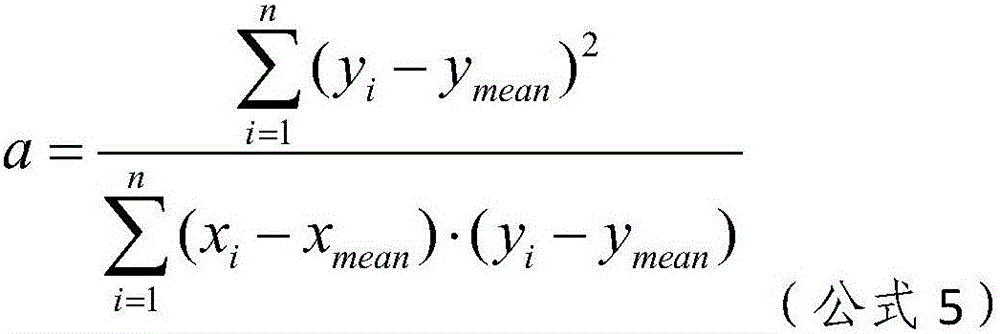Patents
Literature
51 results about "Whole chromosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
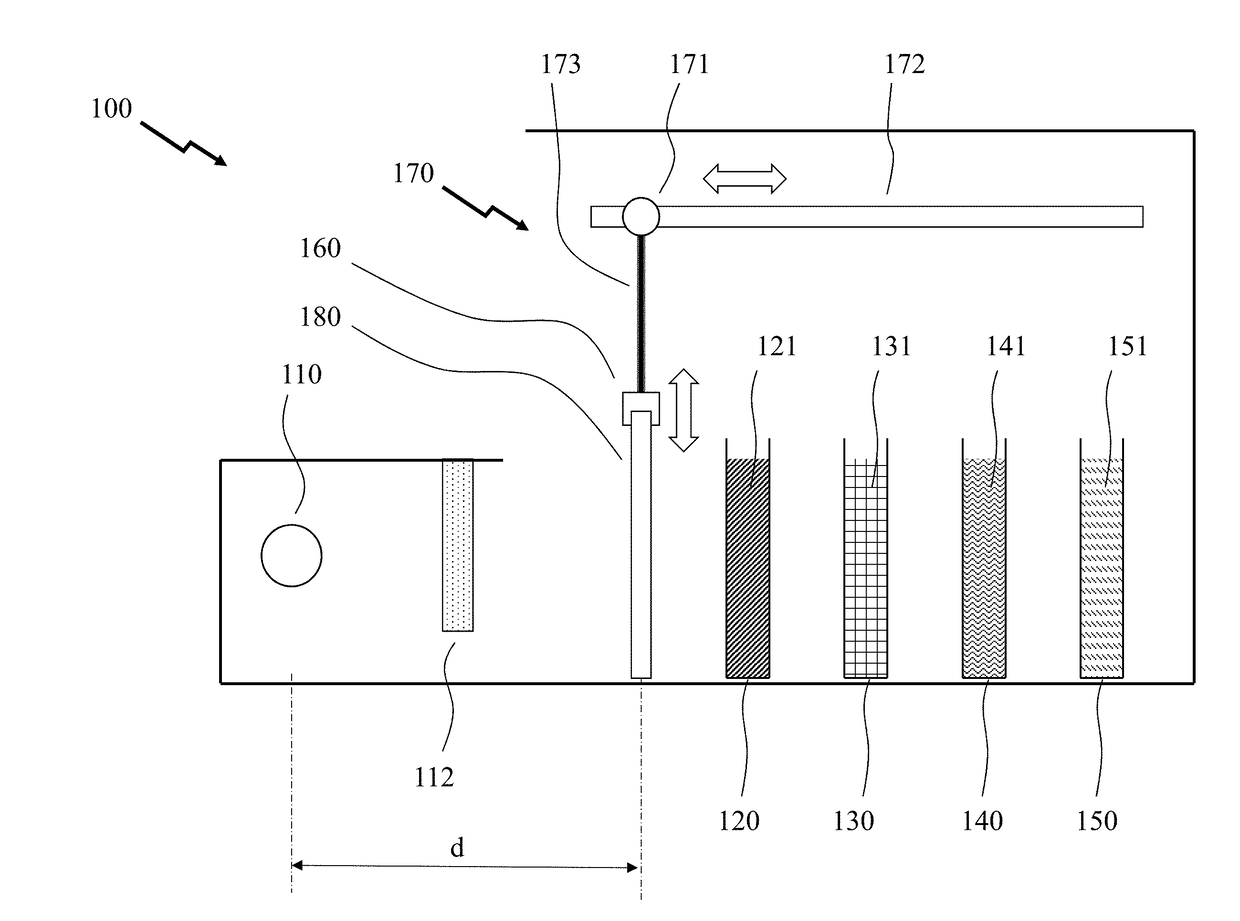
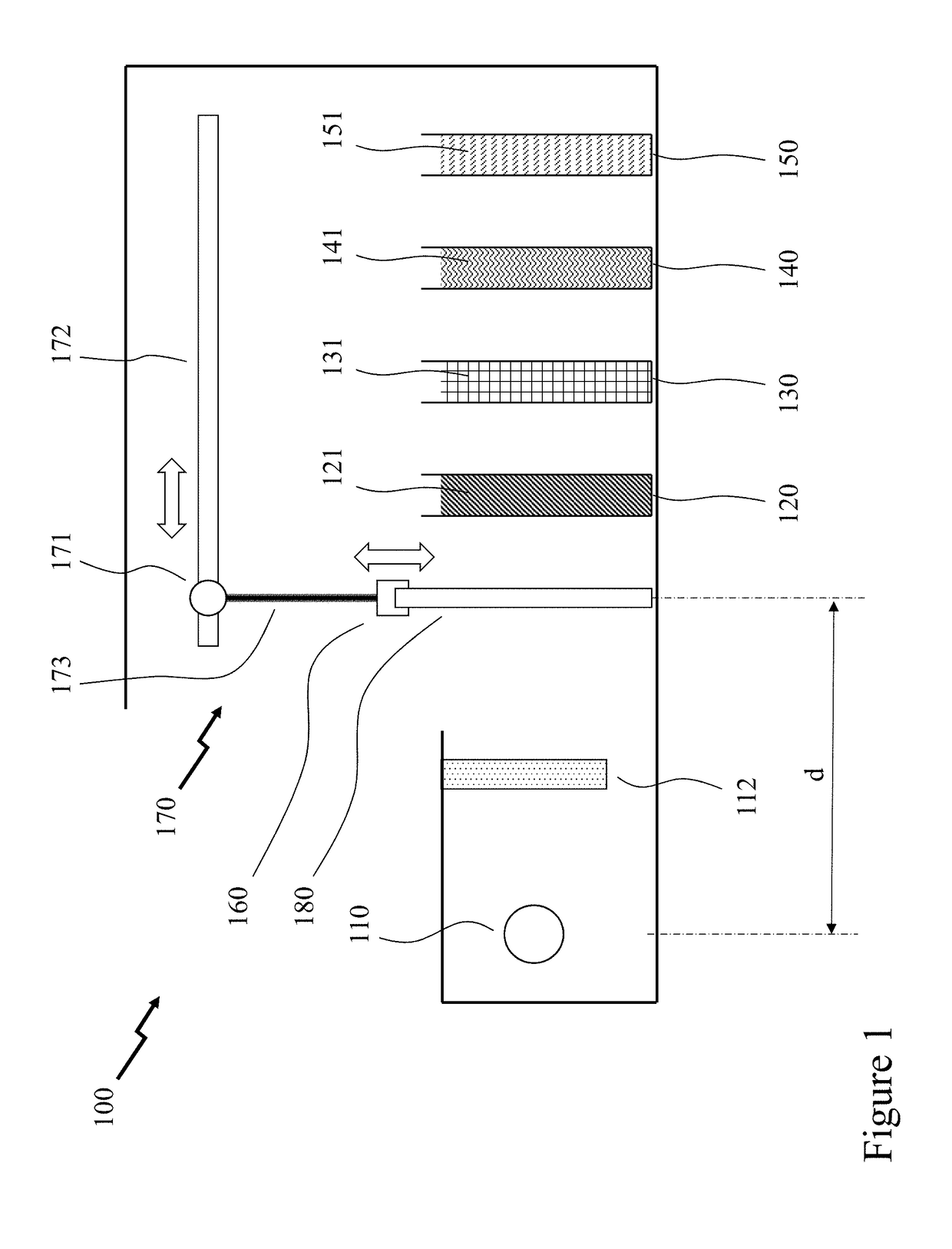
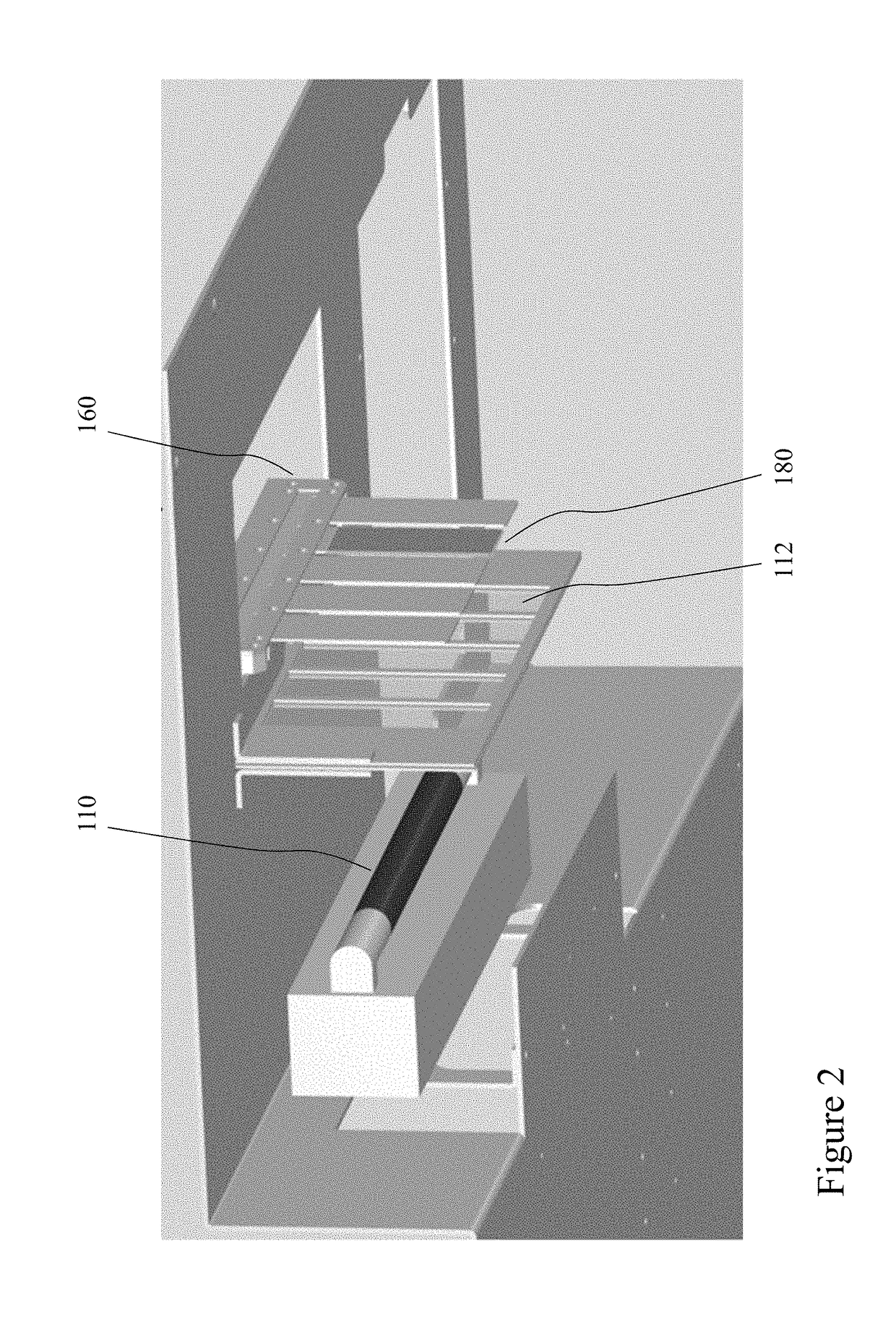
Detecting mutations and ploidy in chromosomal segments
ActiveUS20170107576A1Reduce sensitivityIncreased susceptibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsNucleotideBiology
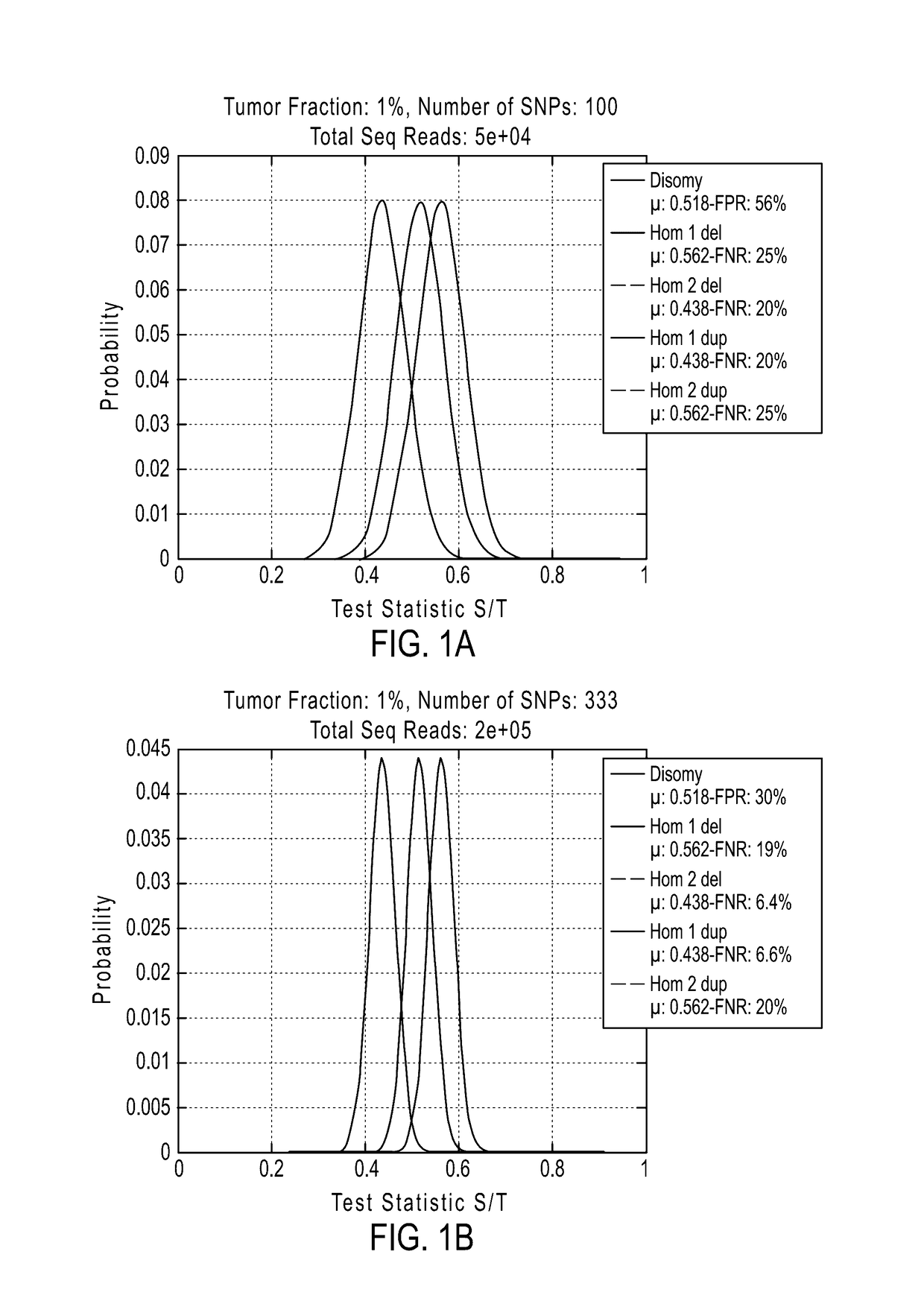
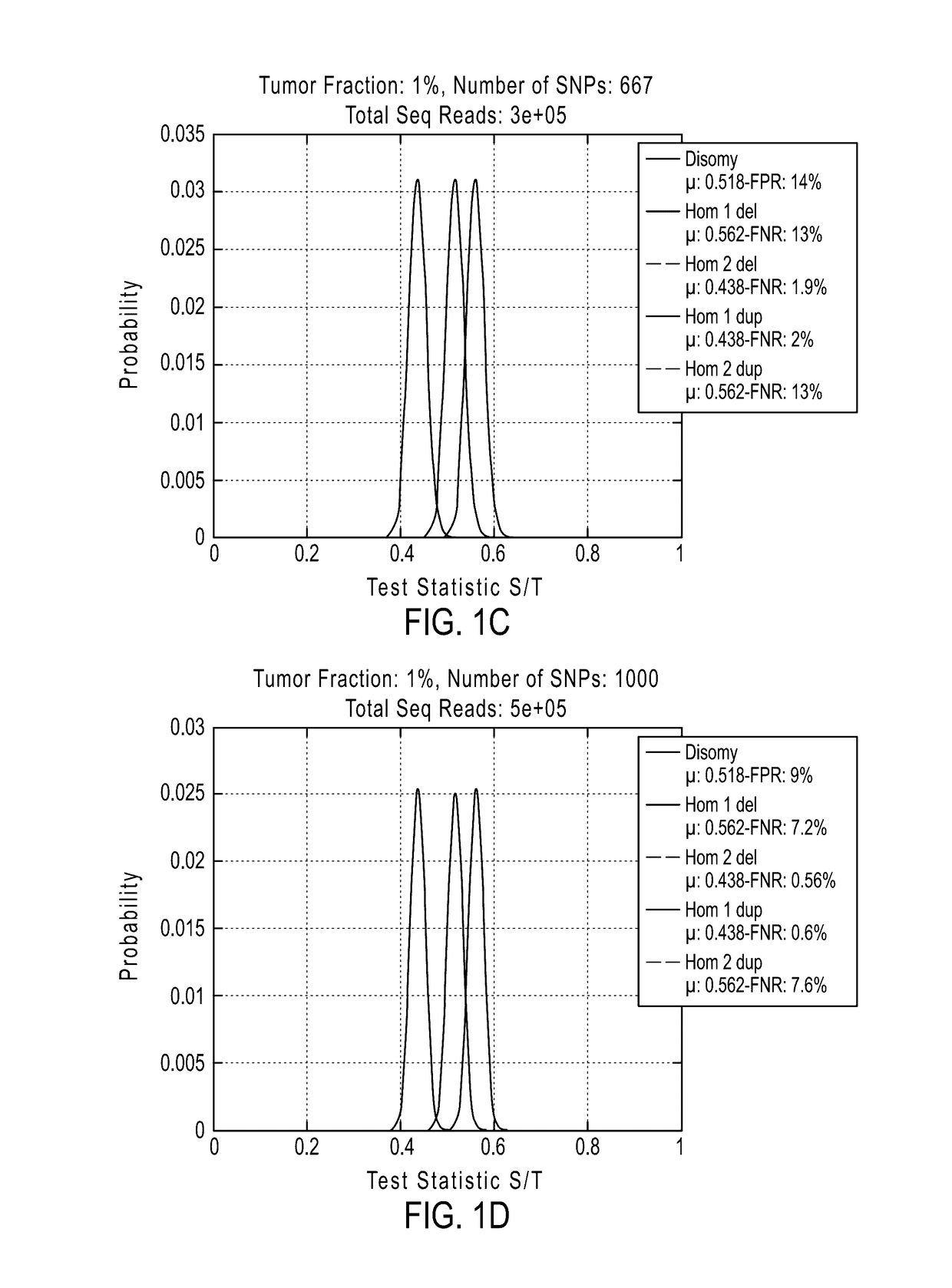
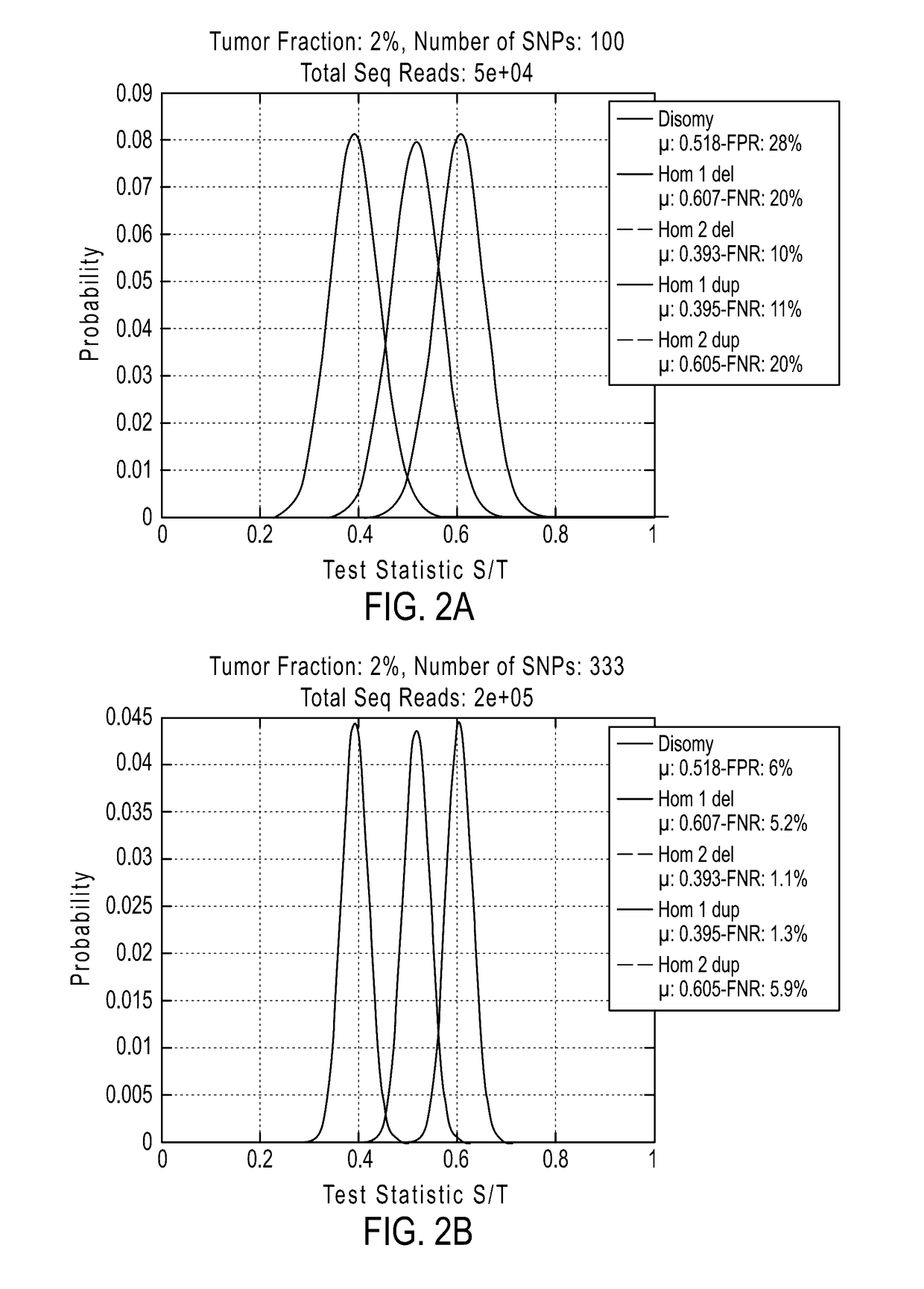
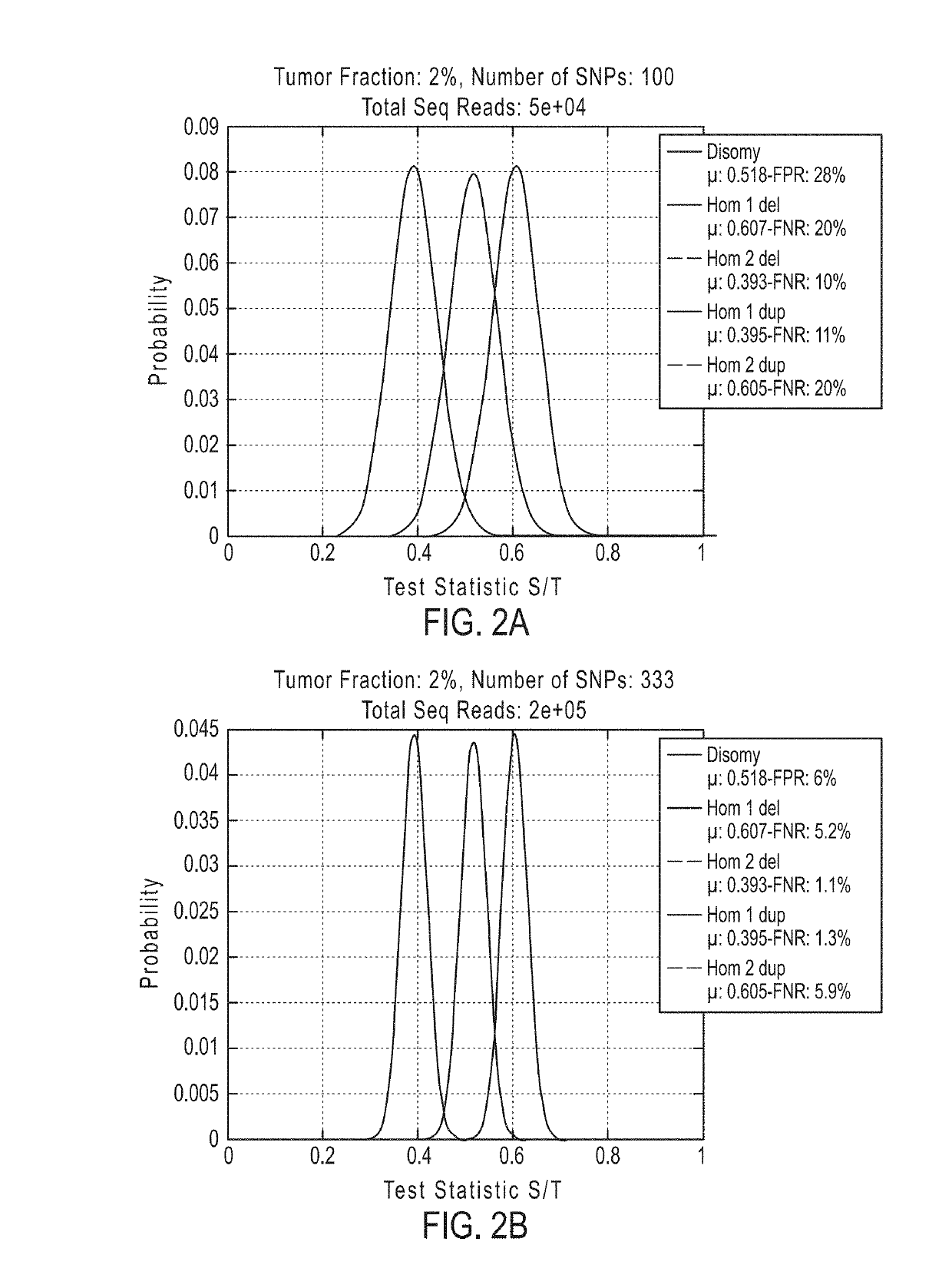
The invention provides methods, systems, and computer readable medium for detecting ploidy of chromosome segments or entire chromosomes, for detecting single nucleotide variants and for detecting both ploidy of chromosome segments and single nucleotide variants. In some aspects, the invention provides methods, systems, and computer readable medium for detecting cancer or a chromosomal abnormality in a gestating fetus.
Owner:NATERA
High resolution chromosomal mapping
ActiveUS20070238105A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStructural analysisGenome
The present invention generally relates to spatial and structural genomic analysis compositions, which can be used for the mapping of chromosomes and structural analyses of chromosomal rearrangements, including the entire chromosome, as well as specific portions or regions of interest of the chromosomes. In some embodiments, multiple portions of the genome can be distinguished, for instance, using a first detection entity and a second detection entity different from the first detection entity. The detection entities may be immobilized relative to oligonucleotides, which may be selected to bind to different locations within the chromosome. For instance, the oligonucleotides may be at least substantially complementary to the chromosome, e.g., substantially complementary to a specific location of the chromosome.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
High resolution chromosomal mapping
ActiveUS8058055B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStructural analysisGenome
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Detecting cancer mutations and aneuploidy in chromosomal segments
ActiveUS20160333416A1Improve throughputIncrease probabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleotideBiology
The invention provides methods, systems, and computer readable medium for detecting ploidy of chromosome segments or entire chromosomes, for detecting single nucleotide variants and for detecting both ploidy of chromosome segments and single nucleotide variants. In some aspects, the invention provides methods, systems, and computer readable medium for detecting cancer or a chromosomal abnormality in a gestating fetus.
