Patents
Literature
89 results about "Below threshold level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
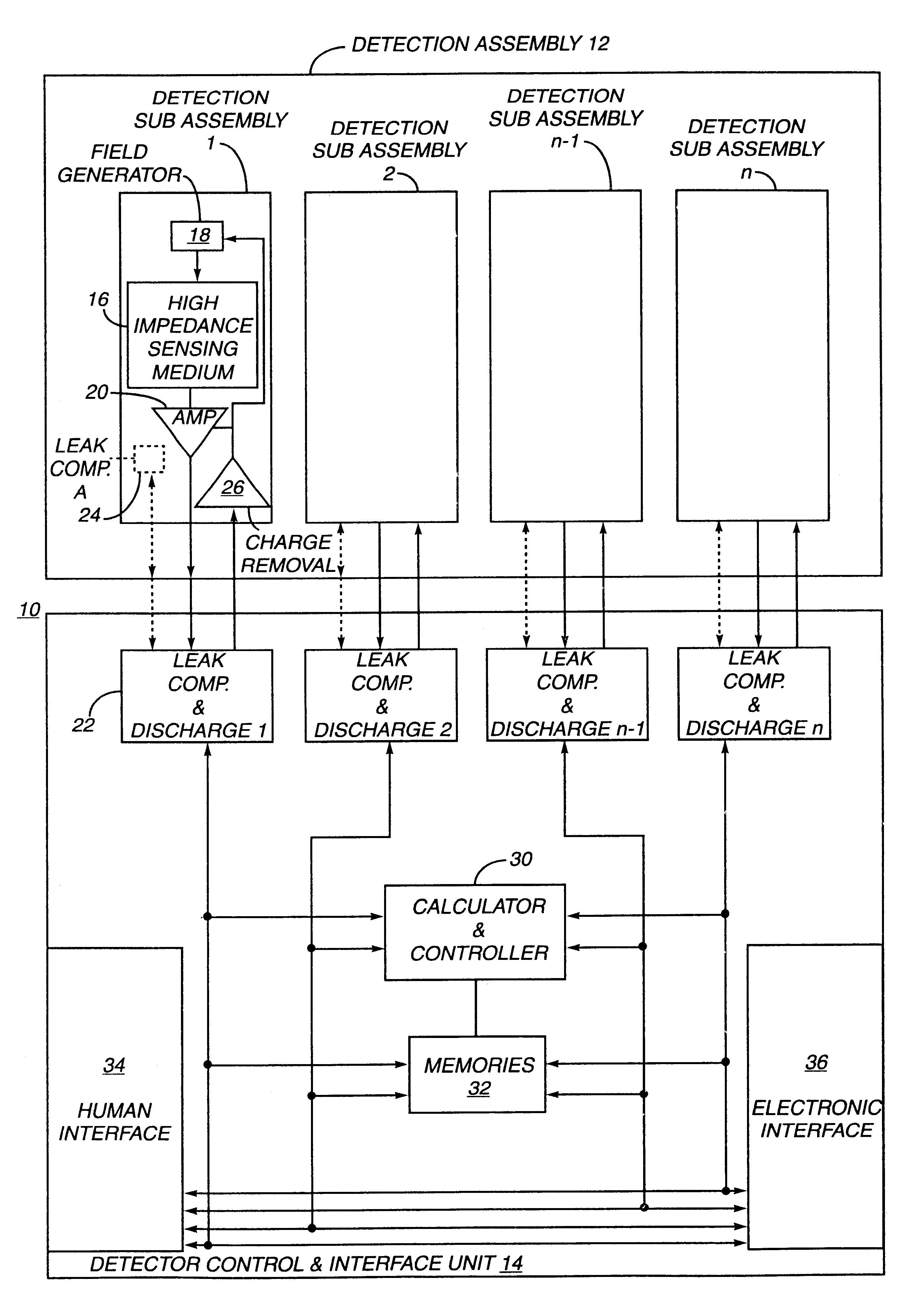
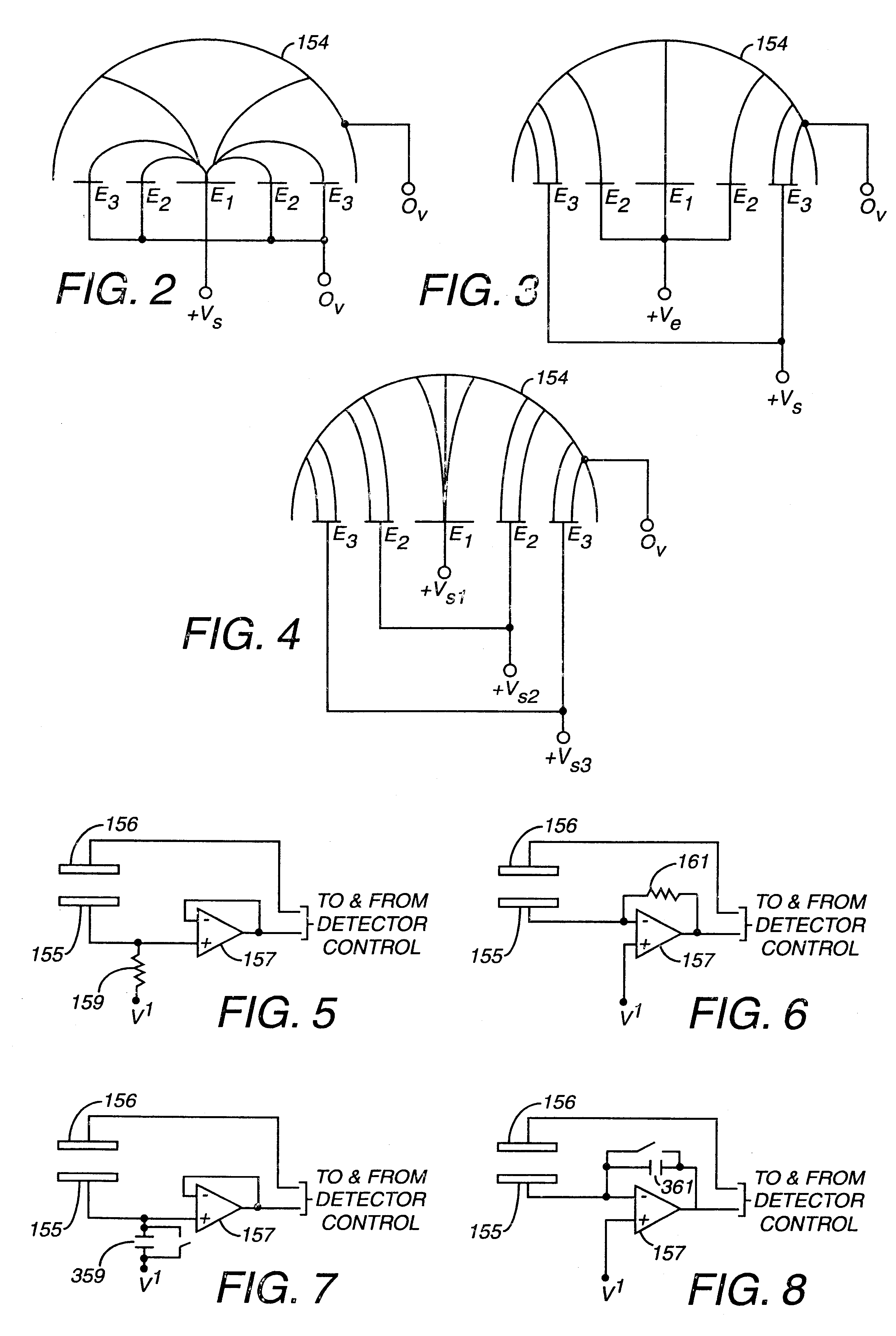
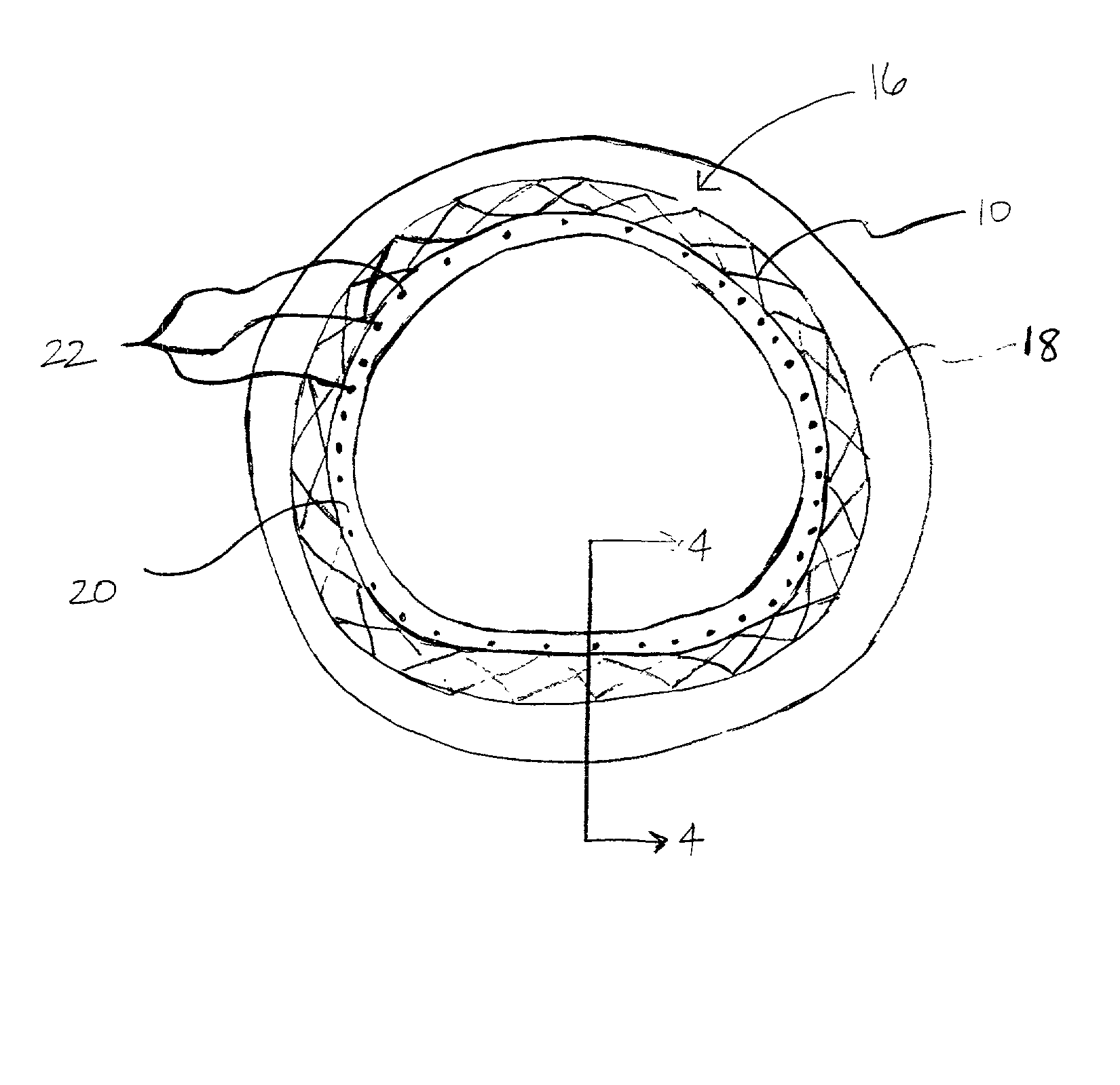
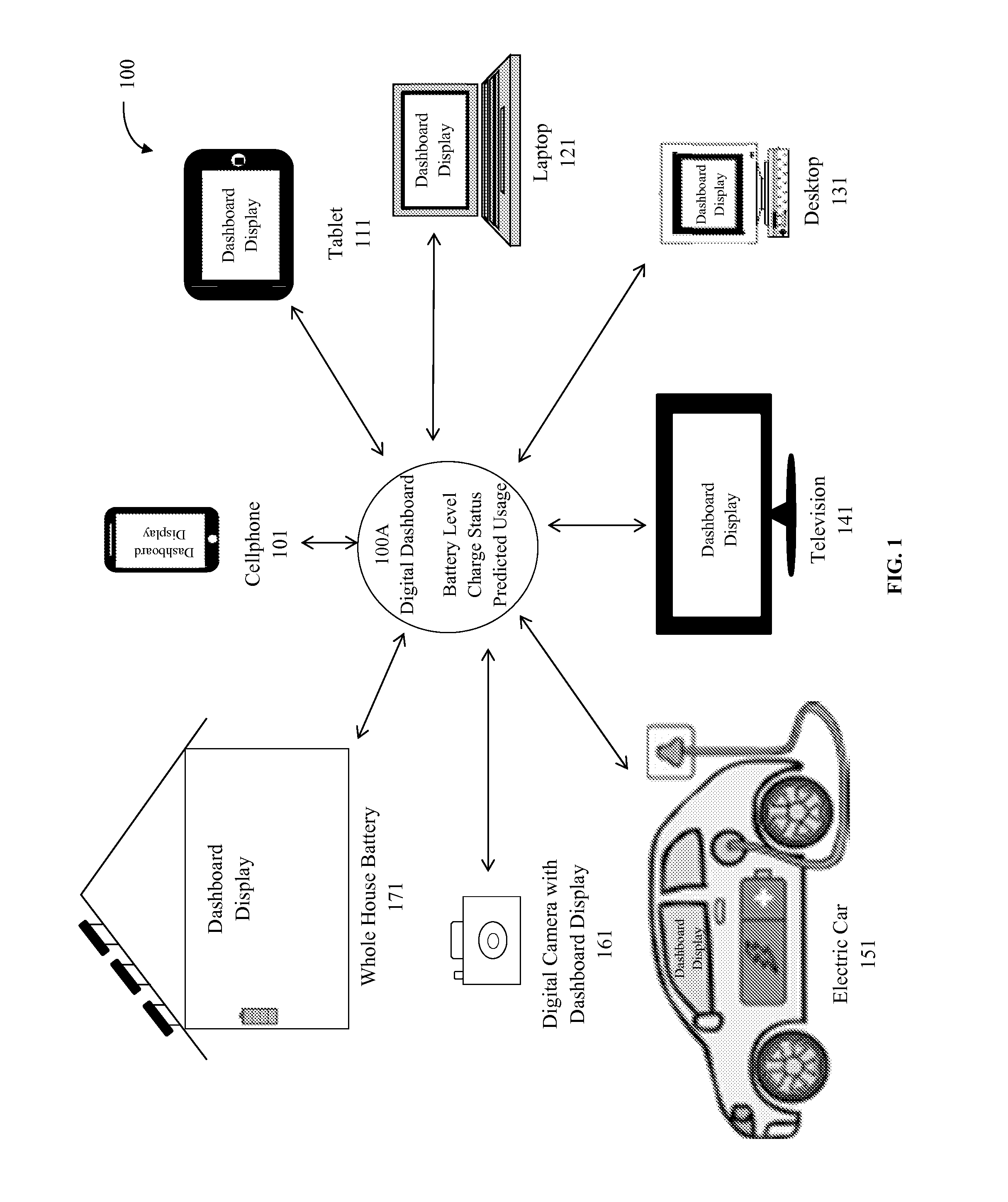
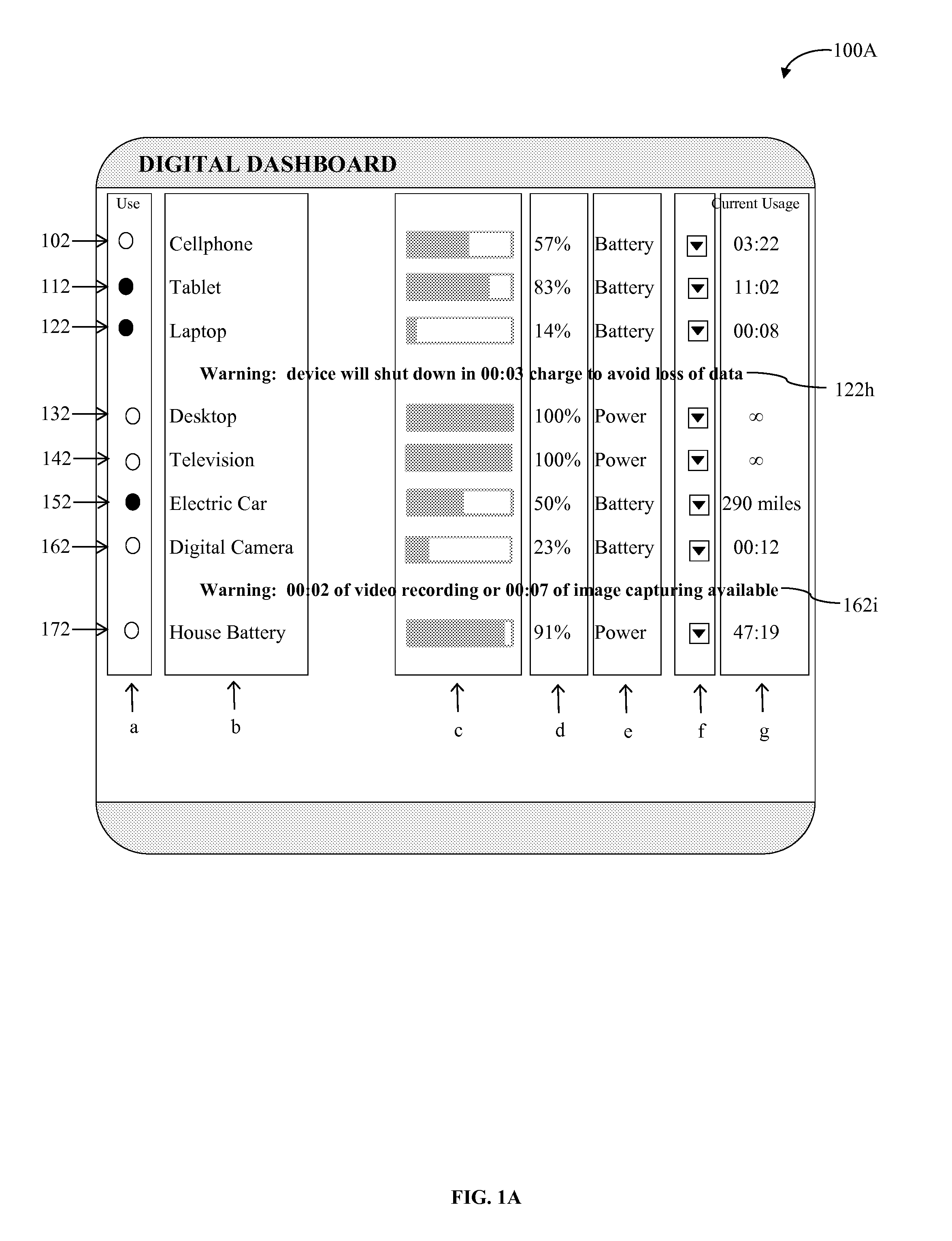
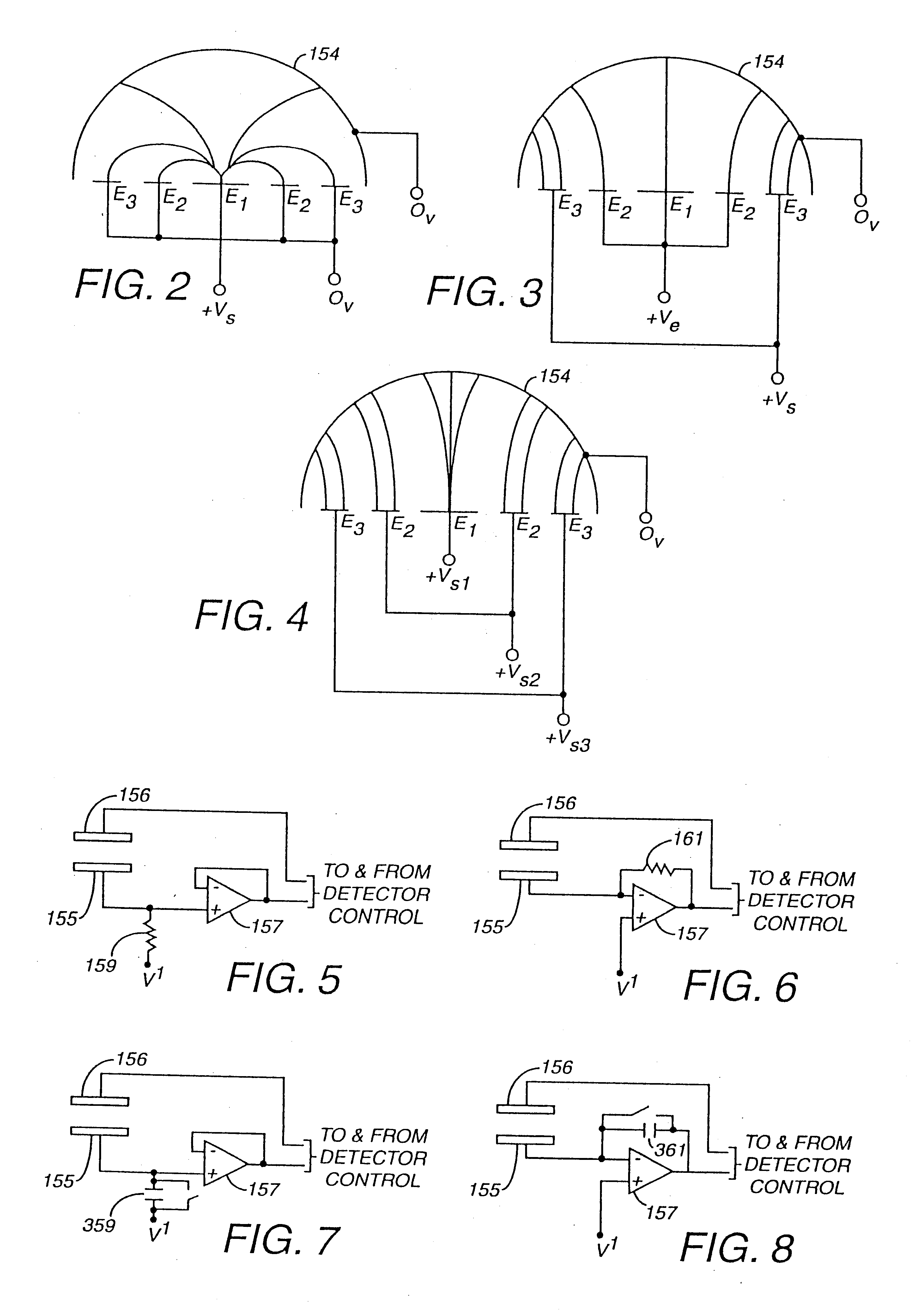
Electronic circuit
InactiveUS6353324B1Improve performanceLimits of linearityPhotometry electrical circuitsMeasurement using digital techniquesCapacitanceEngineering
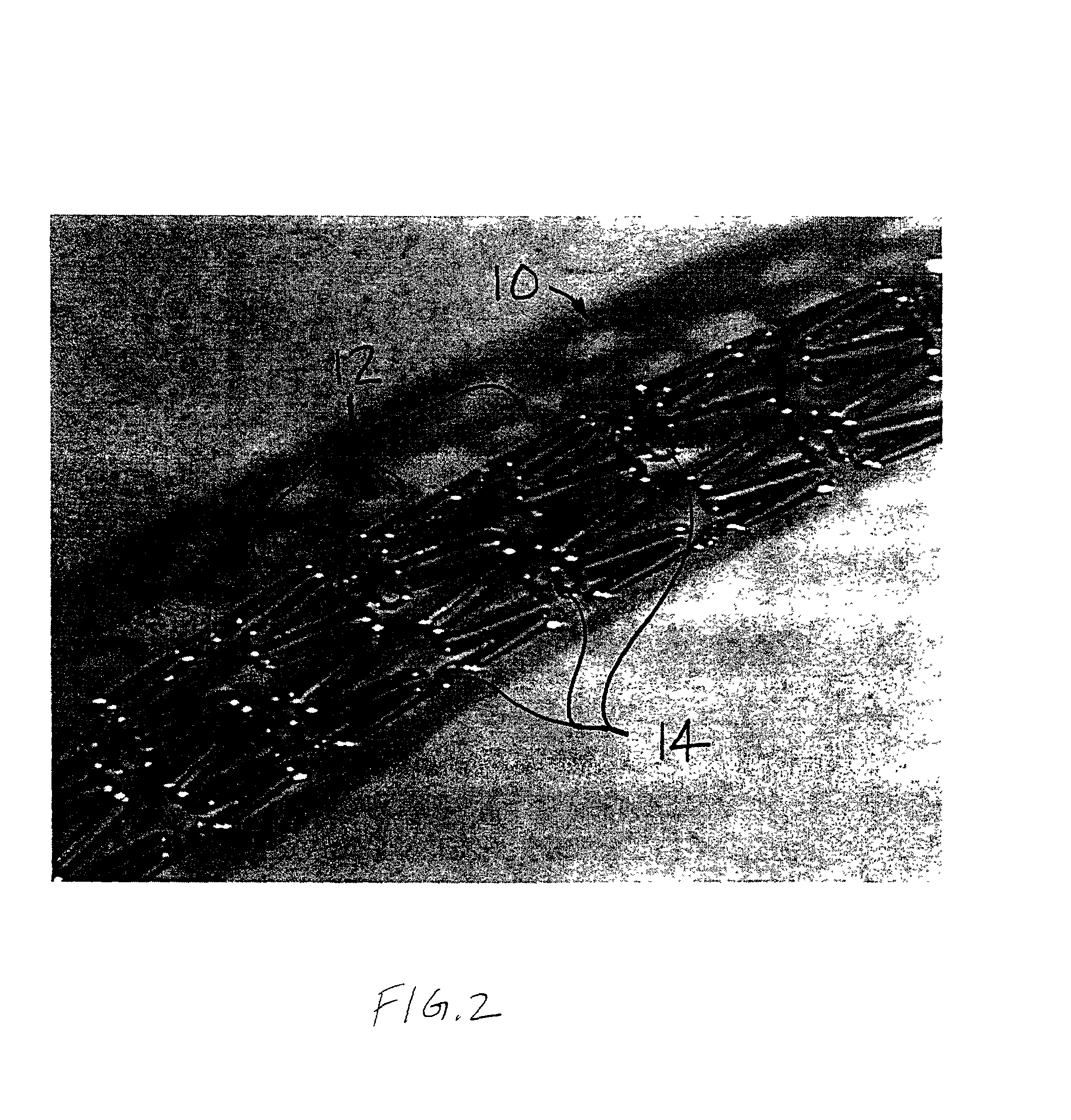
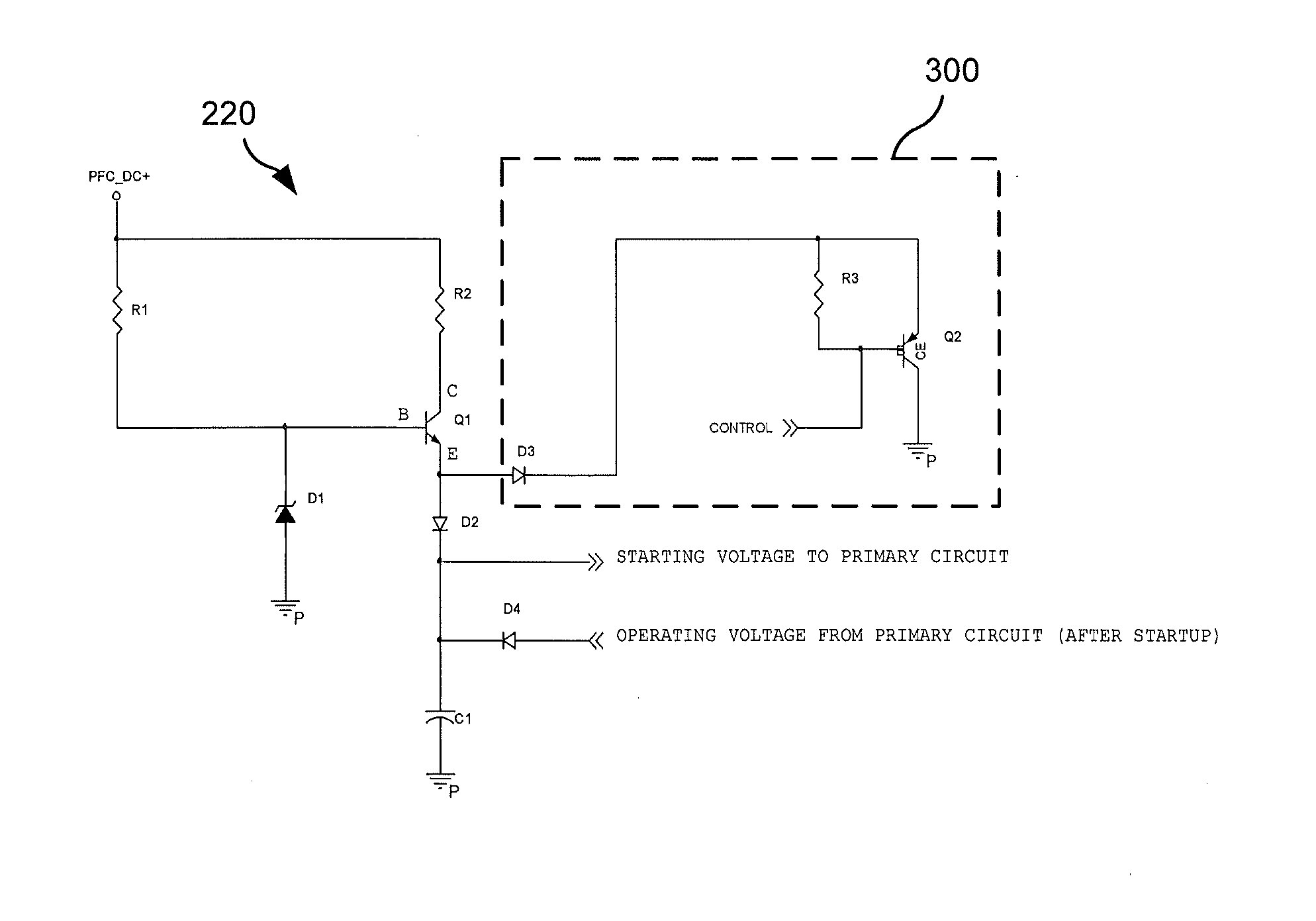
The present invention relates to an electronic circuit and an array of such circuits for precisely measuring small amounts or small changes in the amount of charge, voltage, or electrical currents. One embodiment of the present invention provides an electronic circuit for measuring current or charge that can be used with a variety of sensing media (including high impedance sensing media) that produce a signal by either charge or current production or induction in response to physical phenomena occurring within the sensing media. In another embodiment, the voltage level (bias) of either the sensing or reference electrode can be switched relative to the other upon receipt of a triggering pulse. This changes the polarity of the electric field to cause charge of the opposite polarity to be driven to the sensing electrode, thereby eliminating the need to electrically connect a discharge path to the sensing electrode to clear the charge accumulated at the sensing electrode. This can be supplemented by capacitively coupling a compensation signal to the sensing electrode to cause the amplifier output signal to lessen in magnitude below a threshold level that permits additional charge or current measurements of the same polarity before performing bias reversal. Alternately or in combination with bias reversal and capacitive compensation, sensor performance can be improved by minimizing inaccuracies caused by leakage currents or current drawn from the sensor. Other described methods of reducing leakage currents that can be used alone or in combination with the aforementioned features include the use of guard rings, physical switches or relays, the controlled creation of charges or currents of a specific polarity in a specific region of the sensing medium, controlled leakage over the surface of an insulator, and controlling the environment in which the circuit operates.
