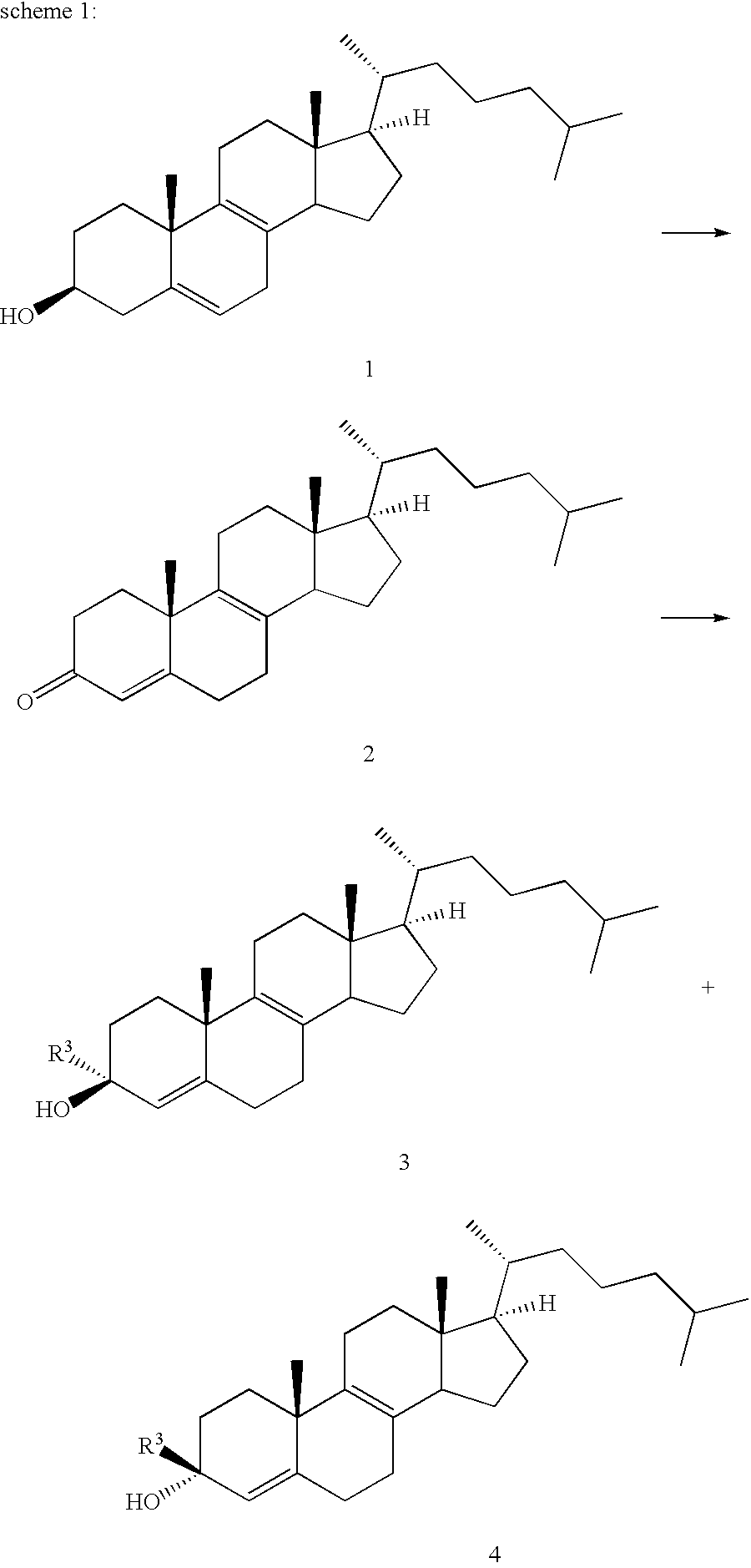
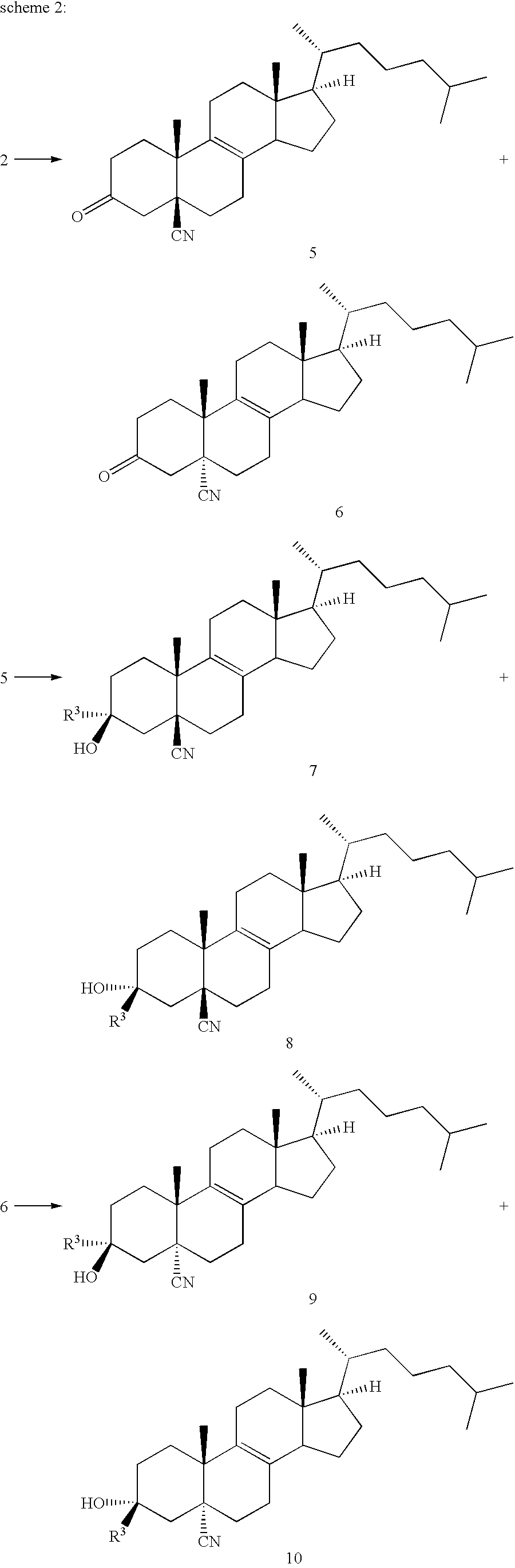
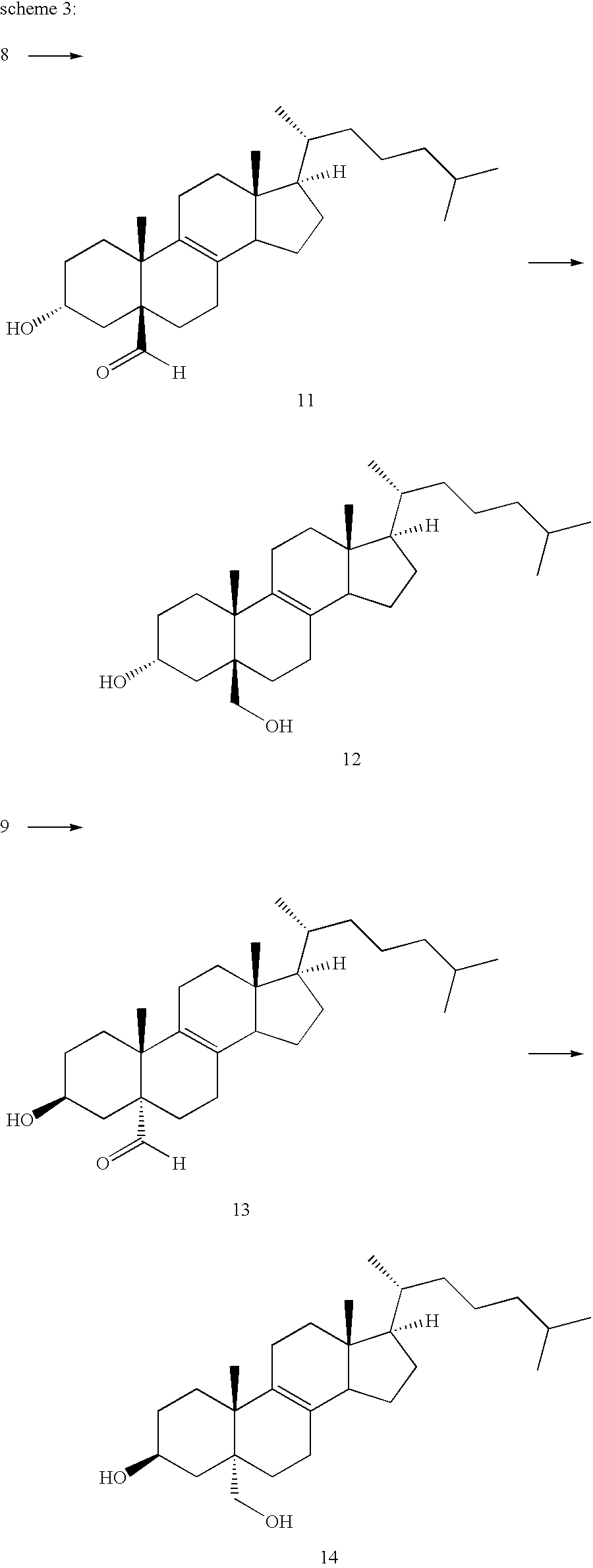
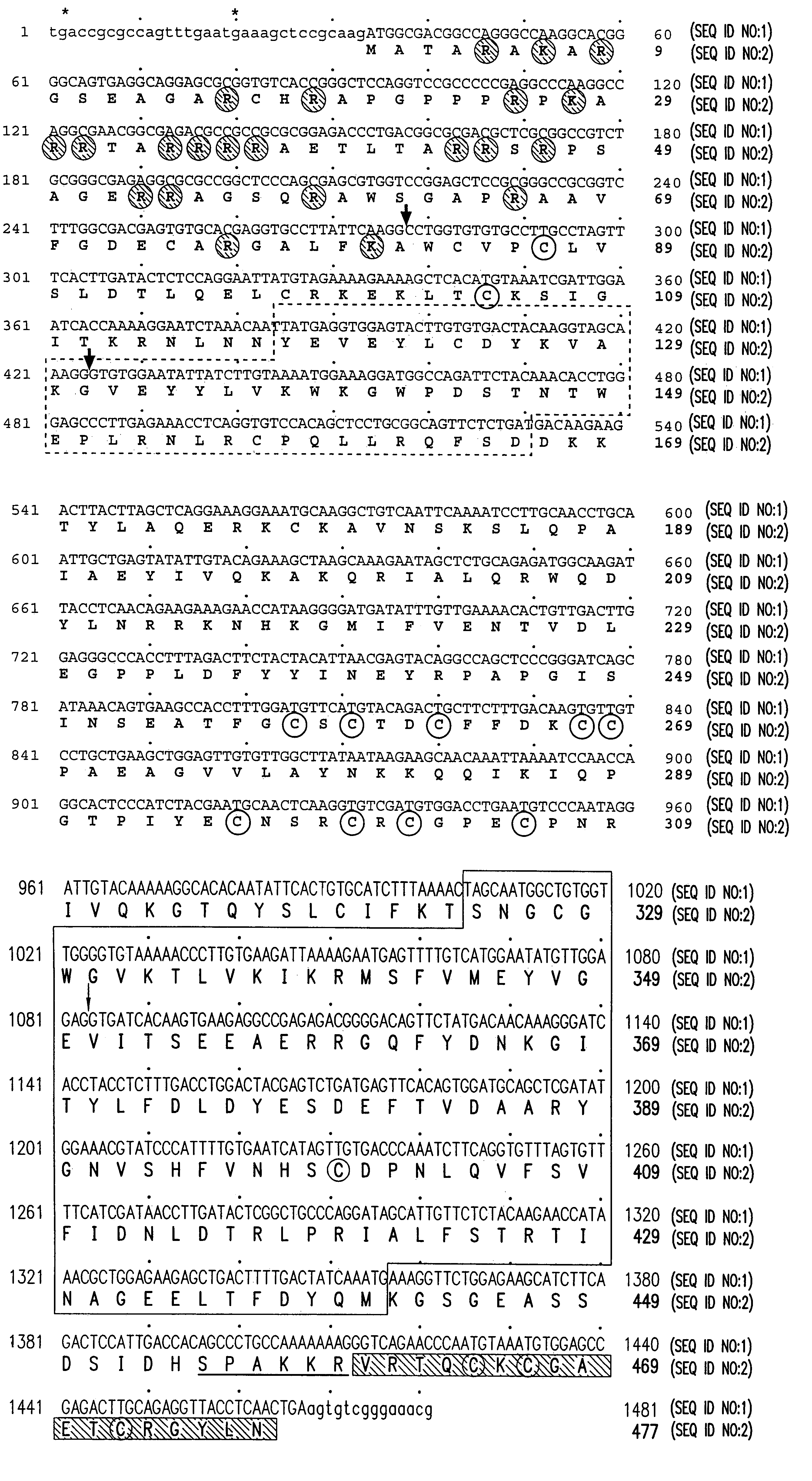Patents
Literature
158 results about "Meiosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Meiosis (/maɪˈoʊsɪs/ ; from Greek μείωσις, meiosis, which means lessening) is a special type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, creating four haploid cells, each genetically distinct from the parent cell that gave rise to them. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multicellular eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Meiotic cell divisions are an essential process during oogenesis and spermatogenesis.
