Molecular marker of multieffect QTLs locus qTLS-4 for regulating and controlling size of rice leaf and application of molecular marker
A technology of leaf size and molecular markers, which is applied in the fields of rice breeding and molecular biology, can solve the problems of relatively few studies on molecular genetic mechanisms, and achieve the effects of good marker polymorphism, accelerated breeding, and accurate QTL positioning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Embodiment 1, acquisition of experimental materials
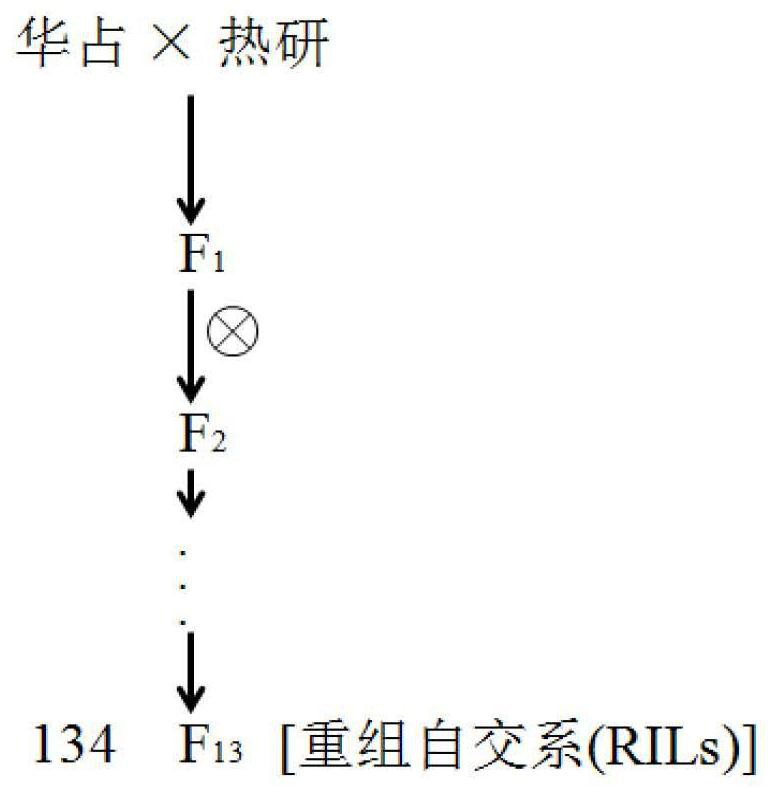
[0063] Huazhan was used as the donor parent, and the local rice variety Reyan was used as the recipient parent to construct RILs by crossing, using the single-seed method (i.e., bagging a single plant of F1 until the phenotype of the offspring did not occur. segregation), finally got 134 stable genetic lines, such as figure 1 .
[0064] Select 60 seeds (F13) of the parent and each strain, soak the seeds for 2 days after surface disinfection, wrap them in a moist towel, put them in a 37°C incubator for 48 hours, and select the seeds with consistent dew and whiteness for sowing. After 30 days, the parents with similar growth conditions and 24 seedlings of each line were selected for transplantation. All rice materials were planted in the experimental field of the School of Chemistry, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua City, Zhejiang Province, and were managed routinely.
Embodiment 2
[0065] Embodiment 2, blade size data measurement
[0066] At the tillering stage, 5 tillers were randomly selected for each line (transplanted parents, line seedlings), and the leaf length, leaf width, and leaf area of flag leaves were measured respectively. Record the data of each group and calculate the average value.
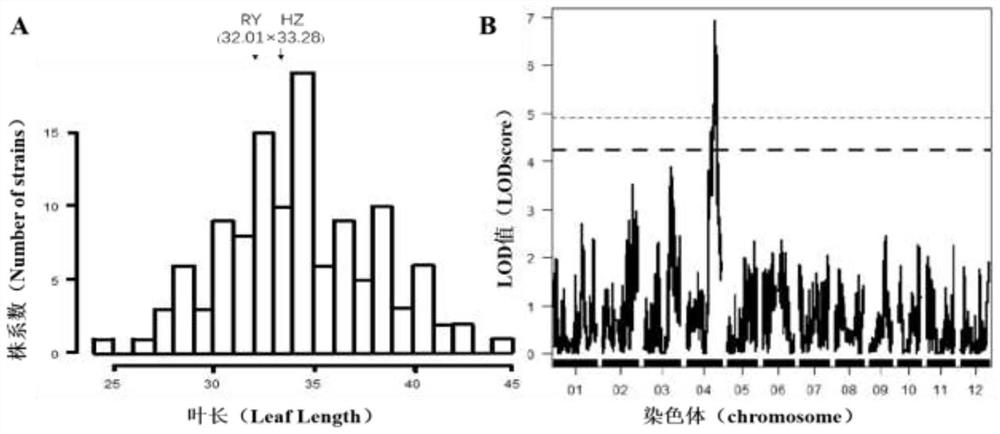
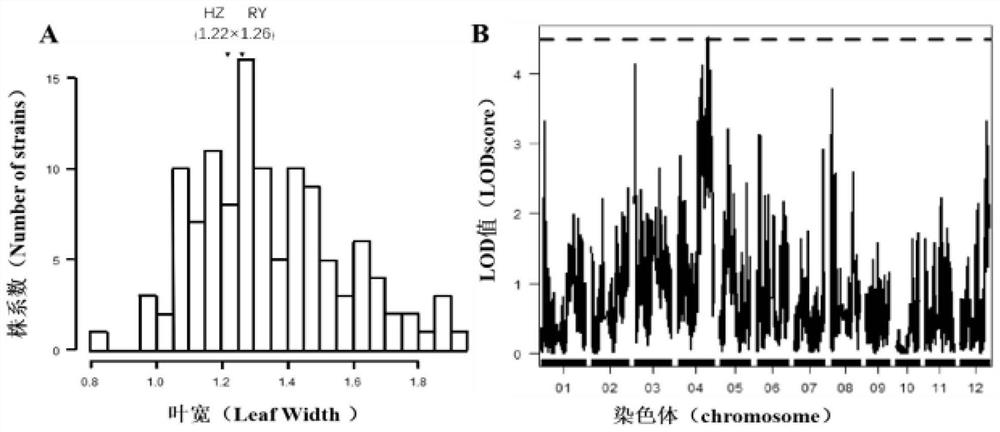
[0067] figure 2 A. image 3 A. Figure 4 In A, RY represents the rice variety Reyan, and HZ represents the rice variety Huazhan; according to figure 2 A. image 3 A. Figure 4 A. It can be known that the data of leaf length, leaf width and leaf area of sword blade are continuous normal distribution and wide range, there are many super-parents, showing the genetic characteristics of quantitative traits.
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3, QTL location analysis
[0069] Use the genetic map constructed by a large number of SNP and Indel markers developed in the laboratory to map the quantitative trait locus (QTL) interval of rice leaf size, and analyze the markers and quantitative trait phenotype values of the entire chromosome group through R-QTL professional software QTLs were mapped to corresponding positions in the linkage group one by one, and their genetic effects were estimated. If a molecular marker with LOD>3 is detected, it is considered that there is a QTL between the two markers corresponding to the highest LOD value. A pleiotropic QTL located between the Indel Fls-1 marker and the Indel Fls-2 marker on chromosome 4 was found in the entire genome, with leaf length LOD values as high as 6.92, leaf width LOD values as high as 4.51, and leaf area LOD values as high as 6.37( figure 2 B. image 3 B. Figure 4 B). Its genetic distance is 87.1-97.4cM, physical distance is 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com