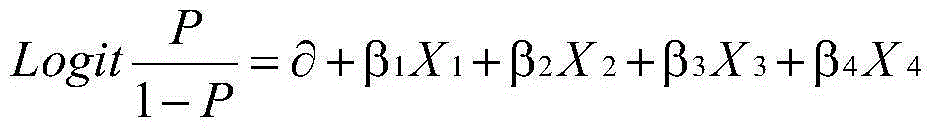Patents
Literature
72 results about "Mitotic Metaphase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
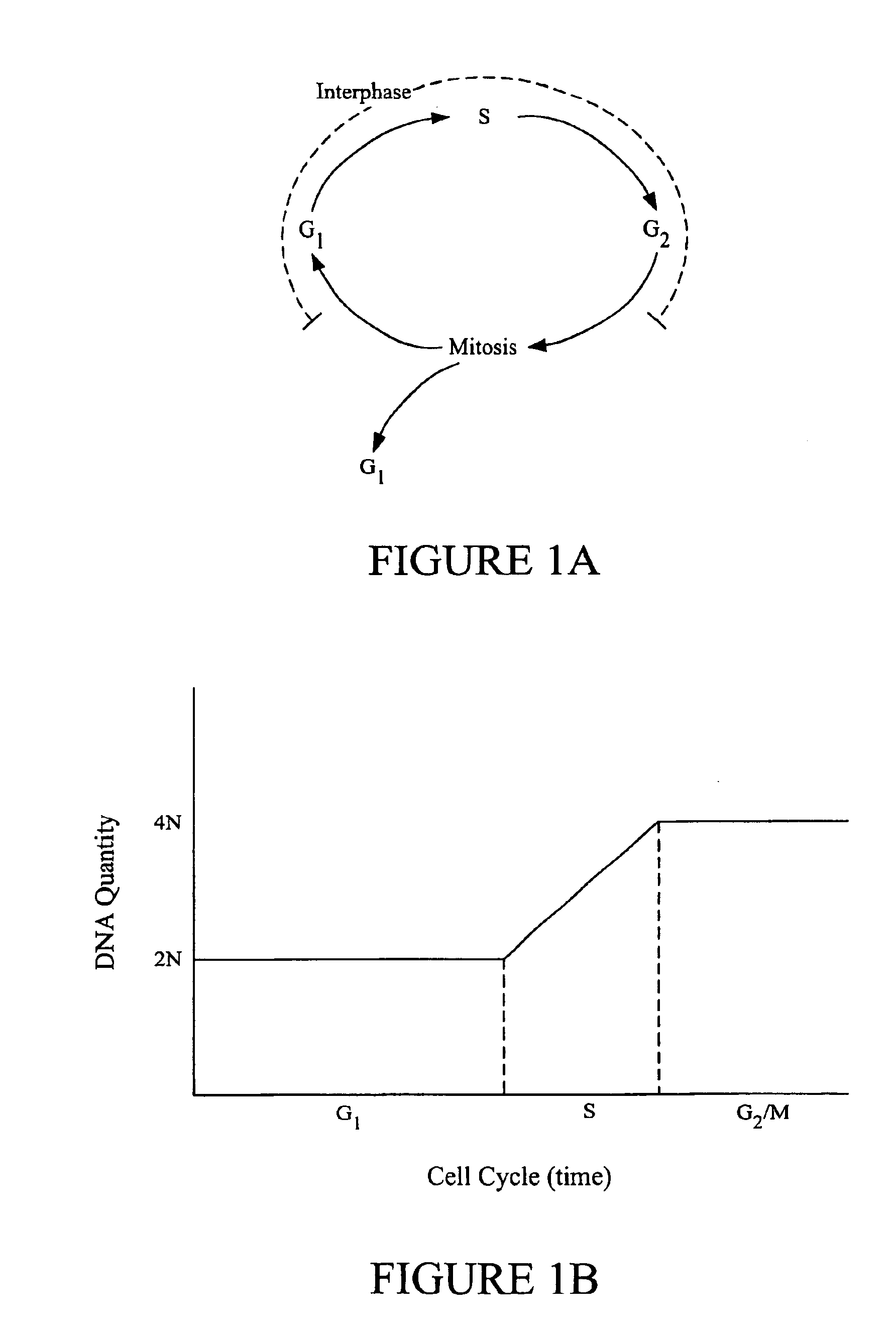
Metaphase (from the Greek μετά, adjacent and φάσις, stage) is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which chromosomes are at their second-most condensed and coiled stage (they are at their most condensed in anaphase).
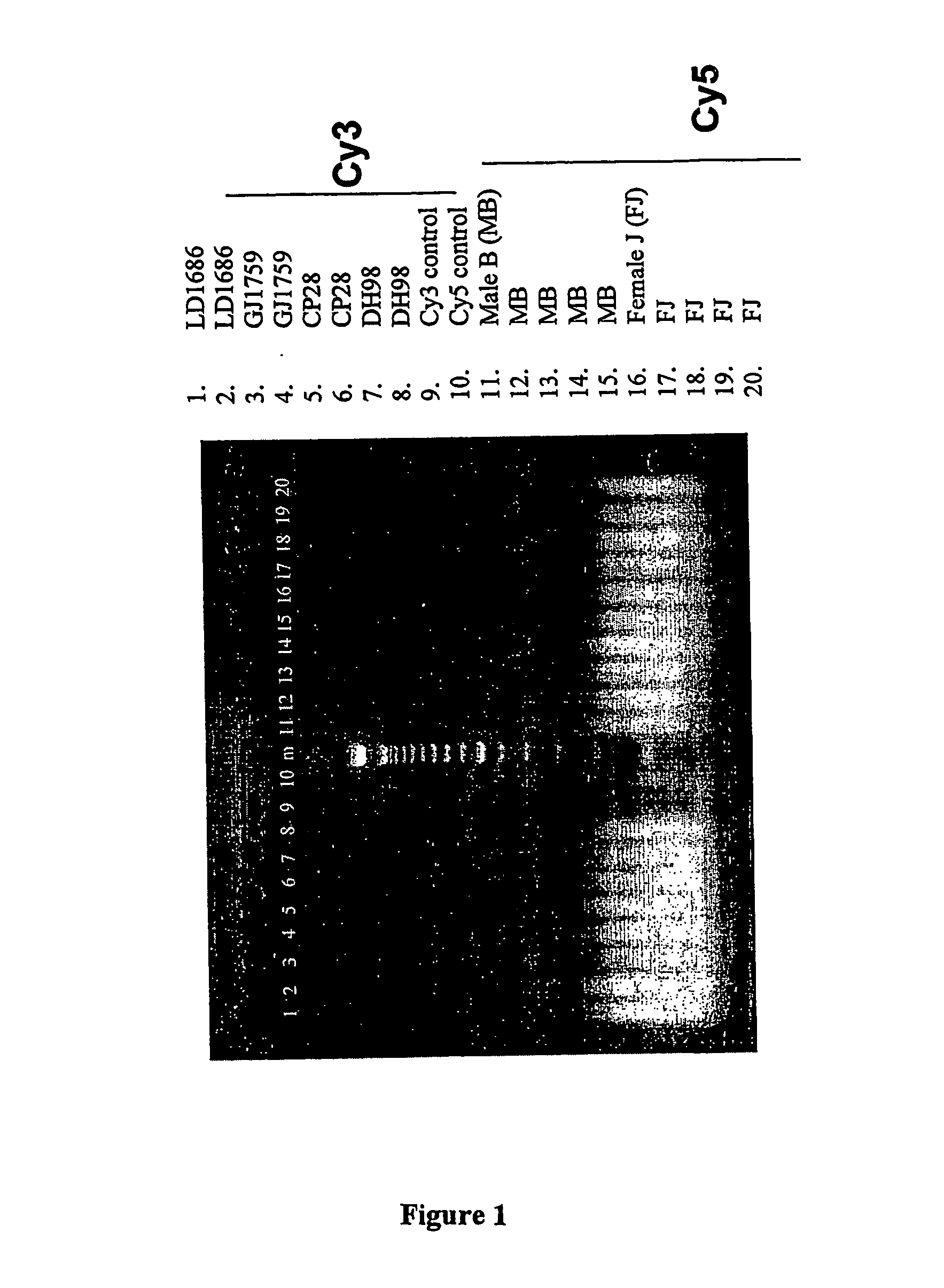
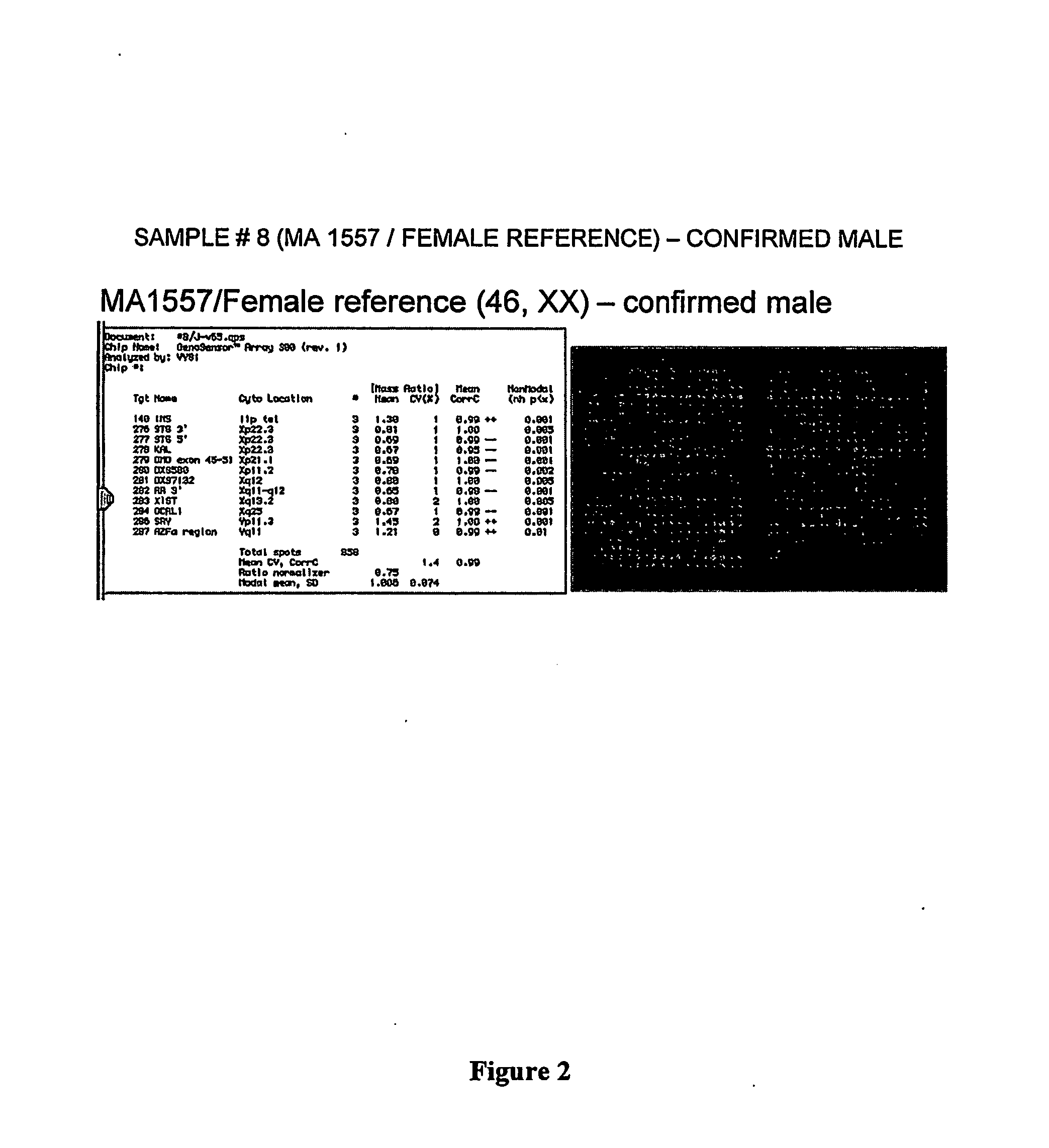
Prenatal Diagnosis Using Cell-Free Fetal DNA in Amniotic Fluid
InactiveUS20070212689A1Rapid determinationAddressing slow performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansCell-free fetal DNAAmniotic fluid
The present invention relates to improved methods of prenatal diagnosis, screening, monitoring and / or testing. The inventive methods include the analysis by array-based hybridization of cell-free fetal DNA isolated from amniotic fluid. In addition to allowing the prenatal diagnosis of a variety of diseases and conditions, and the assessment of fetal characteristics such as fetal sex and chromosomal abnormalities, the new inventive methods provide substantially more information about the fetal genome in less time than it takes to perform a conventional metaphase karyotype analysis. In particular, the enhanced molecular karyotype methods provided by the present invention allow the detection of chromosomal aberrations that are not often detected prenatally such as microdeletions, microduplications and subtelomeric rearrangements.
