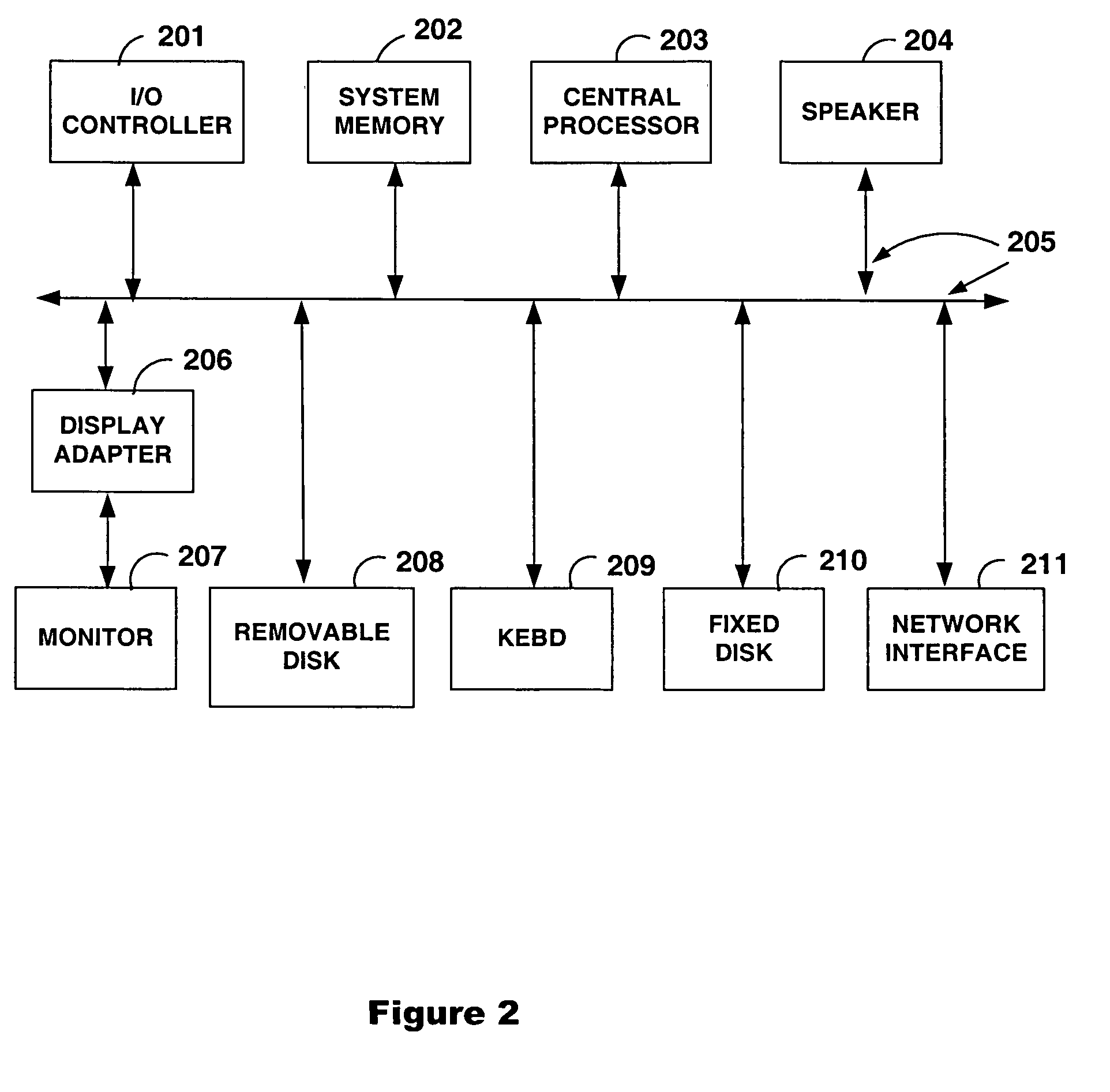
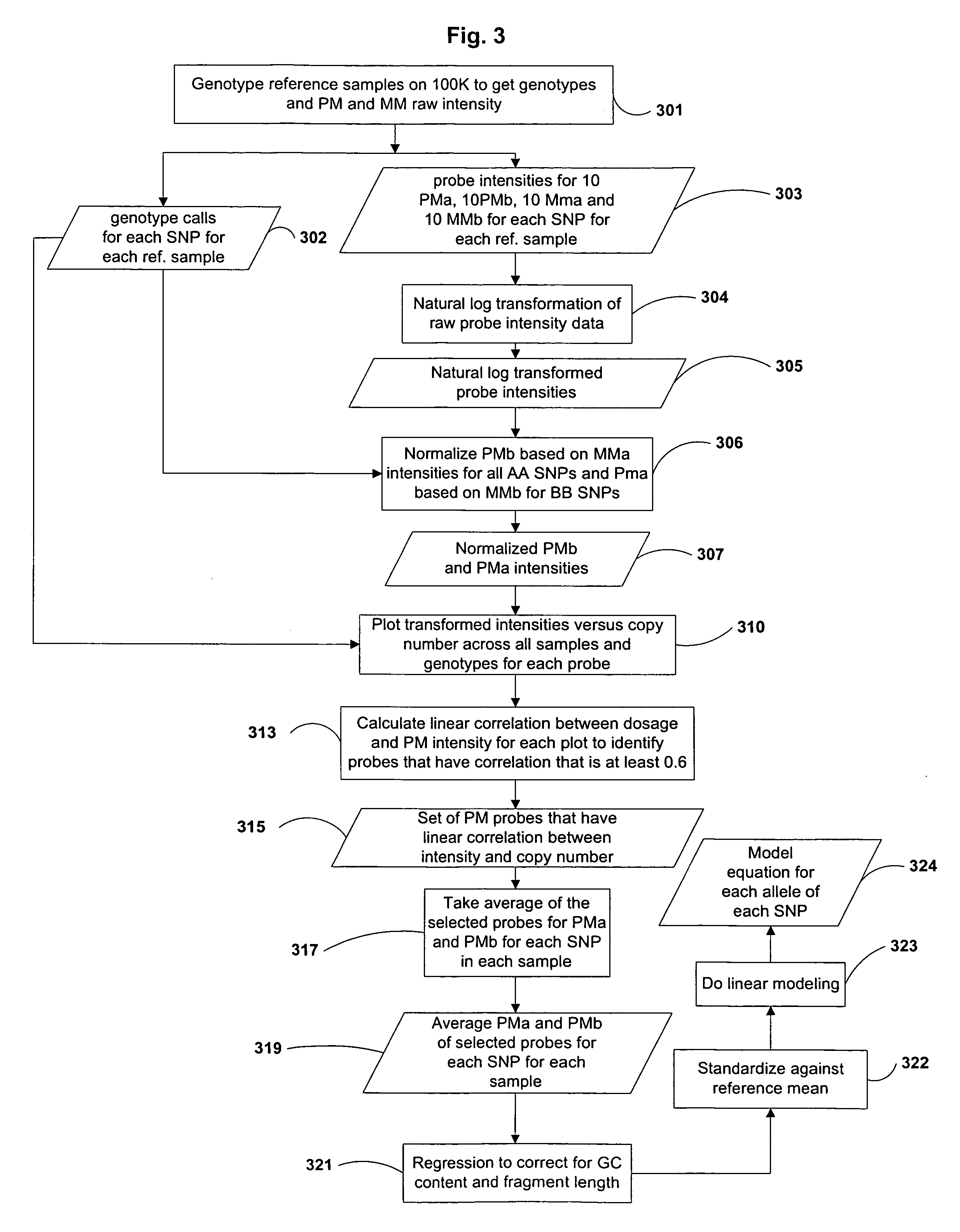
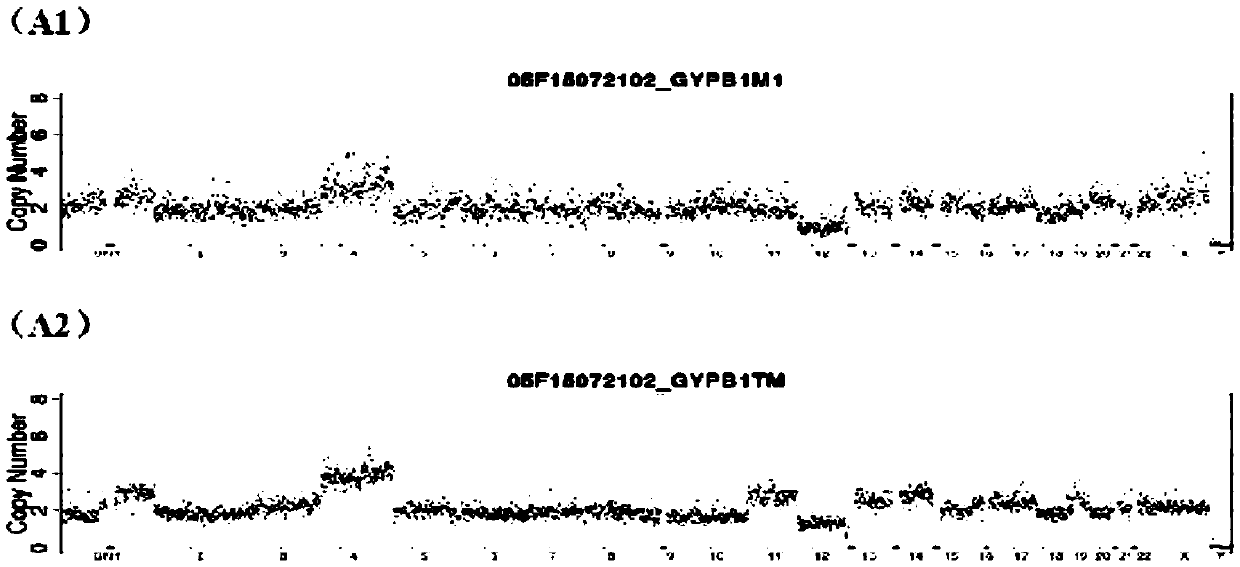
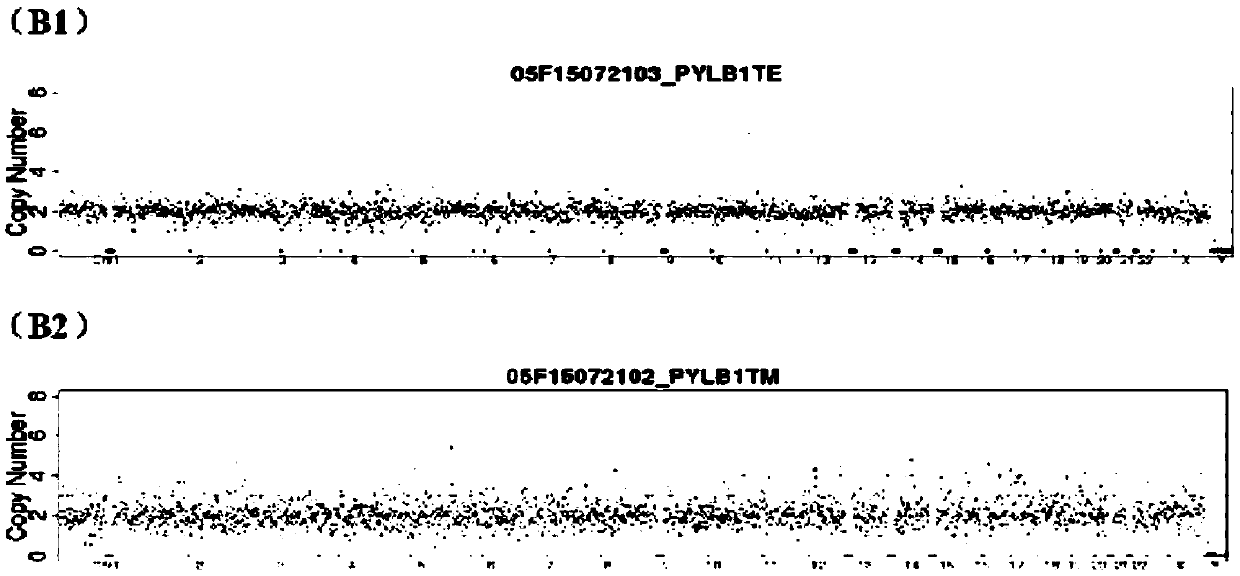
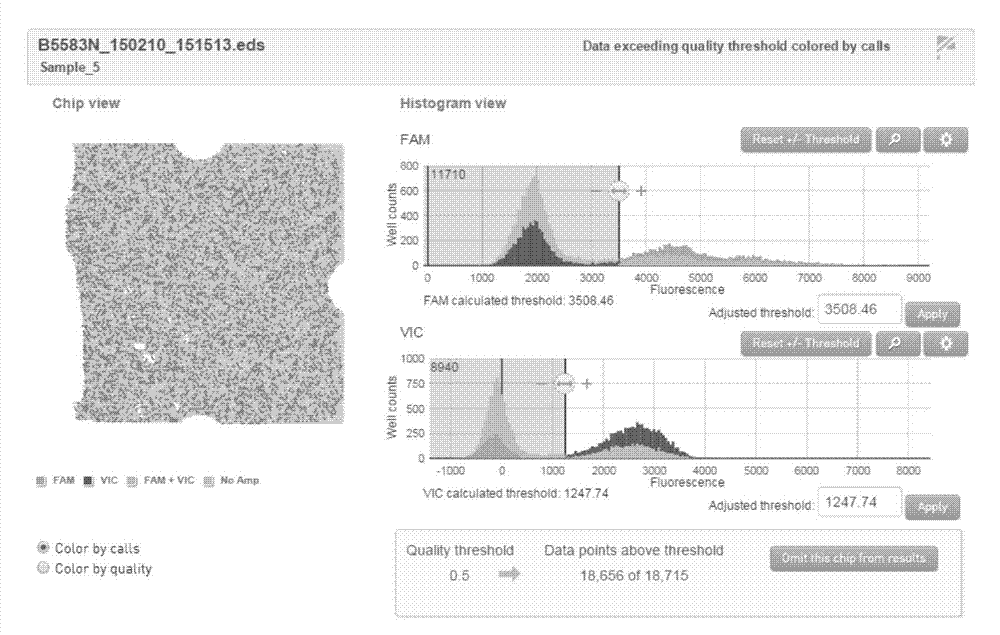
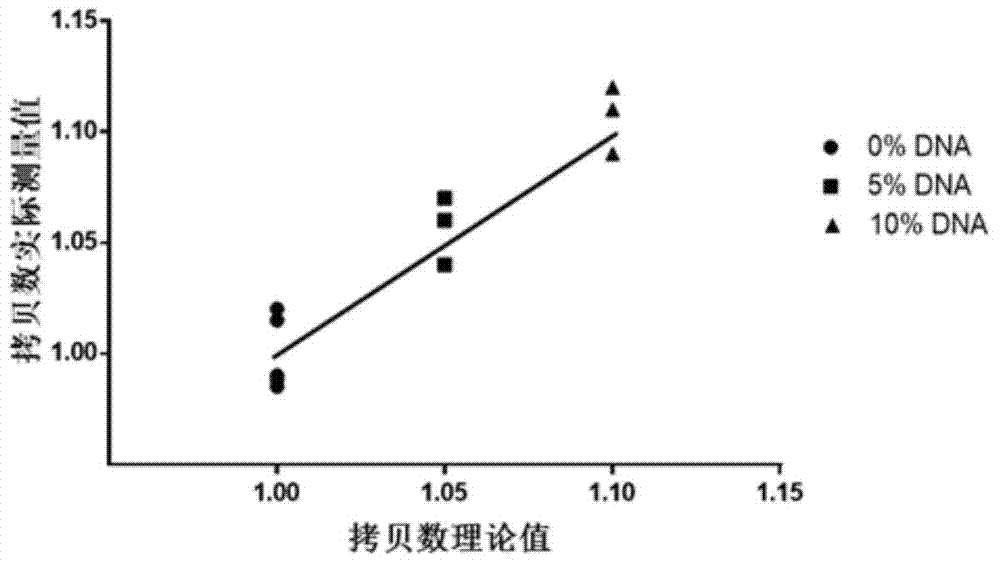
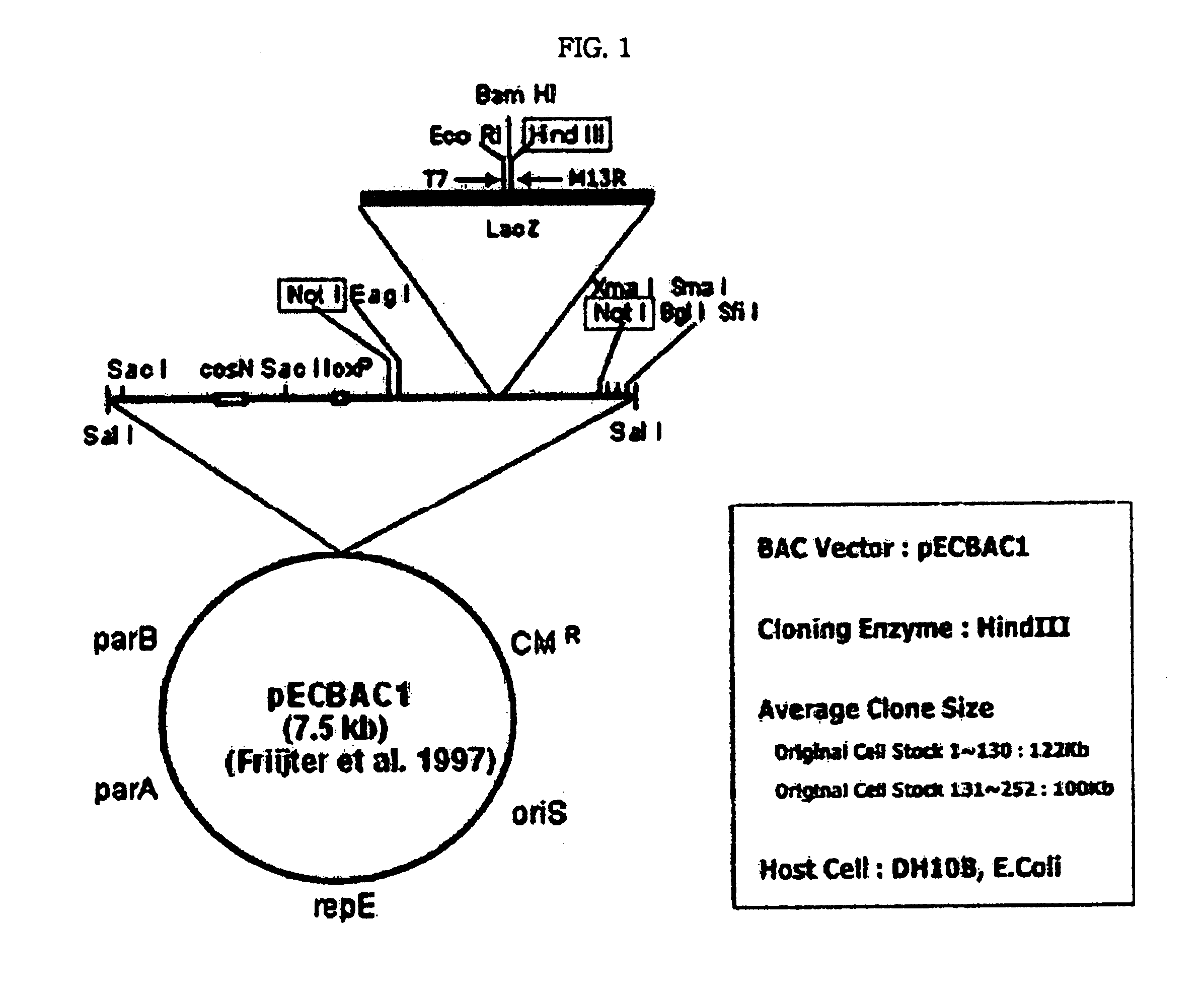
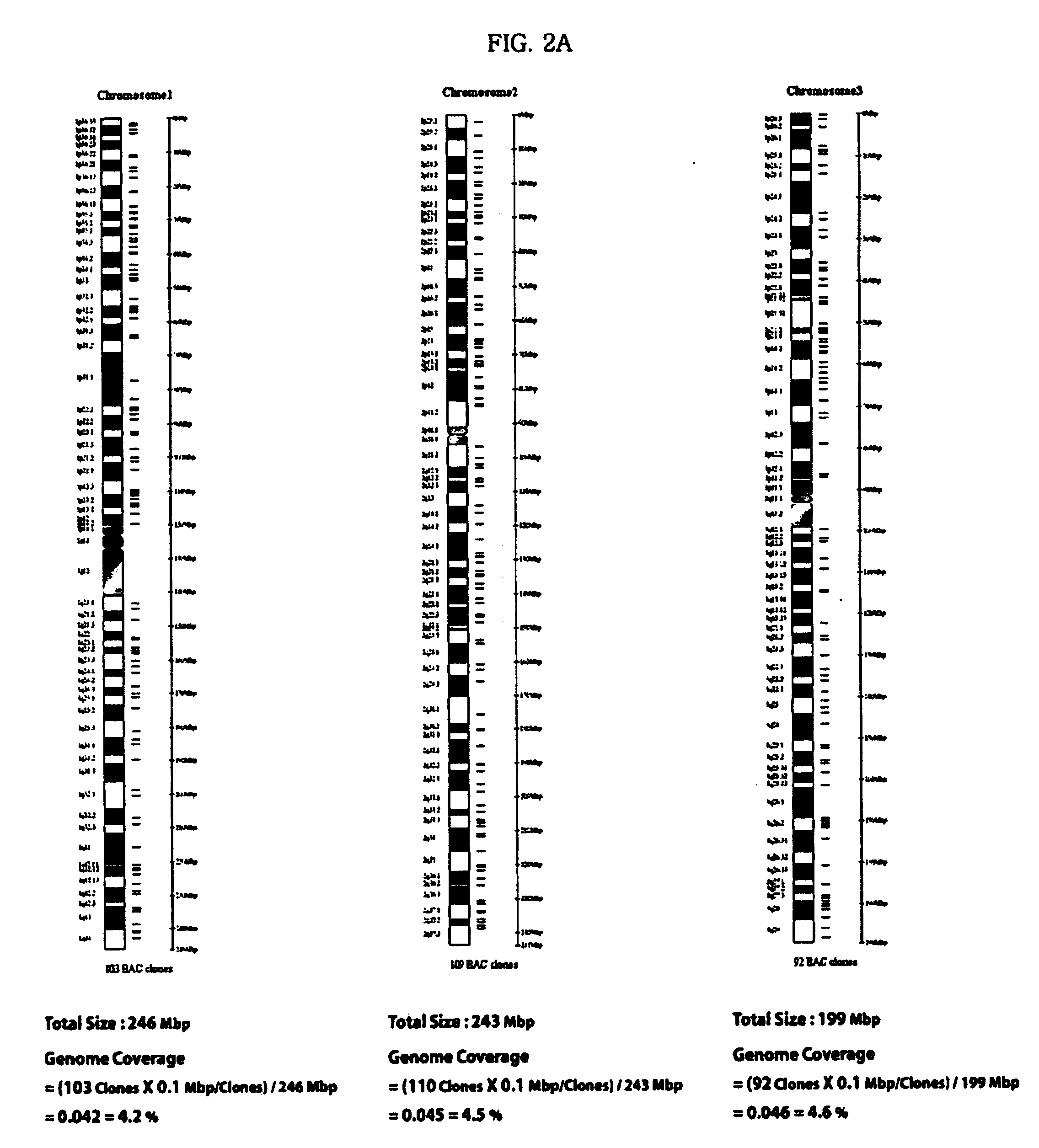
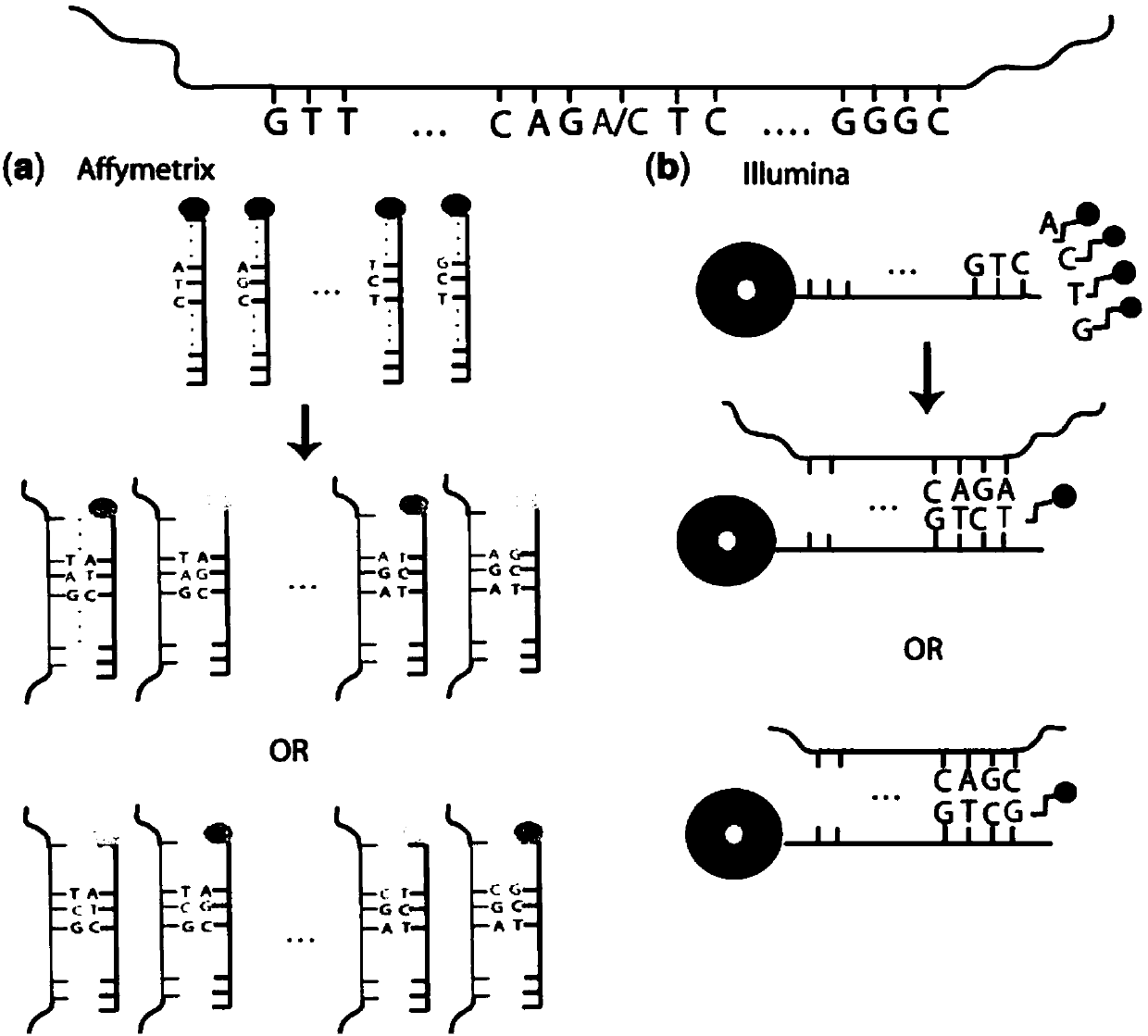
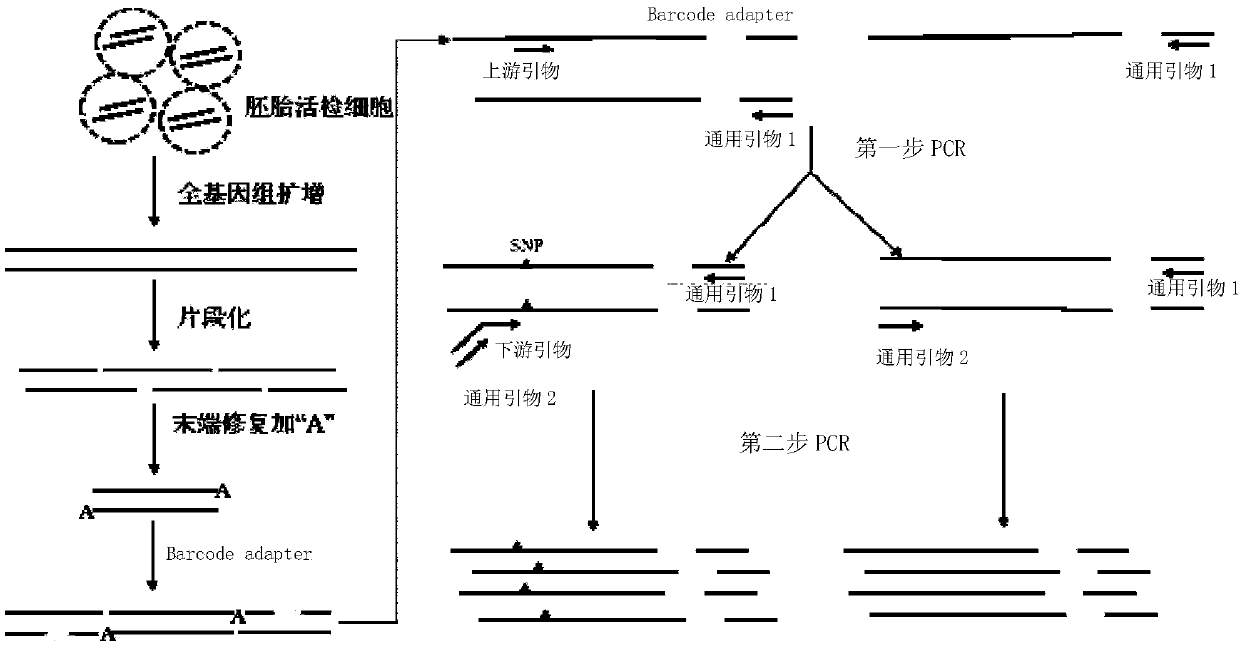
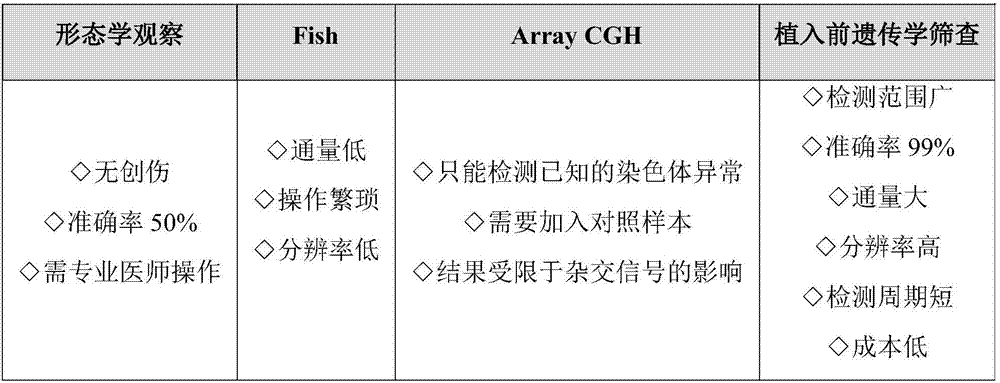
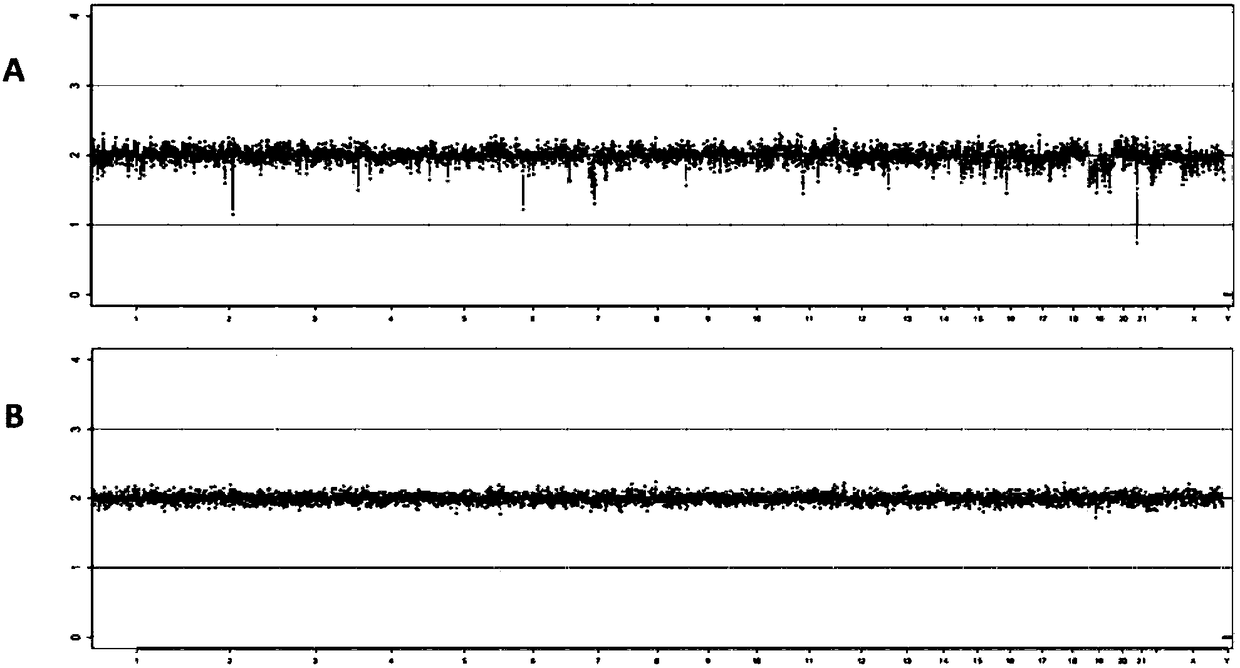
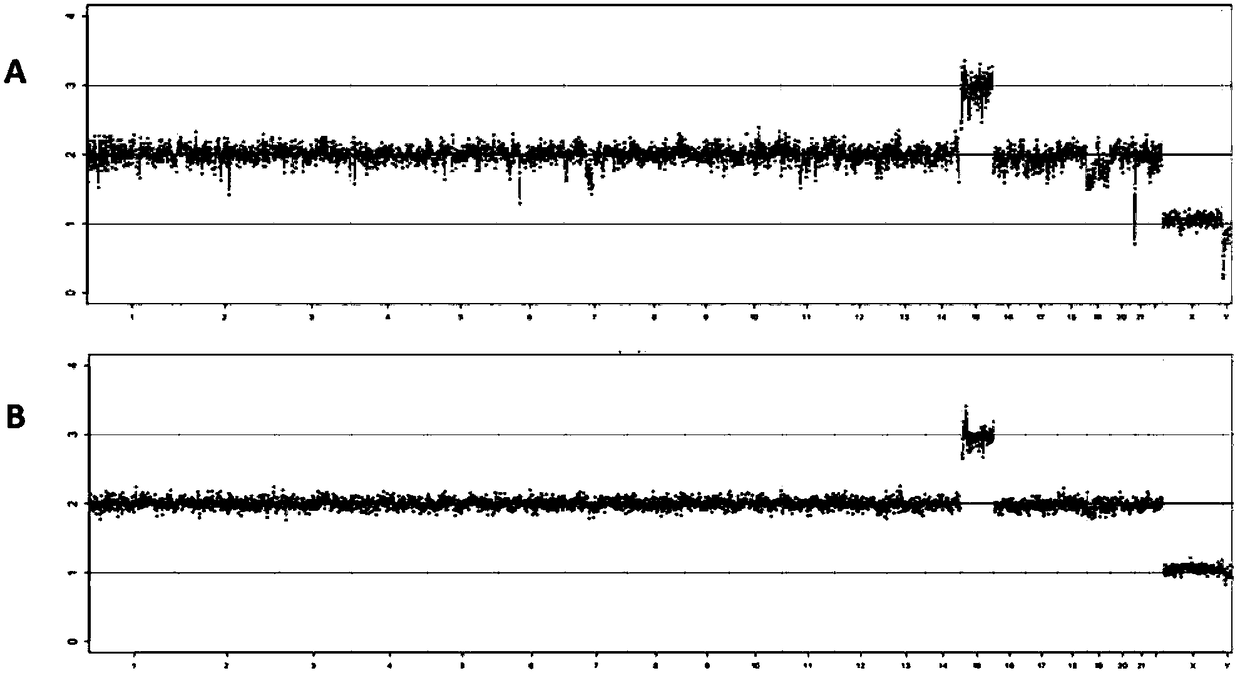
