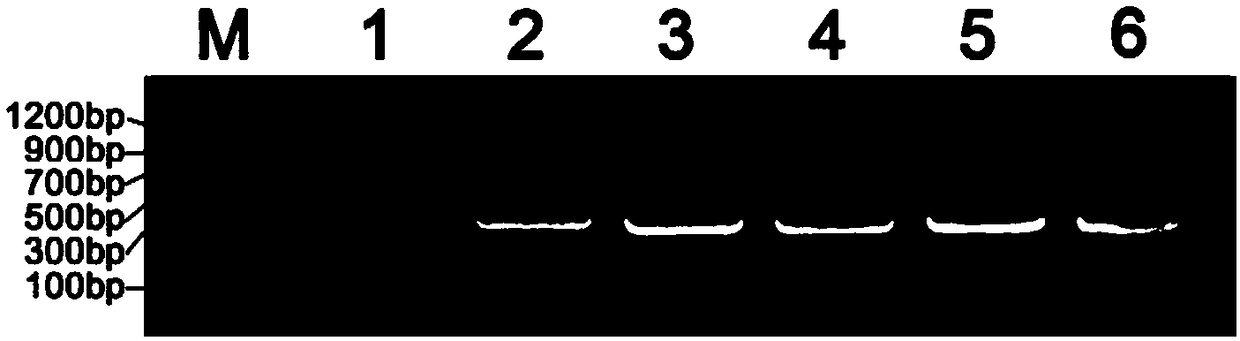
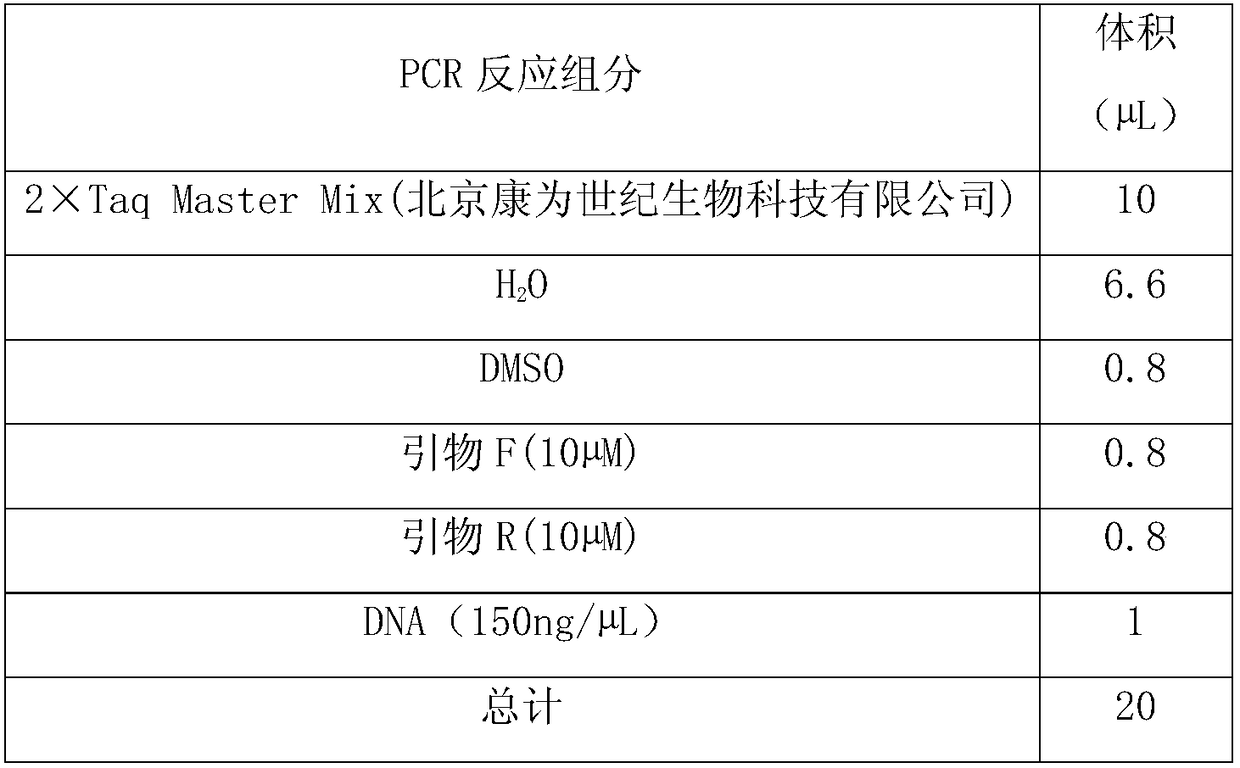
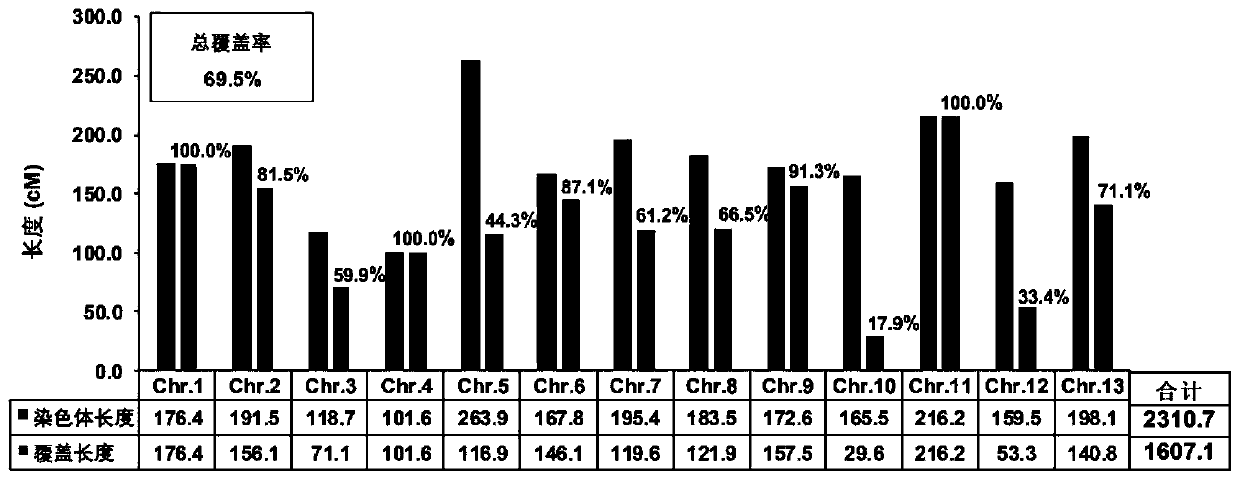
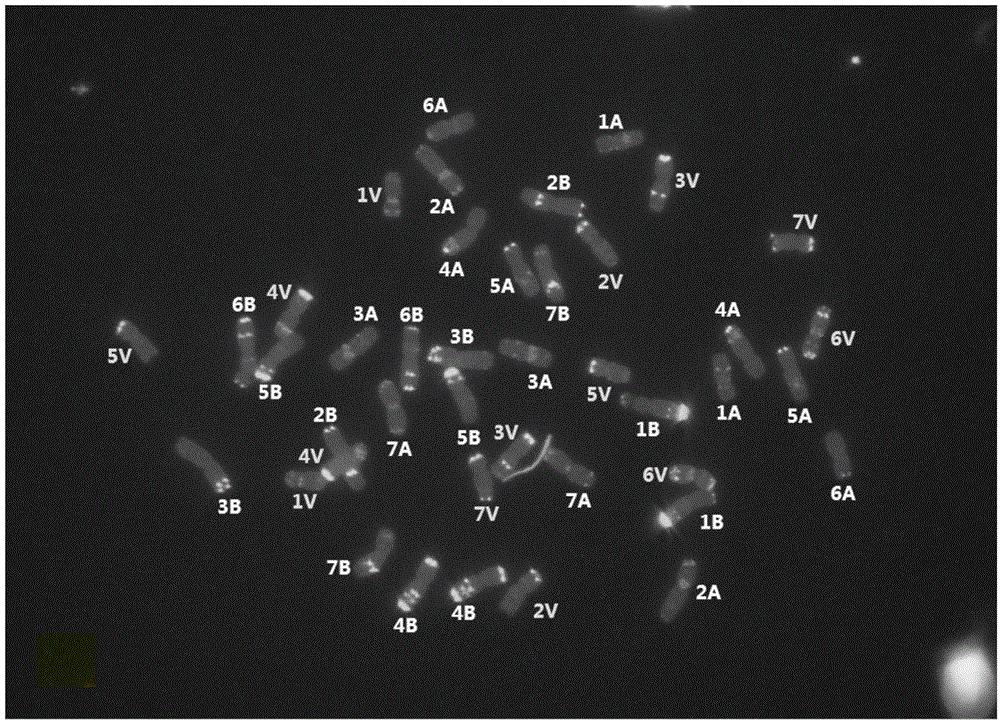
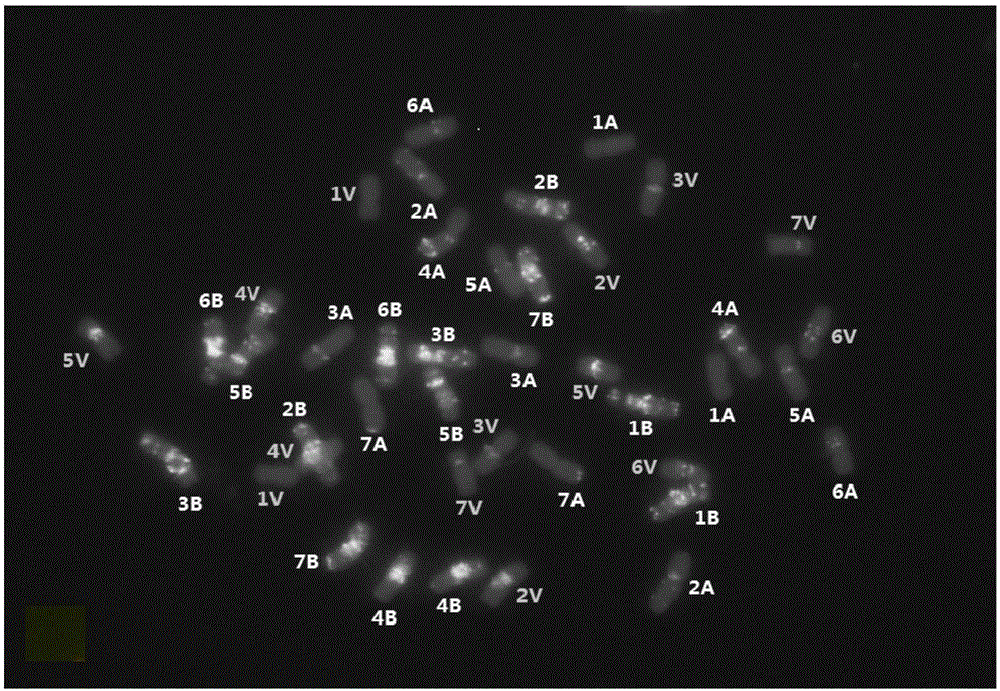
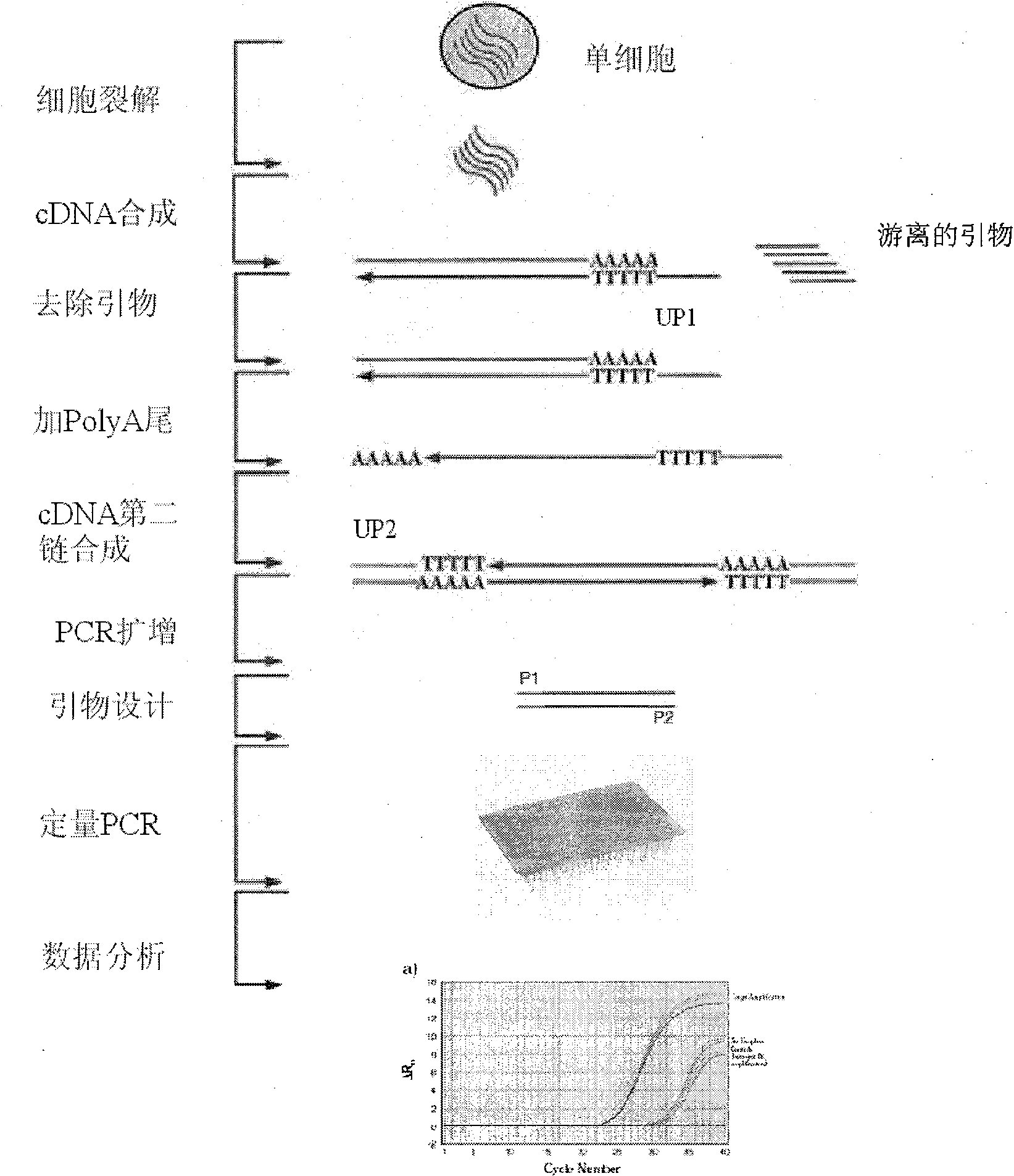Patents
Literature
112 results about "Chromosome fragment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for simultaneous detection of multiple fluorophores for in situ hybridization and multicolor chromosome painting and banding
InactiveUS6066459AImprove throughputShorten the timeRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryChromosome paintingFluorophore
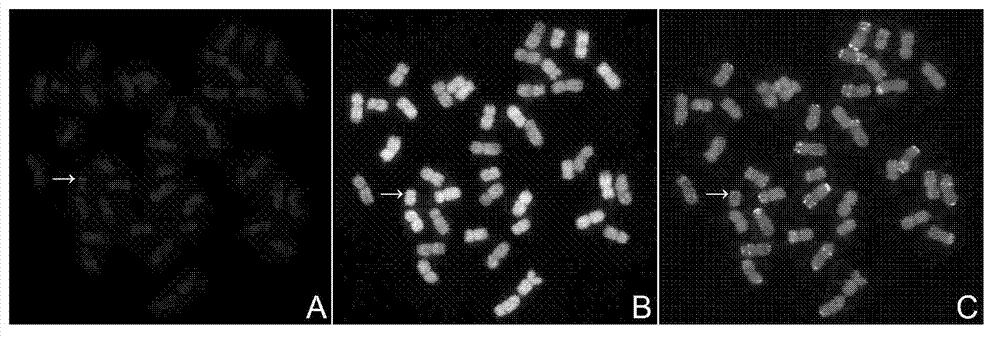
A spectral imaging method for simultaneous detection of multiple fluorophores aimed at detecting and analyzing fluorescent in situ hybridizations employing numerous chromosome paints and / or loci specific probes each labeled with a different fluorophore or a combination of fluorophores for color karyotyping, and at multicolor chromosome banding, wherein each chromosome acquires a specifying banding pattern, which pattern is established using groups of chromosome fragments labeled with various fluorophore or combinations of fluorophores.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
Method for molecular genealogical research
A genealogical research and record keeping system and method for identifying commonalities in haplotypes and other genetic characteristics of two or more individual members of a biological sample. Chromosomal fragments identical by descent identify family ties between siblings, parents and children and ancestors and progeny across many generations. It is particularly useful in corroborating and improving the accuracy of genealogical data, and identifying previously unknown genetic relationships.
Owner:ANCESTRY COM DNA
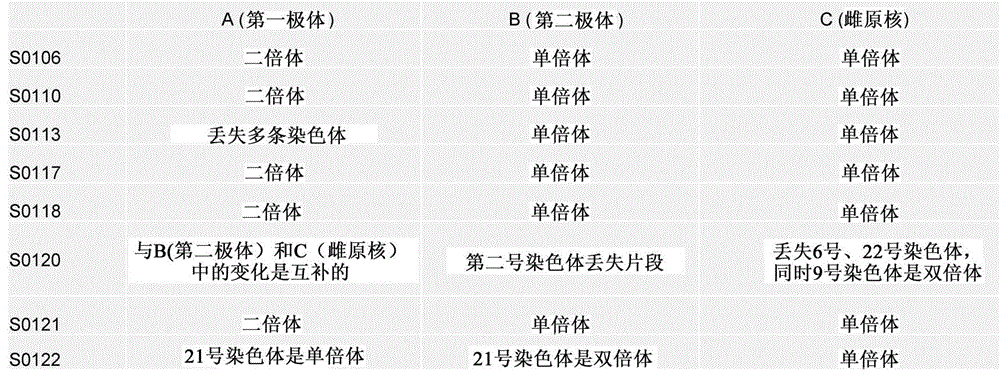
Selection of embryo of test tube baby through sequencing by single cell genome of polar body or embryo
Disclosed is a method for using a first polar body and a second polar body as well as a single-cell embryo to carry out whole-genome non-exponential amplification and high-throughput genome sequencing, so as to perform preimplantation genetic diagnosis for genetic disease and testing for pathogenic genes causing repeated miscarriages. The method of the present invention comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining oocytes and embryos, and carrying out separation and genome amplification of first and second polar bodies and single-cell