Owner:BIANCHI DIANA W +2
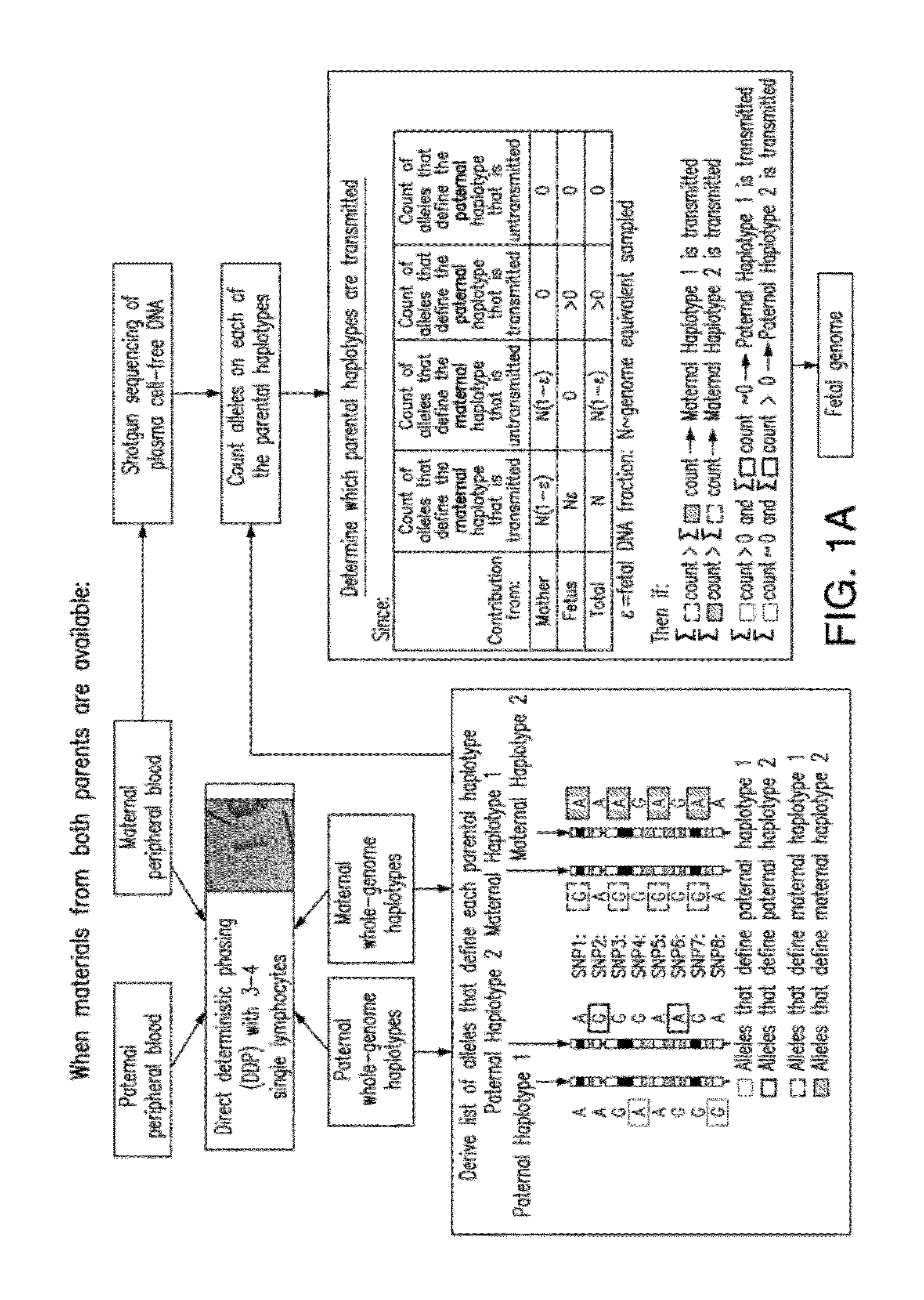
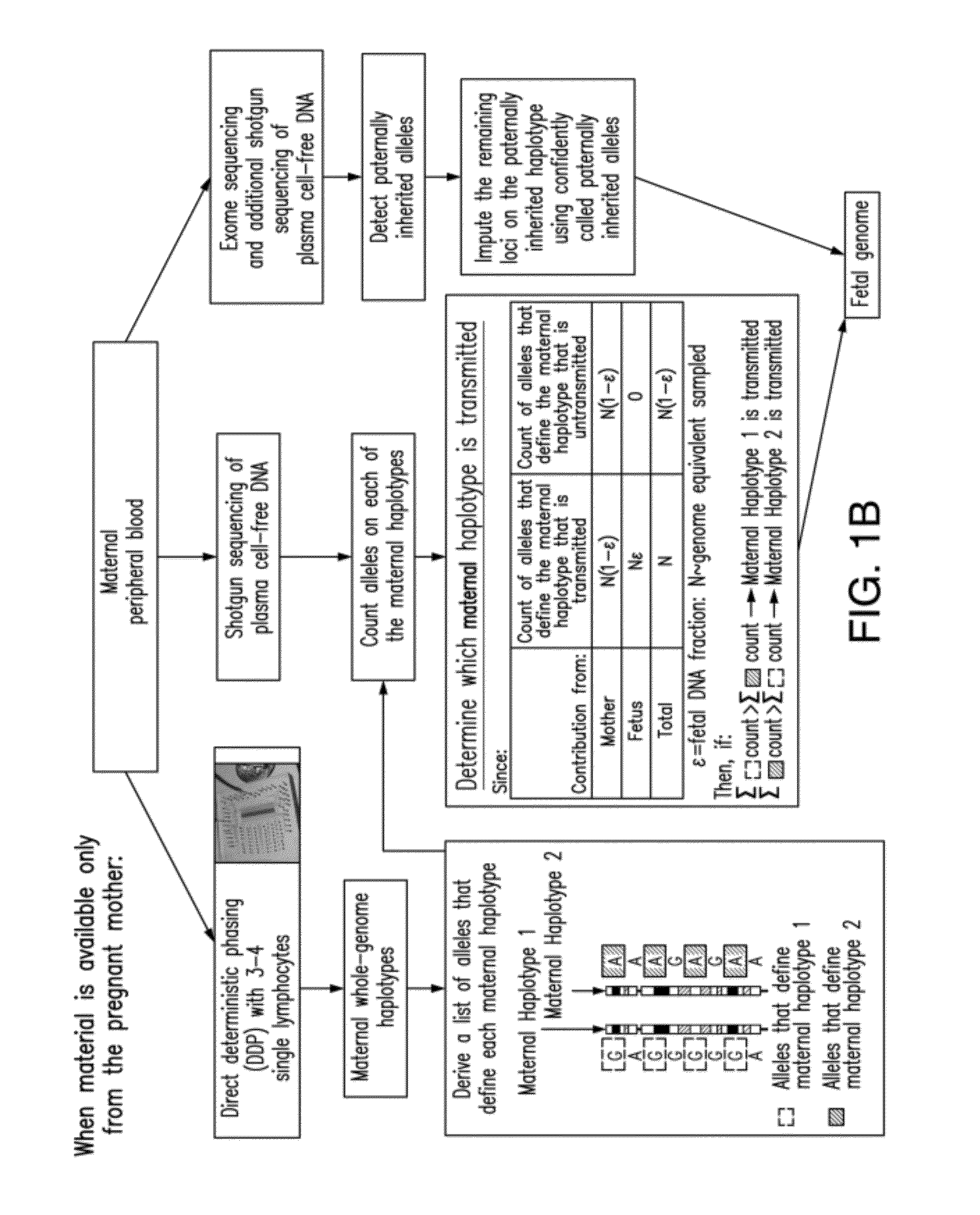
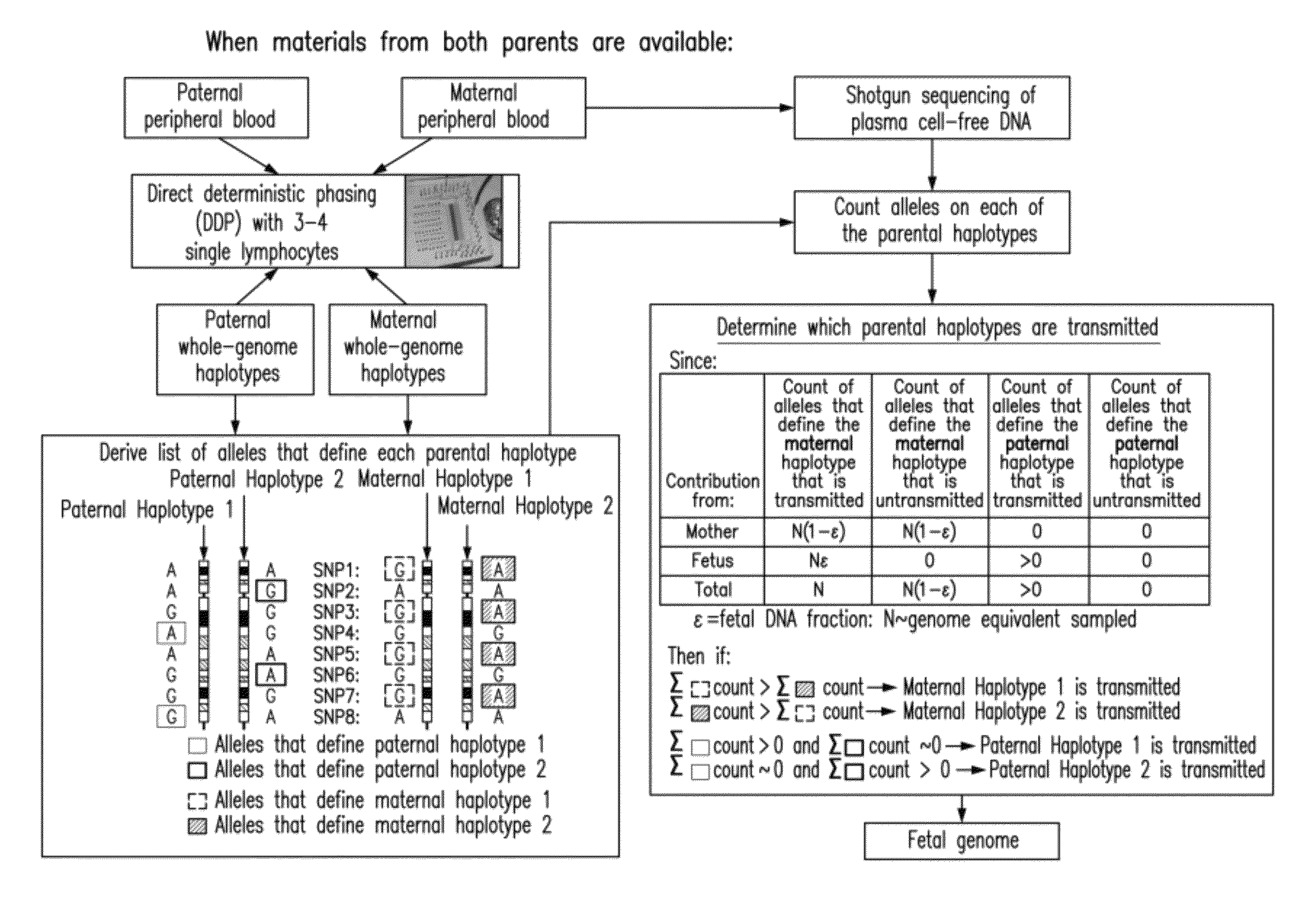
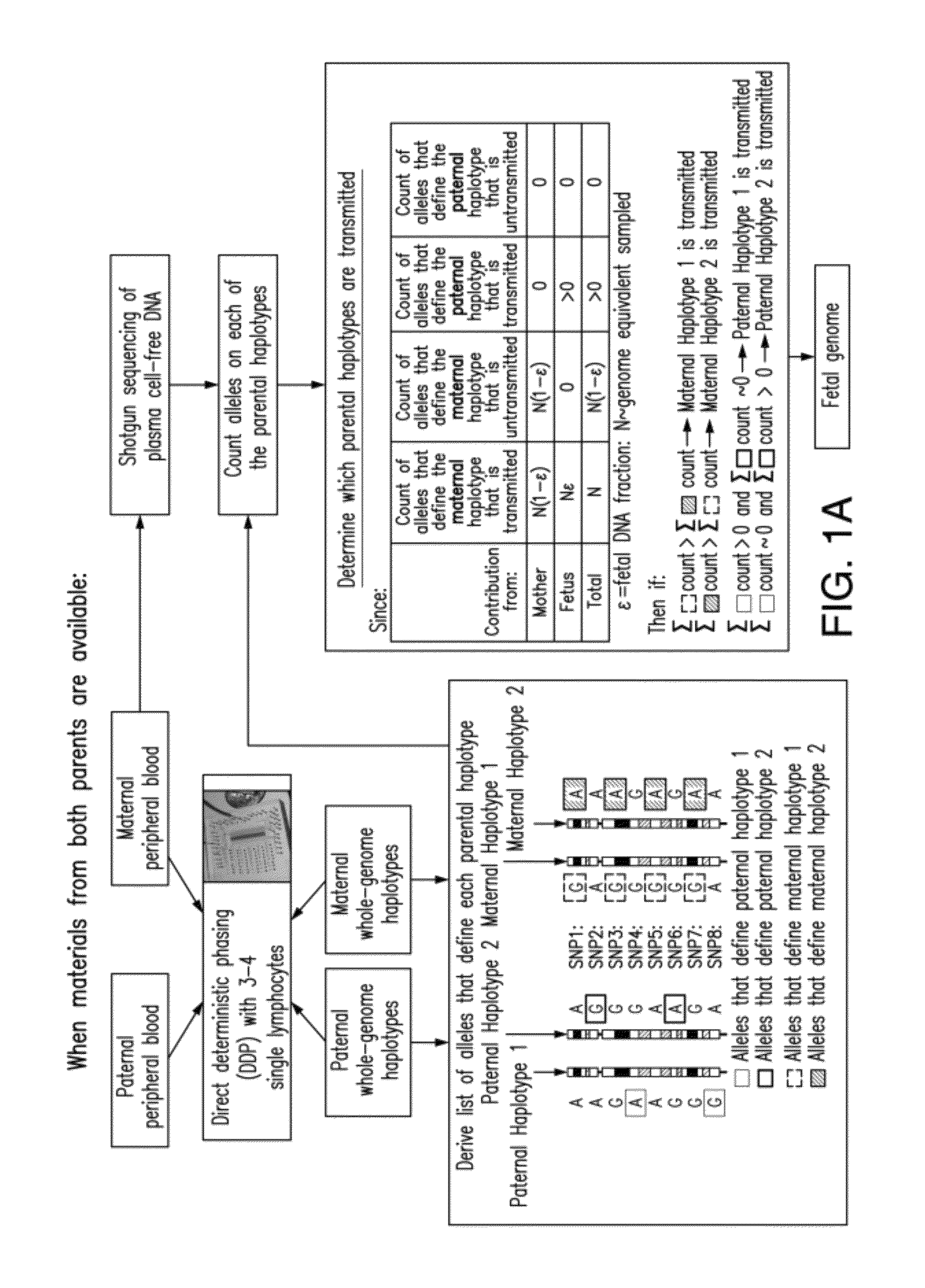
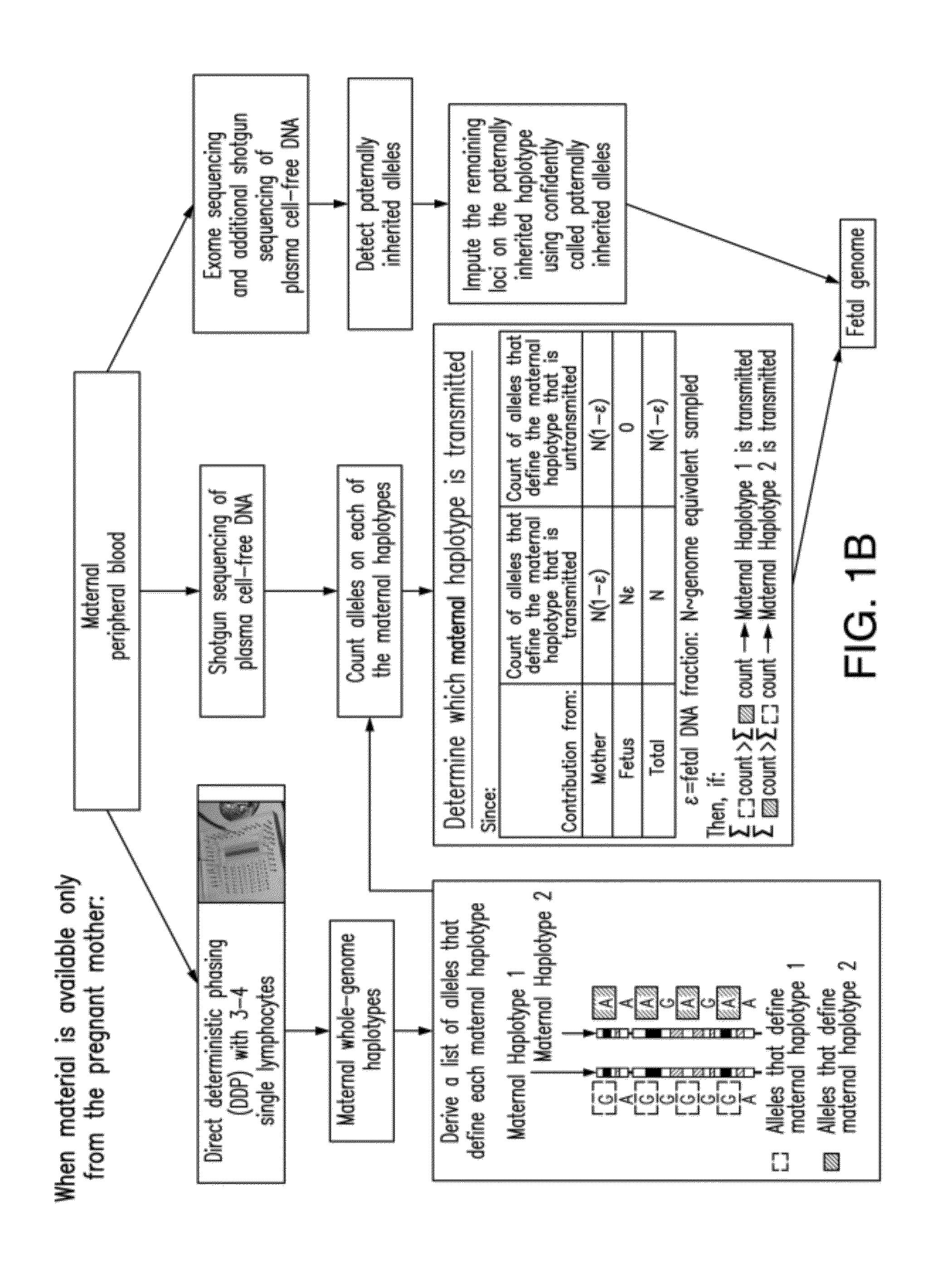
Non-invasive determination of fetal inheritance of parental haplotypes at the genome-wide scale
ActiveUS20120196754A1Reduce riskNon-invasively determiningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSequence analysisSerum samples
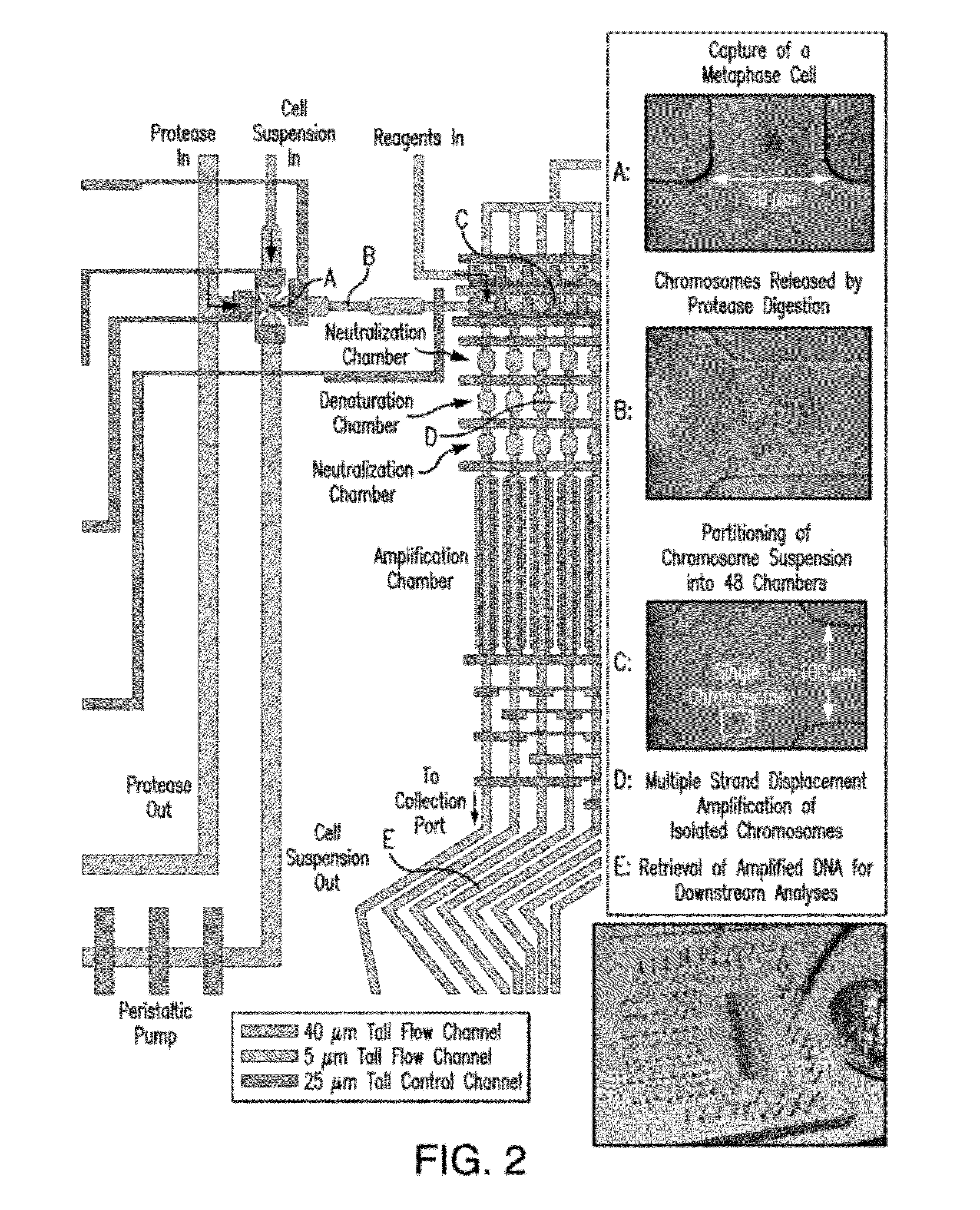
The present invention provides a method, device and a computer program for haplotyping single cells, such that a sample taken from a pregnant female, without directly sampling the fetus, provides the ability to non-invasively determine the fetal genome. The method can be performed by determining the parental and inherited haplotypes, or can be performed merely on the basis of the mother's genetic information, obtained preferably in a blood or serum sample. The novel device allows for sequence analysis of single chromosomes from a single cell, preferably by partitioning single chromosomes from a metaphase cell into long, thin channels where a sequence analysis can be performed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Prenatal diagnosis using cell-free fetal DNA in amniotic fluid
InactiveUS20070111233A1Improved and rapid methodHigh recovery rateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCell-free fetal DNAAmniotic fluid
The present invention relates to improved methods of prenatal diagnosis, screening, monitoring and / or testing. The inventive methods include the analysis by array-based hybridization of cell-free fetal DNA isolated from amniotic fluid. In addition to allowing the prenatal diagnosis of a variety of diseases and conditions, and the assessment of fetal characteristics such as fetal sex and chromosomal abnormalities, the new inventive methods provide substantially more information about the fetal genome in less time than it takes to perform a conventional metaphase karyotype analysis. In particular, the enhanced molecular karyotype methods provided by the present invention allow the detection of chromosomal aberrations that are not often detected prenatally such as microdeletions, microduplications and subtelomeric rearrangements. Also provided are improved methods of extraction of fetal DNA from amniotic fluid.