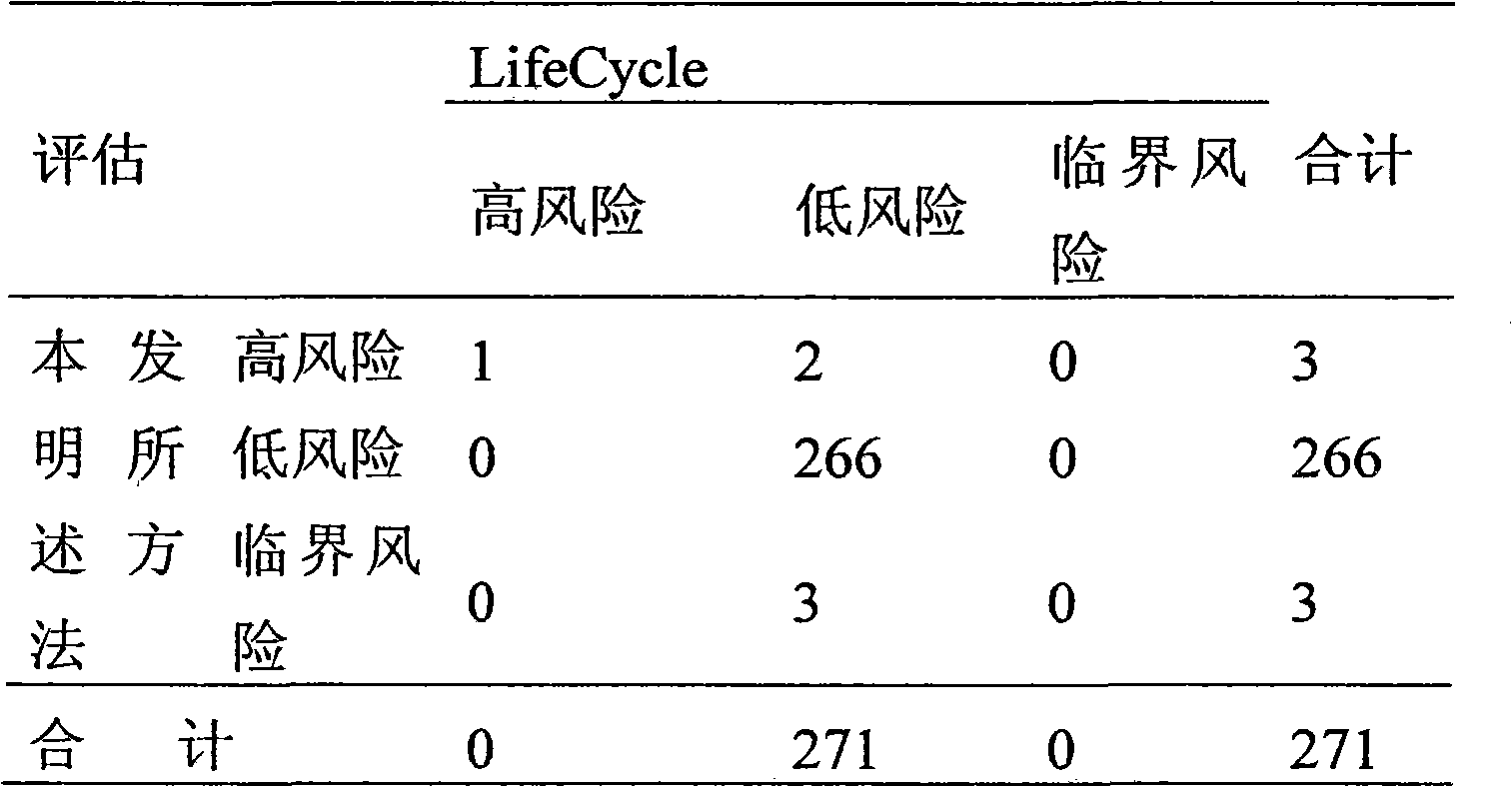
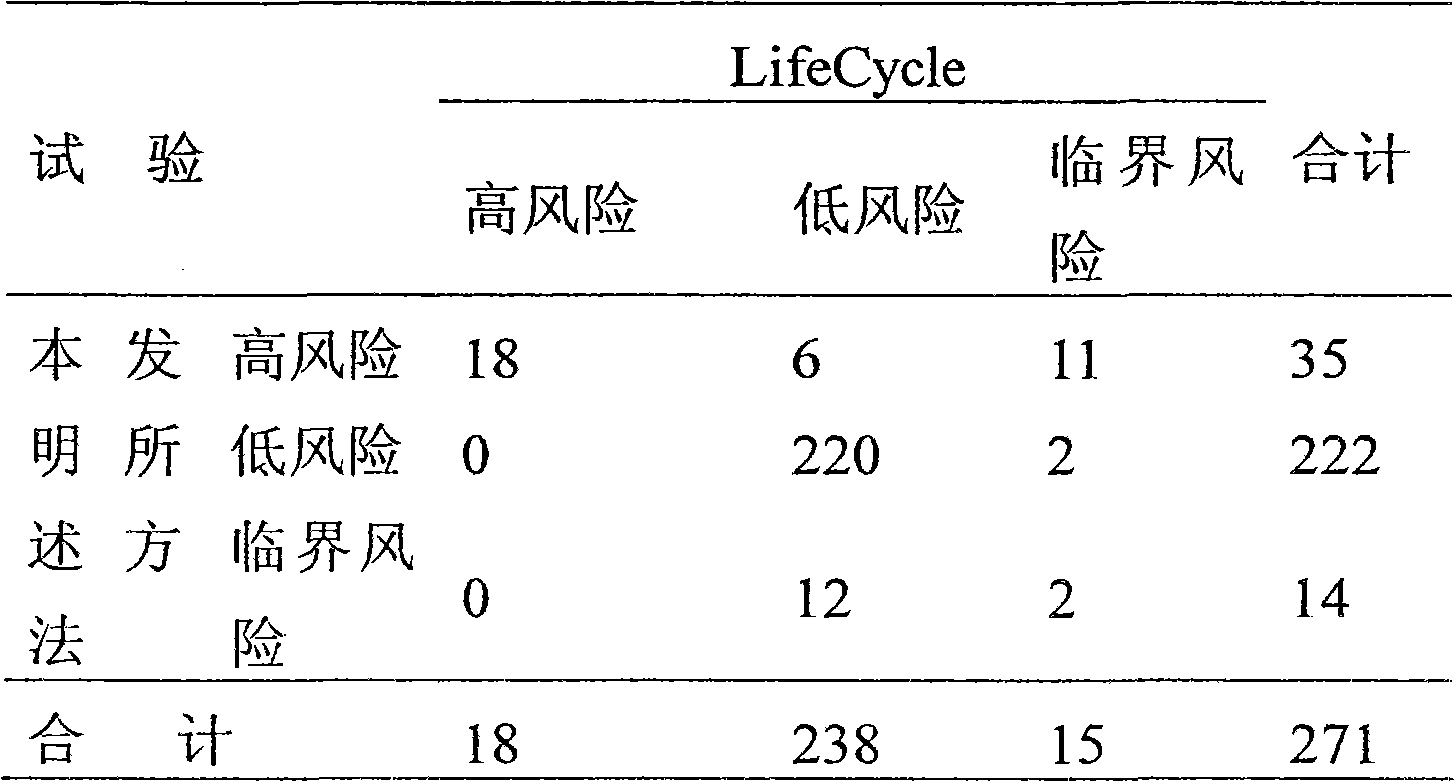
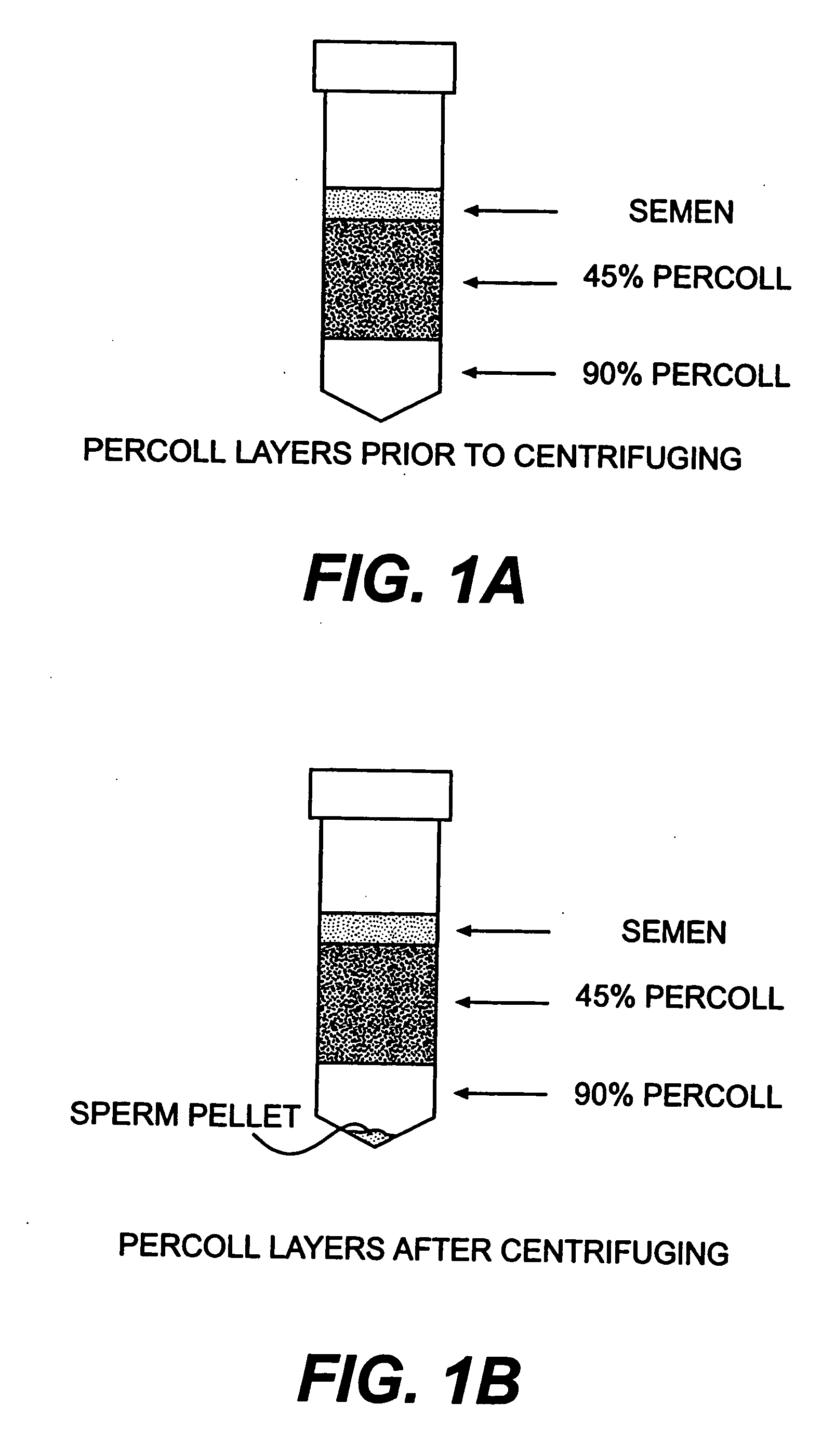
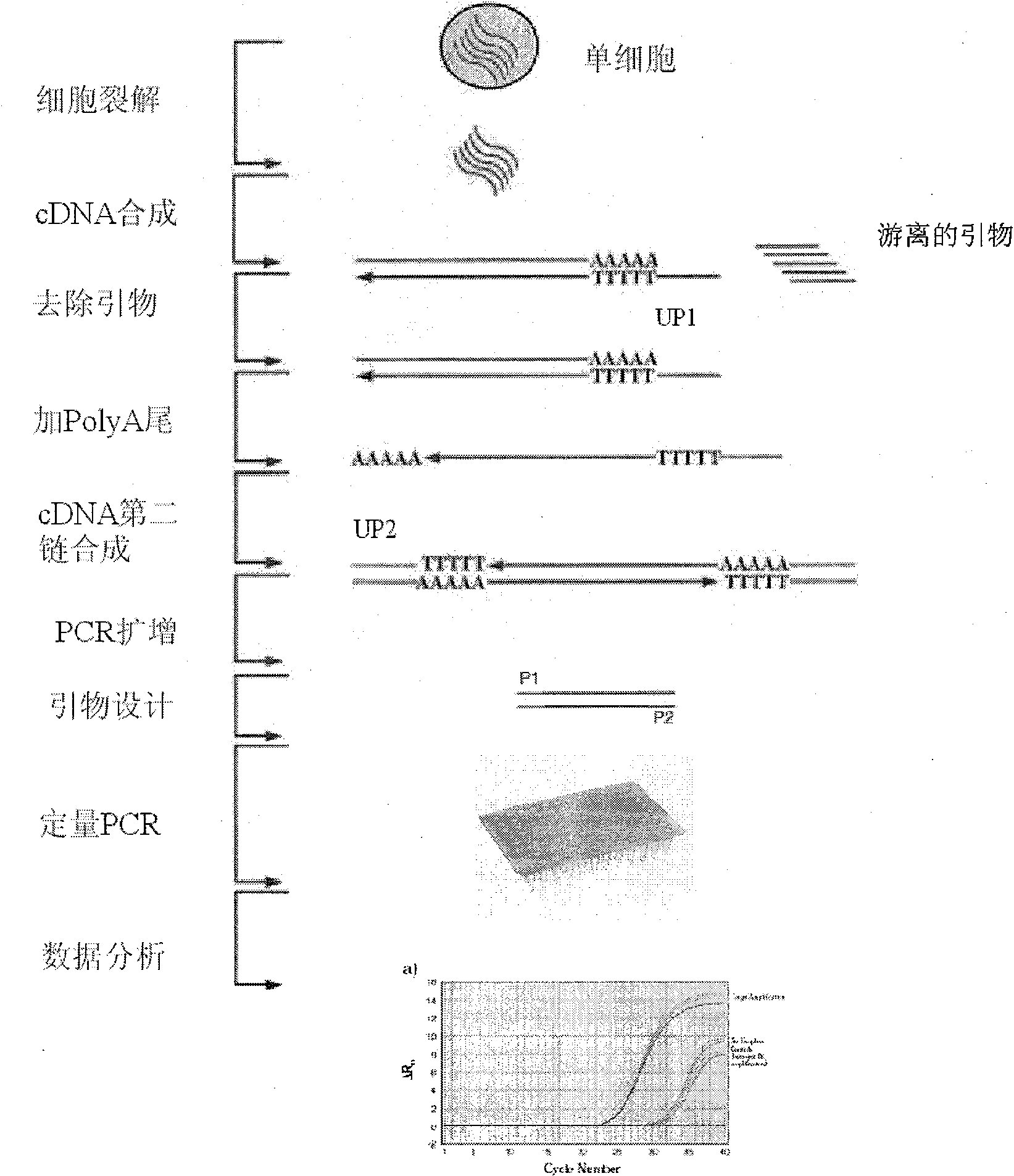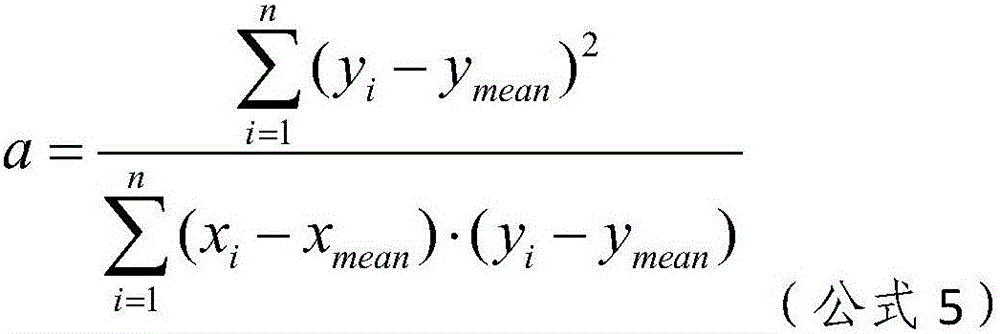Patents
Literature
66 results about "Chromosome abnormality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A chromosomal disorder, anomaly, aberration, or mutation is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. It can be from a typical number of chromosomes or a structural abnormality in one or more chromosomes. Chromosome mutation was formerly used in a strict sense to mean a change in a chromosomal segment, involving more than one gene. The term "karyotype" refers to the full set of chromosomes from an individual; this can be compared to a "normal" karyotype for the species via genetic testing. A chromosome anomaly may be detected or confirmed in this manner. Chromosome anomalies usually occur when there is an error in cell division following meiosis or mitosis. There are many types of chromosome anomalies. They can be organized into two basic groups, numerical and structural anomalies.