Owner:NATERA
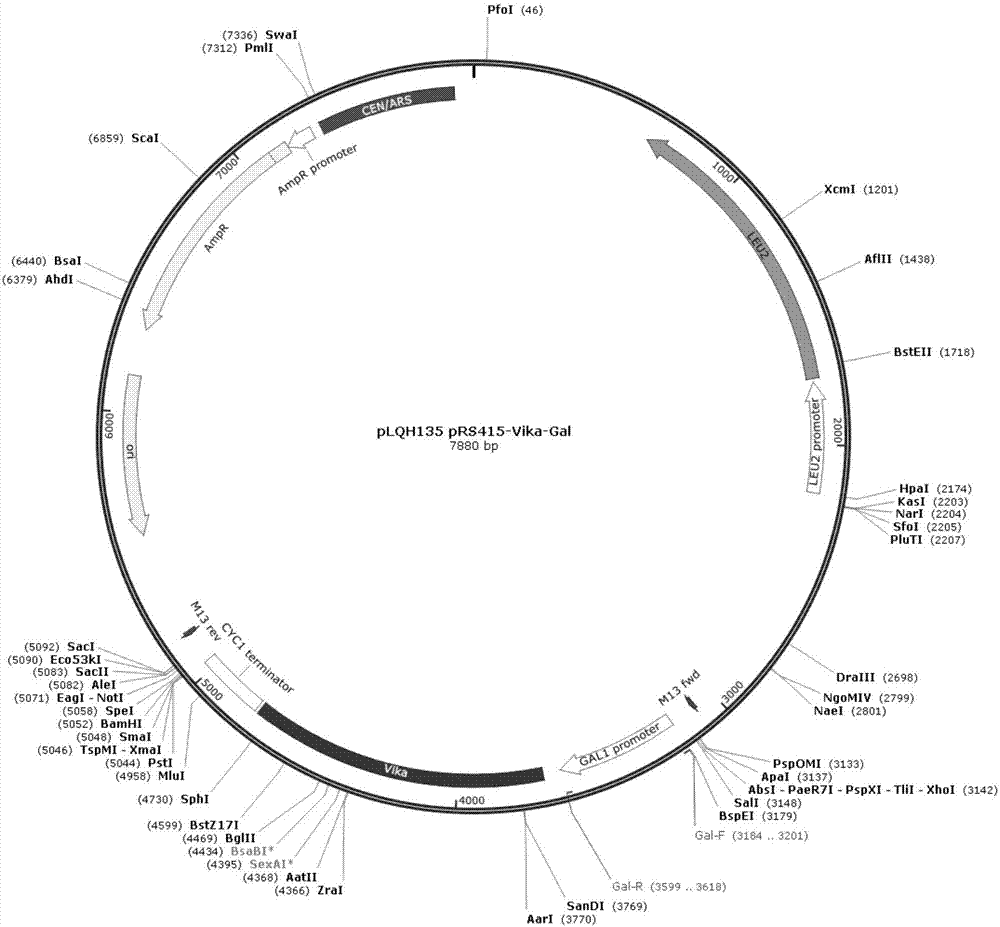
Method for knocking down brewing yeast chromosome
ActiveCN107858346AKnockout simpleKnockout EfficientHydrolasesStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyYeast chromosome
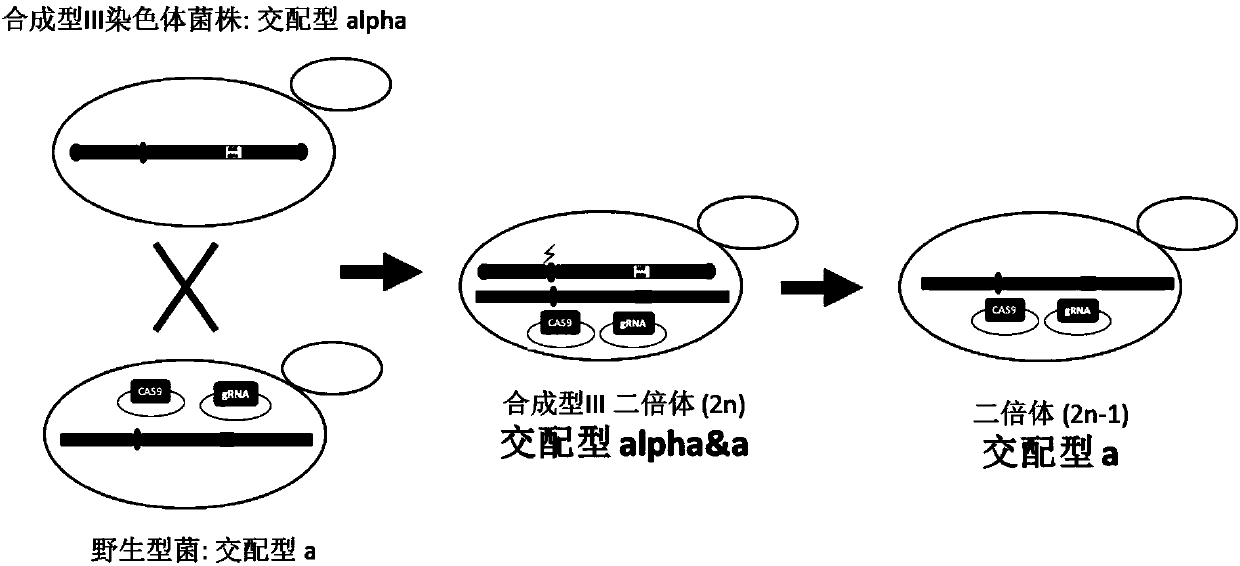
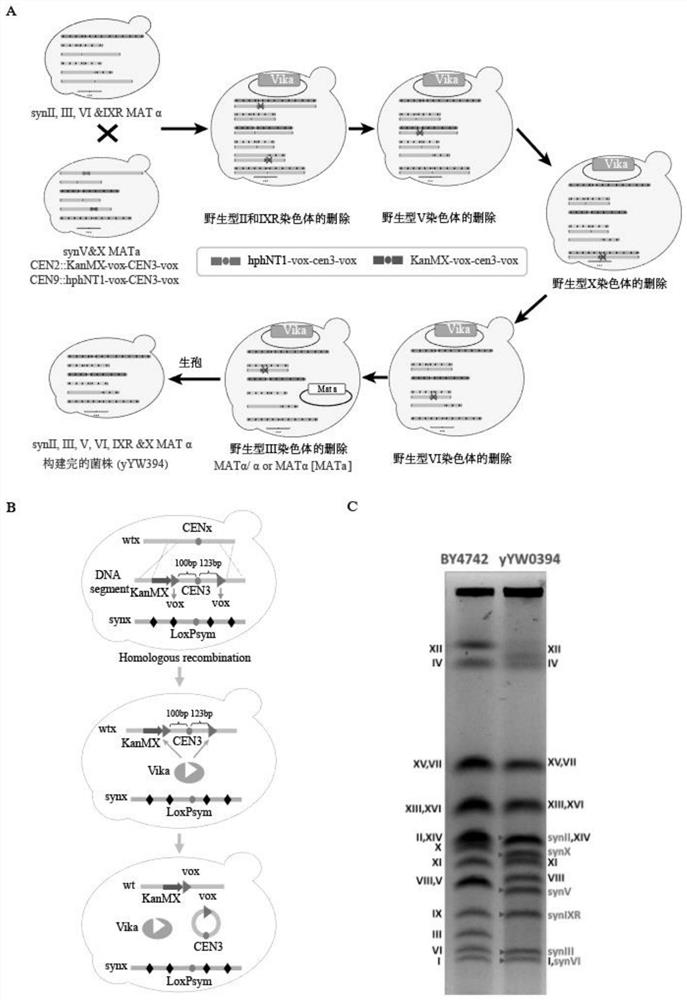
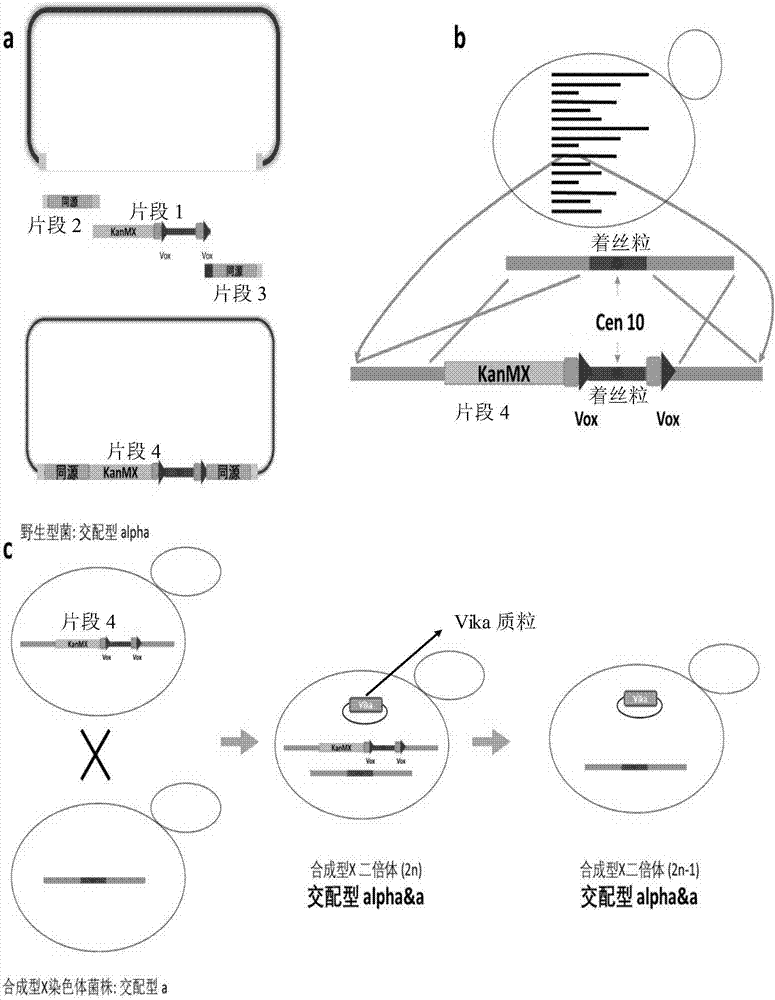
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and specifically discloses a method for knocking down brewing yeast chromosome. The method is characterized in that the complete yeast chromosome is cut according to the CRISPR / Cas9 base technology; a specificity target close to centromere is selected; a corresponding guide RNA is designed to guide Cas9 protein to generate an incision closeto the centromere, thus realizing the knocking down of the whole chromosome. Compared with the conventional method for losing the whole chromosome in manners such as inducing through a Ga1 promoter, and reductional division, the method has the advantages that the brewing yeast chromosome is simply, efficiently and quickly cut; the cross exchange of sister chromatids can be avoided; the chromosome-knocked-down homozygous brewing yeast diploid strain can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Mapping of proteins along chromatin by chromatin cleavage
ActiveUS7790379B2Accurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein insertionProtein C
The present invention is directed to a method for localizing, in chromatin or DNA, the binding loci of a chromatin or DNA binding protein comprising the following steps:a) tethering, directly or indirectly, an enzyme with regulatable activity to said chromatin binding protein,b) transiently activating the regulatable enzymatic activity bound to the targeted chromatin andc) mapping the enzymatically-modified genomic sites introduced by the enzyme into the chromatin.According to an embodiment of the invention, the regulatable enzyme is a regulatable protease. The mapping step may be carried out on specific DNA fragments, or on a chromosome-wide scale or a genome-wide scale.The present invention is also directed to kits for carrying out the methods of the invention.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
Method for gene association analysis on basis of deep learning algorithm
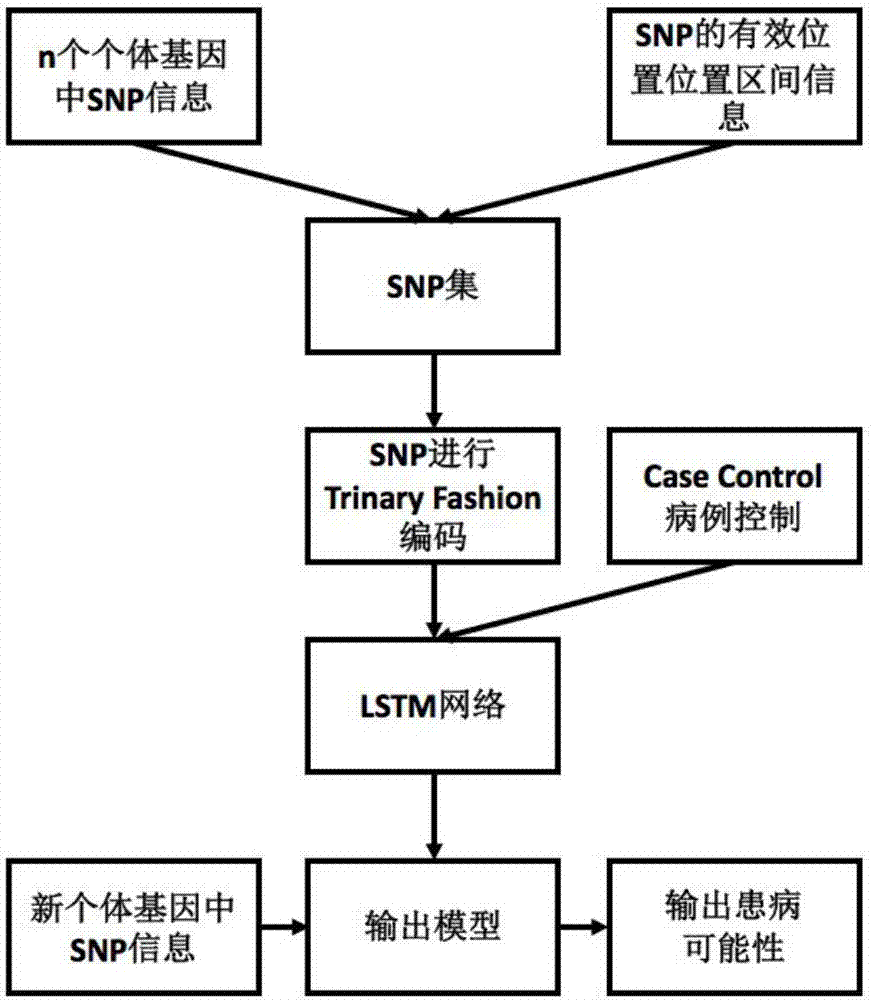
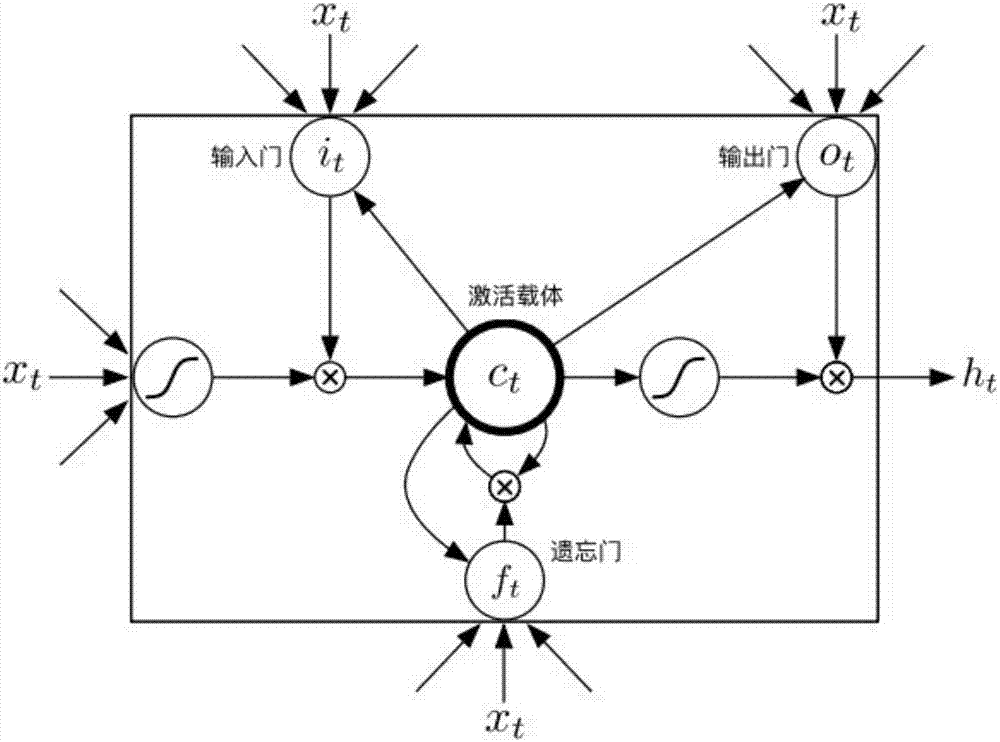
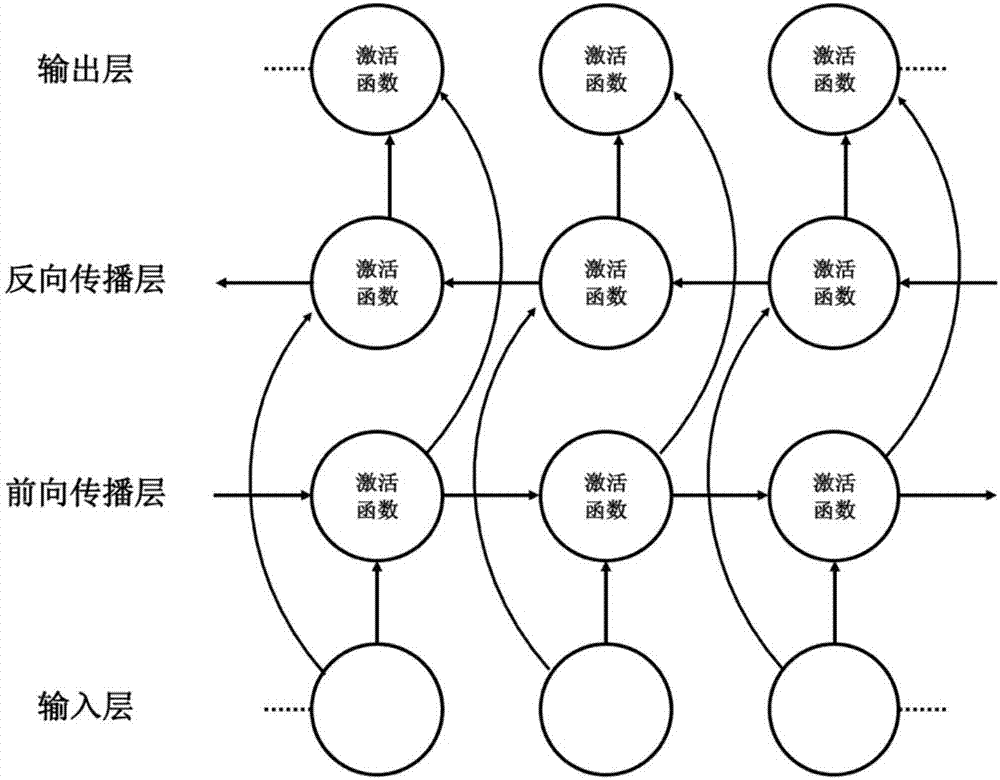
The invention discloses a method for gene association analysis on basis of a deep learning algorithm. The method based on SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) set analysis needs to take SNP information, which comes from different positions of the same individual but is related, as a reference, and SNP of the individual is divided into multiple units according to existing biological knowledge. Firstly, all SNP is divided into multiple SNP sets on the whole chromosome level according to related knowledge of biology such as the principles approaching genomic characteristics. After division ends, each SNP set is input into an established bidirectional LSTM (long short-term memory) network, the network is a circulating neural network, and the state of the network contains old information of the last moment and also is a basis of weight change of the next moment. After LSTM network learning is completed, the attention degree required for input data can be output through network calculation. The method has better sensitivity and specificity and a new field is explored for development and research of the clinical medicine, genetic epidemiology and preventive medicine.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Genome assembling method
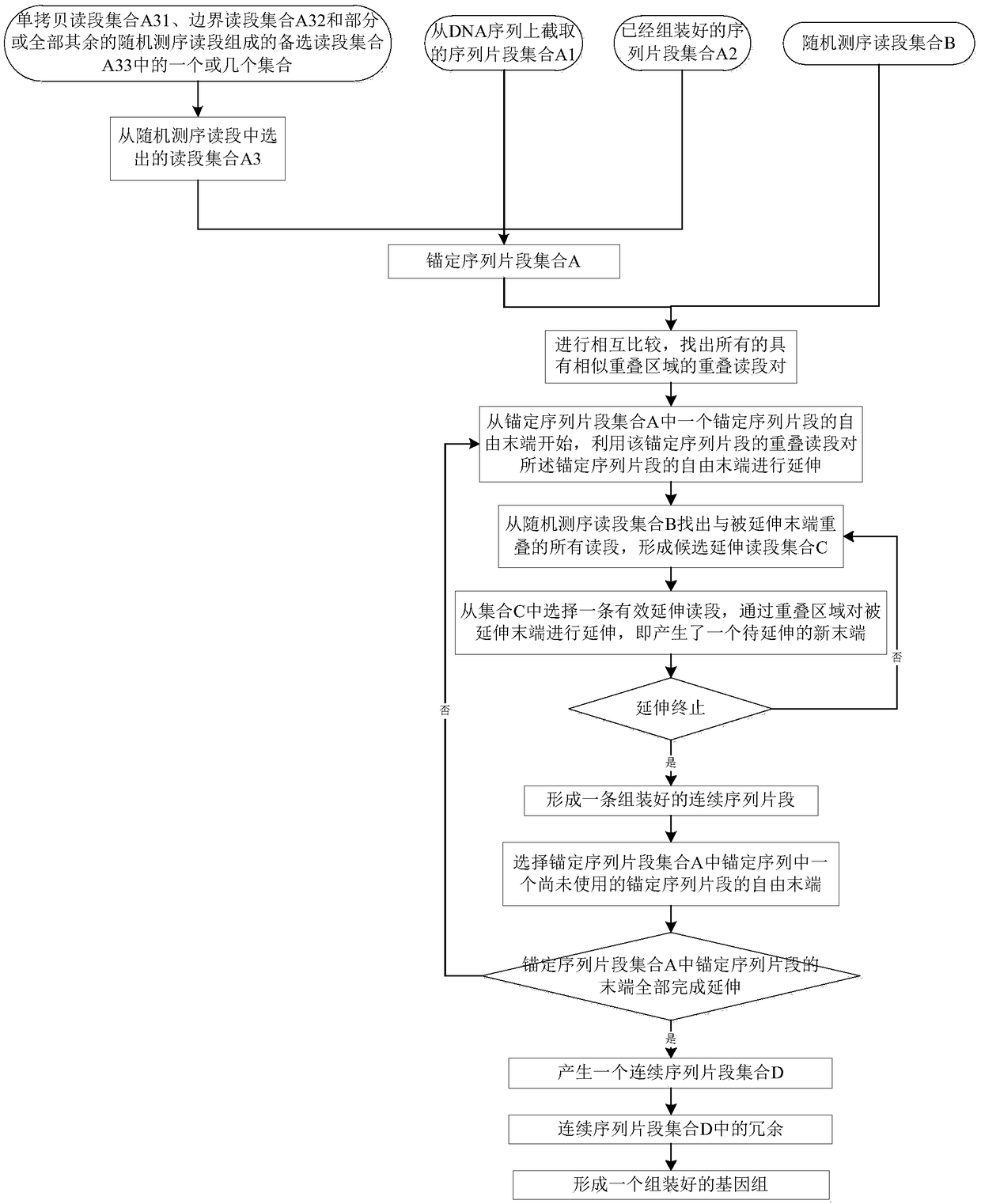
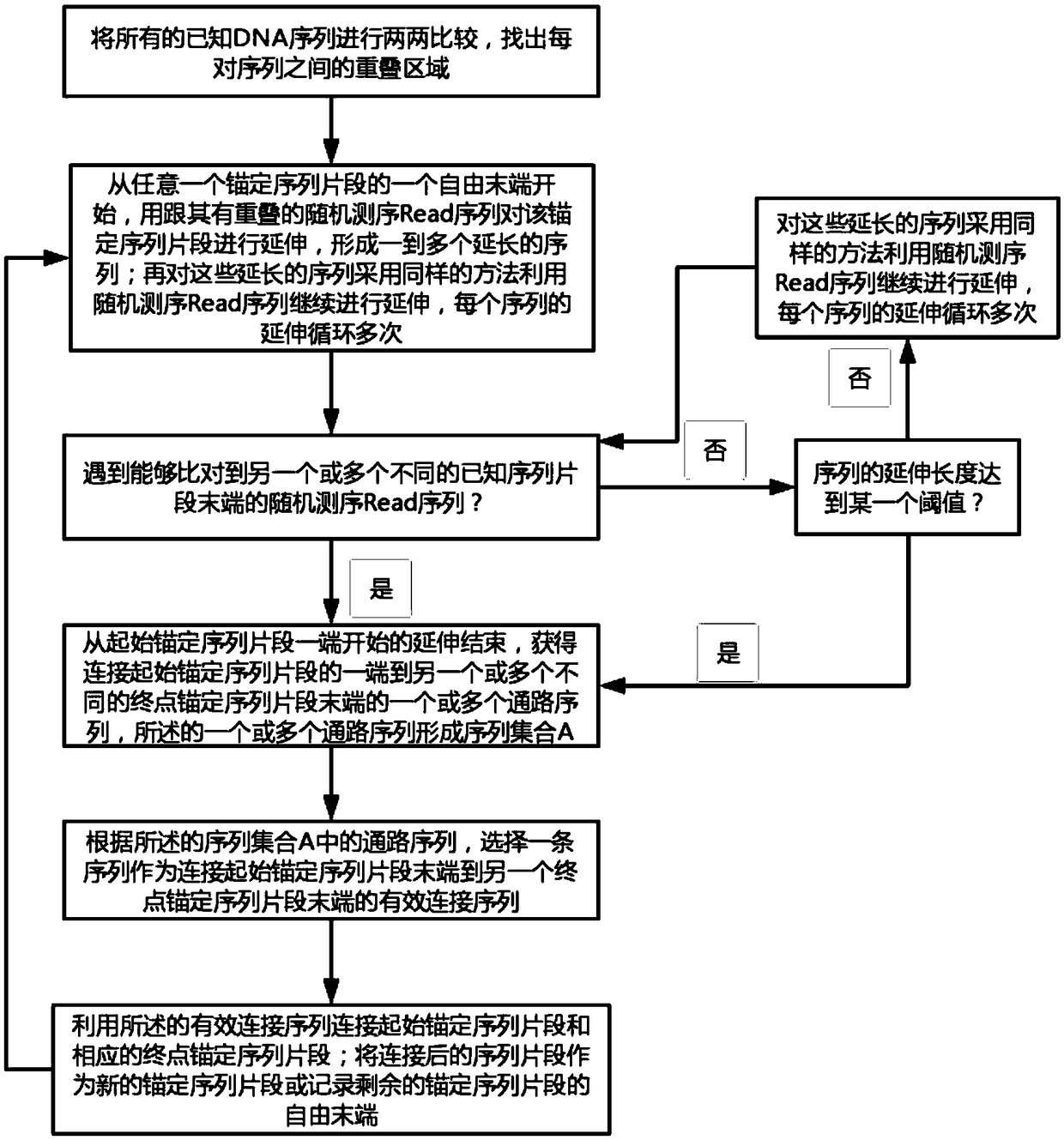
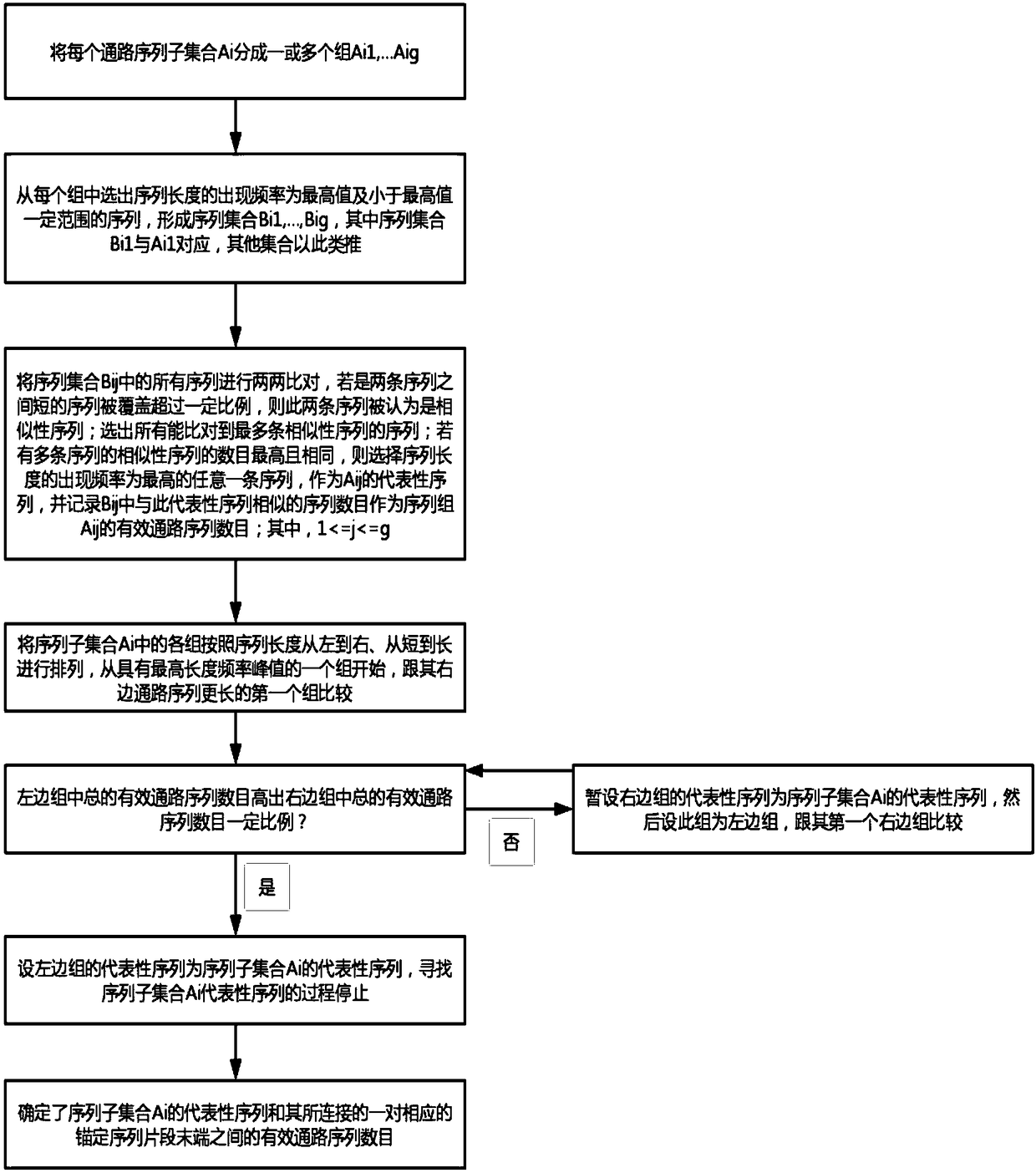
ActiveCN109234267AEfficient assemblySimplify the implementation process of assemblyDNA preparationComputational biologyChromosome
