocarps of the wild dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome (1882) to integrated PDA slope culture medium or pine needle decoction culture medium, culturing until a slope is covered by mycelia to obtain a slope maternal strain, inoculating the slope maternal strain to wheat grain culture medium, culturing until the wheat grain culture medium is covered by mycelia, selecting strains with white, thick and thick mycelia as original strains, sowing the original strains inculture medium for producing layer by layer, covering the culture medium for producing by soil, culturing until the mycelia grow out of the surface of the soil covered on the culture medium for producing, forming a large number of rhizomorphs from the mycelia, expanding the tail ends of the rhizomorphs to form young blastemas and buds, continuing culturing until indusiums have the largest openingdegree, and harvesting the fresh sporocarps of the dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome (1882). Due to the adoption of the method, the biological efficiency of the sporocarps of the dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome (1882) can be 1.5-2.5kg / m<2>. The sporocarps of the dictyophora multicolor berk. and broome (1882) can be used as medicinal raw materials or research materials.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
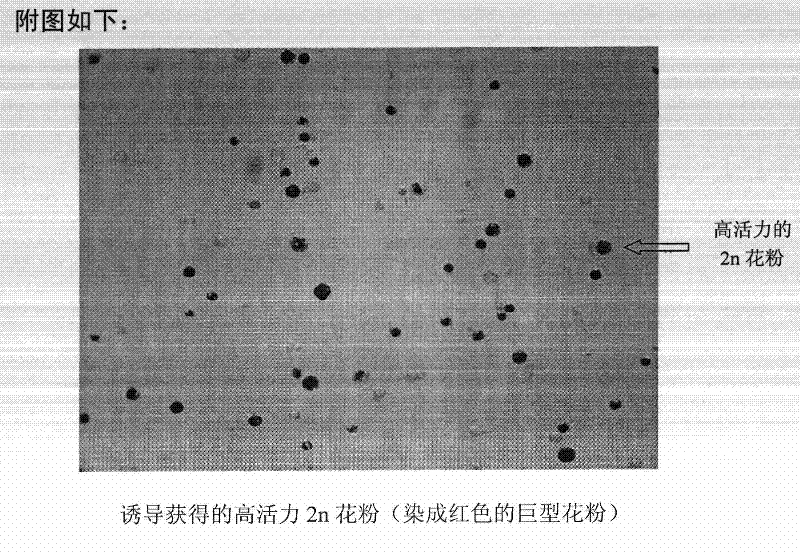
Method for efficiently inducing jujube tree 2n pollen
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
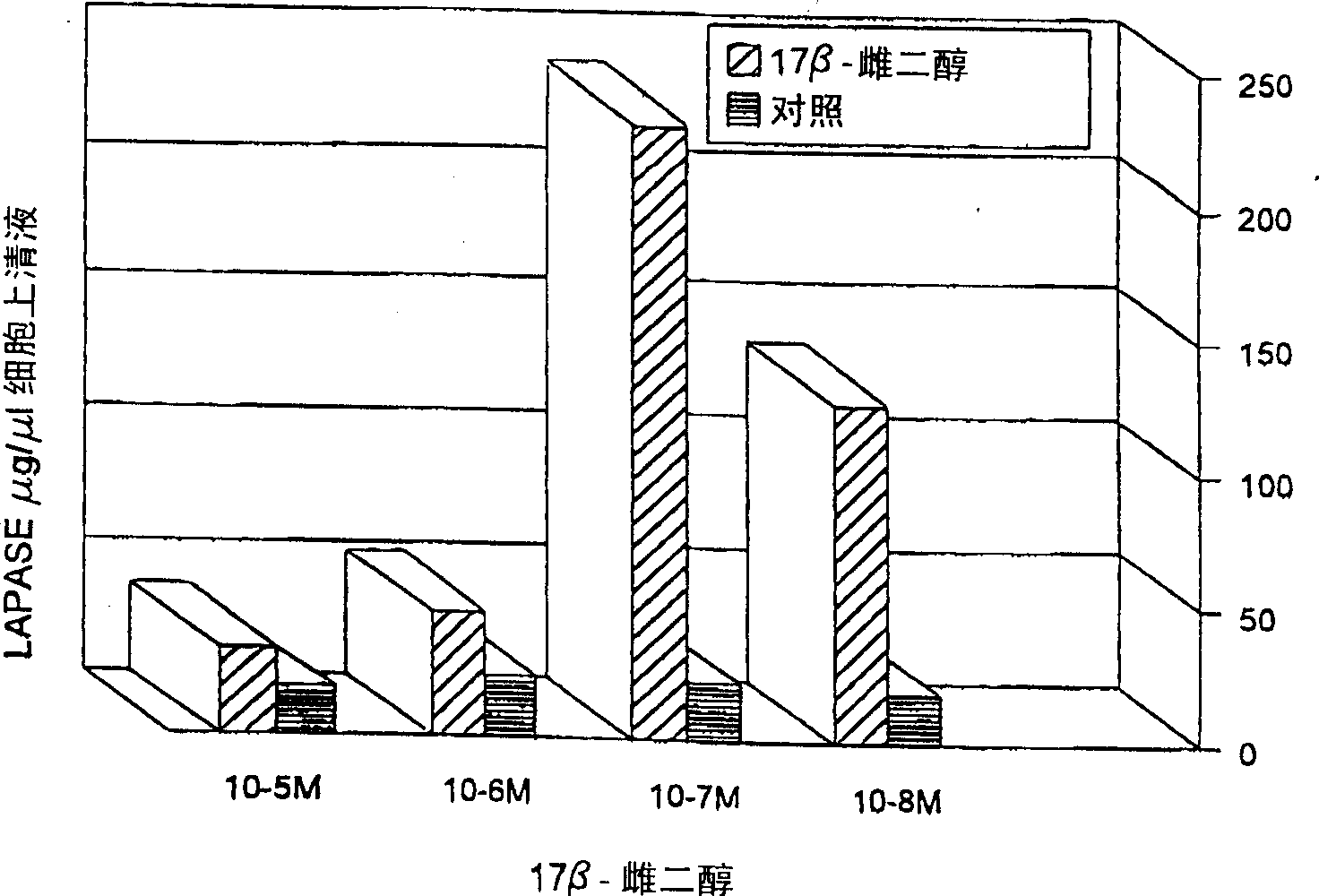
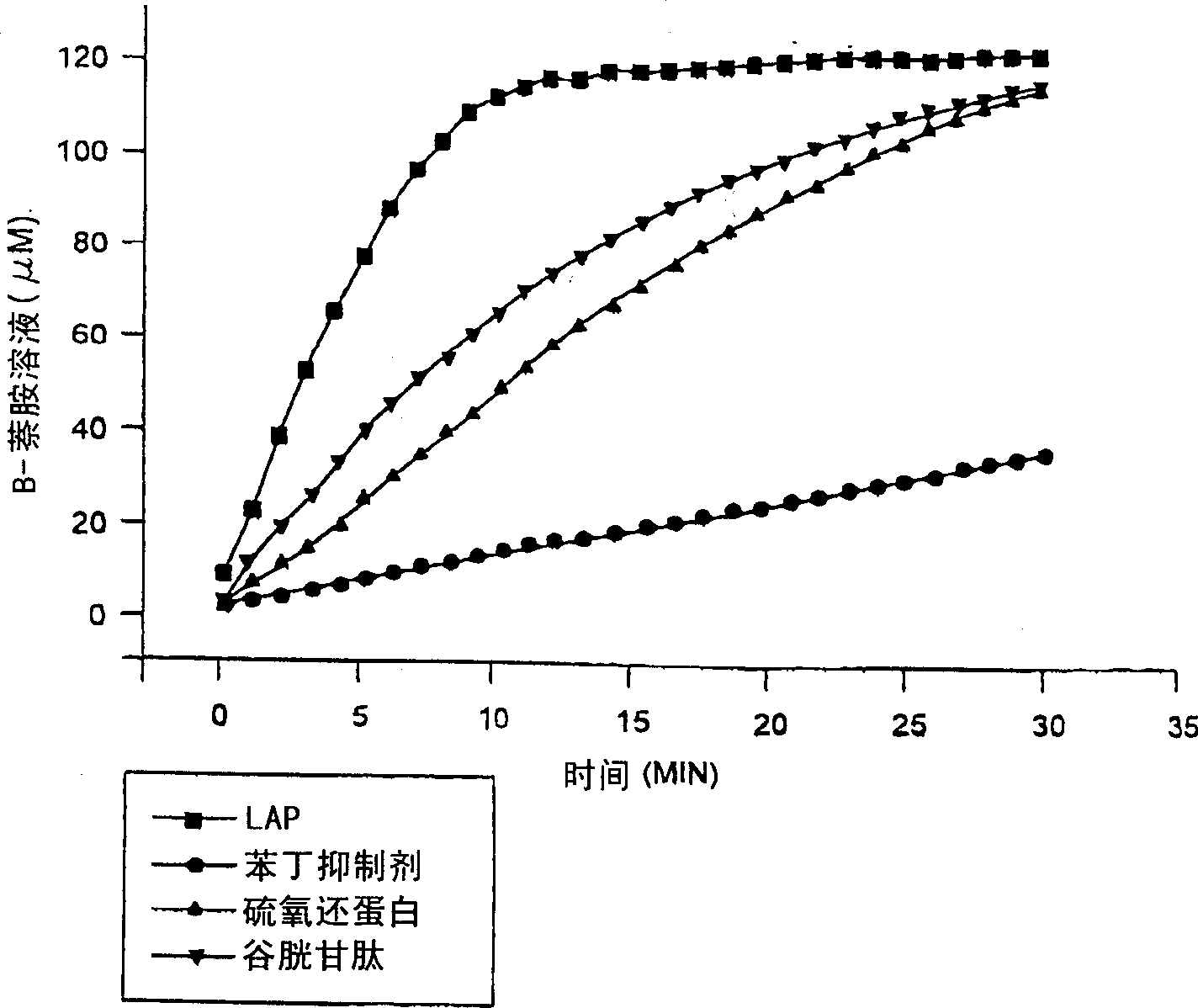
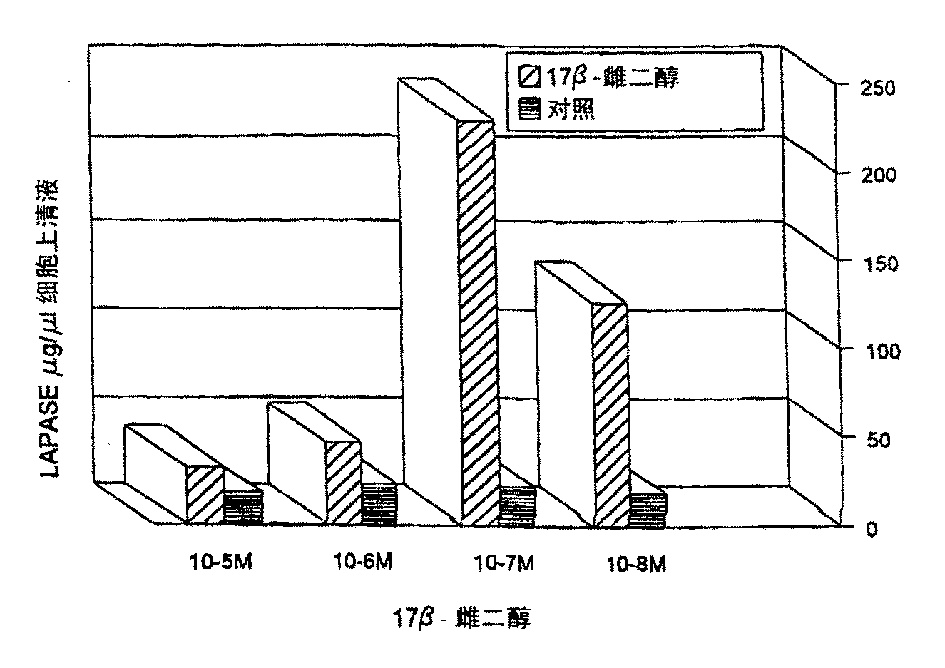
Monoclonal antibody against estrogen-stimulated leucine aminopeptidase
The identification and characterization of risk factors and their molecular implications in the pathophysiology of human diseases such as cancer is essential for designing efficient diagnostic assays and therapeutic compounds. Estrogenic steroids, under normal physiological conditions, have been shown to play a critical function in several tissues. The response of such a variety of tissues to estrogen stimulation can explain in part its active role in the development and progression of different human diseases, particularly breast cancer. Searching for estrogen-responding cellular factors in parental cells of primary human breast