Patents
Literature
79 results about "Granulosa cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A granulosa cell or follicular cell is a somatic cell of the sex cord that is closely associated with the developing female gamete (called an oocyte or egg) in the ovary of mammals.
Methods for the culture of human embryonic stem cells on human feeder cells
InactiveUS7432104B2Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsBone Marrow Stromal CellCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human granulosa feeder cells, muscle cells, Fallopian ductal epithelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and skin fibroblasts and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be alternatively cultured with conditioned medium obtained from a cell culture capable of maintaining human embryonic stem cells in a pluripotent state, wherein the cell culture is a human granulosa cell culture.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Alternative compositions and methods for the culture of stem cells
InactiveUS20050037488A1Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsBone Marrow Stromal CellCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human granulosa feeder cells, muscle cells, Fallopian ductal epithelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and skin fibroblasts and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be alternatively cultured with conditioned medium obtained from a cell culture capable of maintaining human embryonic stem cells in a pluripotent state, wherein the cell culture is a human granulosa cell culture.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
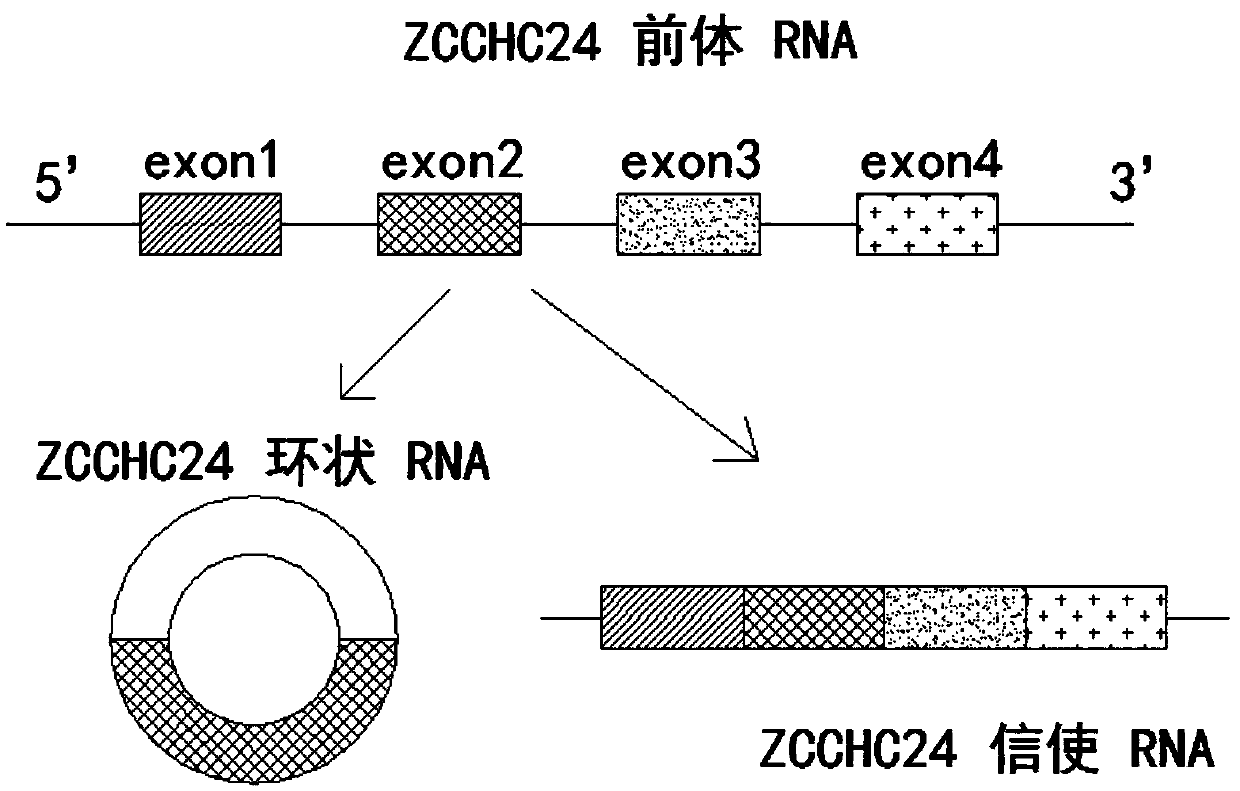
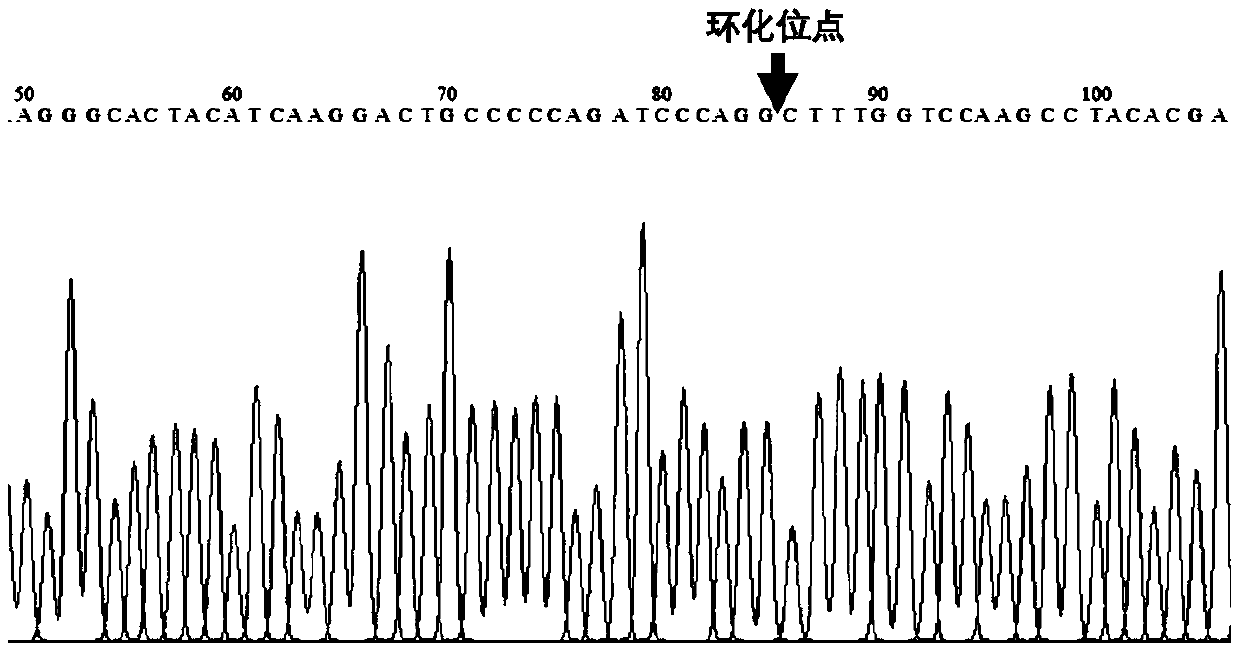
Goat circular RNA, and identification method and functional application thereof
ActiveCN109609656AAccurate detectionPromote proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideRna expression
The invention discloses a goat circular RNA as well as an identification method and functional application thereof. Nucleotide sequences of primers used for detecting the goat circular RNA circ_ZCCHC24 are respectively shown in the SEQ ID NO: 2 and the SEQ ID NO: 3. An over-expression vector constructed by an over-expression vector plasmid construction method of the goat circular RNA circ_ZCCHC24contains a circular RNA expression vector pCD2.1-ciR as well as full-length sequence information of the goat circular RNA circ_ZCCHC24, and is capable of promoting proliferation of goat follicular granulosa cells; and thus, new ideas for further understanding genetic mechanisms of goat follicular granulosa cell development are provided by the goat circular RNA circ_ZCCHC24. Therefore, the goat circular RNA circ_ZCCHC24 is of great significance for studying the genetic essence of goat reproductive traits and breeding high-breed-rate goat breeds.