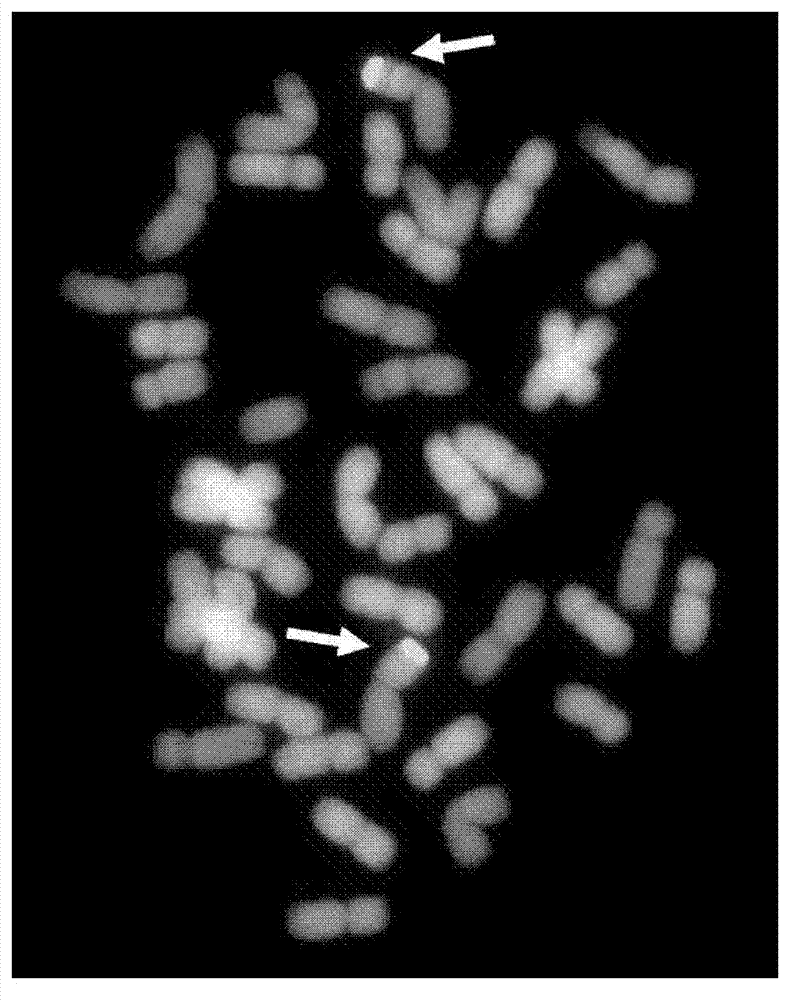
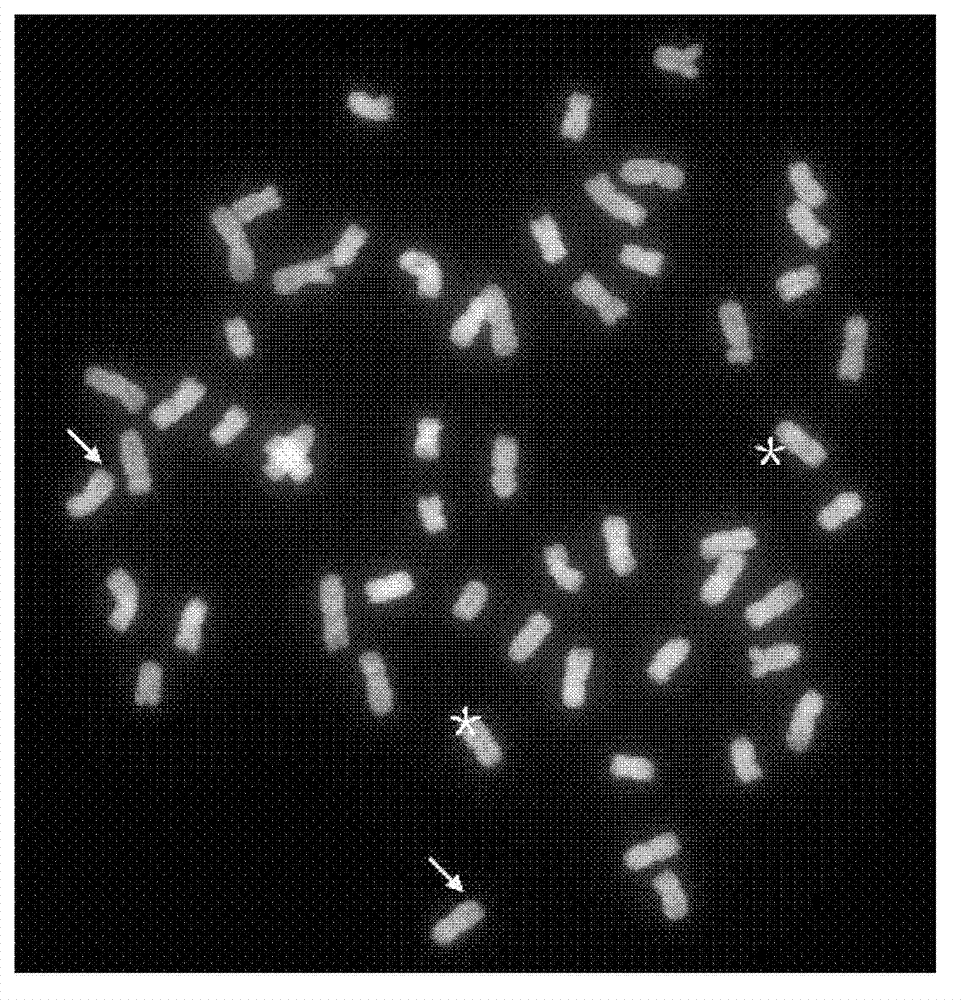
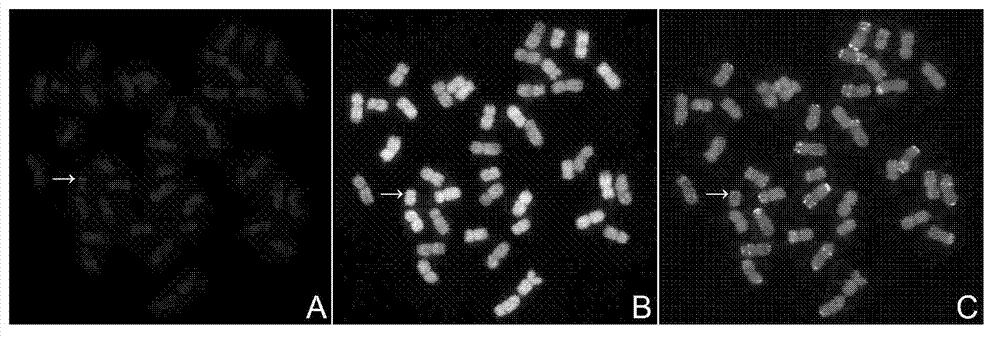
Multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization (MFISH) method for quickly analyzing and identifying alien chromosome of wheat
A fluorescence in situ hybridization and rapid analysis technology, applied in the field of cell biology and molecular biology research, can solve the problems of restricting the development of chromosome engineering, long cycle, difficult to accurately and effectively track and quickly identify recombinant chromosomes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Embodiment 1. Identification of Longchun 23 spring wheat material
[0057] 1. Preparation of Longchun 23 Spring Wheat Mitotic Metaphase
[0058] The Longchun 23 spring wheat used came from the germplasm resources preserved in the Han Fangpu Laboratory of the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (see Yang Wenxiong 2005).
[0059] 1)N 2 O treatment of root tip
[0060] When the root tip grows to 2-3cm, cut it off, put it in a wet centrifuge tube, cover it and put it in a N2O air chamber for 1-3h, the pressure is 10ATM (1.01Mpa);
[0061] 2) root tip fixation
[0062] Fix with 90% acetic acid for 5-10 minutes (no more than 1 hour), and wash with distilled water twice. The fixed root tips can be transferred to 70% ethanol and stored at -20°C for many years;
[0063] 3) Enzymolysis
[0064] Blot the water on the root tip with filter paper, cut off the root tip meristem, and put in 20 μL of a mixture of pectinase and cellulase (en...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Example 2. Chromosomal composition analysis of octoploid Tritite XY784
[0088] 1. Preparation of mitotic metaphases of octoploid Trititum XY784