embryos; (2) establishing a genome sequencing library and sequencing, and carrying out bioinformatic analysis of the genome to obtain a gene spectrum and information concerning the number of copies of chromosomes and fragments thereof; (3) determining the chromosome ploidy of the polar bodies and embryos as well as information concerning defects, replication and point mutation in the chromosome fragments; (4) selecting normal or suitable embryos for implantation.
Owner:HARVARD UNIV +2
Method For Molecular Genealogical Research
InactiveUS20130149707A1Microbiological testing/measurementSequence analysisStudy methodologyOrganism
A genealogical research and record keeping system and method for identifying commonalities in haplotypes and other genetic characteristics of a biological sample of two or more individual members. Chromosomal fragments identical by descent identify family ties between siblings, parents and children and ancestors and progeny across many generations. It is particularly useful in corroborating and improving the accuracy of genealogical data and identifying previously unknown genetic relationships.
Owner:ANCESTRY COM DNA
Method for identifying exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in plant distant hybrids
InactiveCN102876801AOvercome the problem of unsatisfactory detection effectImprovement of Chromosome Production TechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceFluorescence
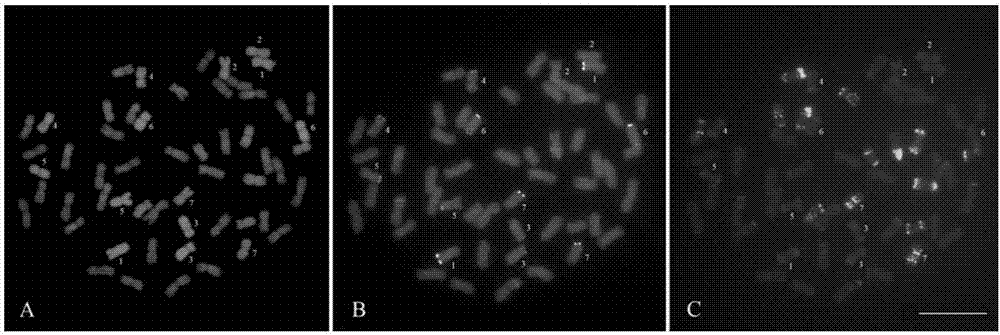
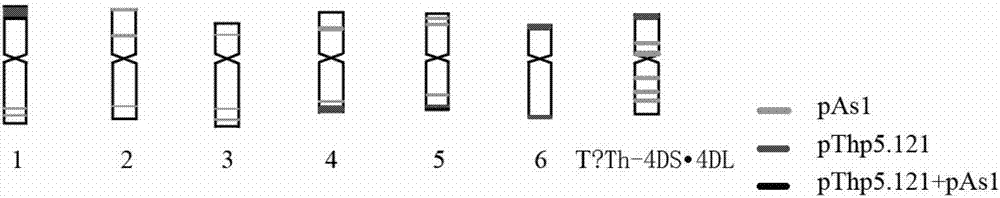
The invention provides a method for identifying exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in plant distant hybrids. The method includes the steps of firstly, microscopically separating monosomes or chromosome segments of chromosomes to be tested of a plant to be tested; secondly, using the separated monosomes or chromosome segments in the first step to build a fluorescence probe of the monosomes or chromosome segments; thirdly, using the fluorescence probe built in the second step to perform fluorescence in situ hybridization to chromosomes in metaphase division of the hybrids; and fourthly, analyzing the fluorescence in situ hybridization result obtained in the third step to determine distribution of fluorescence signals of the chromosomes to be tested of the plant to be tested. Exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in wheat distant hybrids can be identified by the method, and the method is applicable to identification of exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in distant hybrids of other plants.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