Prenatal Diagnosis Using Cell-Free Fetal DNA in Amniotic Fluid
InactiveUS20070212689A1Rapid determinationAddressing slow performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansCell-free fetal DNAAmniotic fluid
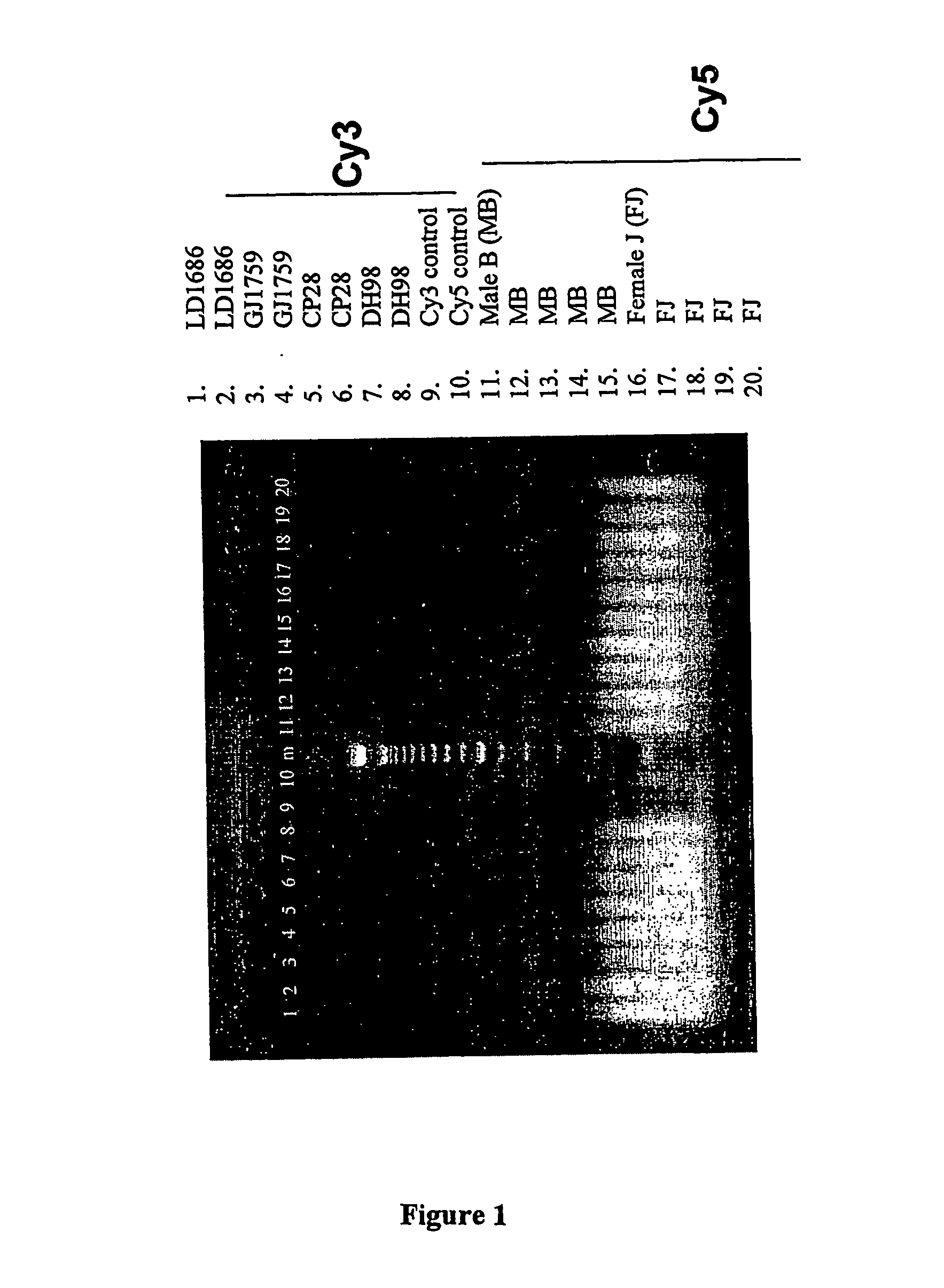
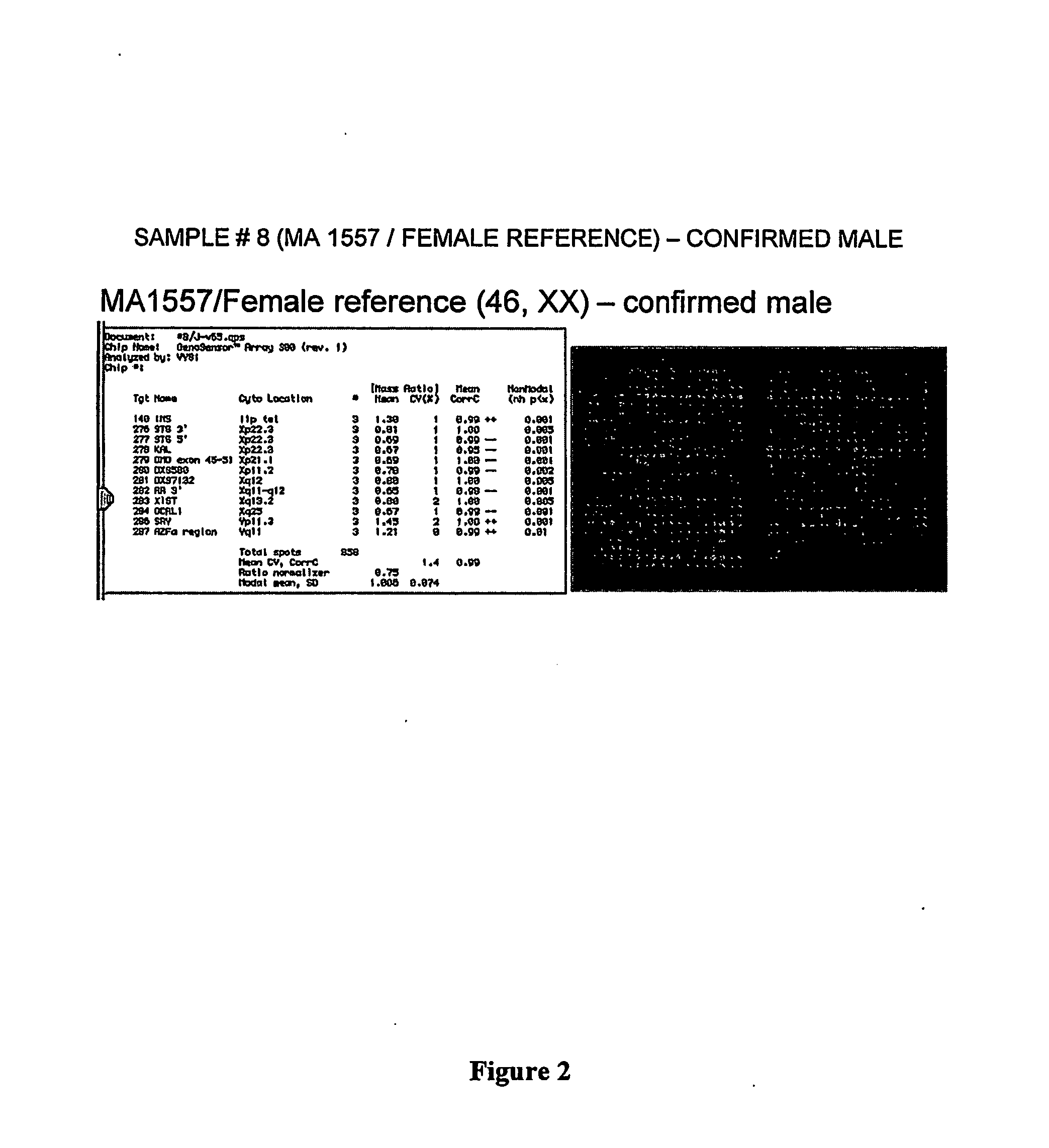
The present invention relates to improved methods of prenatal diagnosis, screening, monitoring and / or testing. The inventive methods include the analysis by array-based hybridization of cell-free fetal DNA isolated from amniotic fluid. In addition to allowing the prenatal diagnosis of a variety of diseases and conditions, and the assessment of fetal characteristics such as fetal sex and chromosomal abnormalities, the new inventive methods provide substantially more information about the fetal genome in less time than it takes to perform a conventional metaphase karyotype analysis. In particular, the enhanced molecular karyotype methods provided by the present invention allow the detection of chromosomal aberrations that are not often detected prenatally such as microdeletions, microduplications and subtelomeric rearrangements.
Owner:BIANCHI DIANA W +2
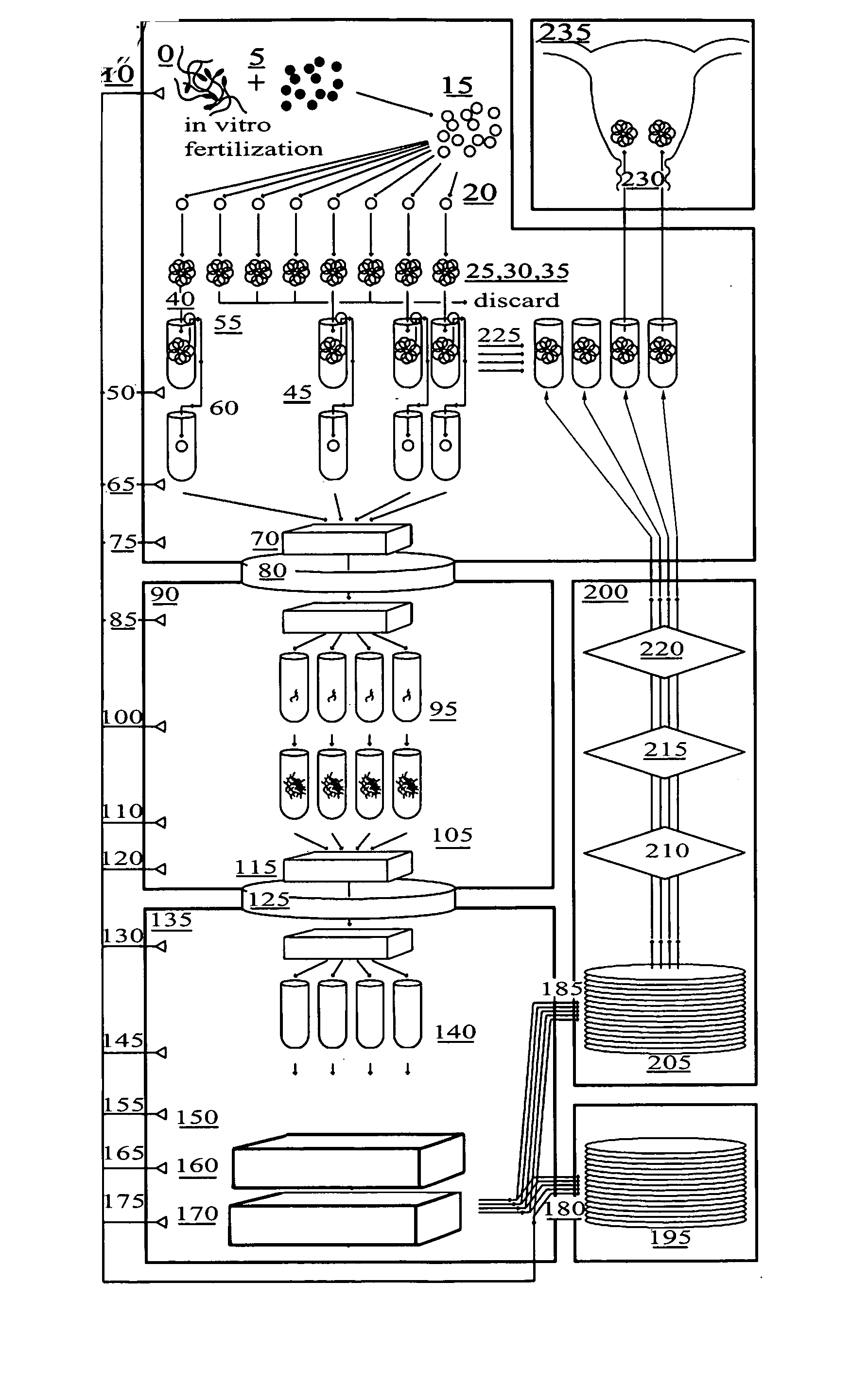
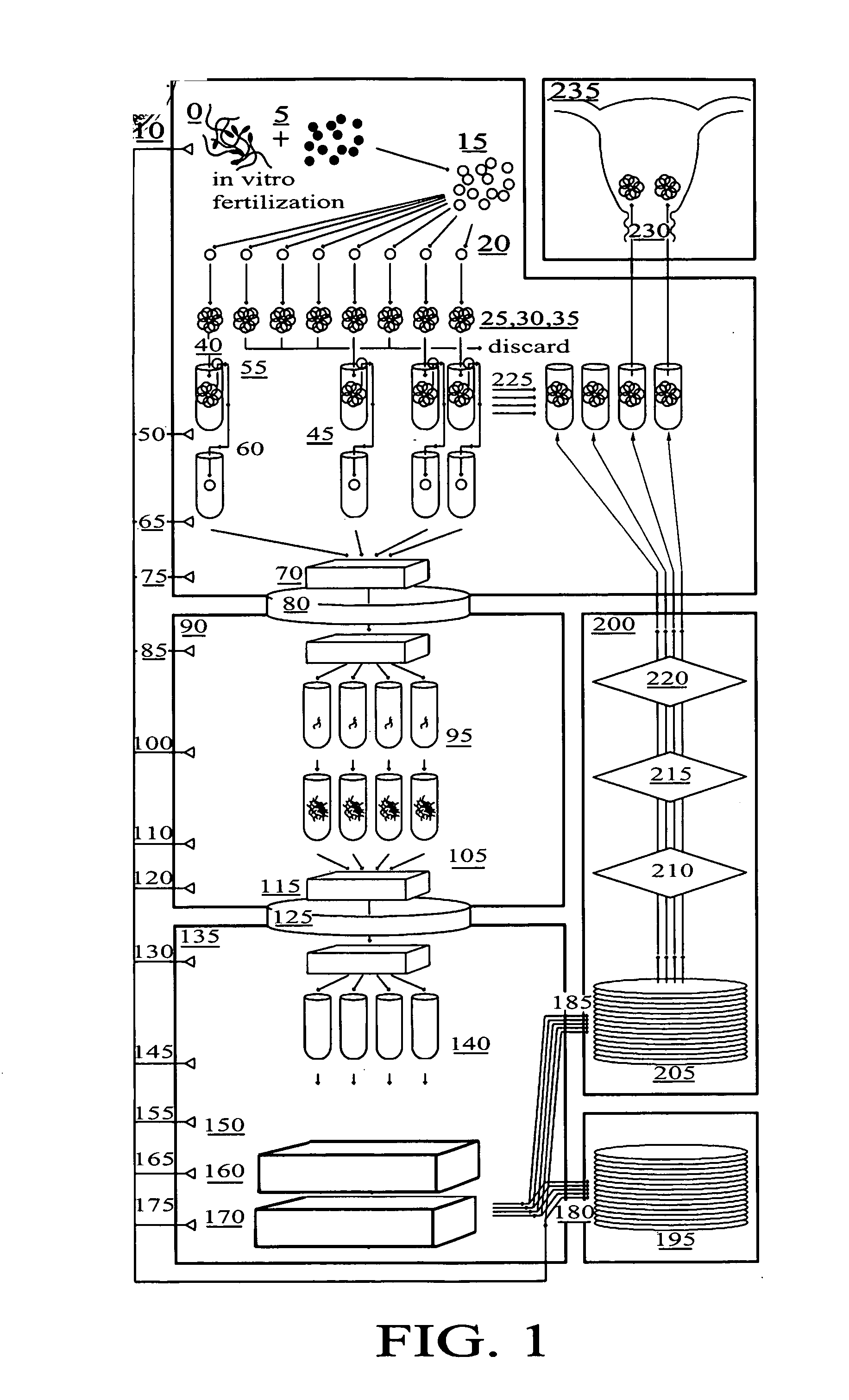
Method for genetic testing of human embryos for chromosome abnormalities, segregating genetic disorders with or without a known mutation and mitochondrial disorders following in vitro fertilization (IVF), embryo culture and embryo biopsy
InactiveUS20080085836A1Reduce significant riskImprove the level ofLibrary screeningLibrary member identificationLess invasiveContamination
We describe a method for interrogating the content and primary structure of DNA by microarray analyses and to provide comprehensive genetic screening and diagnostics prior to embryo transfer within an IVF setting. We will accomplish this by the following claims: 1) an optimized embryo grading system, 2) a less invasive embryo biopsy with reduced cellular contamination, 3) an optimized DNA amplification protocol for single cells, 4) identify aneuploidy and structural chromosome abnormalities using microarrays, 5) identifying sub-telomeric chromosome rearrangements, 6) a modified DNA fingerprinting protocol, 7) determine imprinting and epigenetic changes in developing embryos, 8) performing genome-wide scans to clarify / diagnose multi-factorial genetic disease and to determine genotype / haplotype patterns that may predict future disease, 9) determining single gene disorders with or without a known DNA mutation, 10) determining mtDNA mutations and / or the combination of mtDNA and genomic (nuclear) DNA aberrations that cause genetic disease.
