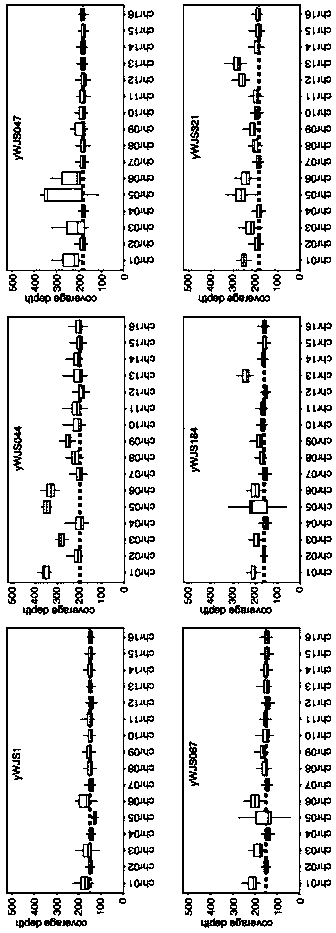
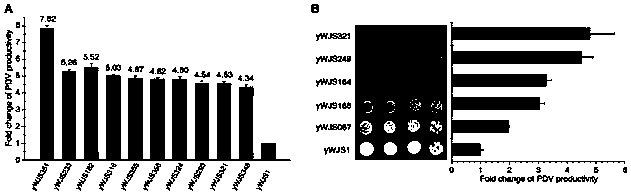Patents
Literature
32 results about "Yeast chromosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Yeast Artificial Chromosome (YAC) Yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) is a human-engineered DNA molecule used to clone DNA sequences in yeast cells. YACs are often used in connection with the mapping and sequencing of genomes.
Method for knocking down brewing yeast chromosome
ActiveCN107858346AKnockout simpleKnockout EfficientHydrolasesStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyYeast chromosome
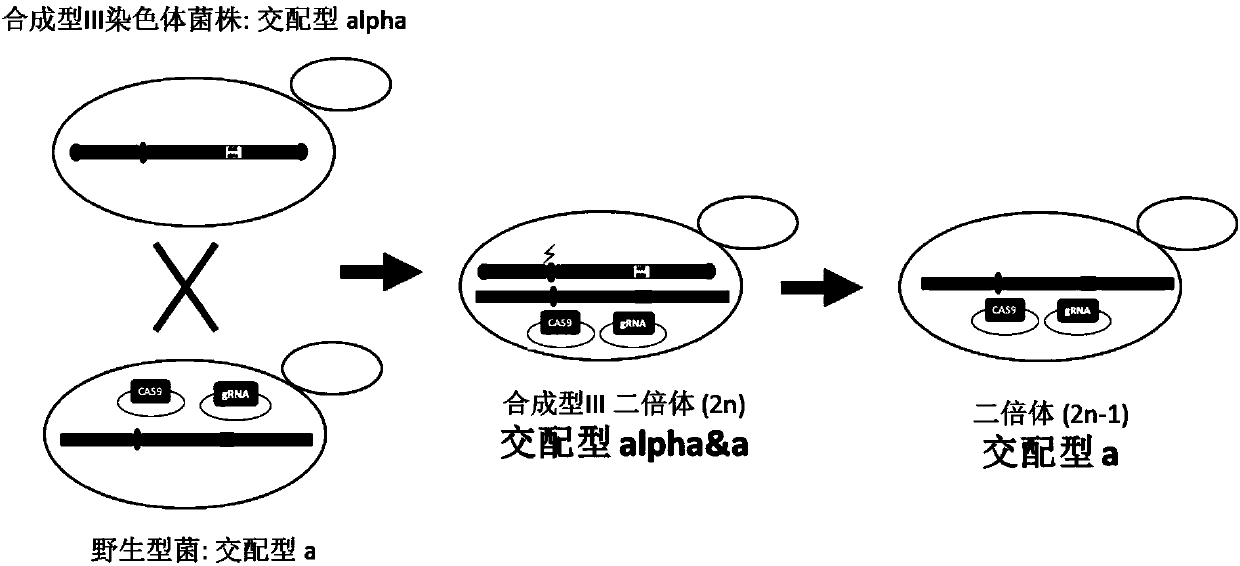
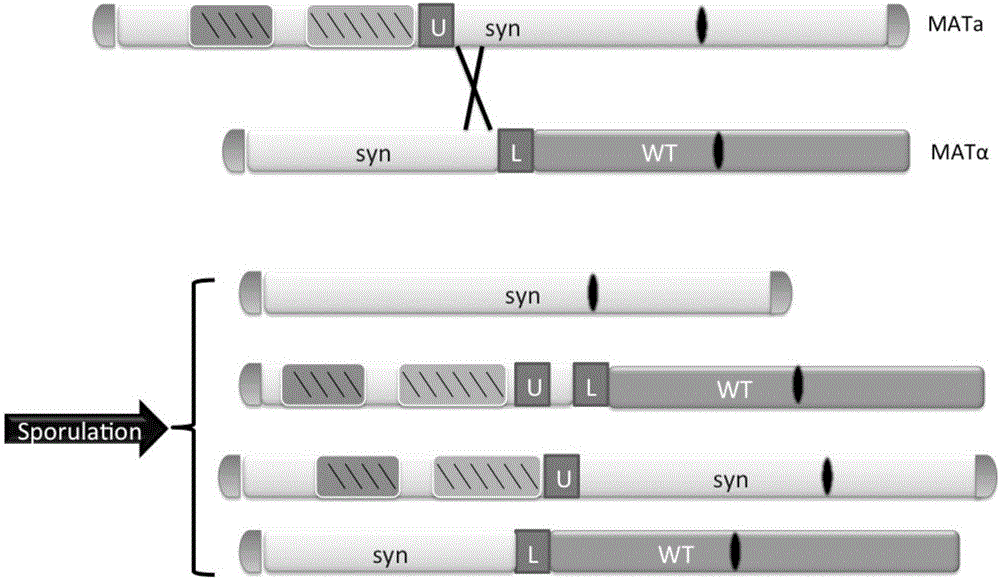
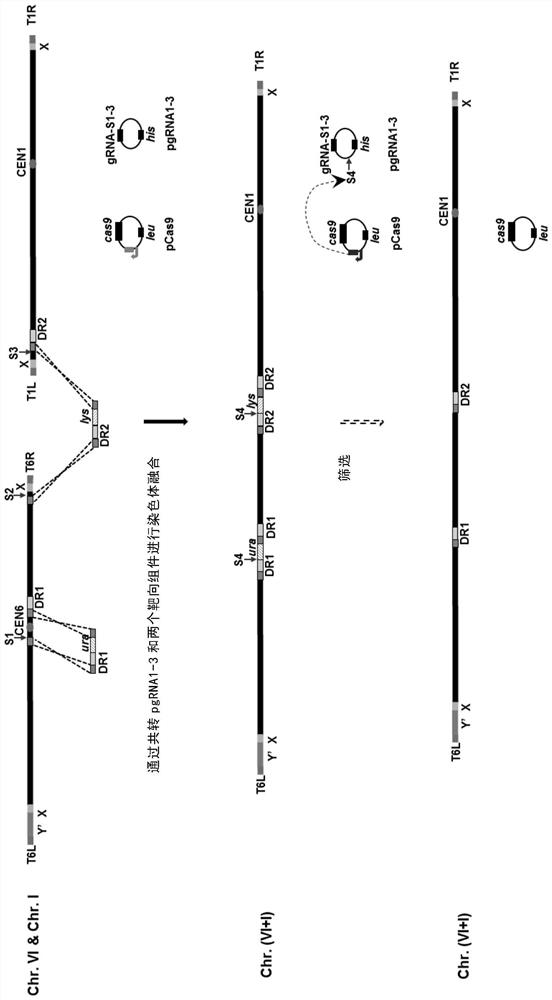
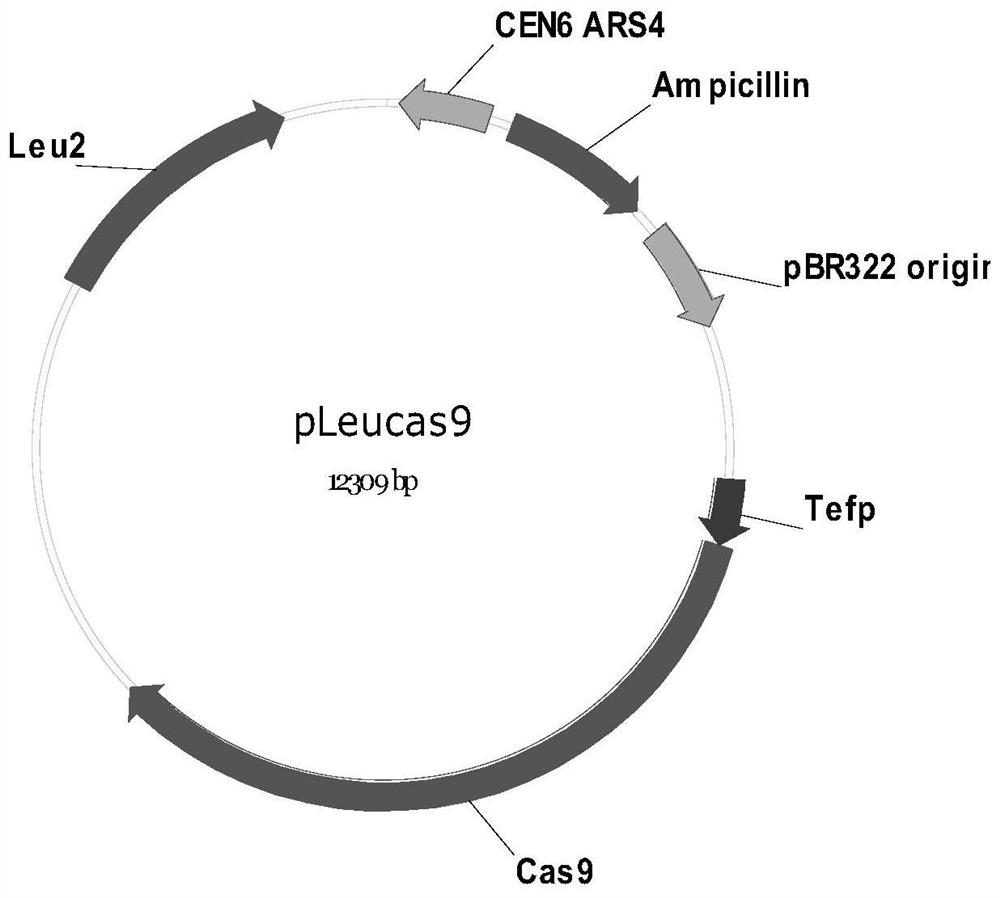
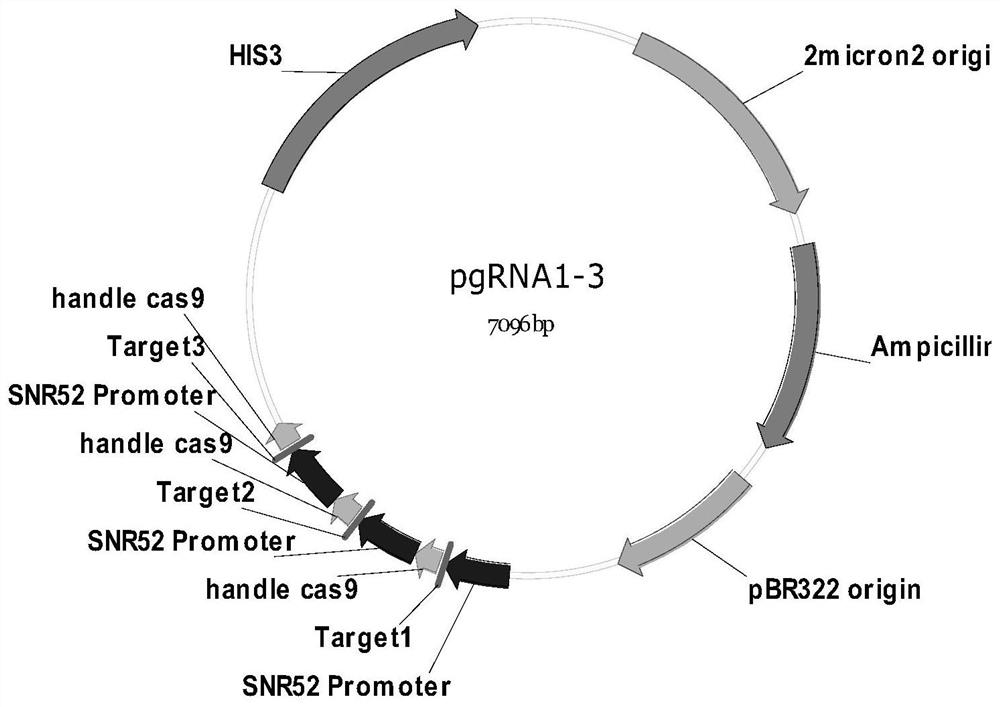
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and specifically discloses a method for knocking down brewing yeast chromosome. The method is characterized in that the complete yeast chromosome is cut according to the CRISPR / Cas9 base technology; a specificity target close to centromere is selected; a corresponding guide RNA is designed to guide Cas9 protein to generate an incision closeto the centromere, thus realizing the knocking down of the whole chromosome. Compared with the conventional method for losing the whole chromosome in manners such as inducing through a Ga1 promoter, and reductional division, the method has the advantages that the brewing yeast chromosome is simply, efficiently and quickly cut; the cross exchange of sister chromatids can be avoided; the chromosome-knocked-down homozygous brewing yeast diploid strain can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation for porcine defensin engineering yeast strain
InactiveCN101275118AIncrease production capacityReduce manufacturing costFungiMicroorganism based processesYeast chromosomeBiotechnology
The present invention provides a preparing method of a porcine defensins engineering yeast strain, firstly, the porcine defensins gene is modified by method of genetic site-directed mutagenesis, mutant of porcine defensins gene having high biological activity is screened, then the porcine defensins gene which codon is optimized is artificially synthesized by the conventional codon of yeast strain, the engineering yeast strain having high yield, strong biological activity for producing porcine defensins is obtained by multiple screens. The porcine defensins engineering yeast strain kills the yeast by heating after fermented, directly used as feed additive by concentrated, having no separating and extracting courses, reducing the production cost of the defensins, improving the economic effect of the production enterprise. The invention provides conditions for mass industrial production of defensins, resolving the displacement of the porcine feed antibiotics additive.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Yeast recombinant collagen
InactiveCN107090458AEasy to operateMaintain natural structureConnective tissue peptidesFungiBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
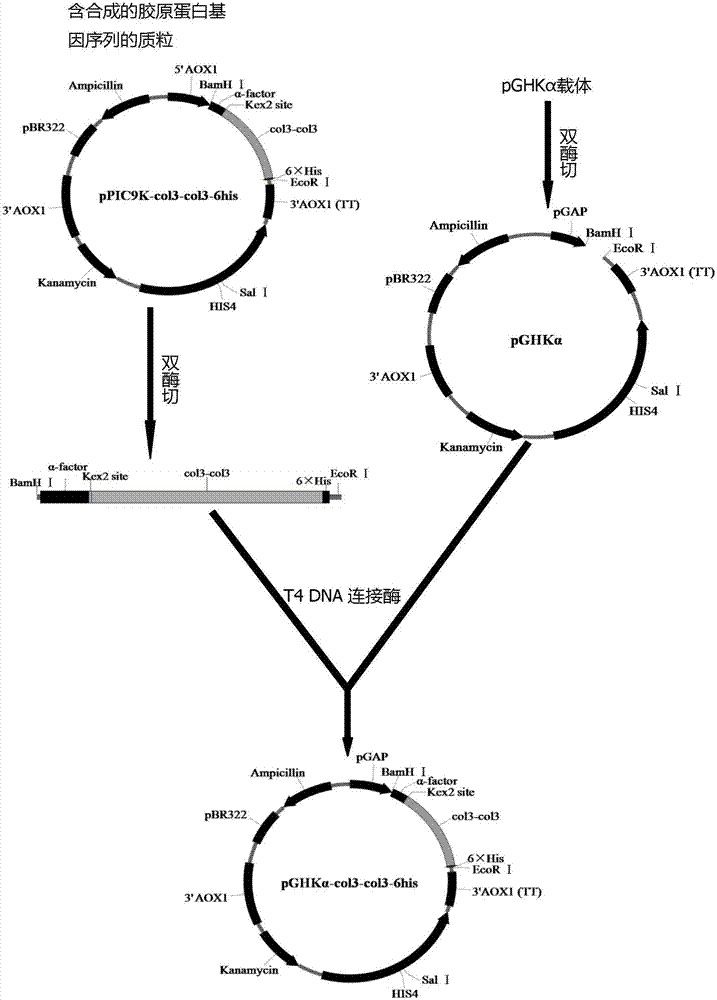
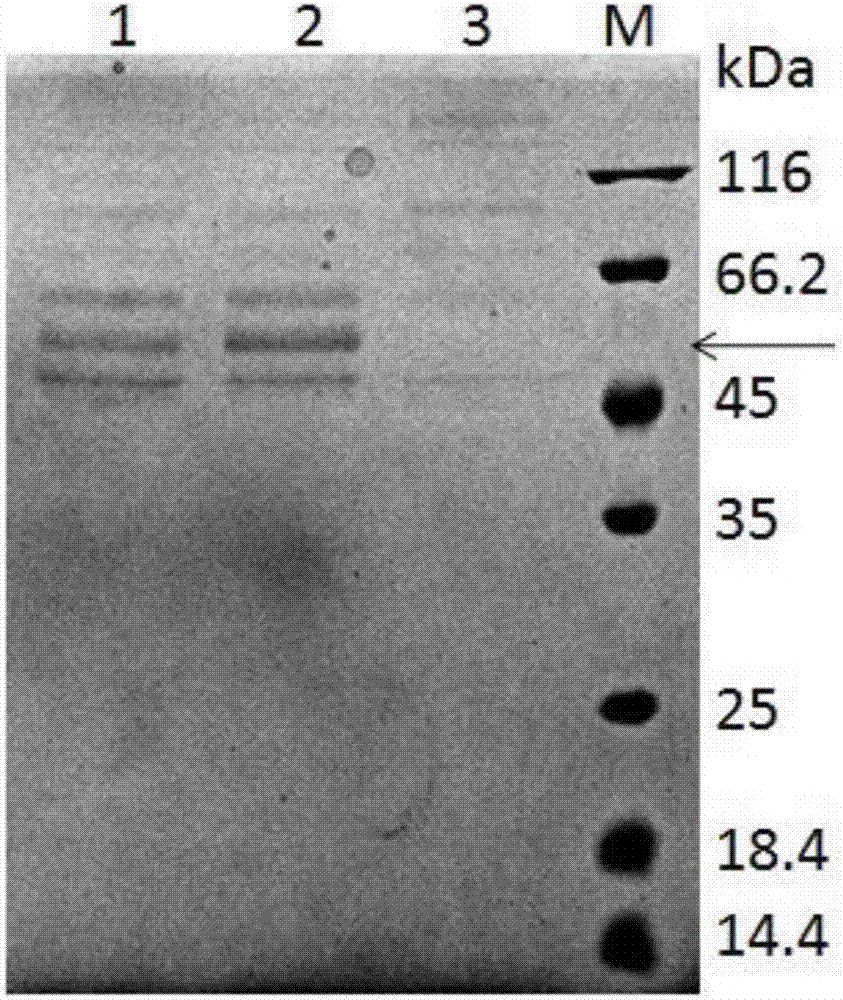
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to a production method for a yeast recombinant collagen, which includes construction of recombinant pichia pastoris engineered strain and production of constitutively and secretively expressed recombinant collagen without methanol induction. The invention first utilizes conventional codons of pichia pastoris at the genetic level to optimize a collagen gene sequence and performs artificial total gene synthesis, the optimized collagen gene sequence is then integrated into yeast chromosome, and thereby a constitutively and secretively expressed recombinant pichia pastoris engineered strain is constructed. The fermentation process is easy to operate, yield is high, and the separation and purification of the product are simple; methanol induction is not needed, the fire-proof and explosion-proof indexes of production equipment and factory buildings are low, and the production environment is environmentally friendly and pollution-free; and no toxic and harmful substances are use, so the product is safer. A specific affinity purification label is carried, the product with higher purity can be easily obtained, and the product can be applied to biomedical materials.