Owner:BRIDGE SEMICON
Apparatus and methods for controlled substance delivery from implanted prostheses
InactiveUS20020082685A1Improve drug delivery efficiencyReduce lossesStentsSurgeryPercent Diameter StenosisControl substances
The present invention provides improved devices and methods for inhibiting restenosis and hyperplasia after intravascular intervention. In particular, the present invention provides luminal prostheses which allow for programmed and controlled substance delivery with increased efficacy to selected locations within a patient's vasculature to inhibit restenosis. The luminal delivery prosthesis comprises a scaffold which is implantable within a body lumen and means on the scaffold for releasing a substance from the scaffold. The substance is released over a predetermined time pattern comprising an initial phase wherein the substance delivery rate is below a threshold level and a subsequent phase wherein the substance delivery rate is above a threshold level.
Owner:ALTAI MEDICAL TECH
Thermally reversible implant and filler
The invention relates to the use of a thermal reversible gel, such as a copolymer composition, as a biological filler or implant. The gel has a semi-solid form at body temperature, but upon cooling to a temperature below a threshold level, the gel is liquefied and can be re-shaped, re-sized, manipulated or removed from the body. The gel may be used as a subcutaneous implant, a biological filler, joint or tissue spacer, for wrinkle filling or other cosmetic implants, as a soft-tissue replacement for reconstructive surgery, or as a barrier within the lumen of a biological structure, such as a blood vessel. The implant may be used to provide reversible birth control by providing, for example, a reversible barrier to the cervix or a reversible blockage of the lumen of the vas deferens.
Owner:CHENG YU LING +3
Systems and Methods for Improving the Reliability of a Multi-Core Processor
InactiveUS20090288092A1Improve reliabilityDelay agingResource allocationMemory systemsMulti processorBelow threshold level
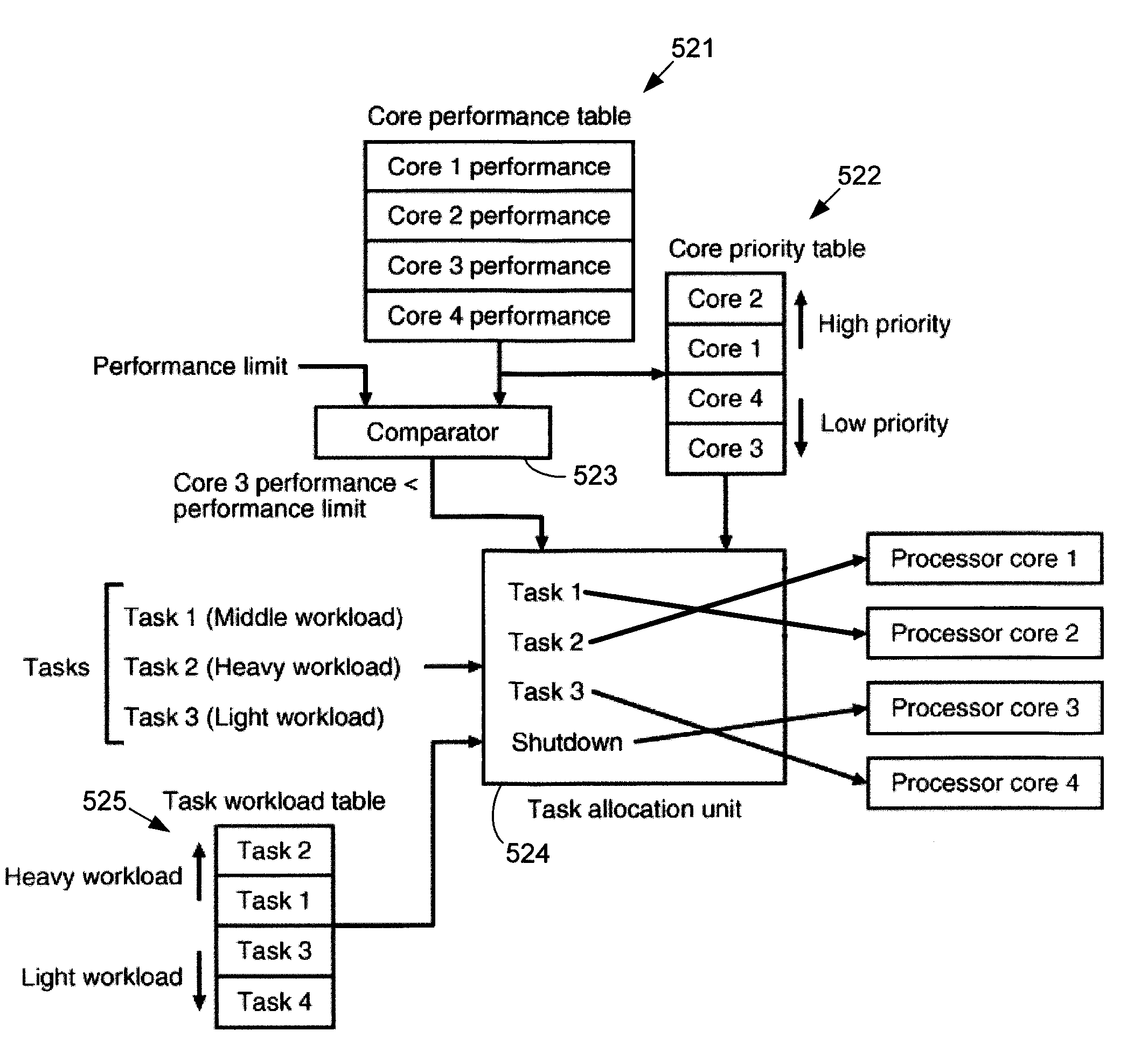
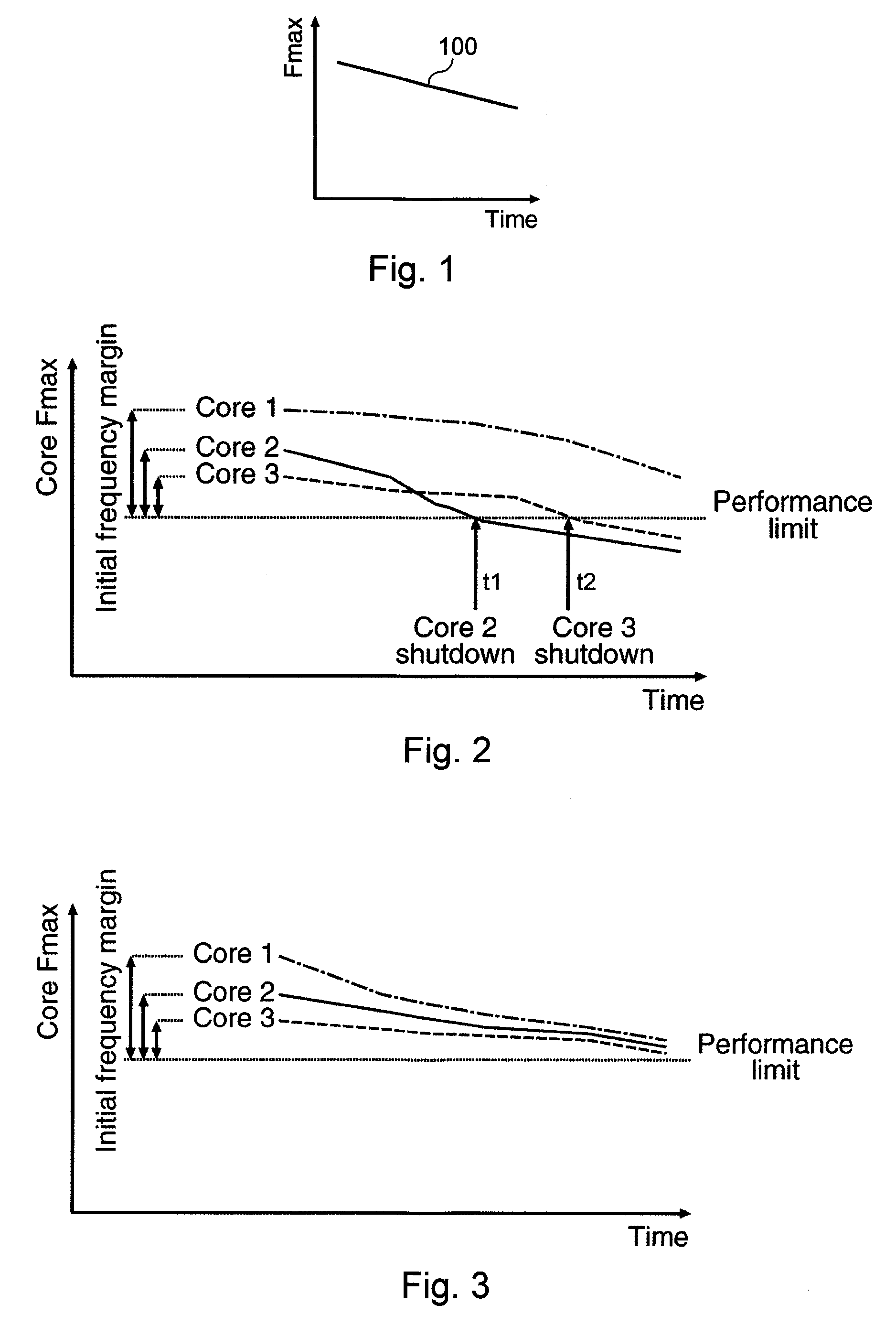
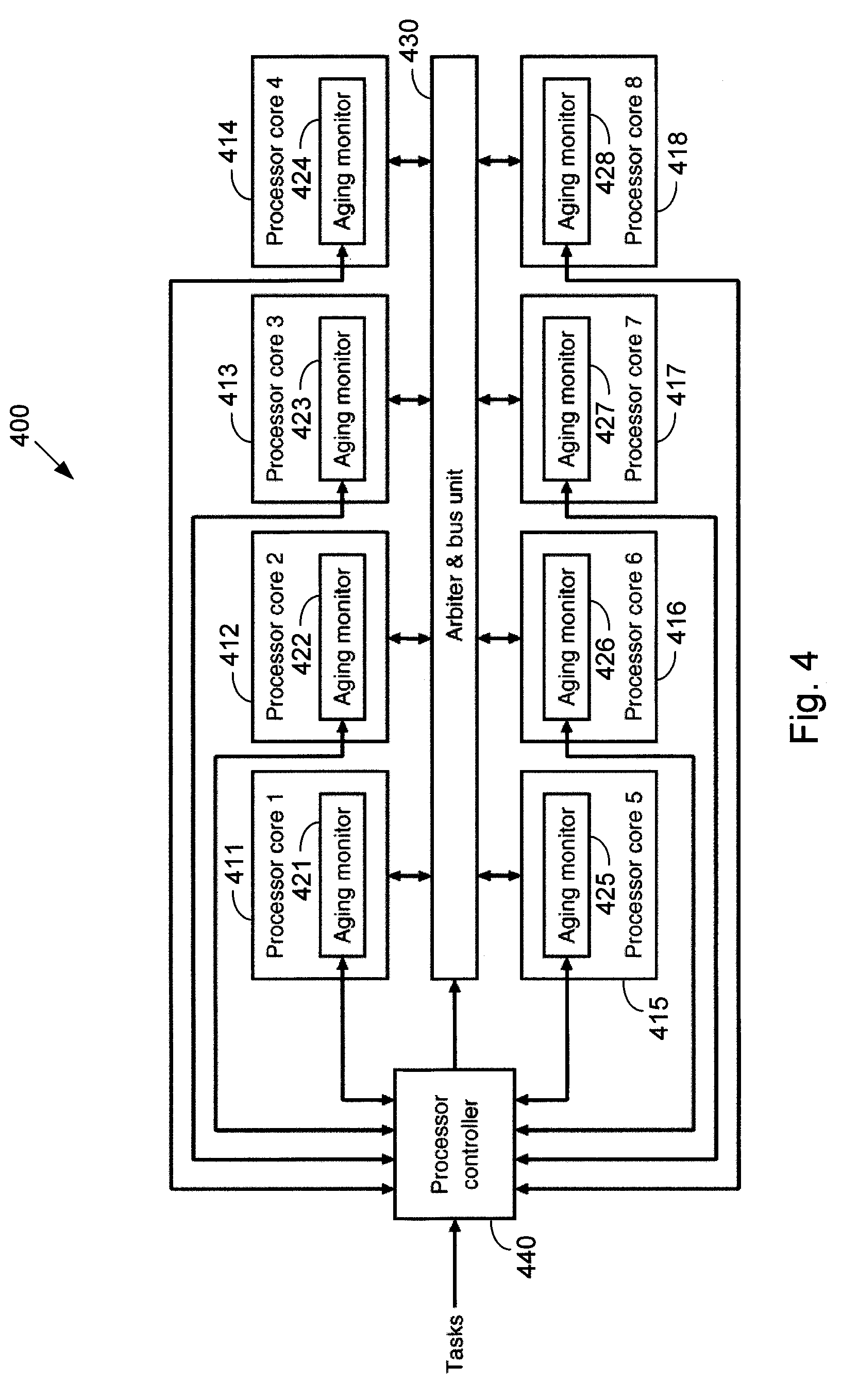
Systems and methods for improving the reliability of multiprocessors by reducing the aging of processor cores that have lower performance. One embodiment comprises a method implemented in a multiprocessor system having a plurality of processor cores. The method includes determining performance levels for each of the processor cores and determining an allocation of the tasks to the processor cores that substantially minimizes aging of a lowest-performing one of the operating processor cores. The allocation may be based on task priority, task weight, heat generated, or combinations of these factors. The method may also include identifying processor cores whose performance levels are below a threshold level and shutting down these processor cores. If the number of processor cores that are still active is less than a threshold number, the multiprocessor system may be shut down, or a warning may be provided to a user.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Device Power and Resource Management
InactiveUS20150323974A1Power managementVolume/mass flow measurementResource Management SystemElectrical battery
Owner:SHUSTER GARY STEPHEN +1
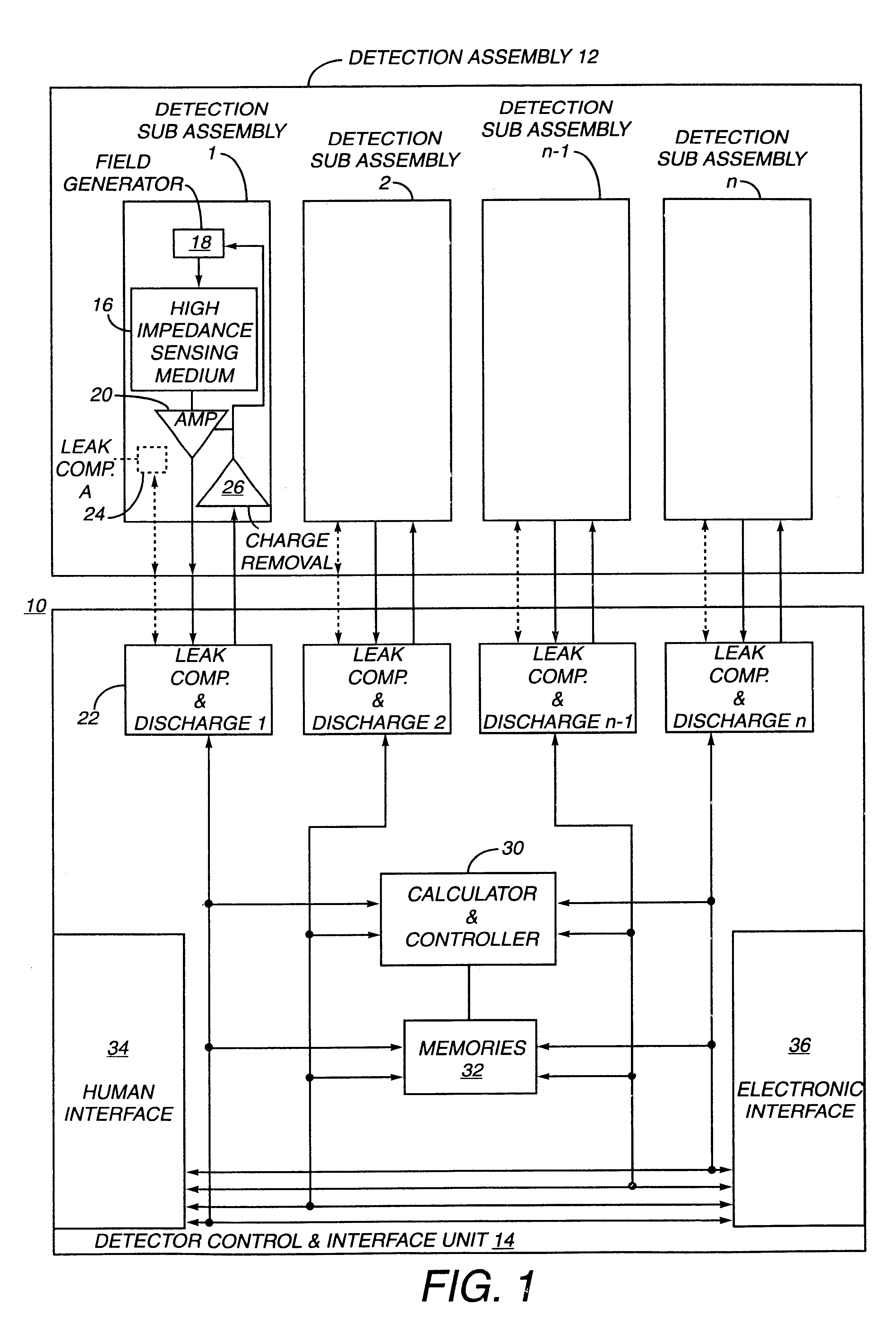
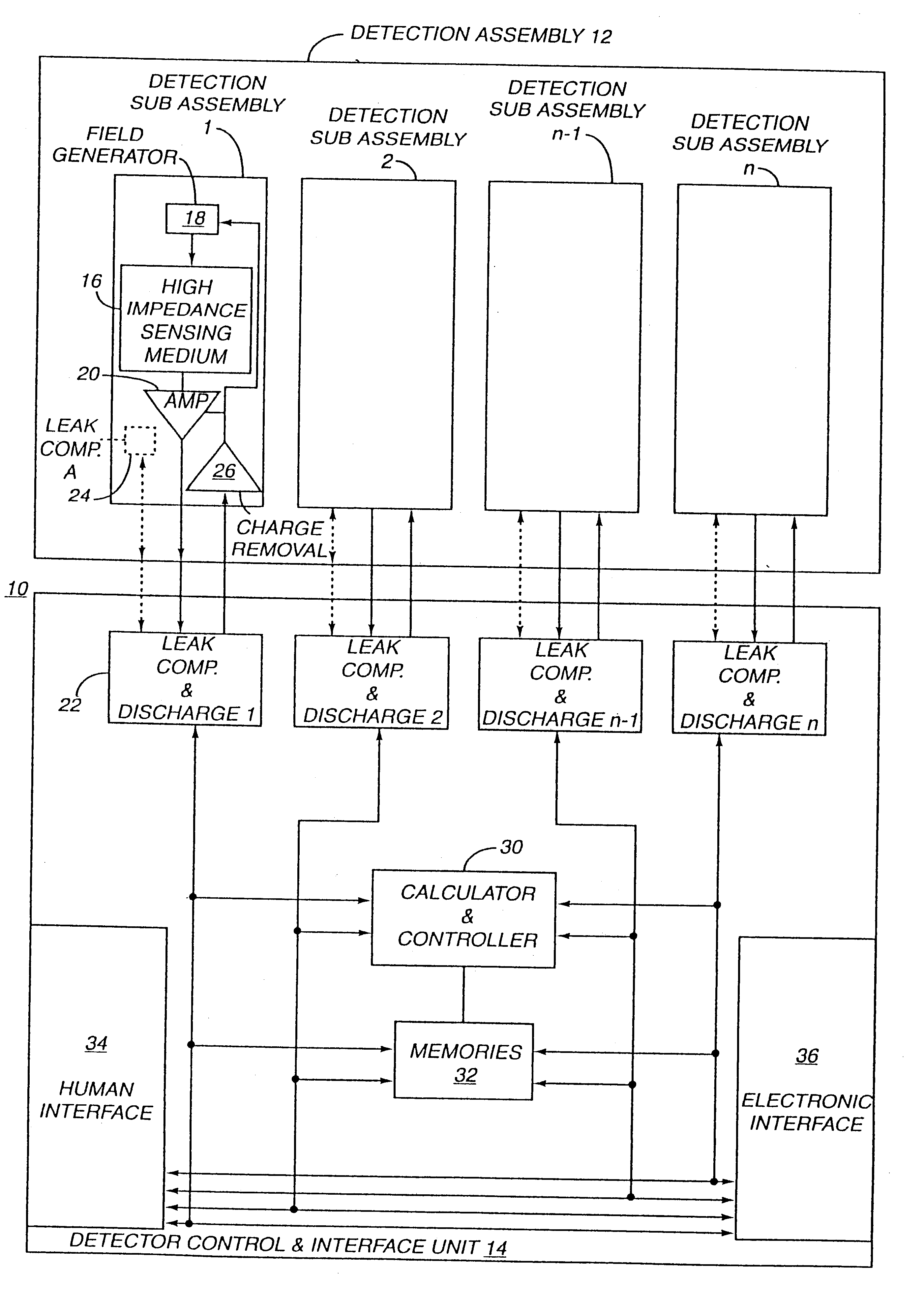
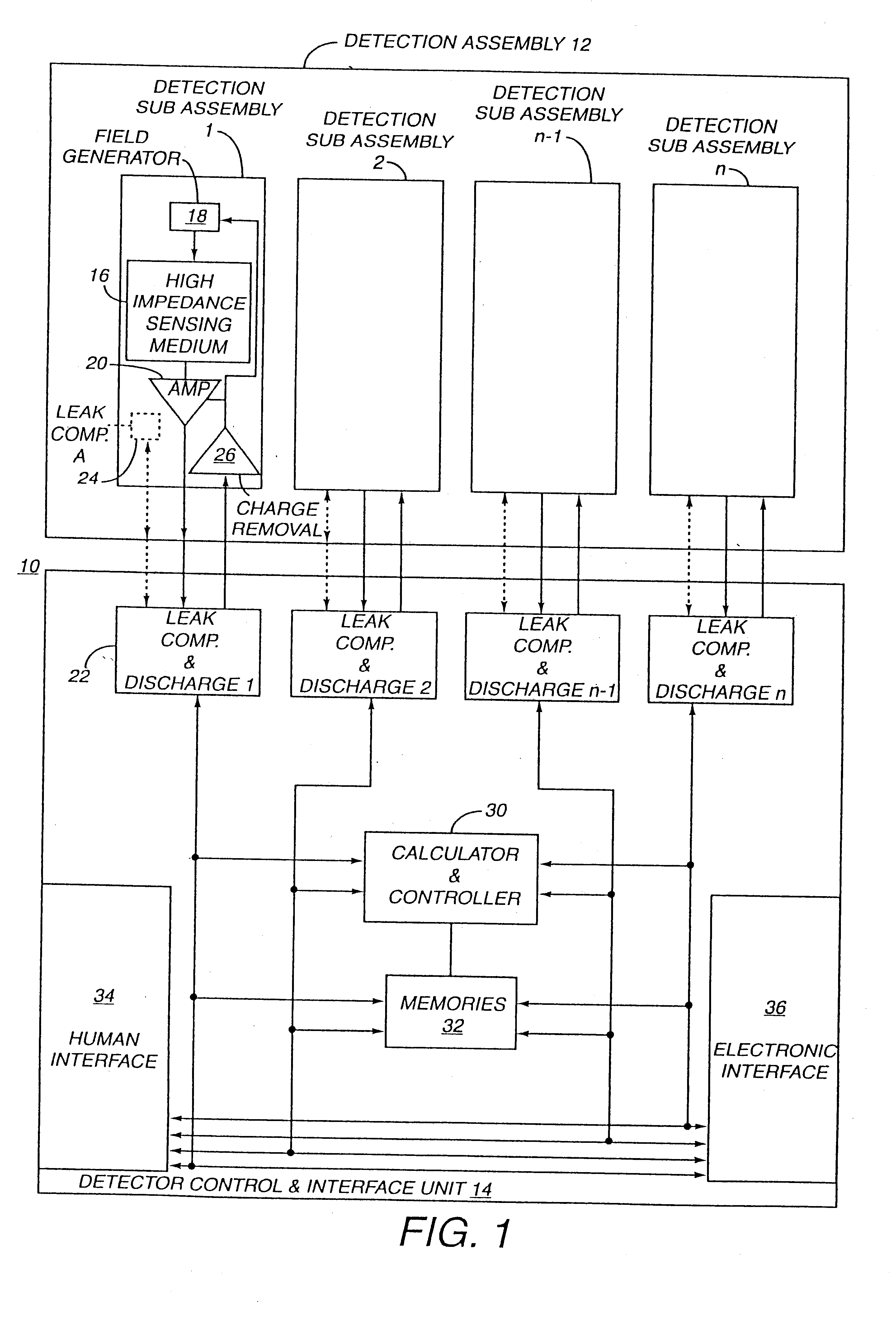
Electronic circuit
InactiveUS6414318B1Improve performanceLimits of linearityElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
The present invention relates to an electronic circuit for measuring small amounts of charge or small electrical currents. One embodiment of the present invention provides an electronic circuit for measuring current or charge that can be used with a variety of sensing media (including high impedance sensing media) that produce a signal by either charge or current production or induction in response to physical phenomena occurring within the sensing media. In another embodiment, the voltage level (bias) of either the sensing or reference electrode can be switched relative to the other upon receipt of a triggering pulse. This changes the polarity of the electric field to cause charge of the opposite polarity to be driven to the sensing electrode, thereby eliminating the need to electrically connect a discharge path to the sensing electrode to clear the charge accumulated at the sensing electrode. This can be supplemented by capacitively coupling a compensation signal to the sensing electrode to cause the amplifier output signal to lessen in magnitude below a threshold level that permits additional charge or current measurements of the same polarity before performing bias reversal. Alternately or in combination with bias reversal and capacitive compensation, sensor performance can be improved by minimizing inaccuracies caused by leakage currents or current drawn from the sensor. Other methods of reducing leakage currents that can be used alone or in combination with the aforementioned features include the use of guard rings, physical switches or relays, the controlled creation of charges or currents of a specific polarity in a specific region of the sensing medium, controlled leakage over the surface of an insulator, and controlling the environment in which the circuit operates.
