Patents
Literature
326 results about "Physical phenomena" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
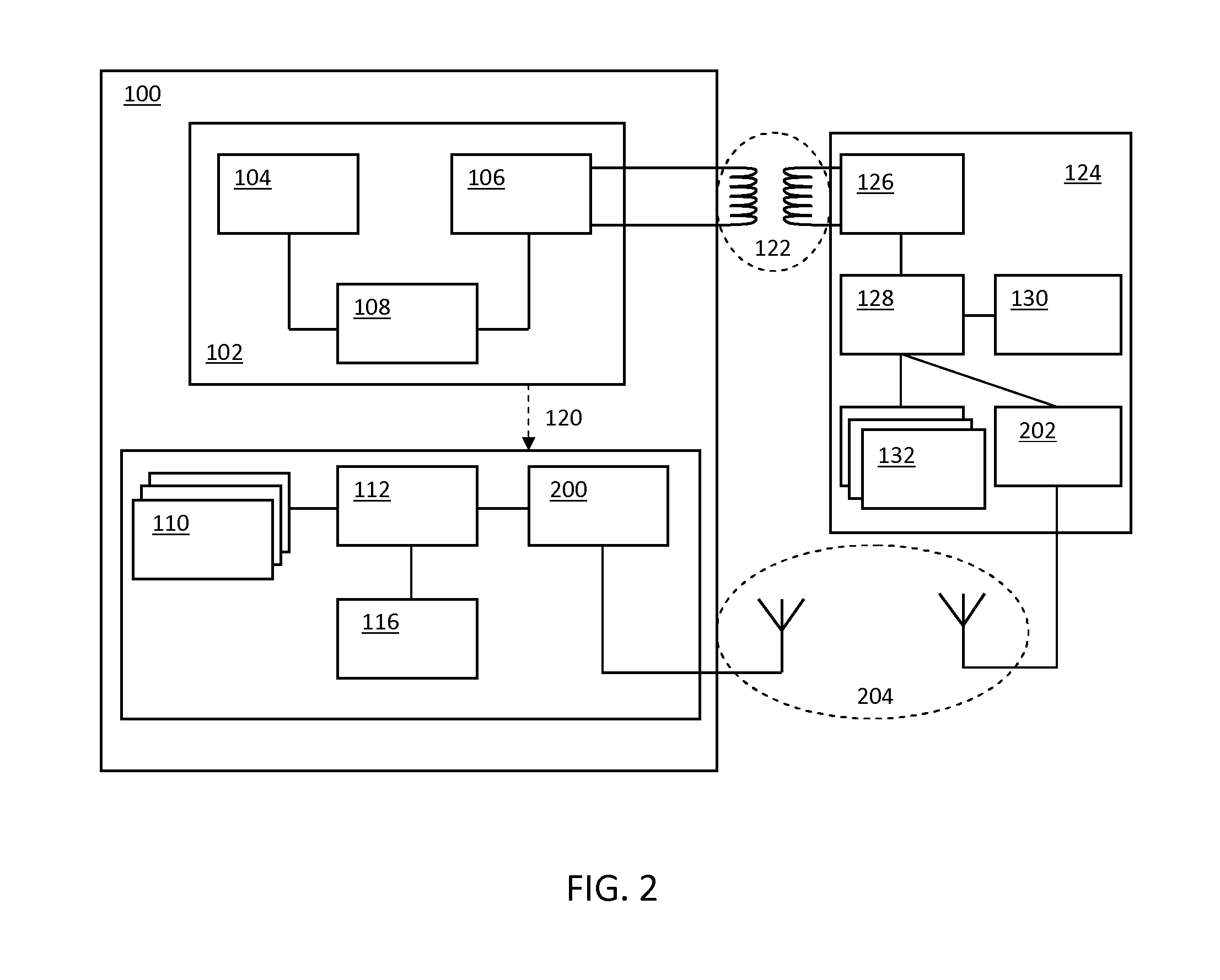
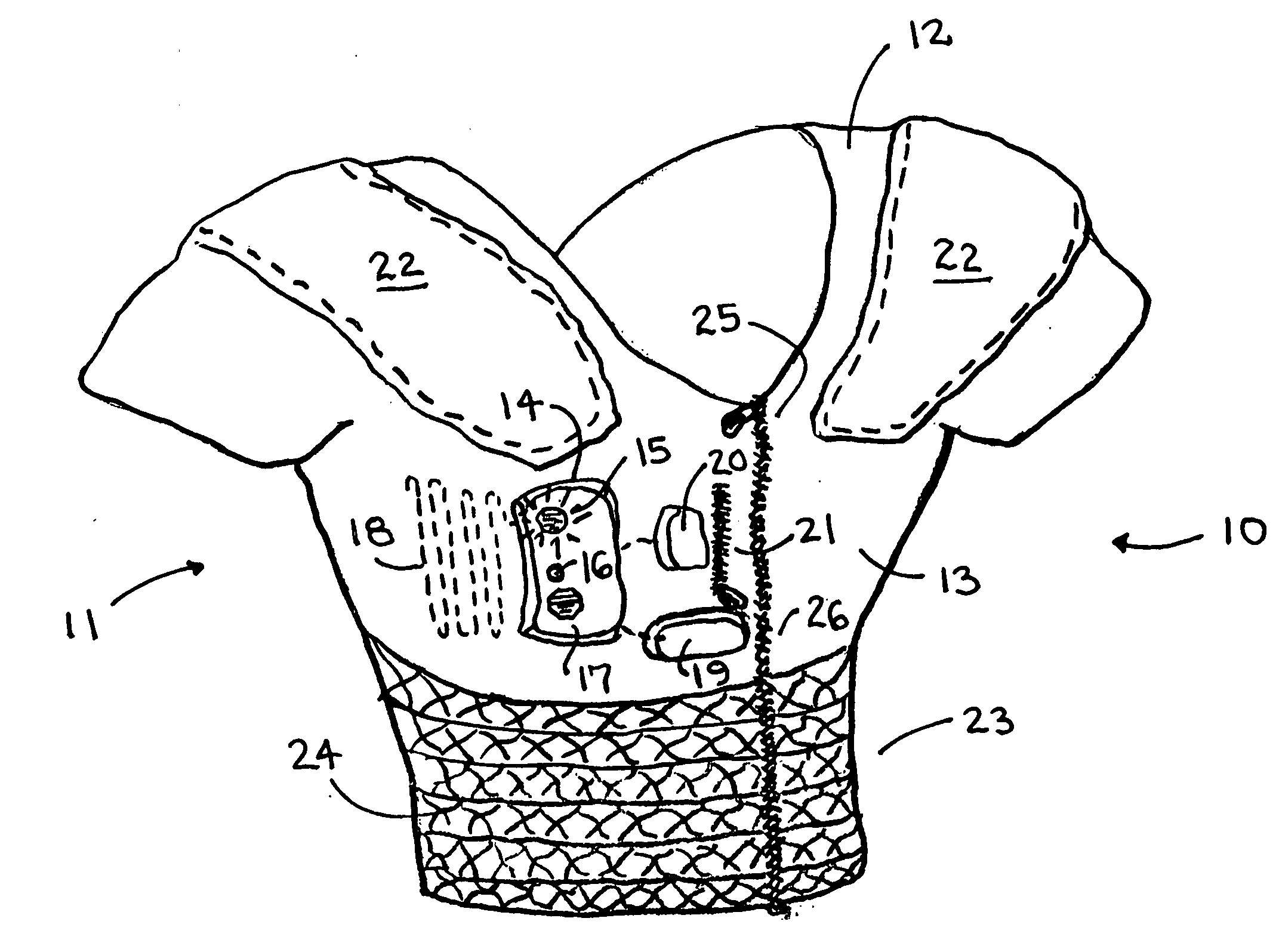
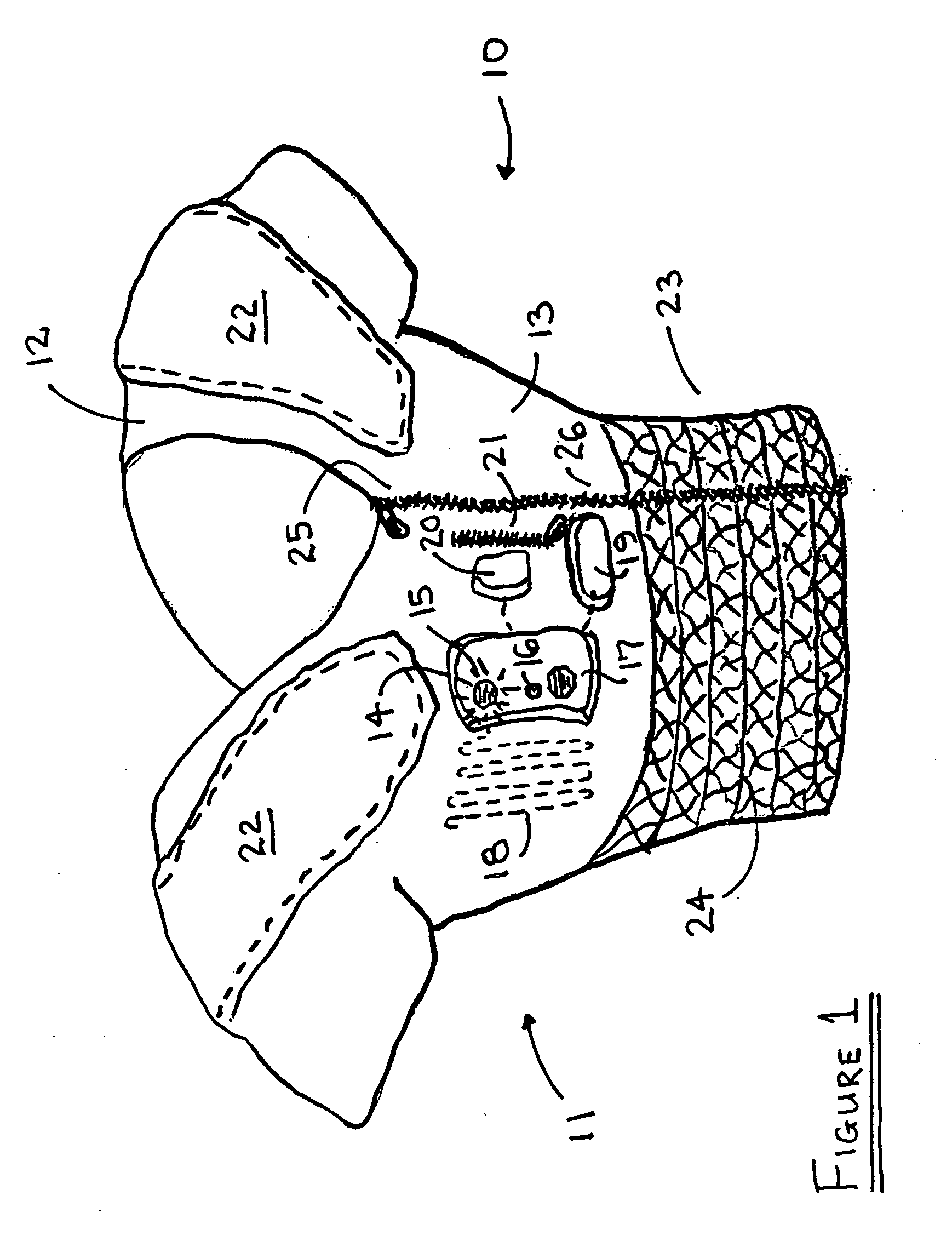
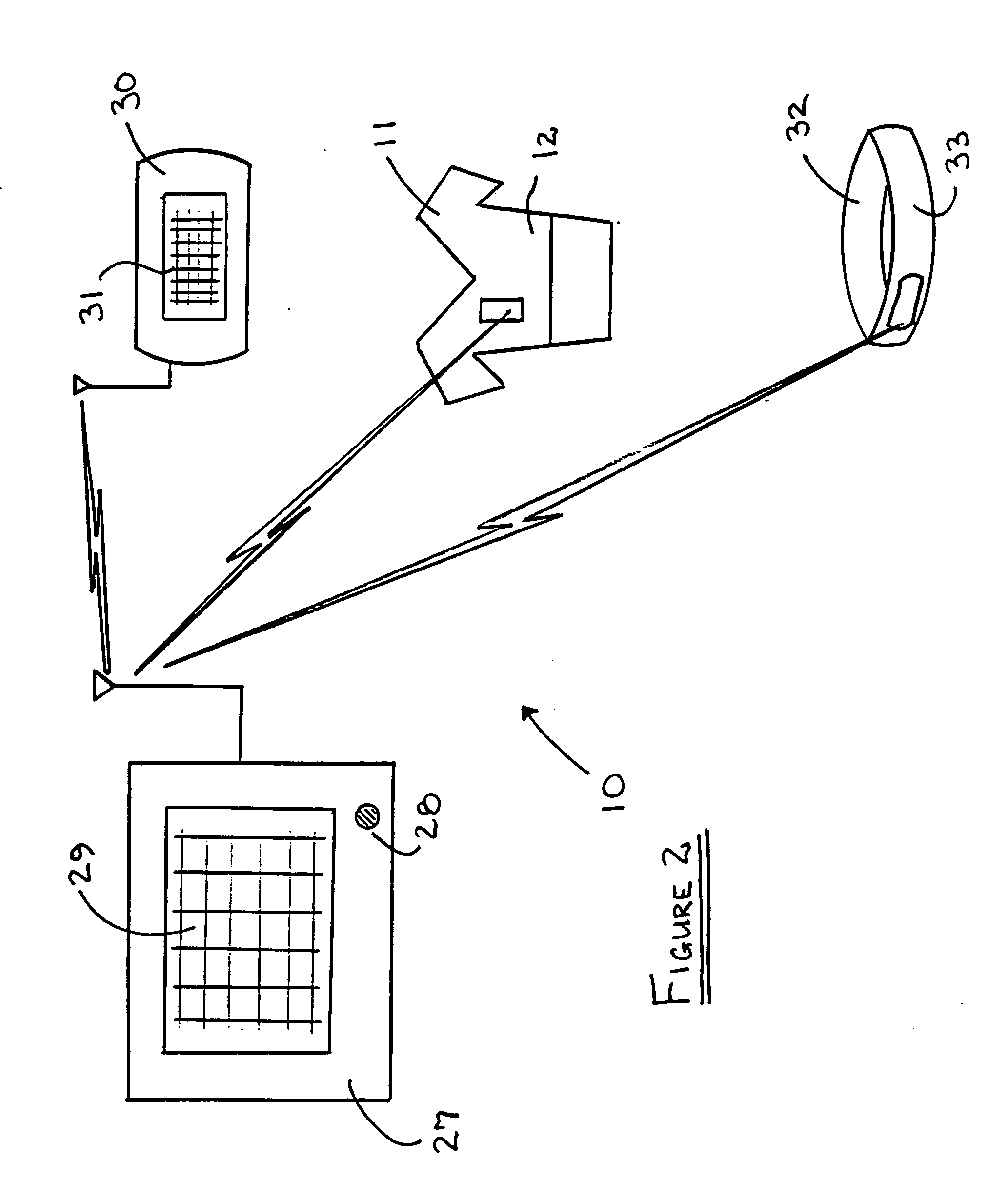
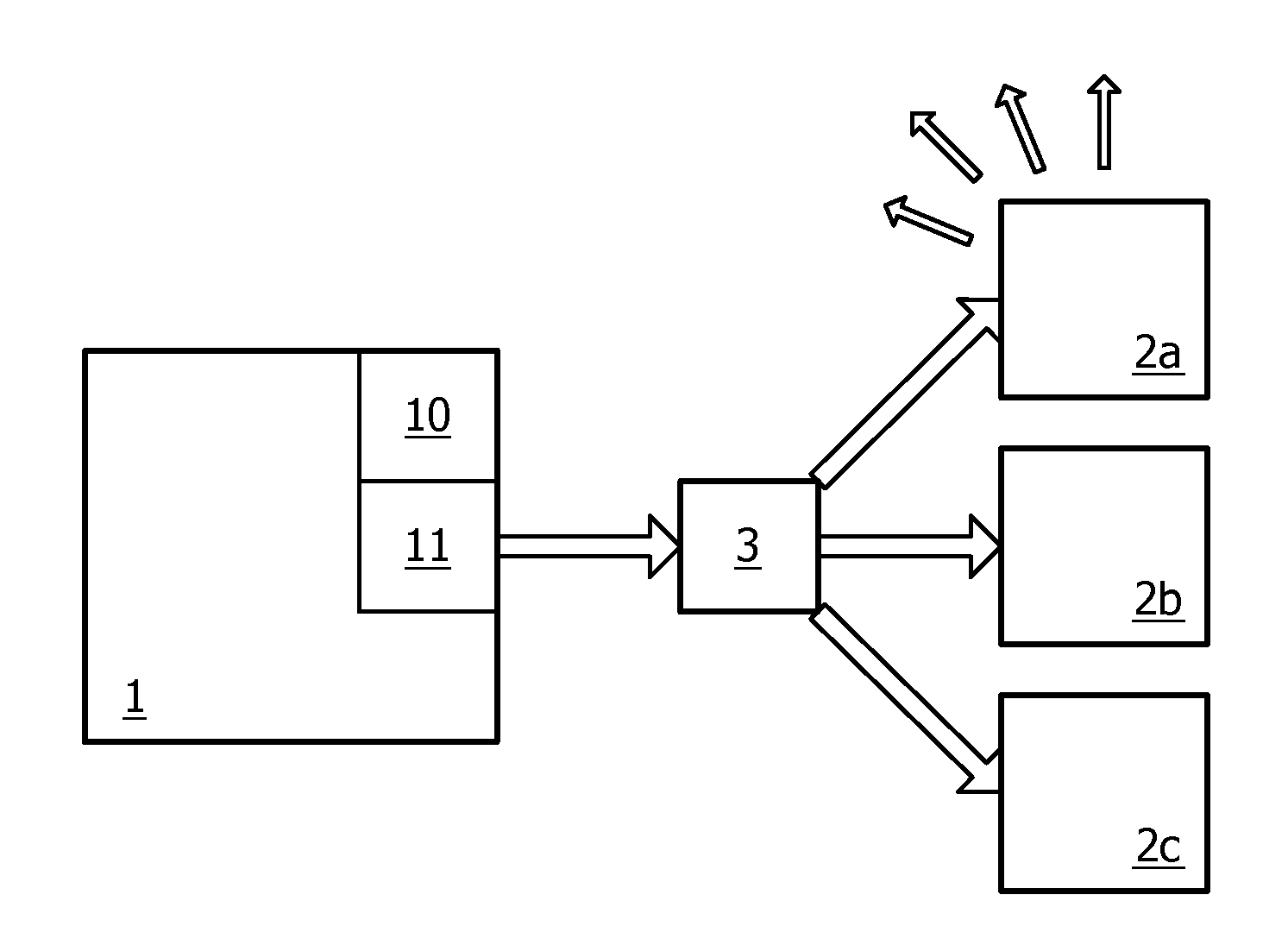
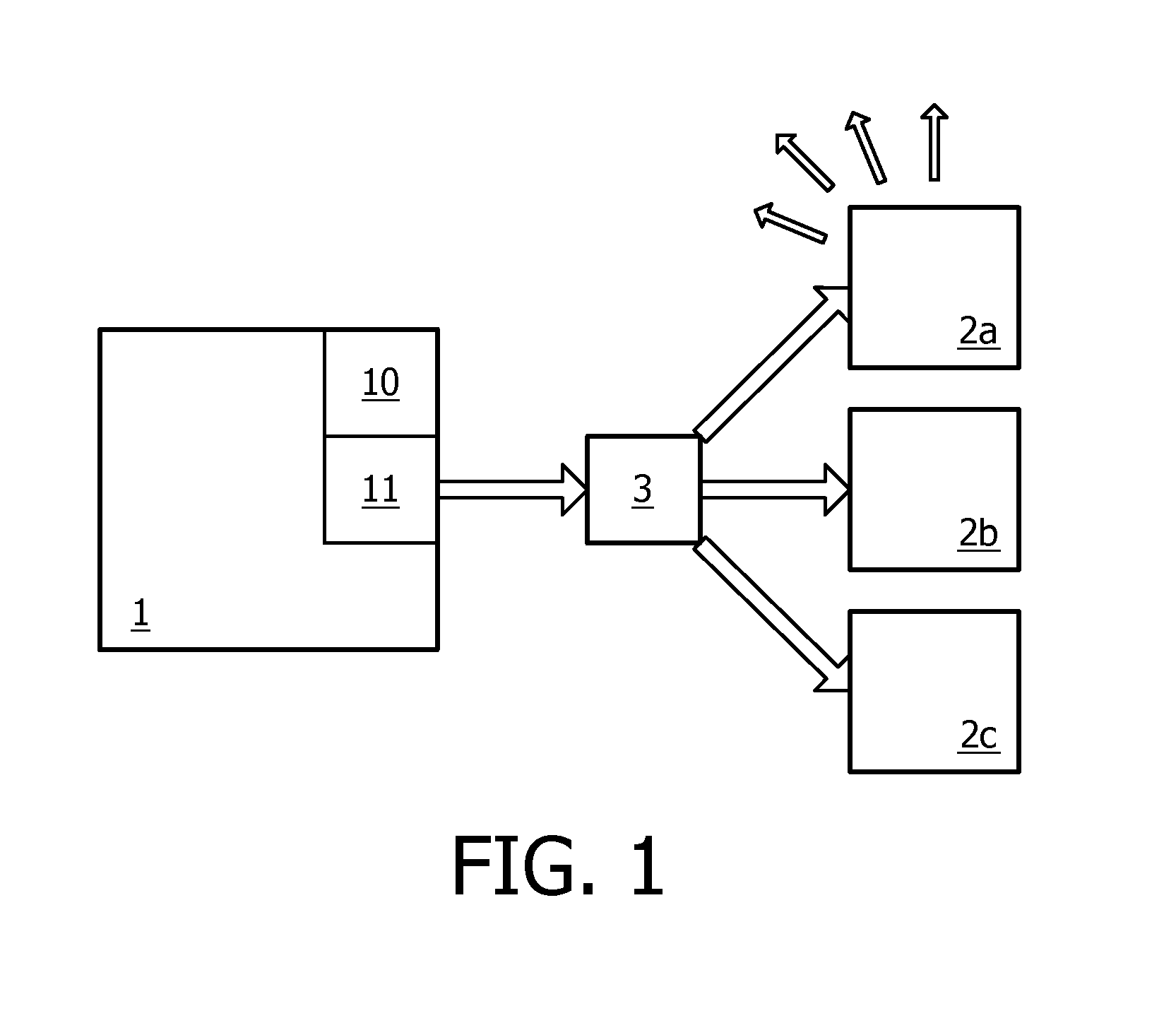
Modular communications apparatus and method
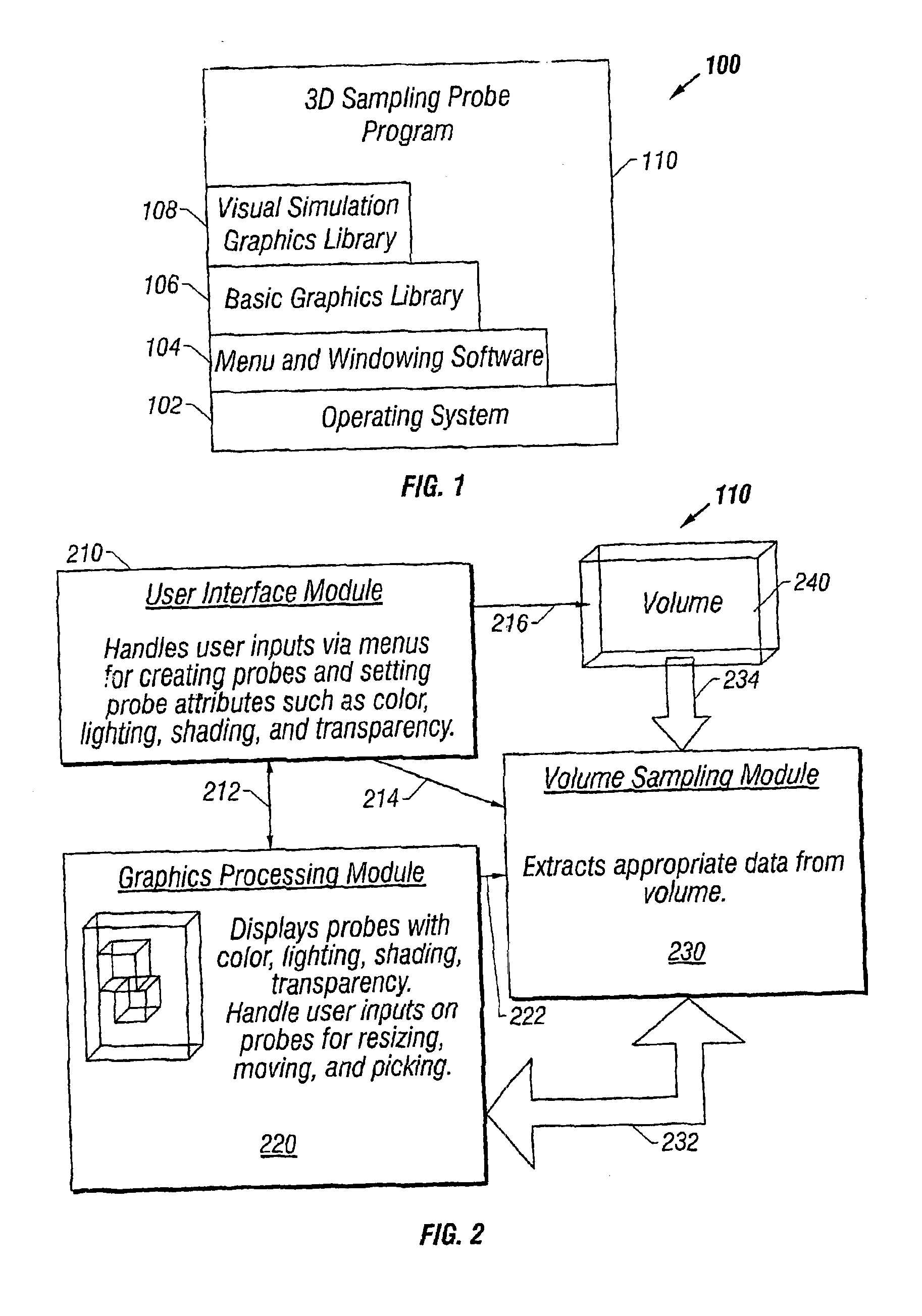
Briefly, and in accordance with an embodiment of the invention, a modular device for providing wireless services and a network of such devices. The modular device may include one or more modules including, but not limited to, a module for providing cell phone services, a module for providing conditioned power to other modules included in the modular device, a module for presenting wireless networking services, a module for bridging to other modular devices arranged in a network, a module for monitoring physical phenomena such as air quality, a module for providing public services such as public service announcements, and a module for storing data. Some embodiments include an integrated enclosure.