Owner:JIANGSU TRAUTEC MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
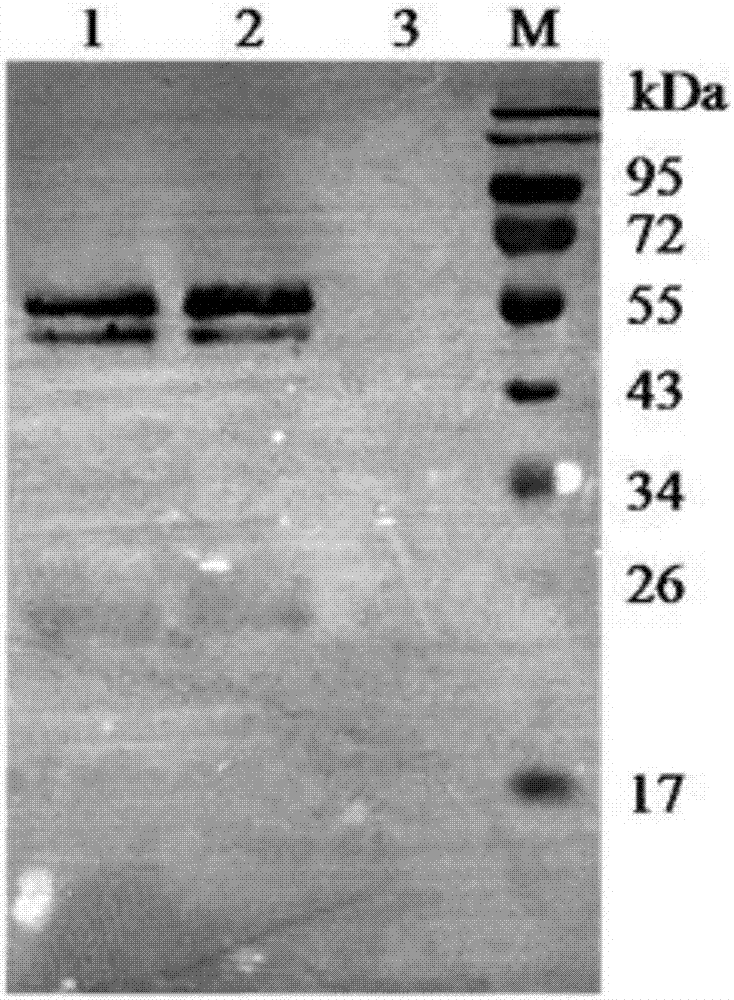
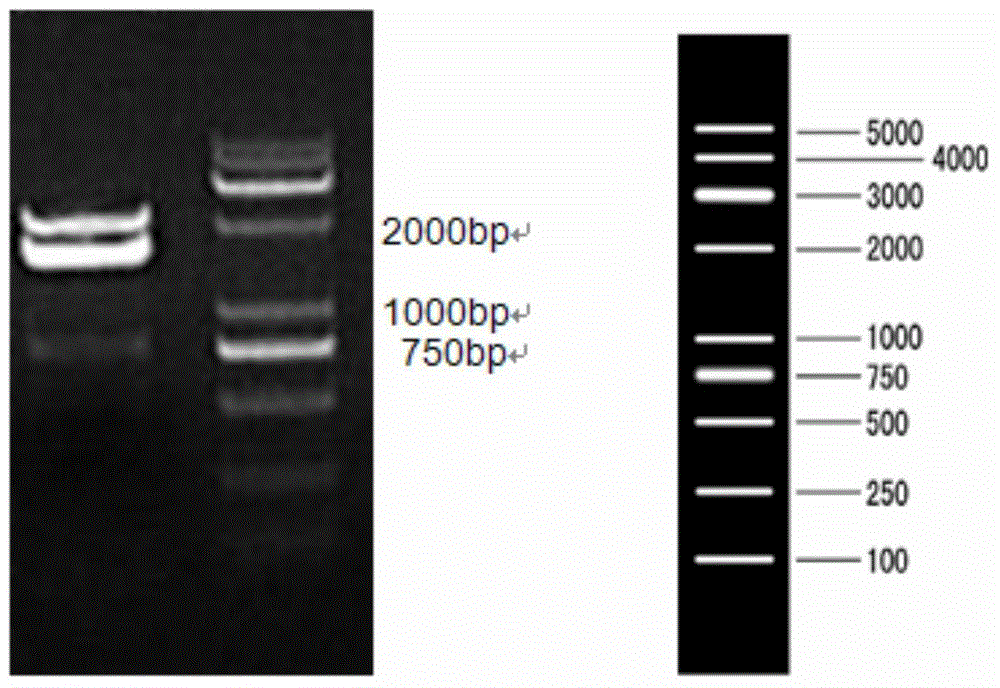
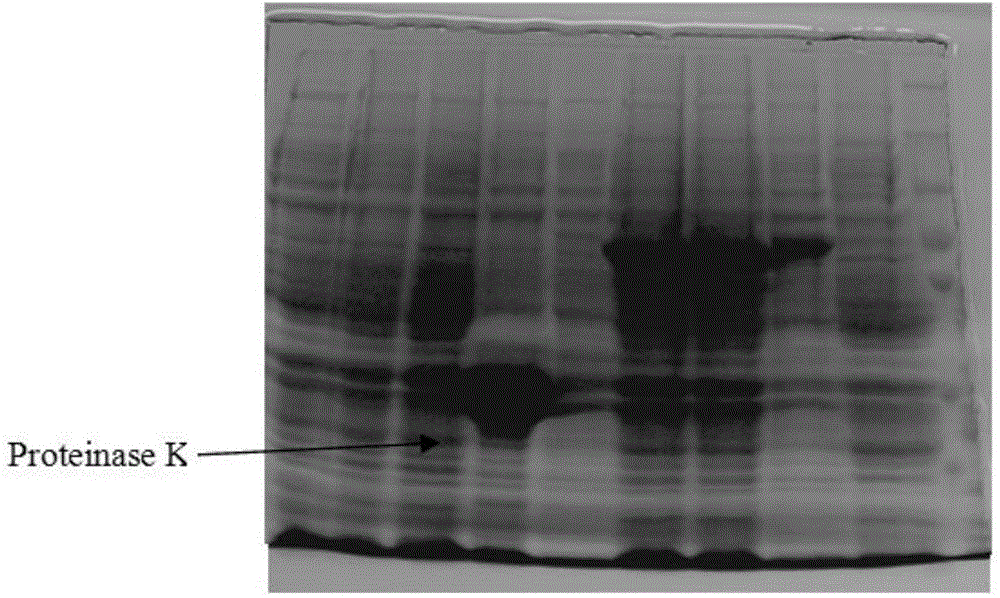
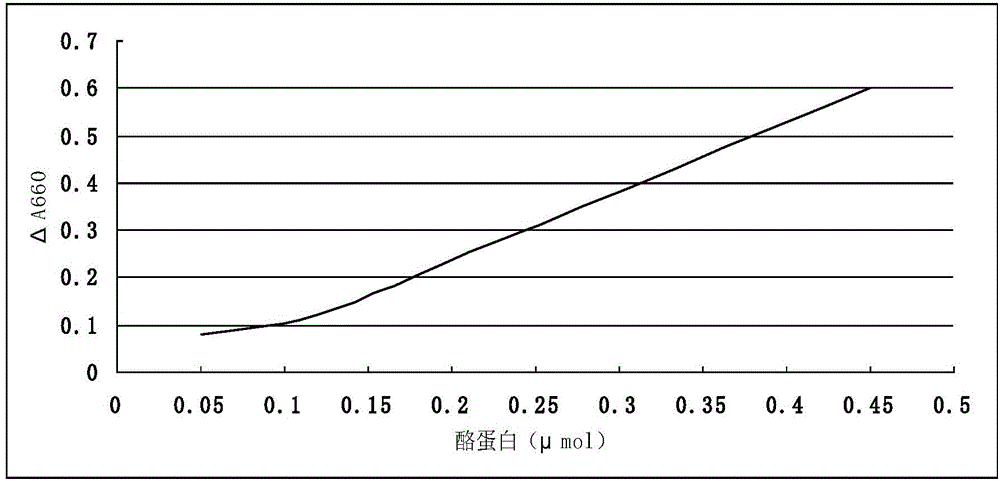
Genetically engineered protease K and production method of protease K
The invention discloses genetically engineered protease K. Enzymatic activity of the protease K is at least two times that of conspecific natural protease, production period can be shortened to 3-4 days, and production efficiency is greatly improved. The production method comprises the following steps of performing synthesis and amplification to obtain protease K genes; cloning and transforming to integrate the protease K genes to yeast artificial chromosome; selecting a high-quality bacterial strain capable of expressing target proteins effectively by screening yeast; performing high-density fermentation to express the protease K by using a high-density fermentation technology; and performing separation and purification on protein to obtain the high-purity and high-activity protease K.
Owner:天津旭晨科技有限公司
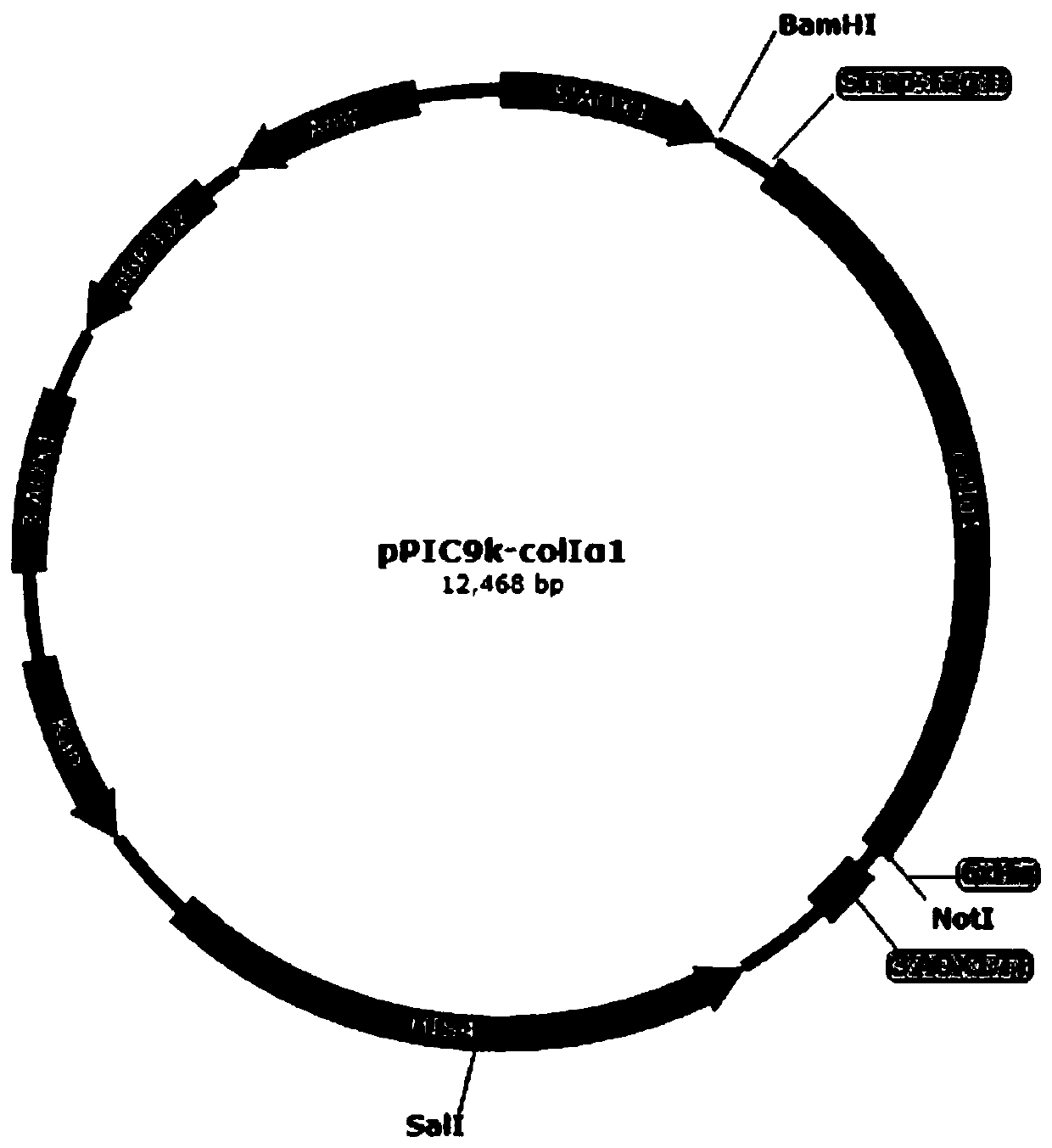
Yeast recombinant human type I collagen alpha 1 chain protein, synthesis method and application thereof
PendingCN110964099AInefficient translationOptimize secondary structureCosmetic preparationsConnective tissue peptidesPichia pastorisYeast chromosome
The invention discloses a yeast recombinant human type I collagen alpha 1 chain protein, a synthesis method and application thereof. The recombinant human type I collagen alpha 1 chain protein of theinvention consists of an N-terminal affinity purification marker, a human type I collagen alpha 1 chain mature peptide sequence and a C-terminal affinity purification marker. The bispecific affinity purification markers designed at the two terminals are beneficial to purification of the recombinant protein and are also beneficial to detection and full-length identification of the recombinant protein. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: firstly optimizing collagen gene sequence by utilizing common codons of pichia pastoris at gene level and synthesizing the whole gene artificially, then constructing a recombinant vector through PCR, enzyme digestion, connection and the like, and integrating into yeast artificial chromosome to construct recombinant pichia pastoris engineeringbacteria for secretory expression of the recombinant human type I collagen alpha 1 chain protein. The bispecific affinity purification marker carried by the recombinant human type I collagen alpha 1chain protein of the invention can be subjected to two-step specific purification to easily obtain high-purity products.
Owner:JIANGSU TRAUTEC MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
A kind of antibacterial polypeptide and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN102295694AMass preparationEfficient preparationAntibacterial agentsBiocidePichia pastorisYeast chromosome