The invention discloses a genome assembling method, comprising the following four steps: sequence comparison, sequence extension, completion of extension and removal of redundancy. Genome-wide assembly is divided into two main steps: assembly of single copy sequence and assembly of remaining sequence, which simplifies the implementation process, makes the whole method fast, efficient and error-free, and greatly improves the continuity of the assembly sequence fragments and the assembly quality. By assembling the whole genome sequence with the method of the invention, the whole genome sequencecan be recovered quickly and efficiently, and the whole chromosome and the whole genome sequence can be recovered more easily. The genome assembling method of the invention can also be used for filling the sequence of the blank region in the genome sequence, in particular, the assembling effect can be greatly improved by combining the genome optical map information or the chromosome grouping sorting information. And for judging whether there is a connection between any two sequences or for estimating a distance between two adjacent sequences.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Noninvasive prenatal biological information detection and analysis method
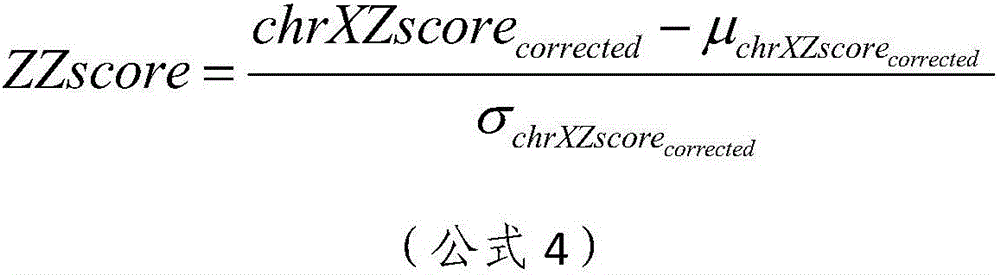
The invention relates to the field of medical detection and particularly discloses a noninvasive prenatal biological information detection and analysis method. For improving the accuracy of analyzing different quantities of to-be-detected samples, different detection and analysis methods are selected according to the different quantities of the to-be-detected samples, and different analysis policies are adopted for parameters obtained by the to-be-detected samples and parameters obtained by a normal reference set, so that the accuracy of analysis is improved to a greater extent. According to the method, the problem of inaccurate regression result caused by great influence of abnormal data on slope due to use of a least square method for regression in a process of correction by using a whole chromosome method in the prior art is well solved by adopting robust regression and CV regression, so that the robustness and accuracy of sample analysis are ensured. A set of analysis method for judging anomaly of sex chromosome by utilizing a ZZ value is originated; and the chromosome anomaly is judged by using the ZZ value method, so that related statistic judgment standards are better met, a result is more accurate, and the reliability of the method for judging the anomaly of the sex chromosome is enhanced.
Owner:北京普康瑞仁医学检验所有限公司
Apparatus and methods for efficient processing of biological samples on slides
InactiveUS20060216744A1Assay rapid and convenientDissolve fastBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideBiochemistry
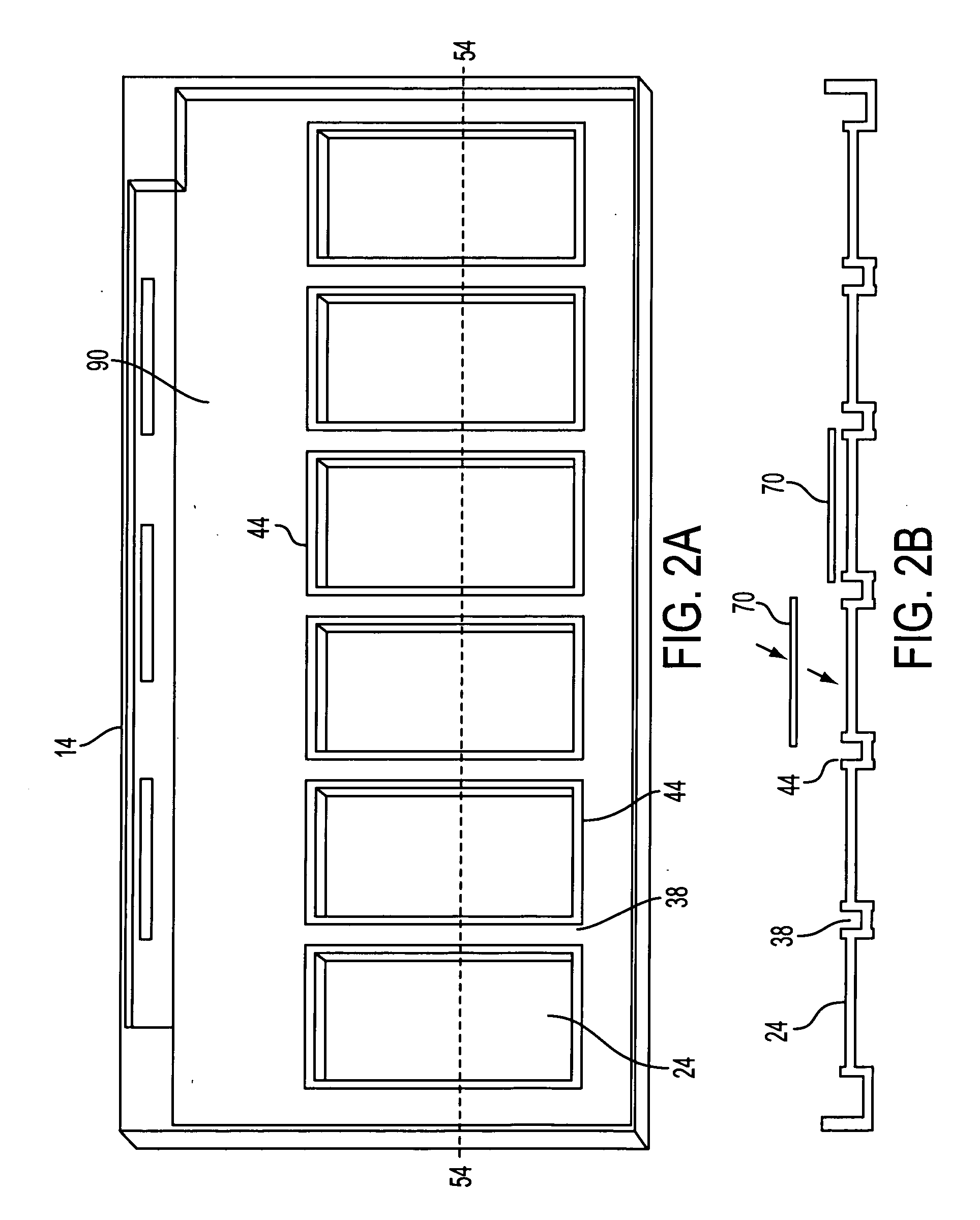
Methods for treating biological samples on microscope slides are set forth. One aspect of the invention is the use of predried reagents in wells on trays onto which the slides are placed, especially the use of predried reagents which dissolve sequentially. Yet another aspect of the invention is the use of external controls placed directly on a microscope slide in conjunction with a biological sample to be assayed. The external controls can be conveniently placed on a membrane which can be affixed to the slide. A further aspect of the invention is a specially designed tray to allow whole chromosome painting of all chromosomes of a cell sample on a single slide. The invention is also drawn to a coverslip with concave wells which act as reaction chambers when placed against a slide and filled with buffer. Preferably a reagent is predried in the well. A further aspect of the invention is a method of reacting samples on slides by placing them into a reaction chamber together with a coverslip which has a predried reagent on it.