Owner:BAMBIC BRITT B +1
Electronic circuit
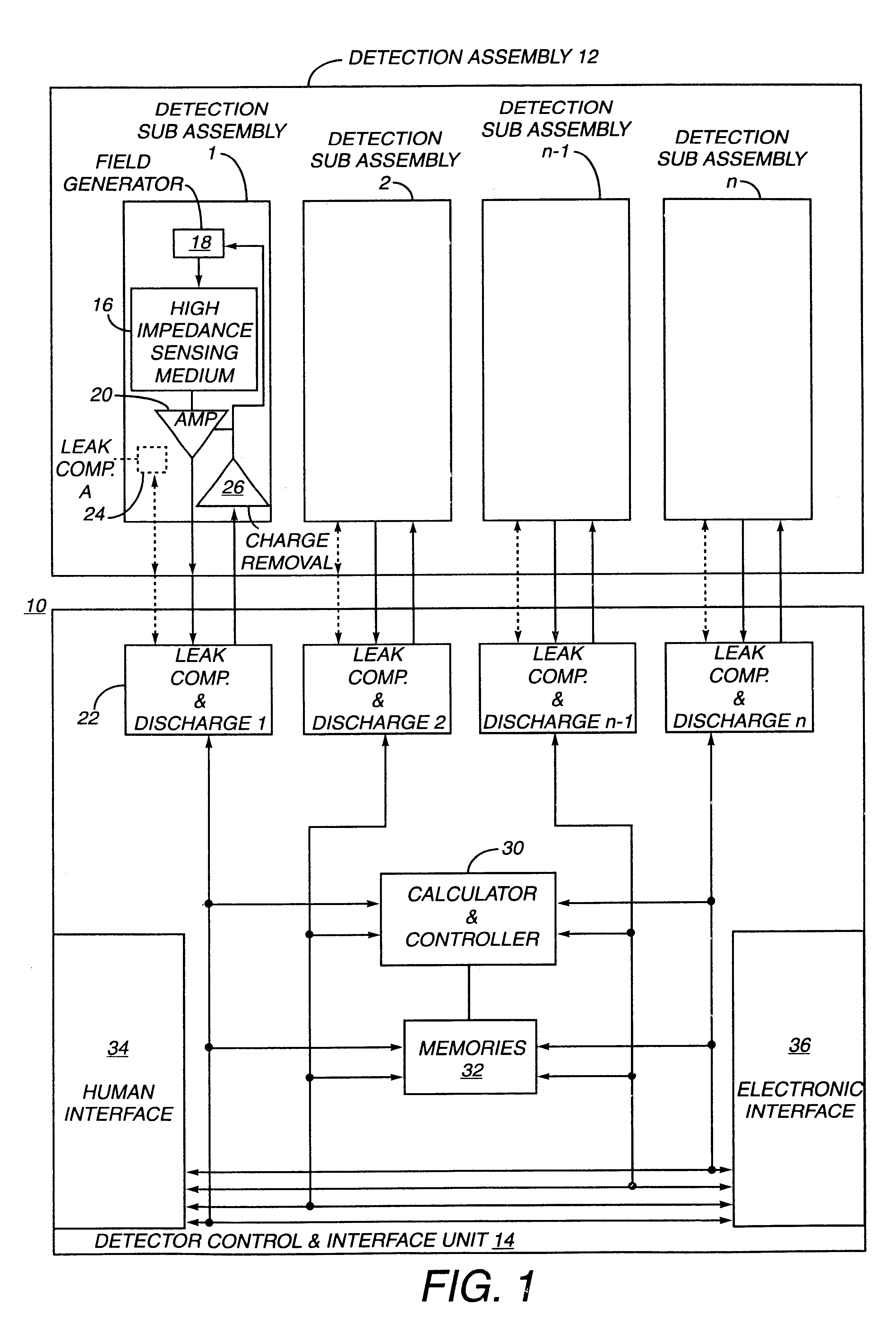
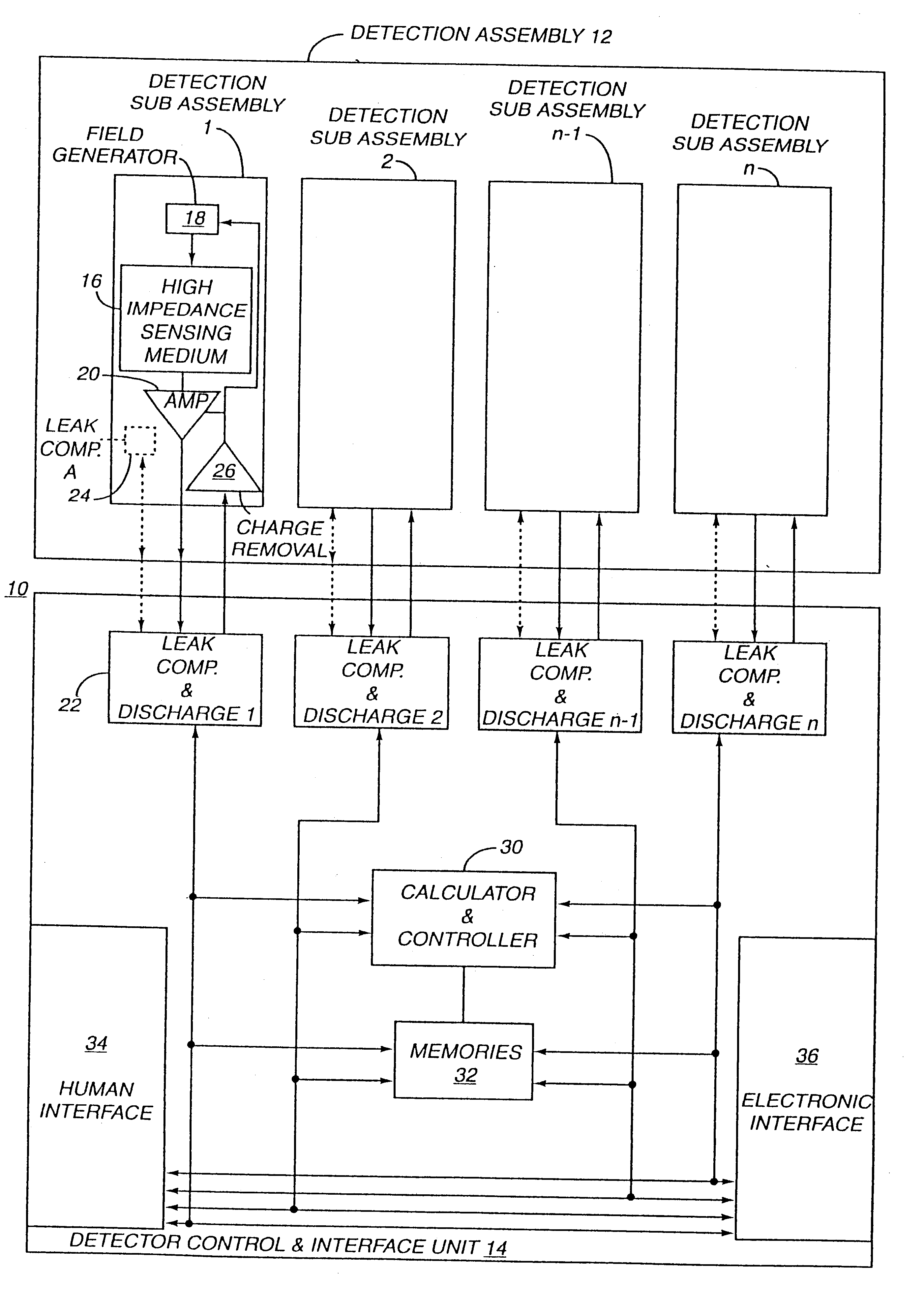
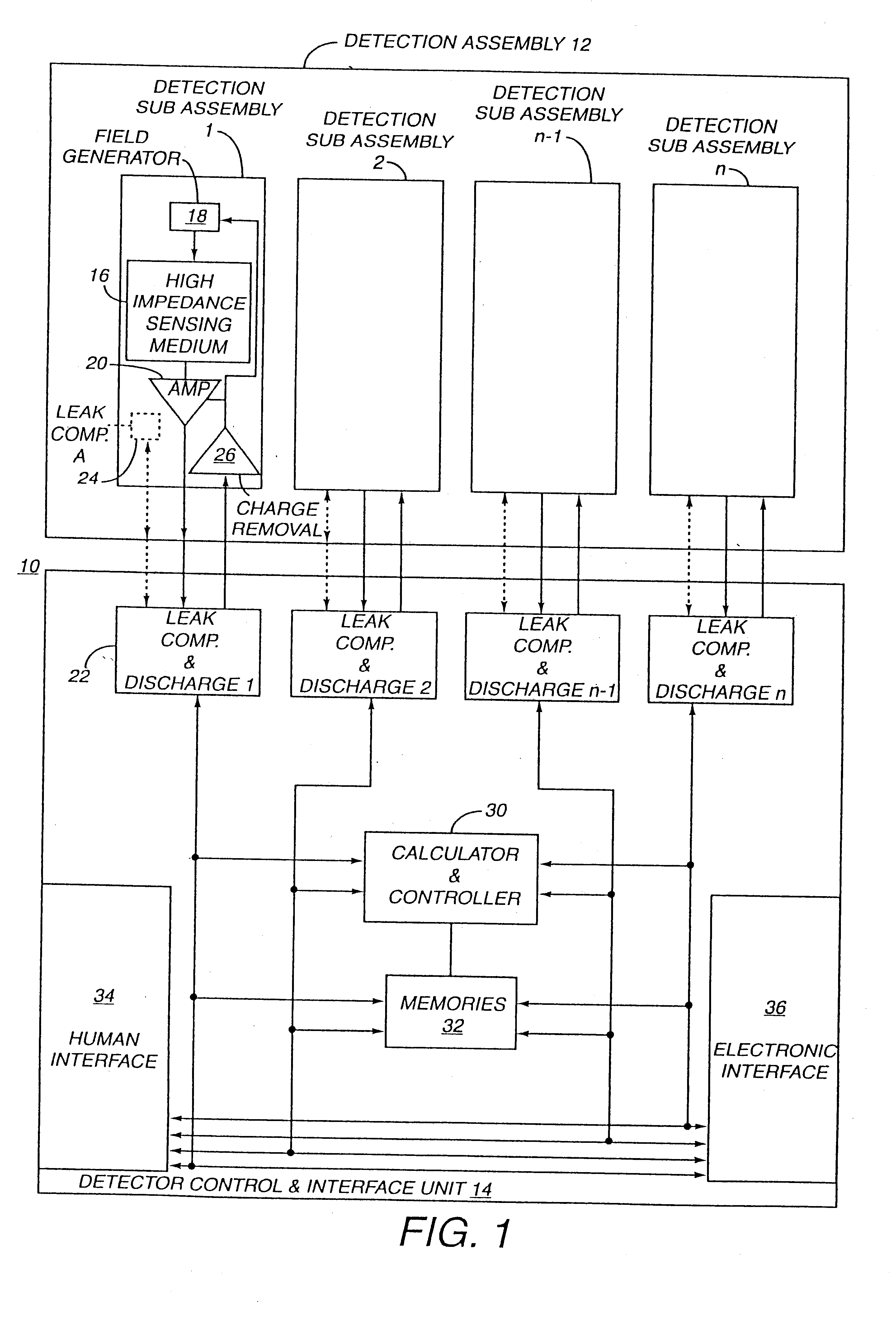
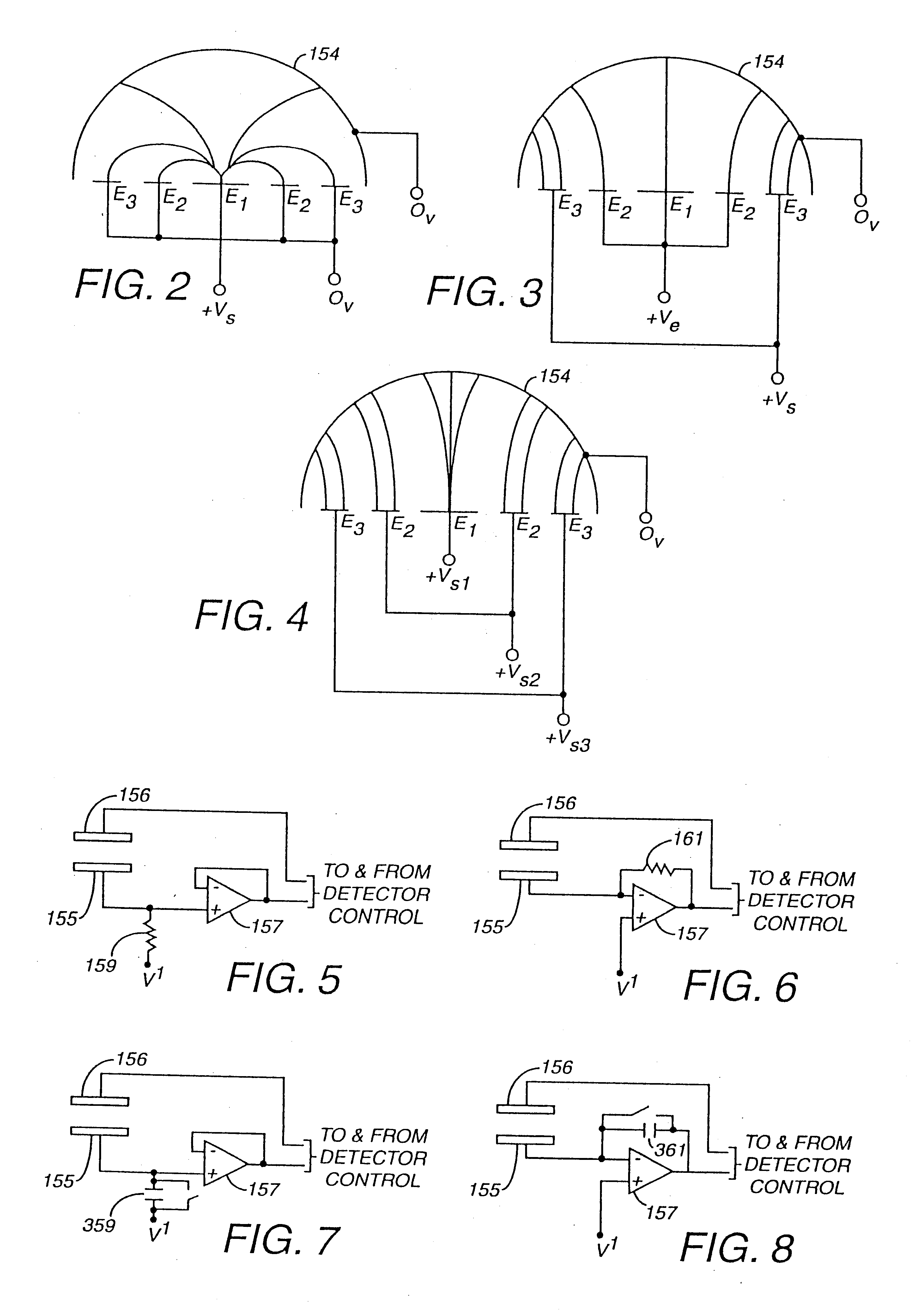
InactiveUS6353324B1Improve performanceLimits of linearityPhotometry electrical circuitsMeasurement using digital techniquesCapacitanceEngineering
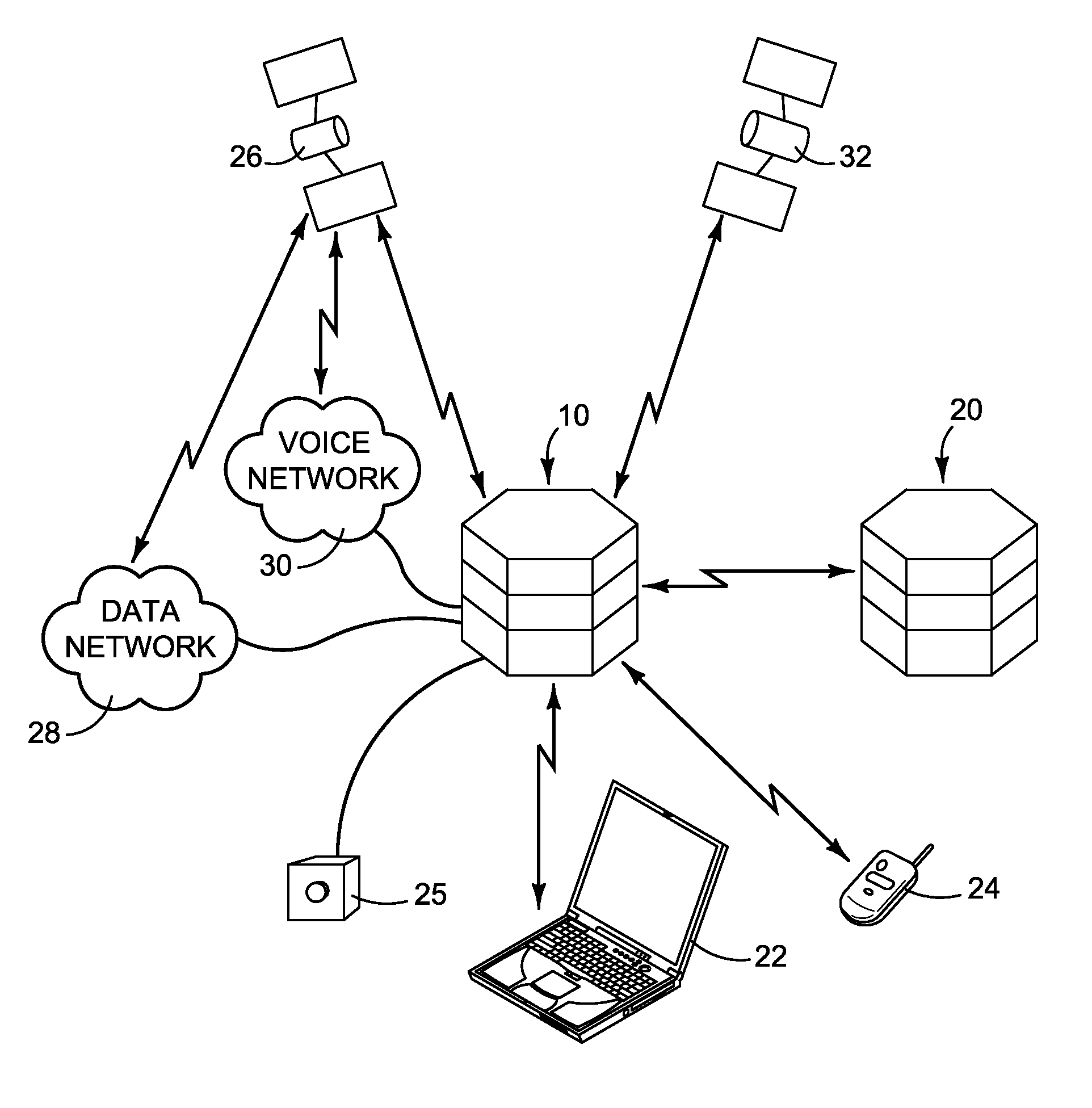
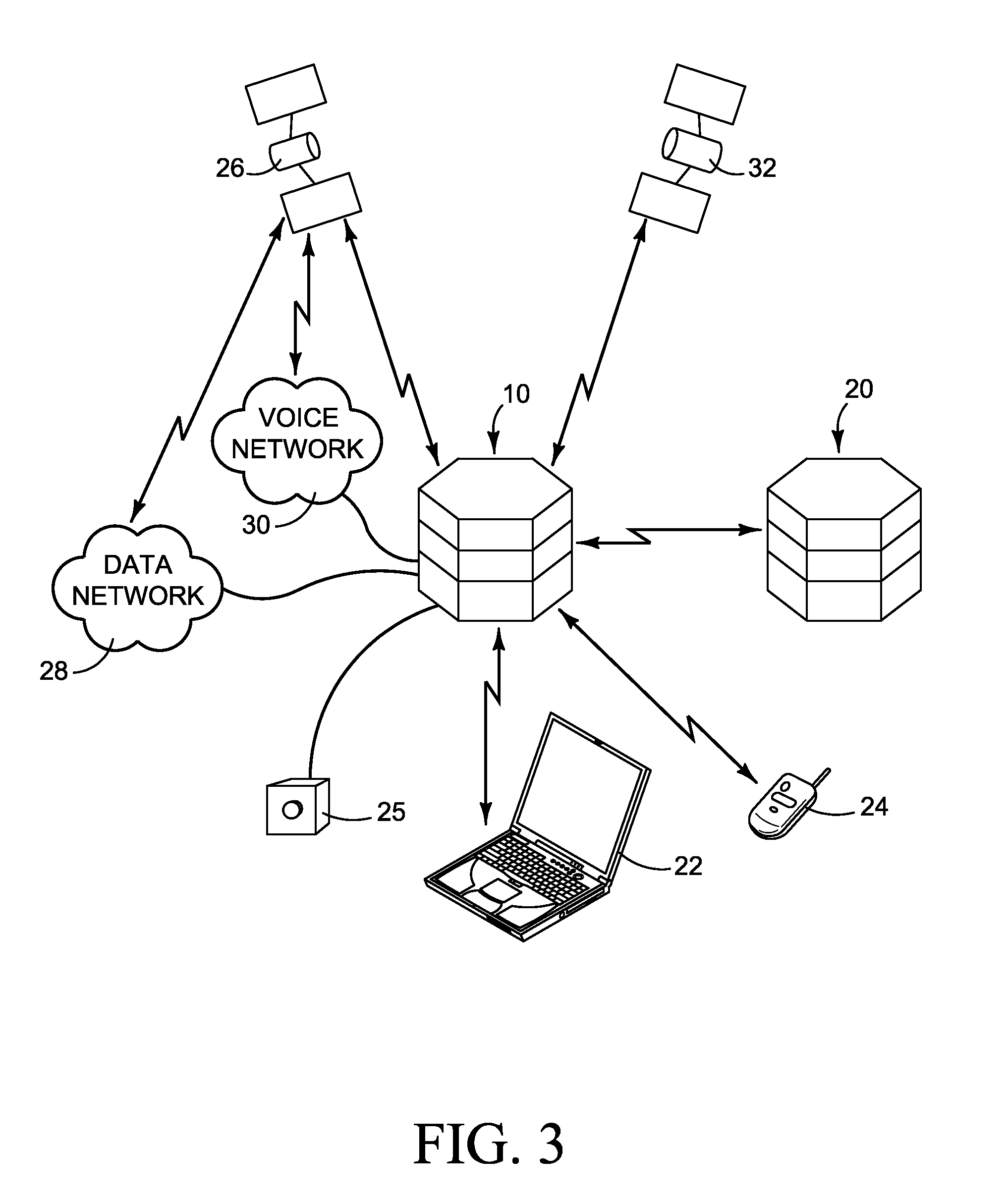
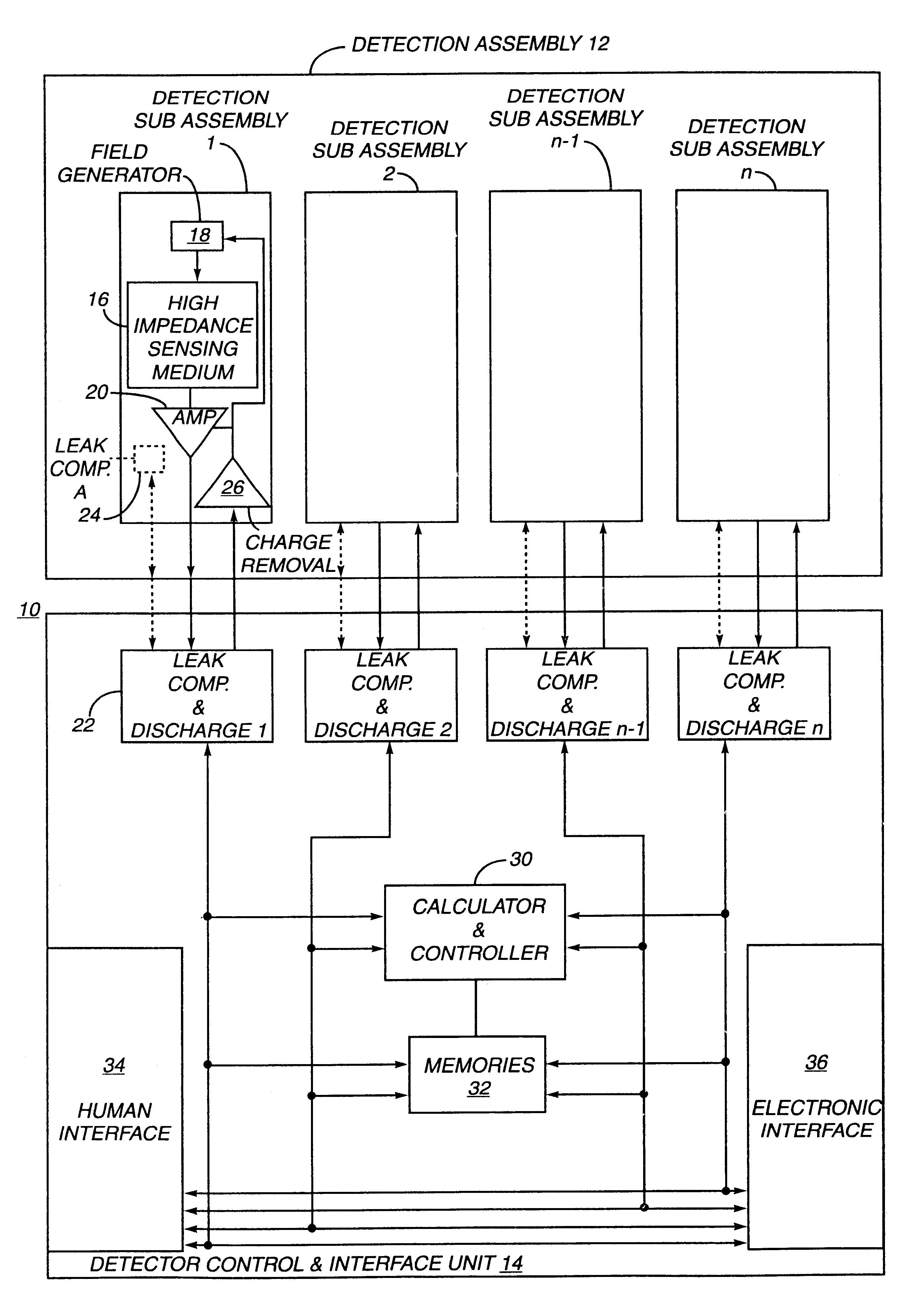
The present invention relates to an electronic circuit and an array of such circuits for precisely measuring small amounts or small changes in the amount of charge, voltage, or electrical currents. One embodiment of the present invention provides an electronic circuit for measuring current or charge that can be used with a variety of sensing media (including high impedance sensing media) that produce a signal by either charge or current production or induction in response to physical phenomena occurring within the sensing media. In another embodiment, the voltage level (bias) of either the sensing or reference electrode can be switched relative to the other upon receipt of a triggering pulse. This changes the polarity of the electric field to cause charge of the opposite polarity to be driven to the sensing electrode, thereby eliminating the need to electrically connect a discharge path to the sensing electrode to clear the charge accumulated at the sensing electrode. This can be supplemented by capacitively coupling a compensation signal to the sensing electrode to cause the amplifier output signal to lessen in magnitude below a threshold level that permits additional charge or current measurements of the same polarity before performing bias reversal. Alternately or in combination with bias reversal and capacitive compensation, sensor performance can be improved by minimizing inaccuracies caused by leakage currents or current drawn from the sensor. Other described methods of reducing leakage currents that can be used alone or in combination with the aforementioned features include the use of guard rings, physical switches or relays, the controlled creation of charges or currents of a specific polarity in a specific region of the sensing medium, controlled leakage over the surface of an insulator, and controlling the environment in which the circuit operates.
