Design and construction methods and application of standardized bio-elements
A construction method and biological technology, applied in the fields of metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, and genetic engineering, can solve the problems of huge cost, difficulty in constructing and optimizing exogenous metabolic pathways, and inability to directly apply yeast and other eukaryotic microorganisms.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
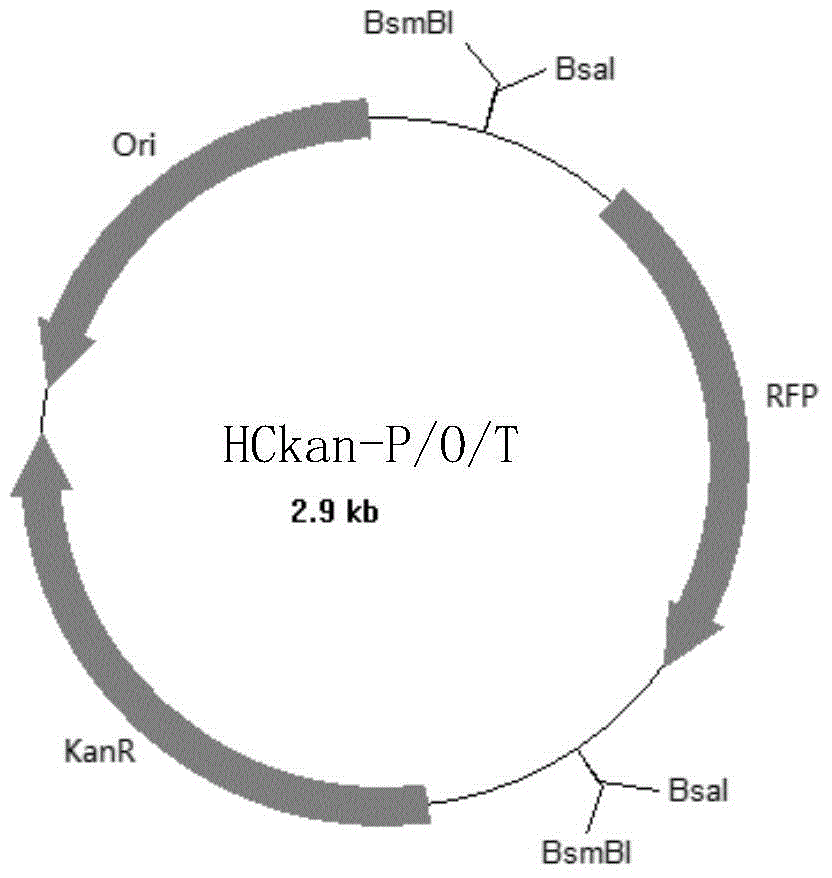
[0126] The construction of embodiment 1, HCkan-P, HCkan-O and HCkan-T
[0127] 1. Using pSMART HCKan as template, using SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2 as primers, use ultra-fidelity DNA polymerase Q5 enzyme for PCR amplification (PCR program: 94°C for 3min; 94°C for 30s, 55°C 30s, 72°C for 40s, 30 cycles; 72°C for 7min; 4°C+∞), the PCR amplification product was obtained, the PCR amplification product was digested with BsaI, and the large vector fragment 1 was obtained. The sequence of the large vector fragment 1 is shown as SEQ ID Shown in No.3.
[0128] Replace the primers with SEQ ID No.4 and SEQ ID No.5, and the remaining experimental steps are the same as the above-mentioned experimental steps to obtain the PCR amplification product, digest the PCR amplification product with BsaI, and obtain the large vector fragment 2, the large vector fragment The sequence of 2 is shown in SEQID No.6.
[0129] Replace the primers with SEQ ID No.7 and SEQ ID No.8, and the remaining experim...