Owner:BRIDGE SEMICON
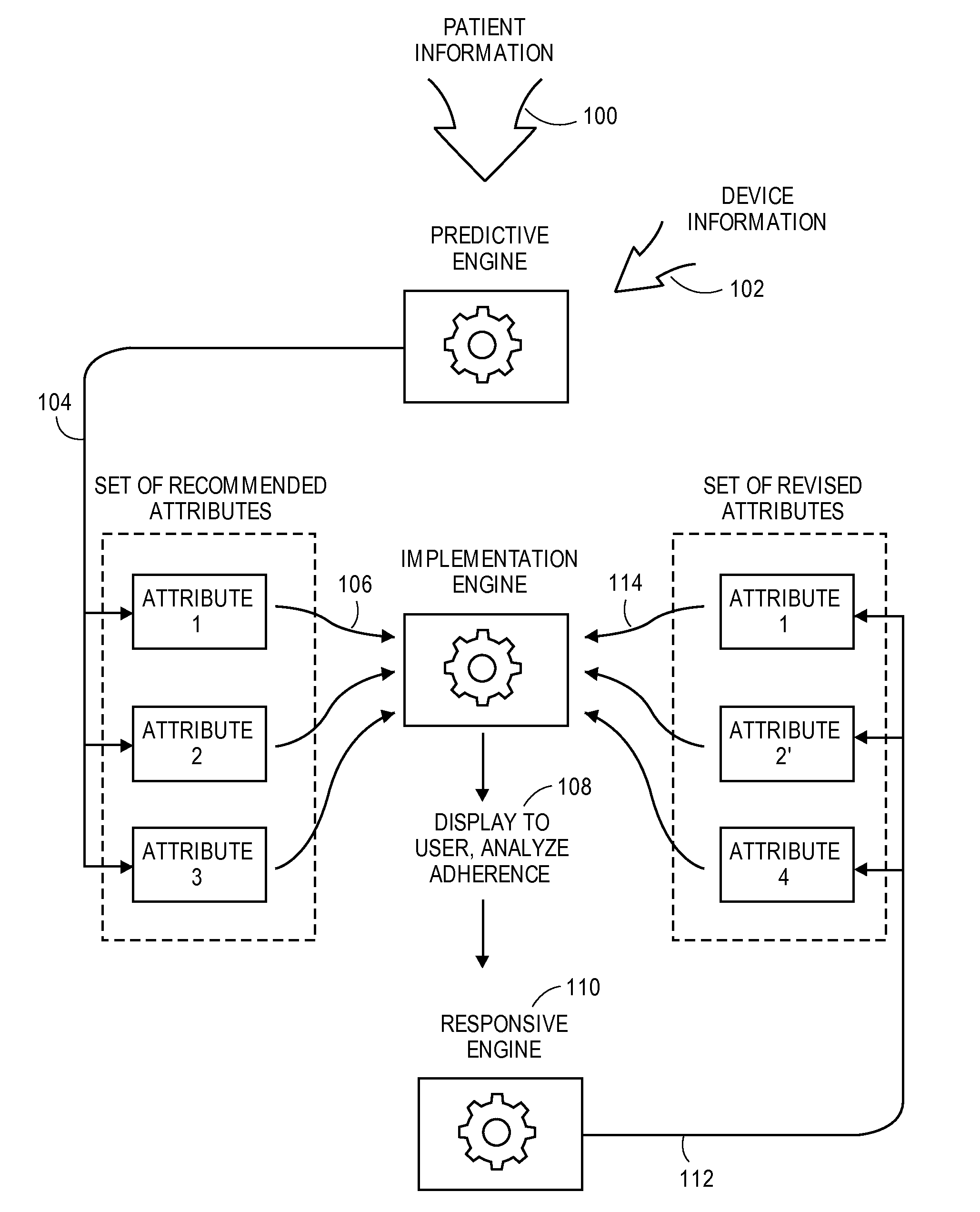
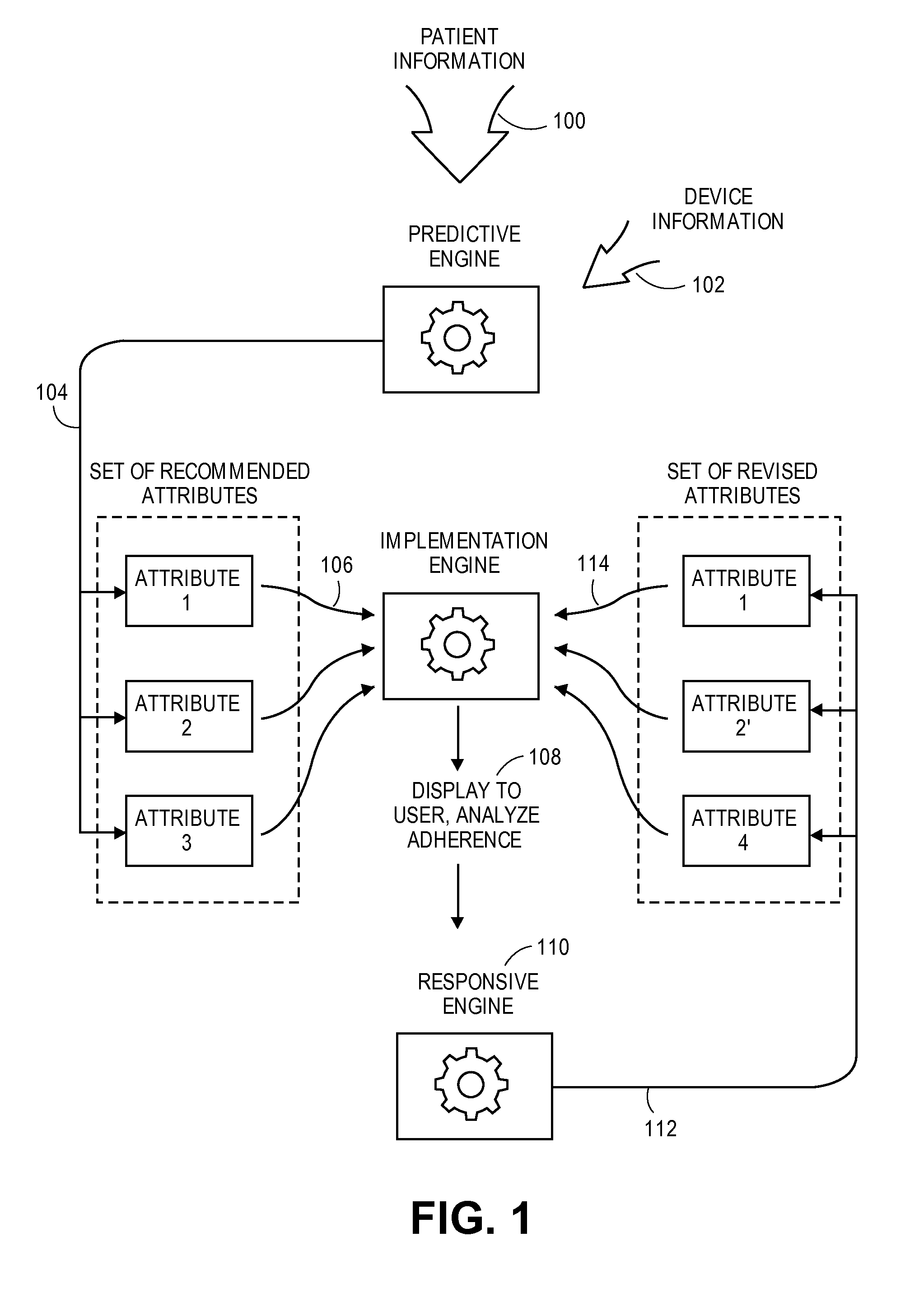
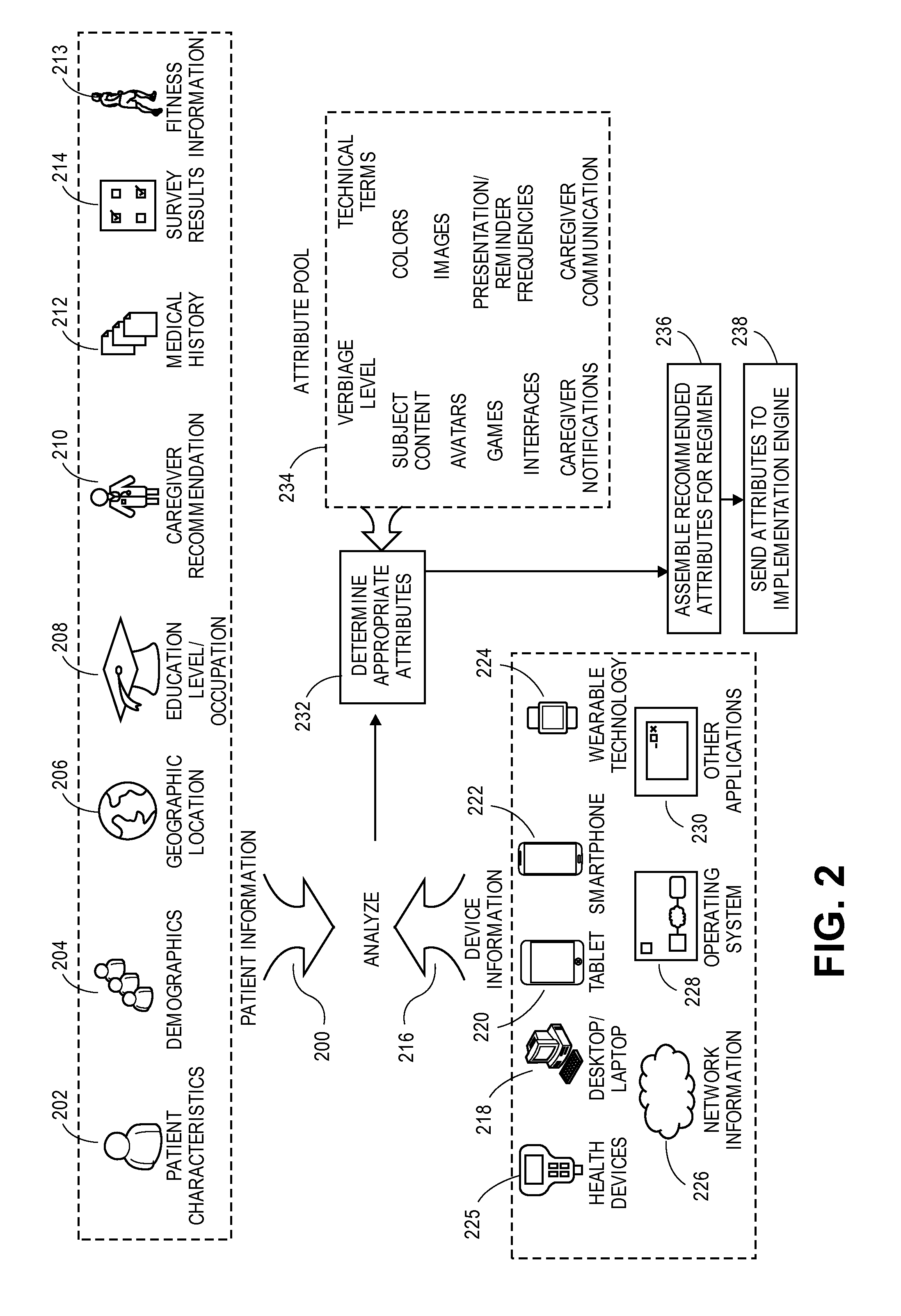
Monitoring and adapting a patient's medical regimen and facilitating communication with a caregiver
A user engagement system such as a medical regimen monitoring the adherence of a patient. The user engagement system customizes the medical regimen to meet the needs of the patient. The system includes a predictive engine for generating a set of recommended attributes for the regimen by analyzing a set of user information, an implementation engine for displaying the regimen to the user and monitoring adherences, and a responsive engine for adapting the regimen to improve an adherence level upon the patient falling below a threshold level by determining a set of revised attributes likely to improve adherence.
Owner:PLAY IT HEALTH
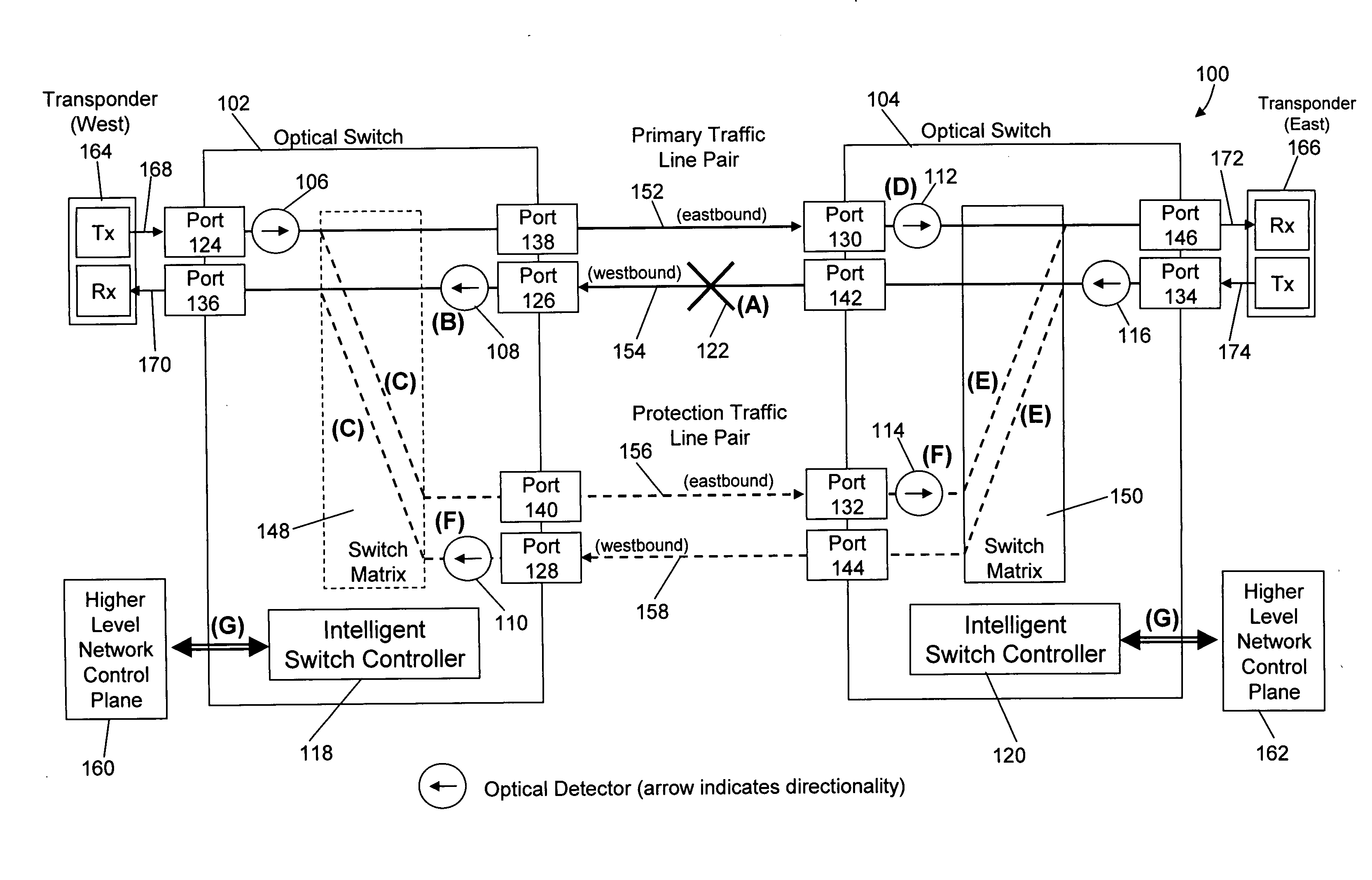
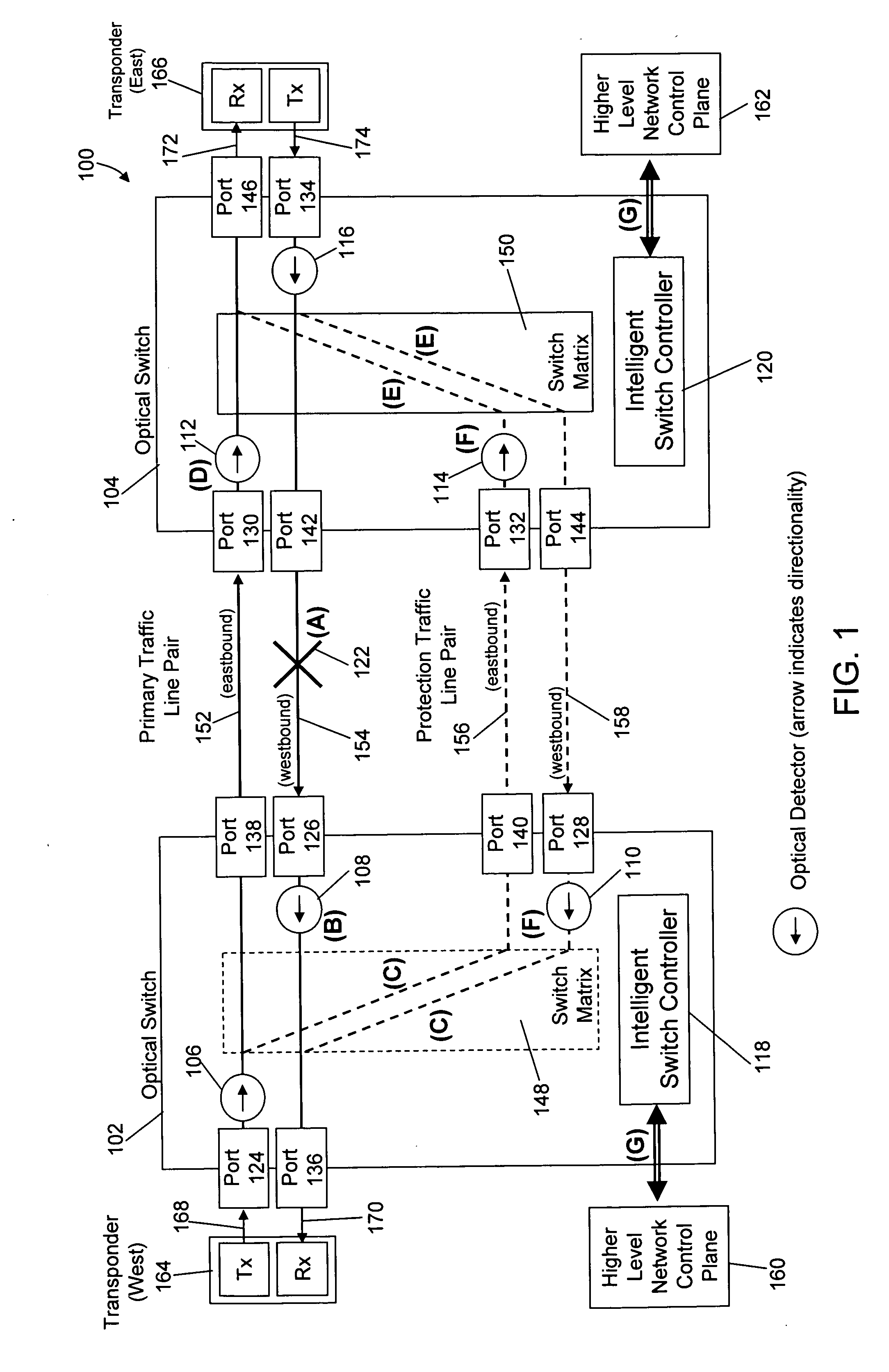
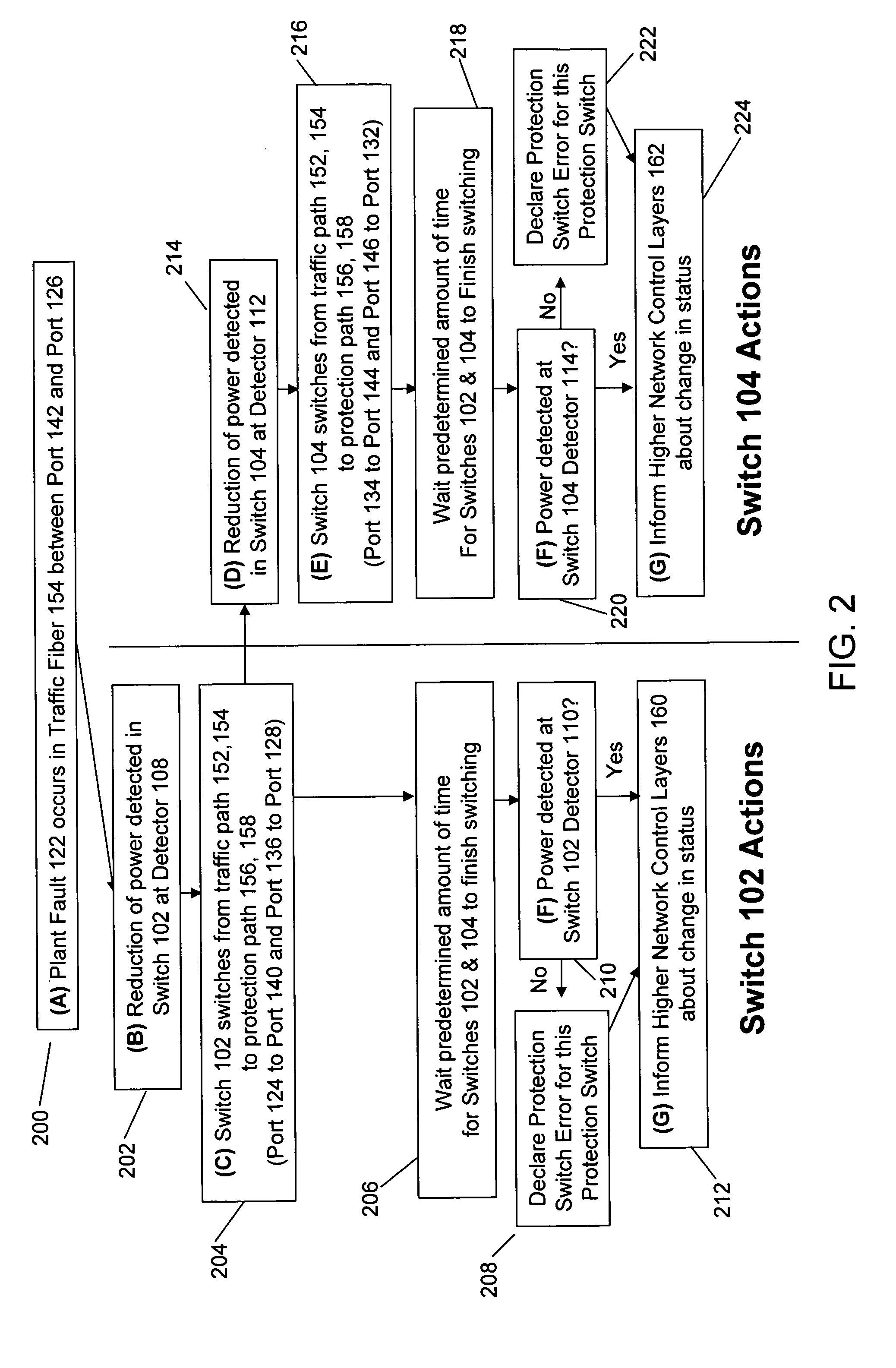
Method and apparatus for network fault detection and protection switching using optical switches with integrated power detectors
ActiveUS20080175587A1Reduced network fault recovery timeShorten recovery timeMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsPower detectorPhysical layer
Current network switching architectures require communication with a higher level network control plane, which can be slow to reroute communications, resulting in unacceptable losses of communications for customers. Examples embodiments of the present invention reroute communications faster detecting optical power of an optical signal at optical switches coupled via optical communication paths, and causing at least one optical communication path between a first optical switch and second optical switch to switch to an alternative optical communication path, in part, through physical layer triggering in an event optical power at at least one of the first or second optical switches falls below a threshold level. Switching in response to physical layer triggering may result in reduced switching times and, consequently, faster restoration of communications to customers after a network fault interruption.
Owner:POLATIS PHOTONICS INC
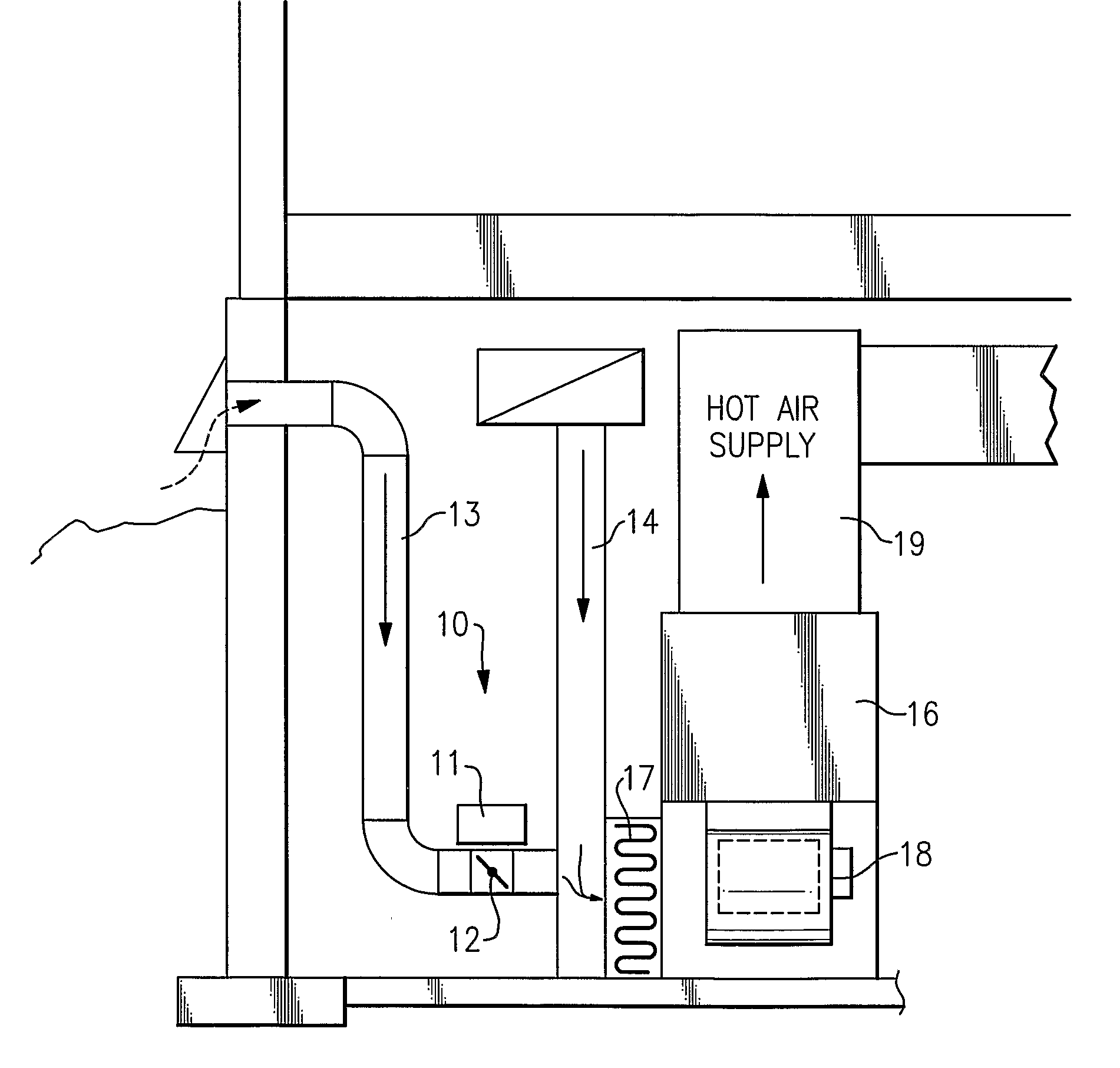
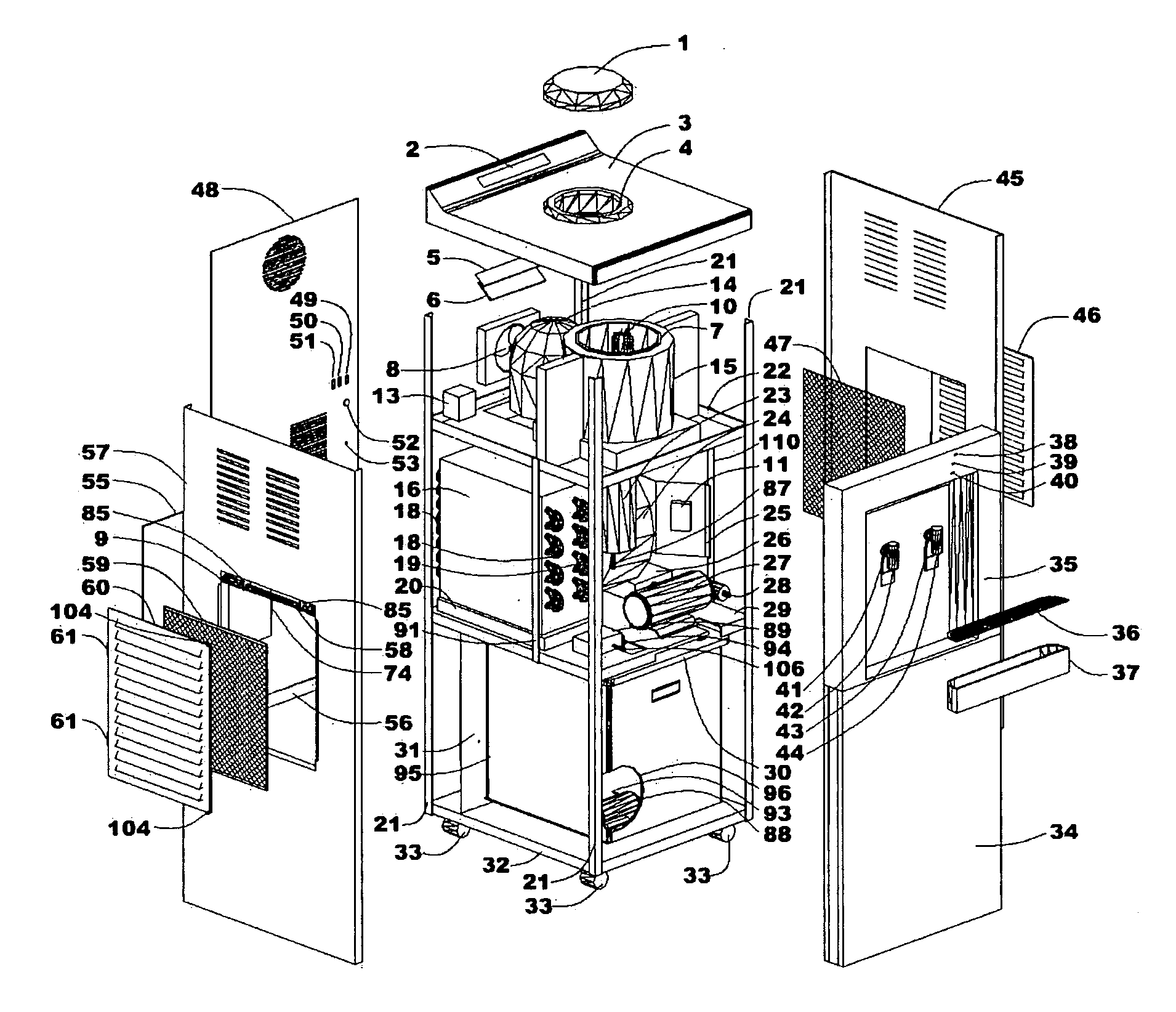
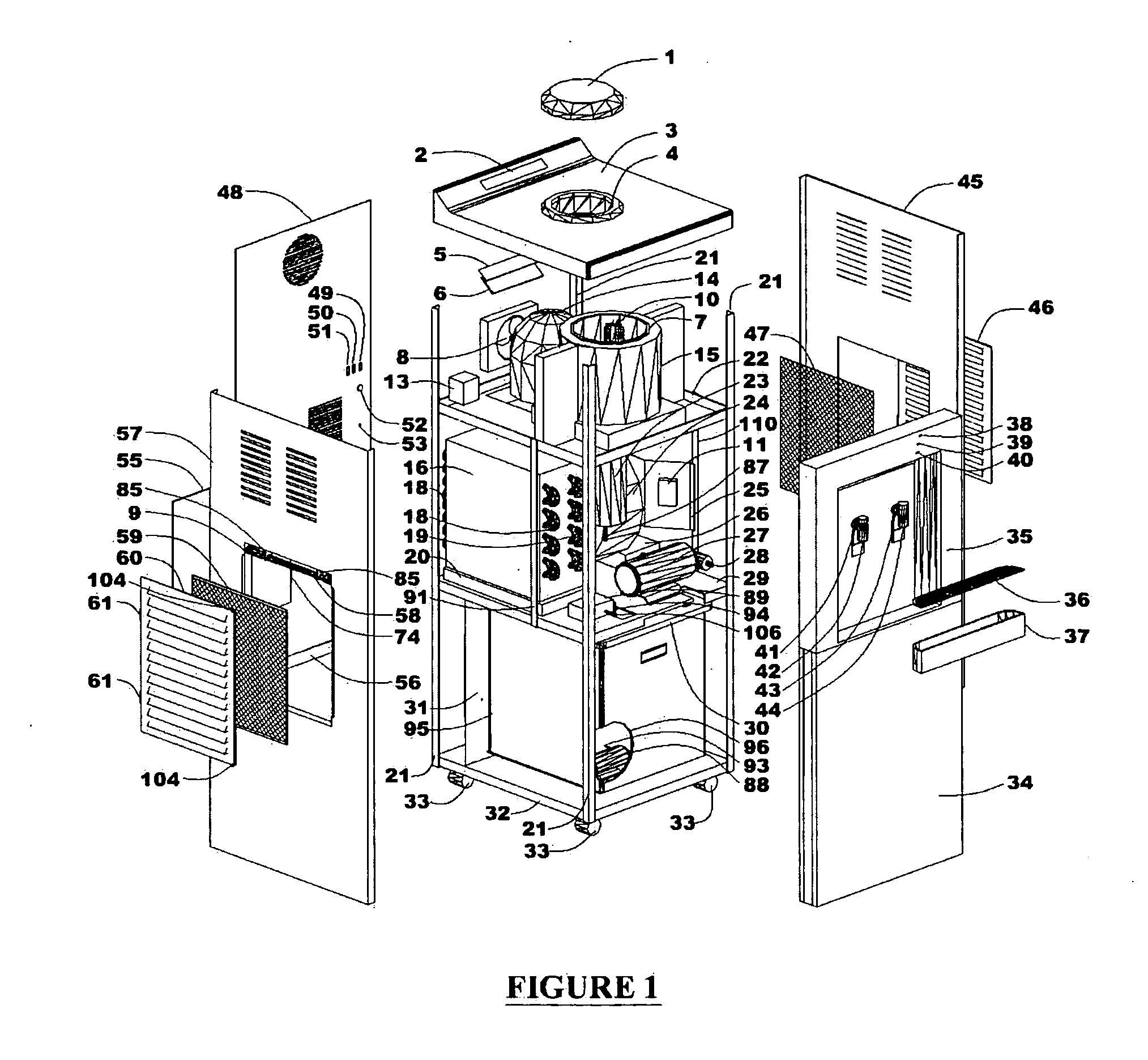
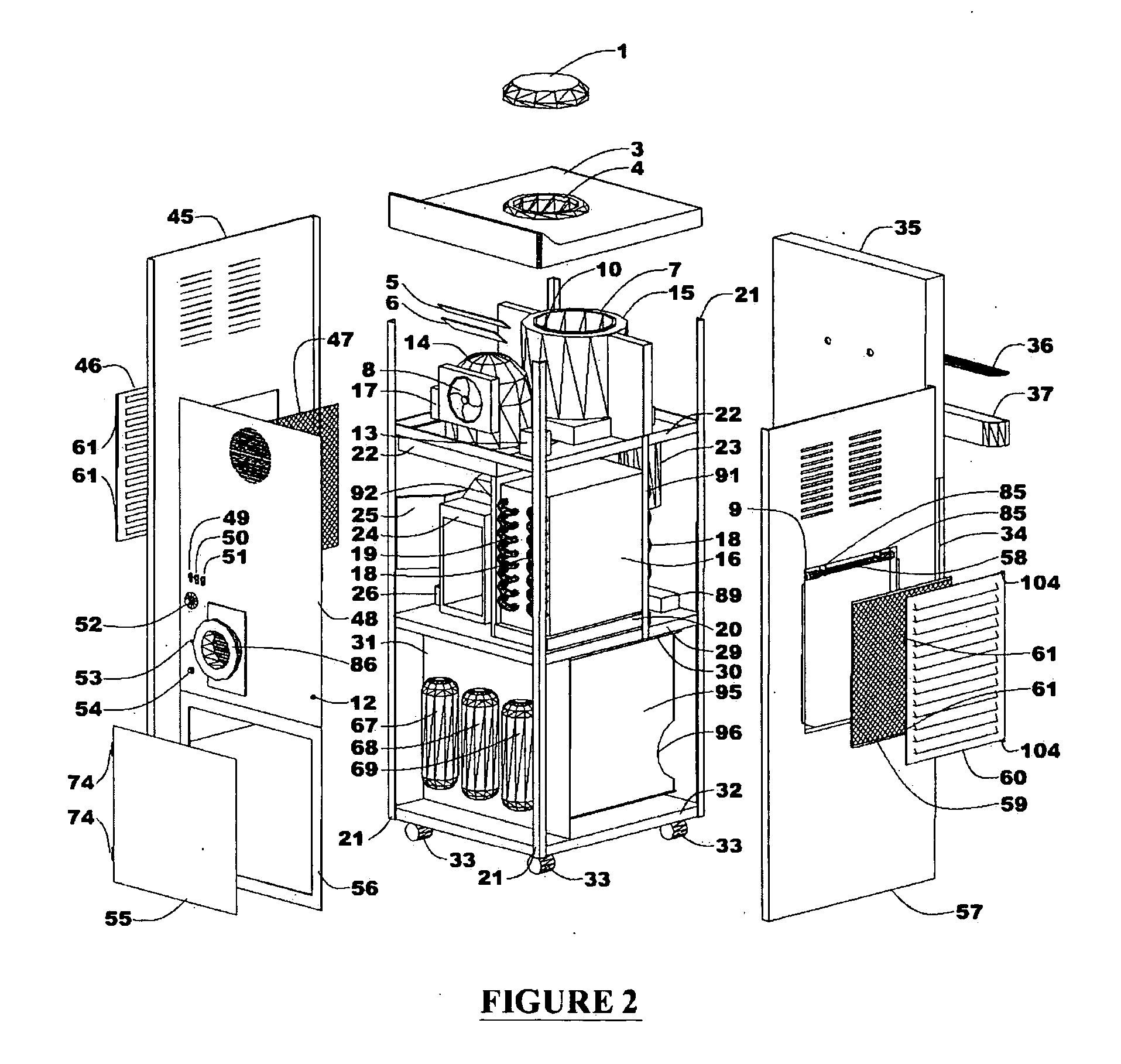
Energy Efficient House Ventilation
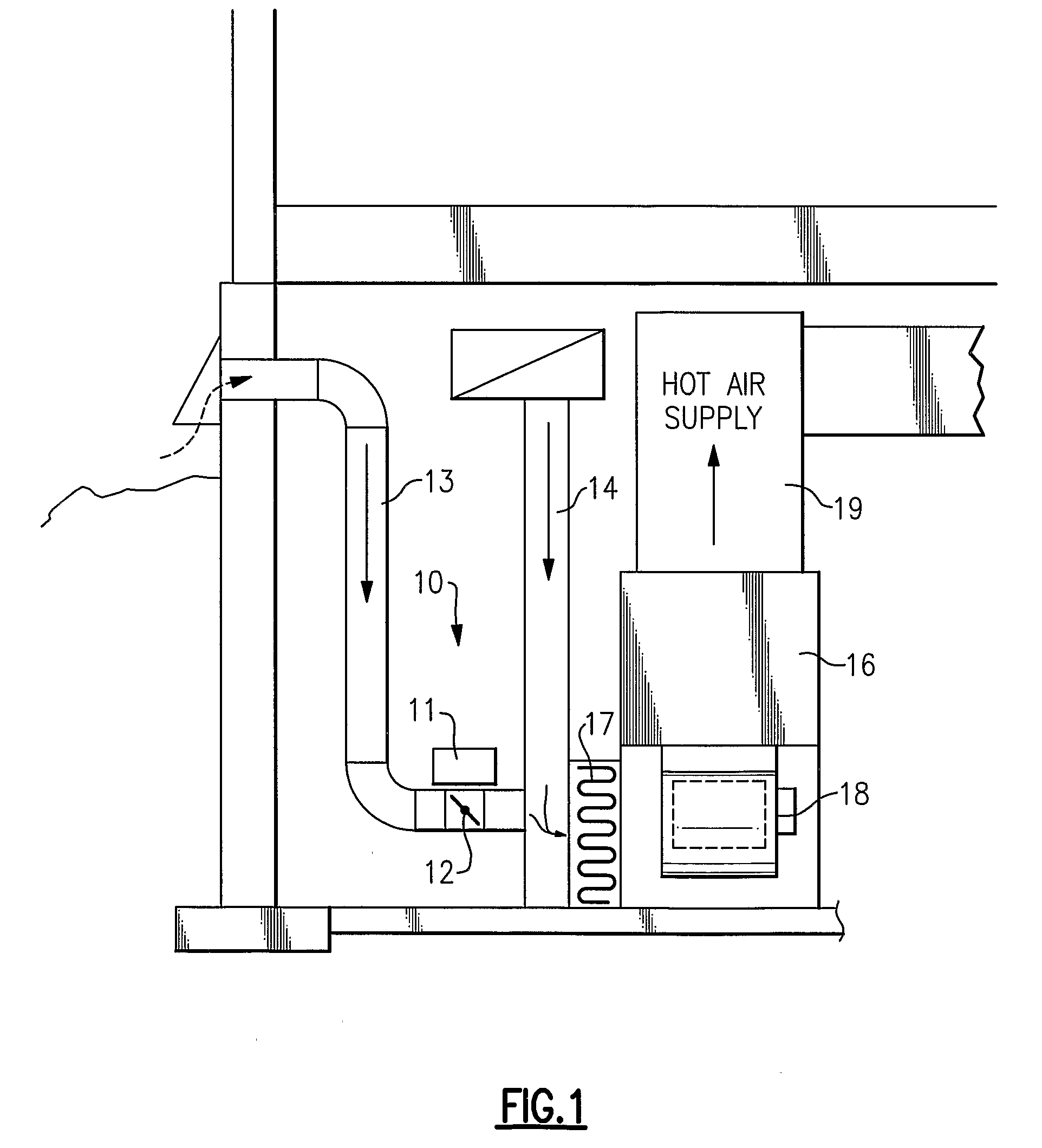
InactiveUS20090001179A1Degree of reductionSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsSpace heating and ventilation control systemsNatural ventilationSnubber
A method and apparatus for maintaining an acceptable level of outside air exchange rate in a structure. The natural ventilation rate is determined as a function of the outdoor air temperature, and the amount of mechanically induced ventilation that is used to supplement the natural air ventilation is controlled such that the sum of the natural occurring ventilation and the mechanically induced ventilation is maintained by a substantially constant predetermined level. One approach is to use a stepper motor to modulate the position of the damper, while another approach is to use an on / off motor damper and to close the damper at outdoor temperatures below a threshold level and to otherwise leave the damper open and use the regular on / off cycle of the system blower to control the flow of outdoor air, with provision for allowing the fan to remain on for a calculated period of time after the system is cycled off to thereby maintain the desired level of ventilation. Can also vary the speed of the furnace blower or a separate ventilation fan motor.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Lighting unit with improved cooling
InactiveUS20040208009A1Effective and relatively cheap mean of coolingIncrease productionPoint-like light sourceElectrical apparatusMotor driveEngineering
Disclosed is a lighting unit comprising at least one light emitting diode (50), means for supplying power to the light emitting diode (50), and a motor driven pump means (18) for generating a stream of fluid for cooling the light emitting diode (50). The pump means is mounted in a resiliently compressible member (48) for absorbing vibrations produced by the pump means (18) which reduces the level of noise produced by the lighting unit. The lighting unit has control means operable to gradually increase or decease the speed of operation of the pump means in response to the power dissipation of the light emitting diode exceeding or falling below, respectively, a threshold level, which makes the noise produced by the pump means less noticeable.