Owner:BRIDGE SEMICON
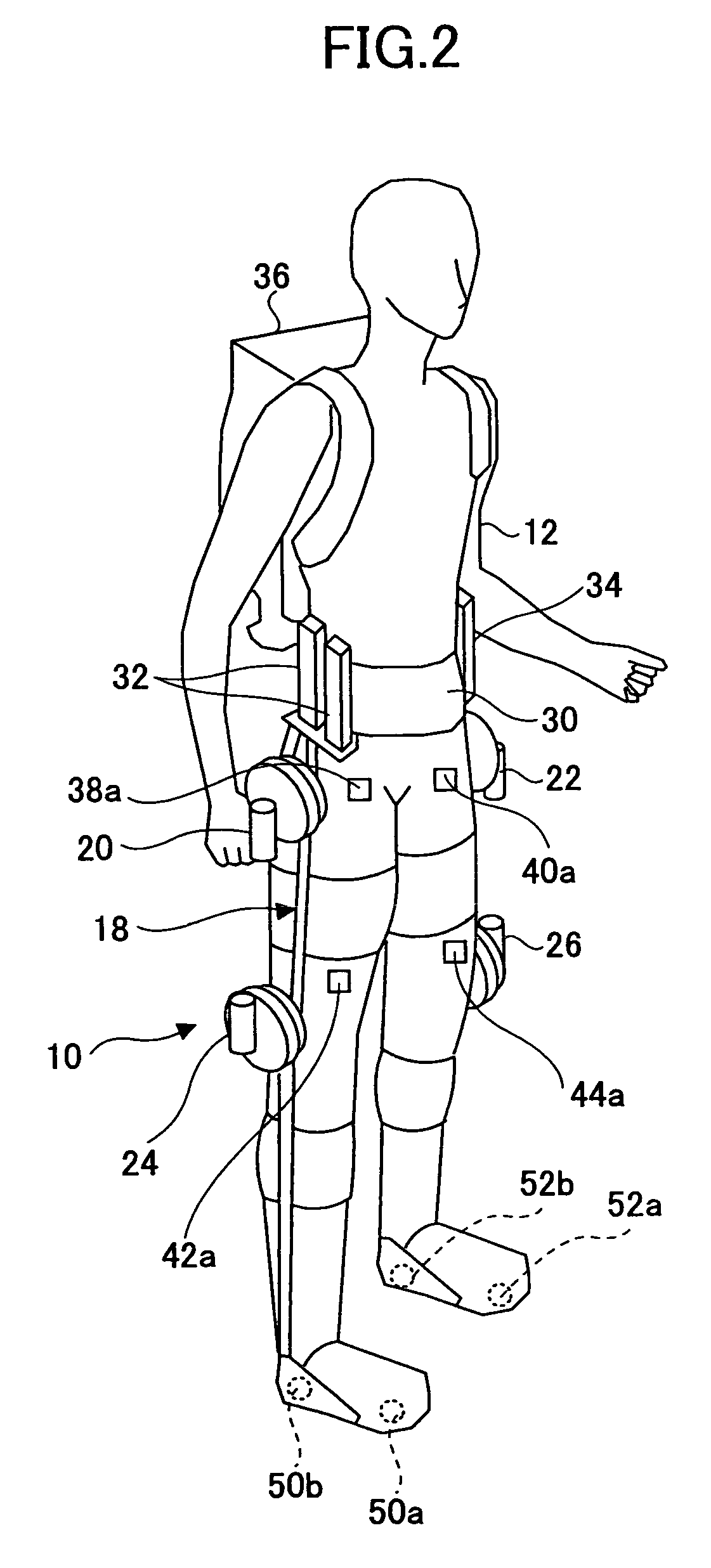
Wearing Type Behavior Help Device, Wearing Type Behavior Help Device Calibration Device, and Calibration Program
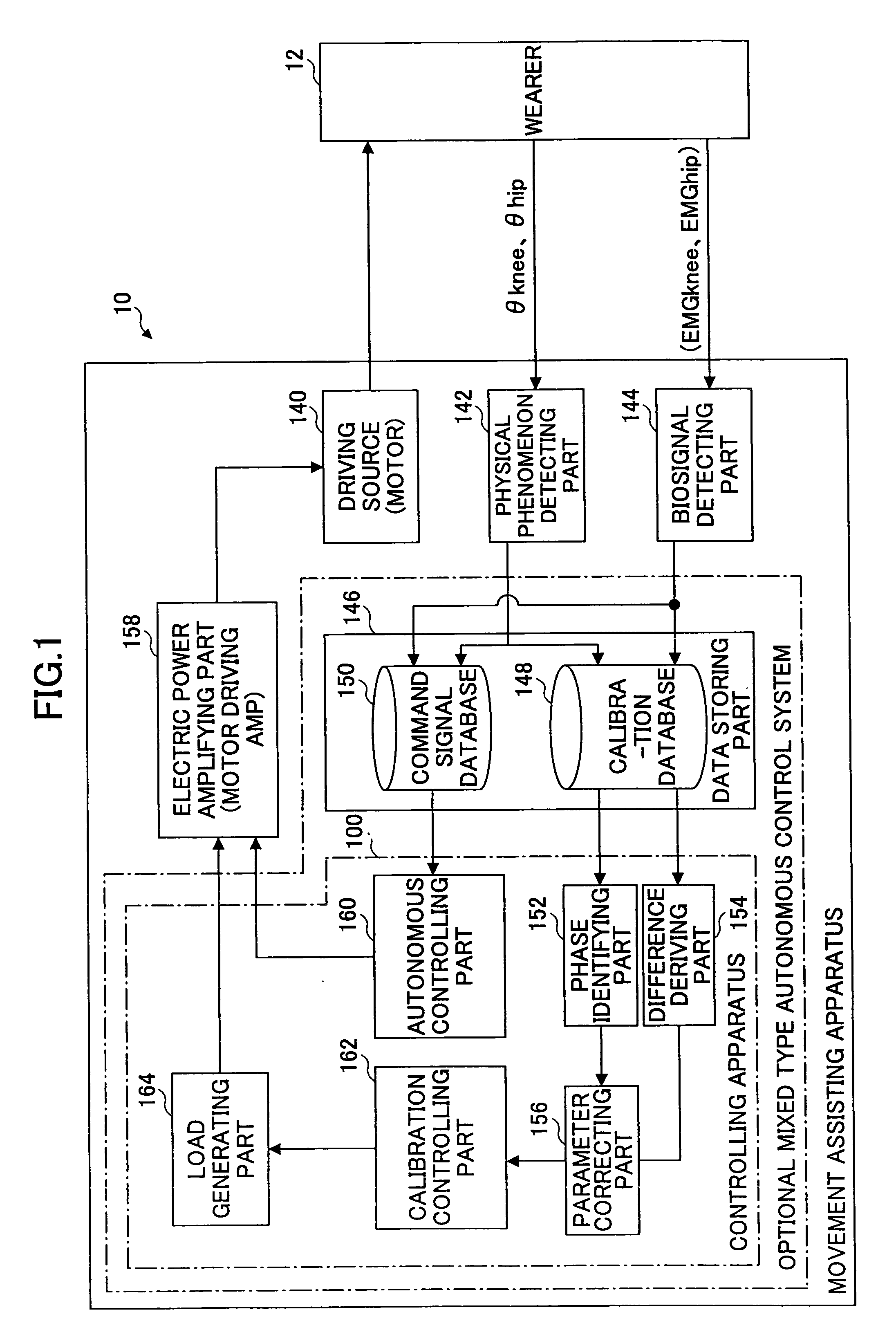
ActiveUS20080234608A1Precise applicationReliable typeProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectromyographyEngineeringSkeletal muscle
[Problem to be Solved]The problem to be solved by the present invention is to reduce the load applied to the wearer by correcting a parameter in correspondence with detectivity of biosignals.[Means to Solve Problem]The calibration controlling part 162 of the movement assisting apparatus 10 enables the power amplifying part 158 to apply a driving force of the driving source 140 as a load (input torque) from the load generating part 164 to the wearer 12 when the wearer 12 wears the movement assisting wearing device. Then, the wearer 12 applied with the driving force of the driving source 140 generates power from the skeletal muscles by performing a predetermined calibration operation. Accordingly, the physical phenomenon detecting part 142 detects joint angle along with the calibration operation, and the biosignal detecting part 144 detects myoelectric signals. In the parameter correction part 156, a parameter K is corrected based on the difference between the load (input torque) and the driving force (muscular strength) being calculated by the difference deriving part 154 with respect to the phase identified by the phase identifying part 152.
Owner:TSUKUBA UNIV OF +1
Using a physical phenomenon detector to control operation of a speech recognition engine
ActiveUS20090182560A1Devices with voice recognitionDevices with sensorSpeech identificationPush-to-talk
A transmission device such as a cell phone or other mobile communication device includes a physical phenomenon detection device to perform a “push to talk” function by detecting the occurrence of a particular physical phenomenon and using such detection to start and stop recording an utterance for subsequent analysis by a speech recognition engine. A method of controlling operation of a speech recognition engine in response to detection of a physical phenomenon includes detecting or sensing, via a physical phenomenon detection unit, a predetermined physical phenomenon representative of an intent to invoke operation of a speech recognition engine. In response to the detection or sensing of the predetermined physical phenomenon, a signal is transmitted to a control unit in a communication device. In response to the receipt of the transmitted signal, the utterance received from a user via the communication device is recorded, and the recorded utterance is provided to a speech recognition engine for operation thereon. The user may thus effectuate operation of the speech recognition engine upon the utterance by causing the physical phenomenon to occur.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC +1
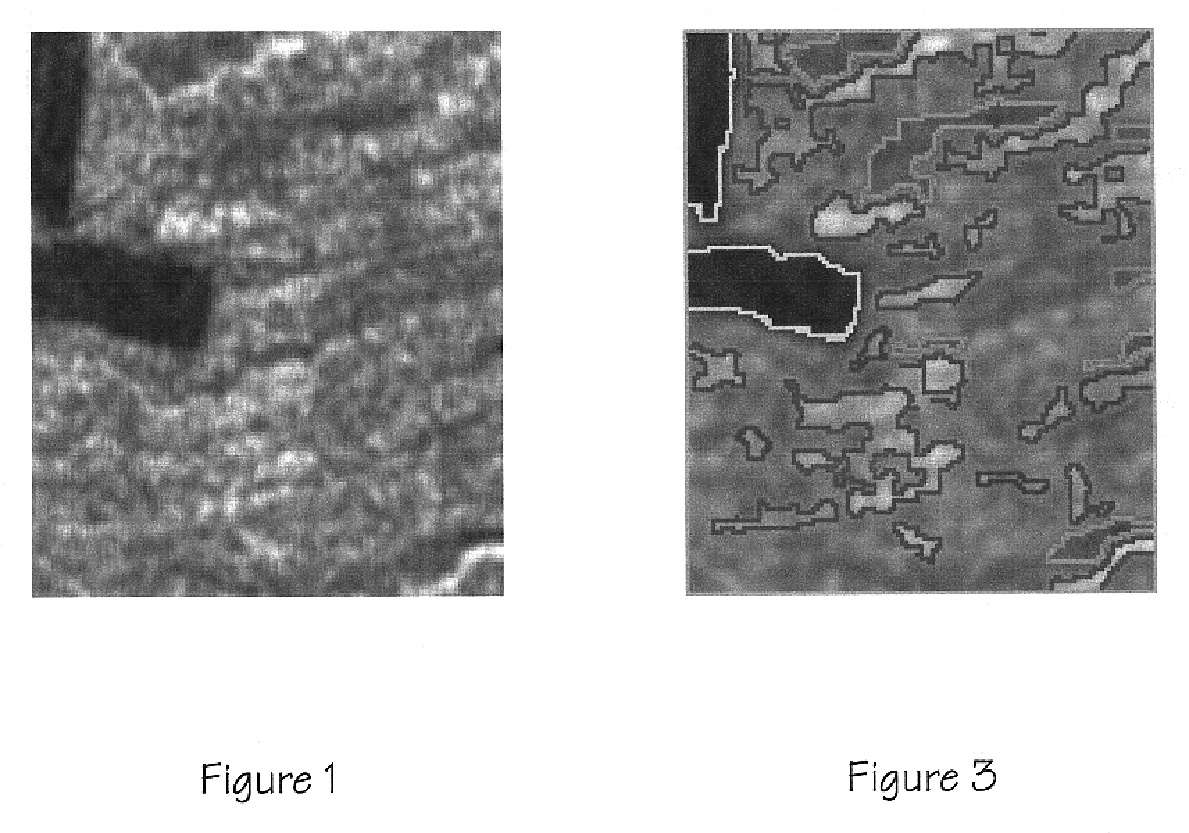
System and method for analyzing and imaging three-dimensional volume data sets
A system and method is provided for quickly tracking a physical phenomena represented within the three-dimensional volume data set. A plurality of planes may be successively displayed in the three-dimensional volume data set from which points are digitized related to the structure of interest to create a spline curve on each plane. The area between the spline curves (1914, 1916, 1918, 1920) is interpolated to produce a surface (1912) representative of the structure of interest, which may for example be a fault plane described by the three-dimensional volume data set. In this manner, the user can more easily and effectively visualize and interpret the features and physical parameters that are inherent in the three-dimensional volume data set.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS CORP
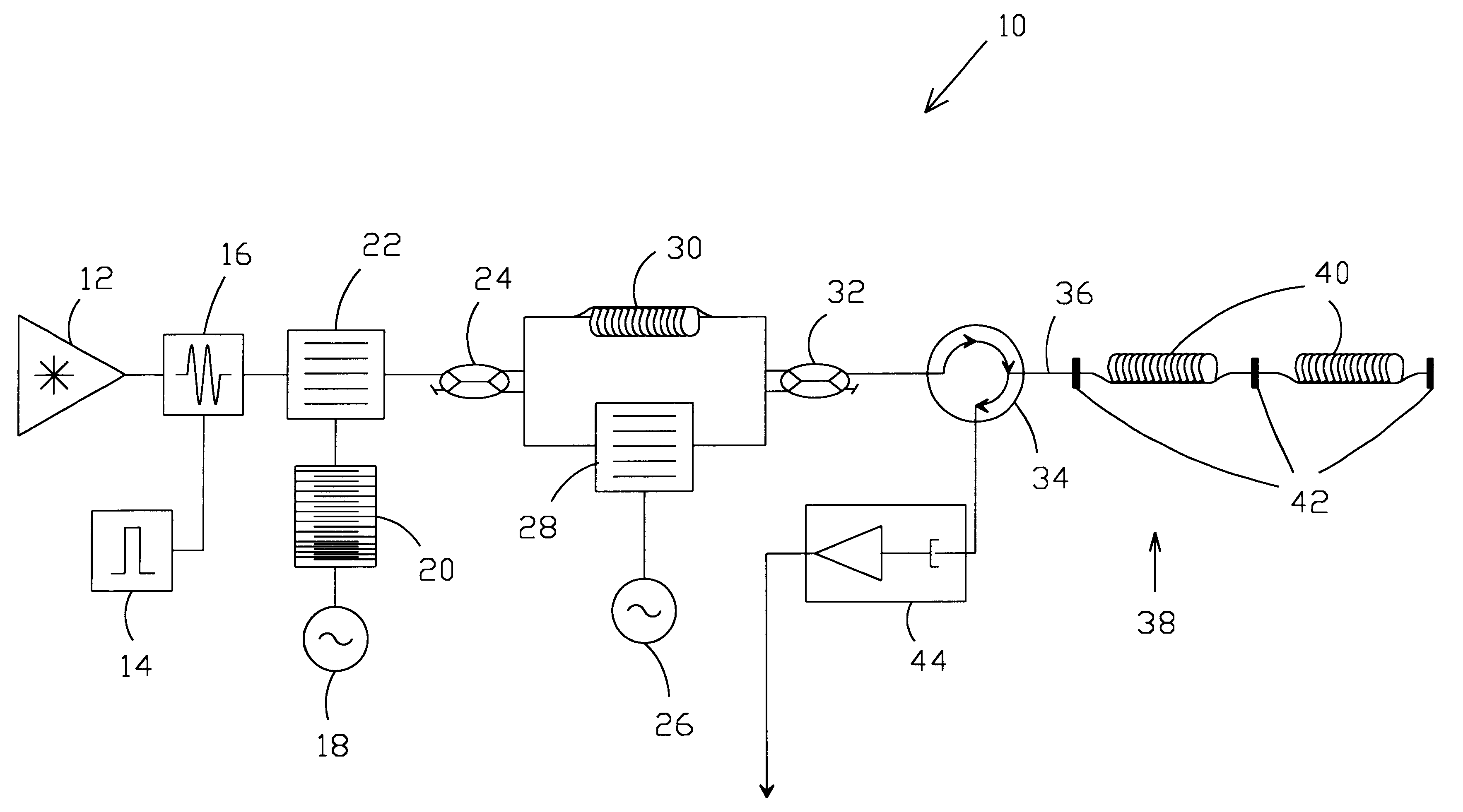
Pulsed system and method for fiber optic sensor
InactiveUS6466706B1Reduce noiseSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementCoupling light guidesSingle fiberTransducer
A system and method is disclosed for generating, propagating, and detecting light pulses for use with a fiber optic transducer array. The system preferably uses two pulses to provide fixed and relatively short interferometer path differences to thereby reduce coherent light noise. The system preferably uses a surface acoustic wave device for chirping the light pulses to thereby spread noise over a wider bandwidth so as to suppress noise. A coherent light source is preferably amplitude modulated to produce an initial pulse. In one embodiment, that initial pulse is chirped and split into two pulses. One of the two pulses is delayed while the other is frequency shifted. The two pulses are combined onto a single fiber optic path and applied to the fiber optic transducer array. After being acted on by the fiber optic transducer array, the two pulses are photodetected and processed to obtain the information about the physical phenomena to be detected.
Owner:NAVY US SEC THE NAVY THE
Calibration method, calibration device and measurement device
ActiveUS20130211761A1Less calibration workProgramme controlElectrical measurementsTelecommunications linkMeasurement device
According to an aspect of the invention a method for calibrating a measurement device is conceived wherein: a calibration device is brought into close proximity of the measurement device such that a data communication link is established between the measurement device and the calibration device; wherein the following steps are performed while the calibration device and the measurement device are in close proximity of each other: the calibration device performs a measurement of at least one physical phenomenon; the measurement device performs a measurement of the same physical phenomenon; the result of the measurement by the measurement device is compared with the result of the measurement by the calibration device; and calibration parameters are computed based on a difference between the result of the measurement by the measurement device and the result of the measurement by the calibration device.
Owner:NXP BV
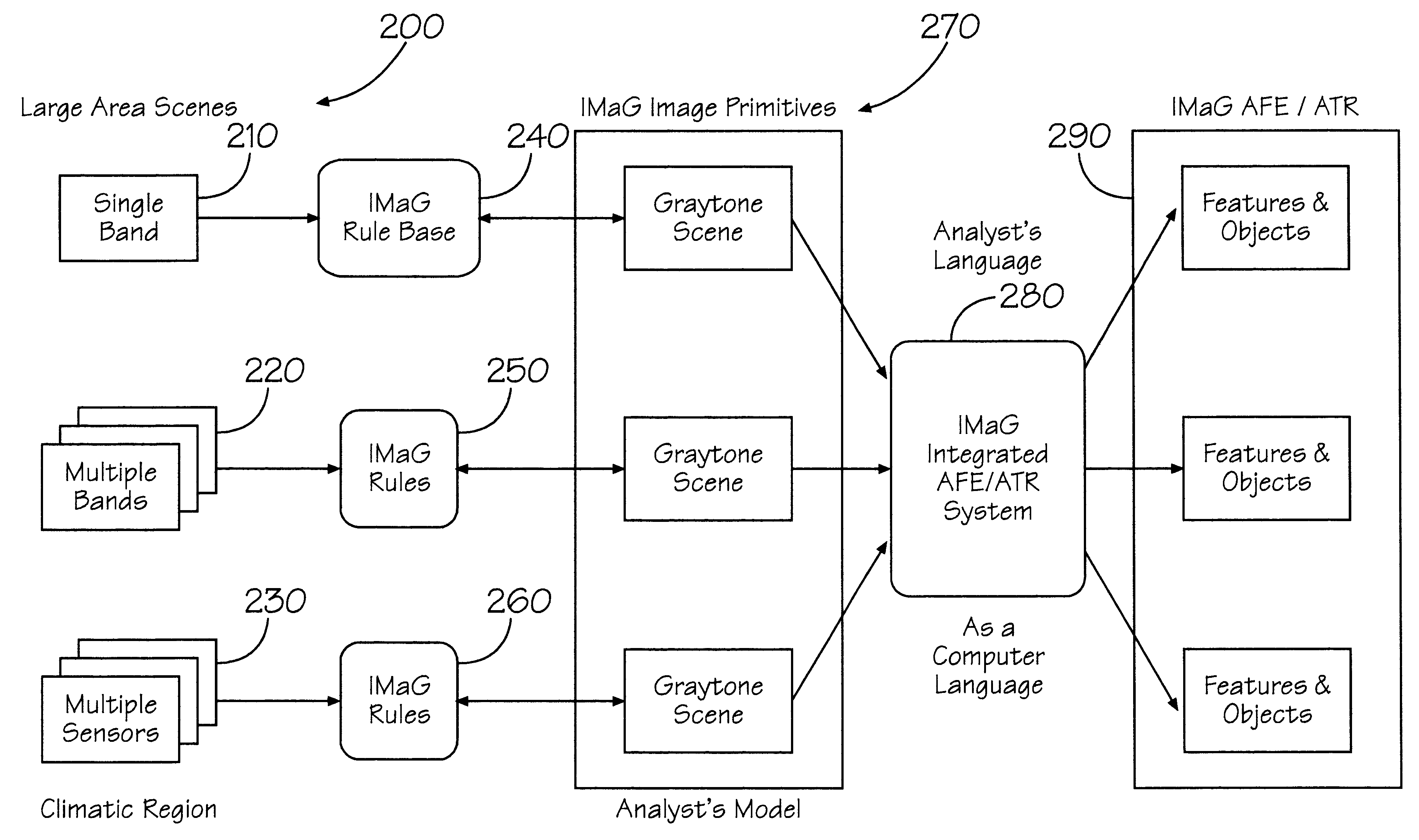
Compiliable language for extracting objects from an image using a primitive image map
InactiveUS6741744B1Easy extractionTedious and costly and error processData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionInformation processing
The invention features a method wherein a recognition environment utilizes pseudo-English as a programming language to extract simple and complex objects with image-and / or map-data as inputs. Based on this human / computer interface in which pseudo-English is a programming language, the object-recognition system has three major logic modules: (1) an input data module; (2) an information-processing module, coupled with the above-noted human computer interface (HCI) module; and (3) an output module that has a feedback mechanism back to the main information-processing and the input-data module. A physical phenomenon (i.e., one that is visible, audible, tactile, etc.) is analyzed by the information-processing module to determine whether it is susceptible to description or articulation. If not, the phenomenon is matched or compared, via the output module, to a known articulatable, physical-phenomenon model and recognizable features are extracted.
