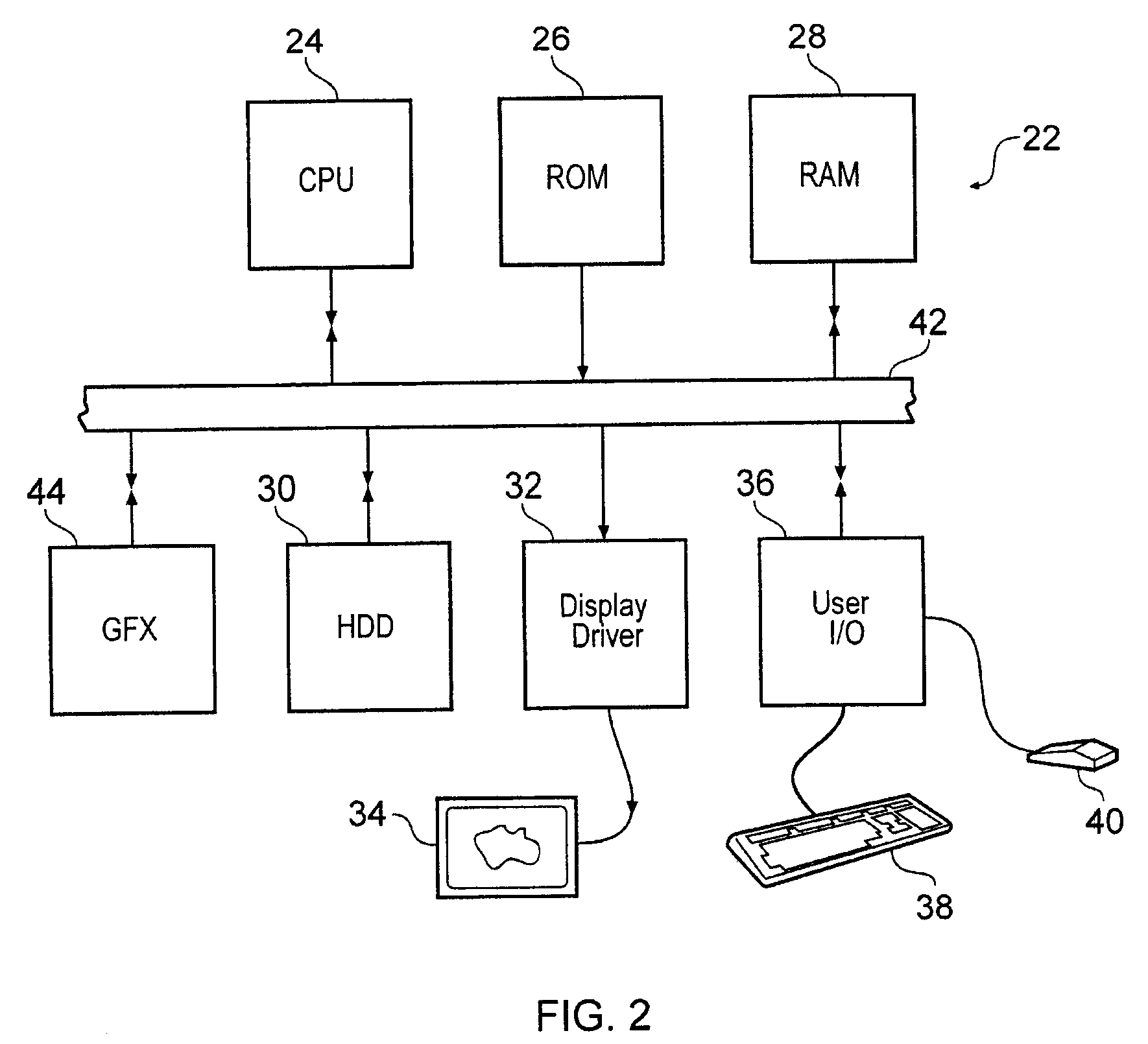
Patents
Literature
66 results about "Automated microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
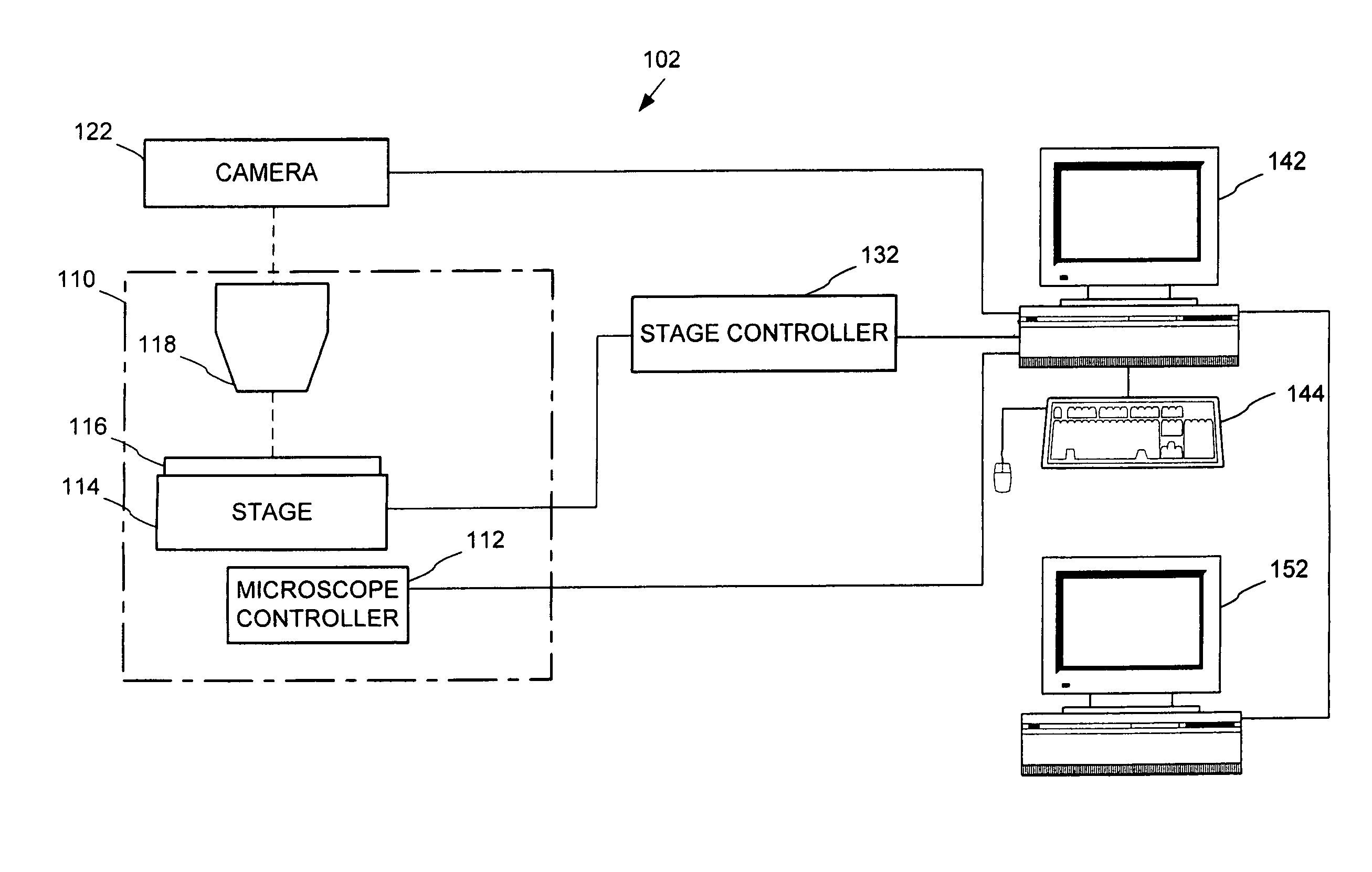
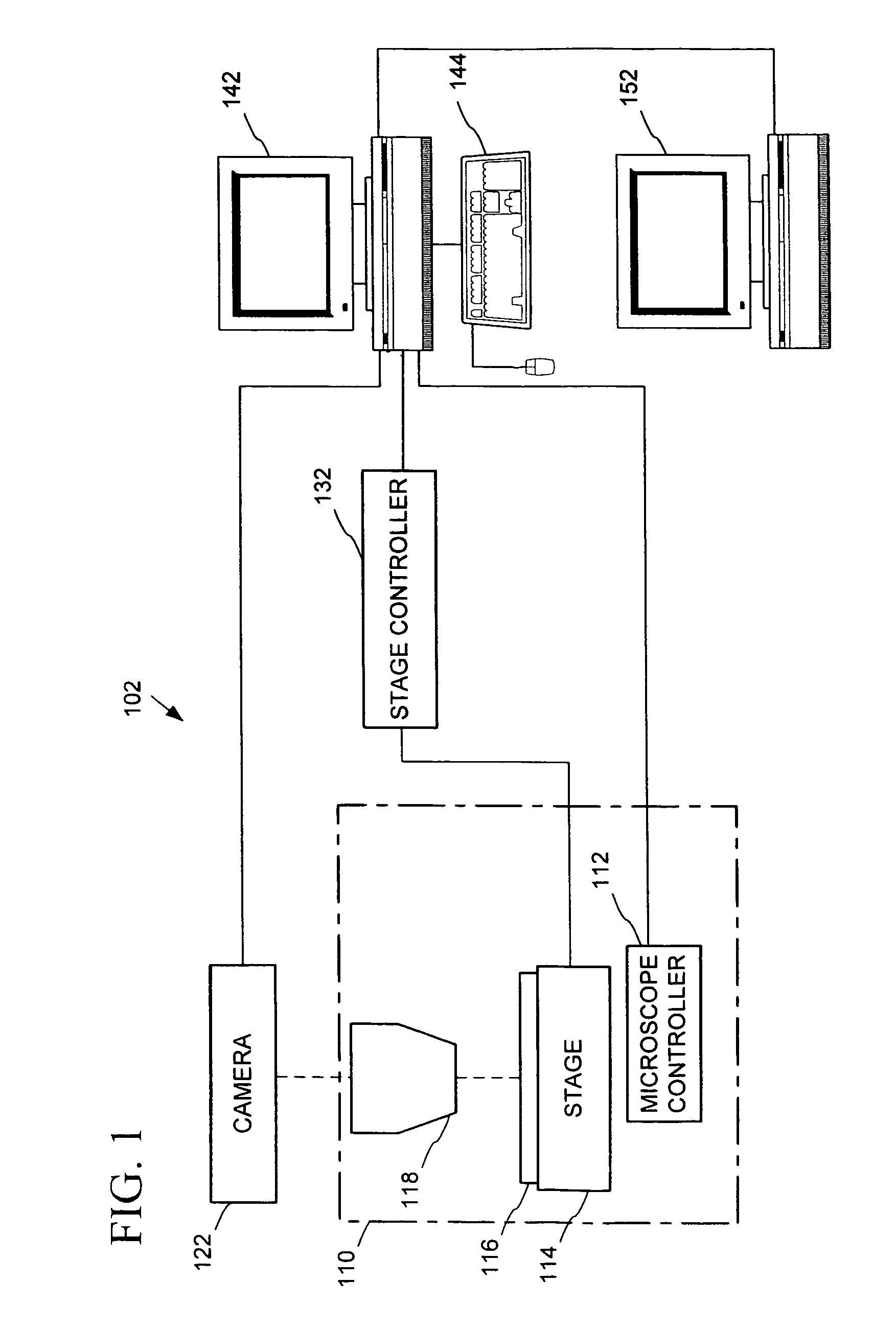
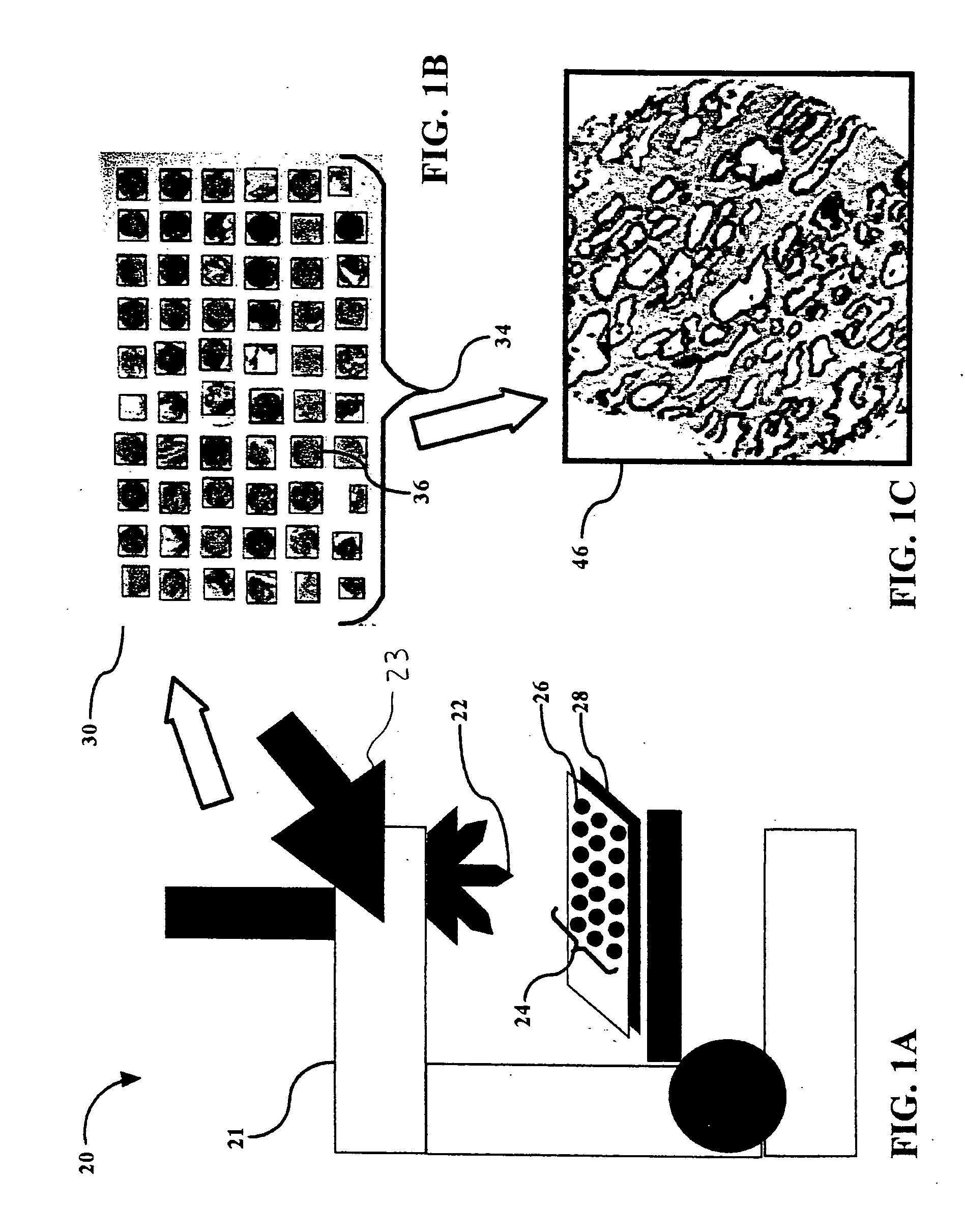
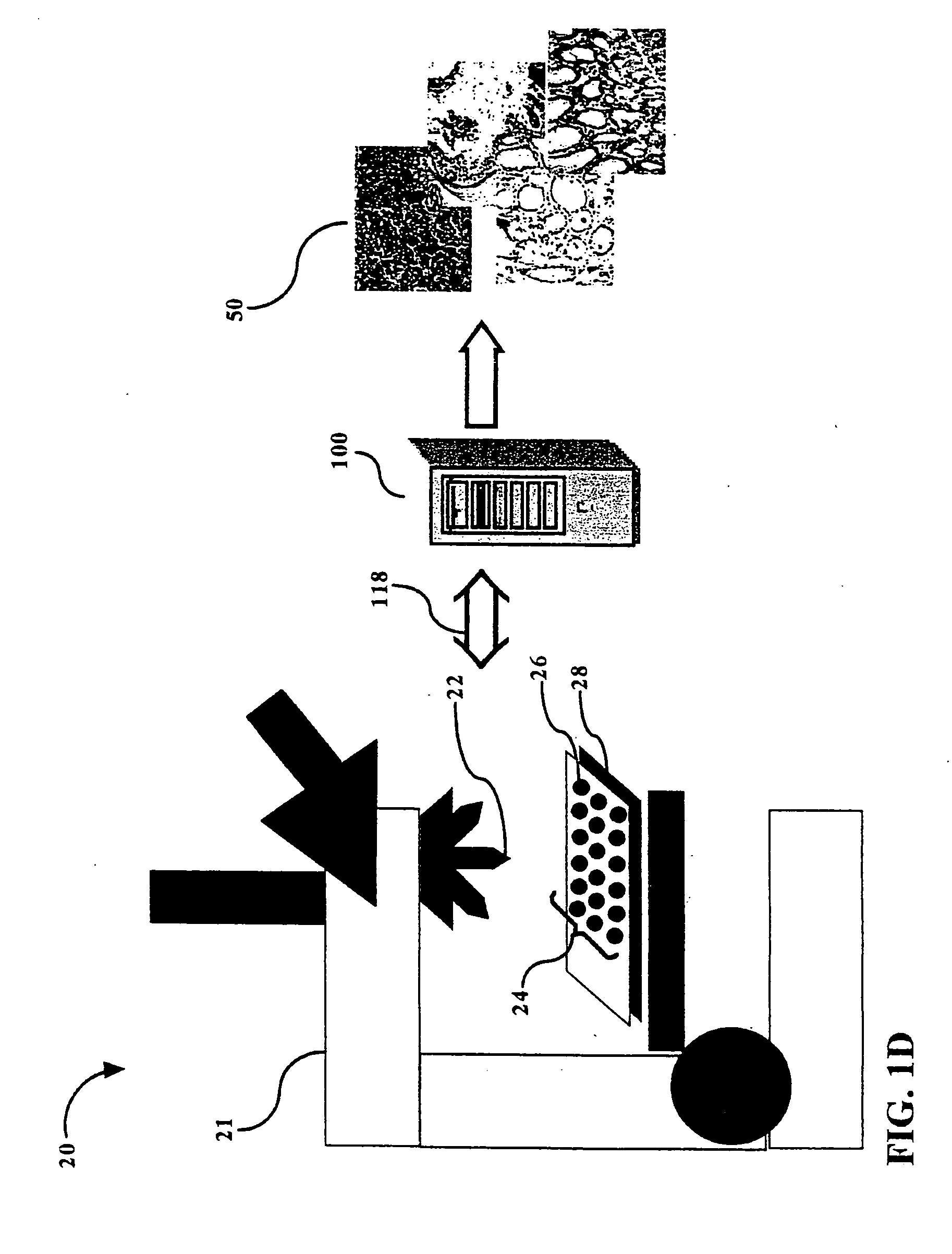
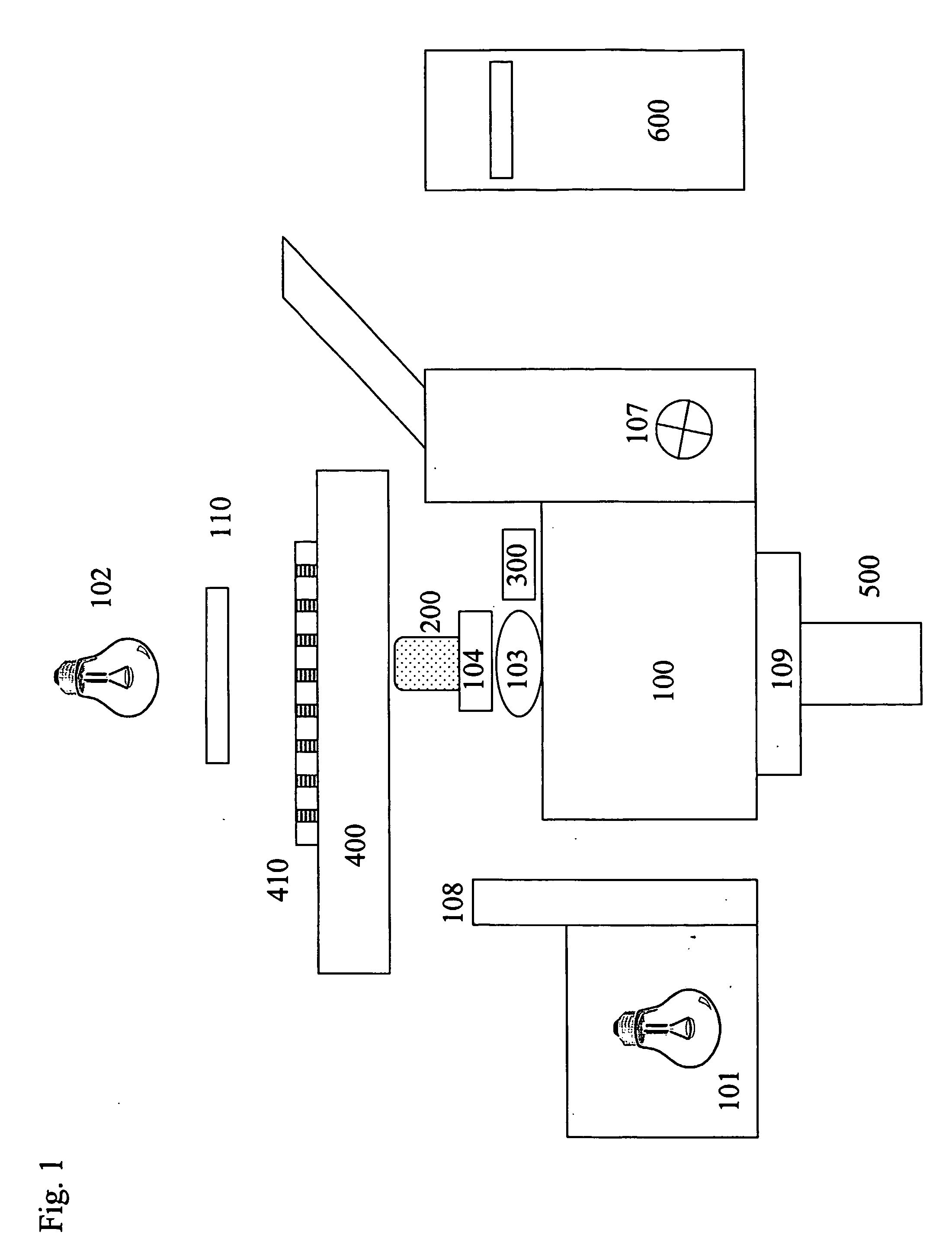
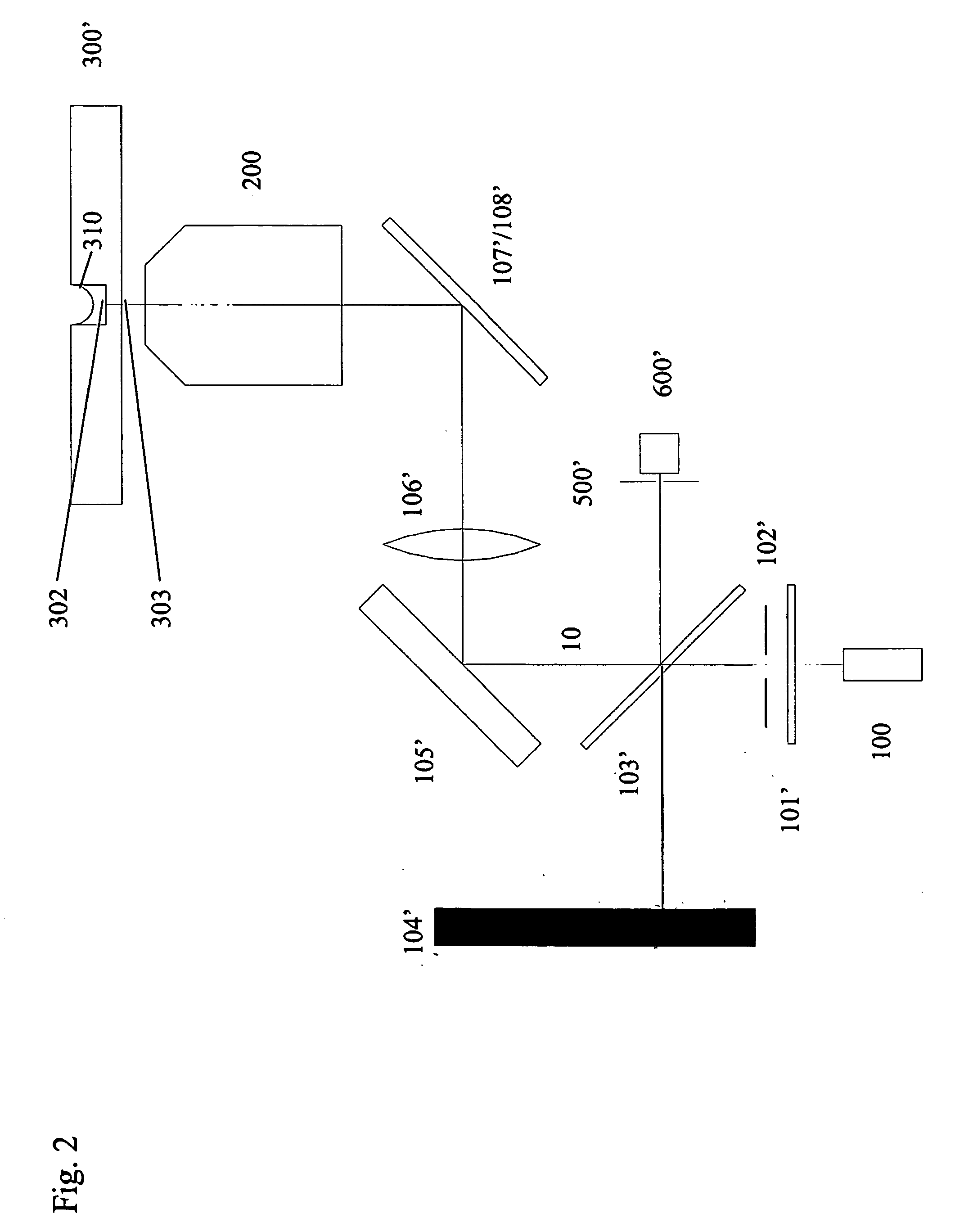
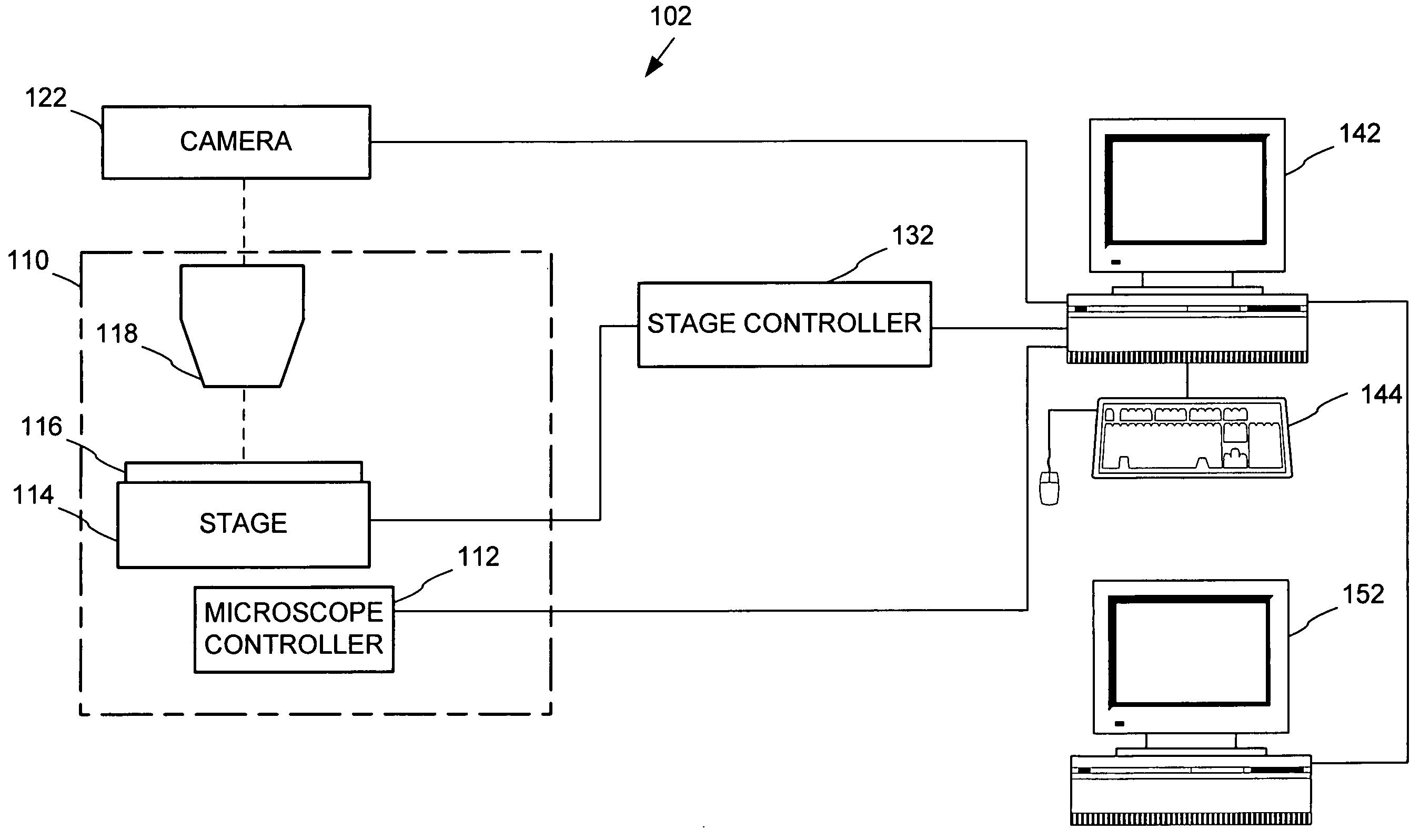
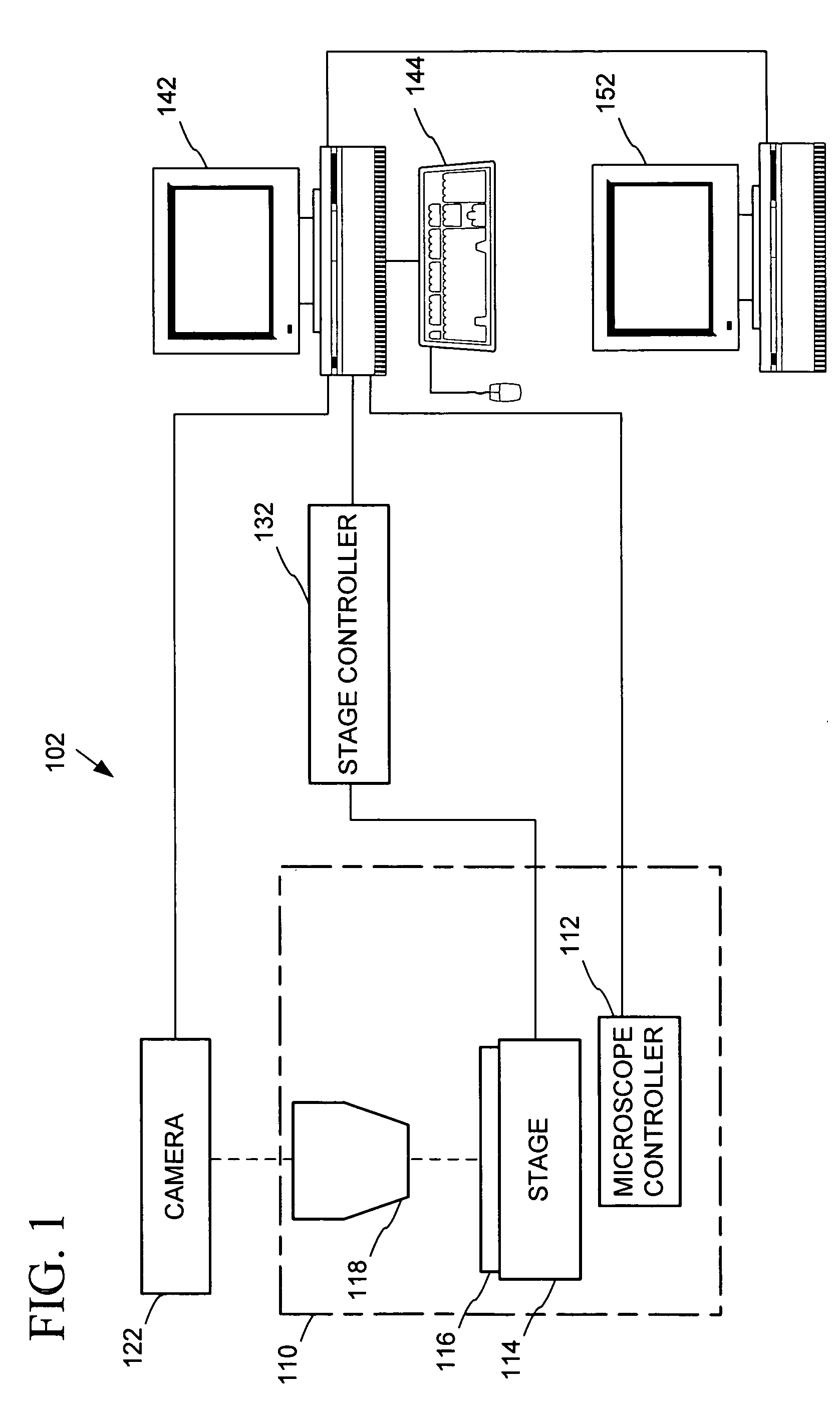
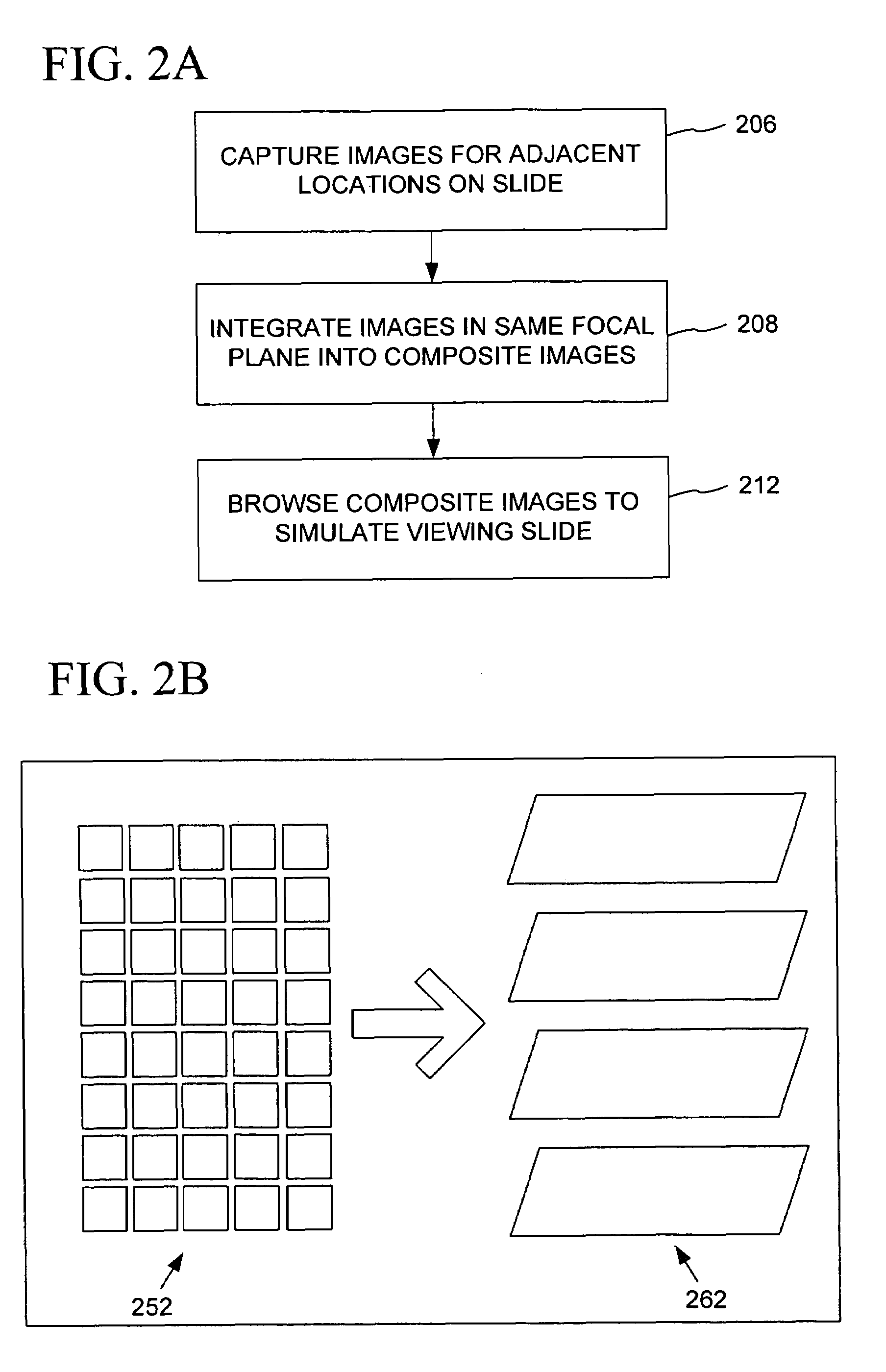
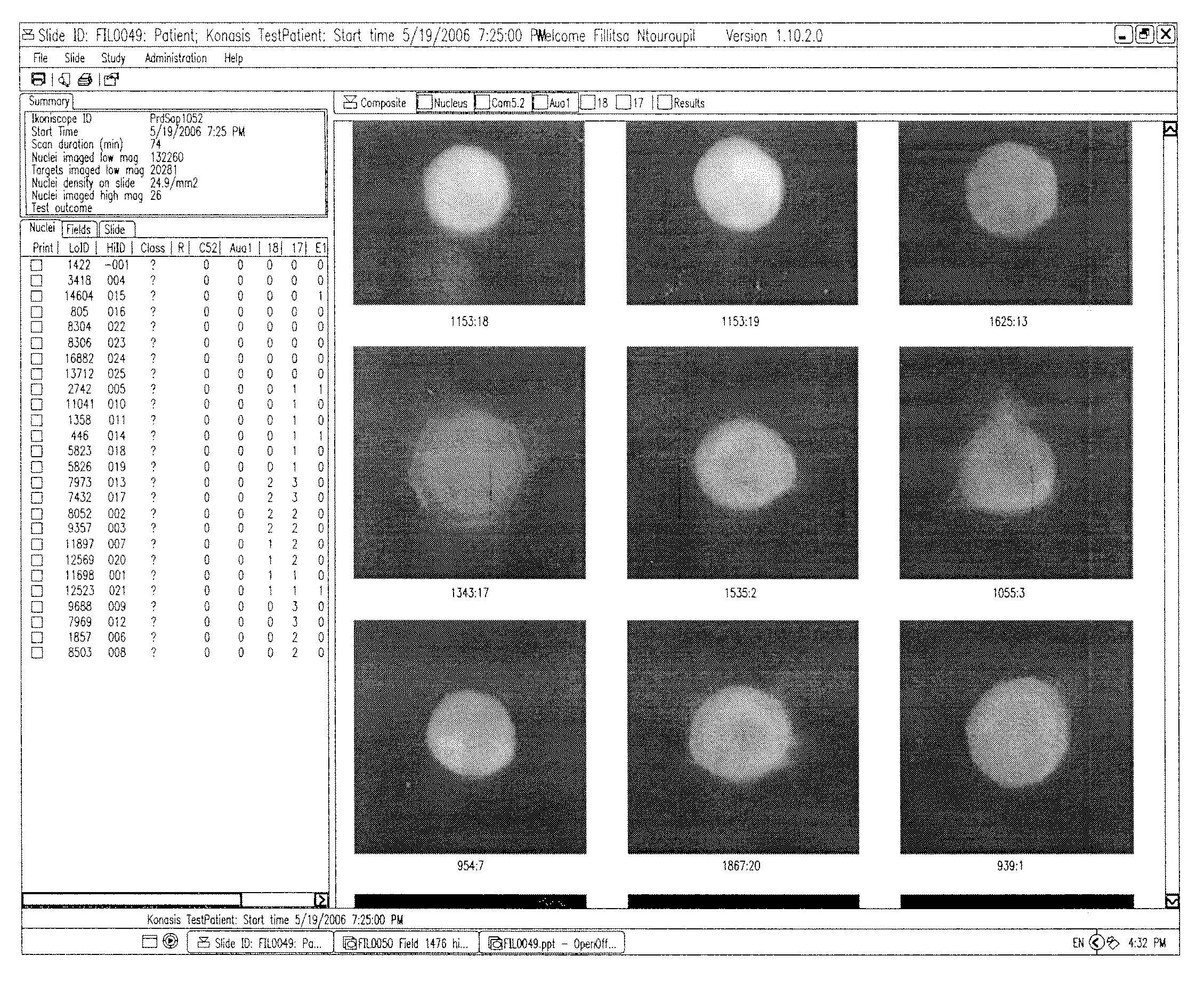
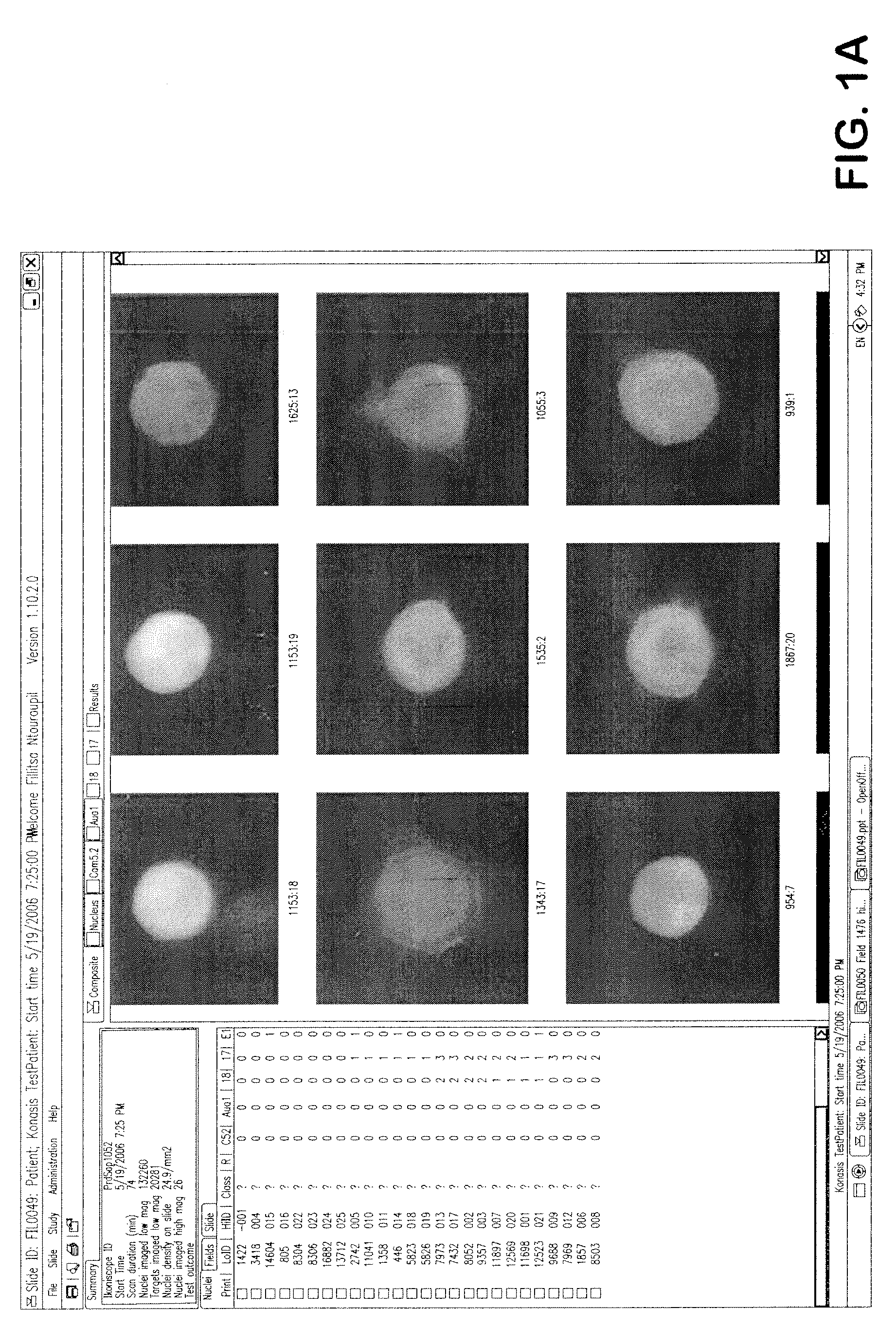
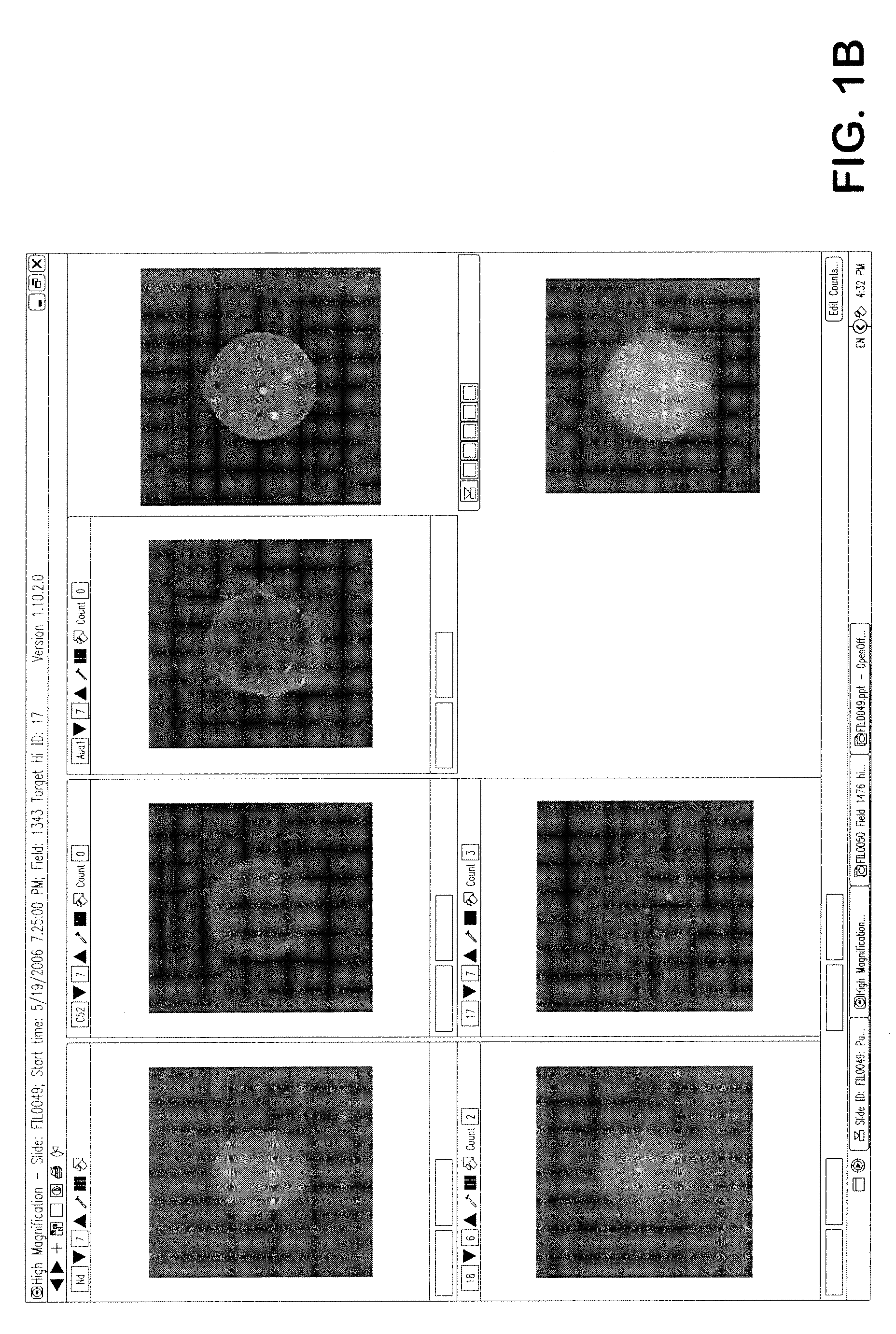
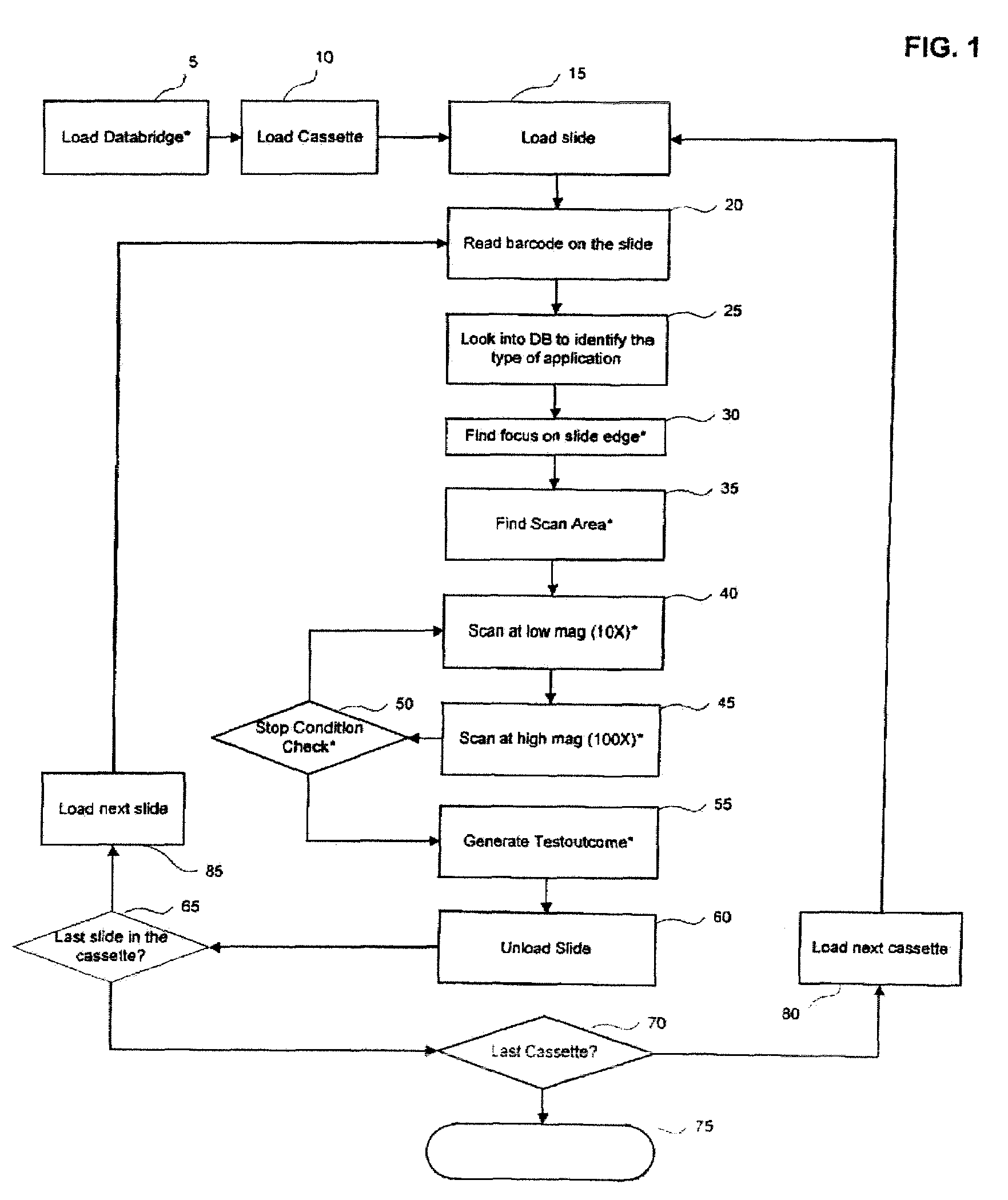
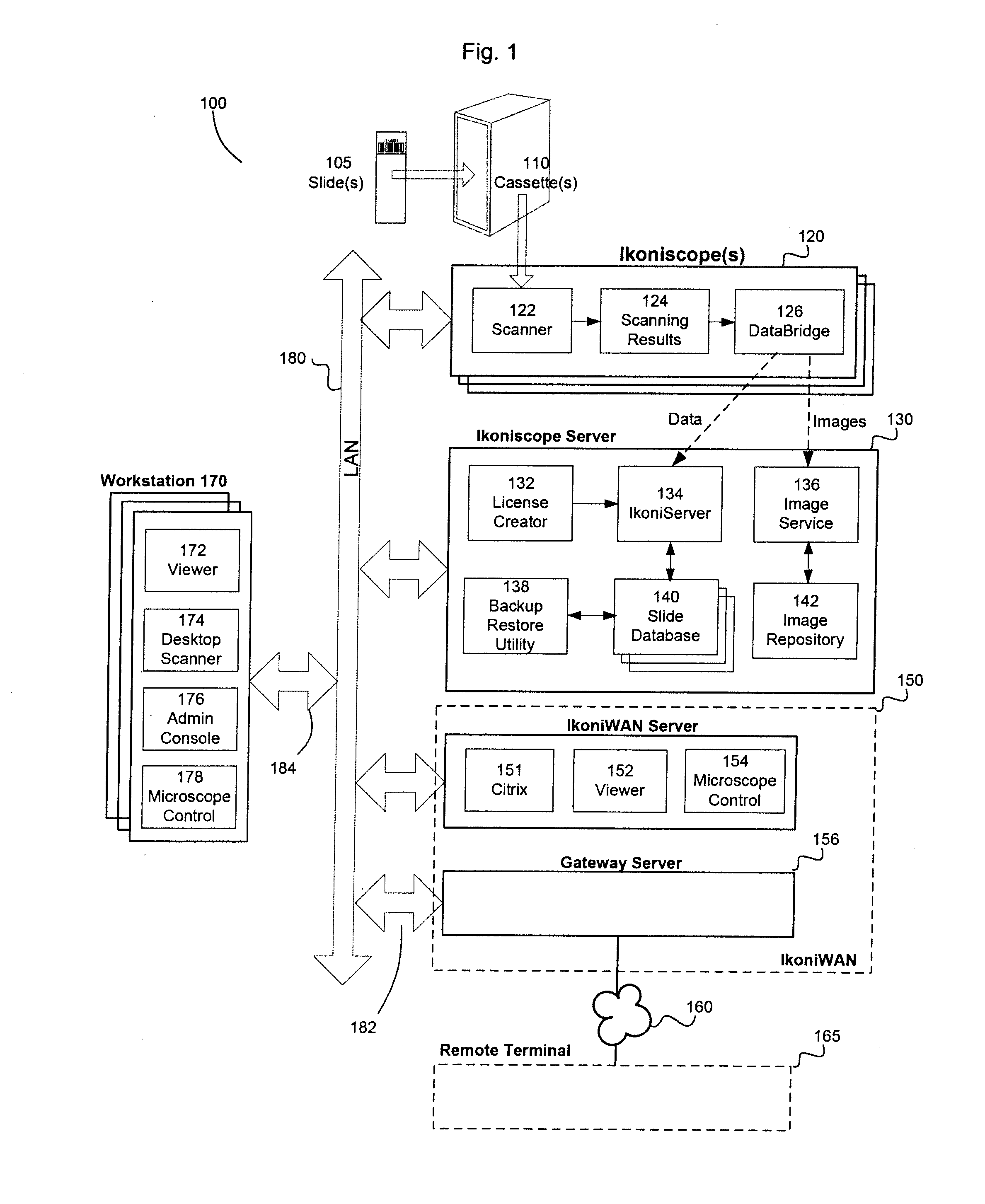
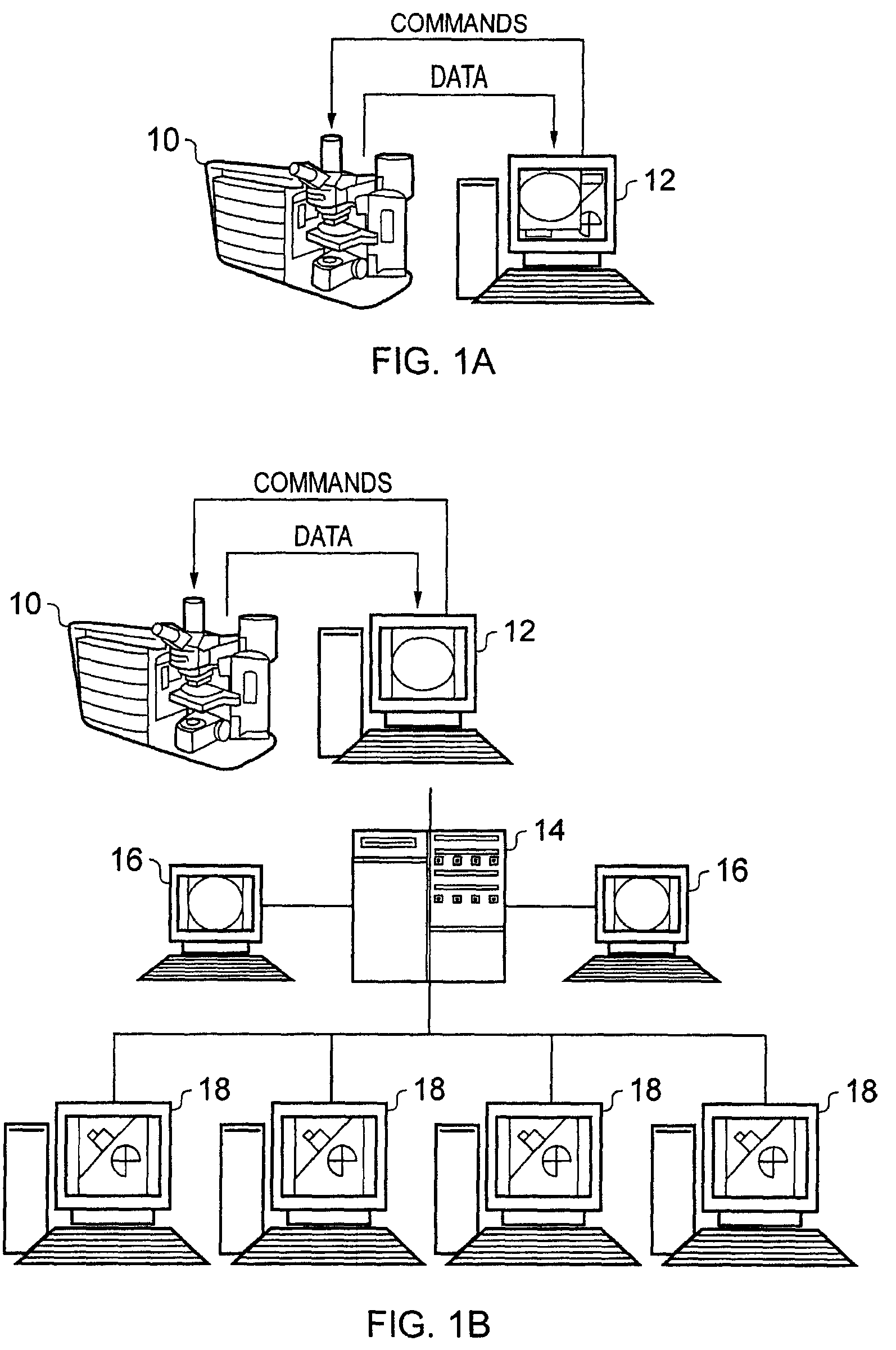
Automated microscopic image acquisition, compositing, and display
InactiveUS7027628B1Inhibition effectSuppress mutationImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageAutomated microscopy
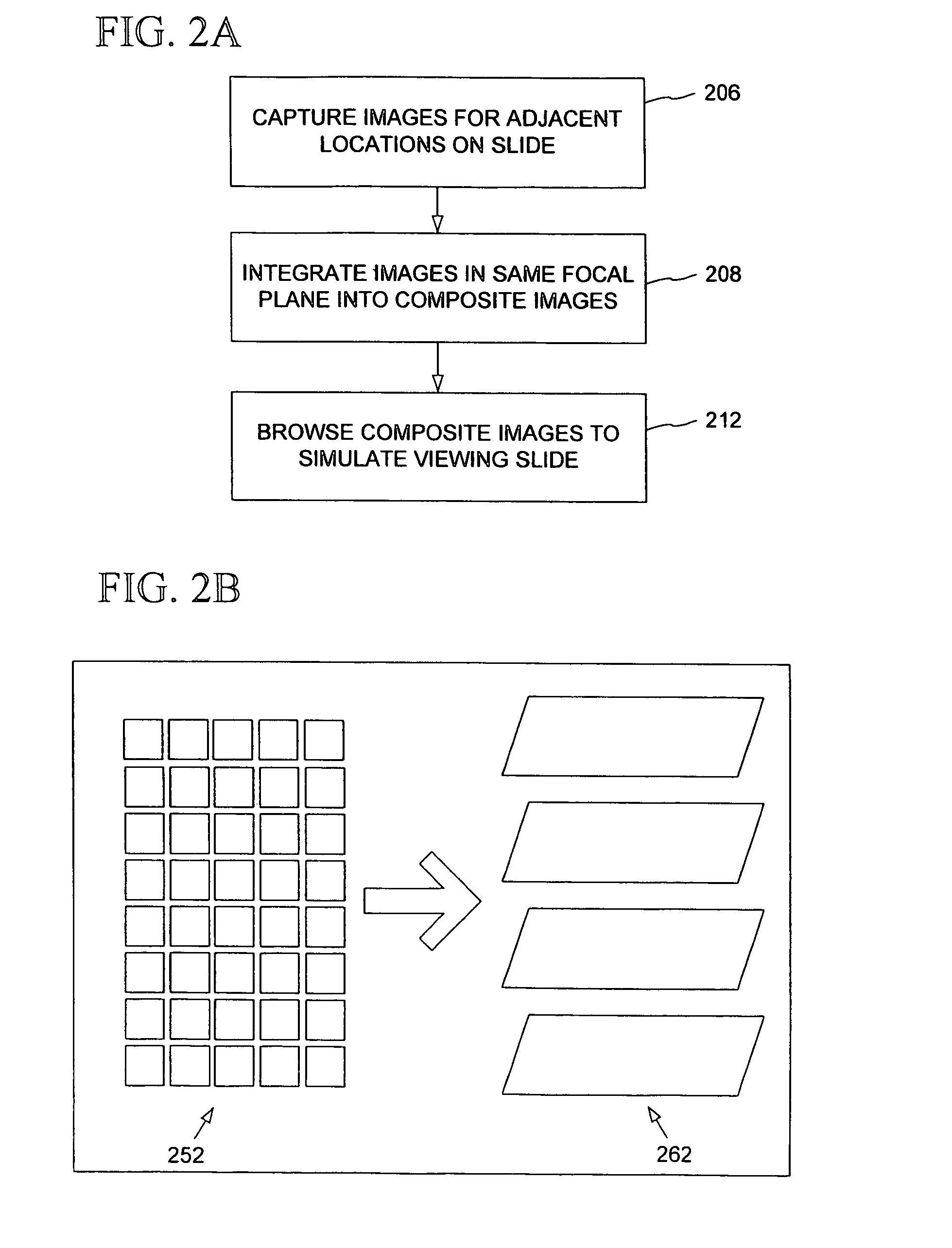
An automated microscope and computer system captures a set of images for a capture area in a plurality of focal planes. The images can then be integrated into composite images for