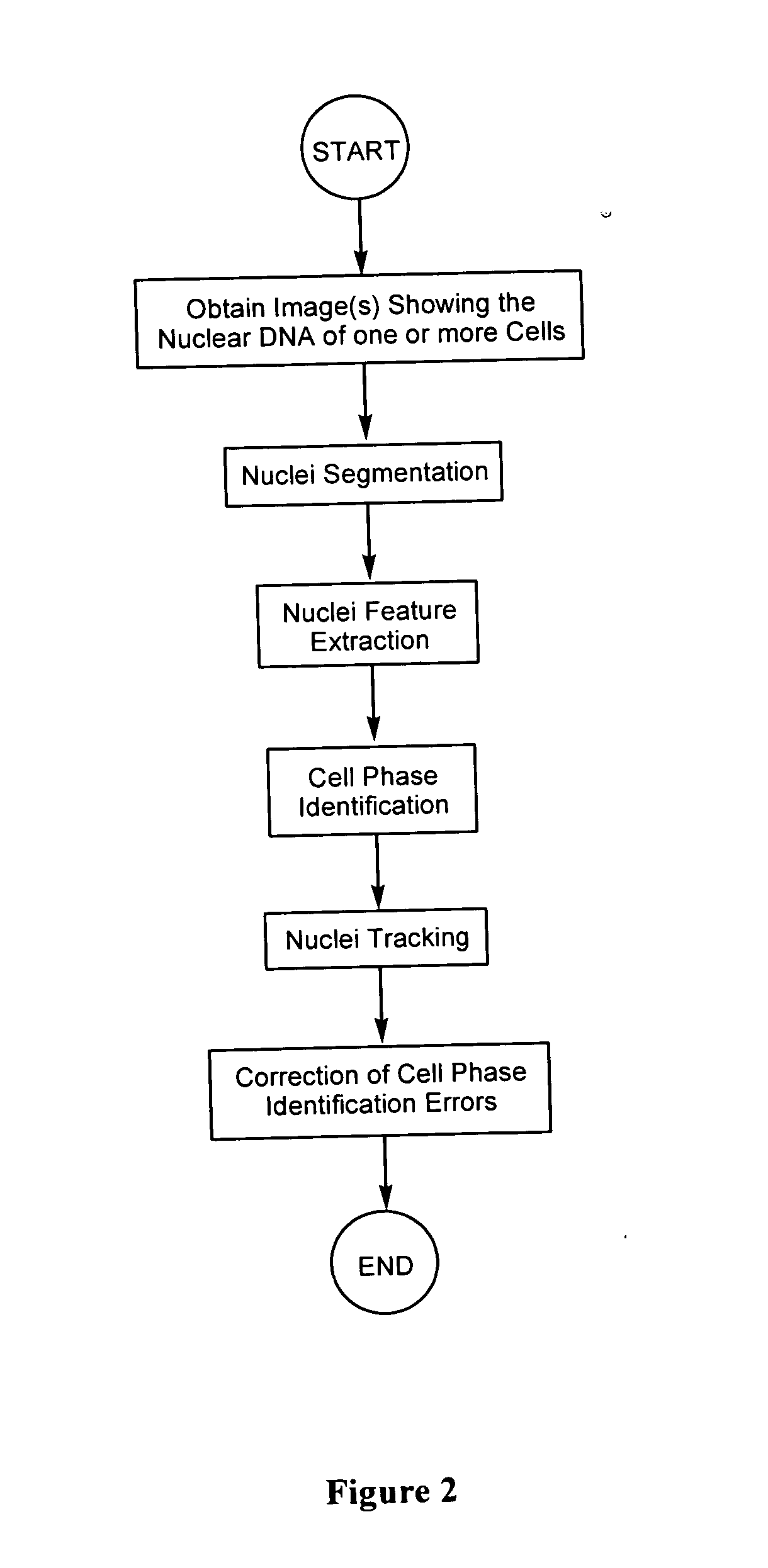
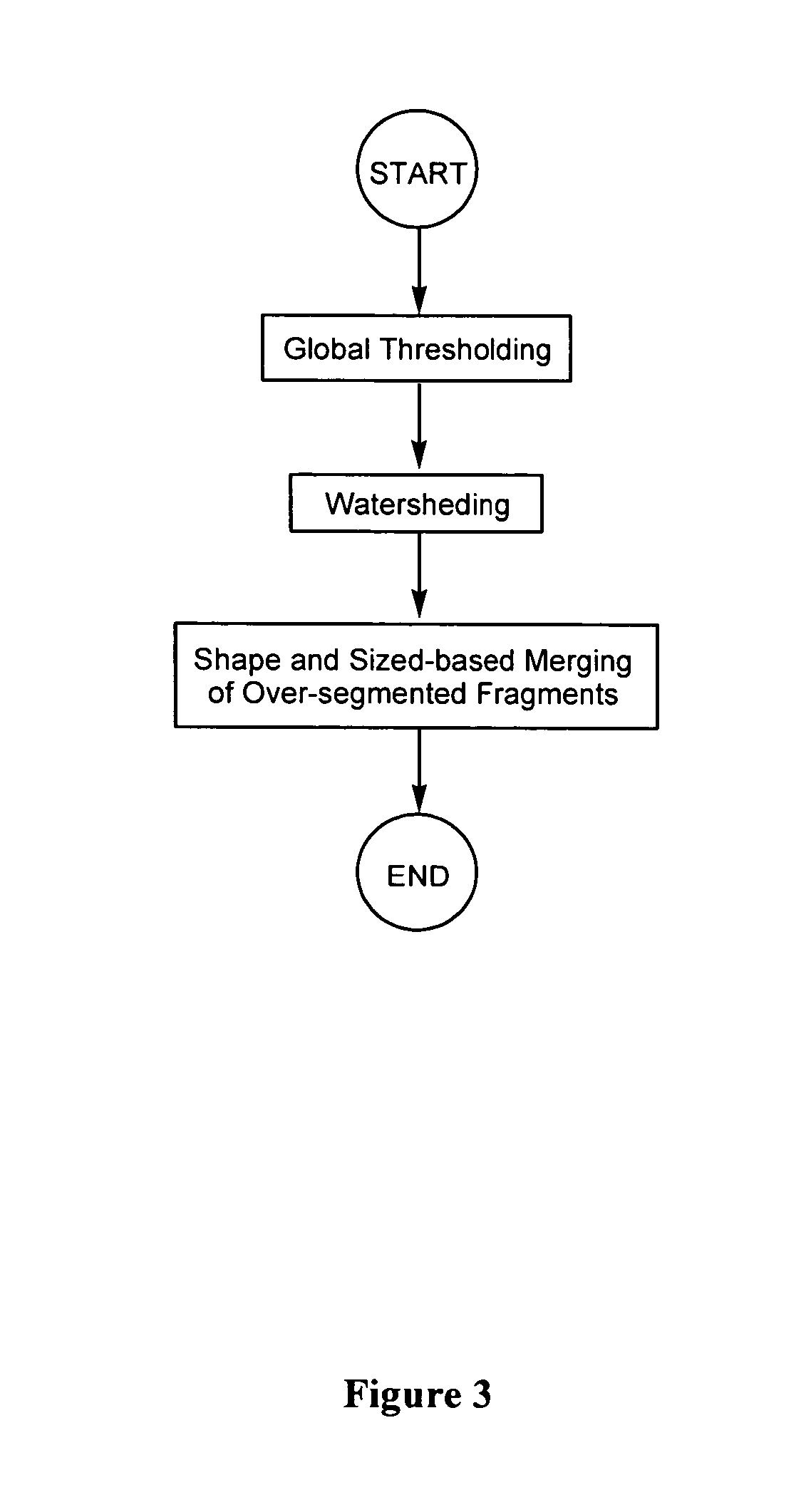
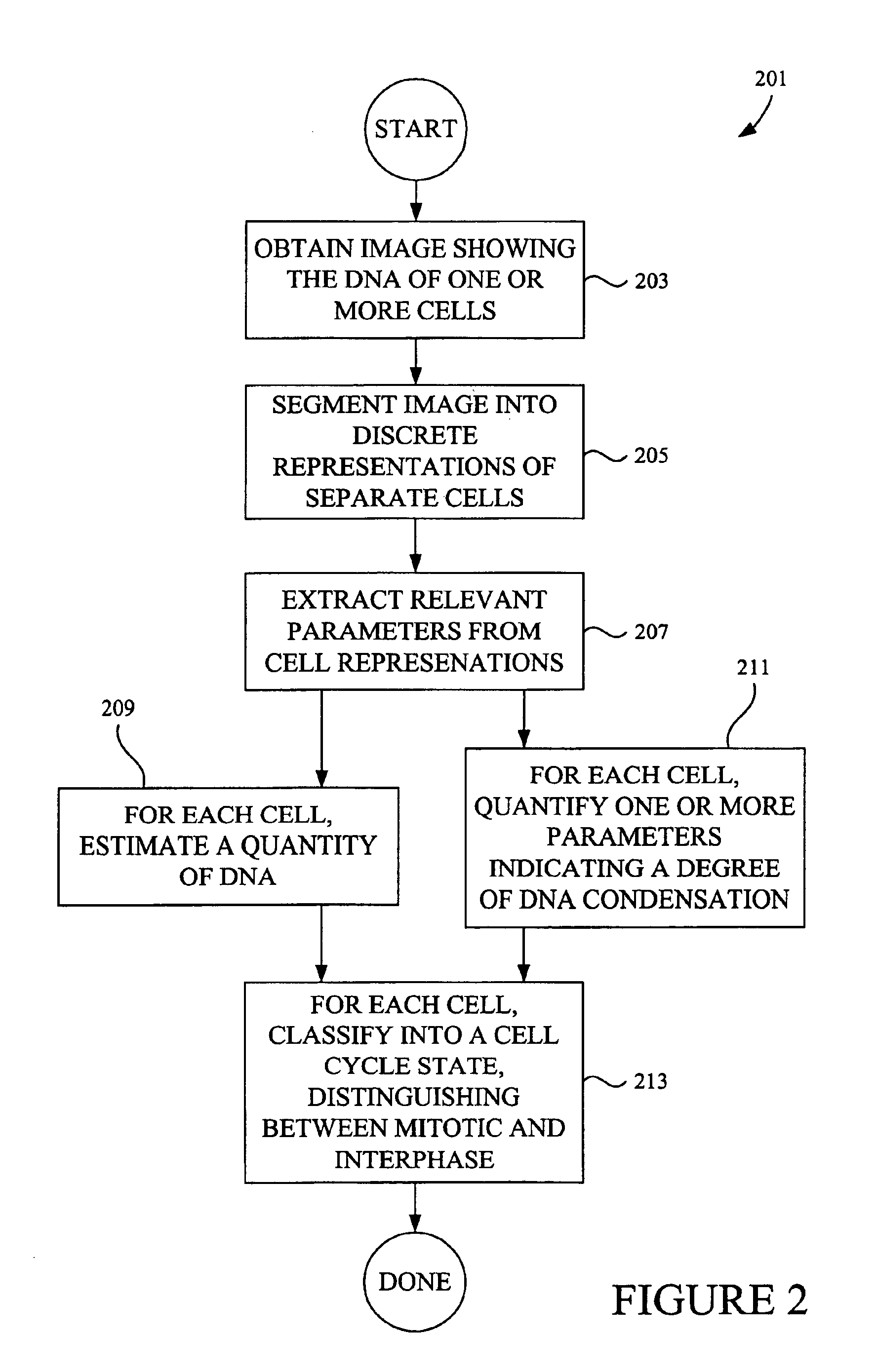
Automated segmentation, classification, and tracking of cell nuclei in time-lapse microscopy
InactiveUS20060127881A1Efficient dynamic cell imaging studyIncrease capacityImage enhancementImage analysisAutomated segmentationInterphase Cell
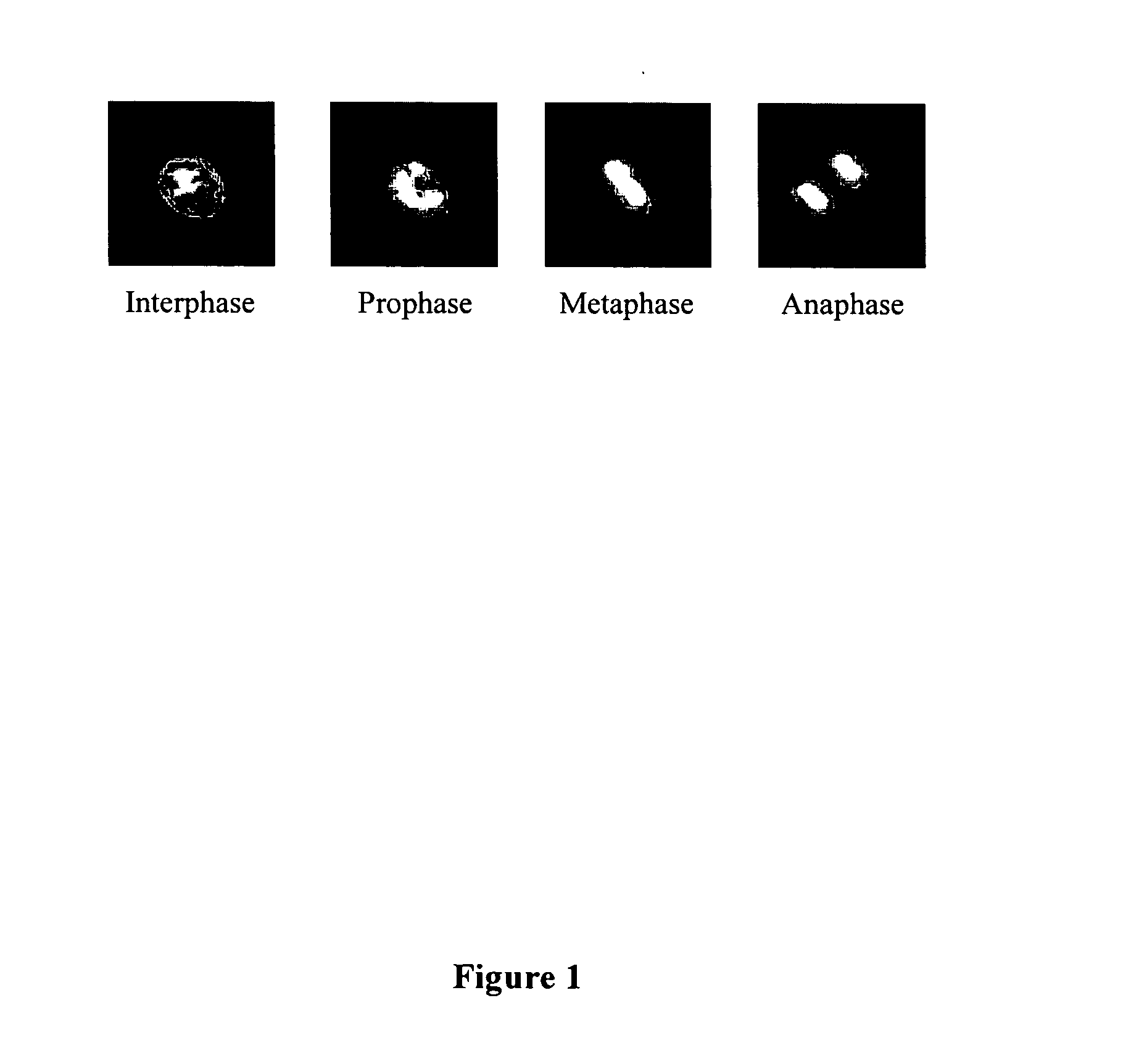
Methods and apparatus are provided for the automated analysis of images of living cells acquired by time-lapse microscopy. The new methods and apparatus can be used for the segmentation, classification and tracking of individual cells in a cell population, and for the extraction of biologically significant features from the cell images. Based upon certain extracted features, the inventive image analysis methods can characterize a cell as mitotic or interphase and / or can classify a cell into one of the following mitotic phases: prophase, metaphase, arrested metaphase, and anaphase with high accuracy.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMENS HOSPITAL INC
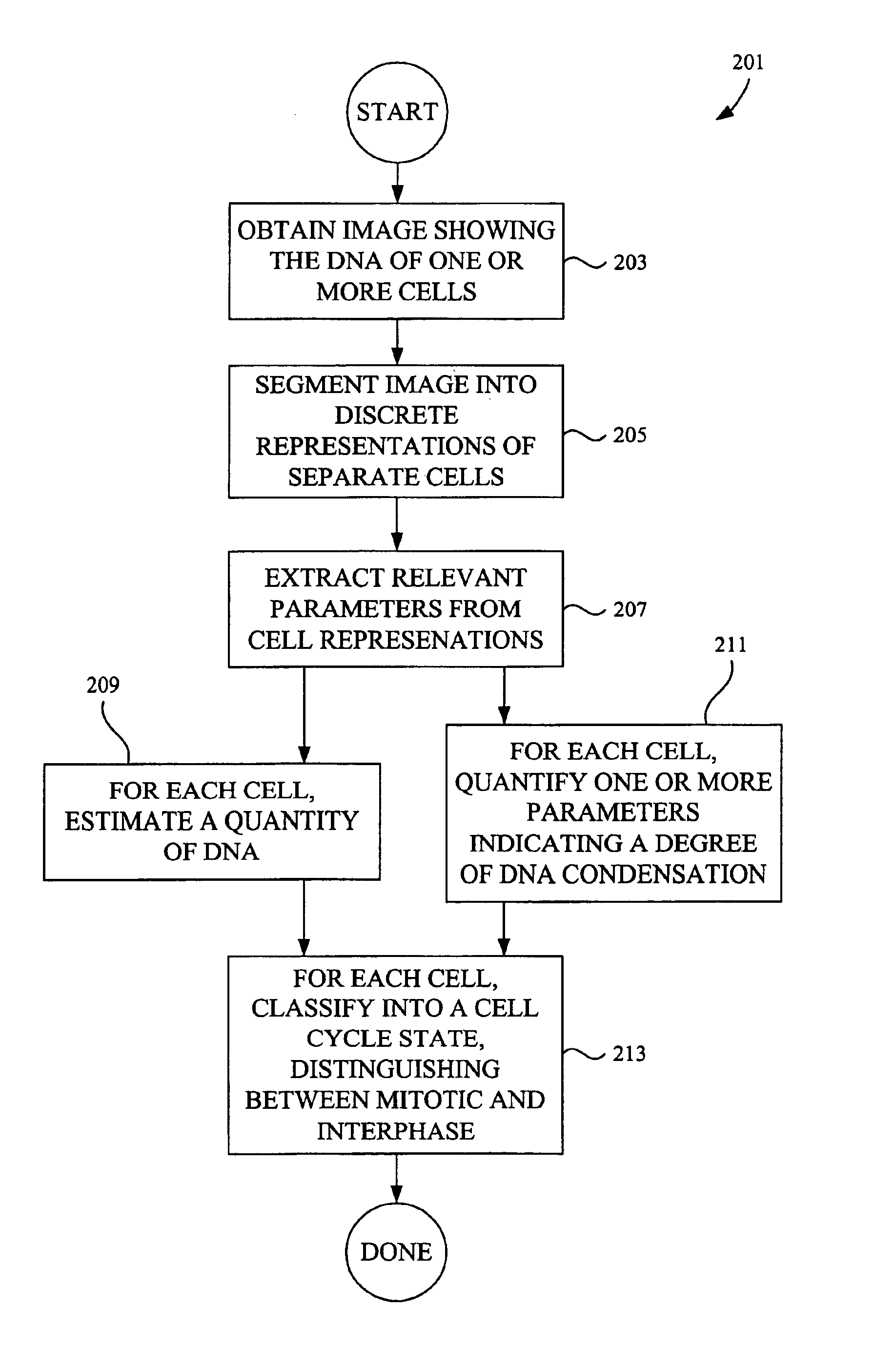
Classifying cells based on information contained in cell images
InactiveUS6876760B1Accurate classificationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisPhases of clinical research
Image analysis methods analyze images of cells and place the cells in particular cell cycle phases based upon certain features extracted from the images. The methods can also quantify the total amount of DNA in a cell based on specific features such as fluorescence intensity from fluorescent molecules that bind to DNA. Further, the methods can characterize a cell as mitotic or interphase based on chosen parameters such as the variance in intensity observed in a cell image and / or the size of a region containing DNA. In one example, image analysis methods can classify the cell into one of the following five phases: G1, S, G2, telophase, and an early stage mitotic phase comprised of prophase, metaphase, and anaphase.
Owner:CYTOKINETICS INC
Electrodynamic profiling of genomic response in the cell
InactiveUS20060127879A1Highly preventive effectMicrobiological testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCell EvaluationHydrogen