Owner:HSU SHIN YI
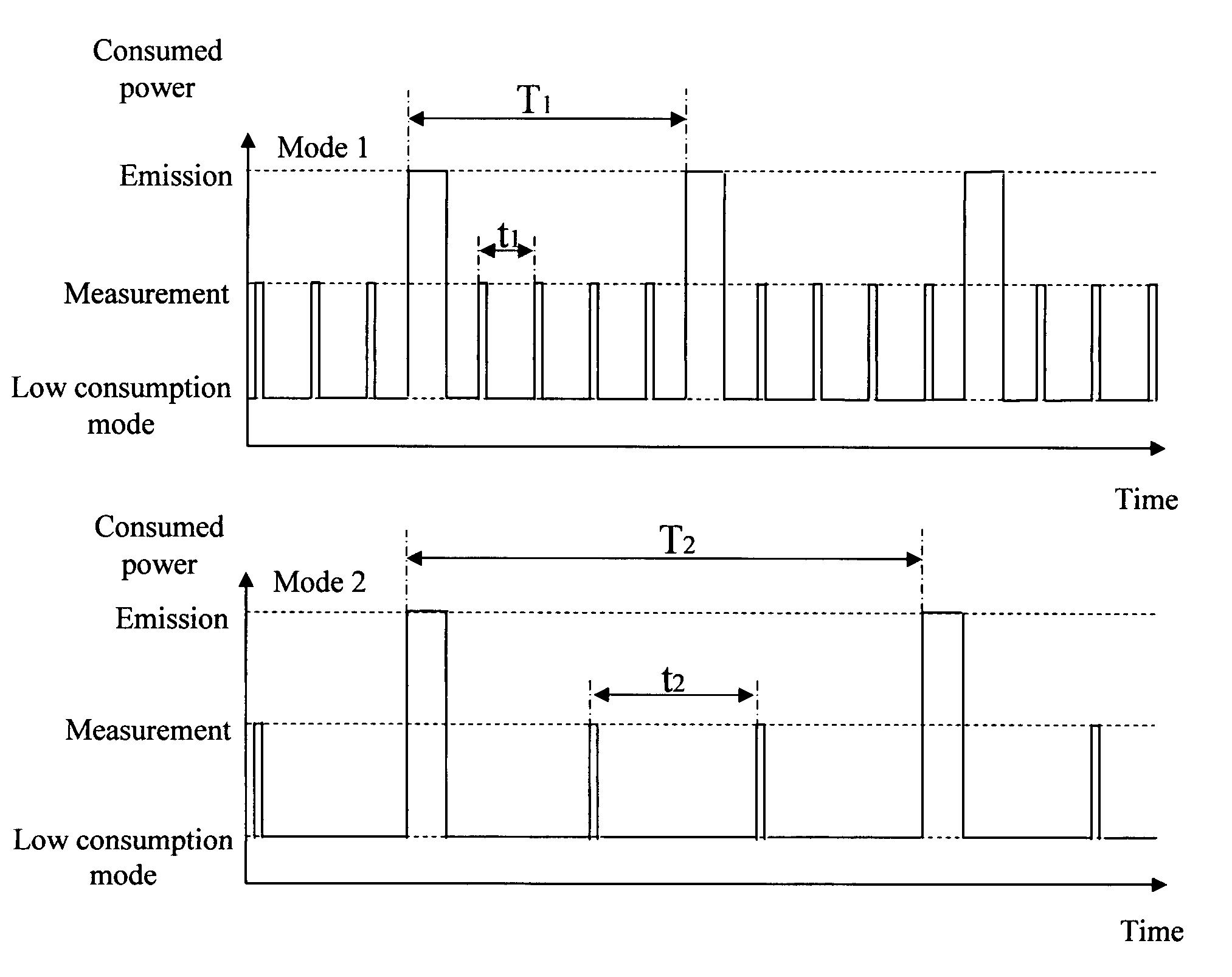
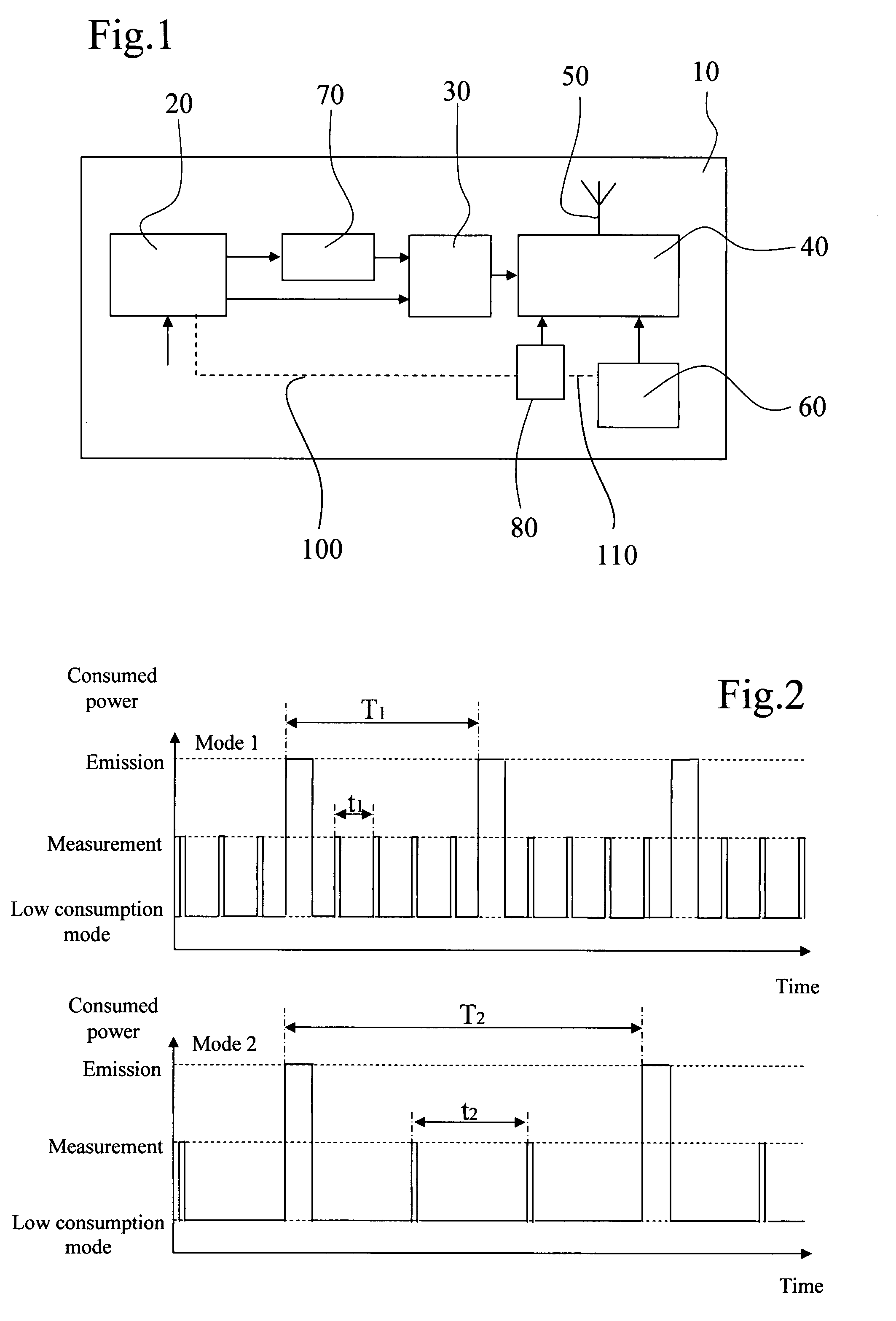
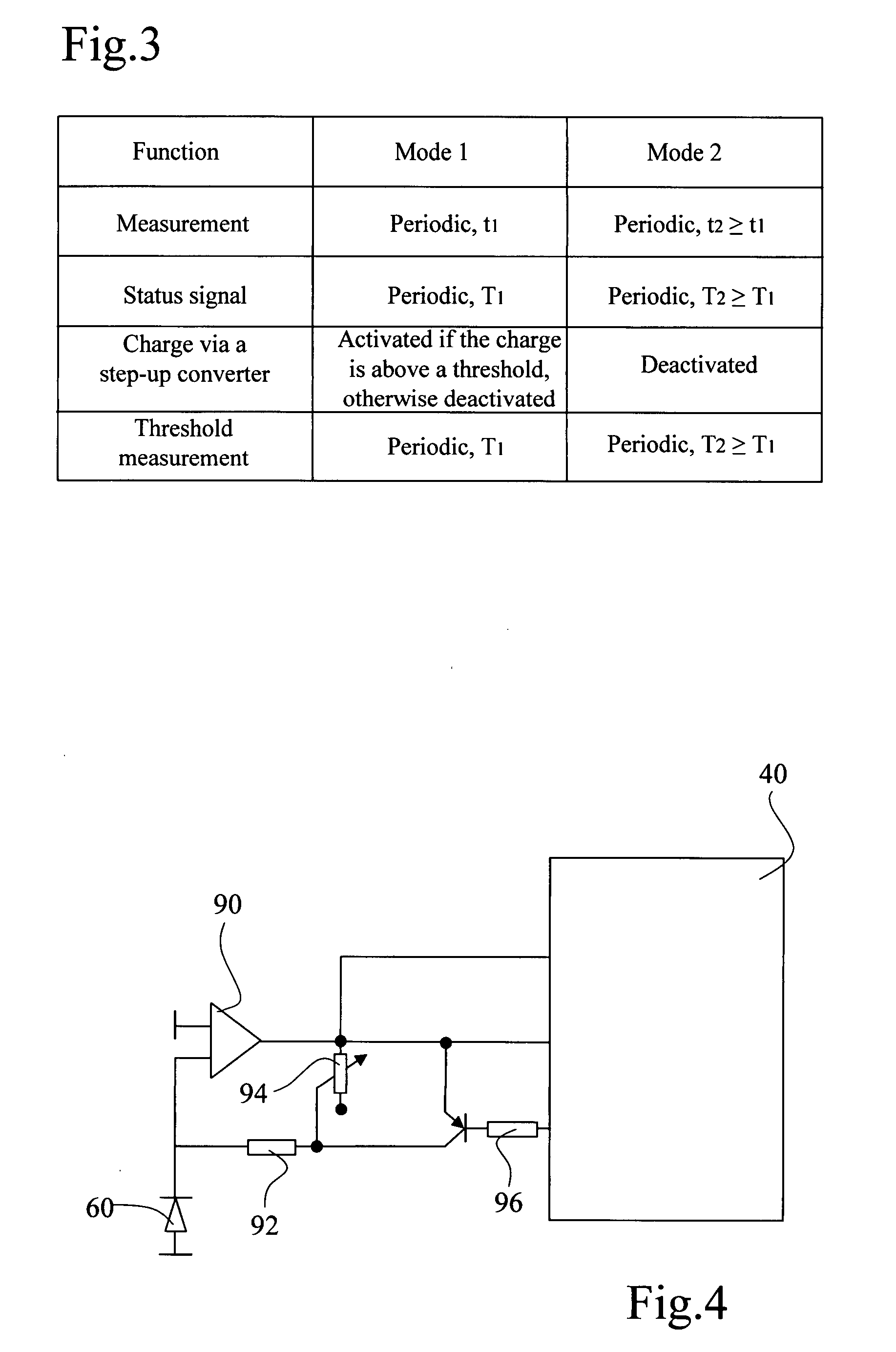
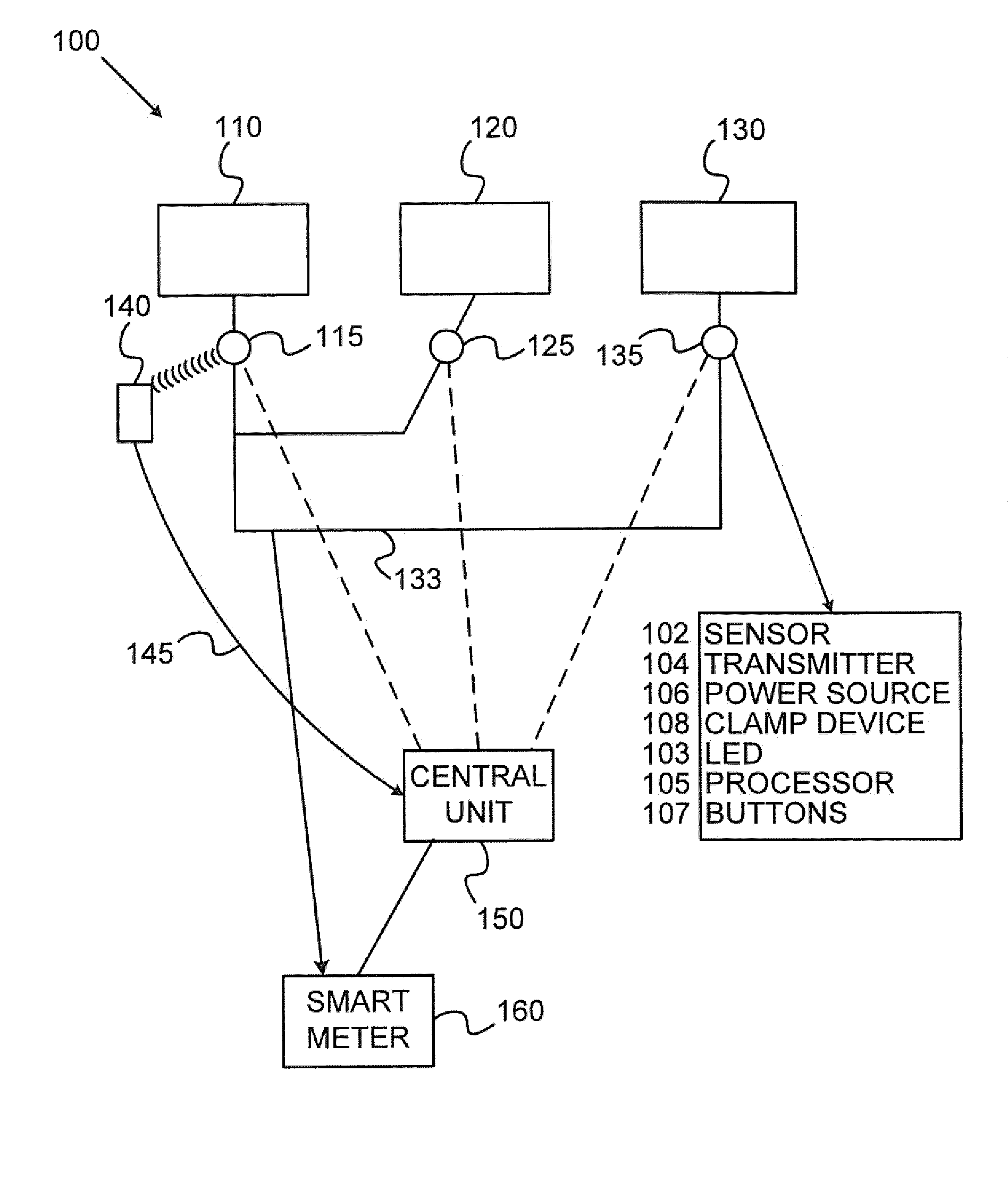
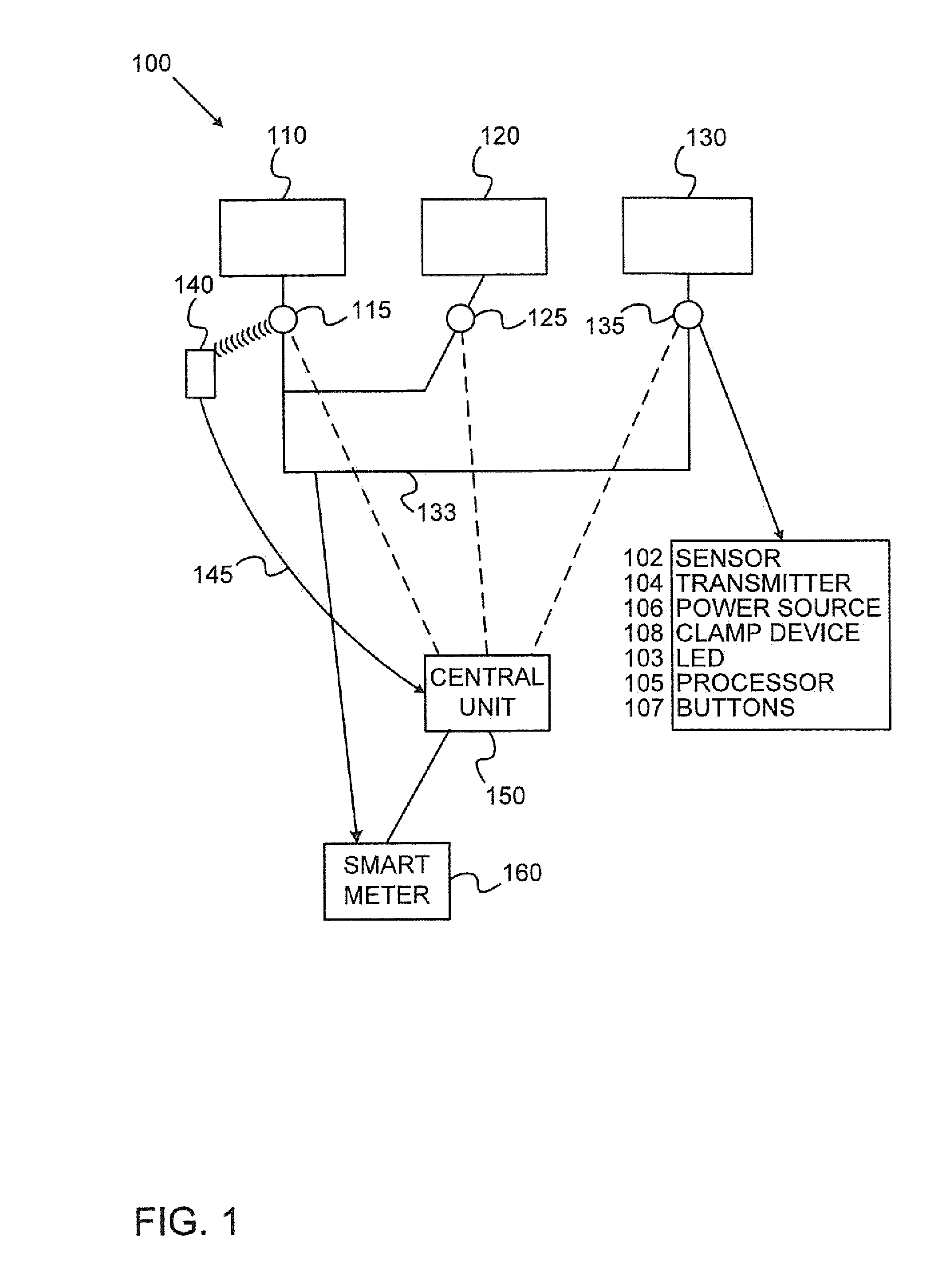
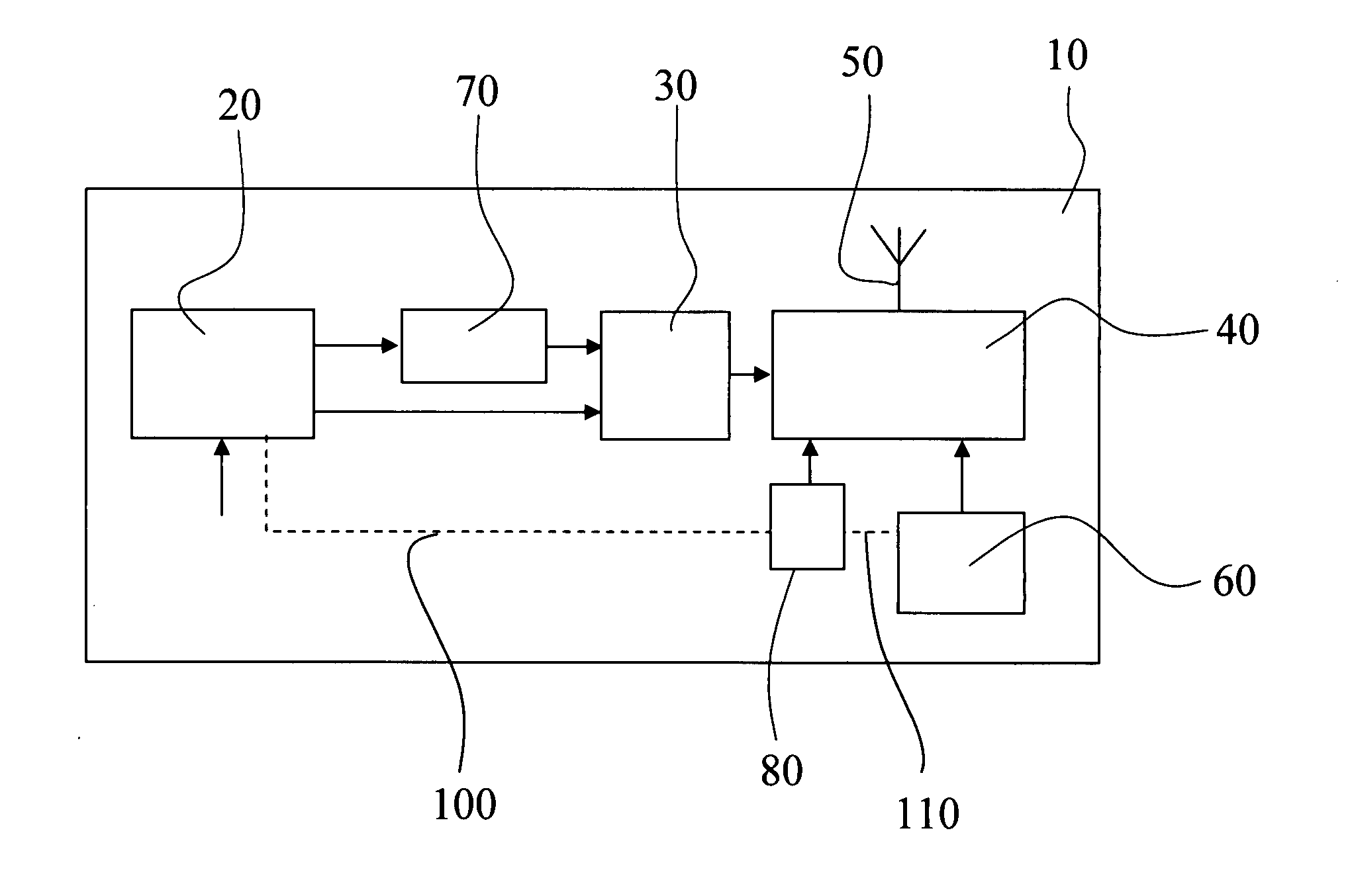
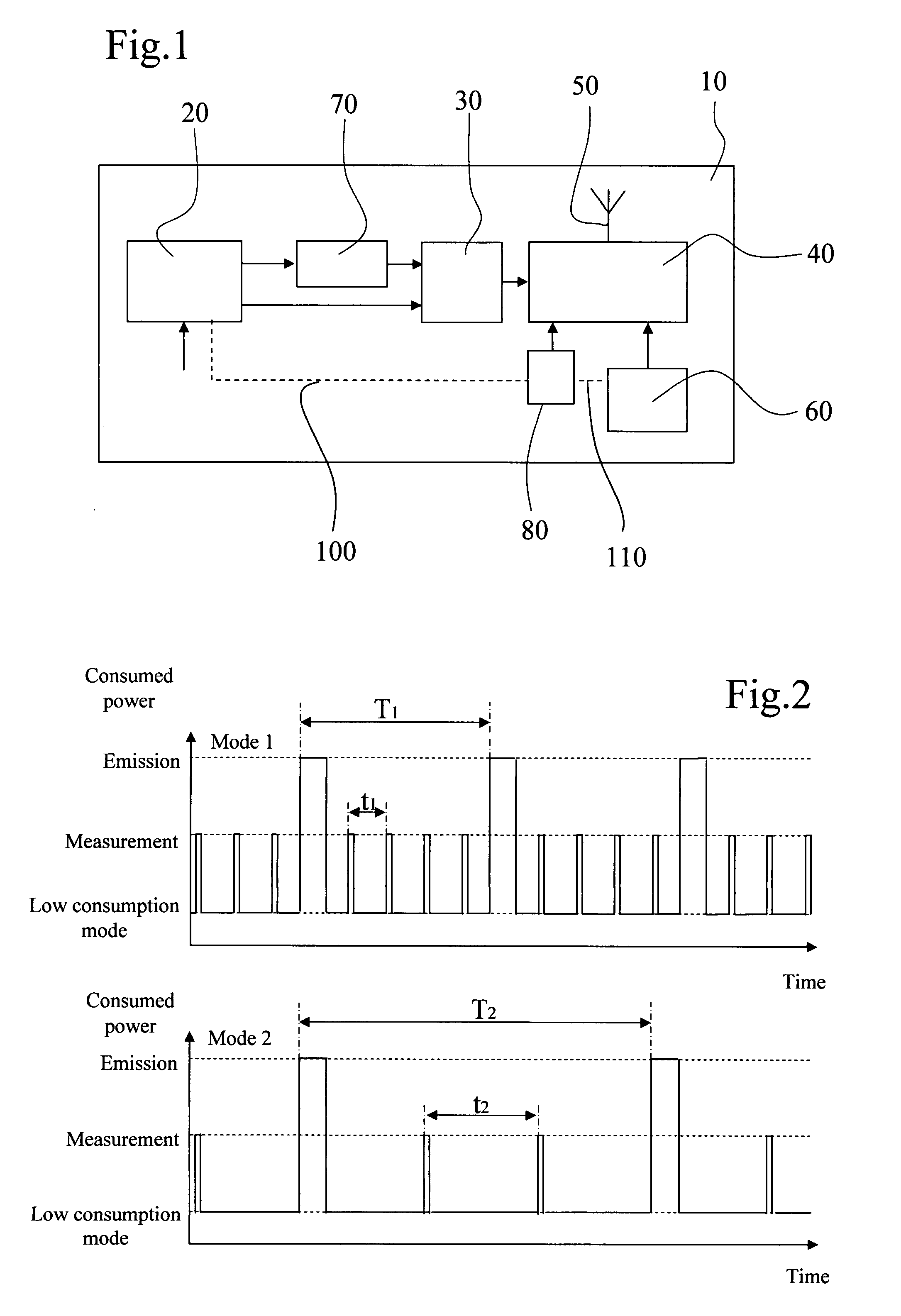
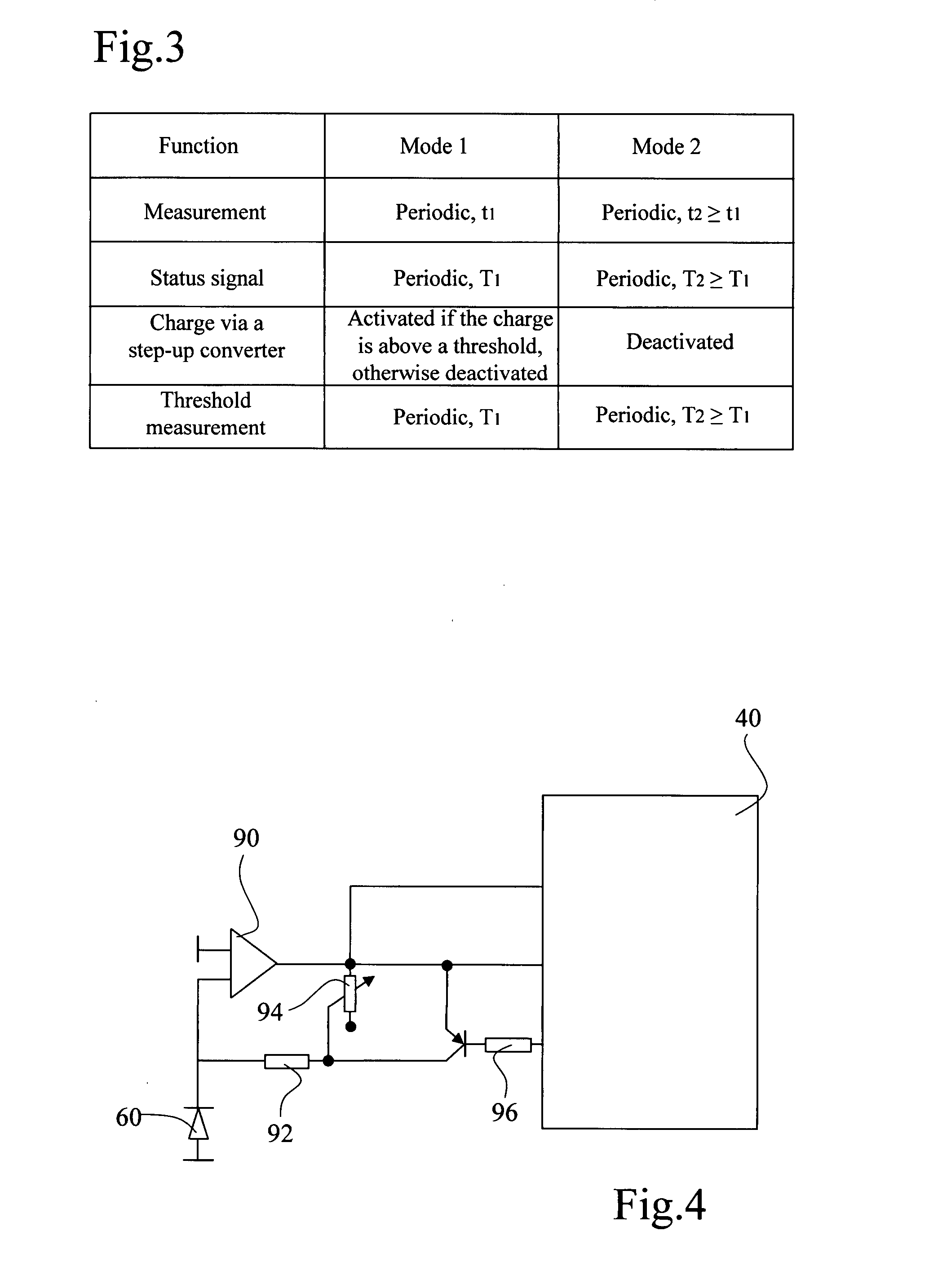
Method of operating a self-powered home automation sensor device for detecting the existence of and/or for measuring the intensity of a physical phenomenon
ActiveUS8106768B2Easy to manageGood anticipationLight dependant control systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsEngineeringOperation mode
The method of operation applies to a self-powered home automation sensor device for detecting the existence of and / or for measuring the intensity of a first physical phenomenon, comprising a means of converting an effect of a second physical phenomenon into electrical energy and a means of determining the instantaneous power of this second physical phenomenon that can be converted into electrical energy, wherein a normal, first mode of operation of the device or an energy-saving second mode of operation of the device is activated according to a value defined on the basis of the determination of the instantaneous power that can be converted into electrical energy.
Owner:SOMFY ACTIVITES SA
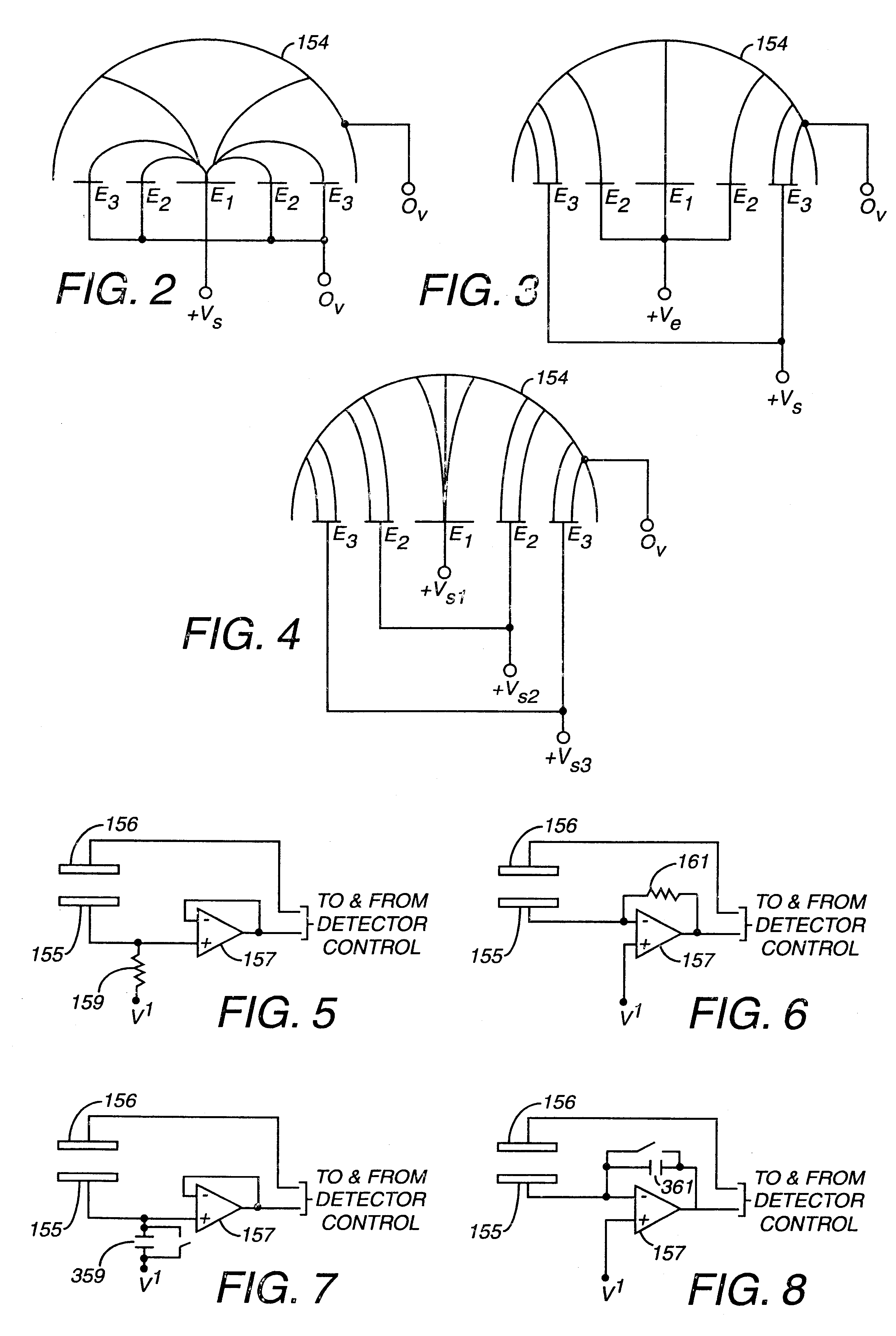
Electronic circuit
InactiveUS6414318B1Improve performanceLimits of linearityElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
The present invention relates to an electronic circuit for measuring small amounts of charge or small electrical currents. One embodiment of the present invention provides an electronic circuit for measuring current or charge that can be used with a variety of sensing media (including high impedance sensing media) that produce a signal by either charge or current production or induction in response to physical phenomena occurring within the sensing media. In another embodiment, the voltage level (bias) of either the sensing or reference electrode can be switched relative to the other upon receipt of a triggering pulse. This changes the polarity of the electric field to cause charge of the opposite polarity to be driven to the sensing electrode, thereby eliminating the need to electrically connect a discharge path to the sensing electrode to clear the charge accumulated at the sensing electrode. This can be supplemented by capacitively coupling a compensation signal to the sensing electrode to cause the amplifier output signal to lessen in magnitude below a threshold level that permits additional charge or current measurements of the same polarity before performing bias reversal. Alternately or in combination with bias reversal and capacitive compensation, sensor performance can be improved by minimizing inaccuracies caused by leakage currents or current drawn from the sensor. Other methods of reducing leakage currents that can be used alone or in combination with the aforementioned features include the use of guard rings, physical switches or relays, the controlled creation of charges or currents of a specific polarity in a specific region of the sensing medium, controlled leakage over the surface of an insulator, and controlling the environment in which the circuit operates.