Treatment of Infertility
InactiveUS6281013B1Degree of side effect can be improvedDegree of improvementBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPhysiologyMeiosis
In an in vitro fertilization method, a woman is treated with a hypothalamic hormone and / or a pituitary hormone or an agonist or antagonist thereof or an active derivative thereof for a short period of time and, thereafter, using in vitro oocyte maturation egg or eggs are retrieved from the woman and are maturated using a meiosis activating compound.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Treatment of infertility
InactiveUS6585982B1Easy to optimizeIVF can be improved substantiallyOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMeiosisInfertility
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Method for knocking down brewing yeast chromosome
ActiveCN107858346AKnockout simpleKnockout EfficientHydrolasesStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyYeast chromosome
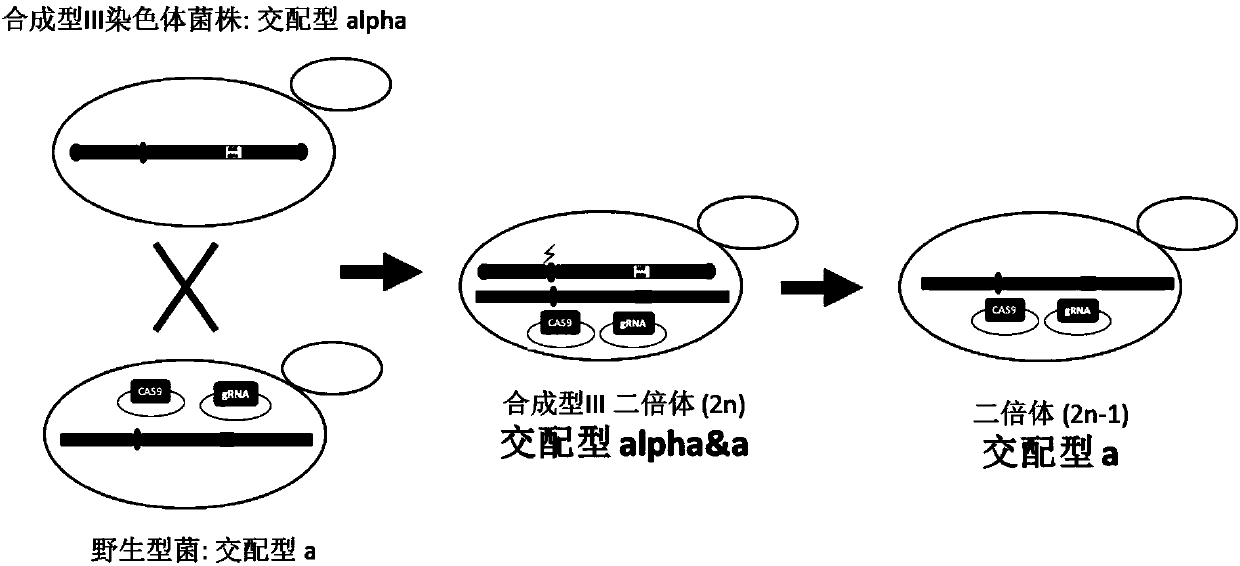
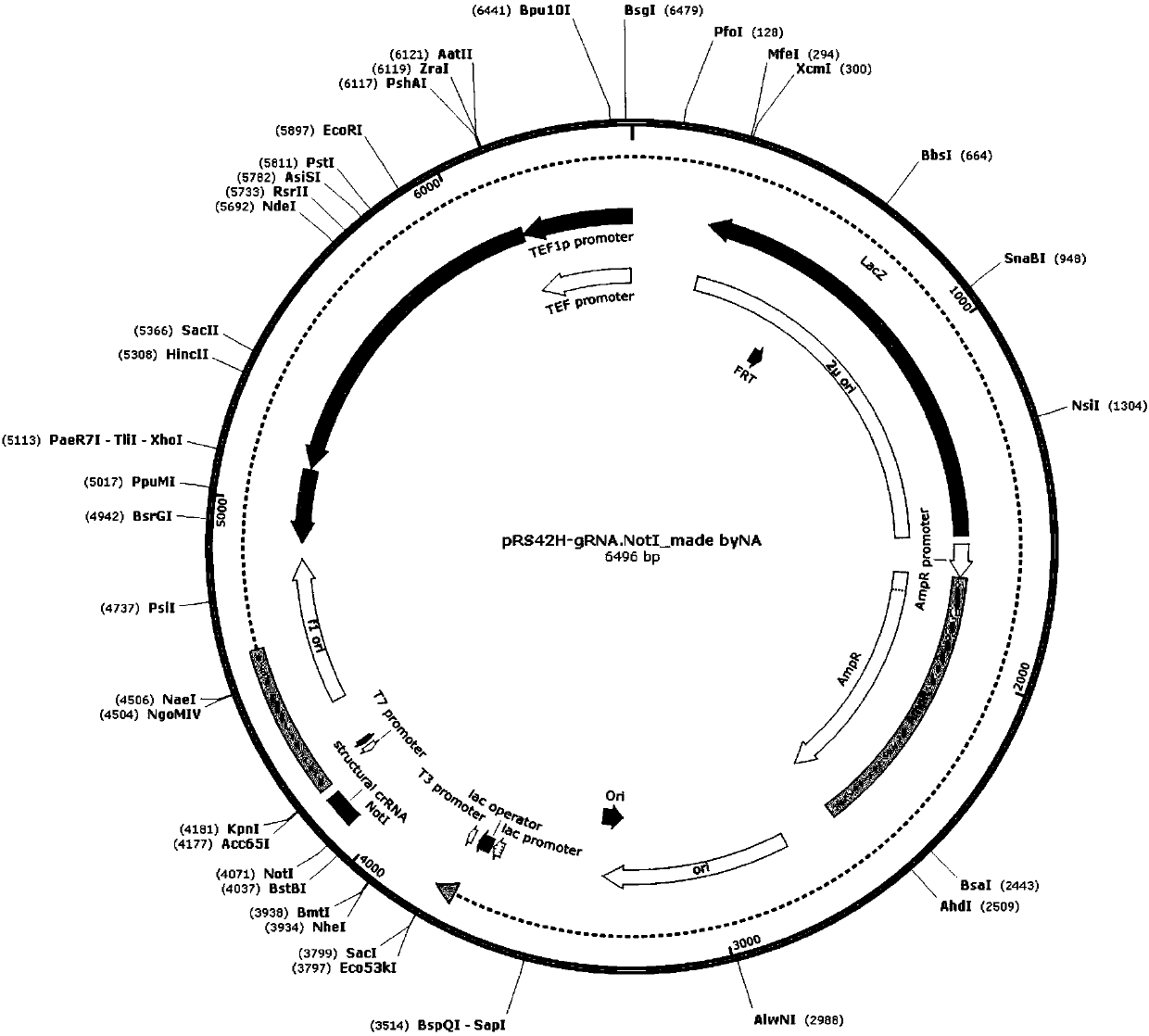
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and specifically discloses a method for knocking down brewing yeast chromosome. The method is characterized in that the complete yeast chromosome is cut according to the CRISPR / Cas9 base technology; a specificity target close to centromere is selected; a corresponding guide RNA is designed to guide Cas9 protein to generate an incision closeto the centromere, thus realizing the knocking down of the whole chromosome. Compared with the conventional method for losing the whole chromosome in manners such as inducing through a Ga1 promoter, and reductional division, the method has the advantages that the brewing yeast chromosome is simply, efficiently and quickly cut; the cross exchange of sister chromatids can be avoided; the chromosome-knocked-down homozygous brewing yeast diploid strain can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Modulation of meiotic recombination
InactiveUS20040023388A1Inhibit cell proliferationReduced growth rateStable introduction of DNAFermentationFunctional activityMeiosis
The invention provides methods of modifying the level of expression or functional activity of factors such as enzymes or other catalytic proteins or structural proteins, alone or in concert, to modify the frequency of meiotic homologous recombination involving the exchange of genetic information between non-sister chromatids from homologous maternal and paternal chromosomes. The steps at which modulation may occur include: homologous chromosome pairing, double-strand break formation; resection; strand invasion; branch migration; and resolution. Methods of plant and animal breeding are also provided that utilize the modulation of meiotic homologous recombination.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD +1
Polyploid rice breeding and detecting method with polyploid meiosis stability gene
ActiveCN1586134ASolve the problem of low seed setting ratePlant genotype modificationRice cultivationOryzaPollen
The present invention provides polyploid rice selectively breeding and identifying method with polyploid meiosis stability (PMeS) gene. The rice selectively breeding process includes: selecting parents; hybridization or complex hybridization; back crossing; doubling chromosome; identifying polyploid; selecting bearing property; observing meiosis behavior; self-crossing to form stable line; and identifying high bearing property. The identifying indexes include: polyploid line of Asia cultivated indica type rice or japonica rice; bearing rate not lower than 65 %; normal meiosis behavior; normal pollen shape and physiological activity and normal dyed pollution with 0.1 5 I-KI not lower than 95 %; bearing rate of hybrid of PMeS polyploid rice and other polyploid rice variety over 70 % and that of PMeS polyploid rice and wild rice variety over 65 %. The present invention solves the problem of low bearing rate of polyploid rice and may be used in breeding polyploid rice variety.
Owner:WUHAN POLYPLOID BIOTECH CO LTD
Method of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation and pharmaceutical kit for use in such method
InactiveUS20060217315A1High implantation ratePremature LH-surgesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMeiosisProgesterones
Owner:PANTARHEI BIOSCI
Methods for inducing targeted stimulation of meiotic recombination and kits for performing said methods
Owner:INST NAT DE RECH POUR LAGRICULTURE LALIMENTATION & LENVIRONNEMENT +1
Nuclear transfer embryo formation method
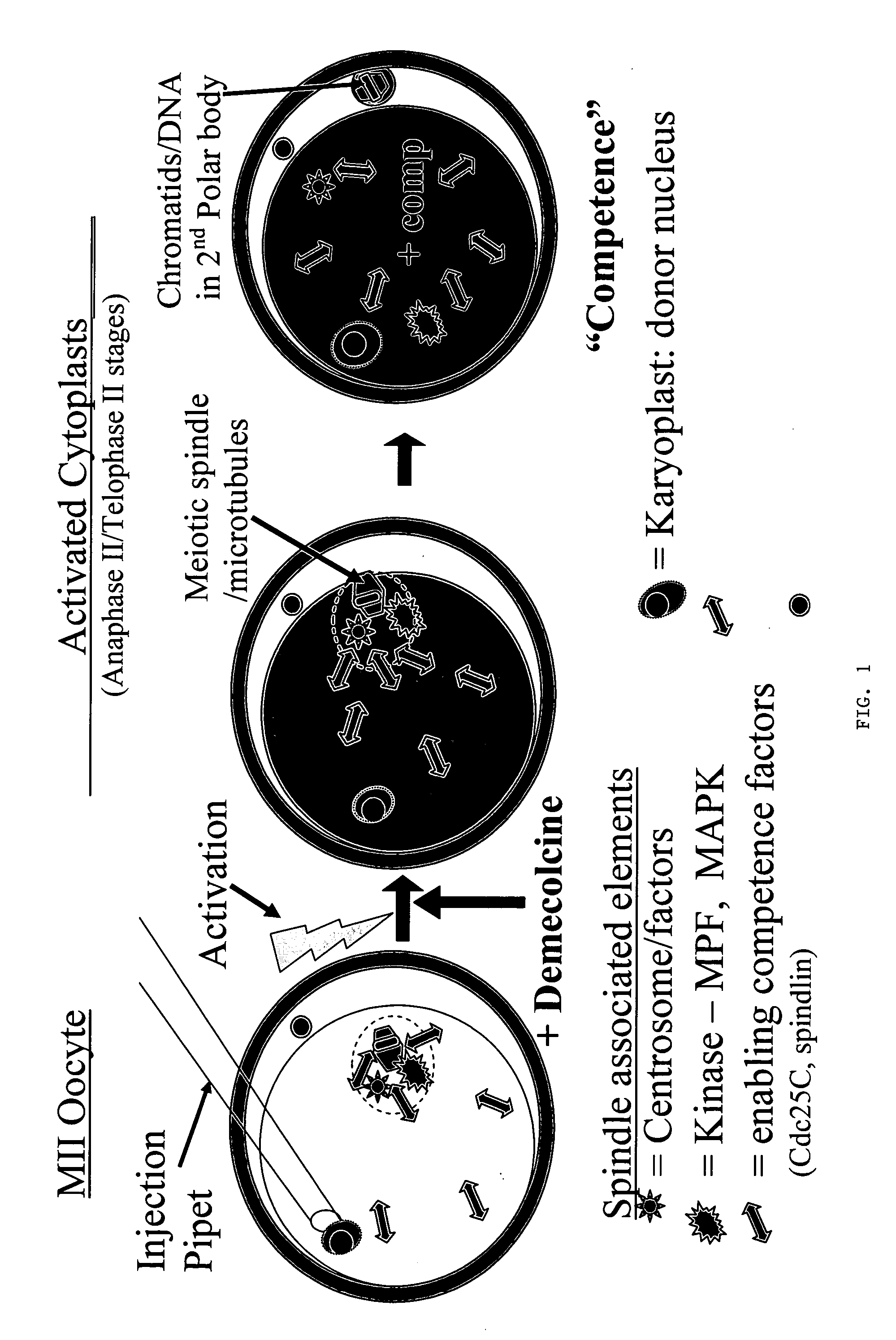
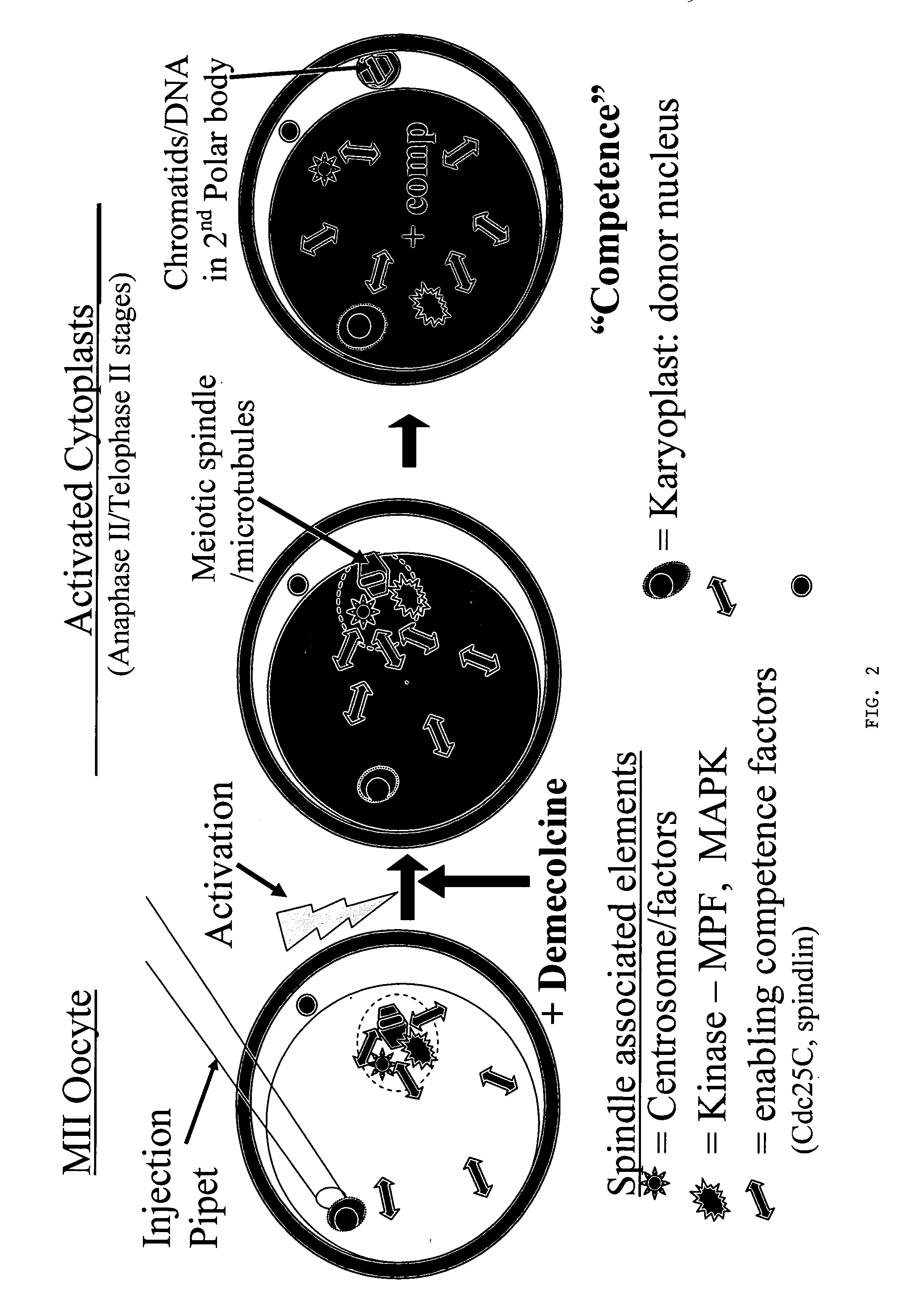
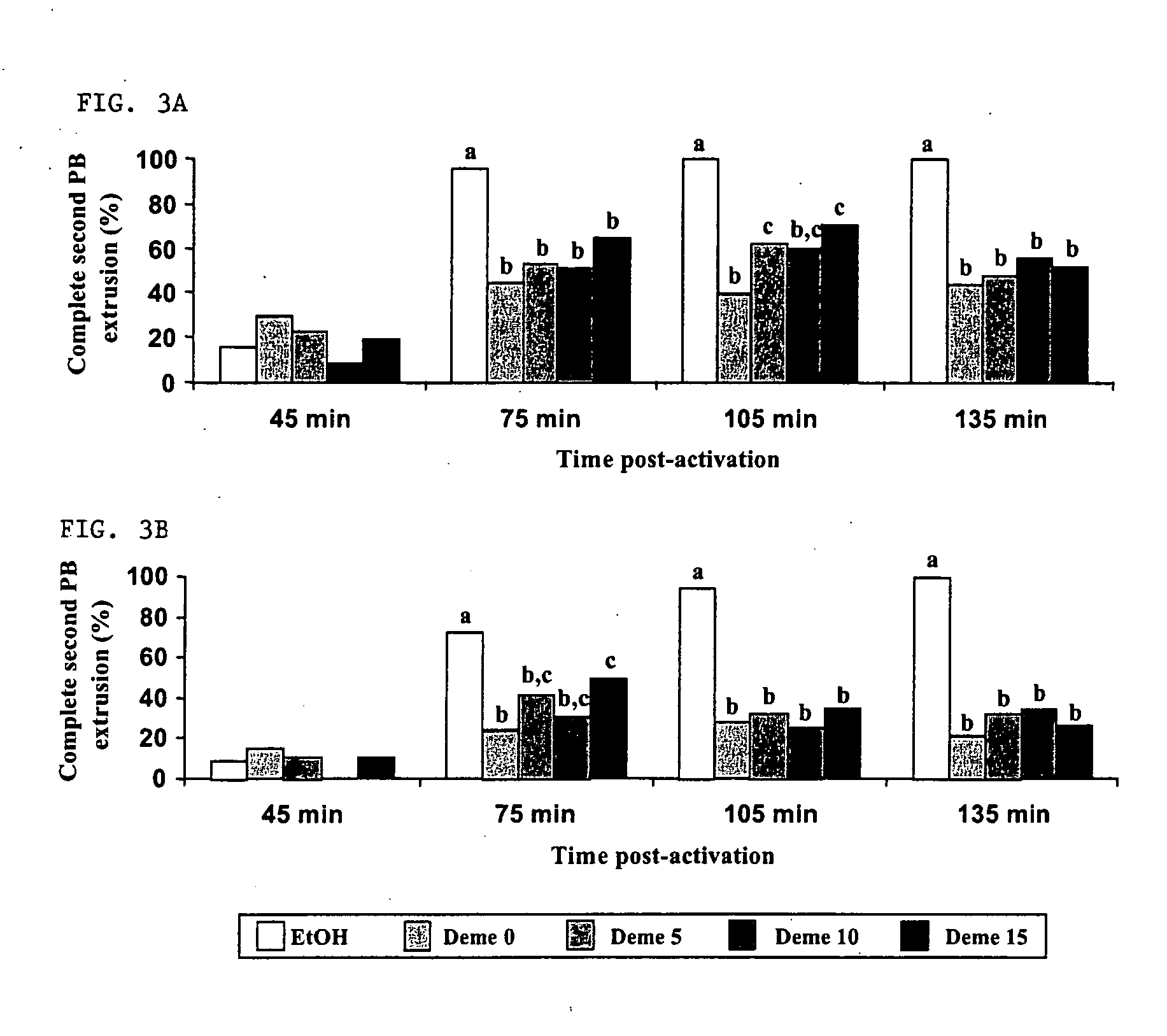
A nuclear transfer embryo is formed by destabilizing microtubules of an oocyte, whereby essentially all endogenous chromatin collects at a second polar body during meiosis of an oocyte. The oocyte is fused with the nucleus of a donor somatic cell of the same species of said oocyte prior to cessation of extrusion of the second polar body from the oocyte, thereby forming the nuclear transfer embryo. In one embodiment, the nuclear transfer embryo is employed to impregnate an animal, such as a mammal. In another embodiment, the donor nucleus is transgenic.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
Method of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation and pharmaceutical kit for use in such method
InactiveUS20050235374A1Easy to solveImprove developmentPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsGanirelixCo administration
One aspect of the present invention is concerned with a method of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation in a mammalian female, said method comprising the co-administration to said female of a substance having follicle stimulating hormone activity (FSH substance) in an amount effective to stimulate multiple follicular development;—gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist in an amount equivalent to a daily subcutaneous dose of at least 0.5 mg ganirelix to prevent a premature LH-surge; and—a LH substance in an amount effective to prevent or suppress symptoms of luteinising hormone (LH) deficiency resulting from the administration of the GnRH antagonist; followed by administering a meiosis and luteinisation inducing substance (ML substance) in an amount effective to stimulate resumption of meiosis and luteinisation, and wherein the LH substance is not obtained from the urine of human females. Another aspect of the to invention relates to a pharmaceutical kit for use in a method of controlled hyperstimulation, which kit comprises:—at least one parenteral or oral dosage unit containing one or more FSH substances in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 50-1500 I.U. FSH;—at least one parenteral dosage unit containing one or more GnRH antagonists in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 0.5-25 mg ganirelix;—at least one parenteral dosage unit containing one or more LH substances in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 50-3000 I.U. recombinant LH; wherein the LH substance is not obtained from the urine of human females.