Owner:PULSAR LIGHT OF CAMBRIDGE
Control of a multi-sectored antenna system to improve channel efficiency
InactiveUS7359362B2Increase data rateAchieve benefitsAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentOmnidirectional antennaSignal quality
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for transferring data over a network
InactiveUS7437428B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksNetwork activitySoftware update
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
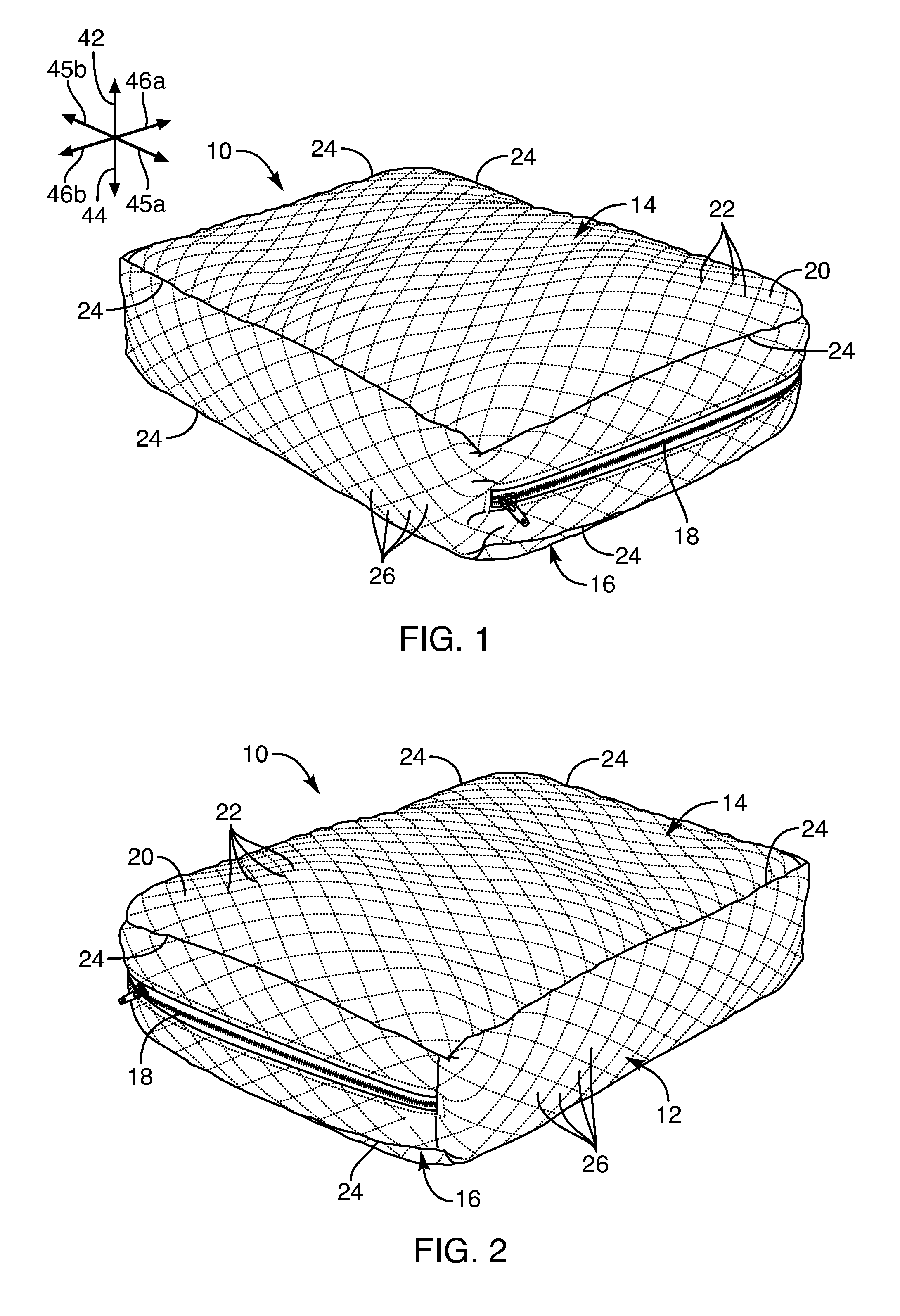
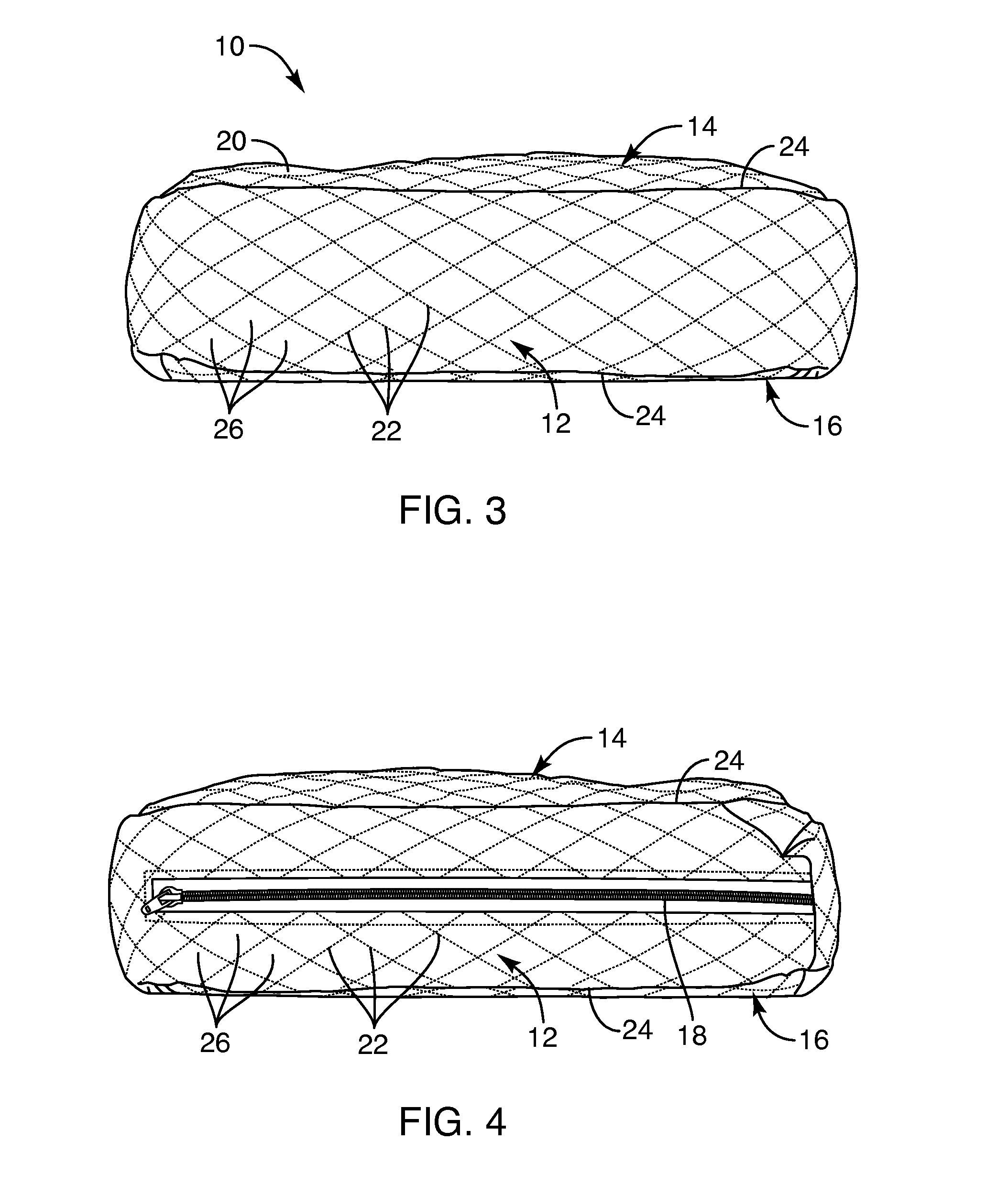
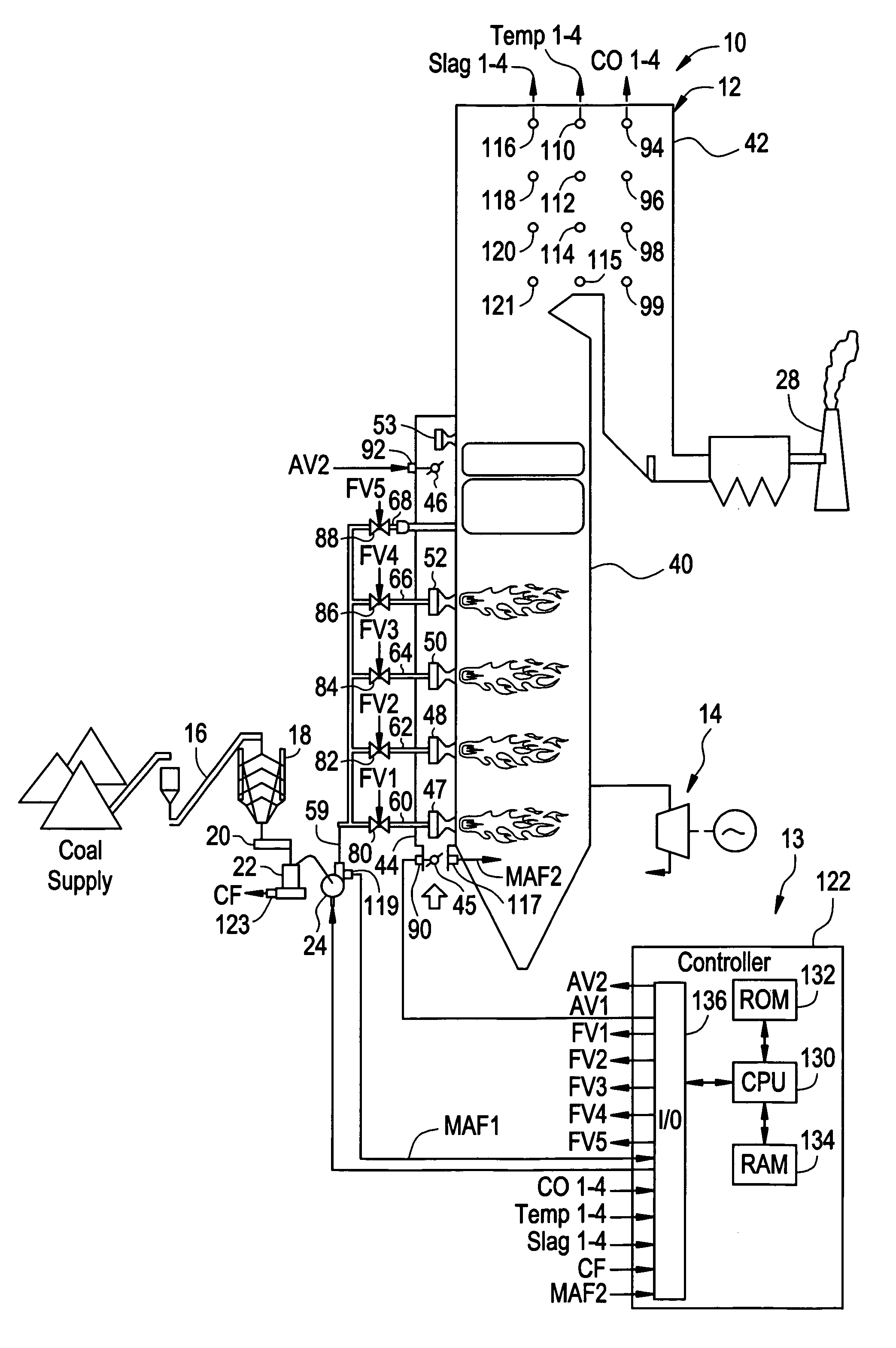
Cpap pillow apparatus and method
Owner:RANDALL BRET
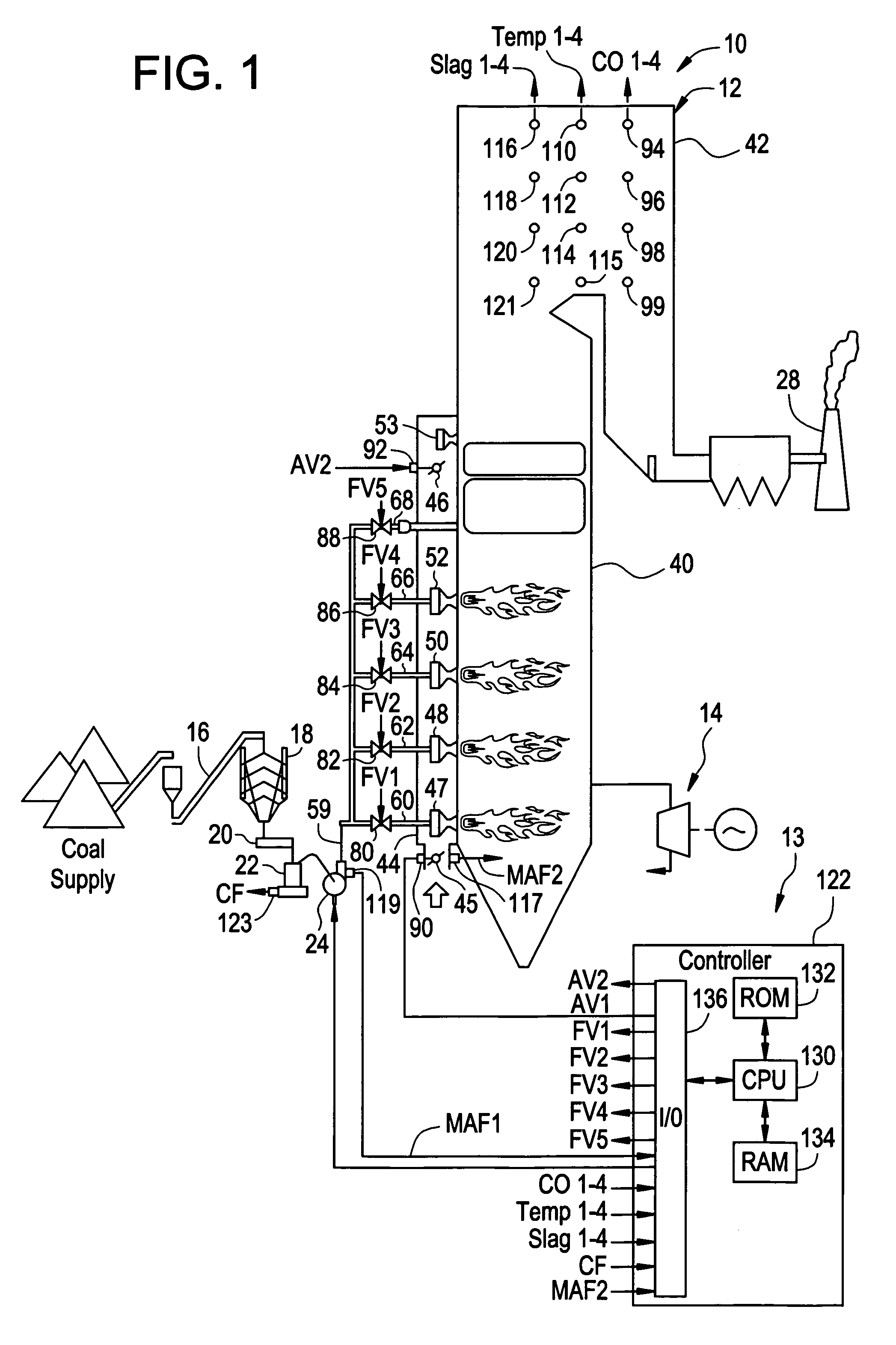
System, method, and article of manufacture for adjusting temperature levels at predetermined locations in a boiler system
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Refrigeration appliance interior lighting system
InactiveUS6951402B1Eliminate the effects ofEliminates blinding effectFurnace componentsElectrical apparatusElectricityEngineering
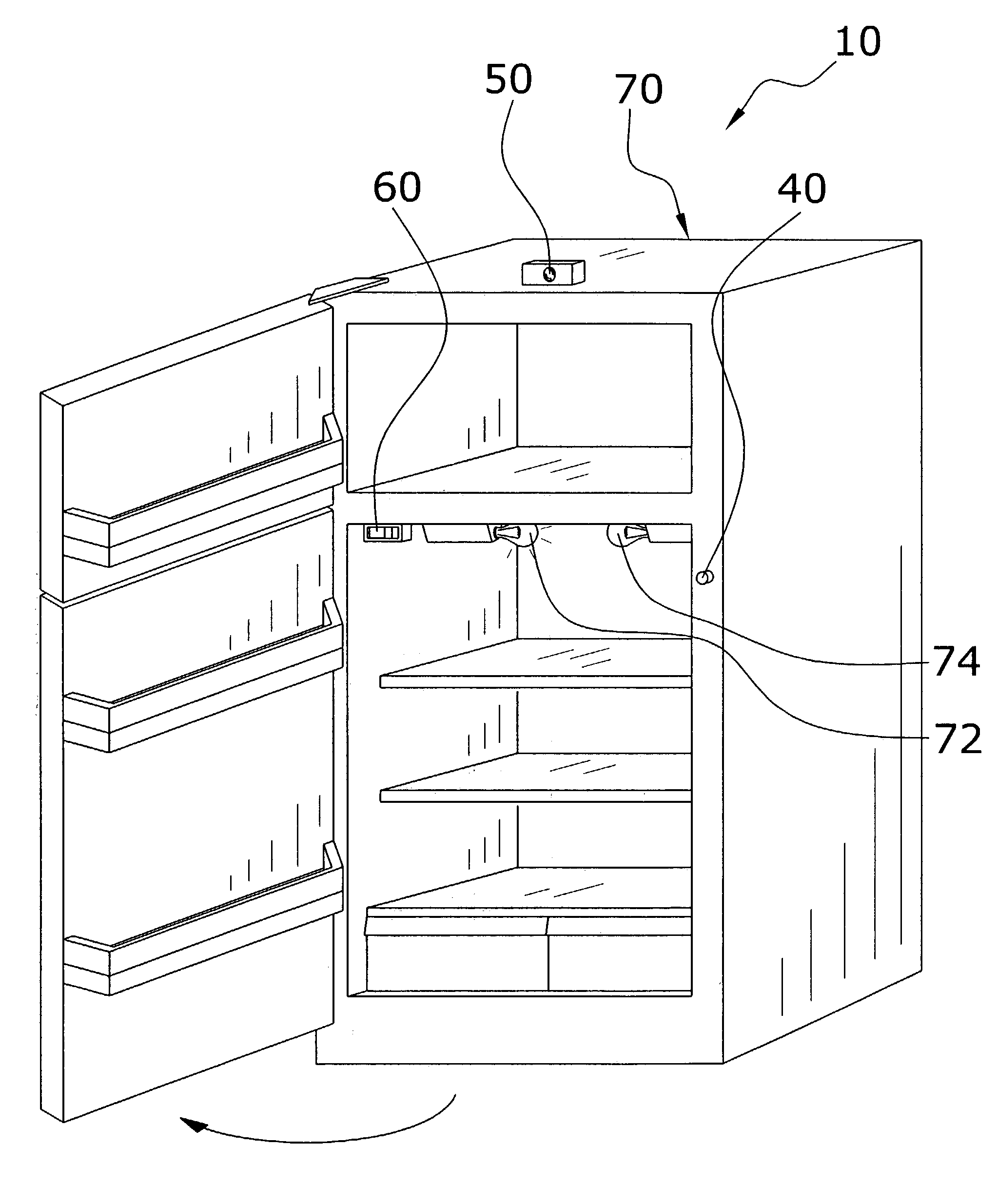
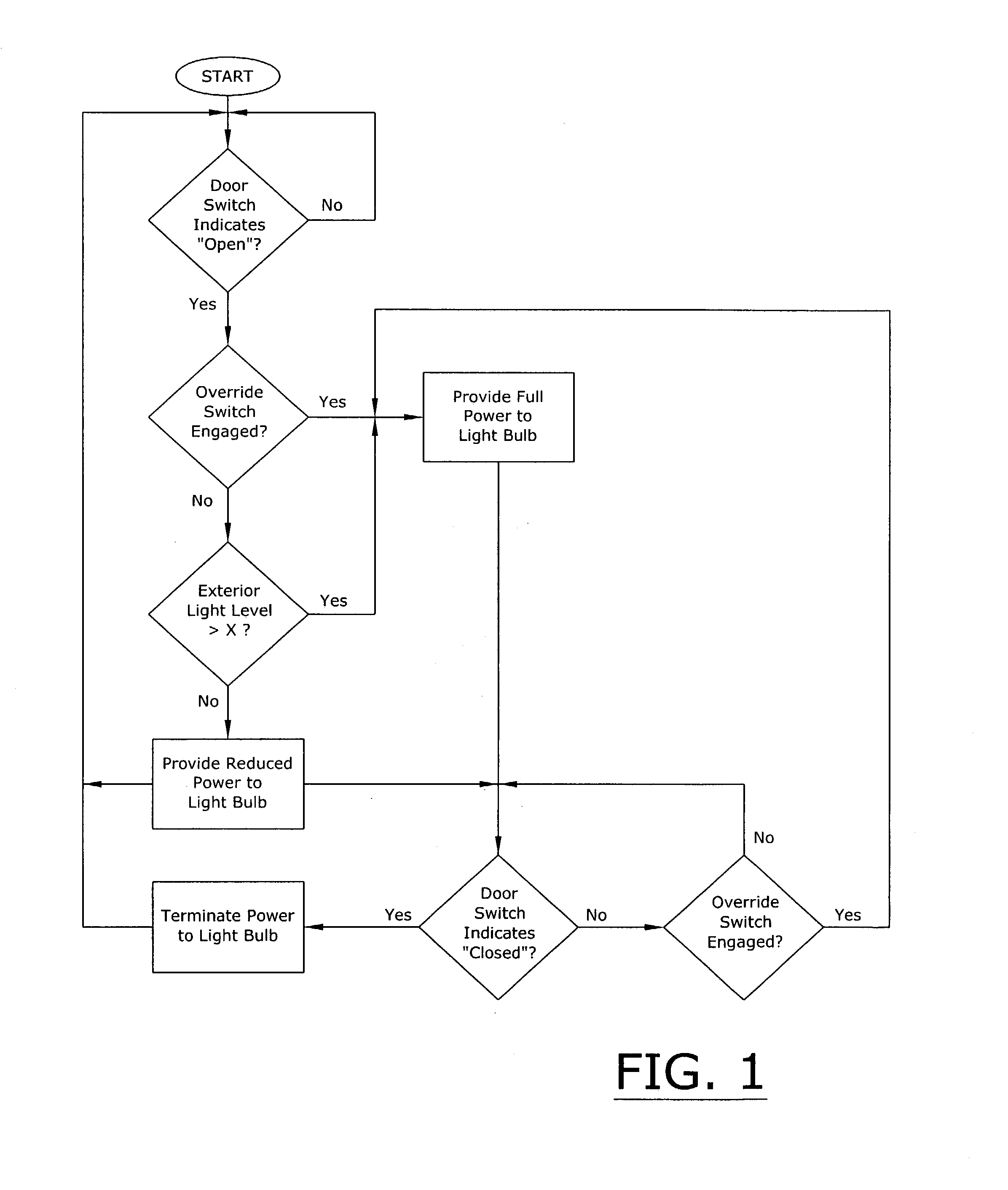
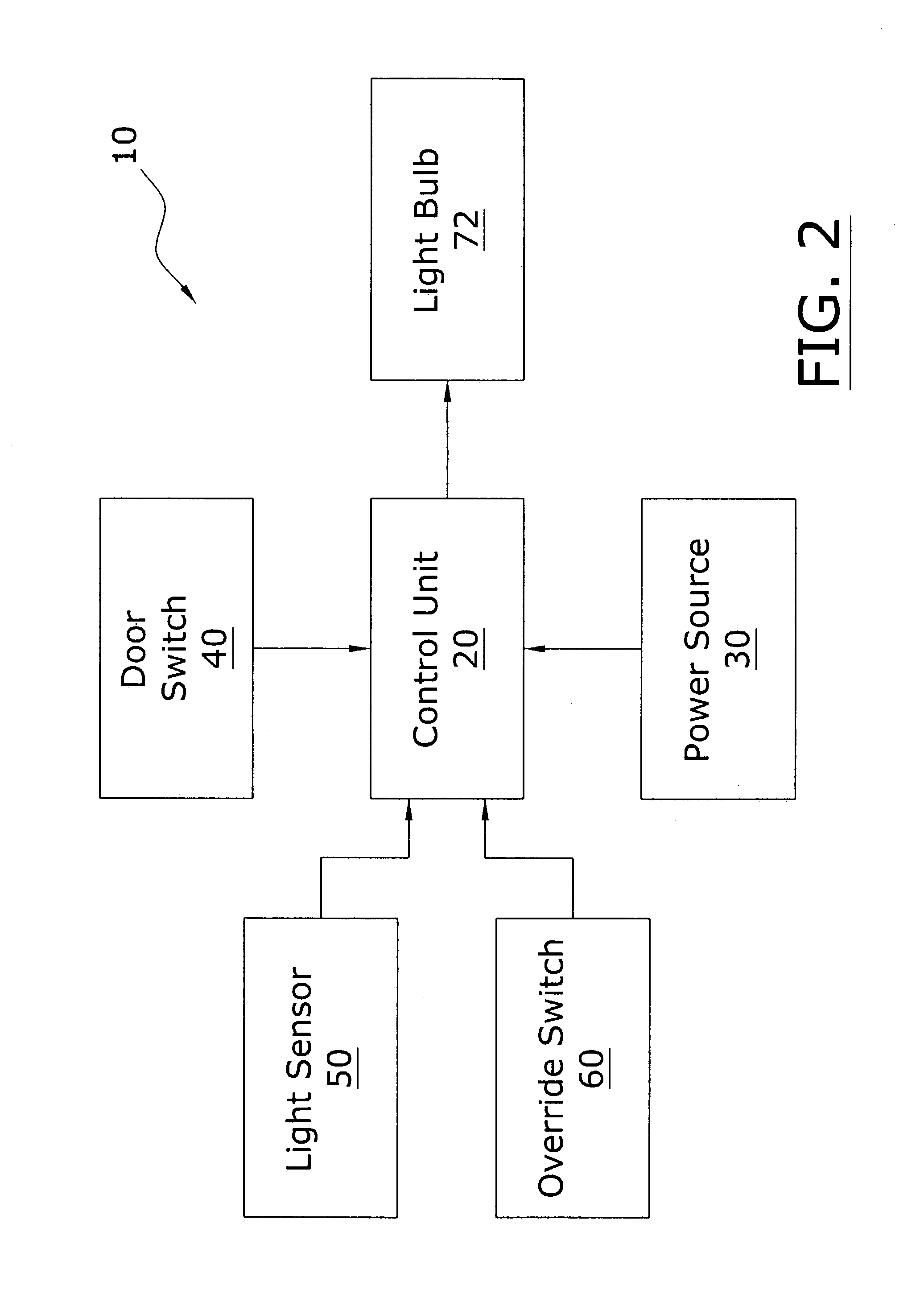
A refrigeration appliance interior lighting system for sensing the exterior light level and adjusting the light level accordingly within the interior of the home appliance. The refrigeration appliance interior lighting system includes a control unit in electrical communication with a first light bulb for controlling the illumination intensity of the first light bulb. A light sensor is positioned to measure the exterior light level and communicates the exterior light level to the control unit. When the exterior light level is above a threshold level, the first light bulb emits a high level of illumination. When the exterior light level is below the threshold level, the first light bulb emits a low level of illumination.