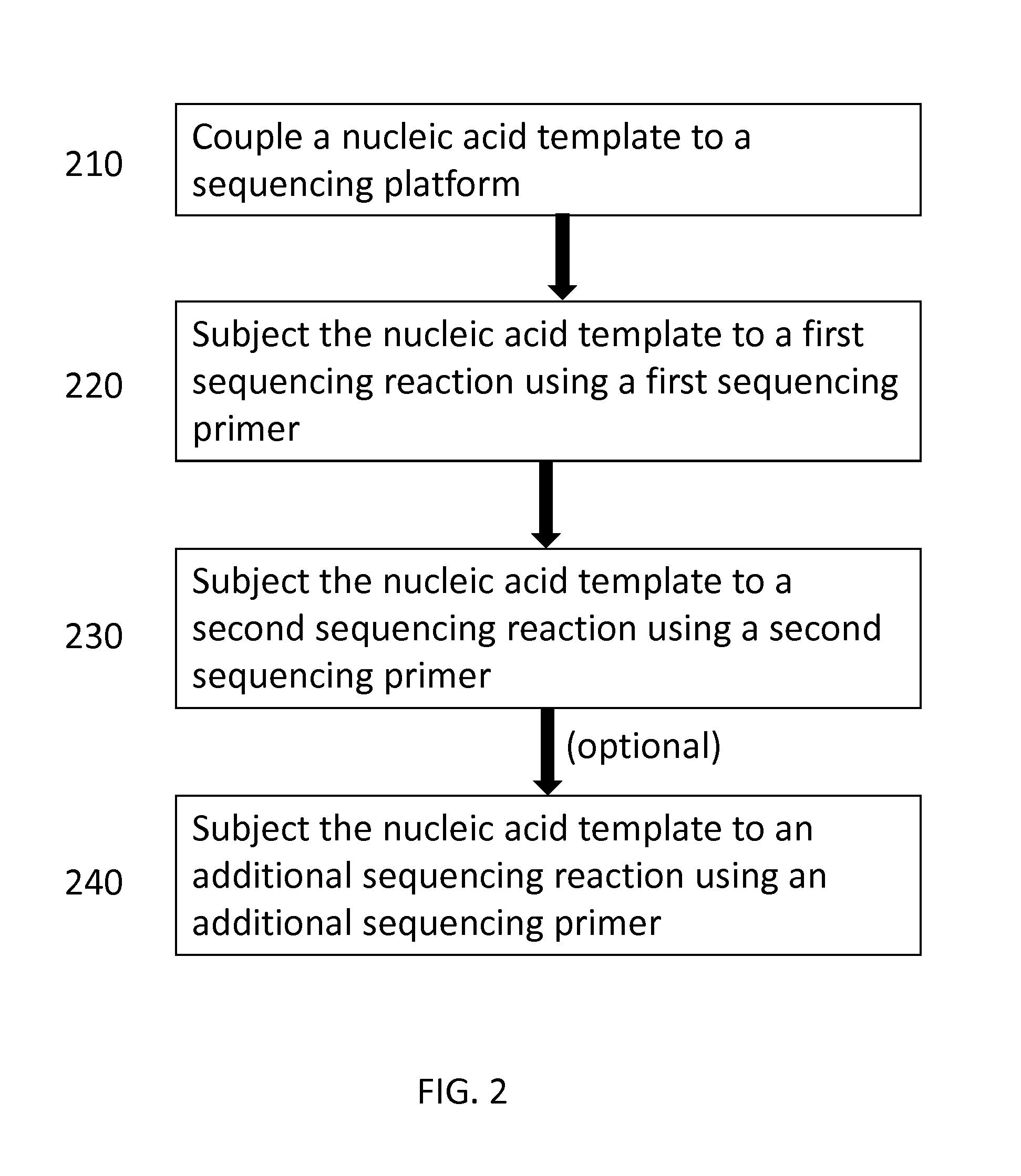
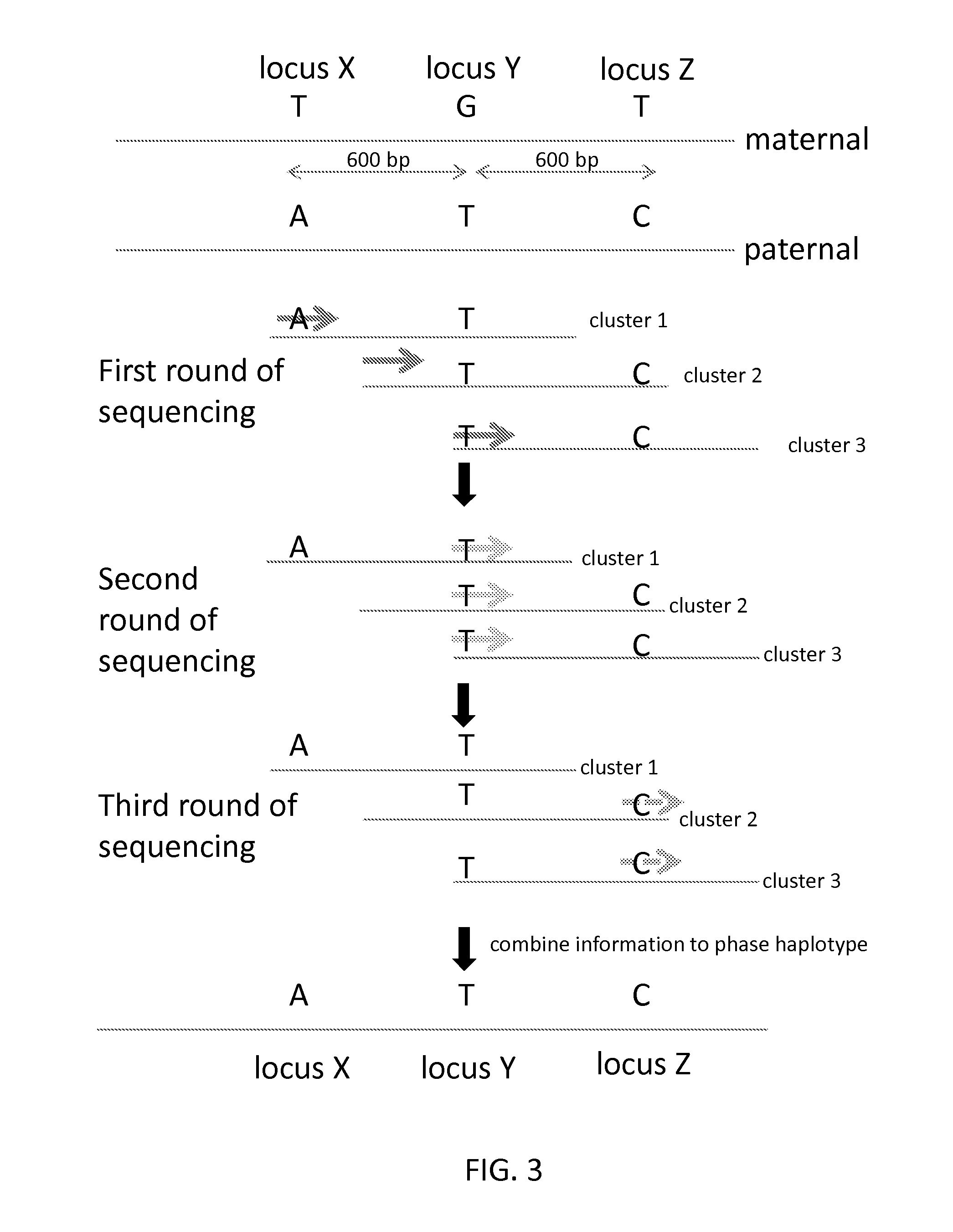
Sequential sequencing
ActiveUS20160251711A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleic acid sequencingExon
Described herein are improved methods, compositions and kits for next generation sequencing (NGS). The methods, compositions and kits described herein enable phasing of two or more nucleic acid sequences in a sample, i.e. determining whether the nucleic acid sequences (which can comprise regions of sequence variation) are located on the same chromosome and / or the same chromosomal fragment. Phasing information can be obtained by performing multiple, successive sequencing reactions from the same immobilized nucleic acid template. The methods, compositions and kits provided herein can be useful, for example, for haplotyping, SNP phasing, or for determining downstream exons in RNA-seq.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization (MFISH) method for quickly analyzing and identifying alien chromosome of wheat
ActiveCN103205500AAvoid deformationAvoid problems such as loss of deformationMicrobiological testing/measurementAlien chromosomeTriticeae
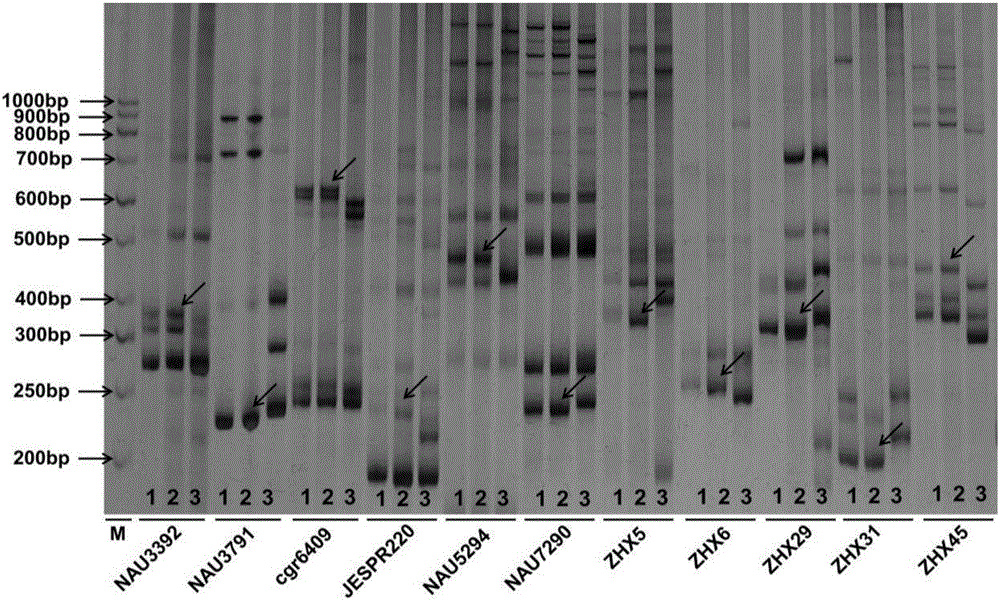
The invention provides a multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization (MFISH) method for quickly analyzing and identifying alien chromosome of wheat. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preprocessing actively dividing tissues in meristematic zone of wheat root tip by N2O and conducting enzymolysis on the actively dividing tissues to obtain a metaphase specimen with clear images and uniform distribution of chromosomes; (2) marking a fluorescent probe of fundamental genome of wheat by nick translation method; (3) conducting fluorescence in situ hybridization on chromosomes at mitosis metaphase obtained in step (1) by using the constructed fluorescent probe in step (2); and (4) analyzing the fluorescence in situ hybridization results obtained in step (3). According to the method provided by the invention, not only can alien chromosomes and chromosome segments in distant hybrid wheat be identified, but also alien chromosomes and chromosome segments of distant hybrids of other crops can be identified.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis on embryo by using new single cell nucleic acid amplification technology