browsing to simulate viewing an item, such as a biological sample, under a microscope. A corrective filter can be constructed from the images to avoid an effect called “tiling.” Before capture, variable focal plane error can be avoided by collecting z locations for a set of points in the capture area. During image browsing, entire composite images can be loaded into memory in compressed form. Compressed image portions can be pre-decompressed to avoid delay as a browsing user navigates throughout the composite images. Pre-decompression can be done by a thread separate from the thread performing navigation operations.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION US SEC THE +1
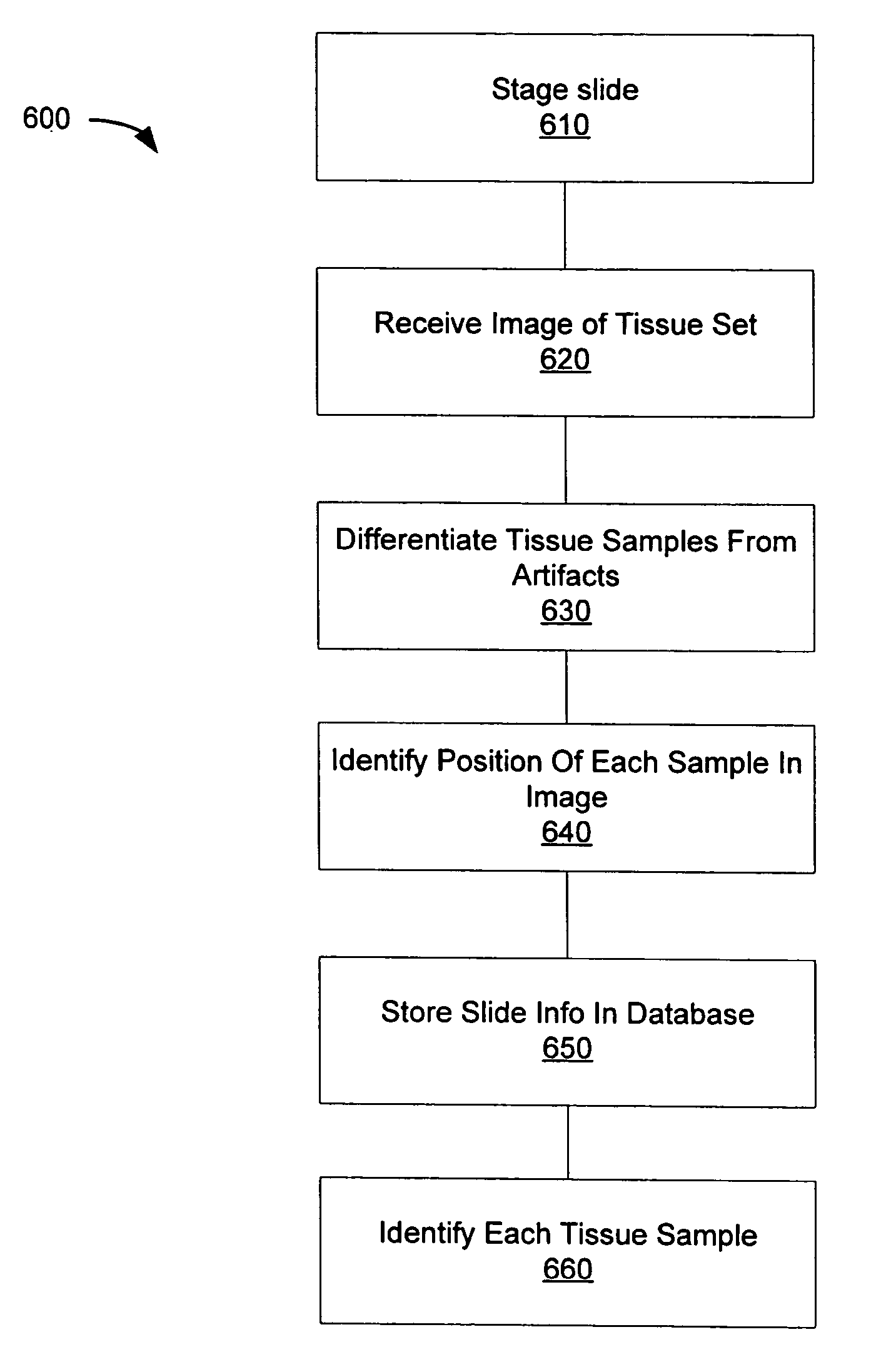
Automated microscope slide tissue sample mapping and image acquisition
A method comprises receiving an image of a tissue-sample set. A position in the image of each tissue sample relative to at least one other tissue sample is electronically identified. Each tissue sample is electronically identified based on the tissue sample position identification.
Owner:THE CHAMBERLAIN GRP INC +1
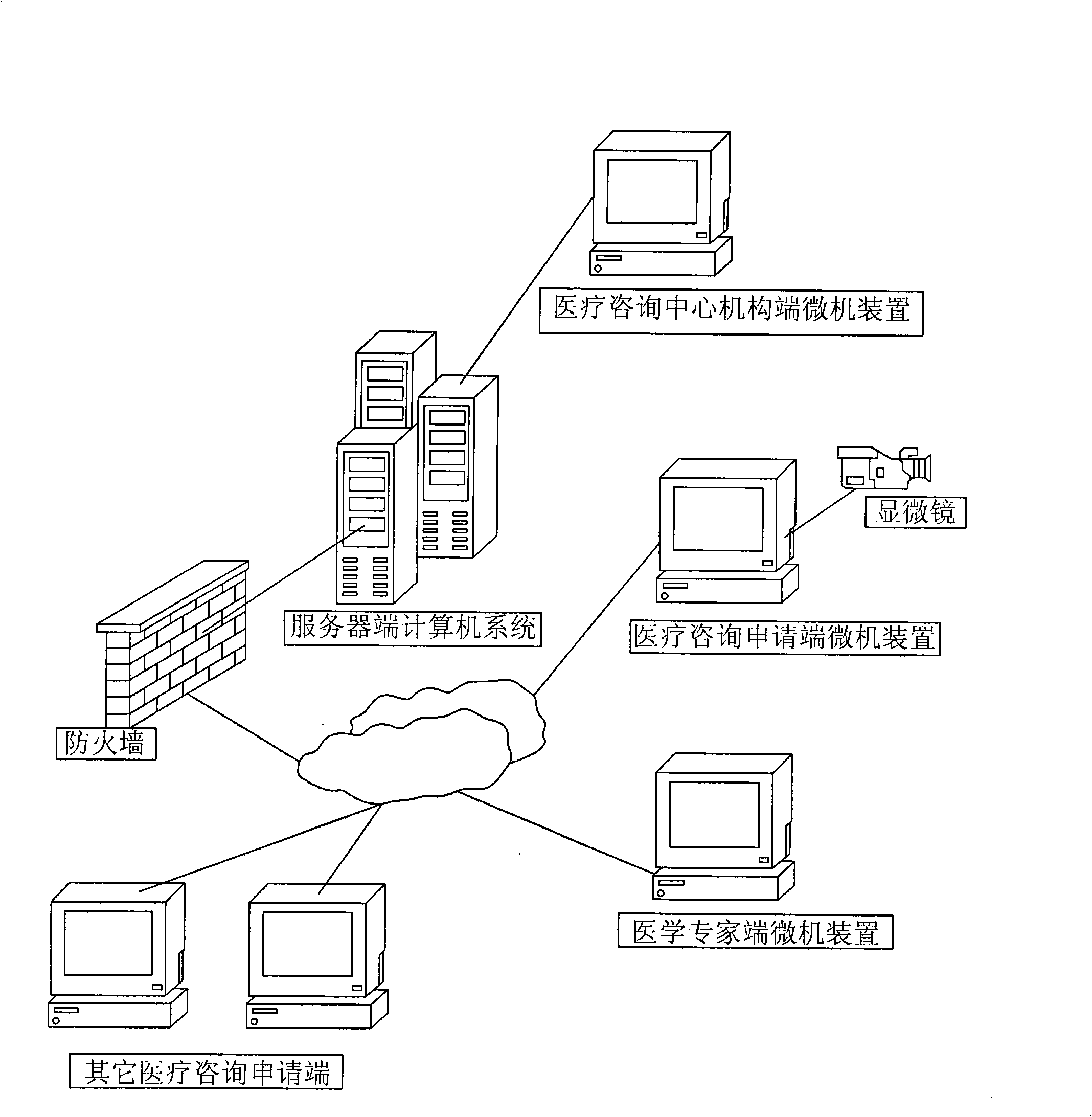
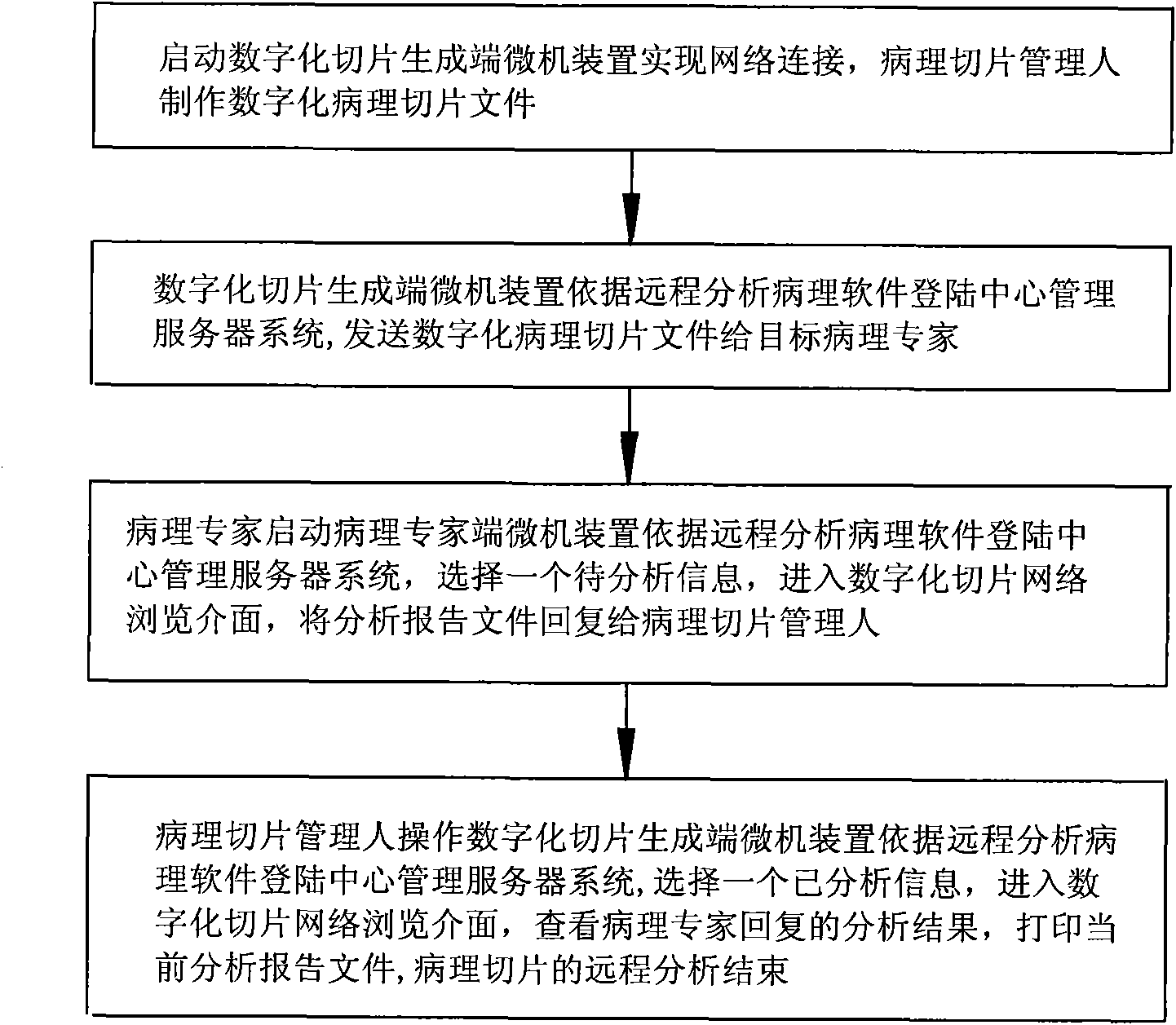