carcinomas obtained from tumour biopsies, two cellular markers, an isoenzyme of putative leucine aminopeptidase (LAPase; EC 3.4.11.1) from parental cells of primary human breast carcinomas obtained from tumour biopsies, and cytosolic NDP-Kinase / Nm23 (EC 2.7.4.6) from HL60 cells were identified. Monoclonal antibodies against each cellular marker have been produced. Determination of the presence of these two markers, either alone or in combination, -can be used to detect breast cancer, and in particular, associated metastatis. Thus, this invention refers to the use of both LAP and NDP-Kinase / Nm23 monoclonal antibodies together in a tandem solid-matrix based immuno-assay for first line confimatory blood-based testing for breast cancer.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF HEALTH
Resurrection hormone composition capable of improving filling fat survival rate and reducing fat fibration and calcification
InactiveCN106754645AImprove survival rateIncrease the scope of applicationCulture processVertebrate cellsAnimal scienceCalcification
The invention discloses a resurrection hormone composition capable of improving filling fat survival rate and reducing fat fibration and calcification. The resurrection hormone composition comprises, by weight, 20-26 parts of mother cells from receptor types, 20-24 parts of glucose base solution, 10-14 parts of recombinant human interleukin-II, 12-14 parts of cell factors, 1-2 parts of human PH (potential of hydrogen) regulators, 5-8 parts of amino acid, 6-9 parts of rh-a FGF (recombinant human-acidic fibroblast growth factors), 4-8 parts of cell growth stimulating activities GRO / MGSA and 0.5-1 part of lytic enzyme. Cells of types of same receptors serve as basic materials, cell organelles and the like in the basic materials are removed, cell sap is reserved, corresponding cell factors for assisting vital movement of the receptors are added, most of needed additives are from cell receptors, possibilities and seriousness of rejection reaction can be greatly reduced to some extent, special matching according to life characteristics of actual receptors can be omitted, production cost and technical requirements are effectively reduced, the application range of fat resurrection hormone is widened, and practicability of the fat resurrection hormone is improved.
