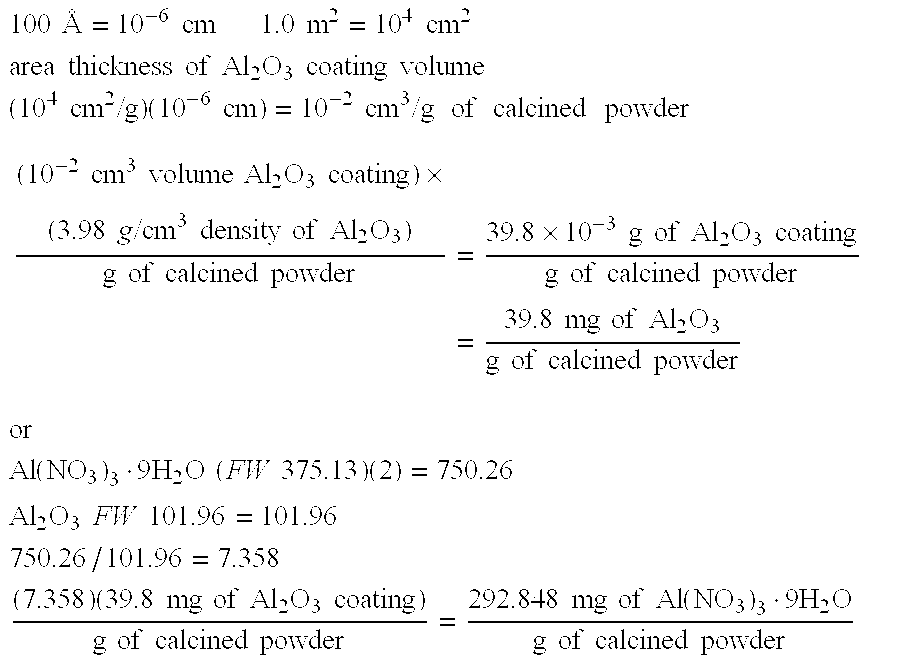Patents
Literature
2967results about How to "Delay aging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
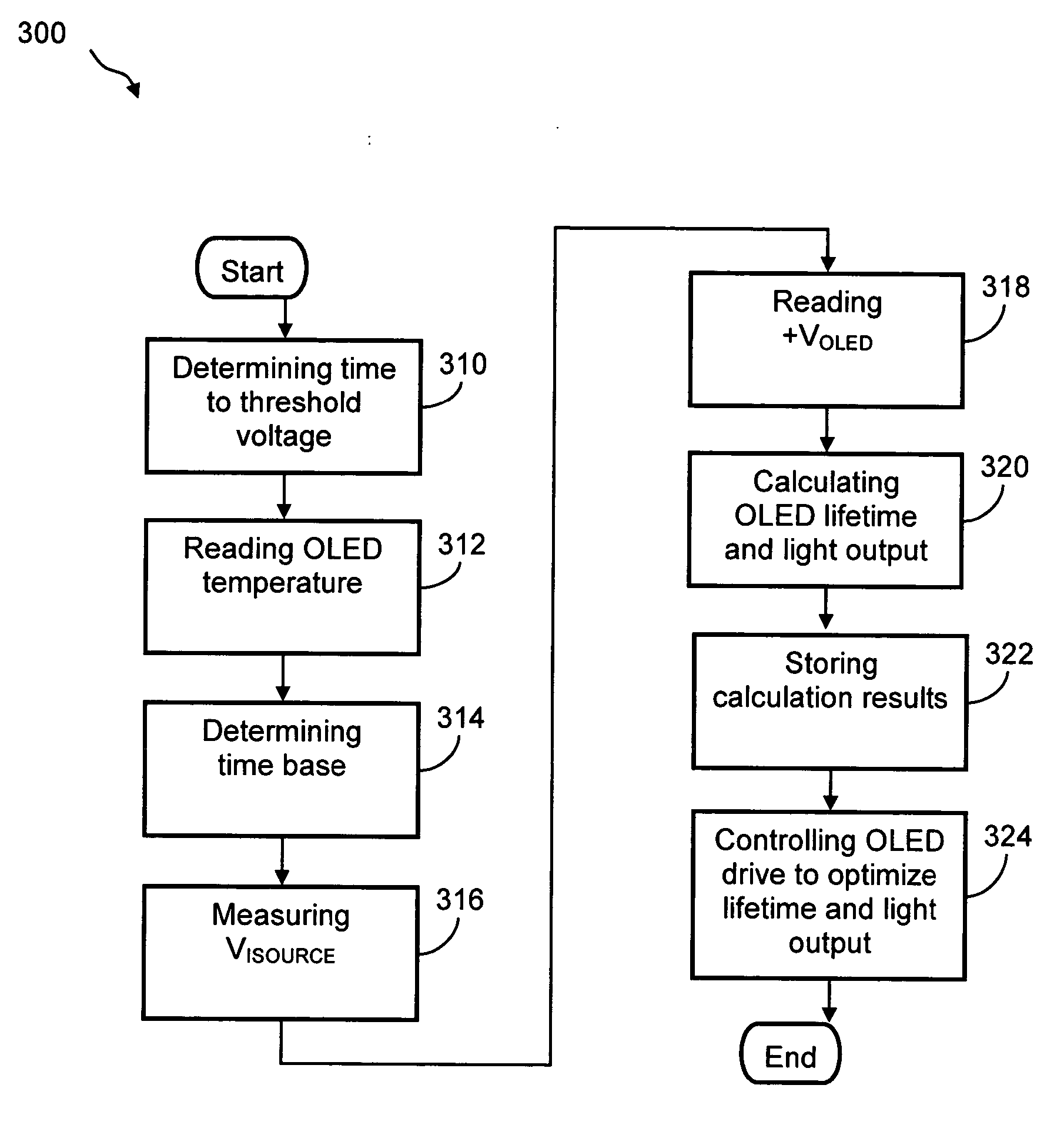
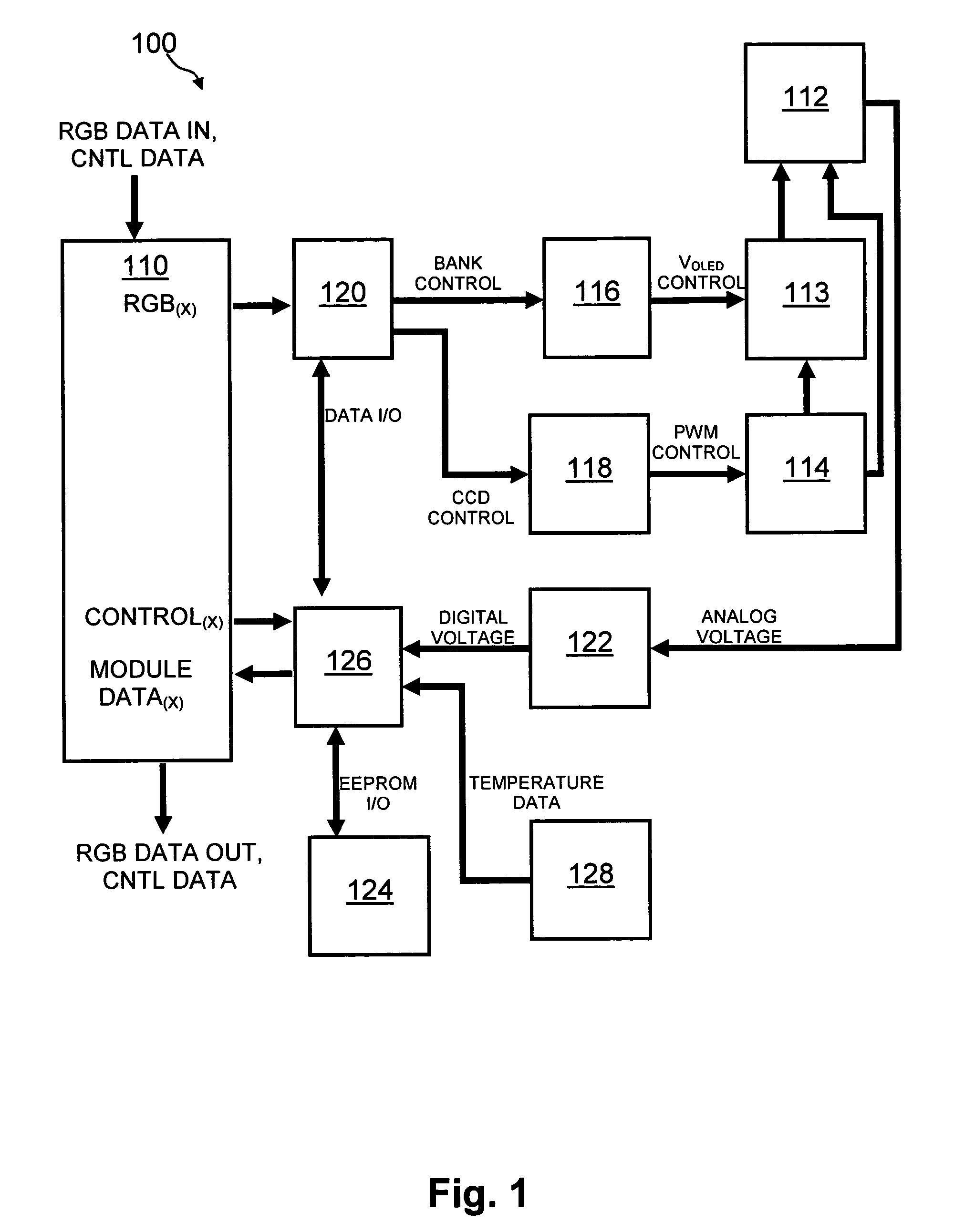
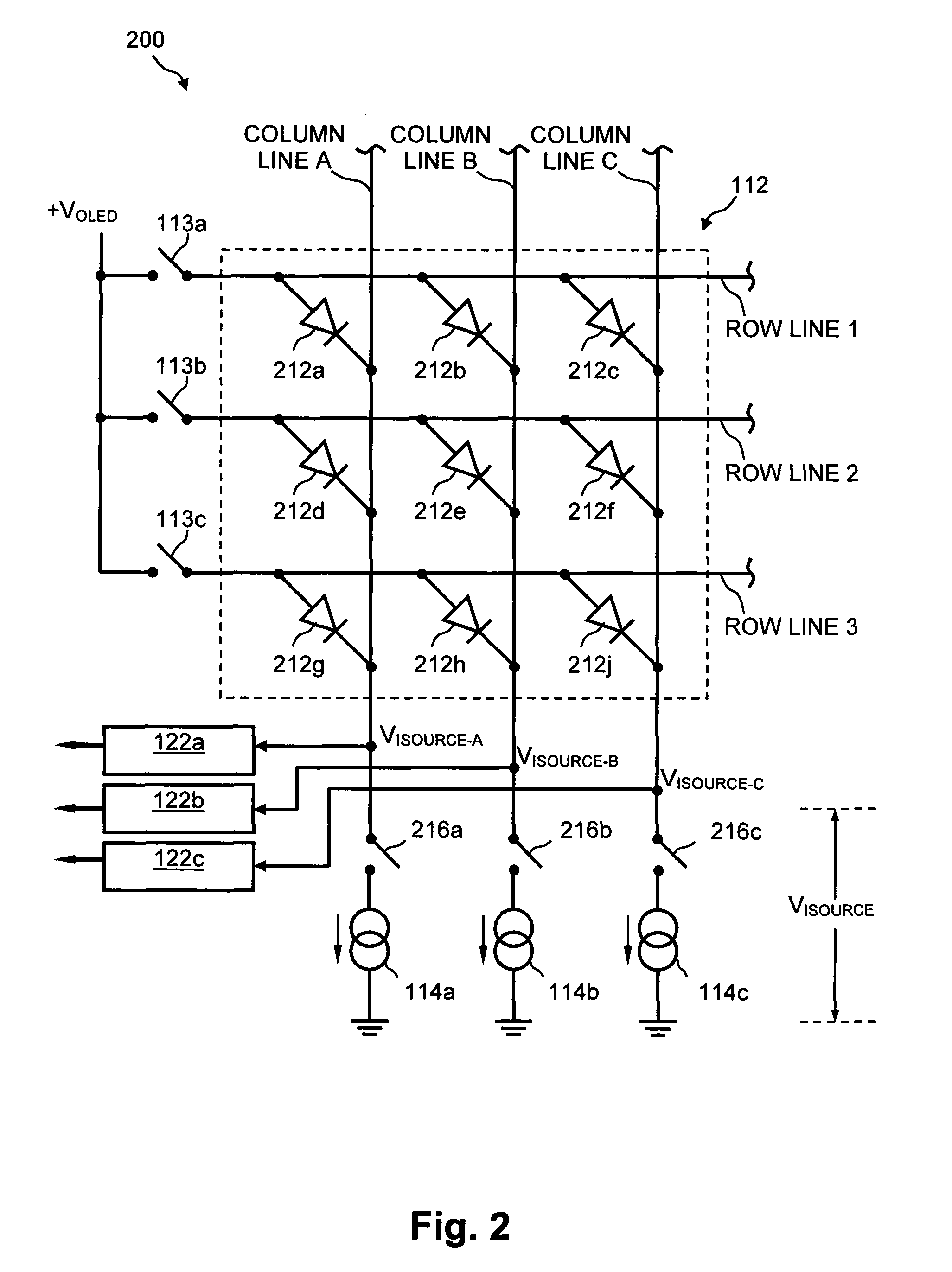
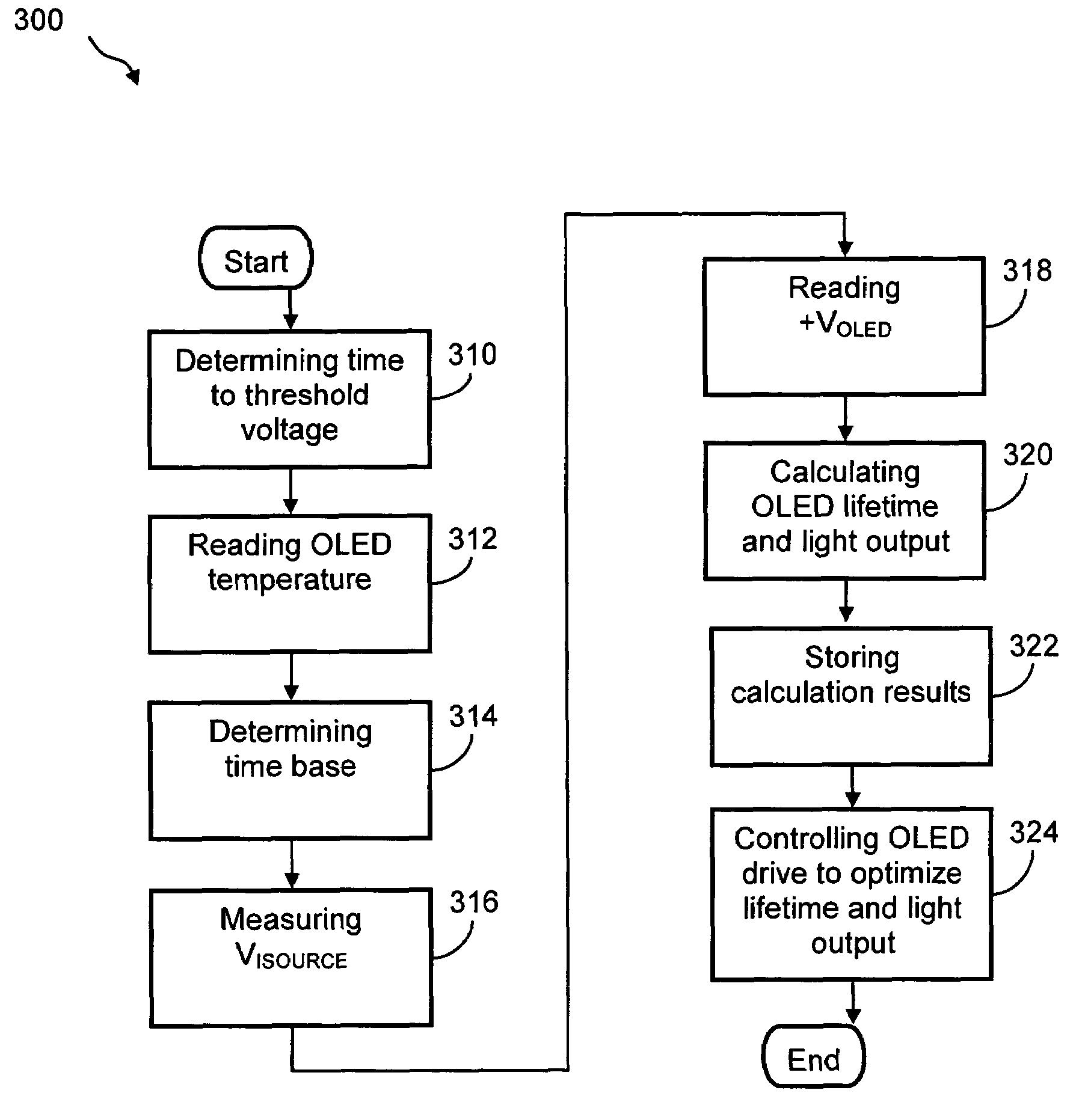
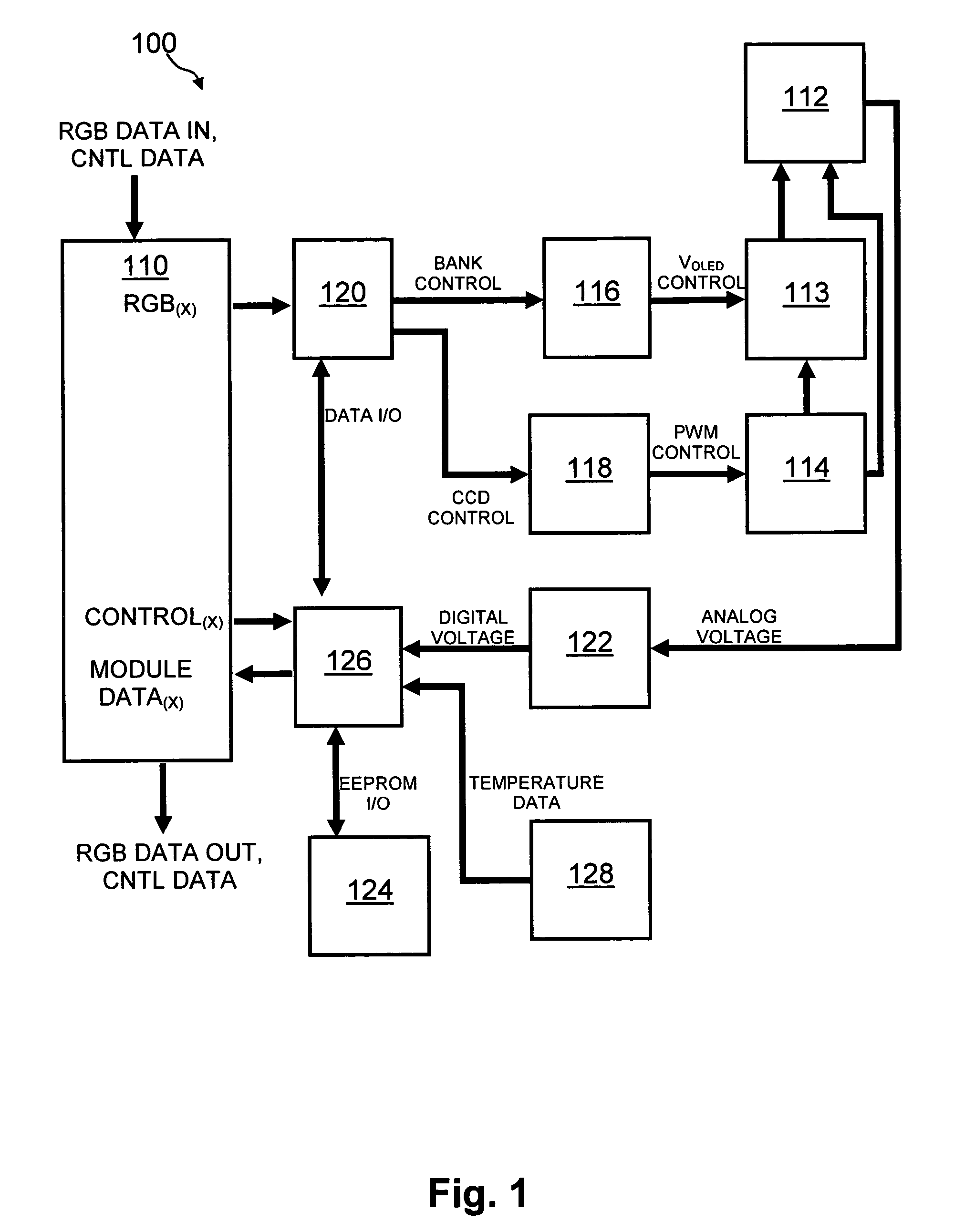
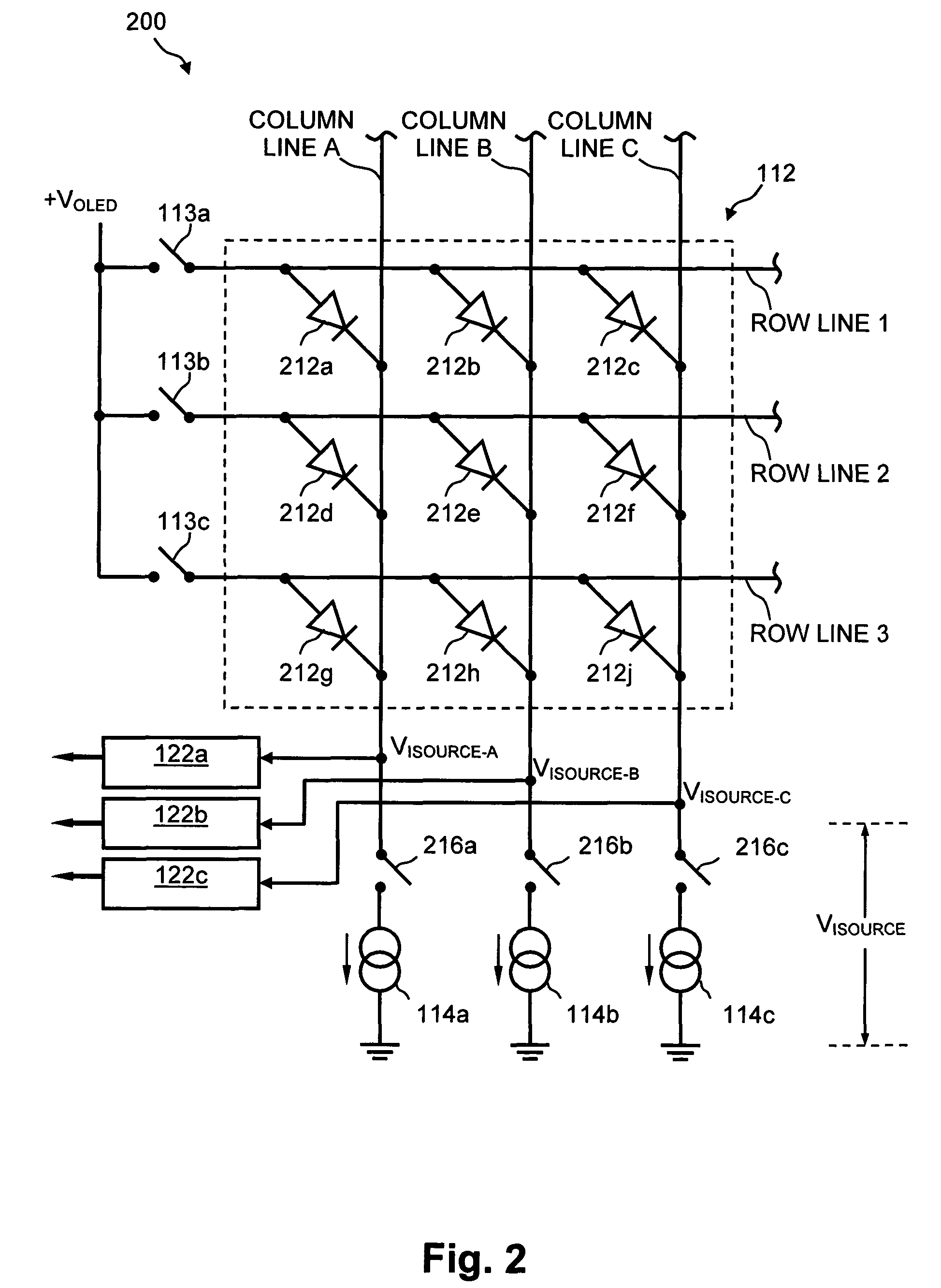
Method and system for measuring and controlling an OLED display element for improved lifetime and light output
InactiveUS20050030267A1Delay agingImprove the display effectCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPre-chargeDisplay device
A method of optimizing lifetime of an OLED display element and an OLED display element with optimized lifetime for possible use in a tiled display, while maintaining light output are described. It compensates an OLED operating parameter such as supply voltage and / or on-time of the operating current based on at least one environmental factor which affects aging and on at least one operating factor which is indicative of aging, e.g. by determining the brightness of an OLED display element. To optimize the light output, pre-charge of the aged OLED display elements can be optimized. The knowledge of the working temperature of OLED tiles may be used to regulate the cooling and thus the working temperature, thus improving the lifetime of the display. Furthermore the intensity and contrast of the display illumination may be set within predefined limits to reduce the aging.