A method of cellular evaluation based on the electronic nature of cells is reveled though cellular reproductions use of a magnetic force. The dynamic process of nuclear response is shown to be electronic in nature relative to DNA mediating electrons hydrogen bonding in bases pairing of DNA though out the a cell cycle and finally during metaphase one see the magnetic component of interaction. The electrostatic understanding of magnetic force is not well defined in physics in the process of electrodynamic. Cells use electrodynamic interaction within the cell are being studied as the basis and using the cell to measure and define electrodynamic interaction with the system that is biological a call. Specifically DNA thought the electronic interaction interactions. It appears infrared spectrum holds promises to help in revel these mechanisms. The promise of understanding or merely evaluation of electrodynamic interaction holds great promise to science with the greatest medical implication to understand genomic responses in cells. Understanding how the DNA interacts within a cell dynamic transition are known to take place and these are regulated thought electrodynamic interaction.
Owner:FUCCIONE ANTHONY STEPHEN
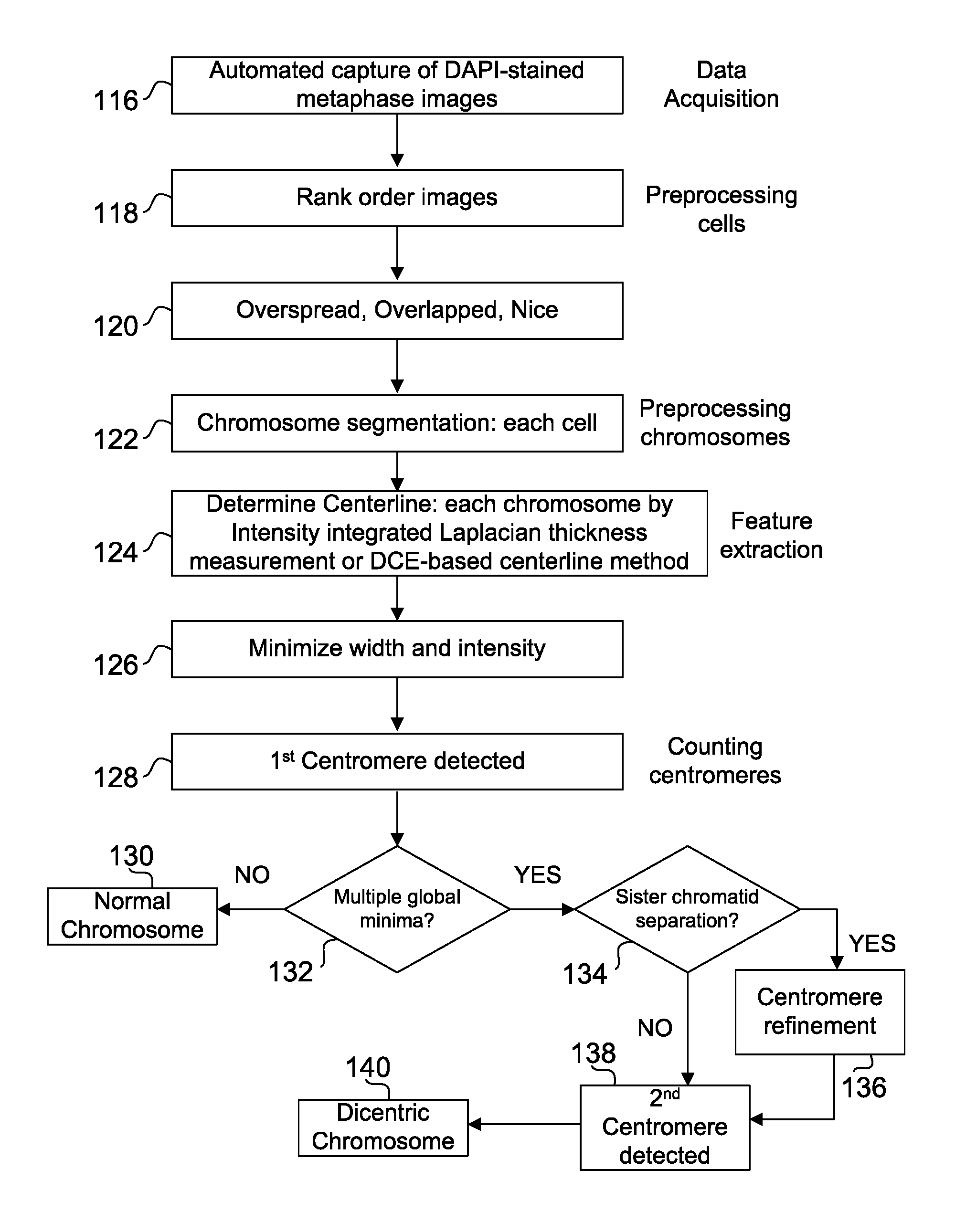
Centromere Detector and Method for Determining Radiation Exposure From Chromosome Abnormalities
ActiveUS20130216118A1Microbiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiation exposureDicentric chromosome
A method for determining radiation exposure from chromosome abnormalities present in a specimen by determining the location or locations of the centromere of each chromosome in a cell in an image of a metaphase cell by segmentation of an accurately drawn chromosome centerline followed by selection of a longitudinal cross-section with the minimum width or intensity or width and intensity; counting the number of centromeres in each chromosome in each cell; computing the frequency of dicentric chromosomes in a population of cells; and determining the radiation dose by comparing the computed frequency of dicentric chromosomes with a previously determined dose-response curve from a calibrated source.