InactiveCN102094083APrevent birthBirth to avoidMicrobiological testing/measurementRecessive inheritanceCentral dogma of molecular biology
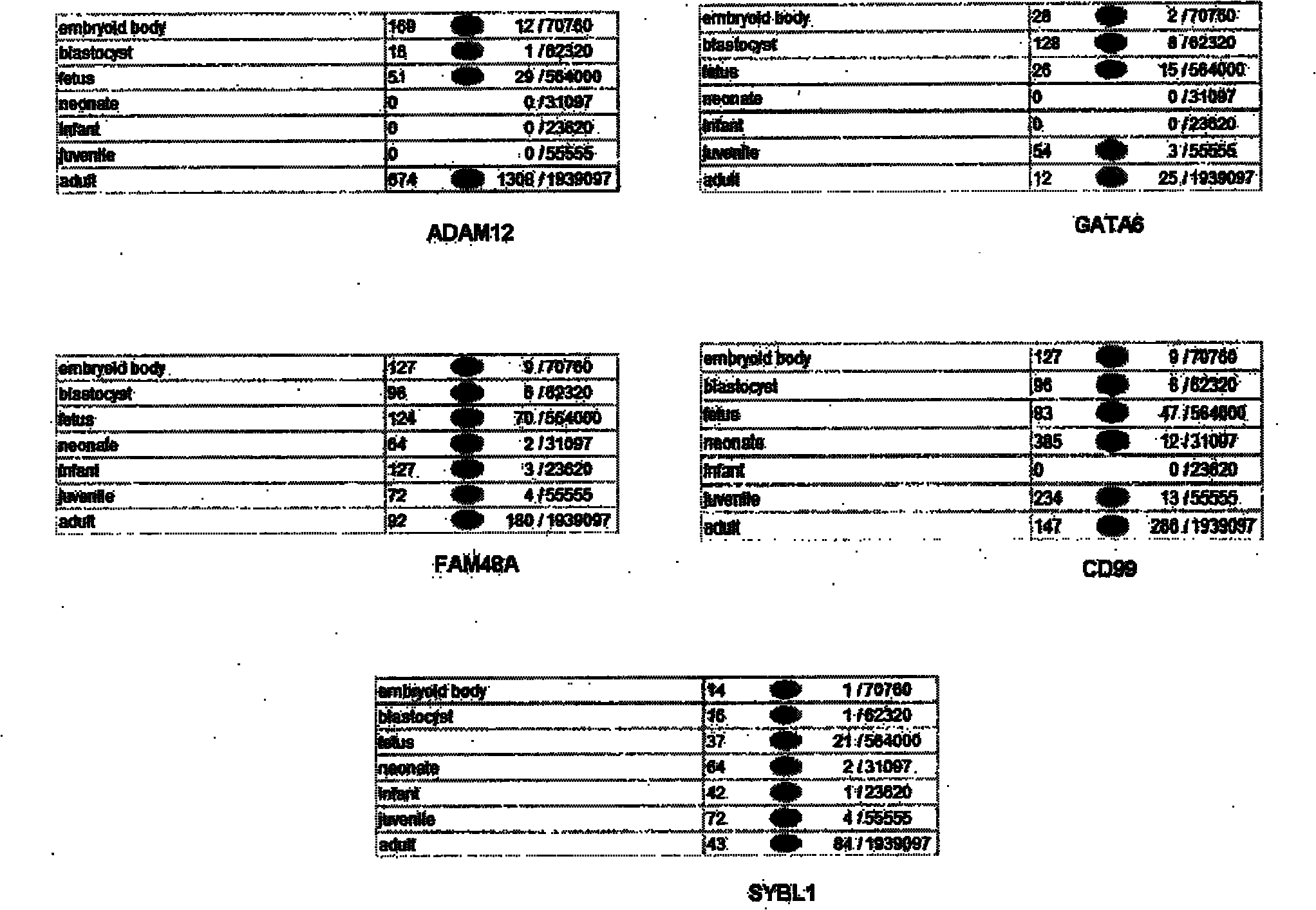
The invention relates to preimplantation genetic diagnosis on an embryo by using new single cell nucleic acid amplification technology, which mainly utilizes the signal amplification action of the mRNA (messenger Ribose Nucleic Acid) to detect the multiplication or deletion of DNAs (Deoxyribonucleic Acids) of certain chromosome segments. According to the central dogma, the mRNA is transcribed by using the DNA as the template, the abnormity of the number of copies of the DNA template can cause the change of the quantity of the mRNAs; and in the transcription process, the multiplication or deletion of the DNA template can be amplified on the mRNA level, and can be easily detected. The main technical method is as follows: the single cell mRNA of a human embryo is subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification after being subjected to reverse transcription and addition of a common primer; by using the amplification product as the template, quantitative PCR with a 96-pore plate is used for detecting the expression level of 8 genes of a single cell or a small amount of cells; and the detection result can be compared with a normal diploid embryo, so as to distinguish the embryo sex of X chromosome recessive inheritance family history, and the multiplication and deletion of Trisomy 21, Trisomy 18, Trisomy 13 and sex chromosome and carry out genetic diagnosis on some common chromosome anomalies.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Gossypium barbadense chromosome segment capable of improving verticillium wilt resistance of gossypium hirsutum and molecular markers
ActiveCN105713976AImprove disease resistanceIncrease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyDisease
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
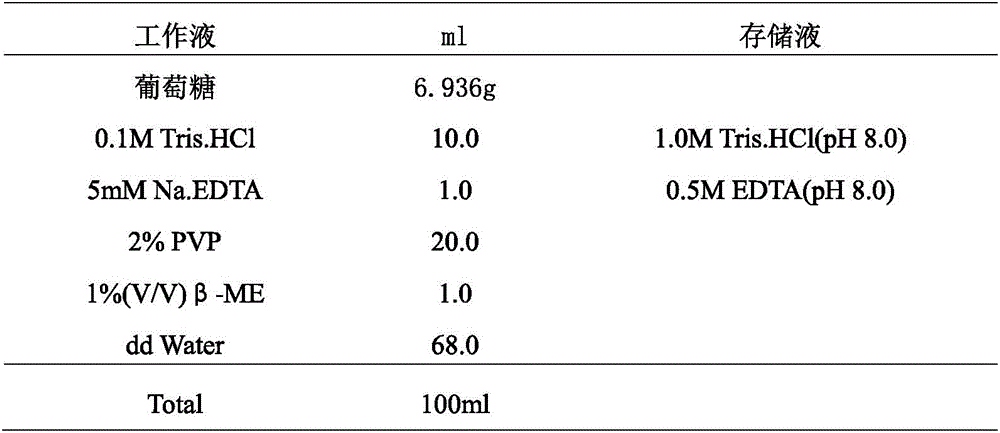
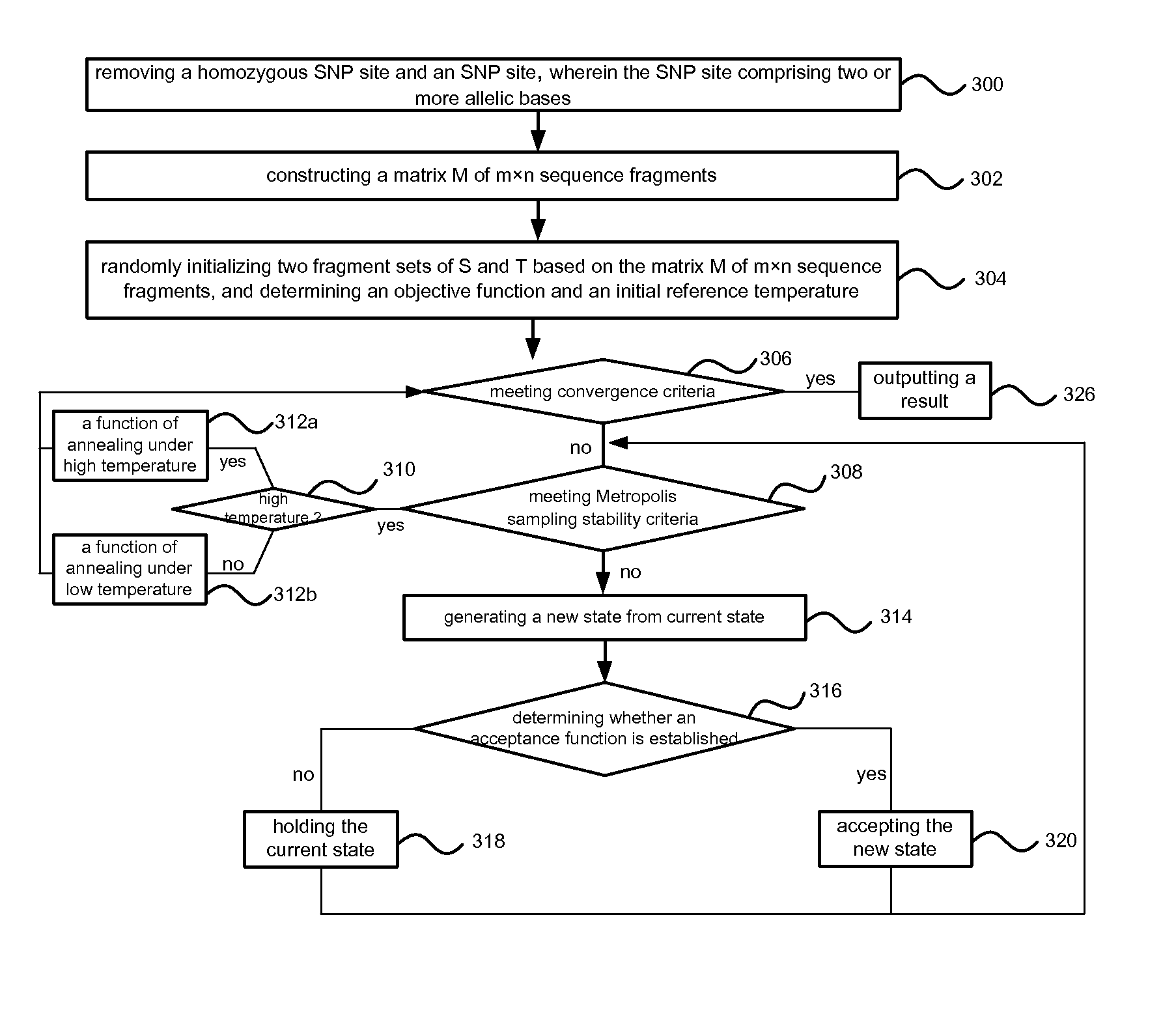
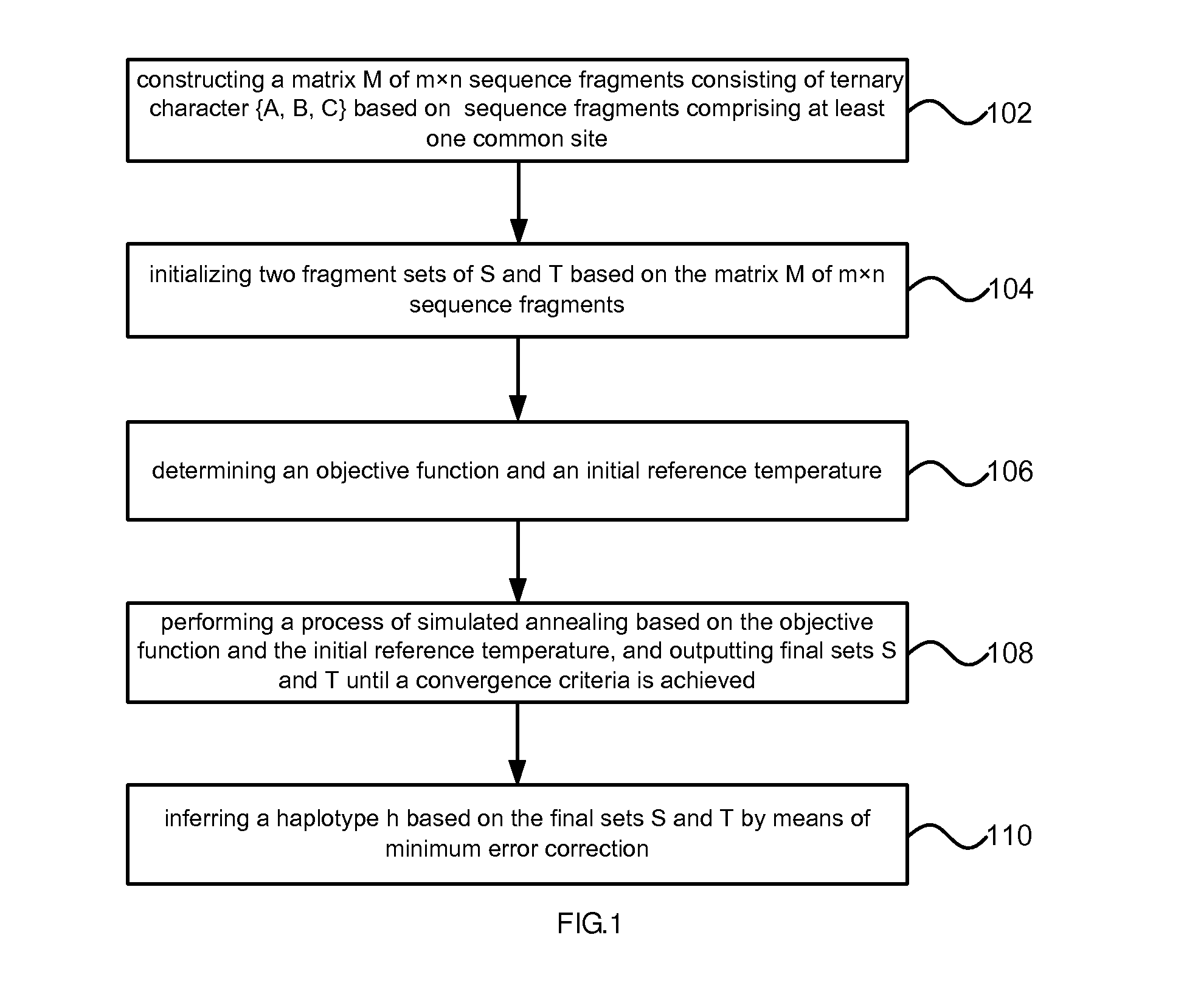
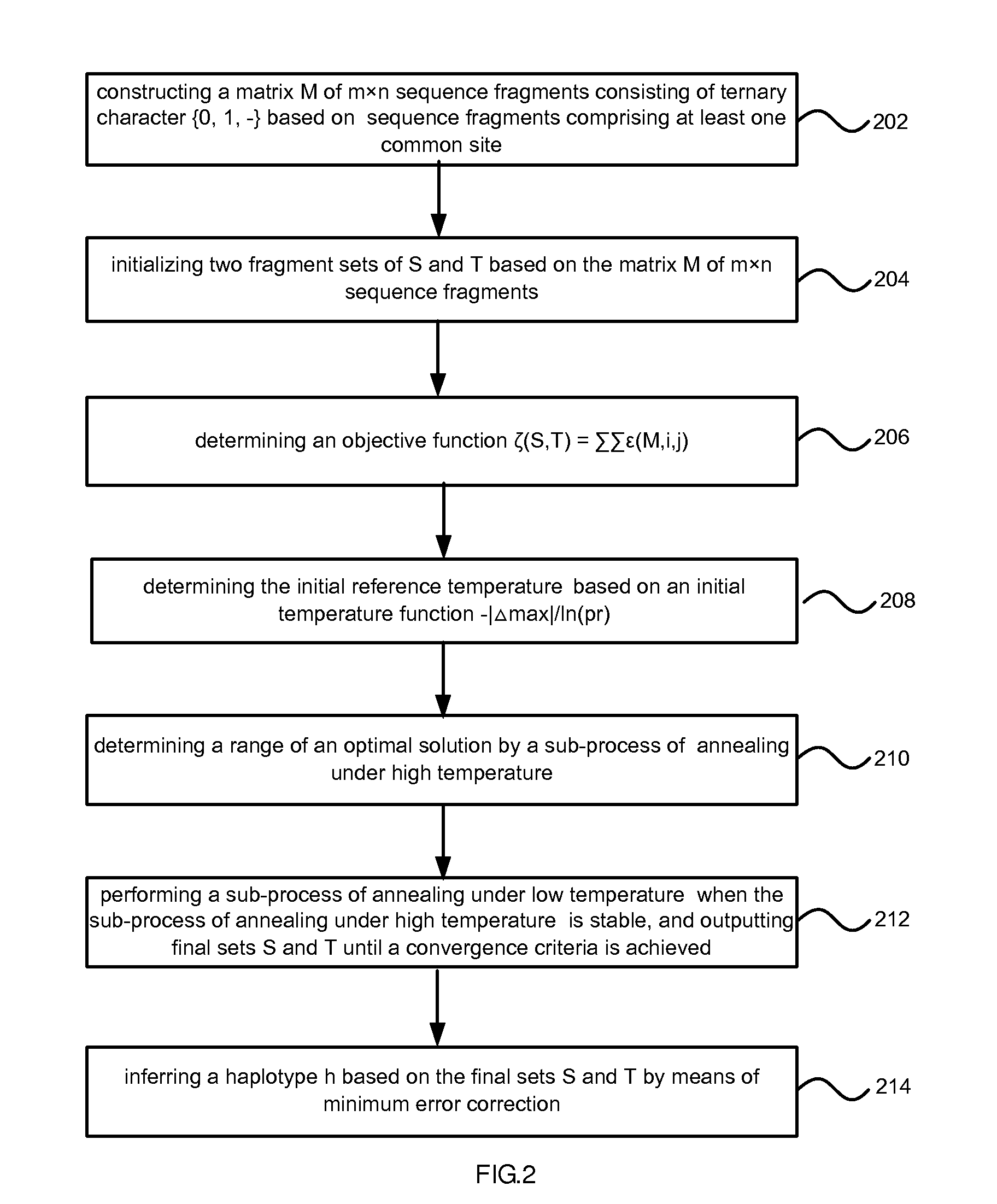
Method of reconstructing haplotype of diploid and system thereof
InactiveUS20150120256A1Improve accuracyHigh speedBiostatisticsComputation using non-denominational number representationMinimum error correctionChromosome fragment