Owner:BRIDGE SEMICON
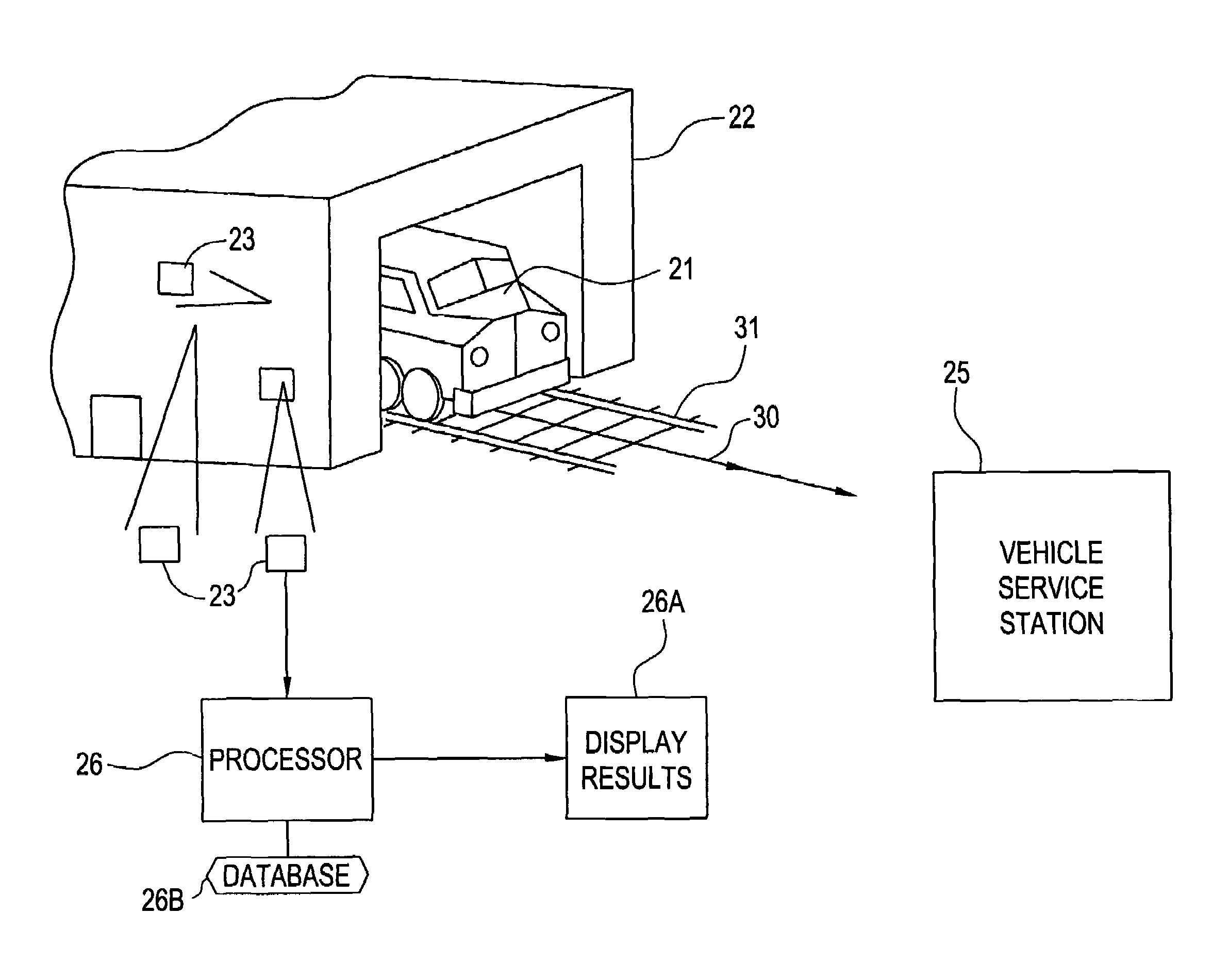
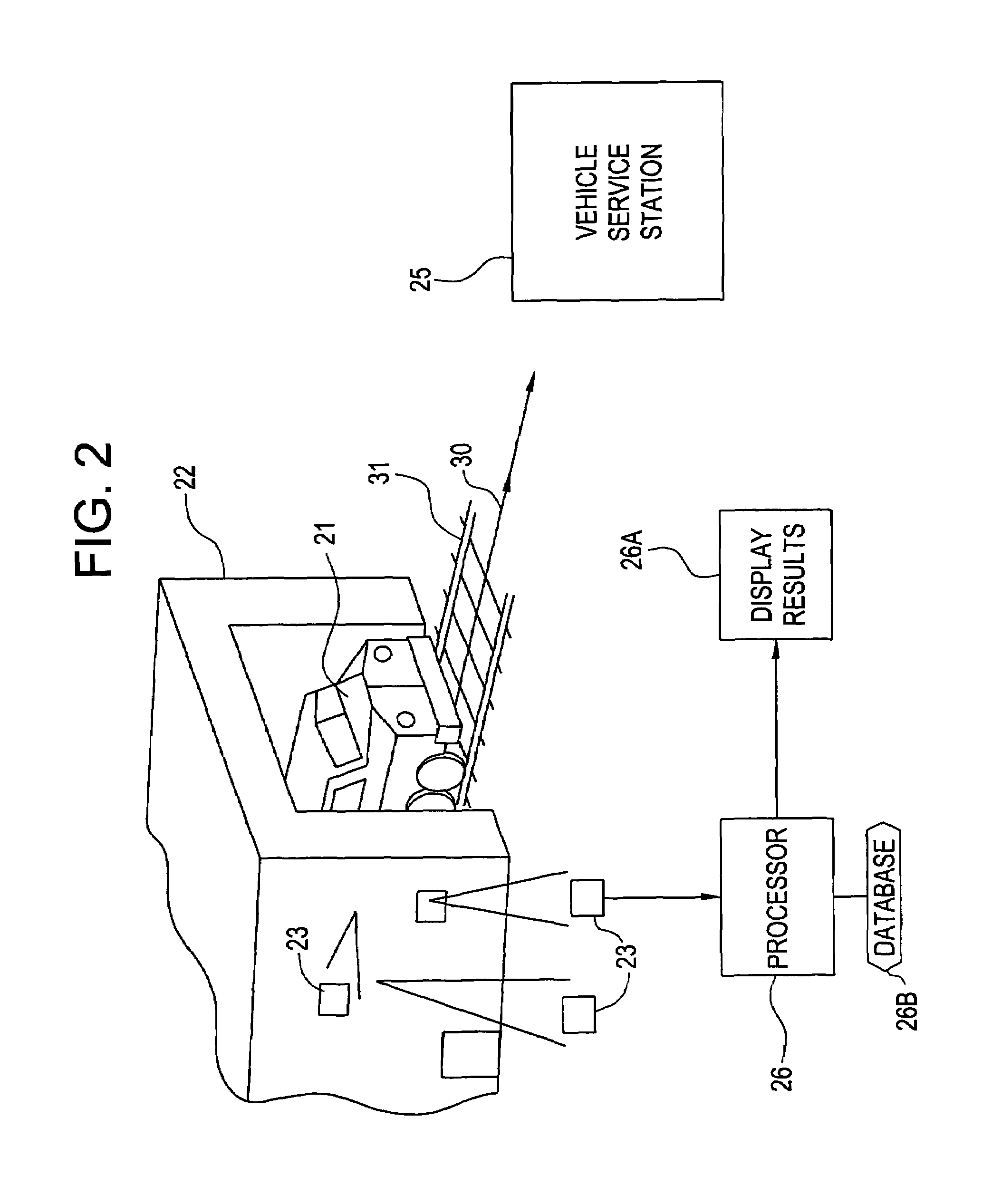
System and method for monitoring the condition of a vehicle
InactiveUS6985803B2Optimize timingVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesData transmissionWireless transmitter
A system for monitoring the condition of a vehicle has at least one wireless transmitter in on the vehicle, and in communication with the vehicle computer system. Data representative of operating parameters generated during the operation of the vehicle is downloaded to the transmitter, which transmits the data to a wireless receiver positioned proximal to a path of travel of the vehicle. The receiver is linked to a processor for transmission of the data to the processor for storage and processing if necessary. The system may also include at least one sensor, positioned proximal the path of travel, for detecting a physical phenomenon emanating from at least one vehicle component. The sensor generates a signal, which is transmitted to the processor. The processor is capable of analyzing the signal generating data indicative of operating condition of the vehicle component. The sensor, and / or receiver, mounted to a structure positioned proximal the path of travel of the vehicle.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Fault diagnosis apparatus for sensors used in a system
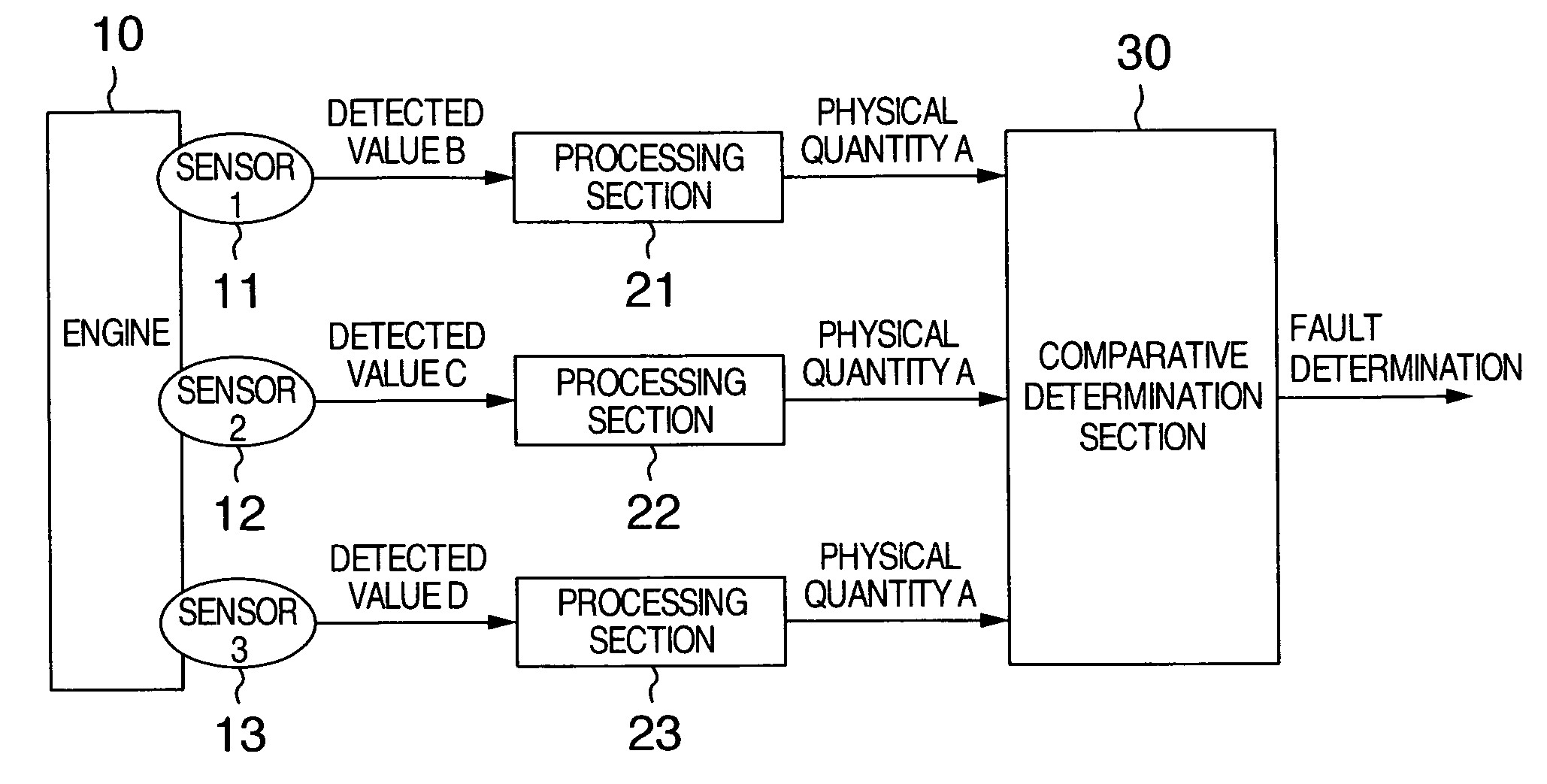
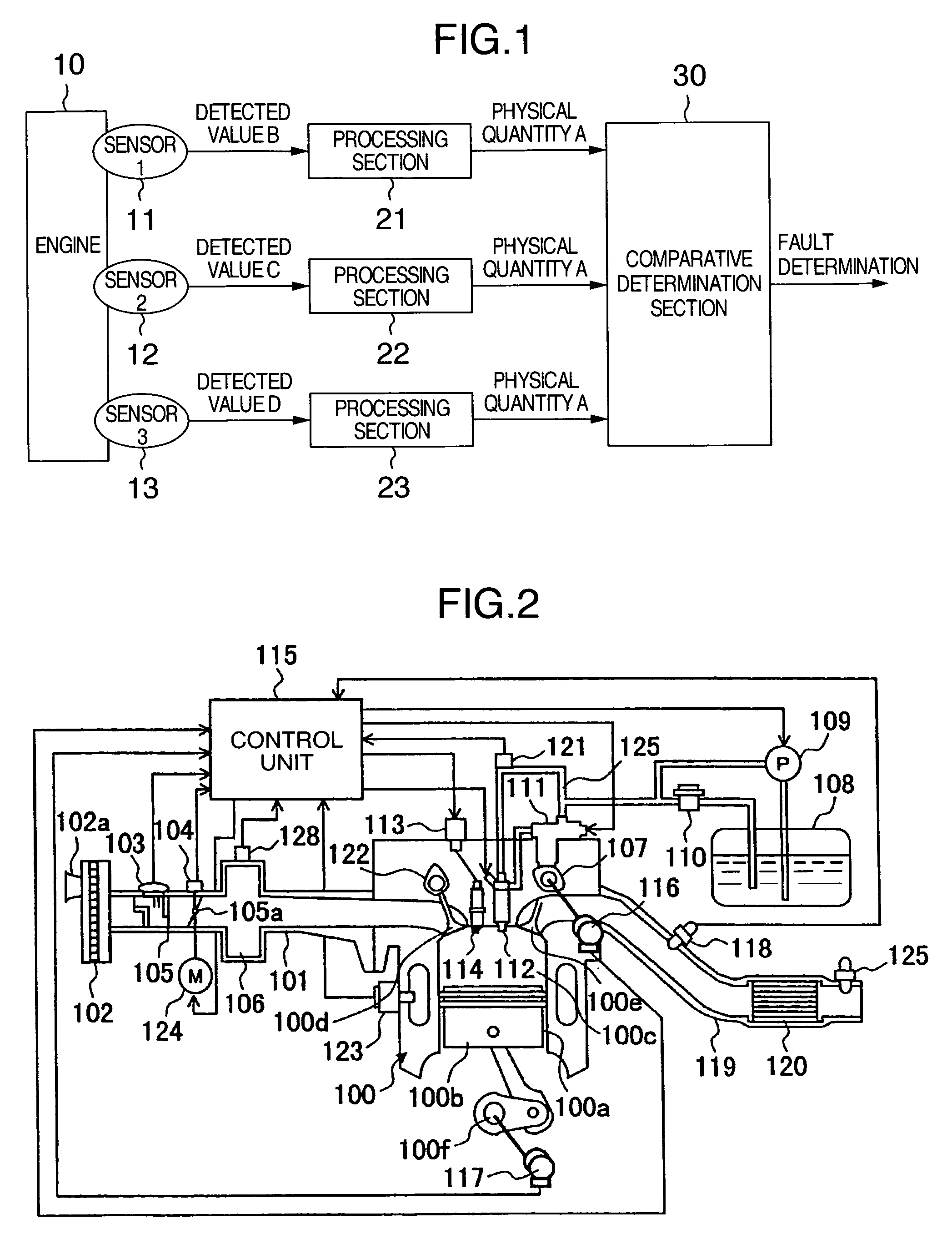
InactiveUS20060287806A1Increase costReduce probabilityAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlEngineeringPhysical quantity
A fault diagnosis apparatus for sensors in an apparatus system has at least three sensors which detect different physical quantities for one physical phenomenon which vary in correlation with one another, the sensors outputting signals indicating the detected physical quantities, wherein outputs from the at least three sensors are converted into one identical physical quantity in accordance with the correlations so that the resulting identical physical quantity can be used to determine whether or not each of the sensors is defective.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
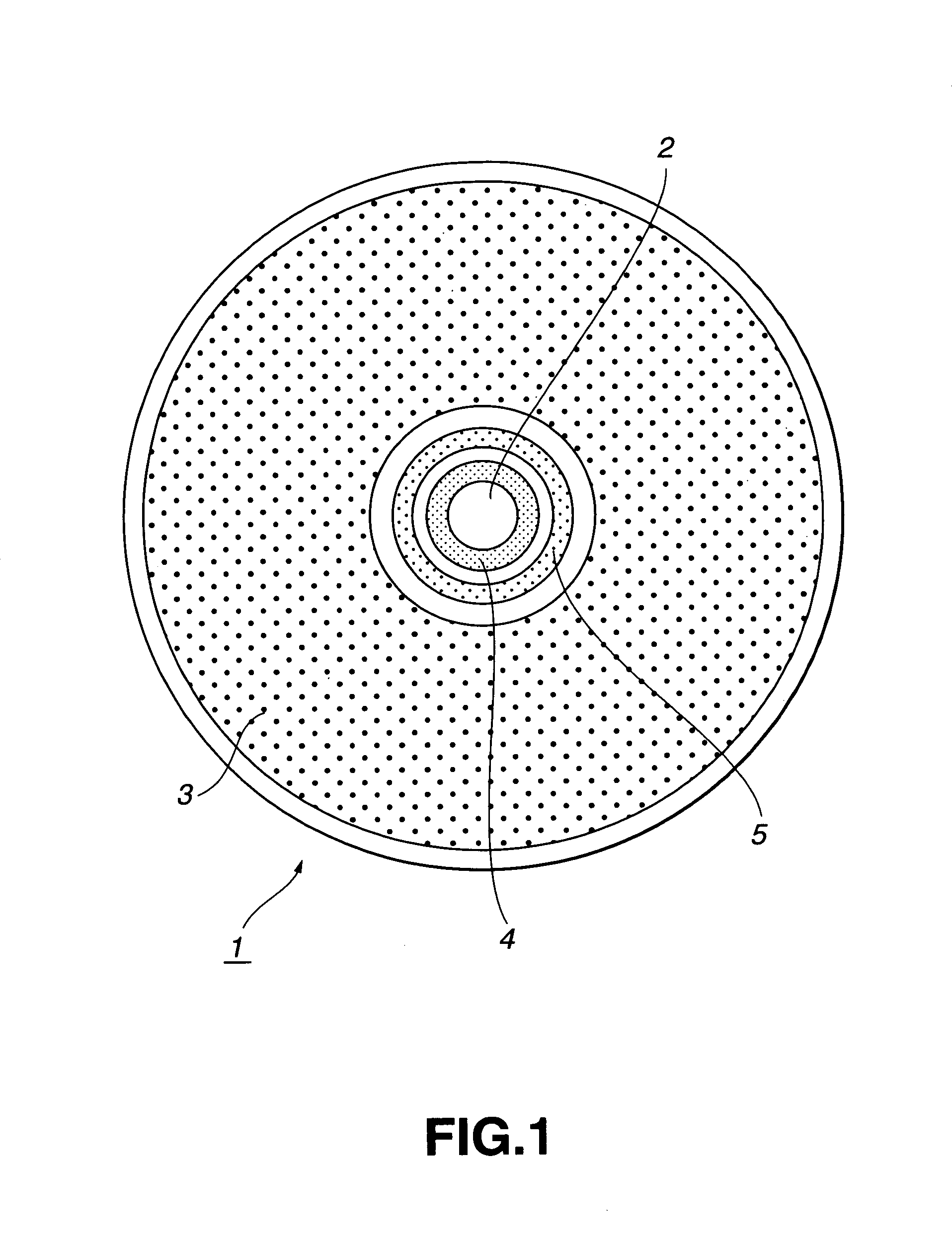
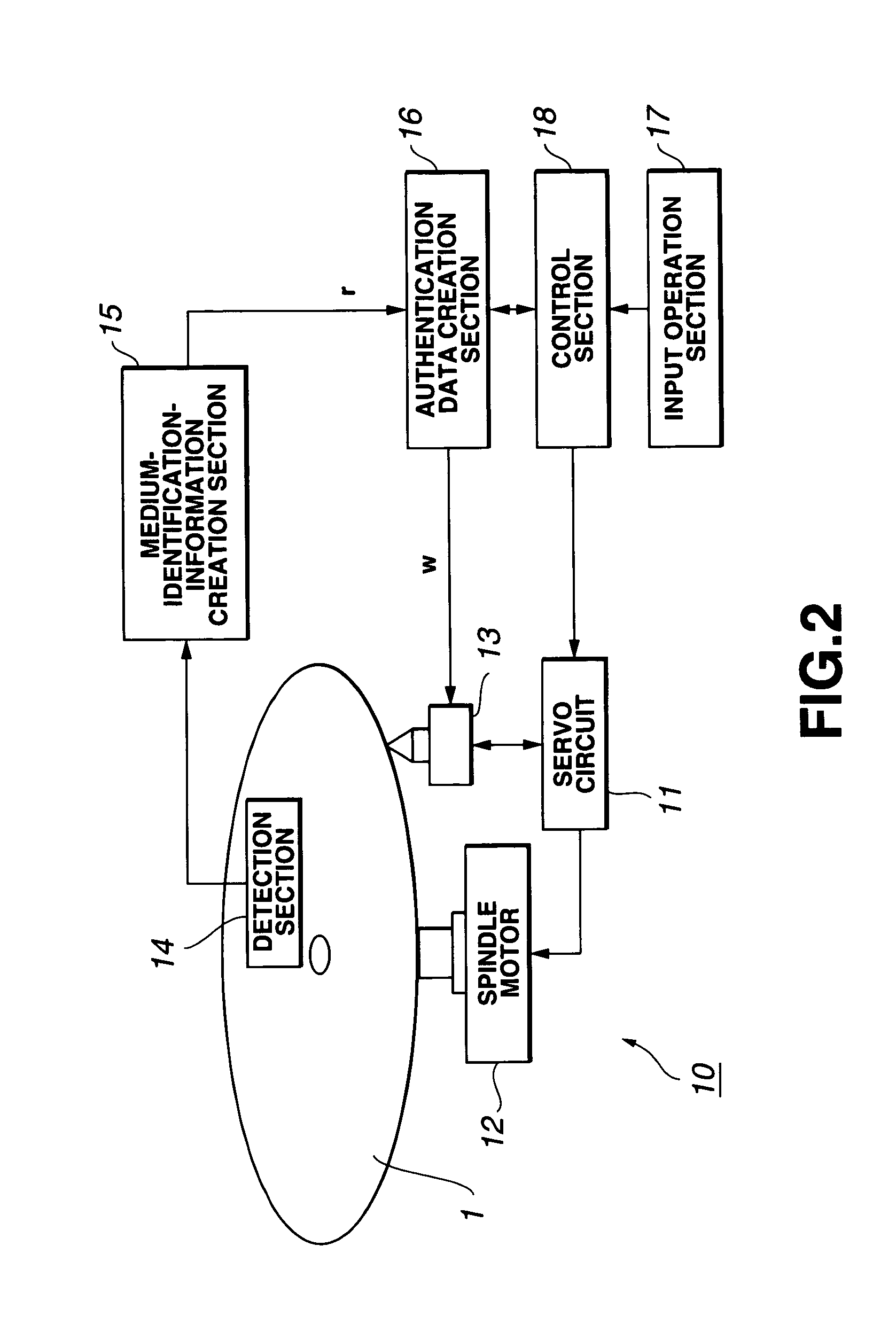
Information recording/reproducing system
An information recording medium 1 is provided with: a user data recording part 3 which records user data; a random-patter-information recording part 4 which records random pattern information from a random physical phenomenon; and an authentication data recording part 5 which records, as authentication data, medium identification information created on the basis of the random pattern information detected from the random-pattern-information recording part 4 and a digital signature for each manufacturer with respect to the medium identification information.