Doctor-patient remote interaction platform and method
InactiveCN101345670AMeet Distance Medical EducationMeet the Telemedicine ExchangeElectric signal transmission systemsData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionVoice communication
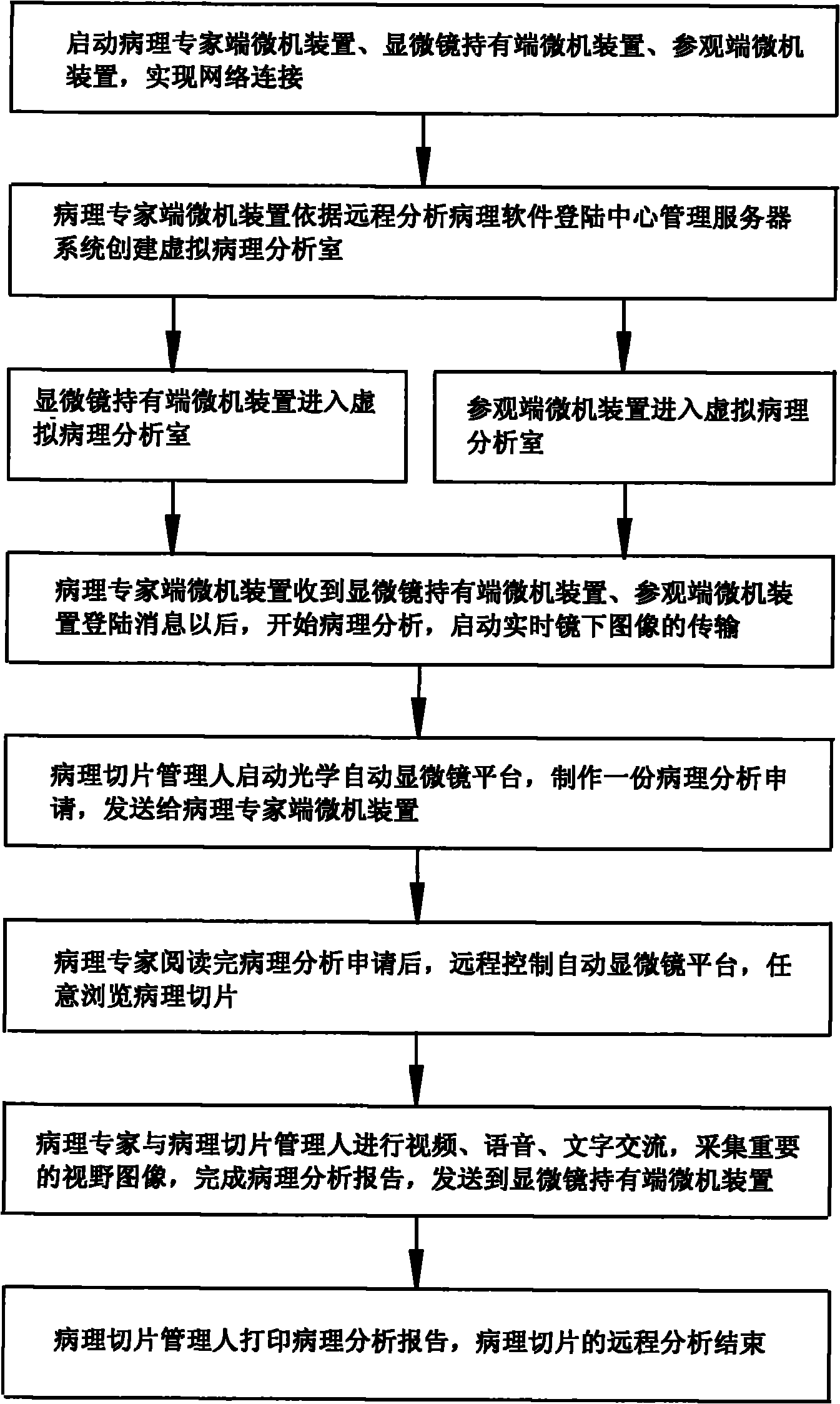
The invention relates to a doctor-patient remote alternation platform and a remote alternation method, comprising: a computer system at a server end, a microcomputer device at a medical referral centre institution end, a microcomputer device at a medical referral application end, a microcomputer device at a medical expert end, which are in a wide area network and realize network connection, thereby realizing facial transmission in a broadcasting mode, medical image of real-time transmission, remote control automatic microscope platform, and alternation speech communication is present on the basis of sharing real-time medical image. Three perfect remote medical solution with different applications are realized, including a pathology remote consultation solution, a pathology remote medical education solutionand a pathology remote medical communication solution.