Provided is a method and system of reconstructing a haplotype of a diploid. The method can include constructing a matrix of sequence fragments consisting of ternary character based on sequence fragments comprising at least one common site, wherein in the matrix of sequence fragments, two allelic bases of an SNP site in chromosome fragments are labeled with A and B respectively; initializing two fragment sets of based on the matrix of sequence fragments; determining an objective function and an initial reference temperature; performing a process of simulated annealing based on the objective function and the initial reference temperature, and outputting final sets until a convergence criteria is achieved; inferring a haplotype based on the final sets by means of minimum error correction.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Artificial selection method and reagents
ActiveUS20140220575A1High precisionCosts for selecting individualsMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryEffective population sizeGenotype
Owner:AGRI VICTORIA SERVICES PTY LTD
Brassica plant resistant to the fungus leptosphaeria maculans (blackleg)
The invention relates to fungal disease resistance, in particular to resistance to blackleg disease caused by Leptosphaeria maculans. Provided are Brassica plants and seeds comprising a fragment of chromosome 8 of a wild B. rapa accession in their genome, wherein this fragment comprises a blackleg resistance locus. Further provided are molecular markers linked to the blackleg resistance locus and methods of using the markers. Brassica plants and seeds with stacked blackleg resistance loci are also provided.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Molecular breeding method for improving cold resistance of rice
InactiveCN105475120AEasy to identifySimple selectivityPlant genotype modificationResistant genesAgricultural science
The invention discloses a molecular breeding method for improving cold resistance of rice. The method comprises the steps that a single chromosome segment substitution line is established by taking a rice line which is weak in cold resistance as a recurrent parent and taking a rice line which is strong in cold resistance as a cool-resistant gene donor; multi-environment multi-repeat cold resistance detection at an object growth development stage is conducted, and the single chromosome segment substitution line with stable cold-resisting QTL is screened; hybridization is conducted, molecular markers closely linked with the cold-resisting QTL are utilized for assisting in selection, and a polymerization line with different gene locus cold-resisting QTL is obtained; cold resistance evaluation at the object growth