The invention relates to an antimicrobial polypeptide, and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the field of biomedicine. The amino acid sequence of the antimicrobial polypeptide provided by the invention is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The preparation method comprises the following steps: after linearizing the coding sequence of the antimicrobial polypeptide with restriction endonuclease, transforming into Pichia pastoris GS115 by an electric shock method, recombining onto the Pichia pastoris chromosome by homology, screening high-expression strains with G418, and inducingthe expression with methanol, thereby obtaining the antimicrobial polypeptide. The test proves that the antimicrobial polypeptide has the functions of inhibiting and killing multiple bacteria, viruses, tumor cells, carcinomatous solid tumors, fungi and protozoa, can not easily generate resistance, and thus, can be used as an ideal antibiotic substitute, biological medicine for human and livestock, feed additive, preservative, bactericide or the like.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Yeast for dietary therapy of diabetes and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101824388AReduce biological activityImprove bioavailabilityFungiMetabolism disorderYeast chromosomeRestriction site
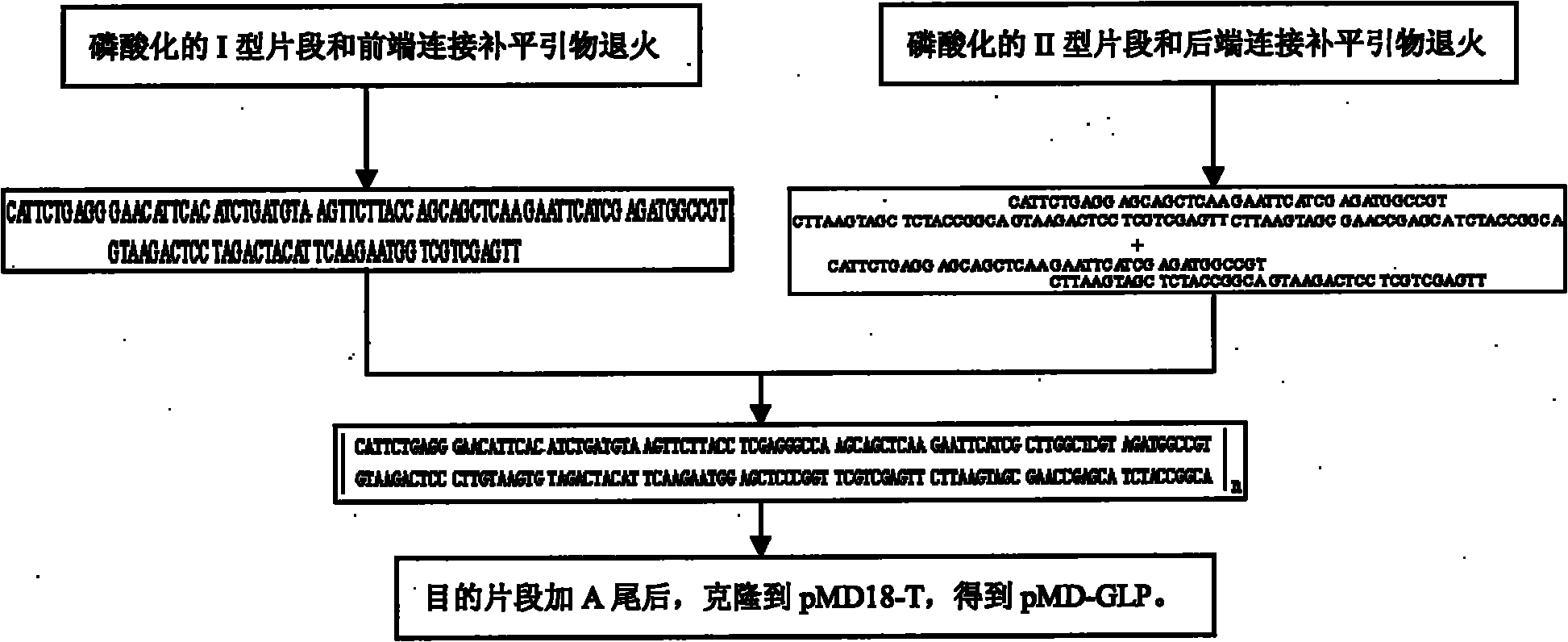
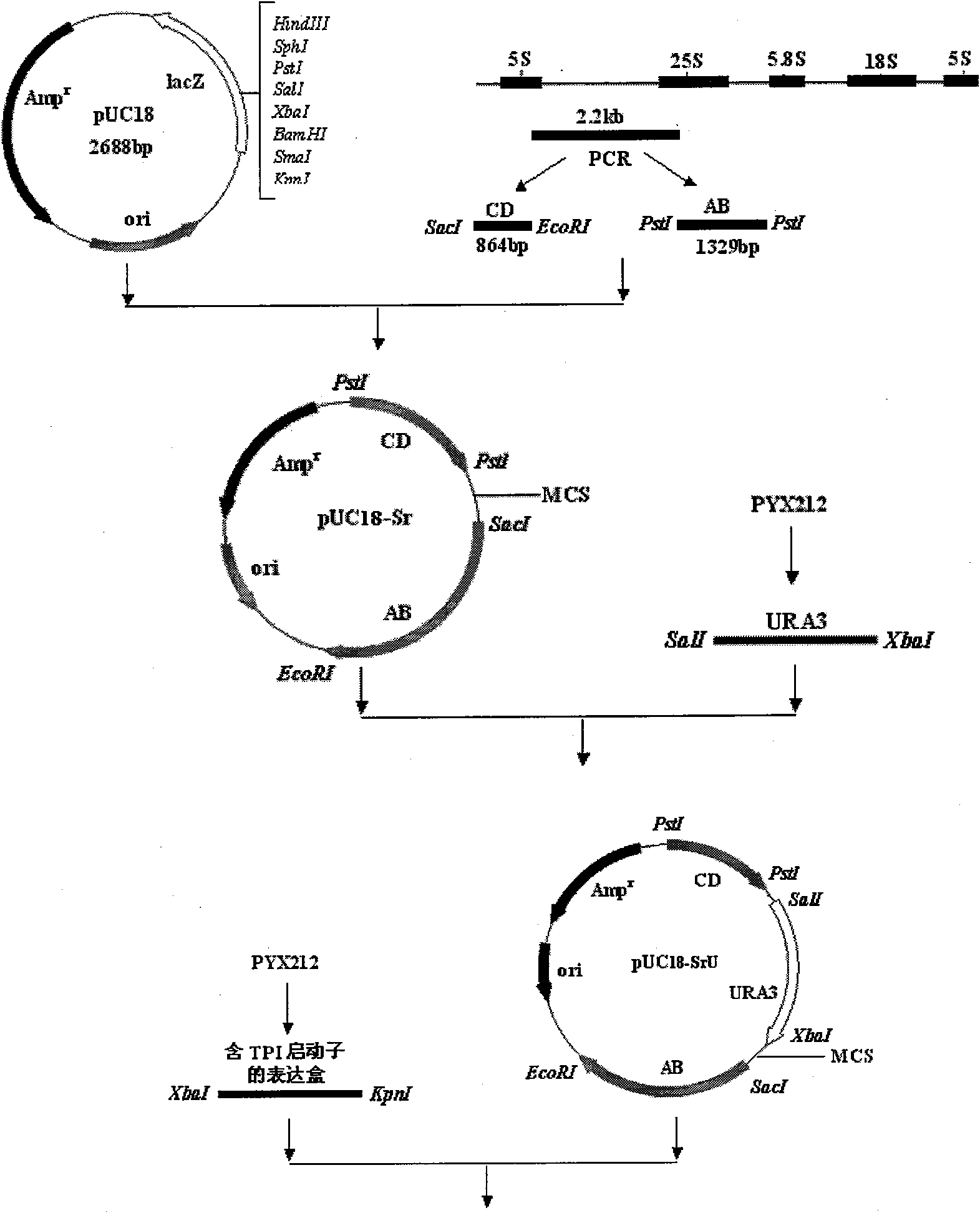
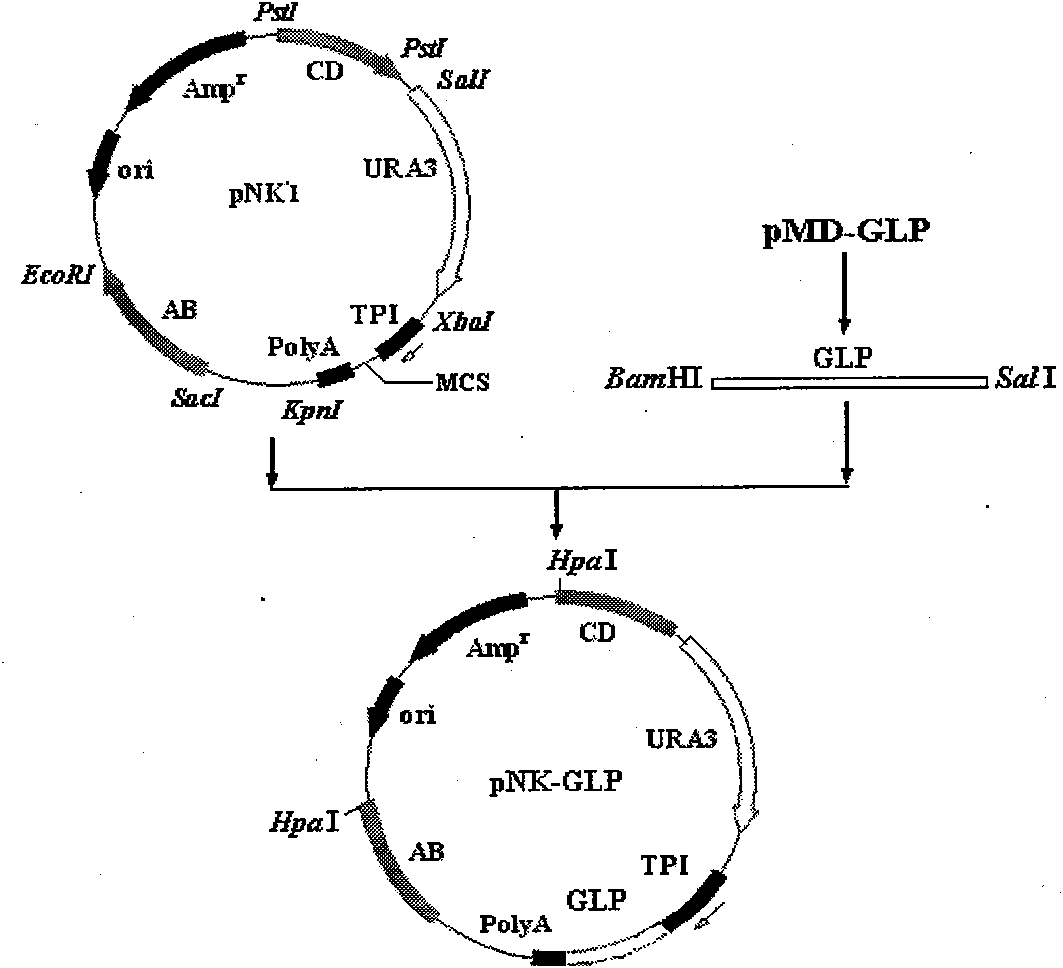
The invention describes a yeast for the dietary therapy of diabetes and a construction method thereof. A saccharomyces cerevisiae genome DNA as a template is used for amplifying two sections of rDNA sequences; pYX212 as a template is used for amplifying a nutritional marker gene URA3 and an expression cassette segment driven by a triosephosphate isomerase promoter; the four amplified products are respectively cloned at corresponding loci of pUC18, and thereby an integrating vector pNK1 is obtained. A DNA synthesization point mutation technique is then utilized to remove the restriction sites of dipeptidase VI and trypsin in the natural GLP-1 molecule, so that type I primer segments, type II primer segments and left and right connected filling primer segments are synthesized, and a ten-repeat tandem rolGLP-1 sequence is obtained by the method of step-by-step annealing and one-step connection, and is cloned in the pNK1, so that pNK-GLP is obtained. The pNK-GLP is then linearized, saccharomyces cerevisiae BJ2407 is transformed, and after screening, recombinant yeast SG2 is obtained. Because the rolGLP-1 gene is integrated in yeast chromosome, the recombinant strain can stably and efficiently express the characteristics of the rolGLP-1 and reduce the blood sugar level of a rat with hyperglycaemia, and can be used in the development of yeast biomedicine for treating diabetes.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
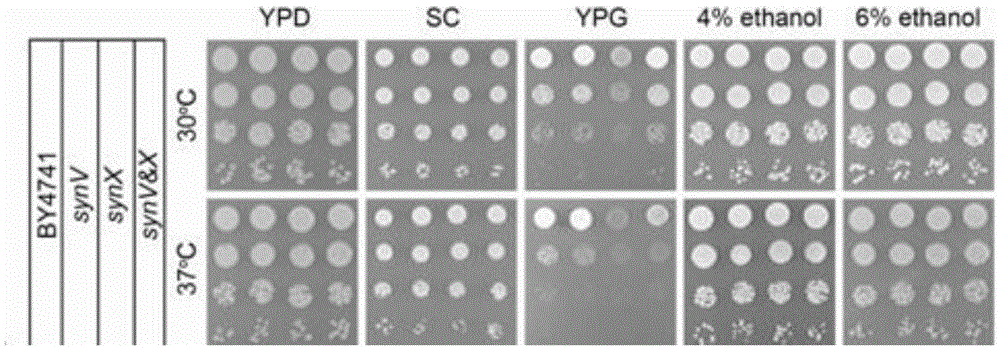
Transfer method for saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomes
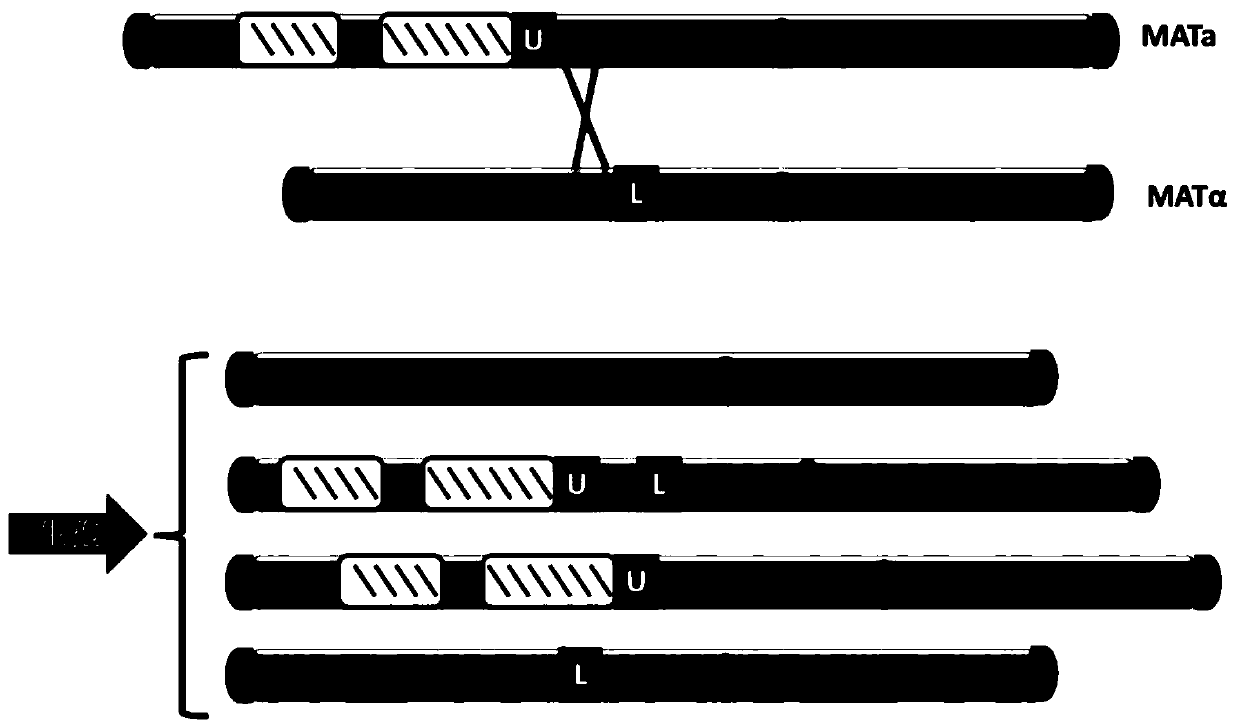
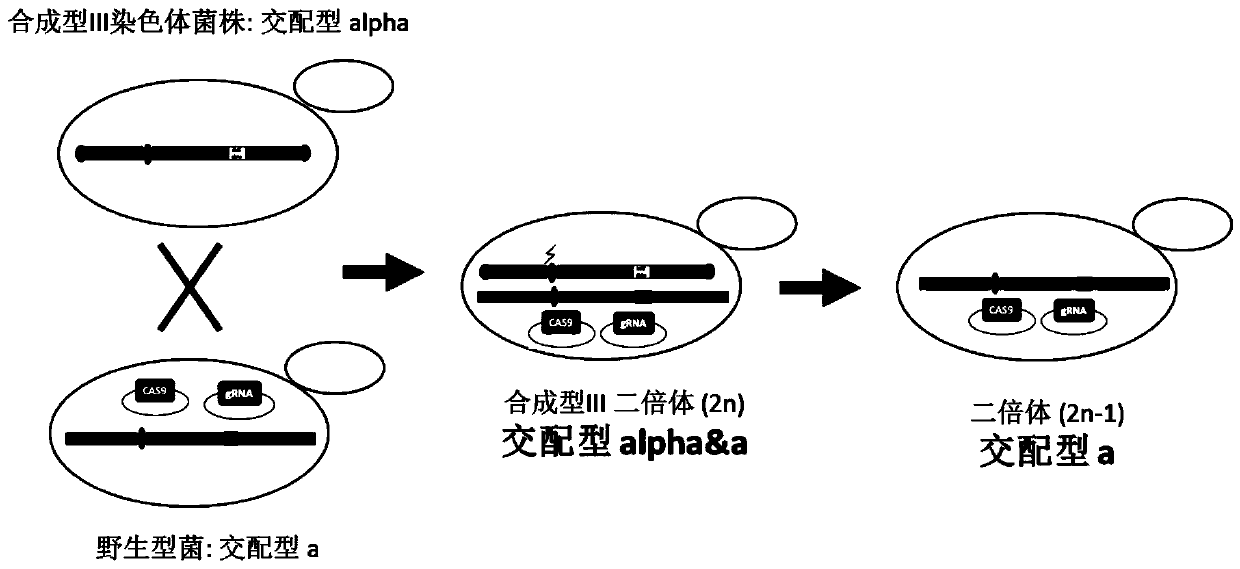
ActiveCN105602934AAchieve transferAvoid cross swapsMicrobiological testing/measurementHybrid cell preparationBiotechnologyYeast chromosome
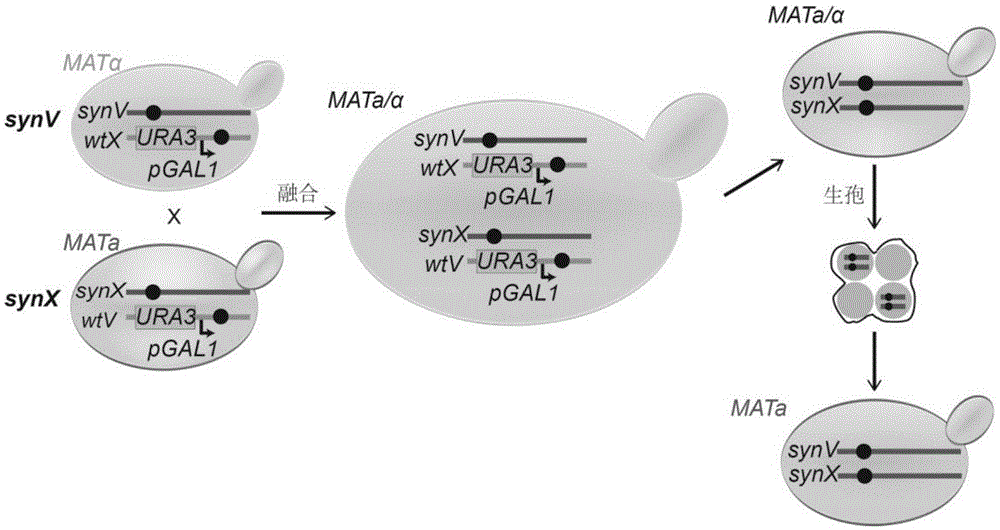
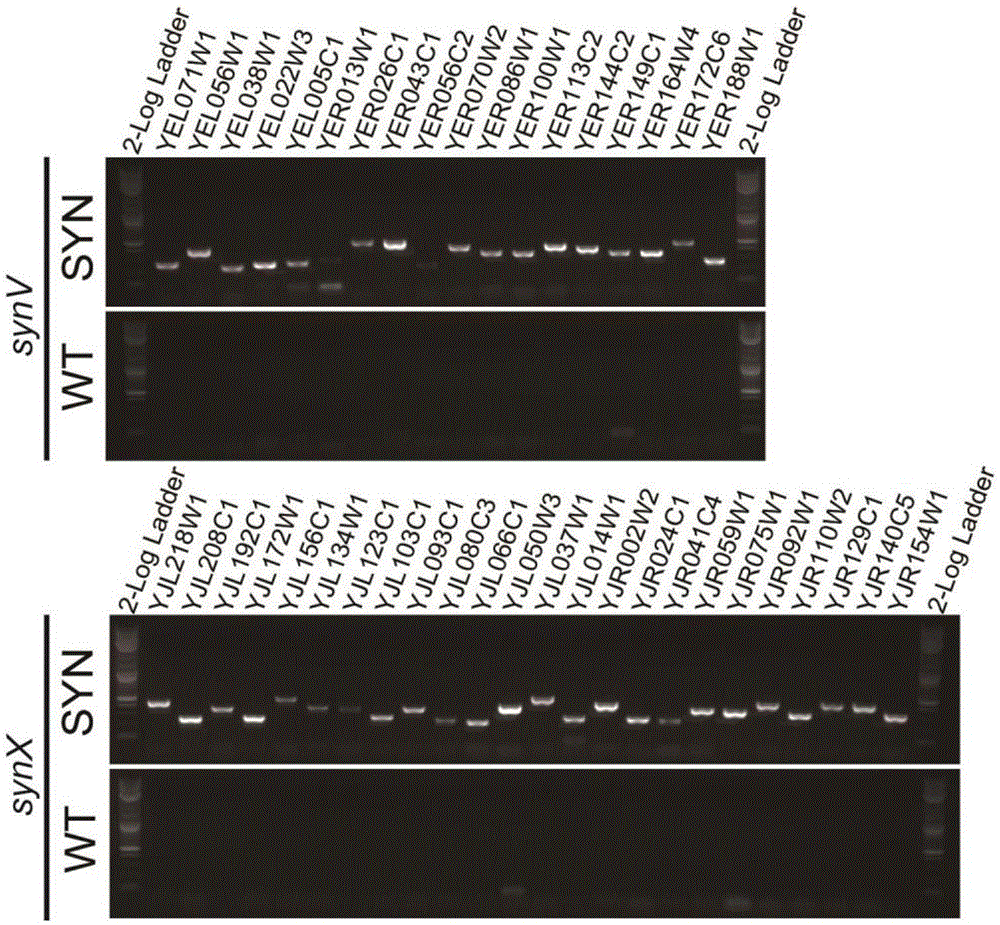
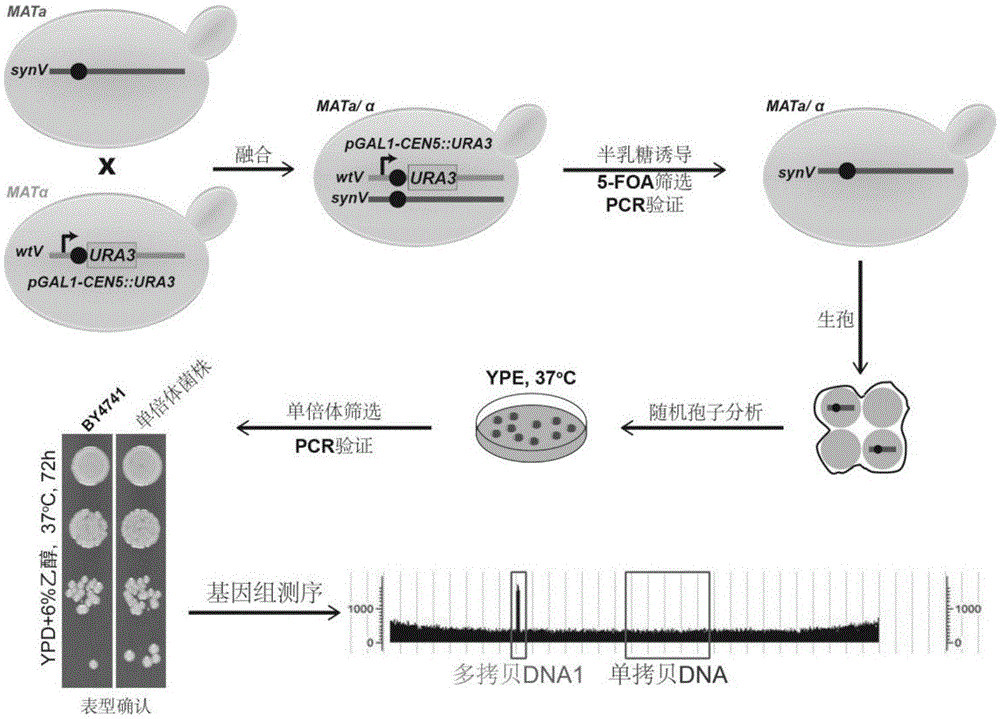
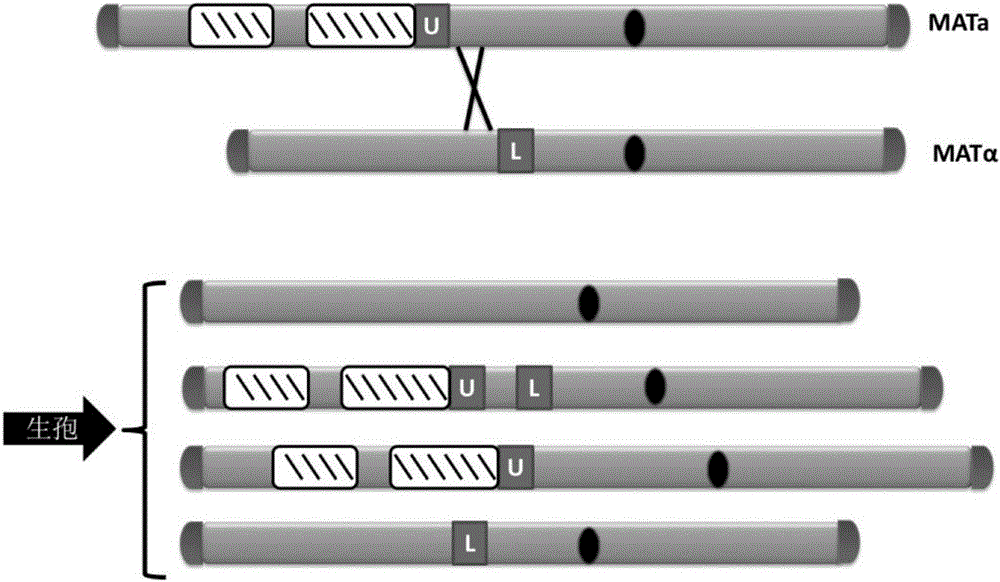
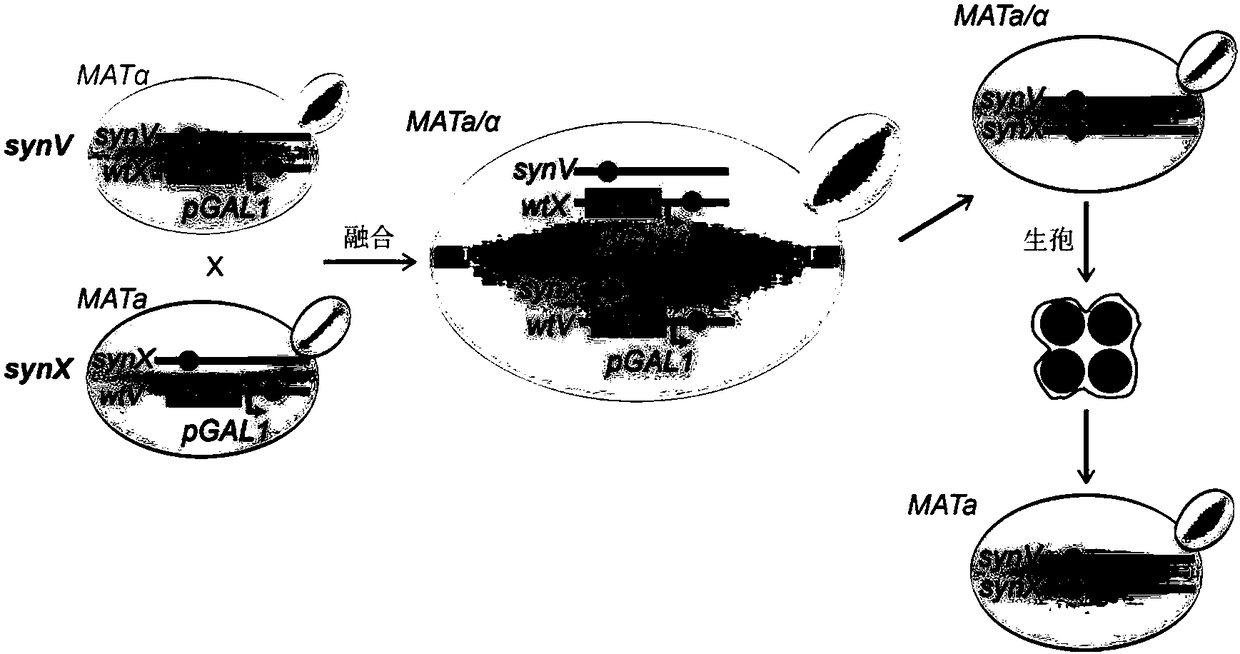