Owner:ZONE IND DE IOURIETTAZ
Method of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation and pharmaceutical kit for use in such method
InactiveUS7815912B2Easy to solveIncrease dosePeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesGanirelixCo administration
One aspect of the present invention is concerned with a method of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation in a mammalian female, said method comprising the co-administration to said female of —a substance having follicle stimulating hormone activity (FSH substance) in an amount effective to stimulate multiple follicular development; —gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist in an amount equivalent to a daily subcutaneous dose of at least 0.5 mg ganirelix to prevent a premature LH-surge; and —a LH substance in an amount effective to prevent or suppress symptoms of luteinising hormone (LH) deficiency resulting from the administration of the GnRH antagonist; followed by administering a meiosis and luteinisation inducing substance (ML substance) in an amount effective to stimulate resumption of meiosis and luteinisation, and wherein the LH substance is not obtained from the urine of human females. Another aspect of the to invention relates to a pharmaceutical kit for use in a method of controlled hyperstimulation, which kit comprises: —at least one parenteral or oral dosage unit containing one or more FSH substances in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 50-1500 I.U. FSH; —at least one parenteral dosage unit containing one or more GnRH antagonists in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 0.5-25 mg ganirelix; —at least one parenteral dosage unit containing one or more LH substances in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 50-3000 I.U. recombinant LH; wherein the LH substance is not obtained from the urine of human females.
Owner:ZONE IND DE IOURIETTAZ
Homologous recombination in plants
InactiveUS20090031444A1Increase the number ofEasy to disassembleTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsMeiosisNucleic acid sequencing
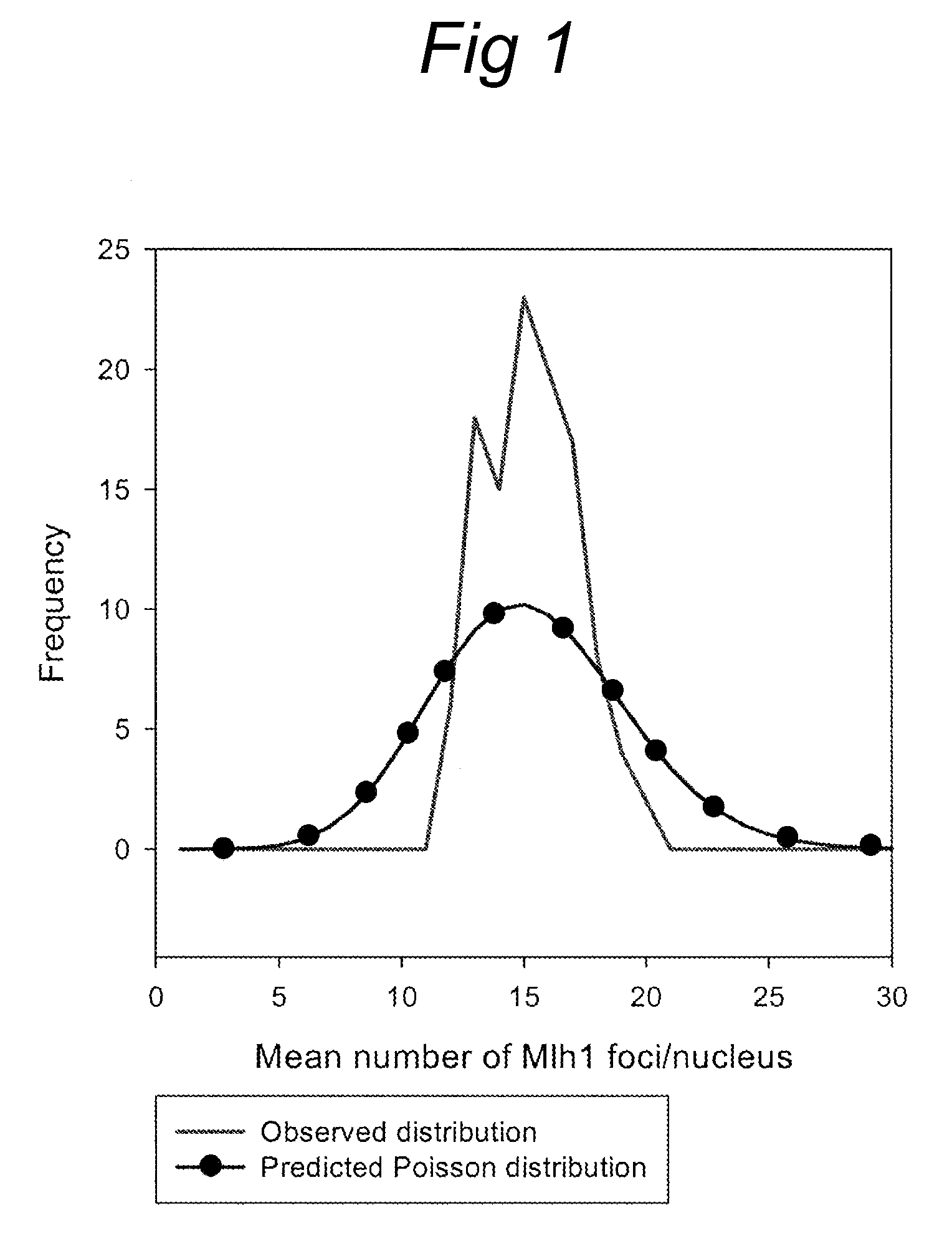
The invention relates to the field of meiotic homologous recombination in plants. Provided are transgenic plants, cytological assays and MLH1 protein and nucleic acid sequences, as well anti-MLH1 antibodies, anti-SMC1, anti-SMC3 and anti-CENP-C antibodies.
Owner:WITTICH PETER EGBERTUS +4
Mammalian SUV39H2 proteins and isolated DNA molecules encoding them
InactiveUS7052889B2High activityInhibit productionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionScreening methodMeiosis