Owner:AMERICAN REGISTRY OF PATHOLOGY
Method for Detecting Chromosome Structure and Gene Expression Simultaneously in Single Cells
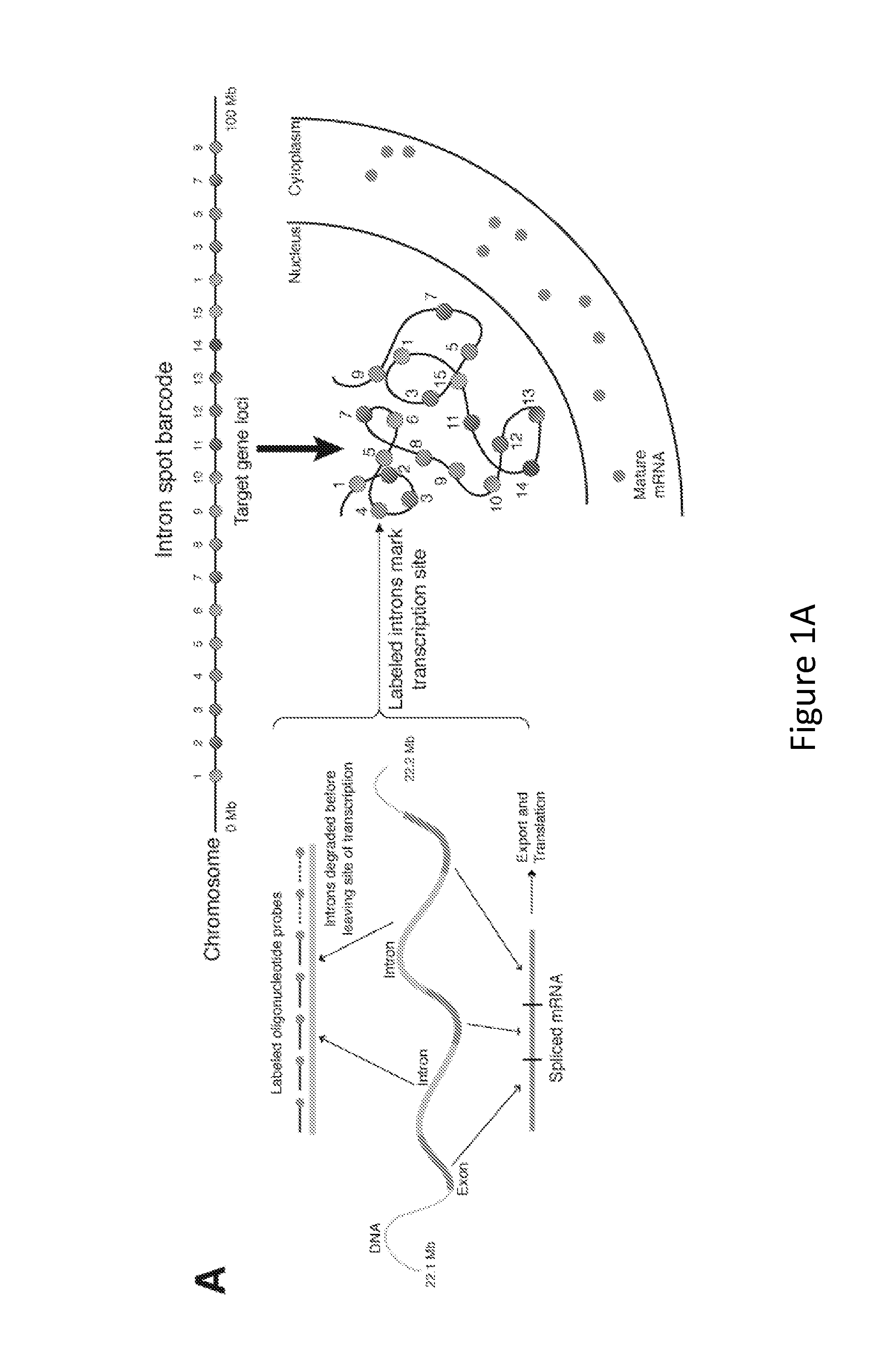
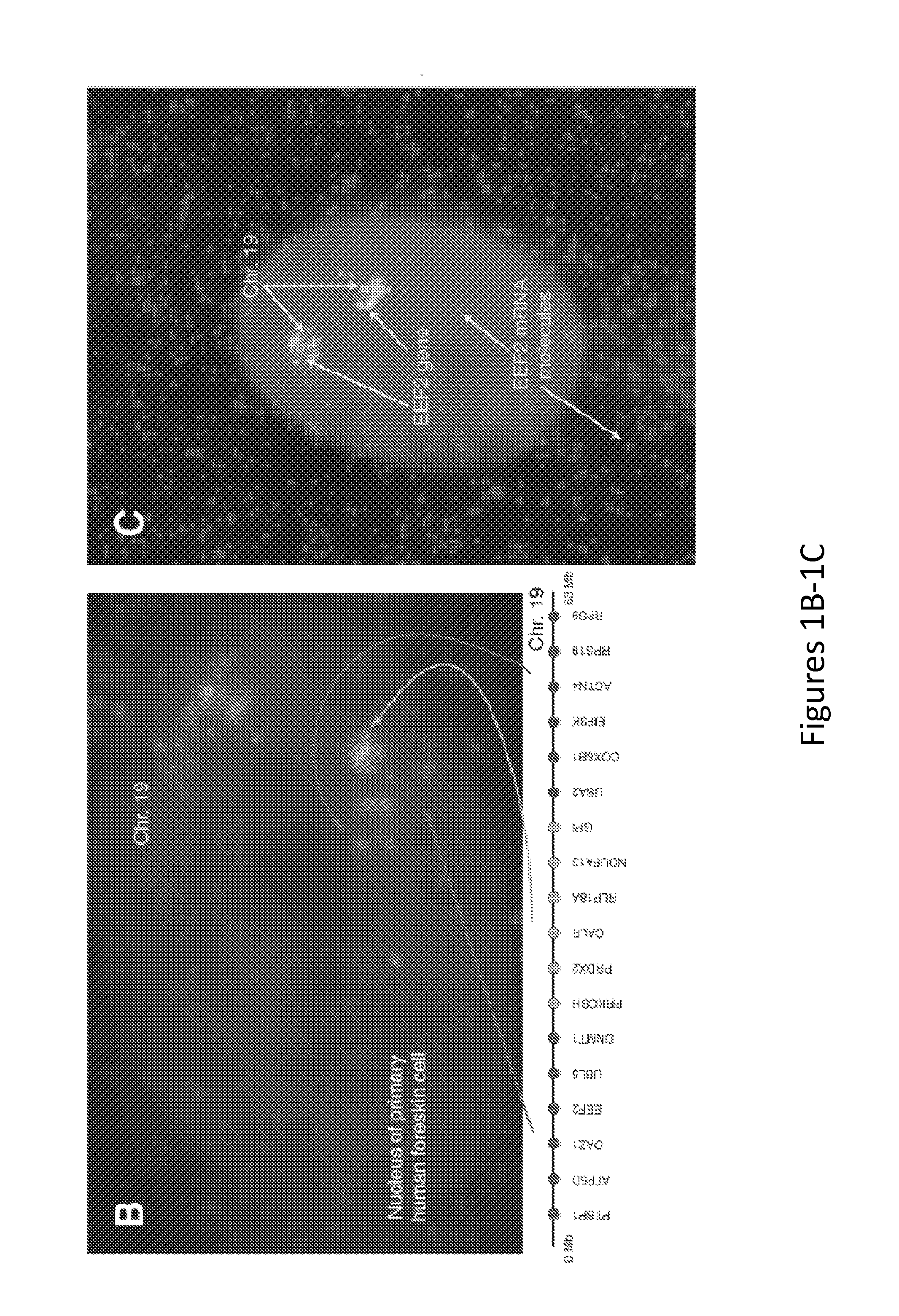
The present invention relates to systems and methods for measuring chromosome structure and gene expression. In one embodiment, the present invention includes an assay for determining the spatial organization of gene expression in the nucleus. The present invention also includes a method based on fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) that simultaneously yields information on the physical position and expression of individual genes. By lighting up a large number of targets on a particular chromosome using a bar-coding scheme, the large scale structure of an entire chromosome can be determined.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method for screening cells and method for detecting oral carcinoma cells
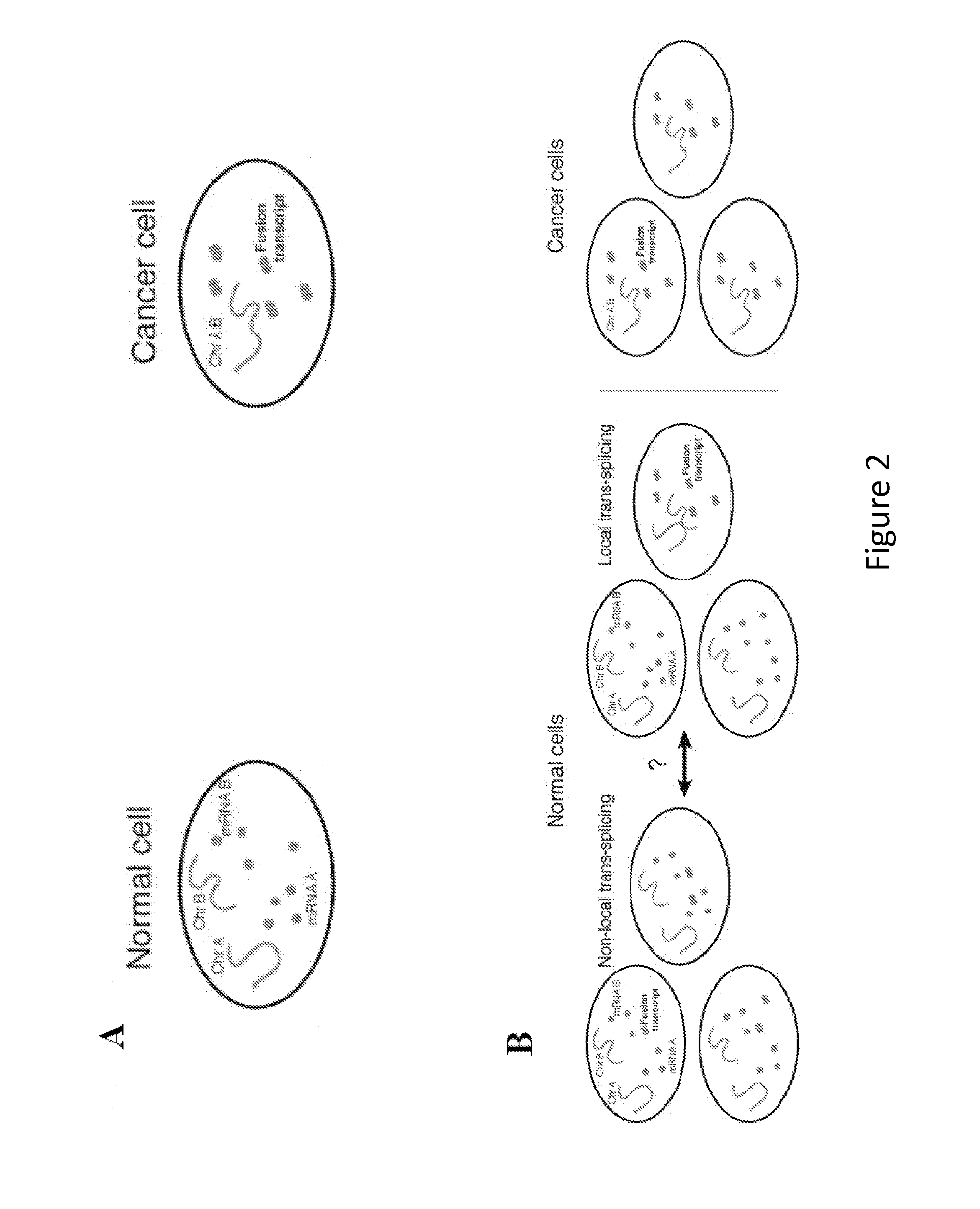
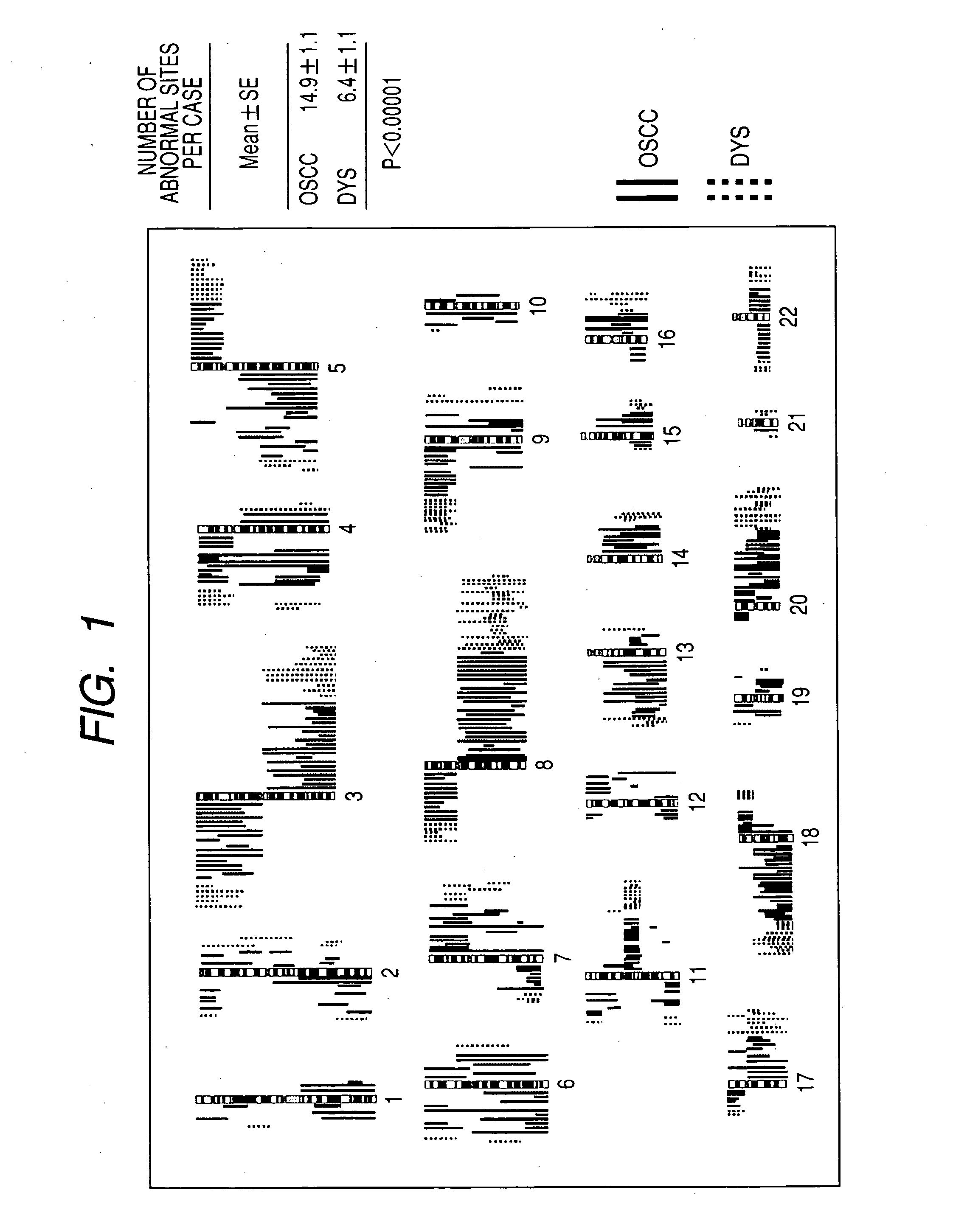
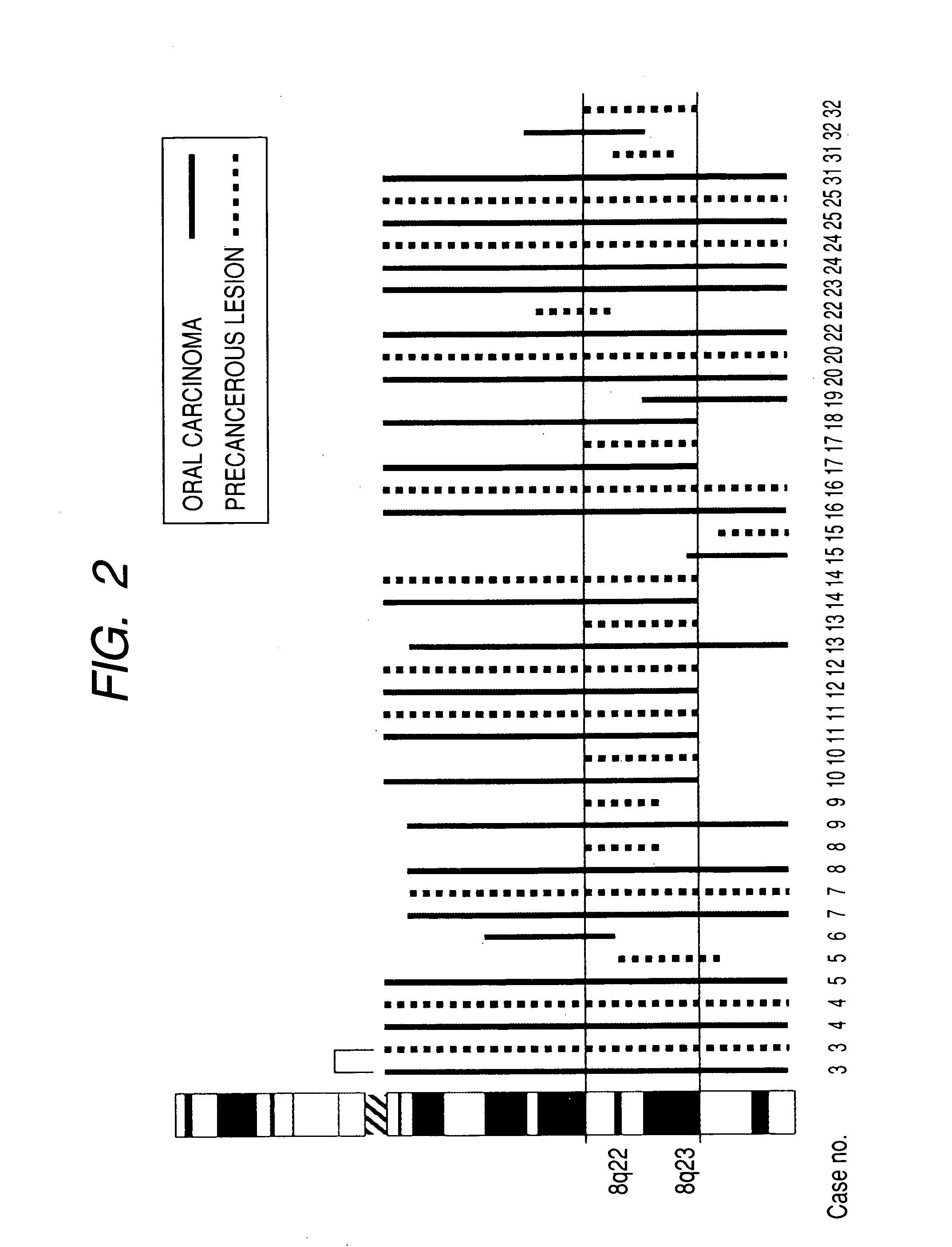
InactiveUS20060068435A1Effective evaluationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNAChromosomal region
The present invention provides a method of detecting oral carcinoma cells with high accuracy, and a method of making possible early detection of oral carcinoma or discrimination between a precancerous lesion and an early cancer in diagnosis of oral carcinoma. The methods are achieved by screening cells for oral carcinoma or precancerous lesion by measuring a DNA copy number in whole chromosomes or a part thereof in a sample, wherein chromosomal regions for which said copy number is measured comprise at least one region selected from the group consisting of: a 22-23 region in the q arm of Chromosome 8, a 14-21 region in the p arm of Chromosome 3 and a 12-22 region in the p arm of Chromosome 5.
Owner:CANON KK
Single cell whole genome amplification method
InactiveCN105296466AGood repeatabilityExcellent uniformityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGenomic sequencingNucleotide
The invention discloses a single cell whole genome amplification method, comprising following steps: (1), performing separating to obtain single cell samples; (2), subjecting the single cell samples to whole genome DNA amplification; (3), subjecting an amplification product to quantitative and qualitative analysis; (4), establishing a genome sequencing library, performing sequencing, and performing genome bioinformatic analysis. The single cell genome DNA amplification method is built and can be used to detect the single, tertiary, multiple and sex chromosome deficiency of a whole chromosome, the insertion and deficiency of few bases, DNA copy number variation, and the genetic variation information of single cell genomes such as single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Owner:SUZHOU BASECARE MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
Method for screening environmental stress response promoters
InactiveCN106520905AEasy to dig, effective and intuitiveMeet the needs of constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceStress conditionsMicrobiology
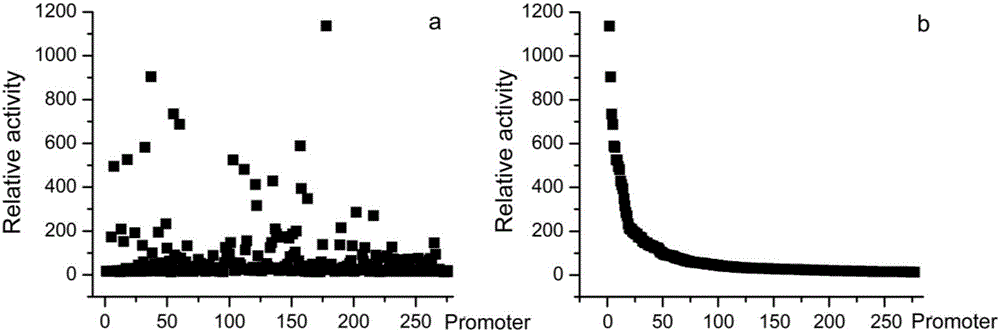
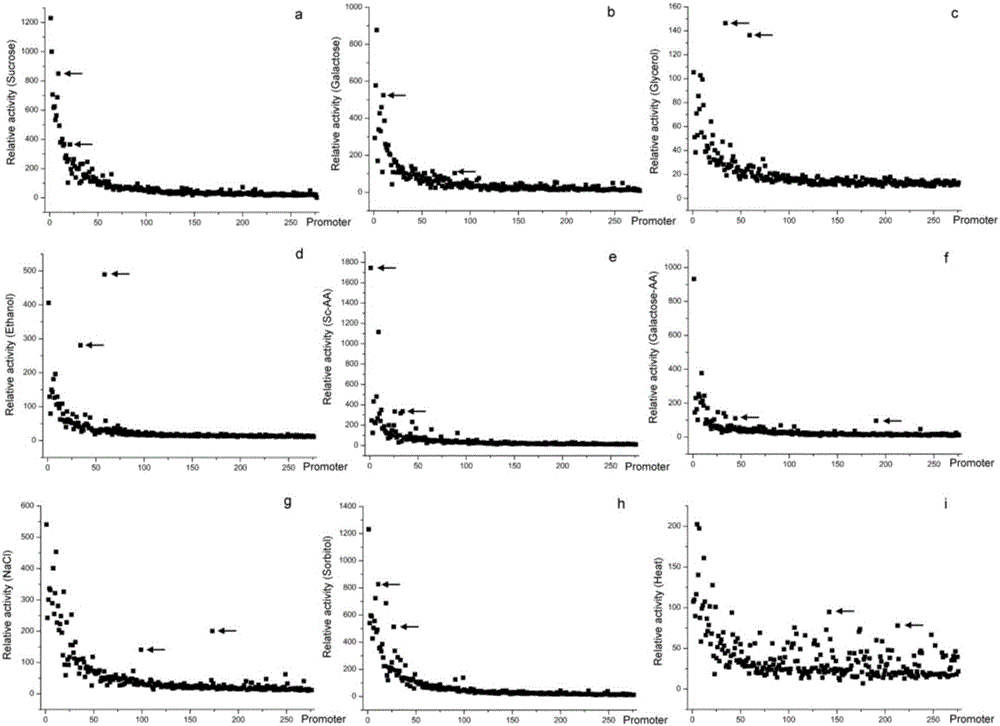
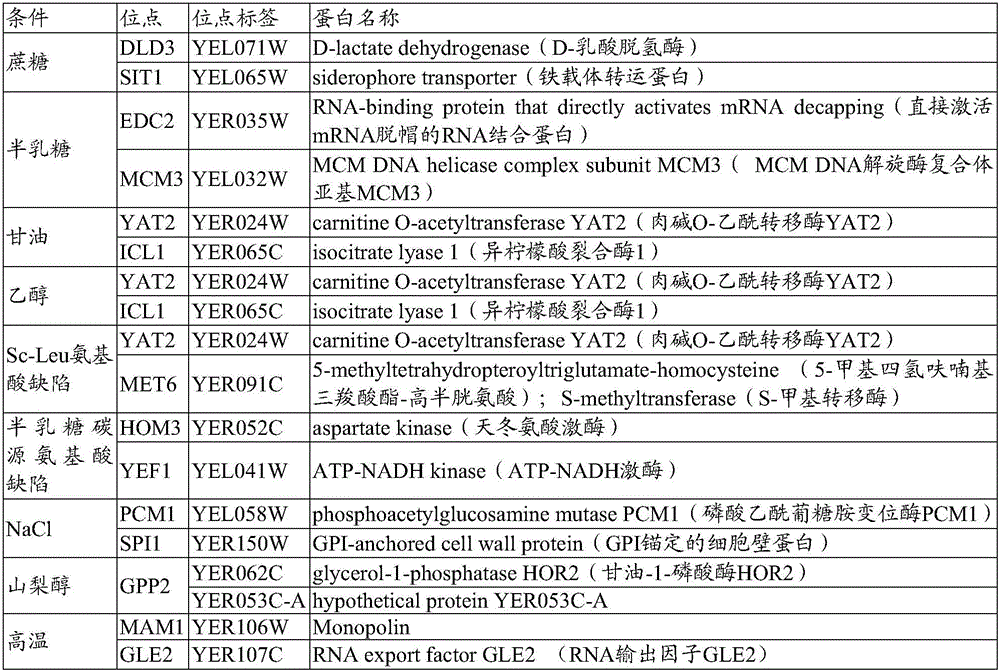
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and provides a method for screening environmental stress response promoters. The method comprises the steps that a promoter library is established, representation strains of the promoter library are activated and then cultivated under different stress conditions, OD600 and the fluorescence intensities are measured, the fluorescence intensities of different component culture media and under different culture conditions are analyzed, and the environmental response promoters are excavated. The method is based on the natural promoter library of saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomes V, quantitative presentation and excavation of promoters of a whole chromosome size under specific culture conditions are achieved, and the promoters giving response to different environment conditions are obtained through screening. The method provided by the invention can be further applied to screening of promoters, giving to response to different environment conditions, of other promoter libraries, and screening of promoters giving response to other conditions, and the target stress response promoters can be excavated systematically, conveniently, effectively and visually.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for separating chromosomes in plant cells by using fluorescence in-situ hybridization