Owner:BARCO NV
Method and system for measuring and controlling an OLED display element for improved lifetime and light output
InactiveUS7262753B2Delay agingImprove the display effectCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPre-chargeDisplay device
A method of optimizing lifetime of an OLED display element and an OLED display element with optimized lifetime for possible use in a tiled display, while maintaining light output are described. It compensates an OLED operating parameter such as supply voltage and / or on-time of the operating current based on at least one environmental factor which affects aging and on at least one operating factor which is indicative of aging, e.g. by determining the brightness of an OLED display element. To optimize the light output, pre-charge of the aged OLED display elements can be optimized. The knowledge of the working temperature of OLED tiles may be used to regulate the cooling and thus the working temperature, thus improving the lifetime of the display. Furthermore the intensity and contrast of the display illumination may be set within predefined limits to reduce the aging.
Owner:BARCO NV
Preparation method of polyurethane-nano kaolin composite material
InactiveCN102002141AGood for uniform dispersionGood for product performancePigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsPigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsDimethyl formamideEthyl acetate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a polyurethane-nano kaolin composite material. The composite material mainly comprises polyurethane and nano kaolin. The preparation method is as follows: firstly, carrying out organic intercalation modification on the nano kaolin to obtain organically modified nano kaolin with larger interlamellar spacing; and then using a body-(in-situ) intercalative polymerization method to prepare the polyurethane-nano kaolin composite material. The preparation method is characterized in that the nano kaolin with lower price and better performance is utilized, the composite material is a novel efficient halogen-free retardant agent, and no benzene, toluene, N,N'-dimethyl formamide, ethyl acetate and other harmful solvents are used, therefore environmental requirements are met. By adding a small amount of kaolin, the mechanical property, heat insulation performance and heat resistance of the polyurethane elastomer can be significantly improved. In addition, the material has simple preparation process, low cost and excellent integrated performance, and can be widely applied to mining equipment, sports equipment, area pavement materials and other industries, thereby having wide market prospects.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
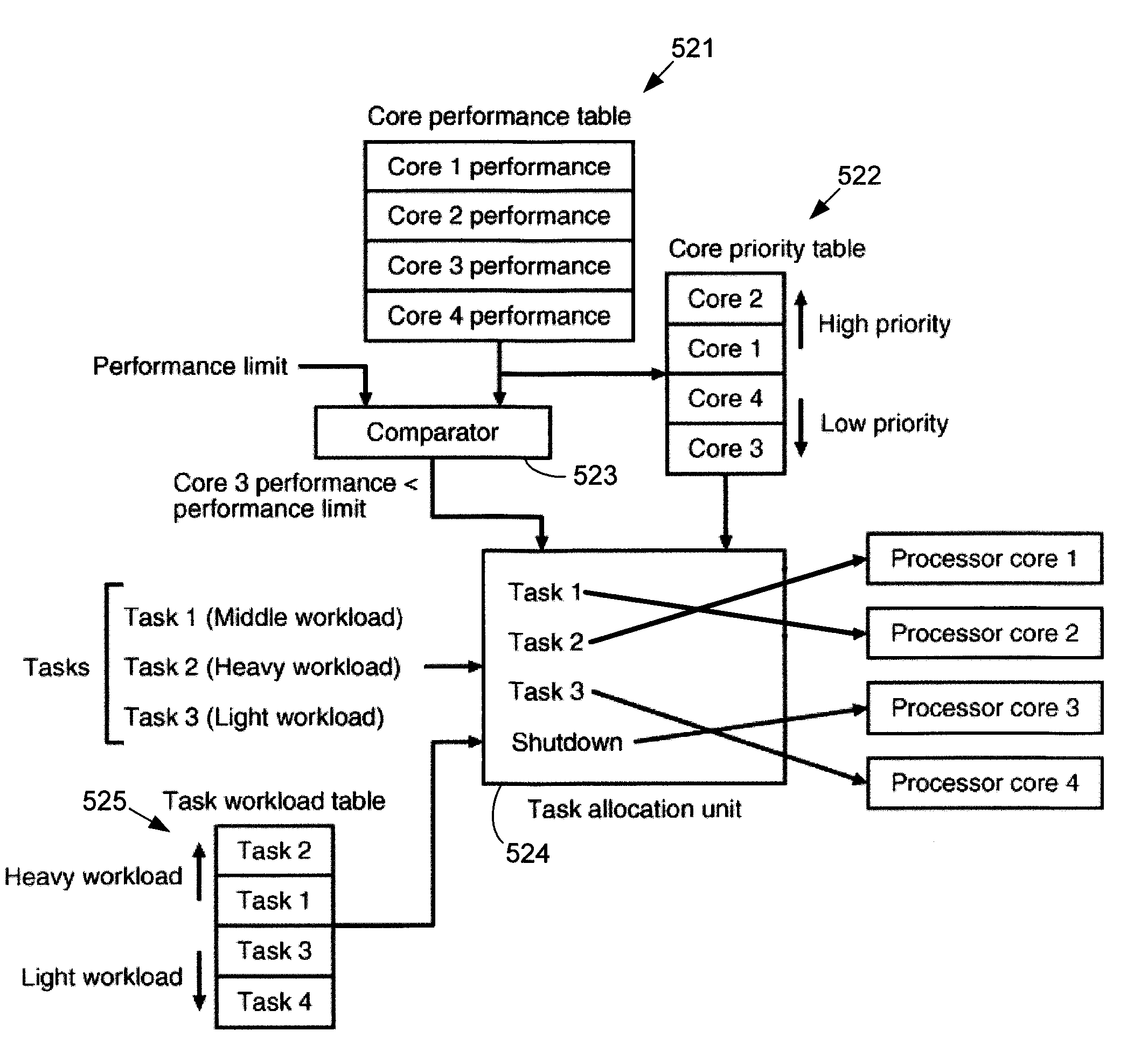
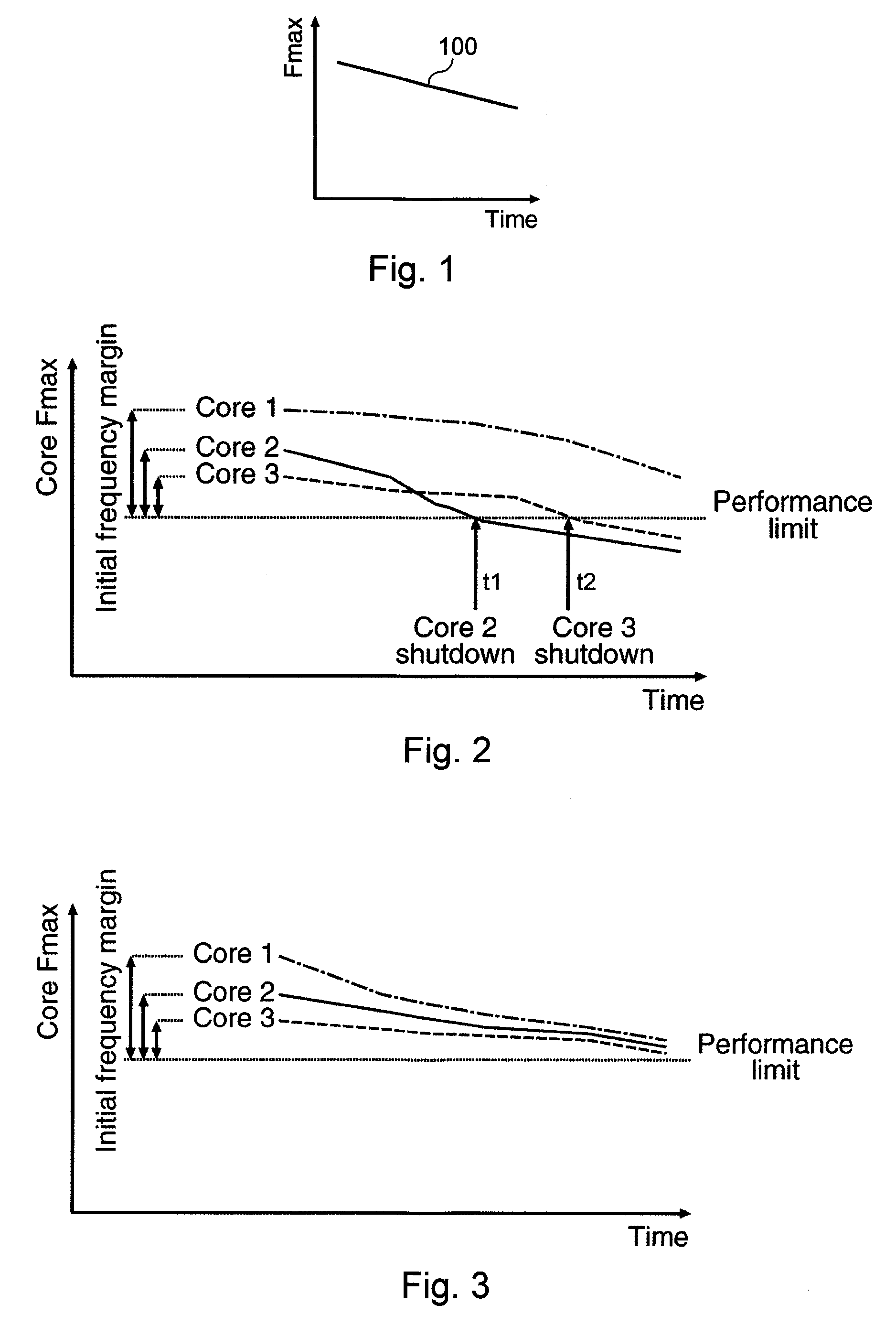
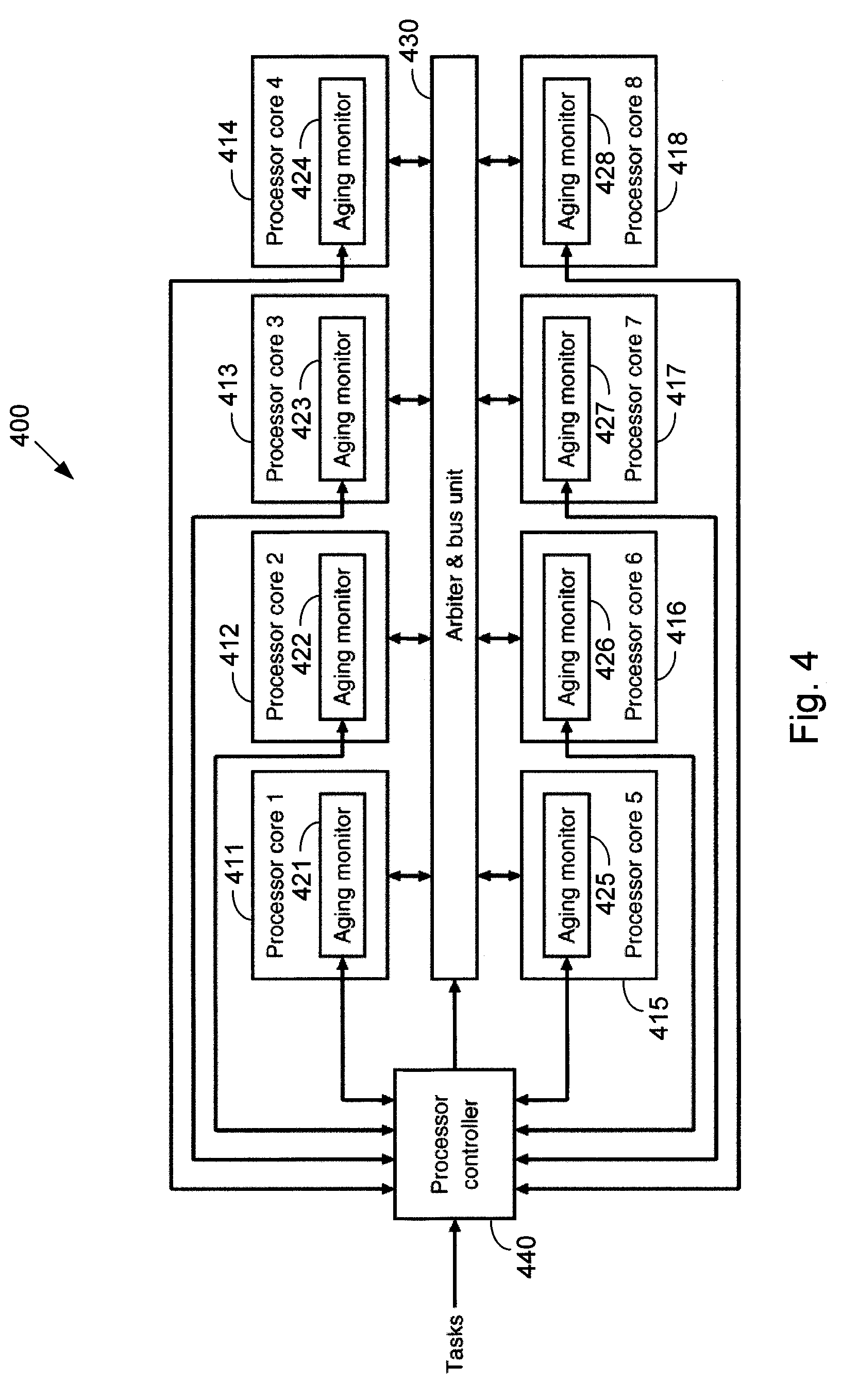
Systems and Methods for Improving the Reliability of a Multi-Core Processor
InactiveUS20090288092A1Improve reliabilityDelay agingResource allocationMemory systemsMulti processorBelow threshold level
Systems and methods for improving the reliability of multiprocessors by reducing the aging of processor cores that have lower performance. One embodiment comprises a method implemented in a multiprocessor system having a plurality of processor cores. The method includes determining performance levels for each of the processor cores and determining an allocation of the tasks to the processor cores that substantially minimizes aging of a lowest-performing one of the operating processor cores. The allocation may be based on task priority, task weight, heat generated, or combinations of these factors. The method may also include identifying processor cores whose performance levels are below a threshold level and shutting down these processor cores. If the number of processor cores that are still active is less than a threshold number, the multiprocessor system may be shut down, or a warning may be provided to a user.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