Murine and human Suv39h2 polypeptide and DNA molecules encoding them. Suv39h2 is a novel member of the Suv3-9 gene family. Suv39h2 is a novel component of meiotic higher order chromatin. It has histone methyltransferase activity and is required, in combination with Suv39h1, for male gametogenesis. Suv39h2 can be used in screening methods to identify modulators of its methyltransferase activity, which are useful in cancer therapy and for male contraception.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Cell cycle progression proteins
InactiveUS20050227301A1Modulating cell cycle progressionImprove progressAntimycoticsAntipyreticMeiosisMitotic cell
The invention describes human genes involved in cell cycle progression, including mitosis and meiosis. The invention also relates to the use of these “cell cycle progression” genes and proteins in the modulation of cell cycle progression in cells and methods for identifying modulators of these genes or proteins and hence modulators of mitosis and meiosis.
Owner:CYCLACEL
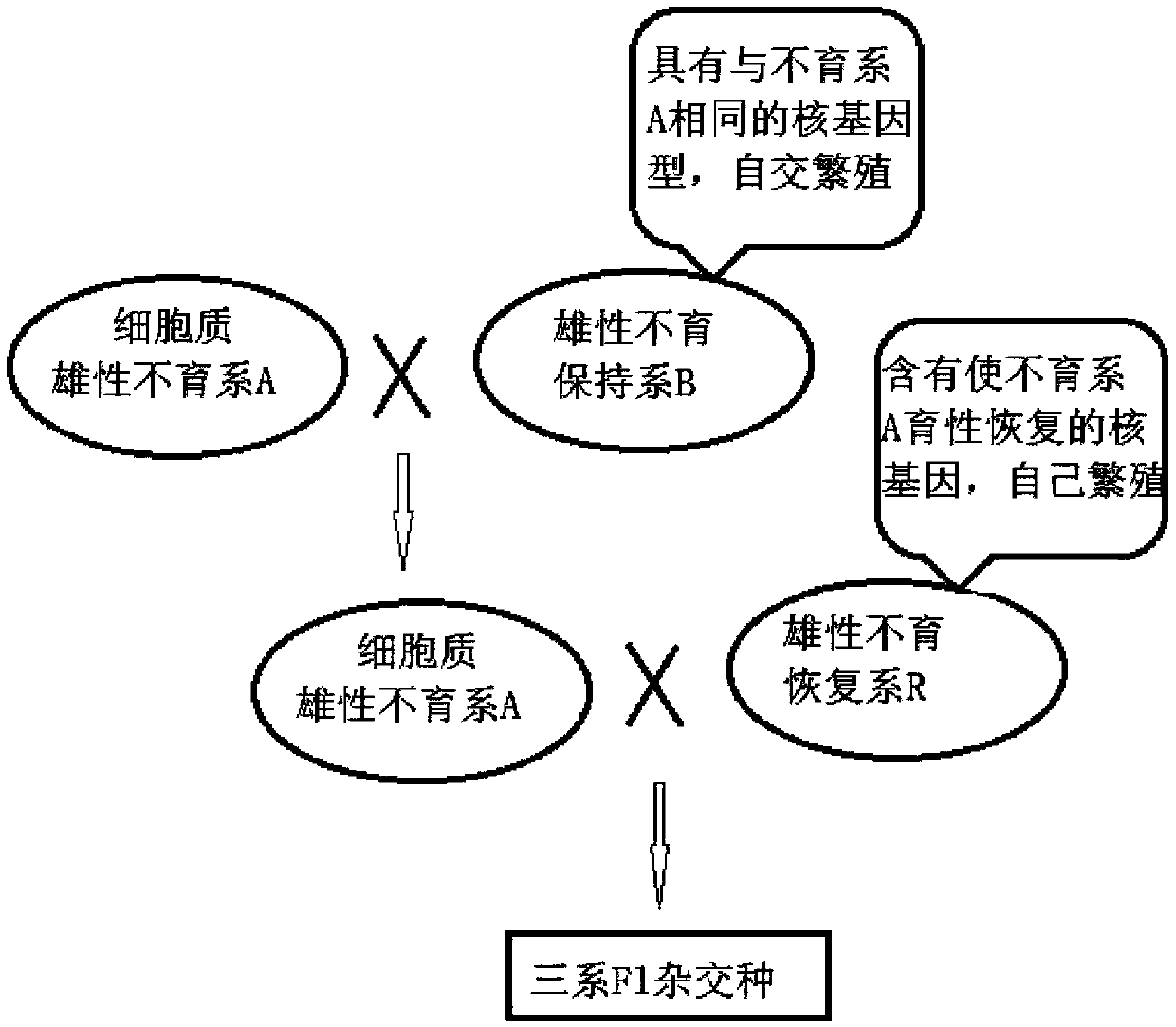
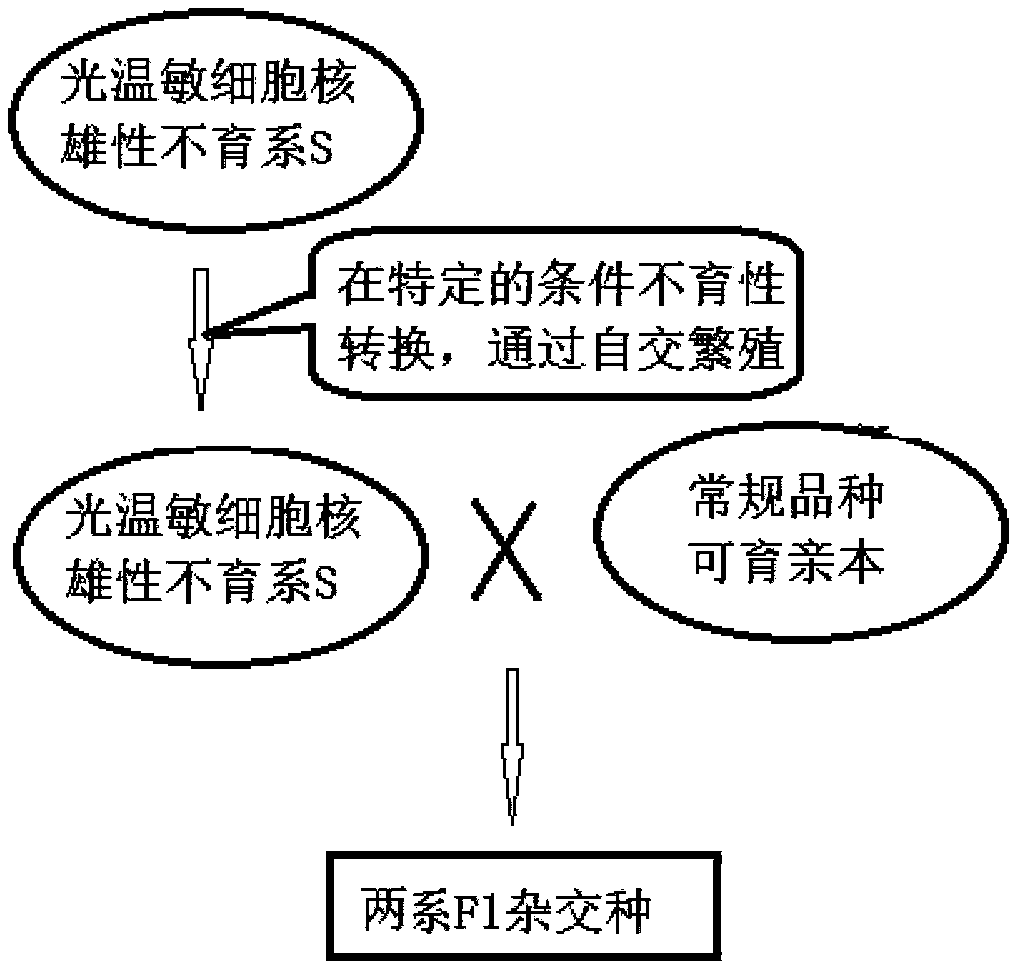
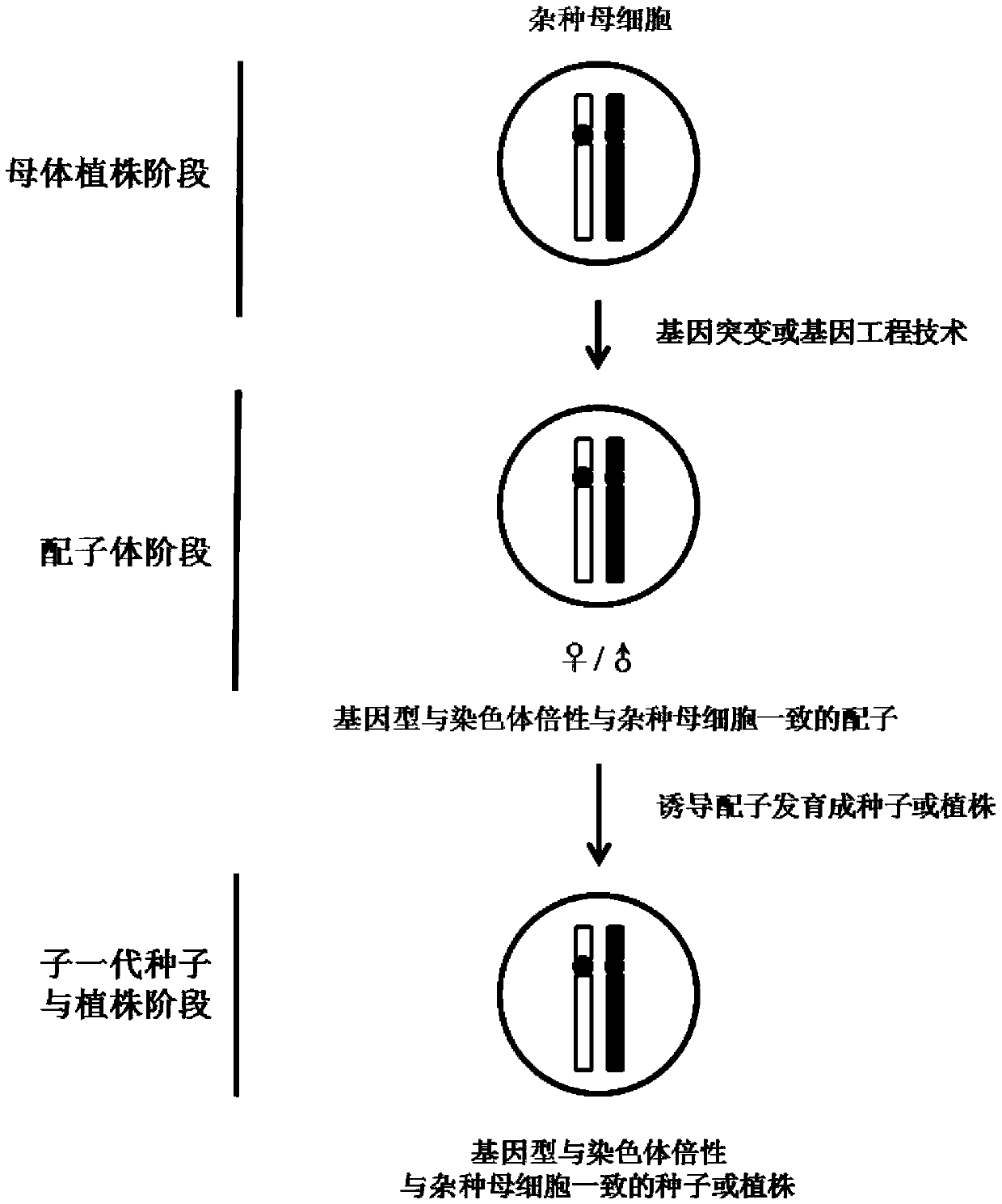
Method for utilizing plant heterosis
The invention discloses a method for utilizing plant heterosis. The method comprises the following steps: S1, converting meiosis of germ cells of a hybrid into similar mitosis by using a gene mutationor genetic engineering technology so as to obtain gametes consistent with a genotype and chromosome ploidy of the hybrid; and S2, inducing the gametes to develop into seeds or plants. By applying thetechnical scheme of the invention, hybrid seeds can generate cloned seeds or plants which are completely consistent with its genotype and chromosome ploidy, so that the heterosis can be utilized fora long time, and the existing problems of difficulty in parent-to-parent hybridization, low seed production yield, high hybrid seed cost and the like caused by inconsistent flowering periods and the like in the utilization of the heterosis are solved.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
In vitro maturing culture method for human immature ovum
InactiveCN1800371AClearly deal with individuationMedical Security GuaranteeGerm cellsCulture fluidMeiosis
The invention discloses a human immaturity ovum external mature culture method, which comprises: preparing for human external mature culture liquid, adding self-body mature follicle liquid to prepare for the culture liquid A, positioning the immaturity ovum of the first inter middle phase in the micro drop of the culture liquid A, adding separated and purified self-body ovum particle cell deposition in the culture liquid A to float into the culture liquid B with self-body ovum particle cell density 1-5*105 / ml, adding the immaturity ovum of the first inter front phase in the micro drop of the culture liquid B.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
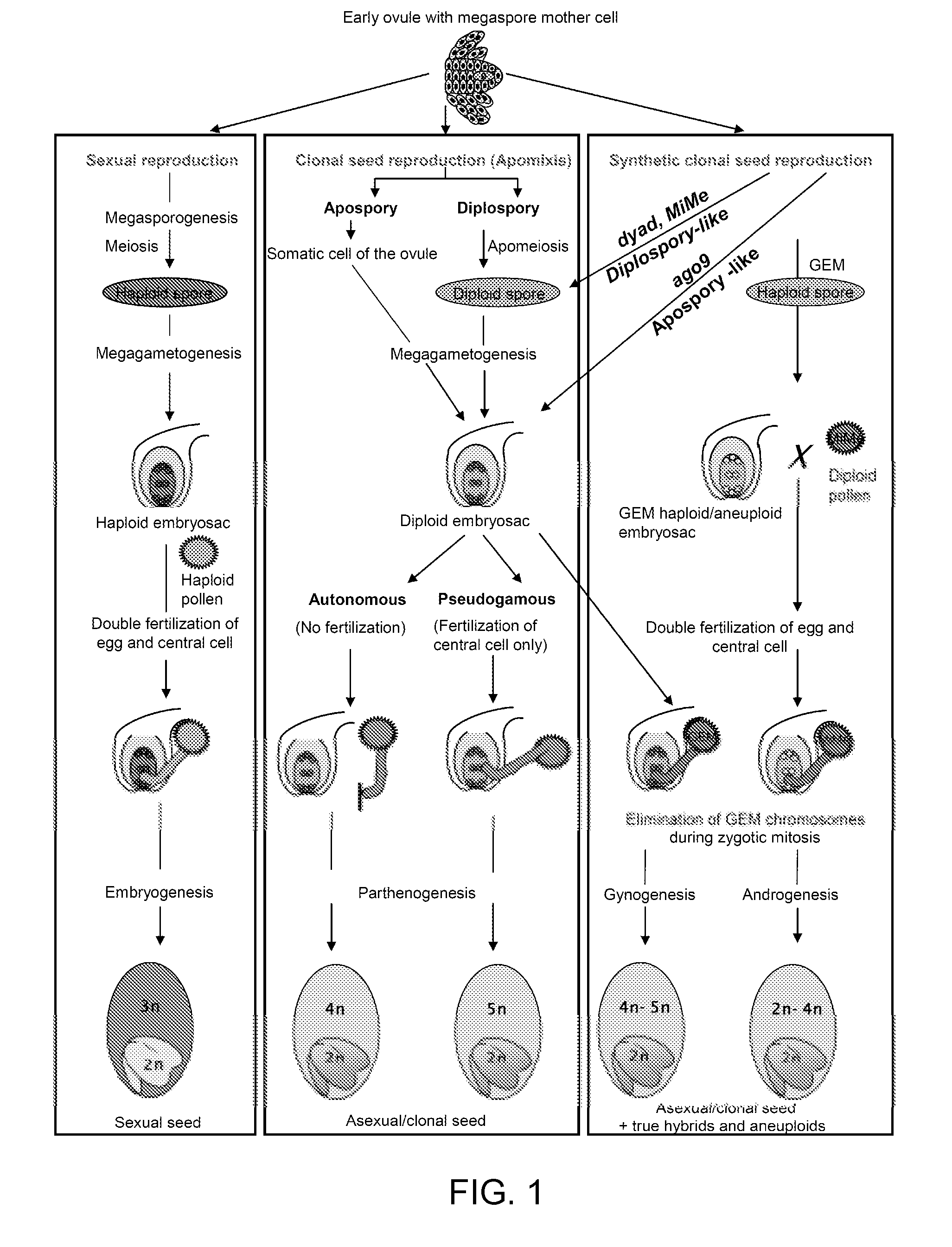
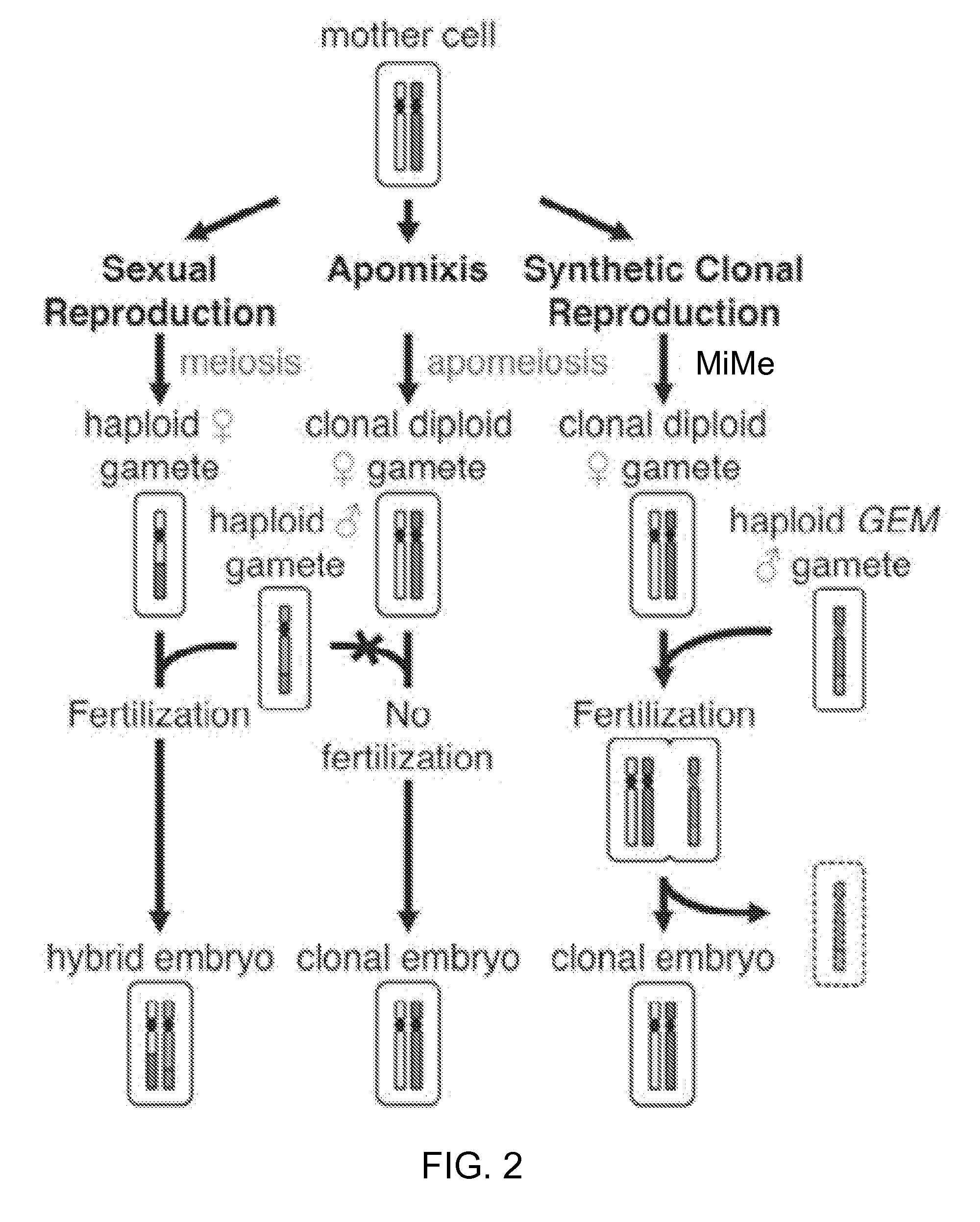