Owner:COPP HEATH R
Combination dehydrator, dry return air and condensed water generator/dispenser
InactiveUS20070175063A1Drying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsEngineeringBelow threshold level
A portable, combination dehydrator, dry return air and condensed water generator / dispenser configured to reduce the humidity in a dry storage unit. In one embodiment, a system draws intake air from the dry storage unit across the condenser of a heat exchanger and condenses water from the air, collecting the water in a storage tank. The dried return air is ducted into the dry storage unit. In one embodiment, the source of the intake air may be selected from either the dry storage unit or an alternative source (e.g., outside air.) The selection of the intake air source may be based on the humidity of the air (e.g., if the humidity of the air in the dry storage unit is above a threshold, the dry storage unit is selected.) If both of the alternate sources of intake air have humidities below a threshold level, operation of the system may be suspended.
Owner:MORGAN MICHAEL +1
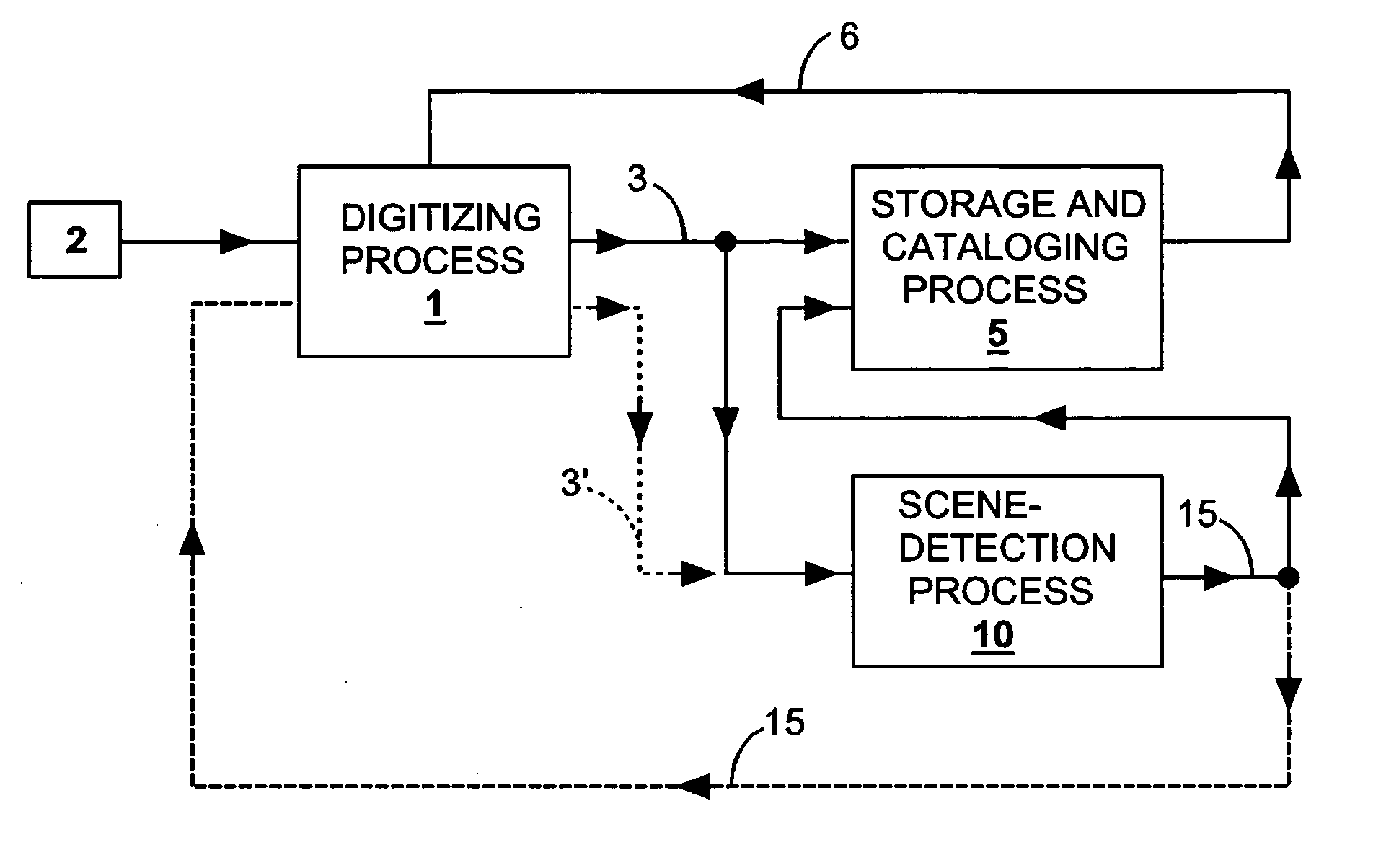
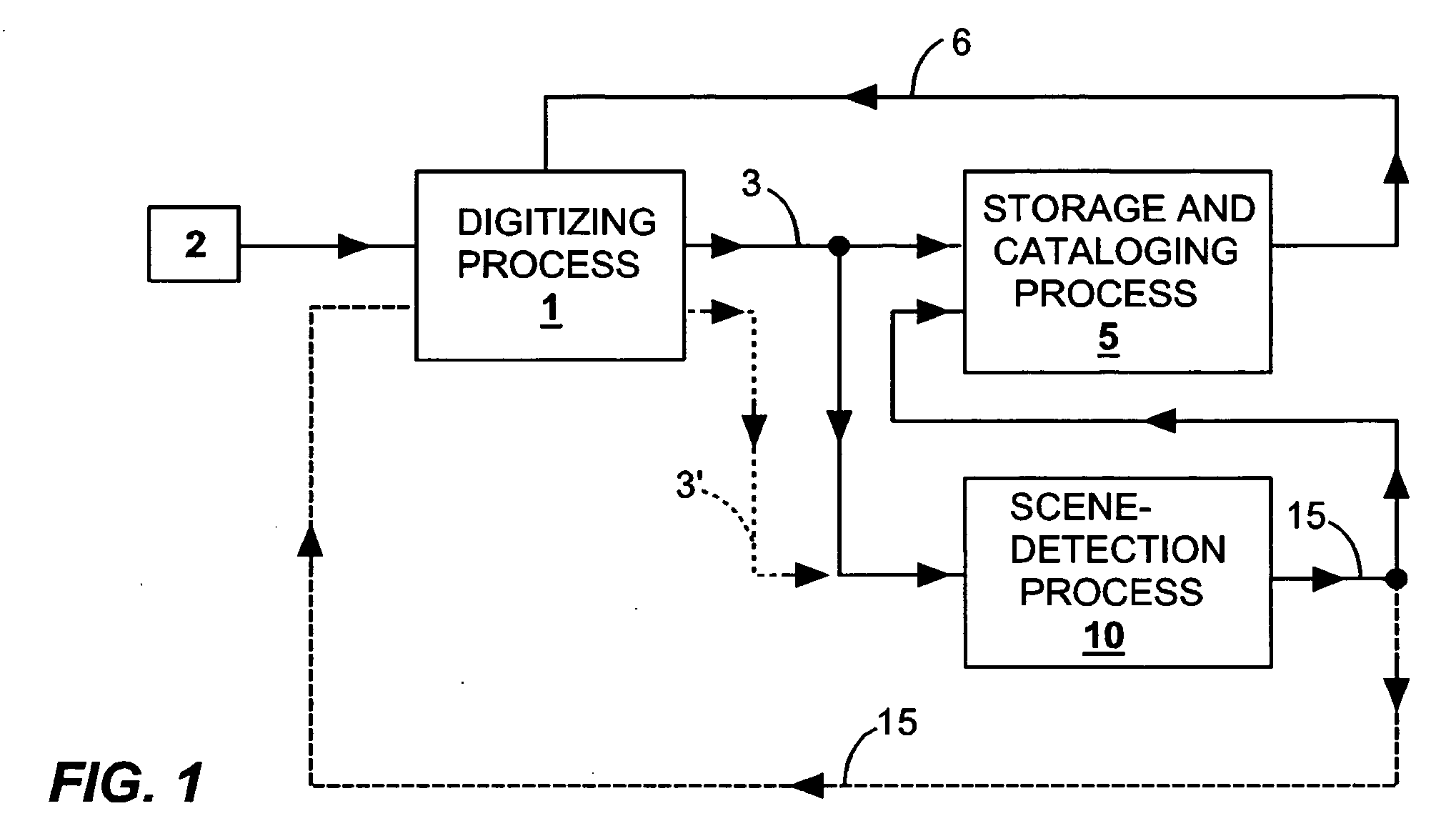
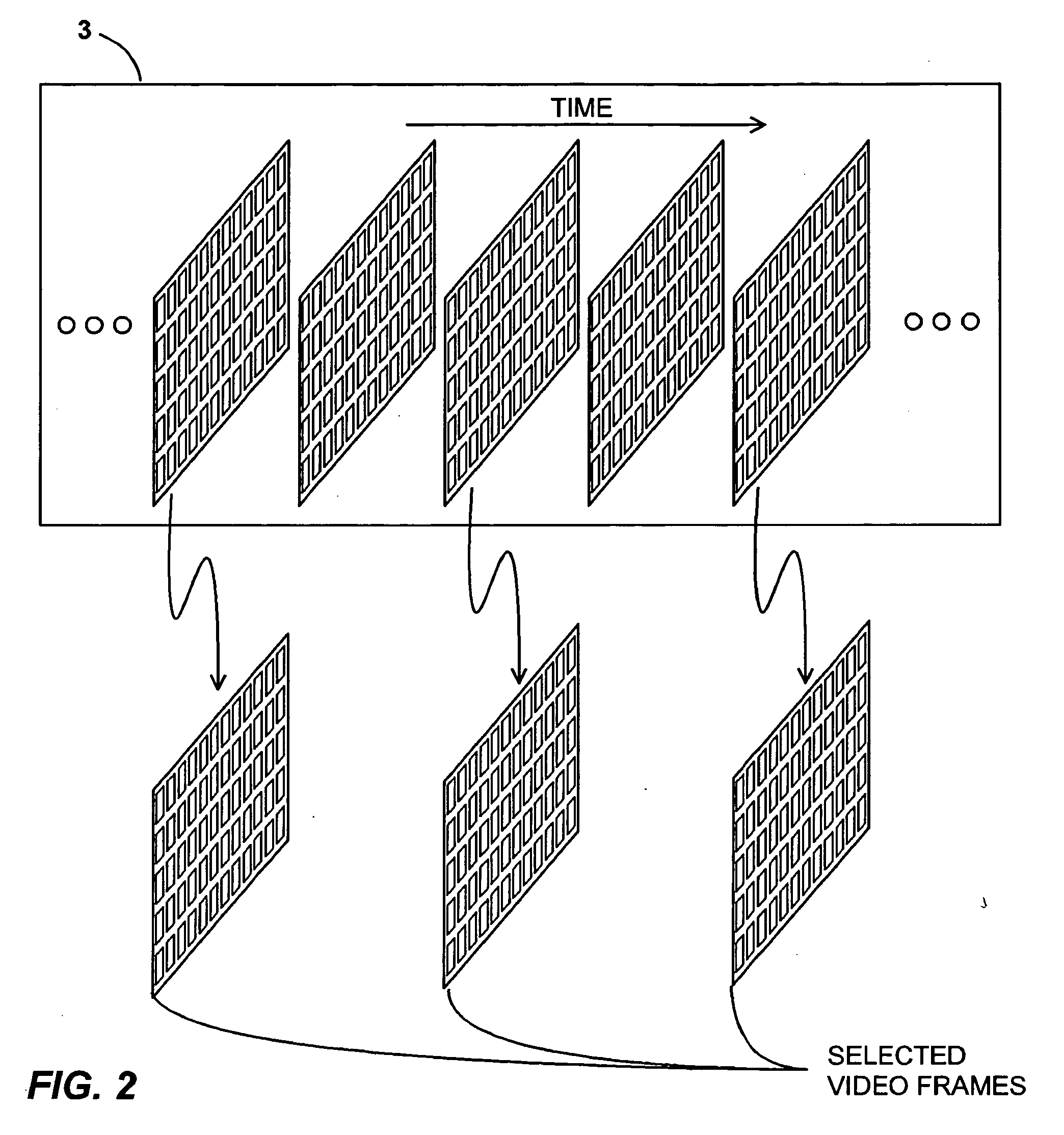
Methods and apparatus for detecting scenes in a video medium
ActiveUS20060165283A1Reliable detectionLower requirementTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer graphics (images)Video record
Owner:TERESIS MEDIA MANAGEMENT
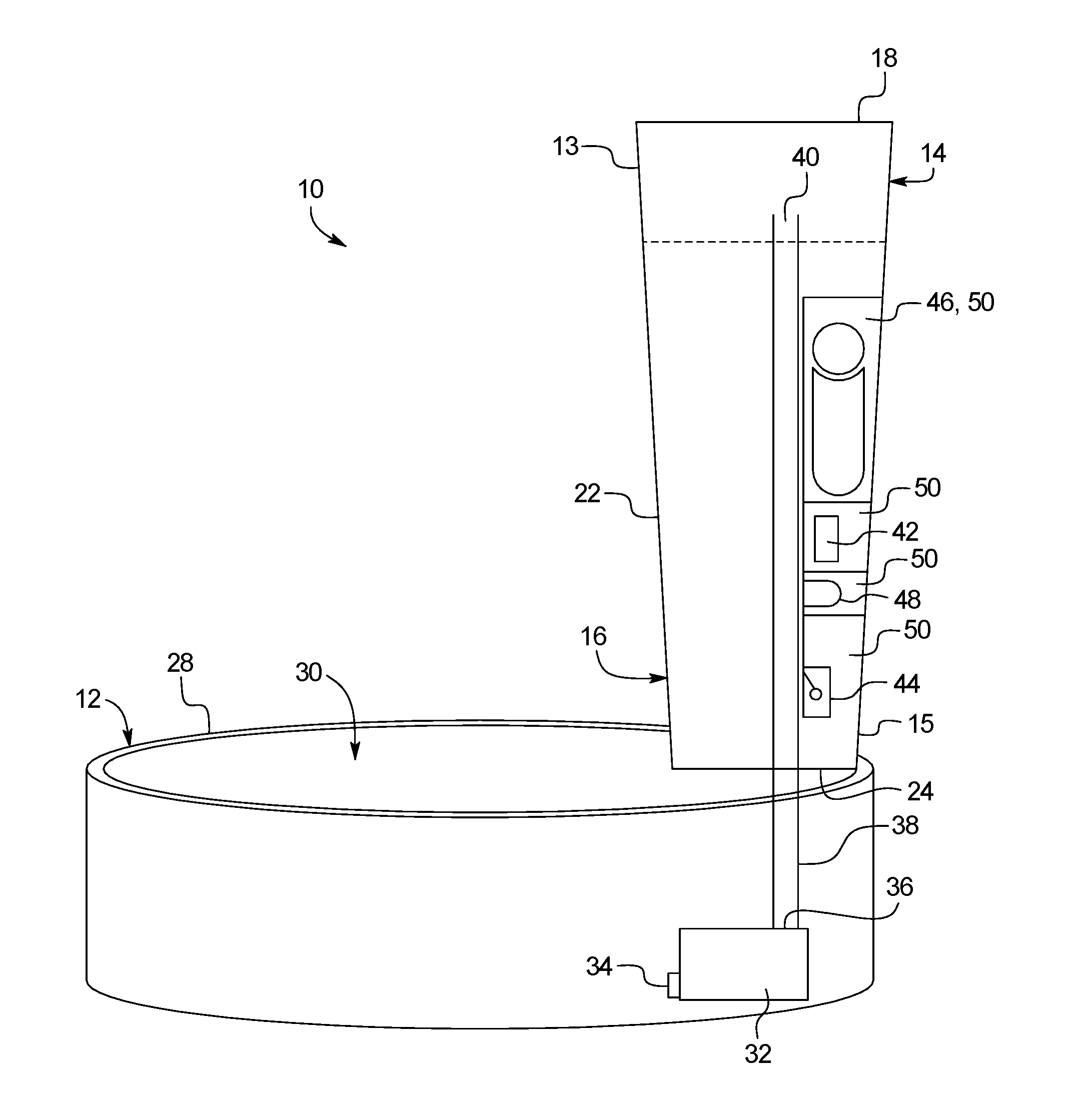
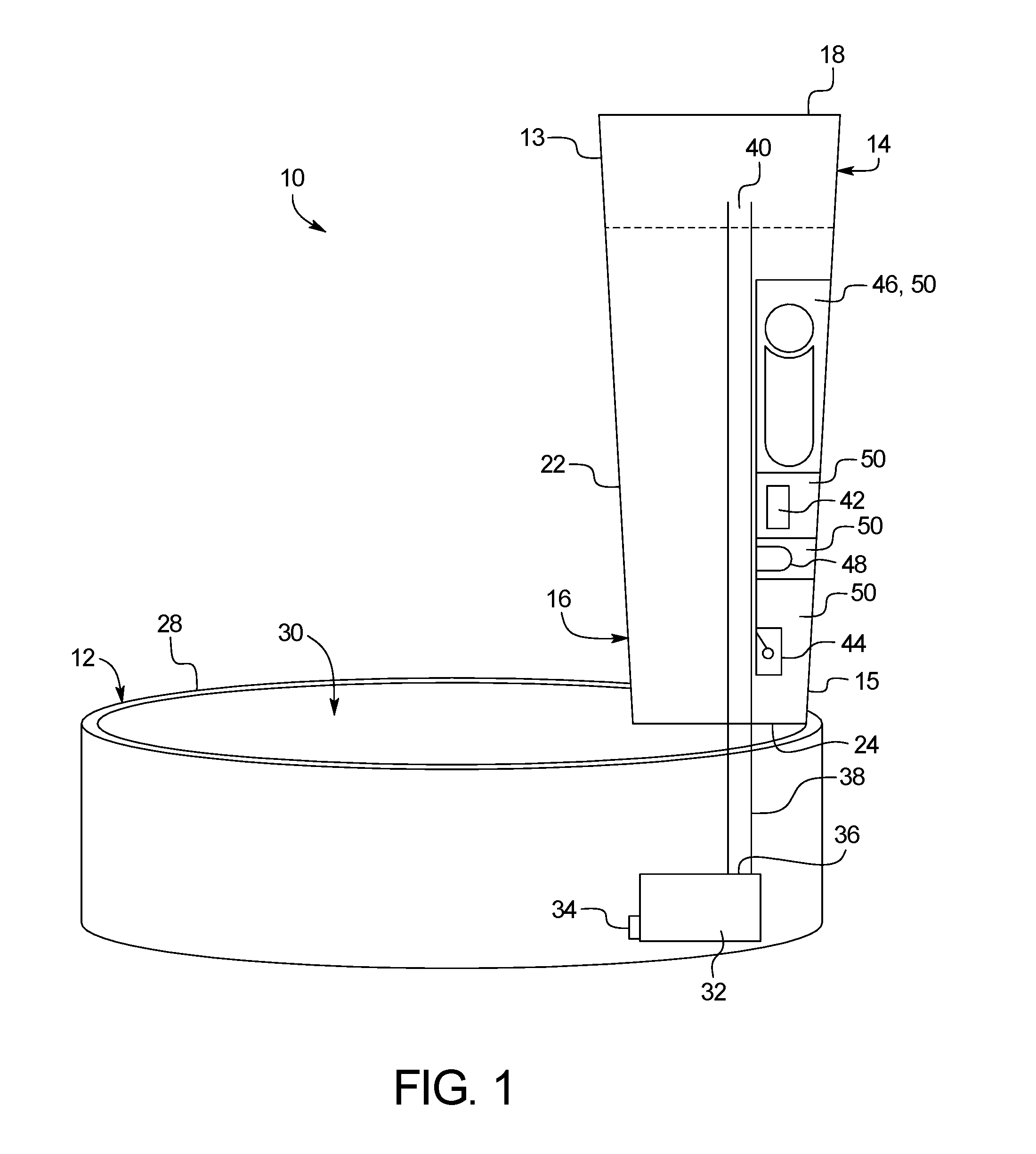
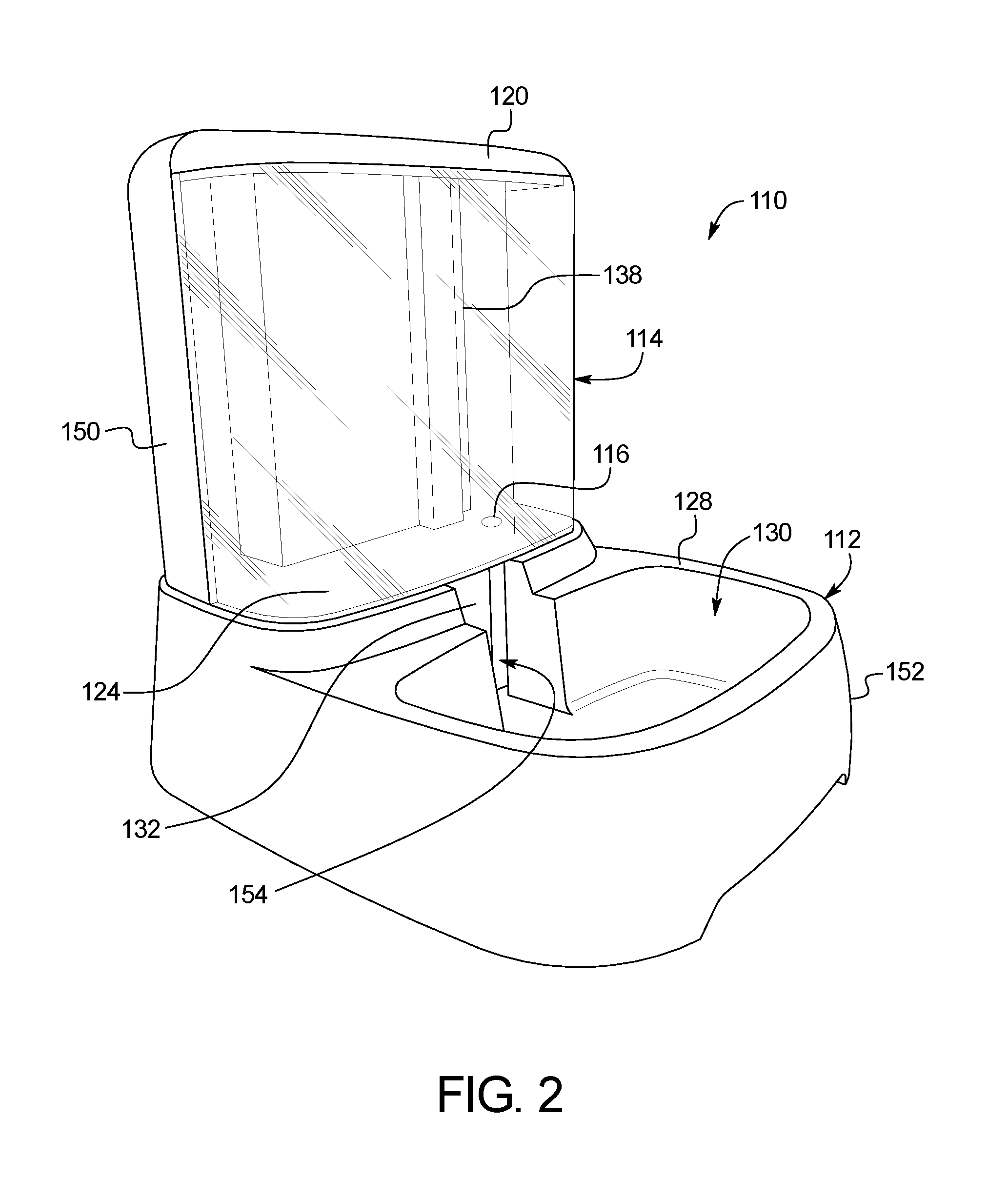
Drinking apparatus for pets
A drinking apparatus includes a drinking receptacle, a liquid reservoir, a pump, a controller, and a liquid detector. The liquid reservoir has a liquid outlet for dispensing liquid into the drinking receptacle. The pump has an inlet in liquid communication with the drinking receptacle, and an outlet in liquid communication with the reservoir. The controller is configured to control the operation of the pump. The liquid level detector is configured to detect when the level of liquid in the reservoir is below a first threshold level. The controller is responsive to the liquid level detector to operate the pump to pump liquid from the drinking receptacle into the reservoir when the liquid level detector indicates that the level of liquid in the reservoir is below the threshold level, and the controller is configured to deactivate the pump at the end of a pumping period.