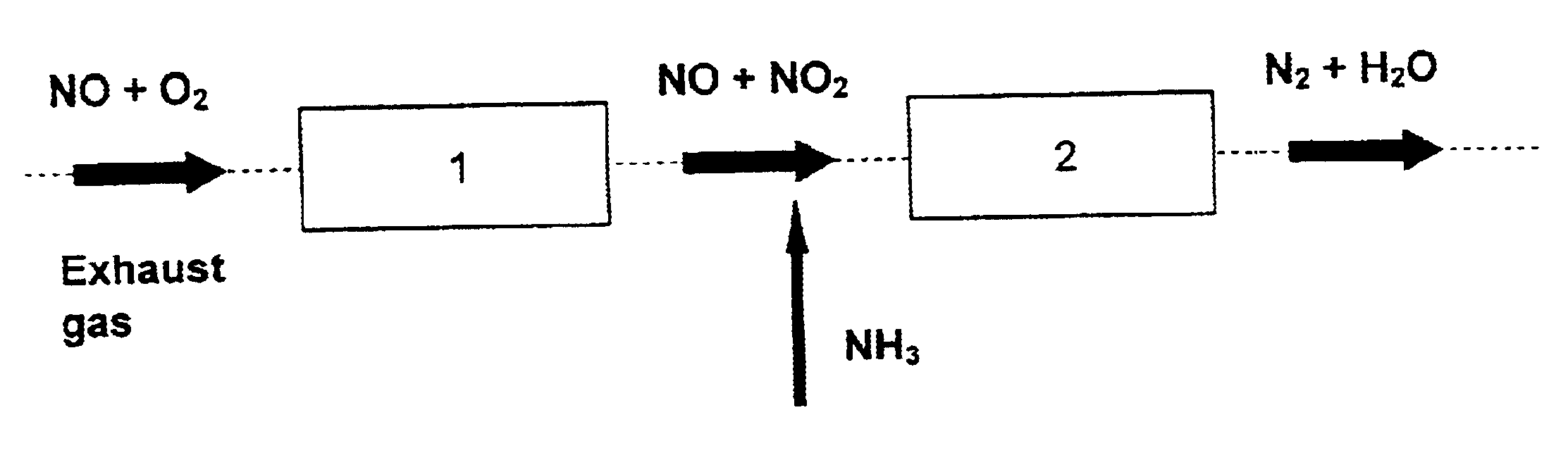
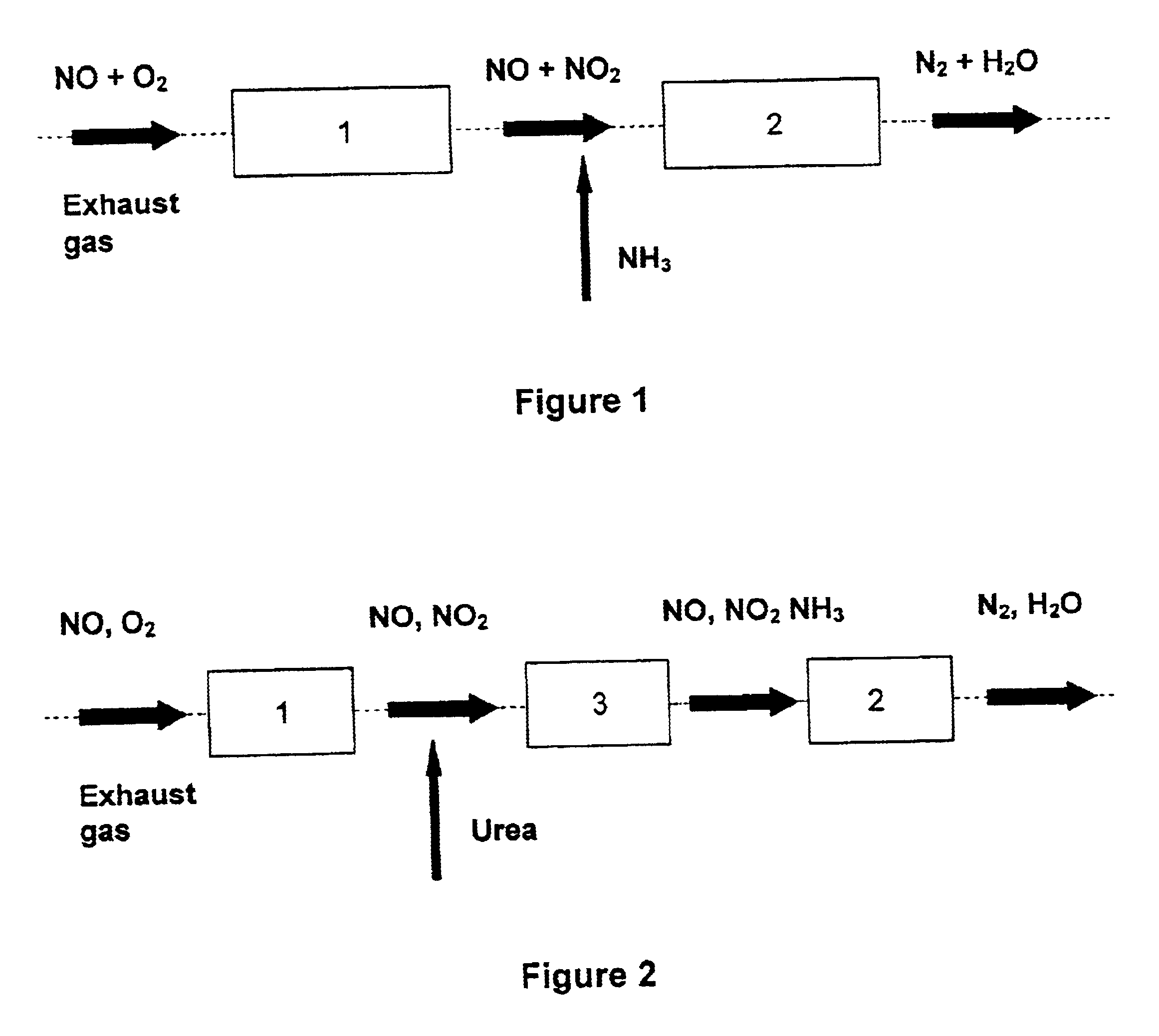
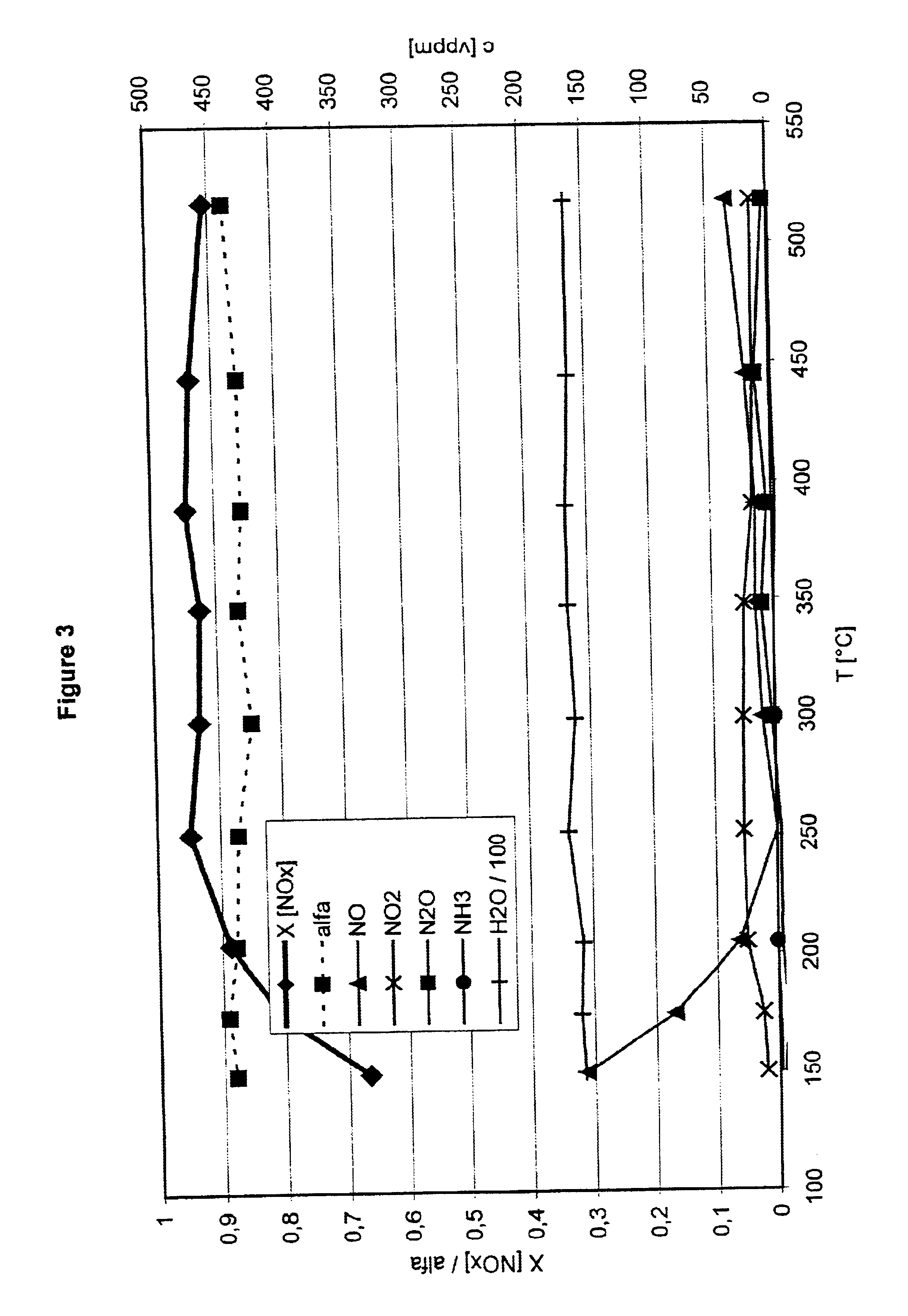
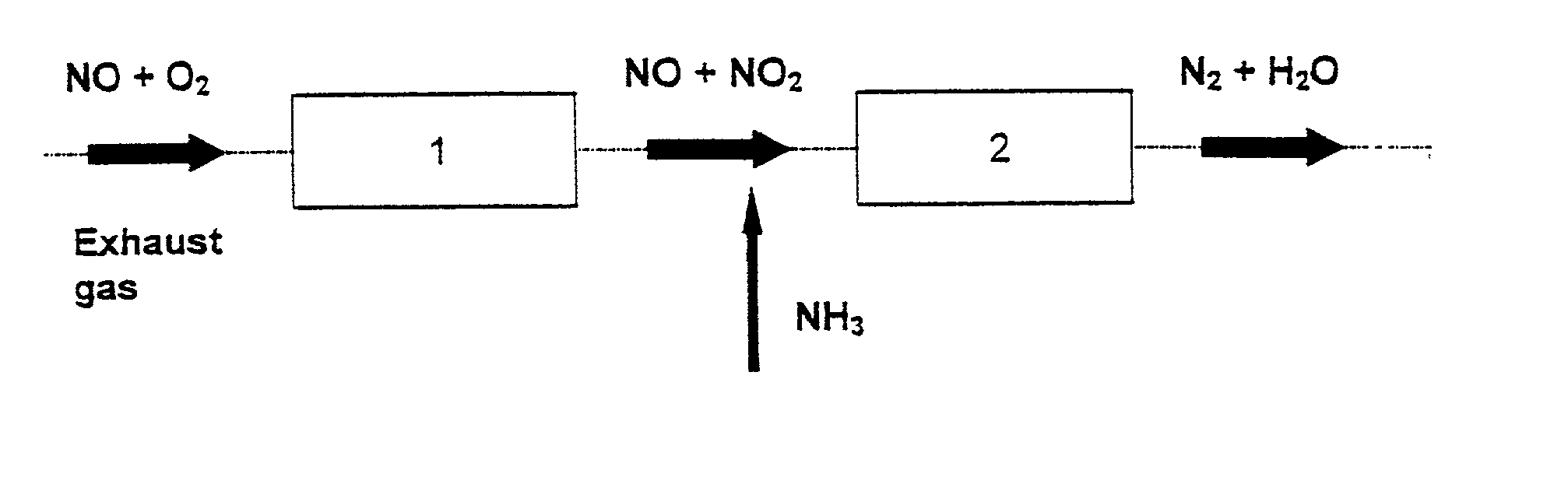
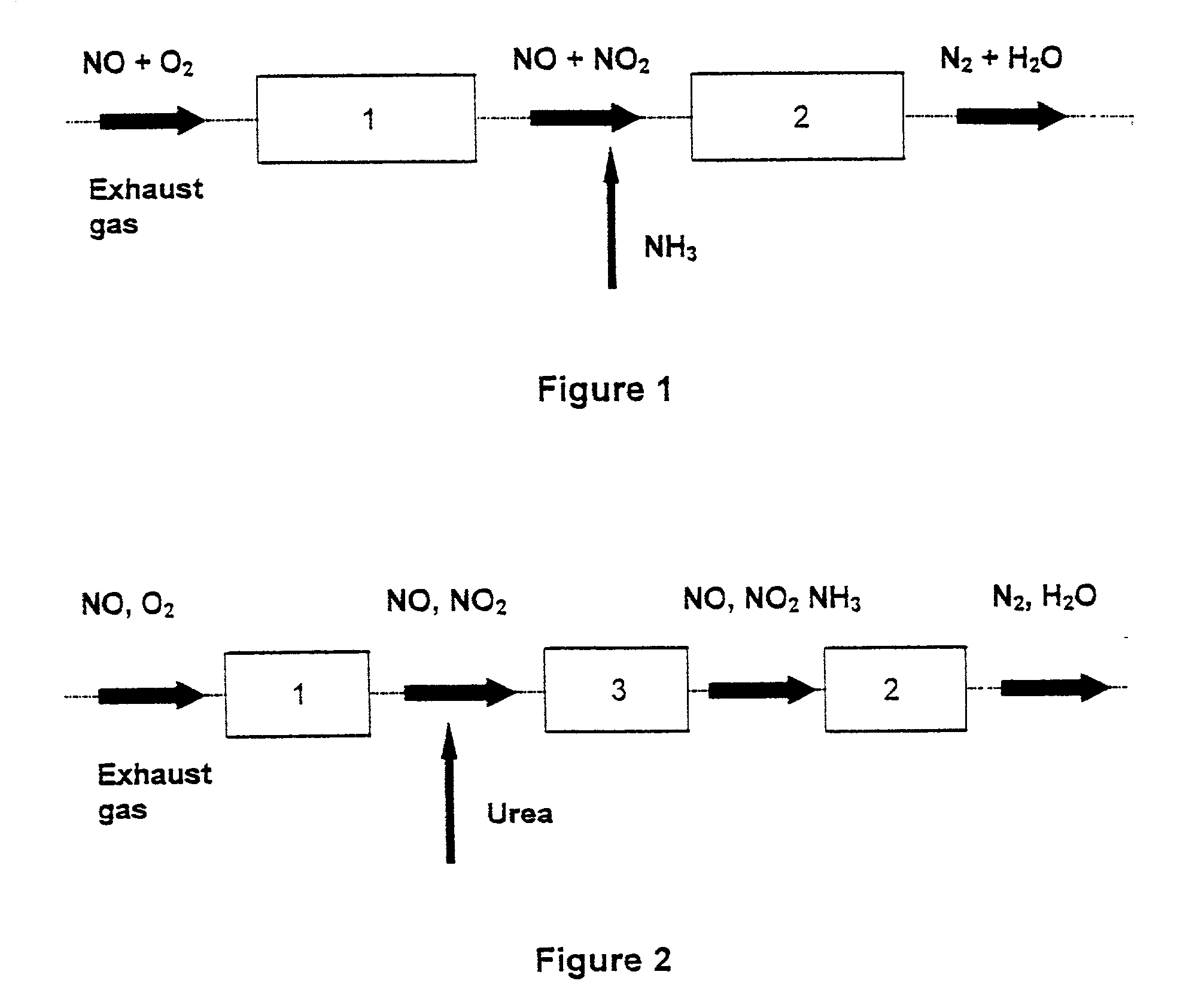
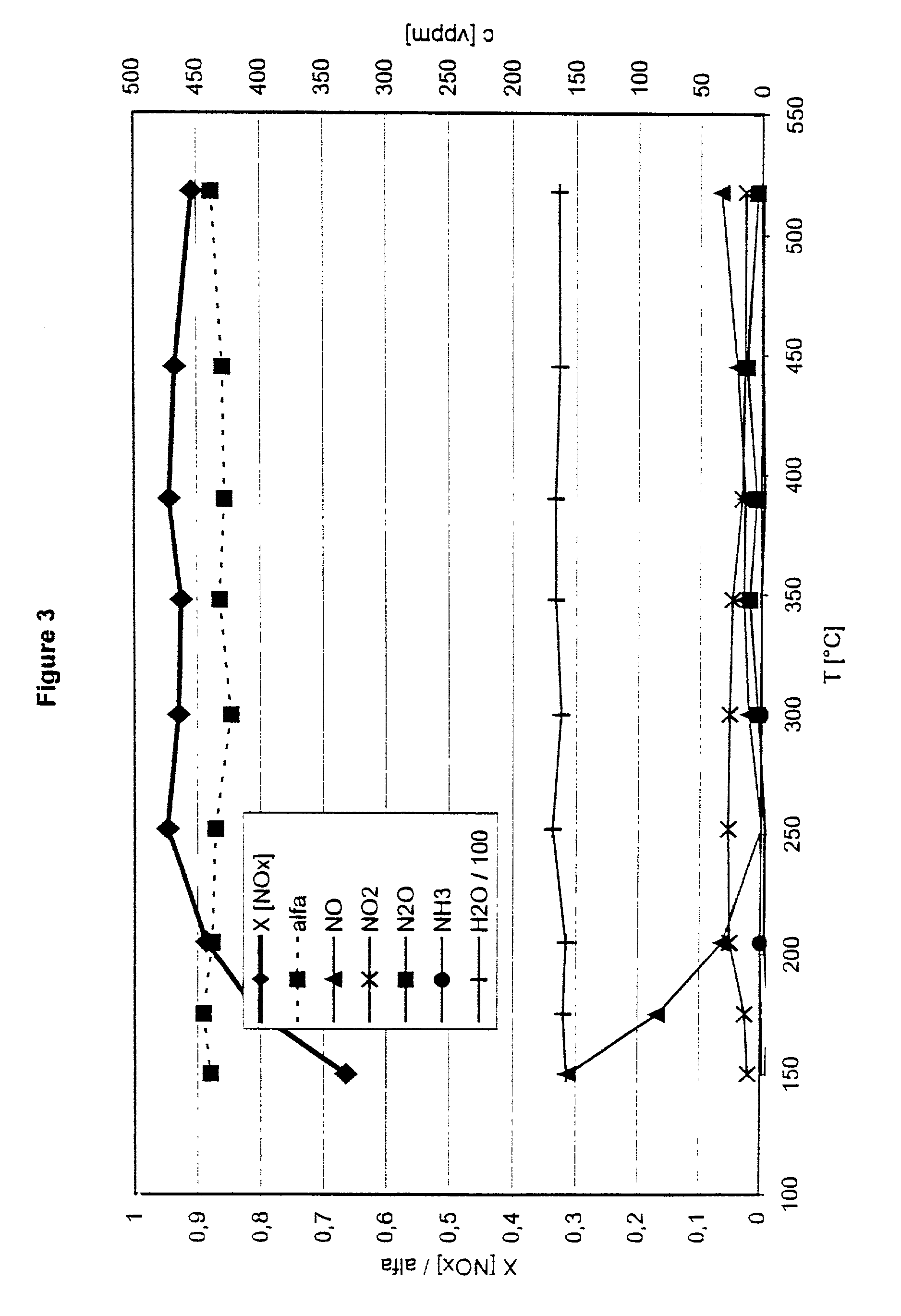
Process and catalyst for reducing nitrogen oxides
InactiveUS6843971B2High activityDelay agingCyanogen compoundsInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineChemistry
A process for reducing the nitrogen oxides present in a lean exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine by selective catalytic reduction on a reduction catalyst using ammonia, wherein a fraction of the nitrogen monoxide present in the exhaust gas is oxidized to nitrogen dioxide before the exhaust gas, together with ammonia, is passed over the reduction catalyst. The reduction catalyst contains a zeolite exchanged with transition metals and oxidation of the nitrogen monoxide is performed in such a way that the exhaust gas contains 30 to 70 vol. % of nitrogen dioxide before contact with the reduction catalyst.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Automobile windscreen cleaning agent
InactiveCN101041793AEasy to cleanDelay agingNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsCleansing AgentsSolvent
The invention discloses a cleaning agent of windscreen for car, which is characterized by the following: allocating alcohol, surface activator, inhibitor, de-icing film former, dye and water; producing the cleaning agent. This invention can delay rubber age of rain scraper and extend durability of windscreen, which is an environment-friendly type cleaning agent.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Process and catalyst for reducing nitrogen oxides
InactiveUS20020039550A1High activityDelay agingInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusNitric oxideInternal combustion engine
A process for reducing the nitrogen oxides present in a lean exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine by selective catalytic reduction on a reduction catalyst using ammonia, wherein a fraction of the nitrogen monoxide present in the exhaust gas is oxidized to nitrogen dioxide before the exhaust gas, together with ammonia, is passed over the reduction catalyst. The reduction catalyst contains a zeolite exchanged with transition metals and oxidation of the nitrogen monoxide is performed in such a way that the exhaust gas contains 30 to 70 vol. % of nitrogen dioxide before contact with the reduction catalyst.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
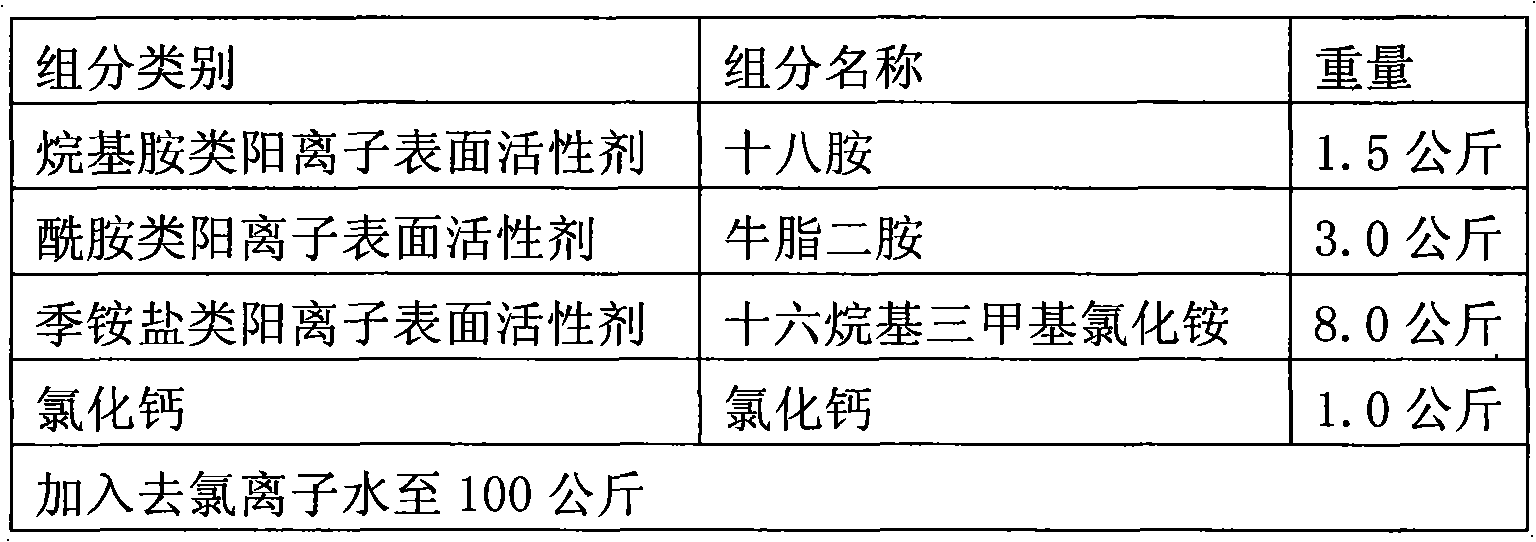
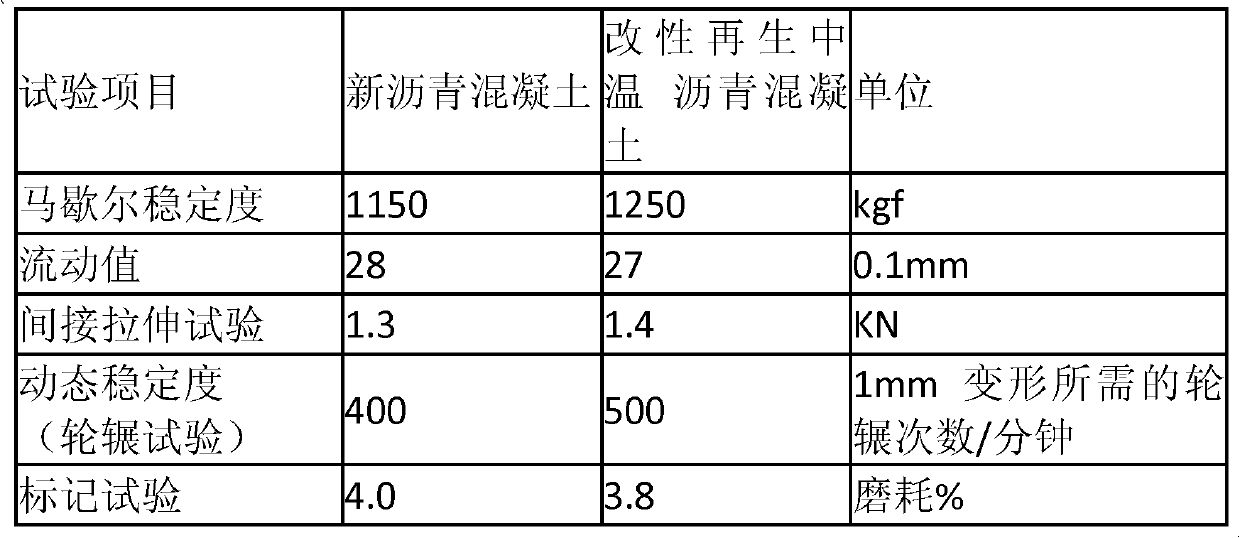
Asphalt warm-mix agent and asphalt mixture mixed by same as well as preparation methods thereof
ActiveCN101899218AWith viscosity reductionWith foamClimate change adaptationBuilding insulationsChlorideRoad surface
The invention relates to an asphalt warm-mix agent, comprising the following components in percentage by weight: 1.0-2.0% of alkylamine type cationic surfactant, 3.0-5.0% of amide type cationic surfactant, 5.0-10.0% of ammonium salt type cationic surfactant, 1.01.5% of calcium chloride, and water with residual percentage. The invention also relates to an asphalt mixture with the pavement applicability basically same as the traditional hot-mix asphalt mixture and the mixing and construction temperature lower than 20-50 DEG C; the purposes of energy saving, emission reduction, longer construction season, asphalt aging reduction and easier compaction are realized by reducing the mixing temperature; the indexes of the compaction degree, the water stability, the high-temperature performance, the low-temperature performance and the like of the pavement after paving the asphalt are not lower than those of hot-mix asphalt mixture at the same stage; and the service life of the asphalt pavement is efficiently guaranteed.