Synthetic Clonal Reproduction Through Seeds
InactiveUS20140298507A1Improve fertilitySeed viabilityTissue culturePlant tissue cultureMeiosisEmbryo
Clonal embryos or seeds produced by conversion of apomeiotic gametes into clonal embryos or seeds. Clonal embryos or seeds are produced by crossing a MiMe plant, as either a female or male, with an appropriate plant which induces genome elimination (genome eliminator, GE). MiMe plants are those in which meiosis is totally replaced by mitosis. In specific embodiments MiMe plants are MiMe-1 plants or MIME-2 plants. In specific embodiments MiMe plants are mutant plants. In a more specific embodiment, the genome eliminator is a haploid inducer exhibiting directed genome elimination of its own genome.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
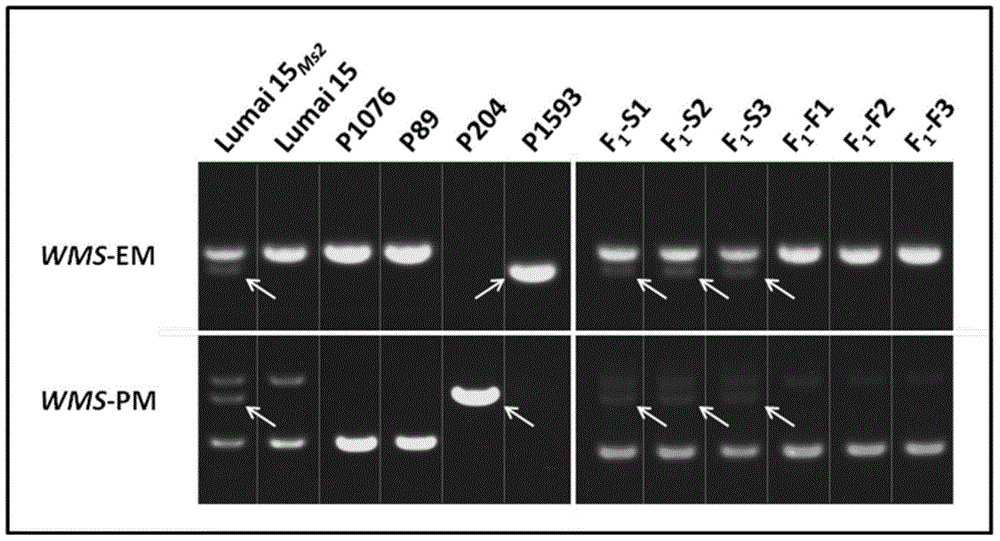
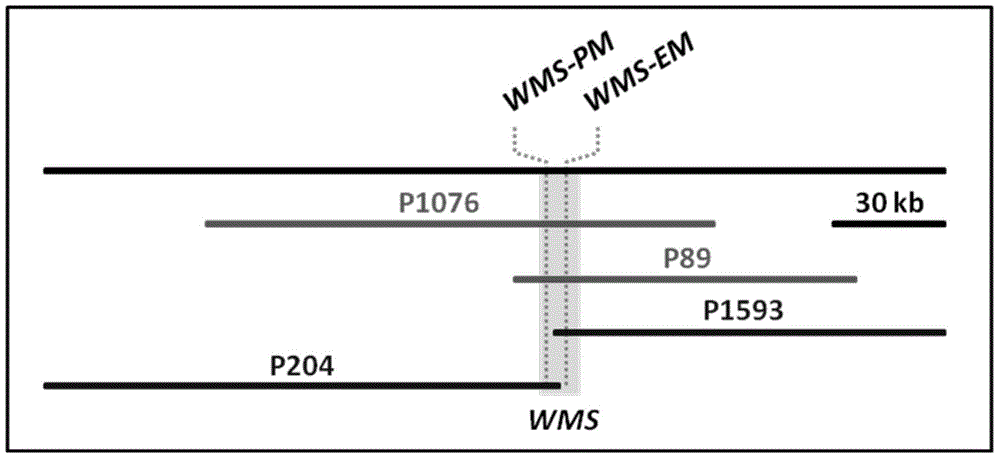
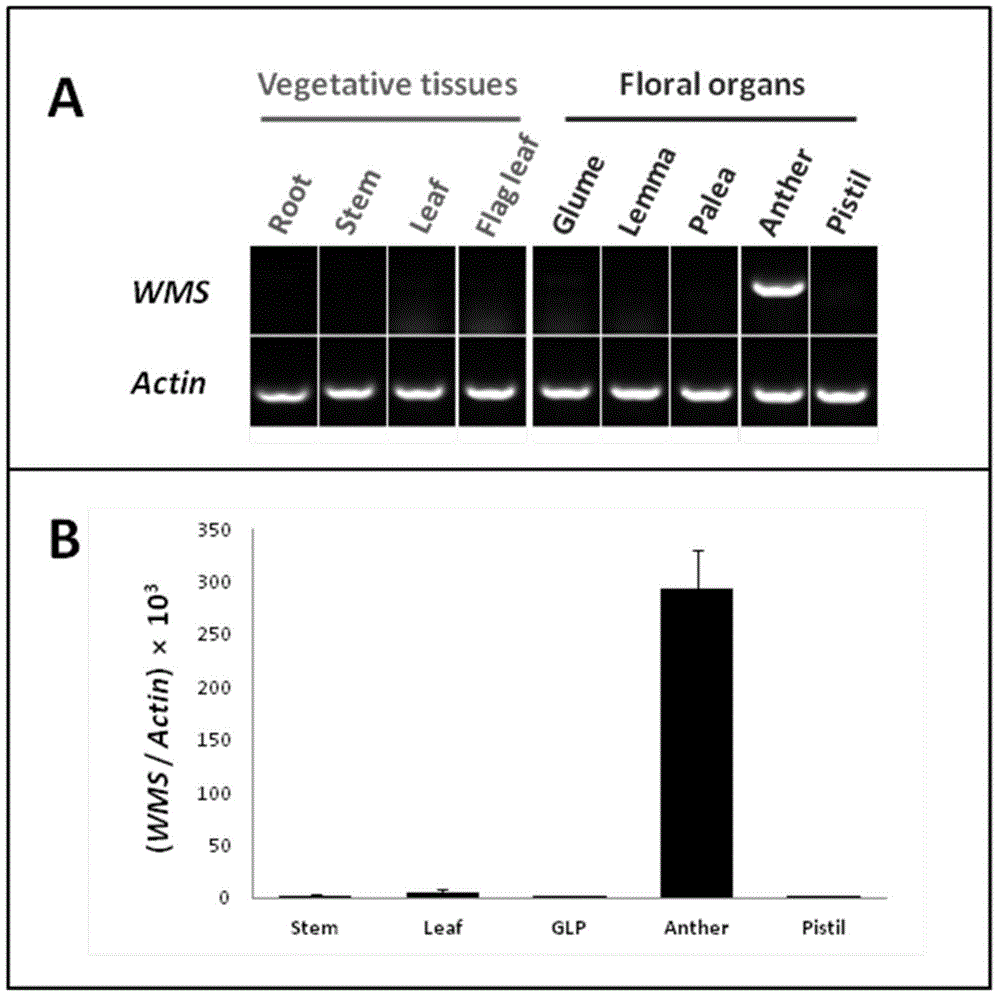
Wheat male sterility genes WMS and application of anther specific promoter thereof
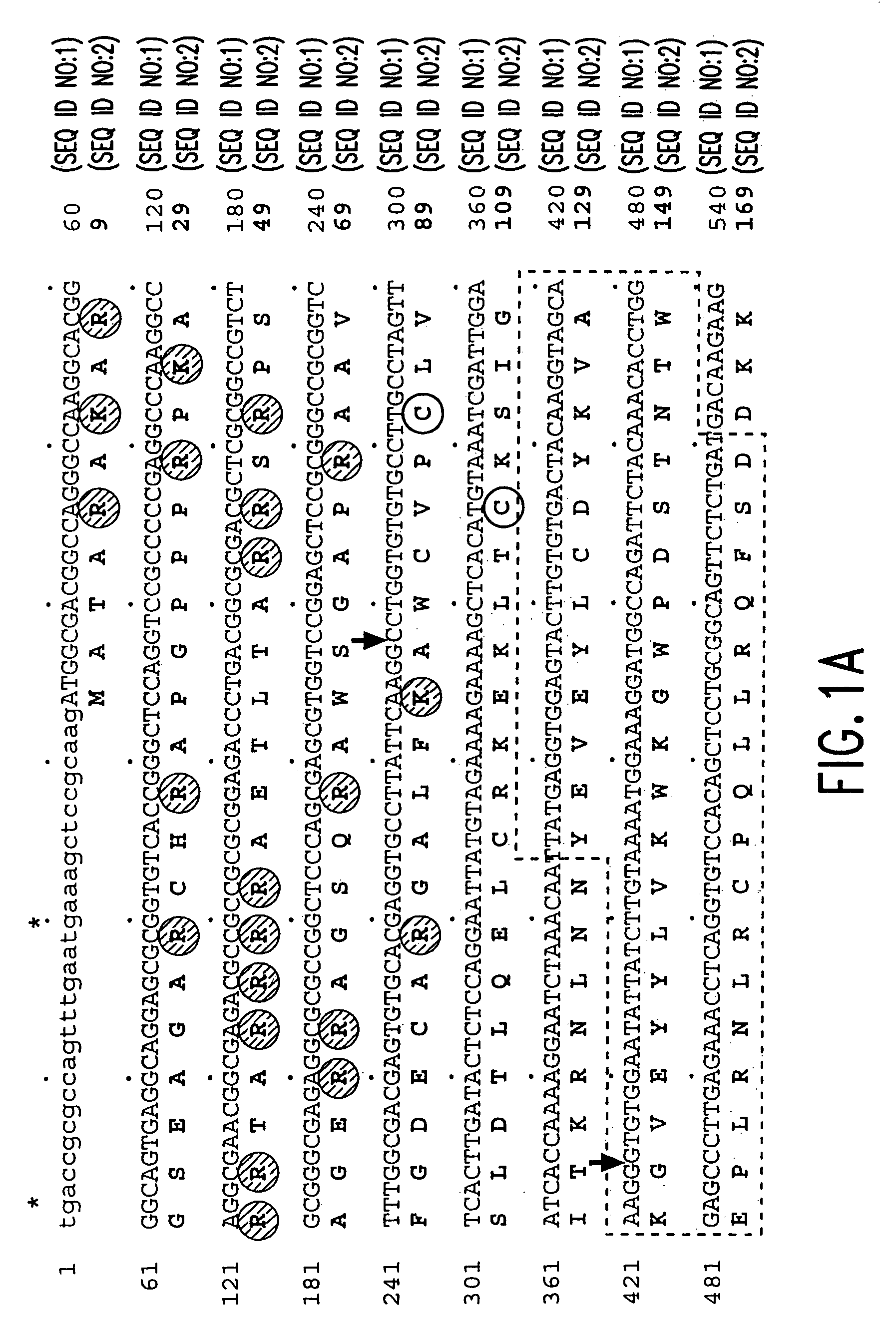
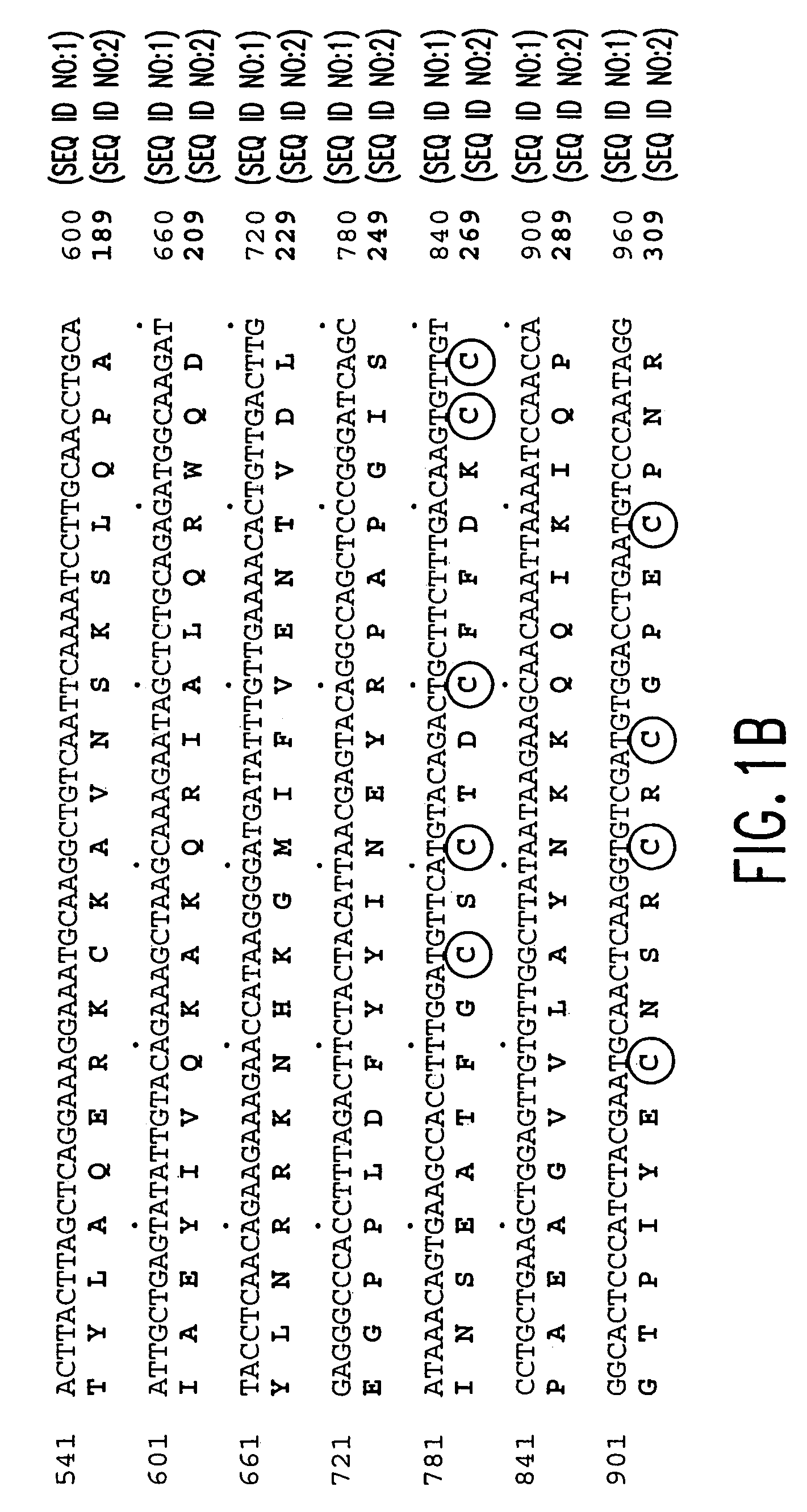
ActiveCN104911194AChange fertilityAchieve anther-specific expressionClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesAgricultural scienceTriticeae
The invention relates to wheat male sterility genes WMS and an application of an anther specific promoter thereof. The anther transcriptomes of the wheat near-isogenic line 'Lu wheat 15' and 'Lu wheat 15+Ms2' ('Lu wheat 15Ms2' for short) during the meiosis early period are compared by means of the RNA sequencing technique, and the genes WMS only expressed in 'Lu wheat 15Ms2' anther tissue are found. The full-length cDNA sequence of the WMS genes is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The amino acid sequence of WMS gene coding protein, namely WMS protein, is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The WMS gene promoter has the activity of triggering anther tissue specificities, the fertility of the stamen of wheat and slender false brome grass can be changed by manually operating the WMS genes. Therefore, the wheat male sterility genes WMS and the application of the anther specific promoter thereof can be used for realizing anther specificity expression of target genes, establishment of plant male sterility, establishment of a plant recurrent selection system and development of the plant hybrid seed production technique.
Owner:泉脉农业科技有限公司
Methods for production of sporeless agaricus bisporus mushrooms
Methods of producing hybrid Agaricus bisporus mushrooms strains derived or descended from at least one wild mushroom strain and having the specified traits of either greatly diminished sporulation or an absence of sporulation, and of obtaining postmeiotic offspring of nonsporlating basidiomycete fungi including Agaricus bisporus, are disclosed.