Owner:CYTOGNOMIX
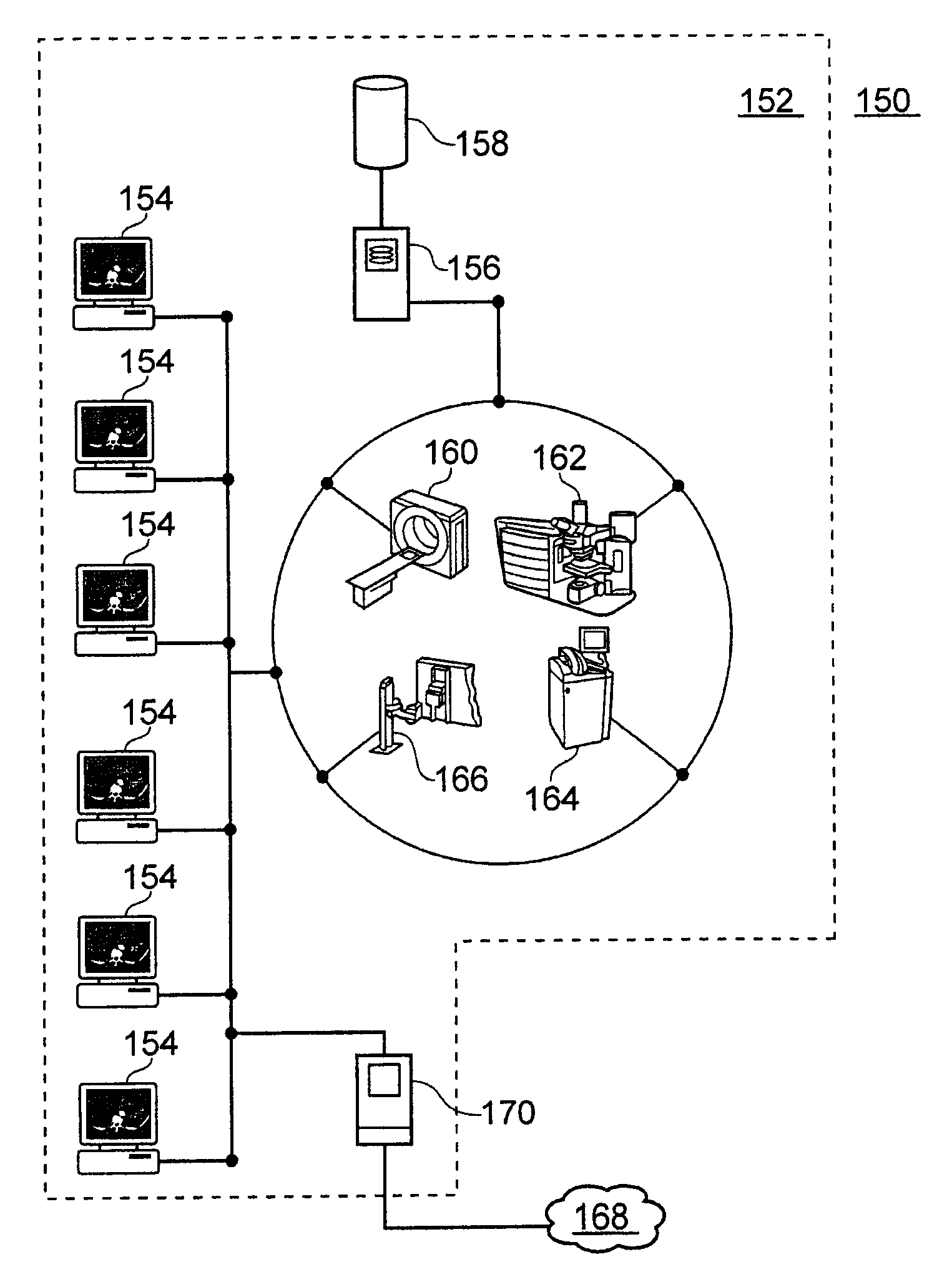
Automated Detection of Cell Colonies and Coverslip Detection Using Hough Transforms
The present invention provides methods and systems for automatic detection of the location of cell colonies on a specimen slide, in particular under the coverslip of a specimen slide. Slide scanning can be performed using an automated microscope with motorized axes. The location of the colonies can be determined by image analysis, which is followed by automatically finding metaphase cells and associating them with each colony. The invention also provides an automated, Hough-transform-based method for identifying the location of the slide coverslip and, if desired, analyzing only the image area contained within the coverslip.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Method for quickly culturing barley anther and used culture media
InactiveCN102577946AReduce dosageReduce workloadPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeHordeum vulgare
The invention discloses a barley anther culture medium, which comprises a pretreatment culture medium, an inducing culture medium and a differentiating / rooting culture medium. The invention further provides a method for rapidly culturing barley anther by using the barley anther culture medium. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) taking a wheat ear of which a microspore develops at a mononuclear metaphase from a field, taking anther out of the wheat ear, putting onto the pretreatment culturing medium, and culturing in a dark environment for 3-5 days; (2) transferring the pretreated anther onto the inducing culture medium, and culturing in a dark environment for 4-5 weeks; (2) transferring callus and a seedling obtained by inducing in the step (2) onto the differentiating / rooting culture medium, performing illumination culturing at the temperature of 22-25 DEG C and at the illumination intensity of 40-60 mumol / m<2> / s for 3-4 weeks, 12 hours every day, to obtain a rooting green seeding. Due to the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the culturing efficiency of the barley anther can be increased remarkably.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for identifying exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in plant distant hybrids
InactiveCN102876801AOvercome the problem of unsatisfactory detection effectImprovement of Chromosome Production TechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceFluorescence
The invention provides a method for identifying exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in plant distant hybrids. The method includes the steps of firstly, microscopically separating monosomes or chromosome segments of chromosomes to be tested of a plant to be tested; secondly, using the separated monosomes or chromosome segments in the first step to build a fluorescence probe of the monosomes or chromosome segments; thirdly, using the fluorescence probe built in the second step to perform fluorescence in situ hybridization to chromosomes in metaphase division of the hybrids; and fourthly, analyzing the fluorescence in situ hybridization result obtained in the third step to determine distribution of fluorescence signals of the chromosomes to be tested of the plant to be tested. Exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in wheat distant hybrids can be identified by the method, and the method is applicable to identification of exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in distant hybrids of other plants.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
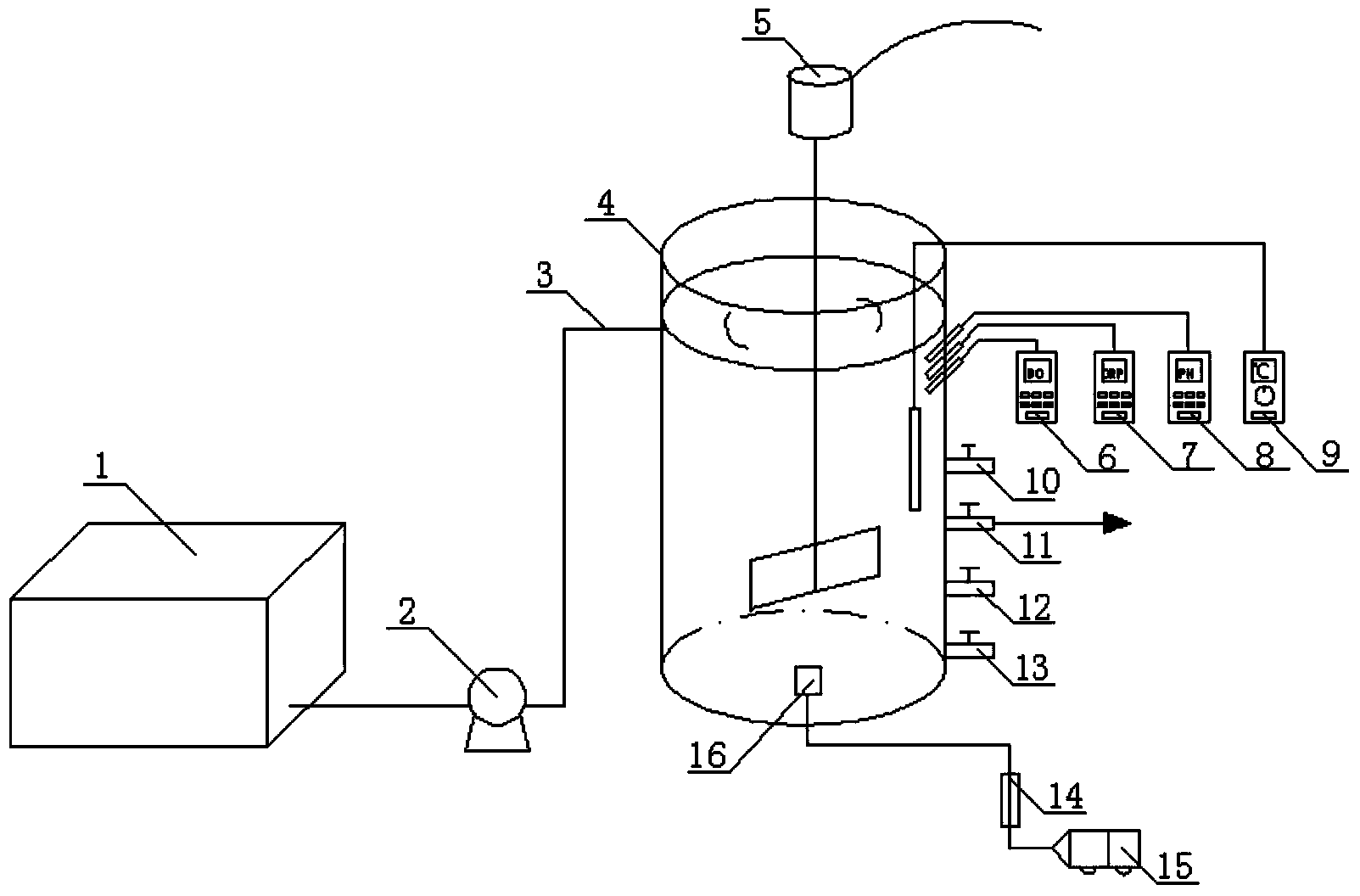
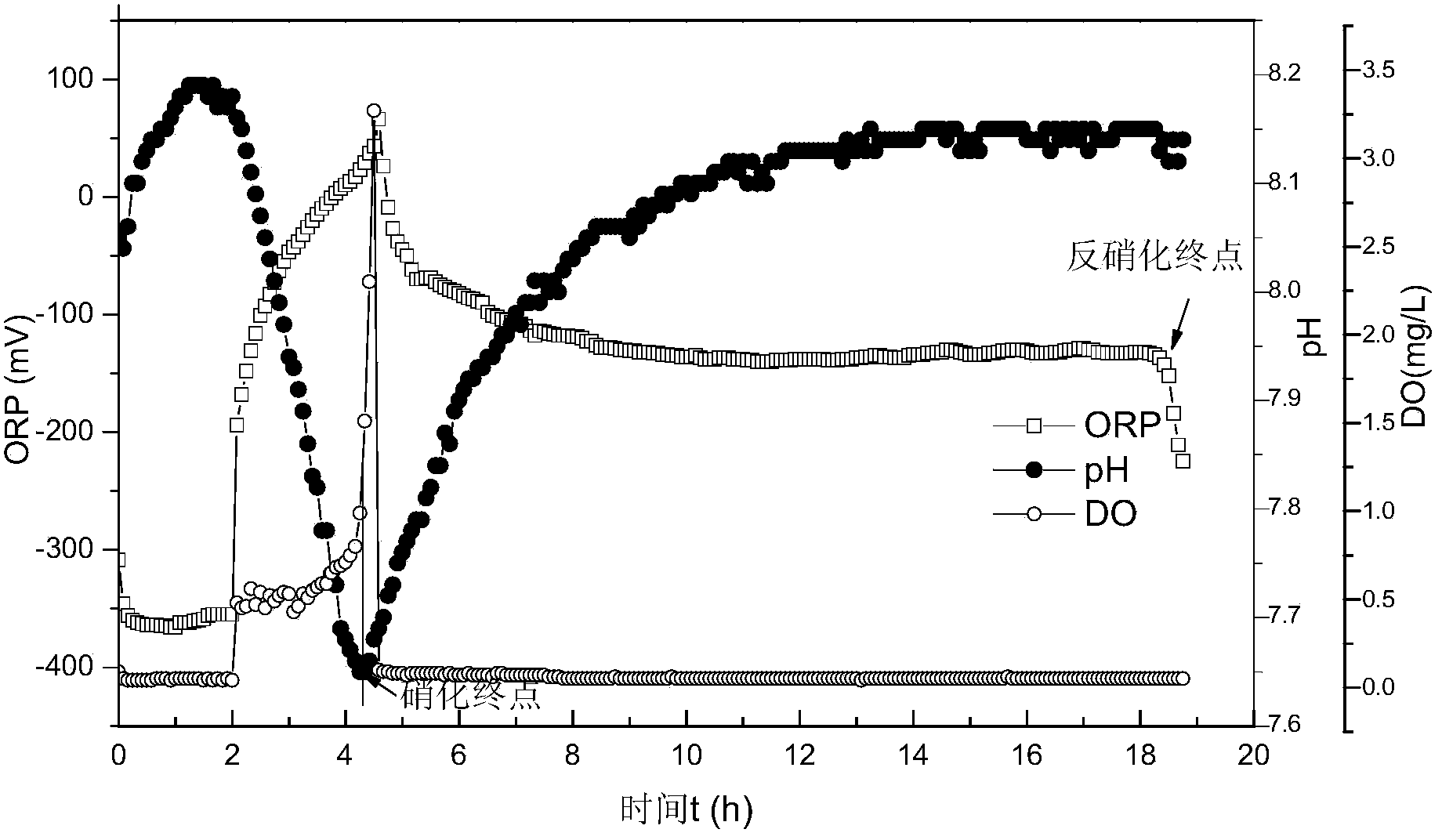
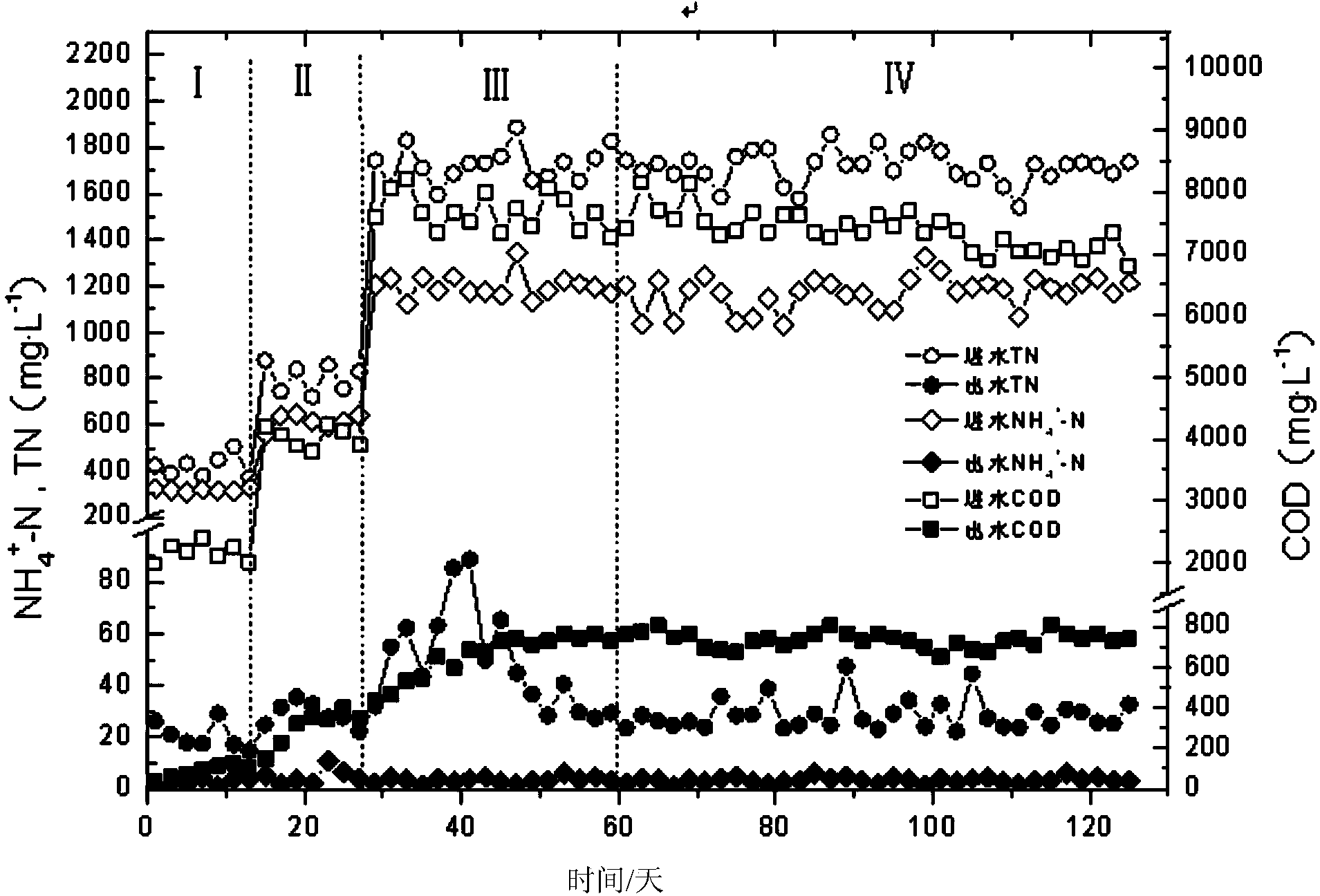
Method for deep denitrification of metaphase landfill leachate through single-stage SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber) post denitrification treatment
ActiveCN103755028AStart fastThe reaction device is simpleTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesVolatile fatty acidsEmission standard
The invention discloses a method for deep denitrification of metaphase landfill leachate through single-stage SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber) post denitrification treatment, which belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment by using biochemical process. Aiming at the characteristics that the landfill leachate is high in organism concentration, high in ammonia concentration, high in C / P ratio (grater than 200), the invention discloses a real-time control method with the combination of 'anaerobic / aerobiotic / anoxic' operation modes, and SBR post denitrification is achieved. Under long-term domestication, glycan bacteria (GAO) can be enriched, volatile organic acids (VFA (Volatile Fatty Acid)) in water are converted into poly-beta-hydroxy-alkanoic acid ester (PHA) through glycogen glycolysis at an anaerobic stage by using GAO, in an aerobiotic stage (the dissolved oxygen is less than 0.8mg / L), when partial nitrification is carried out, most part of PHA is converted into glycogen, and in the anoxic stage, the residual PHA and the glycogen are utilized to perform carbon source denitrification, so that the effluent meets the latest national emission standard. The method has the advantages of simple devices, rapid starting, freedom of external carbon source, good denitrification effect, simplicity in operation, low cost and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
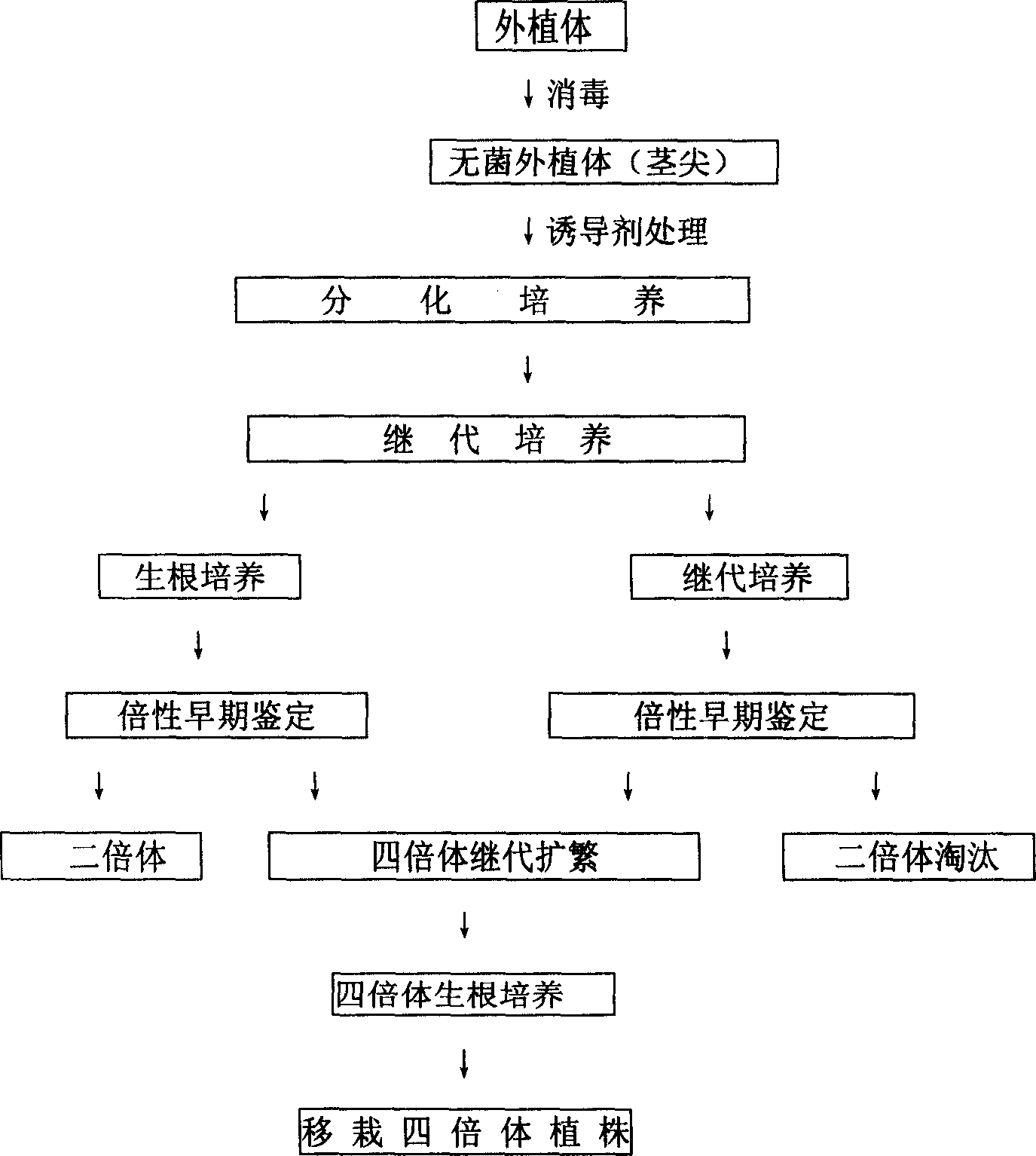
Excised mutagenesis tetraploid method of water melon and ploidy early stage certification technique
InactiveCN1631101AInduction frequency is highLow toxicityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureFluorescenceColchicine
The invention provides an excised mutagenesis tetraploid method of water melon and ploidy early stage certification technique, wherein dinitro toluene herbicide (DNH) is employed to substitute the conventional colchicines as inducer, whose function is to suppress the Mitosis in the metaphase of cell division through the mechanism of interfering spindle, so as to double the tissue cell chromosome. The method has the advantages of increased inducement success rate and substantially shortened time required for inducement.