Owner:天津市市政工程研究院 +1
Chip antenna and mobile communication apparatus using same
InactiveUS6075491ASatisfactory antenna characteristicImprove reliabilitySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A chip antenna 10 includes, inside a rectangular-parallelepiped base 11 having barium oxide, aluminum oxide, and silica as main constituents, a conductor 12 wound in a spiral form along the length direction of the base 11, and an LC parallel resonance circuit 13, which is inserted in the intermediate portion of the conductor 12 and which is connected electrically in series with the conductor 12, and includes, on the surface of the base 11, a power-feeding terminal 14 for applying a voltage to the conductor 12. The conductor 12 is separated into a first conductor 121 and a second conductor 122 by the LC parallel resonance circuit 13. The LC parallel resonance circuit 13 is formed of a coil L1, which is an inductance element, and a capacitor C1, which is a capacitance element, which are connected in parallel.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method, display apparatus and burn-in reduction device for reducing burn-in on display device
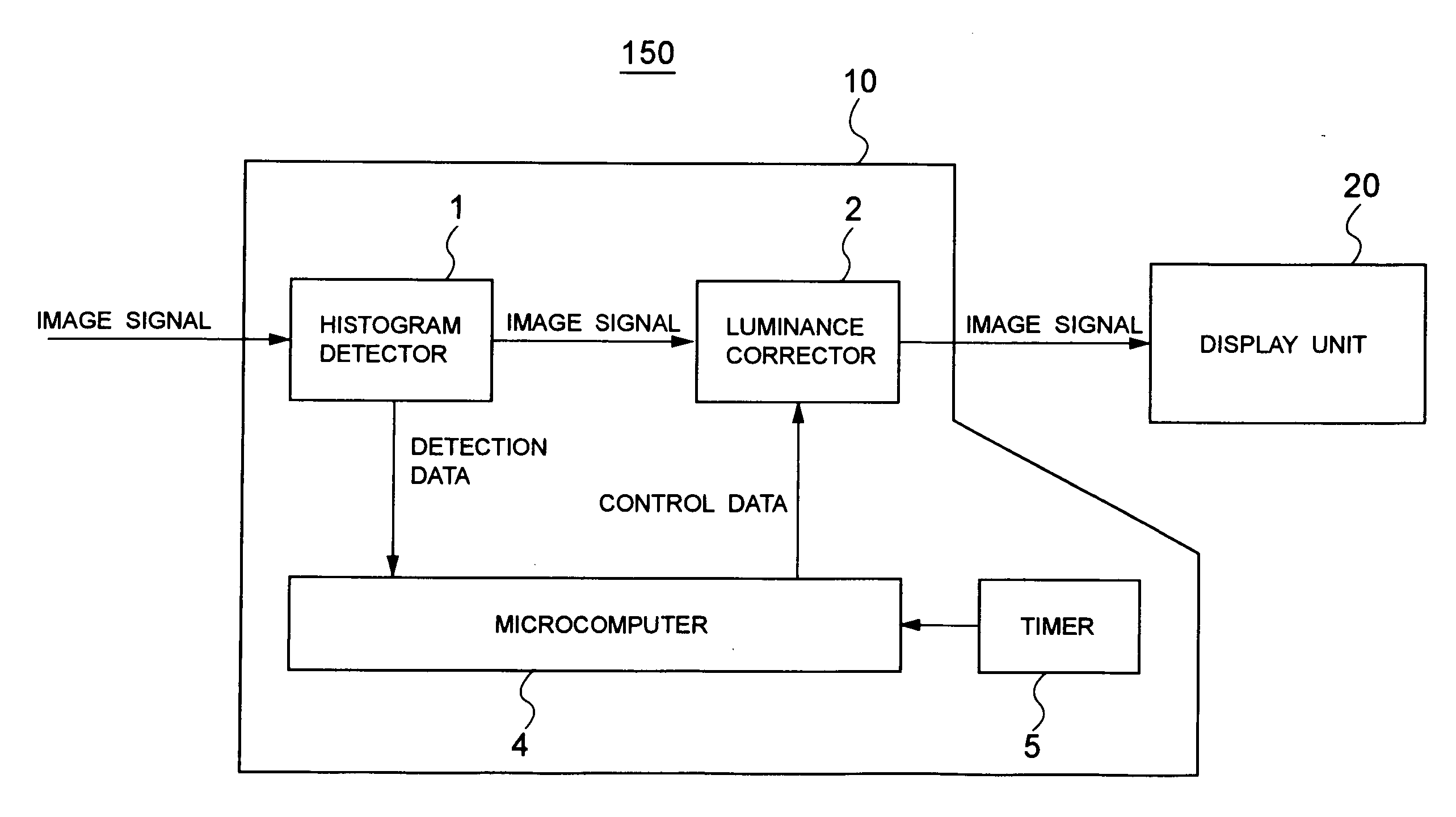
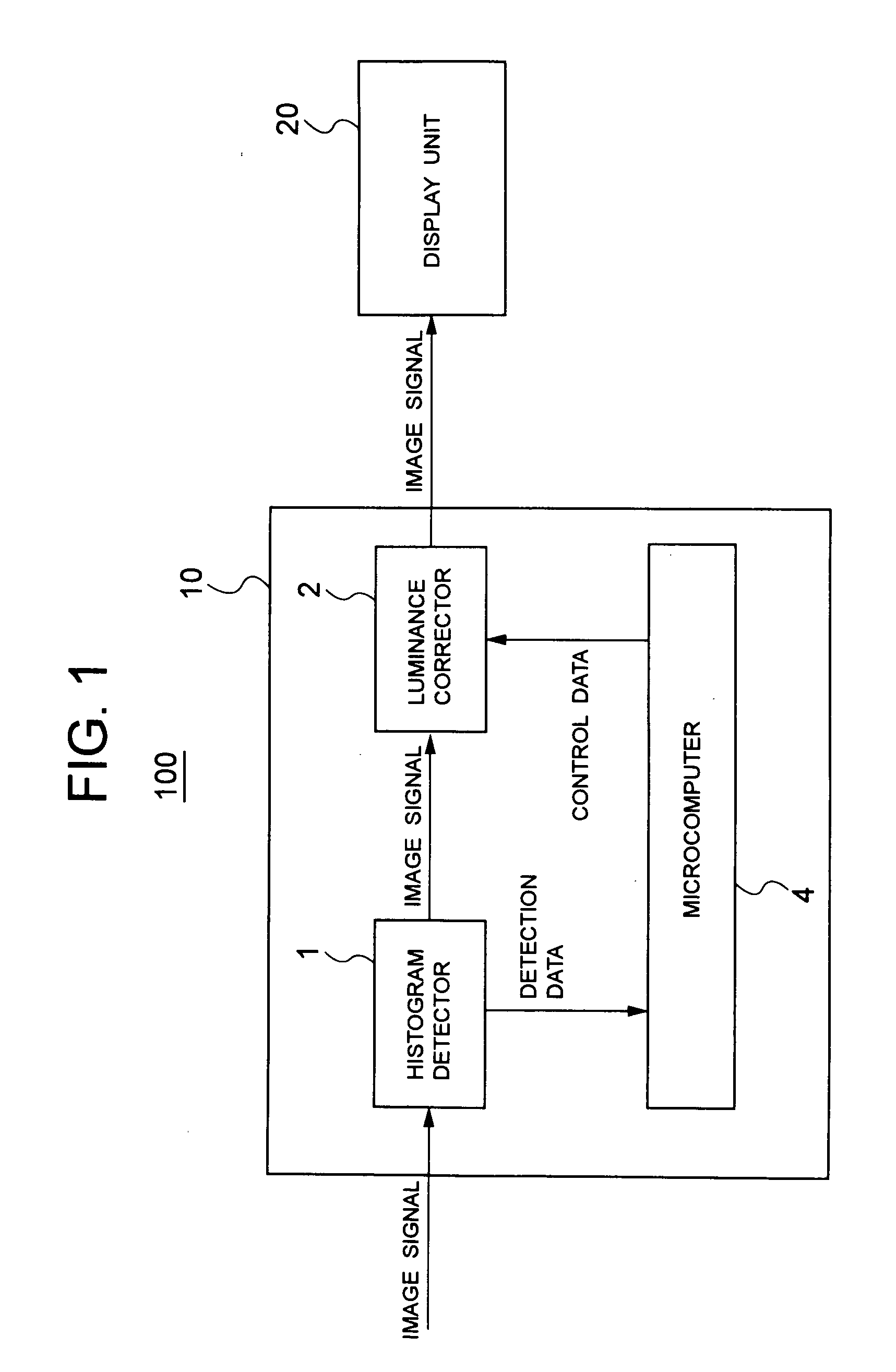
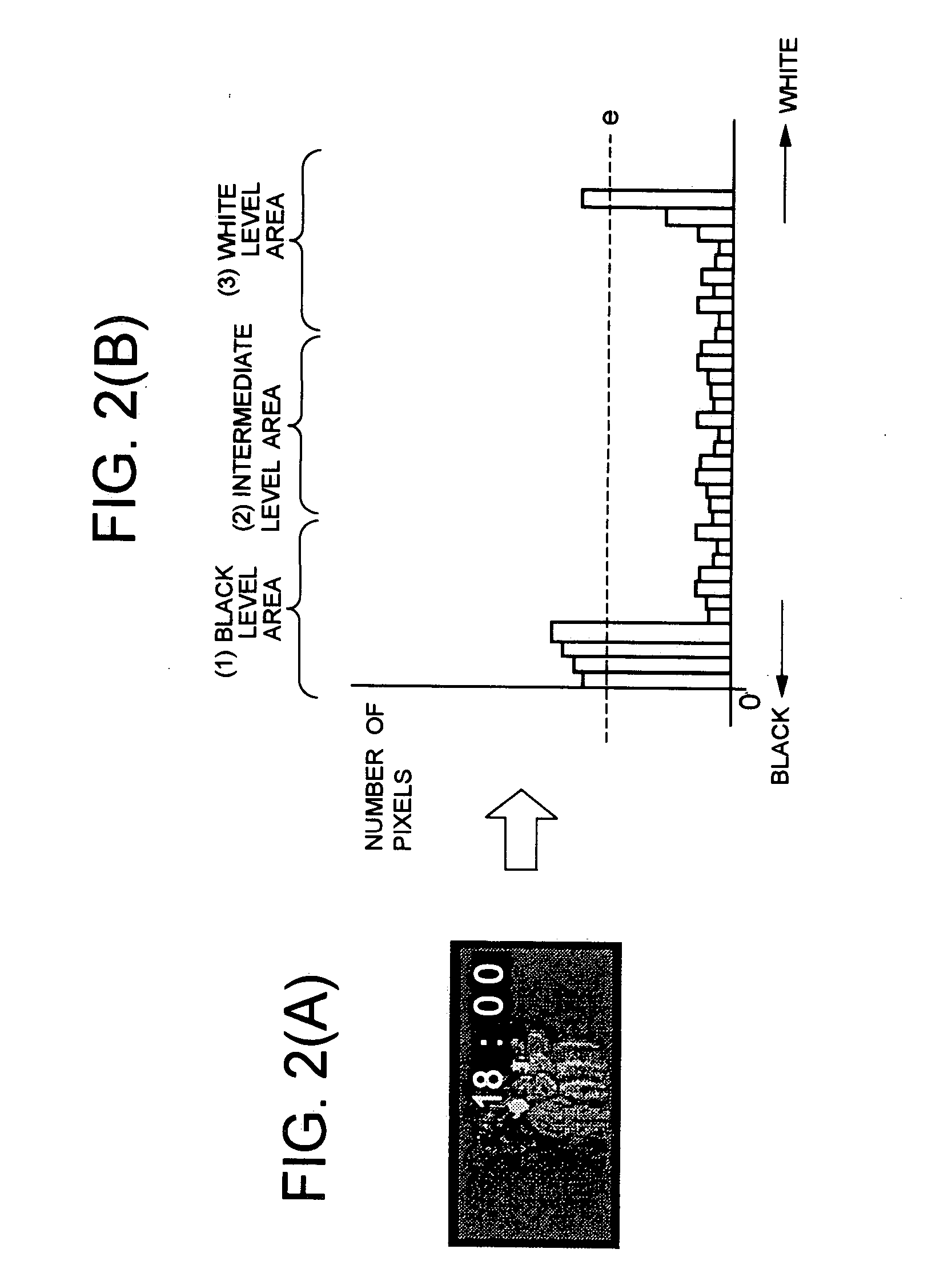
InactiveUS20050212726A1Improve image qualityIncrease the number ofStatic indicating devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceImage signal
Disclosed is a burn-in reduction device capable of favorably reducing burn-in on a screen. The burn-in reduction device comprises luminance level distribution detecting means for detecting a statistical distribution with respect to luminance levels of pixels of an image based on an input image signal; and luminance changing means for changing a luminance level of the input image signal in accordance with the statistical distribution detected by the luminance level distribution detecting means.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
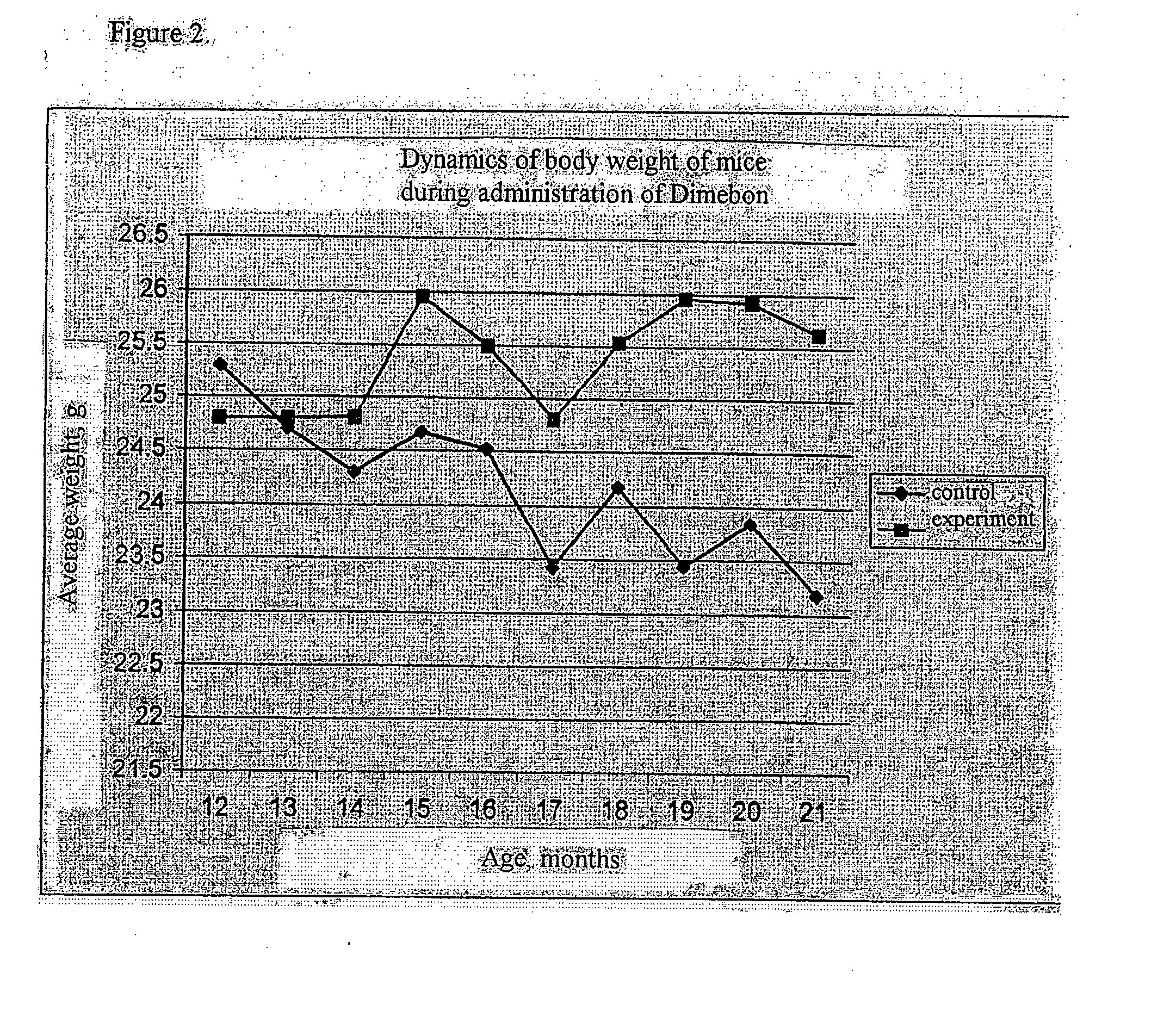
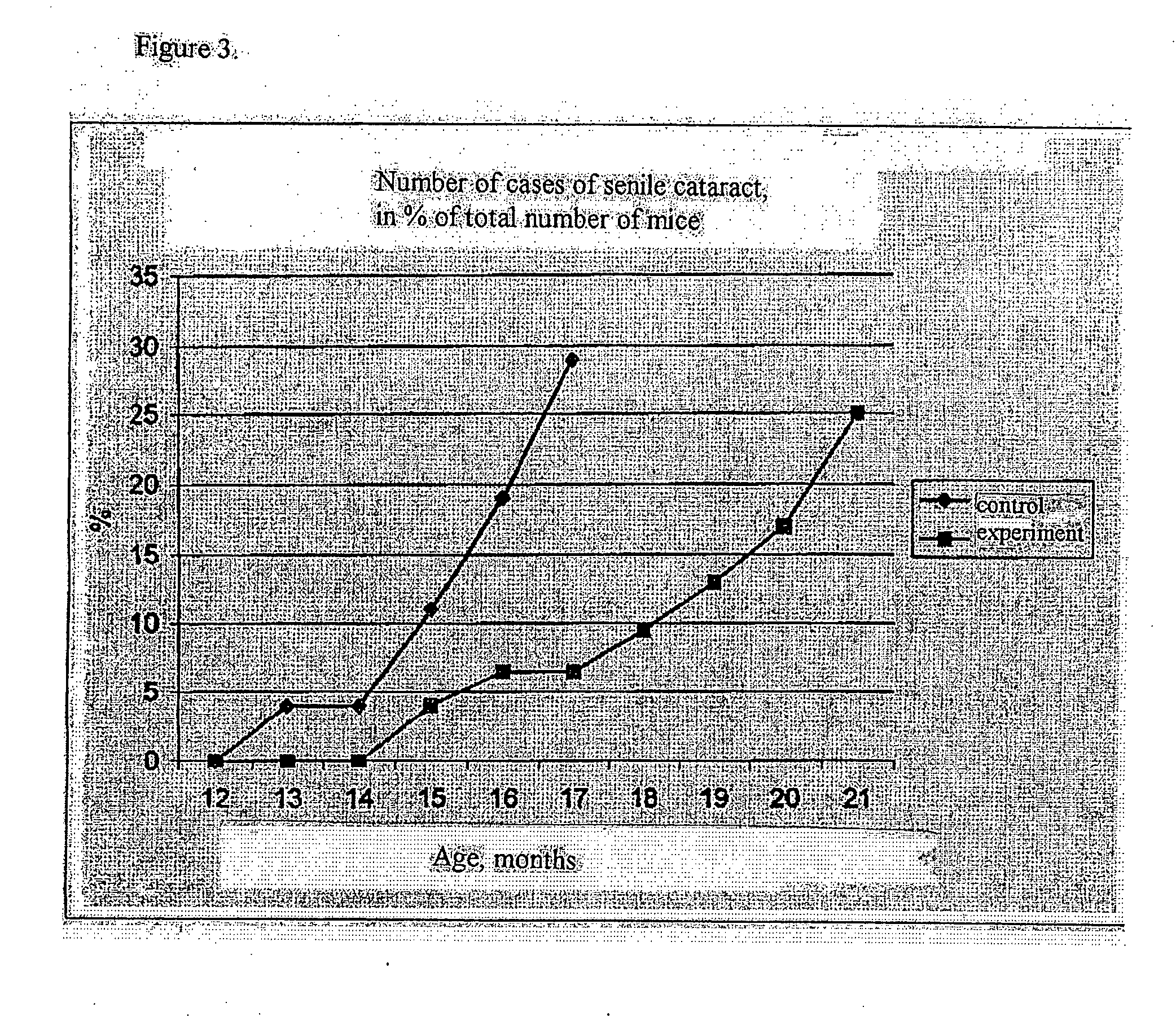
Methods and compositions for slowing aging
InactiveUS20070179174A1Anti agingImprove the quality of lifeBiocideAnimal repellantsQuality of lifePathology diagnosis
The present invention provides a pharmacological agent based on derivatives of hydrogenated pyrido (4,3-b) indoles and uses thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a geroprotector in the series of hydrogenated pyrido (4,3-b) indoles (several derivatives), which can be used for slowing aging, prolonging lifespan of an individual or cells in an individual, and / or improving quality of life of an individual developing or having a risk of developing age-associated manifestations and / or pathologies.