Owner:SYLVAN AMERICA
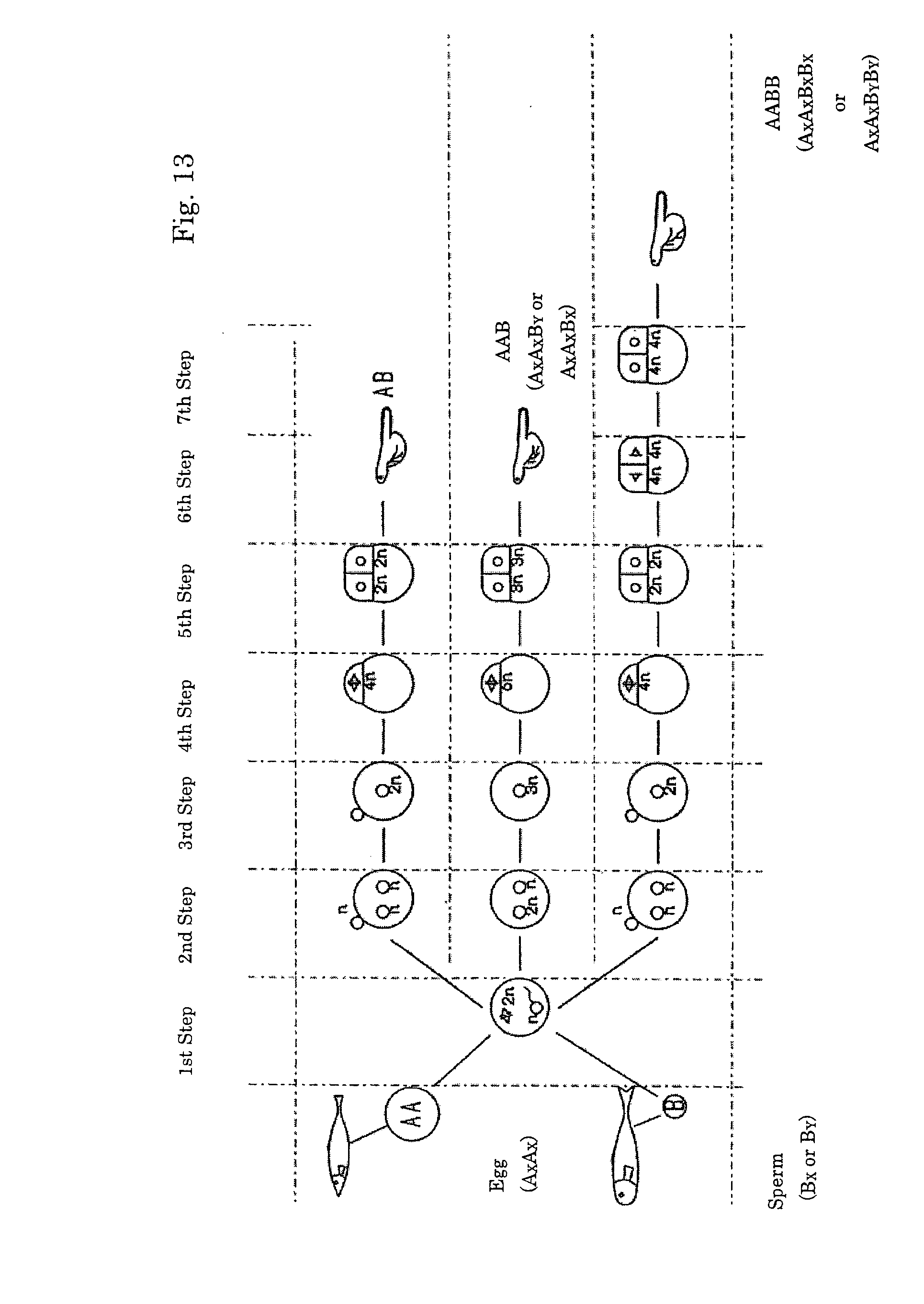
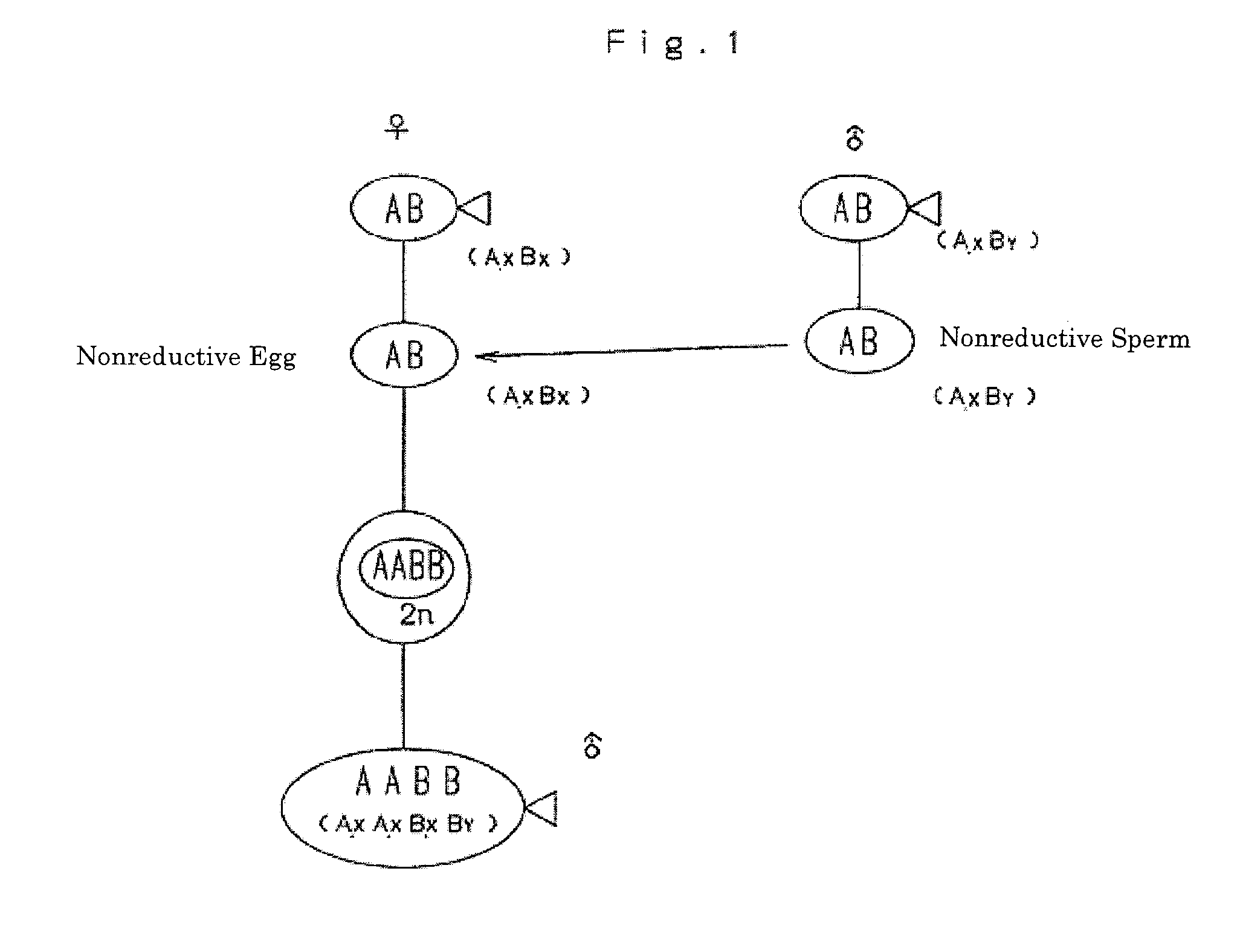
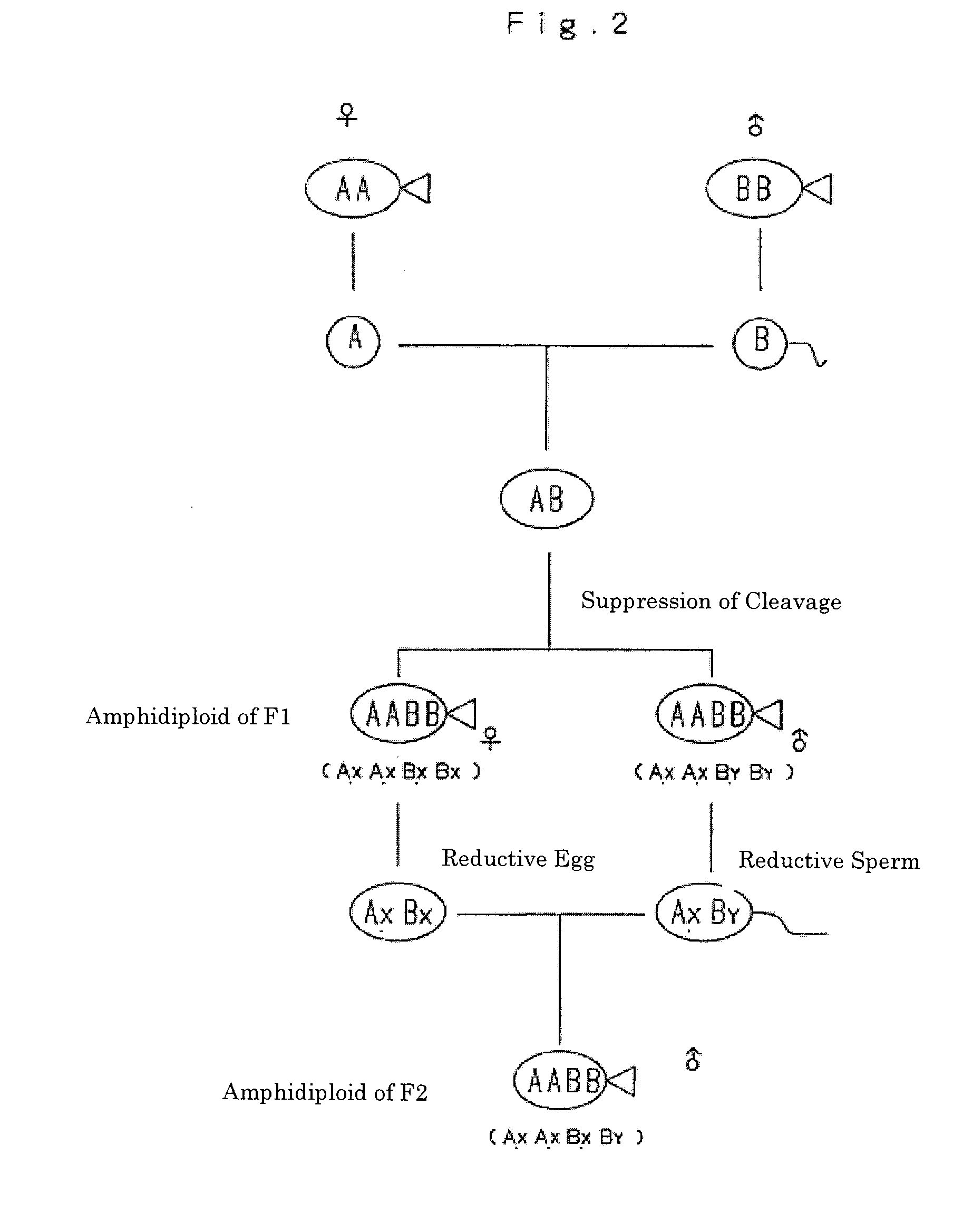
Amphidiploid aquatic animal and method of breeding the same
An amphidiploid aquatic animal according to the present invention has genomes AB of different species and carries fertile XXXY sex chromosomes. Among a large number of aquatic animals of the first filial generation kept in a closed system, a nonreductive sperm of a male and a nonreductive egg of a female are selected. Then the nonreductive egg is fertilized with the nonreductive sperm to create an amphidiploid aquatic animal having fertile XXXY sex chromosomes. Since this amphidiploid has the XXXY sex chromosomes, it can be crossed with an egg AXBX of an F1 hybrid that produces nonreductive eggs, thus ensuring a stable creation of amphidiploids in the subsequent generations by natural crossbreeding. In the meiotic division, one set of the chromosomes of each species is assuredly distributed to each gamete. Therefore, the trait of the first generation (F1) will be perpetually maintained. Since no genetic separation takes place, two sets of the genomes of different species are always inherited to every individual. Therefore, inbreeding depression will not take effect even if relative mating is repeated.
Owner:MATSUMOTO INST OF MICROORGANISMS +1
Immature oocyte in vitro maturation promoting culture medium and application thereof
ActiveCN107460161AImprove the ability of in vitro culture and developmentIncrease available quantityCulture processGerm cellsMaturation oocyteCulture fluid
The invention relates to an immature oocyte in vitro maturation promoting culture medium and application thereof. The immature oocyte in vitro maturation promoting culture medium is screened out through research on effects of different additives on immature oocytes and prepared by adding 20-100 mu M of BAPTA-AM in normal oocyte in vitro maturation culture solution. The immature oocyte in vitro maturation promoting culture medium is safe and free to side and toxic effects, enables meiosis of the immature oocytes, particularly those in level 3 cumulus-oocyte complexes, improves the in vitro development of the oocytes, promotes maturation, improves the cleavage rate and the blastula development rate after the mature oocytes are parthenogenetically-activated and further improves embryo quality. Application of the immature oocyte in vitro maturation promoting culture medium provides favorable support for the technology of in vitro propagation of animal embryos.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
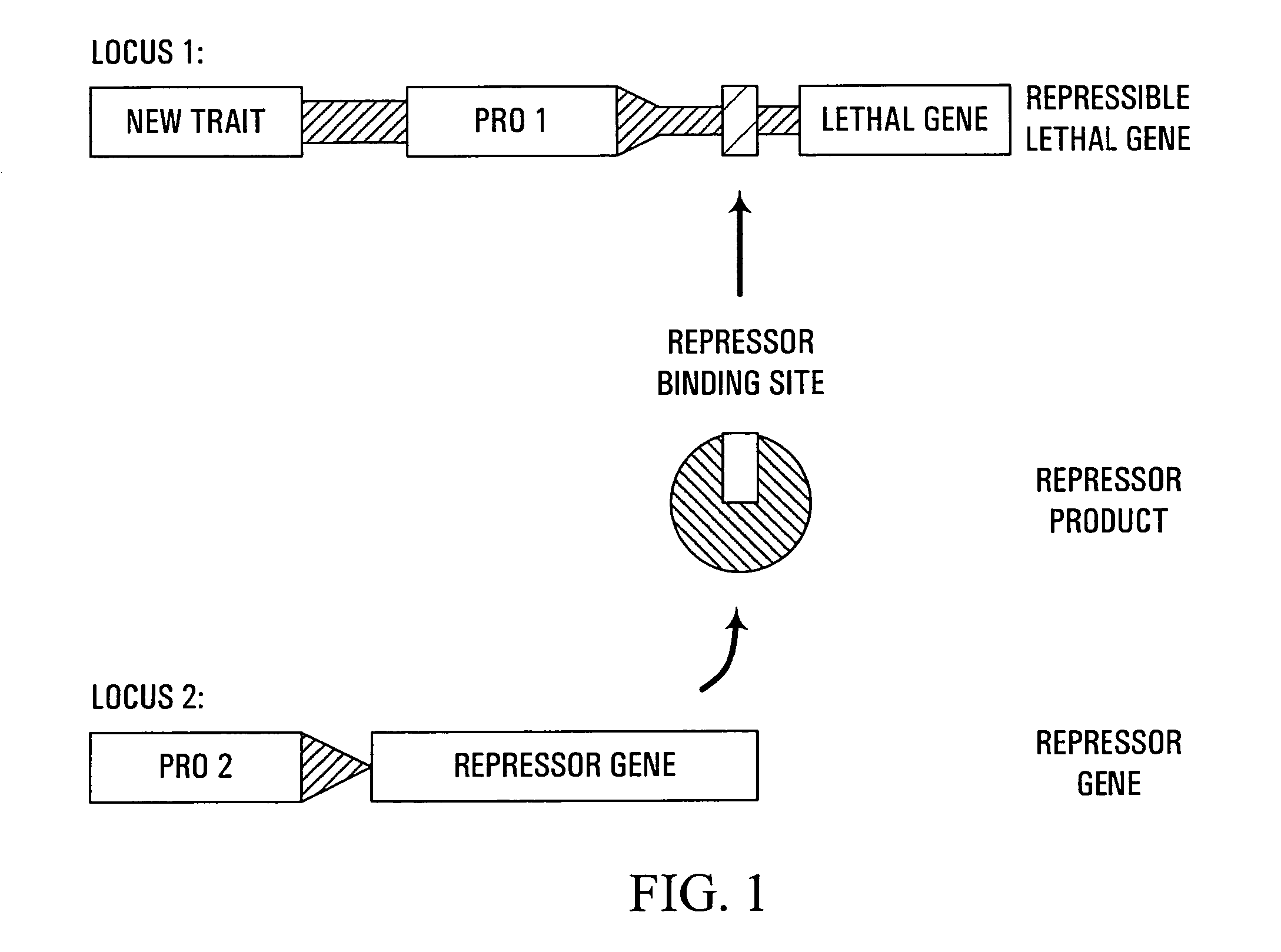
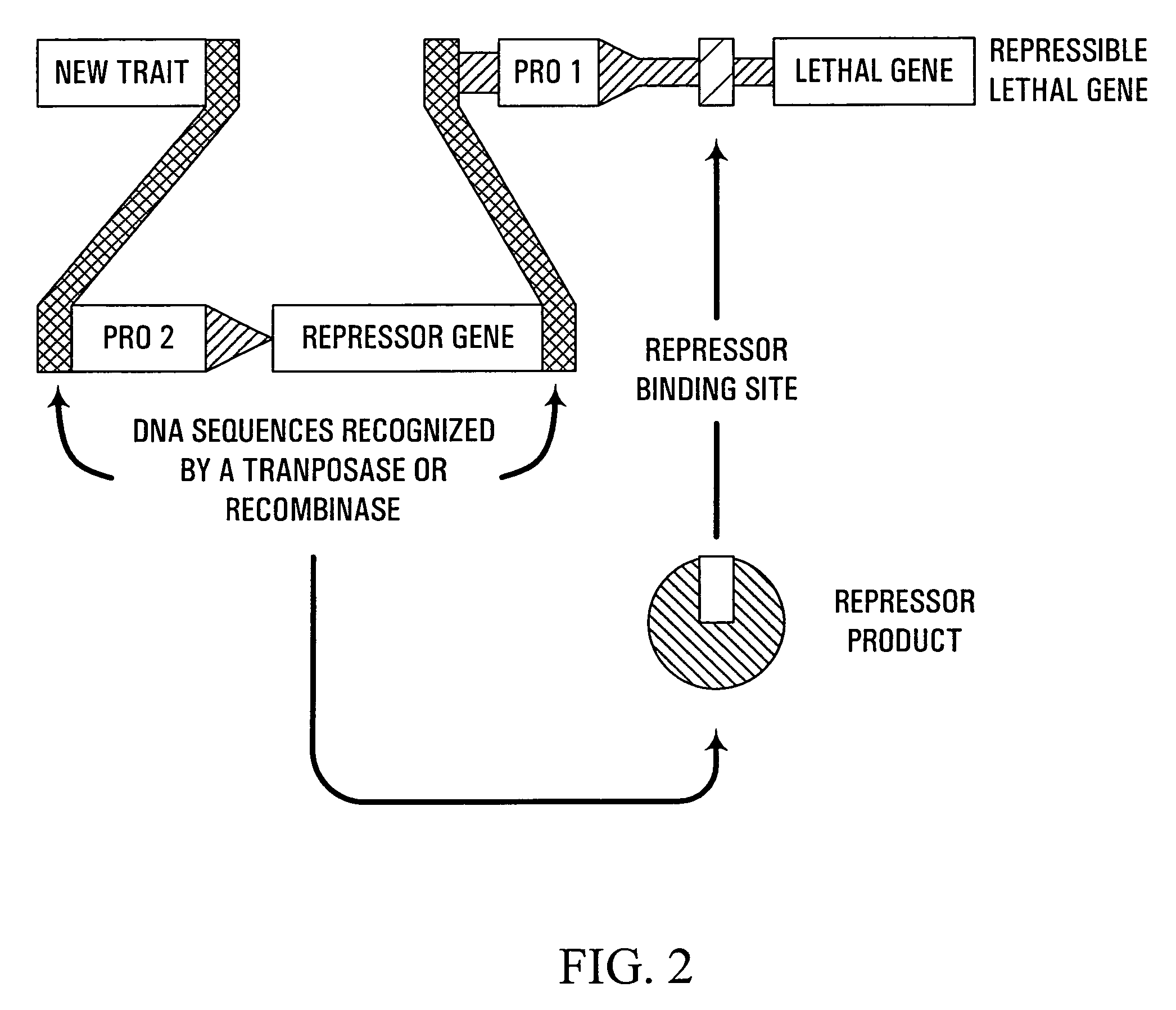
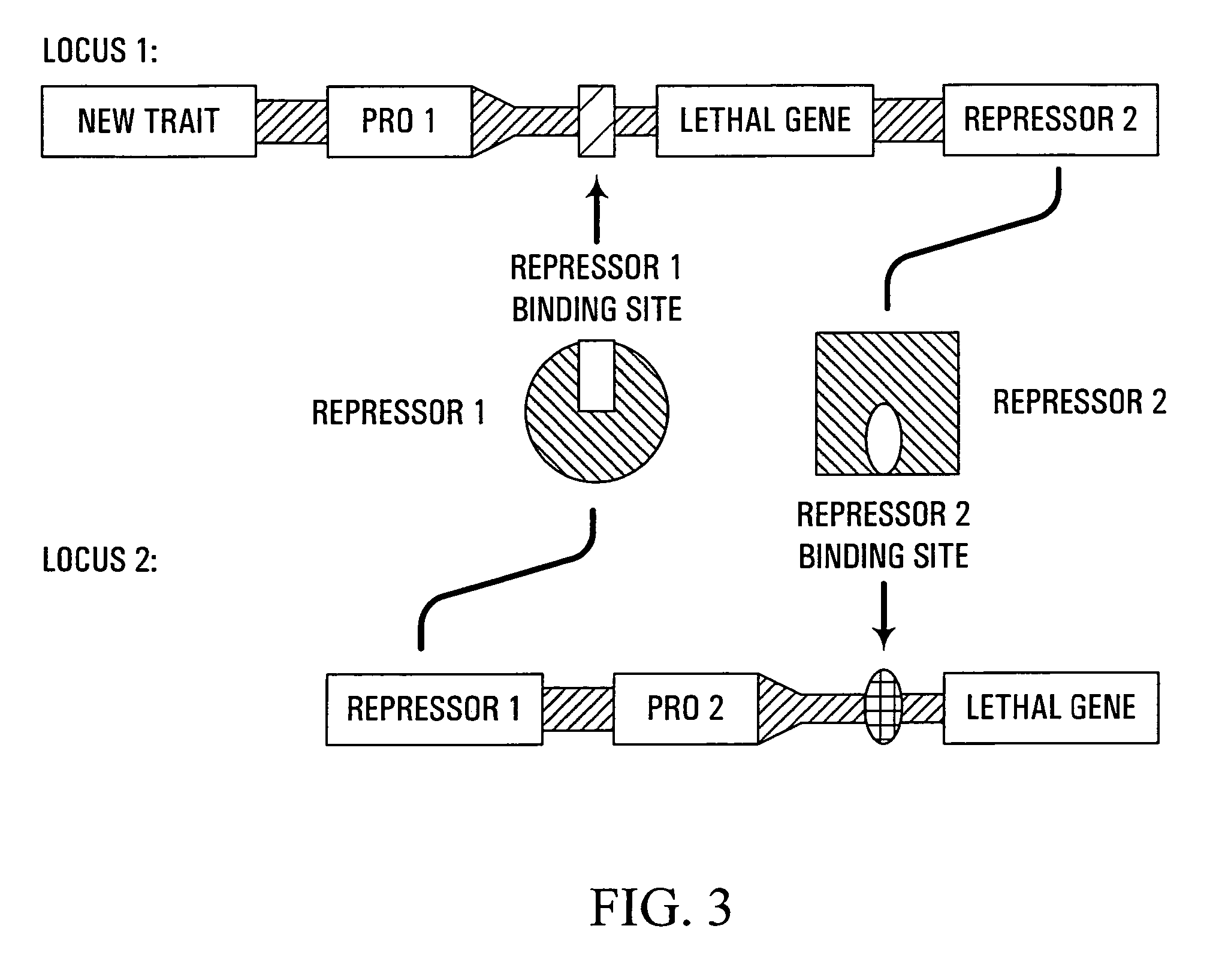
Methods and genetic compositions to limit outcrossing and undesired gene flow in crop plants
InactiveUS7671253B2Avoid spreadingAvoid persistenceSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesMeiosisRecombinant DNA
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Auxiliary genome assembly method based on artificial meiosis
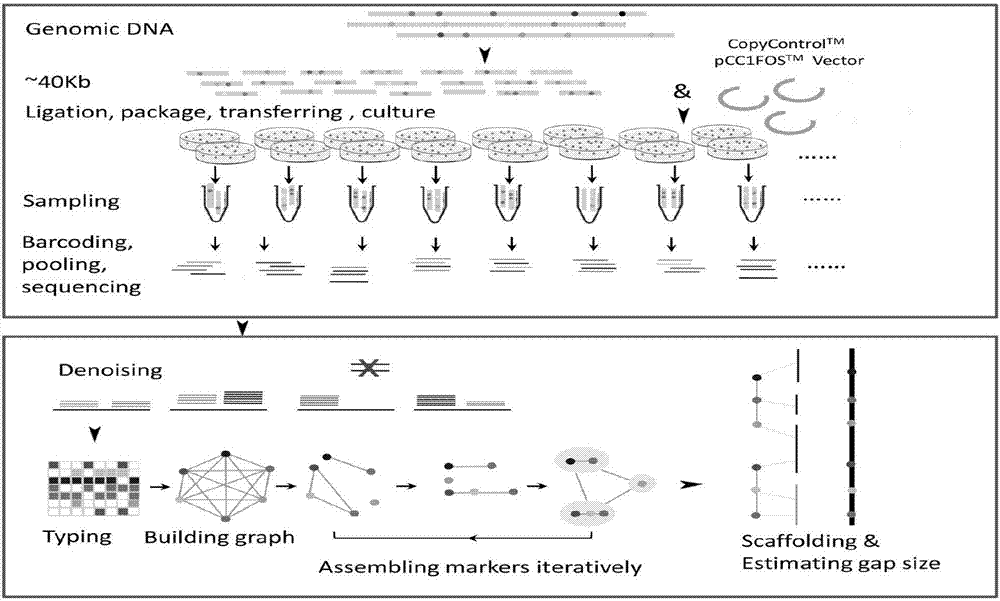
ActiveCN107058298AReduce the possibilityEliminate restriction enzyme digestion PCR clone decoding methodDNA preparationHigh densityAccessory genome
The invention discloses an auxiliary genome assembly method based on artificial meiosis. A genome in a form of clone library is equally divided so as to establish random artificial meiosis samples, and the random artificial samples are treated through Hpall transmethylase and FspEi methyl-modified dependent-type incision enzyme to form and analyze typing markers with high densities; and then sorting information of the typing markers is obtained; therefore, further assembly of scaffold or direct cascade assembly of Pacbio sequencing reads are achieved. Based on an assembly strategy of artificial meiosis, the auxiliary genome assembly method has the advantages of being easy in experiment operation, short in period, low in cost and capable of splicing the genome with high coverage and accuracy, and owns a wide application prospect in species with relatively complicated and highly heterozygous genomes.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
A cultivation method for carassius auratus gynogenesis fries
ActiveCN104904638APure germplasmFast growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaGenetic MaterialsMicrosatellite