Owner:王剑 +1
System and methods for rapid and automated screening of cells
A system for performing automated cell screening in drug discovery, including an automated microscope, a fast autofocus device and a digital imaging system. Processes are implemented in software through which relevant cellular material is segmented and quantified with minimal user interaction. Improvements in the following areas: known methods for image processing are implemented in such a way that automated segmentation is achieved; sets of known measurements (pixel counting, etc.) are implemented as methods which demonstrate aspects of biology in a reliable fashion; components for automated positioning, focusing, imaging and processing of a multiplicity of samples are integrated as systems within which the segmentation and measurement methods may be mounted; and components and methods are adapted into systems which yield more highly automated and more rapid cell screening.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Automated microscopic image acquisition compositing, and display
InactiveUS7305109B1Suppress mutationImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageAutomated microscopy
An automated microscope and computer system captures a set of images for a capture area in a plurality of focal planes. The images can then be integrated into composite images for browsing to simulate viewing an item, such as a biological sample, under a microscope. A corrective filter can be constructed from the images to avoid an effect called “tiling.” Before capture, variable focal plane error can be avoided by collecting z locations for a set of points in the capture area. During image browsing, entire composite images can be loaded into memory in compressed form. Compressed image portions can be pre-decompressed to avoid delay as a browsing user navigates throughout the composite images. Pre-decompression can be done by a thread separate from the thread performing navigation operations.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
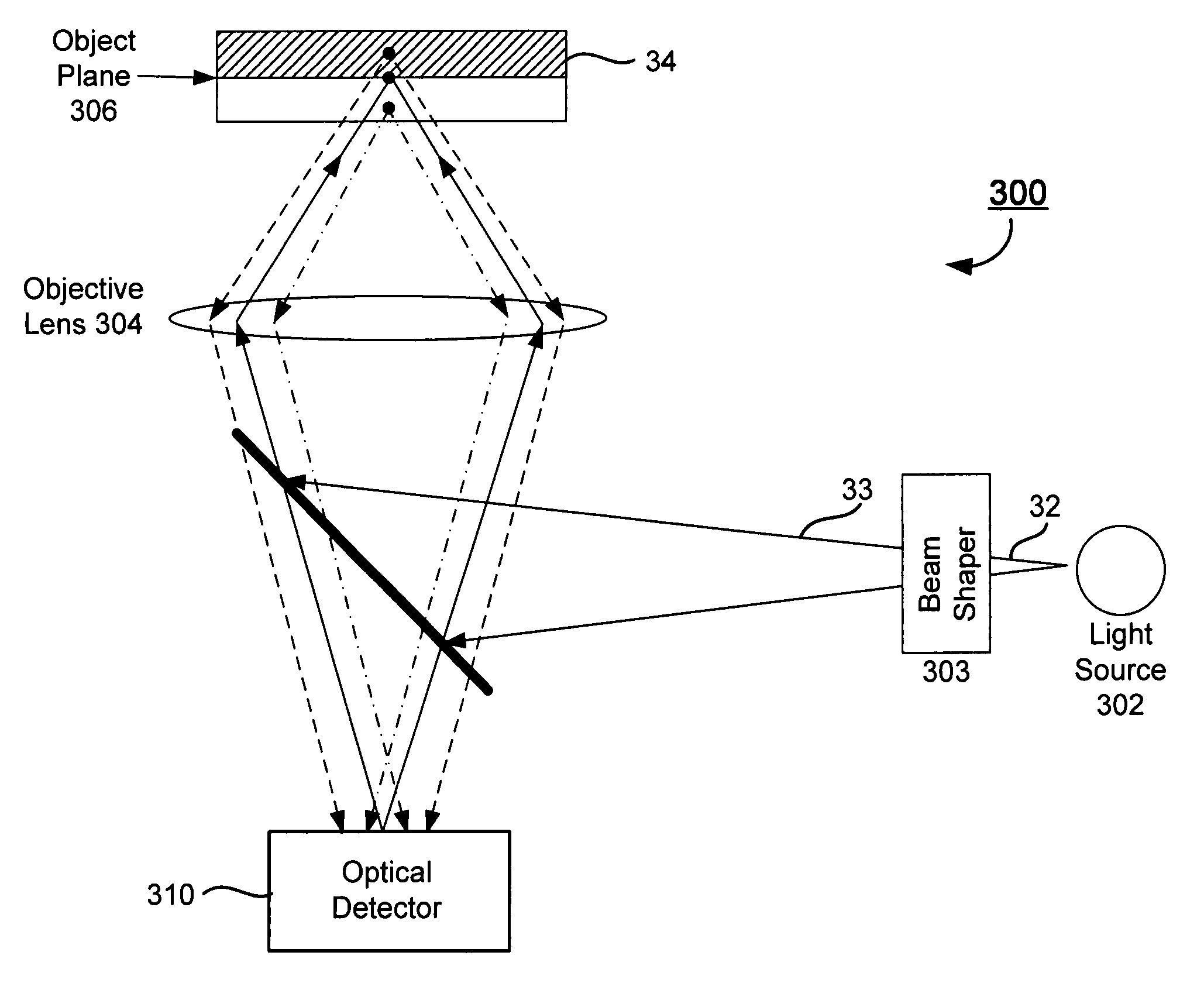
System and method for utilizing an autofocus feature in an automated microscope
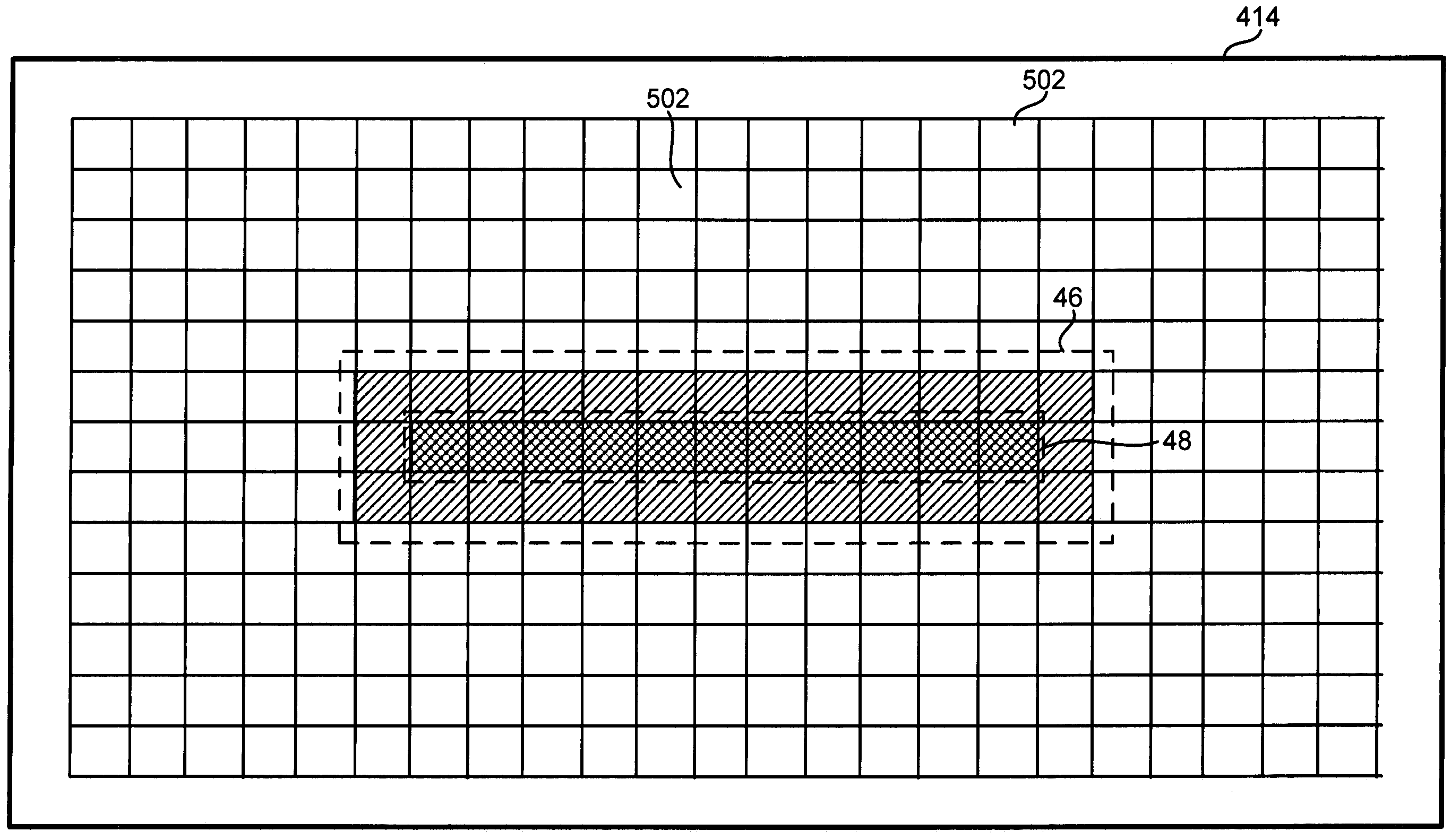
ActiveUS20070152130A1Increase speedImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansAutomated microscopyLight beam
The invention relates to a method for adjusting focus in an automated microscope. The method may comprise the steps of: providing an optical detector for image acquisition, wherein the optical detector comprises an array of sensor pixels; designating a region of interest in the array of sensor pixels to emulate a confocal aperture; directing a light beam to illuminate an object according to a predefined pattern, thereby forming an image of the illuminated pattern at the optical detector, wherein the image of the illuminated pattern substantially overlaps the designated region of interest; detecting a light intensity from sensor pixels located within the designated region of interest; and adjusting a relative focal position of an objective lens based on the detected light intensity.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
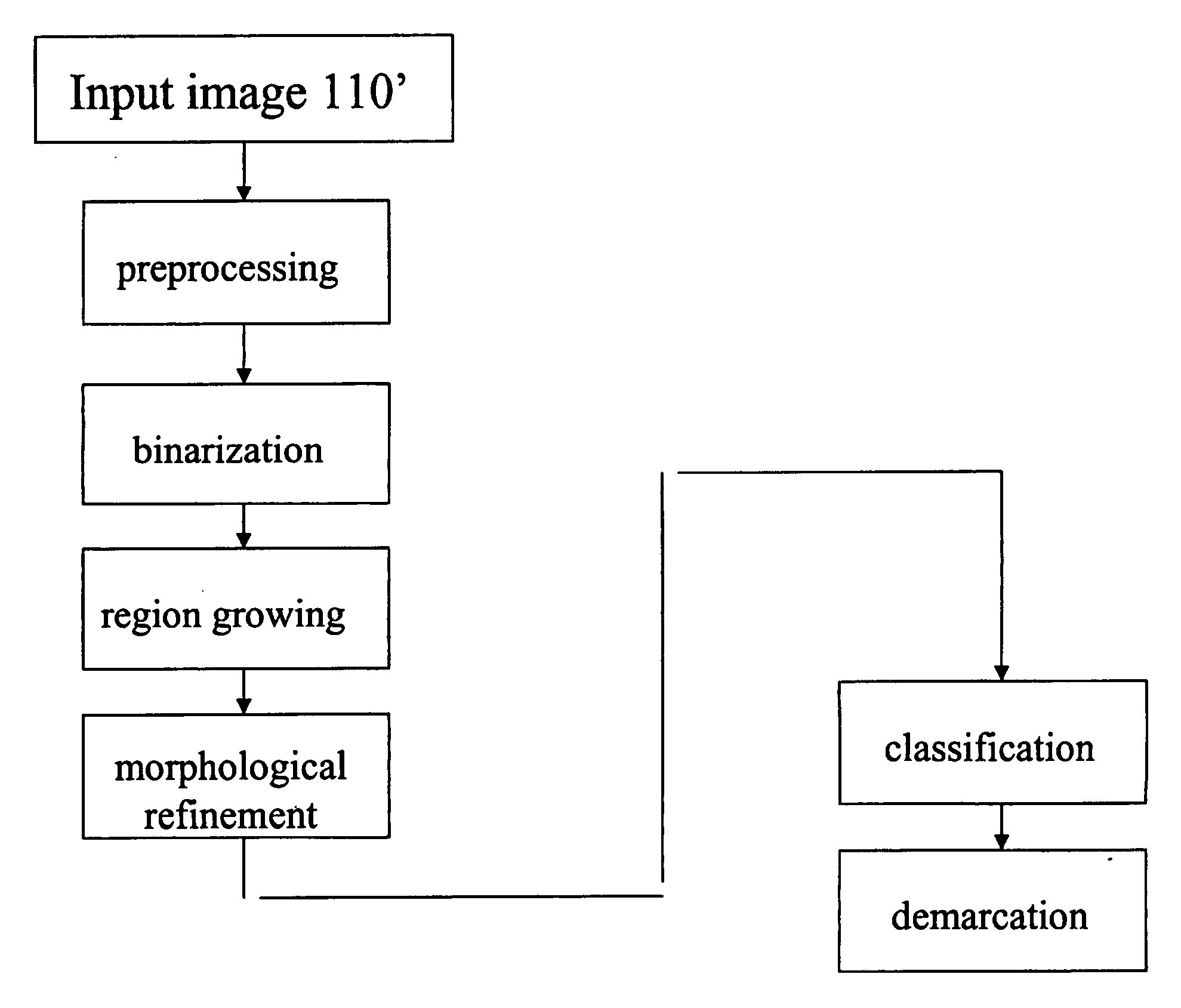
Morphological analytical apparatus and method for erythrocytes
ActiveCN102359938AReduce the impact of errorsBiological neural network modelsColor/spectral properties measurementsAutomated microscopyRed blood cell
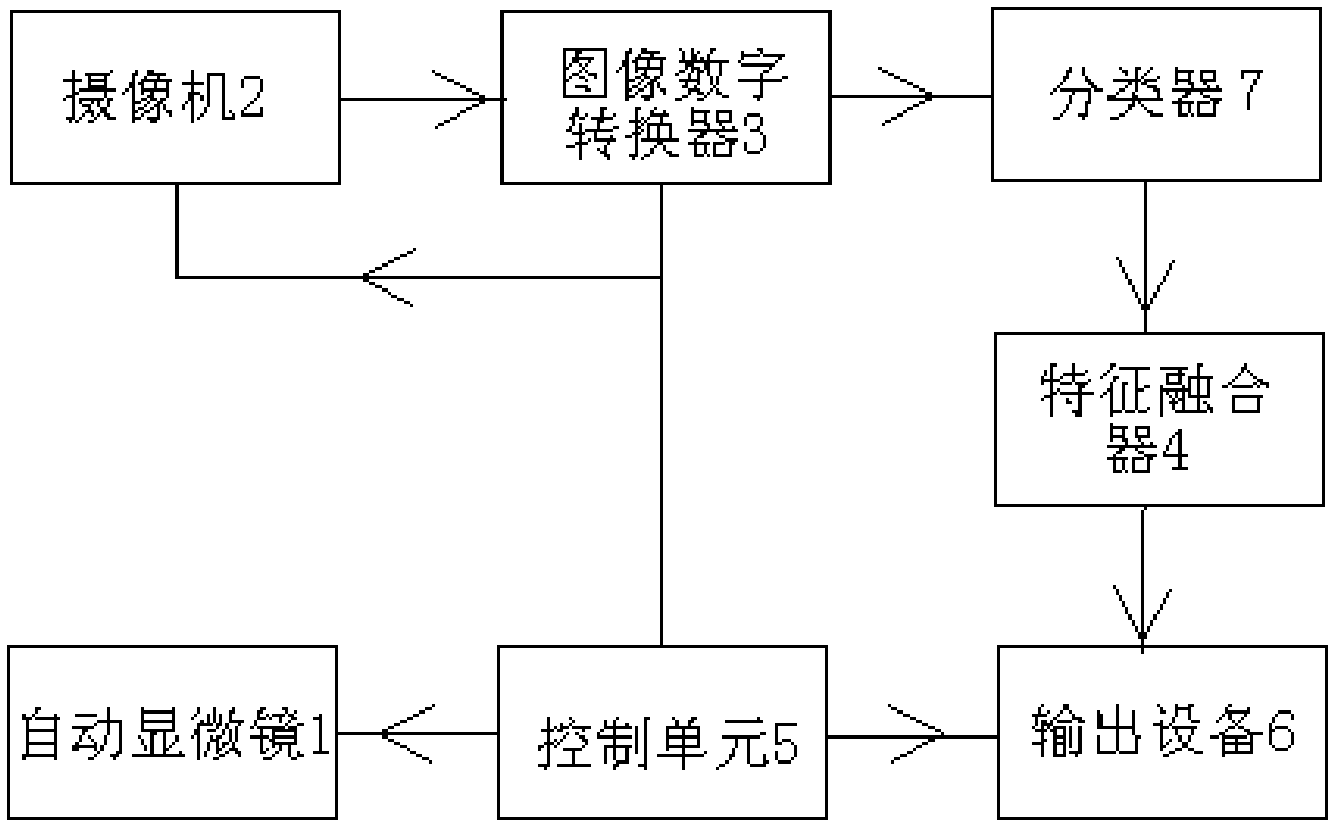
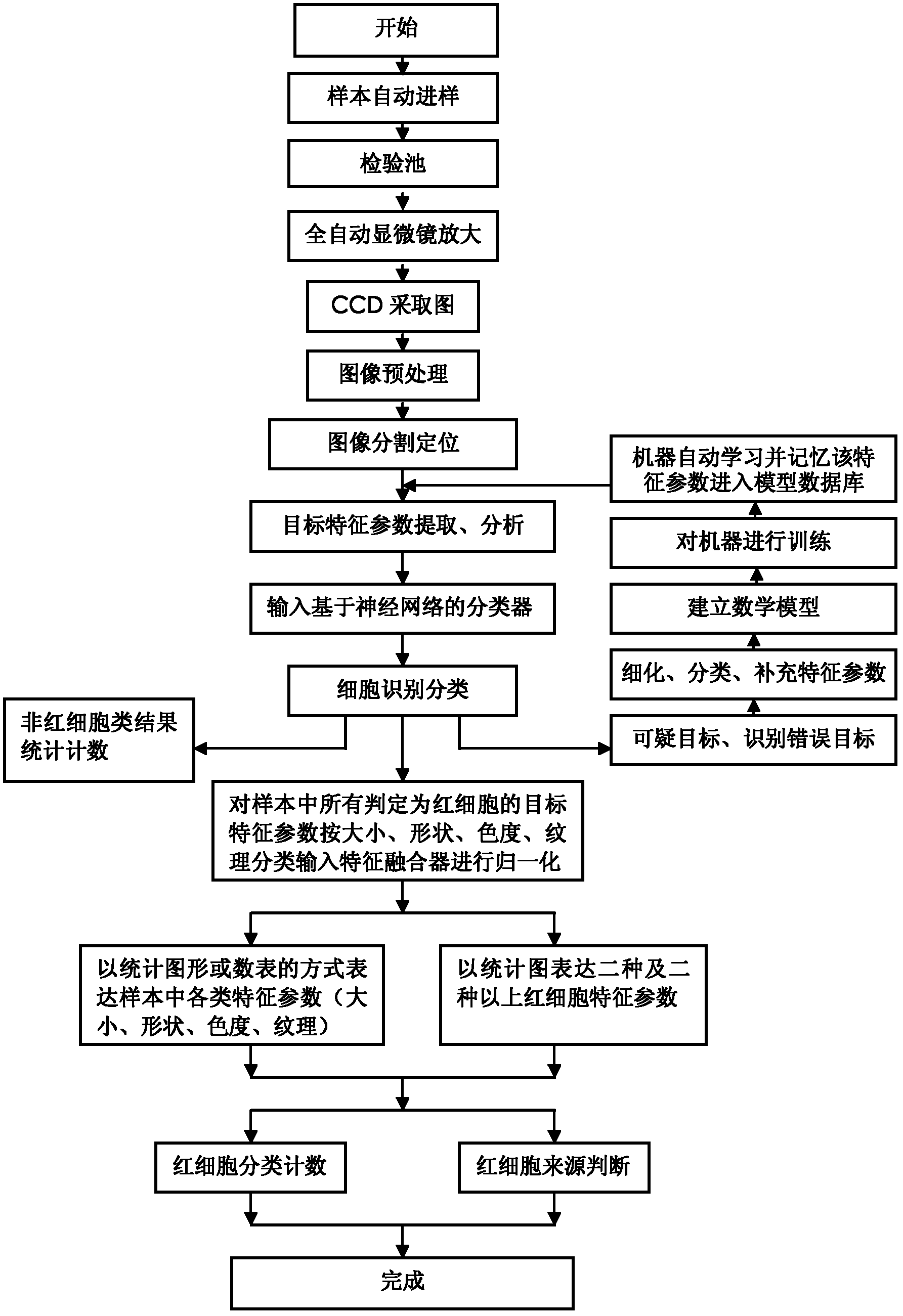
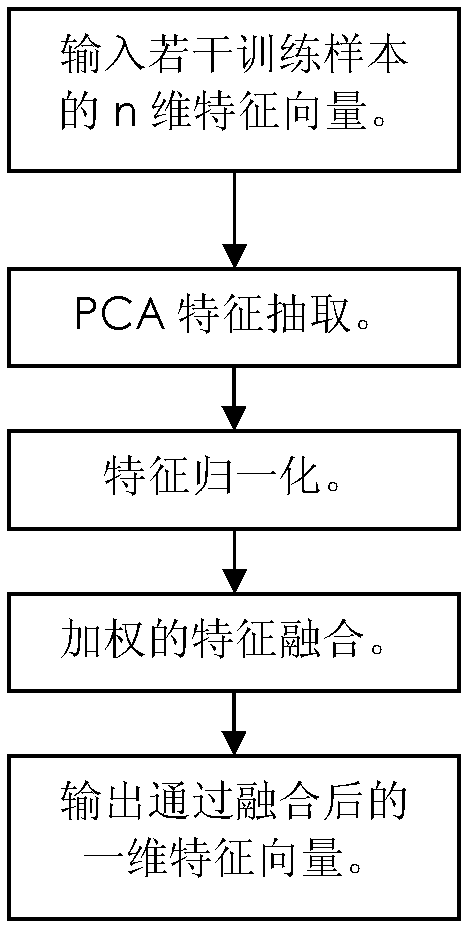
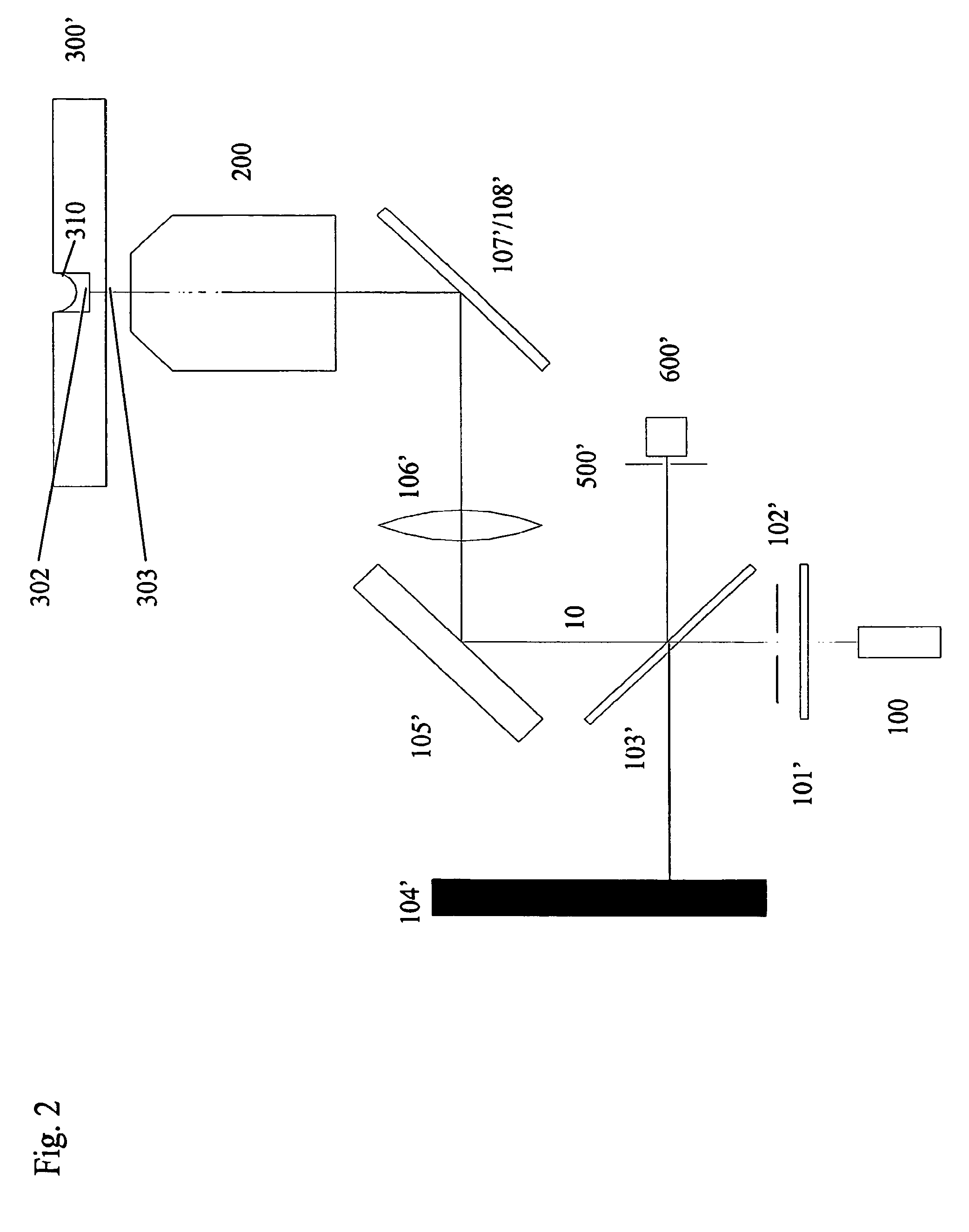
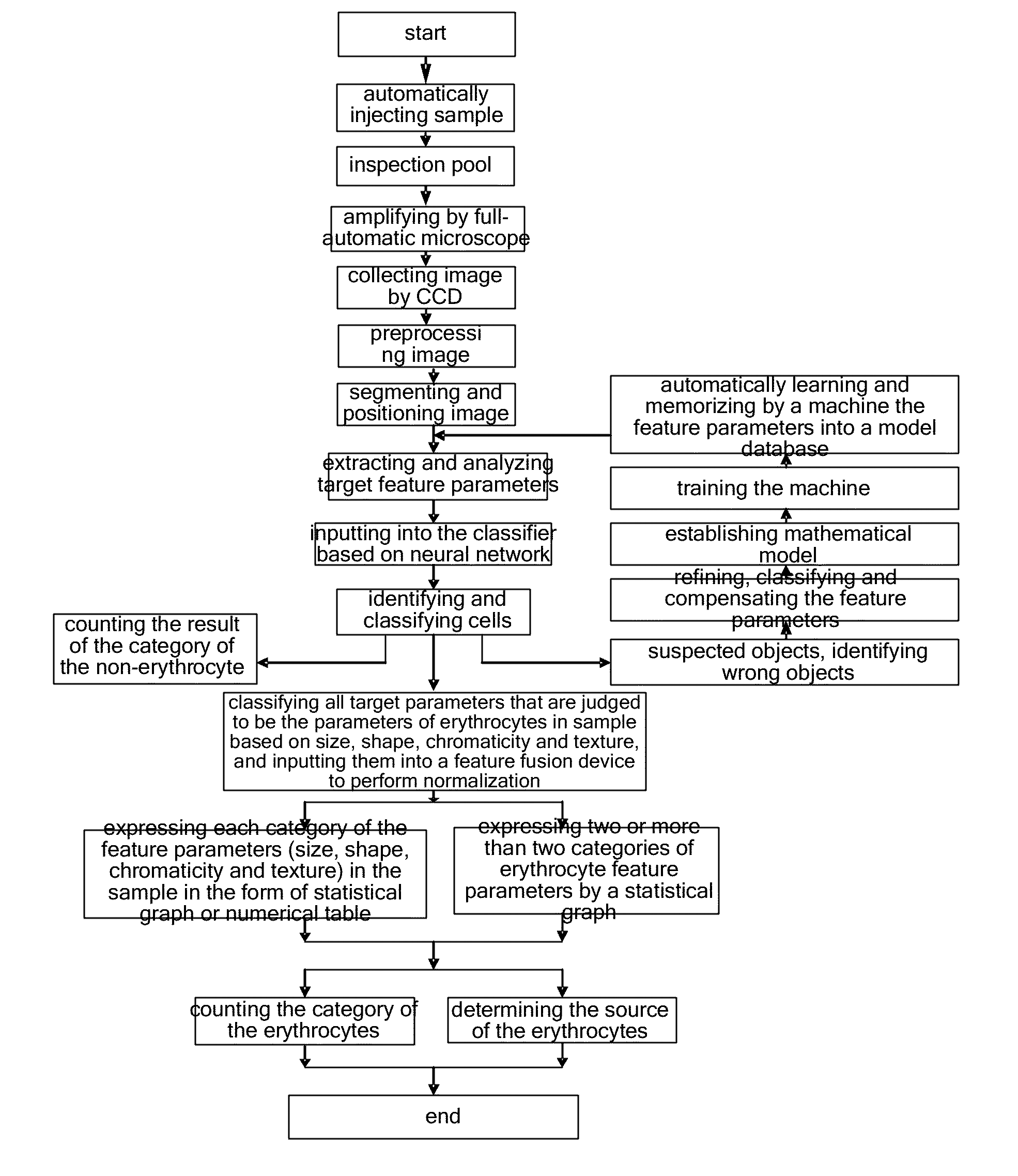
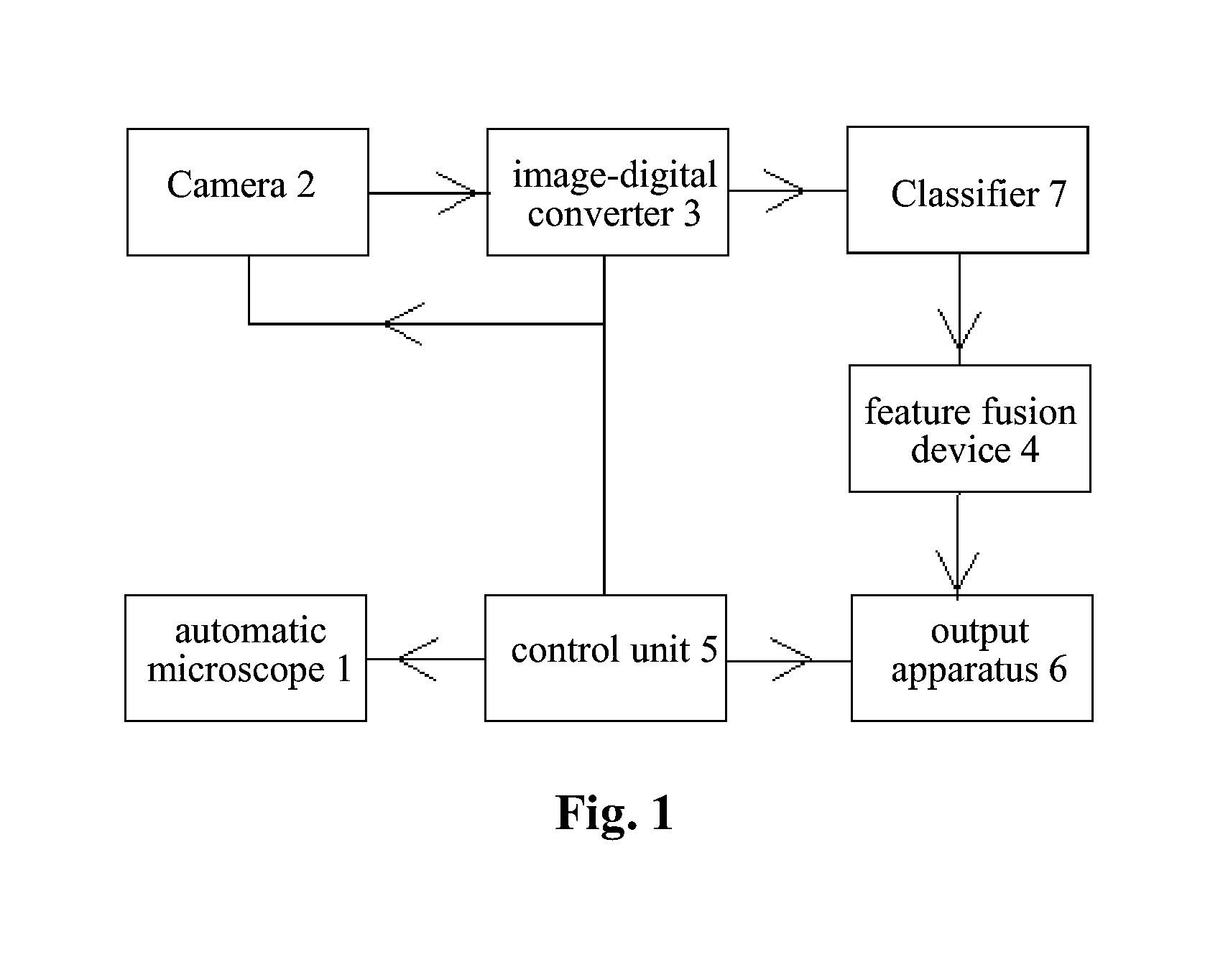
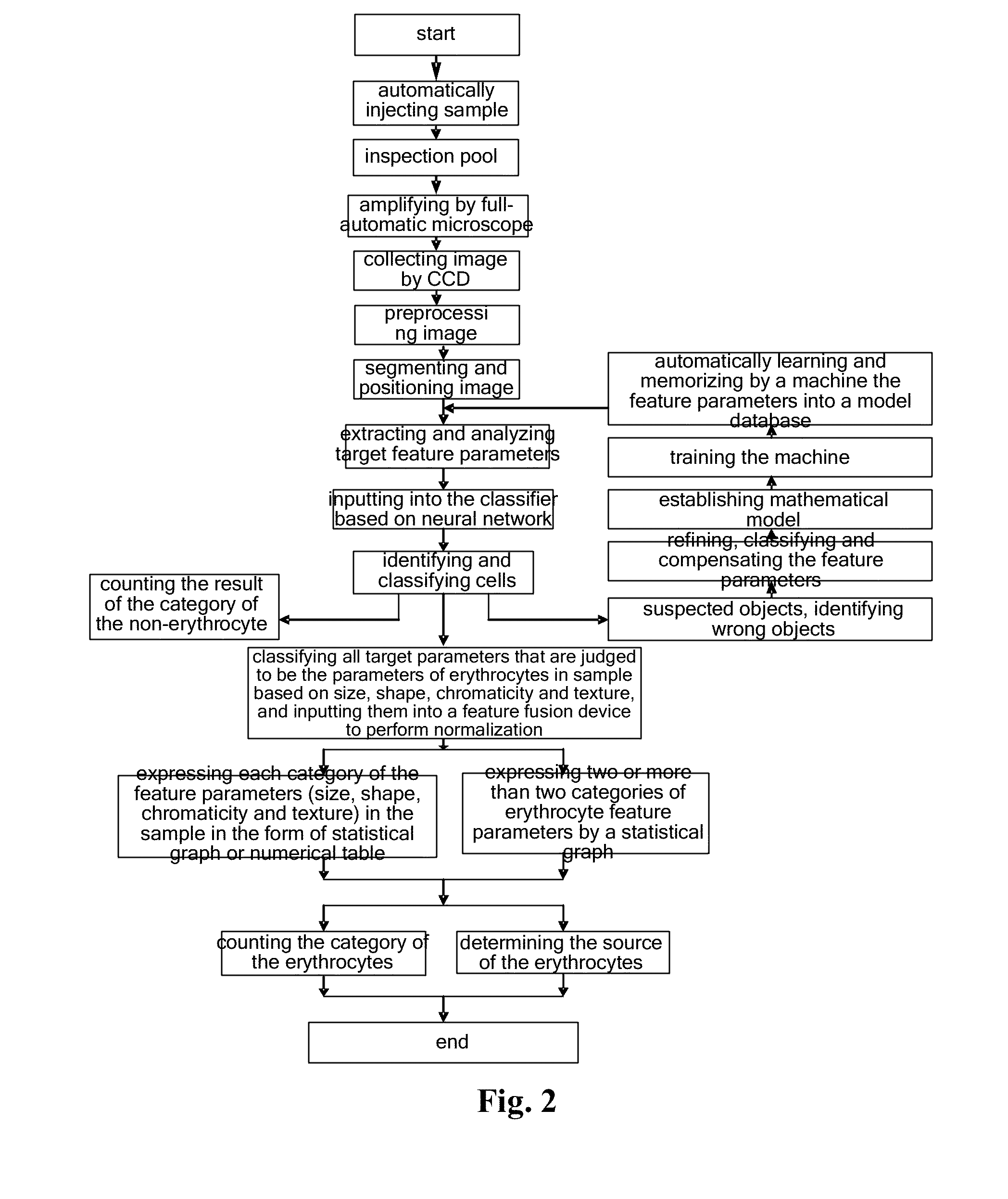
The invention discloses a morphological analytical apparatus and method for erythrocytes. According to the invention, a sample is placed under an automatic microscope and amplified, morphological images of all the cells in the sample are collected by a CCD (charge-coupled device) and digitalized by an image digitizer, and then segmentation and positioning of the images and extraction of target characteristic parameters are carried out; morphological characteristic parameters of every erythrocyte are separated with a classifier established on the basis of a neural network; normalization treatment is carried out on morphological characteristic parameter data of every variety of erythrocytes with a characteristic fusion cage established on the basis of fuzzy clustering; statistical analysis is carried out on each variety of obtained normalization parameters; comprehensive statistical analysis is carried out on a plurality of the normalization parameters and is expressed with figures or numerical tables so as to determine whether morphology of the erythrocytes is normal; and sources and properties of the erythrocytes can be identified through detection of erythrocytes with abnormal morphology.