Owner:MEDIVATION TECH INC
Temperature-adjusted and modified recycled ascon composition for reusing 100% of waste ascon for road pavement, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN102448907AImprove qualityLow production temperatureIn situ pavingsSolid waste managementCost savingsParticle-size distribution
Provided is a temperature-adjusted and modified recycled ASCON composition for reusing 100% of waste ASCON for road pavement, and a method for manufacturing same, wherein the composition is used in asphalt pavement as a material for the wearing course, surface course, binder course, and base course, and the method comprises: feeding 100 wt % of waste ASCON aggregate having up to a 53 mm particle size distribution into a mixer via a feeding inlet for new aggregate; adding 0.1 to 20 wt % of a recycling modifier and 0.1 to 20 wt % of a temperature-adjusting additive to the waste ASCON via the feeding via the inlet for new aggregate; and homogeneously mixing said materials at 5 to 180 DEG C for 0.5 to 3 minutes. The recycling modifier improves the physical properties of recycled ASCON, while the temperature-adjusting additive adjusts the temperatures for producing and constructing recycled ASCON. The present invention may provide economic, social and technological conveniences by improving the overall recycling technology of waste ASCON. The conveniences may be achieved by virtue of: cost-saving in production by using only waste ASCON without any new materials; saving waste disposal costs; preventing the destruction of nature to obtain aggregate; reducing the consumption of new asphalt; preventing environmental pollution through the reuse of waste products; preventing the early occurrence of plastic deformation and fatigue cracks due to improving the quality of the recycling modifier; economic benefits from the prolonged lifespan of road pavement; the possibility of being used as a material for the wearing course and surface course of major roadways; saving energy in the production and construction of recycled ASCON by adding the temperature-adjusting additive; and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Owner:许政道
External skin care product capable of adjusting skin immunity and delaying skin aging
ActiveCN103520081ARegulate immunityDelay agingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyCentella asiatica extract
The invention discloses an external skin care product capable of adjusting skin immunity and delaying skin aging. The external skin care product is characterized by comprising powder, an aqueous solution and emulsion, wherein the powder comprises oligopeptide-1 and ginsenoside; the aqueous solution comprises glycyrrhiza glabra root extract, artemisia capillaris flower extract, mulberry root extract, jujube fruit extract, scutellaria root extract, hydrolyzed rice protein and nicotinamide; and the emulsion comprises hgytantriol bifida ferment lysate, creatine, carnosine, alpha glucosyl hesperidin, hexapeptide-3, centella asiatica extract, coenzyme Q10 inclusion complex, opuntia ficus-indica stem extract, rhodiola rosea extract, saussurea involucrate extract, pseudo-ginseng root extract and Chinese angelica extract inclusion complex. According to the external skin care product, the powder, the aqueous solution and the emulsion are jointly used, and the external skin care product can reduce wrinkle and pachulosis, even skin tone and improve skin elasticity and skin firmness, so that the skin is finer and smoother and looks young.
Owner:INFINITUS (CHINA) CO LTD
Methods for identifying agents which alter histone protein acetylation, decrease aging, increase lifespan
InactiveUS20030207325A1Extend your lifeEasy to identifyCompound screeningSenses disorderADPRibosylationNad dependent
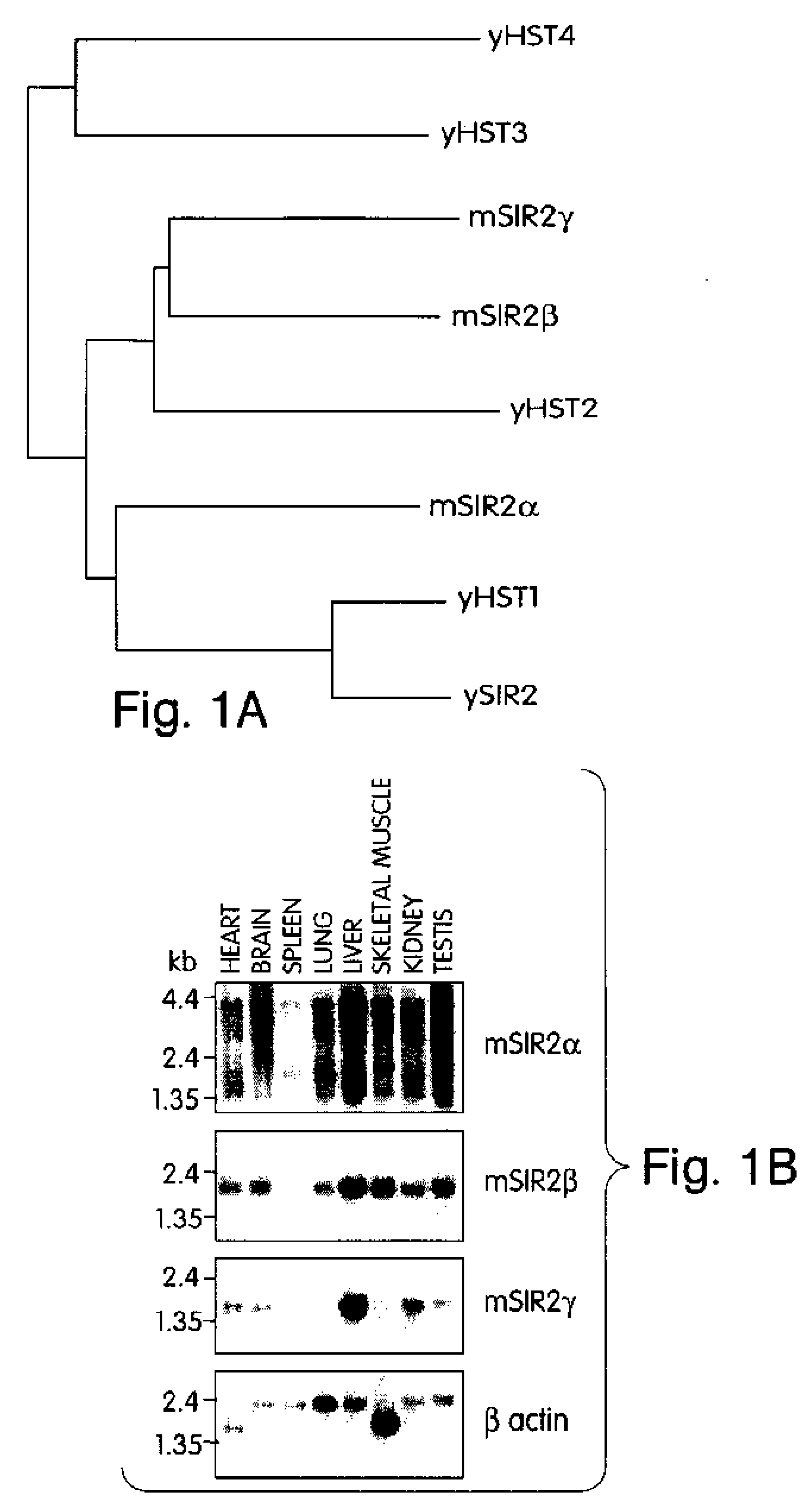
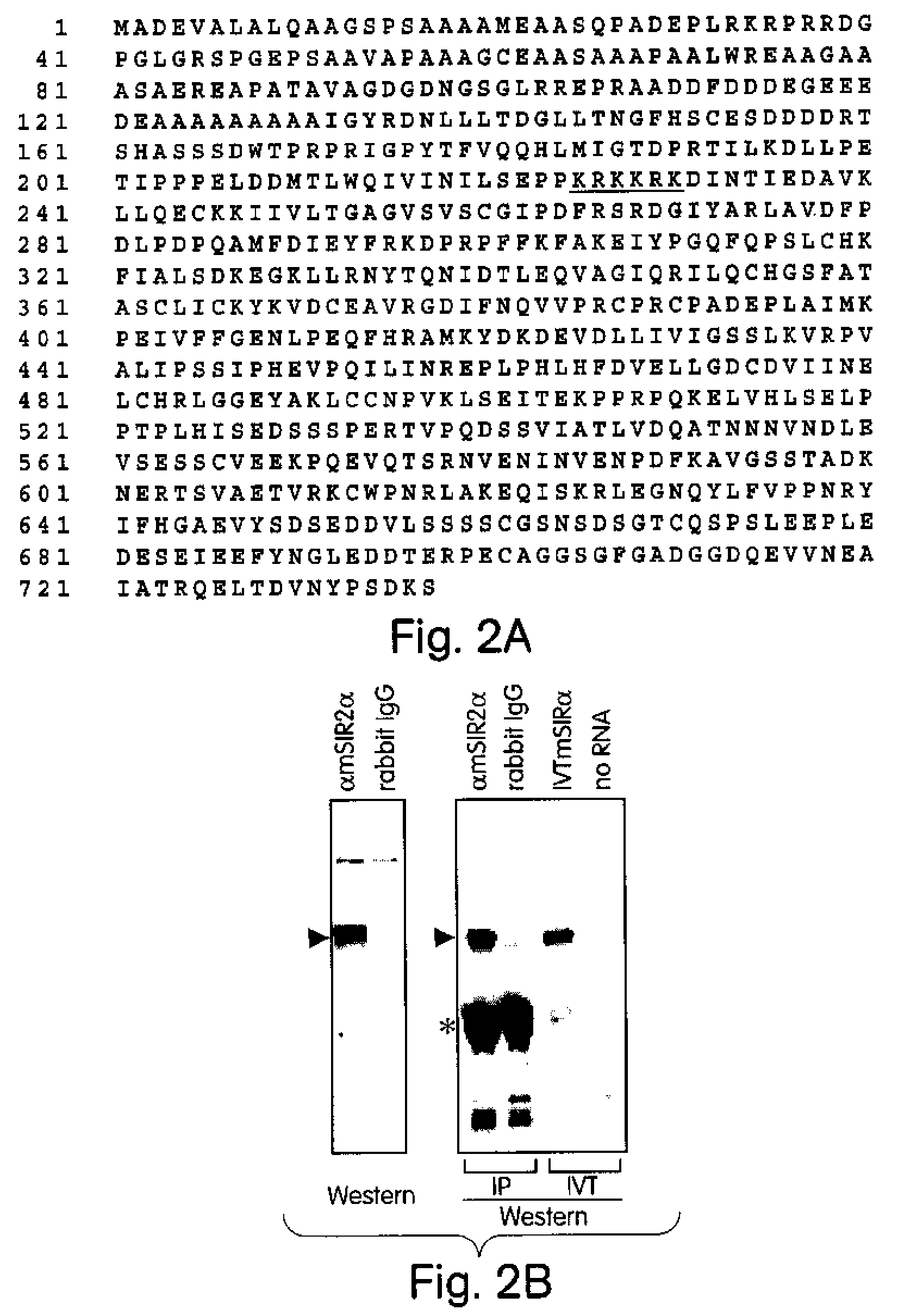
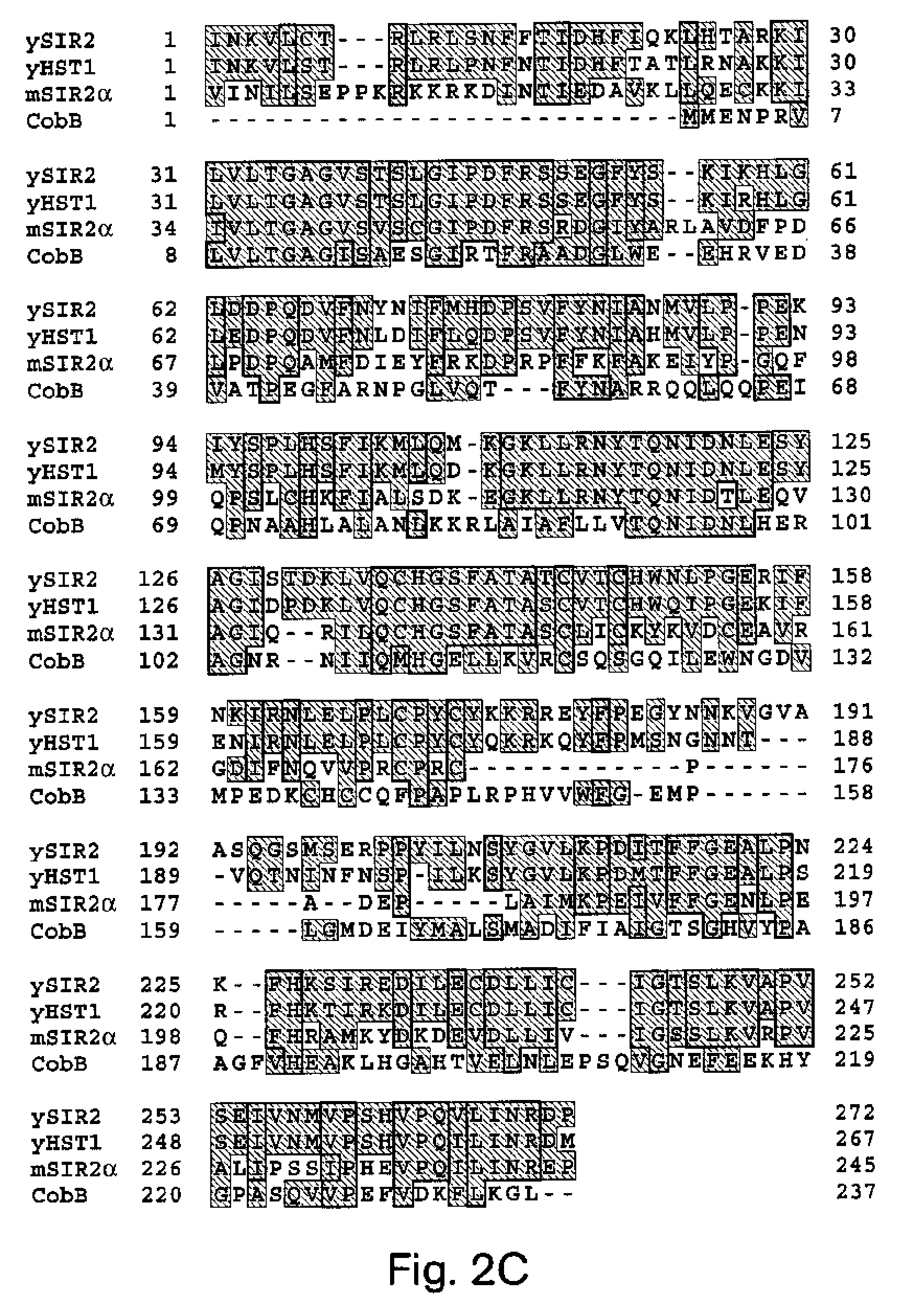
Abstract of the Disclosure Methods of identifying agents which alter the NAD-dependent acetylation status and mono-ADP-ribosylation of nuclear proteins are disclosed. The methods further include identifying agents which alter the life span or aging of a cell or an organism by determining the level of NAD-dependent acetylation and / or ADP ribosylation of a nuclear protein. The invention also relates to a mammalian Sir2 protein which acetylates or deacetylates nuclear proteins in a NAD-dependent manner and has mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Host cells producing the Sir2 protein and antibodies to the Sir2 protein are also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
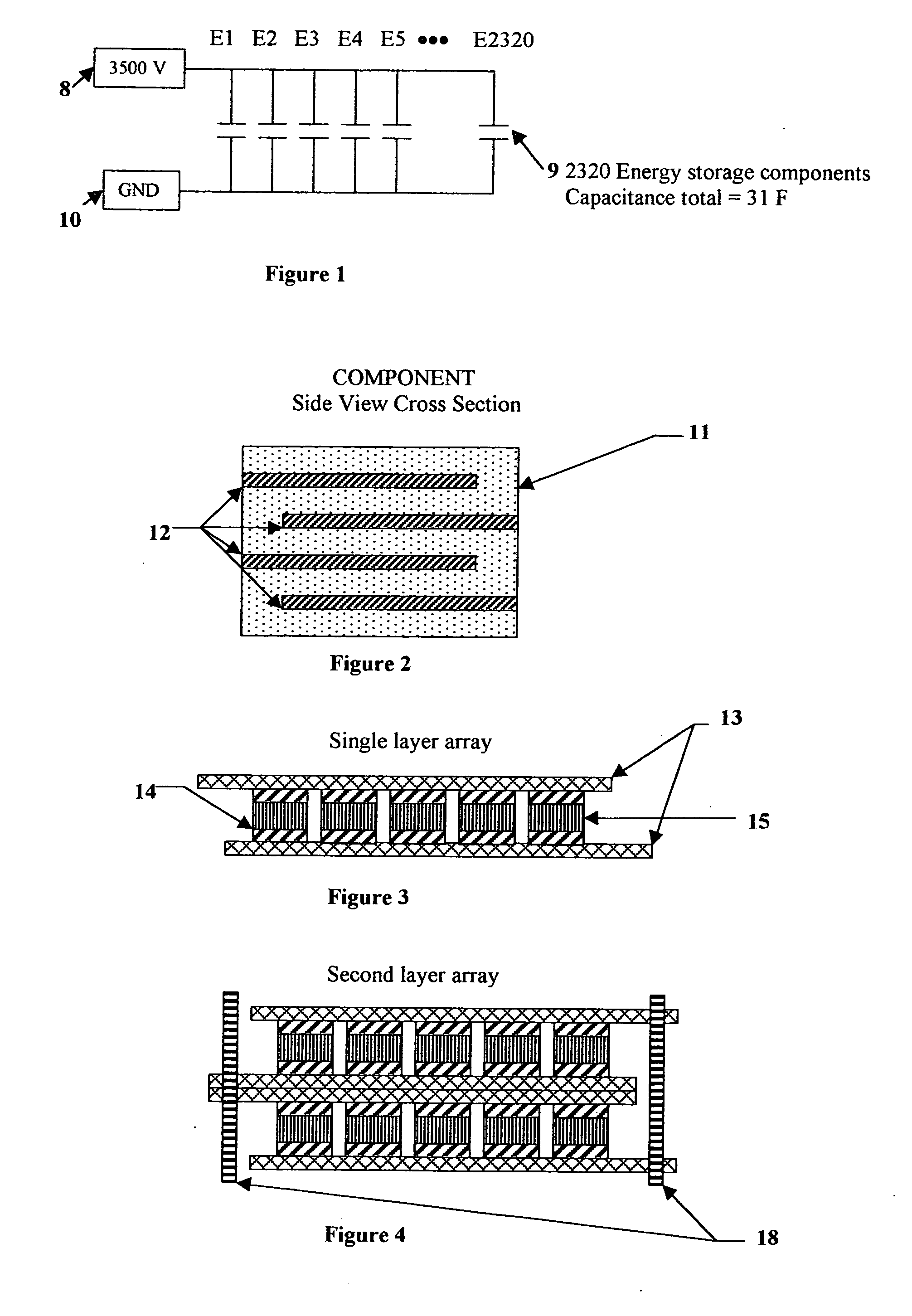
Electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) utilizing ceramic and integrated-circuit technologies for replacement of electrochemical batteries
InactiveUS20060210779A1Fast chargingSolution to short lifeStacked capacitorsPrimary cellsBarium titanateElectrical battery
An electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) has as a basis material a high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate ceramic powder. This powder is double coated with the first coating being aluminum oxide and the second coating calcium magnesium aluminosilicate glass. The components of the EESU are manufactured with the use of classical ceramic fabrication techniques which include screen printing alternating multilayers of nickel electrodes and high-permittivitiy composition-modified barium titanate powder, sintering to a closed-pore porous body, followed by hot-isostatic pressing to a void-free body. The components are configured into a multilayer array with the use of a solder-bump technique as the enabling technology so as to provide a parallel configuration of components that has the capability to store electrical energy in the range of 52 kW·h. The total weight of an EESU with this range of electrical energy storage is about 336 pounds.