Owner:KEARNS WILLIAM G +1
Methods for identifying DNA copy number changes
InactiveUS20050064476A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenomic DNANormal tissue
Methods of identifying changes in genomic DNA copy number are disclosed. Methods for identifying homozygous deletions and genetic amplifications are disclosed. An array of probes designed to detect presence or absence of a plurality of different sequences is also disclosed. The probes are designed to hybridize to sequences that are predicted to be present in a reduced complexity sample. The methods may be used to detect copy number changes in cancerous tissue compared to normal tissue. The methods may be used to diagnose cancer and other diseases associated with chromosomal anomalies.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Methods for identifying DNA copy number changes
Methods of identifying allele-specific changes in genomic DNA copy number are disclosed. Methods for identifying homozygous deletions and genetic amplifications are disclosed. An array of probes designed to detect presence or absence of a plurality of different sequences is also disclosed. The probes are designed to hybridize to sequences that are predicted to be present in a reduced complexity sample. The methods may be used to detect copy number changes in cancerous tissue compared to normal tissue. The methods may be used to diagnose cancer and other diseases associated with chromosomal anomalies.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Method for generating cloned animals using chromosome shuffling
InactiveUS20020174449A1Population uniformImprove quality controlNew breed animal cellsFermentationSpecific chromosomeMammal
The present invention concerns the use of chromosomal replacement techniques in the context of producing cloned and transgenic animals, in order to correct chromosome abnormalities or alter autosomal genotypes, and provide for novel breeding pairs by replacing the sex chromosome in animals to be cloned. Replacement of a sex chromosome, or an X or Y chromosome, will result in animals that are autosomally isogenic and sexually non-isogenic (AISN), with "autosomally isogenic" meaning that the paired sets of autosomes (non-sex chromosomes) in each animal are isogenic or identical. Also included in the invention are animals that are both "autosomally" and "allelically" isogenic whereby each particular pair of chromosomes is internally isogenic or identical within a single animal as well as between animals. Such animals are particularly useful in generating a line of cloned mammals using sexual reproduction, without having to undergo nuclear transfer in order to propagate cloned animals.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
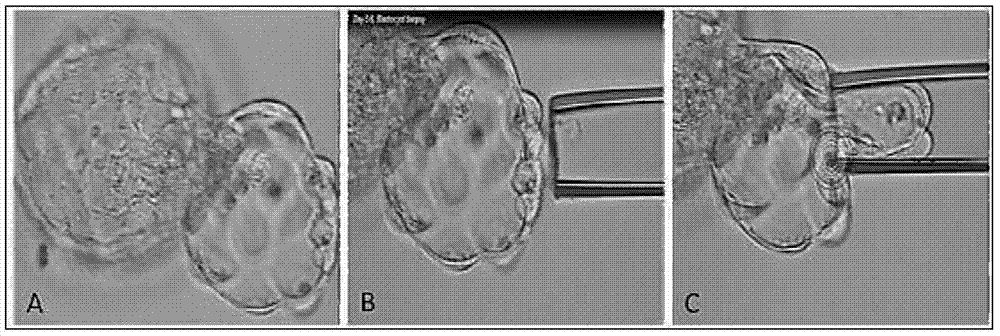
Method for detecting embryo chromosome abnormality by utilizing blastula culture solution
ActiveCN105368936AAvoid lostAvoid damageMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisEmbryoNon invasive
Owner:XUKANG MEDICAL SCI & TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Detection of chromosoal abnormalities associated with breast cancer
InactiveUS7094534B2Avoid saturationHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for detecting embryo chromosome abnormalities by using blastula-stage embryo cells
InactiveCN104711362AAvoid harmA large amountMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh cellCell separation
The invention discloses a method for performing genome amplification by using embryo blastula-stage cells, performing chromosome detection on the preimplantational embryo by combining a high-flux sequencing technique and screening out the chromosome normal embryo. The method can comprehensively and completely analyze the genetic variation information of the embryo genome, thereby instructing the preimplantational embryo selection, reducing the hereditary diseases and enhancing the success rate of test tube babies. The method comprises the following steps: blastula-stage trophocyte separation; genome amplification; DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segmentation; and Proton library establishment, mounting sequencing and sequencing data analysis. By using the blastula-stage embryo to perform trophocyte separation detection, the method avoids the injuries of cleavage-stage cell separation to the embryo, obtains higher cell quantity than the cleavage stage, and enhances the success rate and amplification effect of genome amplification. After the blastula-stage embryos are subjected to the natural elimination process, the high-quality blastula-stage embryo is selected for detection, thereby saving the cost.
Owner:SUZHOU BASECARE MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
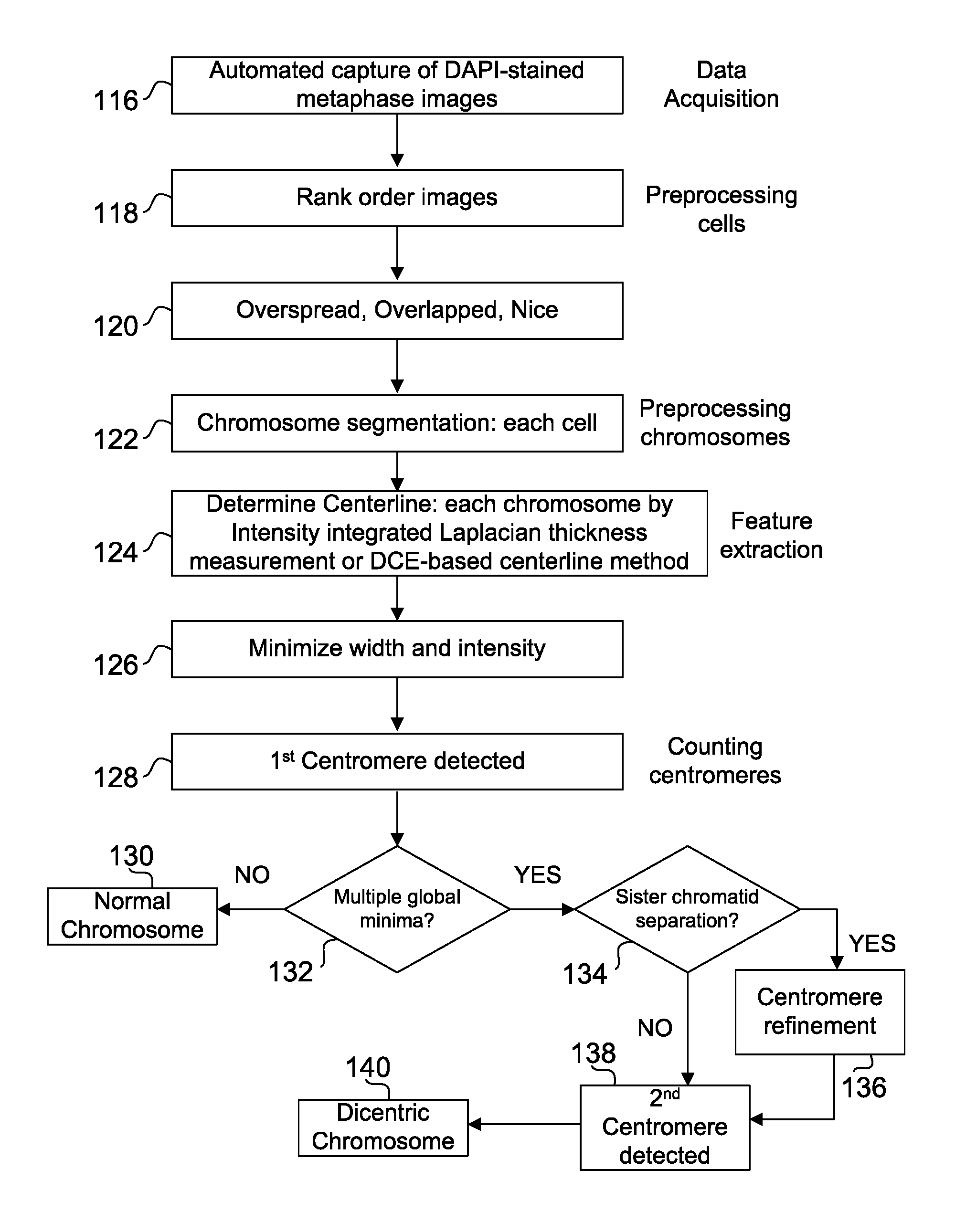
Centromere Detector and Method for Determining Radiation Exposure From Chromosome Abnormalities
ActiveUS20130216118A1Microbiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiation exposureDicentric chromosome
A method for determining radiation exposure from chromosome abnormalities present in a specimen by determining the location or locations of the centromere of each chromosome in a cell in an image of a metaphase cell by segmentation of an accurately drawn chromosome centerline followed by selection of a longitudinal cross-section with the minimum width or intensity or width and intensity; counting the number of centromeres in each chromosome in each cell; computing the frequency of dicentric chromosomes in a population of cells; and determining the radiation dose by comparing the computed frequency of dicentric chromosomes with a previously determined dose-response curve from a calibrated source.
Owner:CYTOGNOMIX
Method for detecting embryonic chromosome abnormality by virtue of blastochyle free DNA
InactiveCN104450923AProbability of small developmental abnormalitiesSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFragment sizeEmbryo
The invention relates to a method for detecting embryonic chromosome abnormality by virtue of blastochyle free DNA. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring blastochyle free DNA, detecting the blastochyle DNA, carrying out whole genome amplification of the free DNA, analyzing a product of the whole genome amplification, implementing fragmenting treatment on genome DNA, carrying out quantitative analysis and fragment size analysis on fragmented target DNA, constructing a library, sequencing by virtue of a computer and analyzing biological information. By virtue of high-throughput sequencing, the method disclosed by the invention can be used for overcoming shortcomings of a conventional DNA analysis method which is merely used for researching partial region of a single cell genome, and is capable of completely analyzing the genetic information of the single cell genome; the method is simple and convenient to operate, time-saving and efficient; meanwhile, by using the blastochyle free DNA as a detection sample, the method is convenient and safe to sample, so that the probability of later embryonic development abnormality is reduced and embryo is protected from being influenced in later development.
Owner:SUZHOU BASECARE MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
Medical diagnosis support device, image processing method, image processing program, and virtual microscope system
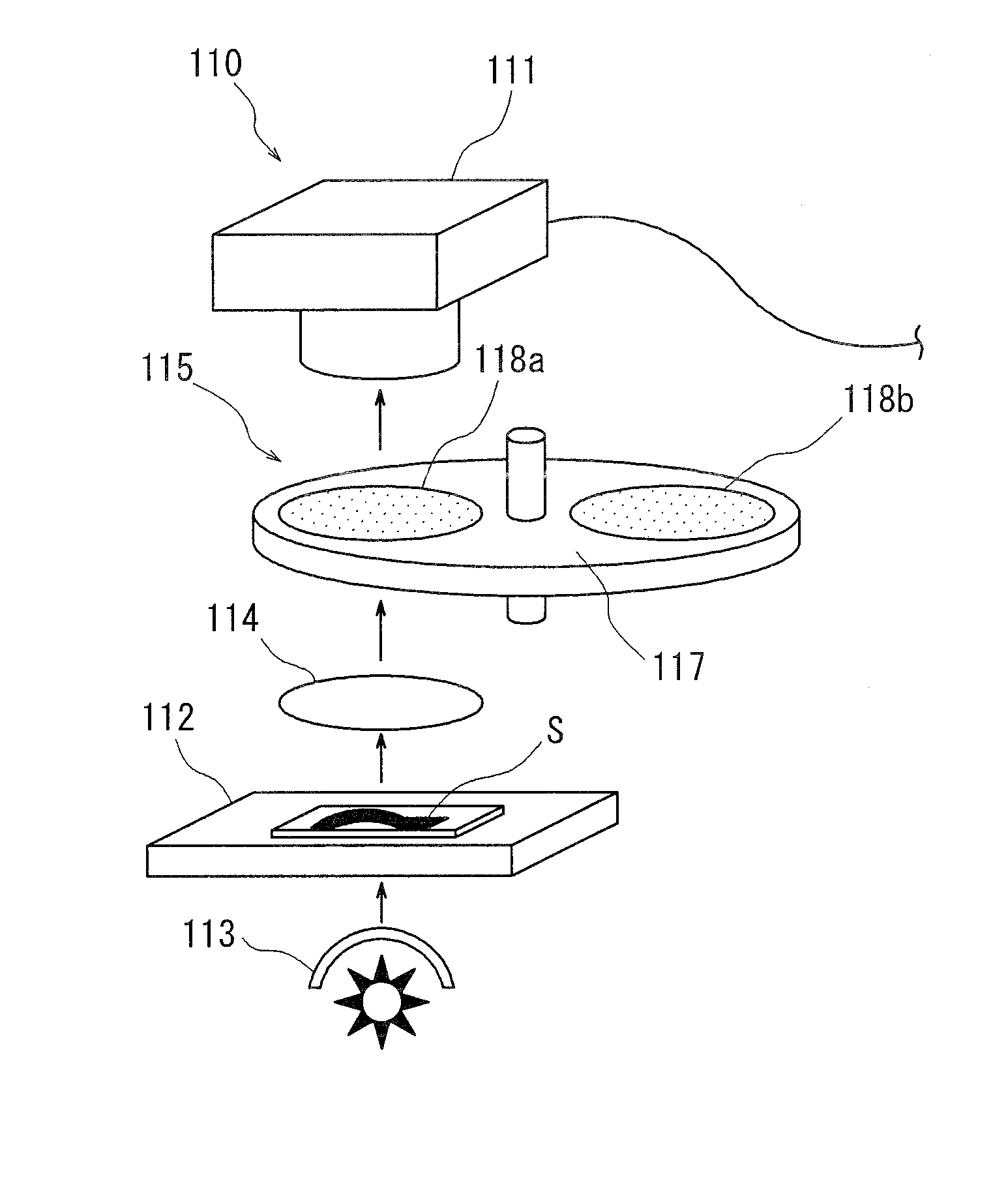
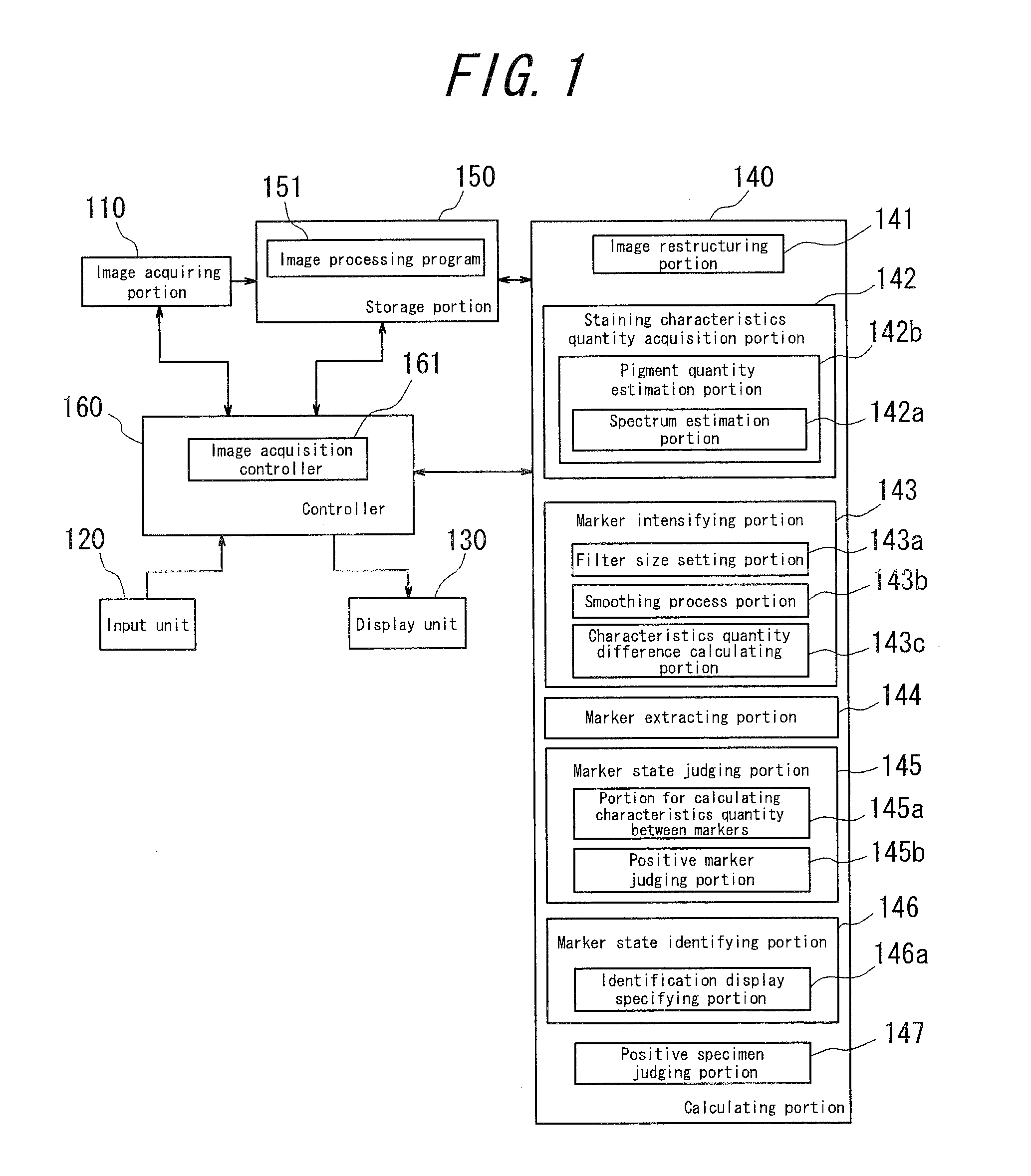
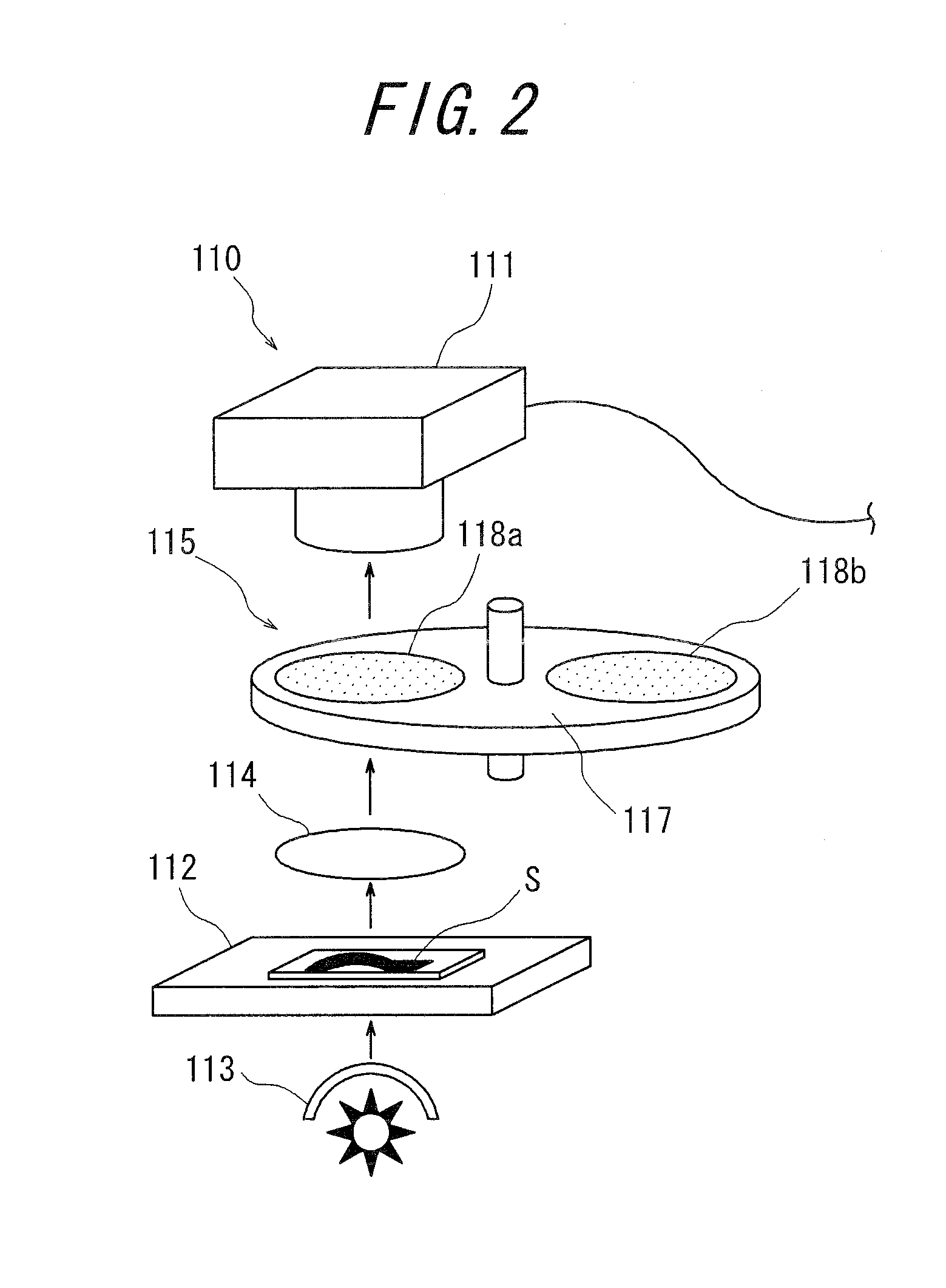