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to a transfer method for saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomes. A synthetic No.V chromosome saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a synthetic No.X saccharomyces cerevisiae strain are fused into a diploid strain through an endoreduplication backcross method, the wild No.V chromosome and No.X chromosome are induced to be lost through galactose, and screening is conducted through an SC+5-FOA culture medium; a saccharomyces cerevisiae haploid strain carrying the synthetic No.V and No.X chromosomes is obtained through spore splitting. Compared with existing achievements, the transfer method has the advantages that transfer of the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomes is rapidly achieved; cross swap of sister chromatids is avoided, and the saccharomyces cerevisiae haploid strain with the chromosomes transferred is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
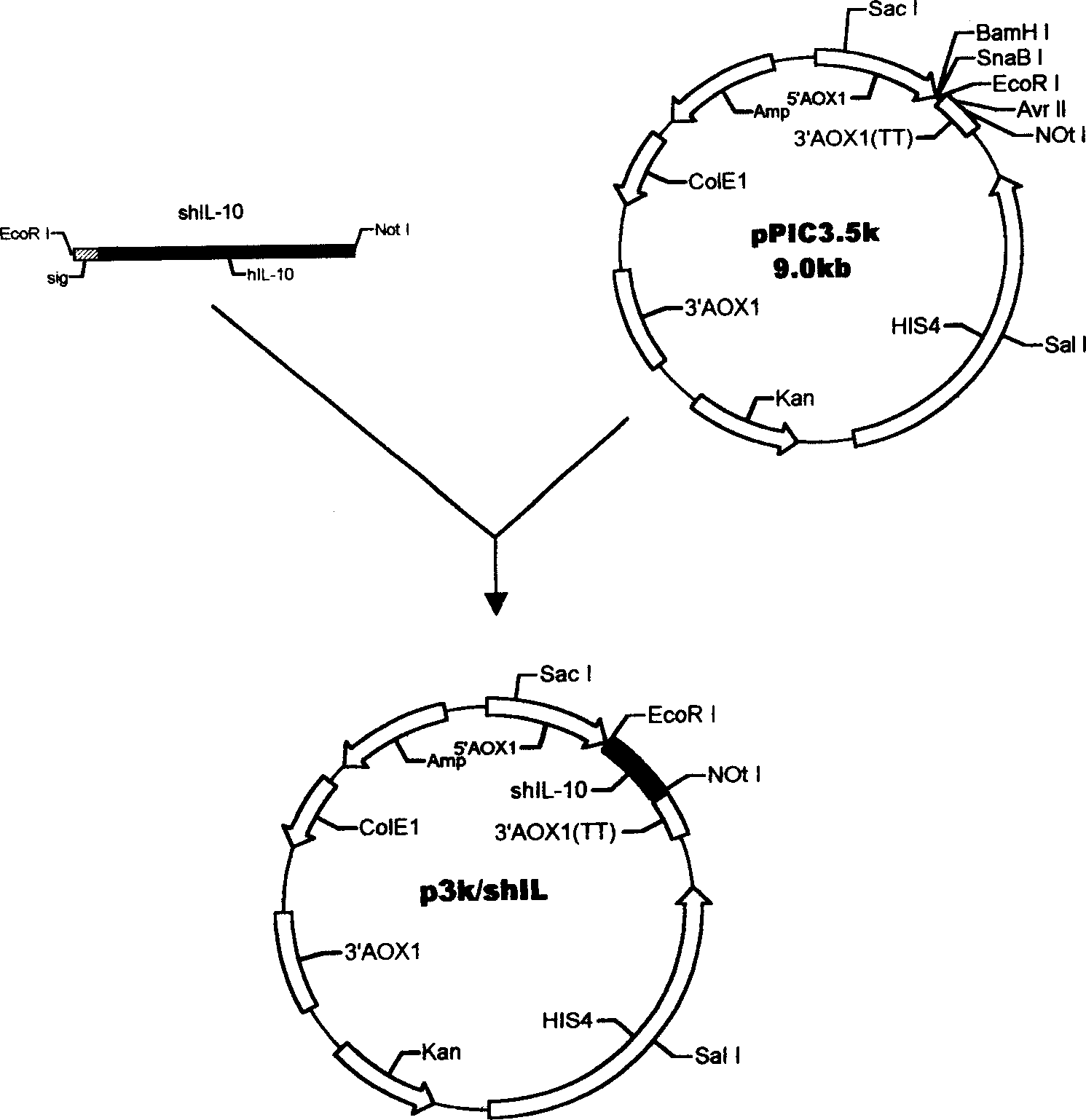
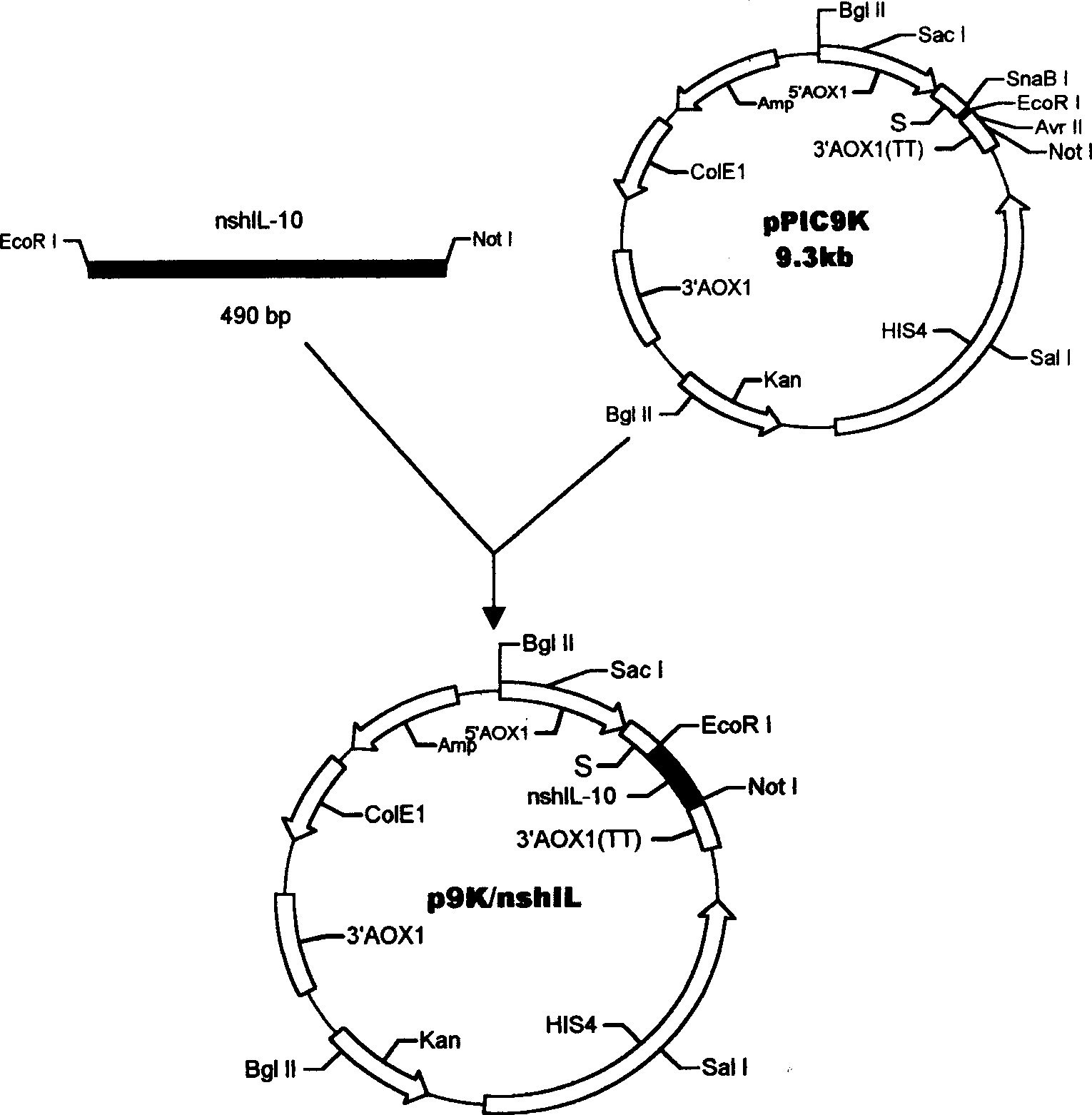
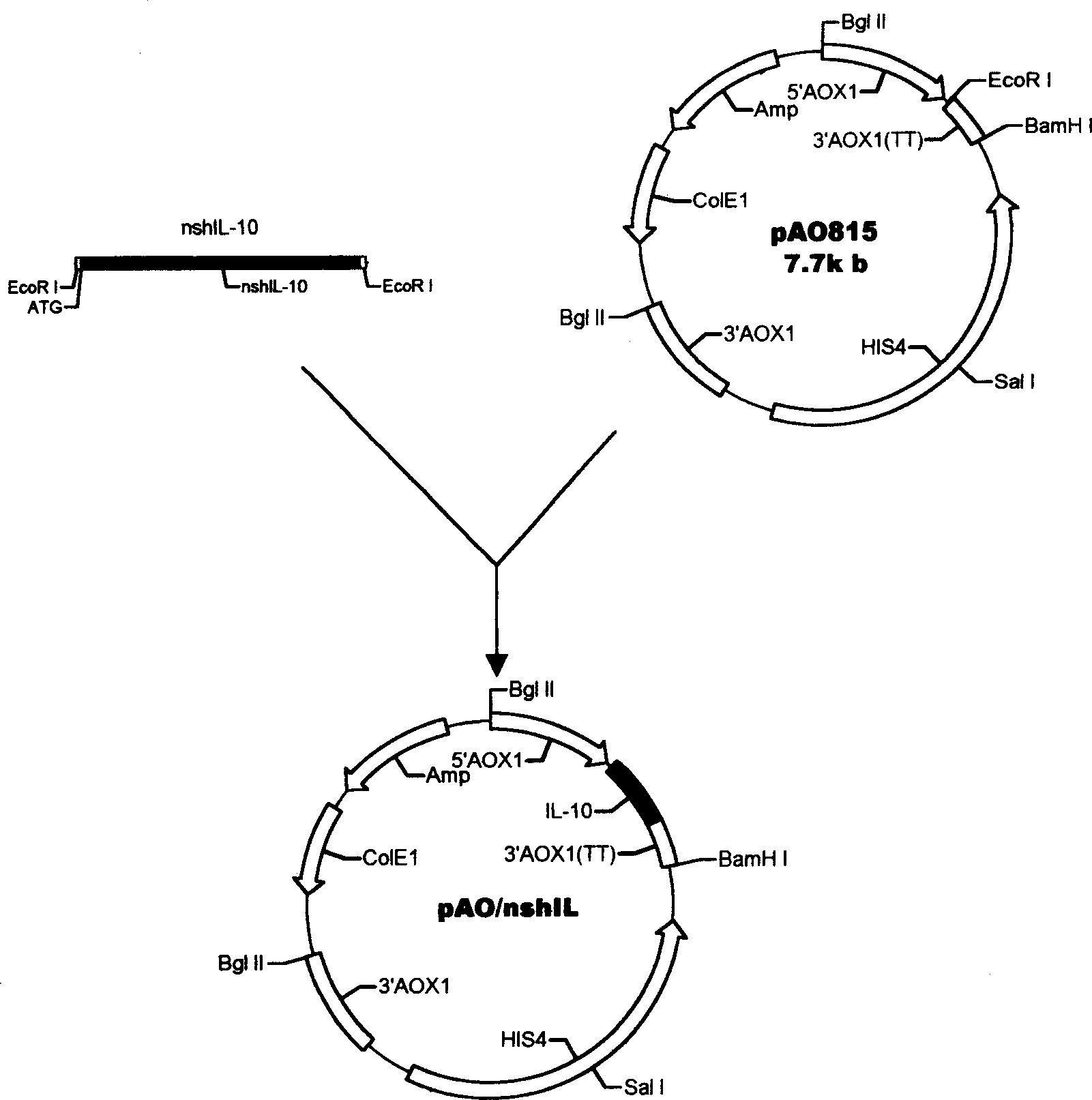
Method for yeast cell to express human interleukin 10
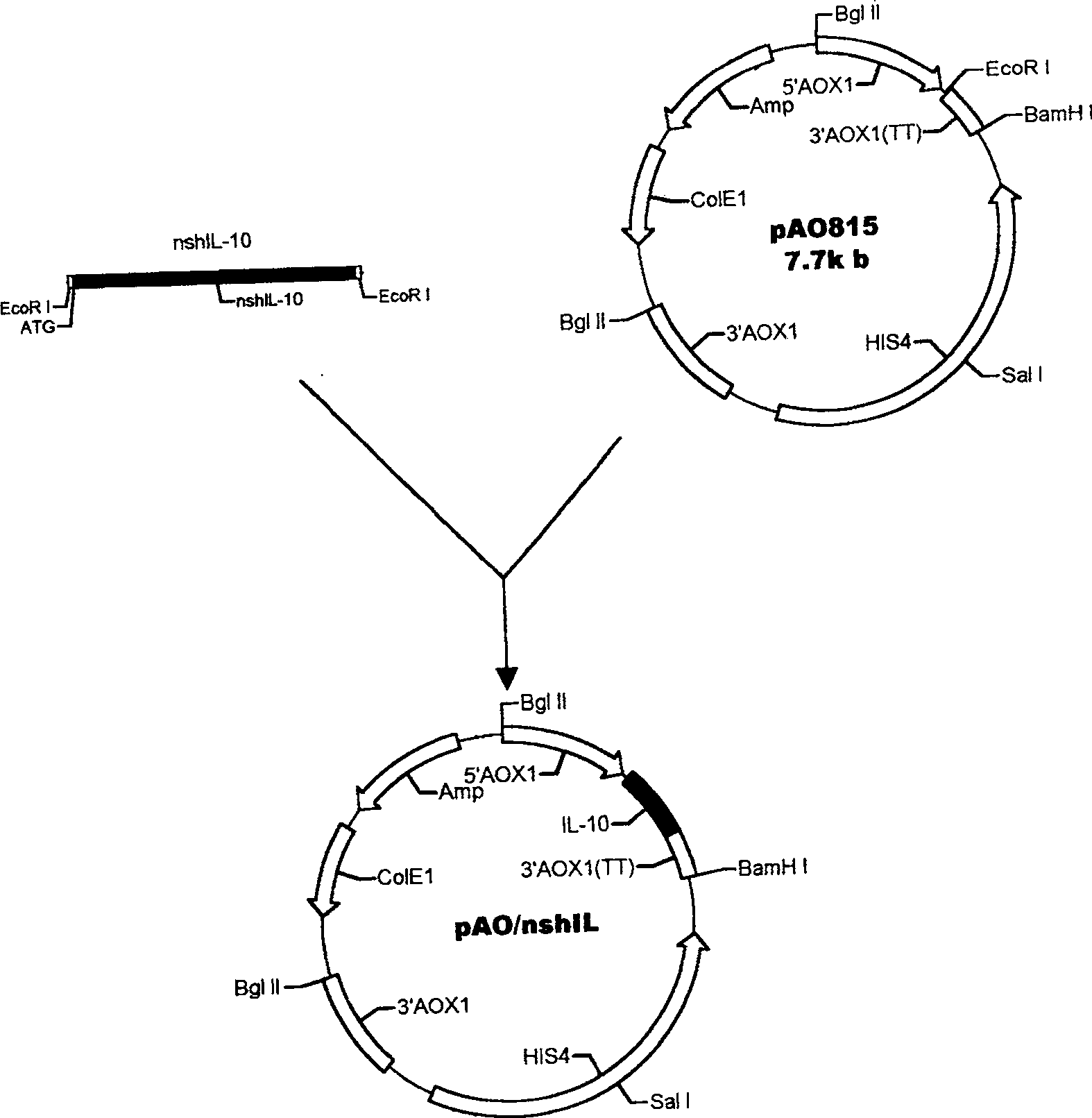
InactiveCN1506463AAvoid degradationSimple structureFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyYeast chromosome
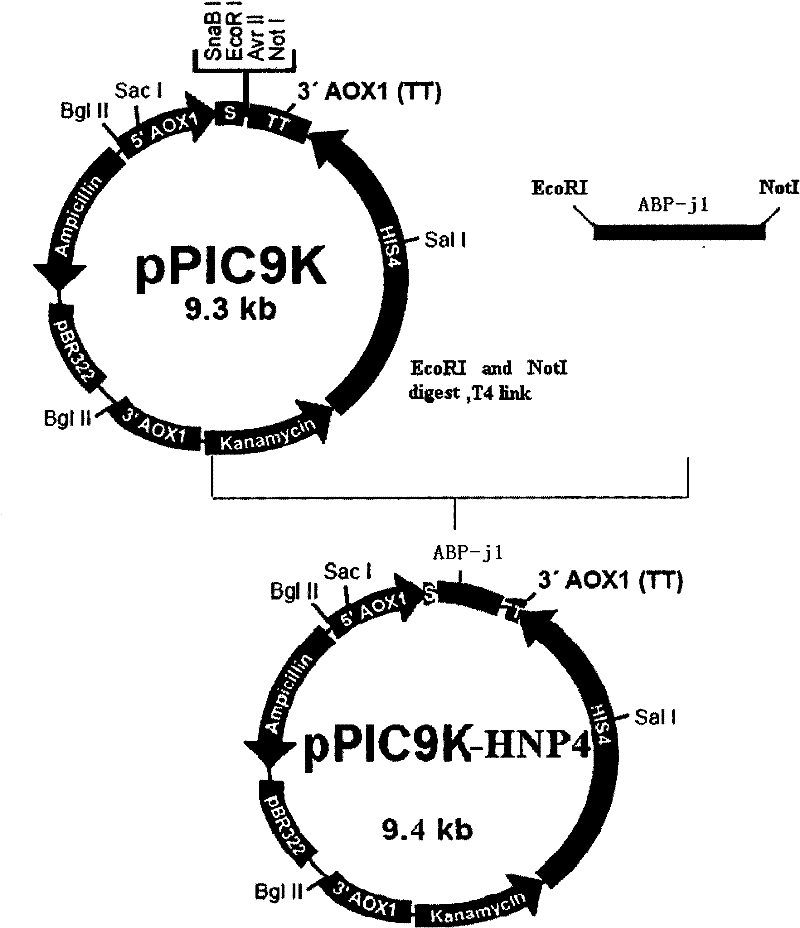
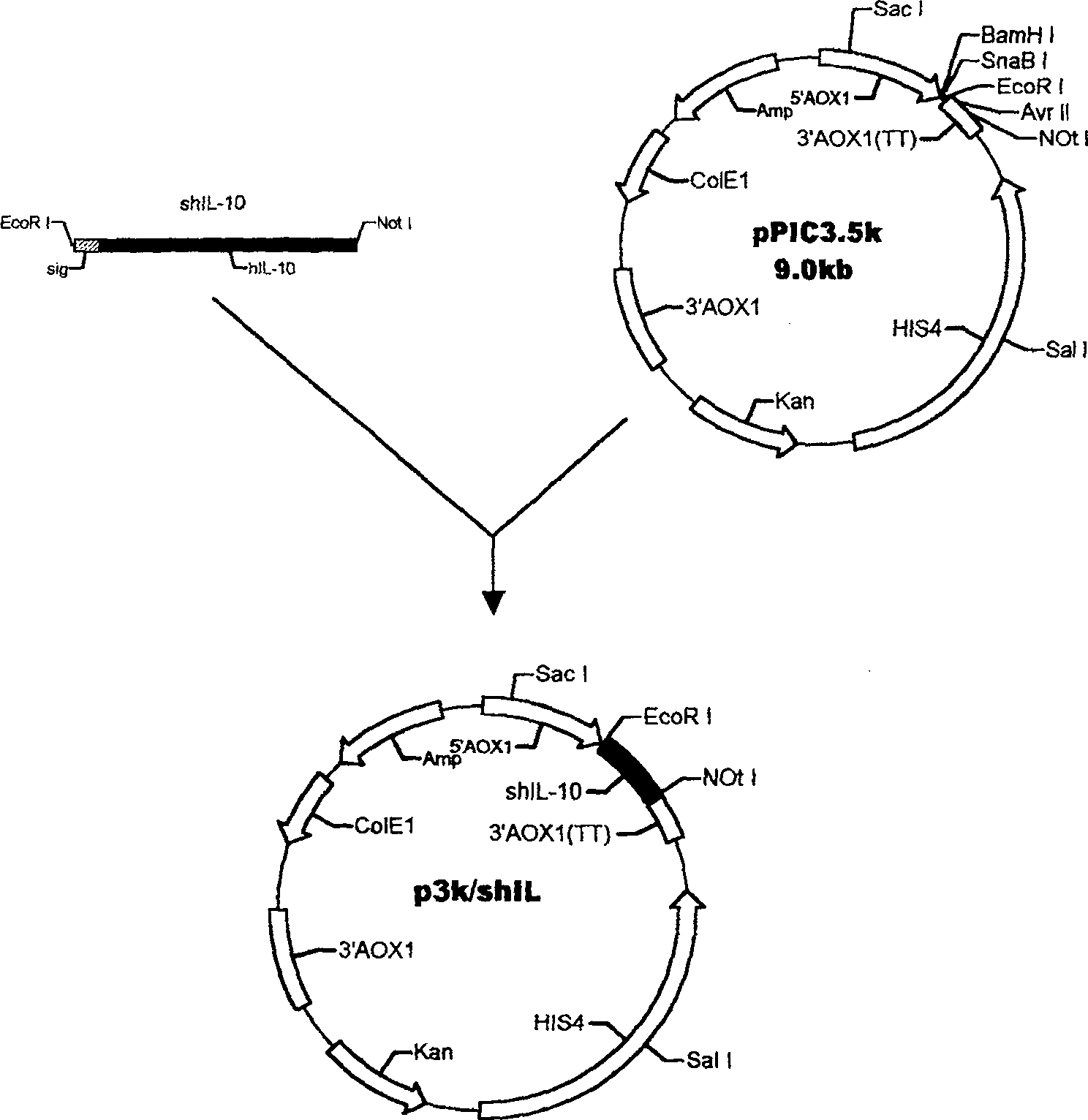
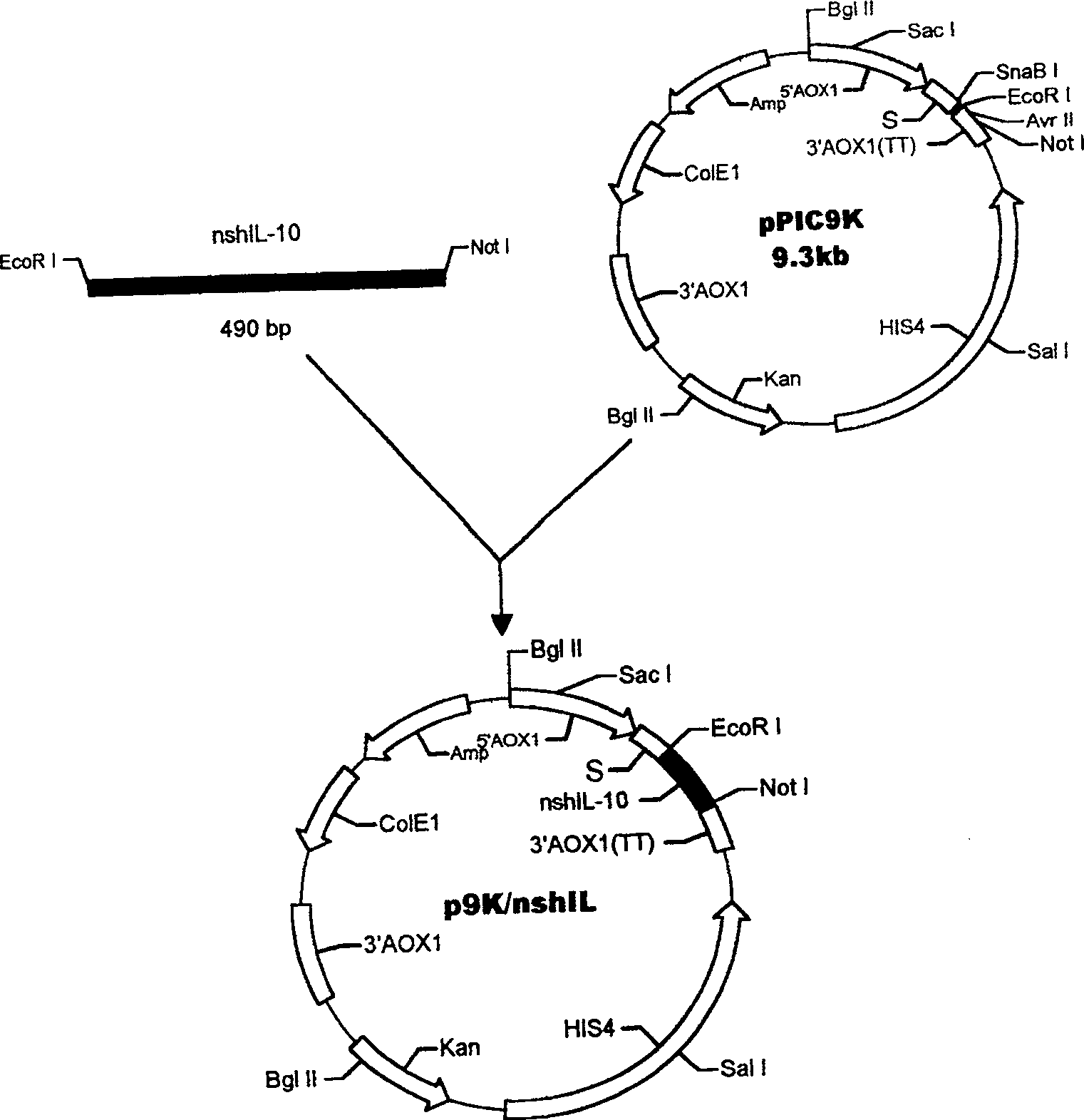
The method for yeast cell to express human interleukin 10 (hIL-10) has the technological scheme including artificially synthesizing all-gene sequence of hIL-10 including signal-carrying hIL-10 sequence, named shIL-10, and no-signal hIL-10 sequence, named nshIL-10; adding to the ends with EcorR I enzyme incising sequence and Not I enzyme incising sequence or with EcorR I enzyme incising sequences; double incising with EcorR I and Not I the integral expression vector pPIC3.5K and Ppic9K of destination gene shIL-10, nshIL-10 and Pichia yeast; constituting recombinant plasmid pPIC3.5K / shIL-10 and Ppic9K / nshIL-10; converting Pichia yeast cell via electrical perforation and plasmodic granule process; integrating recombinant plasmid and destination gene to yeast chromosome; and applying methanol to induce Pichia yeast for intracellular soluble expression and extracellular secretion type expression. The present invention is superior to expression in colibacillus.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
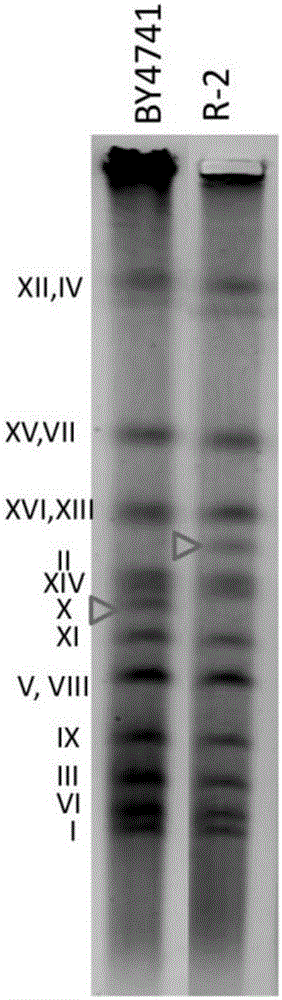
Method for detecting klenow fragment repetition position in saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome
ActiveCN105624306AQuick checkEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementYeast chromosomeGenomic sequencing
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, in particular to a method for detecting a klenow fragment repetition position in a saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome.By combining genomic sequencing with endoreduplication backcrossing, the position of repeated klenow fragment genome DNA in the chromosome is confirmed quickly.Through the endoreduplication backcrossing method, the position of the repeated klenow fragment genome DNA in the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome can be detected efficiently and quickly and repaired, repeated klenow fragment genome DNA is deleted, there is no need to precisely confirm the position of a klenow fragment repetition site or conduct cumbersome experimental data analysis on saccharomyces cerevisiae to be detected, operation is easy, and the experimental period is short.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Yeast recombined human-source I-type collagen alpha1 chain protein, synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN109988234AImprove cutting efficiencyImprove start-up efficiencyCosmetic preparationsConnective tissue peptidesPichia pastorisYeast chromosome