Owner:EESTOR
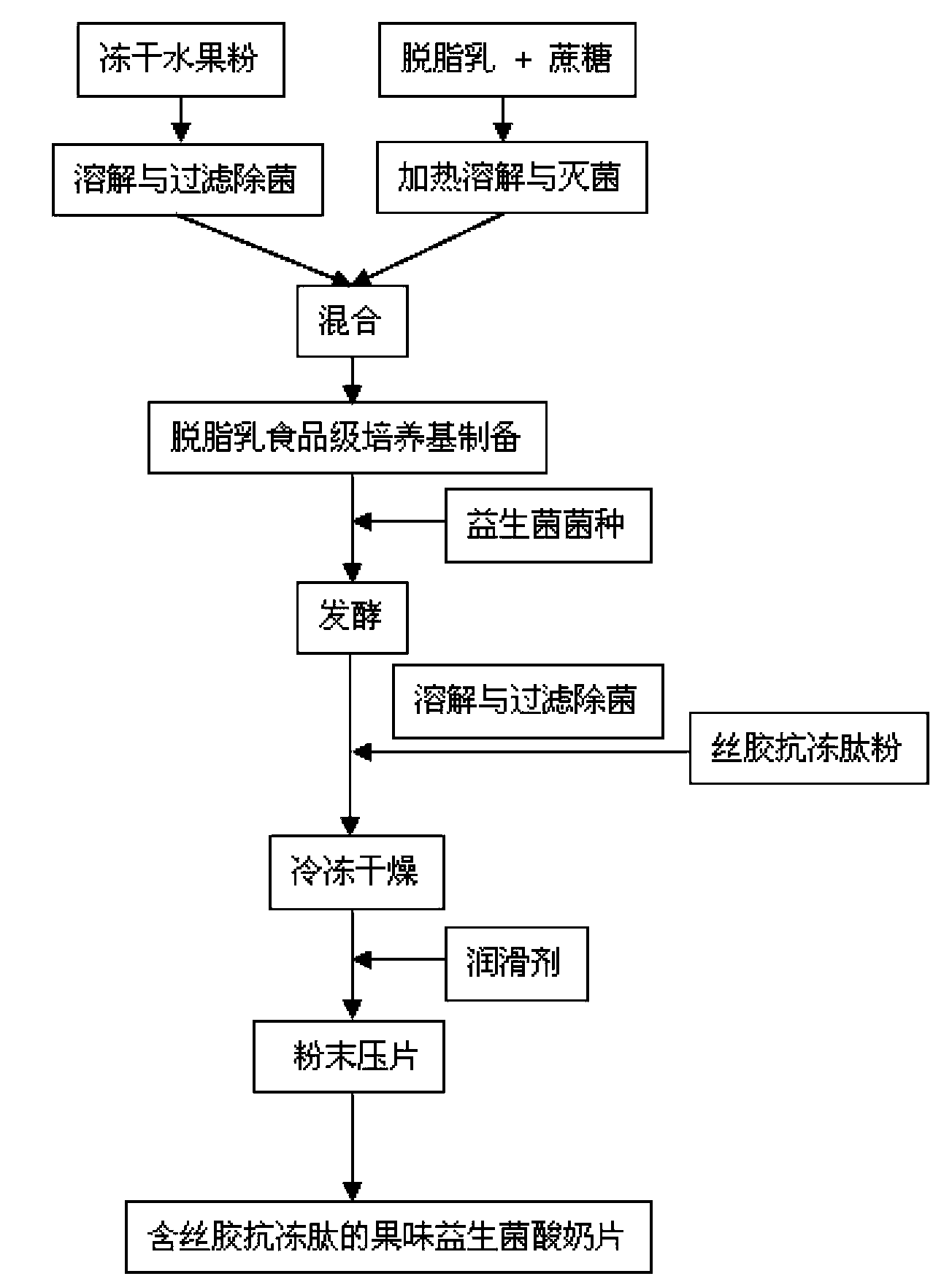
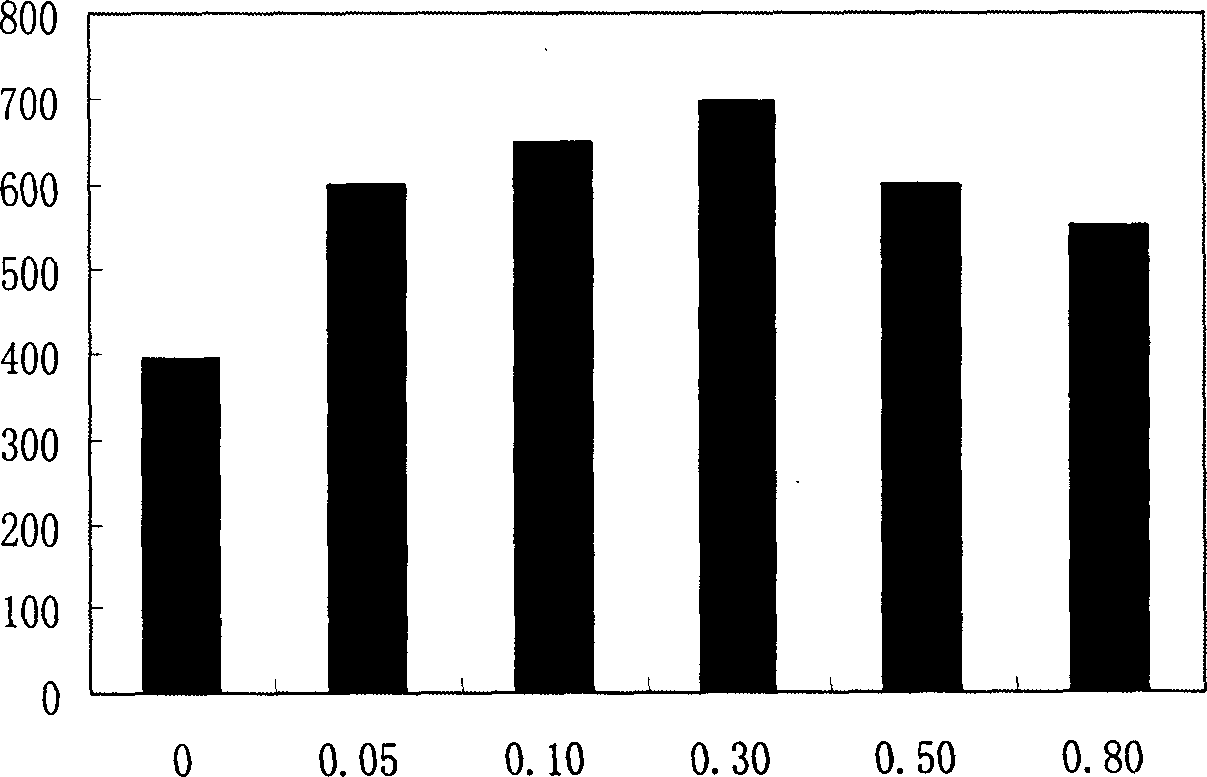
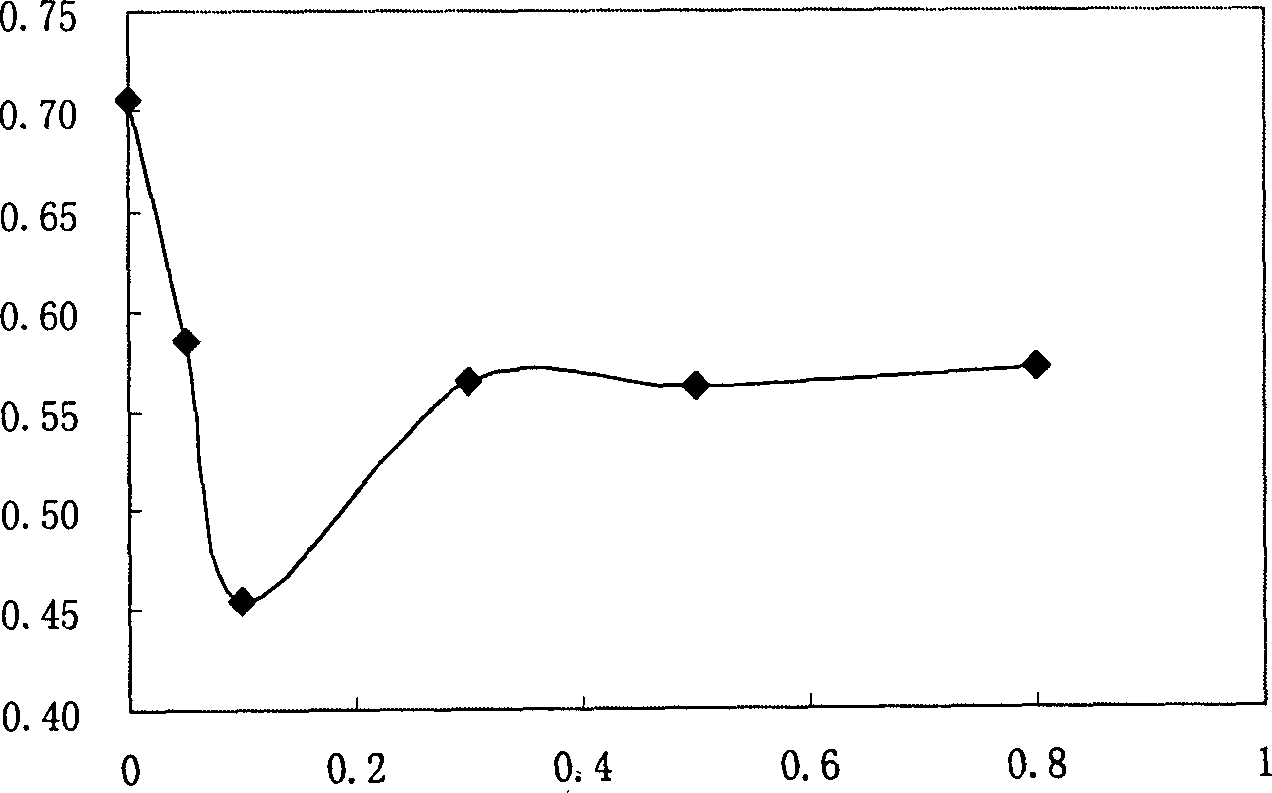
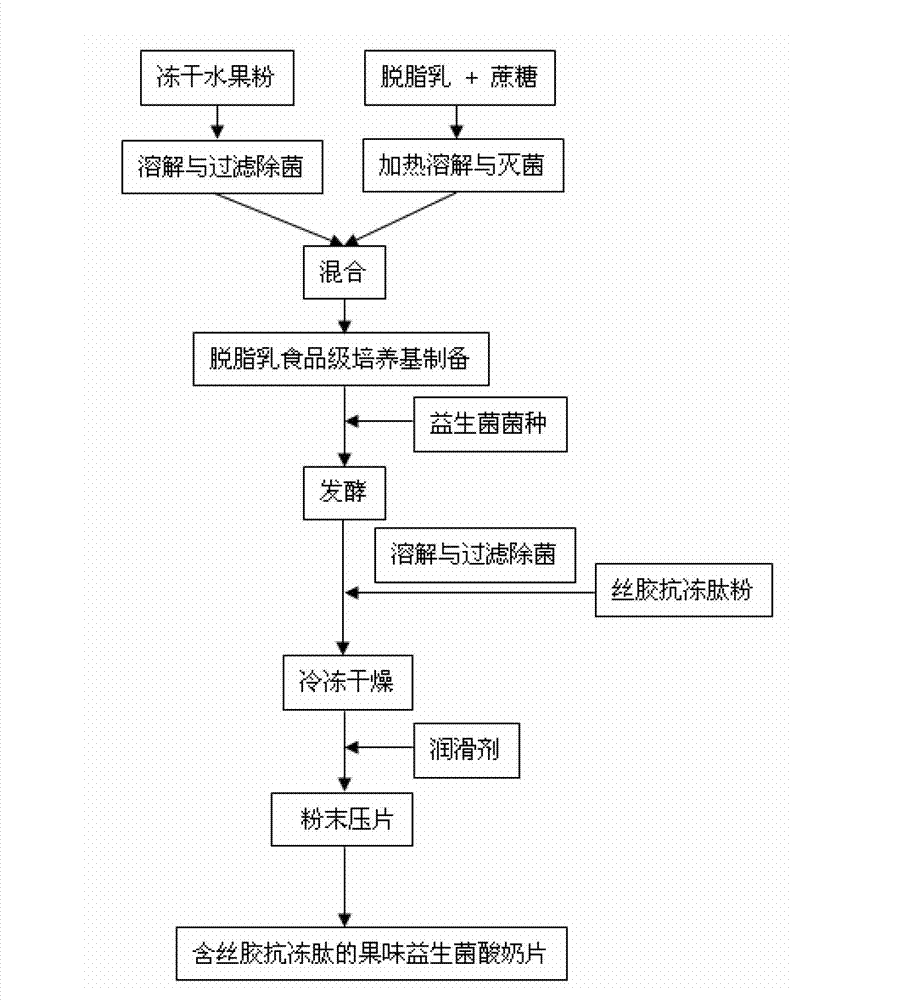
Fruity probiotic yogurt slice containing antifreeze sericin peptide and method for preparing same
ActiveCN103109930BRich in physiological functionsRich in antioxidantMilk preparationProbiotic yogurtBiotechnology
The invention discloses a fruity probiotic yogurt slice containing antifreeze sericin peptide. The raw materials for preparing the fruity probiotic yogurt slice comprise 10-14 parts of skimmed milk powder, 2-5 parts of sucrose, 1-3 parts of sericin peptide, 1-4 parts of fruit material, 0.1-0.6 part of lyophilized active probiotics and 0.1-0.4 part of magnesium stearate. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the product which is the fruity probiotic yogurt slice. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: preparing a skimmed-milk food-grade culture medium, fermenting the probiotics, adding the antifreeze sericin peptide, freezing and drying fermented milk in vacuum, and pressing powder into slices. As the fruity probiotic yogurt slice contains the antifreeze sericin peptide and the lyophilized fruit powder which is rich in the vitamin B group, the number of the probiotics in the fruity probiotic yogurt slice can be increased, the retention time of the activity of the probiotics can be prolonged, and the taste, flavor and nutritional and healthcare values of the fruity probiotic yogurt slice can be improved. The fruity probiotic yogurt slice can serve as a functional food for supplementing the vitamin B group, improving the immunity and promoting the intestinal health.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Thermoplastic low-smoke halogen-free flame-retardant environment-friendly sheath material for power cables and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103122097ADoes not affect physical and mechanical propertiesDoes not affect processabilityInsulated cablesPigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsCrack resistanceDimethyl methylphosphonate
The invention discloses a thermoplastic low-smoke halogen-free flame-retardant environment-friendly sheath material for power cables and a preparation method thereof. The thermoplastic low-smoke halogen-free flame-retardant environment-friendly sheath material for power cables comprises the following components in parts by weight: 60-80 parts of EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate), 20-30 parts of HDPE (high-density polyethylene), 10-15 parts of EPDM (ethylene-propylene-diene monomer), 15-25 parts of compatiblizing agent, 100-150 parts of halogen-free flame retardant, 0.5-1 part of antioxidant 1035, 0.5-1 part of antioxidant DSTP, 1-2 parts of ethylene bis stearamide, 3-5 parts of DCP (dicumyl peroxide), 2-4 parts of zinc oxide, 1-2 parts of calcium stearate, 10-20 parts of dimethyl methyl phosphonate, 30-40 parts of nano kaolin, 2-3 parts of stearic acid and 0.5-1 part of isopropyl tri(dioctylpyrophosphate)titanate. The sheath material disclosed by the invention has the advantages of excellent physical and mechanical properties, excellent flame retardancy, favorable high / low temperature resistance, favorable oil resistance, favorable solvent resistance, favorable wear resistance, favorable ozone resistance, favorable aging resistance, high flexibility, crack resistance and the like, is very durable, environment-friendly and pollution-free, and can completely satisfy the requirements for modern power cables.