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Endothelial cell growth factor, methods of isolation and expression
A novel growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells has been identified in conditioned medium of bovine pituitary derived folliculo stellate cells. This factor, named folliculo stellate derived growth facto (FSdGF) or vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), was purified to homogeneity by a combination of heparin sepharose affinity chromatography, Bio Gel P-60 exclusion chromatography, Mono S ion exchange chromatography and hydrophobic chromatography on a C4 reverse phase HPLC column. The factor is also found in the murine AtT-20 cell line. Alternatively, the growth factor is purified by a first reverse phase HPLC using acetonitrile gradient followed by a second reverse phase HPLC using an isopropanol gradient. FSdGF, having a molecular weight of about 43,000 da, was characterized as a glycoprotein composed of two homologous sub units with MW of about 23 kDa. FSdGF was a potent mitogen for vascular endothelial cells with activity detectable at 10 pg / ml and saturation at 500 pg / ml. It did not stimulate the proliferation of other cell types such as bovine corneal endothelial cells, adrenal cortex cells, granulosa cells, BALB / MK cells or BHK-21 cells. Microsequencing revealed an amino terminal sequence containing no significant homology to any known protein. The release of FSdGF by pituitary cells and its unique target cell specificity indicate that FSdGF is useful in angiogenesis.
Owner:FERRARA NAPOLEONE +2
Method for in vitro culture of ovarian follicles
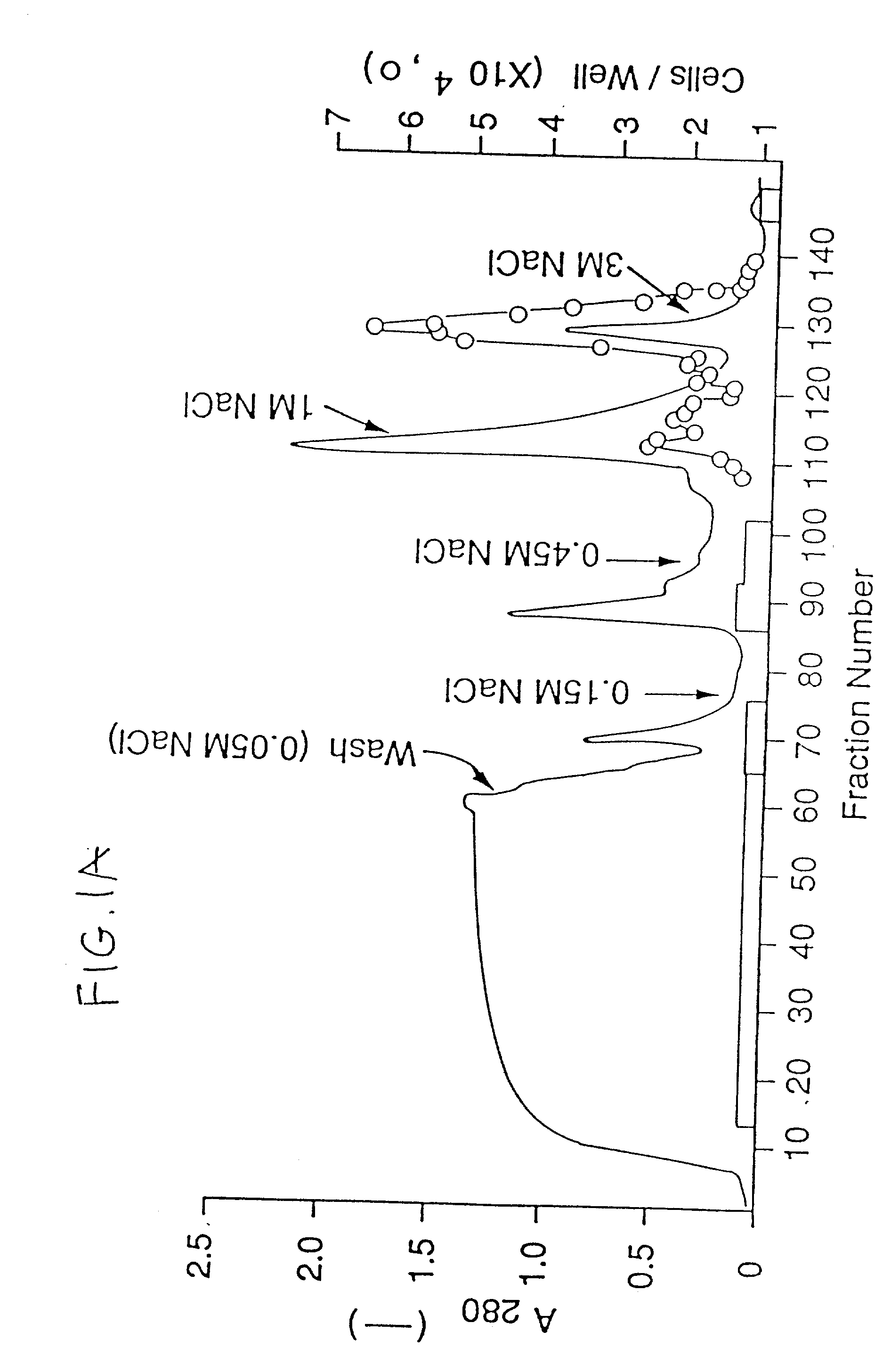
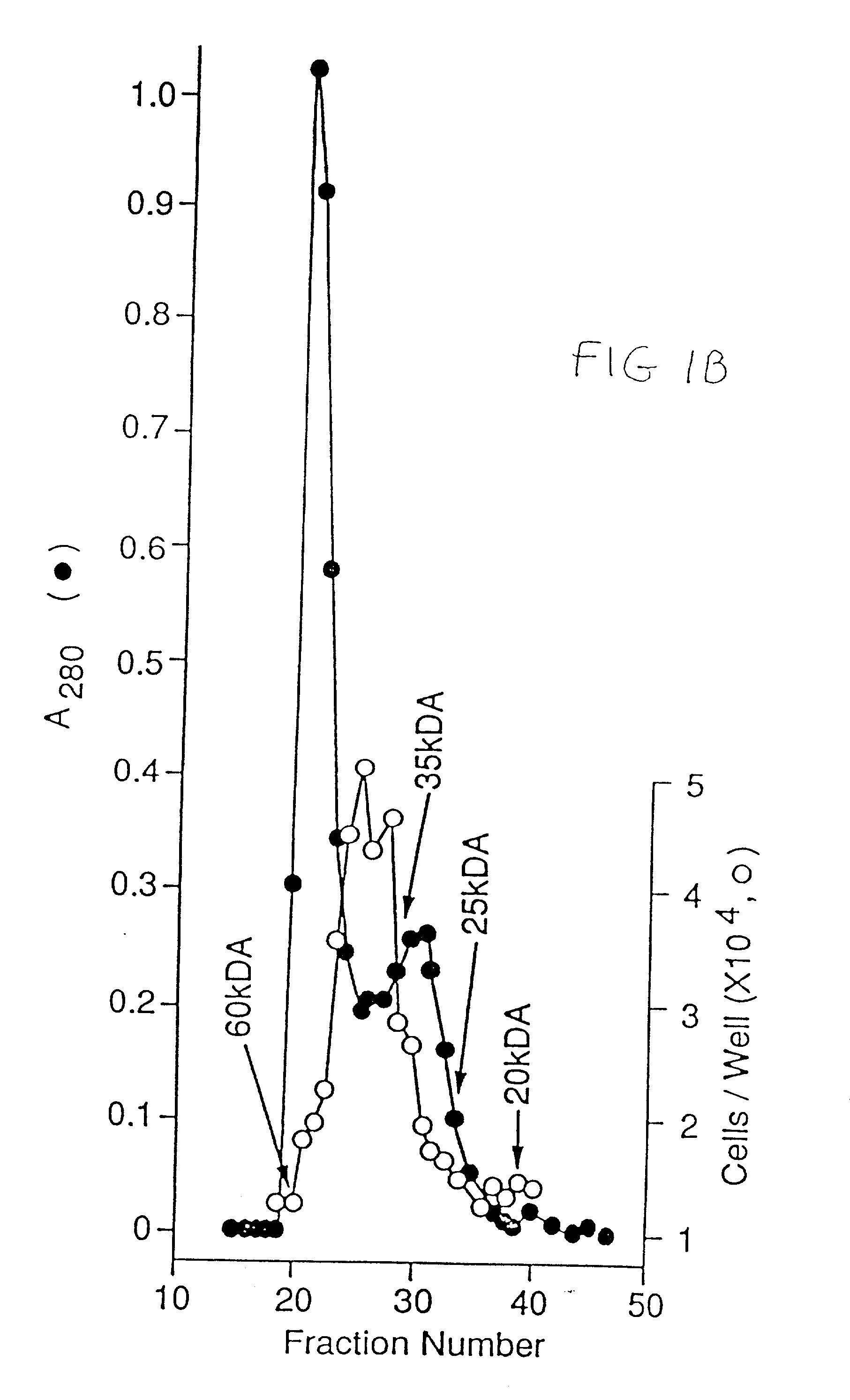
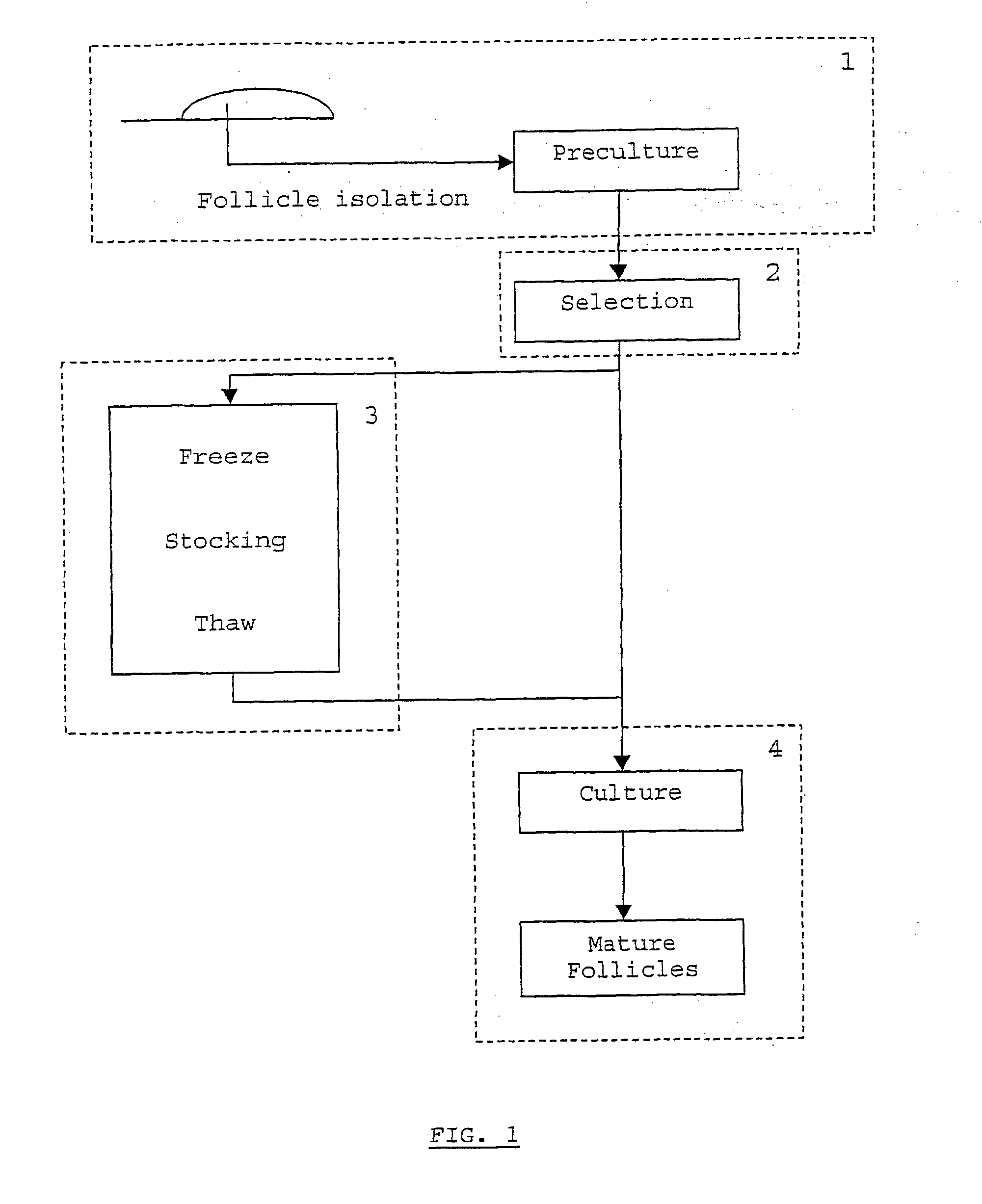
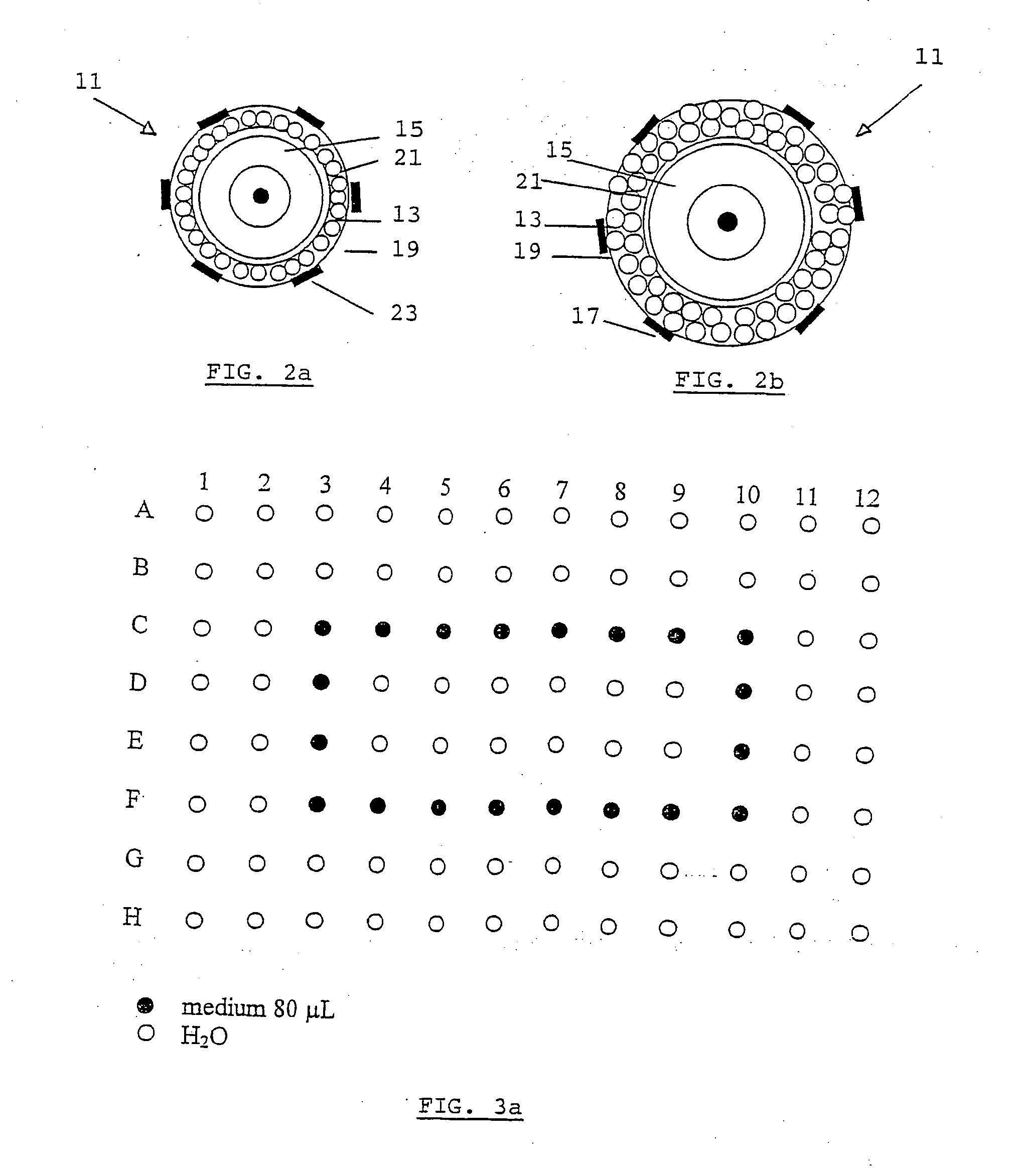
The present invention is related to a method for in vitro culture of mammalian ovarian follicles for bioassay purposes, comprising the following subsequent steps:-providing a suitable container for the in vitro culture,-selecting a follicle from an ovary of a mammal, said follicle comprising at least a theca or pre-theca cell, a granulosa cell and an oocyte,-an optional first culture step using an attachment prohibiting first medium free from oil,-a second culture step using an attachment promoting second medium free from oil arranged to, and-the retrieval of the matured follicle.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL
Immature oocyte in-vitro maturation culture solution and application thereof
ActiveCN107475181AImprove maturity rateIncreased potential for later developmentNew breed animal cellsCulture processMaturation oocyteCulture fluid
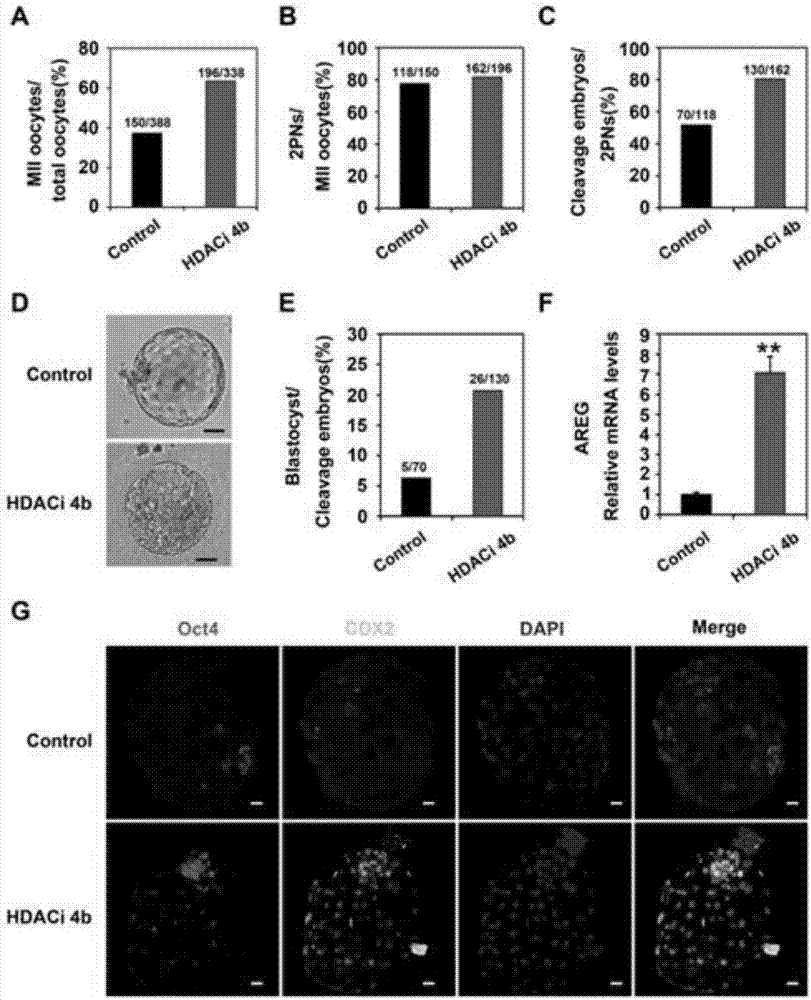
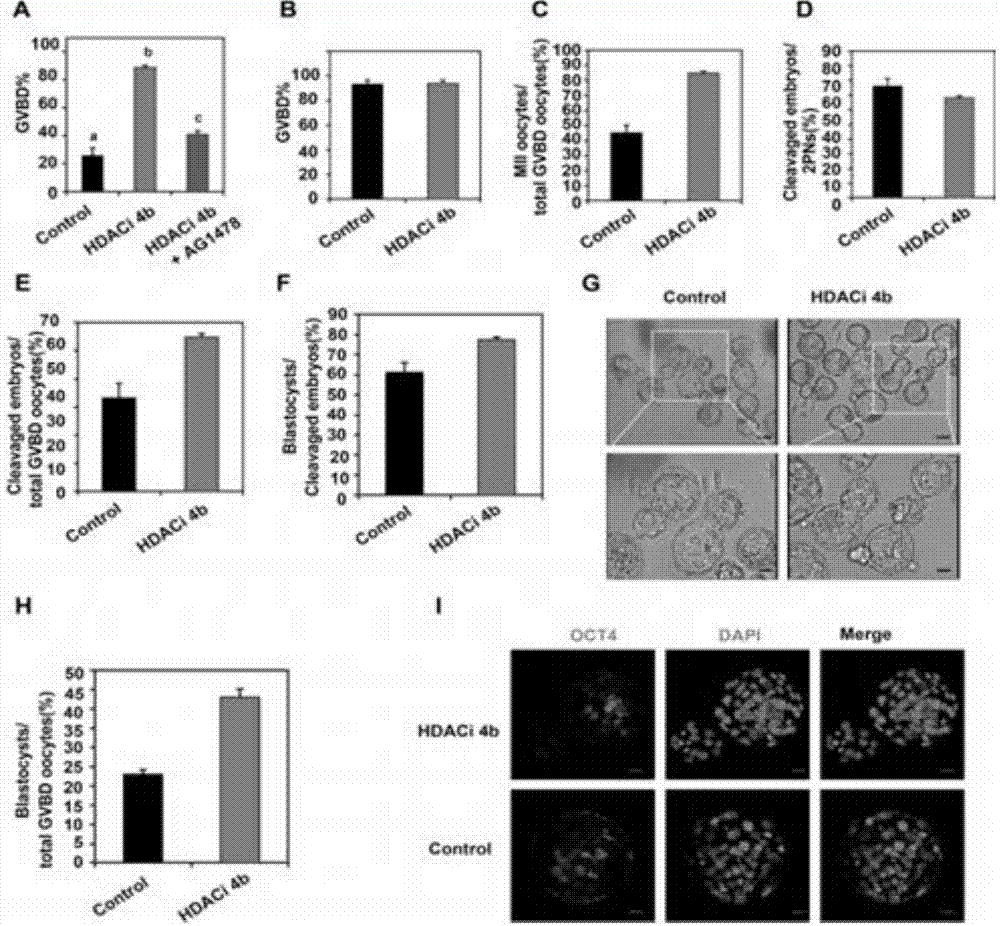
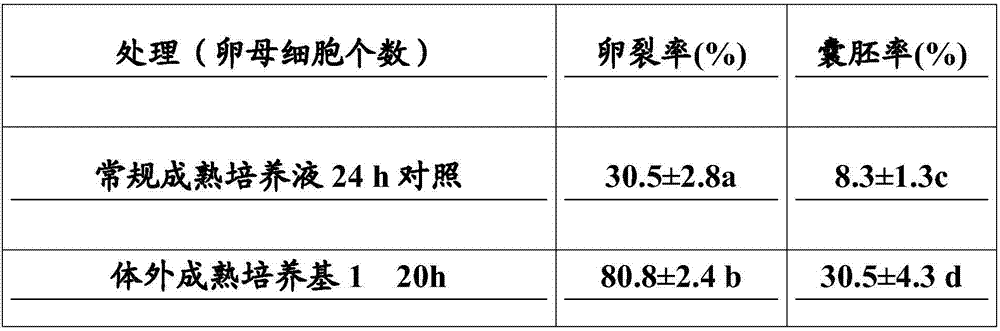
The invention relates to cell culture and particularly discloses an immature oocyte culture scheme which can promoting in-vitro maturation of immature oocytes. Specially, the scheme adopts follicular granulosa cells and a culture solution for culturing the follicular granulosa cells, wherein the culture solution for culturing the follicular granulosa cells contains CNP or its variants or analogues and an HDAC (histone deacetylase) inhibitor. The invention further provides an in-vitro maturation culture solution containing the CNP or its variants or analogues and the HDAC inhibitor and related compositions and application of a culture medium, the culture solution and the compositions in promotion of in-vitro maturation of immature oocytes.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Mammalian oocyte development competency granulosa markers and uses thereof
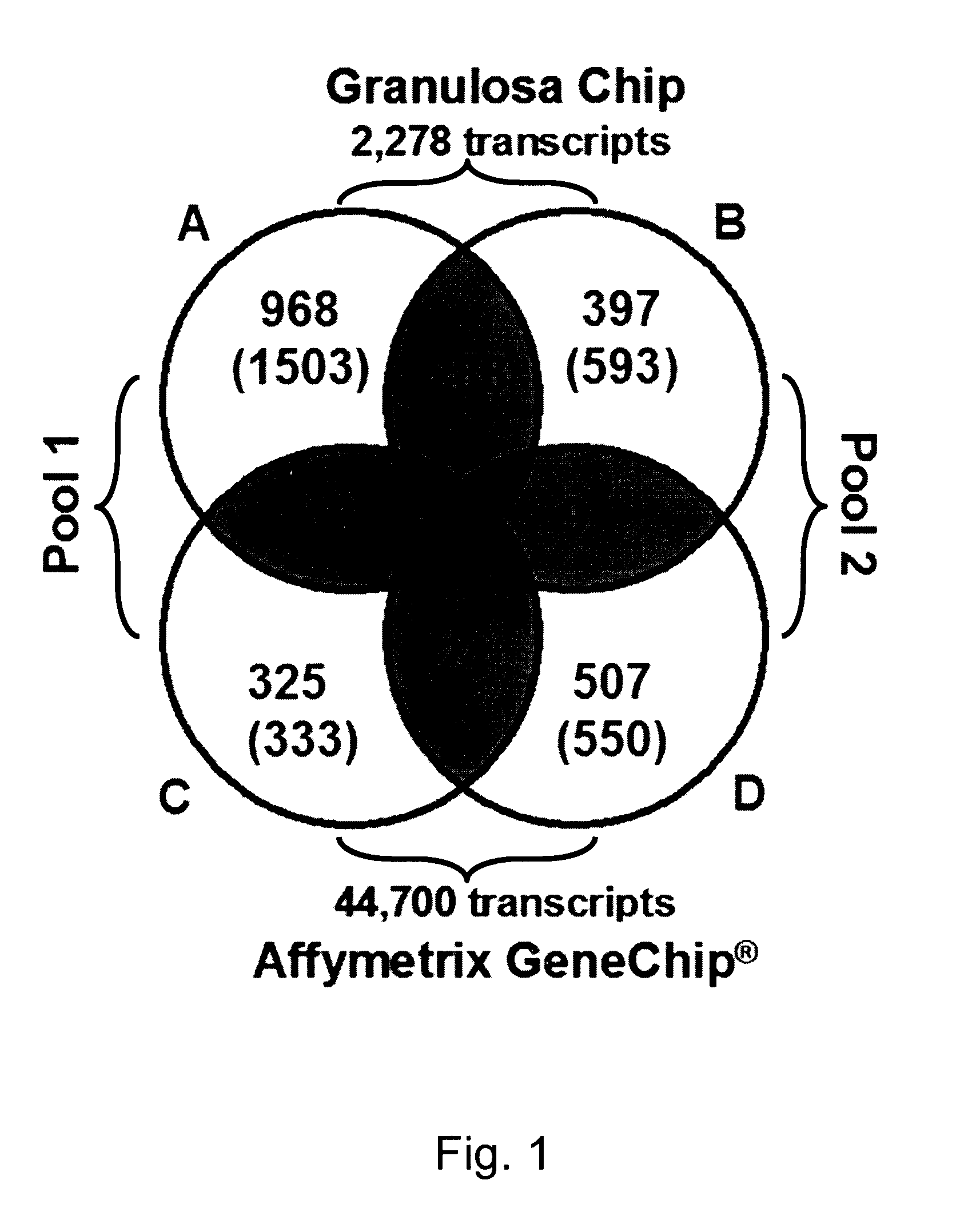
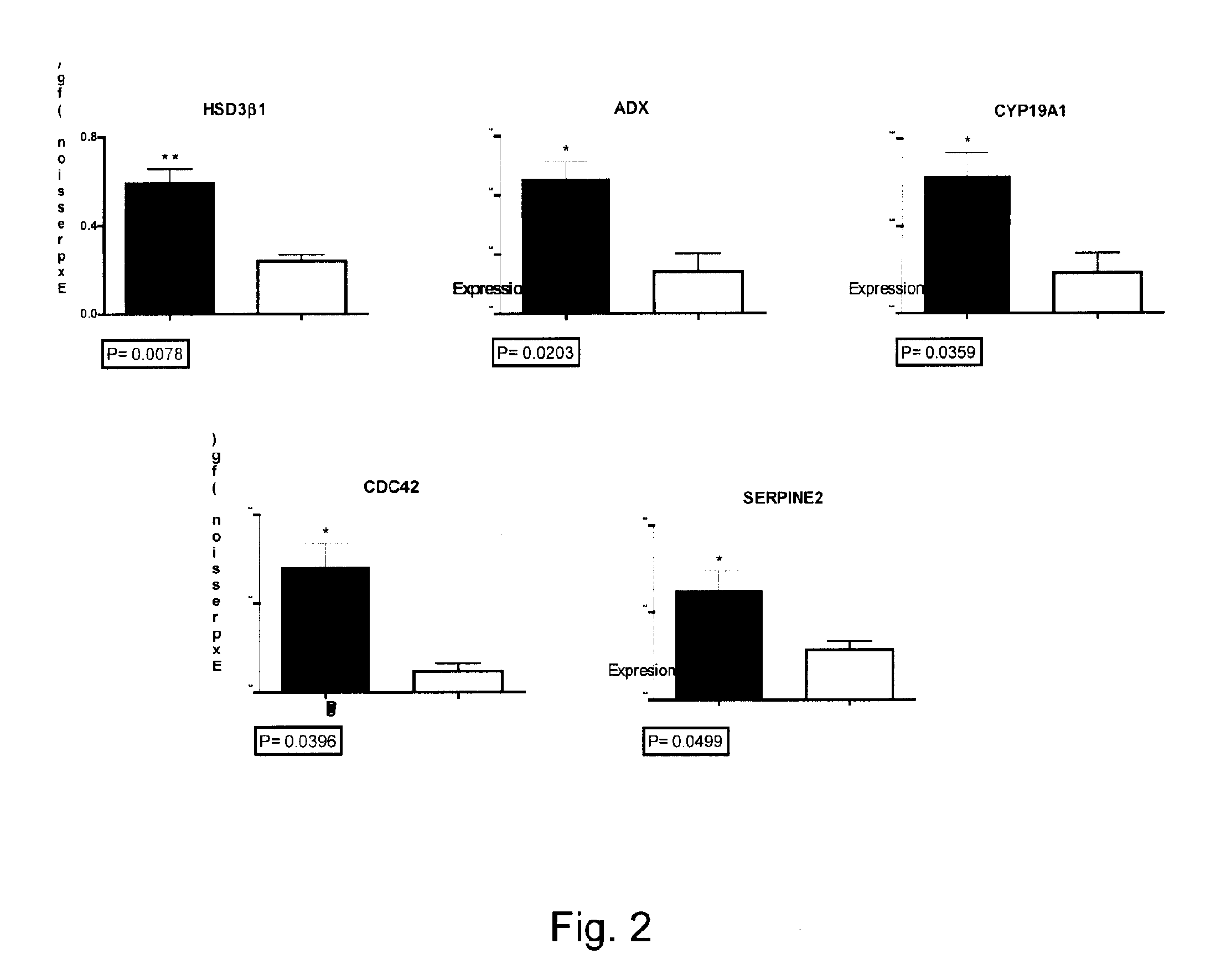
The present invention relates to the competence of oocytes for uterine implantation and development into living individuals. The invention more particularly relates to markers that are detected and measured in granulosa cells collected along with the oocytes during oocyte aspiration as it is done in assisted reproduction techniques. Markers include cytochrome P450 aromatase (CYP19A1), cell division cycle 42 (CDC42), 3-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 (3βHSD1), serpm peptidase inhibitor clade E member 2 (SERPINE 2), and adrenodoxm (ADX) that are detected and measured, using RT-PCR.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Method for separating different kinds of single cells in ovary
The invention provides a method for obtaining single oocyte and single granulosa cells thereof by separating early follicles of mammals. By means of the method, the early follicles of the mammals can be separated to obtain single oocyte with activity and the corresponding granulosa cells thereof. The invention further provides a kit for obtaining the single oocyte and the single granulosa cells thereof of the early follicles of the mammals.