The invention discloses yeast recombined human-source I-type collagen alpha1 chain protein, a synthesis method and an application thereof. The recombinant human-source I-type collagen alpha1 chain protein is composed of N-terminal affinity purification marker, human-source I-type collagen alpha1 chain mature peptide sequence and C-terminal affinity purification marker, and the double specific affinity purification markers are designed at two ends of the protein, so that purification of the recombinant protein is facilitated, and detection and full-length identification of the recombinant protein are facilitated. The synthesis method includes utilizing pichia pastoris idiomatic codon to optimize a collagen gene sequence and performing artificial whole-gene synthesis on a gene level; building a recombinant vector through PCR, enzyme digestion and connection, and integrating the recombinant vector into yeast chromosome to build a recombinant pichia pastoris engineered strain secreting andexpressing the recombined human-source I-type collagen alpha1 chain protein. The double specific affinity purification markers carried by the protein is supportive of two-step specific purification,and easiness in acquiring a high-purity product is realized.
Owner:JIANGSU TRAUTEC MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
DNA construct for transforming a yeast
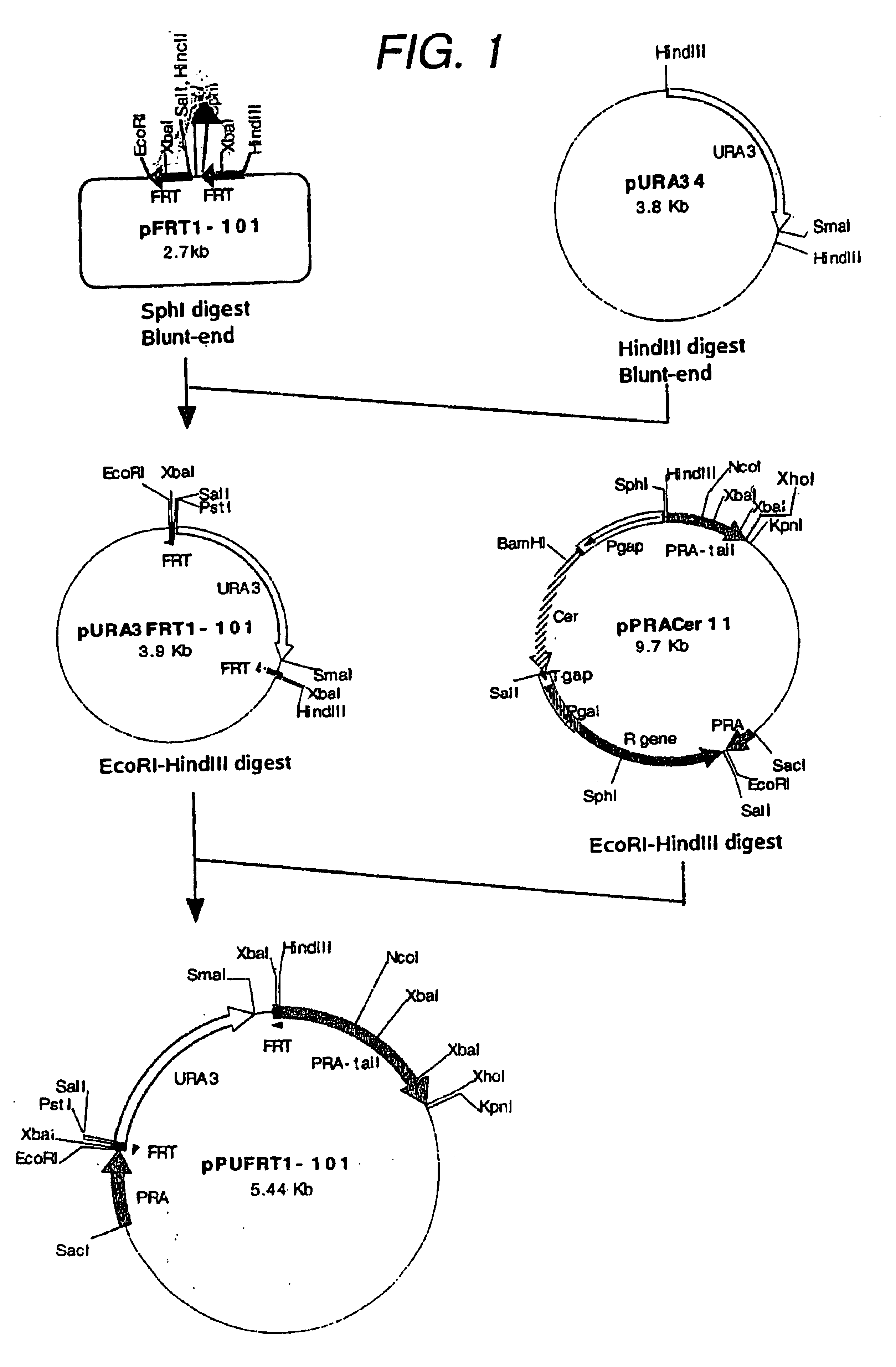
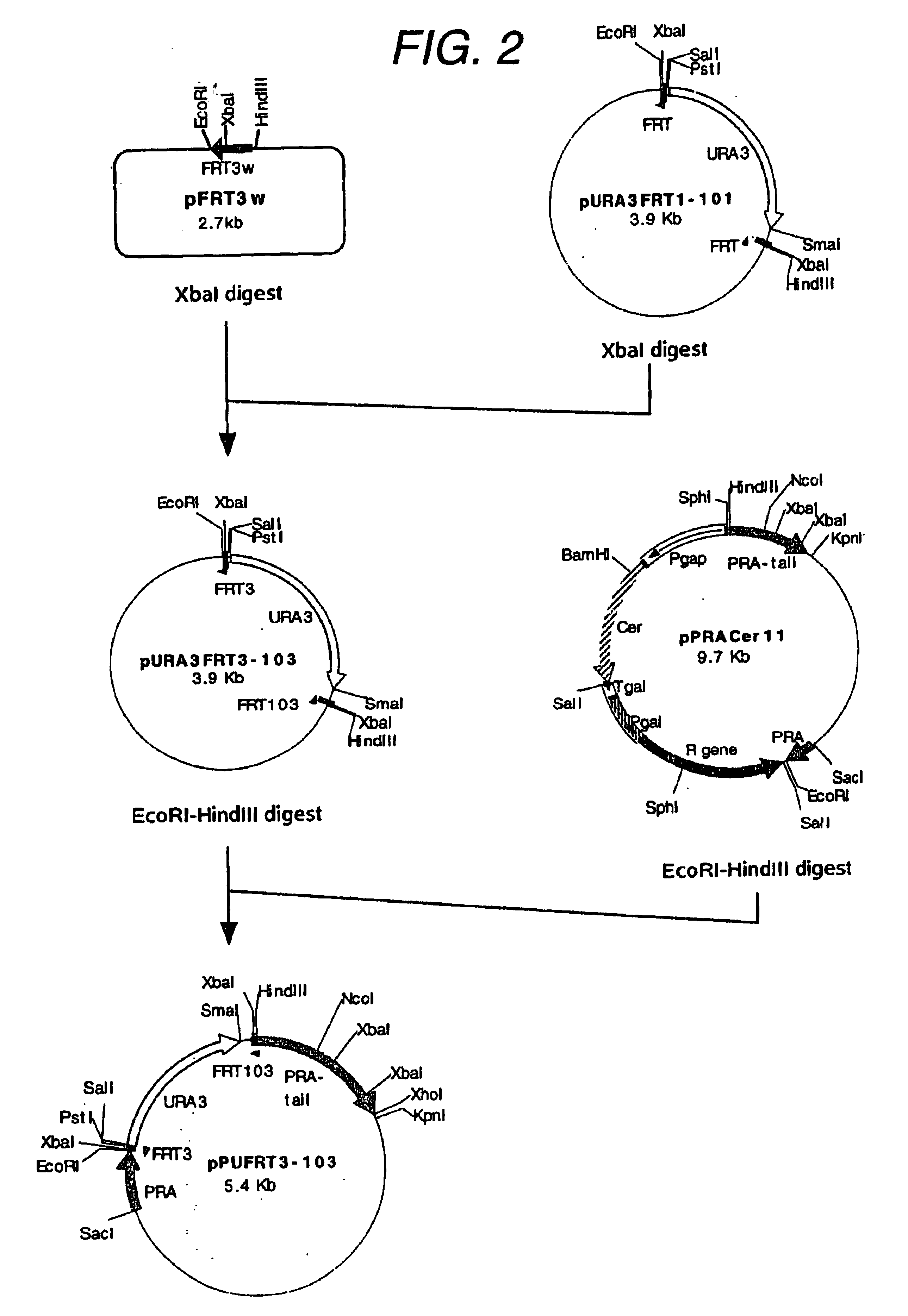
A DNA construct comprising:(1) a selective marker gene,(2) a galactose-inducible growth inhibition sequence,(3) a pair of FRT sequences in the same orientation flanking (1) and (2), and(4) a DNA fragment capable of recombining with a yeast chromosomal DNA located at each end of (3),wherein said FRT sequences contain the following sequence: 5'-GAAGTTCCTATAC TTTCTAGA GAATAGGAACTTC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1)or a sequence substantially identical to said sequence.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and construction method thereof
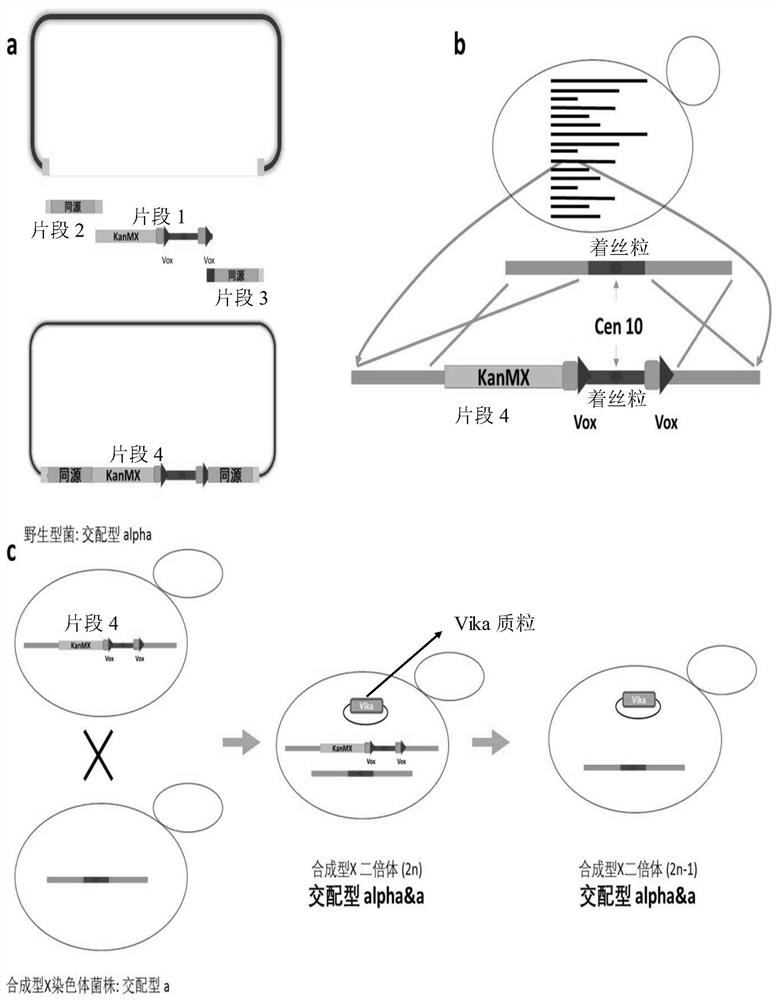
ActiveCN113046255AAchieve knockoutAchieve integrationFungiStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyYeast chromosome
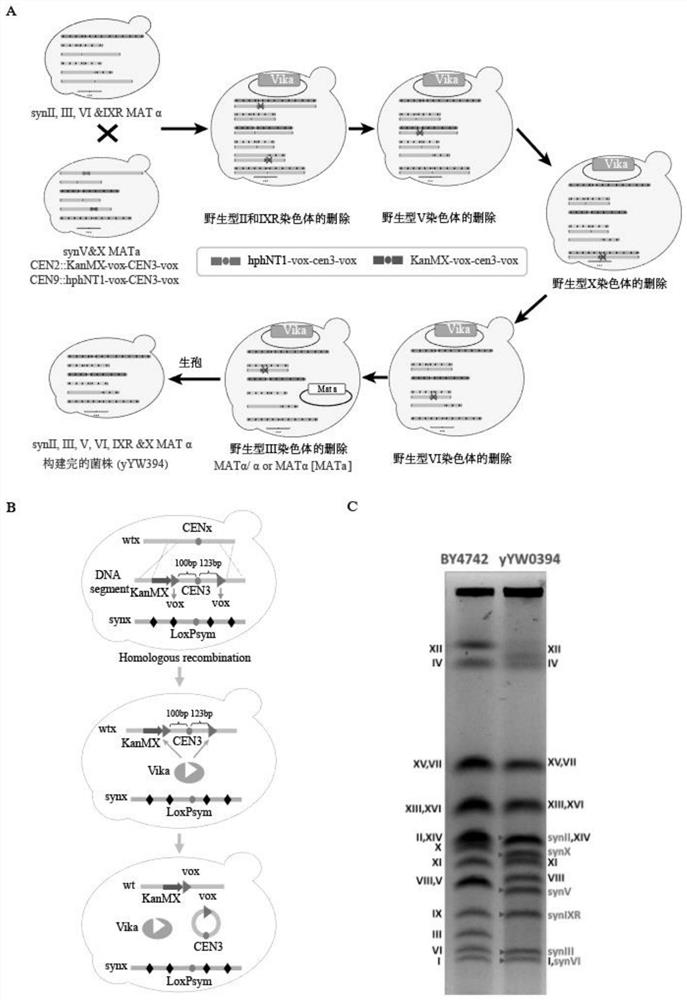
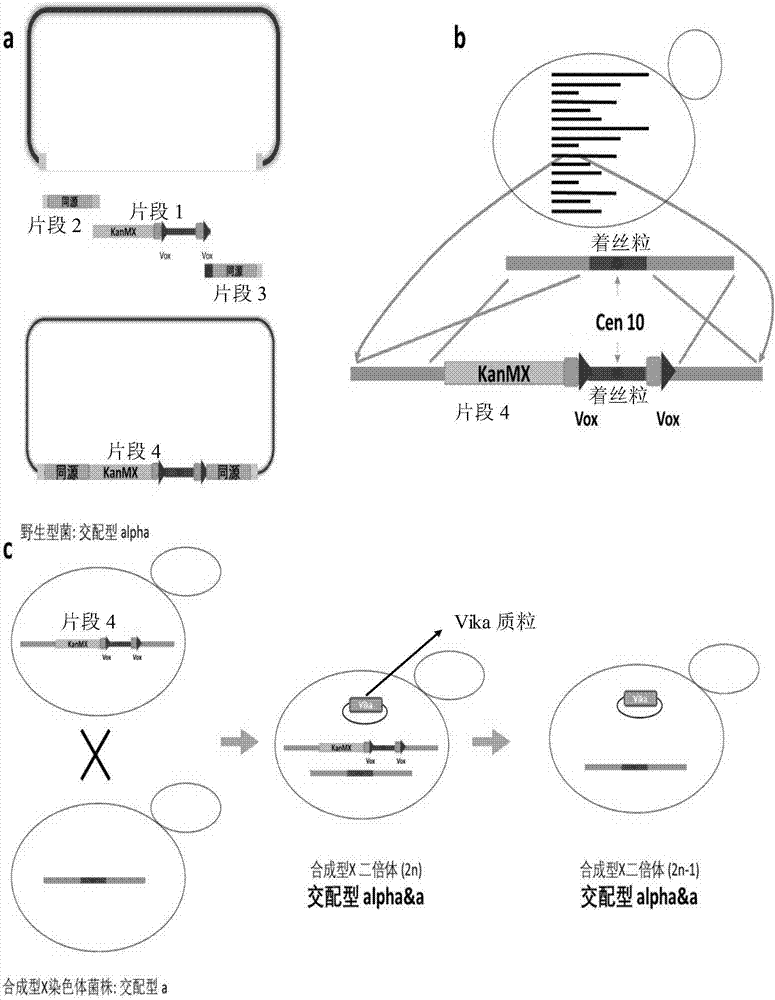
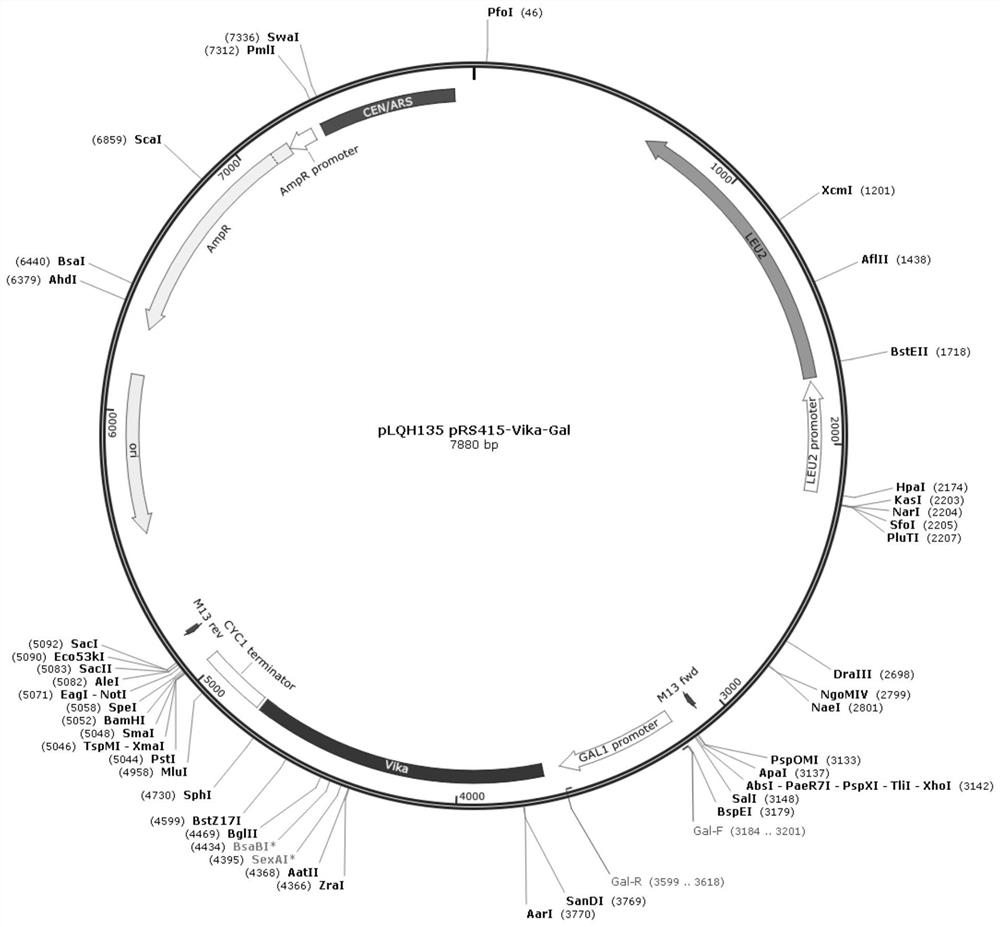
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and a construction method thereof. According to the yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and the construction method thereof, a complete yeast chromosome is cut off by using a Vika / vox technology, so that homologous recombination is generated by chromosome centromeres, the whole chromosome is knocked out, six synthetic chromosomes are integrated, and a large-scale rearrangement event is generated. Compared with existing achievements, the yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and the construction method thereof have the following beneficial effects that cutting of the yeast chromosome is achieved simply, efficiently and quickly; cross exchange of sister dyeing monomers is avoided, and haploid yeast integrated by the six synthetic chromosomes is obtained; and very large-scale genome rearrangement is generated simply, efficiently and quickly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for knocking out saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome
ActiveCN107988202AAchieve knockoutIncrease success rateStable introduction of DNAHybrid cell preparationYeast chromosomeSite-specific recombination
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and in particular discloses a method for knocking out a saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome. According to the method, a Vika / vox technology is utilized for removing a complete yeast chromosome, and chromosome centromeres are specifically recombined into a ring by virtue of loci, so that knockout of the whole chromosome is realized. Compared with a method for realizing elimination of the whole chromosome in a reduction mitosis manner, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that cutting of the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome is more simply, efficiently and rapidly realized, crossing over of sister chromatids is avoided, and a saccharomyces cerevisiae homozygous diploid bacterial strain with the chromosome knocked out is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Novel promoter and use thereof
InactiveCN104220600AImprove expression levelImprove productivityActivity regulationBiofuelsHeat resistanceKluyveromyces marxianus
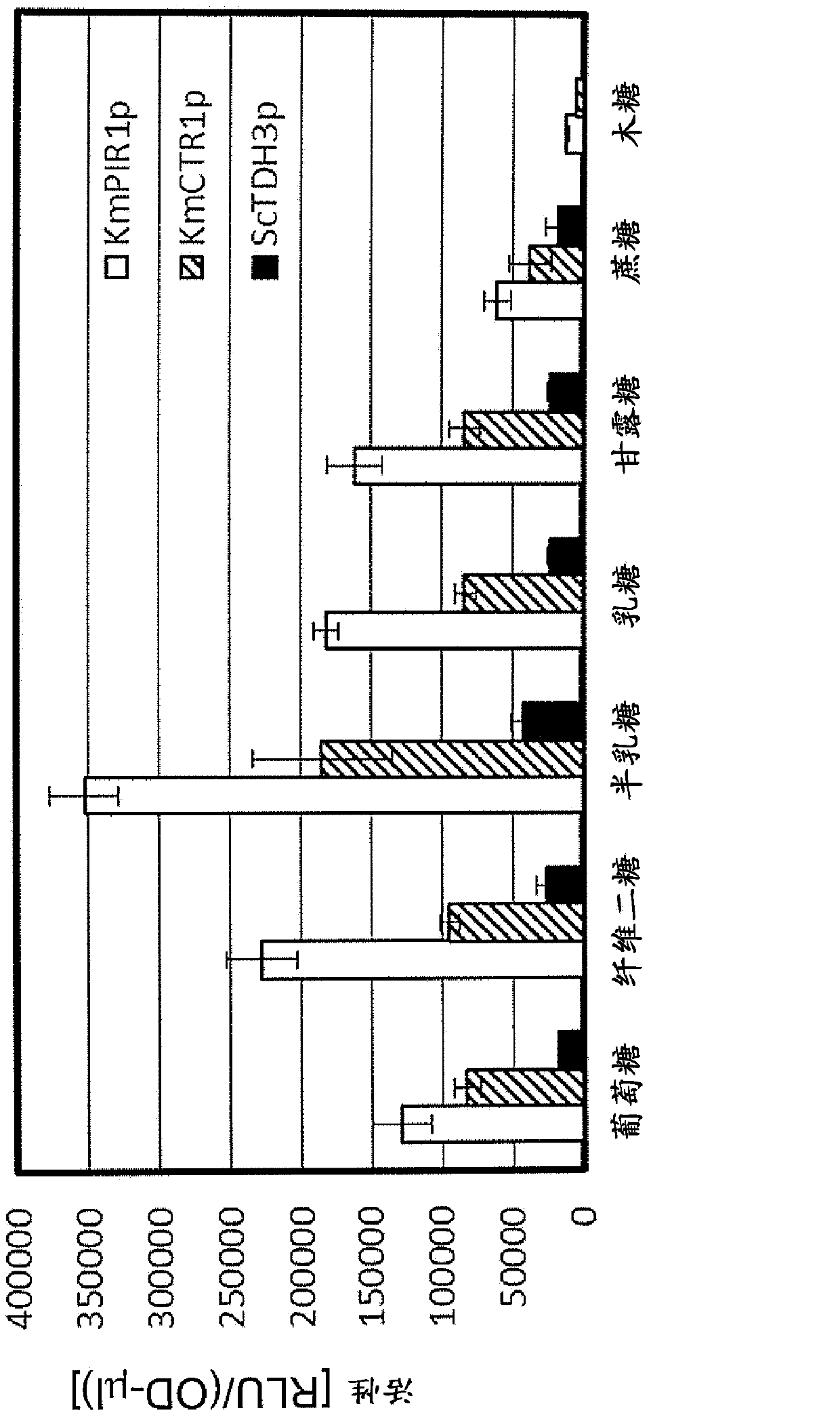
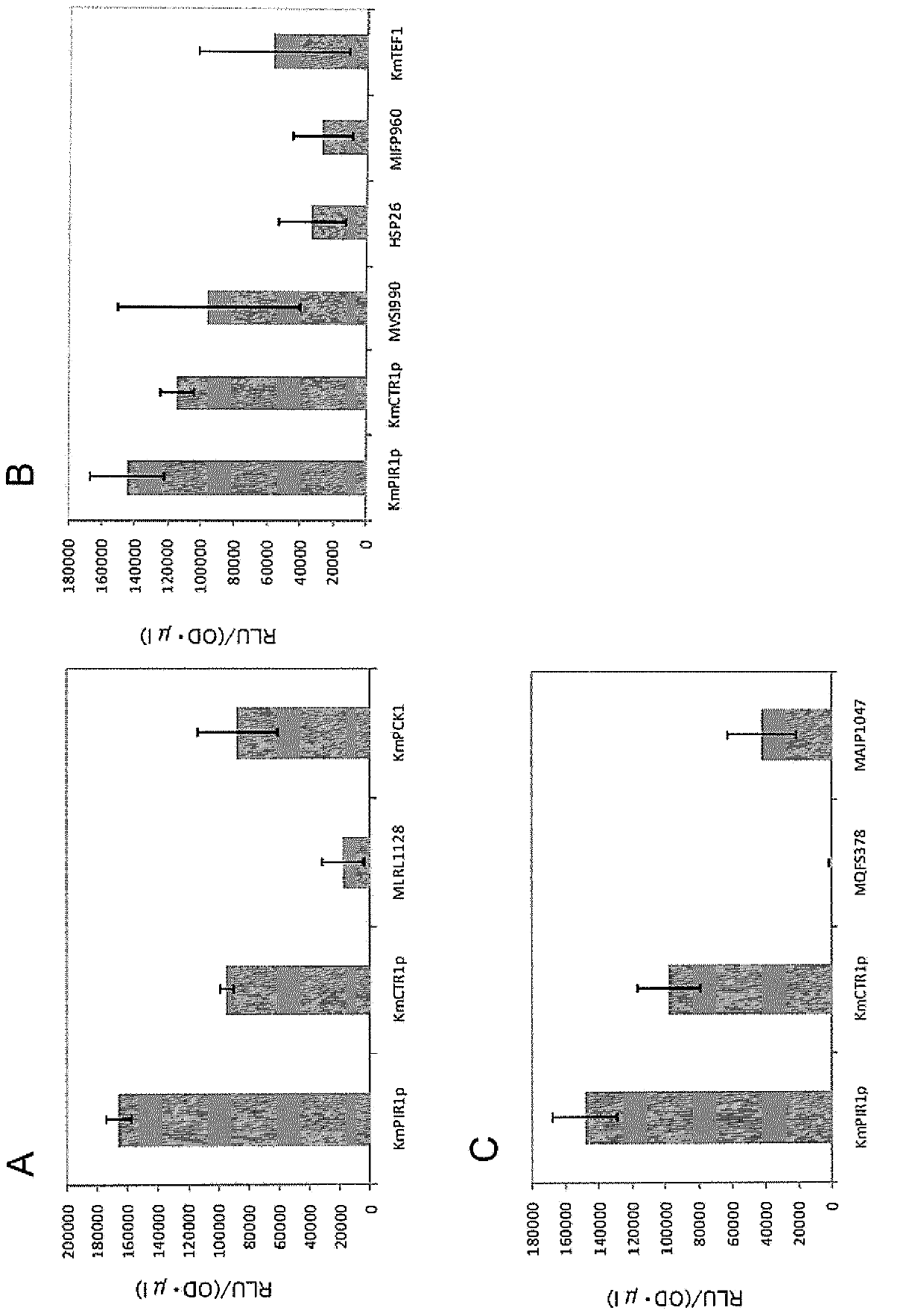
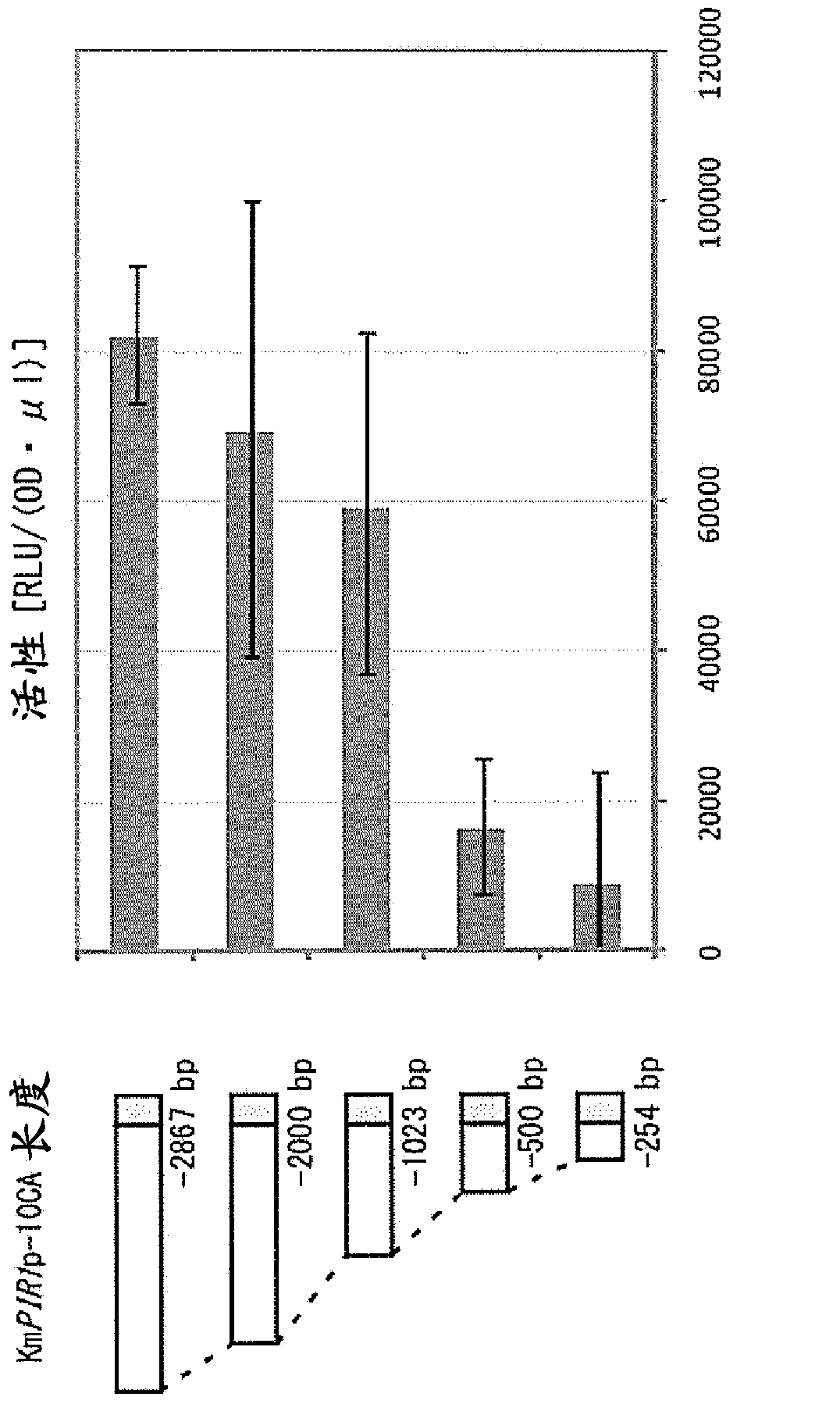
The promoter of the present invention causes a desired gene to be highly expressed, especially in thermotolerant yeast. The promoter is located upstream of the PIR1 gene or the CTR1 gene on the Kluyveromyces marxianus chromosome and comprises a region controlling expression of the PIR1 gene or the CTR1 gene.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Method for expressing desmodus rotundus salivary plasminogen activator in pichia pastoris
InactiveCN101914568AImprove biological activityImprove solubilityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesYeast chromosomeBiotechnology
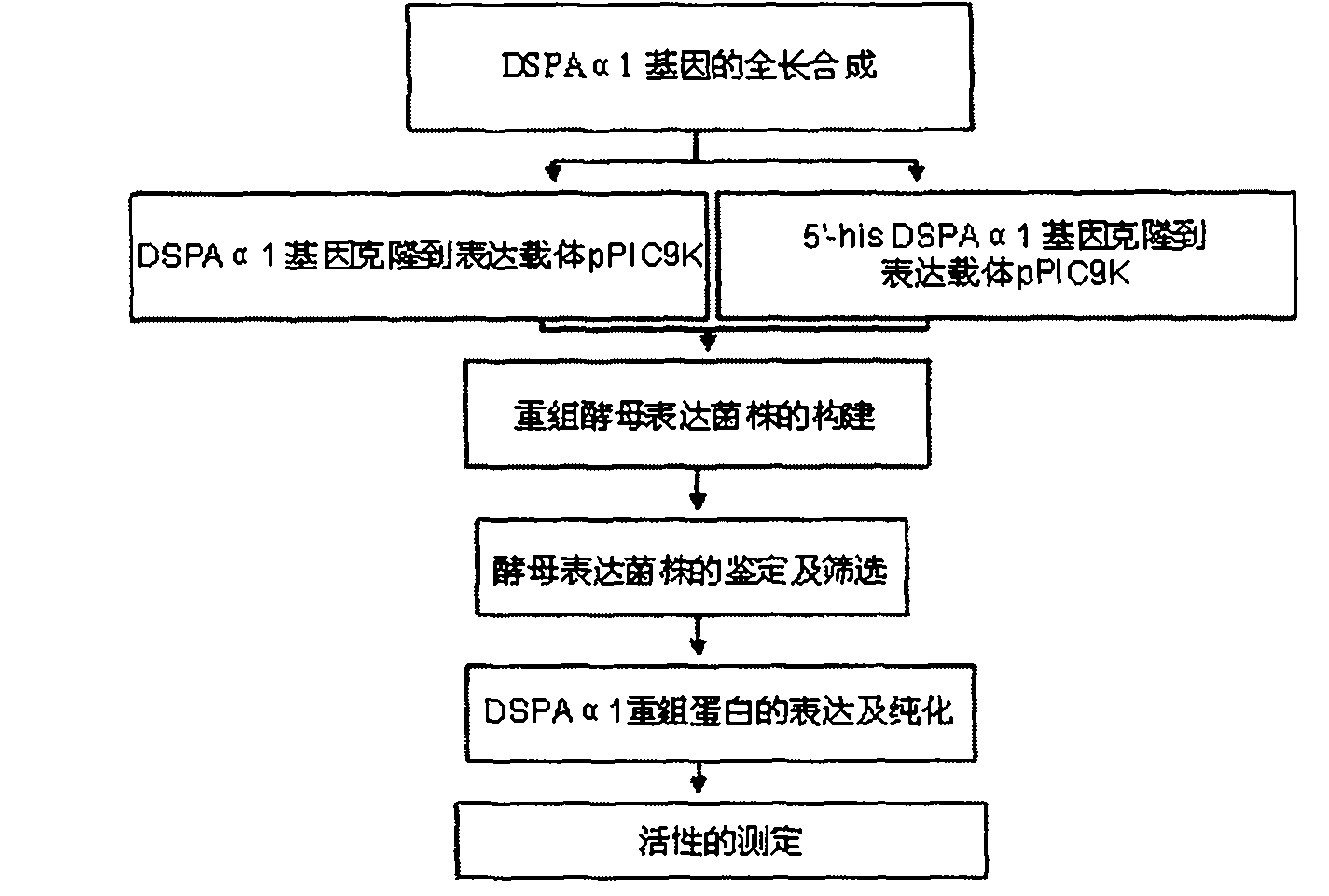
A method for expressing a desmodus rotundus salivary plasminogen activator in pichia pastoris is realized by the following steps: artificially synthesizing the full-length gene of the desmodus rotundus salivary plasminogen activator (Bat-PA) in vitro, then cloning the full-length gene on an expression vector pPIC9K and then transforming a linearized recombinant plasmid to a yeast cell by electroporation to be stably integrated on a yeast chromosome. The method stably and efficiently expresses the Bat-PA, especially DSPAalpha1 in pichia pastoris, thus lowering the production cost, improving the expression quantity and ensuring the generated recombinant protein to have the bioactivity of the natural protein. The purified protein can be used for treating various thrombotic cardio-cerebro vascular diseases.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
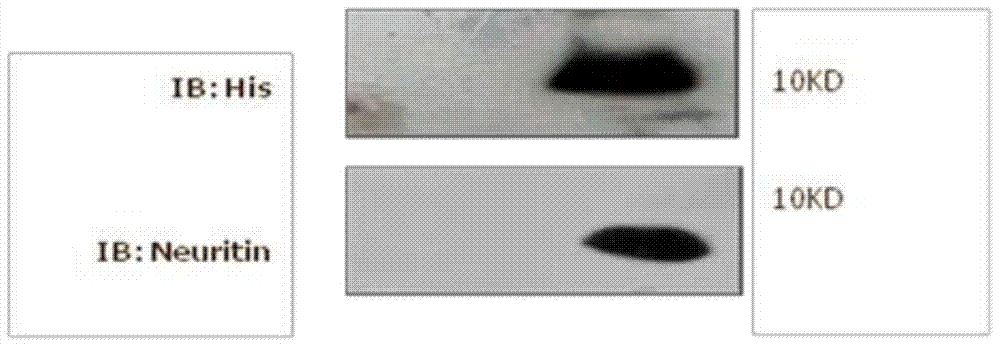
Pichia yeast recombinant bacterial strain highly expressing Neuritin truncated protein, and application thereof