Owner:티안지우안
Method for efficiently inducing generation of adventitious roots of Pinus densiflora tissue culture plantlets
ActiveCN101589690BQuality improvementLess callusHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSaccharumSucrose
The invention discloses a method for efficiently inducing the generation of adventitious roots of Pinus densiflora tissue culture plantlets, which uses growing young Pinus densiflora tissue culture plantlets as explants, and adopts a 'two-step method', namely firstly, inducing the generation of adventitious root blastemas in a culture medium containing 1 / 2 to 1 / 4 of WPM, 0.1 to 0.2 mg / L NAA, 1.0 to 2.0 mg / L IBA and 0.5 to 1.5 percent sucrose, and secondly, transferring the explants into a culture medium containing 1 / 2 of the WPM, 0.5 to 1.0 g / L AC and 2.0 percent of the sucrose to promote the expression and the extension of the adventitious roots so as to finish the generation process of the adventitious roots. By adopting the method, the generation ratio of the adventitious roots of the Pinus densiflora tissue culture plantlets is high, the root system develops well and the transplant survival rate is high, thus the method lays a solid foundation for the mass production of Pinus densiflora tissue culture regeneration plants for resisting pine wood nematode diseases, and simultaneously has important reference value for the cultivation of other Pinus species tissue culture plantlets.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
A strain producing phospholipase c and its screening method
ActiveCN103509736BAccurately determineOvercoming the Shortcomings of ScreeningBacteriaMicroorganism based processesYolkHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a bacterial strain capable of producing phosphatidase C, and a screening method thereof. The bacterial strain is Pseudomonas fluorescens P.f-9103, and preservation number is CCTCC No.M2013298. The bacterial strain is obtained by screening and separation from soil near oil workshops. Morphological characteristics are that: the shape of a bacterial colony is round, the surface of the colony is salient, the color is white, and the bacterial colony is nontransparent and yellows with the increasing of age; the colony is smooth, is relatively viscous and dense, and is easy to be stirred up, and the edge is smooth; the colony has a flagellum, is capable of moving, and produces no blastema; the bacterial strain is gram negative, the optimum growth temperature is 25 to 30 DEG C, and pH value is 7.0 to 7.6. The screening method comprises following steps: primary screening is performed on LB medium containing yolk; then phosphatide is taken as a substrate, and enzymatic reaction is performed; and reaction products are analyzed by HPLC so as to realize secondary screening. According to the method, natural phosphatide is taken as the substrate, so that problems caused by inactivity of phosphatidase C on phosphatide substrate analogue NPPC are avoided. Sources of primary screening raw material are abundant, operation is convenient, secondary screening is accurate and rapid, and the screening method is suitable for high throughput screening of the bacterial strain capable of producing phosphatidase C.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for inducing doubling of pollen chromosome of Eucommia ulmoides
A method for reduplicating the pollen chromosomes of eucommia tree by inducing features that a high-temp reduplicating device of tree is used to heat the male flower buds of eucommia tree in the meiophase of pollen metrocytes at 45-47 deg.C for 2 hr to increase the 2n pollen percentage to 45-70%, especially in the diakinasis-metaphase I.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for quickly detecting fruiting performance of pleurotus nebrodensis
InactiveCN101824461BStrong identification and detection reliabilityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceHypha
The invention discloses a method for quickly detecting the fruiting performance of pleurotus nebrodensis, which comprises the following steps of: inoculating pleurotus nebrodensis strains into the center of a solid culture medium, culturing for 7 to 10d at the temperature of 22 to 26 DEG C under a dark condition and culturing again for 3 to 5d after hyphae overgrow with a culture dish; then, freezing the culture dish at the temperature of 0 to 4 DEG C under a dark condition for 3 to 5d; and afterwards, putting the culture dish at the temperature of 8 to 12 DEG C under the illumination of 200 to 800Lux for carrying out recovering culture for 10 to 20d and selecting the strains which can form white blastemas with dense texture, i.e. the strains with better fruiting performance. The method has high identification and detection accuracy, short time and high efficiency, lowers the breeding or production cost and is suitable for the quick detection and identification of the fruiting performance of the pleurotus nebrodensis strains on a large scale.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A method of inducing jujube 2n pollen based on branch instillation technology
InactiveCN102972288BIncrease the chance of occurrenceEfficient inductionPlant genotype modificationFiberPollen
The invention discloses a method for simply and efficiently inducing jujube 2n pollen based on a stem dripping technology. The method comprises the following steps of: drilling bases of stems of a jujube tree by using colchicines as a mutagenic agent at an exuberant meiosis stage of jujube pollen mother cells; and directly dripping the colchicines to the stems, so that medicine liquor is upwards transported by the xylems, and spindle fibers are prevented from being generated in the reduction mitosis process of the pollen mother cells so as to induce the pollen chromosome to be doubled to obtain the 2n pollen. The method provided by the invention is applied to introducing the 2n pollen; the introducing time is easily grasped, and the 2n pollen introducing can be carried out on a plurality of jujube trees within one year; and the high-proportion 2n pollen is obtained to quicken the sexual polyploidization breeding process of the jujube trees.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com