Owner:AVE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Automated microscopic cell analysis
InactiveUS20170328924A1Eliminate Bubble ProblemsSolve insufficient capacityReagent containersPreparing sample for investigationWhite blood cellRed blood cell
Disclosed in one aspect is a method for performing a complete blood count (CBC) on a sample of whole blood by metering a predetermined amount of the whole blood and mixing it with a predetermined amount of diluent and stain and transferring a portion thereof to an imaging chamber of fixed dimensions and utilizing an automated microscope with digital camera and cell counting and recognition software to count every white blood cell and red blood corpuscle and platelet in the sample diluent / stain mixture to determine the number of red cells, white cells, and platelets per unit volume, and analyzing the white cells with cell recognition software to classify them.
Owner:MEDICA CORP
System and methods for rapid and automated screening of cells
A system for performing automated cell screening in drug discovery, including an automated microscope, a fast autofocus device and a digital imaging system. Processes are implemented in software through which relevant cellular material is segmented and quantified with minimal user interaction. Improvements in the following areas: known methods for image processing are implemented in such a way that automated segmentation is achieved; sets of known measurements (pixel counting, etc.) are implemented as methods which demonstrate aspects of biology in a reliable fashion; components for automated positioning, focusing, imaging and processing of a multiplicity of samples are integrated as systems within which the segmentation and measurement methods may be mounted; and components and methods are adapted into systems which yield more highly automated and more rapid cell screening.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Device and Method for Erythrocyte Morphology Analysis
ActiveUS20140185906A1Reduce impactBiological particle analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionStatistical analysisFeature parameter
The disclosure provides a device and a method for performing morphological analysis for erythrocytes, wherein the method for performing morphological analysis for erythrocytes comprises: collecting a morphological image of each of cells in a sample through a Charge Coupled Device (CCD) after amplifying the sample through an automatic microscope; segmenting and positioning the image and extracting target feature parameters after digitizing the image through an image-digital converter; isolating morphological feature parameters of each of the erythrocytes through a classifier established on the basis of the neural network, and normalizing each type of the morphological feature parameters of the erythrocytes through a feature fusion device established on the basis of fuzzy clustering; performing a statistical analysis on each type of normalized parameters obtained or performing a comprehensive statistical analysis according to a plurality of types of parameters, and expressing the result of the statistical analysis or the comprehensive statistical analysis in the form of graph or numerical table, thereby judging whether the morphology of the erythrocyte is normal. The source and property of the erythrocytes can be identified according to the detection for each type of the erythrocytes with the abnormal morphology.
Owner:CHANGSHA HIGH TECH IND DEV ZONE AVE SCI & TECH IND CO LTD
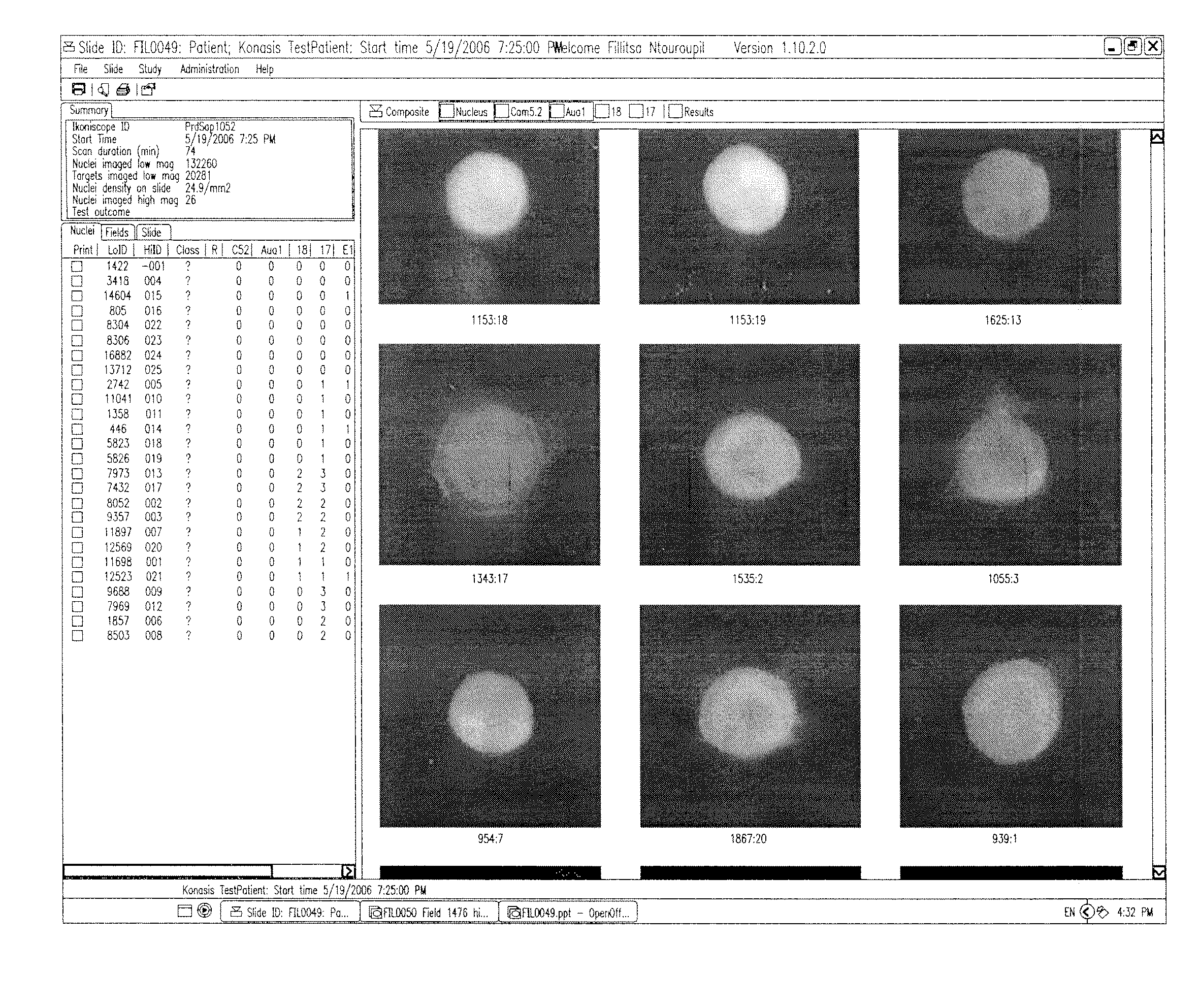
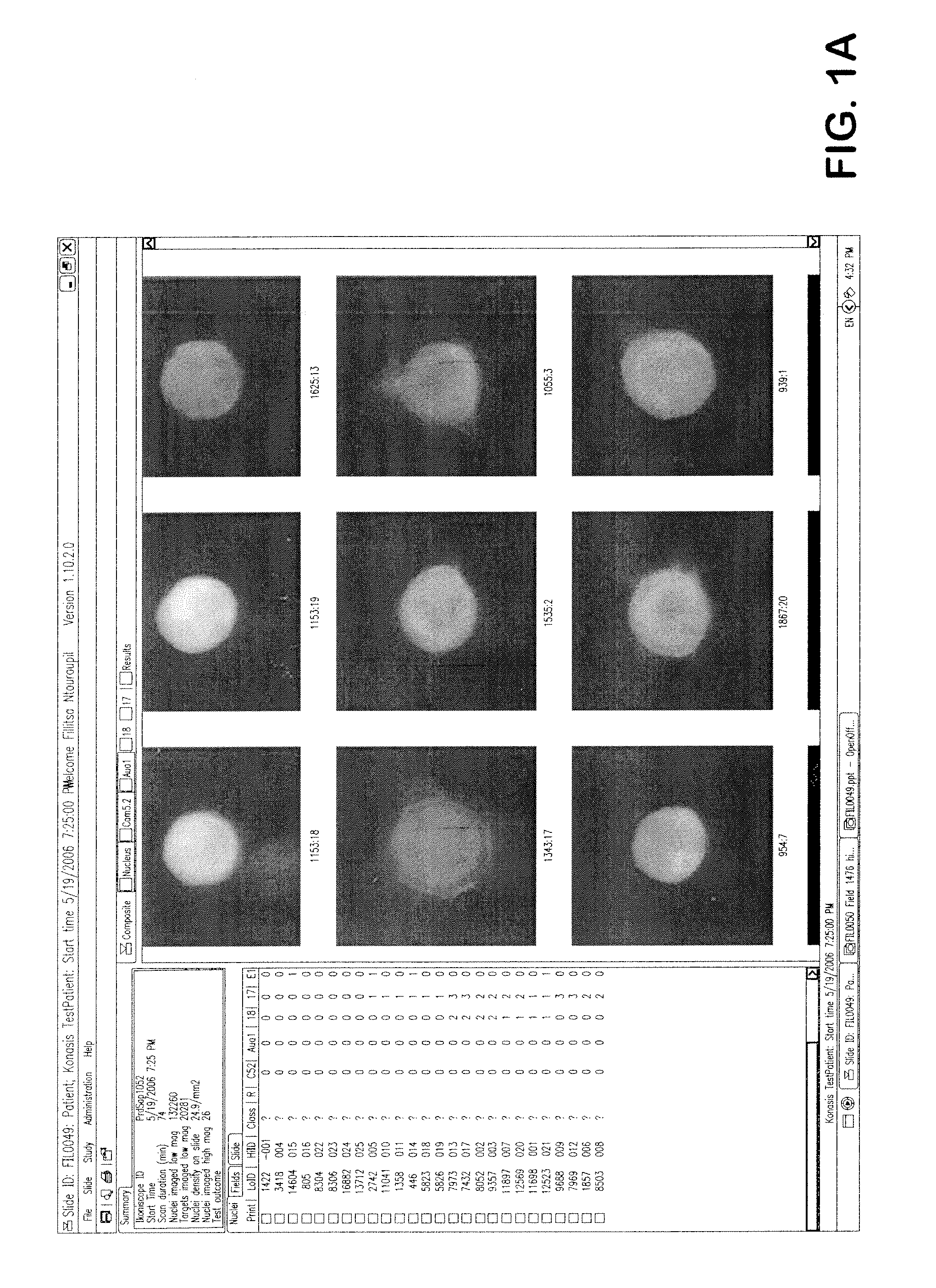
Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood with an automated scanning fluorescence microscope