Owner:ANHUI HUAJIN CABLE GROUP
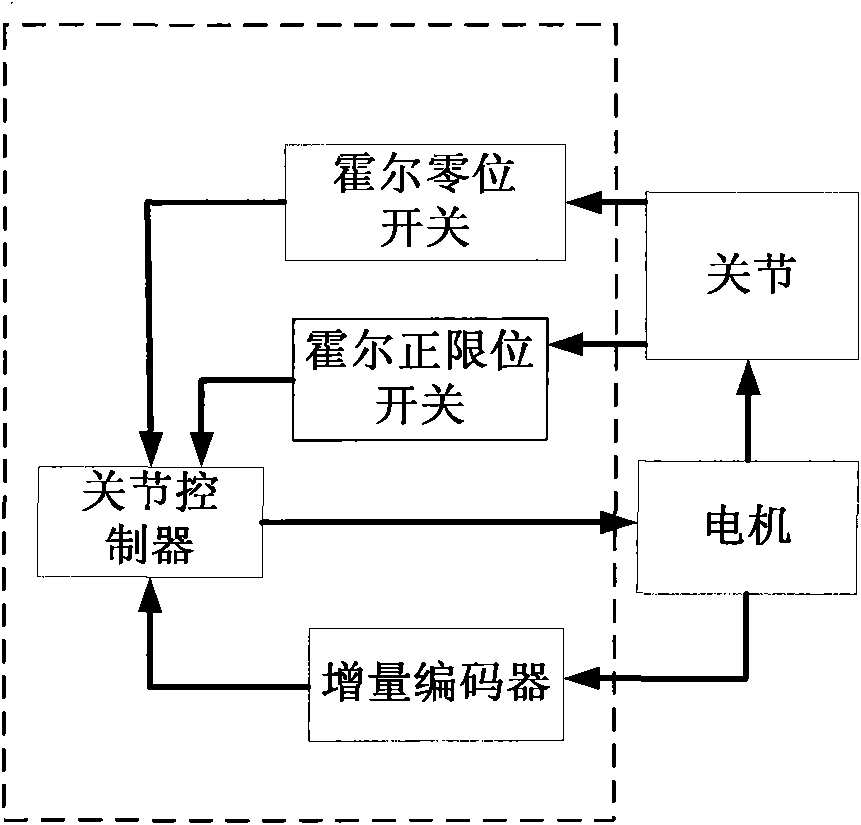
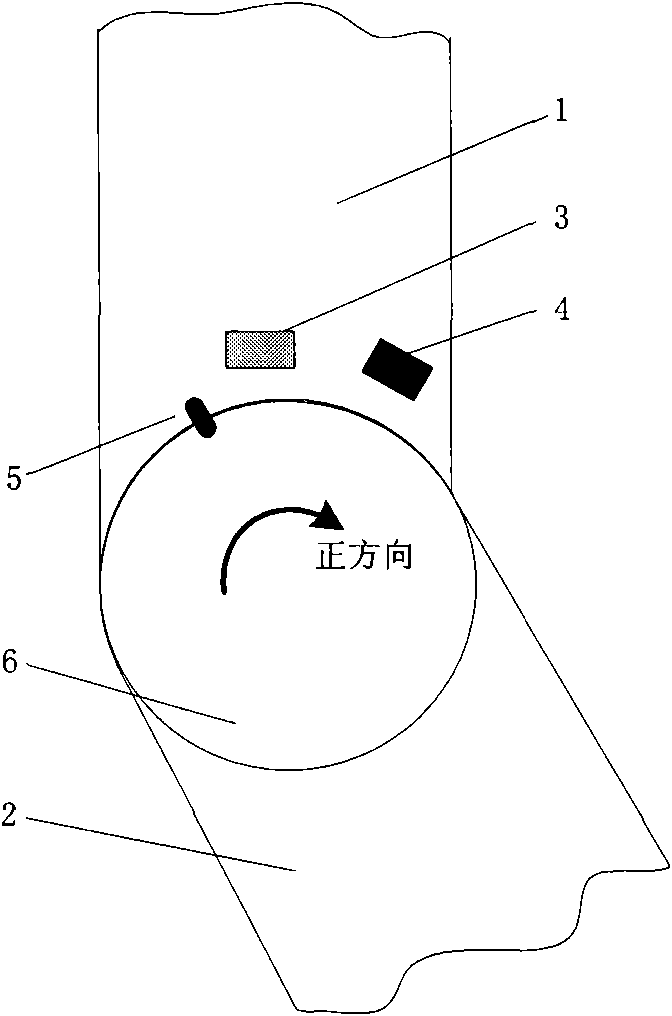
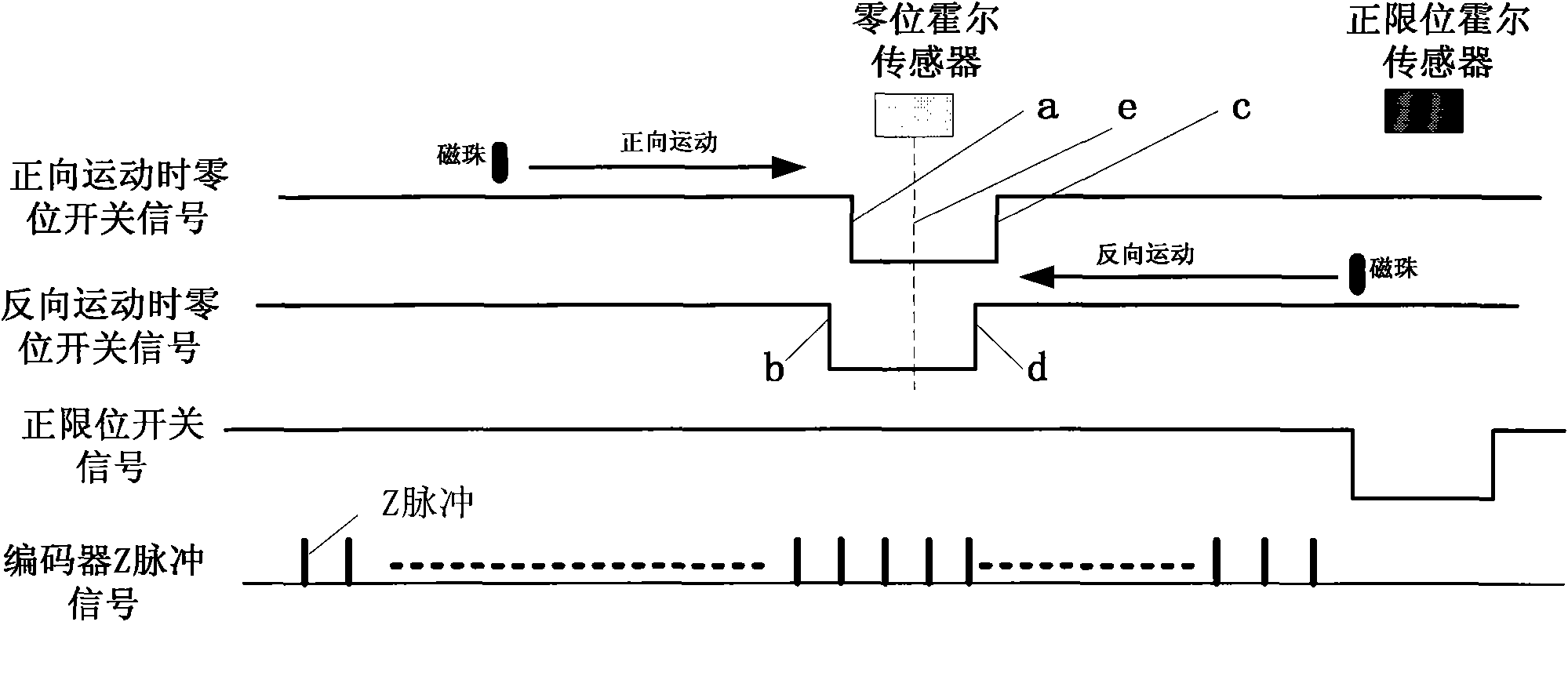
A Hall-switch-based system for accurately positioning the initial position of the joint of a robot
The invention discloses a Hall-switch-based system for accurately positioning the zero position of the joint of a robot. On the basis of utilizing a Hall zero position switch as a position sensor, the joint rotates to the same direction when powered up and the system ingeniously selects and ascertains the zero position of the joint of the robot by using the hysteretic characteristic of the Hall signal and a Z pulse of a motor shaft, achieving the automation for accurately positioning the zero position of the joint of the robot. The system has the advantages of strong anti-interference capability, high stability, high precision, low cost and simple structure.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
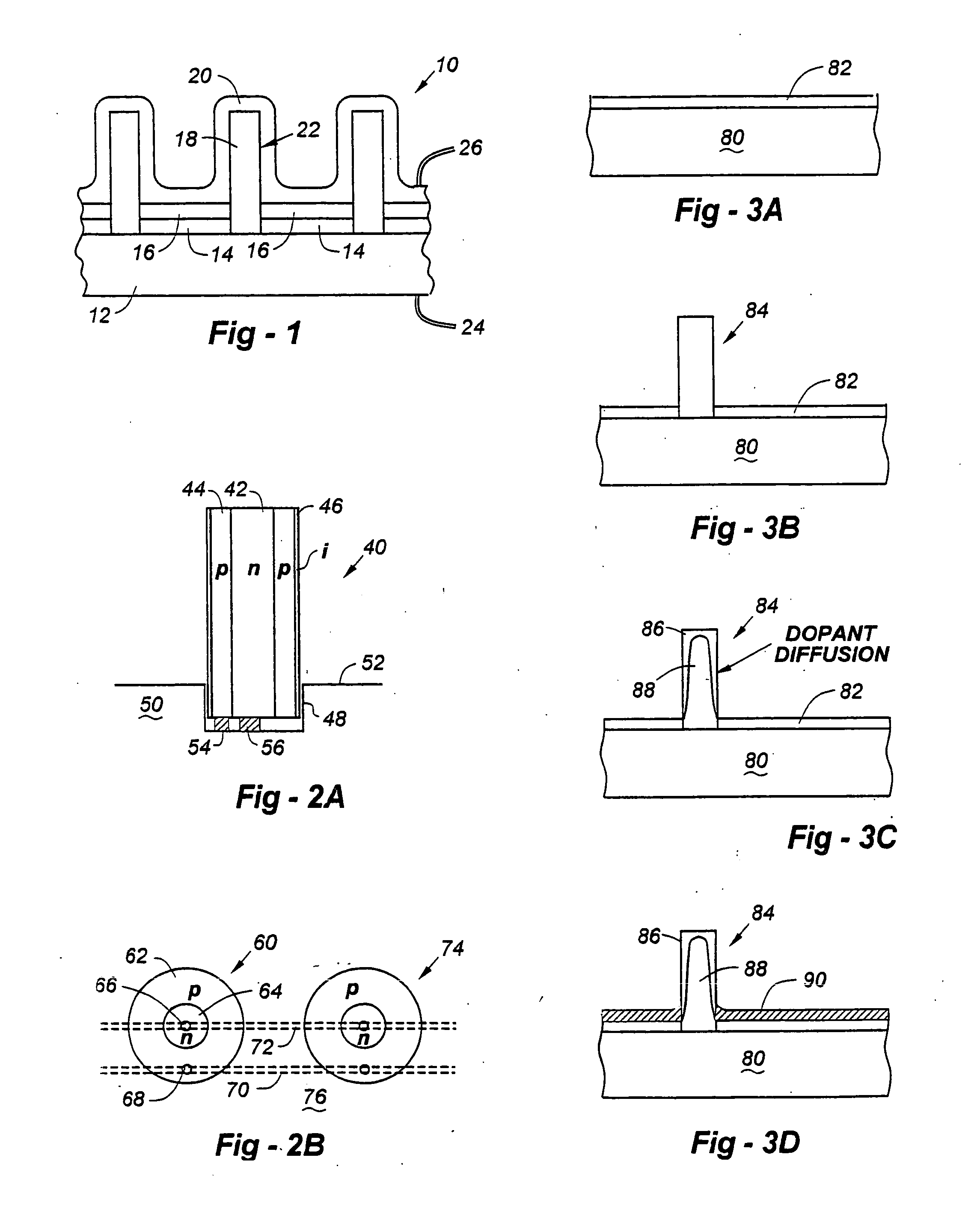
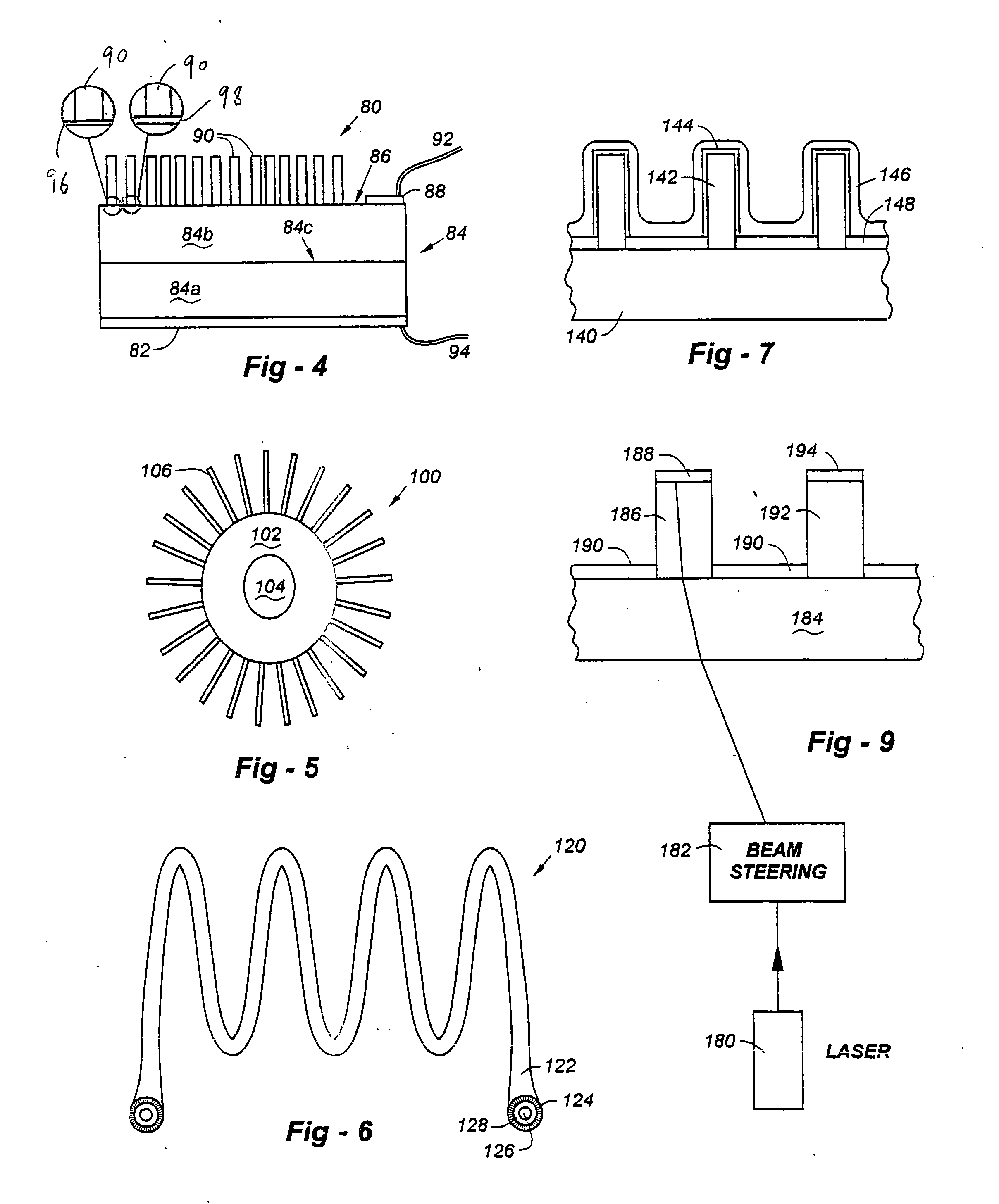
Optoelectronic devices employing fibers for light collection and emission
InactiveUS6969897B2Avoid mechanical damageDelay agingSolar heating energySolar heat devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceFiber
An optoelectronic device, such as a solar cell, light-emitting device, or photodetector, comprises a substrate, a number of fibers supported by the substrate so that an end of each fiber is in electrical communication with the substrate surface; an optional first layer, covering the substrate, though which the fibers protrude, and a second layer overlaid on at least part of the first layer and exposed fiber surfaces. The second layer may be electrically conducting, and electrically isolated from the substrate surface by the first layer. The second layer can be in electrical communication with each fiber, and an electrically conducting path can exists between the second layer and the substrate surface through each fiber. The substrate, in whole or in part (such as the substrate surface) can be electrically conducting. The electrically conducting path may comprises a semiconductor p-n junction, so that the optoelectronic device emits light, provides a photovoltaic potential, and / or is sensitive to light, for example acting as a photoresistor, photodetector, and the like.
Owner:KIM II JOHN
Soothing repair serum containing bifida ferment lysate and preparation method of essence
InactiveCN110101651AIntegrity guaranteedInhibition releaseCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsIrritationSkin color
The invention discloses a soothing repair serum containing a bifida ferment lysate. The soothing repair serum is prepared from, by weight, 1-10 parts of polyhydric alcohol, 1-10 parts of a moisturizing agent, 0.5-10 parts of a skin moisturizing agent, 0.5-5 parts of an emulsifying agent, 0.1-2 parts of a thickening agent, 0.1-2 parts of a pH adjusting agent, 0.1-5 parts of an anti-allergy soothingagent, 0.1-10 parts of a skin conditioning agent, 0.1-1 part of a preservative, 0.01-0.05 pat of essence and the balance deionized water, wherein the sum of the weight parts of all the components is100. The soothing repair serum can obviously reduce wrinkles, reduce the content of pigment, improve the glossiness of skin, brighten the skin color, improve the skin elasticity, repair the skin barrier and reduce moisture loss; the soothing repair serum is free of irritation to the skin, has the functions of preventing skin aging and perpetually moisturizing the skin and makes the skin in a healthy natural bright white status.
Owner:DOCTOR PLANT GUANGDONG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Metal/ ceramic nano composite additive of self-rehabilitation and its preparation method
The invention relates to a metal / ceramic nano complex self-repairing additive, which comprises metal nano micropowder and nano natural ore powder as main material, detergent, catalyst, antioxidant, and solvent, and can be used in lube, grease and ultrasonic medium. The advantages of this invention include: it can form rapidly high-hardness self-repairing protection layer on a plurality of metal friction surfaces with thickness adjustable to optimize gap and improve surface physical and chemical property, and has wide application in friction dual parts.
Owner:JIANGSU MOLEDN PETROCHEM
Pre-mixed flour of mochi bread with prolonged shelf life, mochi bread and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101971868AElasticity adjustableIncrease elasticityDough treatmentModified nutritive productsAlcohol sugarsFermentation
The invention discloses pre-mixed flour of mochi bread with prolonged shelf life, mochi bread and a preparation method thereof. The pre-mixed flour of mochi bread comprises the following components: 30 to 50% of modified starch, 5 to 10% of water-milled glutinous rice flour, 7 to 13% of non reducing sugar, 6 to 10% of sugar alcohol, 1.8 to 3.8% of edible colloid, 2 to 3% of edible emulsifier, 1 to 3% of salt, 1 to 3% of full-cream milk powder and 20 to 30% of self-raising flour. To produce the mochi bread from the pre-mixed flour of the mochi bread, the pre-mixed flour of the mochi bread is uniformly mixed with whole eggs, water, syrup and soybean oil to obtain the required properties, and then the mixture is baked to obtain the mochi bread without fermentation. The preparation method of the mochi bread is simple, and the prepared mochi bread has honeycomb internal phase and is softer than the common bread and not sticky; moreover, the shelf life of the mochi bread is obviously prolonged that the mochi bread can be stored for a month at normal temperature.