Owner:SDIVF R&D CENT LTD
Determination of oocyte quality
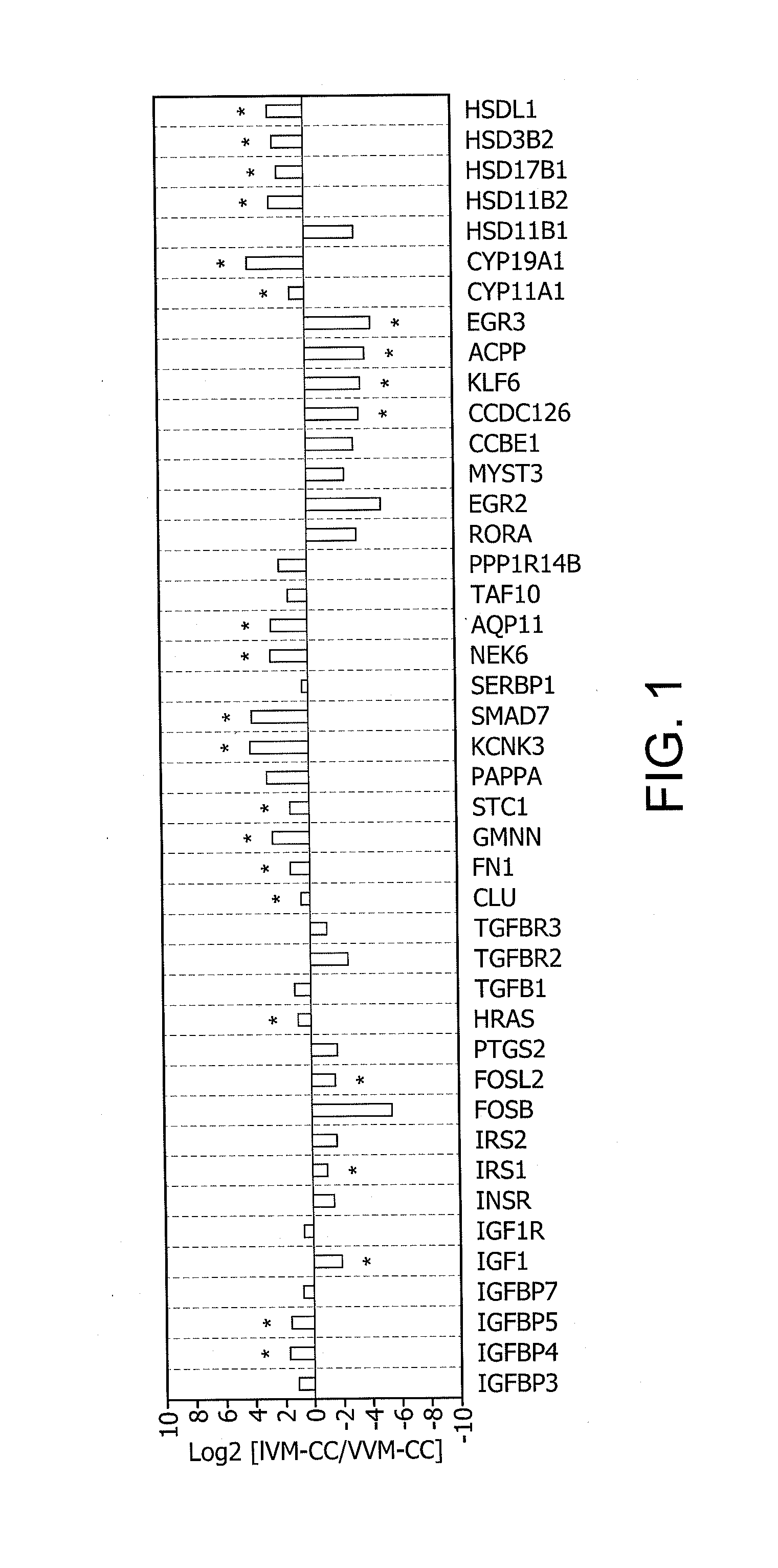
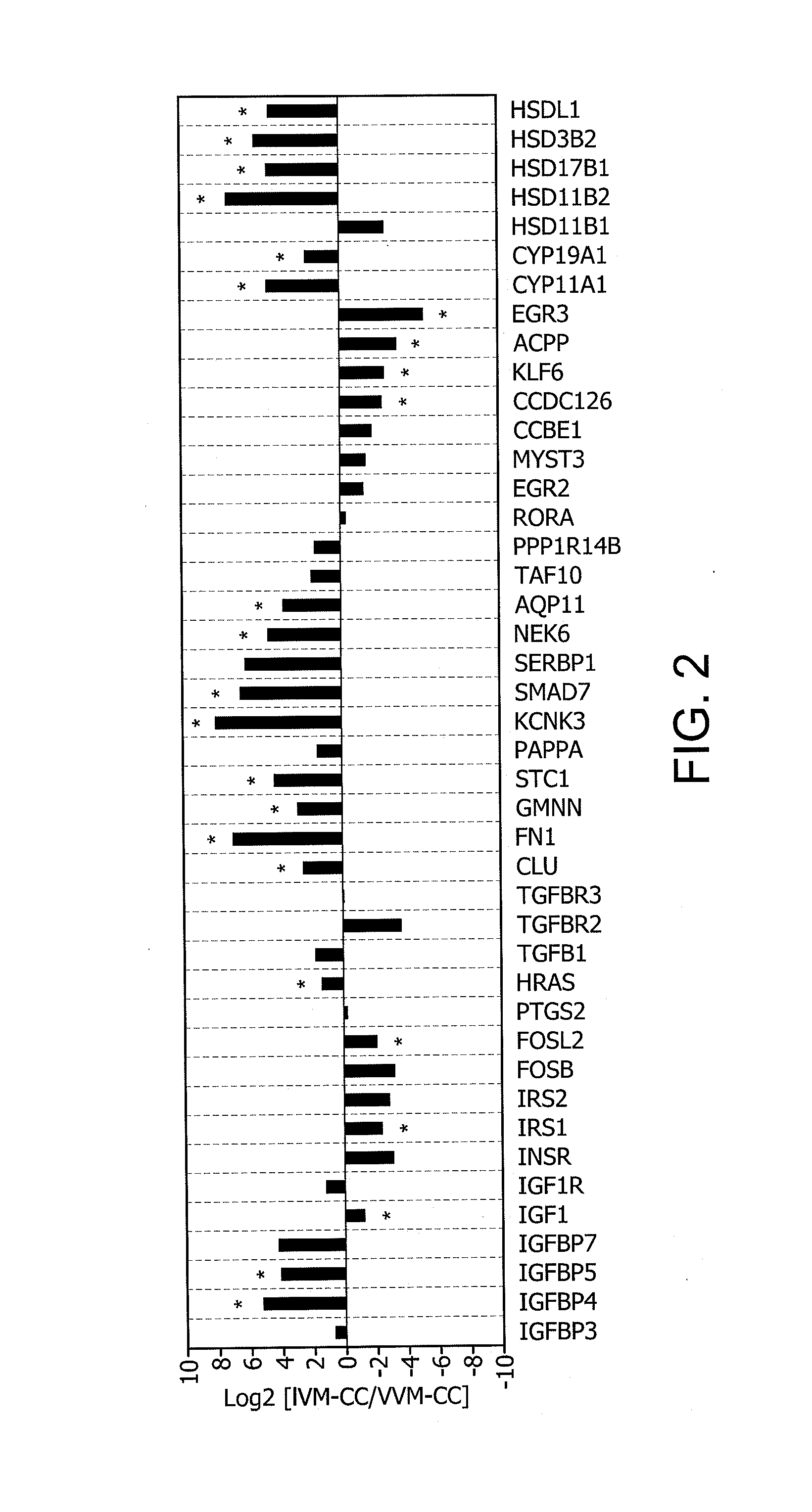
A method for evaluating the quality of mammalian oocytes comprises determining the expression level of one or more of the genes ACPP, AQP11, CCDC126, CLU, CYP11 A1, CYP19A1, EGR3, FN1, FOSL2, GMNN, HRAS, HSD3B2, HS-D17B1, HSD11B2, HSDL1, IGF1, IGFBP4, IGFBP5, IRS1, KCNK3, KLF6, NEK6, SMAD7 or STC1 in a test sample derived from a cumulus cell or granulosa cell associated with the oocyte, and comparing the expression level of said at least one marker gene expression in the sample with the expression level in a control. Differential expression of the gene between the sample and the control is indicative of the quality of the oocyte.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
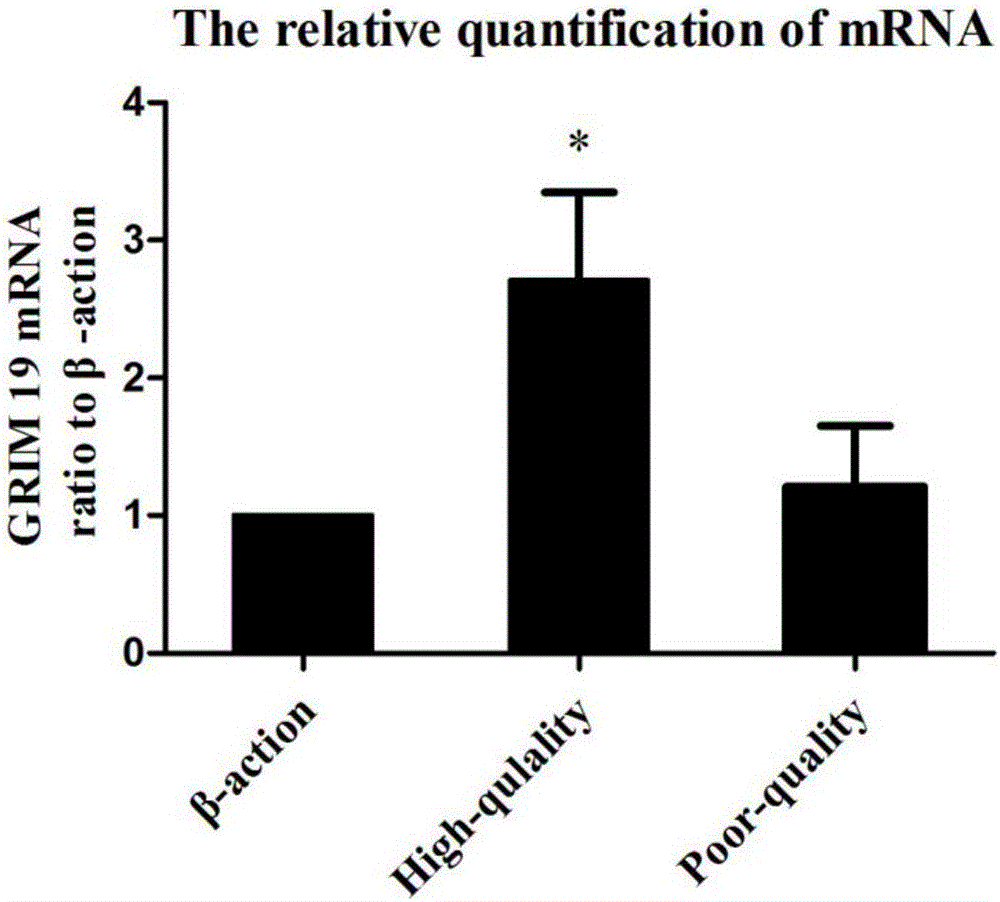
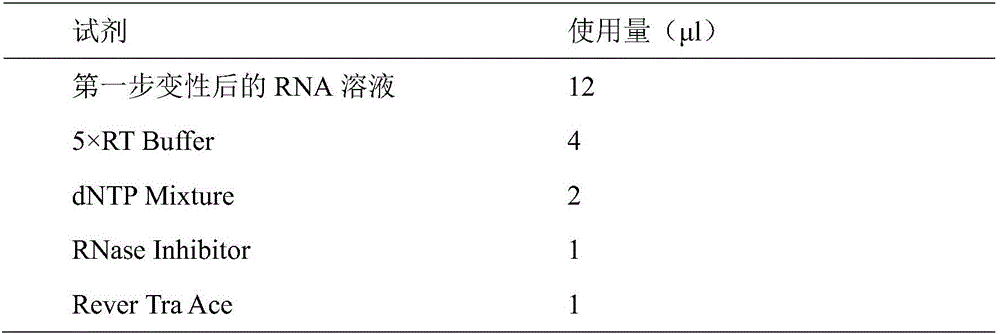
Method for evaluating developmental potential of oocyte by utilizing relative expression of GRIM19 in granulosa cell
ActiveCN105861709ANon-invasive injuryReduce stimulationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNumerical rangeGranulosa cell
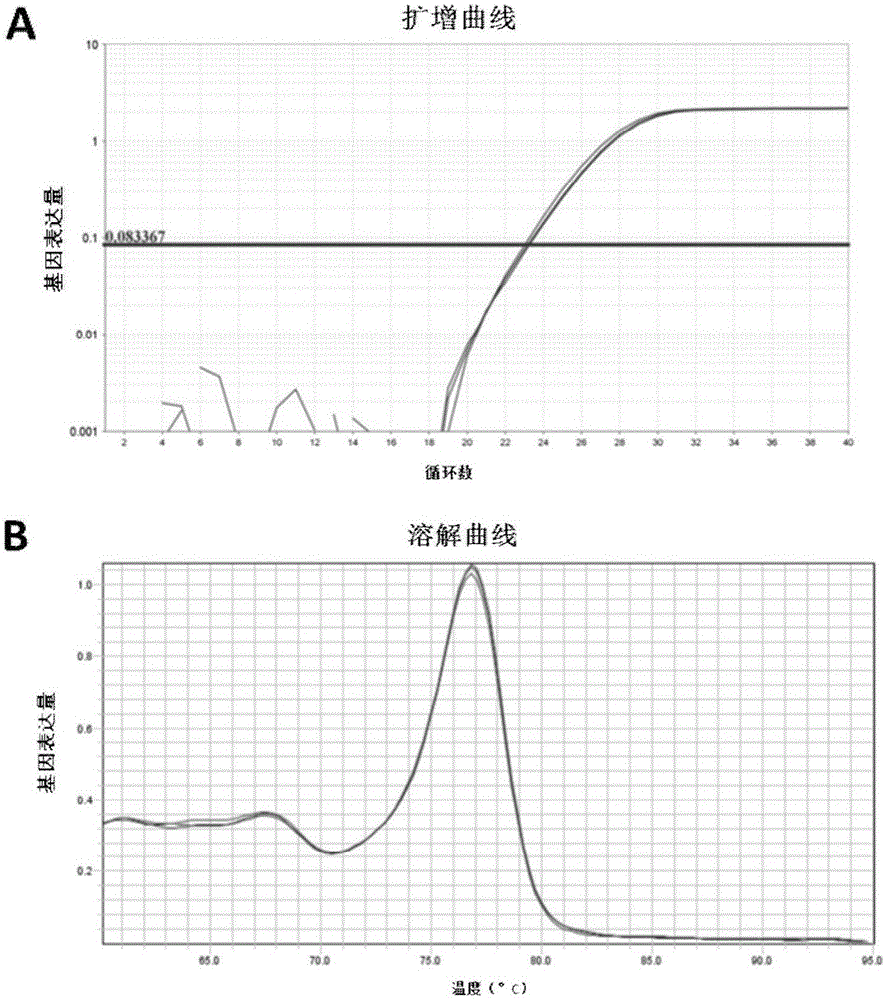
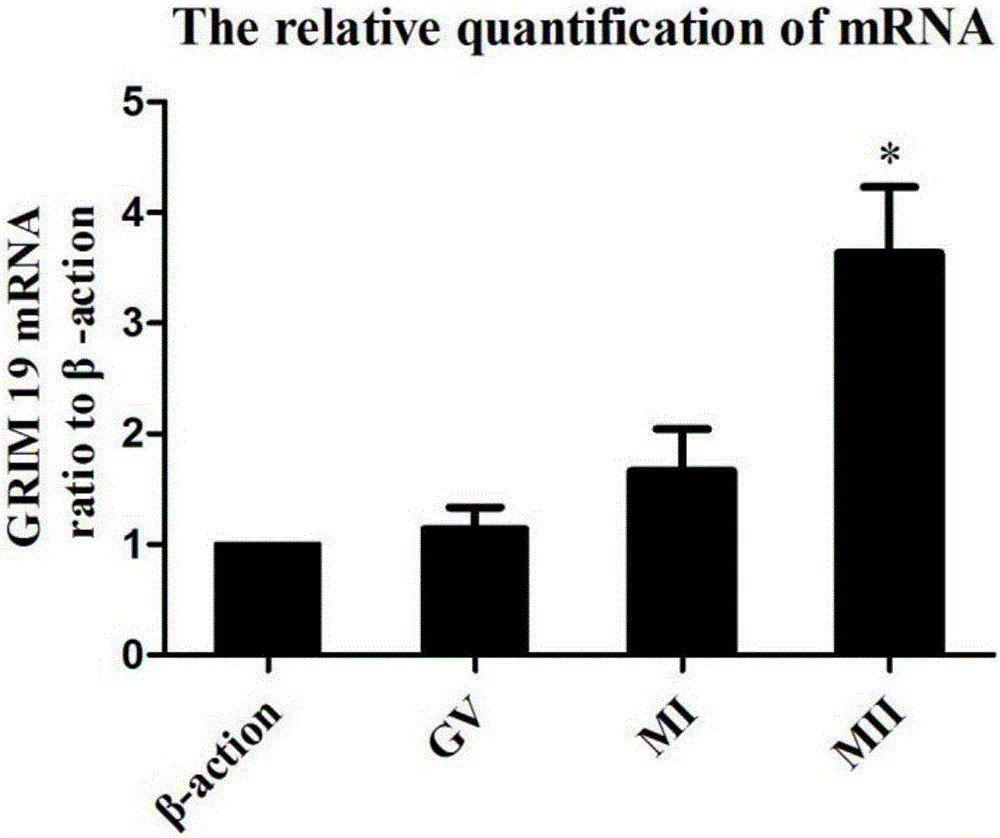
The invention discloses a method for evaluating developmental potential of an oocyte by utilizing the relative expression of GRIM-19 in a granulosa cell. When the relative expression of the GRIM-19 in the granulosa cell of the oocyte is 0.16-0.35, the obtained oocyte is judged to be high in developmental potential; when the relative expression of the GRIM-19 is 0-0.12, the obtained oocyte is judged to be low in developmental potential; a beta-actin gene is selected for internal reference. The method disclosed by the invention is a more objective, accurate and quantizable oocyte quality evaluation method, is noninvasive without repeatedly taking out an incubator for observation, so that the adverse environmental stimulation is reduced. Due to being quantizable, the method disclosed by the invention has a specific numerical range, is easy to operate and solves the problem that due to artificial subjective factors, the judgment standards are not unified.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
Endothelial cell growth factor methods of isolation and expression
InactiveUS20060025577A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsGranular leucocyteGranulosa cell
A novel growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells has been identified in conditioned medium of bovine pituitary derived folliculo stellate cells. This factor, named folliculo stellate derived growth facto (FSdGF) or vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), was purified to homogeneity by a combination of heparin sepharose affinity chromatography, Bio Gel P-60 exclusion chromatography, Mono S ion exchange chromatography and hydrophobic chromatography on a C4 reverse phase HPLC column. The factor is also found in the murine AtT-20 cell line. Alternatively, the growth factor is purified by a first reverse phase HPLC using acetonitrile gradient followed by a second reverse phase HPLC using an isopropanol gradient. FSdGF, having a molecular weight of about 43,000 da, was characterized as a glycoprotein composed of two homologous sub units with MW of about 23 kDa. FSdGF was a potent mitogen for vascular endothelial cells with activity detectable at 10 pg / ml and saturation at 500 pg / ml. It did not stimulate the proliferation of other cell types such as bovine corneal endothelial cells, adrenal cortex cells, granulosa cells, BALB / MK cells or BHK-21 cells. Microsequencing revealed an amino terminal sequence containing no significant homology to any known protein. The release of FSdGF by pituitary cells and its unique target cell specificity indicate that FSdGF is useful in angiogenesis.