InactiveCN101580832AIntegrity guaranteedBroaden the range of separationLibrary creationDNA preparationChemical treatmentFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for separating chromosomes in plant cells by using fluorescence in-situ hybridization. The method for separating the chromosomes in the plant cells comprises the following steps of: the fluorescence in-situ hybridization is carried out on the plant cells, the single chromosome of which is picked; by comparing with the corresponding fluorescence in-situ hybridization map of the normal plant cells, the picked single chromosome is defined to be which chromosome, thus separating a purpose chromosome. The method has the advantages of being capable of separating the chromosomes with similar types and specific bands, widening the separating range of the chromosomes, avoiding the unnecessary chemical processing in the manufacture process of the chromosome specimens, preventing the DNA of the chromosomes from being damaged, guaranteeing the completeness of the separated DNA. A microclone library of the whole chromosomes of the wheat can be obtained by applying the invention.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting differential methylation region of plant genomes
The invention provides a method for detecting a differential methylation region of plant genomes, and belongs to the technical field of genomics and bioinformatics. Single-locus methylation data on whole genomes of a treatment group and a control group is obtained separately through methylation sequencing of the whole plant genomes; single-locus methylation information on the whole genomes of thetreatment group and the control group is read separately and stored by section; stored methylation information of each section of the whole genomes is stored with 200 bp as a window and 50 bp as a step length sliding window, and the scanned methylation information is stored into a python dictionary by section; the methylation information, stored in the python dictionary, of each section of the whole genomes is screened, and the methylation information of each section in each window is counted according to the obtained single-locus methylation information on the effective whole genomes. By means of the method, the python dictionary is utilized for storing a whole chromosome with 50 bp as a section, subsequent operations are facilitated, and a lot of time is saved.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Oligonucleotide library for specific identification of whole short arm of ninth chromosome of cultivated rice and specific identification method
ActiveCN107099849AAnalysis and Research ReorganizationResearch reorganizationNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementOryzaAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and in particular relates to an oligonucleotide library for specific identification of a whole short arm of ninth chromosome of cultivated rice and specific identification method. The oligonucleotide library comprises total 2258 oligonucleotides shown in SEQIDNO.1-2258. The invention also discloses the specific identification method of the ninth chromosome of the cultivated rice, first, total 2258 oligonucleotide probes with fluorescent marks are prepared by use of the specific oligonucleotide library, fluorescent in-situ hybridization of the total 2258 oligonucleotide probes is performed, and the ninth chromosome of the cultivated rice can be identified according to fluorescence signal. The ninth chromosome of the cultivated rice can be identified by use of Paintes Probes of the whole chromosome arm, chromosome recombination, aberrations and homologous genes can be analyzed and studied, and the evolutionary relationship between chromosomes of different species origins can also be studied.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Staining and staining pre-treatment methods and devices
Staining nucleotides within chromosomes is an important technique used in cytogenetics to produce a visible karyotype by staining condensed chromosomes. Such techniques are useful, for example, in identifying genetic diseases through the photographic representation of the entire chromosome complement. Prior to the steps of selective dissolving and staining of nucleotides within the chromosomes an aging step is performed to increase the selective solubility between different nucleotides. Within the prior art this aging step is a time consuming process taking several days. Accordingly, it would be beneficial to provide a staining pretreatment method which can be performed in a short period of time.