InactiveUS8088715B2Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningAutomated microscopyFluorescence microscope
An automated, highly sensitive, specific and potentially quantitative detection method using an automated microscope for identifying and enumerating rare cancer cells in blood and other fluids.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
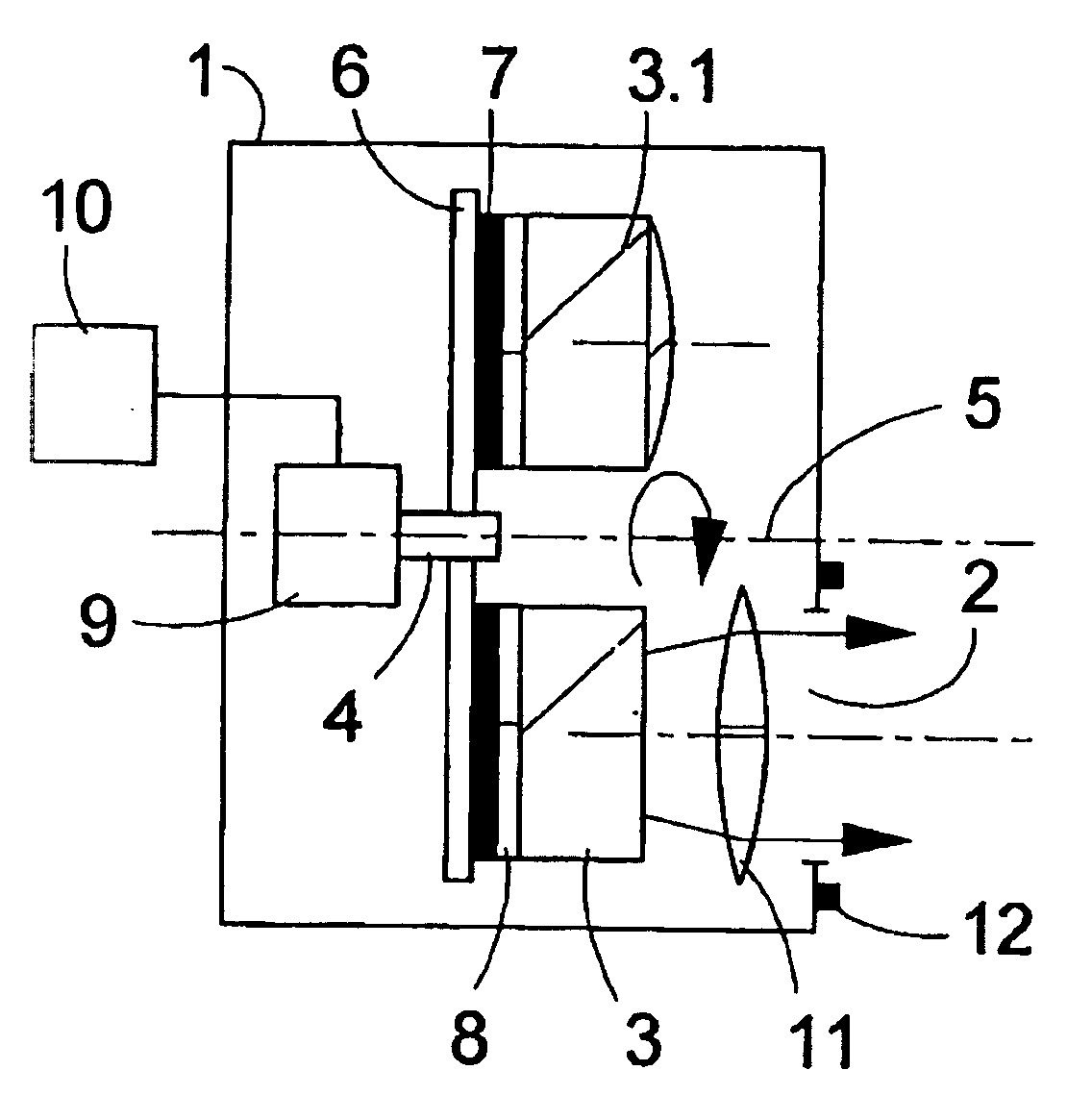
Assembly for illuminating objects with light of different wavelengths
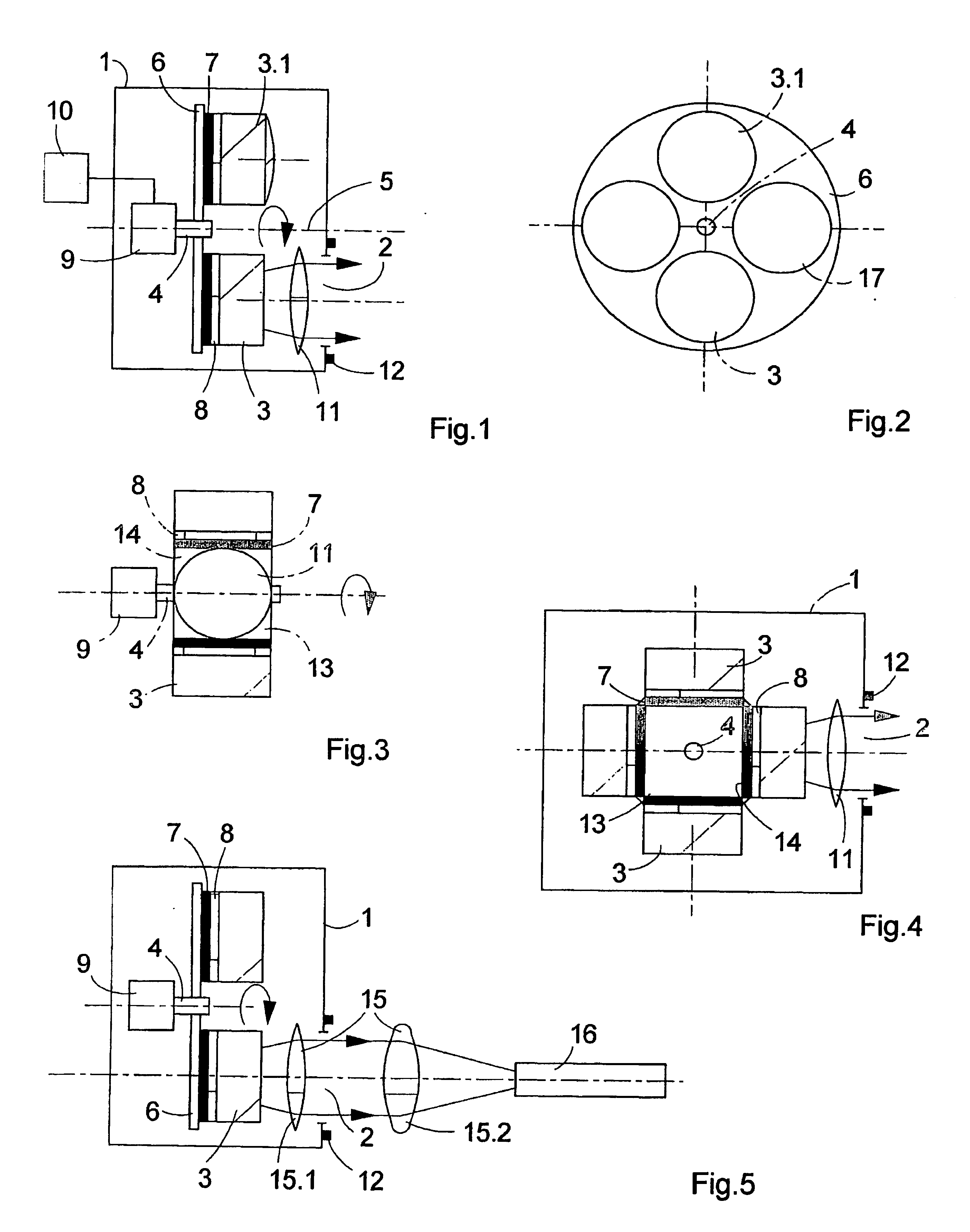
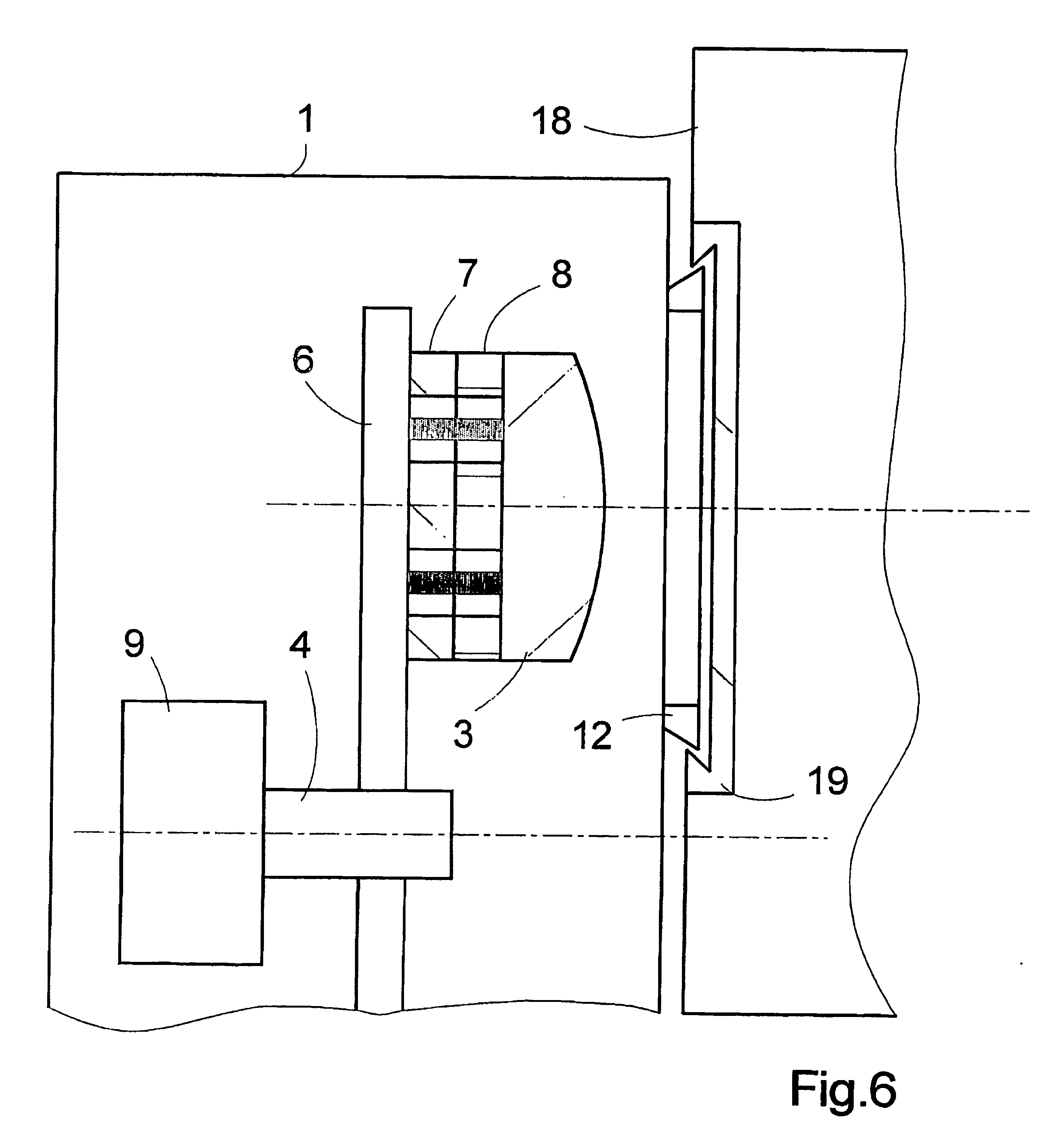
ActiveUS20060187542A1Accurate and fast positioningLighting support devicesVehicle interior lightingRotational axisAutomated microscopy
The invention relates to an assembly for illuminating objects with light of different wavelengths in microscopes, automatic microscopes and devices for fluorescent microscopy applications. Said assembly comprises LED light sources for illuminating the objects, which are positioned in the illumination beam path of the microscope or device. A receiving element (6; 13) that can be rotated about a rotational axis (5) is provided with respective fixing elements (7) for at least one LED (3; 3.1). The receiving device (6; 13) is situated in a housing (1) that can be placed on or positioned in the device housing (18). A drive unit (9) for the defined adjustment of the receiving device (6; 13) is provided in such a way that the LED (3; 3.1) can be positioned in front of a light emission opening of the housing (1) with the respective focal point wavelength that is required for measuring and / or observation purposes.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
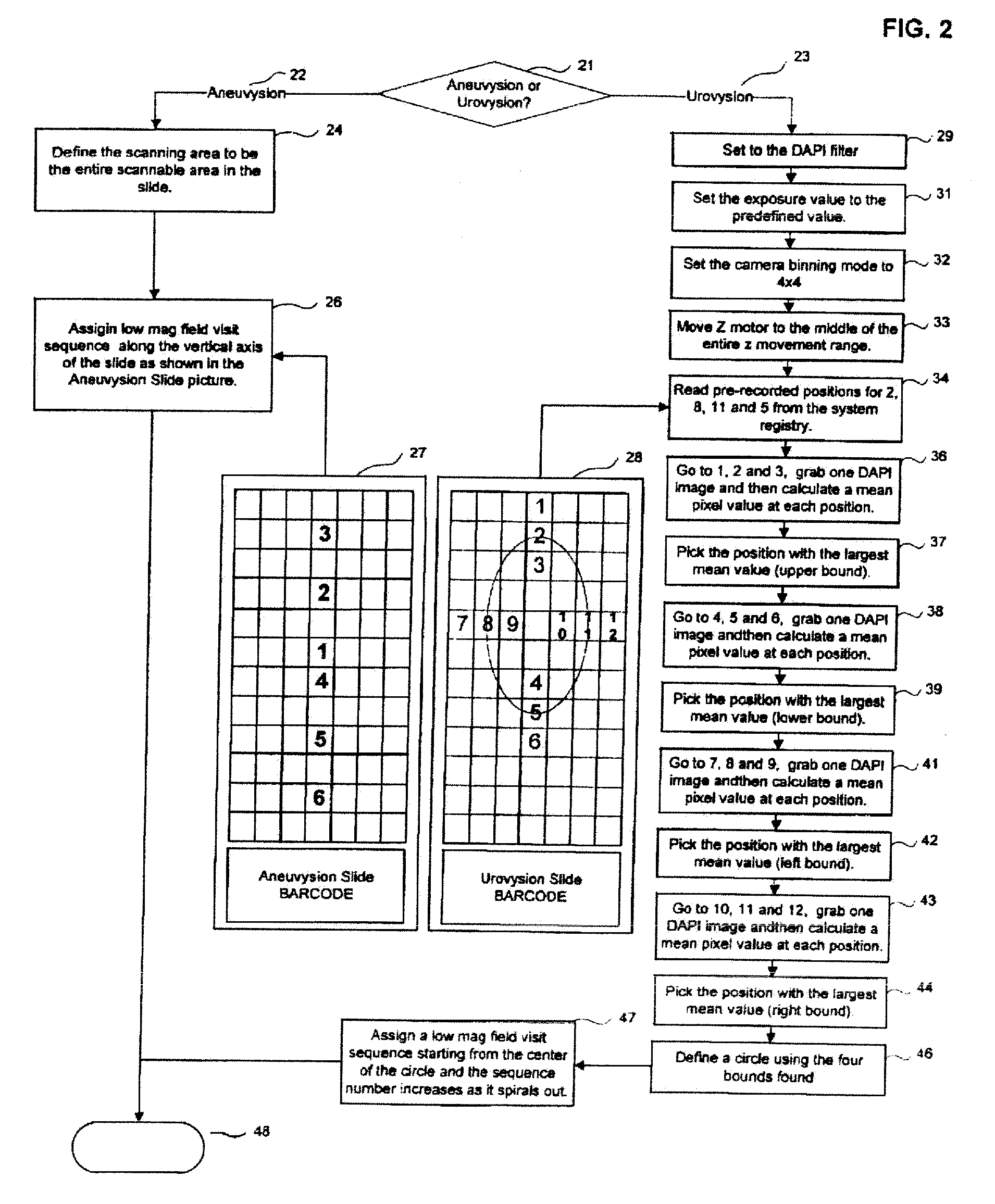
Automated Detection of Cell Colonies and Coverslip Detection Using Hough Transforms
The present invention provides methods and systems for automatic detection of the location of cell colonies on a specimen slide, in particular under the coverslip of a specimen slide. Slide scanning can be performed using an automated microscope with motorized axes. The location of the colonies can be determined by image analysis, which is followed by automatically finding metaphase cells and associating them with each colony. The invention also provides an automated, Hough-transform-based method for identifying the location of the slide coverslip and, if desired, analyzing only the image area contained within the coverslip.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
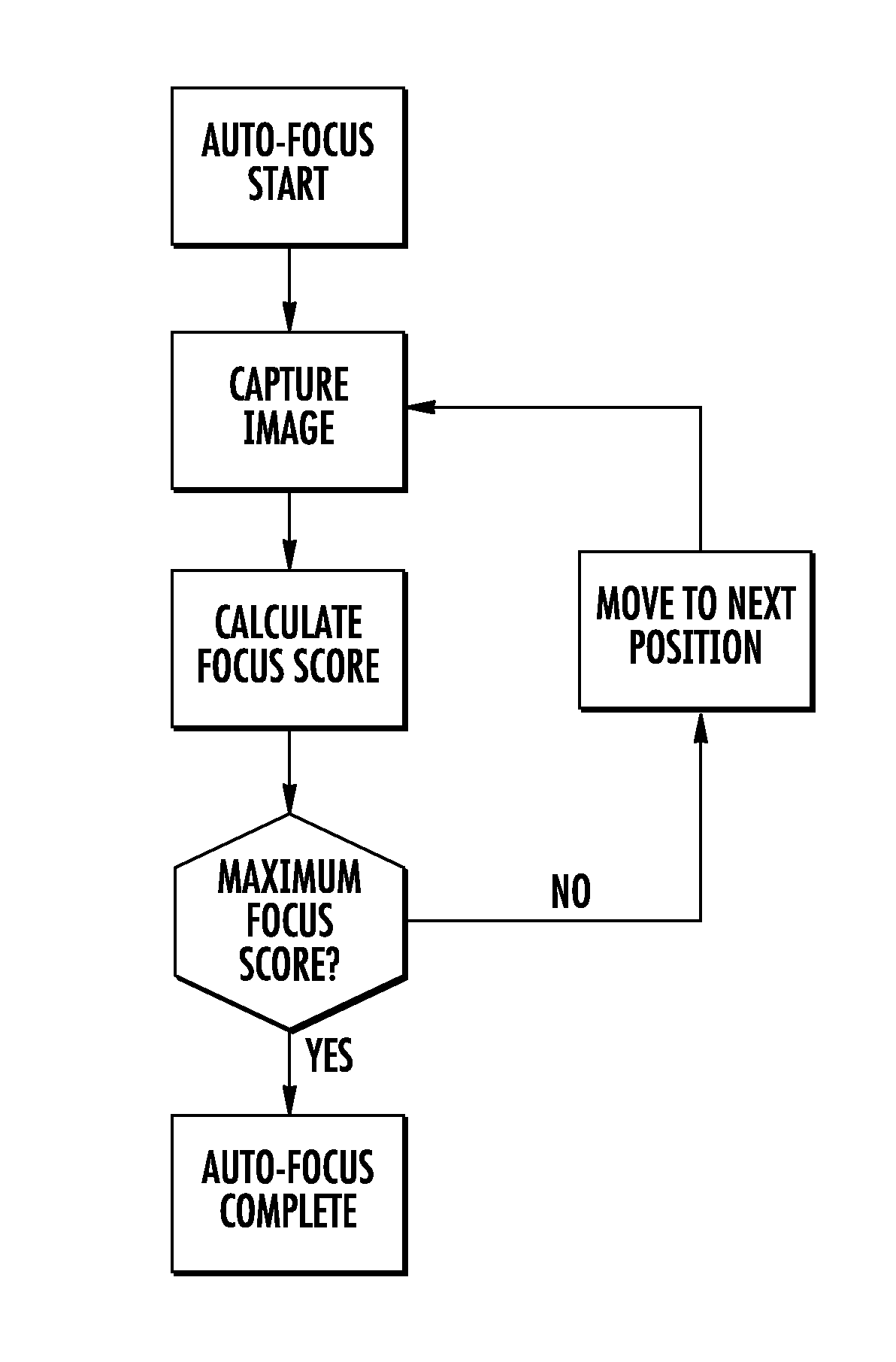
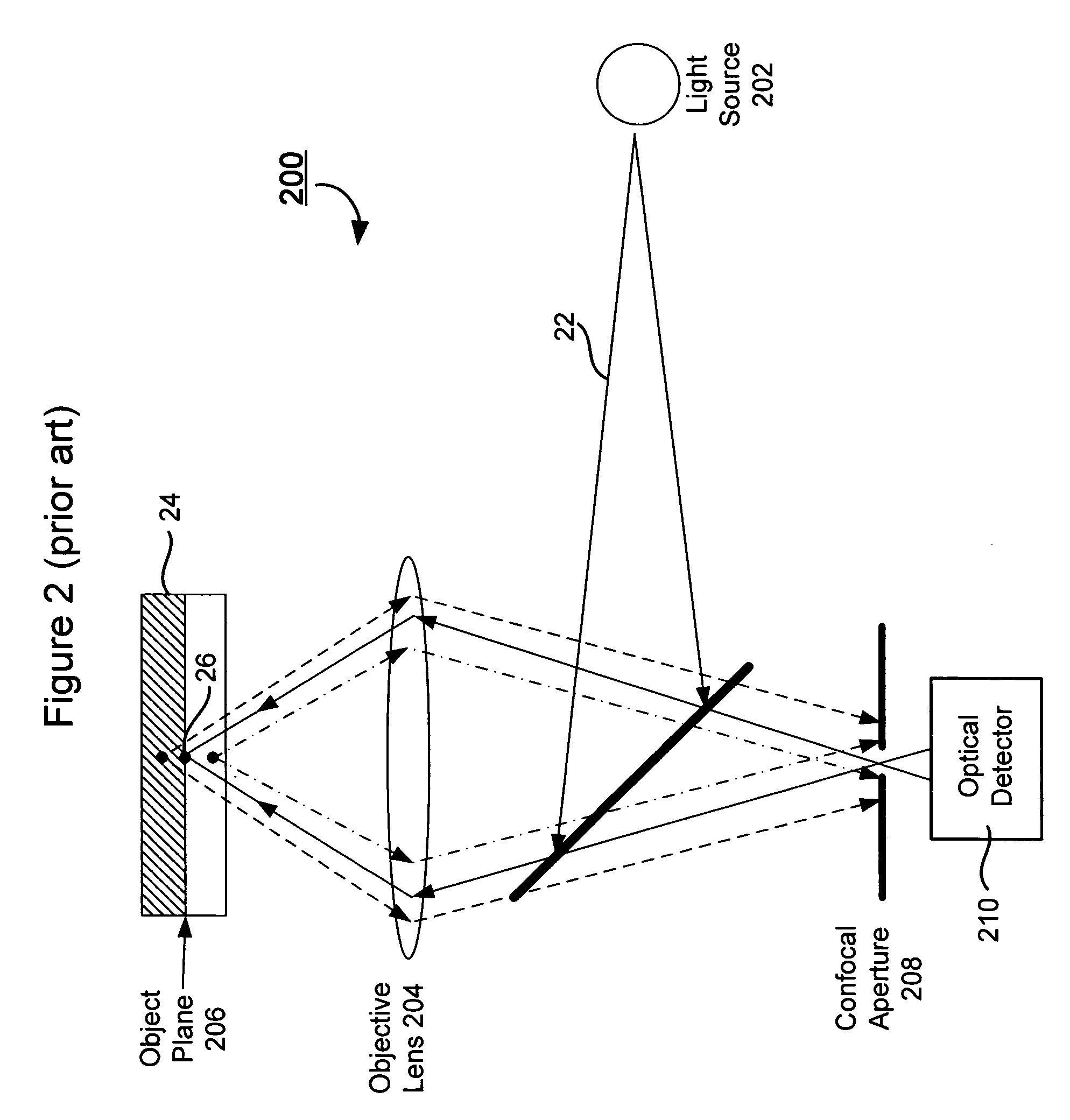
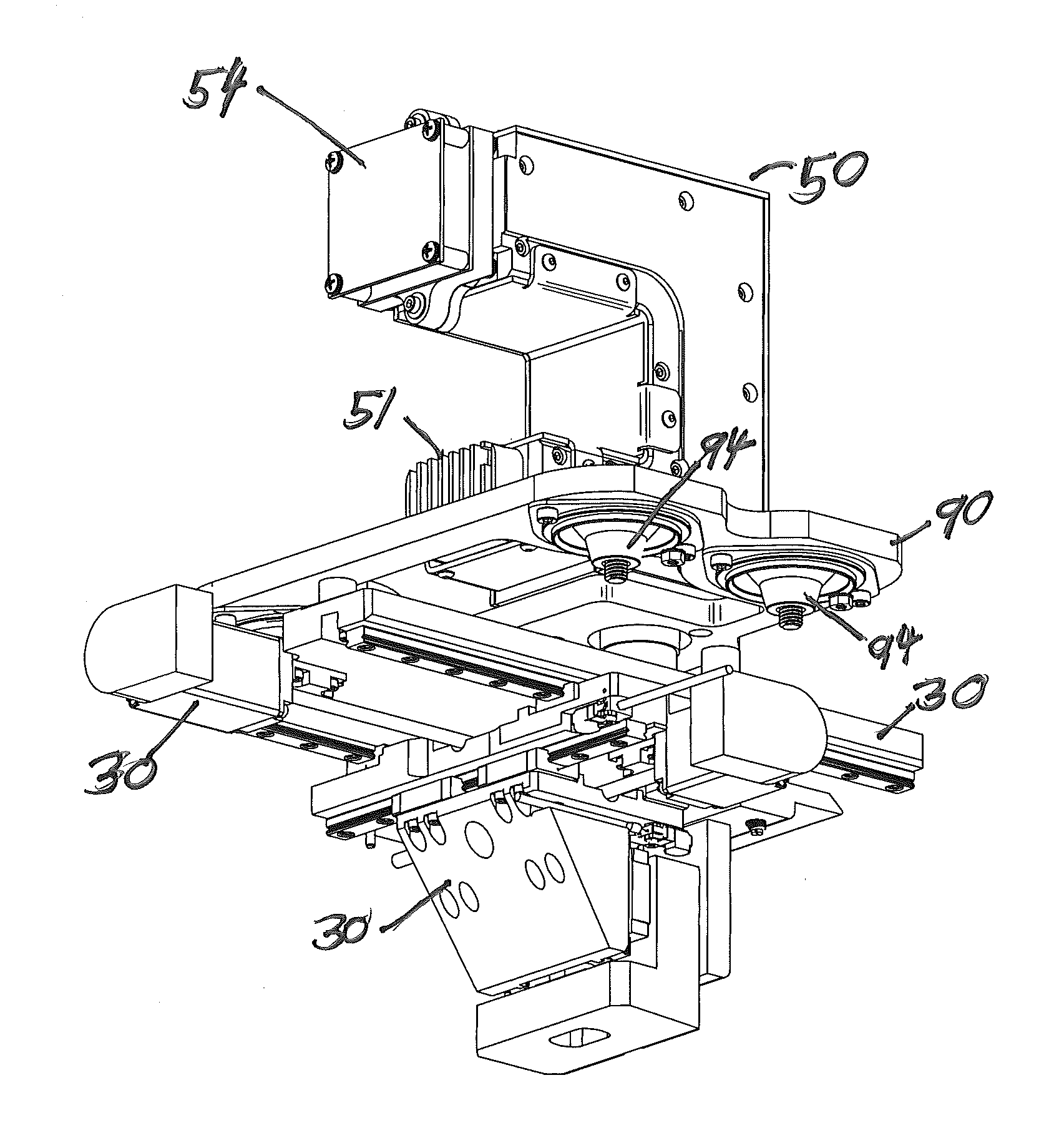
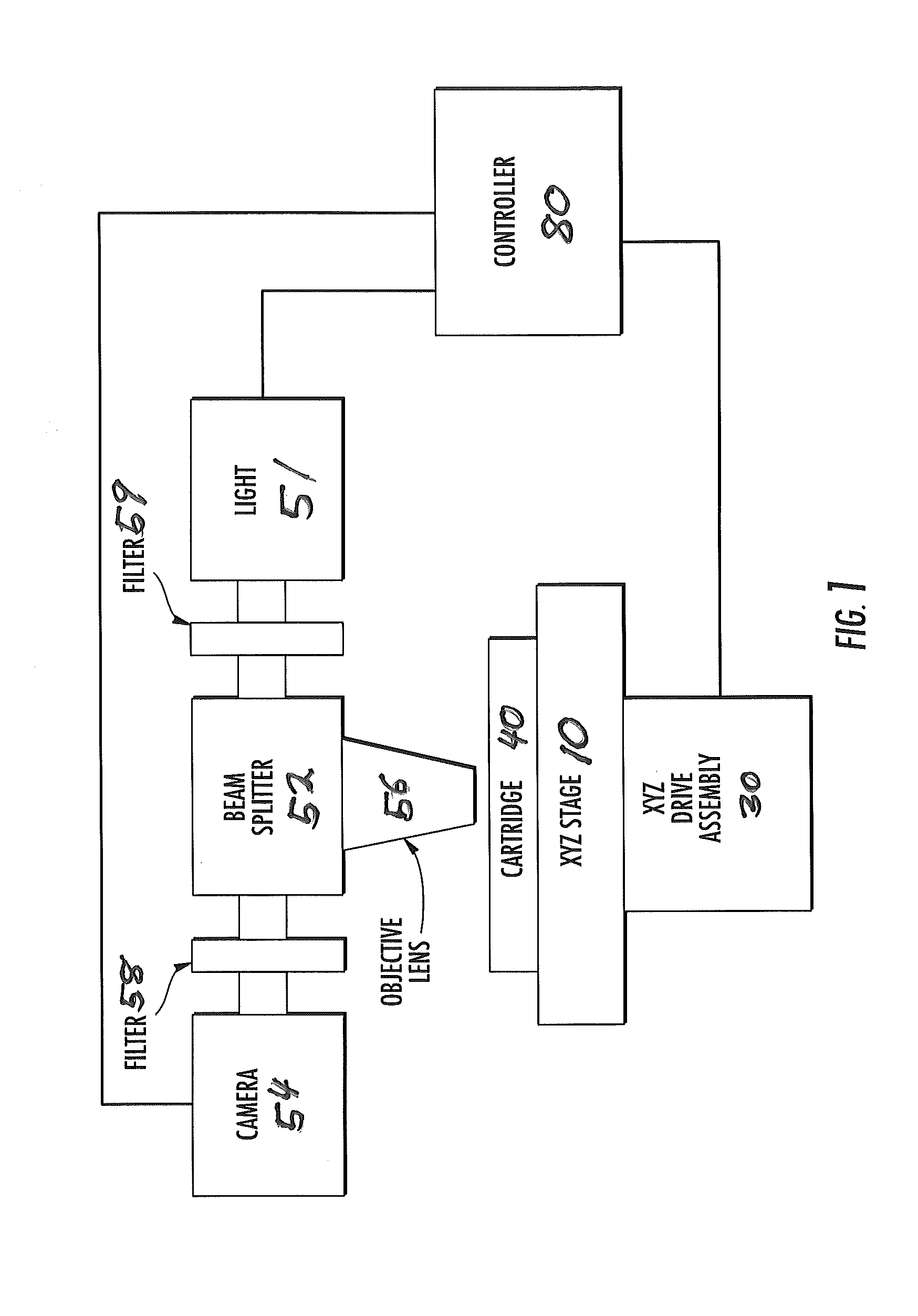
Autofocus method for imaging a biological sample and cartridge for use therein
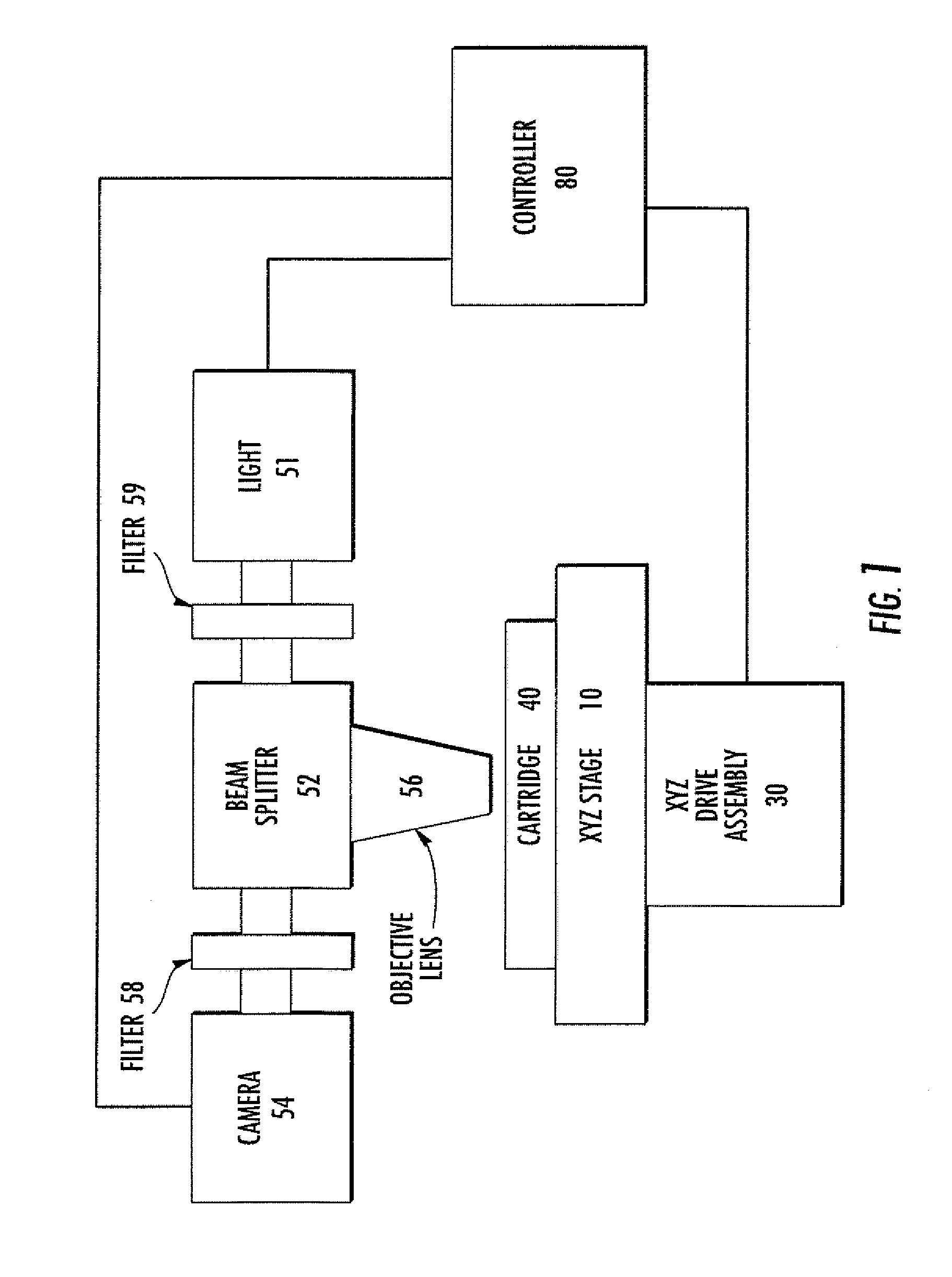
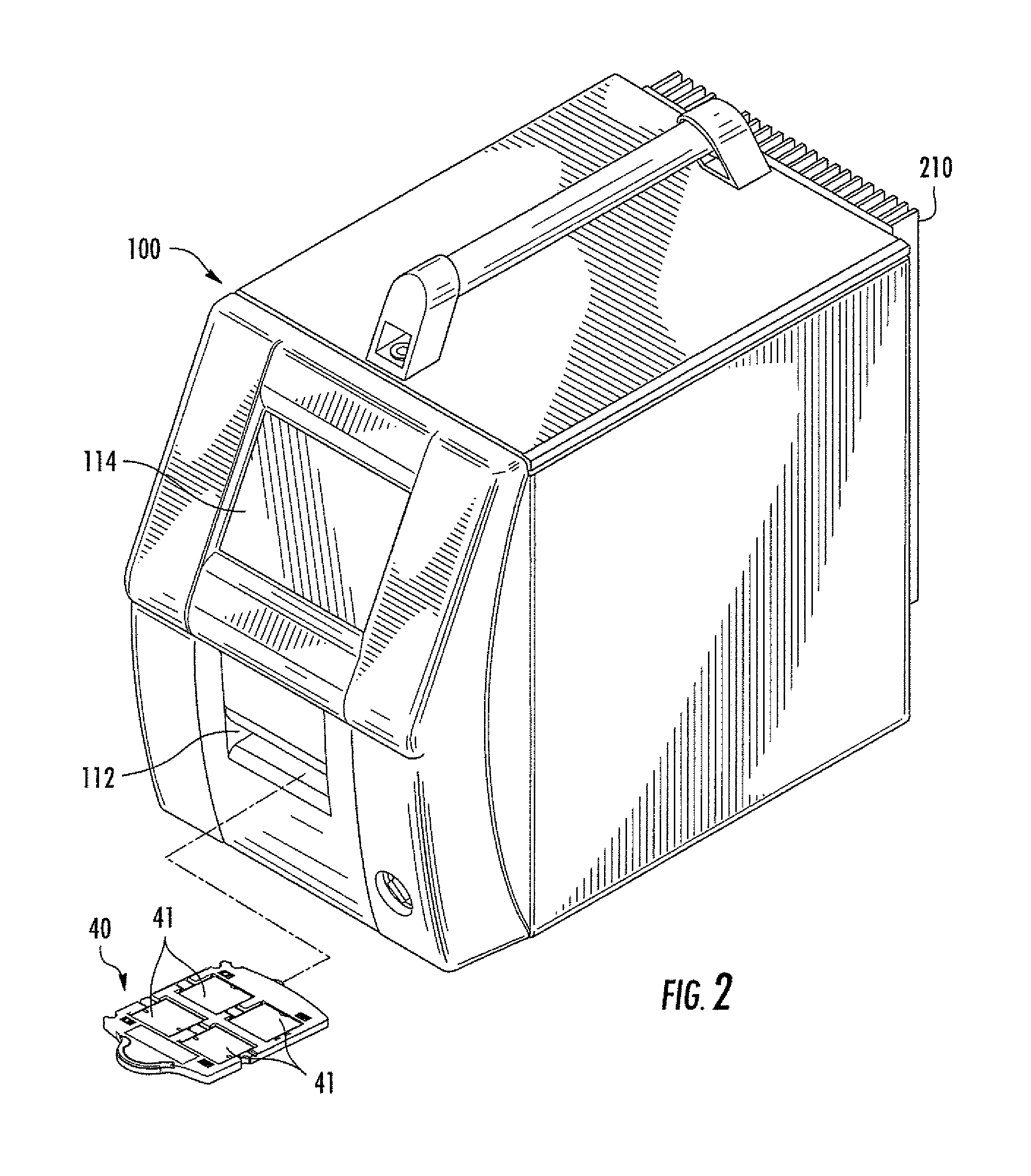
A method of automatically focusing a microscope on a specimen is carried out by capturing an image from each of a plurality of focal planes in or on said specimen, calculating a focus score for each of said images, selecting the focal plane corresponding to the image having the best focus score, and then repositioning said specimen relative to said microscope so that said microscope is focused on said selected focal plane, the method includes a plurality of exogenous targets in or on said specimen, which aids in focusing in the event particular objects of interest, such as cells / pathogens that may or may not be in the sample, are not present, or are present in low numbers. Automated microscopes and microscope cartridges useful in such methods are also described, along with methods of detecting pathogens in biological samples.