InactiveUS20100322502A1Easily and precisely determine chromosome abnormality and/or gene amplificationEasy to confirmImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingStaining
The present invention provides a medical diagnosis support device, which is capable of acquiring information to support medical diagnosis for easily and precisely determining chromosome abnormality and / or gene amplification related to cancer or genetic disorder.The medical diagnosis support device for acquiring information to support medical diagnosis from an image of a specimen stained by multiple staining, the image is obtained by photographing the stained specimen with transmitted light, the device comprises: staining characteristics quantity acquisition means for acquiring characteristics quantity of each staining, based on a pixel value of the image of the stained specimen; marker intensifying means for intensifying a marker, based on the characteristics quantity of each staining thus acquired; marker extracting means for extracting the marker of each staining, based on the characteristics quantity in which the marker has been thus intensified; marker state judging means for judging a state of the marker, based on the marker of each staining thus extracted; and marker state identifying and displaying means for identifying and displaying the marker state, based on the judgment result.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP +1
Application of MDPCR (multiple digital PCR (polymerase chain reaction)) technology to chromosome aneuploidy screening
InactiveCN104846103AShort half-lifeIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention provides application of an MDPCR (multiple digital PCR (polymerase chain reaction)) technology to chromosome aneuploidy screening. Concretely, the invention discloses a method for performing NIPS (non-invas ive prenatal screening) including Down's syndrome, Edward's syndrome, Patau syndrome and other chromosome abnormality diseases on pregnant women by the MDPCR technology. The method has the advantages that early, safe, non-invas, accurate and fast effects are achieved, the method is suitable for large-scale detection and clinic application, and the like; intrauterine infection, abortion and death in the pregnancy middle and later periods of the pregnant women can be avoided; the goals of bearing and rearing better children are achieved.
Owner:NANJING JENOMED BIOTECH CO LTD
Detection method for chromosome abnormality and microarray chip
The present invention relates to a method of detecting a chromosome abnormality and a microarray chip for detecting a chromosome abnormality. More specifically, the present invention is directed to a method of detection for chromosome abnormality in order to easily diagnosing the health condition and disease of the subject by detecting of the chromosome abnormality rapidly and precisely, and to providing a probe for diagnosis of disease by identifying chromosome abnormality specific to the disease.
Owner:MACROGEN INC
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis on embryo by using new single cell nucleic acid amplification technology
InactiveCN102094083APrevent birthBirth to avoidMicrobiological testing/measurementRecessive inheritanceCentral dogma of molecular biology
The invention relates to preimplantation genetic diagnosis on an embryo by using new single cell nucleic acid amplification technology, which mainly utilizes the signal amplification action of the mRNA (messenger Ribose Nucleic Acid) to detect the multiplication or deletion of DNAs (Deoxyribonucleic Acids) of certain chromosome segments. According to the central dogma, the mRNA is transcribed by using the DNA as the template, the abnormity of the number of copies of the DNA template can cause the change of the quantity of the mRNAs; and in the transcription process, the multiplication or deletion of the DNA template can be amplified on the mRNA level, and can be easily detected. The main technical method is as follows: the single cell mRNA of a human embryo is subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification after being subjected to reverse transcription and addition of a common primer; by using the amplification product as the template, quantitative PCR with a 96-pore plate is used for detecting the expression level of 8 genes of a single cell or a small amount of cells; and the detection result can be compared with a normal diploid embryo, so as to distinguish the embryo sex of X chromosome recessive inheritance family history, and the multiplication and deletion of Trisomy 21, Trisomy 18, Trisomy 13 and sex chromosome and carry out genetic diagnosis on some common chromosome anomalies.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
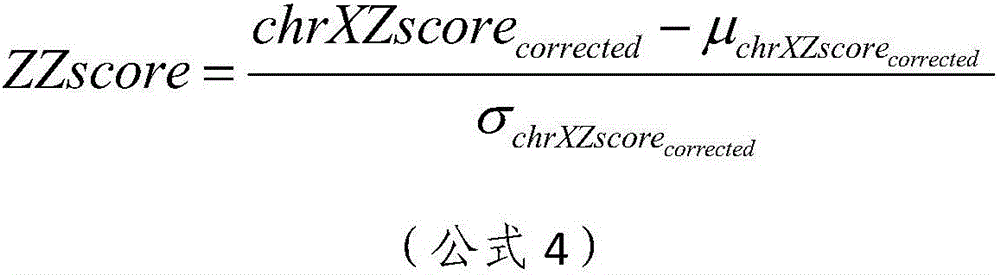
Noninvasive prenatal biological information detection and analysis method
The invention relates to the field of medical detection and particularly discloses a noninvasive prenatal biological information detection and analysis method. For improving the accuracy of analyzing different quantities of to-be-detected samples, different detection and analysis methods are selected according to the different quantities of the to-be-detected samples, and different analysis policies are adopted for parameters obtained by the to-be-detected samples and parameters obtained by a normal reference set, so that the accuracy of analysis is improved to a greater extent. According to the method, the problem of inaccurate regression result caused by great influence of abnormal data on slope due to use of a least square method for regression in a process of correction by using a whole chromosome method in the prior art is well solved by adopting robust regression and CV regression, so that the robustness and accuracy of sample analysis are ensured. A set of analysis method for judging anomaly of sex chromosome by utilizing a ZZ value is originated; and the chromosome anomaly is judged by using the ZZ value method, so that related statistic judgment standards are better met, a result is more accurate, and the reliability of the method for judging the anomaly of the sex chromosome is enhanced.
Owner:北京普康瑞仁医学检验所有限公司
Highly aggressive human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain with add(11)(q23) chromosome abnormality
The invention belongs to the field of microbial animal cell lines, and relates to a new human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain CHH-1. The in vitro isolate of the mononuclear cell of the marrow of a patient with firstly-diagnosed acute B lymphocytic leukemia undergoes cell primary culture to obtain the highly aggressive human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain with add(11)(q23) chromosome abnormality, the preservation number of the cell strain is CGMCC No.11797, and the highly aggressive human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain with add(11)(q23) chromosome abnormality is named as human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain CHH-1, has a same clone source with patient's leukemia cells, can be infinitely and stably passed in vitro, and has the characteristics of clonality add(11)(q23) genetic abnormality, high tumorigenicity and high aggressiveness. The new human acute B lymphocytic leukemia cell strain CHH-1 provides a new good cell model for researches of human acute lymphocytic leukemia with No.11 chromosome long arm structure abnormality and development of biomedicines, and has wide prospect and great practical values in revelation of the pathogenesis of the human acute lymphocytic leukemia and development of medicines.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