Owner:DOSKOCIL MFG
Driver device and driving method for driving a load, in particular a light unit
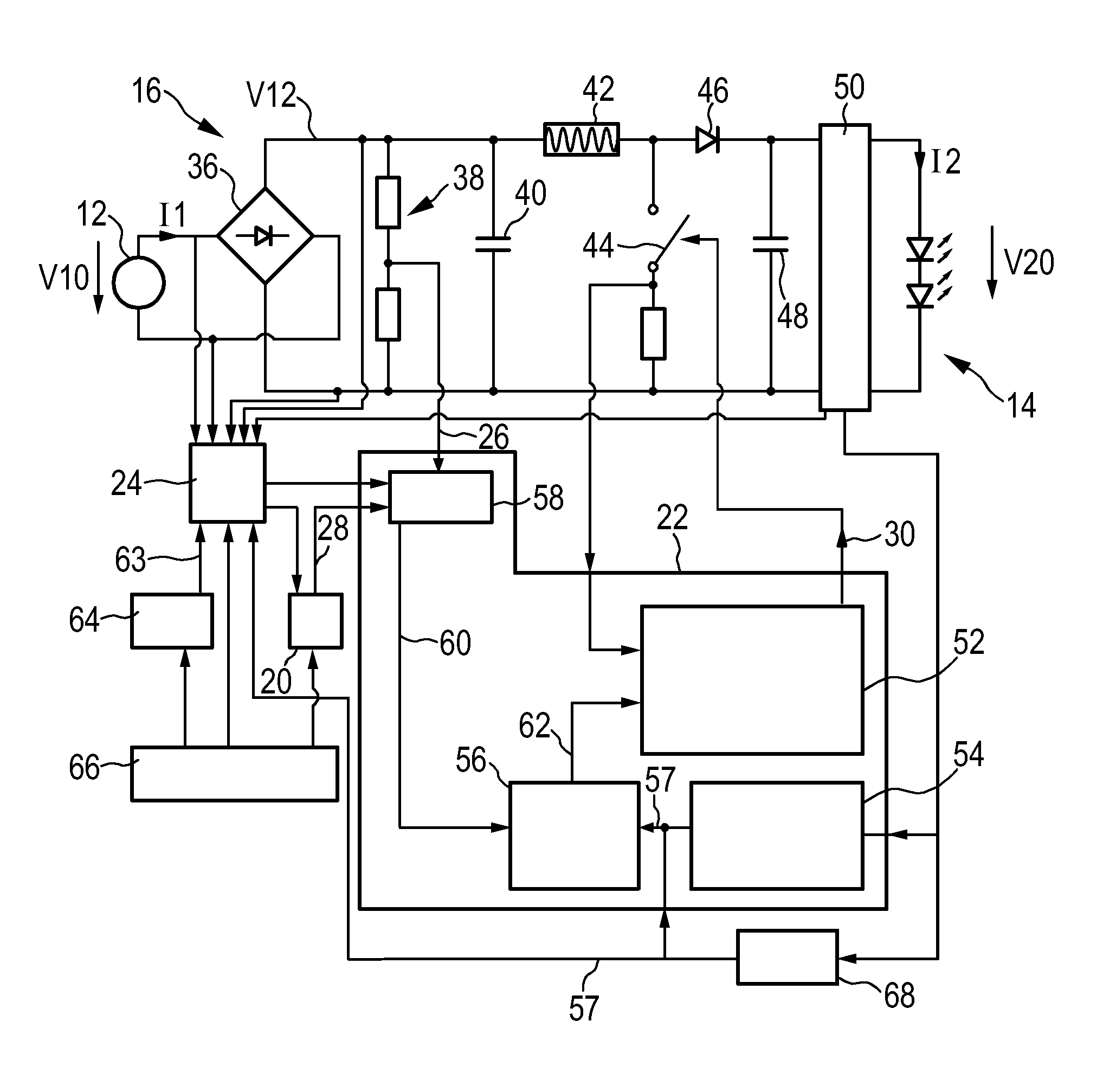
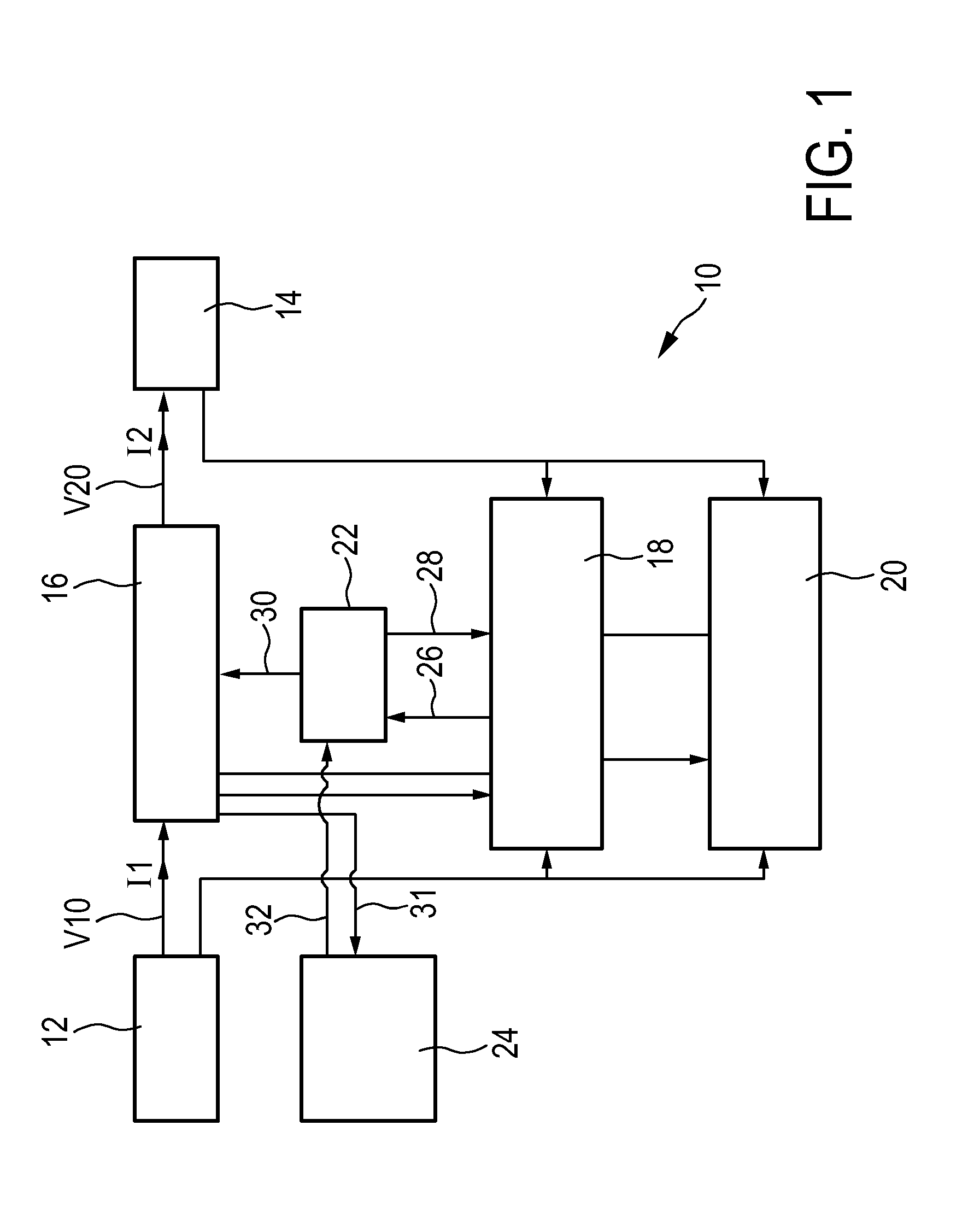
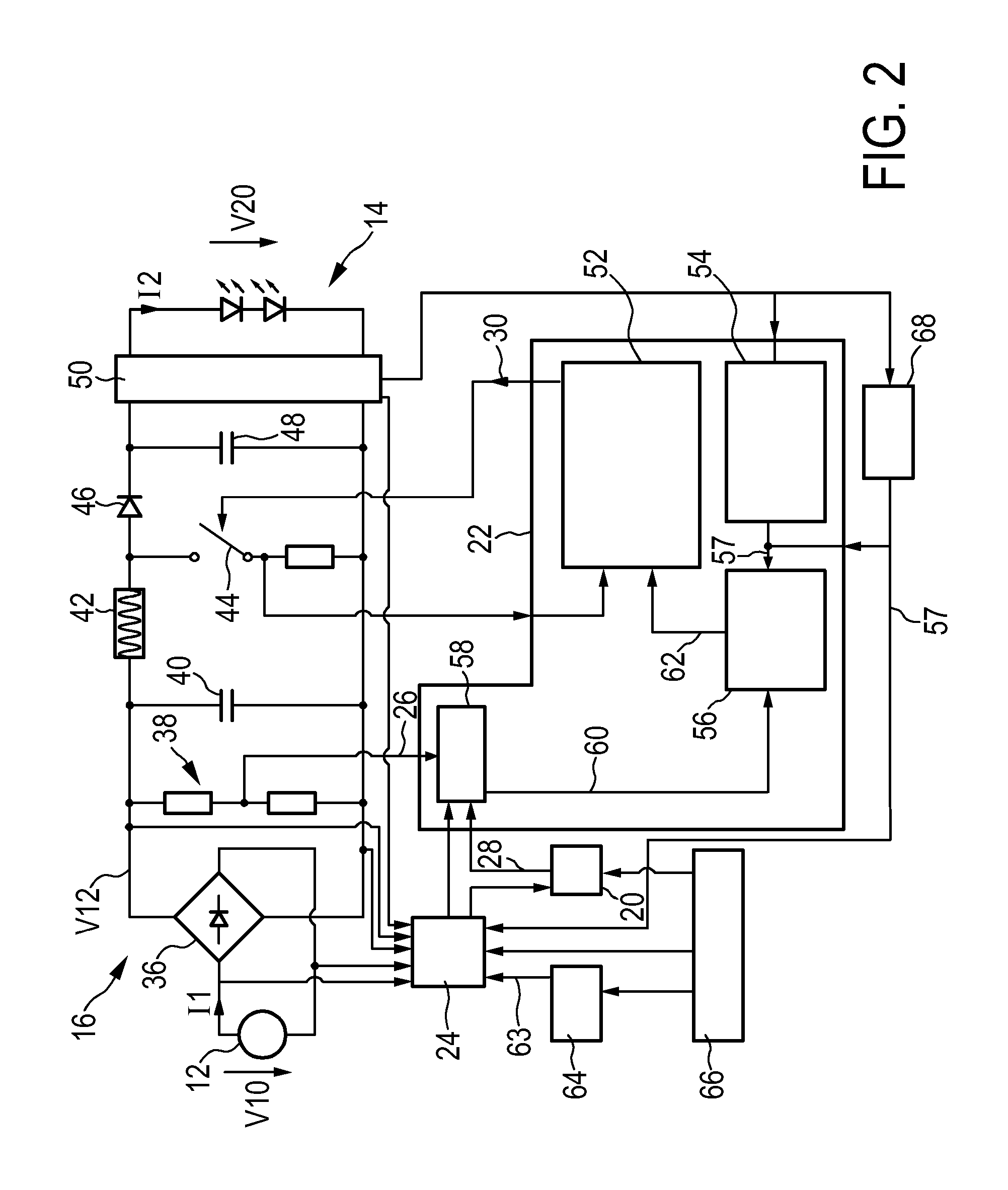
ActiveUS20150208479A1Stable power to loadStable strengthEfficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesElectricityBelow threshold level
The present invention relates to a driver device (10) for driving a load (14), in particular a light unit (14) having one or more light emitters, comprising input terminals for receiving an input voltage (V10) from an external power source (12), output terminals for providing electrical power to the load for powering the load (14), a driver stage (16) connected to the input terminals and to the output terminals, wherein the driver stage (16) is adapted to control an input current (I1) drawn from the external power supply (I2) and to control the electrical power provided to the output terminal shaving a predefined level, a detection device (24) for measuring at least one electrical parameter (V10, V12, I2, V20) of the driver stage (16) and for determining an input voltage deviation from predefined supply conditions on the basis of the electrical parameter (V10, V12, I2, V20), wherein the driver stage (16) is adapted to control the input current (I1) according to predefined conditions if the input voltage deviation is lower than a threshold level (63) and to allow a deviation of the input current (I1) from the predefined conditions if the input voltage deviation exceeds the threshold level (63).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
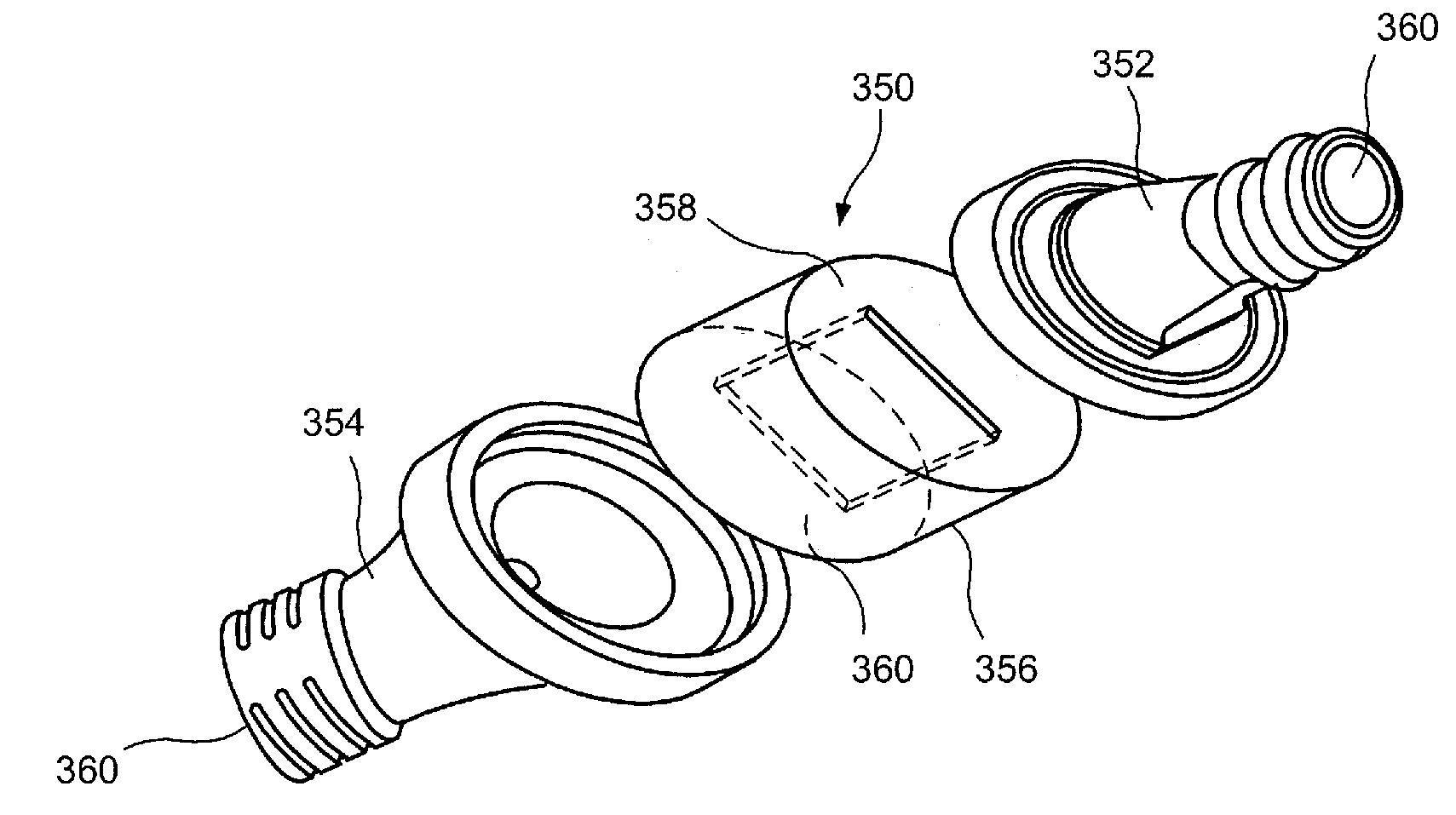
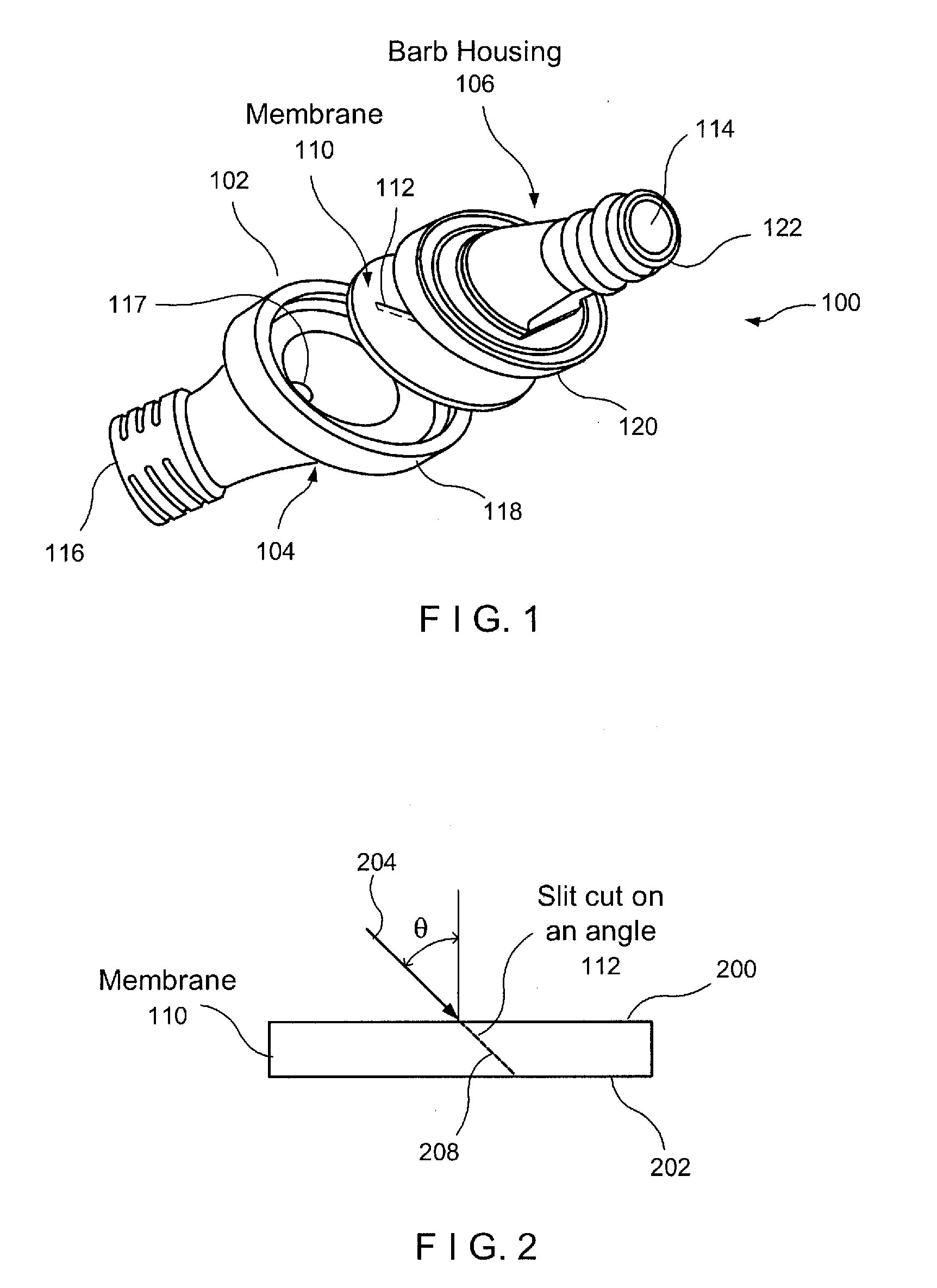
Pressure Activated Valve with Angled Slit
A pressure actuated valve comprises a first membrane having a slit extending through the membrane at a nonzero draft angle relative to a perpendicular to a surface of the membrane, material of the membrane biasing the slit closed so that the slit remains closed when a fluid pressure applied to the membrane is below a threshold level and, when the fluid pressure is at least the threshold level, edges of the slit separate from one another to permit fluid flow through the membrane.
Owner:NAVILYST MEDICAL
Dynamic Loading of Power Supplies
ActiveUS20110234123A1The scope of application is limitedWell formedElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLoad circuitControl signal
A circuit for altering a level of impedance presented to a power supply including a power supply line includes an energy dissipating circuit, a detection circuit configured to generate a control signal indicative of a power consumption level in a load circuit coupled to the power supply line, and an activation circuit configured to controllably couple the energy dissipating circuit to the power supply line in response to the control signal. Methods of operating a solid state lighting apparatus including a power supply and a solid state lighting device coupled to the power supply include detecting a level of power consumption by the solid state lighting device, and coupling an energy dissipating circuit to the power supply in response to the level of power consumption by the solid state lighting device falling below a threshold level.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC +1
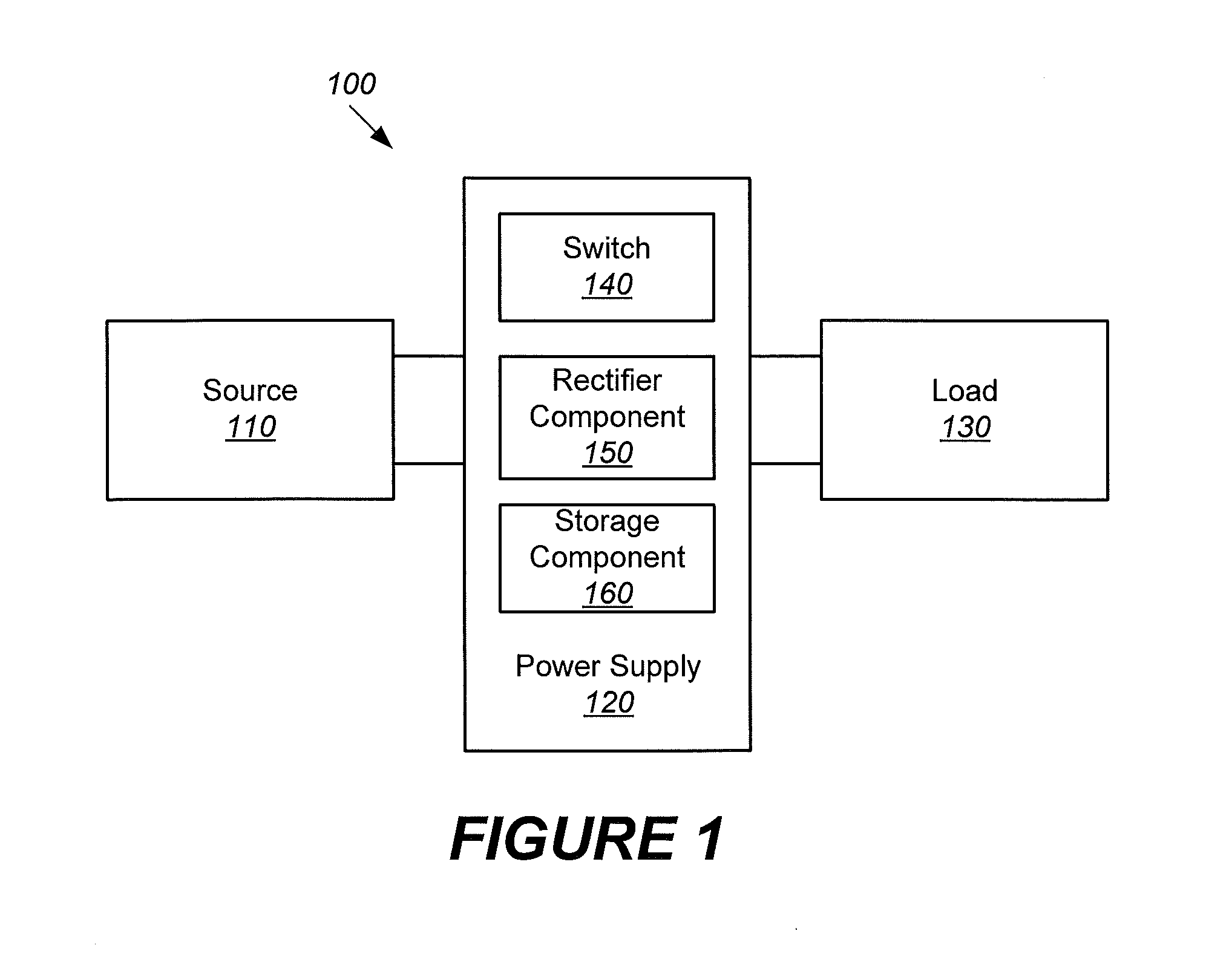
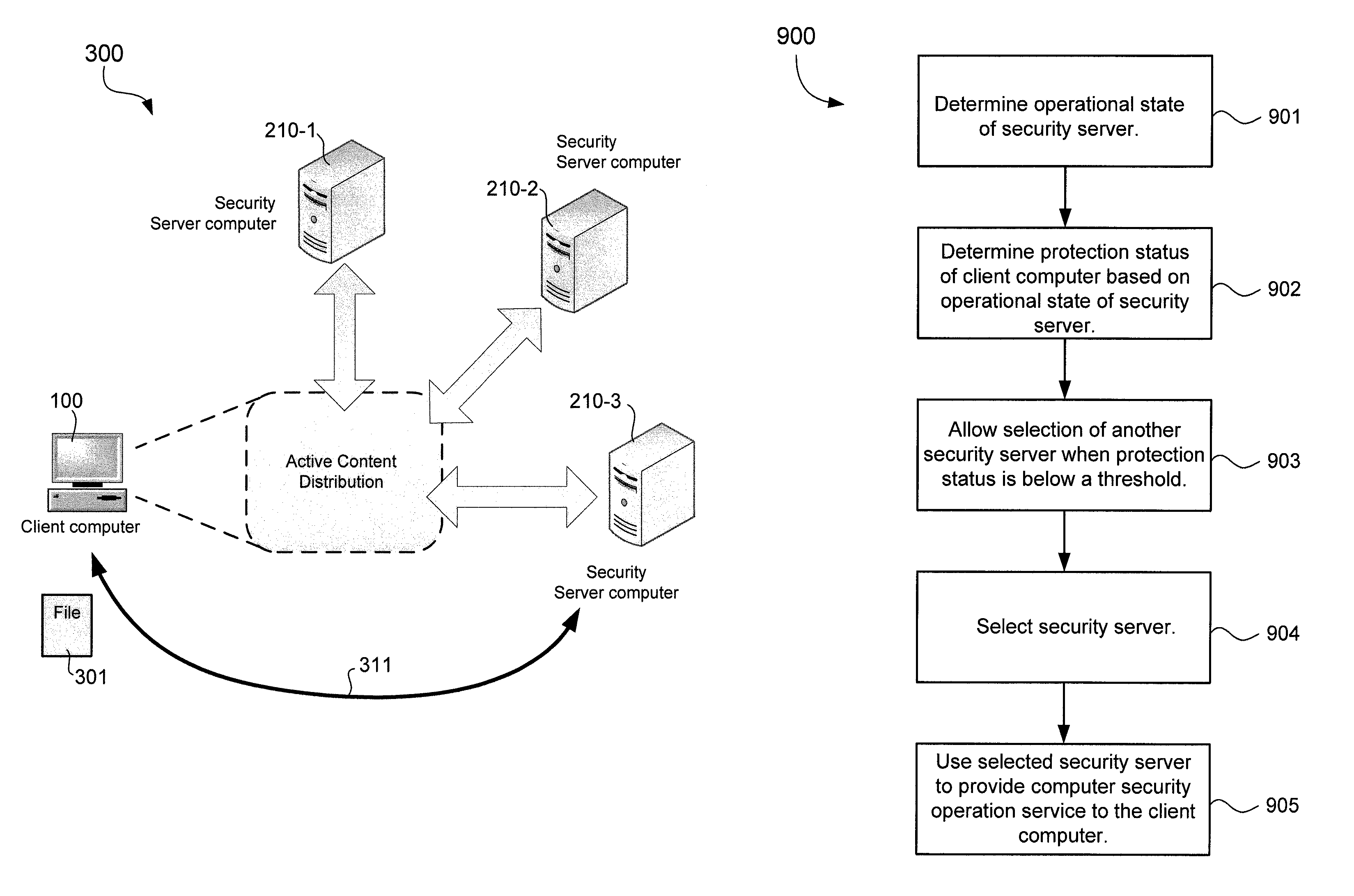
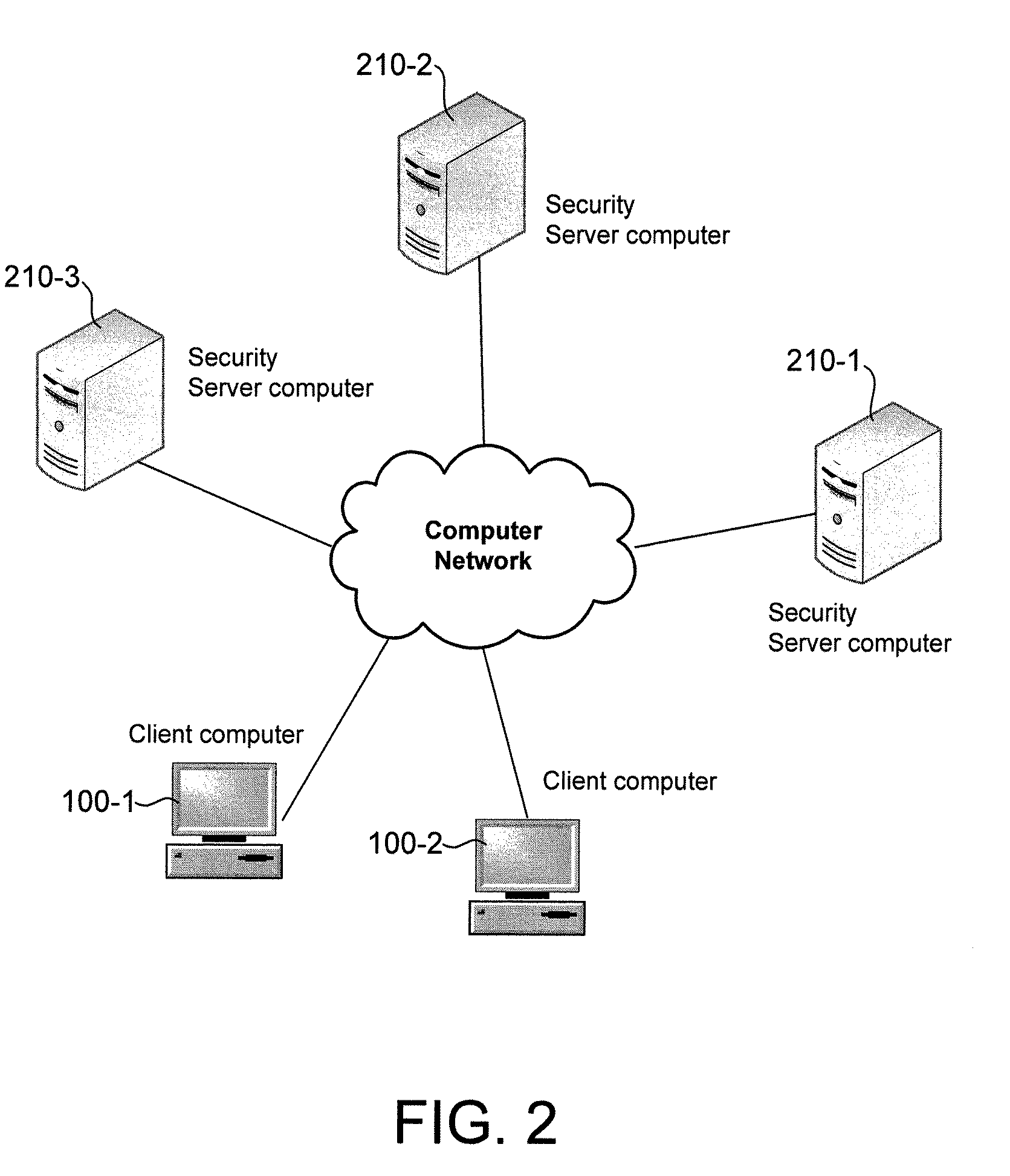
Selection of remotely located servers for computer security operations