Owner:刘文革 +1
Non-invasive determination of fetal inheritance of parental haplotypes at the genome-wide scale
ActiveUS8877442B2Non-invasively determiningReduce riskMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsSequence analysisSerum samples
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Szechuan pickled tuber vegetable fermentation composite microbial agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102406104AUniform qualityAchieve controllabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentAirlift
The invention discloses a preparation method for a Szechuan pickled tuber vegetable fermentation composite microbial agent. The microbial agent comprises microbe powder 1, microbe powder 2 and microbe powder 3; the microbe powder 1 is prepared by inoculating 10L of Bacillus coagulans CICC 10144 strain culture solution in a logarithmic metaphase into a 1,000L airlift fermentor for high-density culture; the microbe powder 2 is prepared by inoculating 10L of Leuconostoc mesenteroides CGMCC 1.20 strain culture solution in a logarithmic metaphase into a 1,000L fermentor for culture; the microbe powder 3 is prepared by inoculating 5L of Lactobacillus plantarum CICC 6067 culture solution, 5L of Lactobacillus brevis CICC 6042 culture solution and 5L of Pediococcus acidilactici CGMCC 1.4 culture solution in a logarithmic metaphase into a 1,000L fermentor for co-culture; and the three kinds of microbe powder are mixed in a ratio of 2:5:5 and the mixture is subjected to vacuum packaging to form the Szechuan pickled tuber vegetable fermentation composite microbial agent. The problem that a microbial agent for producing Szechuan pickled vegetables at present is lacked is solved, and productioncontrollability and standard operation for industrially producing the Szechuan pickled vegetables are realized.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV +1
Improved method for detecting and identifying transgenic wheat with high sensitivity and high efficiency
InactiveCN103160612AOvercome the problem of unsatisfactory detection effectImprovement of Chromosome Production TechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell divisionFluorescence
The invention discloses an improved method for detecting and identifying transgenic wheat with high sensitivity and high efficiency. The improved method comprises the steps of: (1) carrying out pretreatment and enzymolysis on tissue with vigorous cell division in a meristematic zone at a root tip of wheat through N2O gas to obtain a metaphase mitotic phase specimen with clear image and good dispersion of chromosomes; (2) marking a fluorescent probe of a target fragment to be detected (for example, a transgenic fragment carried by a transgenic carrier) by utilizing a nick translation method; (3) carrying out fluorescent in-situ hybridization on the metaphase mitotic phase chromosomes of the transgenic wheat obtained in the step (1) by utilizing the fluorescent probe of the target fragment of the transgenic carrier constructed in the step (2); and (4) analyzing fluorescent in-situ hybridization results obtained in the step (3), and comparing the fluorescent in-situ hybridization results with a contrast material to determine the distribution of fluorescent signals in the transgenic wheat to be detected. The improved method provided by the inventions can be applied to chromosomal localization of exogenous transgenic wheat with the sensitivity reaching 2-3kb, and also can be applied in the identification of transgenic signals of other crops.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
One-step seedling culture method of wheat anther
InactiveCN101554136AReduced induction of adventitious budsEasy to operatePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsLate phasePollen
The invention discloses a one-step seedling culture method of wheat anther, which comprises the following steps of: selecting young spike of wheat with wheat pollen cells developing to mononuclear metaphase to late phase, and pretreating for 2 days at low temperature (2-4 DEG C); after conventional disinfection, stripping anther tissue from the pretreated young spike of wheat, and inoculating the anther tissue on one-step seedling culture medium for shade culture; and when growing visible callus, placing the cultured anther tissue under 1500Lx lighting conditions and culturing for a week, and then increasing the light intensity to 3000Lx-4000Lx and continuously culturing for two weeks to produce pollen plants with vigorous roots and seedlings. The method omits two necessary technical operation links of induction of adventitious buds and induction of adventitious roots by the pollen callus, the culture cost is reduced by nearly 50%, the culture days are shortened by 40-50 days, the average induction rate of green seedlings is equivalent to that of multistep seedling, the albino seedling rate is generally reduced by 10 percent, and test-tube seedlings are vigorous and has developed root system, connecting parts of rootstalks have little or no callus tissue residues, and the transplantation survival rate of the test-tube seedlings is high.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
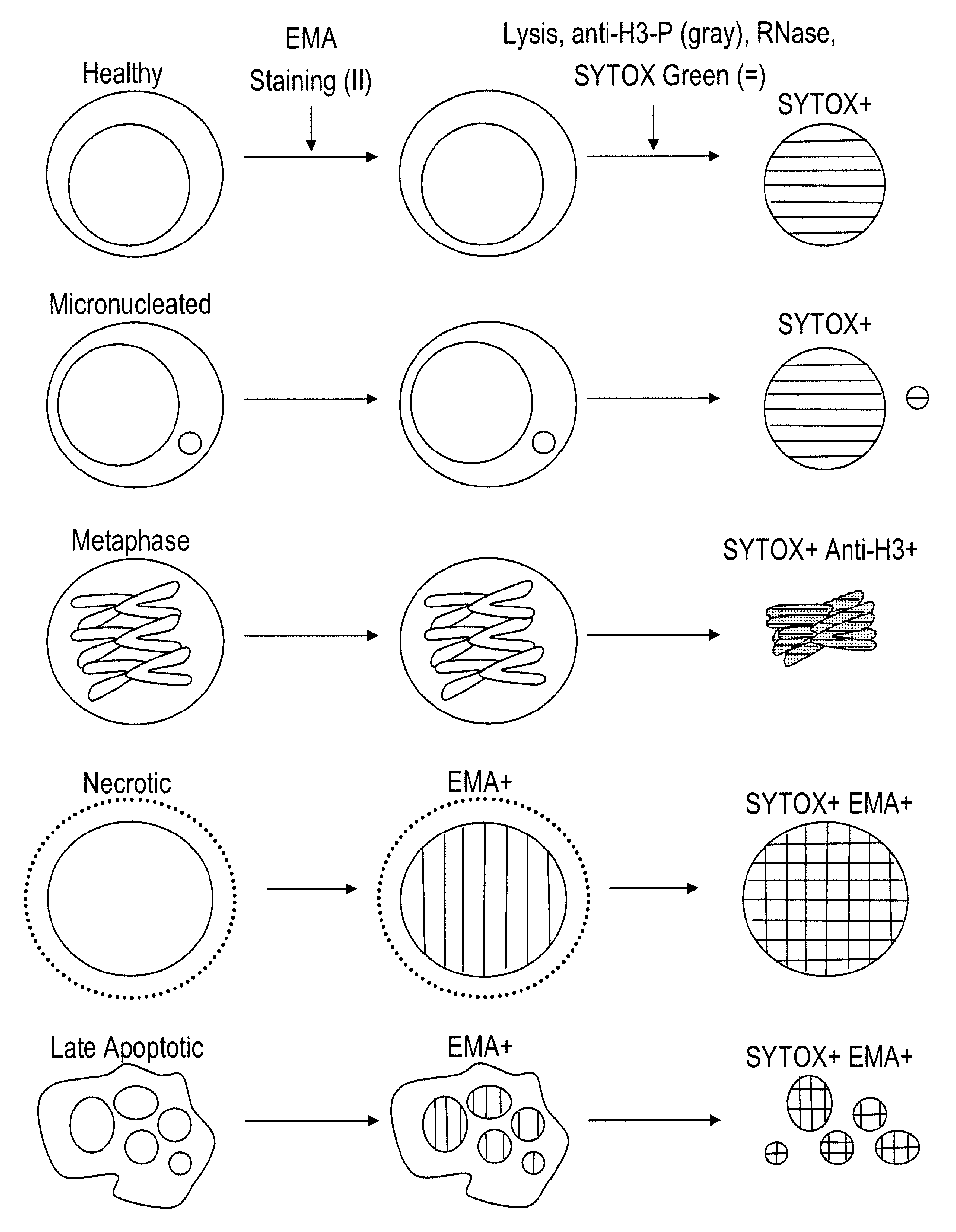
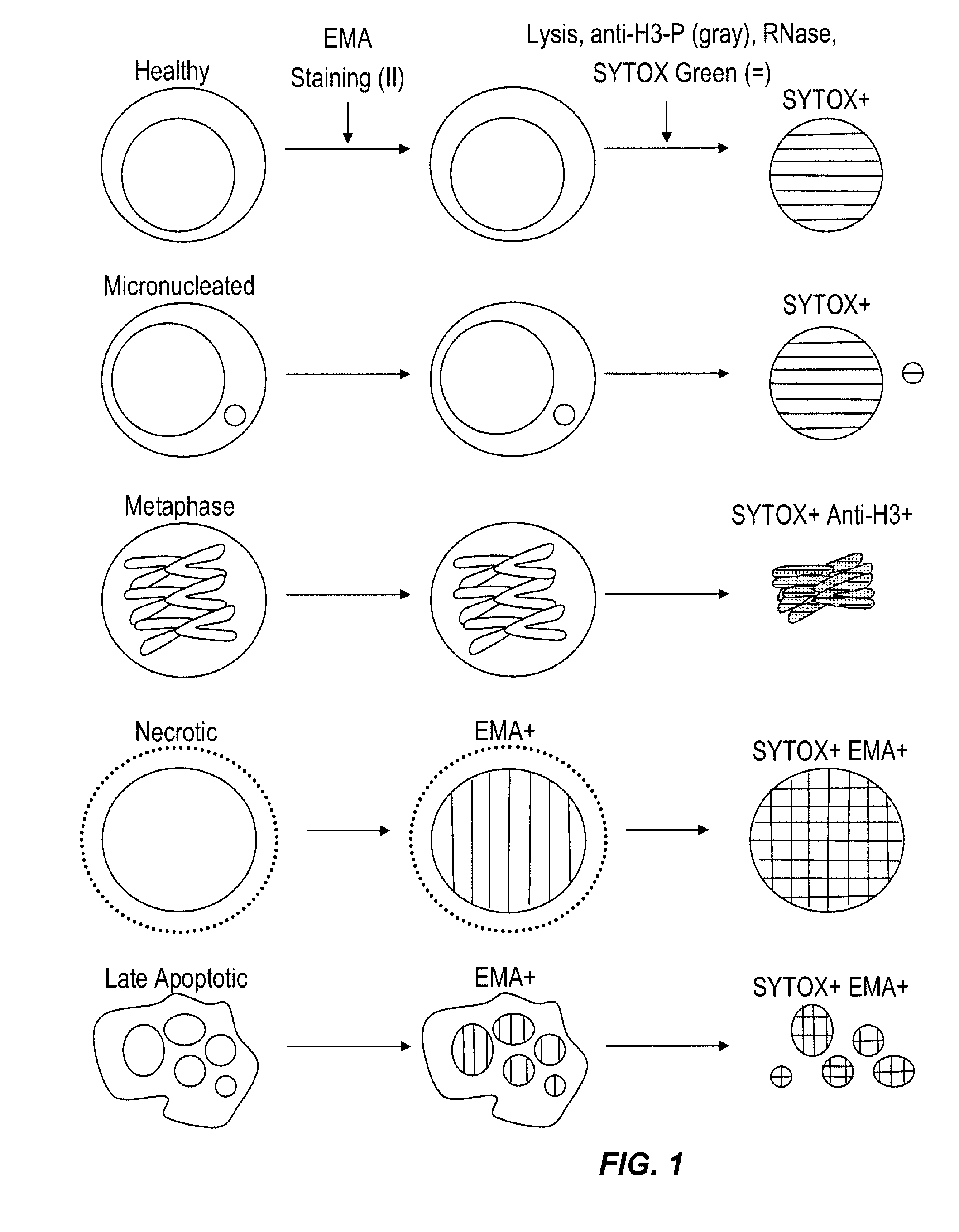
Method for enumerating eukaryotic cell micronuclei with an emphasis on simultaneously acquiring cytotoxicity and mode of action information
InactiveUS20140017673A1Fast and reliable and accurateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMode of actionMetaphase chromosome
The present invention relates a method for the enumeration of eukaryotic cell micronuclei, while simultaneously acquiring cytotoxicity and mode of action information. The method utilizes differential labeling of chromatin from dead and dying cells to distinguish the chromatin from micronuclei, nuclei, and metaphase chromosomes, and differential labeling of metaphase events to provide additional information regarding cytotoxicity and genotoxic modes of action. Counting of micronuclei events relative to the number of nuclei and quantifying perturbations to the proportion of metaphase events can be used to assess the DNA-damaging potential of a chemical agent, the DNA-damaging potential of a physical agent, the effects of an agent which can modify endogenously-induced DNA damage, the effects of an agent which can modify exogenously-induced DNA damage, and genotoxic mode of action.