Owner:ADVANCED ANIMAL DIAGNOSTICS
System and method for utilizing an autofocus feature in an automated microscope
ActiveUS7297910B2Increase speedImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansAutomated microscopyLight beam
The invention relates to a method for adjusting focus in an automated microscope. The method may comprise the steps of: providing an optical detector for image acquisition, wherein the optical detector comprises an array of sensor pixels; designating a region of interest in the array of sensor pixels to emulate a confocal aperture; directing a light beam to illuminate an object according to a predefined pattern, thereby forming an image of the illuminated pattern at the optical detector, wherein the image of the illuminated pattern substantially overlaps the designated region of interest; detecting a light intensity from sensor pixels located within the designated region of interest; and adjusting a relative focal position of an objective lens based on the detected light intensity.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Methods for Detecting Fluorescent Signals in a Biological Sample
ActiveUS20090250629A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAutomated microscopyFluorescence
Owner:IKONISYS INC
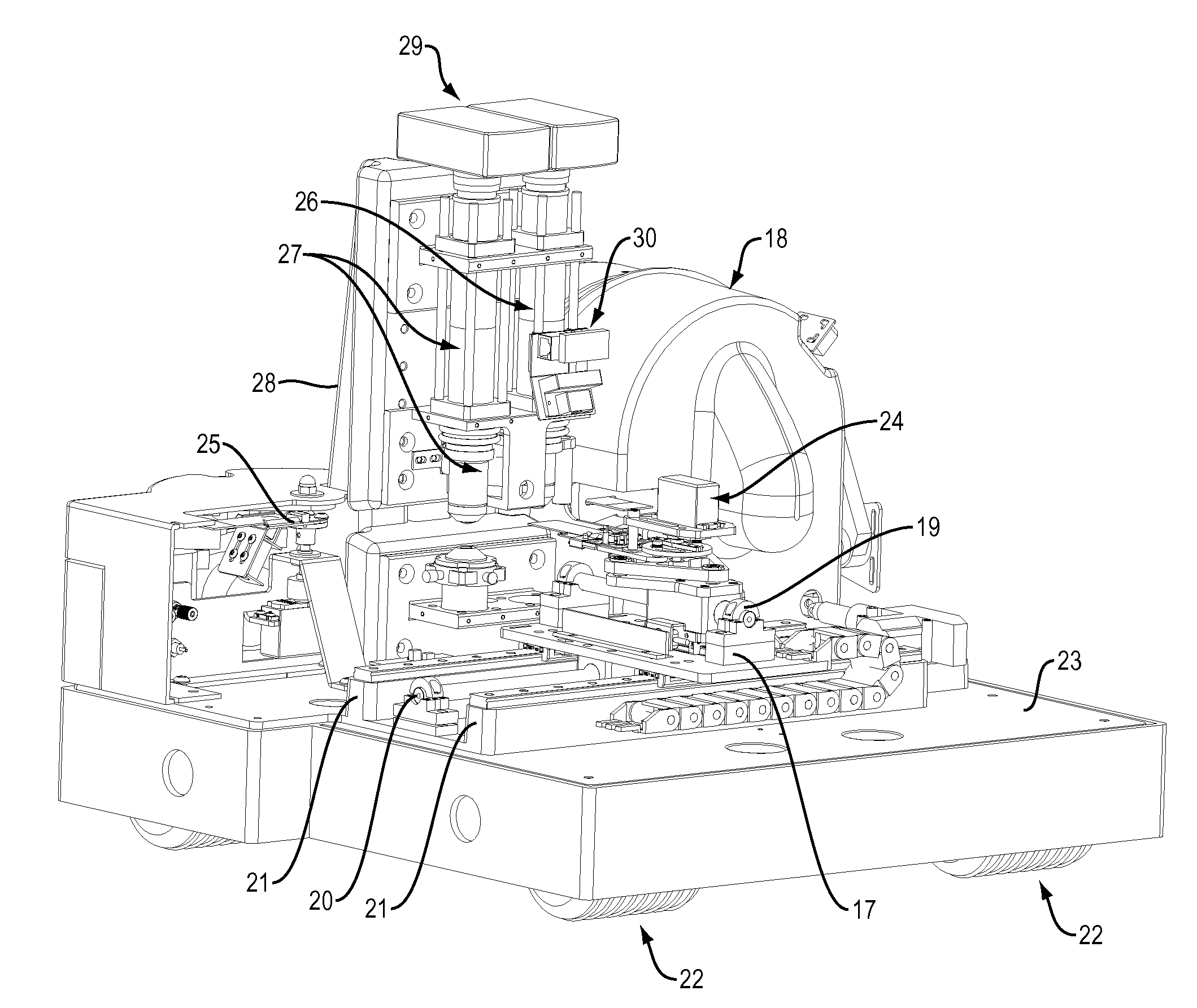
Automated microscope for blood cell analysis
ActiveUS8067245B2Low costQuality improvementWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationBlood gas analysisRed blood cell sample
An apparatus and method of automated blood cell analysis uses technologies from other systems to create a new, robust, improved type of automated microscope, which uses electronic motors and a closed loop control system to minimize ambient factors, such as jarring and temperature changes. Pre-stained blood smear slides are first coated with a thin film of oil and are loaded into a carousel from which they can individually be analyzed. The slides are moved under a low magnification microscope; an optimal area of examination is determined; a focal plane map is calculated for that area, and the positions of white blood cell candidates are computed. The slide is then moved under a high power microscope where a refined focal plane map is computed and the individual white blood cell candidates are imaged. The cells are preclassified and the images are made available for analysis by the technician. Additionally, samples of red blood cells, equivalent to what the technician would do manually, are imaged and presented to the technician for evaluation. The technician may make notes on those cells, both red and white blood cells and archive them.
Owner:MEDICA CORP
Microscope enclosure system
ActiveUS20090116101A1Fault location by increasing destruction at faultMicroscopesAutomated microscopyEngineering
Owner:IKONISYS INC
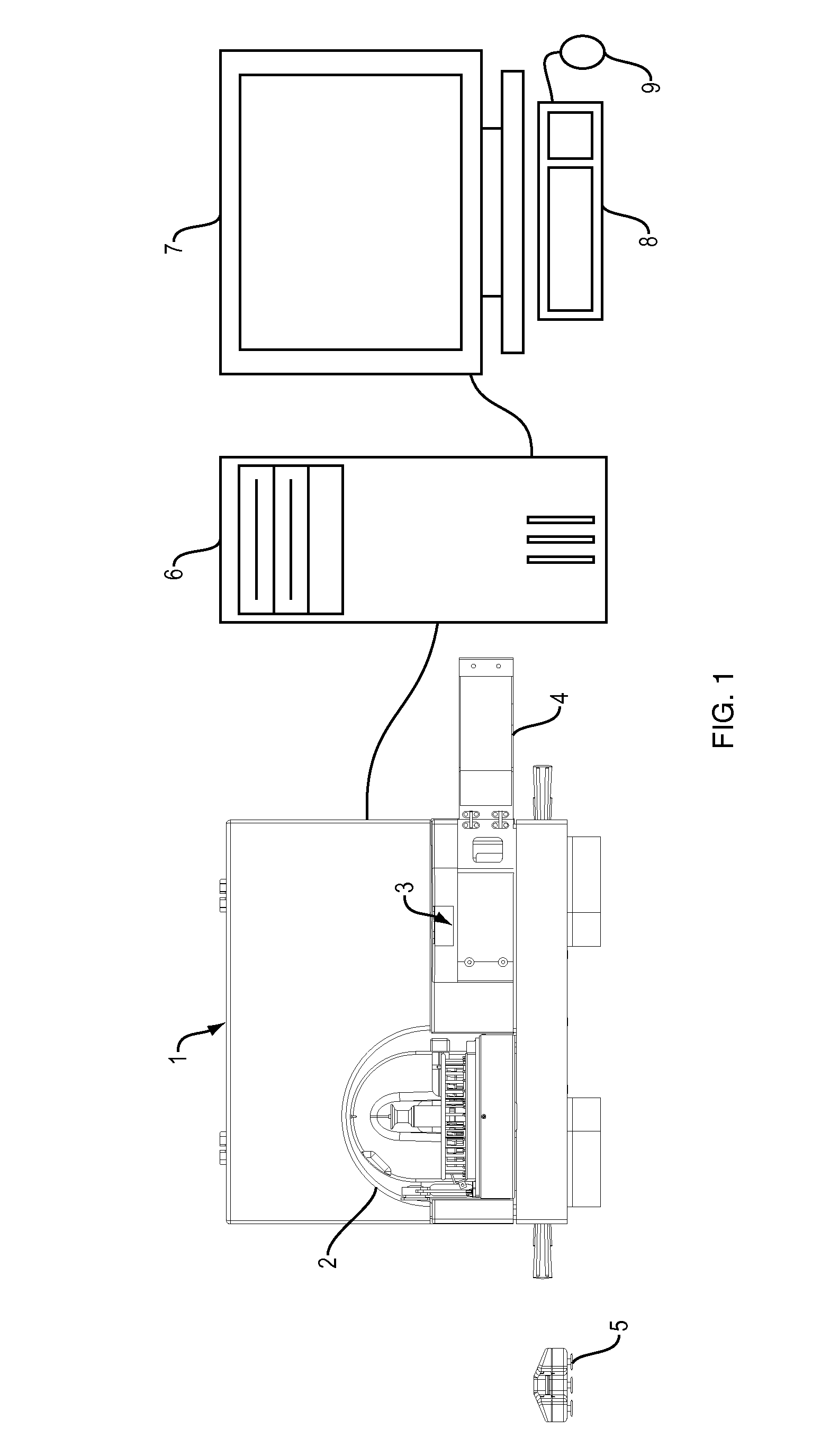
Diagnostic apparatus
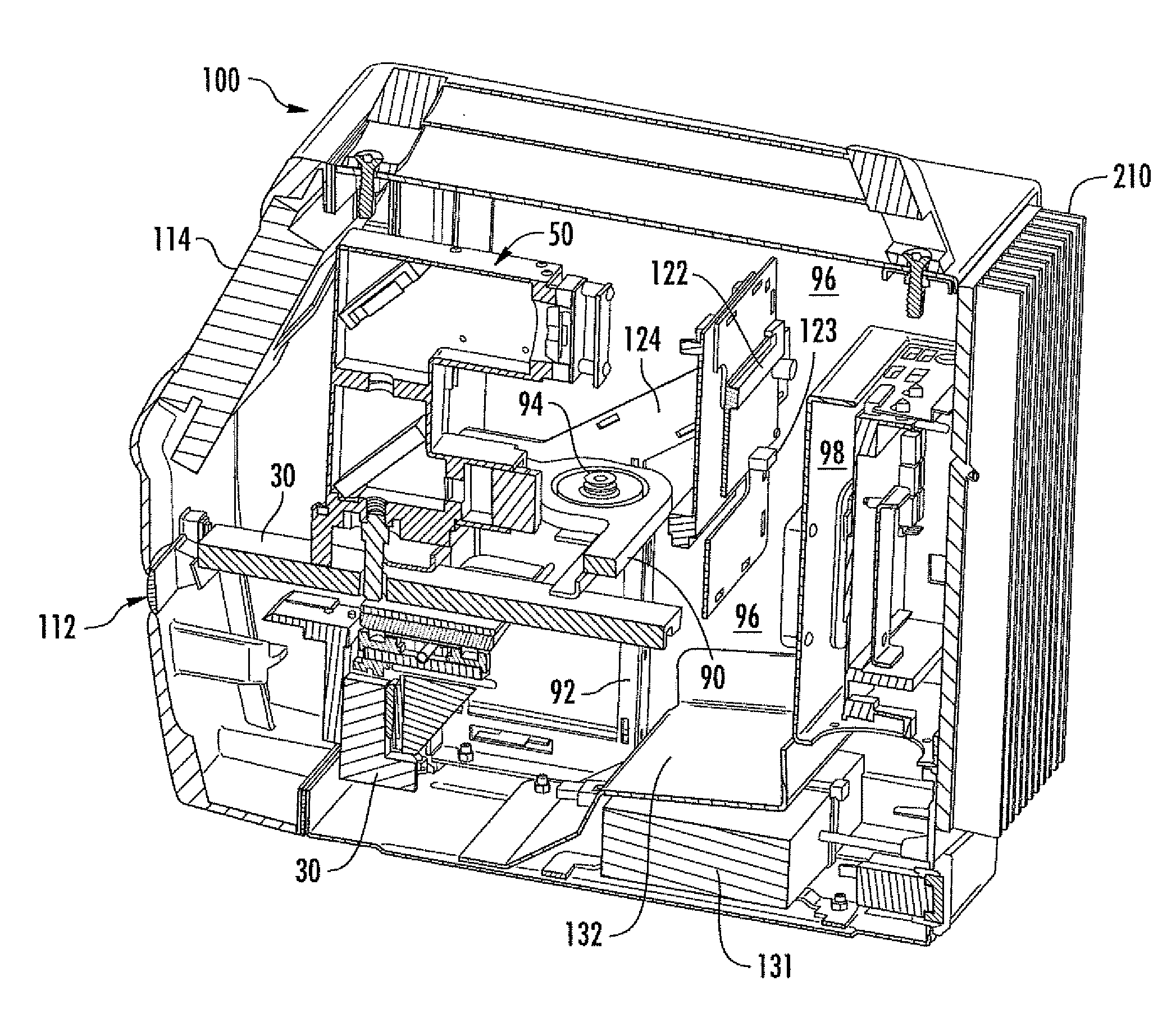
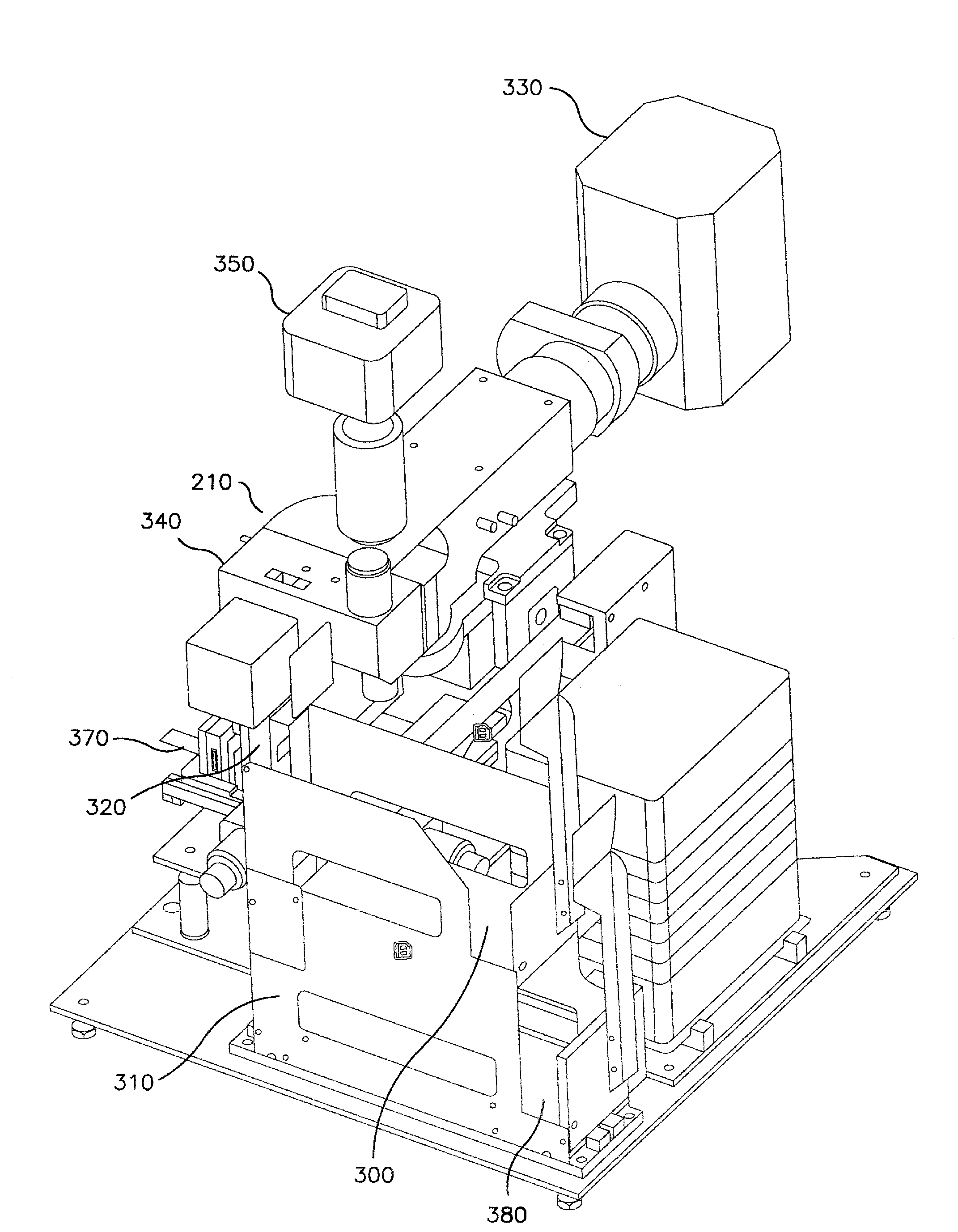
An automated microscope apparatus comprises an outer housing having an external wall; optionally but preferably an internal wall in the housing configured to form a first compartment and a separate second compartment in the outer housing; a microscope assembly in the housing (preferably in the first compartment); a microprocessor in the housing (preferably in the second compartment), and (optionally but preferably) a heat sink mounted on the housing external wall, preferably adjacent the second compartment, with the microprocessor thermally coupled to said heat sink and operatively associated with the microscope assembly. Systems and methods employing the same are also described, along with component parts thereof.
Owner:ADVANCED ANIMAL DIAGNOSTICS
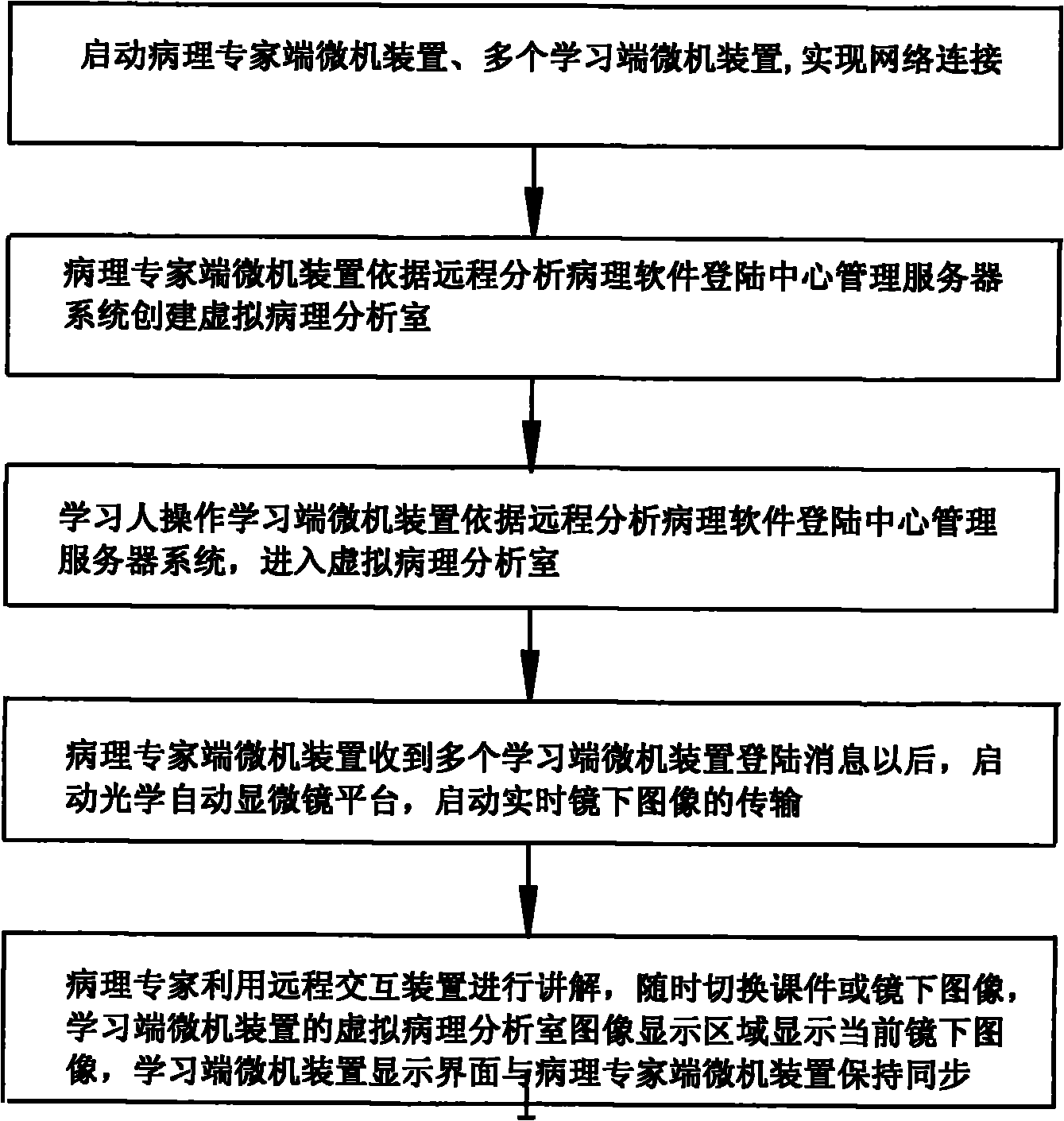
Method for remotely analyzing pathological section
ActiveCN102253922ARealize remote controlActive casual browsingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAutomated microscopyRemote analysis
The invention relates to a method for remotely analyzing a pathological section. A person who participates in analysis performs information communication according to a remote network platform; the remote network platform comprises a central management server system, a pathological expert-side microcomputer device, a microscope holding-side microcomputer device and a visit-side microcomputer device; and the central management server system, the pathological expert-side microcomputer device, the microscope holding-side microcomputer device and the visit-side microcomputer device are in a wide area network environment and realize network connection, so broadcast surface transmission can be realized, real-time medical images are transmitted, an automatic microscope platform can be controlledremotely, and interactive voice communication is realized on the basis of sharing the real-time medical images. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that: the mailing of the pathological section is eliminated; a patient does not need to go to different cities; difficulty in finding an expert can be eliminated; efficiency is improved; the precious time of the expert is saved; and the significance of pathology in the field of medicine can be remarkably improved.