A client computer may be configured to perform computer security operation services, such as malicious code scanning and protection against online threats, using one of several remotely located server computers. The client computer may be configured to determine an operational state of the server computers and determine a protection status of the client computer resulting from use of a server computer of a particular operational state. The protection status may have one of at least three levels and indicate vulnerability of the client computer. The client computer may determine the operational state of a server computer based on available bandwidth for network communication between the client computer and the server computer. The client computer may be configured to allow for automatic or manual selection of another server computer when the currently selected server computer results in the client computer having a protection status below a threshold level.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
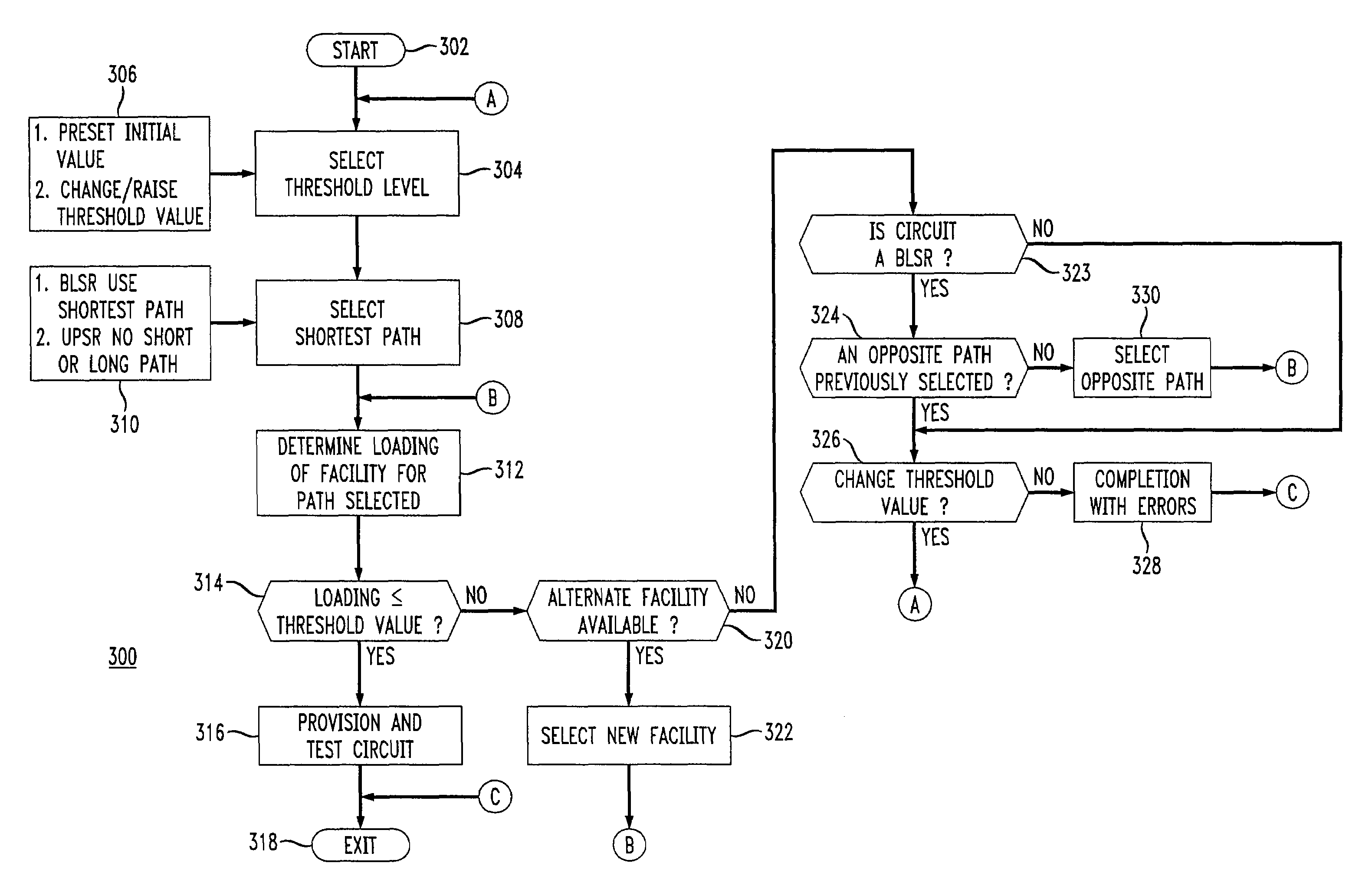
Method and apparatus for SONET/SDH ring load balancing
InactiveUS7509403B1Easy to useAvoid utilizationError preventionTransmission systemsBalanced circuitBelow threshold level
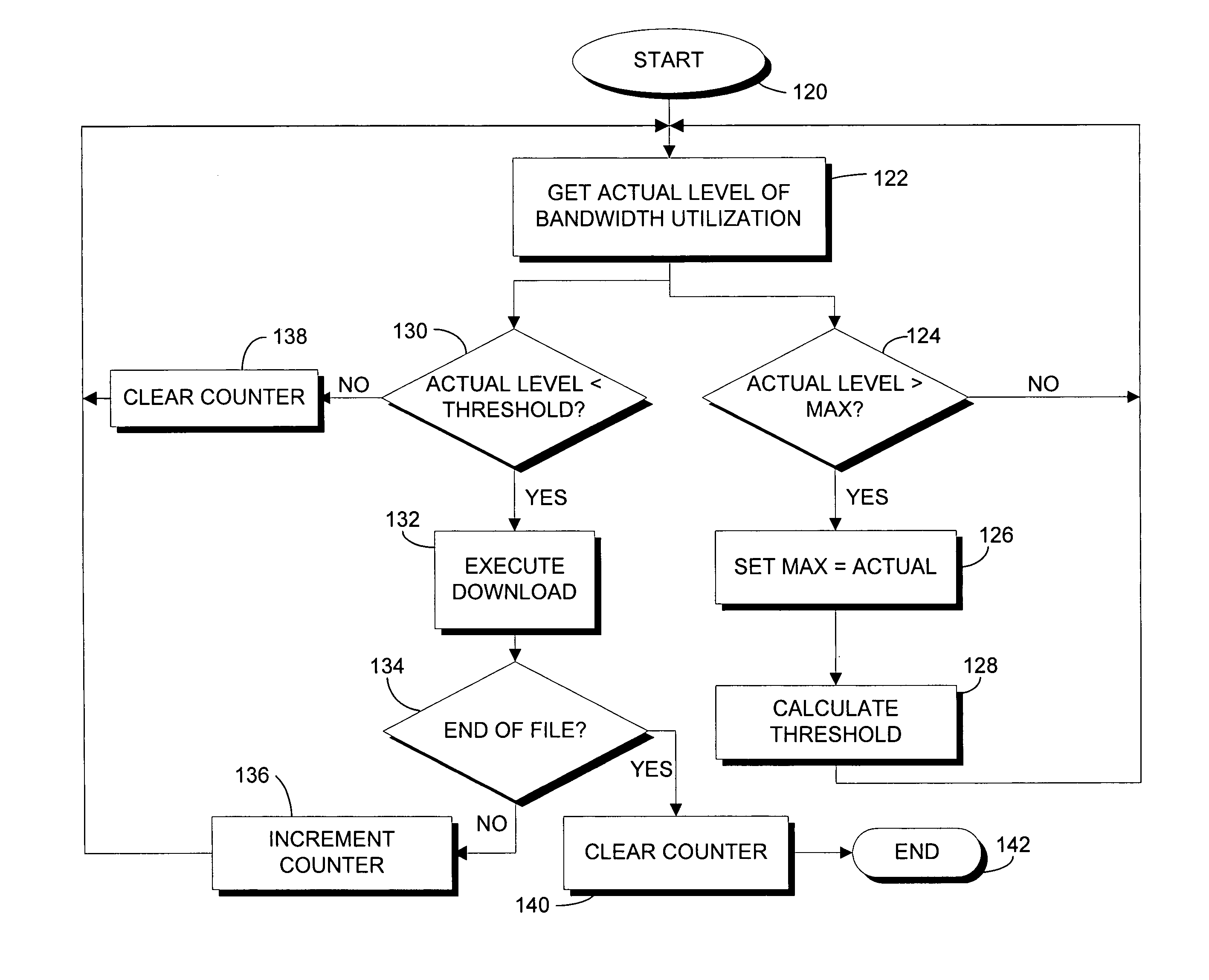
A method and apparatus for providing a load balanced circuit path between a source node and a destination node within a SONET ring comprising a plurality of nodes and connected by links by iteratively selecting facilities within a link that have bandwidth utilization levels that are below a threshold level. In an alternative embodiment, an alternate path is selected in case facilities meeting the threshold level can not be found. The threshold level is changed incrementally if facilities and links within the first path and / or alternate path do not meet the threshold levels.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Adaptive bass processing system
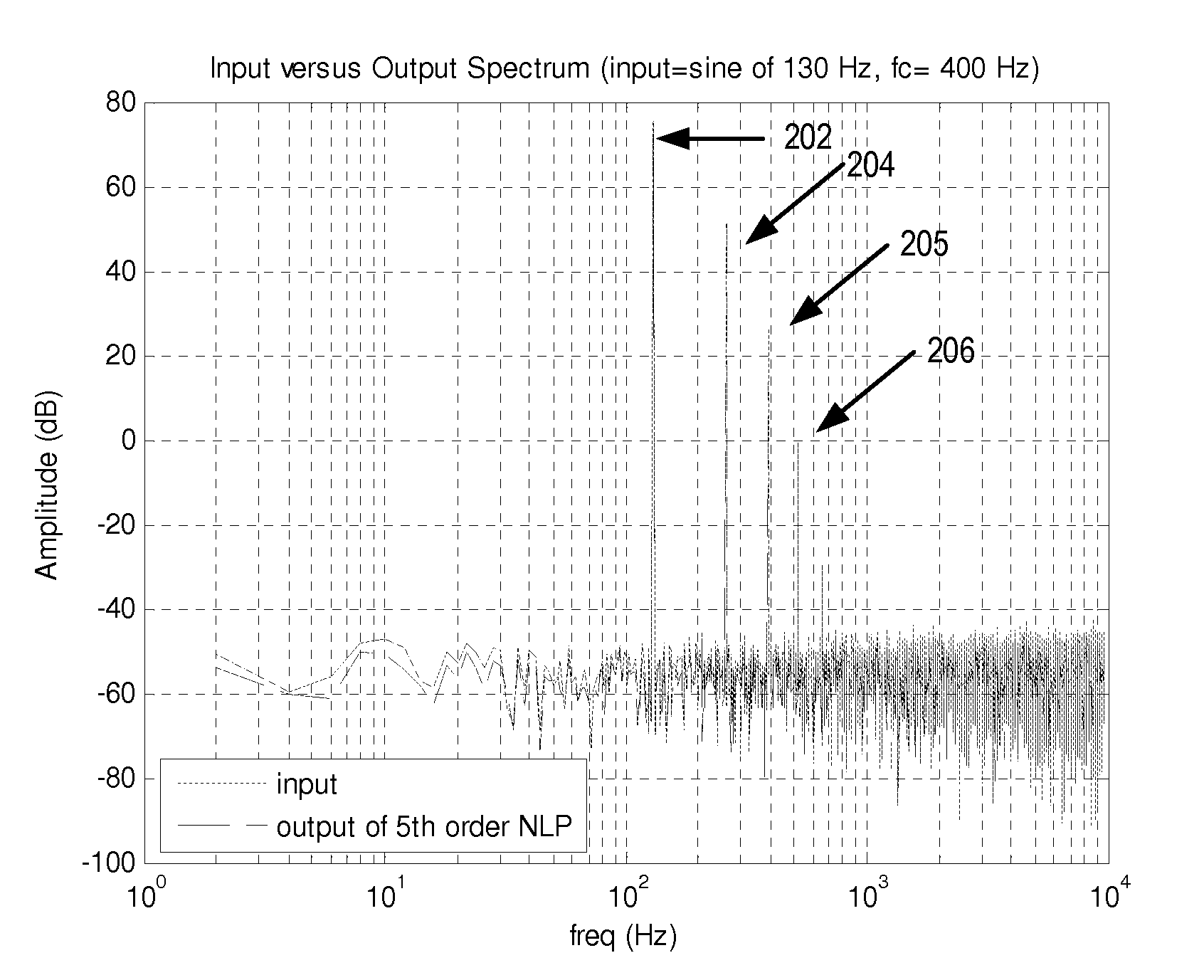
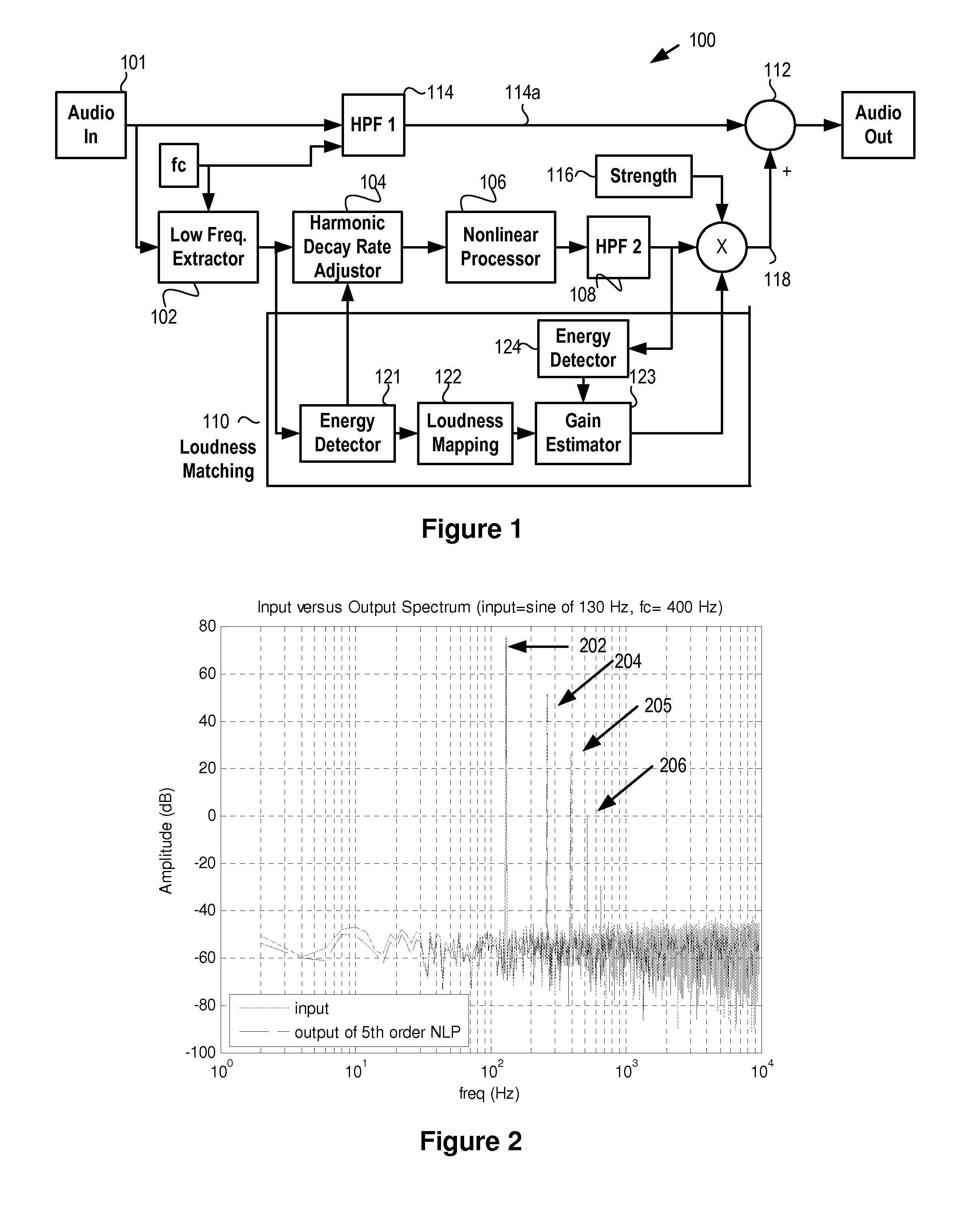
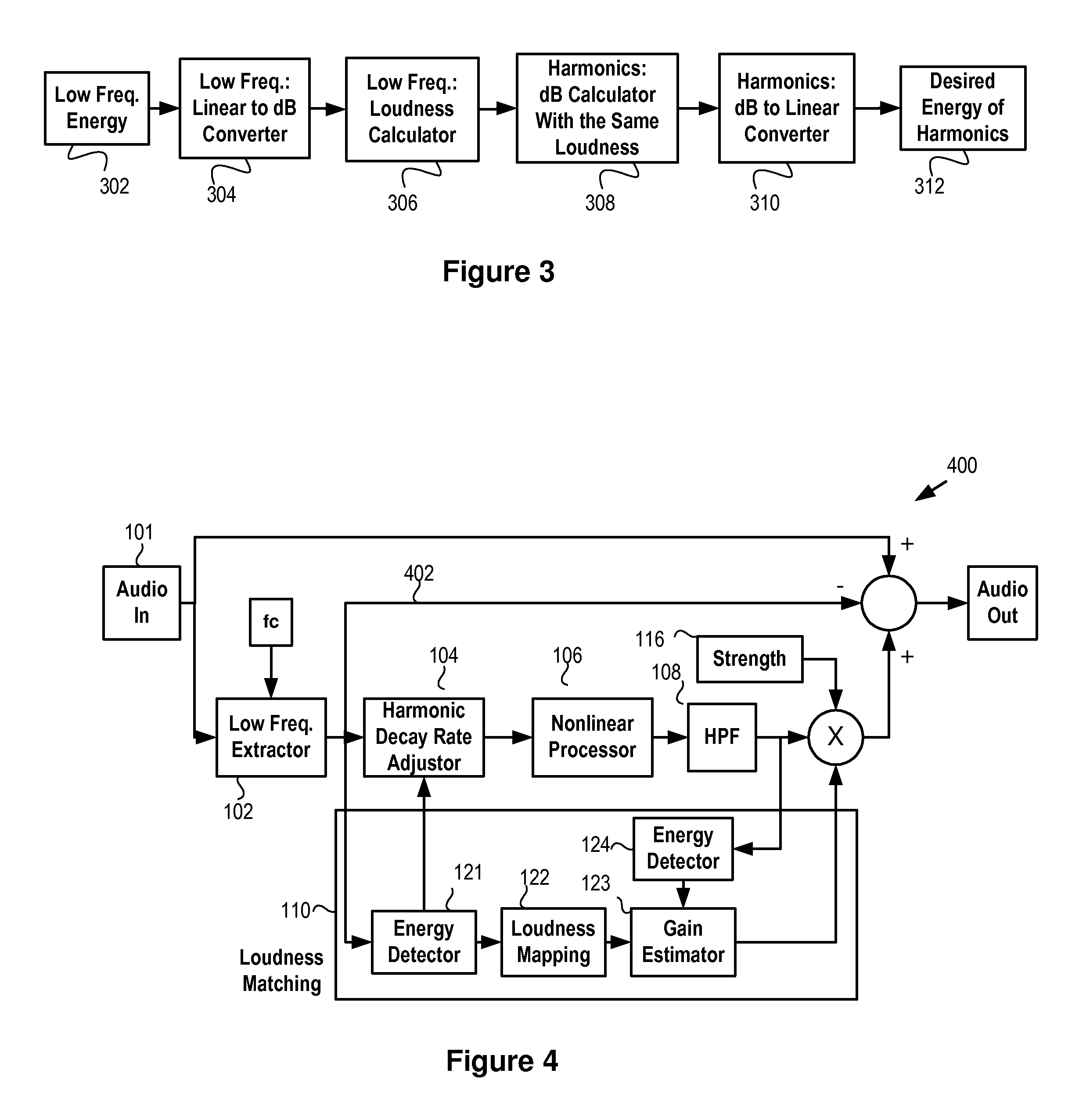
InactiveUS20150146890A1Good audioGeneration is simple and effectiveGain controlFrequency response correctionHarmonicTransducer
An effective and simple psychoacoustic bass generation system generates a harmonic signal having inter-modulation controllable to remain below a threshold level and includes a high-pass filter configured to pass harmonics which are reproducible with fidelity by the loudspeaker or other transducer and a loudness matching block configured to compensate the loudness of the desired harmonics to match the loudness of the original signal.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
Indirect Fluid Flow Measurement
ActiveUS20100094268A1Surgical instruments for heatingSuction devicesEngineeringBelow threshold level
A method for ablating tissue comprising controlling a heating element using a variable phase angle control to heat an ablation fluid to a desired temperature and determining a heating percentage corresponding to a percentage of a maximum available heating power represented by a current level of power supplied to the heating element and, when the heating percentage remains below a threshold level for a predetermined period of time, indicating a flow obstruction condition of the fluid.
Owner:MINERVA SURGICAL
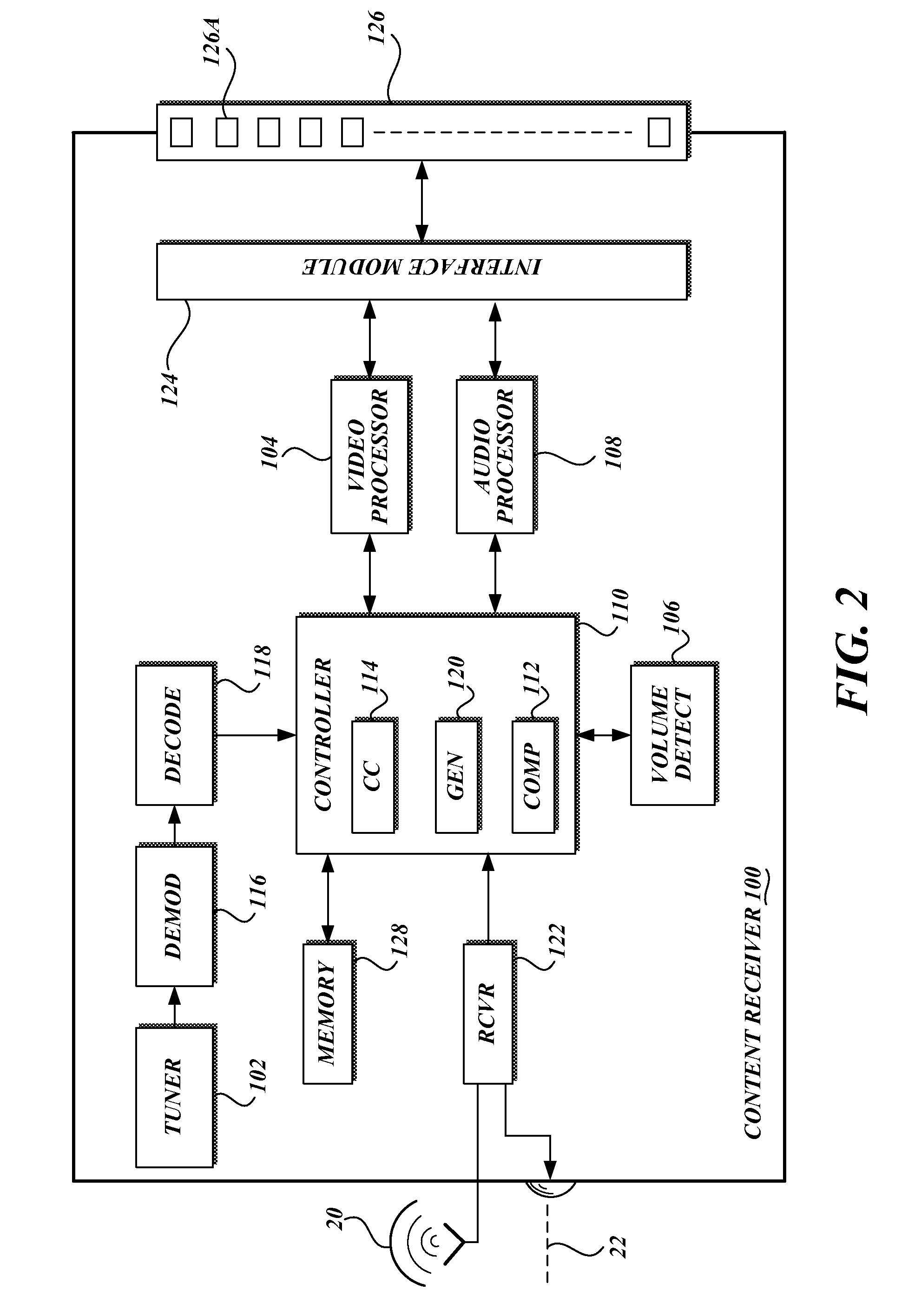
Volume level-based closed-captioning control
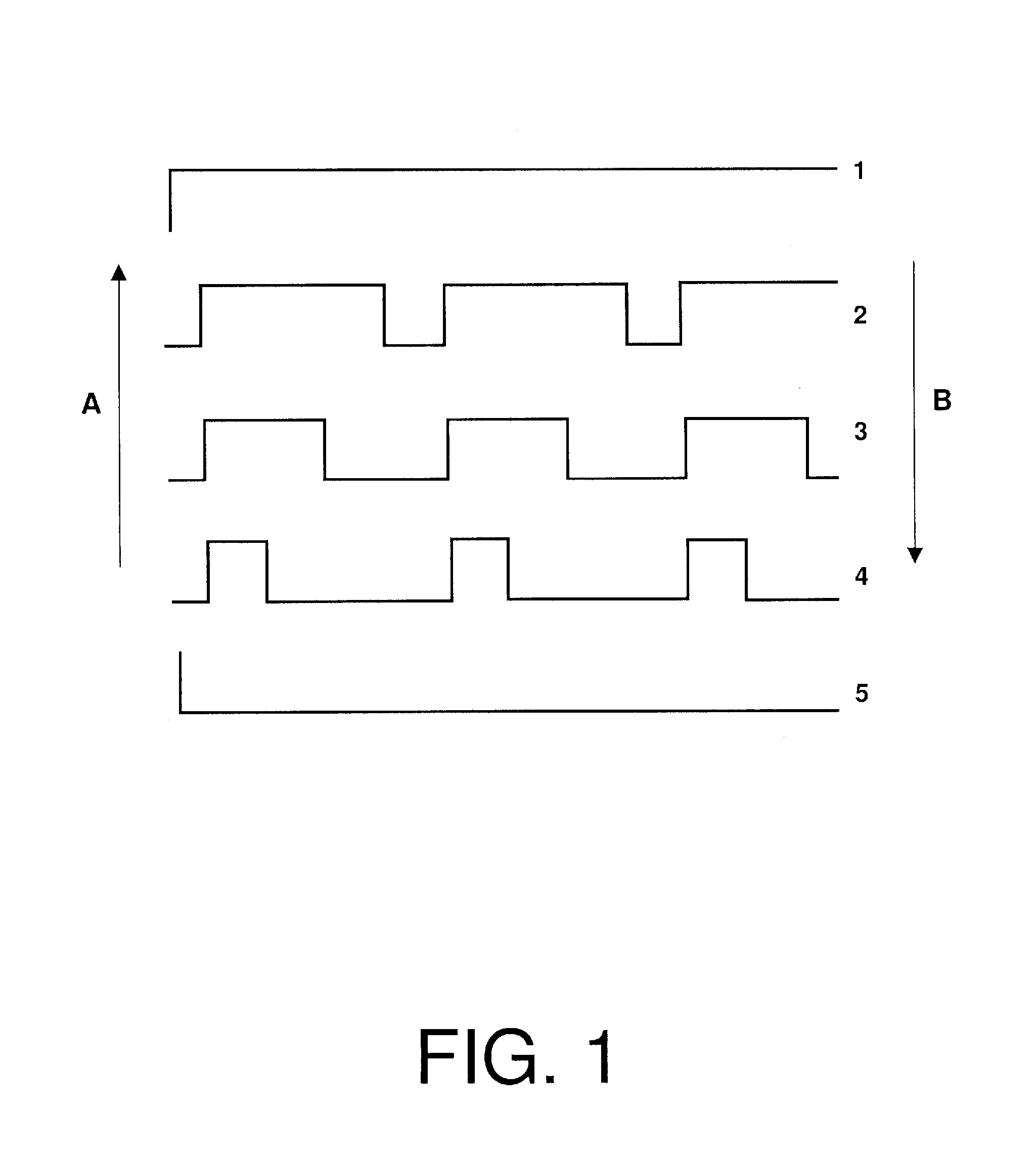
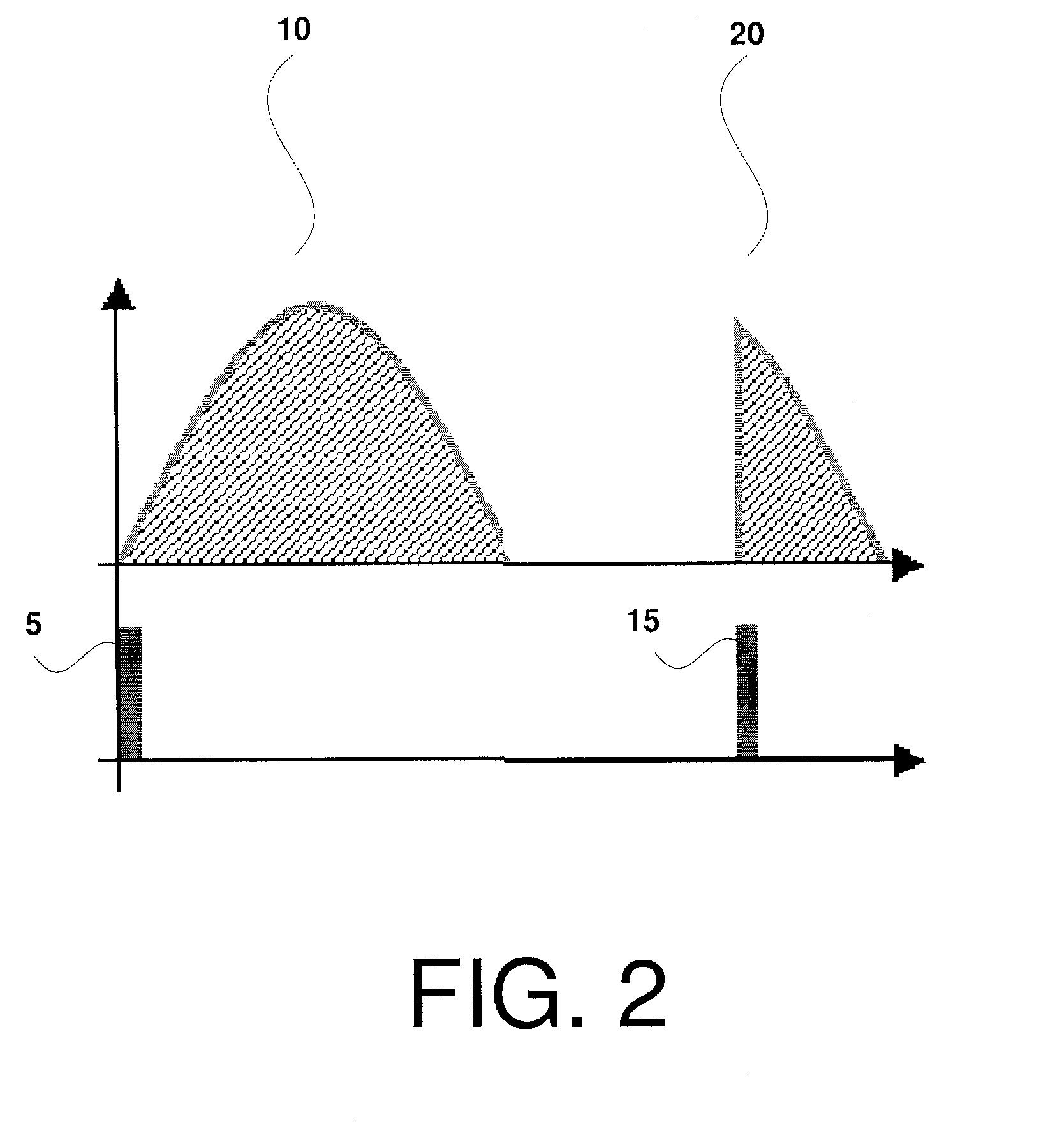
ActiveUS20140184905A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationClosed captioningContent determination
Methods and apparatus are provided for a control of closed captioning based on an audio volume level. A content receiver detects that a volume of an audio of a video presentation has been adjusted by a user, and determines the adjusted audio volume level that results from the adjustment. The content receiver compares the resulting adjusted audio volume level to a threshold level. When the content determines that the adjusted audio volume level is under the threshold level, it enables closed captioning of the video presentation, thus presenting the user with both audio and closed captioning. When the content receiver determines that the adjusted audio volume level is above the threshold level, it disables closed captioning for the video presentation. The content receiver may use a microphone to determine the adjusted audio volume level.