Owner:FERRARA NAPOLEONE +2
Culture method for differentiating primordial germ cells into functionally mature oocytes
The present invention addresses the problem of providing a method for differentiating primordial germ cells into functionally mature GV stage oocytes by in vitro culture. The present invention pertains to a method for differentiating primordial germ cells into functional GV stage oocytes in vitro including (a) a step for forming secondary follicles by culturing primordial germ cells and feeder cells adjacent to the primordial germ cells under conditions that eliminate the effects of estrogen or factors having a similar function to estrogen, (b) a step for partially cleaving the bonds between the granulosa cell layer and the thecal cell layer among the oocyte, granulosa cell layer, and thecal cell layer that constitute the formed secondary follicles, and (c) a step for differentiating the oocytes into functional GV stage oocytes by culturing the oocytes and granulosa cell layer that constitute the secondary follicles and the thecal cell layer in medium including a polymer compound.
Owner:TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE +2
Method for detecting chromosome abnormality of embryos by aid of blastocyst cultivation solution without zona pellucida
The invention provides a method for detecting chromosome abnormality of embryos by the aid of blastocyst cultivation solution without zona pellucida. The method which is particularly an in-vitro non-therapeutic method for detecting the chromosome abnormality of the embryos by the aid of the blastocyst cultivation solution includes steps of (a), providing the cultivation solution from blastocyst cultivation systems; (b), carrying out gene detection on the cultivation solution so as to authenticate whether chromosomes of the embryos are abnormal or not. The zona pellucida of the embryos in the blastocyst cultivation systems is removed before the embryos are cultivated, the embryos are cultivated in the blastocyst systems for 3-6 days, and preferably, the cultivation solution is separated from the cultivation systems after 4 days. The method has the advantages that contamination and interference risks due to redundant sperms and parent-source granular cells in IVF (in-vitro fertilization) and ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) technical procedures can be eliminated, and whether the chromosomes of the embryos are abnormal or not can be accurately authenticated.
Owner:XUKANG MEDICAL SCI & TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
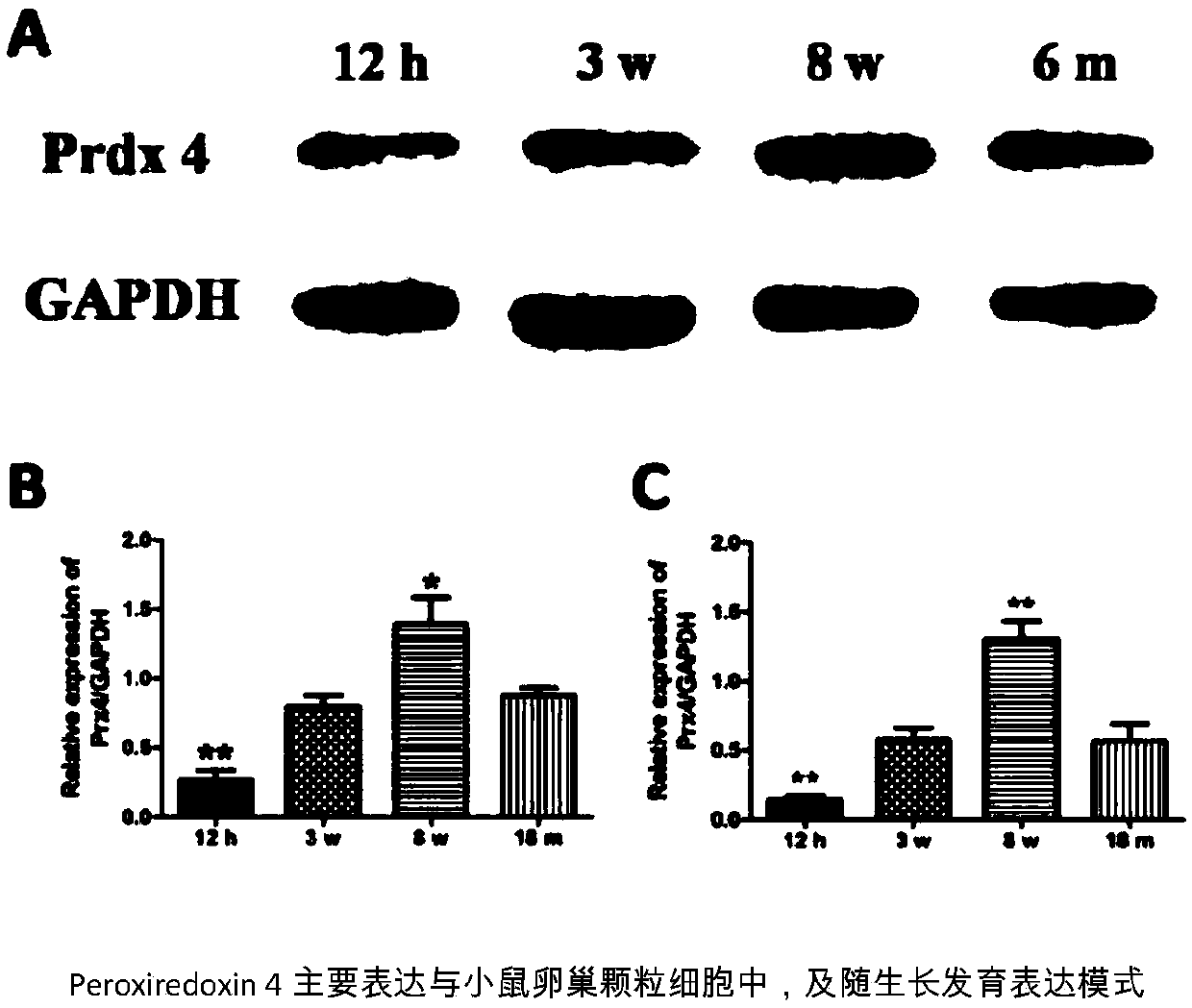
Application of enhancing antioxidation of oocyte cultured in vitro by Peroxiredoxin 4 protein
PendingCN109517788ADelay agingImprove fertilization rateCell culture active agentsGerm cellsMaturation oocyteImmature oocyte
The invention provides an application of enhancing antioxidation of an oocyte cultured in vitro by a Peroxiredoxin 4 protein. The maturing rate of the immature oocyte cultured in vitro can be improvedby improving the resistance of particle cells in oxidative stress and improving the antioxidation of the oocyte. Aging of the oocyte is also delayed through an antioxidant stress mechanism in the cell, and the fertility rate and the clinical pregnancy rate of the oocyte in an assisted breeding process are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL WITH NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
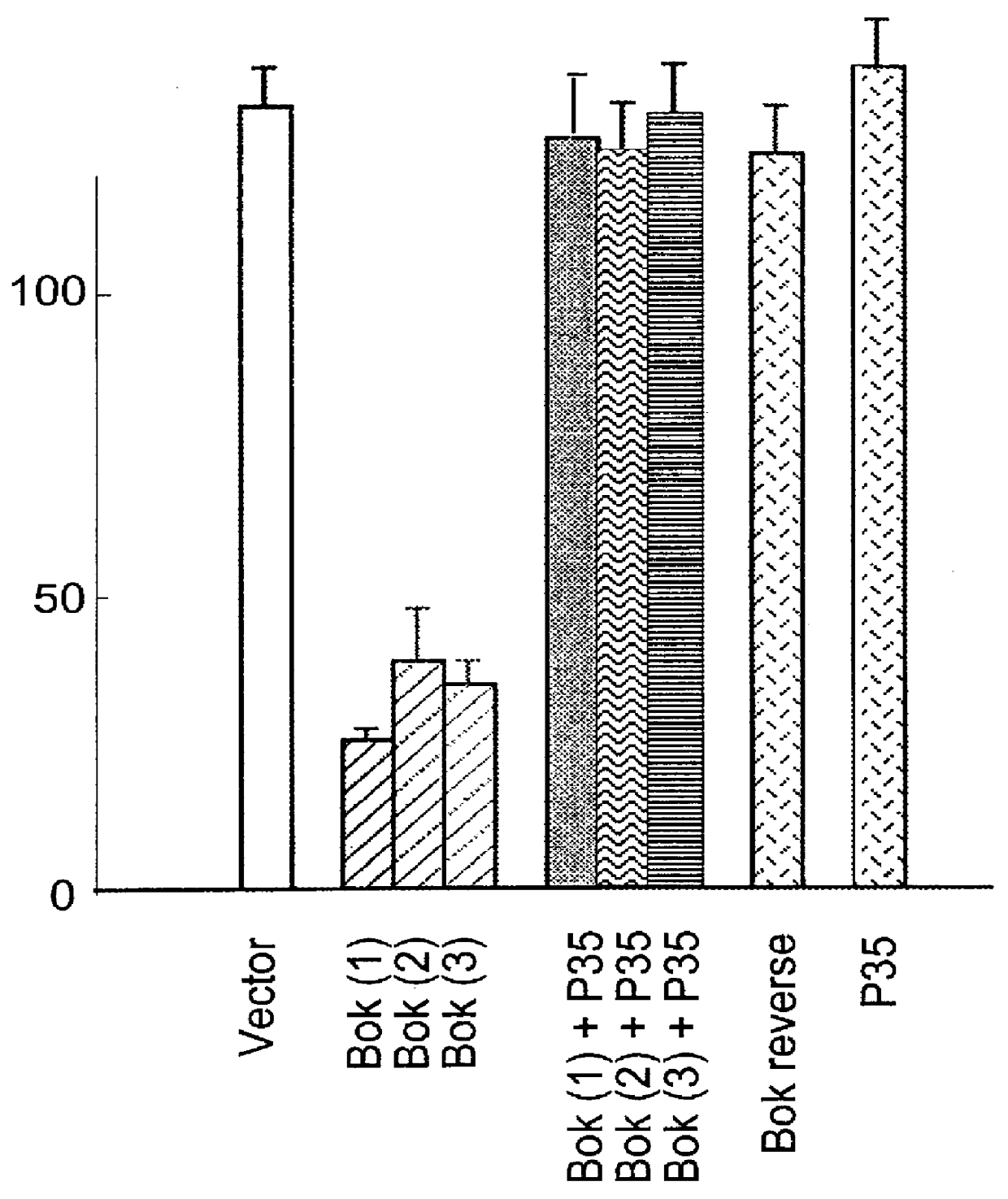
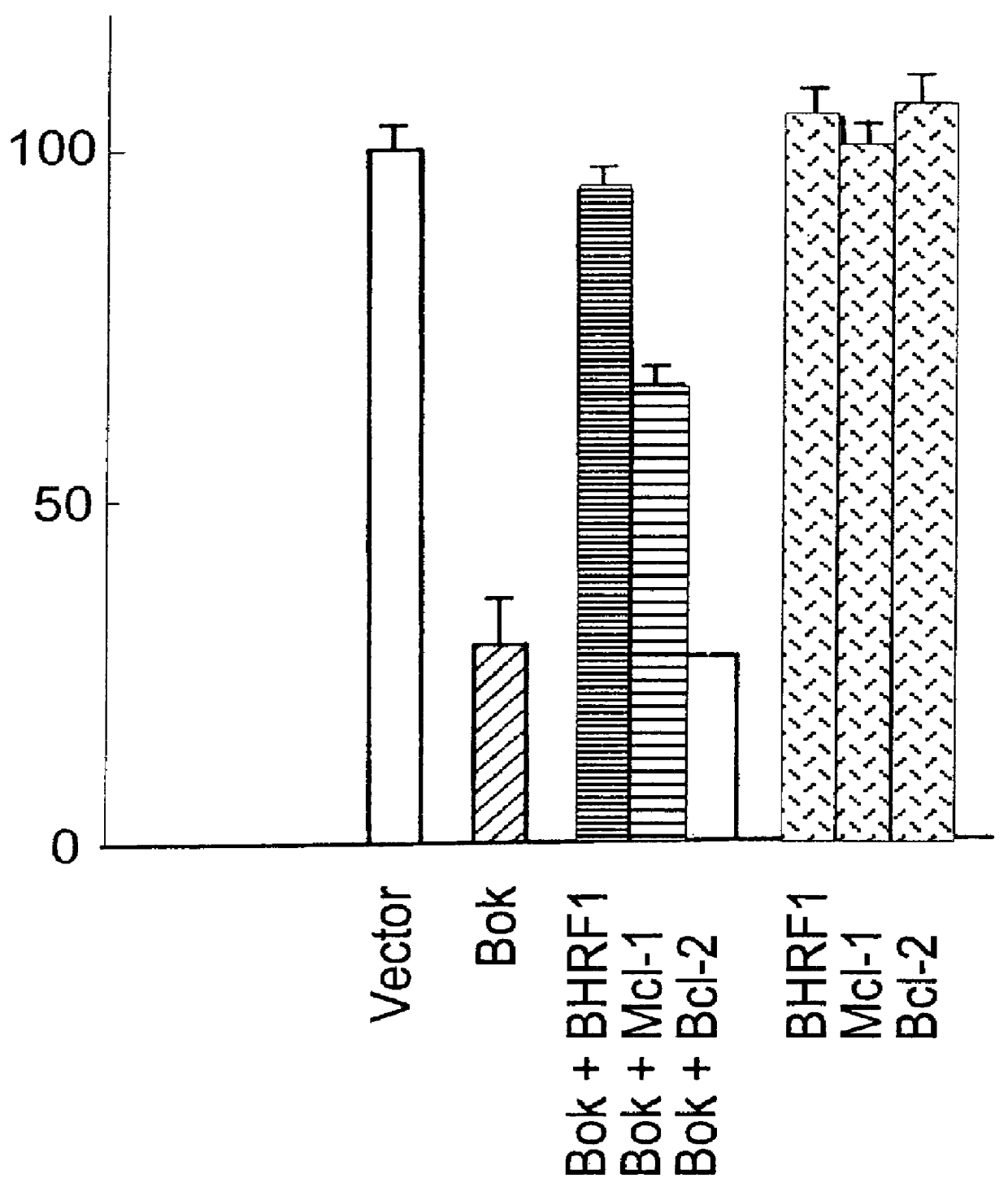
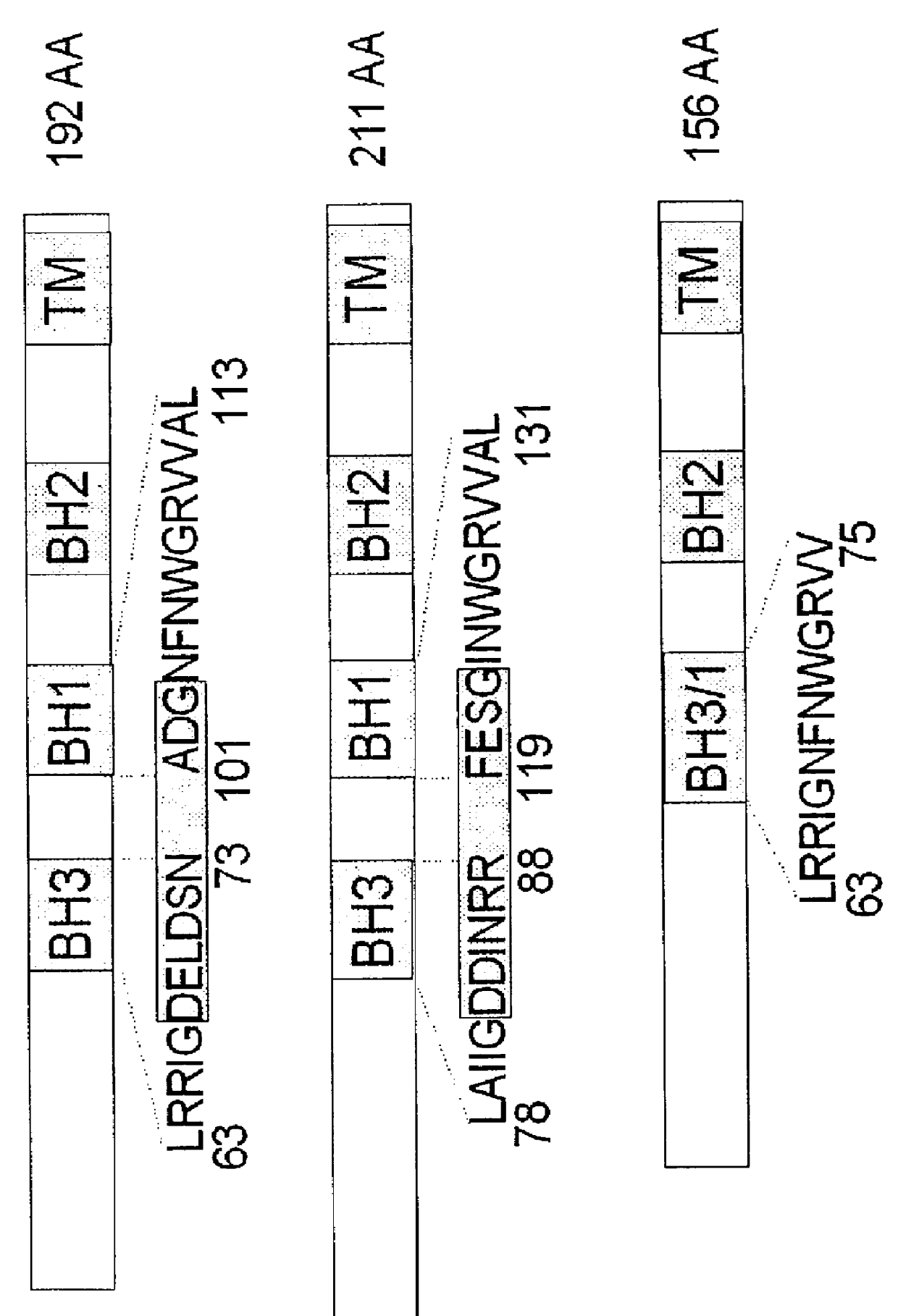
Mammalian pro-apoptotic Bok genes and their uses
Nucleic acid compositions encoding a pro-apoptotic protein, Bok (Bcl-2-related ovarian killer) are identified. Bok has conserved Bcl-2 homology domains 1, 2 and 3 and a C-terminal transmembrane region present in other Bcl-2 related proteins, but lacks the BH4 domain found only in anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. Over-expression of Bok induces apoptosis. Cell killing induced by Bok is suppressed by co-expression with selective anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. Bok is highly expressed in the ovary, testis and uterus, particularly in granulosa cells, the cell type that undergoes apoptosis during follicle atresia. Identification of Bok as a new pro-apoptotic protein with wide tissue distribution and hetero-dimerization properties facilitates elucidation of apoptosis mechanisms in reproductive and other tissues, and provides a means for manipulating apoptosis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Biomarker of granulosa cells used for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) diagnosis, and screening method and diagnostic kit thereof
PendingCN110747269AGood technical versatilityQuick fixMicrobiological testing/measurementGranular leucocyteGranulosa cell
The invention relates to a biomarker of granulosa cells used for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) diagnosis as well as a screening method and a diagnostic kit thereof. The novel diagnostic biomarker is discovered by screening PCOS-related biomarkers in the whole genome by adopting combined analysis of RNA-seq, miRNA-seq and MBD-seq. The biomarker comprises miR-429, miR-141-3p and miR-126-3p, and / or XIAP gene, BRD3 gene, MAPK14 gene and SLC7A5 gene. Compared with the prior art, the biomarker of granulosa cells used for PCOS diagnosis has the advantages of being high in detection sensitivity, high in accuracy and so on.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
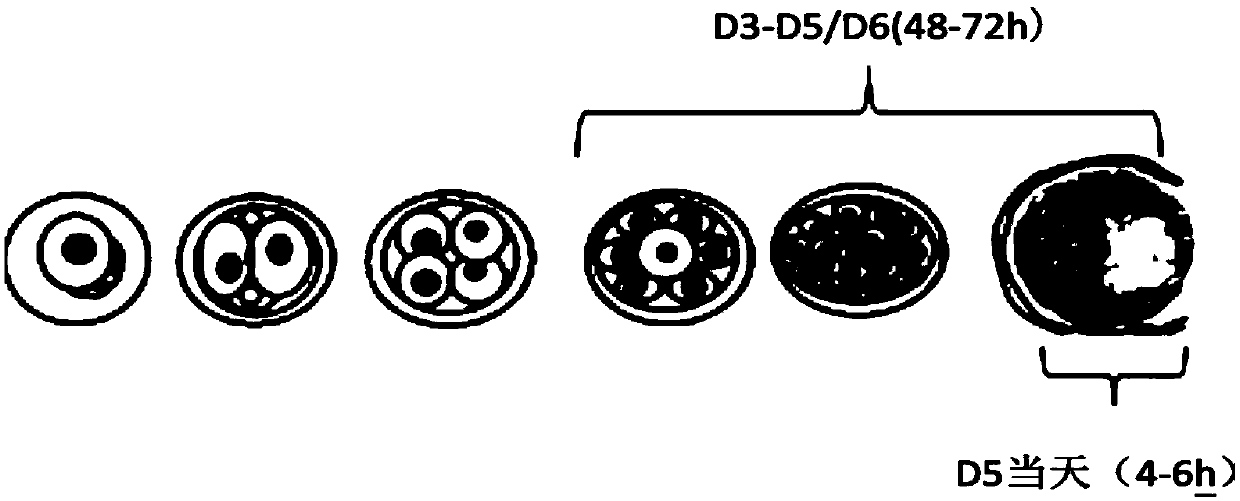
Method for detecting embryo health by using blastocyst culture solution, and product
ActiveCN109536581ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell freeEmbryo