Owner:SONY CORP
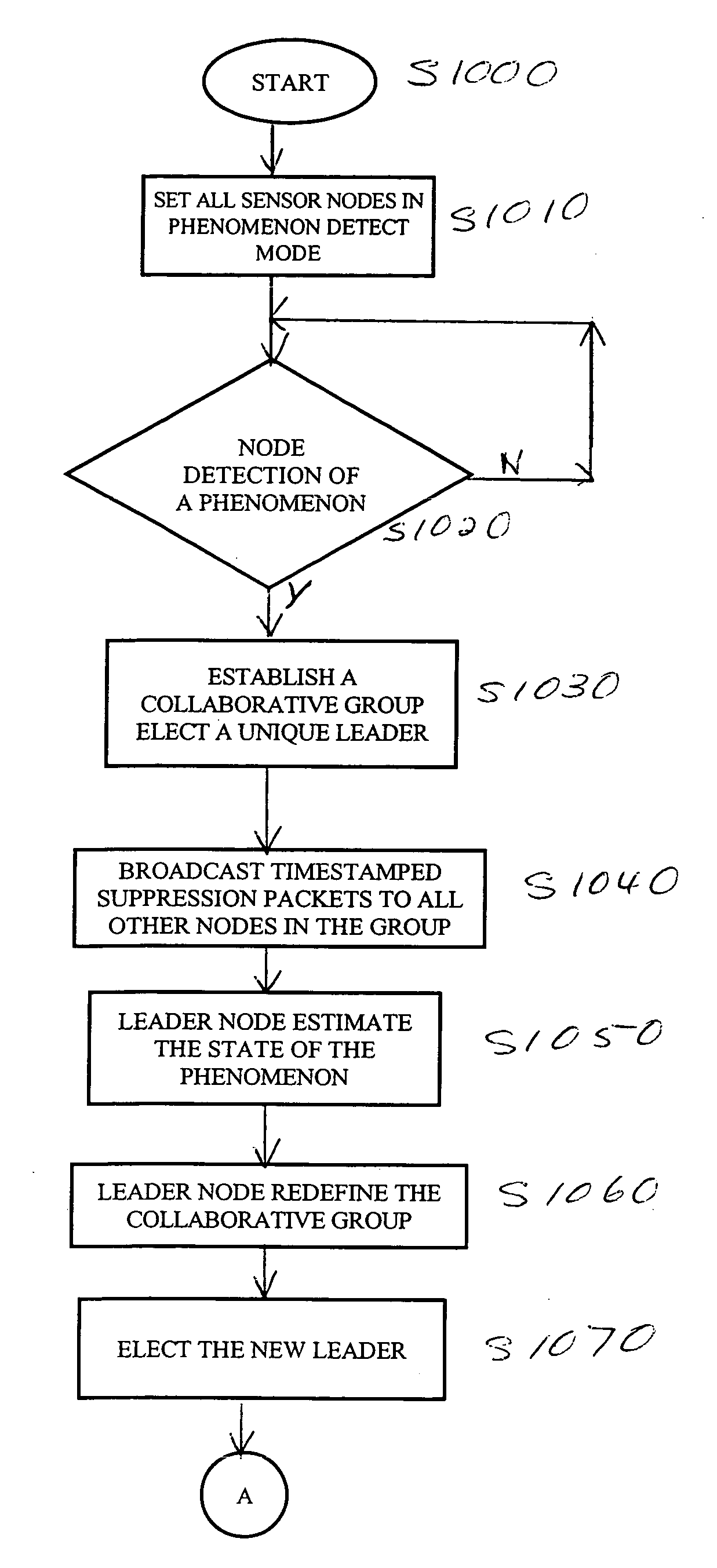
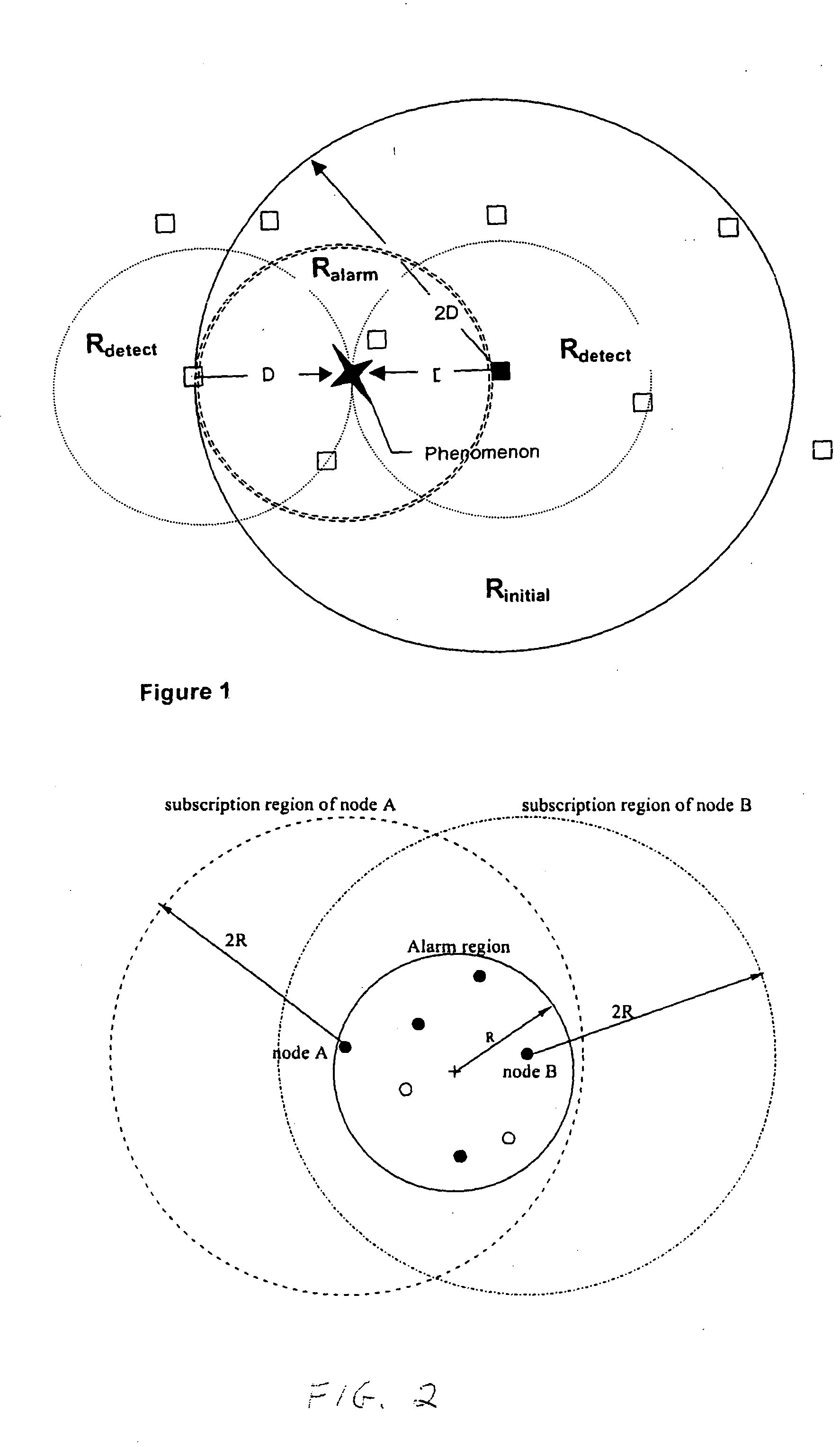
Systems and methods for distributed group formation and maintenance in geographically based networks
InactiveUS20050055417A1Minimizing distance measureParticular environment based servicesNetwork topologiesIndependent groupNew device
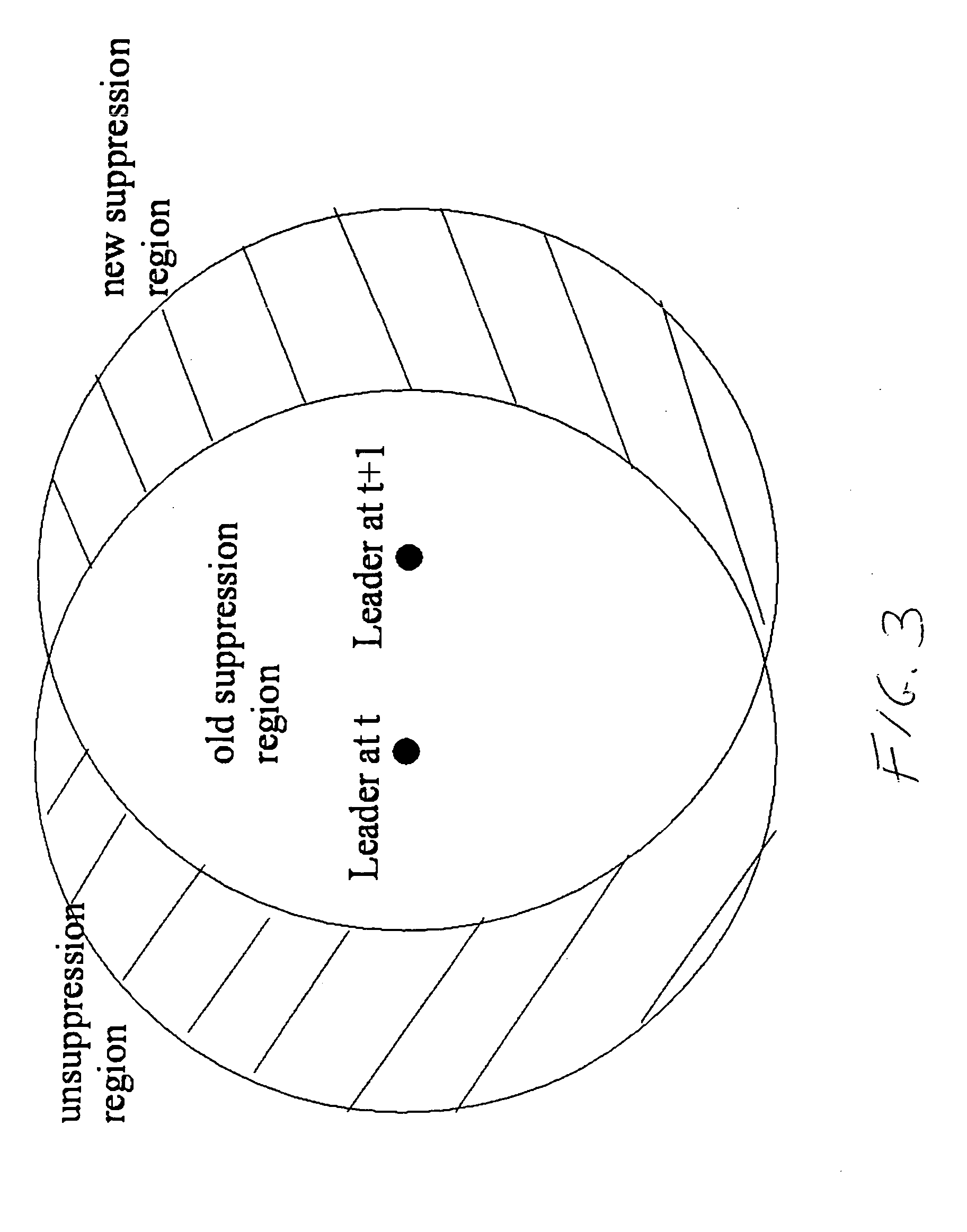
In a distributed sensor network, one or more devices, for example, forming a collaborative group, are associated with a physical phenomenon based on geographical proximity. The sensor network is capable of detecting new phenomena and changing the membership of the collaborative group as the phenomenon changes. Sensors not associated with a detected phenomenon are available to detect new phenomenon, and one group may exist per phenomenon. Upon detection of a phenomenon, a group of nodes is formed and a leader node is elected. As the phenomenon changes over time, new devices come into proximity of the phenomenon and are prevented from forming independent groups associated with the phenomenon. This accomplished in a decentralized way with communication restricted to local neighbors. In a tracking sensor network using a relatively small number of sensors, the sensors are active and maintain a coherent belief associating their measurements with a single common vehicle.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Water safety device
InactiveUS20060012483A1Energy supplyNavigational aids with satellite radio beacon positioningTransducerBiological activation
A water safety device includes a transmitter device adapted for operation with an alarm and search console. The transmitter device includes an alerting unit and an associated activation sensor. Activation of the alerting unit results in the transmission from the alerting unit to the alarm and search console of a tracking signal. The activation sensor may be any transducer or combination of transducers capable of sensing physical phenomenon generally concomitant a fall into water from a boat or ship. The alerting unit is adapted to immediately begin transmission of a predetermined signal for tracking of the life preserver and transmitter device by the alarm and search console following activation by the activation sensor. The alerting unit may be adapted to cause automated inflation of one or more inflatable bladders upon any indication that the wearer of the water safety device has fallen from the boat or ship.
Owner:ETHINGTON BILLY
Method for controlling transmissions from a resource-restricted device, and batteryless device
ActiveUS20120056728A1Reduce leakage currentReduce the probability of collisionError prevention/detection by using return channelElectric signal transmission systemsControl equipmentEmbedded system
The present invention relates to a method for controlling transmissions of a batteryless device (1) operating in a wireless network, the method comprising the following steps: the batteryless device (1) transmitting a frame including elements for controlling operation of a remote device (2a), or controlled device, the batteryless device being configured with a predetermined number of planned retransmissions of the control frame, the batteryless device sensing a change in the physical phenomenon induced by operation of the controlled device (2a), the batteryless device determining, based on the sensing step, the success or failure of the frame transmission, in case the transmission has succeeded, the batteryless device omitting further retransmissions of the control frame. The present invention also relates to a batteryless device carrying out such method.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
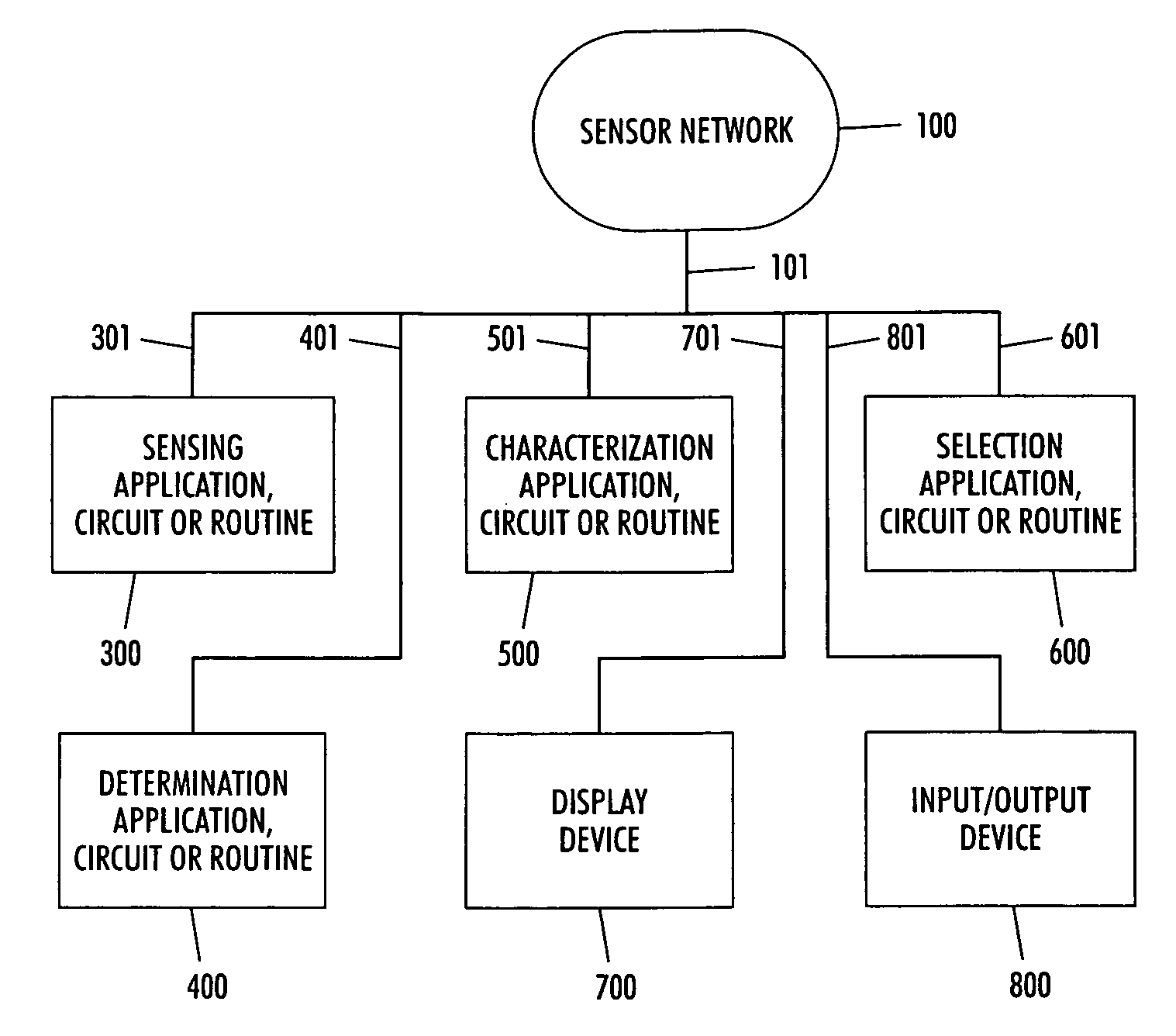
Systems and methods for characterizing the coverage of ad hoc sensor networks
InactiveUS7091902B2Simple and intuitive wayAccurate measurementTesting/calibration apparatusPosition fixationQuality of serviceGraphics
Owner:MAJANDRO LLC
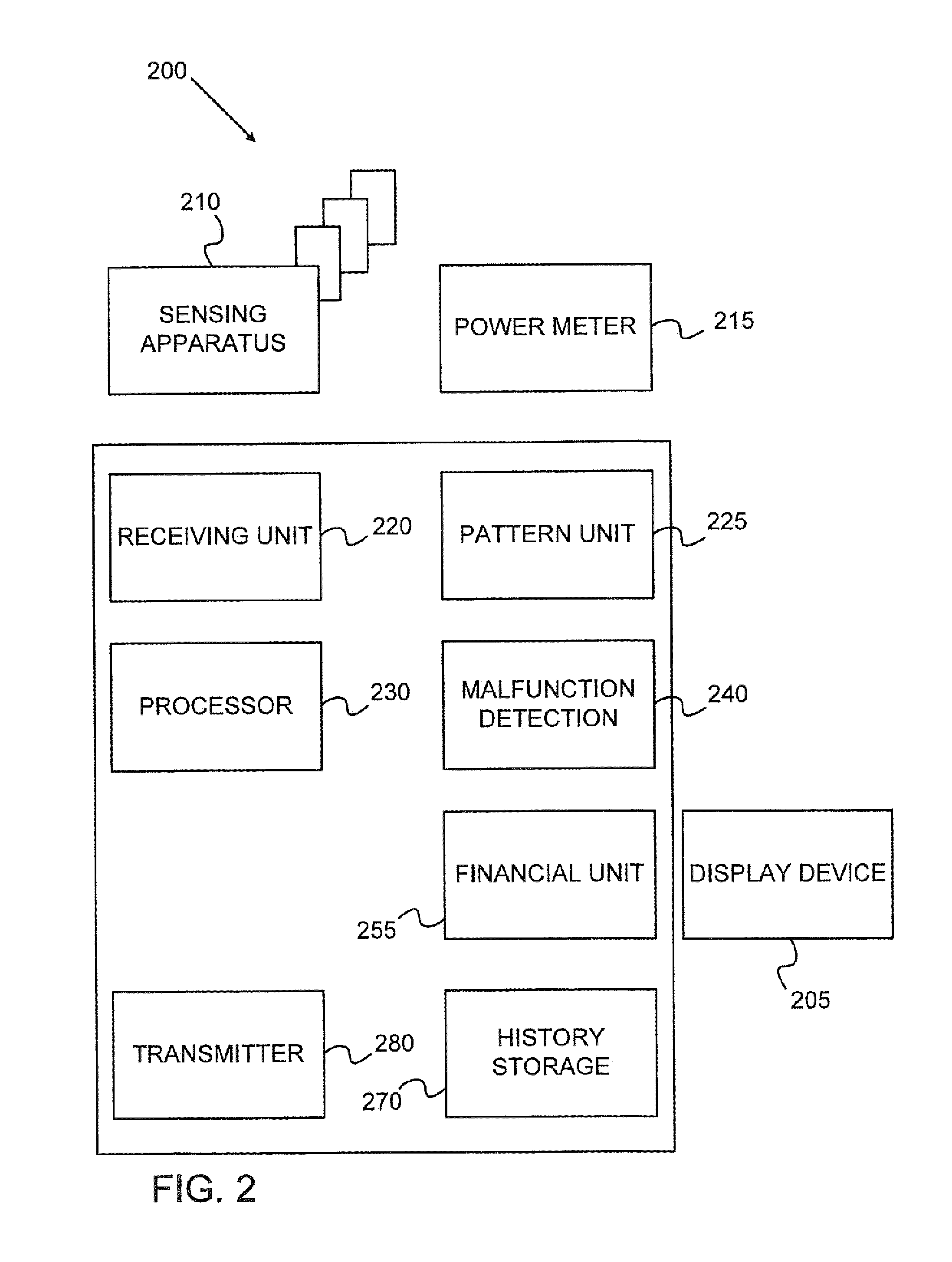
System for measuring electrical power
InactiveUS20110037455A1Decrease and increase powerTariff metering apparatusCurrent/voltage measurementSubject matterElectrical devices
The claimed subject matter discloses a system for measuring power consumption of an electrical appliance. The system comprises a sensing module for sensing physical phenomenon, located externally to the electrical appliance. The system further comprises a transmitter for transmitting information representing the physical phenomenon sensed by the sensing module and a power device. The physical phenomenon sensed by the sensing module provides indication on whether the electrical appliance is ON or OFF and whether the power consumption of the electrical appliance increased or decreased. In some cases, the indication is one or more scalars representing the sensed physical phenomena.
Owner:OREN NAVOT +1
Resonance driven changes in chain molecule structure
InactiveUS6060293AEfficient inductionPeptide preparation methodsElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentChemical industryDisease
PCT No. PCT / DK96 / 00158 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 26, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 26, 1997 PCT Filed Apr. 1, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 30394 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 3, 1996The invention relates to the technical application of electromagnetic radiation such as microwaves and radiowaves and application of ultra sound to chain molecules. In particular, the present invention relates to the utilization of topological excitations such as wring, twist and torsional modes, e.g., for generating structure, such as in folding, refolding or renaturation, and denaturation or unfolding of peptides, polypeptides, proteins, and enzymes; for generating changes in molecular affinity; for stimulating drug receptor interactions; and for changing molecular communication, is described. The technique is based on a new understanding of the underlying physical phenomenon and can also be applied to other chain molecules and biologically active biomolecules and tailored polymers such as glucoproteins, antibodies, genomic chain molecules such as DNA and RNA as well as PNA, carbohydrates, and synthetic and natural organic polymers. The invention is especially applicable for solving problems related to inclusion bodies and aggregation when using recombinant DNA and protein engineering techniques. Furthermore, the invention can be utilized in therapeutic treatment and in development and production of pharmaceuticals. The area of applicability ranges from biotechnological industry, food industry, drug industry, pharmacological industry, chemical industry, and concerns, e.g., the treatment of conditions and diseases related to influenza, hepatitis, polio, malaria, borrelia, diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, Creutzfeldt Jakob disease, other prion related diseases, multiple sclerosis, cataract, heart diseases, cancer, and aging.
Owner:PROKYON
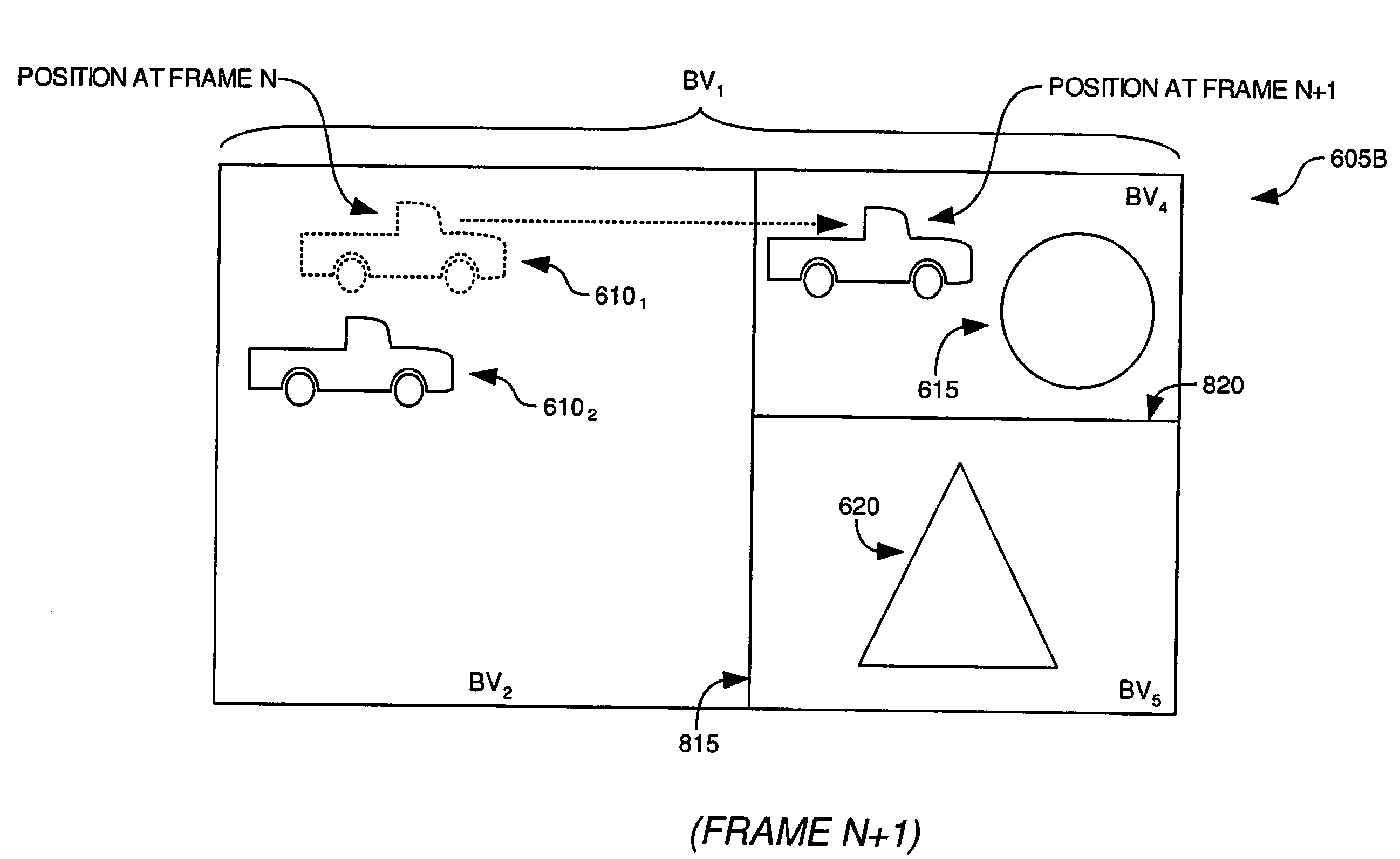
Integrated Acceleration Data Structure for Physics and Ray Tracing Workload
According to embodiments of the invention, a data structure may be created which may be used by both an image processing system and by a physics engine. The data structure may have an initial or upper portion representing bounding volumes which partition a three dimensional scene and a second or lower portion representing objects within the three dimensional scene. The integrated acceleration data structure may be used by an image processing system to render a two dimensional image from a three dimensional scene, and by a physics engine to perform physics based calculations in order to simulate physical phenomena in the three dimensional scene. Furthermore, the physics engine may update the integrated acceleration data structure in response to changes in position or shape of objects due to physical phenomena.