development stage is conducted on the polymerization line, and an excellent line of which the cold resistance is significantly improved is obtained through screening. According to the molecular breeding method, identification and selection on the cold resistance are simple, rapid and economical, the excellent line which is excellent in genetic background and significantly enhanced in cold resistance can be rapidly obtained, and the breeding efficiency and accuracy are improved.
Owner:RICE RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
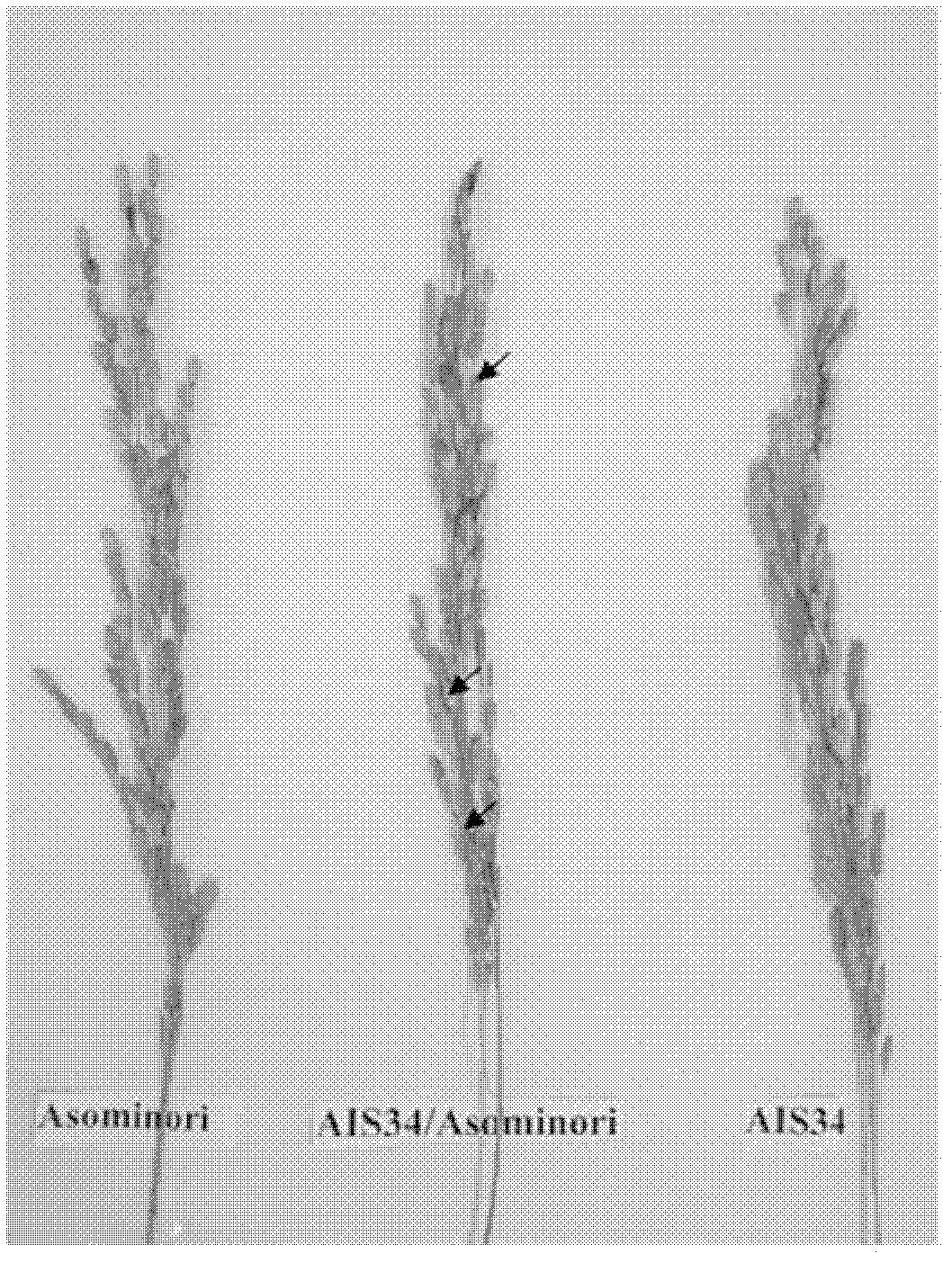
Method for separating two tightly linked rice sterile genes
InactiveCN103374616AReduce molecular marker distanceEasy to separateMicrobiological testing/measurementMarker-assisted selectionF1 generation
The invention relates to a method for separating two tightly linked rice sterile genes, belonging to the field of rice molecular genetics. The method comprises the following steps of: hybridizing a chromosome segment replacement line AIS34 serving as a female parent and Asominori serving as a male parent, from the F1 generation, hybridizing by selecting semisterile plants to obtain a BC1F1 group, performing continuous backcross by selecting the semisterile plants through marker-assisted selection with combination of phenotype identification in the backcross group, performing backcross till the BC4F1 generation, and then performing selfing to obtain a separated group, and respectively positioning a pollen sterile gene and a spikelet sterile gene which are tightly linked with each other. The result shows that through the adoption of the method, the pollen sterile gene is finely positioned in a 33kb area, and meanwhile, an oogamete sterile gene which is tightly linked is finely positioned in a 90kb area.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Resistance to rust disease in wheat
ActiveUS20160222406A1Improve the immunityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyDisease
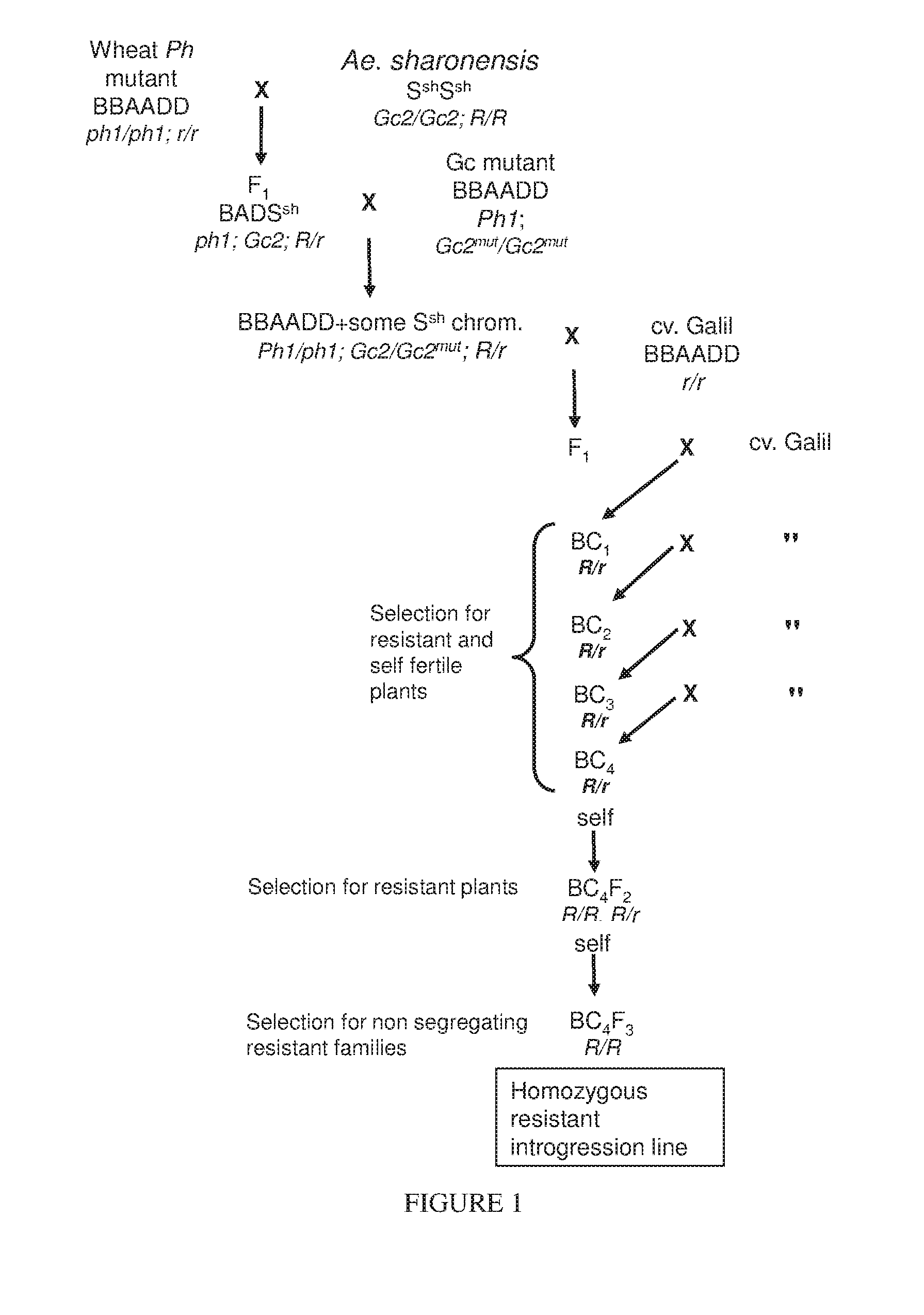
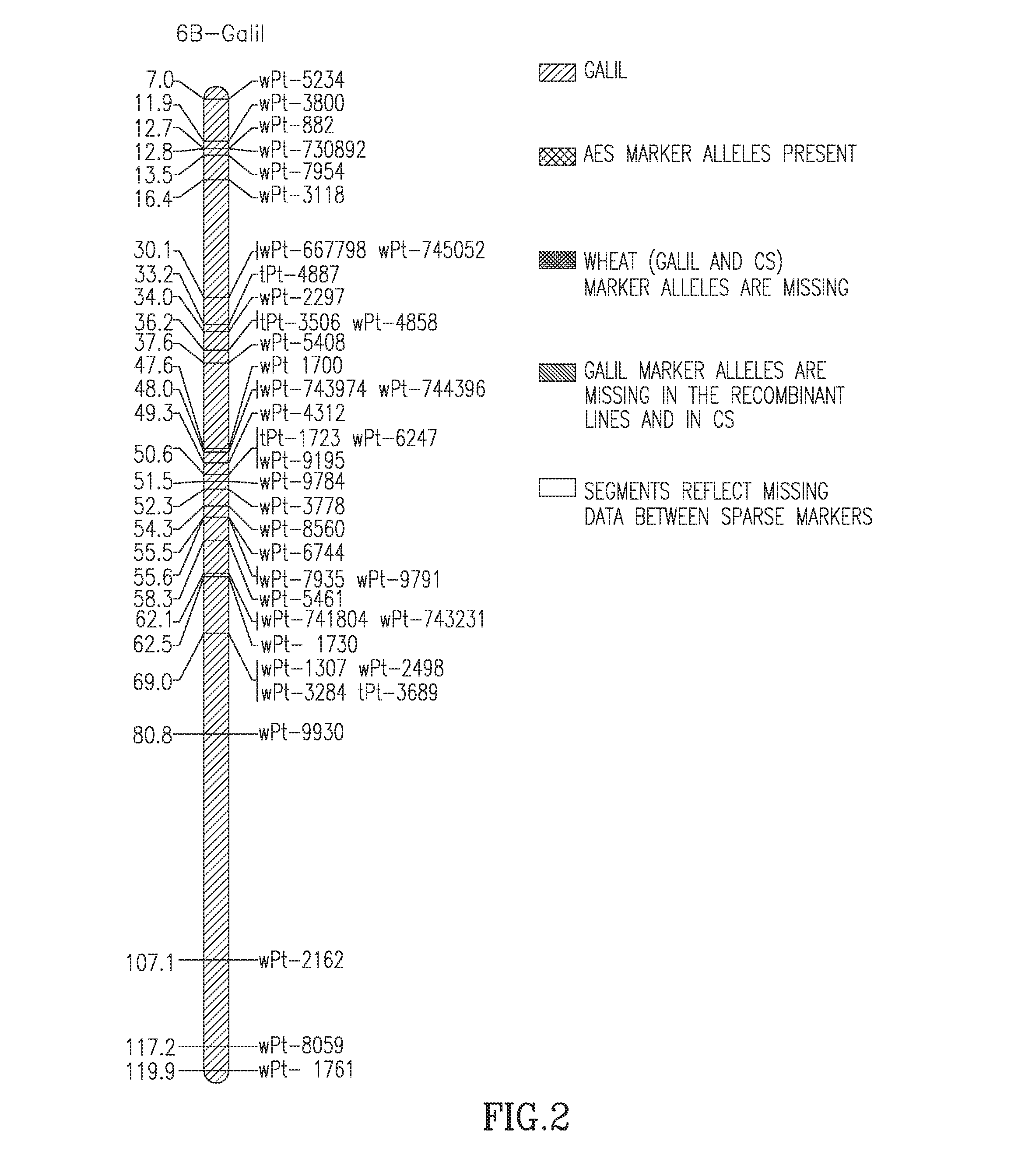
The present invention provides wheat cultivars that are resistant to leaf rust and / or stripe rust disease caused by strains of the fungus Puccinia and to means and methods for producing same. Particularly, the present invention provides wheat cultivars comprising a chromosome segment of Ae. sharonensis, the chromosome segment confers, enhances, or otherwise facilitates resistance of the wheat plants to leaf rust and / or stripe rust disease.