The invention provides a method for detecting embryo health by using a blastocyst culture solution, and a product. In particular, the invention provides the method for detecting embryo health by usinga blastocyst culture solution in vitro. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (a) providing a first blastocyst culture system, wherein the first blastocyst culture system contains blastocysts with culture days of D5-D6 in vitro; (b) transferring the blastocysts to a second blastocyst culture system containing a fresh blastocyst culture solution for liquid exchange cultureso as to obtain a cultured blastocyst culture solution, wherein the liquid exchange culture time is T1; (c) taking out the cultured blastocyst culture solution to obtain a cell-free cultured blastocyst culture solution, namely a detection sample; and (d) performing gene detection on the detection sample to identify the health condition of the blastocysts. The method provided by the invention canremove the risk of pollution interference of superfluous sperms and maternal granulosa cells in the IVF and ICSI technical processes, and can accurately identify the health condition of embryos.
Owner:XUKANG MEDICAL SCI & TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD +2
Separation, primary culture and subculture method for granular cells in follicles in porcine ovary GV period
PendingCN112852712AOptimize the acquisition methodThe cultivation method is simpleCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsGranular cellFollicle
The invention discloses a separation, primary culture and subculture method for granulosa cells in follicles in a pig ovary GV period. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a cyst-free healthy pig ovary, and cleaning the ovary; separating granular cells; carrying out primary culture on the granular cells for 48 hours; changing liquid in a culture bottle for primary culture; after changing the liquid, continuously culturing the cells for 36 hours, and cleaning, digesting and terminating the cultured cells; and finally, sub-packaging and subculturing the cells for 48 hours. The invention provides a pollution-free ovary collection method, optimizes a granulosa cell acquisition and culture method, and further provides a primary granulosa cell subculture method. Granular cells obtained by the method are almost free of pollution, high in cell uniformity, high in consistency in the growth and development period, high in cell survival rate, high in success rate of making oxidative stress models and the like, and high in result consistency, practicability, stability and feasibility. In addition, the number of obtained cells is large, many subsequent experiments can be carried out, the number of times of going to a slaughter house is reduced, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:DALI UNIV
Recombinant human granulosa cell enzyme solution and preparation method of same
The invention relates to a recombinant human granulosa cell enzyme solution and a preparation method of same and belongs to the technical field of artificial assisted reproduction. The recombinant human granulose cell enzyme solution is prepared by dissolving recombinant human granulosa cell enzyme dry powder, which is obtained by processing ovum, in a salt solution containing antibiotics and an indicator. In the invention, by means of a physiological work solution, which is prepared by means of non-animal-sourced recombinant bio-engineering high-tech hyaluronidase (a.k.a. recombinant human granulosa cell enzyme) dry powder, is 80 units (I.U.) and has functional available concentration, not only are granule cells surrounding the ovum effectively digested, which is beneficial to introcytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) technology of the ovum, but also possibility of animal-sourced pathogen and toxin are effectively excluded, thereby greatly improving safety of assisted reproduction.
Owner:瑞柏生物(中国)股份有限公司
Method for in vitro culture of ovarian follicles
The present invention is related to a method for in vitro culture of mammalian ovarian follicles for bioassay purposes, comprising the following subsequent steps: - providing a suitable container for the in vitro culture, - selecting a follicle from an ovary of a mammal, said follicle comprising at least a theca or pre-theca cell, a granulosa cell and an oocyte, - an optional first cultur e step using an attachment prohibiting first medium free from oil, - a second culture step using an attachment promoting second medium free from oil arranged to, and - the retrieval of the matured follicle.
Owner:艾格森特瑞斯有限公司
JY-1 Regulation Of Granulosa Cell Function And Early Embryonic Development In Cattle
InactiveUS20090263406A1Altering in vivo fertilityImprove fertilityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMammalGranulosa cell
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating fertility in mammals. In general, the invention relates to a novel protein produced by oocytes named JY-1, and nucleic acids encoding the JY-1 protein, for controlling folliculogenesis and early embryonic development, particularly in monoovulatory species. In particular, the present invention provides nucleic acid and amino acid sequences encoding JY-1, vectors for the expression of JY-1, host cells expressing JY-1, RNAi probes for reducing levels of JY-1 message, and antibodies to JY-1. Specifically, developing and mature oocytes express JY-1 in vivo, while granulosa cells treated in vitro with recombinant JY-1 (rJY-1) protein reduced cell proliferation while increasing progesterone synthesis and estradiol production. Further, reducing JY-1 protein in developing embryos in vitro using inhibitory siRNA constructs corresponded with arrested blastocyte maturation.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV OFFICE OF INTPROP
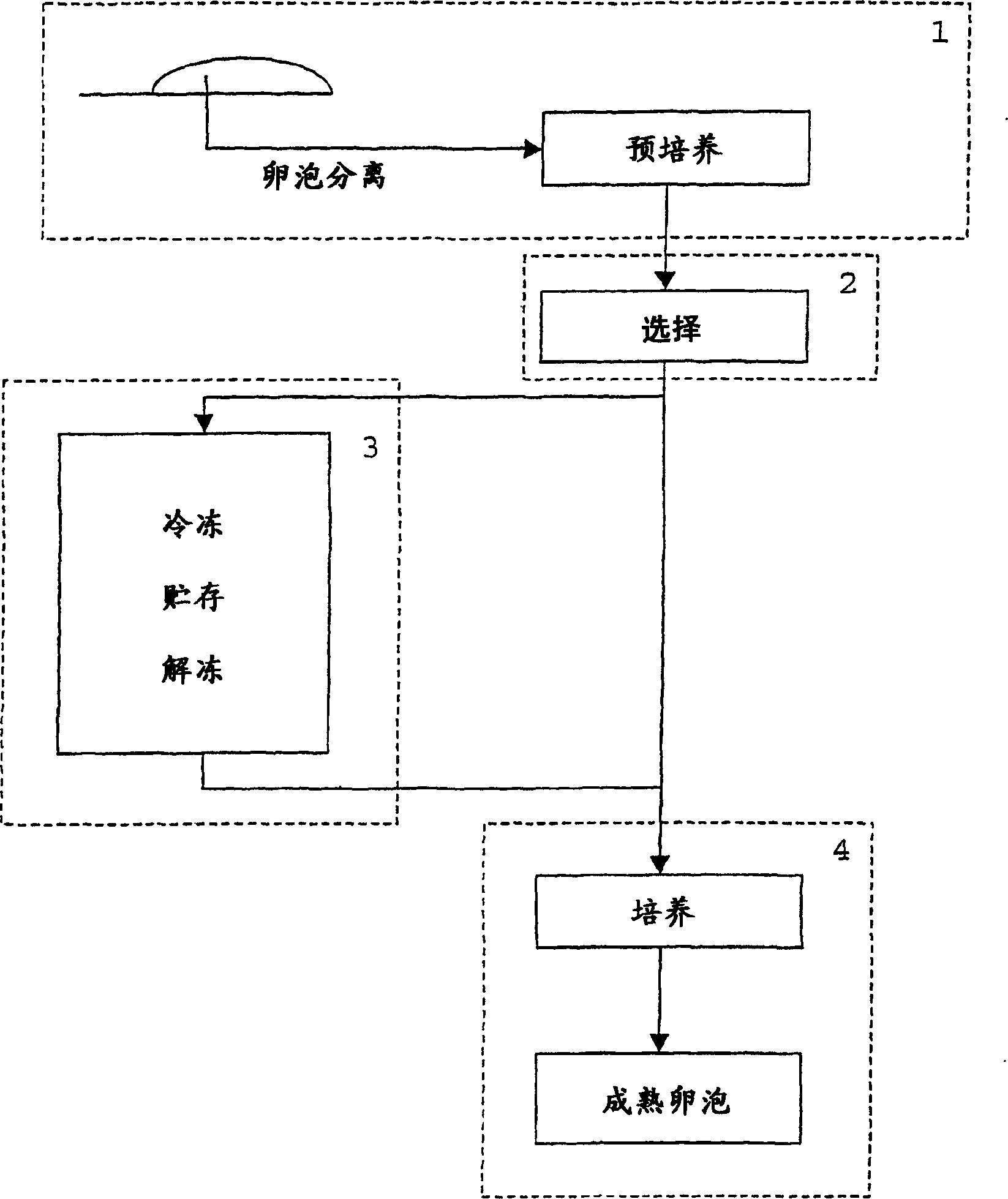
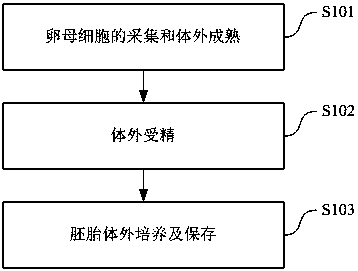
Method for culturing in-vitro fertilized embryo of mammal
The invention relates to a method for culturing an in-vitro fertilized embryo of a mammal. The method comprises the following steps of collection and in-vitro maturation of an oocyte; in-vitro fertilization; in-vitro culture and preservation of the embryo. During in-vitro fertilization, mature COCs are cultured in a fertilization culture solution. During in-vitro culture of the embryo, granulosa cells around the embryo are removed by an egg stripping needle, the embryo is cultured in an embryo culture liquid, and the available embryo after culture is completed is cryopreserved in a freezing liquid with liquid nitrogen. The method has excellent technical effects described in the description.