Owner:DISH TECH L L C
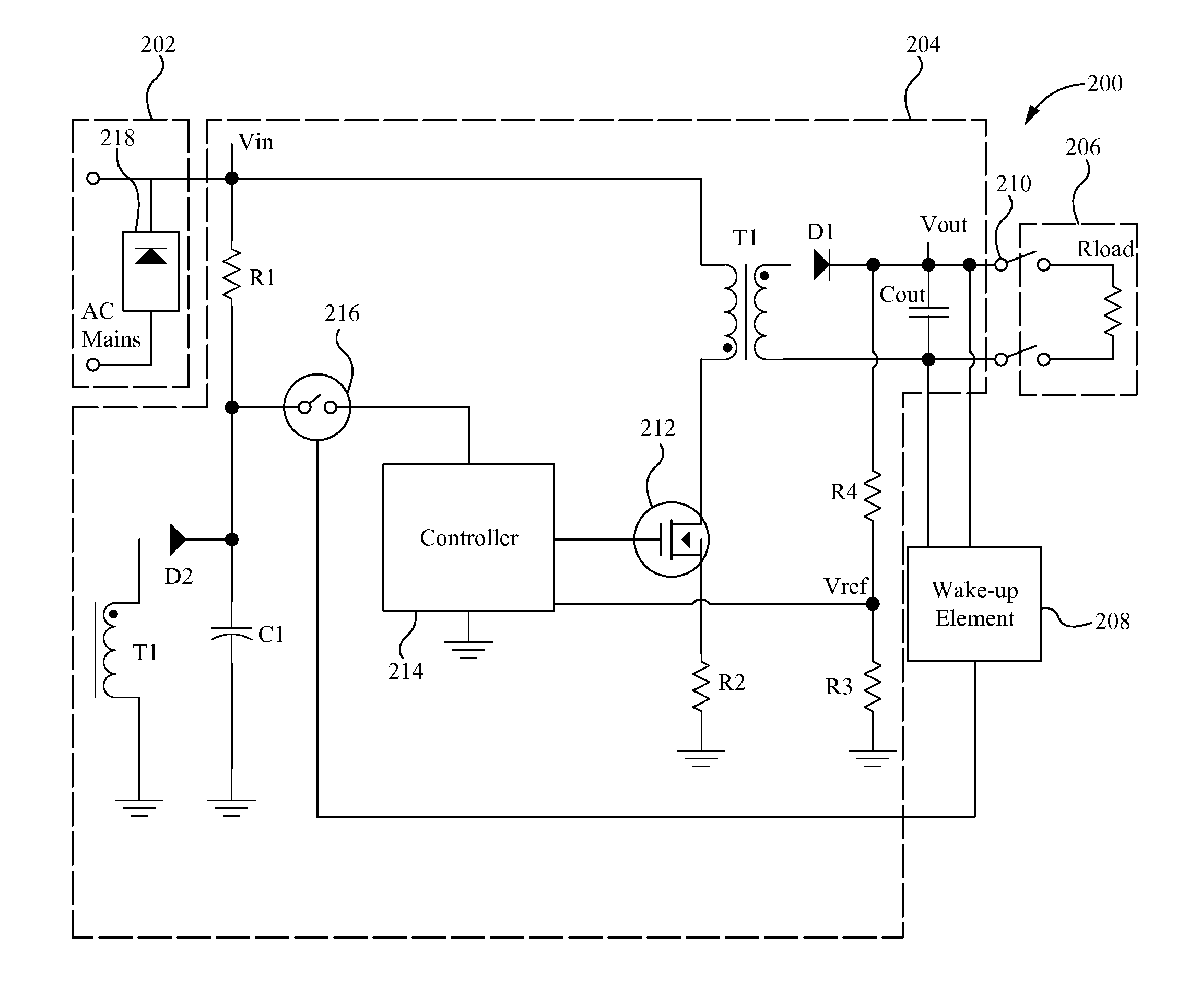
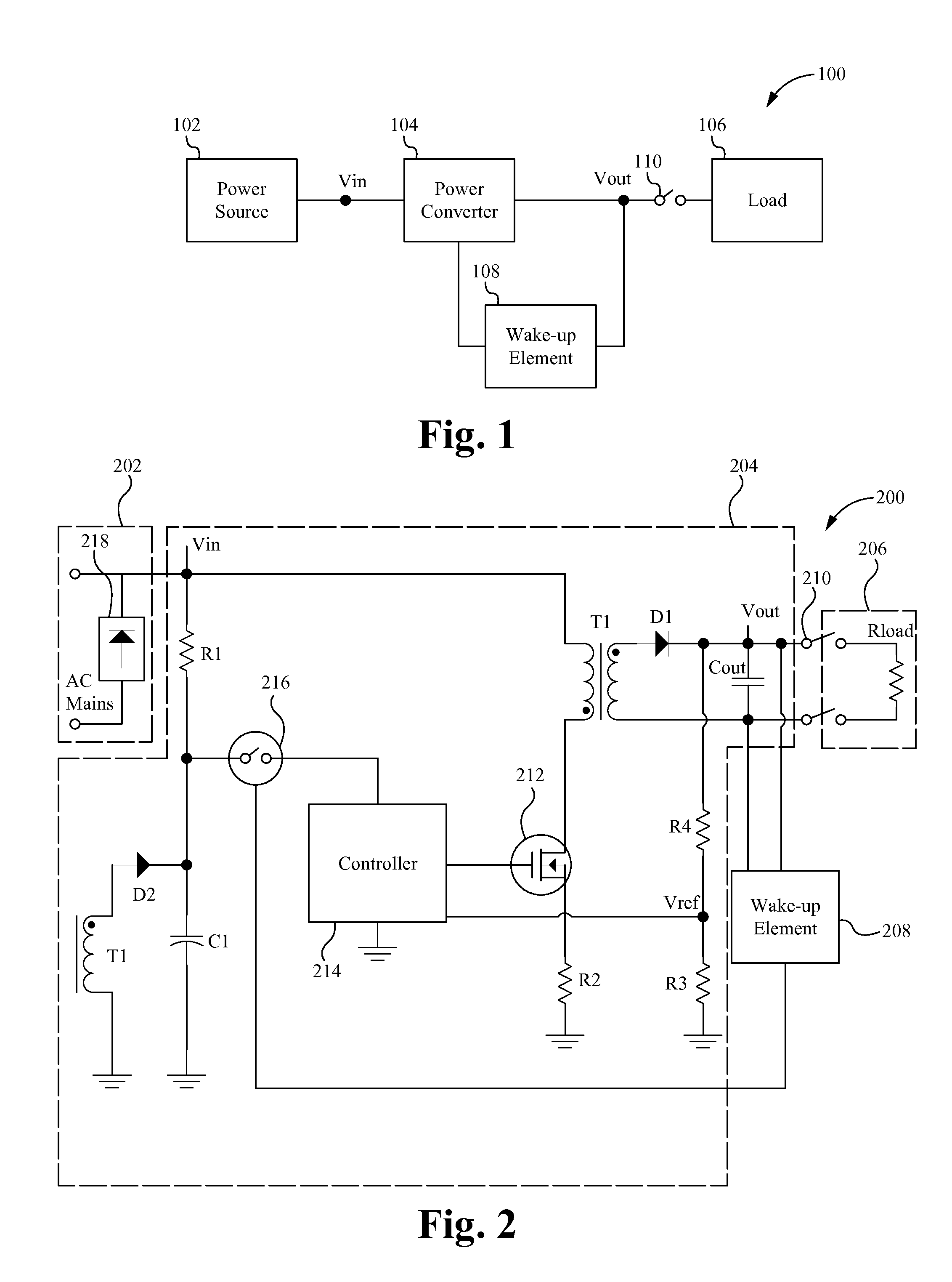
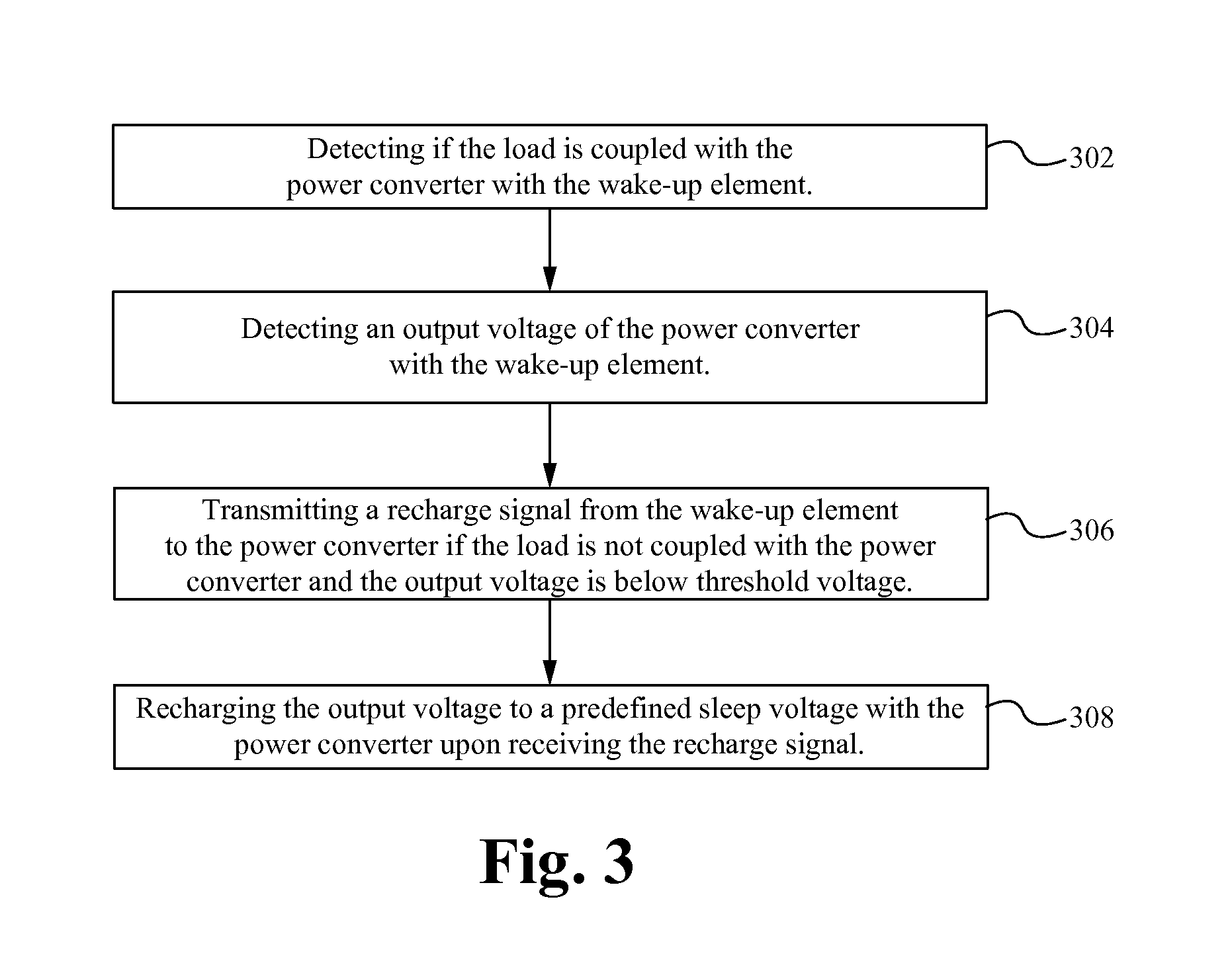
Power converters with quasi-zero power consumption
ActiveUS20140016359A1Maximize efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringBelow threshold level
A power converter system, method and device powers a load when coupled to the load and draws a quasi-zero amount of power from the power supply when not coupled to the load. The power converter system maintains an output voltage such that the power converter system is able to properly “wake-up” when a load is coupled by intermittently operating the power converter for a preselected number of cycles when it is detected that the output voltage has fallen below a threshold level.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
Systems and methods for executing a training program based on player DNA
ActiveUS20180290060A1Reduce network trafficIncreased network trafficVideo gamesTeaching apparatusProgram planningSkill sets
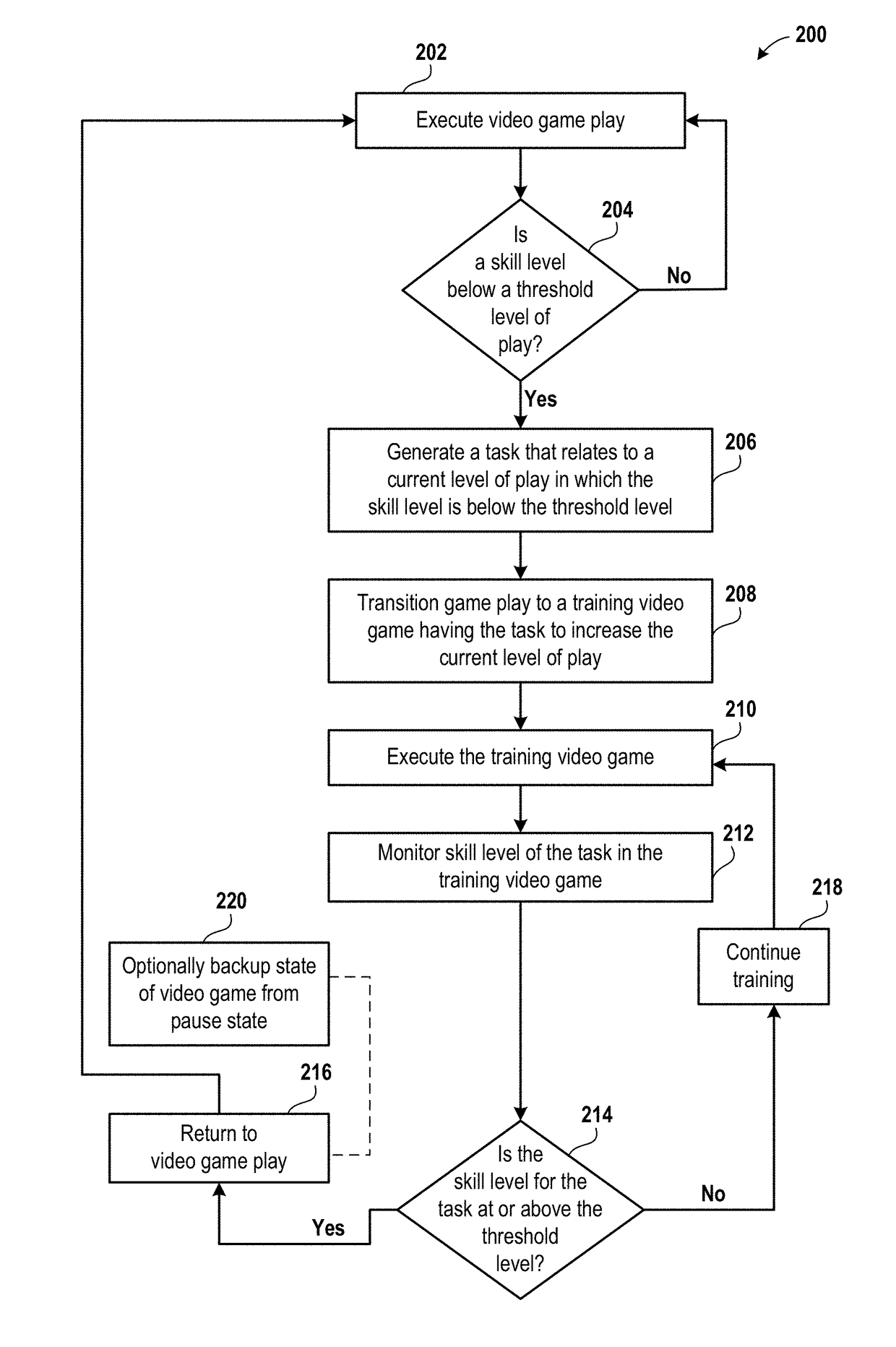
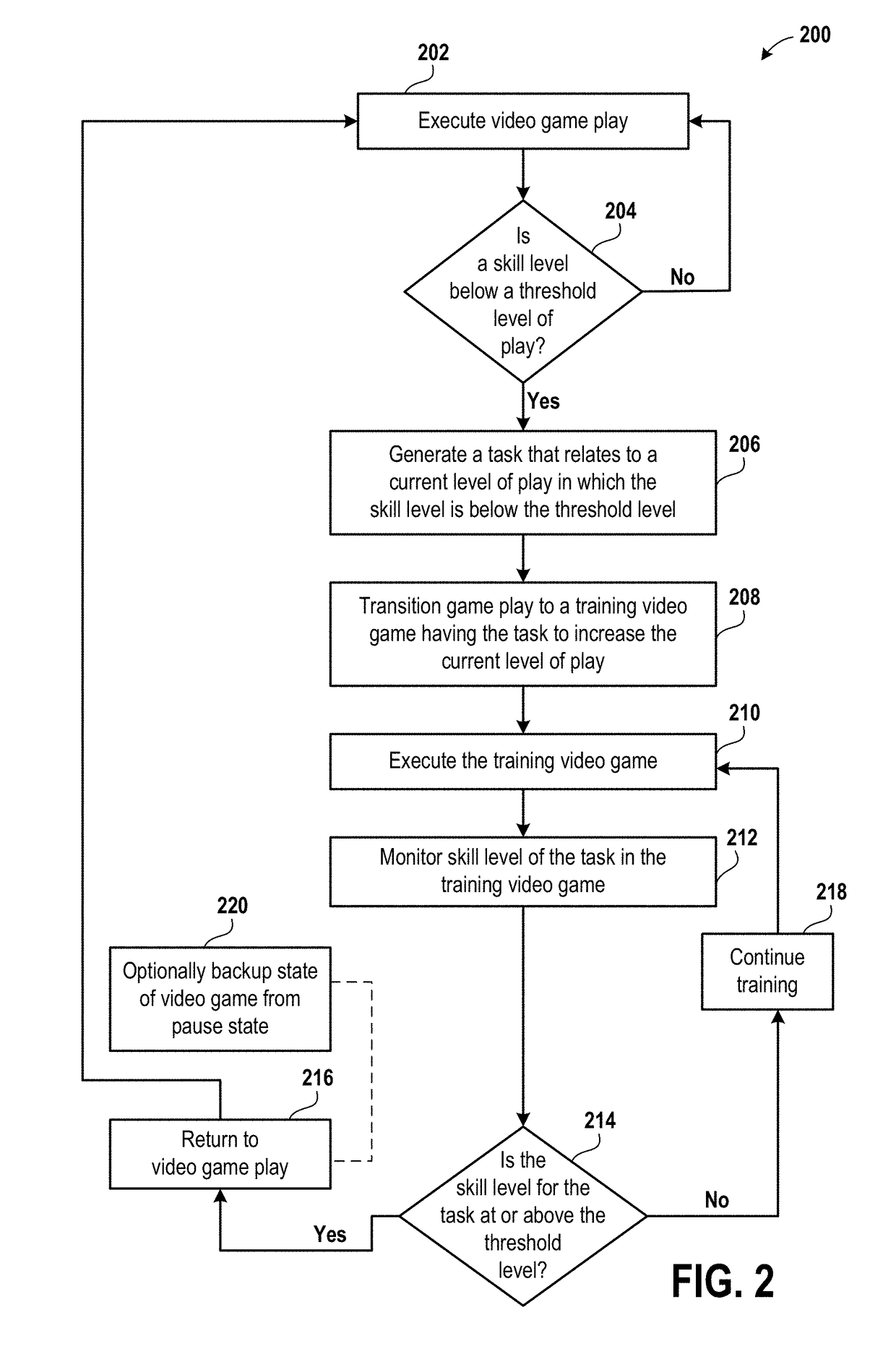
A method for executing a training program based on player DNA is described. The method includes executing a video game and determining whether a skill level of a user is below a threshold level of play. The method includes generating a task that relates to a current level of play of the video game in which the skill level is below the threshold level and transitioning the video game to a training video game program having the task to increase the current level of play. The method includes executing the training video game program and monitoring the skill level for the task in the training video game program. The method includes determining whether the skill level for the task exceeds the threshold level. The method includes returning to an execution of the video game upon determining that the skill level for the task exceeds the threshold level.
Owner:SONY INTERACTIVE ENTRTAINMENT LLC
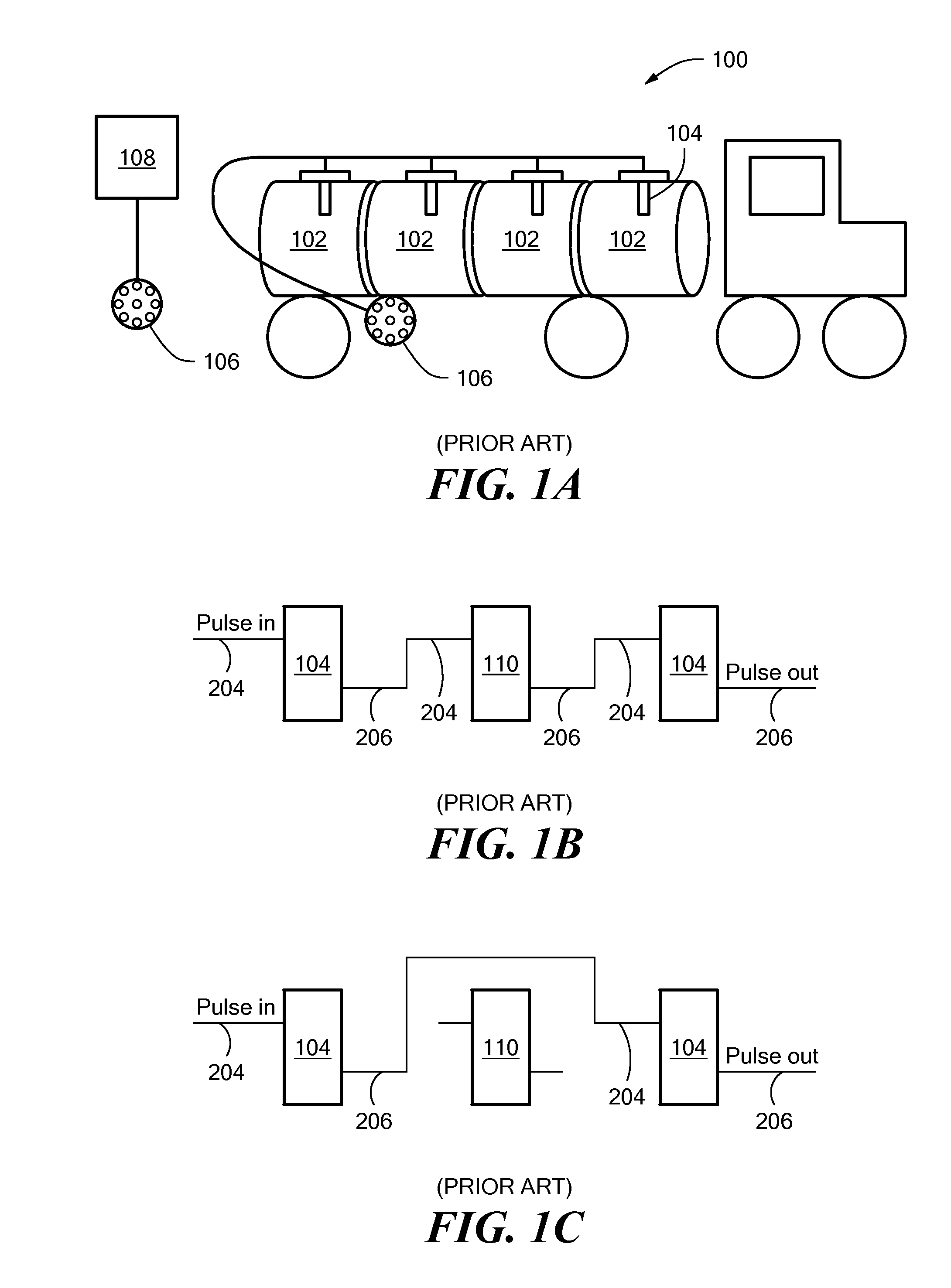
Truck compartment verification system with alternate truck id
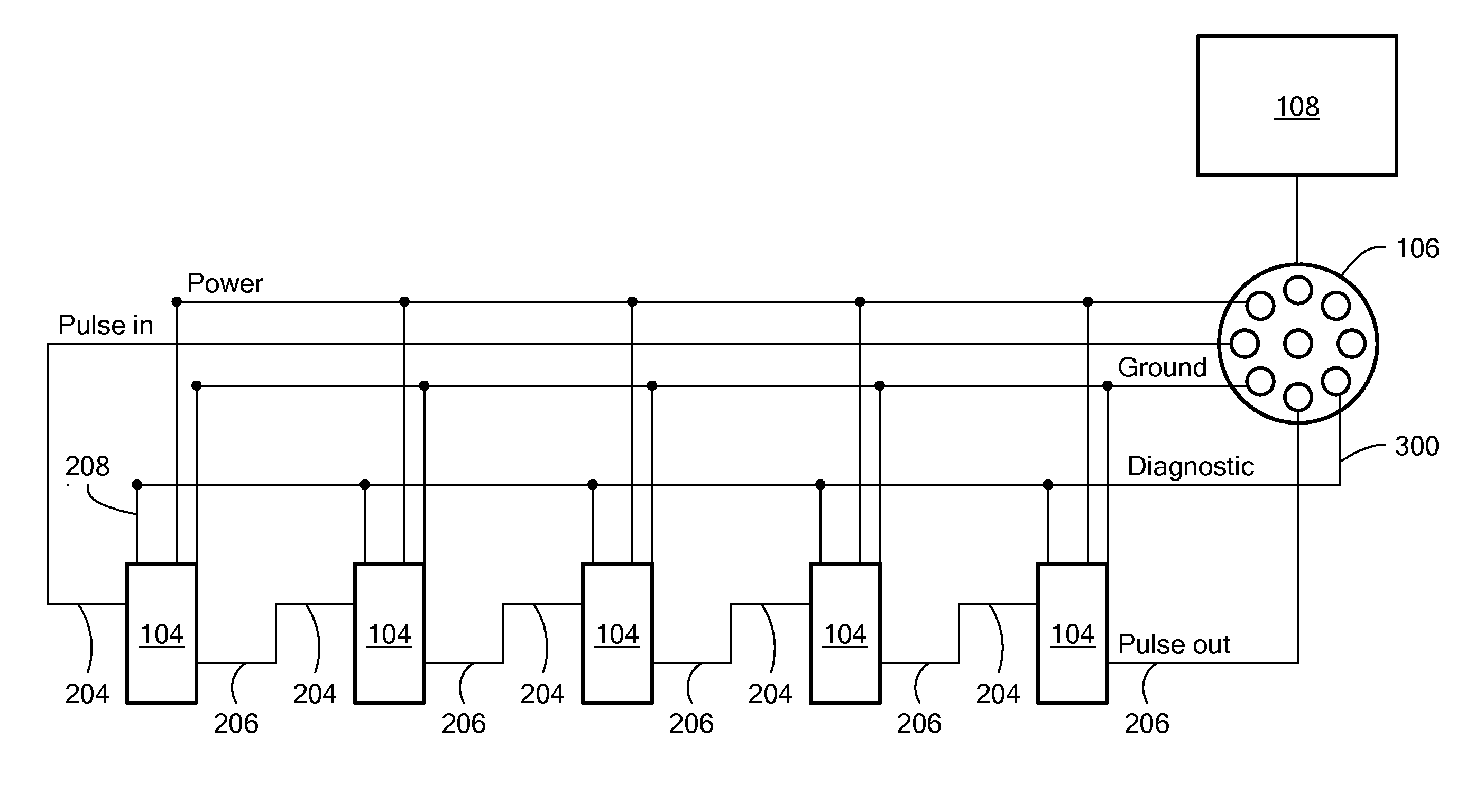
A fluid overfill detection and control system for controlling the transfer of fluid into a transport vehicle having multiple fluid compartments includes a plurality of overfill sensors that are connected in series with one another and that each produces an output pulse when the fluid level in its associated compartment is below a threshold level. A diagnostic line connected to each of the overfill sensors provides a diagnostic signal indicative of the number of overfill sensors that generate an output pulse, while a module on the vehicle provides an indication of the total number of overfill sensors located in the vehicle. To prevent a hazard due to the possible bypass of a overfill sensor, the controller compares the overfill sensor count signal to the diagnostic signal and inhibits the transfer of fluid into the vehicle if the values do not match.
Owner:SCULLY SIGNAL CO
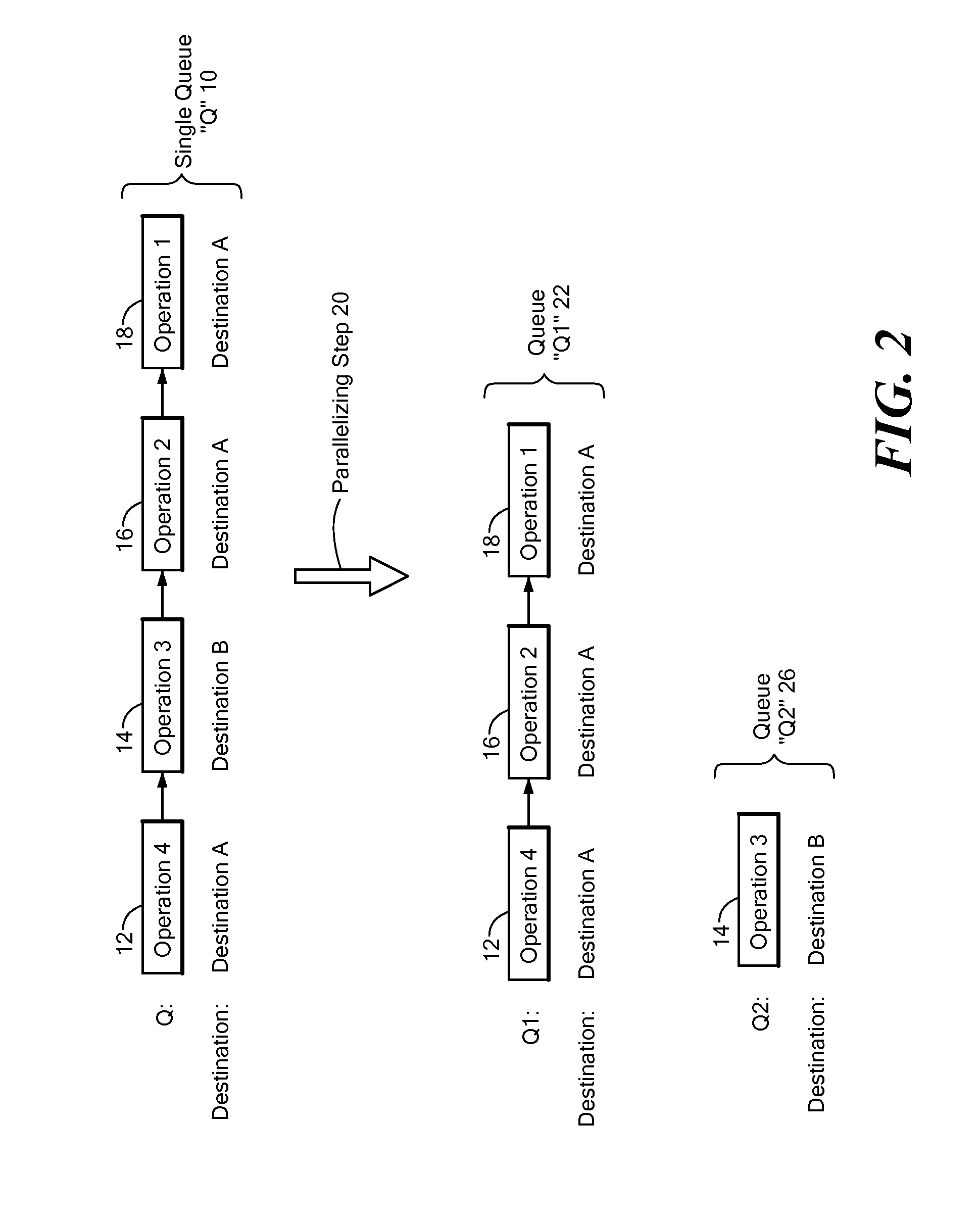
Method and system for dynamic queue splitting for maximizing throughput of queue based operations while maintaining per-destination order of operations
InactiveUS20080123671A1Reduce continuityImprove parallelismData switching by path configurationOrder of operationsBelow threshold level
A system for providing dynamic queue splitting to maximize throughput of queue entry processing while maintaining the order of queued operations on a per-destination basis. Multiple queues are dynamically created by splitting heavily loaded queues in two. As queues become dormant, they are re-combined. Queue splitting is initiated in response to a trigger condition, such as a queue exceeding a threshold length. When multiple queues are used, the queue in which to place a given operation is determined based on the destination for that operation. Each queue in the queue tree created by the disclosed system can store entries containing operations for multiple destinations, but the operations for a given destination are all always stored within the same queue. The queue into which an operation is to be stored may be determined as a function of the name of the operation destination. Just as a single queue may be split into two queues, if one of the two queues starts backing up, the disclosed system may further split that queue into two. Thus each queue in the queue tree may be split into two new queues if its performance falls below a threshold level. Successively more bits from a function applied to destination names for operations may be used to determine specific queues into which operations should be placed as the depth of the queue tree increases.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com