Embodiment 2
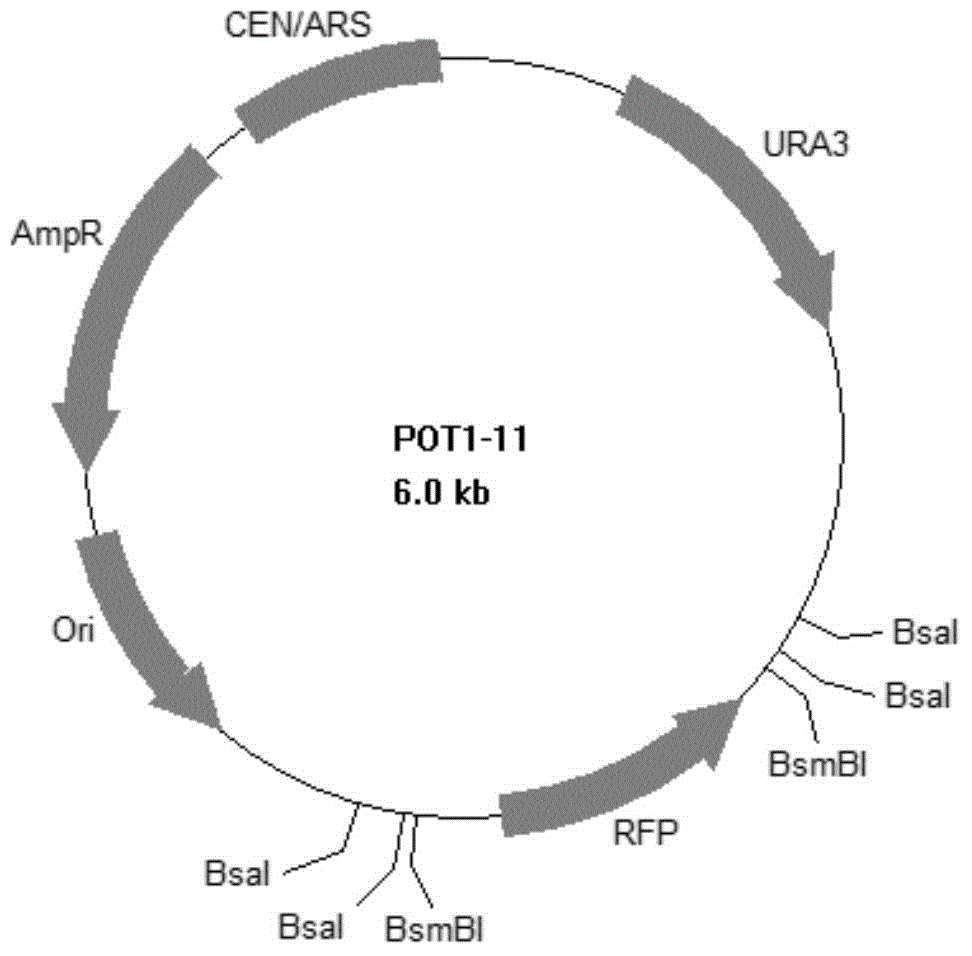
[0137] Embodiment 2, the construction of POT1-11
[0138] 1. Removal of BsaI and BsmBI sites on yeast vector pRS416
[0139] Using pRS416 as template, using F1 and R1 as primers, PCR amplification was performed using ultra-fidelity DNA polymerase Q5 enzyme (PCR program: 94°C for 3min; 94°C for 30s, 55°C for 30s, 72°C for 30s, 30 cycles; 72 ℃7min; 4℃+∞), a 2426bp PCR amplification product was obtained, and the PCR amplification product was digested with BsaI to obtain gene fragment A.
[0140] The primers were replaced with F2 and R2, and the remaining experimental steps were the same as the above-mentioned experimental steps to obtain a 1484bp PCR amplification product, which was digested with BsaI to obtain gene fragment B.
[0141]The primers were replaced with F3 and R3, and the remaining experimental steps were the same as the above-mentioned experimental steps to obtain a 1054bp PCR amplification product, which was digested with BsaI to obtain gene fragment C.
[0142] ...
Embodiment 3
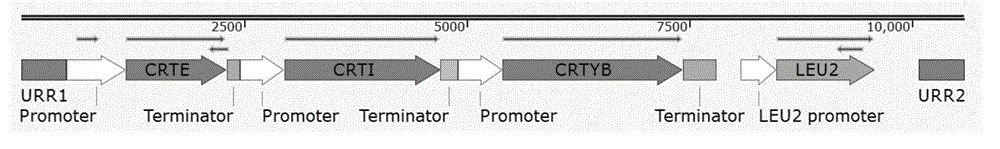
[0161] Example 3, rapid assembly of β-carotene exogenous synthesis pathway in vitro
[0162] 1. The construction of each plasmid HCKan-P-TDH3, HCKan-P-ADH1, HCKan-P-TEF2 containing the promoter
[0163] (1) Acquisition of TDH3 promoter, ADH1 promoter and TEF2 promoter
[0164] Extract the genomic DNA of yeast BY4741, use it as a template, use F5 and R5 as primers, and use ultra-fidelity DNA polymerase Q5 enzyme to perform PCR amplification (PCR program: 94°C for 3min; 94°C for 30s, 55°C for 30s, 72°C 40s, 30 cycles; 72°C 7min; 4°C+∞), a 687bp PCR amplification product a1 was obtained, which contained a TDH3 promoter. The sequence of the TDH3 promoter is shown in SEQ ID No.42.
[0165] F5: 5'-agcgtgggtc tcgggcttca ttatcaatac tgccatttca aagaatacg-3';
[0166] R5: 5'-gtgctgggtc tcacatcttt gtttgtttat gtgtgtttat tcgaaact-3'.
[0167] The primers were replaced with F6 and R6, and the remaining experimental steps were the same as the above-mentioned experimental steps to obtain a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com