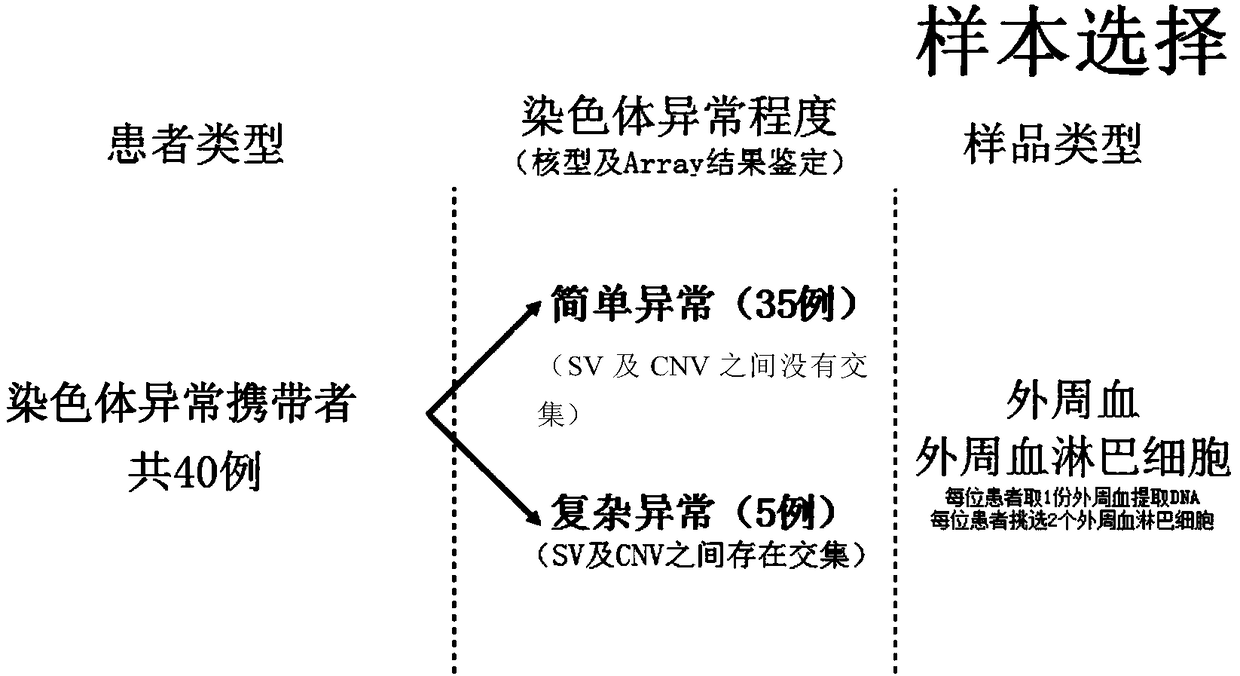
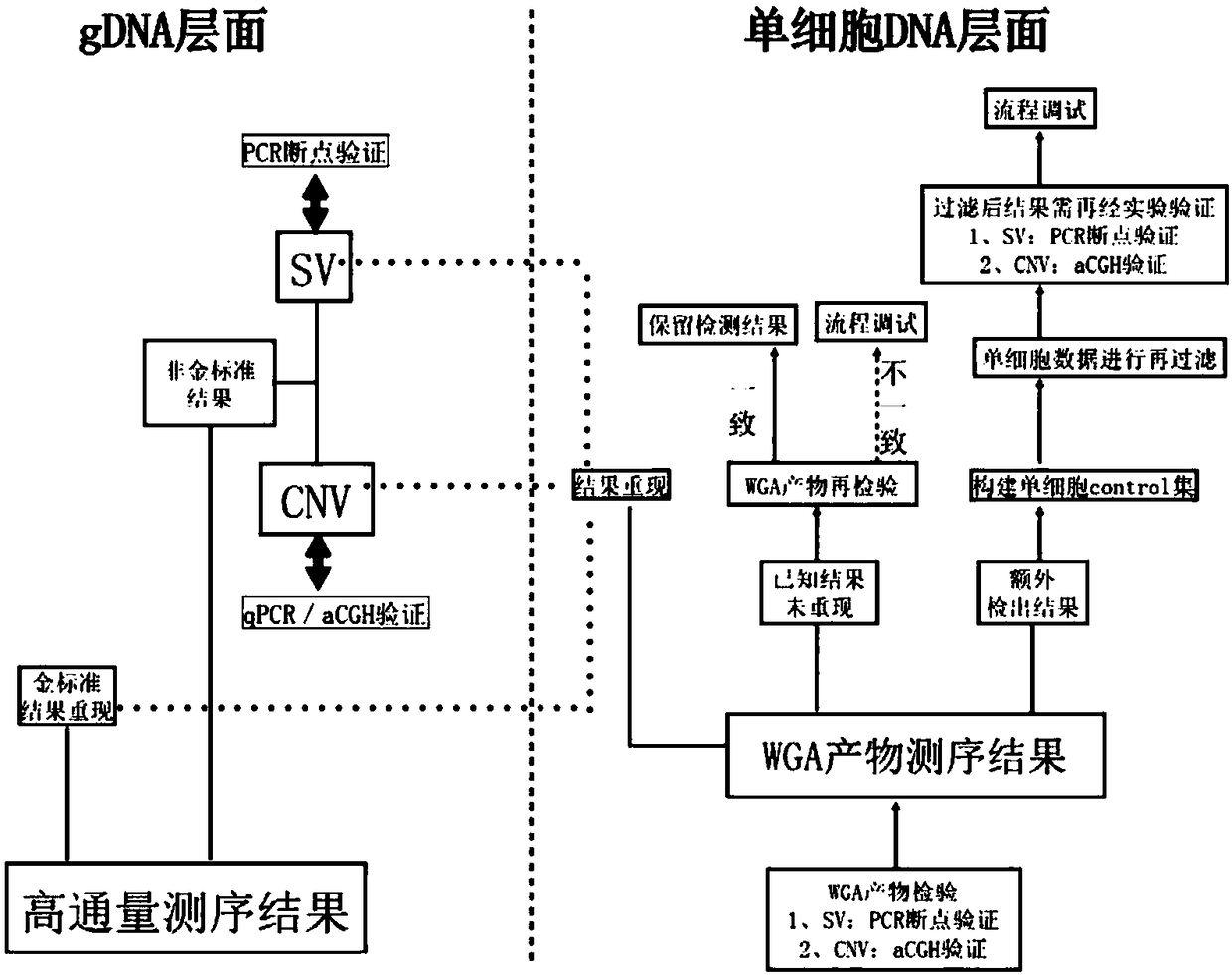
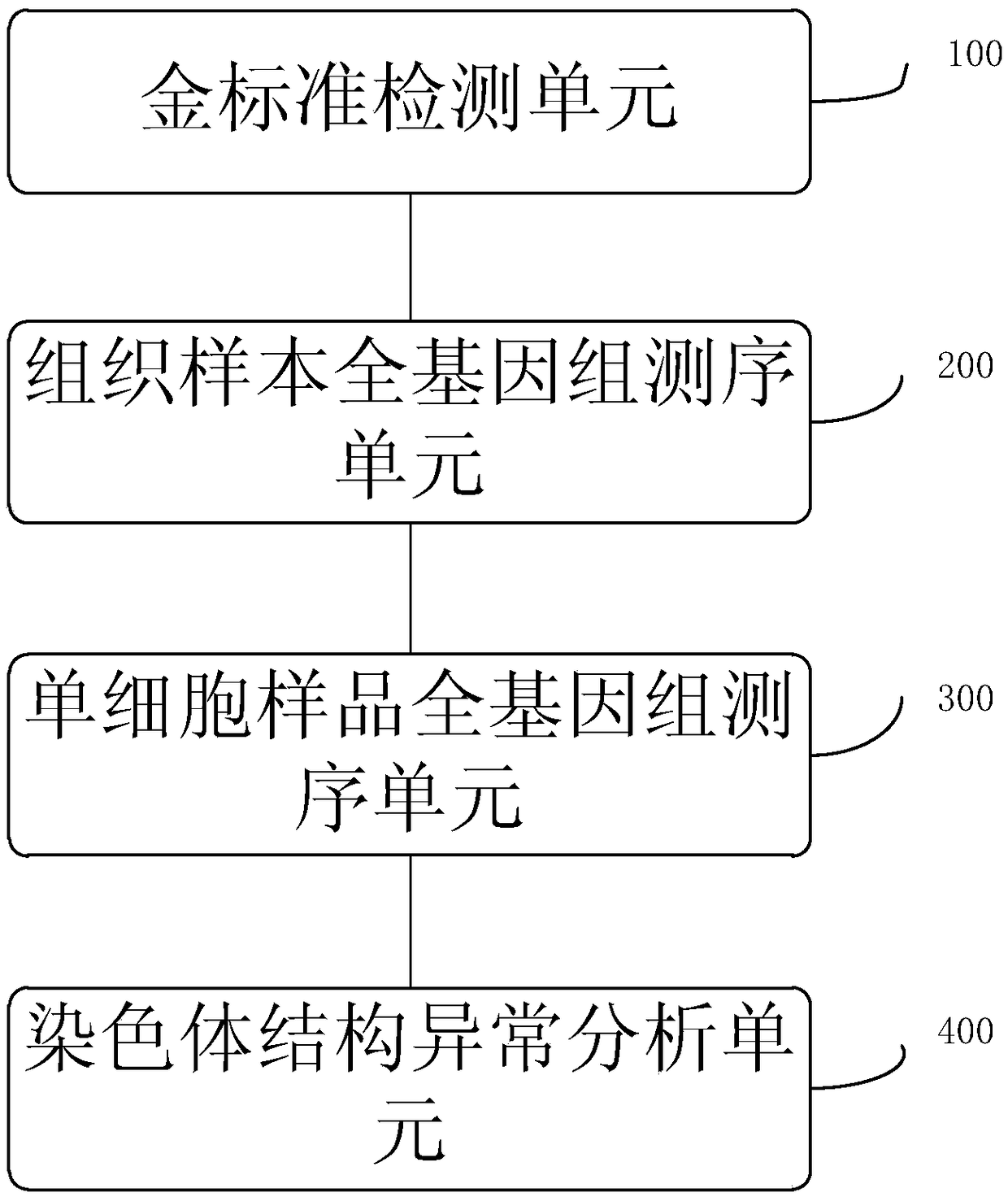
Method and system for determining individual chromosome structure abnormity
PendingCN109280702AImprove the detection rateMicrobiological testing/measurementWhole genome sequencingTissue sample
The invention provides a method for determining an individual chromosome structure abnormity. The method includes the following steps: (1) determining first candidate chromosome structure abnormity types of an individual by using at least one of karyotyping and microarray chip analysis to obtain a first candidate chromosome abnormality type set; (2) performing whole genome sequencing on tissue samples of the individual and preforming first data analysis on obtained sequencing results to obtain a second candidate chromosome abnormality type set; (3) performing whole genome sequencing on singlecell samples of the individual and preforming second data analysis on obtained sequencing results to obtain a third candidate chromosome abnormality type set; and (4) determining a final chromosome structure abnormity type of the individual based on the first candidate chromosome abnormality type set, the second candidate chromosome abnormality type set and the third candidate chromosome abnormality type set.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
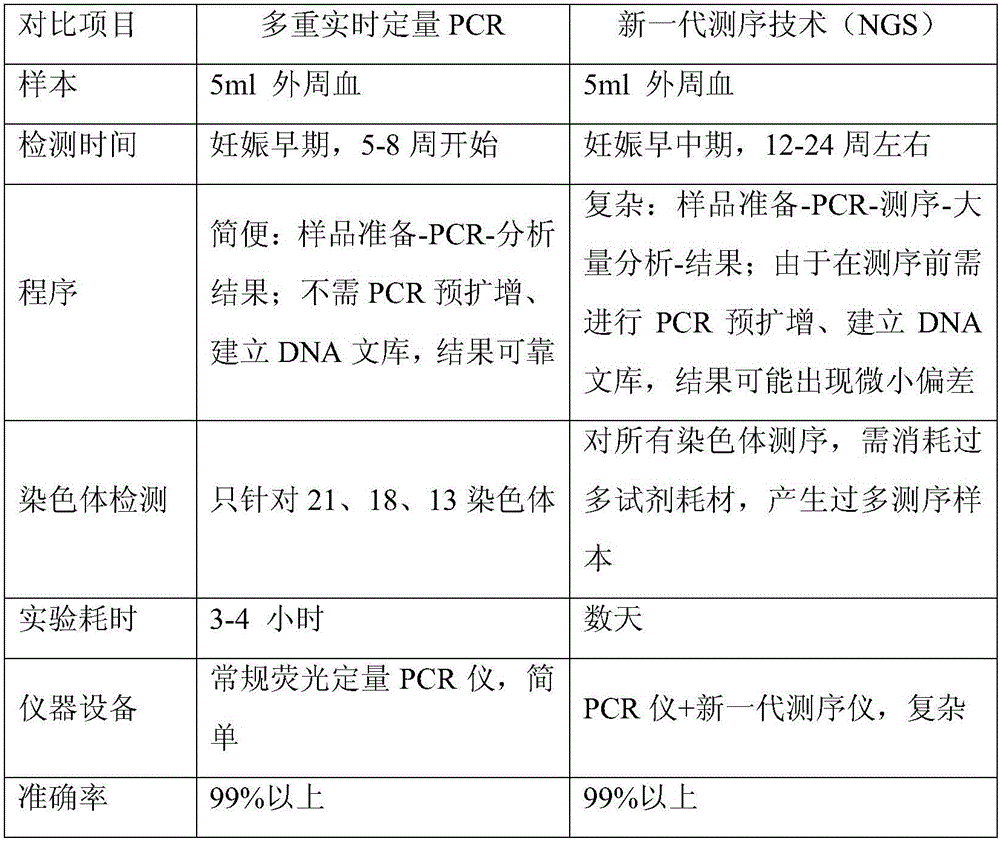
Kit for multiplex real-time quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection of chromosome aneuploid and application of kit
ActiveCN106191233AShort half-lifeIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPrenatal screeningS syndrome
The invention discloses a kit for multiplex real-time quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection of chromosome aneuploid and application of the kit. The kit comprises n1 primer pairs used for amplifying multiple genes and non-genetic locus of a target chromosome and related probes and n2 primer pairs used for amplifying multiple genes and non-genetic locus of a reference chromosome and related probes, wherein the target chromosome is a chromosome subject to chromosome quantitative variation diseases, the reference chromosome is one or multiple chromosomes, and n1 and n2 are greater than or equal to 1 respectively. The kit can be used for noninvasive prenatal screening of Down's syndrome, Edward's syndrome, PaDow's syndrome and other chromosome abnormality diseases of pregnant women. The kit has the advantages of early stage, safety, noninvasiveness, accuracy, quickness and suitability for large-scale detection and clinical application, intrauterine infection, abortion and death of fetuses at middle and late stages of pregnancy of women can be avoided, and the objective of bearing and rearing better children is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JENOMED BIOTECH CO LTD
Automatic chromosome segmentation and classification method based on deep learning
ActiveCN113658150AFully automatedRealize intelligenceImage enhancementImage analysisSupport vector machineClassification methods
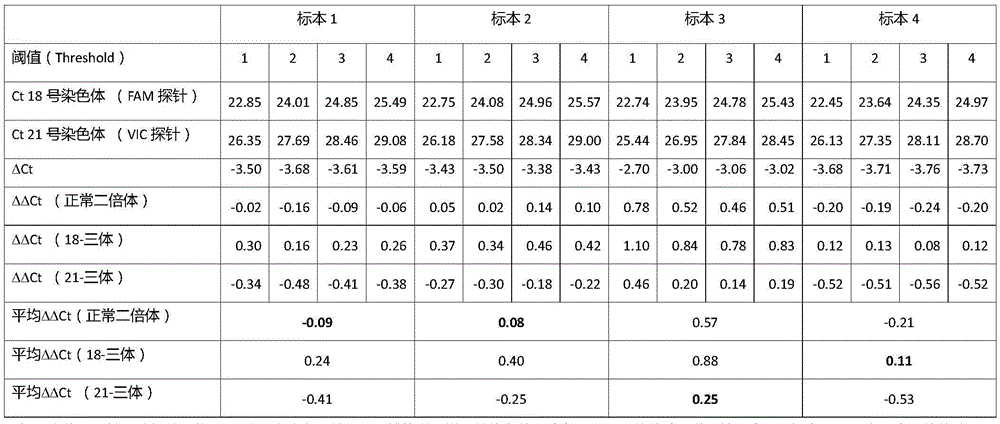
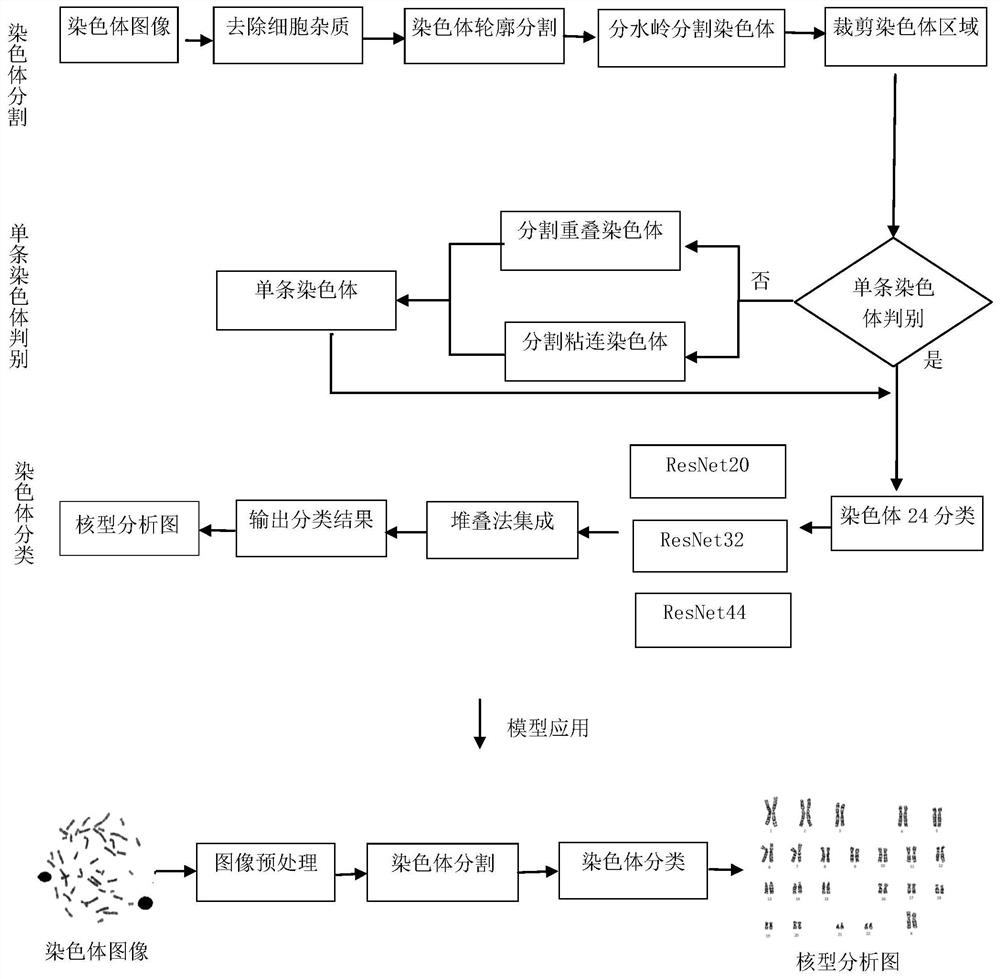
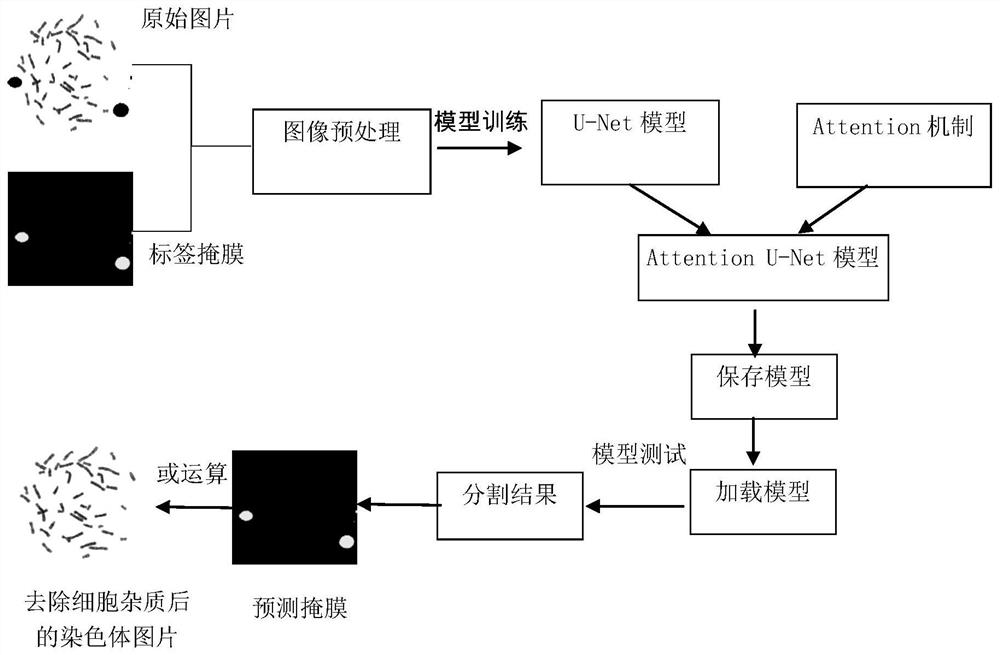
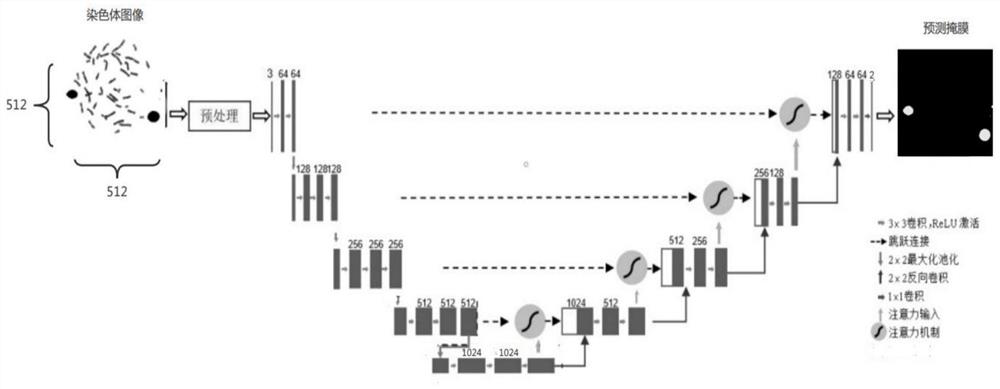
The invention discloses an automatic chromosome segmentation and classification method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a chromosome image and filtering cell impurities by using an Attention U-Net model; segmenting chromosomes and cutting out each chromosome region image; extracting features from the obtained chromosome region, training a support vector machine, a random forest and a logistic regression classifier, and carrying out model integration by adopting a voting method so as to identify overlapped adhesion chromosomes or single chromosomes; respectively designing independent segmentation modules for the overlapped adhesion chromosomes, segmenting the overlapped chromosomes by utilizing a method of separating and then splicing, and segmenting the adhesion chromosomes by utilizing a convex defect point detection method; and respectively inputting the chromosome training data with marked types into 24 classification models ResNet20, ResNet32 and ResNet44 for training, then carrying out model integration by using a stacking method, and outputting a final chromosome classification result and a chromosome karyotype analysis chart so as to carry out chromosome anomaly identification.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Genetic abnormality screening method for embryos
The present invention discloses a genetic abnormality screening method for embryos. The present invention discloses a device. The device comprises a detection device, a genetic disease screening device and a chromosome abnormality screening device; the detection device is used for acquiring target area data of an embryo father, an embryo mother, a propositus and an embryo, and full genome data ofthe embryo; the target area data are genotypes of SNP loci in genetic disease related genes and peripheral regions; the genetic disease screening device is used for screening genetic diseases: effective SNP loci are selected according to target area data of a father and target area data of a mother; haplotypes are established according to genotypes of the effective SNP loci of the embryo father, embryo mother and propositus, and then genetic diseases are screened by performing haplotype linkage analysis on the embryo; and the chromosome abnormality screening device is used for screening chromosome abnormality and judging whether the embryo has chromosome abnormality according to the whole genome data of the embryo. The genetic abnormality screening method for embryos has great applicationand popularization value for genetic screening before embryo implantation.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Method for detecting mutation and HRD scoring of tumor patient to guide medication
PendingCN112820351ACalculation speedEasy to detectDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsAllele ImbalanceWhite blood cell
The invention relates to a method for for detecting mutation and HRD scoring of tumor patient to guide medication, which comprises the following steps: detecting a tumor tissue sample and a control leukocyte sample thereof on the basis of taking a BAM file as an input file, and detecting mutation information of an HRR pathway in panels of different sample types and large-fragment chromosome abnormality HRD caused by gene recombination repair defects, the method for detecting the tumor tissue sample comprises the following steps: 1) detecting mononucleotide mutation of an HRR pathway; 2) detecting the loss of heterozygosity (LOH), telomere allele imbalance (TAI) and large fragment state transition (LST) of the HRR region, wherein the HRD score is equal to the weighted sum of LOH, TAI and LST scores; the invention provides a mutation and HRD scoring medication guidance method for tumor patients. According to the method, a traditional method that the HRD value score is calculated through whole genome detection and is not beneficial to clinical actual effect is optimized, the calculation speed is increased, the detection effect is good, the detection result is accurate, and the requirements of actual application can be well met.