Owner:陈生
Automated microscope slide read system
InactiveUS20070242349A1Improve efficiencySamplingLaboratory glasswaresMicroscope slideAutomated microscopy
Owner:IKONISYS INC
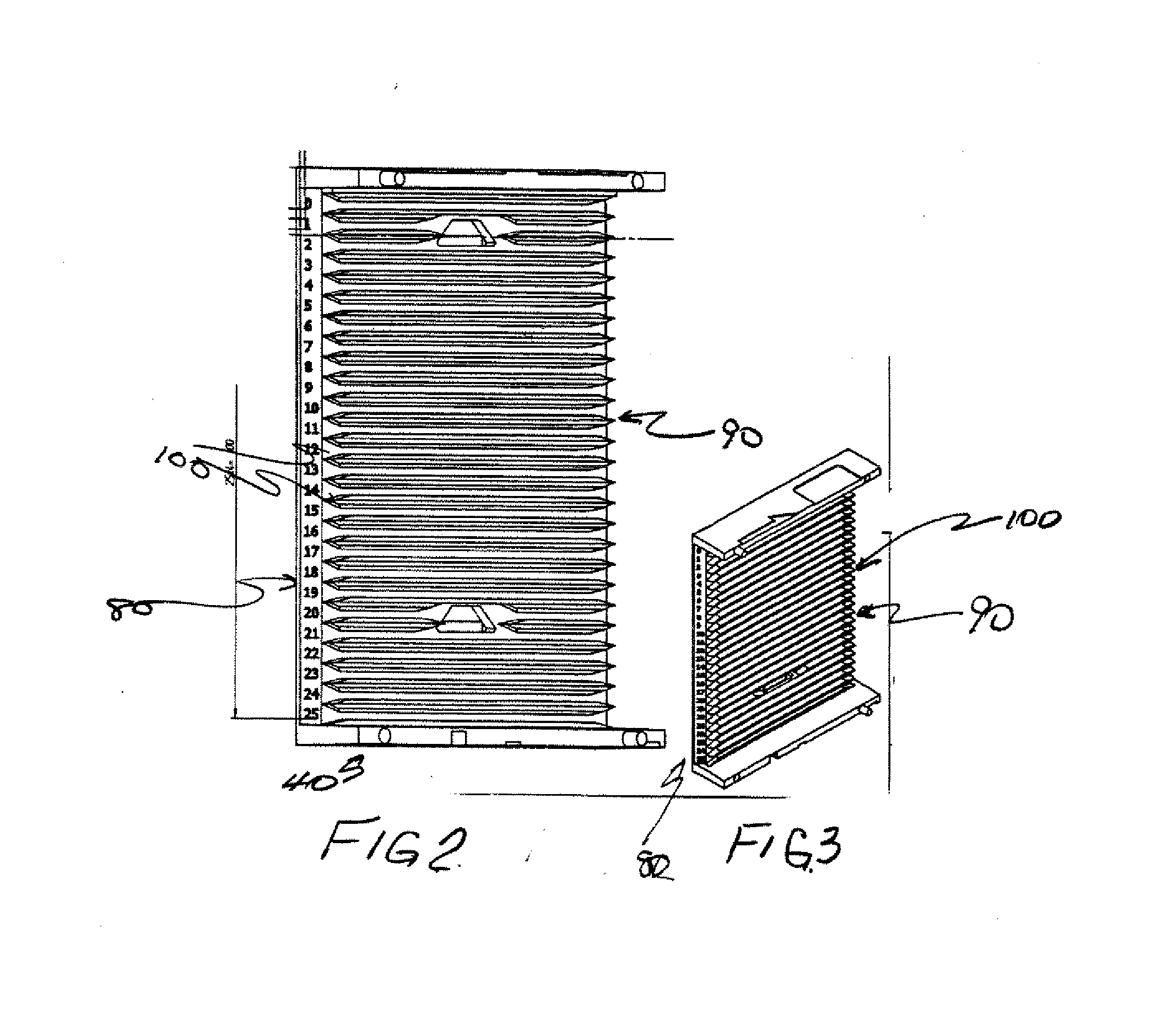
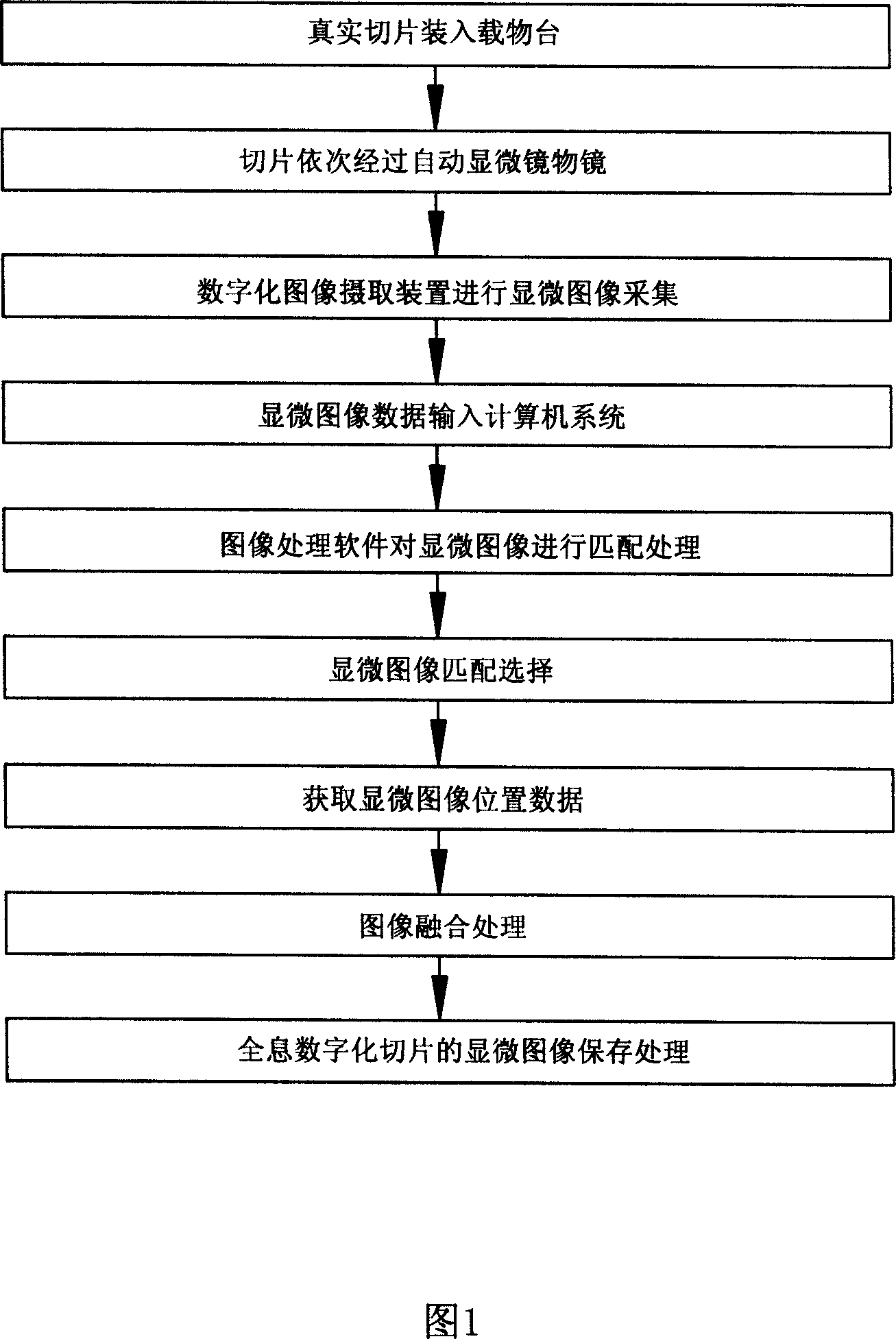
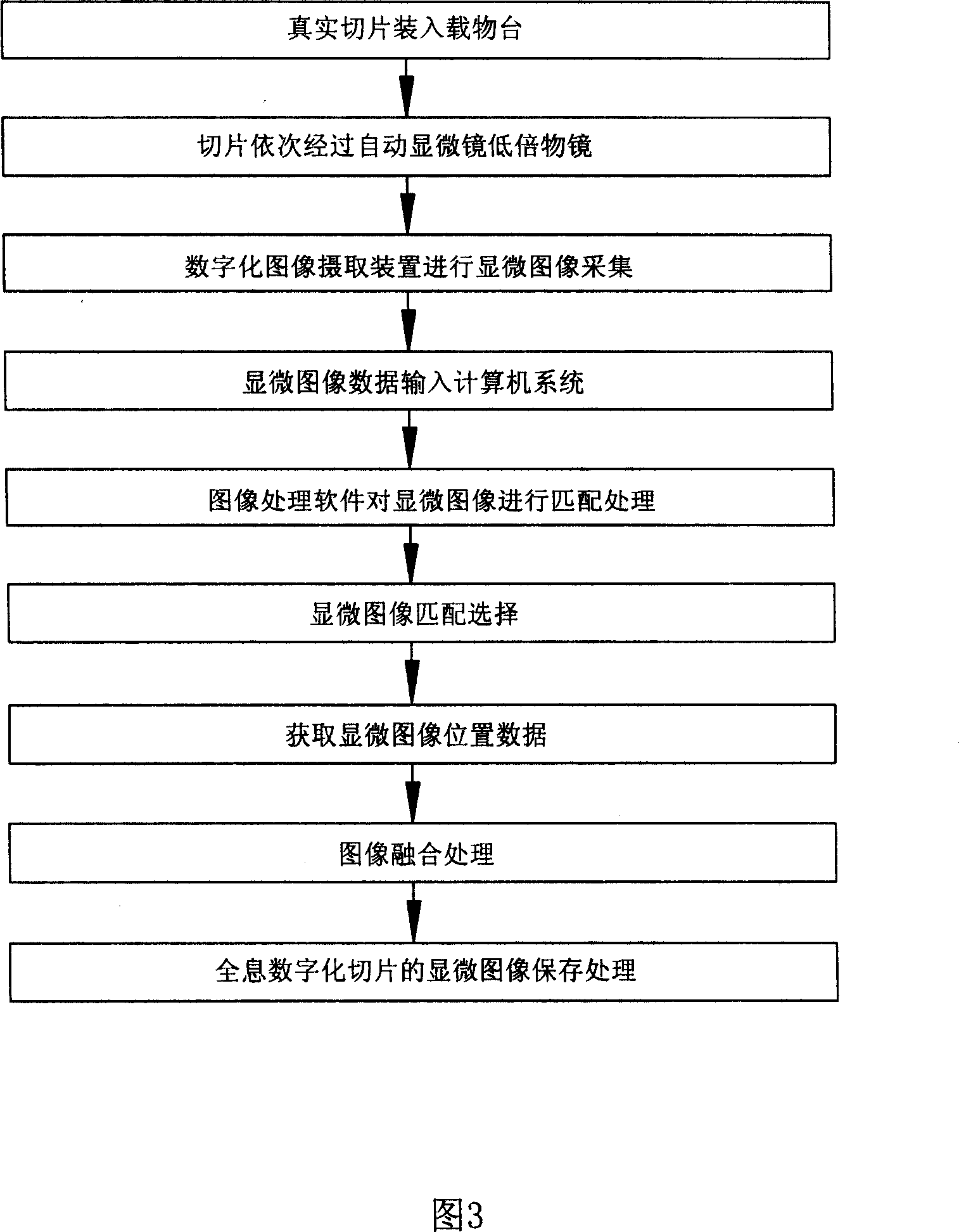
Method for preparing microscopic image of holographic digitalized sliced sheet
ActiveCN101093280AIncrease storage capacityIncrease repeatabilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMicroscopic imageMatch treatment
A method for preparing microscopic image of hologram digitalized slab includes using automatic microscope to collect microscopic image information of a slab to generate sequenced multiple microscopic image unit data, carrying out matching treatment on relevant position between each two adjacent microscopic image units to obtain position data of each microscopic image unit, carrying out fusing treatment on overlapped portion between each two adjacent microscopic image units according to visual habits of human eyes for generating microscopic image of hologram digitalized slab then compressing said image blocking-store it in image file.
Owner:陈生
Diagnostic apparatus
ActiveUS20140009596A1Image analysisDigital data processing detailsAutomated microscopyBiomedical engineering
An automated microscope apparatus, comprises an outer housing having an external wall; optionally but preferably an internal wall in said housing, and configured to form a first compartment and a separate second compartment in said outer housing; a microscope assembly in said housing, preferably in said first compartment; and a microprocessor in said housing, preferably in said second compartment; and optionally but preferably a heat sink mounted on said housing external wall, preferably adjacent said second compartment, with said microprocessor thermally coupled to said heat sink and operatively associated with said microscope assembly.
Owner:ADVANCED ANIMAL DIAGNOSTICS
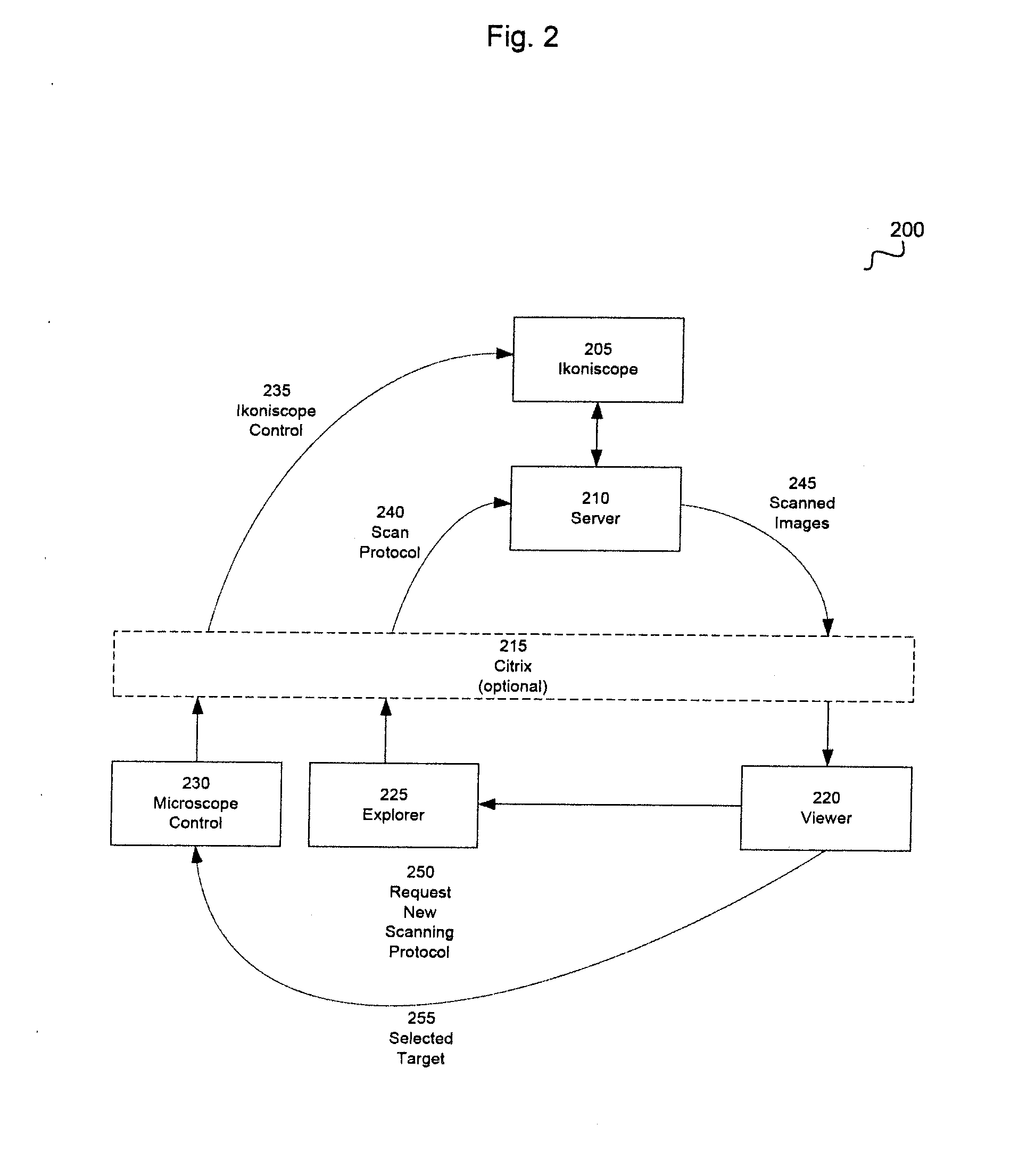
System and method for remote control of a microscope
InactiveUS20140049634A1Improve integrityColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsAutomated microscopyRemote control
Owner:IKONISYS INC
Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood with an automated scanning fluorescence microscope
InactiveUS20090123054A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningAutomated microscopyCirculating cancer cell
An automated, highly sensitive, specific and potentially quantitative detection method using an automated microscope for identifying and enumerating rare cancer cells in blood and other fluids.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
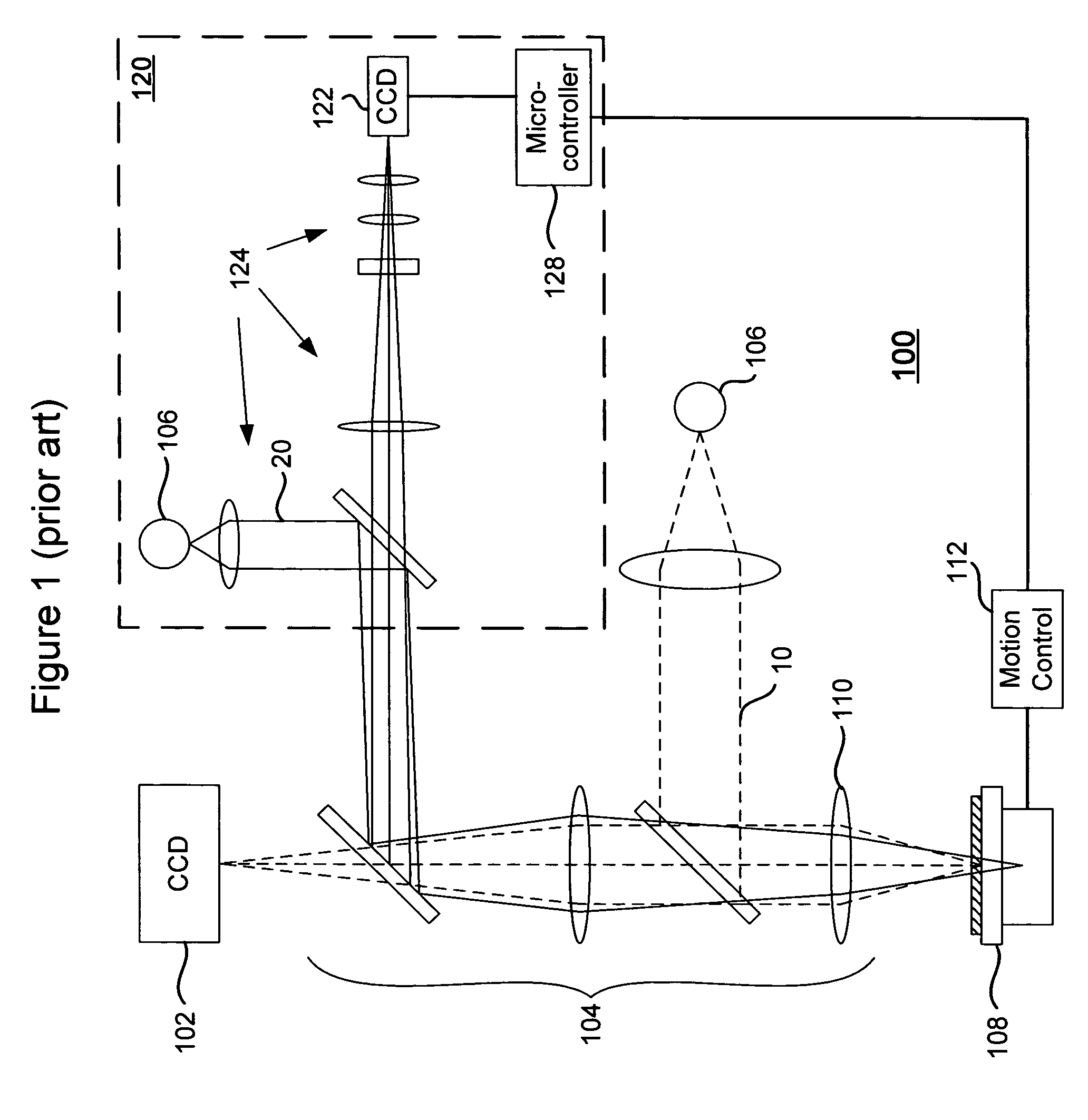
Dynamic scanning automatic microscope and method
An automatic microscope is disclosed which incorporates dynamic scanning of the microscope slide and other interchangeable optical path components.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
Microscope enclosure system
Owner:IKONISYS INC
Automated detection of cell colonies and coverslip detection using hough transforms
The present invention provides methods and systems for automatic detection of the location of cell colonies on a specimen slide, in particular under the coverslip of a specimen slide. Slide scanning can be performed using an automated microscope with motorized axes. The location of the colonies can be determined by image analysis, which is followed by automatically finding metaphase cells and associating them with each colony. The invention also provides an automated, Hough-transform-based method for identifying the location of the slide coverslip and, if desired, analyzing only the image area contained within the coverslip.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Automatic focusing method for automatic microscope
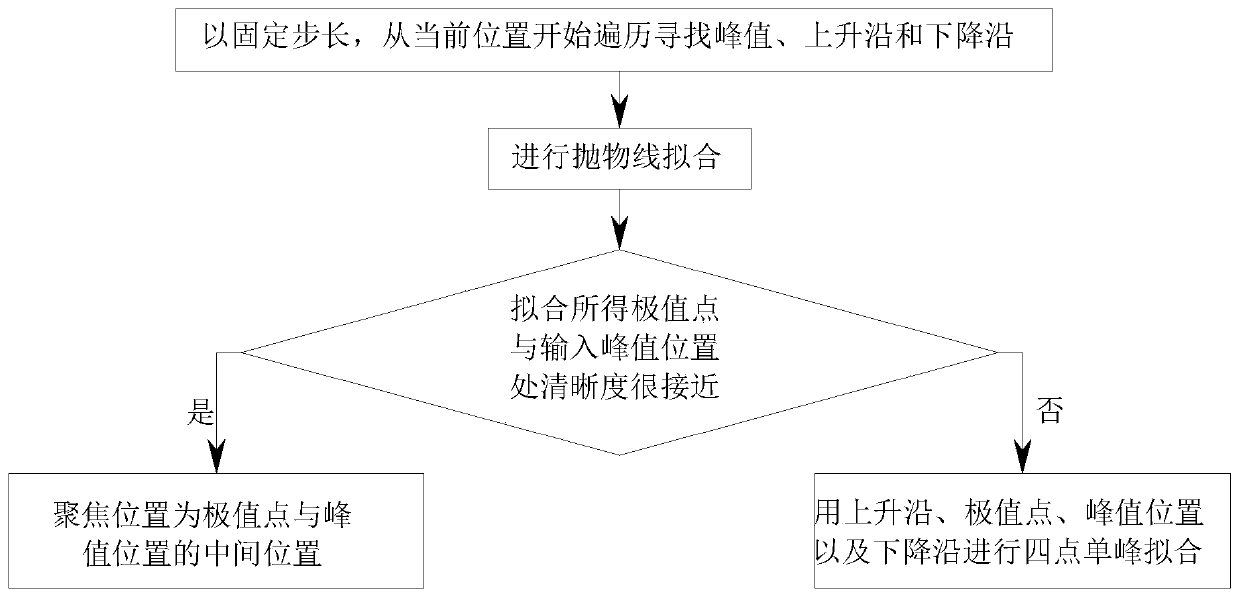
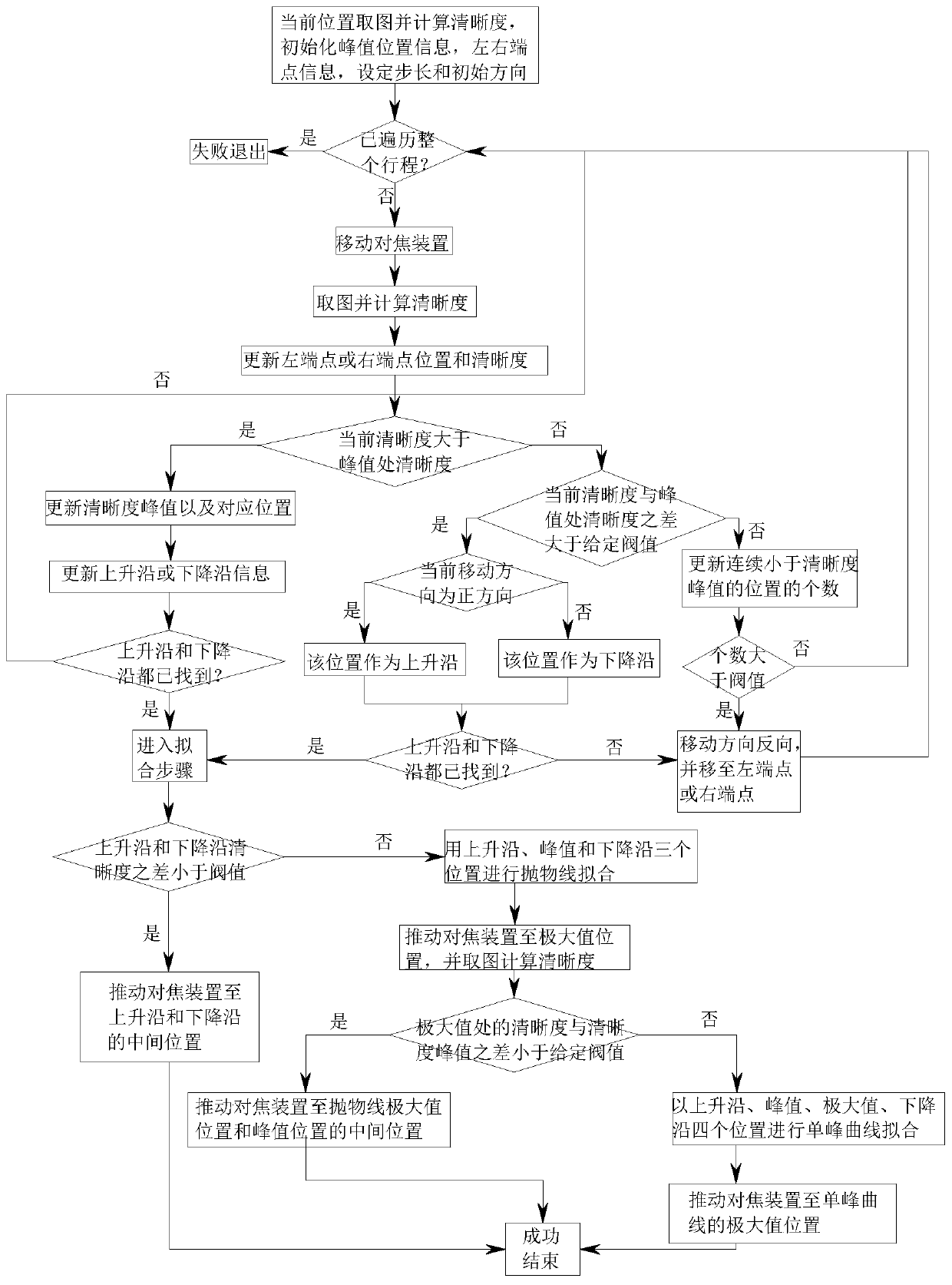
ActiveCN110865453AFast focusingFix too many searchesMicroscopesMountingsAutomated microscopyEngineering
The invention discloses an automatic focusing method for an automatic microscope. The method comprises the following steps of: a preprocessing step of moving a focusing device on the automatic microscope onto a slide, acquiring an image of a current position, calculating definition of the image, setting the definition and a position of the current position as initial definition and position,, andsetting a preset step length and an initial direction; a searching step of searching a peak value with the preset step length and acquiring a rising edge and a falling edge; and a fitting step of fitting the peak value and the rising edge as well as the falling edge, finding out an optimal focal plane position and moving the focusing device on the automatic microscope to the position so as to complete the focusing process. By foreground region extraction, measurement of the peak value and the rising edge as well as the falling edge, parabola fitting and four-point single-peak fitting, the automatic focusing method for the automatic microscope solves the problems that a conventional automatic focusing method is insufficient in focusing speed and accuracy and particularly is lower in accuracy when focusing is carried out on a view field with an ultralow contrast or an ultra few foreground contents.
Owner:MOTIC XIAMEN MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS SYST +1
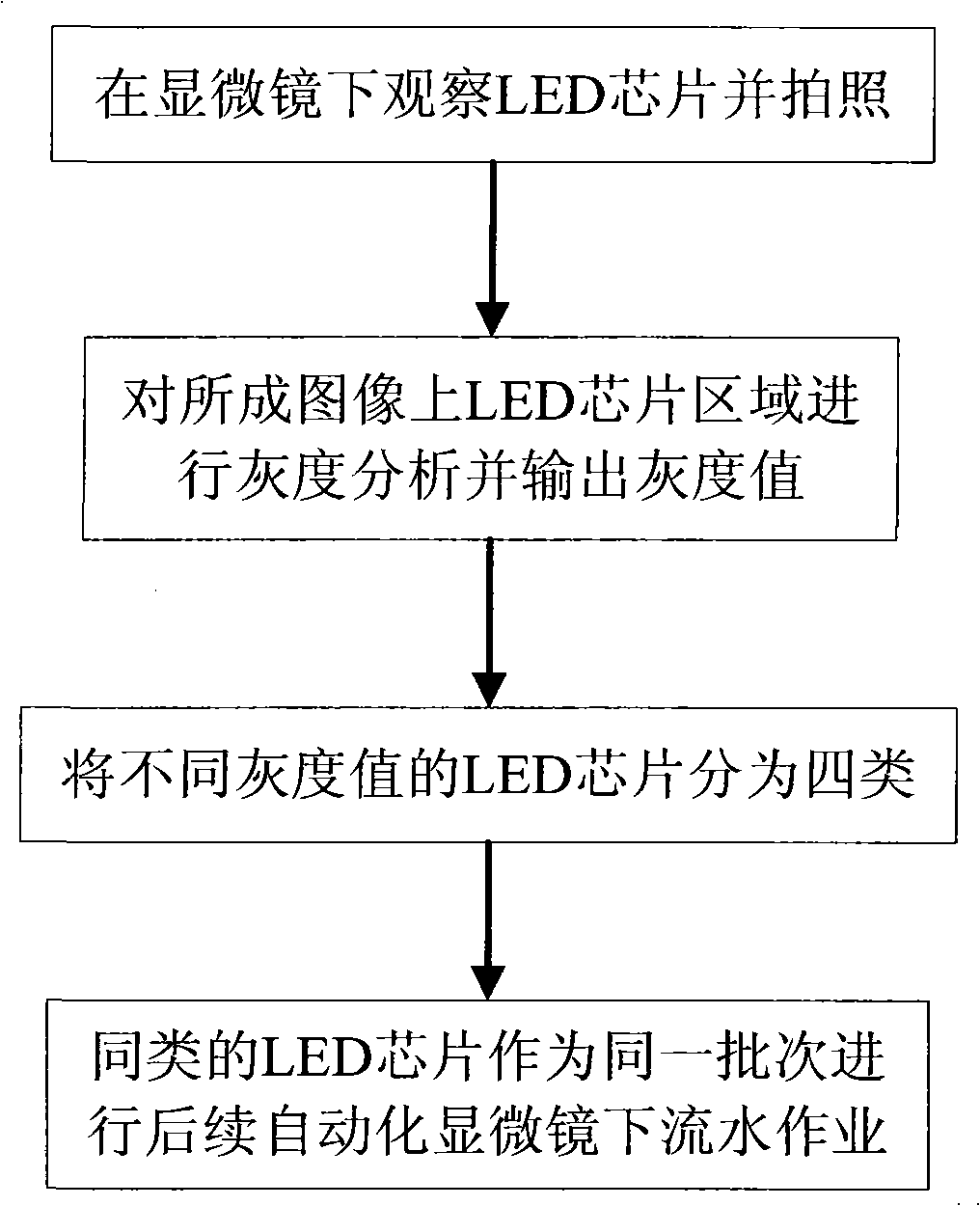
Surface roughness recognizing and classifying method for LED chip
ActiveCN101335226AUniform brightnessAvoid misuseSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementUsing optical meansAutomated microscopyMicroscope
The invention discloses an identification and classification method for the roughness of LED chip surfaces; the method includes the following steps: (1) the LED chip is put under a microscope to observe p electrode area and N electrode area in the LED ship and the microscopic images are photographed; (2) a gray scale identification system is utilized to identify the gray scale for the P electrode area and N electrode area of the LED chip in the microscopic images and the value of gray scale is output; (3) the observed LED chips are classified into four types; (4) when an operation under microscope is necessary, LED chips of the same types classified according to the step (3) are deemed as the same batch and operated in the way of line production. According to the classification method of the invention, classified LED chips can be easily recognized when the chips are under automatic microscopic operation. The classification method of the invention can be used for the classification of LED chips of different surface roughness.
Owner:EPILIGHT TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com