Owner:TECH INNOVATION MOMENTUM FUND ISRAEL
Improved and simplified plant chromosome fluorescence in-situ hybridization method
ActiveCN105296649AFew reaction stepsShorten experiment timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant rootsQuinoline
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Development and application of tenfold elytrigia elongate blue-grained character special molecular marker and fluorescence in situ hybridization probe
ActiveCN108396026AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHybridization probeFluorescence
The invention discloses development and application of a tenfold elytrigia elongata blue-grained character special molecular marker and a fluorescence in situ hybridization probe. A specificity locusamplified fragment sequencing technique is utilized for sequencing common wheat, blue-grained wheat (blue 58) and elytrigia elongata; an elytrigia elongata 4Ag chromosome specific DNA sequence is obtained through sequence data comparative analysis; on the basis of the elytrigia elongate 4Ag chromosome specific DNA sequence, the elytrigia elongate 4Ag chromosome-derived blue-grained character special molecular marker and the special fluorescence probe are developed. The molecular marker and the probe provided by the invention can be used for identifying a blue-grained phenotype during a processof transferring a chromosome segment to the wheat from elytrigia elongata, so that not only a foundation is laid for positioning and cloning a blue aleurone gene, but also a basis is provided for marker-assisted selection of a blue-grained character.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
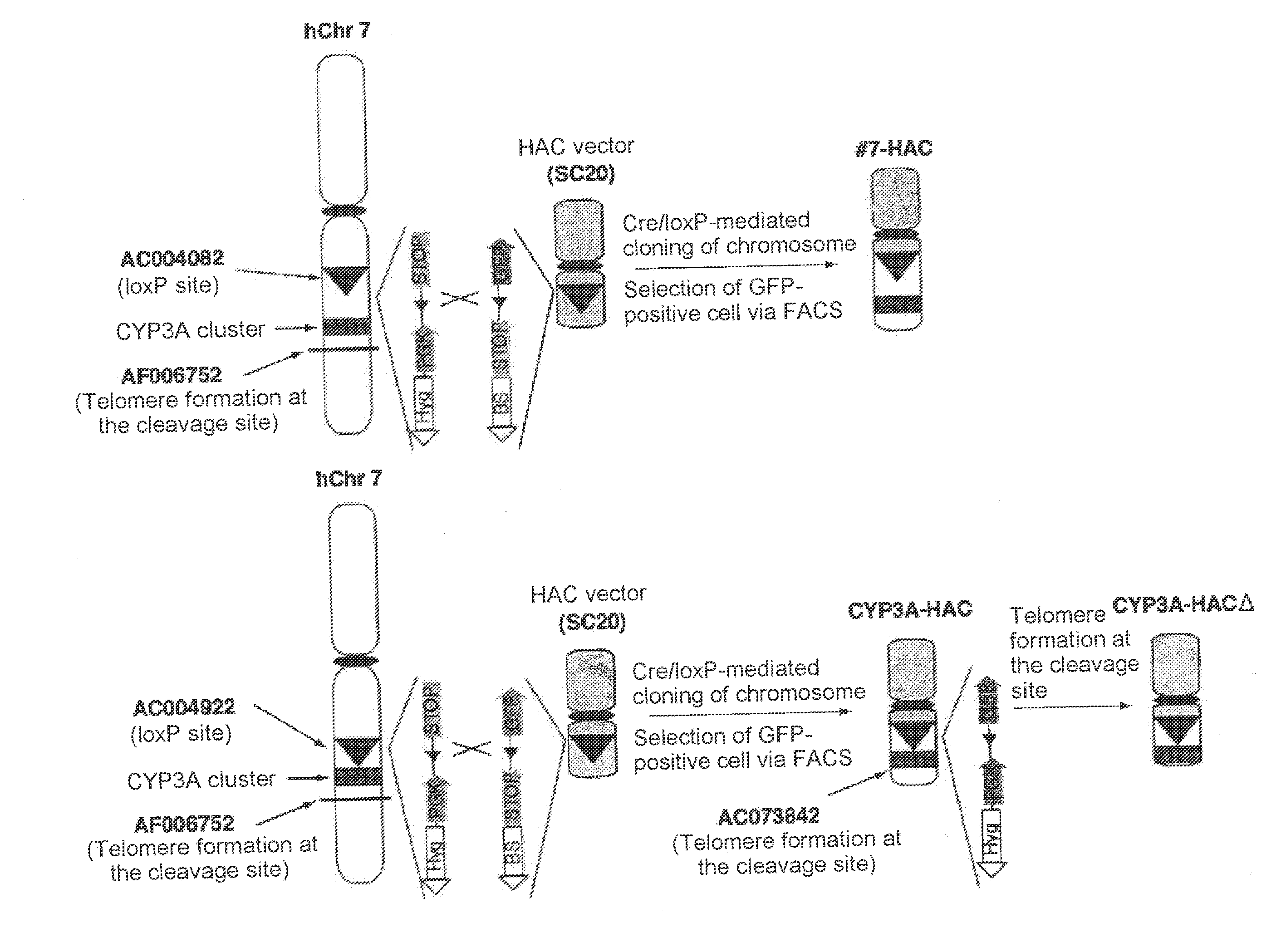
Mammalian artificial chromosome vector comprising human cytochrome p450 gene (cluster) and non-human mammalian animal retaining the same
InactiveUS20110023138A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsGene clusterMammal
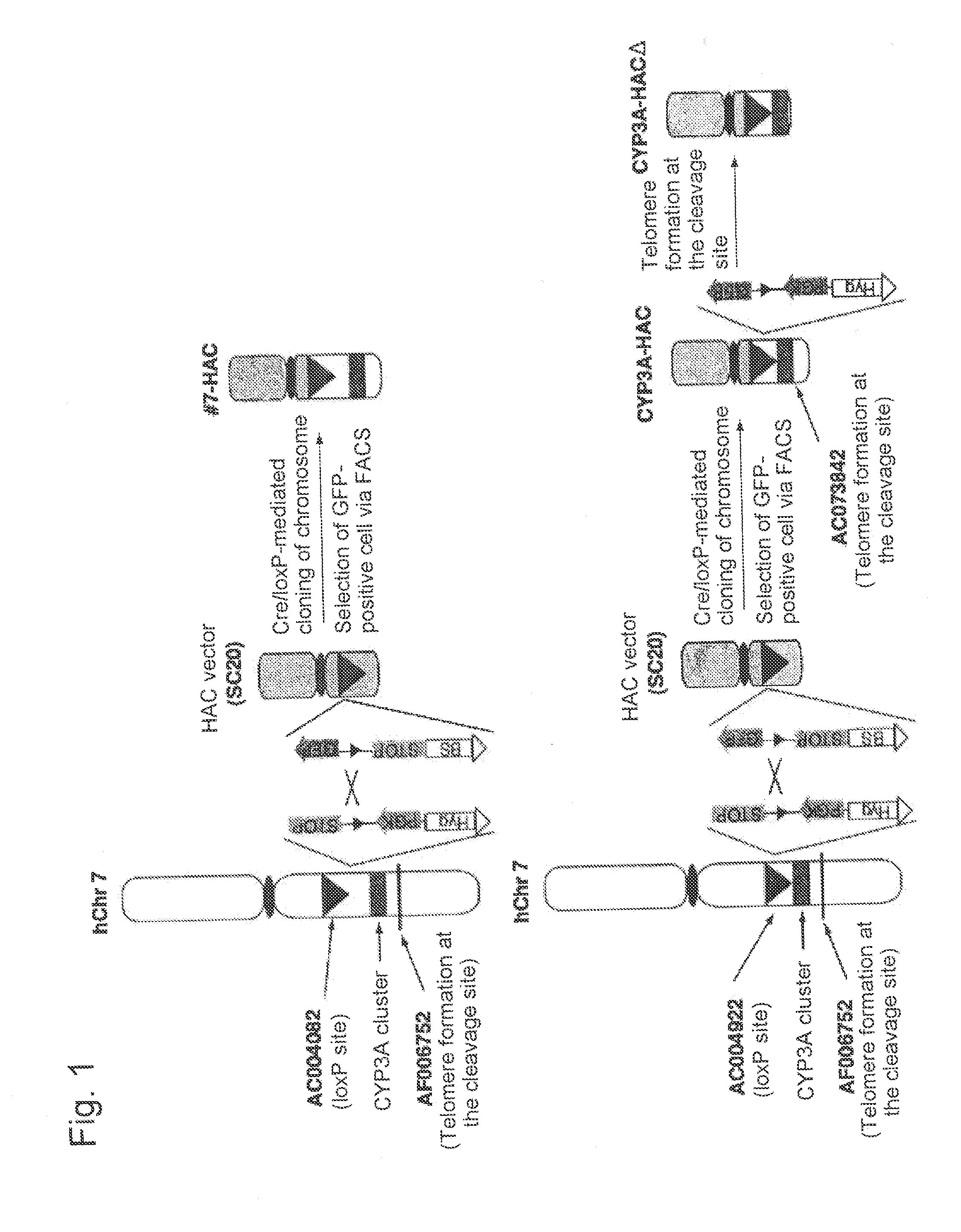
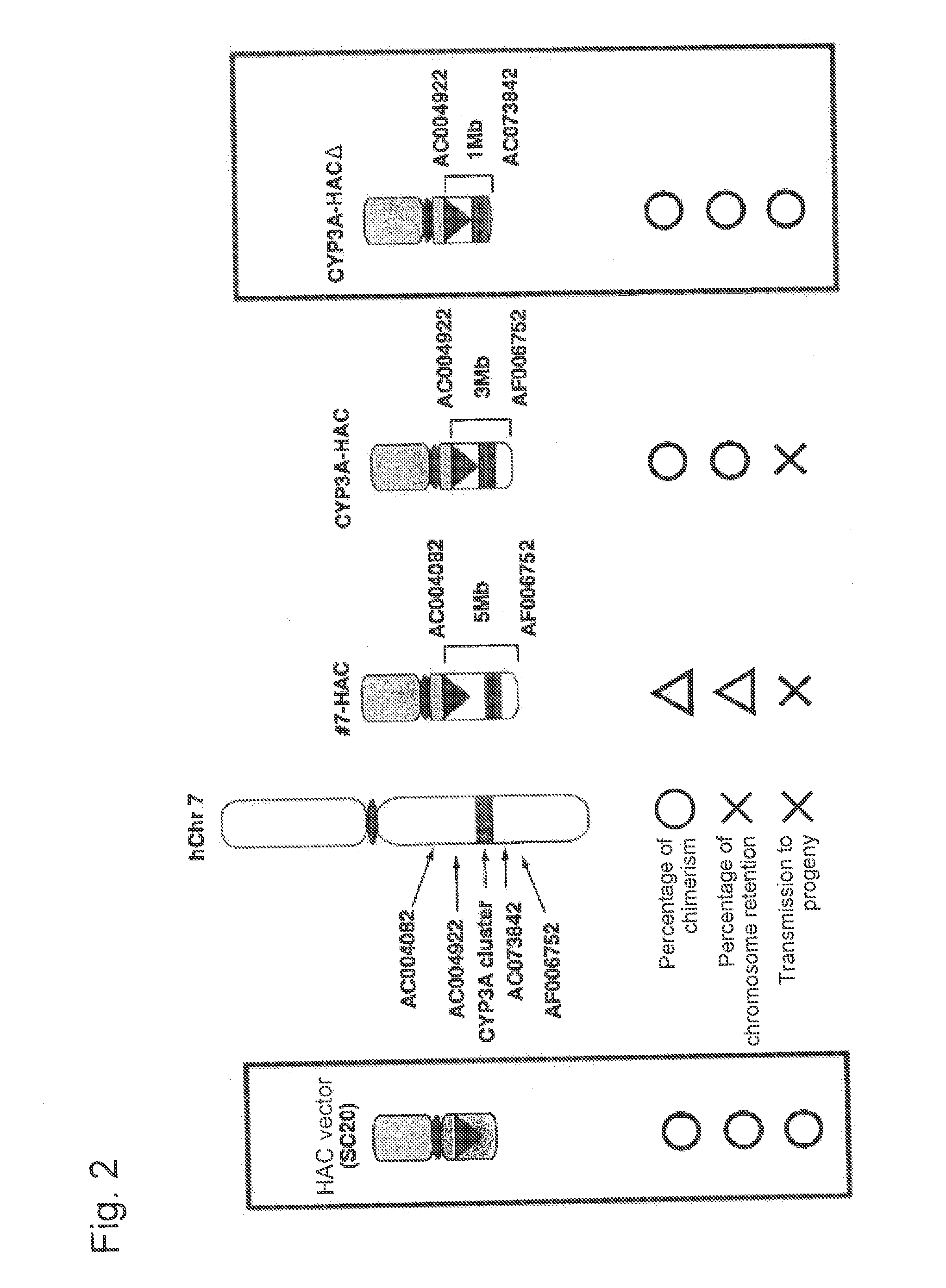
This invention relates to a mammalian artificial chromosome vector, which retains a human chromosome 7 fragment comprising human cytochrome P450 genes and is transmittable to progeny, wherein the human chromosome 7 fragment retains a region of approximately 1 Mb±500 Kb in size comprising at least a human CYP3A gene cluster, which region is located between chromosome markers AC004922 and AC073842, and to a non-human mammalian animal retaining the vector.
Owner:TOTTORI UNIVERSITY +1
Immune stimulating composition comprising bacterial chromosomal DNA fragments having methylated CpG sequences and non-toxic lipopolysaccharides
InactiveUS20060166923A1Economic and effective and specificIncrease doseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAdjuvantBacterial chromatophore
The present invention relates to immune stimulating composition comprising methylated bacterial chromosomal DNA fragments and non-toxic lipopolysaccharides. The composition of the present invention can be industrially applied the effective materials for treating cancers and adjuvant.