Owner:IBM CORP
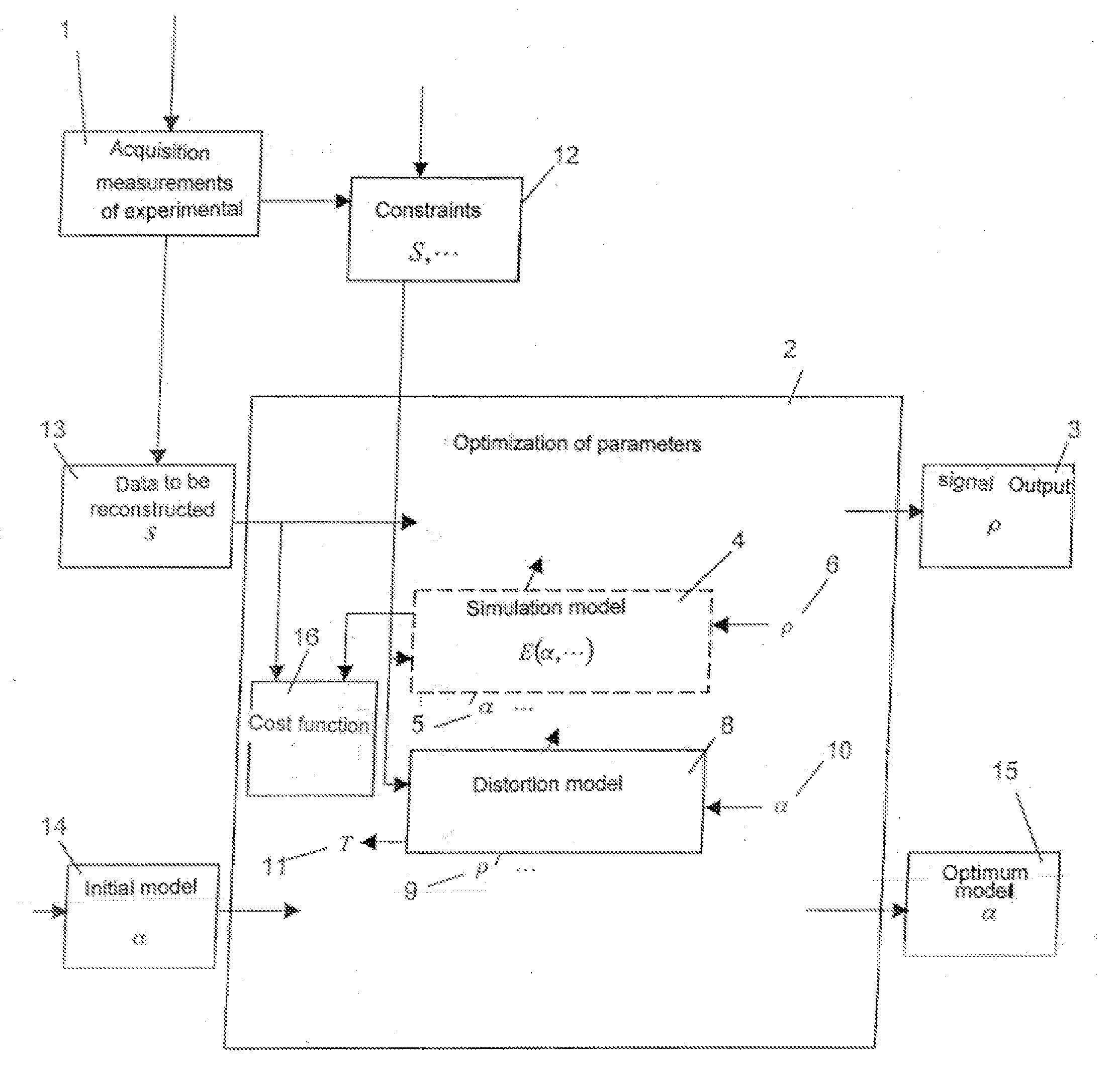
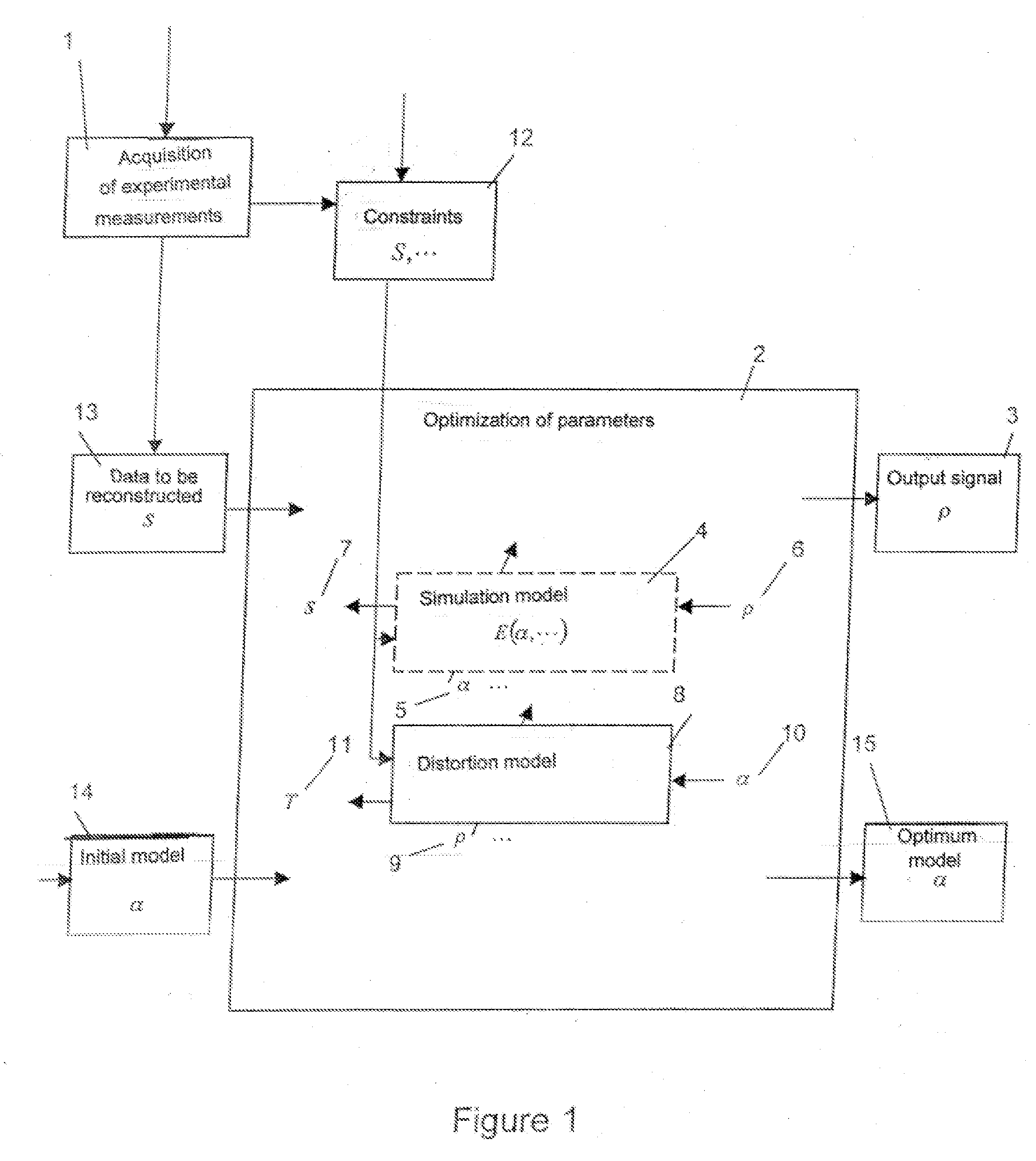
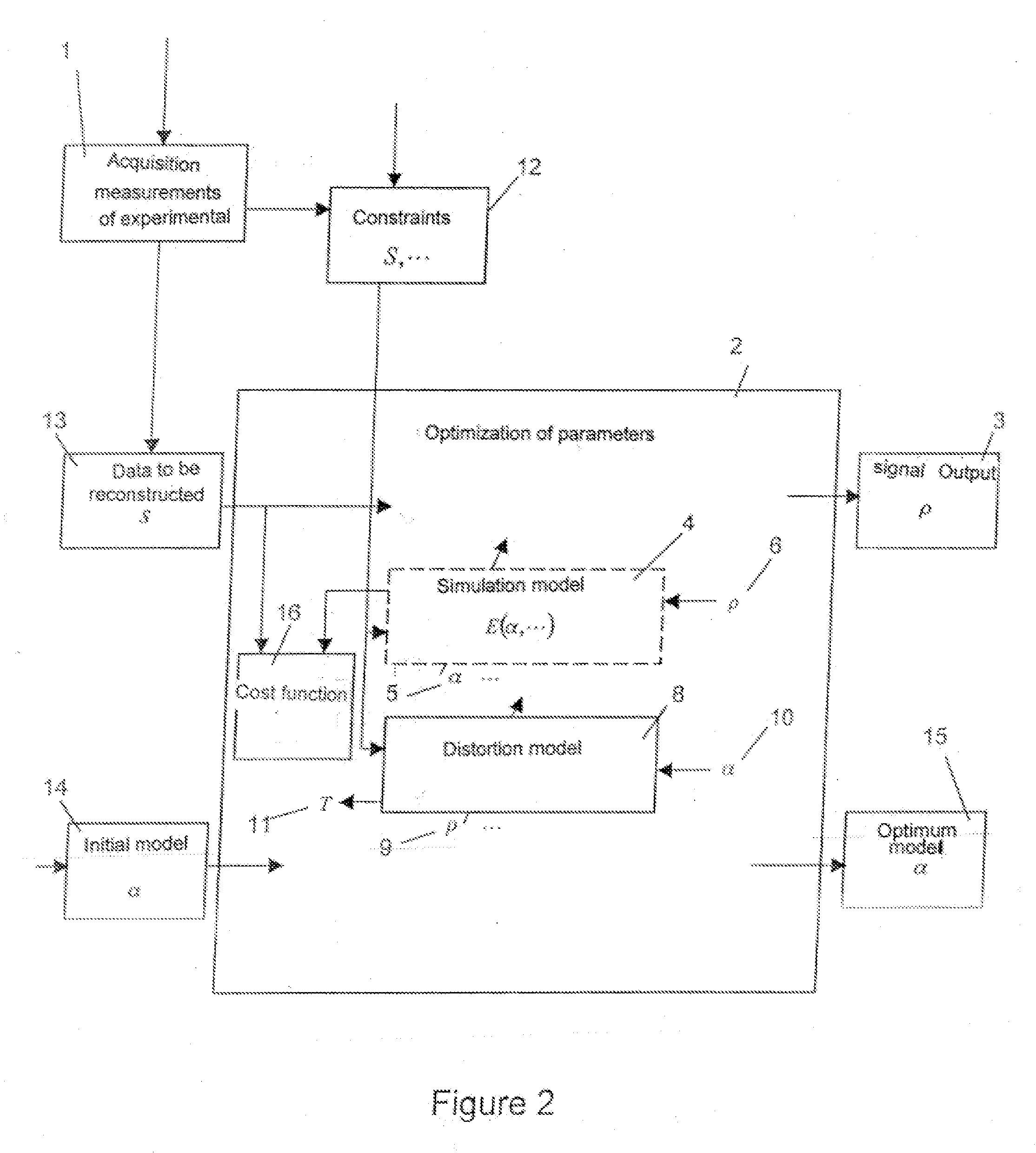
Method for reconstructing a signal from distorted experimental measurements and device for its implementation
ActiveUS20110022375A1Magnetic measurementsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusMedical imagingComputer science
A method for acquiring (1) experimental measures with interferences of a physical phenomenon, and for reconstructing (2) a point-by-point signal (3) representative of the phenomenon according to at least one dimension that can vary during the experimental measure acquisition, using at least one simulation model (4) of at least one acquisition chain of the experimental measures including at least one interference, and at least one model (8) of each interference in each acquisition chain, each interference model being determined at least from the measures themselves, wherein the simulation and interference models include adjustable parameters (6, 10) depending on experimental conditions, wherein at least one adjustable parameter of one of the models is coupled to at least one adjustable parameter of the other model, and in that the adjustable parameters are optimized in a coupled manner. A device for MRI imaging, NMR, or medical imaging using such a method is described.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LORRAINE
Using a physical phenomenon detector to control operation of a speech recognition engine
A transmission device such as a cell phone or other mobile communication device includes a physical phenomenon detection device to perform a “push to talk” function by detecting the occurrence of a particular physical phenomenon and using such detection to start and stop recording an utterance for subsequent analysis by a speech recognition engine. A method of controlling operation of a speech recognition engine in response to detection of a physical phenomenon includes detecting or sensing, via a physical phenomenon detection unit, a predetermined physical phenomenon representative of an intent to invoke operation of a speech recognition engine. In response to the detection or sensing of the predetermined physical phenomenon, a signal is transmitted to a control unit in a communication device. In response to the receipt of the transmitted signal, the utterance received from a user via the communication device is recorded, and the recorded utterance is provided to a speech recognition engine for operation thereon. The user may thus effectuate operation of the speech recognition engine upon the utterance by causing the physical phenomenon to occur.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC +1
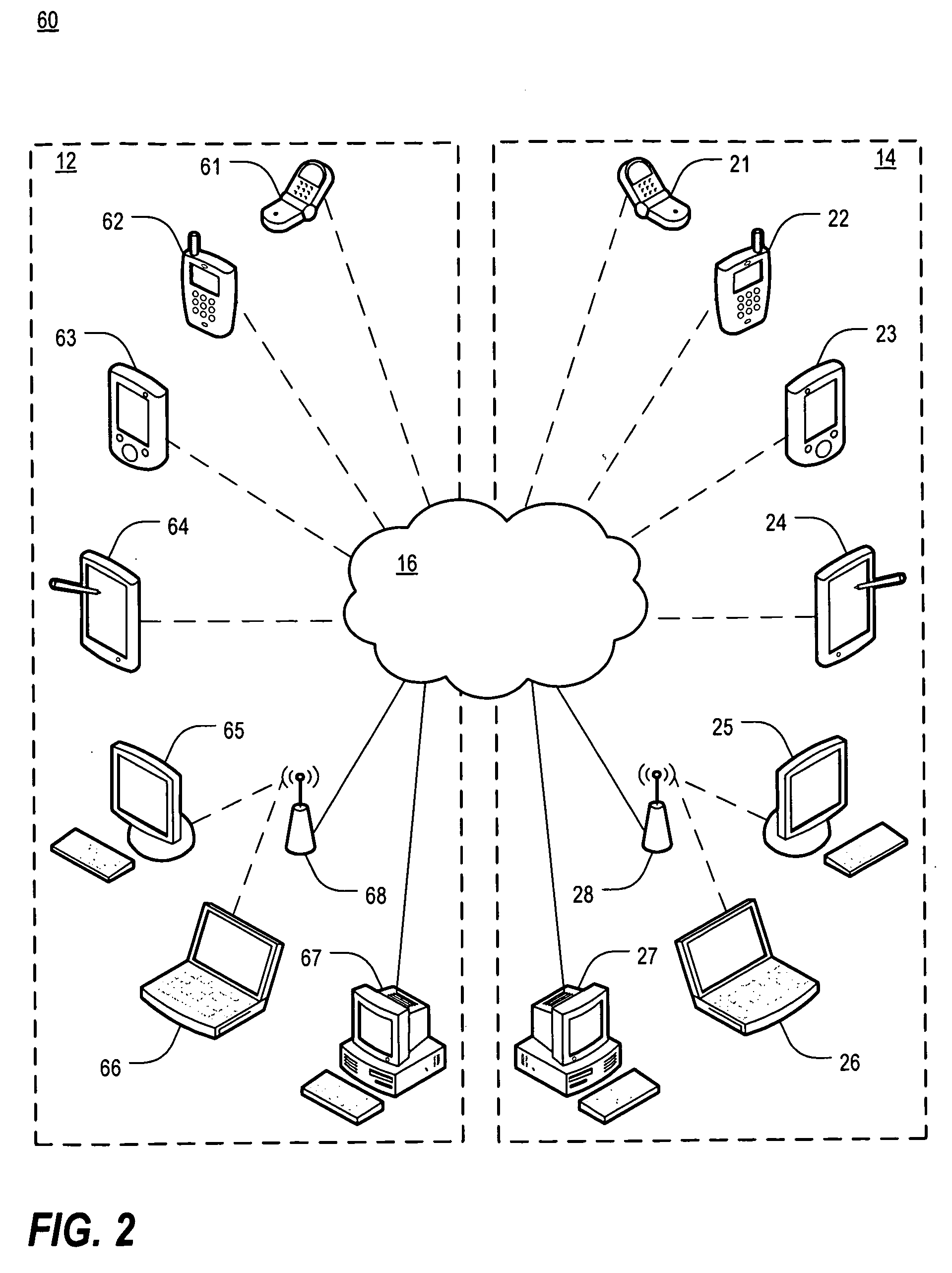
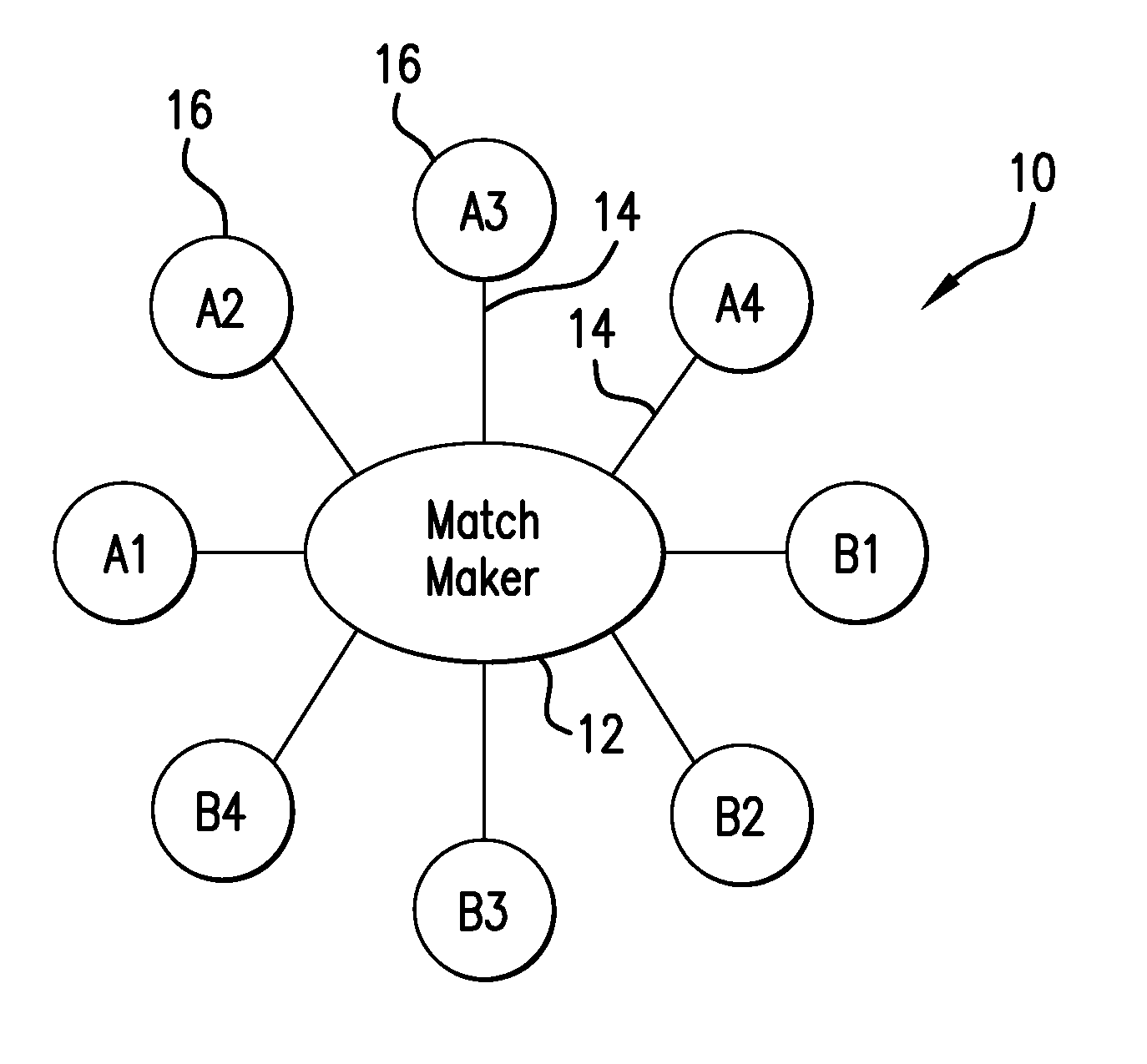
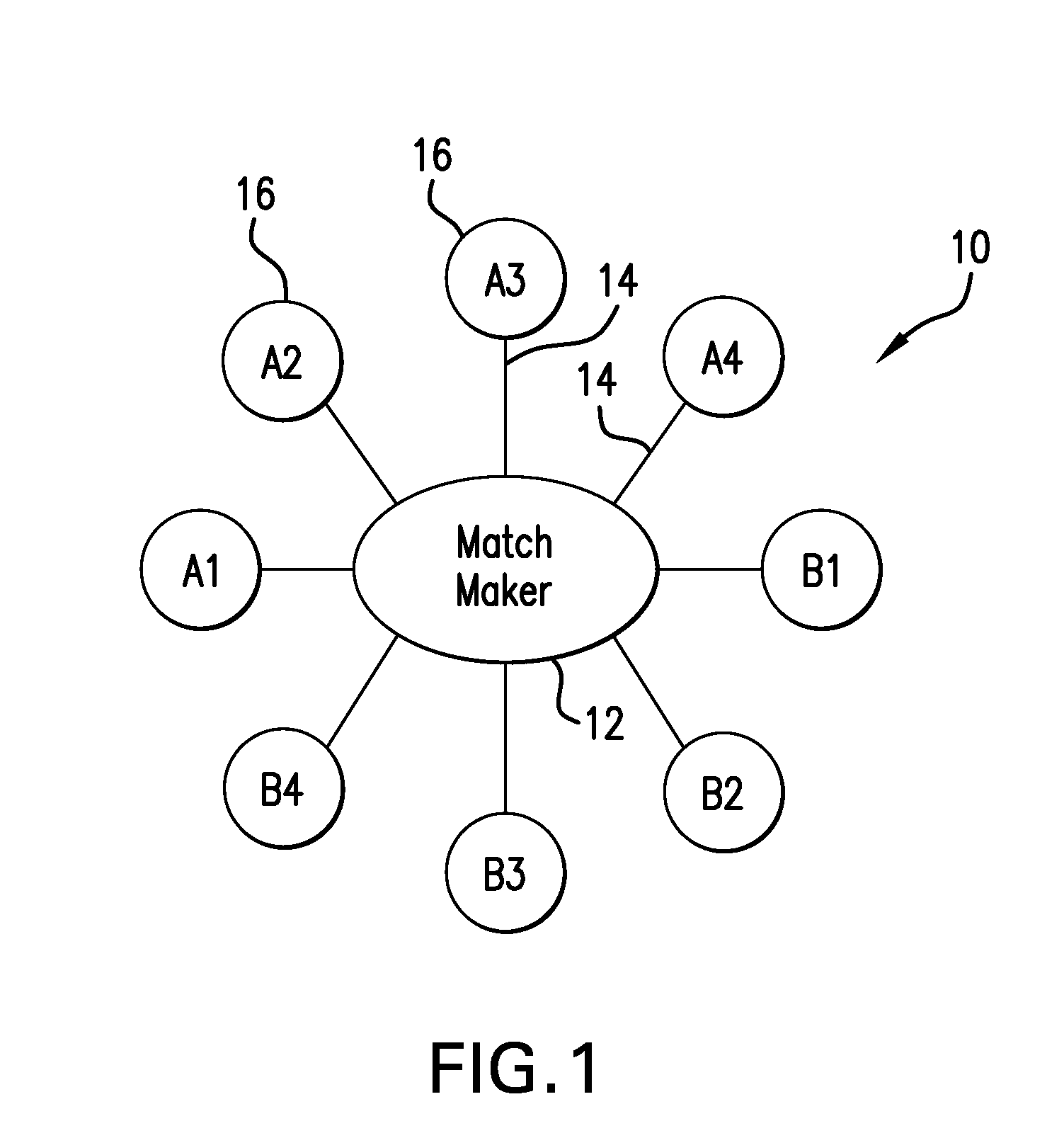
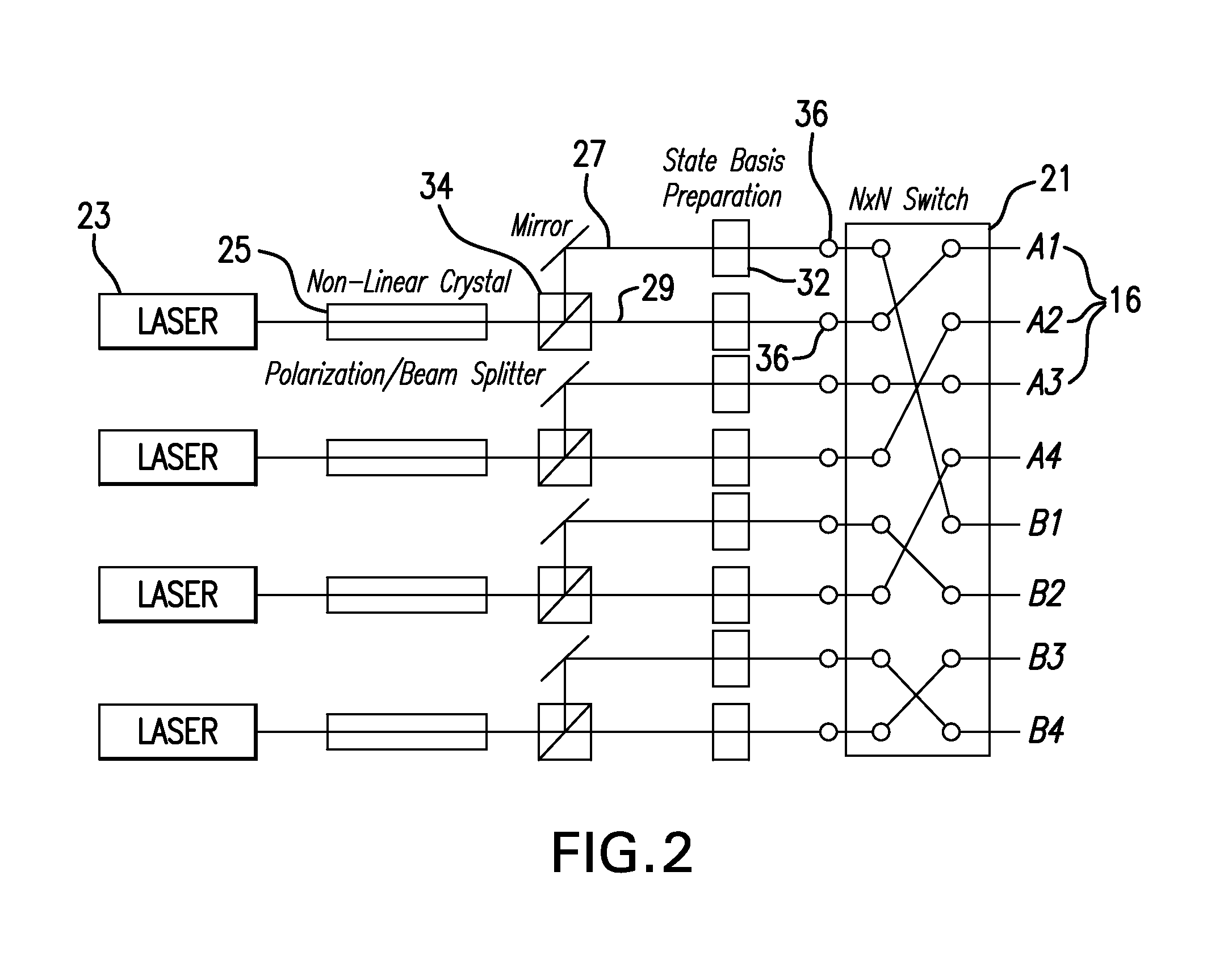
Incorruptible public key using quantum cryptography for secure wired and wireless communications
ActiveUS20160112192A1Communication securitySecure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationElectric digital data processingFuture proofQuantum
A hardware system and encryption method that generates encryption keys based on quantum mechanical phenomena that can be delivered directly, over public wired and wireless channels, to communicating devices. The encryption strength is derived from physical phenomena and not mathematical complexity and, therefore, is “future proof” against advances in computational power. The present invention allows pre-existing networked devices to communicate securely within a geographically defined “protection zone.”
Owner:QUBITEKK
Method for the numerical simulation of a physical phenomenon with a preferential direction
ActiveUS7239990B2Improving numerical toolReduce Simulation CostsComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationPartition of unityAdvection
The invention provides a method of simulating behavior of a flow interacting with an object. The invention improves the accuracy of the approximation of the spatial pth derivative Dp, p≧1, and therefore reduces the cost of the simulation. It includes in the approximation values of the parameter at points which do not lay on grid lines passing through the point of computation P, and by using these values to optimize the approximation. The use of these additional points depends on a preferential direction, such as determined by the advection direction of the flow. The points used in the approximation extend beyond a unit cube on the computational grid. The simulation is in three or more dimensions. The numerical simulation produces output which can be used in the design or optimization of the object which interacts with the flow. In certain cases, it is the output by itself which is important.