Owner:LITRON LAB
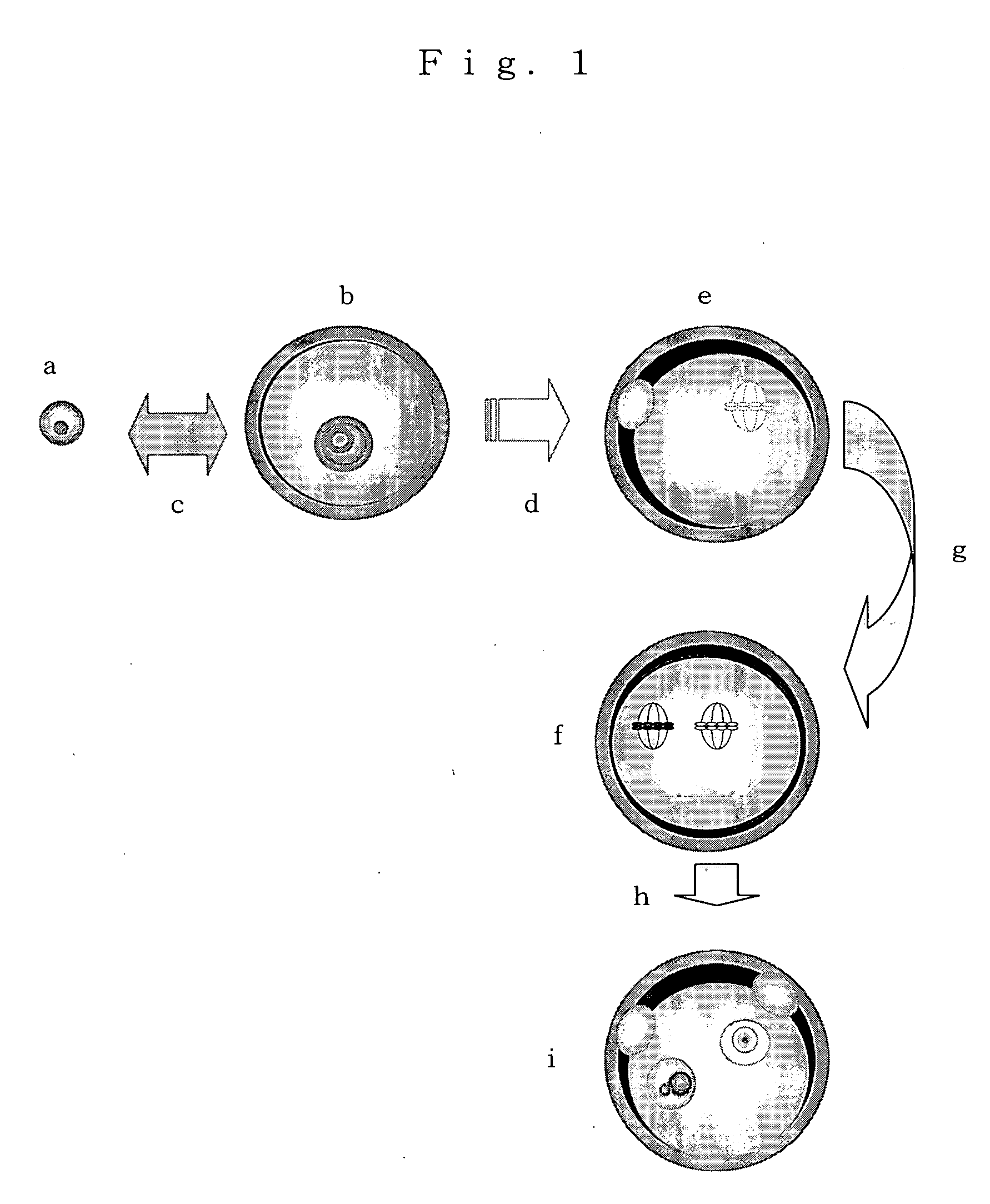
Method of constructing nuclear-transplanted egg parthenogenetic embryo and parthenogenetic mammal
The present invention is to provide a method of constructing a nucleus-implanted egg, a parthenogenetic embryo and a parthenogenetic mammal each having 2 haploid genome sets originating in mammarian ova, and provides methods of constructing a nucleus-implanted egg having a haploid genome set derived from ng ovum and a haploid genome set from fg ovum, a parthenogenetic embryo and a parthenogenetic mammal, which includes the steps of (1) introducing a primitive ovarian follicle egg (ng ovum) into a nucleus-deleted egg in a germinal vesicle stage (GV stage egg) and then developing them to MII phase (second meiosis metaphase) by in vitro maturing and culturing to prepare a first nucleus-implanted egg, and (2) extracting MII phase chromosome from said first nucleus-implanted egg and introducing it into other MII phase egg (fg ovum) to prepare a second nucleus-implanted egg, wherein ovum from which an imprinted gene that undergoes gene modification posteriori during the generation of sperm is deleted is used as the ng ovum or fg ovum.
Owner:TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE
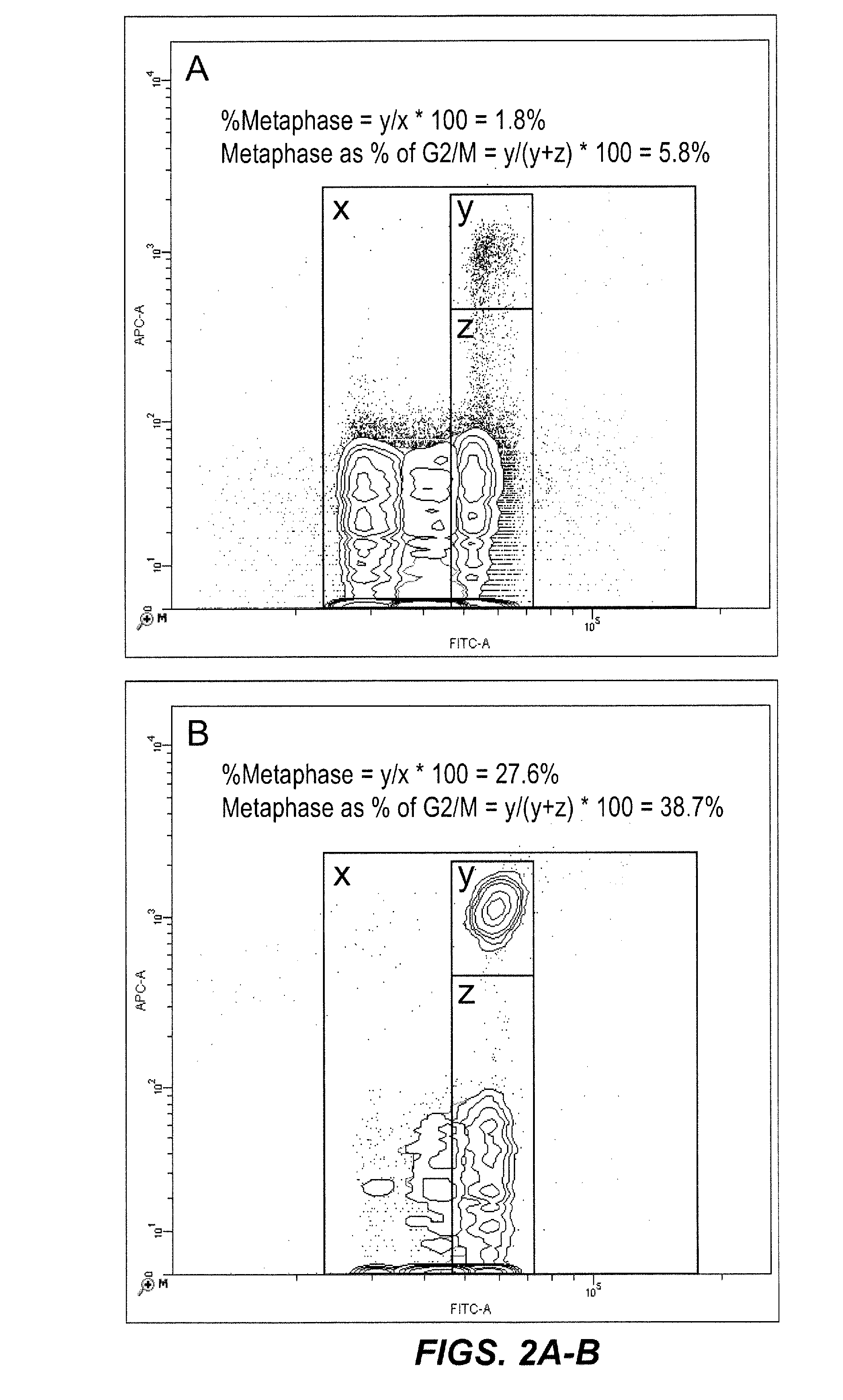
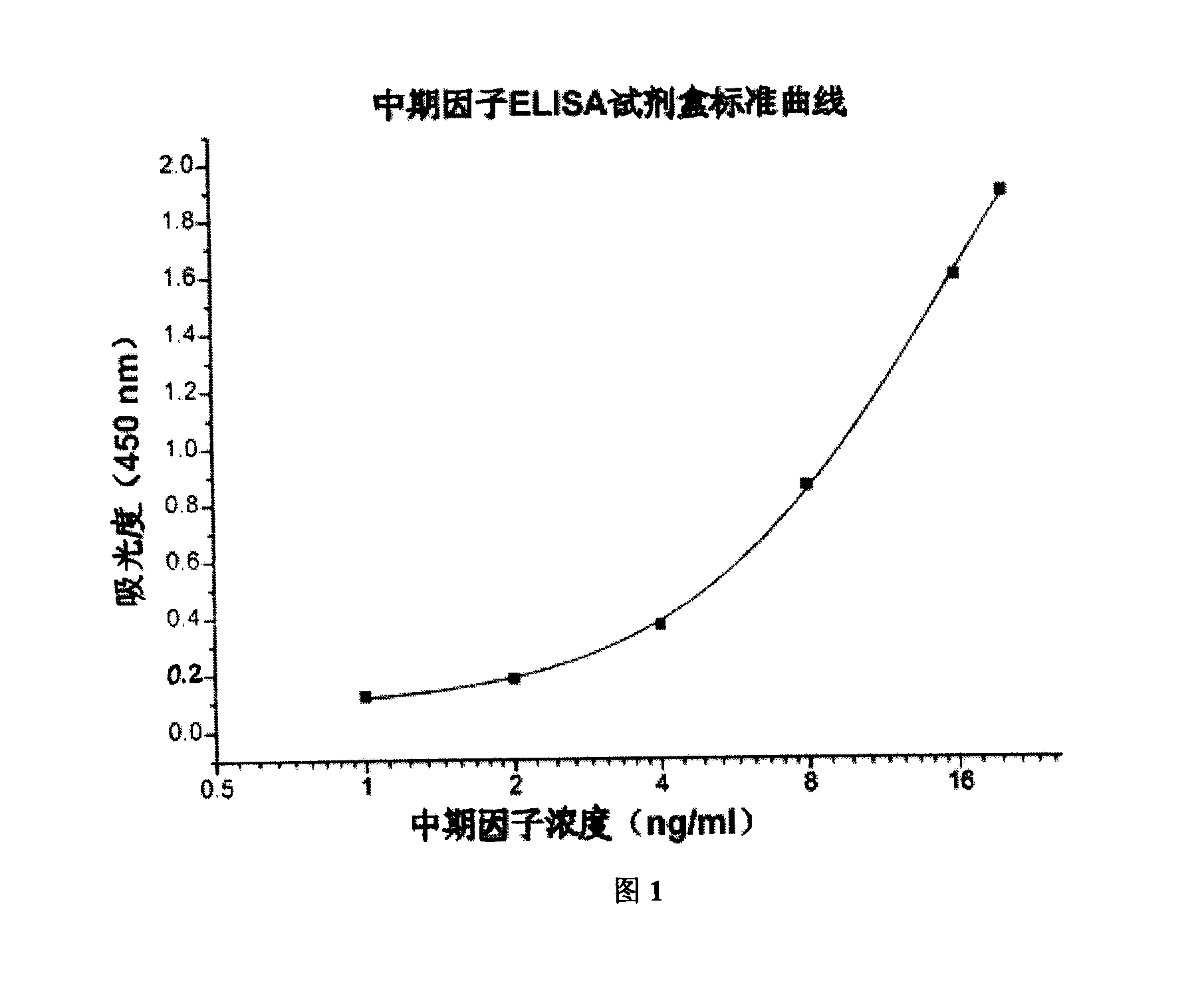
ELISA reagent box for detecting metaphase factor concentration and method of use thereof
The invention provides an ELISA kit to detect the concentration of Midkine and a method of application thereof. The kit comprises monoclonal antibodies of mouse anti-human MK coated on an enzyme marker; polyclonal antibodies of rabbit anti-human; polyclonal antibodies of goatanti rabbit IgG marked with horse radish peroxidase (HRP); His-MK expressed with procaryon in colibacillus E.coli and affinity purified with N ends having six His labels. The application method comprises coating a microlon ELISA plate with commercial monoclonal antibodies of Midkine of mouse anti-human; adding specimens to be detected, and multiple resistance of Midkine of rabbit anti-human and rabbit anti-human IgG marked with HRP for joint incubation after the plate is sealed; adding substrate solution of TMB for reaction and visualization; finally, terminating the reaction with vitriol, and detecting the absorbance at the position of 450nm. A standard curve is drawn with the concentration of standard samples and corresponding absorbance. In this way, the concentration of Midkine in the specimens to be detected can be got through the absorbance and the corresponding standard curve.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for sheeting peanut root tip cell chromosome in mitosis metaphase
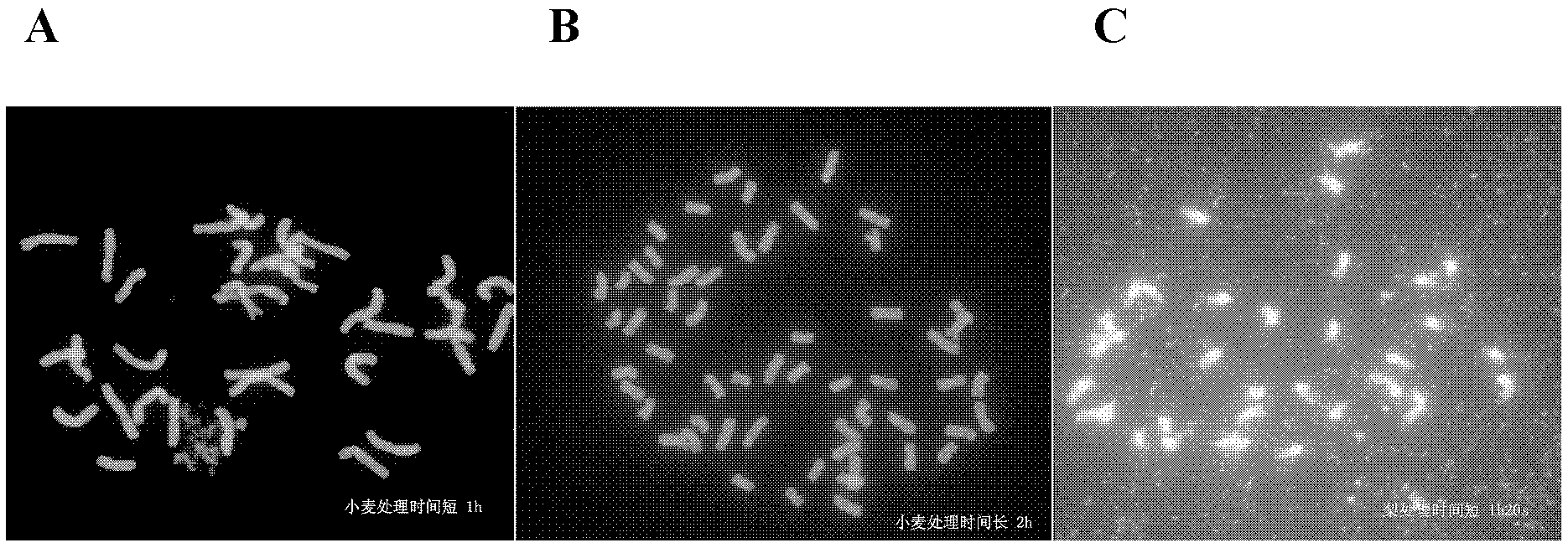
InactiveCN102589943AChromosomal dispersionProduction is not idealPreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyCell wall
The invention relates to a method for sheeting peanut root tip cell chromosome in the mitosis metaphase, which comprises the following steps that: a peanut root tip is selected, and paradichlorobenzene is utilized for soaking pretreatment; the root tip is put into carnoy stationary liquid for room temperature treatment; acetic acid is used for soaking, the root tip of a meristematic zone is cut and put on a glass slide, the center of a cover glass is tapped to disperse the cells, a cell wall is heated by fire for dissociating and softening, and a filter paper is used for removing the excess acetic acid; the cell which is in the mitosis metaphase and has smoothly dispersed chromosome is sheeted and refrigerated, the cover glass is removed, and the glass slide is dehydrated; and stain zoning or fluorescence in-situ hybridization are carried out. The obtained sheet has leveled cells and dispersed chromosome, and more cells are in the metaphase; and the acetic acid medium is used for direct compression, the reagent has small influence to the chromosome, so the method is easy to operate and control, has simple steps and high sheeting efficiency. The method is suitable to not only peanuts but also sesame, paddy, corns, soybeans, green beans or tomatoes and other various plants, and has good operability.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
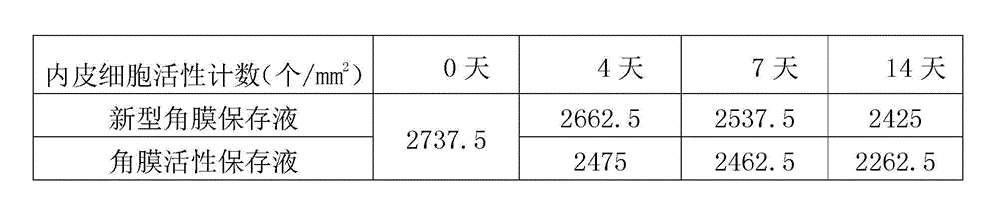
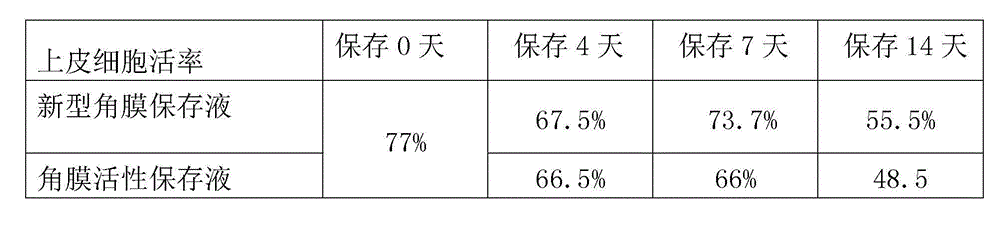
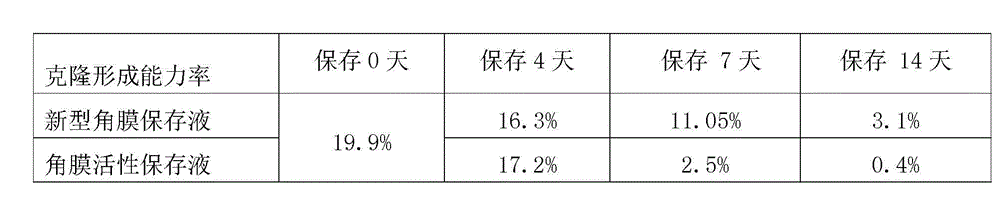
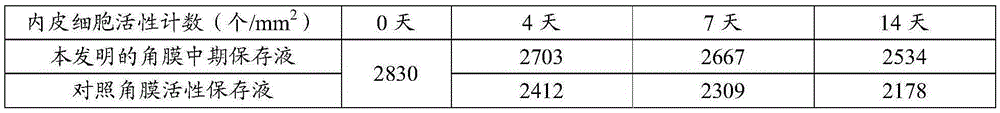
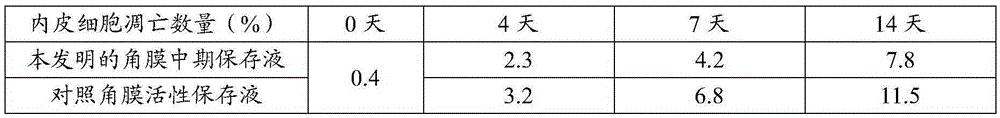
Cornea metaphase preservation solution, and preparing and using methods thereof
The invention provides a cornea metaphase preservation solution, and preparing and using methods thereof. The cornea metaphase preservation solution is a cell culture minimum essential medium (MDM) with chondroitin sulfate, low molecular dextran, L-glutamine, dexamethasone, tobramycin, 2-hydroxyethyl and Y-27632 added. The preservation solution not only can keep activity and normal morphology of cornea endothelial cells, but also can enhance viability of corneal limbus epithelial cells and improve clone ability of corneal limbus stem cells. And especially, a medium to long term preservation effect is obvious, phenomena of deformation, conjugation and the like of endothelial cells of a control group cornea do not appear in long term preservation, endothelial morphology of the control group cornea is consistent with endothelial morphology of a cornea preserved for 4 days, and the endothelial cells of the control group cornea are still regular and few in cell conjugation phenomena. The preservation solution can effectively prevent cell apoptosis phenomena during the process of preserving isolated cornea materials, increases activity and clone forming ability of the corneal limbus stem cells, and enables the cornea to maintain a transparent feature in a long preservation time.