Owner:ADSTEC CORP
Yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and construction method thereof
ActiveCN113046255AAchieve knockoutAchieve integrationFungiStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyYeast chromosome
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and a construction method thereof. According to the yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and the construction method thereof, a complete yeast chromosome is cut off by using a Vika / vox technology, so that homologous recombination is generated by chromosome centromeres, the whole chromosome is knocked out, six synthetic chromosomes are integrated, and a large-scale rearrangement event is generated. Compared with existing achievements, the yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and the construction method thereof have the following beneficial effects that cutting of the yeast chromosome is achieved simply, efficiently and quickly; cross exchange of sister dyeing monomers is avoided, and haploid yeast integrated by the six synthetic chromosomes is obtained; and very large-scale genome rearrangement is generated simply, efficiently and quickly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for knocking out saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome
ActiveCN107988202AAchieve knockoutIncrease success rateStable introduction of DNAHybrid cell preparationYeast chromosomeSite-specific recombination
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and in particular discloses a method for knocking out a saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome. According to the method, a Vika / vox technology is utilized for removing a complete yeast chromosome, and chromosome centromeres are specifically recombined into a ring by virtue of loci, so that knockout of the whole chromosome is realized. Compared with a method for realizing elimination of the whole chromosome in a reduction mitosis manner, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that cutting of the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome is more simply, efficiently and rapidly realized, crossing over of sister chromatids is avoided, and a saccharomyces cerevisiae homozygous diploid bacterial strain with the chromosome knocked out is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
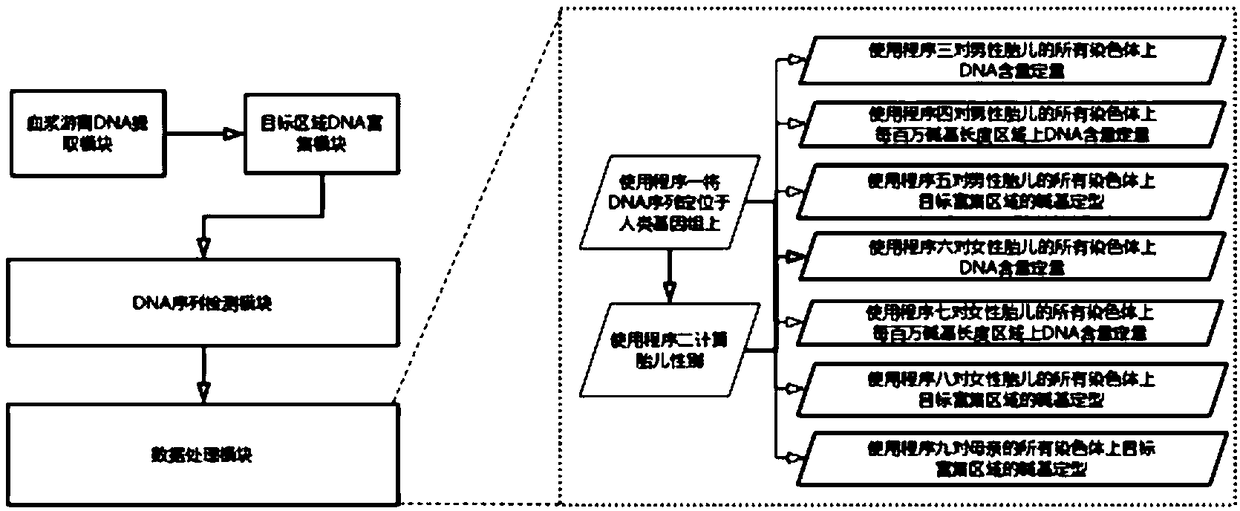
Prenatal non-invasive fetal chromosome detection system based on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragment enrichment and sequencing technology
ActiveCN109321641AHigh precisionRealize detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementEnrichment methodsA-DNA
The invention discloses a method for detecting prenatal fetal chromosome abnormality based on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragment specific enrichment. The method obtains free DNA by obtaining peripheral blood of a pregnant woman and using a DNA enrichment technique; a probe hybridization capture enrichment method is used in a DNA enrichment operation; the enrichment method simultaneously enrichesspecific fragments of a mother and a fetus without needing individual enrichment of fetal DNA. The detection method not only realizes the detection of the whole chromosome content of the fetus, but also realizes the detection of fetal local chromosome content. The method is high in accuracy when being applied to the detection of the fetal chromosome abnormality by means of plasma free DNA of thepregnant woman.
Owner:苏州首度基因科技有限责任公司
A structured grid load balancing method based on LPT local optimization
ActiveCN109885401AImprove fitnessIncrease speedResource allocationGenetic modelsMutation operatorGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses a structured grid load balancing method based on LPT local optimization, and aims to overcome the defects of an existing load balancing method and improve the load balancing rate and the calculation speed. The technical scheme is based on a genetic algorithm on the whole, and includes totally eleven steps of configuring parameters, initializing populations, calculating theadaptability, carrying out the local optimization on the LPTSize / 2 chromosome fragments with the maximum fragment value and the LPTSize / 2 chromosome fragments with the minimum fragment value in each chromosome by adopting an LPT method, carrying out the condition judgment, carrying out update judgment, performing population updating, selecting operators, crossing the operators and varying the operators, and outputting the best load balancing mode. According to the invention, a plurality of chromosome fragments with maximum and minimum chromosome fragment values in each chromosome are locally optimized; the fitness of the whole chromosome is improved, the population updating is carried out, the population is not prone to premature, a program is not prone to ending too early, a globally optimal solution can be obtained, and the parallel computing load balance rate of the whole structured grid is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Use of PARP inhibitors to treat breast or ovarian cancer patients showing a loss of heterozygosity
InactiveCN105917007AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisComputerized systemDeleterious mutation
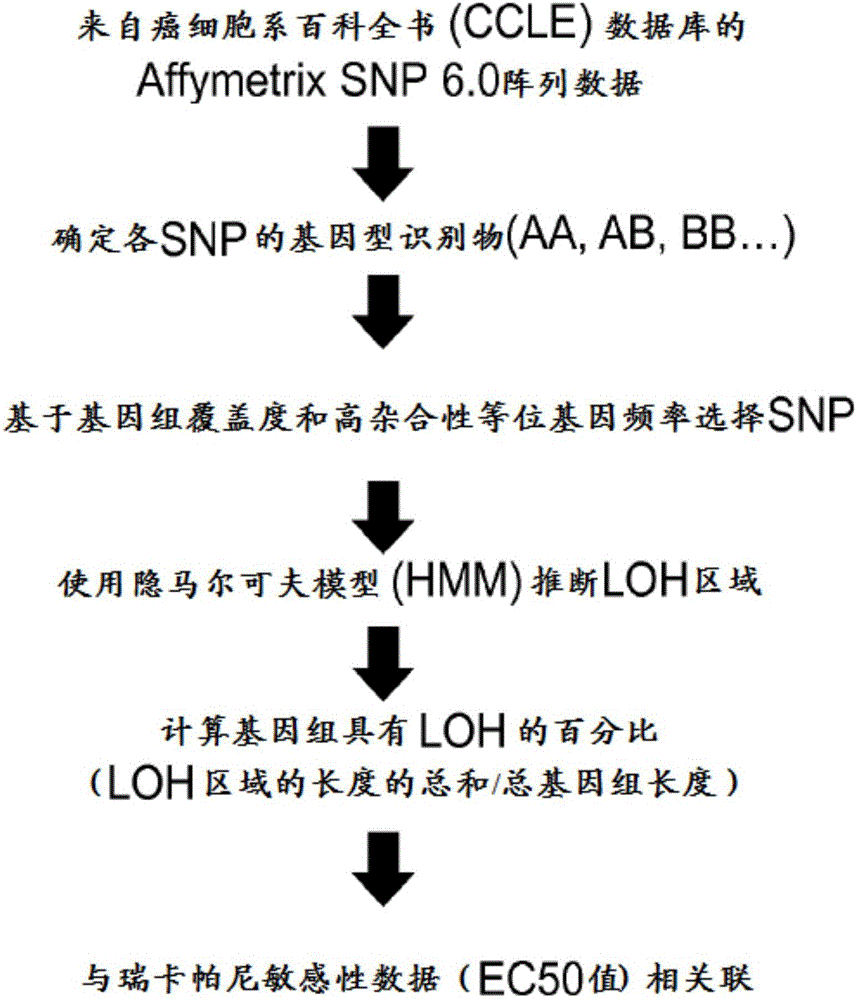
In one embodiment, the subject invention relates to a method for treatment of a breast or ovarian cancer patient that includes receiving assay results stating that the patient's tumor exhibits LOH, and administering a PARP inhibitor. In one embodiment, the subject invention comprising: classifying said cancer patient, with the computer system, as being likely to respond to a PARP inhibitor if the data comprises i) one or more deleterious mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2, or ii) a percentage of the genome having greater than 10 percent LOH as determined by the sum of the lengths of each individual LOH region divided by the total genome length, wherein an LOH region is defined as the presence of homozygosity at multiple contiguous single nucleotides, but excludes whole chromosome or chromosome arm LOH.
Owner:CLOVIS ONCOLOGY INC
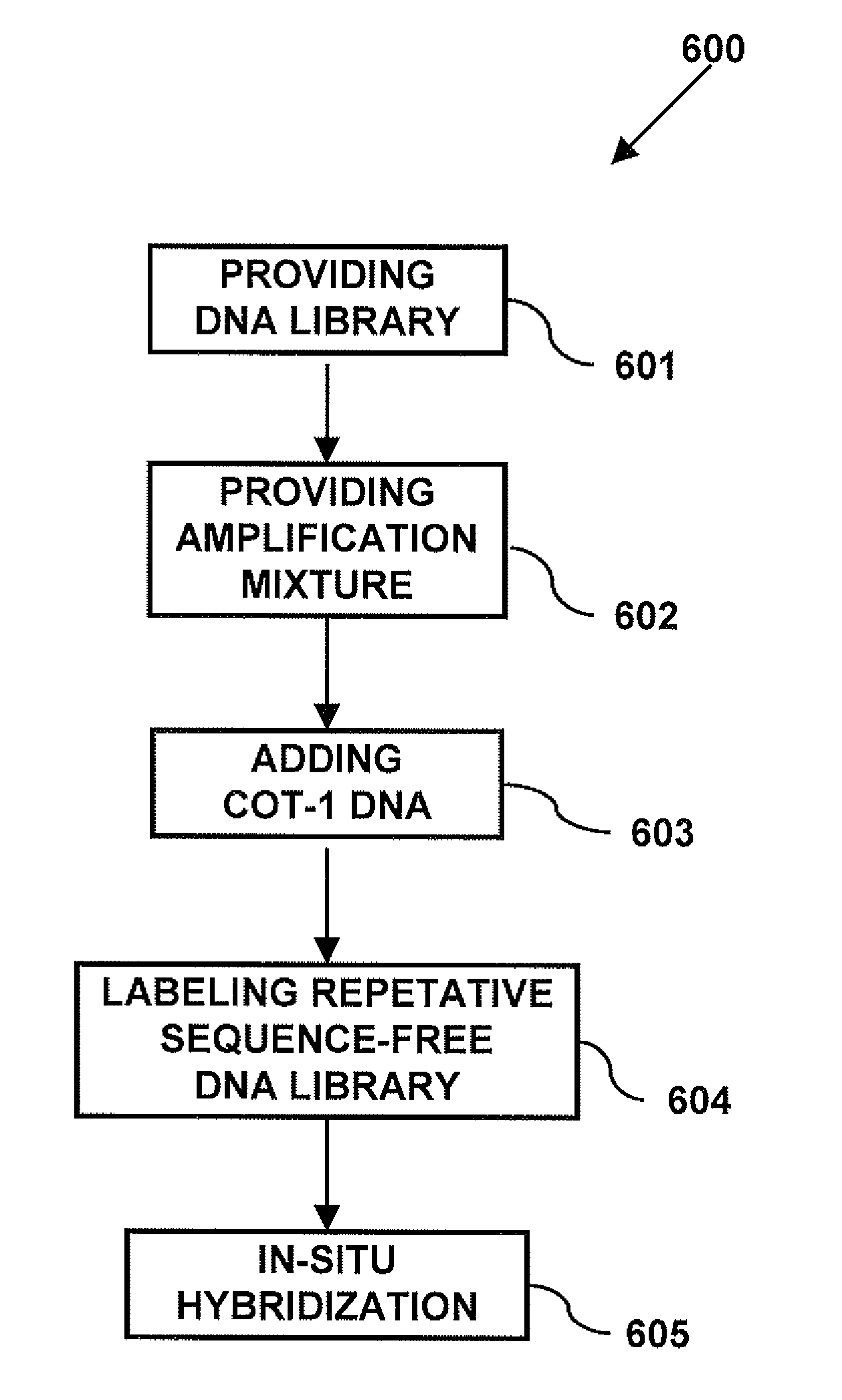
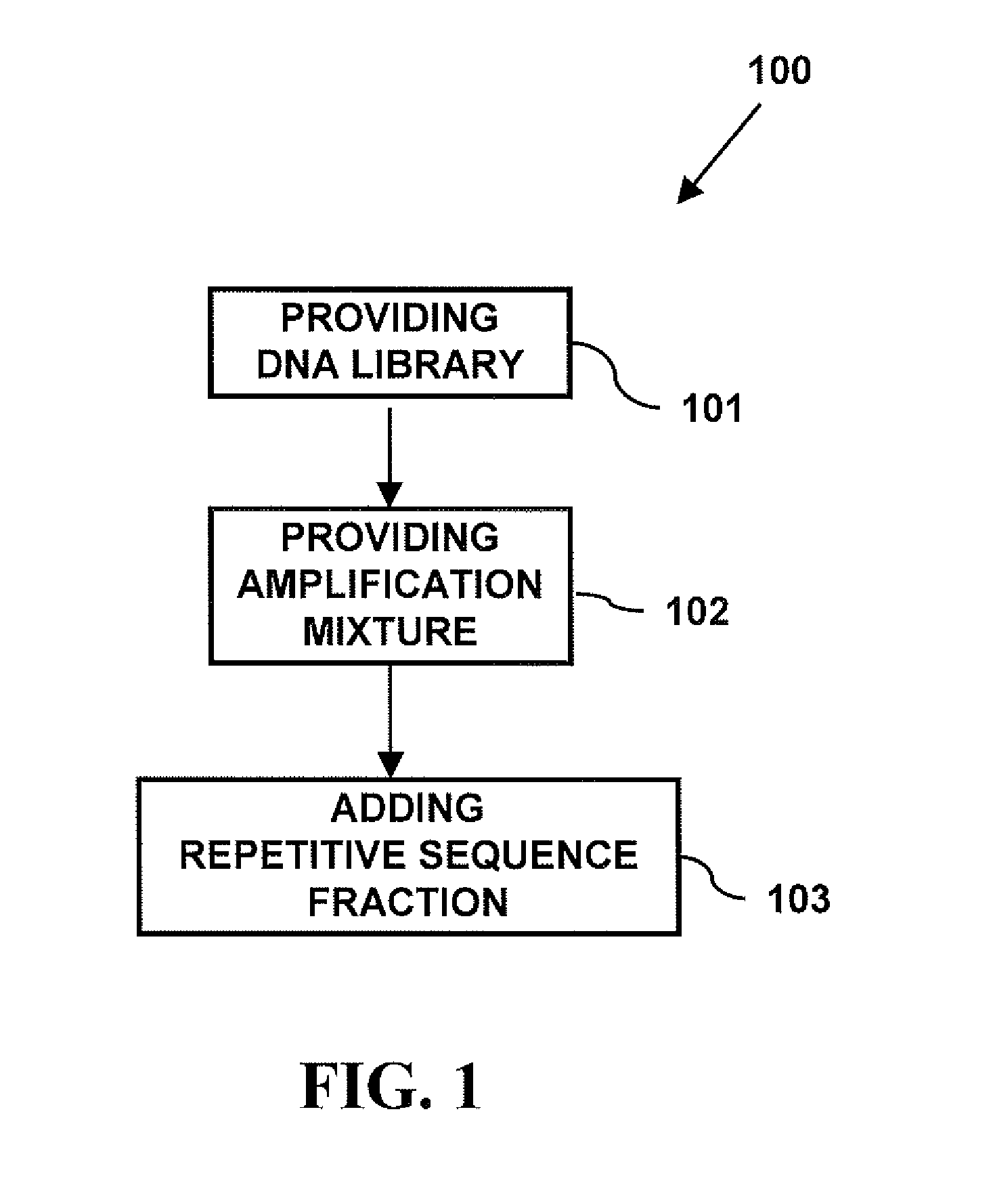
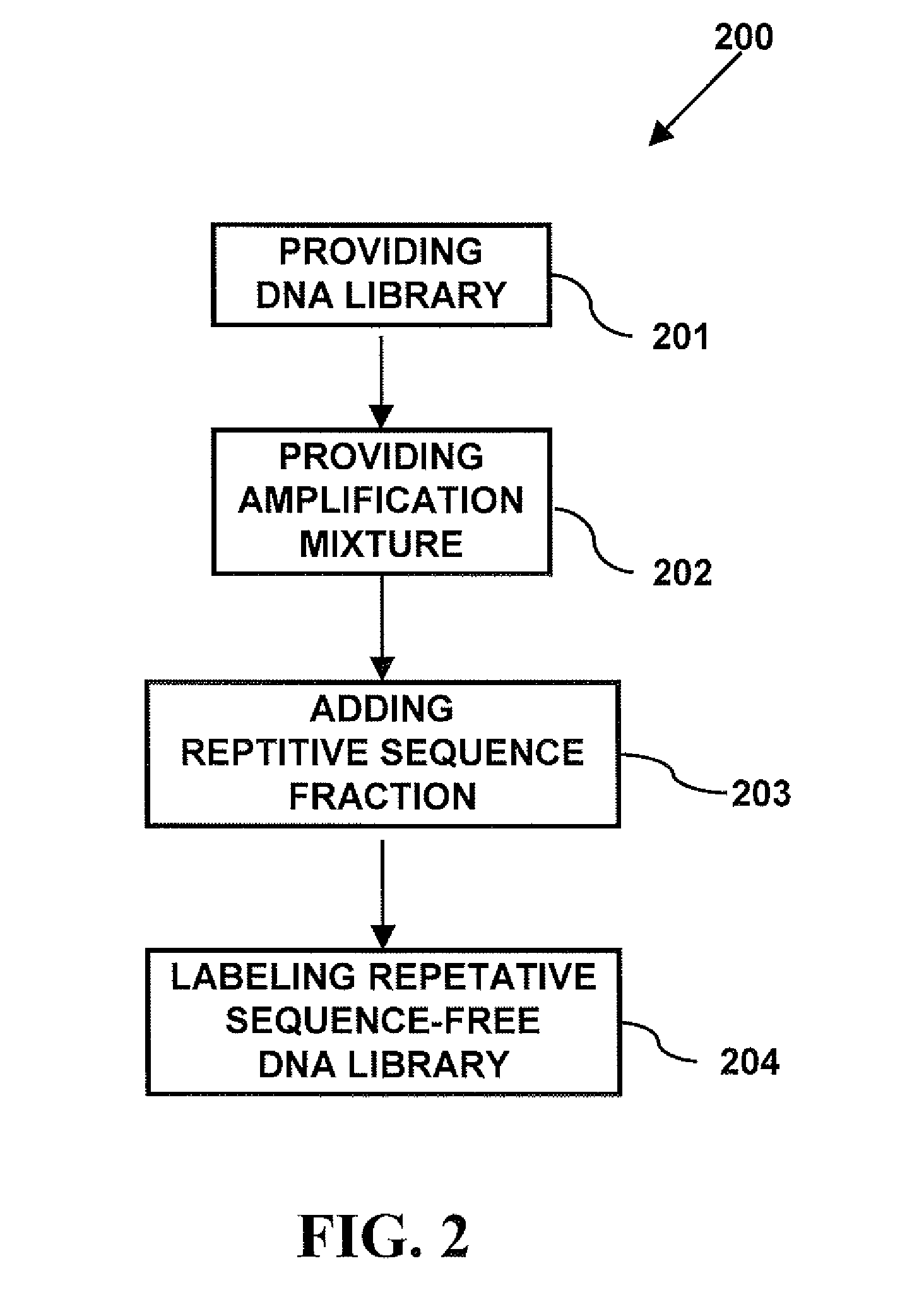
Repetitive Sequence-Free DNA Libraries
InactiveUS20110015085A1Low costStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCDNA libraryRepetitive Sequences
A method of creating a repetitive sequence-free DNA library comprising the steps of providing a DNA library, providing an amplification mixture from the DNA library, and adding a repetitive sequence fraction DNA to the amplification mixture to produce the repetitive sequence-free DNA library. The invention also provides a method of creating a whole chromosome painting probe comprising the steps of providing a DNA library, providing an amplification mixture from the DNA library, adding a repetitive sequence fraction DNA to the amplification mixture to produce the repetitive sequence-free DNA library, and labeling the repetitive sequence-free DNA library to produce the whole chromosome painting probe. The invention also provides a method of in-situ hybridization comprising the steps of providing a DNA library, providing an amplification mixture from the DNA library, adding a repetitive sequence fraction DNA to the amplification mixture to produce the repetitive sequence-free DNA library, labeling the repetitive sequence-free DNA library to produce the whole chromosome painting probe, and using the painting probe in in-situ hybridization.