The invention provides a cultivation method for carassius auratus gynogenesis fries. The method comprises the steps of selecting sexually mature diploid carassius auratus parents and collecting sperm and ovums; performing ultraviolet irradiation on Hanks liquid-diluted sperms to inactivate genetic materials thereof; performing artificial insemination on the inactivated sperms and the ovums; restraining the discharge of second polar bodies of meiosis by using a cold shock method to double genomes of the ovums and thus to cultivate viable carassius auratus gynogenesis diploid fries. Microsatellite marker identification proves that the genetic materials of all the gynogenesis fries are from the female parent; morphological measurement indicates part of the gynogenesis fries has obvious early growth dominance. The method has the advantages of simple operation, high efficiency, stability and high practicality.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
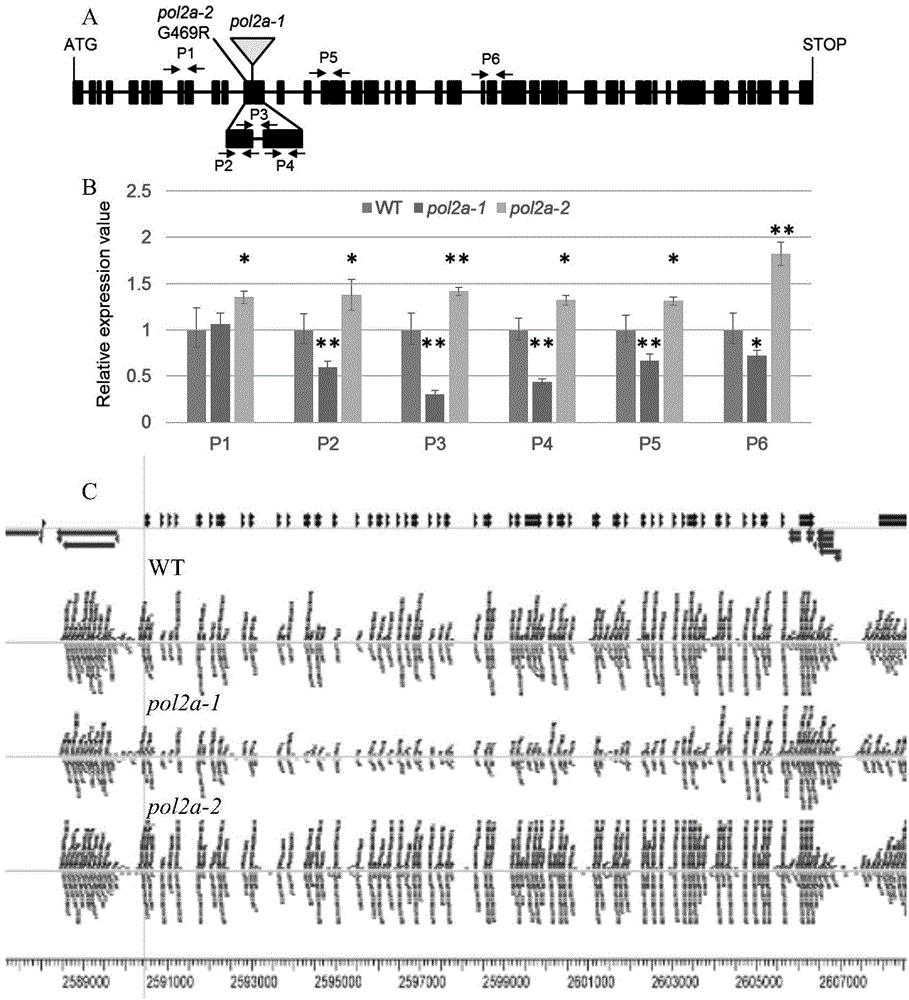
Function and application of arabidopsis thaliana POL2A gene in reduction division recombination
InactiveCN104928303APromote aggregationEasy to separateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyMeiosis
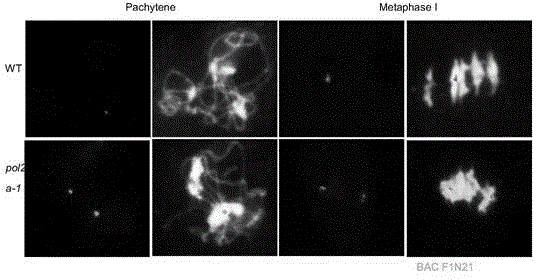
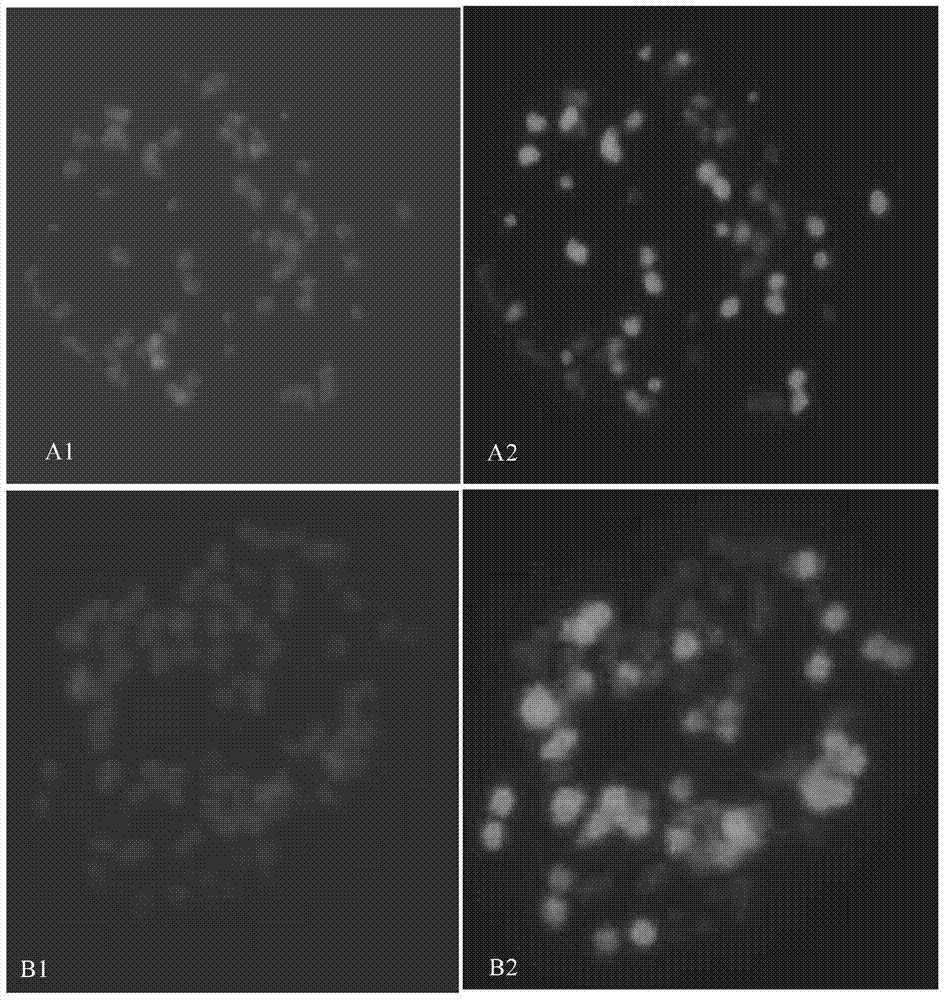
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and particularly relates to a function and application of an arabidopsis thaliana POL2A gene in reduction division recombination. The application comprises the following steps of using sequence characteristics of coding POL2A protein and the authentication of the new function of the gene in reduction division, i.e. using a fluorescent label site system to analyze the influence of POL2A to reduction division recombination frequency and distribution, and providing a fluorescent label-containing genetic material; providing the function of the gene of analyzing how complete mutation of the gene causes embryo death in reduction division, and providing the technology of a series of cell biology and the like. The important function of POL2A in reduction division recombination is proved in an eukaryote for the first time; the function is used, the modern biotechnology method is used, and the recombination frequency of a generic material in a reduction division process is controlled, so that aggregation of excellent characters is quickened, separation of the excellent characters in a hybrid offspring is delayed, and the aim of propelling and improving breeding study level is fulfilled.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for interspecific hybrid genome in-situ hybridization of crambe cordifolia
InactiveCN104745695AEasy to shapeGood dispersionMicrobiological testing/measurementDispersityConcentration ratio
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop molecular breeding, and in particular relates to a method for interspecific hybrid genome in-situ hybridization of crambe cordifolia. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a probe marker, preparing a slide, performing in-situ hybridization, performing signal detection and the like. In the slide preparation process, a chromosome slide which is good in morphology and good in dispersity in the meiosis period of crambe cordifolia can be obtained under appropriate enzymolysis conditions by using an acetic acid extension flame drying method. When probes and chromosomes are modified, appropriate temperature and time can be selected, appropriate blocking DNA and a probe concentration ratio can be confirmed, fluorescent in-situ hybridization images with clear signals can be obtained, and different interspecific chromosomes of hybrid crambe cordifolia species can be clearly identified, so that genome in-situ hybridization can be well applied to cytological detection of crambe cordifolia species with characteristics of a large number of chromosomes, small morphology and the like, and novel techniques and methods are provided for identification and structural research on crambe cordifolia chromosomes, evolution research on crambe cordifolia, and the like.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Polyploid rice breeding and detecting method with polyploid meiosis stability gene
ActiveCN100344223CSolve the problem of low seed setting ratePlant genotype modificationRice cultivationBiotechnologyOryza