Owner:SHANDONG EYE INST
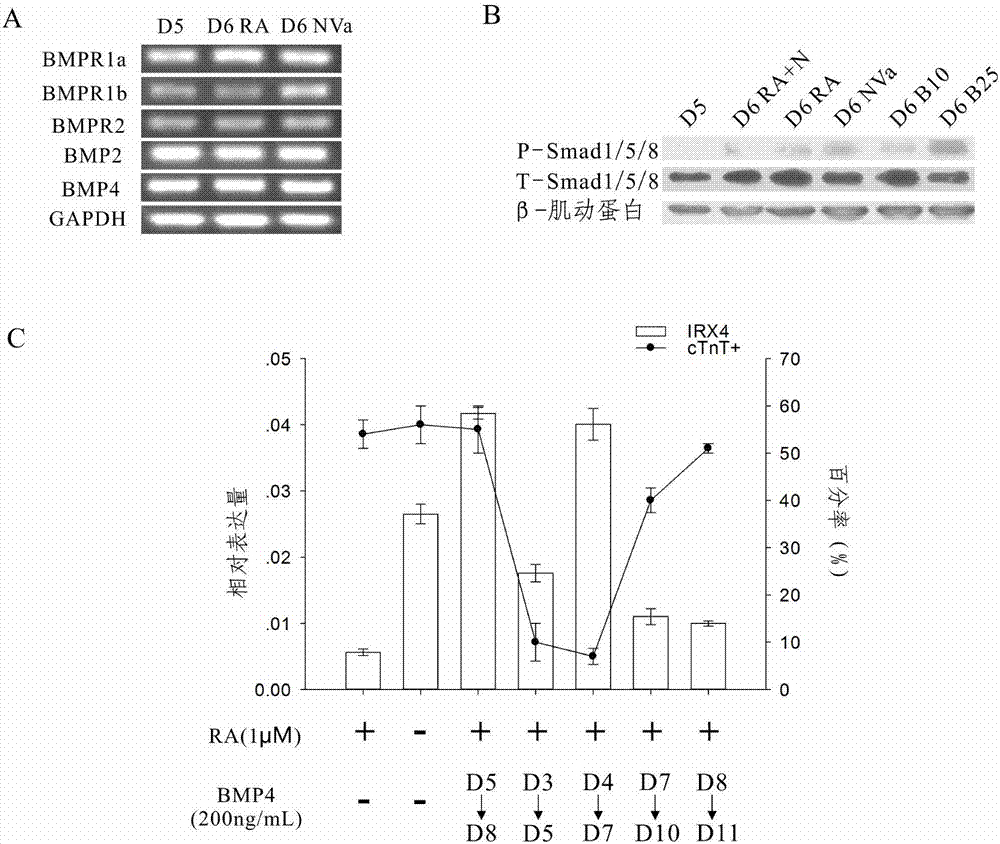
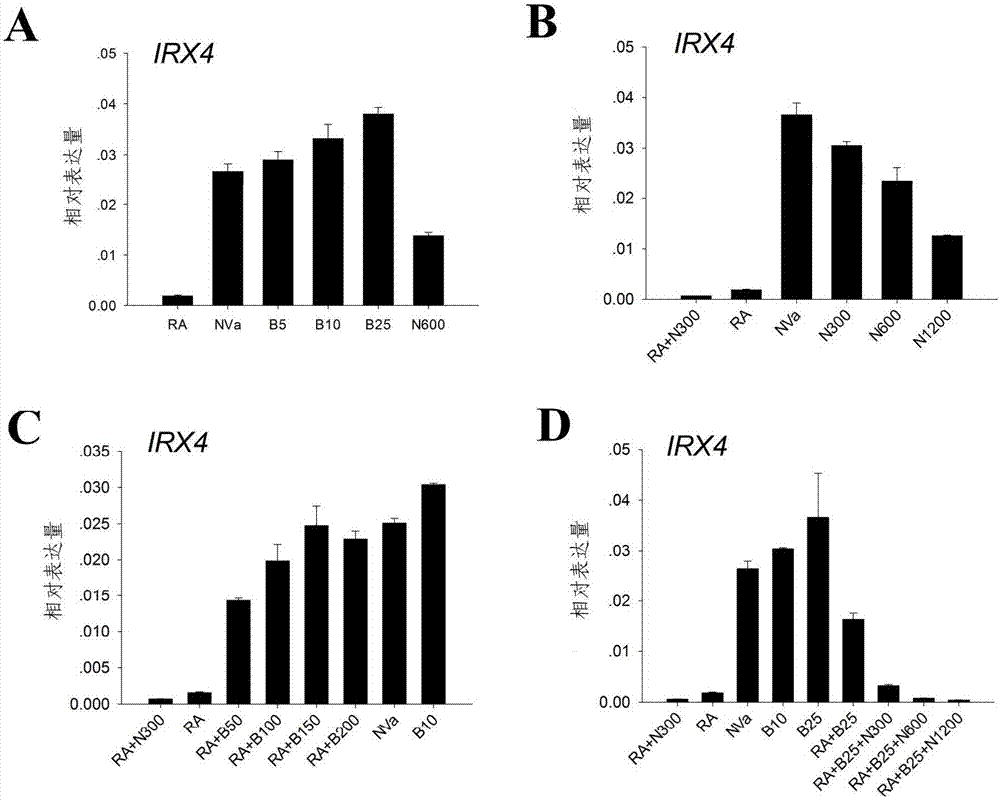
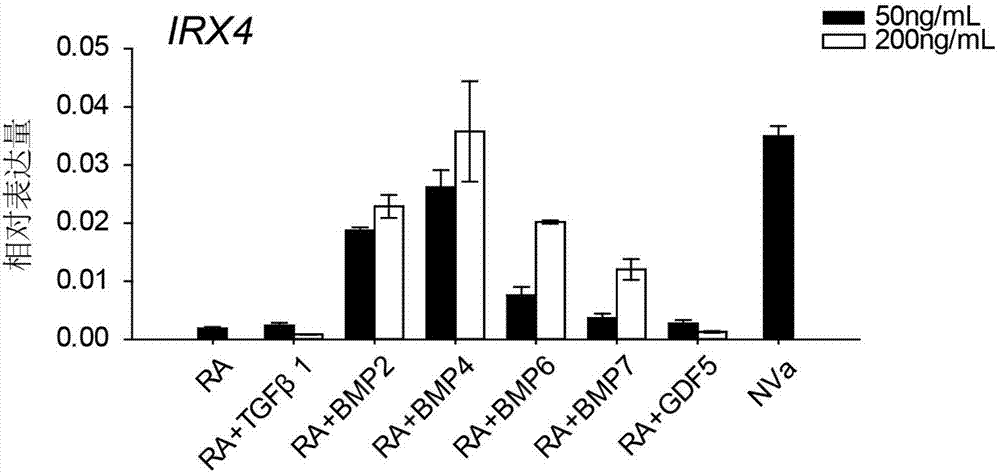
Method for differentiating as ventricular muscle cells by in-vitro induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveCN107460164AHigh purityDrug screeningSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCells transplantationHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
The invention provides a method for differentiating as ventricular muscle cells by in-vitro induced pluripotent stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: through maintaining, amplifying, and culturing pluripotent stem cells in vitro, in the metaphase of pluripotent stem cell cardiac muscle differentiation, namely the differentiation stage from mesoblastema or cardiac muscle precursor cells to the cardiac muscle cells, adding a substance for directly or indirectly activating an Smad1 / 5 / 8 signal channel to a culture medium, and enabling the stem cells to be directionally differentiated as the ventricular muscle cells. The ventricular muscle cells with the biology activity and function can be successfully obtained by using the method. A regulation mechanism in the differentiation process from the cardiac muscle precursor cells to the ventricular muscle cells is presented, and the human ventricular muscle cells obtained by the differentiation can be extensively applied for the myocardial infarction therapy by the cell transplantation and the cardiac toxicology analysis and the development of cardiac related drugs.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Down's syndrome screening method based on machine learning at progestational stage and pregnant metaphase
ActiveCN108847285AEffective predictionSave human resourcesHealth-index calculationComputing modelsMajority classScreening method
The invention relates to a Down's syndrome screening method based on machine learning at the progestational stage and the pregnant metaphase. The method comprises steps that ns fields of pregnant women's Down's screening result data at the pregnant metaphase are selected as training characteristics; Ns samples are added to a data set A; the samples of the data set A are preprocessed to make the number of samples in a minority class set be balanced with the number of samples in a majority class set to obtain a synthetic data set; samples in the synthetic data set are processed to obtain a prediction model for determining whether a fetus has the Down's syndrome, and the prediction model is utilized to predict a tested sample to obtain the prediction result. The method is advantaged in that the process of artificially dividing the indicator threshold is avoided, human resources are saved, and relatively high accuracy and relatively low false positive rate can be achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Automated detection of cell colonies and coverslip detection using hough transforms
The present invention provides methods and systems for automatic detection of the location of cell colonies on a specimen slide, in particular under the coverslip of a specimen slide. Slide scanning can be performed using an automated microscope with motorized axes. The location of the colonies can be determined by image analysis, which is followed by automatically finding metaphase cells and associating them with each colony. The invention also provides an automated, Hough-transform-based method for identifying the location of the slide coverslip and, if desired, analyzing only the image area contained within the coverslip.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Down's syndrome risk assessment method for prenatal screening in pregnant metaphase
InactiveCN105069277AEligible for prenatal screeningImprove screening effectSpecial data processing applicationsDoubling testObstetrics
The present invention discloses a Down's syndrome risk assessment method for prenatal screening in pregnant metaphase, which includes the following steps: 1) collecting serological index testing results of pregnant women who meet the requirement of age, gestation age and weight; 2) determining gestation ages; 3) determining a median of a serological index of normal pregnant women of each of pregnancy days to obtain a regression formula of the median of the serological index of the normal pregnant women of each of pregnancy days relative to pregnancy days; 4) determining a multiple of the median of the tested pregnant women; 5) adjusting the multiple of the median of the tested pregnant women by the regression formula; 6) establishing a coefficient of a risk assessment formula of Down's syndrome by Logistic regression; 7) establishing the risk assessment formula of a triple test scheme and a double test scheme of Down's syndrome. The method based on pregnancy days and applied to prenatal screening aims at Chinese pregnant women, and has high positive rate and low false positive.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for identifying carnation chromosome number by bud
InactiveCN101613755AAddressing the Disadvantages of Poor DispersionSolve hard-to-count puzzlesMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBudMaterial resources
The invention provides a method for identifying carnation chromosome number by bud, comprising: obtaining bud anther, ovary wall and corolla tissue, pre-treating ice water mixture, fixing by stationary liquid, dyeing, dissociating with hydrochloric acid, tabletting and microscopic examining. Compared with the traditional method that a root tip tissue is used for chromosome tabletting, the invention solves the disadvantages of few visual filed cells, difficult microscopic examination and poor chromosome dispersion during root tip chromosome tabletting, and overcomes the problems of long rootage period for carnation cutting seedling and time and labor wasting for cutting; compared with stem tip chromosome tabletting, the invention overcomes the interference problem of non-meristematic cell or reserve substance or secretion, chromosome tabletting can be realized only by using buds, which does not damage plant growing state and has convenient material resource; in addition, a plurality of metaphase cells exist, so that the difficulties of small carnation chromosome, huge quantity and hard counting of the chromosome can be solved. Thus, when plants bloom, the effective method is that the bud is used for chromosome tabletting.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cornea metaphase preservation liquid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105284788AImprove survivabilityLess fusionDead animal preservationCorneal endothelial cellTobramycin
The invention discloses a cornea metaphase preservation liquid and a preparation method thereof. The cornea metaphase preservation liquid is an MEM cell culture medium, which comprises the following components: chondroitin sulfate (20-26 g / L), low molecular dextran (8-12 g / L), L-glutamine (0.37-0.38 mg / L), fetal calf serum (2-5.5%), tobramycin (0.08-0.12 g / L), Hepes (9-10 g / L), and rapamycin (0.9-1.1 nM / L). The provided cornea metaphase preservation liquid can protect corneal endothelial cells, can avoid the phenomenon of necrosis and fusion of endothelial cells due to long time preservation, and prolongs the cornea preservation time more effectively.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine for treating metaphase and advanced liver cancer
InactiveCN101129970ACompatibility is simpleLow costAnthropod material medical ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseLate phase
The invention provides a Chinese medicinal capsule for treating late phase liver cancer, wherein the recipe includes Bupleurum root, zedoary, pinellia tuber, dried orange peel, amomum fruit each 12g, Hypericum japonicum Thunb. , raw astragalus root, oldenlandia, dandehon herb each 30g, pilose asiabell root, poria cocos wolf each 20g, white atractylodes rhizome, fructus akebiae each 15g, centipede 2 pieces, haw, medicated leaven, malt each 10g, licorice root 6g, artemisia capillaris thumb, red phaseolus bean each 30g, rhubarb horsetails 6g, poria peel, polyporus umbellatus, oriental water plantain rhizome, waxgourd peel each 30g, notoginseng powder 3g, bletilla tuber 12g, garden burnet root 15g. The Chinese medicament has simplified recipe, easy preparing process and low price.
Owner:尹克山
Centromere detector and method for determining radiation exposure from chromosome abnormalities
ActiveUS8605981B2Microbiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiation exposureDicentric chromosome
A method for determining radiation exposure from chromosome abnormalities present in a specimen by determining the location or locations of the centromere of each chromosome in a cell in an image of a metaphase cell by segmentation of an accurately drawn chromosome centerline followed by selection of a longitudinal cross-section with the minimum width or intensity or width and intensity; counting the number of centromeres in each chromosome in each cell; computing the frequency of dicentric chromosomes in a population of cells; and determining the radiation dose by comparing the computed frequency of dicentric chromosomes with a previously determined dose-response curve from a calibrated source.
Owner:CYTOGNOMIX
Effective nuclear reprogramming in mammals using CDK2 inhibitors
InactiveUS6906238B2Convenient timeOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureMammalGenetic Materials
The present invention provides methods of producing a cloned non-human mammalian nuclear transfer (NT) embryo and methods for producing a cloned non-human mammal. Embodiments of the methods include introducing donor genetic material into a metaphase I oocyte; introducing donor genetic material into a non-enucleated oocyte; introducing donor genetic material obtained from a donor cell that is at metaphase into an oocyte; introducing donor genetic material into an oocyte, and naturally activating the oocyte or the NT embryo; and introducing donor genetic material obtained from a donor cell that is at late G1 phase into an oocyte.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com