Owner:江苏医联生物科技有限公司
Detection kit for chromosome abnormality before embryo implantation
PendingCN107267628AImprove amplification uniformityReduce analysis biasMicrobiological testing/measurementImage resolutionEmbryo
The invention discloses a detection kit for chromosome abnormality before embryo implantation. The kit is characterized by comprising a single cell amplification reagent, a fragmentation reagent, a library construction reagent, a DNA purification reagent, and negative and positive quality control substances. The invention also discloses a detection method of the aforementioned kit. Compared with the prior art, the invention establishes a method using embryo blastula stage cells for preimplantation chromosome detection, adopts innovative single cell amplification technology, improves the uniformity (97% or above) and coverage (92% or above) of single cell amplification, and has the advantages of rapid detection, wide coverage, high resolution, high accuracy and moderate flux.
Owner:SUZHOU BASECARE MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
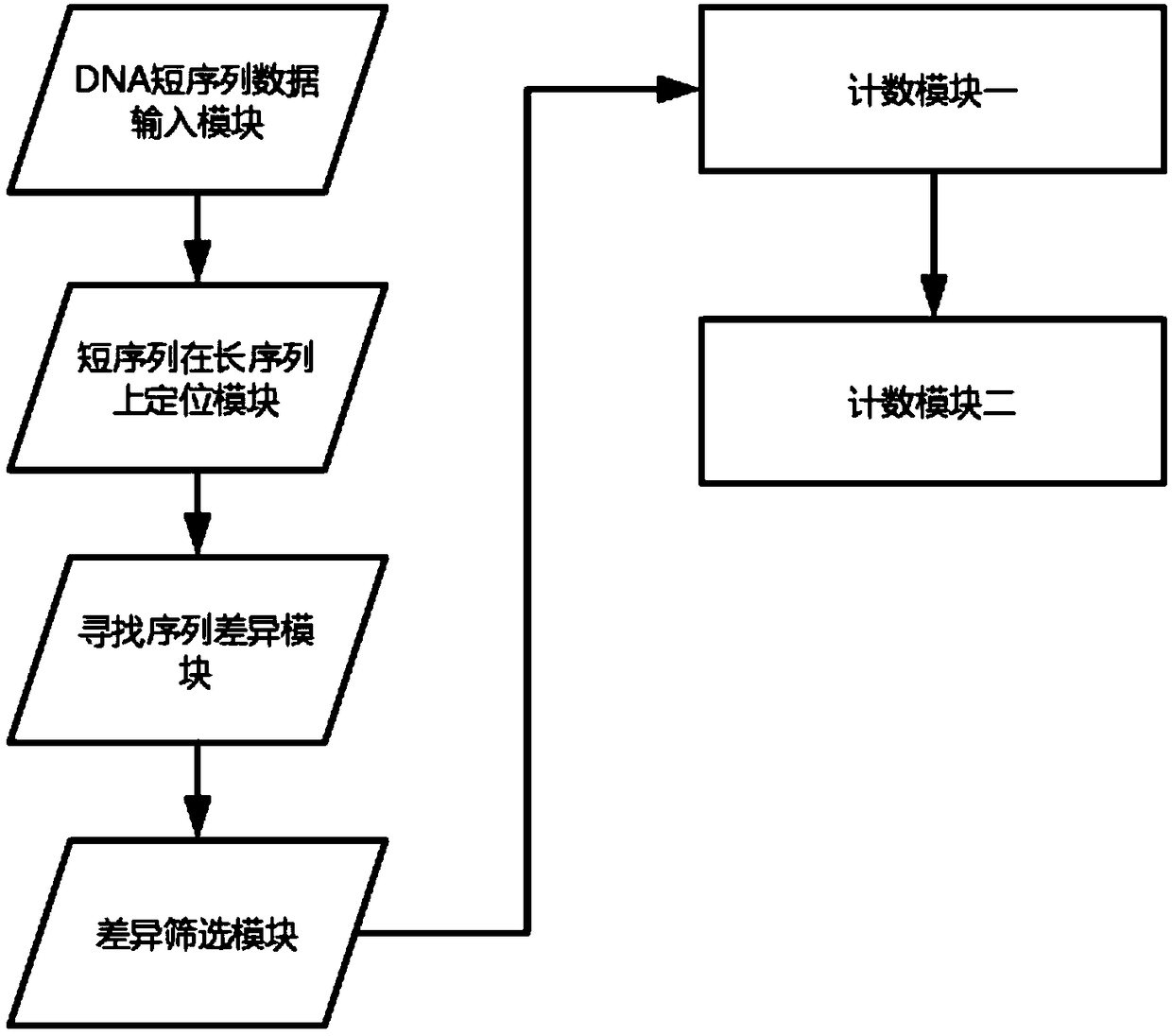
Fetus chromosome detecting system based on DNA variation counting
ActiveCN109402247AReduce adverse effectsPredict chromosomal abnormalitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementPlasma glucoseDNA
The invention provides a fetus chromosome detecting method based on DNA variation counting. The method comprises the steps of obtaining and sequencing free DNA of plasma in a peripheral blood sample of a pregnant woman, comparing the free DNA of the plasma with human reference sequences, namely DNA long sequences on 24 chromosomes, counting the number of variation in the free DNA of the plasma andconducting comparison. The invention further discloses a system for achieving the detecting method. The system comprises a DNA short sequence data input module, a module for positioning short sequences on the long sequences, a module for founding sequence difference, a difference screening module, a first counting module and a second counting module, wherein the modules are sequentially and electrically connected. According to the fetus chromosome detecting method based on DNA variation counting and the system for achieving the method, by detecting chromosomes in peripheral blood of the pregnant woman, whether there is chromosome abnormality or not in a fetus is judged, thus harmful effects on the pregnant woman and the fetus in a detecting process are greatly reduced, and by calculatingthe variation number to judge the chromosome abnormality of the fetus, compared with a method that a sequence number is calculated simply, the fetus chromosome detecting method based on DNA variationcounting is more accurate.
Owner:苏州首度基因科技有限责任公司
Chromosome preparation method, as well as required culture medium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102443623AQuality improvementEasy to check and analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementPhytohemagglutininsPrenatal diagnosis
The invention discloses a chromosome preparation method, as well as a required culture medium and a preparation method thereof, and is used for solving karyotype analysis problem of chromosome. The culture medium consists of RPMI (Roswell Park Memorial Institute) 1640, heparin sodium, HEPES (2-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethanesulfonic acid), L-glutamine, NaHCO3, benzylpenicillin potassium, streptomycin sulphate, bovine serum and phytohemagglutinin (PHA). The detection method comprises the following steps: implanting 0.3 to 0.4ml of human peripheral blood into the culture medium; adding colchicinamide in 2-4 hours before culture is terminated to realize that the cell is terminated in anaphase; culturing the cell after 68 to 72 hours to harvest the cell; performing hypotonicity for 40 minutes, three times of fixation, banding, dyeing and other treatments; and performing chromosome analysis under a microscope to determine whether the peripheral blood supplier has a phenomenon of chromosome abnormality. The culture medium disclosed by the invention has convenience for use, simpleness in operation, low cost and low patient detection fee, and is suitable for genetic diagnosis, infertility and prenatal diagnosis in each level of hospitals.
Owner:苏州苏大赛尔免疫生物技术有限公司
Screening kit for seventh chromosome abnormality diseases of fetus
The invention discloses a screening kit for the seventh chromosome abnormality diseases of a fetus. The screening kit comprises a reagent for detecting the PLGF (placental growth factor) level of the serum or urine of a pregnant woman. The invention further discloses an application for the screening kit for the seventh chromosome abnormality diseases of a fetus in detection for the PLGF level of the serum or urine of a pregnant woman. The kit disclosed by the invention can be used for evaluating whether the seventh chromosome of the fetus is normal or not, and is good in clinical application prospect.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
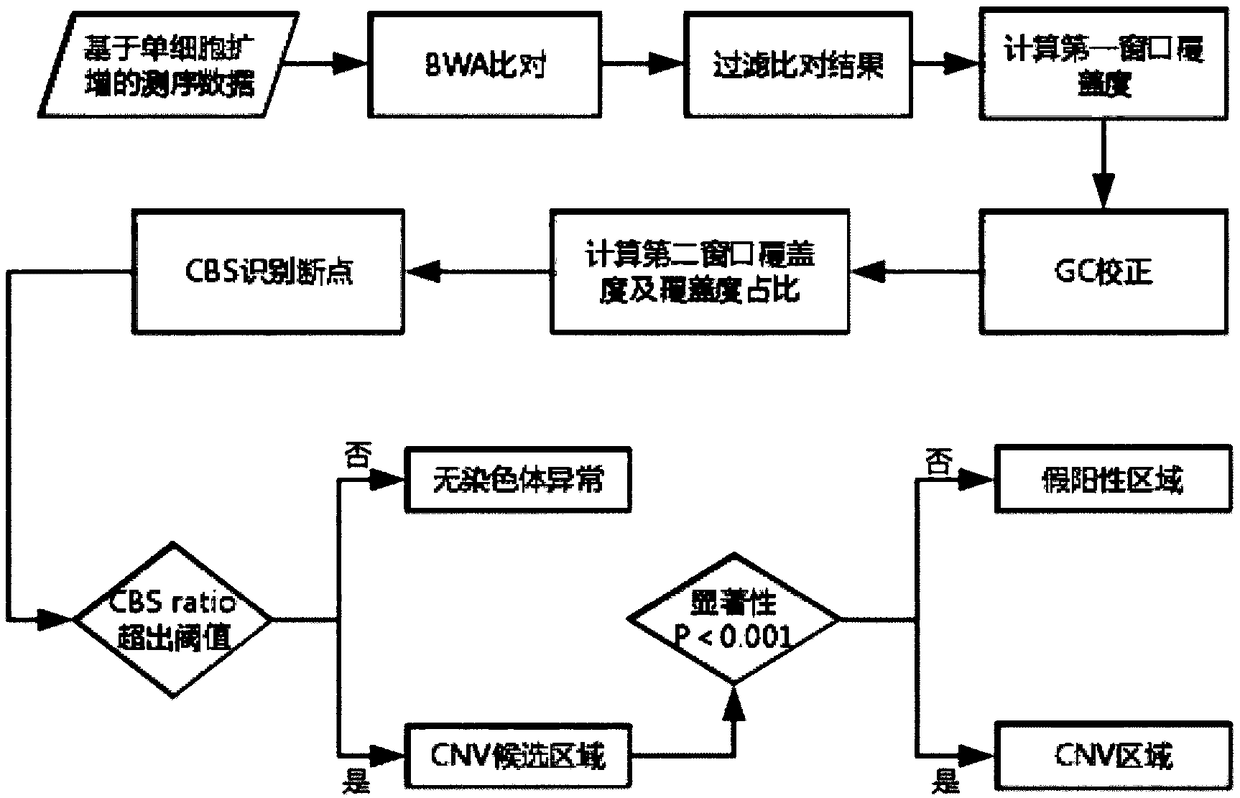
Chromosome abnormality detection device
ActiveCN108268752AImprove uniformityImprove the detection rateBiostatisticsSequence analysisPositive sampleFalse positive paradox
The invention discloses a chromosome abnormality detection device. Aiming at solving the problems that conventional chromosome abnormality detection and analysis are based on a reads number statistical model, can only remove duplicate reads compared in the same initial position of a genome but cannot remove mutually overlapped reads with different initial positions, the device can effectively remove the duplicate reads and overlapping areas caused by amplification preference of a whole genome of a single cell by introduction of a sequence coverage statistical model, data uniformity is remarkably improved, then data noise is reduced, detection rate of positive specimens is increased, and false positive rate is reduced.
Owner:CAPITALBIO GENOMICS
Method for prenatal screening chromosome abnormality and application thereof
InactiveCN101603083AImprove the detection rateReduce false positive rateMicrobiological testing/measurementSerum markersObstetrics
The invention discloses a method for prenatal screening chromosome abnormality and an application thereof. The invention comprises the following steps: totally calculating various measurement indicators of normal pregnant women in China to obtain the median of serum marker of single pregnancy people in each gestational week, the median of serum marker of double pregnancy people in each gestational week and the median of translucent thickness of fetal nape of normal pregnant women in each gestational week; detecting the serum marker, fetal number, translucent thickness of fetal nape of the detected pregnant women to determine the gestational weeks of the pregnant women; correcting according to the weight of the detected pregnant women and finally calculating the multiples of the median value (MoM value) of serum marker; then comparing correspondingly the multiples of the median of serum marker of the detected women with the median of serum marker of normal pregnant women according to the gestational weeks of the pregnant women and fetal number, calculating the likelihood ratio of the serum marker of the detected pregnant women to obtain the risk rates of 21 trisome, 18 trisome or 13 trisome and the risk rate of NTD risk.
Owner:GUANGDONG WOMEN & CHILDREN HOSPITAL +1
Method for detecting chromosome abnormality of embryos by aid of blastocyst cultivation solution without zona pellucida
The invention provides a method for detecting chromosome abnormality of embryos by the aid of blastocyst cultivation solution without zona pellucida. The method which is particularly an in-vitro non-therapeutic method for detecting the chromosome abnormality of the embryos by the aid of the blastocyst cultivation solution includes steps of (a), providing the cultivation solution from blastocyst cultivation systems; (b), carrying out gene detection on the cultivation solution so as to authenticate whether chromosomes of the embryos are abnormal or not. The zona pellucida of the embryos in the blastocyst cultivation systems is removed before the embryos are cultivated, the embryos are cultivated in the blastocyst systems for 3-6 days, and preferably, the cultivation solution is separated from the cultivation systems after 4 days. The method has the advantages that contamination and interference risks due to redundant sperms and parent-source granular cells in IVF (in-vitro fertilization) and ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) technical procedures can be eliminated, and whether the chromosomes of the embryos are abnormal or not can be accurately authenticated.
Owner:XUKANG MEDICAL SCI & TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Method for generating cloned animals using chromosome shuffling
InactiveUS20040139489A1Population uniformImprove quality controlGenetic material ingredientsGenetic engineeringSpecific chromosomeMammal
The present invention concerns the use of chromosomal replacement techniques in the context of producing cloned and transgenic animals, in order to correct chromosome abnormalities or alter autosomal genotypes, and provide for novel breeding pairs by replacing the sex chromosome in animals to be cloned. Replacement of a sex chromosome, or an X or Y chromosome, will result in animals that are autosomally isogenic and sexually non-isogenic (AISN), with "autosomally isogenic" meaning that the paired sets of autosomes (non-sex chromosomes) in each animal are isogenic or identical. Also included in the invention are animals that are both "autosomally" and "allelically" isogenic whereby each particular pair of chromosomes is internally isogenic or identical within a single animal as well as between animals. Such animals are particularly useful in generating a line of cloned mammals using sexual reproduction, without having to undergo nuclear transfer in order to propagate cloned animals.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Centromere detector and method for determining radiation exposure from chromosome abnormalities
ActiveUS8605981B2Microbiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiation exposureDicentric chromosome
A method for determining radiation exposure from chromosome abnormalities present in a specimen by determining the location or locations of the centromere of each chromosome in a cell in an image of a metaphase cell by segmentation of an accurately drawn chromosome centerline followed by selection of a longitudinal cross-section with the minimum width or intensity or width and intensity; counting the number of centromeres in each chromosome in each cell; computing the frequency of dicentric chromosomes in a population of cells; and determining the radiation dose by comparing the computed frequency of dicentric chromosomes with a previously determined dose-response curve from a calibrated source.
Owner:CYTOGNOMIX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com