Owner:NANJING DRUM TOWER HOSPITAL
Application of FGFR1 genes to granulosa cells of sows
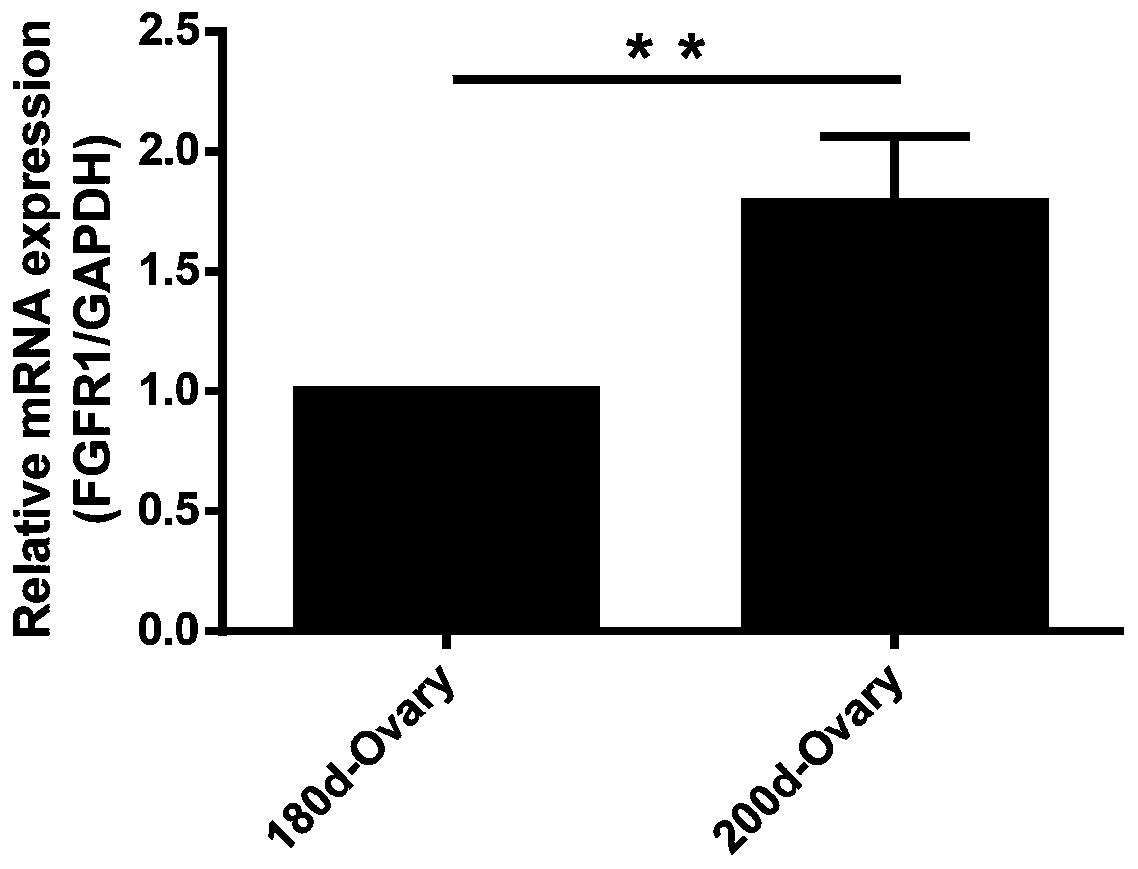
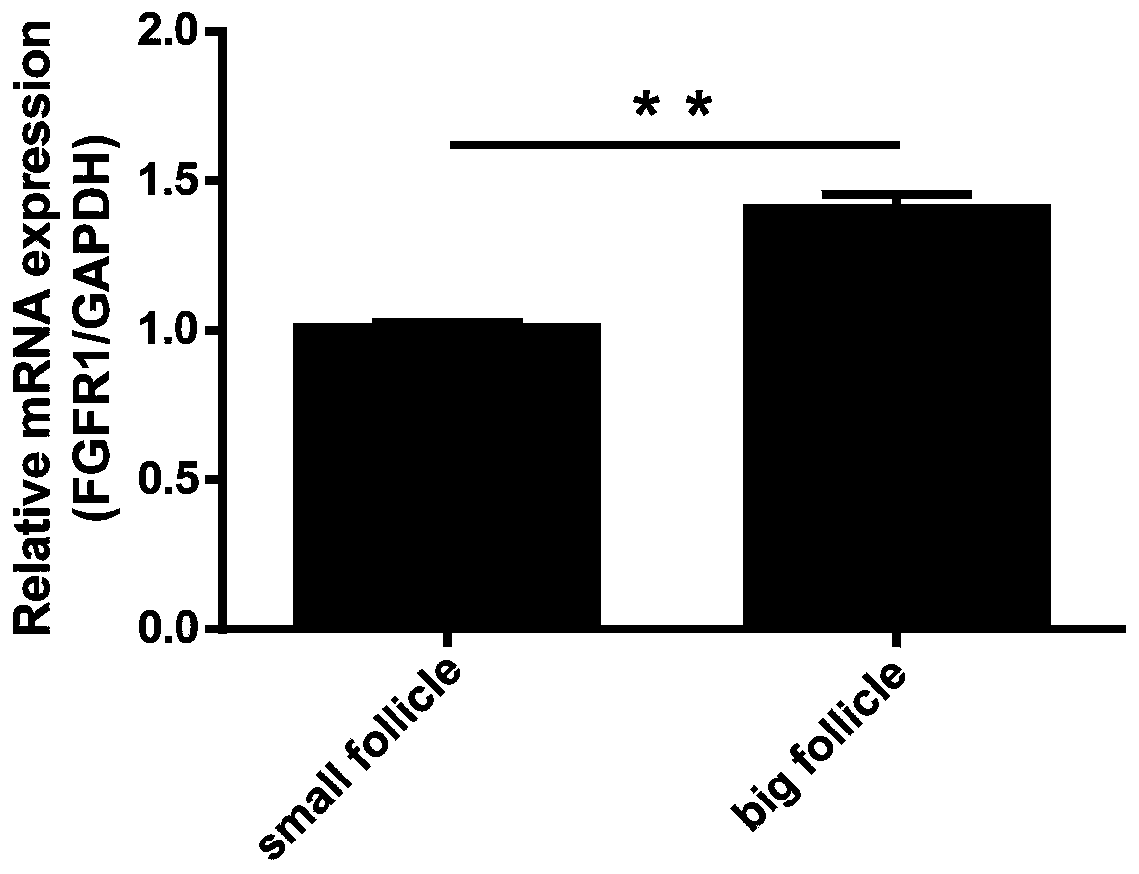
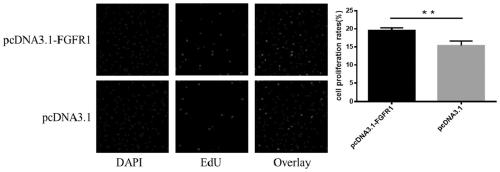
ActiveCN109852680AHigh proliferation rateReduce proliferation rateMicrobiological testing/measurementVertebrate cellsApoptosisGranulosa cell
The invention discloses an application of FGFR1 genes to granulosa cells of sows, and belongs to the technical field of cell engineering and genetic engineering. The FGFR1 genes can be used for detecting the relative expression quantity of FGFR1 mRNA in ovarian tissues of sows of 180 days old (the ovarian is immature ) and sows of 200 days old (the ovarian is mature), and granulosa cells of different size, and the proliferation and apoptosis situation of the granulosa cells after overexpression / interference FGFR1, so as to accumulate materials for the molecule mechanism in the development process of the granulosa cells of the sows. Besides, the results show that the FGFR1 genes participate in promoting proliferation of the granulosa cells, and restraining the apoptosis of the granulosa cells, and further, the results indicate that the FGFR1 genes can participate in development and mature of the granulosa cells of the sows.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
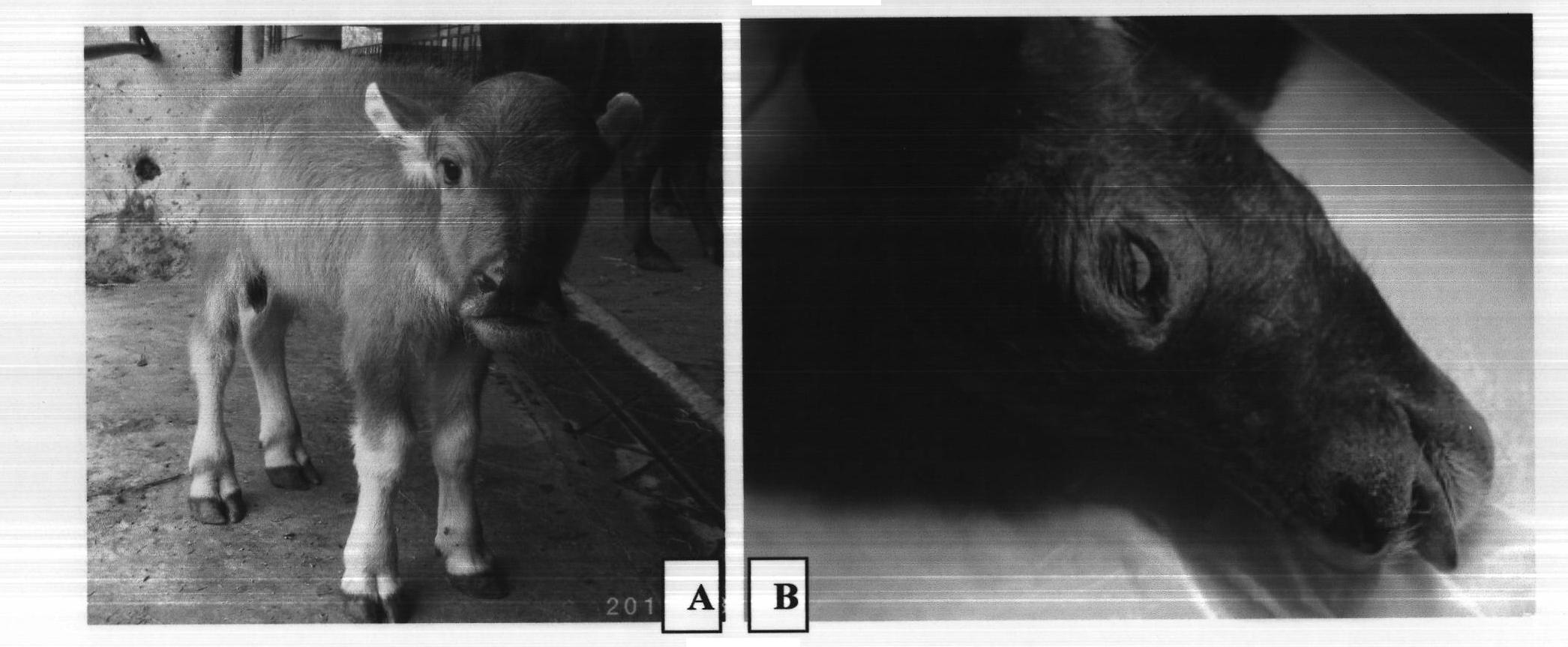
Method for breeding transgenic buffalos by using somatic cell nuclear transfer technology
InactiveCN102250954AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionWater buffaloFull Term Pregnancy
The invention discloses a method for breeding transgenic buffalos by using somatic cell nuclear transfer technology, which comprises: obtaining buffalo fetal fibroblasts (BFF) by separation from buffalo fetuses and culture, implanting a transgenic vector (pCE-EGFP-IRES-neo), which carries a neomycin resistant gene and an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene, into the BFF by an electroporation process, and selecting BFF into which the EGFP gene is transferred by using G418; transplanting the BFF into which the EGFP gene is transferred into denucleated oocytes of the buffalo to construct cloned embryos, treating the cloned embryos for 5 minutes with ionomycin at a concentration of 5 mu mol / L, culturing cloned embryos in 6-dimethyl-aminopurine at a concentration of 2mmol / L for 3 hours, performing chemical activation treatment, co-culturing the cloned embryos in granulose cell monolayer liquid drops for 6 to 7 days, and obtaining the transgenic cloned blastaea; selecting transgenic cloned blastaea in which the EGFP is expressed under a reversed fluorescence microscope, and transplanting the transgenic cloned blastaea into receptor buffalos; and obtaining the transgenic buffalos after full-term pregnancy. After the irradiation by an ultraviolet lamp, the EGFP marker genes are obviously expressed in the heads and limbs of the transgenic buffalo calves, and this proves the method disclosed by the invention can successfully breed transgenic cloned buffalos.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Follicular granulosa cell anti-senescence technology
InactiveCN1628857ABoost estrogen levelsImprove staminaGenetic material ingredientsDrug compositionsPhysiologyGranulosa cell
The invention provides a follicular granulosa cell anti-senescence technology, wherein animal follicular granulosa cells are employed for transplantation, the process comprises the steps of (1) placing ovarium of pig or sheep into curling, (2) culturing the follicular granulose cells, shearing ovarium into small blocks, carrying out grinding, sieving, slaking, purifying and placing into culture bottle, then charging QM-1640 culture liquid containing AB-serum, loading into CO2 incubator for culturing, (3) the application method comprises injecting the ovarian follicle granular cells into human body muscle or waist subarachnoid cavity.