Owner:EYEGENE INC
Method for increasing disease-resistant breeding efficiency of hybrid rice
InactiveCN106636354AImprove breeding efficiency for disease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationSalt resistanceAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for increasing the disease-resistant breeding efficiency of hybrid rice, and belongs to the field of disease-resistant breeding of the hybrid rice. The method comprises the following steps: creating germplasm containing a bacterial blight resistance gene and rice blast resistance gene chromosome segment or a salt resistance gene and rice blast resistance gene chromosome segment by utilizing a molecular marker-assisted selection technology, and respectively hybridizing with a three-line maintainer line, a two-line sterile line or a restoring line; screening resistant individual plants for each segregative generation in a seedling stage by utilizing bacterial blight germs until screening out a new maintainer line B-resistant plant, a two-line sterile line S-resistant plant or a new restoring line R-resistant plant which obtains genetic stability and accords with breeding purposes; matching by using a sterile line containing the bacterial blight resistance gene and rice blast resistance gene chromosome segment and a restoring line containing the salt resistance gene and rice blast resistance gene chromosome segment, thus obtaining a hybrid variety containing the bacterial blight resistance gene, the rice blast resistance gene and the salt resistance gene. The method provided by the invention is simple and quick, and the disease-resistant breeding efficiency of the hybrid rice is increased.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
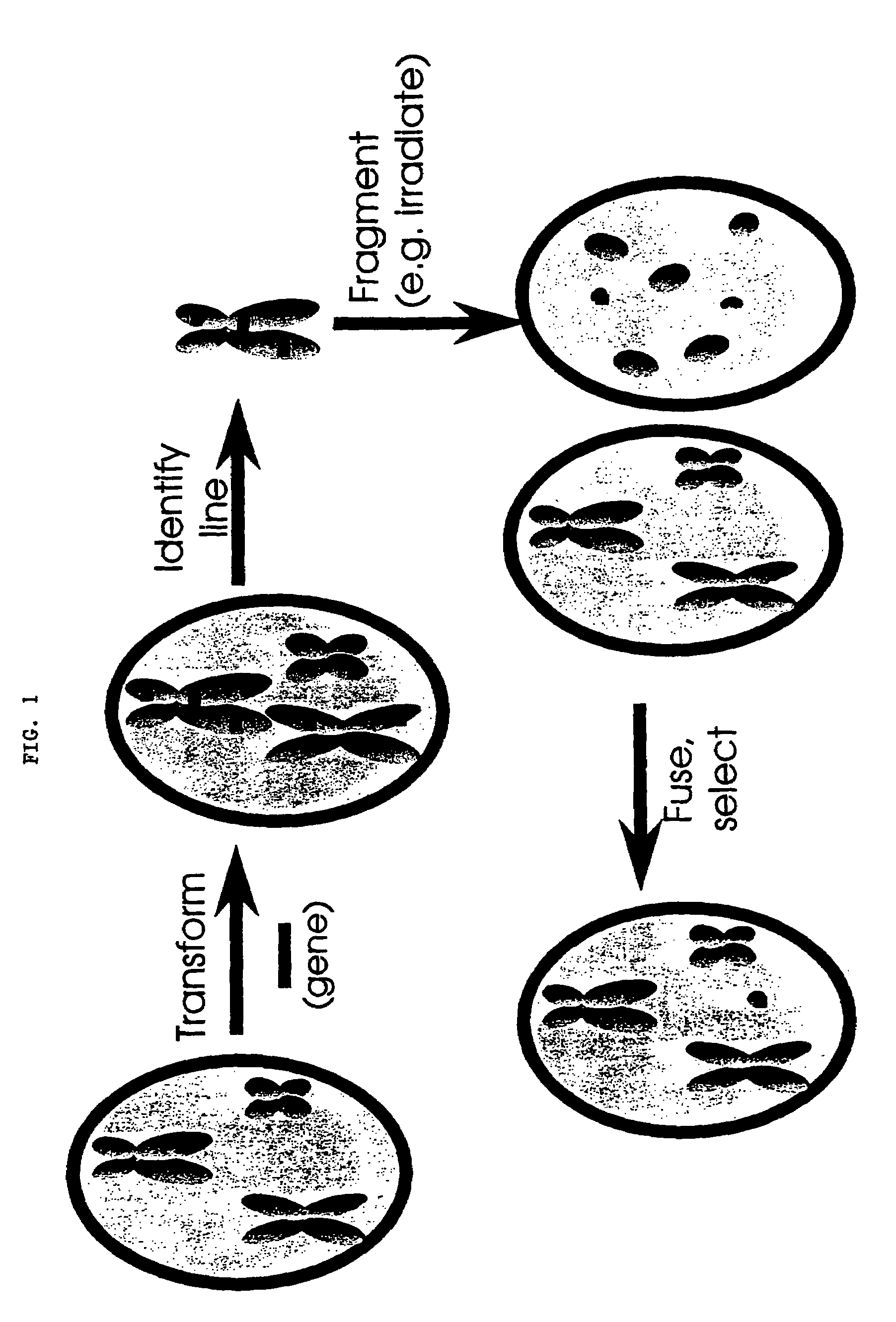
Method of making plant artificial chromosomes
InactiveUS7247768B1Repair damageOther foreign material introduction processesFused cellsProtoplastPlant chromosomes
Disclosed are methods of making plant artificial chromosomes. In one embodiment, the method entails: (a) preparing recombinant protoplasts of a first plant species containing an exogenous nucleic acid (e.g., DNA) of interest; (b) producing chromosome fragments of chromosomes contained in the recombinant protoplasts; (c) fusing the recombinant protoplasts of (b) with protoplasts of a second plant species to produce fused protoplasts, wherein the first and second plant species may be the same or different; and (d) identifying fused protoplasts of (c) or cells derived from the fused protoplasts of (c) that contain chromosome fragments that exhibit normal plant chromosomal properties. The chromosome fragments may be moved from one plant species to another. Whole plants, plant cell cultures and intermediates of same are also provided.
Owner:ICON GENETICS
Development and application of decaploid agropyron elongatum tandem repeat sequence specific probe
ActiveCN107475390AImproved genetic traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgropyron elongatumAgricultural science
The invention discloses development and application of a decaploid agropyron elongatum tandem repeat sequence specific probe. According to the development and the application, a specific length amplified fragment sequencing technology (SLAF-seq) is utilized to perform sequencing on common wheat, a common wheat-decaploid agropyron elongatum translocation line and decaploid agropyron elongatum, a decaploid agropyron elongatum specific sequence is acquired through sequence data comparative analysis, and the tandem repeat sequence specific probe is developed based on the decaploid agropyron elongatum specific sequence. The tandem repeat sequence specific probe provided by the invention can be used for rapidly identifying decaploid agropyron elongatum chromosomes and identifying a translocation line in a process that chromosome fragments of agropyron elongatum are transferred into the wheat, providing an important way of molecular marker-assisted selection to improve the wheat hereditary property and also providing an important application basis for wheat molecular breeding, phyletic evolution and germplasm resource identification.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Artificial selection method and reagents
InactiveUS20120144508A1Small sizeConserve costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingChromatophoreChromosome fragment
The present invention provides methods for estimating the breeding value of individuals in populations such as those having small effective population size (Ne) e.g., to identify selection candidates having high breeding values, wherein the methods comprise inferring one or more genotypes for one or more markers at a locus or QTL to be the same as for an ancestor or founder or a subset of ancestors and / or founders from which a corresponding chromosome segment is derived and estimating the breeding value of the individual based on the inferred genotype(s).
Owner:AGRI VICTORIA SERVICES PTY LTD
Lophopyrum elongatum genome-specific molecular markers and application thereof
InactiveCN102676515AGood repeatabilityStable amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideRe engineering
The invention belongs to the field of crop genetic breeding, in particular 36 Lophopyrum elongatum genome-specific molecular markers. The 36 genome-specific molecular markers are obtained by the following steps: according to a nucleotide sequence of 18srRNA gene disclosed by National Center of Biotechnology Information (NCBI), designing primers in the sequence between two RsaI loci, removing homologous sequences between two genome DNA by using a suppression subtractive hybridization technology, enriching differential sequences, obtaining Lophopyrum elongatum specific DNA segments, sequencing the DNA segments, and redesigning primers according to sequences without homology with wheat. The markers can be used for identifying translocation lines in the process of transferring chromosome segments from Lophopyrum elongatum to wheat, can be used for linkage analysis of scab-resistant gene, and can serve as specific molecular markers for identifying chromatin of the Lophopyrum elongatum to be applied to scab-resistant and stress-resistant breeding of wheat.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Drought-resistant related SSR sequence derived from abnormal cotton and application thereof
ActiveCN111349712AImprove selection efficiencyHigh speedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyAssociated organism
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Nucleic acid probes for identifying haynaldia villosa chromosomes and application thereof
InactiveCN106350594APromote diffuse distributionFast and more accurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleic Acid ProbesHaynaldia villosa
The invention provides a pair of oligonucleotides and nucleic acid probes prepared from the same. The two nucleic acid probes can form better dispersive distribution on most of haynaldia villosa chromosomes, and by combining the nucleic acid probes with known oligomeric nucleic acid probes Oligo-pTa535, the haynaldia villosa chromosomes and / or chromosome segments in the genetic background of wheat can be identified quickly and accurately. The technology has the advantages of time saving, labor saving, low cost and capability of reaching a similar GISH (genomic in situ hybridization) effect.
Owner:SAAS BIOTECH & NUCLEAR TECH RES INST
Line design
ActiveUS20140007286A1Efficient constructionEfficient methodVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationChromosome fragmentGenetically modify
The present invention relates to a method for genetically modifying the genome of a hybrid plant by replacing one or more of its chromosomes or chromosome fragments with the corresponding chromosome or chromosome fragment of one or more donor parents. The invention uses the reverse breeding technique to construct a novel type of substitution and introgression libraries that can be used for accelerated breeding and hybrid correction. These libraries and their use are also part of this invention.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Specific molecular markers for detection of Aegilops comosa 2M, 3M, 6M and 7M chromosomes in wheat, kit and method
ActiveCN106011299AEffective detection meansActive industrialization valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGermplasmAegilops comosa
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, in particular to specific molecular markers for detection of Aegilops comosa 2M, 3M, 6M and 7M chromosomes in wheat, and the specific molecular markers are DNA base sequences respectively shown as SEQ ID No.1 and -18 in the sequence table. A to-be-detected chromosome sample and a specific molecular marker composition are put into a kit to conduct amplification. The specific molecular markers and the kit can be used for detection or assisted detection of the existence of Aegilops comosa 2M, 3M, 6M and 7M chromosomes in wheat. The invention provides an effective detection means for screening and identification of wheat-Aegilops comosa distant hybridization new germplasms involving Aegilops comosa 2M, 3M, 6M and 7M chromosomes, provides a detection method for transfer of excellent genes on Aegilops comosa 2M, 3M, 6M and 7M chromosomes to wheat by means of chromosome segments, and has positive industrialization value.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for rapidly identifying thinopyrum intermedium 4St chromosome
ActiveCN113265483AQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMolecular genetics
The invention discloses a method for rapidly identifying an thinopyrum intermedium 4St chromosome, and relates to the technical field of plant molecular genetic breeding. The method comprises the following steps: plant genome DNA is extracted, and PCR amplification is carried out; and if any target fragment is obtained through amplification, an thinopyrum intermedium 4St chromosome gene exists. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention can be used for rapidly detecting the 4St chromosome or the 4St chromosome segment in chromosome engineering lines (chromosome addition lines, substitution lines, translocation lines and double diploids) of the thinopyrum intermedium in the distant hybridization process of the wheat and the thinopyrum intermedium. The method has important value for theoretical research and practical application of wheat genetic breeding.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker of multieffect QTLs locus qTLS-4 for regulating and controlling size of rice leaf and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN112126703ASize predictionSpeed up breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyA-DNA
The invention discloses a multieffect QTLs locus for regulating and controlling a size of a boot leaf of rice. The QTLs locus is located on a DNA fragment of a chromosome 4# of the rice, is called after qTLS-4, has a genetic distance of 87.1cM-97.4cM and a physical distance of 28747360bp-29507404bp and plays a role in regulating and controlling the size of the boot leaf of the rice. The inventionfurther discloses a molecular marker of the multieffect QTLs locus qTLS-4 for regulating and controlling the size of the boot leaf of the rice. The molecular marker comprises two pairs of molecular markers Indel Fls-1 and Indel Fls-2 which are closely chained. According to the molecular marker, whether a rice variety or line has the QTLs for regulating and controlling the size of the boot leaf ofthe rice or not is detected by using a molecular marker method, and thus, a breeding progress of excellent varieties of the rice is accelerated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com