The present invention provides polyploid rice selectively breeding and identifying method with polyploid meiosis stability (PMeS) gene. The rice selectively breeding process includes: selecting parents; hybridization or complex hybridization; back crossing; doubling chromosome; identifying polyploid; selecting bearing property; observing meiosis behavior; self-crossing to form stable line; and identifying high bearing property. The identifying indexes include: polyploid line of Asia cultivated indica type rice or japonica rice; bearing rate not lower than 65 %; normal meiosis behavior; normal pollen shape and physiological activity and normal dyed pollution with 0.1 5 I-KI not lower than 95 %; bearing rate of hybrid of PMeS polyploid rice and other polyploid rice variety over 70 % and that of PMeS polyploid rice and wild rice variety over 65 %. The present invention solves the problem of low bearing rate of polyploid rice and may be used in breeding polyploid rice variety.
Owner:WUHAN POLYPLOID BIOTECH CO LTD
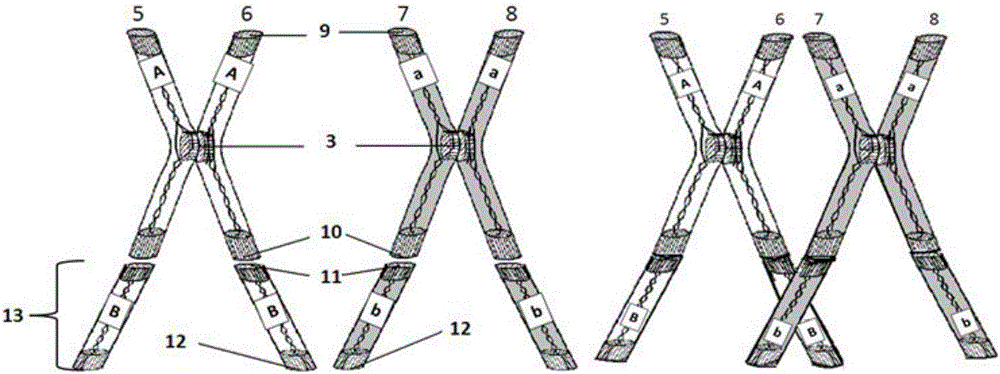
Teaching model for demonstrating cell division
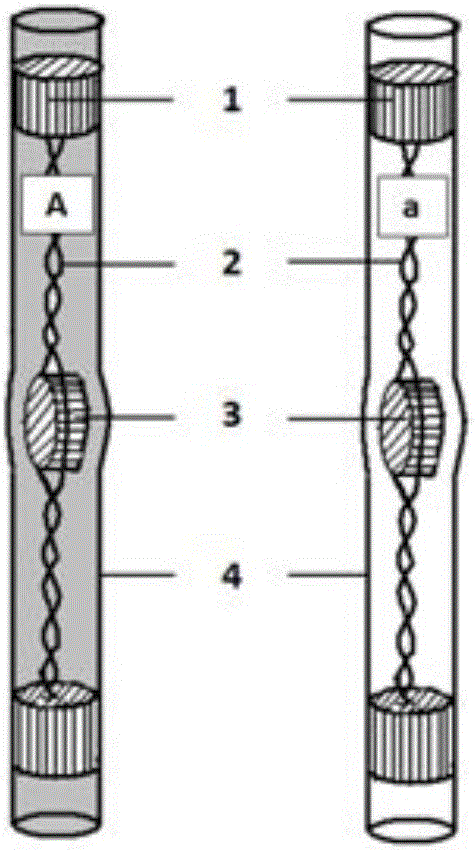
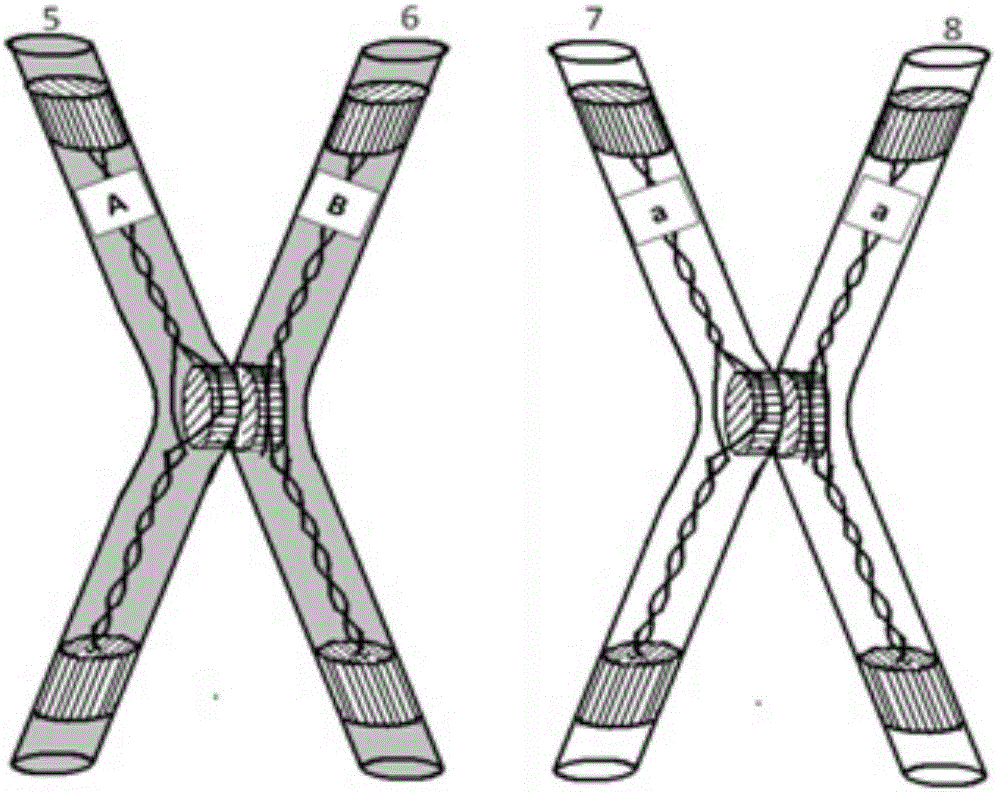
A teaching model for demonstrating cell division is composed of a flexible transparent chromosome magnetic model, a homologous chromosome cross exchange model, and a cell division telescopic rope model. The flexible transparent chromosome magnetic model is used for demonstrating the behavior relationship of chromosome, chromatid, DNA and gene in the processes of mitosis and meiosis, demonstrating the relationship between meiosis and the basic genetic laws and demonstrating the chromosome number and structure variation. The homologous chromosome cross exchange model is used for demonstrating cross exchange in the tetrad stage of meiosis. The cell division telescopic rope model is used for demonstrating depression and hanging division in the middle of cytomembrane in the process of animal cell division and demonstrating a dynamic change process in which a cell plate is extended to a cell wall and one cell is divided into two cells in the late stage of plant cell separation.
Owner:郭士安
Immunofluorescence microscopy observation method for marine bivalve meiosis device
InactiveCN101639441AEasy to operateOperation time savingBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceCytochemistryFluorescence
The invention relates to cytochemistry and cellular immunology, which are particularly used for observing a marine bivalve meiosis device through immunofluorescence microscopy. A sample can be observed after pre-treatment of fixing and the like, dyeing and flaking. The sample is fixed by phosphate buffered saline (PBS) of paraformaldehyde at a mass percentage concentration of 2 to 6 percent; then,permeabilization treatment and sealing treatment are performed sequentially; immunofluorescence dyeing is performed on sample spindle bodies, and fluorescence dyeing is performed on chromosomes withthe phosphate buffered saline containing propidium iodide of which the concentration is 5 to 20 mg of per liter; and the sample is flaked after dyeing for observation through fluorescence microscopy.The cytological immunofluorescence observation method is suitable for observing the spindle bodies and the chromosomes of the marine bivalve meiosis device synchronously, has the advantages of simpleand direct operation, high definition and high study efficiency, and is a qualitative, positioning and quantitative cytological immunofluorescence observation method which inosculates forms and functions.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
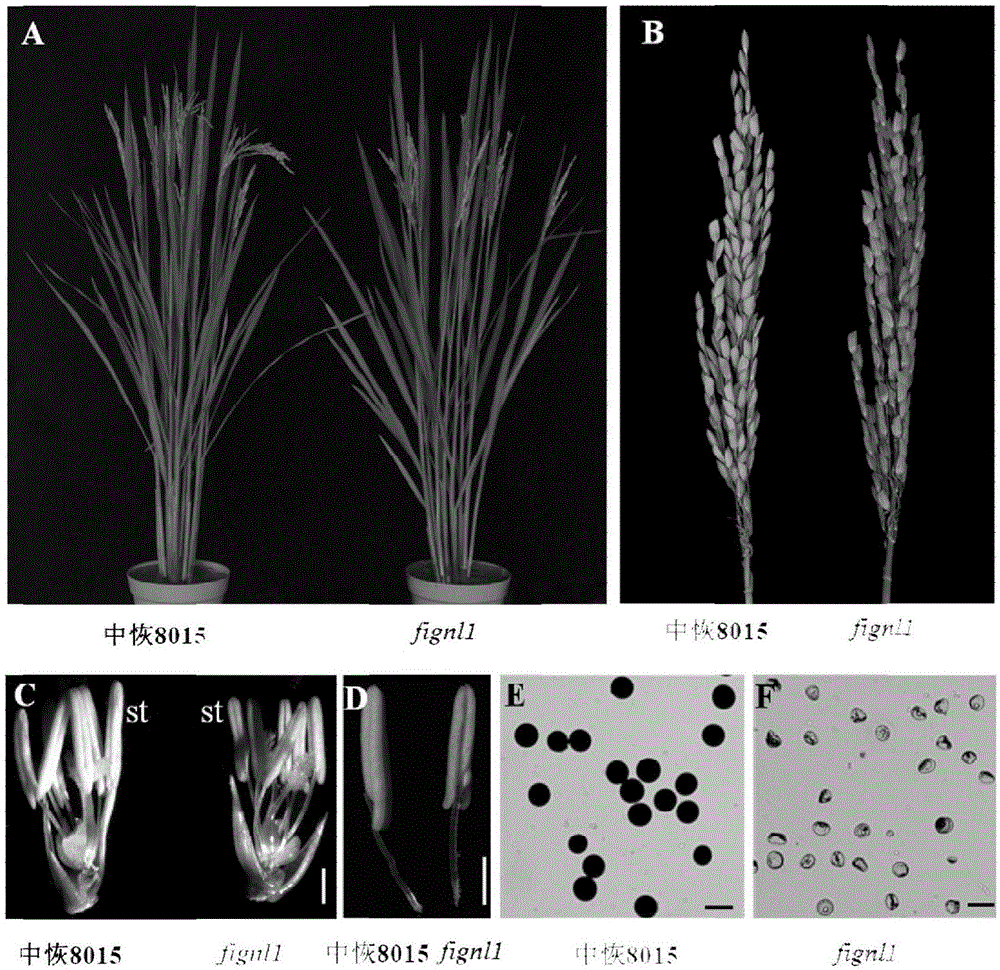
Oryza sativa male sterility gene OsFIGNL1 (Oryza sativa Fidgetin-like 1) and application thereof
The invention relates to an oryza sativa male sterility gene OsFIGNL1 (oryza sativa Fidgetin-like 1) and an application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene OsFIGNL1 is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. One function lost mutant of OsFIGNL1 is obtained through <60>Co-gamma mutagenesis, and the mutant in a field planting environment shows the following characteristics: vegetative growth of plants are normal, male plants are sterile, pollen is 100% typically abortive, and development of female gametes is not affected. Meiosis squashing operation shows that chromosome behaviors are severely affected by function loss of OsFIGNL1 during meiosis, and developmental defects of microspores are caused finally. The mutant can be applied to breeding of new dominant varieties of oryza sativa hybrids. The gene OsFIGNL1 can serve as a functional gene for regulating meiosis of oryza sativa to be applied to oryza sativa heterosis creation work in future and has huge development and utilization value and broad market application prospect.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com