InactiveCN104774777ABiologically activeStable passageFungiNervous disorderEucaryotic cellBiotechnology
The invention discloses a pichia yeast recombinant bacterial strain highly expressing a Neuritin truncated protein, and an application thereof. The recombination bacterial strain is Pichia pastoris and has a preservation number of CGMCC NO:9912. Compared with Neuritin truncated proteins expressed by Escherichia coli and sold in the present market, the Neuritin truncated protein expressed by the pichia yeast recombinant bacterial strain has the following advantages: an exogenous protein expressed by eukaryotic cells has post-translational modification bioactivity, and exogenous gene is stably integrated in yeast chromosome, and can realize stable passage and easy large scale culture. A suitable concentration of Neuritin can promote the regeneration and function recovery of early stage sciatic nerves after injuries, provides a new method for treatment of peripheral neuropathy injury, and has good application prospect.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Design and construction methods and application of standardized bio-elements
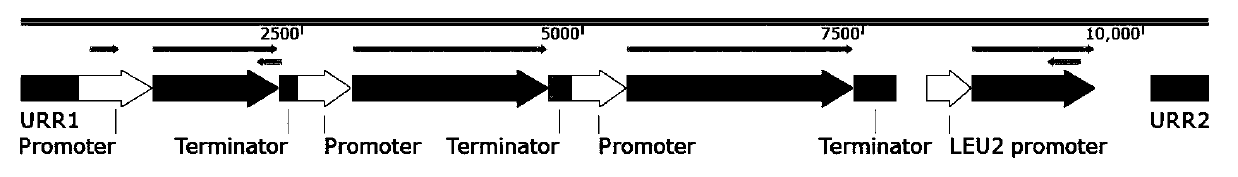
The invention discloses design and construction methods and application of standardized bio-elements. The construction method of the standardized bio-elements comprises the following steps that 1, a target genophore group, a promoter carrier group and a terminator carrier group are constructed. A series of standardized bio-elements are designed and constructed based on a yeast system, restriction enzymes II can be utilized for assembling the standardized bio-elements into an ultralong foreign DNA fragment, the foreign DNA fragment is a target product synthesis route composed of multiple genes, and the fragment is integrated to a specific site of a yeast chromosome through yeast homologous recombination for stable expression; a heterogenetic source in the target product yeast can be synthesized, optimum expression of the target product can be achieved by optimizing the promoters of all the genes, and therefore unique advantages and great significance are achieved in the optimization process of target product synthesis.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method of differentiating beer yeast
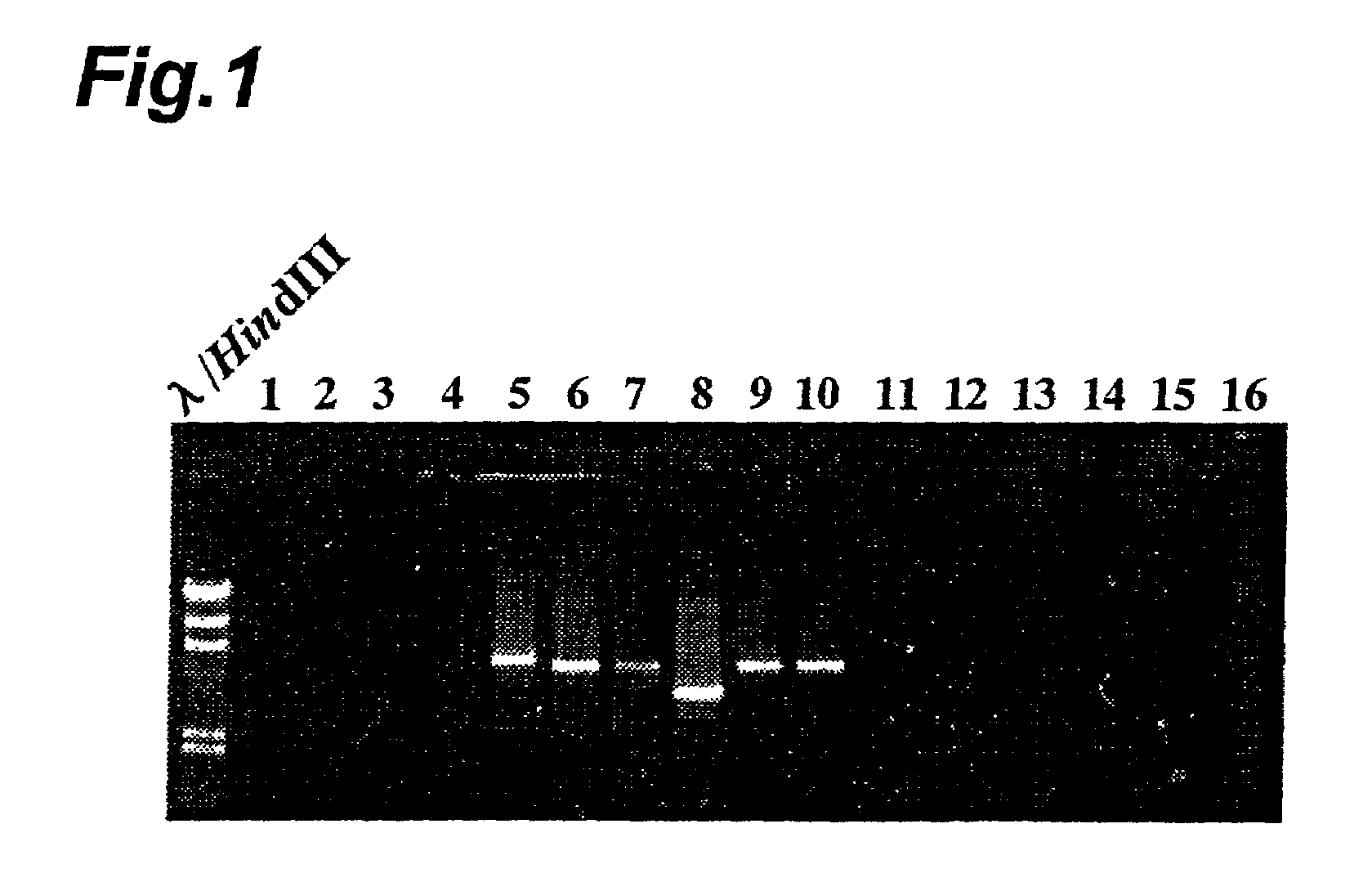
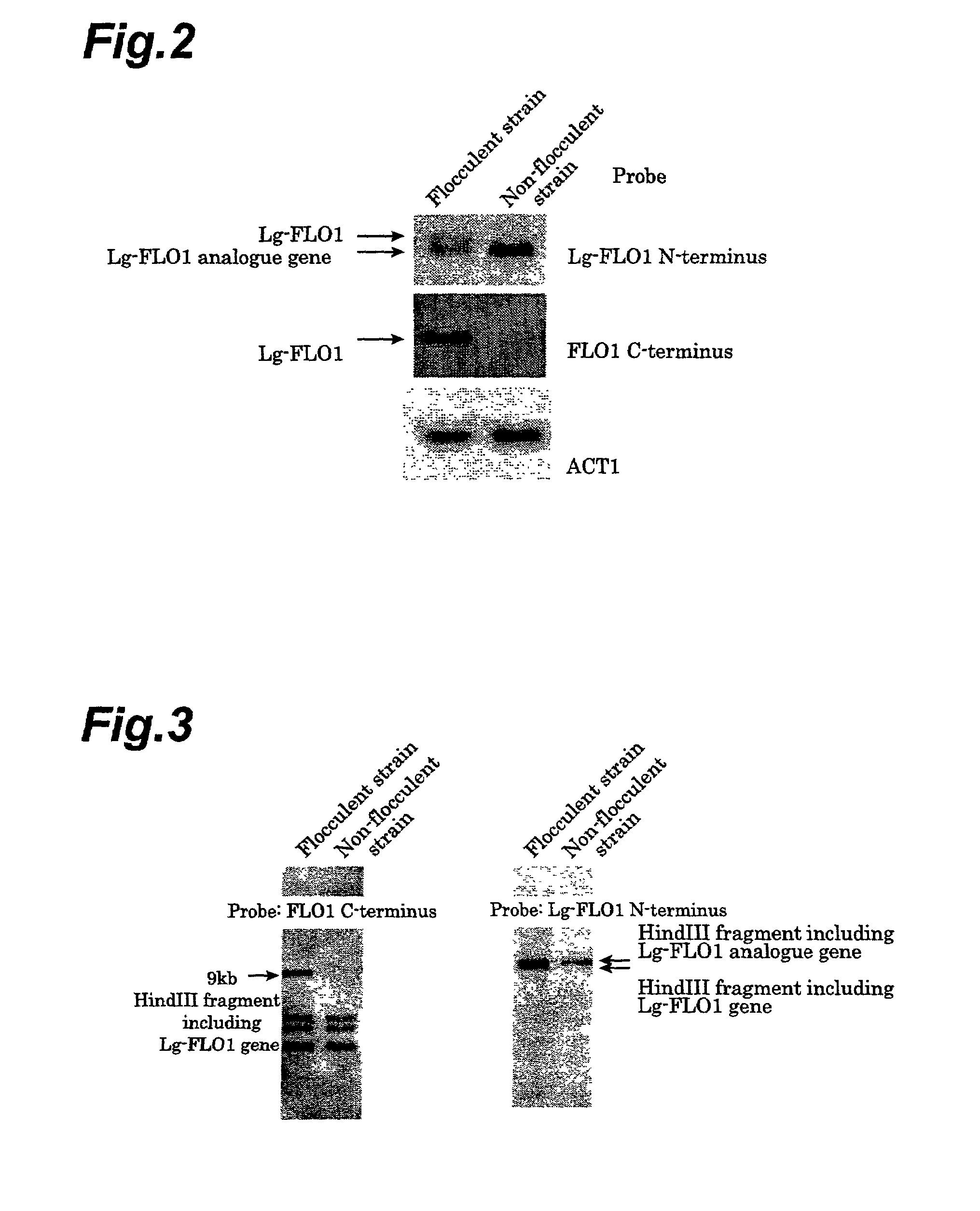
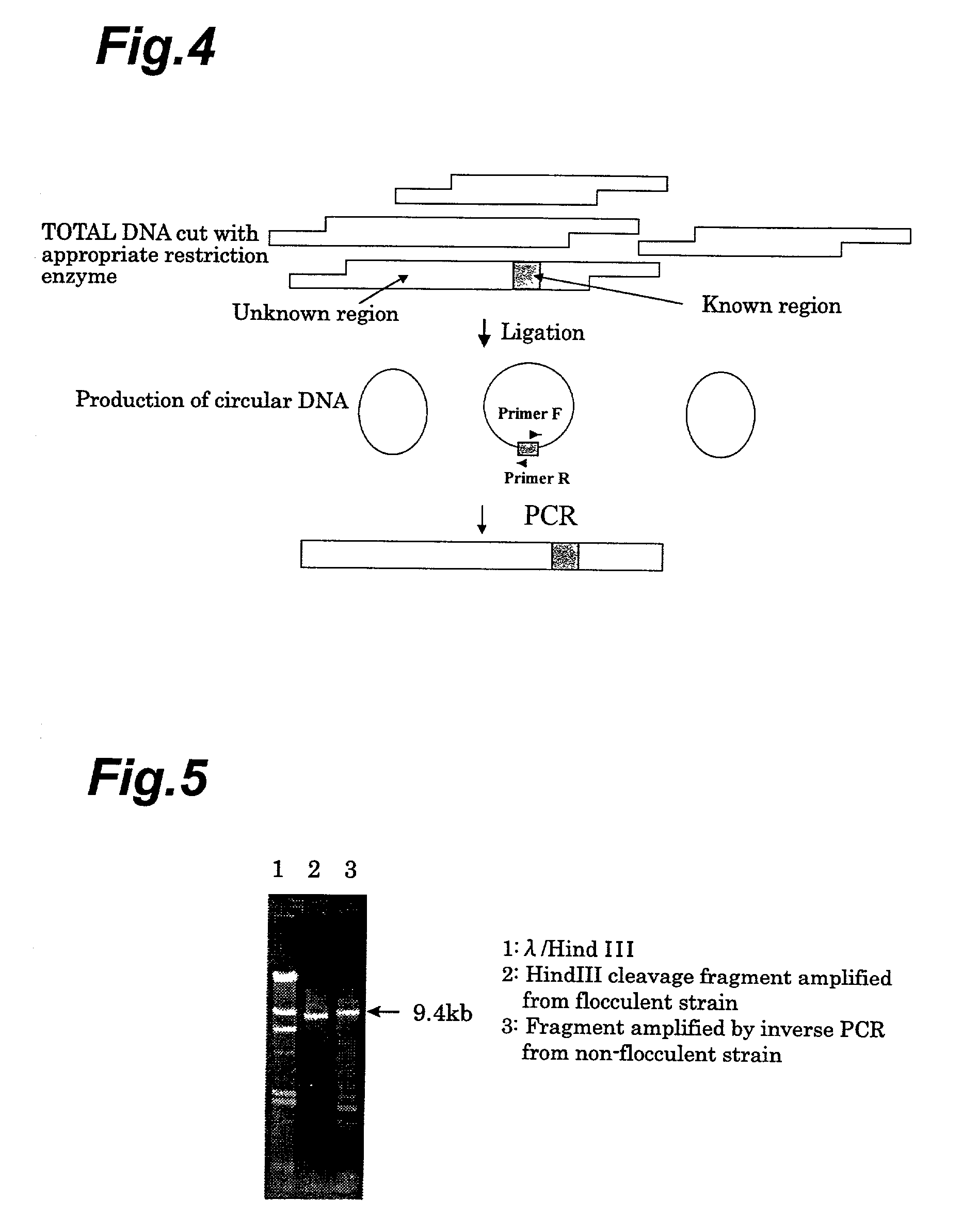
InactiveUS7504239B2High precisionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyYeast chromosome
The method of differentiating beer yeast of the invention is a method which comprises a first step of synthesizing a primer capable of amplifying the linker portion between a base sequence (A) and a base sequence (B) in a novel gene (C) which has the base sequence (B) comprising a portion of yeast chromosome IX linked downstream from the base sequence (A) comprising a portion of the N-terminal end of yeast gene Lg-FLO1, and which includes the base sequences listed as SEQ. ID. Nos. 1-6 of the Sequence Listing; a second step of carrying out a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) using the primer synthesized in the first step and DNA separated from a yeast specimen; and a third step of differentiating whether the yeast is bottom-fermenting yeast or wild yeast, based on the PCR amplification product obtained from the second step.