Owner:刘玉来 +2
Method for in vitro culture of ovarian follicles
The present invention is related to a method for invitro culture of mammalian ovarian follicles for bioassay purposes, comprising the following subsequent steps: - providing a suitable container for the invitro culture, selecting a follicle from an ovary of a mammal, said follicle comprising at least a theca or pre-theca cell, a granulosa cell and an oocyte, an optional first cultur e step using an attachment prohibiting first medium free from oil, a second culture step using an attachment promoting second medium free from oil arranged to, and the retrieval of the matured follicle.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating premature ovarian failure as well as preparation method and application of traditional Chinese medicine composition
The invention belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines, and particularly discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating premature ovarian failure. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 8-20 parts of radix rehmanniae preparata, 6-10 parts of fructus corni, 10-30 parts of Chinese yam, 10-15 parts of fructus lycii, 6-10 parts of tortoise-plastron glue, 6-10 parts of deer-horn glue, 10-25 parts of semen cuscutae, 6-10 parts of radix cyathulae, 10-15 parts of fructus psoraleae, 10-15 parts of herba taxilli, 10-15 parts of radix dipsaci, 6-10 parts of ginseng, 10-30 parts of radix astragali, 6-10 parts of rhizoma atractylodis macrocephalae, 10-15 parts of radix angelicae sinensis, 10-15 parts of radix paeoniae alba, 6-10 parts of pericarpium citri reticulatae and 6-10 parts of radix glycyrrhizae preparata. The traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating premature ovarian failure can effectively inhibit apoptosis of granulosa cells, promote follicular maturation and improve ovarian reserve capacity, and is high in safety.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
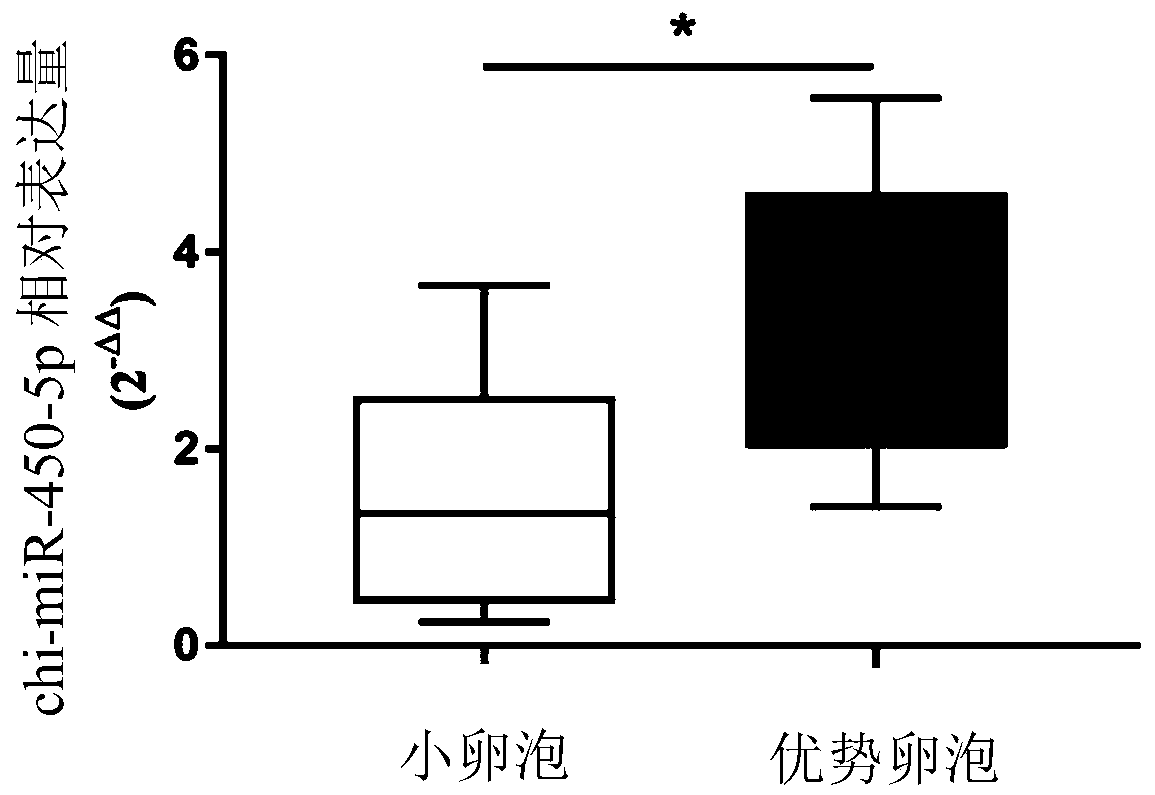
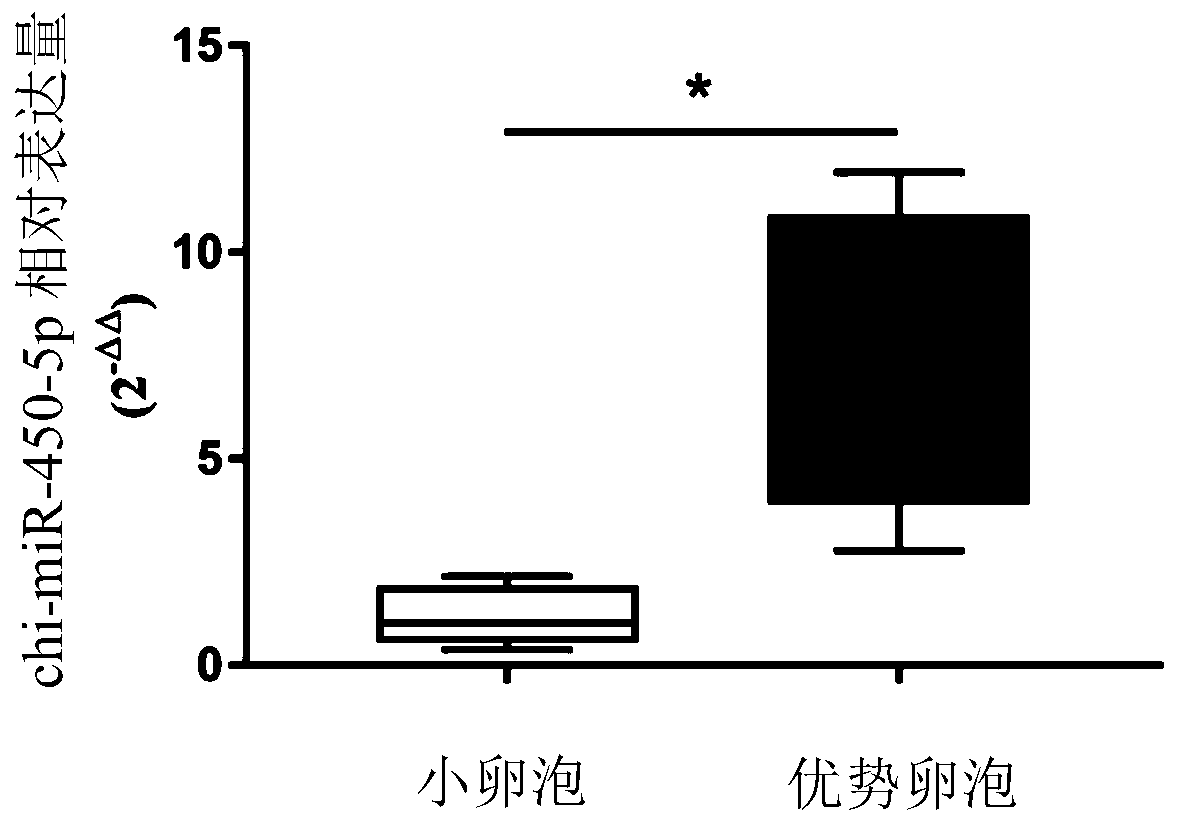
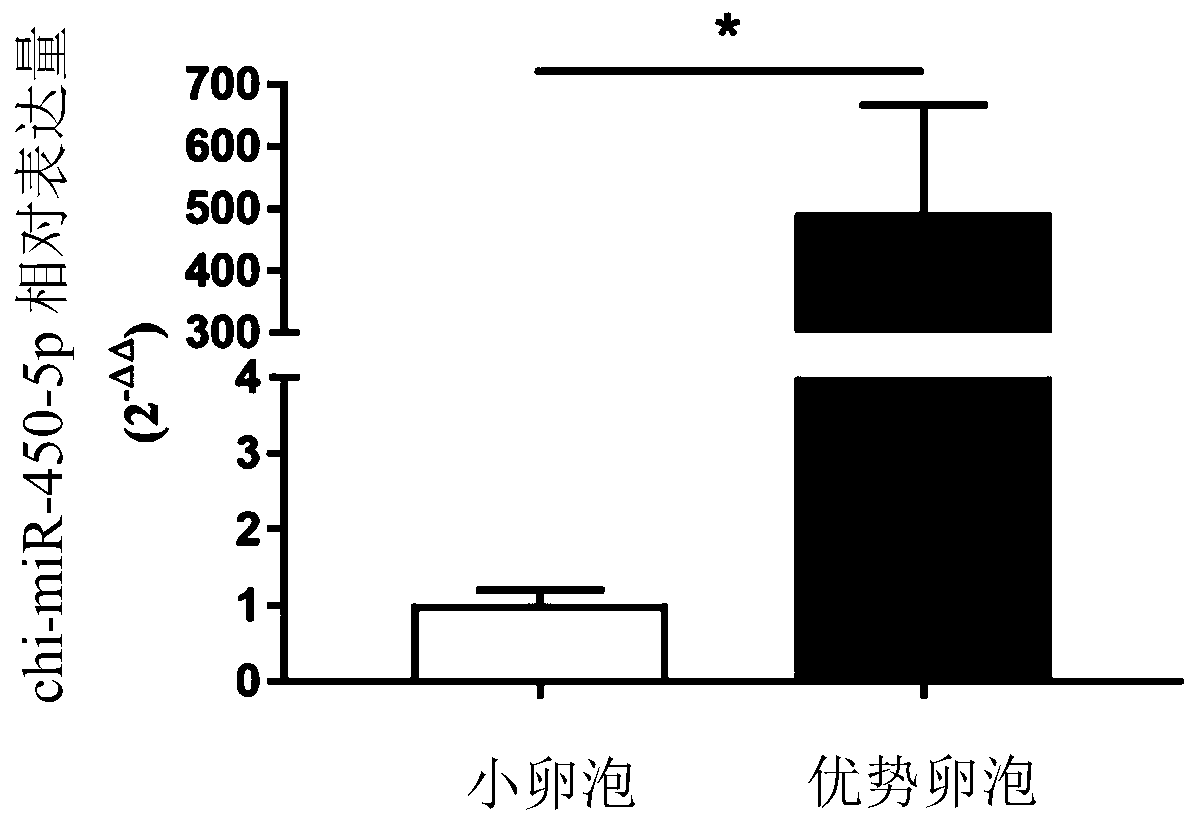
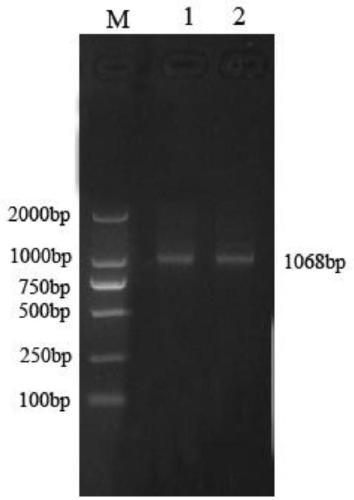
Application of chi-miR-450-5p as miRNA marker for maturation of goat follicles
ActiveCN111118170AProven reliabilityDemonstrated universalityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGranular leucocyteGranulosa cell
The invention discloses an application of chi-miR-450-5p as an miRNA marker for maturation of goat follicles. The chi-miR-450-5p provided by the invention can reflect the maturation of goat follicles,and has reliability, universality and repeatability as a follicle development marker. The invention also discloses a test kit for detecting the development condition of the goat follicles. Accordingto the invention, through separation of follicle granulosa cells, the expression mode of the chi-miR-450-5p in dominant follicles and small follicle granulosa cells is verified, and a basis is provided for perfecting a goat follicle growth and development, ovulation gene regulation and non-coding regulation network.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Human ovarian mesothelial cells and methods of isolation and uses thereof
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
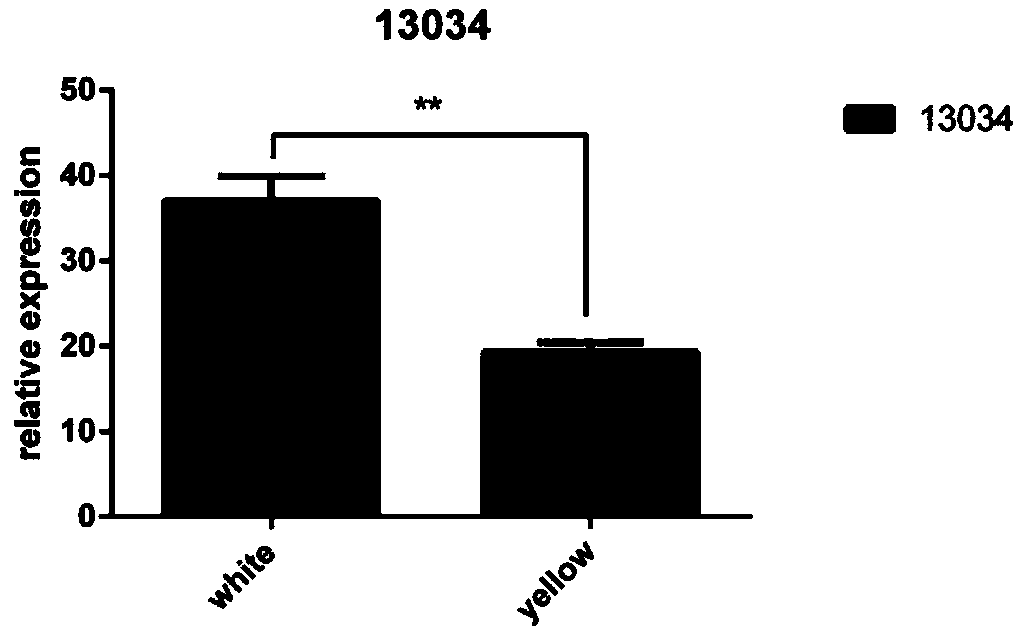
Laying duck circRNA circ_13034 and detection reagent, method and application thereof
ActiveCN108977554AImprove reproductive performanceHigh expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and provides laying duck circRNA circ_13034 and a detection reagent, a method and an application thereof. A cDNA sequence corresponding to the laying duck circRNA circ_13034 provided by the invention is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention further provides a fluorescent quantitative PCR detection primer pair and a detection kit ofthe laying duck circRNA. The detection primer pair has nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 and SEQ ID NO: 3. The invention further provides an overexpression vector of the laying duck circRNAcirc_13034 and a construction method thereof. The invention further provides application of the laying duck circRNA and the overexpression vector in differentiation of laying duck follicle developmentconditions and detection of cell proliferation and differentiation conditions of laying duck follicle granulosa cells as molecular markers. The application has an important significance in researching inheritance of proliferation character of laying duck and improving reproductivity of the laying duck.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com