[0089] The octoploid Trititti XY784 used came from the germplasm resources preserved in the Li Zhensheng Laboratory of the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Zhang Xueyong et al.1995).
[0090] 1) N2O treatment root tip with embodiment 1.1
[0091] 2) Root tip fixation Same as Example 1.2
[0092] 3) Enzymolysis Same as Example 1.3
[0093] 4) drop sheet is the same as embodiment 1.4
[0094] 5) Microscopic examination is the same as in Example 1.5
[0095] 2. Probe labeling of AA group, DD group and decaploid E. elongatum group
[0096] 1) CTAB method extracts plant genomic DNA with embodiment 2.1
[0097] 2) Probe labeling is the same as in Example 2.2
[0098] 3) with embodiment 2.3
[0099] 4) with embodiment 2.4
[0100] 3. Fluorescence in situ hybridization identificat...
Embodiment 3
[0109] Example 3. Preparation of metaphase chromosomes of different plants
[0110] The present invention will be further described below with reference to specific examples, but those skilled in the art should understand that the present invention is not limited to these specific examples.
[0111] 1. Seed Germination
[0112] (1) Put the seeds in a petri dish lined with moist filter paper, and germinate in an incubator at 21-23°C.
[0113] 2. Plant chromosome specimen preparation
[0114] 1) With embodiment 1.1.
[0115] 2) With embodiment 1.2.
[0116] 3) With embodiment 1.3.
[0117] 4) With embodiment 1.4.
[0118] 5) With embodiment 1.5.
[0119] 3. In Situ Hybridization
[0120] 1) Use the method of procedure 1 to prepare mitotic metaphase chromosome samples.
[0121] 2) with embodiment 3.2
[0122] 3) Same as embodiment 3.3
[0123] 4) When performing the second in situ hybridization, put the hybridized chromosome specimen into 2×SSC to wash off the antifade ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com