Owner:SAPPORO BREWERIES
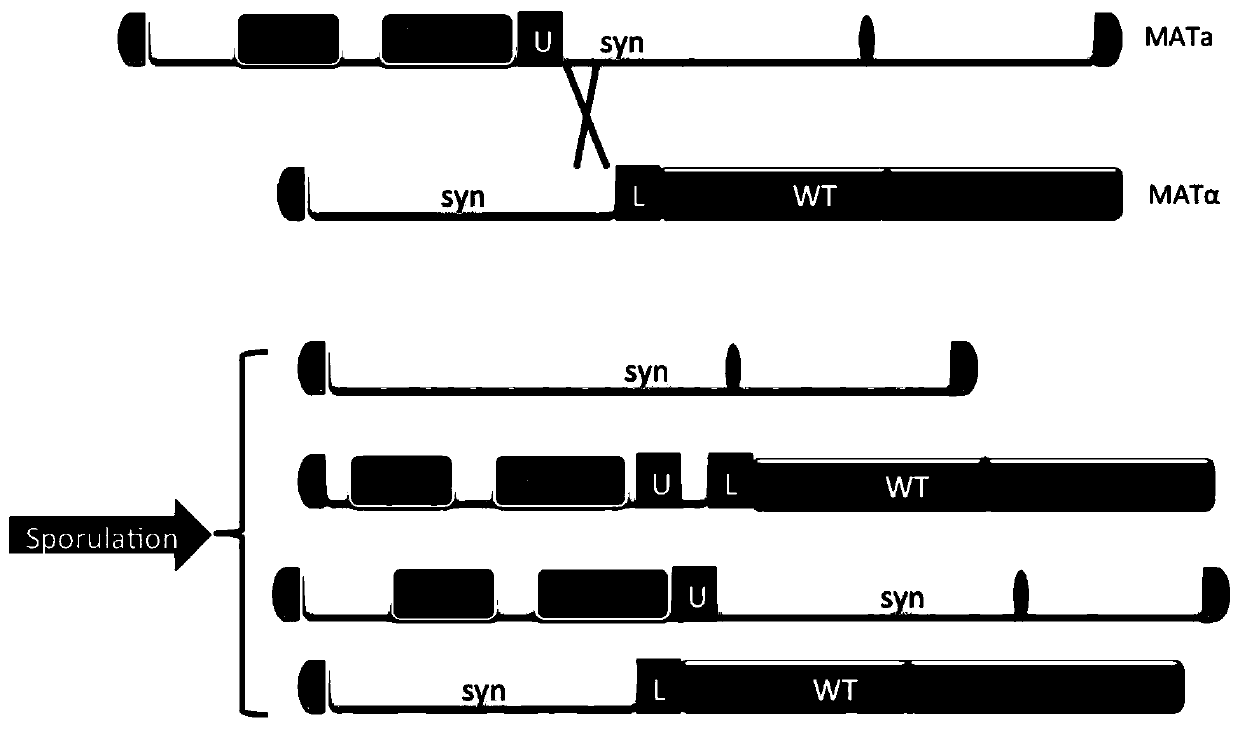
Method for repairing anomaly of yeast chromosome structure
ActiveCN106755116ARepair Structural VariationsExchangeFungiStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyYeast chromosome
The invention relates to the field of genome engineering and discloses a method for repairing the anomaly of a yeast chromosome structure. According to the method disclosed by the invention, yeast chromosomes, which have chain exchange at a design region, are rapidly screened by utilizing an efficient homologous recombination mechanism and a screening label of yeast, and exchange between an sequence with the abnormal yeast chromosome structure and a normal chromosome sequence is realized, so that the aim of efficiently repairing the variation of the yeast chromosome structure in a large scale is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Design and construction methods of standardized biological components and their applications
The invention discloses design and construction methods and application of standardized bio-elements. The construction method of the standardized bio-elements comprises the following steps that 1, a target genophore group, a promoter carrier group and a terminator carrier group are constructed. A series of standardized bio-elements are designed and constructed based on a yeast system, restriction enzymes II can be utilized for assembling the standardized bio-elements into an ultralong foreign DNA fragment, the foreign DNA fragment is a target product synthesis route composed of multiple genes, and the fragment is integrated to a specific site of a yeast chromosome through yeast homologous recombination for stable expression; a heterogenetic source in the target product yeast can be synthesized, optimum expression of the target product can be achieved by optimizing the promoters of all the genes, and therefore unique advantages and great significance are achieved in the optimization process of target product synthesis.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Chromosome Transfer Method of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN105602934BAchieve transferAvoid cross swapsMicrobiological testing/measurementHybrid cell preparationYeast chromosomeBiotechnology
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to a transfer method for saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomes. A synthetic No.V chromosome saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a synthetic No.X saccharomyces cerevisiae strain are fused into a diploid strain through an endoreduplication backcross method, the wild No.V chromosome and No.X chromosome are induced to be lost through galactose, and screening is conducted through an SC+5-FOA culture medium; a saccharomyces cerevisiae haploid strain carrying the synthetic No.V and No.X chromosomes is obtained through spore splitting. Compared with existing achievements, the transfer method has the advantages that transfer of the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomes is rapidly achieved; cross swap of sister chromatids is avoided, and the saccharomyces cerevisiae haploid strain with the chromosomes transferred is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A method for repairing structural abnormality of yeast chromosome
ActiveCN106755116BRepair Structural VariationsExchangeFungiStable introduction of DNAYeast chromosomeYeast
The invention relates to the field of genome engineering and discloses a method for repairing the anomaly of a yeast chromosome structure. According to the method disclosed by the invention, yeast chromosomes, which have chain exchange at a design region, are rapidly screened by utilizing an efficient homologous recombination mechanism and a screening label of yeast, and exchange between an sequence with the abnormal yeast chromosome structure and a normal chromosome sequence is realized, so that the aim of efficiently repairing the variation of the yeast chromosome structure in a large scale is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Gene element and application of same to variation of chromosome number, copy number and structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN108913611ARealize the structureAchieving Continuous VariationFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast chromosome
The invention especially relates to a generation method for the variation of the chromosome number of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, belonging to the field of synthetic biology. According to the invention,in virtue of the characteristics of genome rearrangement of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and through genome rearrangement of the ring chromosomes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, an aneuploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with chromosome number variation is obtained, the continuous variation of the circular chromosome copy number of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is realized, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with continuously evolved phenotypes is obtained, and correlation between structural variation and phenotype enhancement is revealed. According to the invention, the variation of the chromosome number, the copy number and the structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is realized and the structural variation is revealed by using a chromosome rearrangement method, and a novel research means is provided for obtaining aneuploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains and studying the relationship between chromosome structure variation and functions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for yeast cell to express human interleukin 10
InactiveCN100494386CAvoid degradationSimple structureFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyYeast chromosome
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method for producing gene engineering recombination 192 peptide human growth hormone
InactiveCN100543141CStable genetic traitsFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, in particular to a method for producing genetic engineering recombinant 192 peptide human growth hormone. The technical scheme is as follows: (1) Obtaining the 192-peptide human growth hormone gene: using the pHil-D2 plasmid as a shuttle plasmid, the growth hormone cDNA is transferred into yeast cells, and through homologous recombination with genes on the chromosomes of yeast cells, The genetically engineered hGH yeast was constructed; (2) expression system: the strain of Pichia pastoris was used as the expression host to express 192 peptide human growth hormone in the way of intracellular expression; (3) the hGH yeast was induced to express and produce human growth hormone.
Owner:周琪
A method for knocking out the chromosome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN107858346BKnockout simpleKnockout EfficientHydrolasesStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyYeast chromosome
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and specifically discloses a method for knocking down brewing yeast chromosome. The method is characterized in that the complete yeast chromosome is cut according to the CRISPR / Cas9 base technology; a specificity target close to centromere is selected; a corresponding guide RNA is designed to guide Cas9 protein to generate an incision closeto the centromere, thus realizing the knocking down of the whole chromosome. Compared with the conventional method for losing the whole chromosome in manners such as inducing through a Ga1 promoter, and reductional division, the method has the advantages that the brewing yeast chromosome is simply, efficiently and quickly cut; the cross exchange of sister chromatids can be avoided; the chromosome-knocked-down homozygous brewing yeast diploid strain can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
An Efficient Yeast Chromosome Fusion Method
The invention relates to an efficient yeast chromosome fusion method. The invention discloses a method for performing yeast chromosome fusion by using a CRISPR / Cas9 system and a homologous recombination system in yeast. The method of the invention can realize rapid and efficient chromosome fusion.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
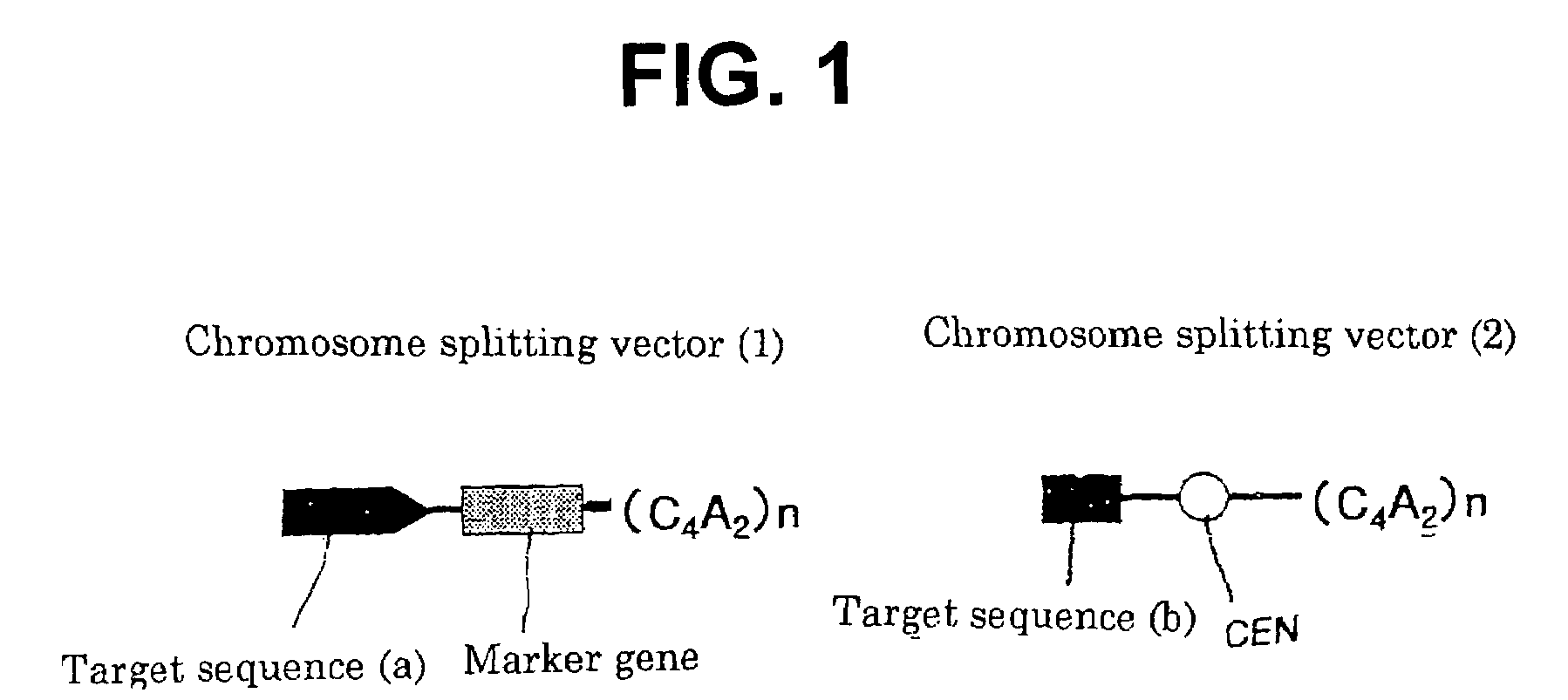
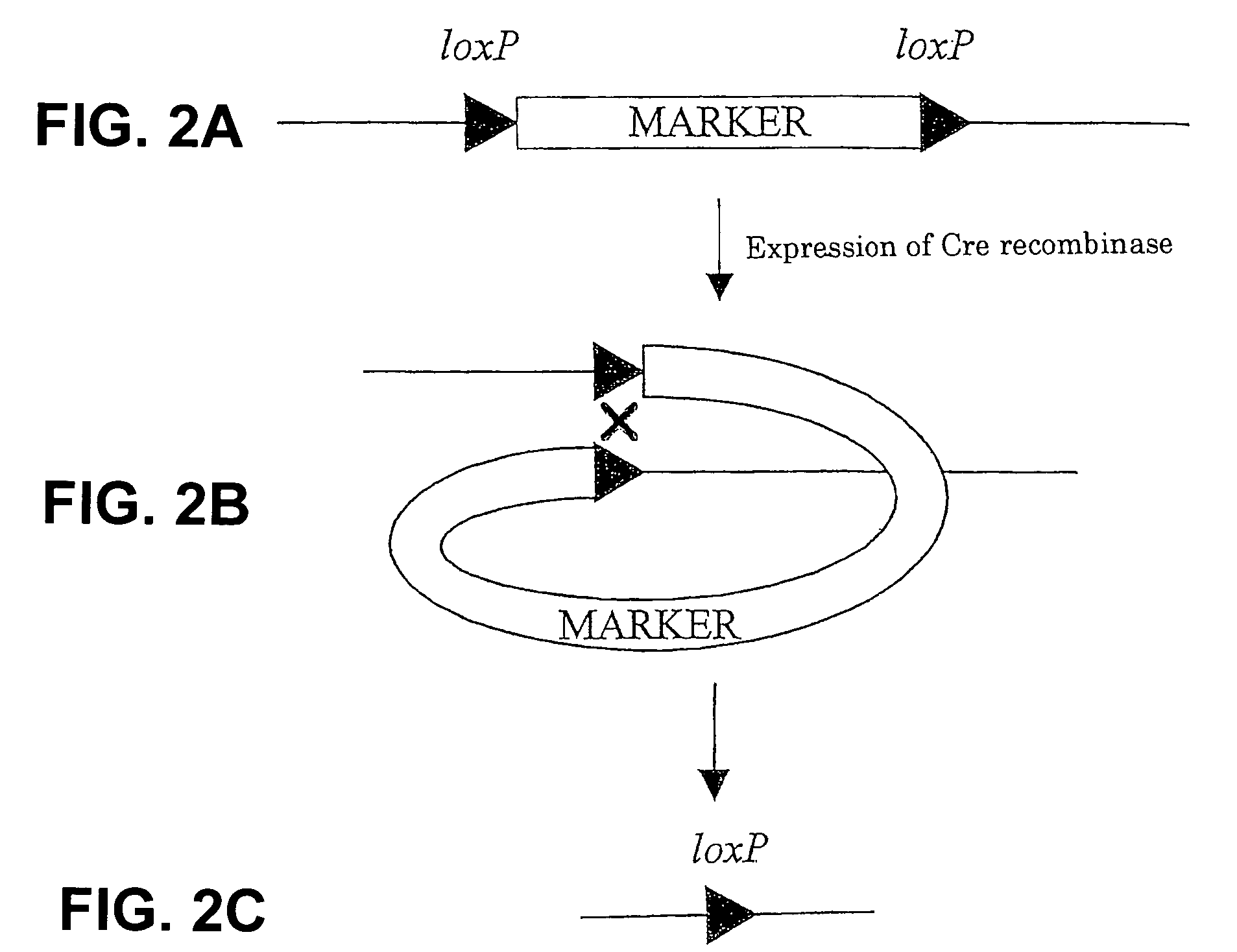
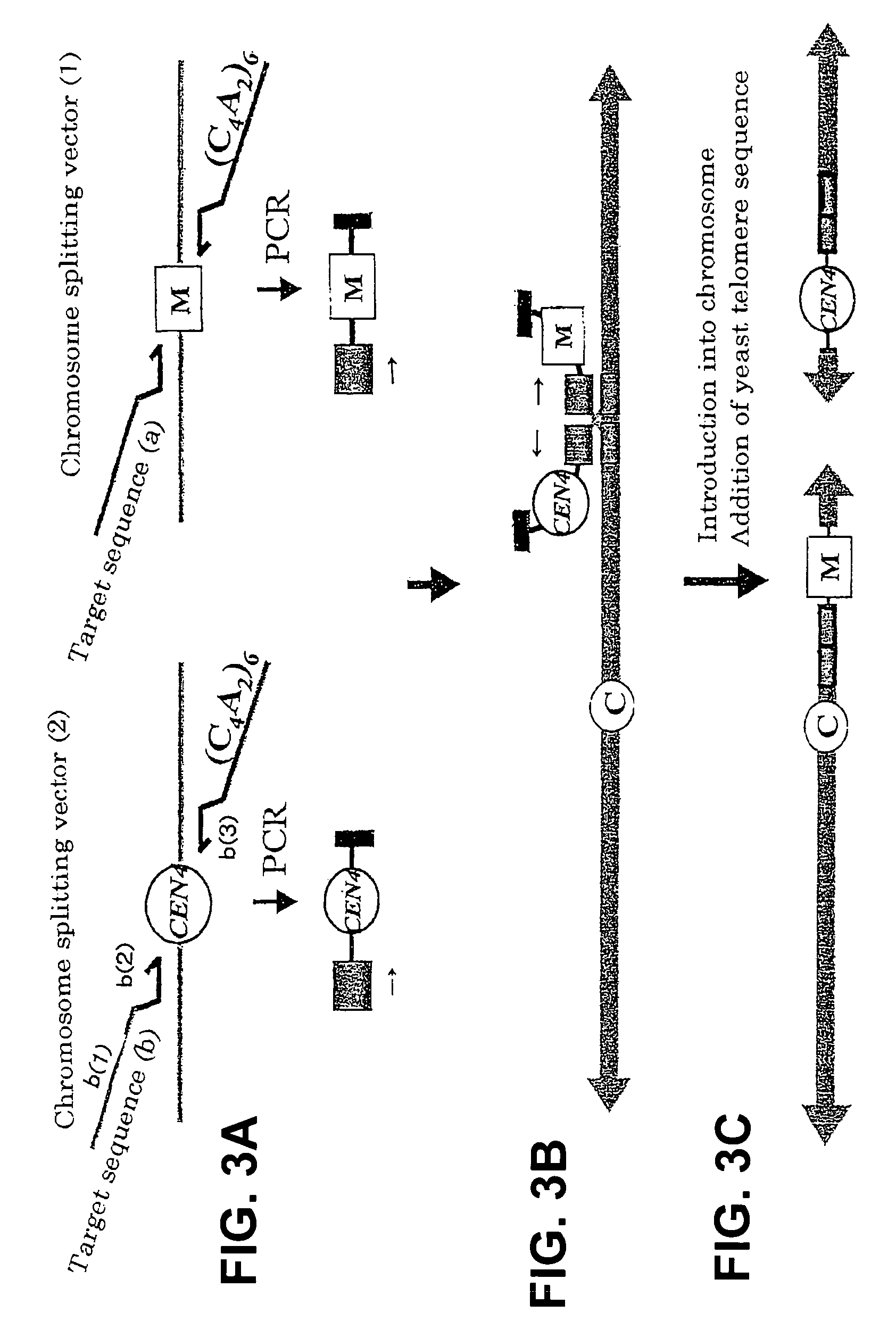
Method for modifying chromosomes
The present invention provides a simple method for splitting and loss of a chromosome in yeast. The method for modifying a chromosome in yeast includes preparing a linear chromosome splitting vector (1) having a target sequence (a), a marker gene sequence and (C4A2)n sequence in this order; preparing a linear chromosome splitting vector (2) having a target sequence (b), a centromere sequence of a yeast chromosome and (C4A2)n sequence in this order; and introducing the chromosome splitting vectors (1) and (2) into yeast. Herein, n is each independently an integer of 6 to 10. Although this chromosome splitting vector has a repetitive sequence of 5′-CCCCAA-3′, it can be amplified specifically with PCR, so that a chromosome splitting vector can be prepared significantly simply and easily, compared with the conventional DNA splitting method. It seems that a yeast telomere sequence is bound to the (C4A2)n sequence of the split chromosome generated by splitting with the chromosome splitting vector, and therefore the fragment can function as an intact chromosome.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
A method for knocking out Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomes
ActiveCN107988202BSimple knockoutEfficient knockoutStable introduction of DNAHybrid cell preparationYeast chromosomeChiasma
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and in particular discloses a method for knocking out a saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome. According to the method, a Vika / vox technology is utilized for removing a complete yeast chromosome, and chromosome centromeres are specifically recombined into a ring by virtue of loci, so that knockout of the whole chromosome is realized. Compared with a method for realizing elimination of the whole chromosome in a reduction mitosis manner, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that cutting of the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome is more simply, efficiently and rapidly realized, crossing over of sister chromatids is avoided, and a saccharomyces cerevisiae homozygous diploid bacterial strain with the chromosome knocked out is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com