Owner:广州合诚实业有限公司
Fruity probiotic yogurt slice containing antifreeze sericin peptide and method for preparing same
ActiveCN103109930ARich in physiological functionsRich in antioxidantMilk preparationProbiotic yogurtBiotechnology
The invention discloses a fruity probiotic yogurt slice containing antifreeze sericin peptide. The raw materials for preparing the fruity probiotic yogurt slice comprise 10-14 parts of skimmed milk powder, 2-5 parts of sucrose, 1-3 parts of sericin peptide, 1-4 parts of fruit material, 0.1-0.6 part of lyophilized active probiotics and 0.1-0.4 part of magnesium stearate. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the product which is the fruity probiotic yogurt slice. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: preparing a skimmed-milk food-grade culture medium, fermenting the probiotics, adding the antifreeze sericin peptide, freezing and drying fermented milk in vacuum, and pressing powder into slices. As the fruity probiotic yogurt slice contains the antifreeze sericin peptide and the lyophilized fruit powder which is rich in the vitamin B group, the number of the probiotics in the fruity probiotic yogurt slice can be increased, the retention time of the activity of the probiotics can be prolonged, and the taste, flavor and nutritional and healthcare values of the fruity probiotic yogurt slice can be improved. The fruity probiotic yogurt slice can serve as a functional food for supplementing the vitamin B group, improving the immunity and promoting the intestinal health.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Optoelectronic devices employing fibers for light collection and emission
InactiveUS20050285121A1Delay agingSolar heating energySolar heat devicesFiberElectrical resistance and conductance
An optoelectronic device, such as a solar cell, light-emitting device, or photodetector, comprises a substrate, a number of fibers supported by the substrate so that an end of each fiber is in electrical communication with the substrate surface; an optional first layer, covering the substrate, though which the fibers protrude, and a second layer overlaid on at least part of the first layer and exposed fiber surfaces. The second layer may be electrically conducting, and electrically isolated from the substrate surface by the first layer. The second layer can be in electrical communication with each fiber, and an electrically conducting path can exists between the second layer and the substrate surface through each fiber. The substrate, in whole or in part (such as the substrate surface) can be electrically conducting. The electrically conducting path may comprises a semiconductor p-n junction, so that the optoelectronic device emits light, provides a photovoltaic potential, and / or is sensitive to light, for example acting as a photoresistor, photodetector, and the like.
Owner:KIM II JOHN
Method of preparing heat-proof xylanase, heat-proof beta-xylosidase or heat-proof beta-glucosidase
The invention discloses a making method of heat-proof xylanase, heat-proof beta-xylosidase or heat-proof beta-glucosidase, which comprises the following steps: adopting agricultural waste as carbon source; fermenting Paecilomyces thermophila J18 at 40-60 deg.c to obtain the ferment liquid with heat-proof xylanase, heat-proof beta-xylosidase or heat-proof beta-glucosidase; purifying; obtaining electrophoretic grade product.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Aqueous solar heat reflection thermal insulation nanometer coating material
The present invention discloses an aqueous solar heat reflection thermal insulation nanometer coating material, which comprises, by mass, 30-45% of a film forming material, 19-38% of a pigment filler, 1-2% of nanometer powder, 3-15% of an auxiliary agent, and 15-40% of deionized water, wherein the film forming material comprises an aqueous fluorocarbon emulsion and / or an acrylic acid polymer elastic emulsion, the pigment filler comprises one or a plurality of materials selected from rutile type titanium dioxide powder, mica powder, diatomite, ultra-fine calcium carbonate, vacuum ceramic micro-beads and hollow glass beads, the nanometer powder comprises one or a plurality of materials selected from nanometer silica and nanometer zinc oxide, and the auxiliary agent comprises one or a plurality of materials selected from a dispersant, a leveling agent, a defoamer, a preservative, a pH value adjustment agent, a thickening agent, a film forming agent and an anti-freezing agent. The aqueous solar heat reflection thermal insulation nanometer coating material has characteristics of low thermal conductivity coefficient, high thermal radiation reflection efficiency, easy construction and long service life, and can be widely used for the outdoor.
Owner:BEIJING CEEVIN NEW MATERIALS
Nanomer vibration-reducing noise-reducing self-repairing material and its prepn process
InactiveCN1740290AAutomatically adjust thicknessOptimizing friction pair clearanceBase-materialsMachine partsRepair material
The nanometer vibration-reducing and noise-reducing self repairing material is prepared with nanometer level metal powder and natural ore powder as main material and through adding several kinds of supplementary material and certain technological process, and is added into lubricating oil or ultrasonic medium as high performance repair material. The present invention features that the high performance repair material can create high hardness self-repairing lubricating film fast on the surface of metal friction pairs to regulate the interval of the friction pair, reduce friction coefficient, raise bearing capacity, leveling the friction surface, reduce vibration and noise caused by the unbalance, friction and damage of the moving machine parts, and prolong the service life of the machine parts. The present invention may be used widely in improving performance of mechanical friction parts.
Owner:JIANGSU MOLEDN PETROCHEM
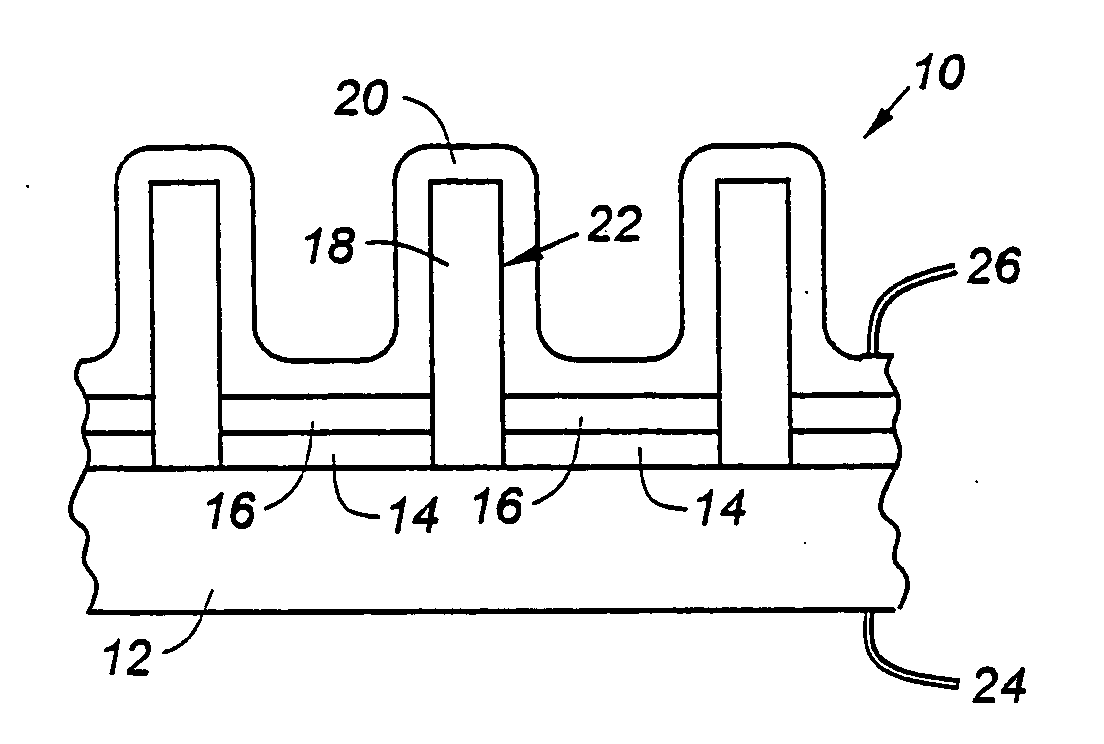
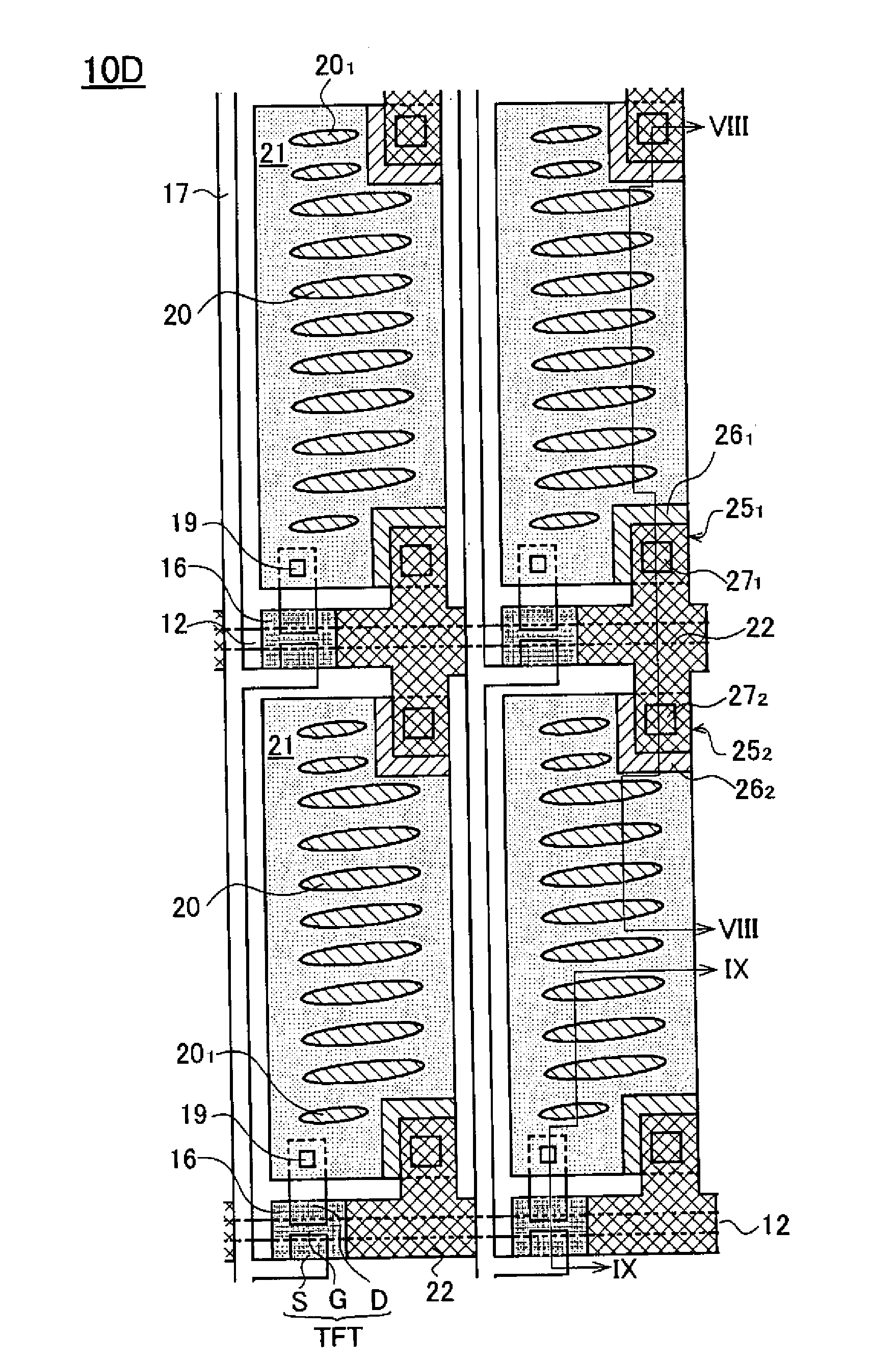
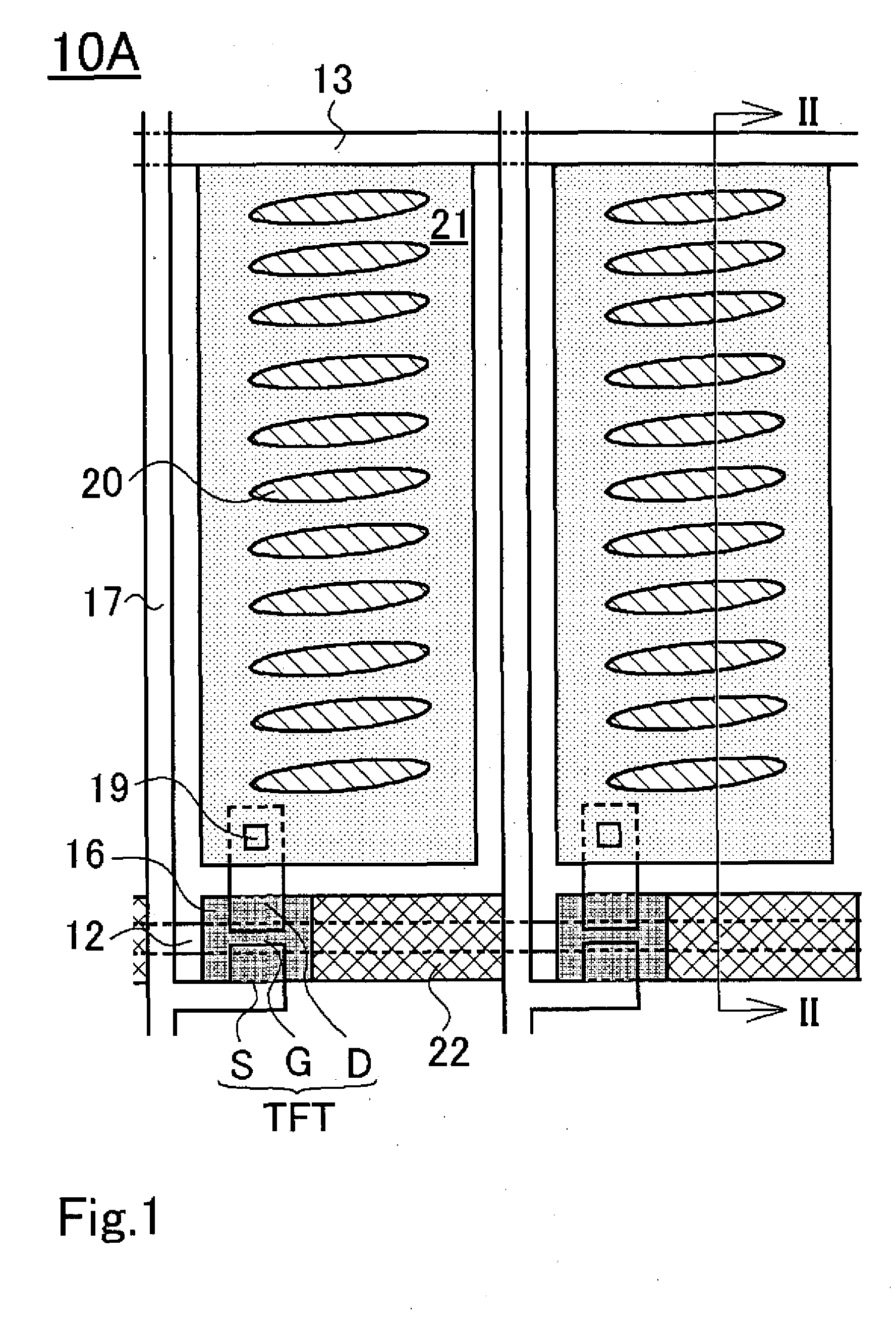
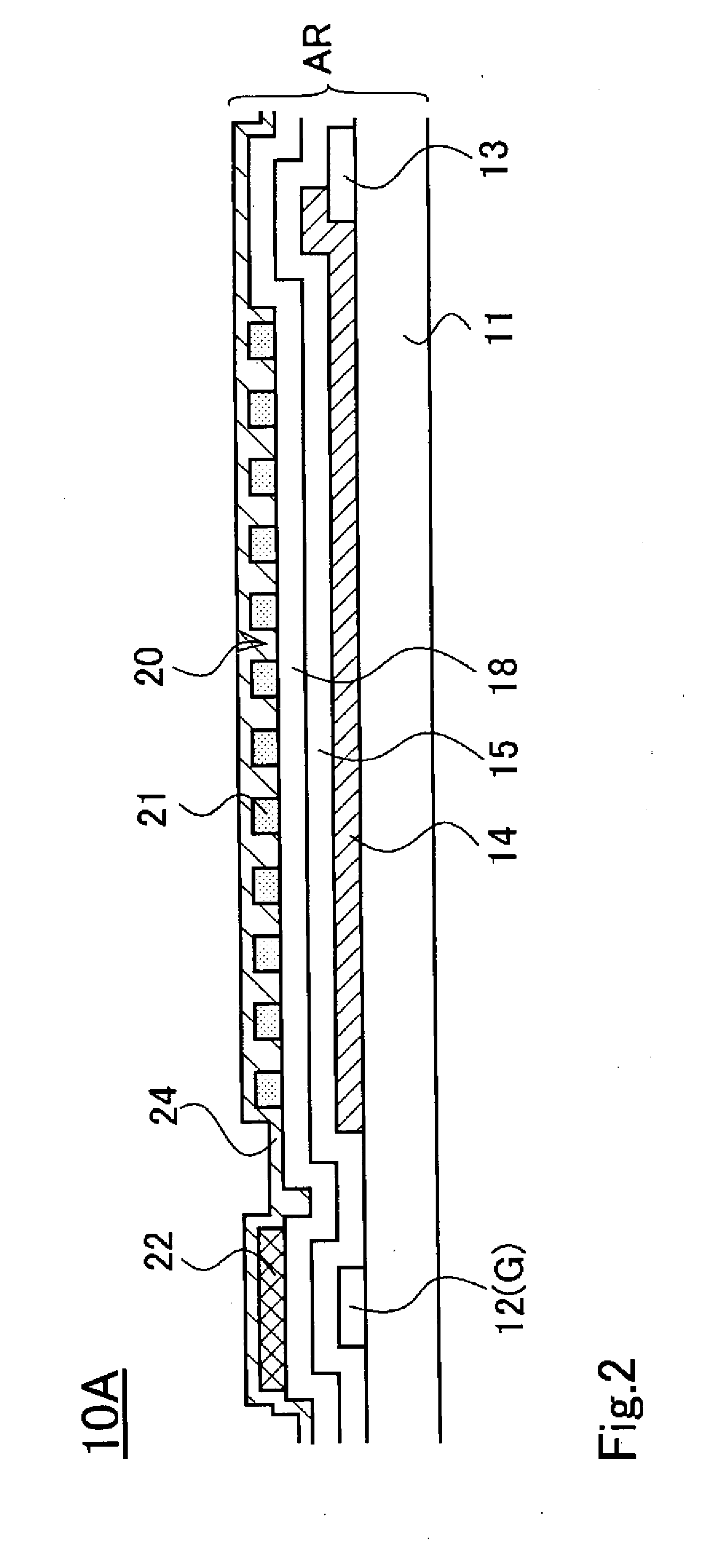
Transverse field type liquid crystal display panel
A transverse field type liquid crystal display panel has multiple scan lines 12 and common wires 13 provided in parallel, multiple signal lines 17 provided in the direction crossing the scan lines 12, and common electrodes 14 and pixel electrodes 21 formed in the regions delimited by the multiple scan lines 12 and signal lines 17. At least part of the surface of an insulator laid over the scan lines 17 is covered by shield electrodes 22 constituted of a conductive material. Thanks to such structure, there can be provided a transverse field type—that is, an IPS mode or FFS mode—liquid crystal display panel that is equipped with a device for preventing burn-in due to the voltage that is applied to the scan lines.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
Plants with improved yield and stress tolerance
InactiveUS20080301841A1Greater stringencySmall sizeSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationEctopic expressionPolynucleotide
Polynucleotides incorporated into expression vectors have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. The encoded polypeptides of the invention have been shown to confer at least one regulatory activity and confer greater size, greater organ size, greater biomass, greater yield, curlier leaves, darker coloration, greater tolerance to water deprivation, delayed flowering, delayed development, delayed senescence, greater tolerance to cold, and / or greater tolerance to hyperosmotic stress as compared to a control plant.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Probiotic fruit and vegetable enzyme drink and preparation method thereof
PendingCN107348272AHigh activityHigh nutritional valueFood ingredient for microbe protectionNutritive valuesLactobacillus paracasei
The invention provides a probiotic fruit and vegetable enzyme drink and a preparation method thereof. Fruits and vegetables as well as four-in-one PPHR Lactobacillus powder (including Lactobacillus paracasei, L. plantarum, L. helveticus and L. rhamnosus) are mixed and the obtained mixture is fermented, and the obtained fermented product is the probiotic fruit and vegetable enzyme drink. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method has the advantages that the fermentation process can be shortened, the fermentation process can be simplified, the nutritional value of fruit and vegetable juice can be increased, the fruit and vegetable juice is endowed with higher oxidation resistance, and the application range of Lactobacillus in food, particularly drinks, is broadened.
Owner:恒利康生物科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com