Owner:CHRISTIAN ALLEN T +2
Detecting cancer mutations and aneuploidy in chromosomal segments
ActiveUS10262755B2Improve throughputIncrease probabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleotideBiology
The invention provides methods, systems, and computer readable medium for detecting ploidy of chromosome segments or entire chromosomes, for detecting single nucleotide variants and for detecting both ploidy of chromosome segments and single nucleotide variants. In some aspects, the invention provides methods, systems, and computer readable medium for detecting cancer or a chromosomal abnormality in a gestating fetus.
Owner:NATERA
Method for preparing single blastomere chromosome
InactiveCN1884522AImprove efficiencyQuality improvementFermentationPlant genotype modificationBiologyBiopsy
The invention provides a method for preparing individual blastomere chromosome, and the said method is as follows: removing germ hill from normal fertilized ovum in prokaryotic period and performing enucleation to obtain cell plastid, in addition selecting individual human blastomere by biopsy, performing electric anabranch to the said blastomere and the cell plastid to obtain heterocaryon, introducing the prematured chromosome to conglomerate to shape with the obtained heterocaryon, then performing low permeability to the introduced heterocaryon, afterwards fixing and colouring the heterocaryon, finally obtaining the said individual blastomere chromosome. The invention obtains the method for preparing individual blastomere chromosome with high efficiency and fine quality by further improving and perfecting the electric anabranch solution, chromosome evoked solution, low permeability solution and mounting step, the prepared chromosome is of intelligible shape and of high quality, the method connected with G-bandings or chromosome paint-on and probe FISH technology can overcome the shortage existed in present interphase nucleus FISH technology and can make the PGD diagnostic range extended to the whole chromosome complement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Stapler with adapter
InactiveCN101076434BAvoid accidental slidingSimple structureStapling toolsPhysical MapsBase sequence
To provide a method and an apparatus for decoding genome base sequences in which whole genome base sequences can be restored by recovering DNA from a chromosome while recording the presence position and determining the base sequences, and a method and an apparatus for preparing a genome physical map in which positioning of a genome library clone onto a genome is carried out by recovering DNA froma specific position on the chromosome and utilizing a part of the base sequence information. The shape of the chromosome is precisely acquired by an AFM search needle 7 also having a scraping mechanism, and minute fragments at accurate positions on the chromosome are continuously scraped. The scraped chromosome fragments are charged to an extraction means 8 of DNA and the extracted DNA is transferred to an amplification means 9. The amplified DNA is cloned to an adequate vector and a base sequence of a clone is successively determined by a base sequence-determining means 10. The resultant base sequence data are fed to a data processing mechanism 11, and the base sequences of the fragments and the whole chromosomes are restored.
Owner:ROMEO MAESTRI & FIGLI
Genome assembly method for constructing overlength continuous DNA (DeoxyriboNucleic Acid) sequence
The invention discloses a genome assembly method for constructing an overlength continuous DNA (DeoxyriboNucleic Acid) sequence. The genome assembly method comprises the following steps: S1, finding out an overlapping region between each pair of known DNA sequences; S2, starting from a free tail end of any anchoring sequence fragment, extending the anchoring sequence fragment by using a Read sequence overlapped with the anchoring sequence fragment, cycling for multiple times until the Read sequence which can match the tail end of the other anchoring sequence fragment is encountered and obtaining one or more path sequences; S3, selecting at most one sequence from all the path sequences as an effective linker sequence for linking the tail end of a starting anchoring sequence fragment to thetail end of another endpoint anchoring sequence fragment; S4, linking the starting anchoring sequence fragment with the corresponding endpoint anchoring sequence fragment by utilizing the effective linker sequence; taking the effective linker sequence as a new anchoring sequence fragment after linking or recording the free tail end of the remaining anchoring sequence fragment and switching to S2;repeating S2 to S4 and finally, forming the overlength continuous DNA sequence. The genome assembly method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the sequences of the whole chromosome and the whole genome are more favorably restored.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Assessment of risk of aneuploidy
ActiveUS20150337381A1Reduce in quantityLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningChromosome regionsWhole chromosome
The present disclosure relates generally to methods and materials for use in detecting abnormalities of the number of whole chromosomes or chromosome regions (aneuploidy). It has particular utility for assessing the risk of aneuploidy of eggs (i.e., oocytes), fertilised eggs or embryos developed therefrom in the context of in vitro fertilisation.
Owner:HANDYSIDE ALAN
Multiplexed Method for Detecting DNA Mutations and Copy Number Variations
PendingUS20200362408A1Efficient countingStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementTarget geneWhole chromosome
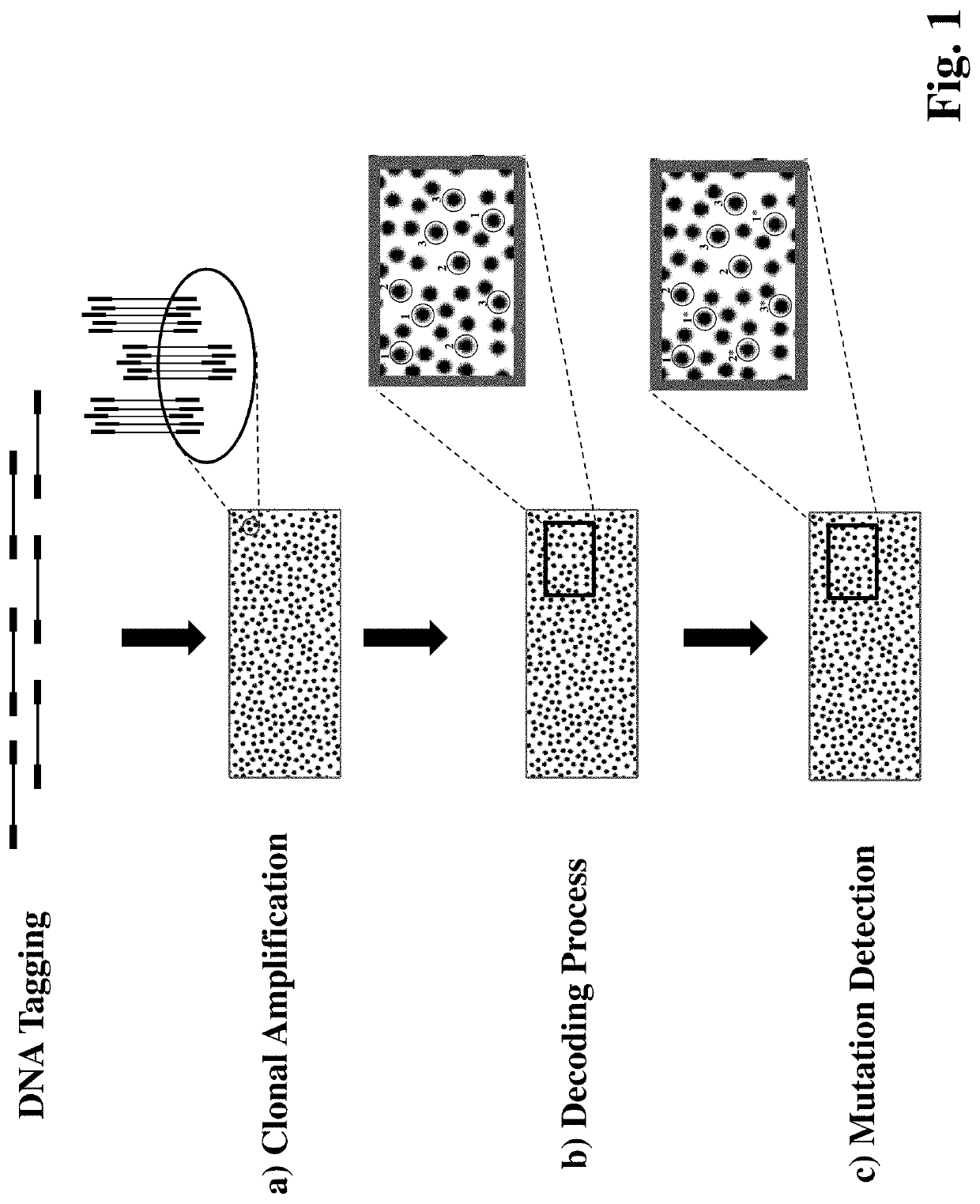
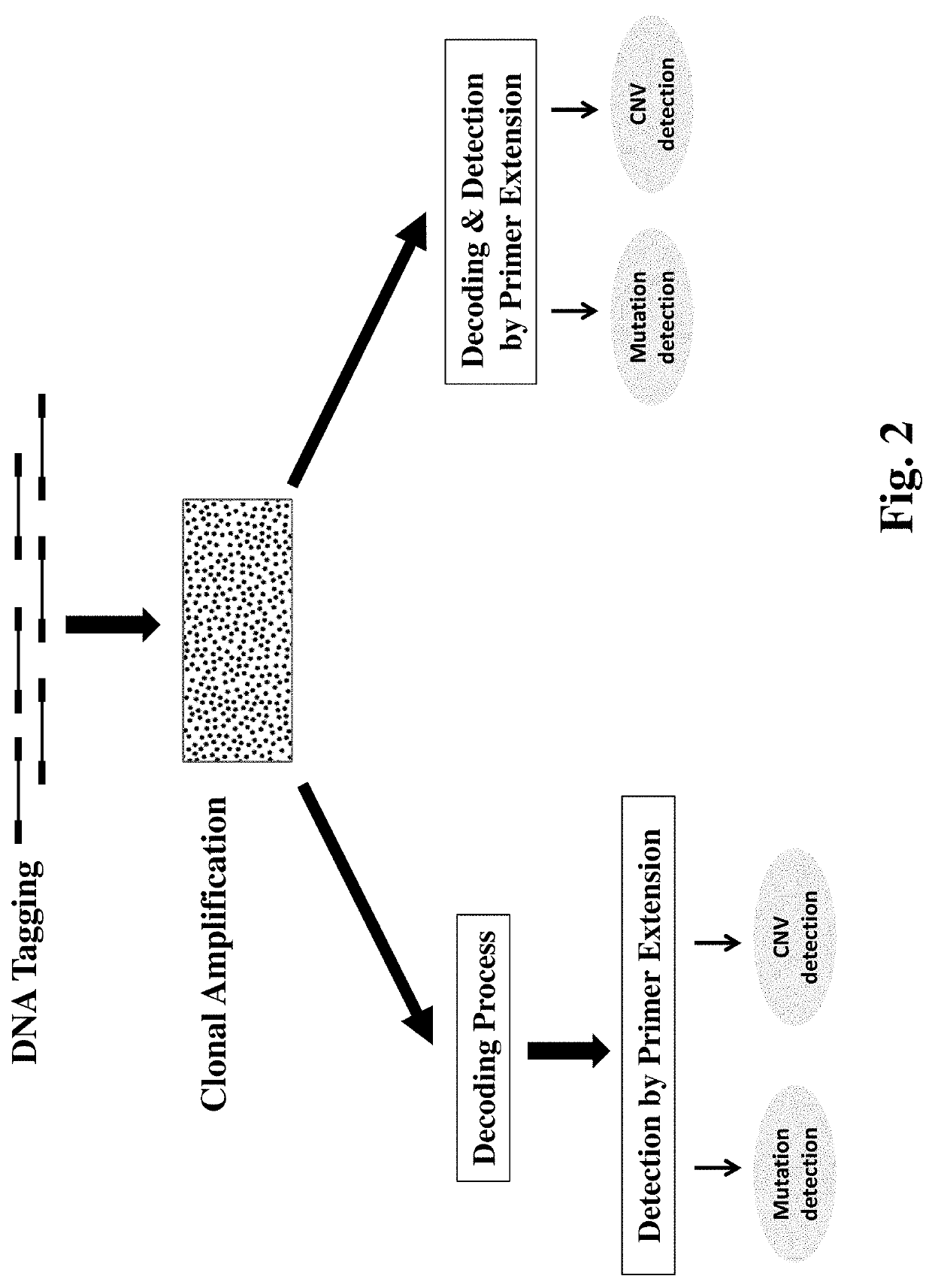
Disclosed is a method for simultaneously detecting a large number of mutations of different target genes with high specificity and sensitivity. It exploits single-molecule clonal amplification techniques, a hybridization-based decoding technique and a primer extension-based detection method to enable simultaneous measurement of hundreds and thousands of mutation DNAs in a sample. Also disclosed is a method for detecting copy number variation with high sensitivity and accuracy. The invention provides a method for efficiently and accurately counting thousands and millions of sequences from a plurality of target regions, enabling detection of copy number variation at the whole genome, the whole chromosome, sub-chromosomes or single gene level.
Owner:WANG YAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com