Owner:STRUIJS ROBERT
Exterior parts
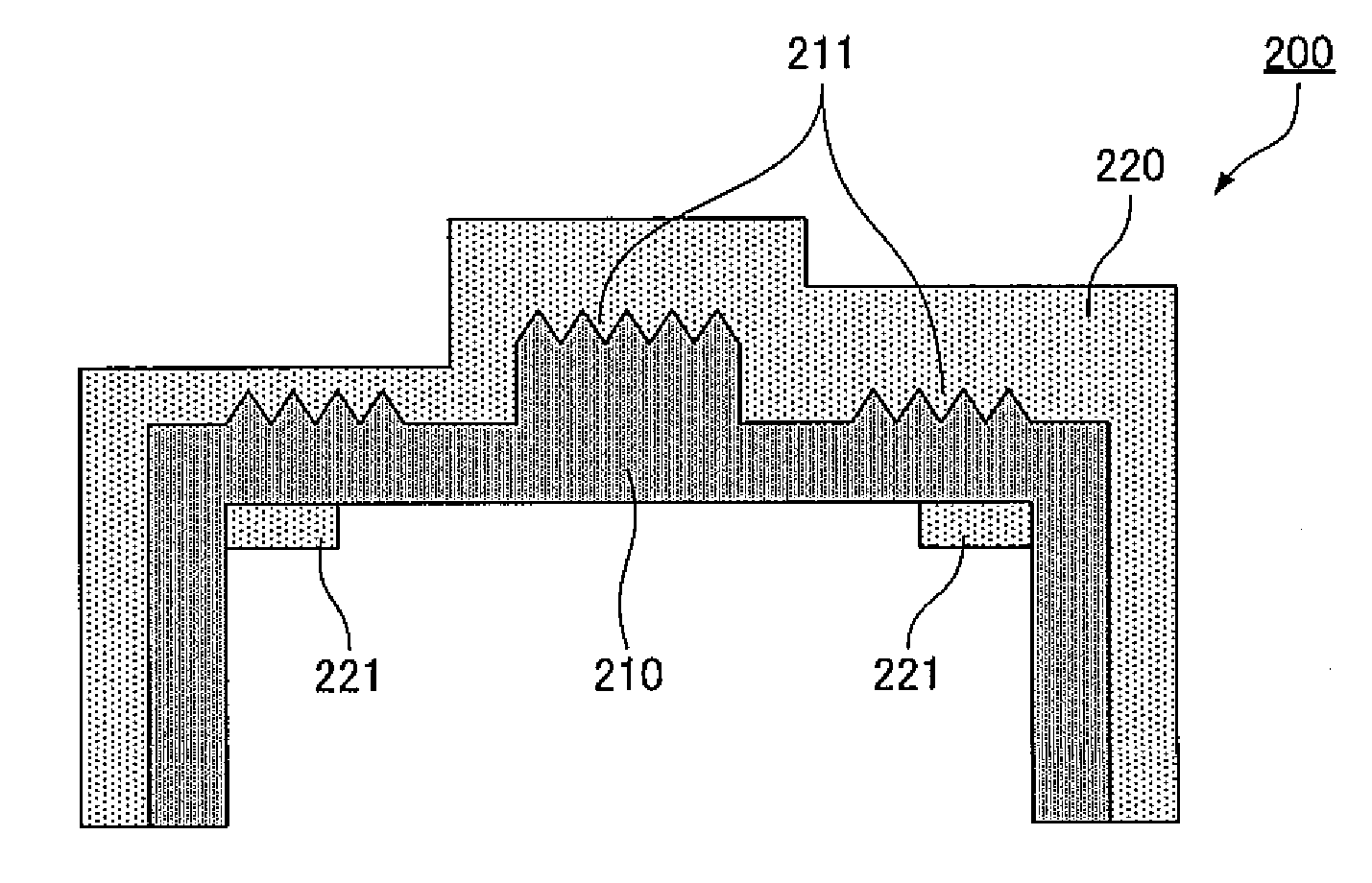
InactiveUS20110033670A1Improve suppression propertiesSimple moldingLayered productsDiffusing elementsEngineeringPhysical phenomena
An exterior part (200) includes (a) a structure color generation portion (210) having a minute shape (structure color generation region (211)) formed therein, light in a visible light range being produced from the minute shape by a physical phenomenon such as interference or diffraction with the incidence of light, and (b) a resin portion (220) that is made of resin having a light transmitting property and serves as the outer surface of a product, (c) the structure color generation portion (210) and the resin portion (220) are formed by molding, and (d) the structure color generation portion (210) is made of resin different from the resin of the resin portion (220), and covered with the resin portion (220).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
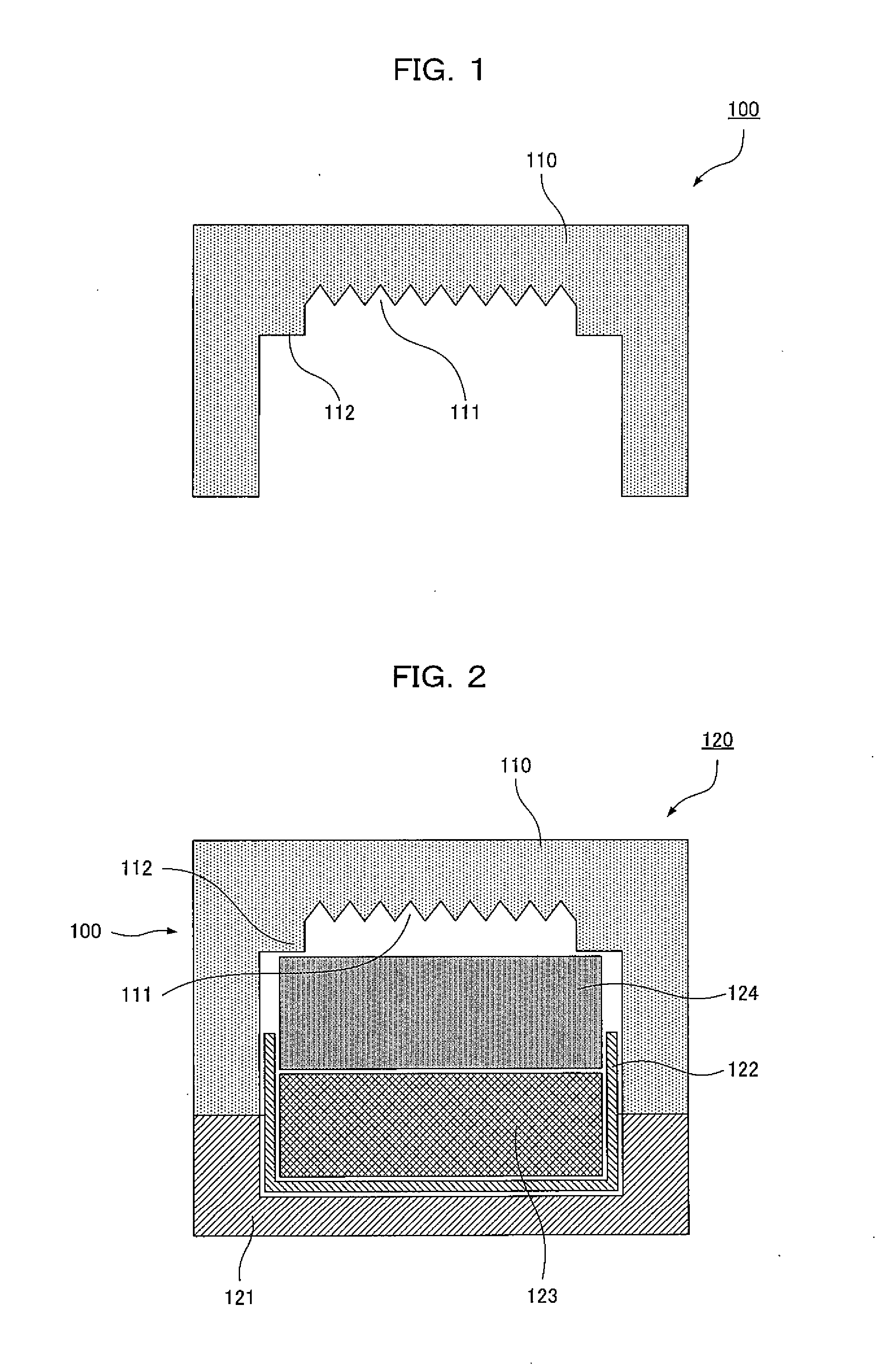
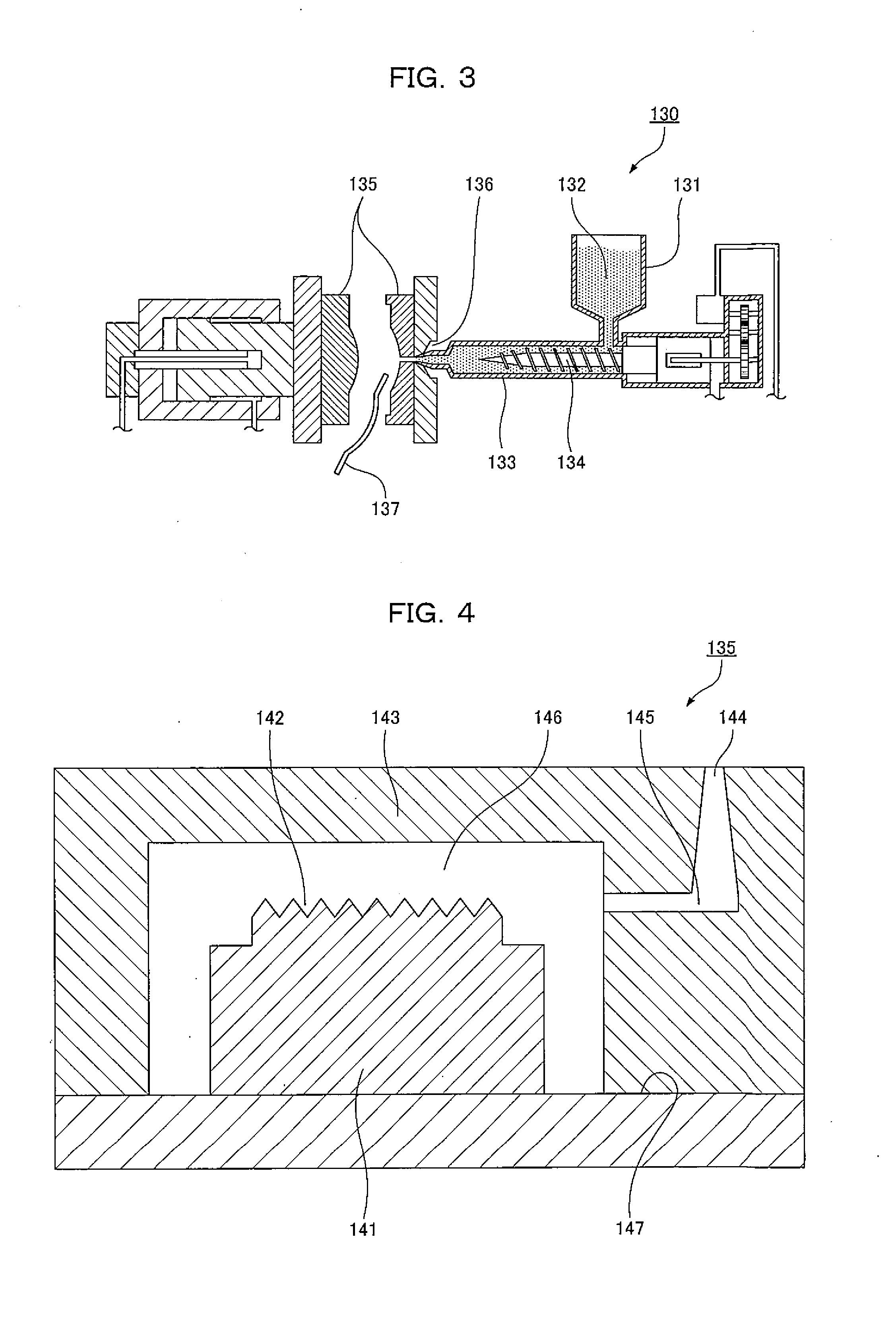
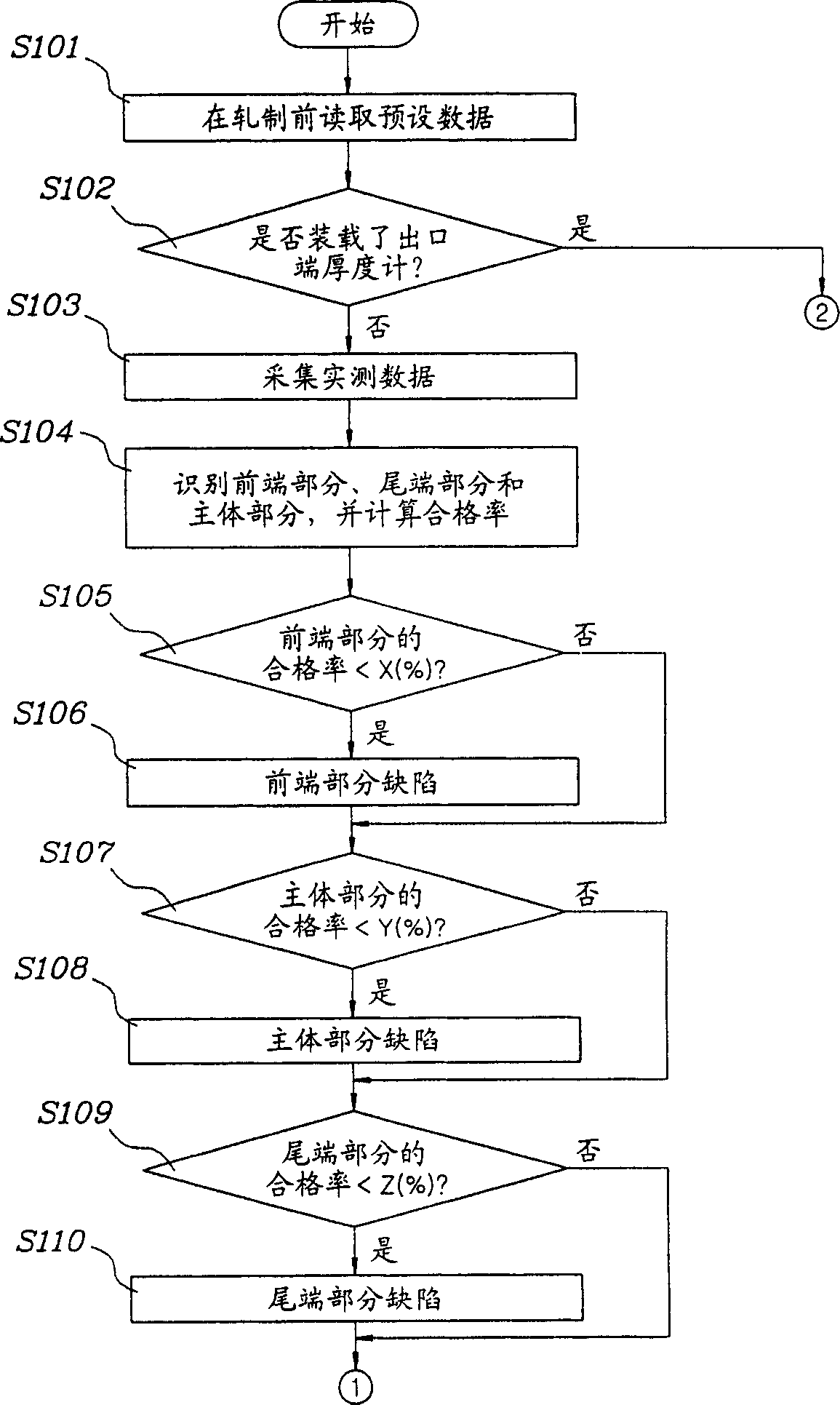
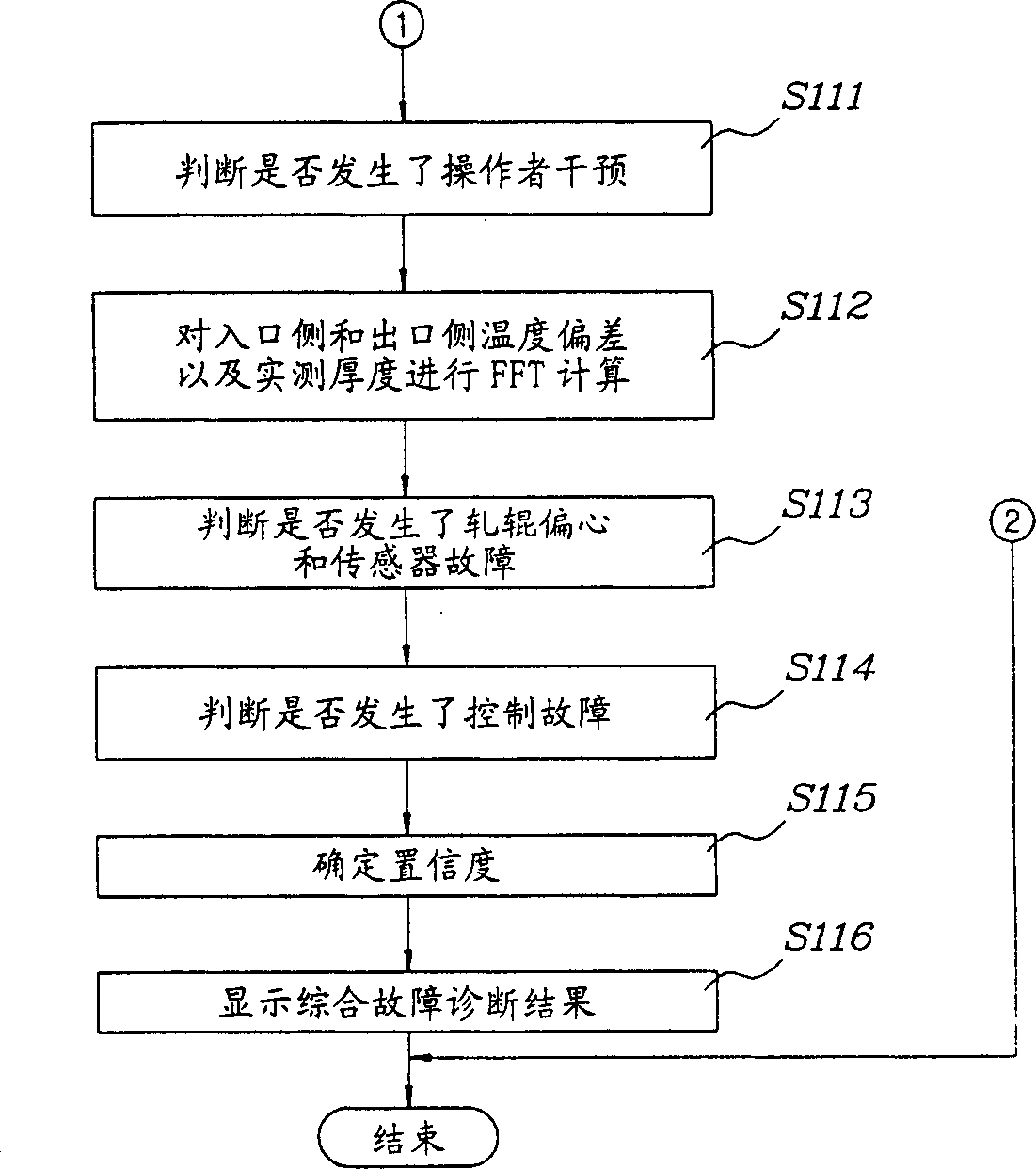
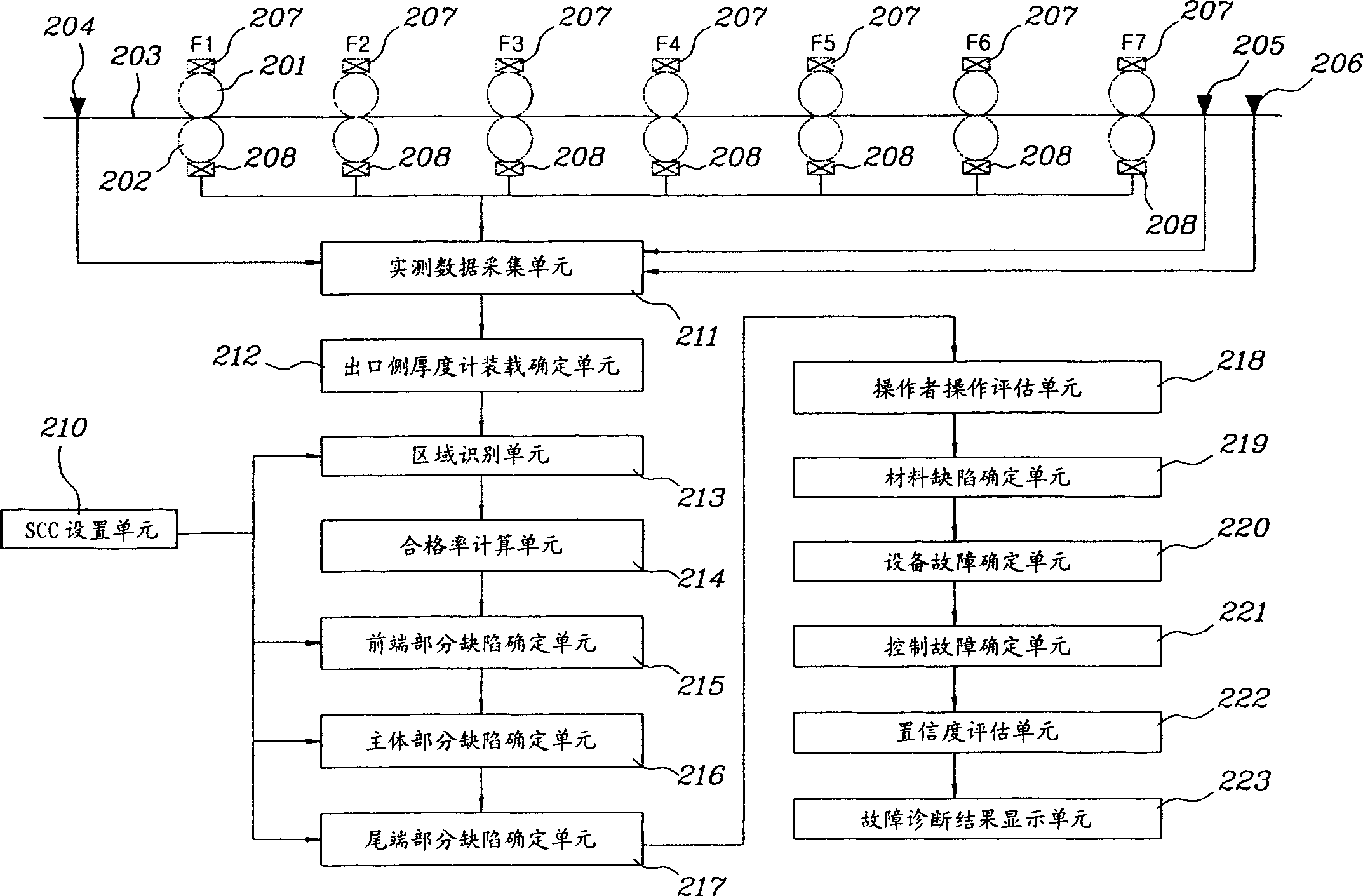
Fault diagnosis apparatus and method for hot fine rolling band steel
InactiveCN1502424ADiagnosing Thickness DefectsRoll mill control devicesElectric testing/monitoringReal-time dataCollections data
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
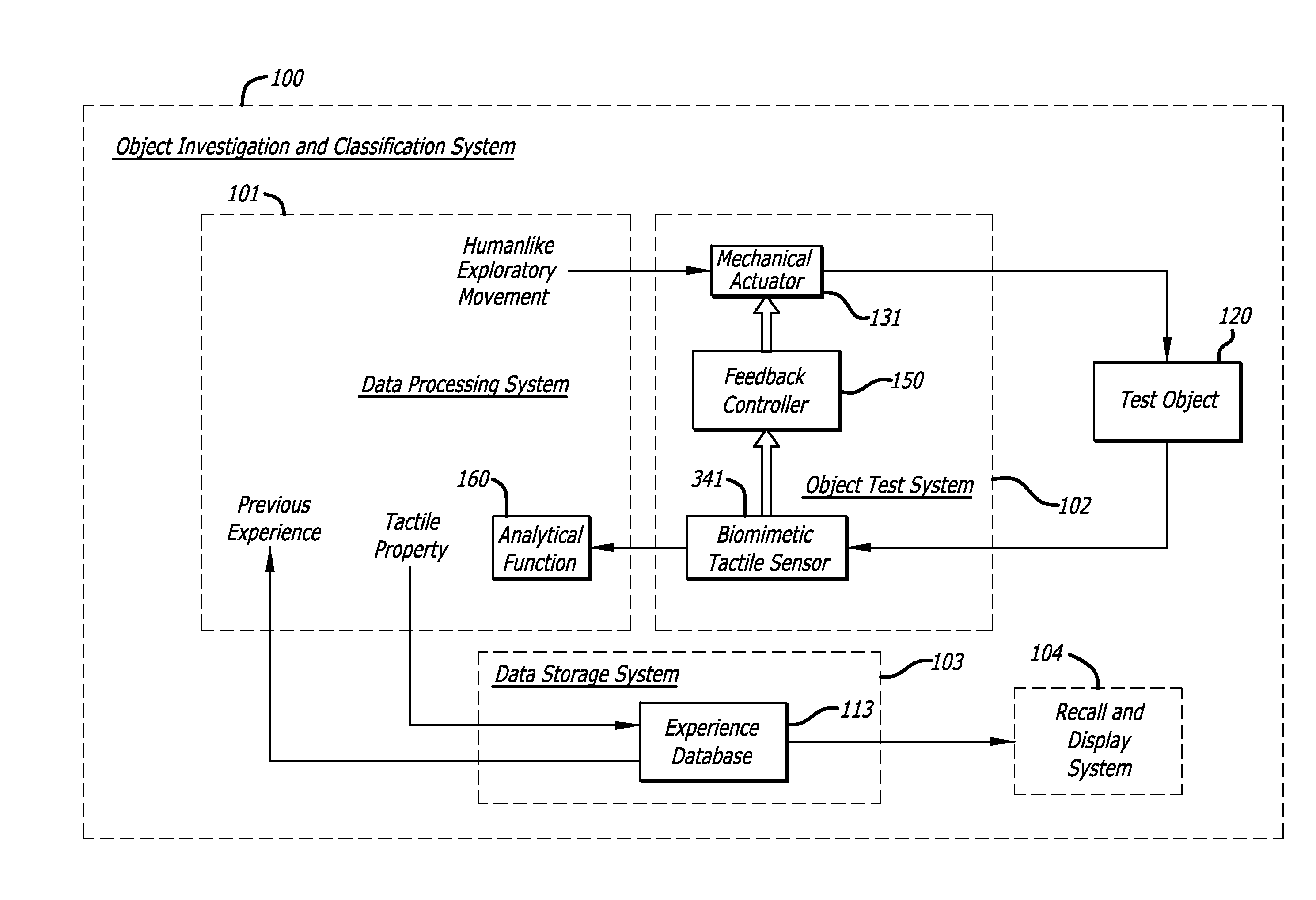
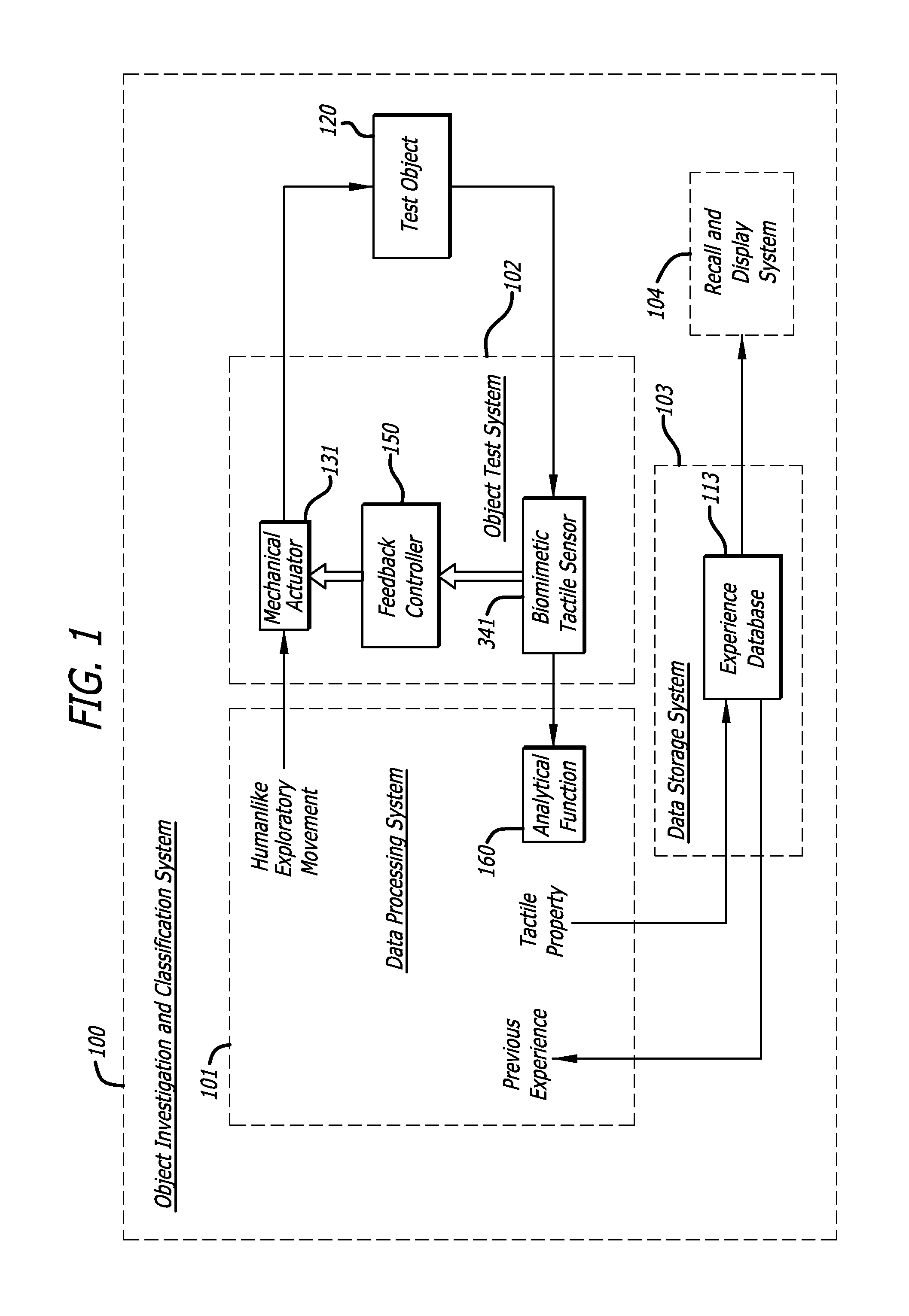
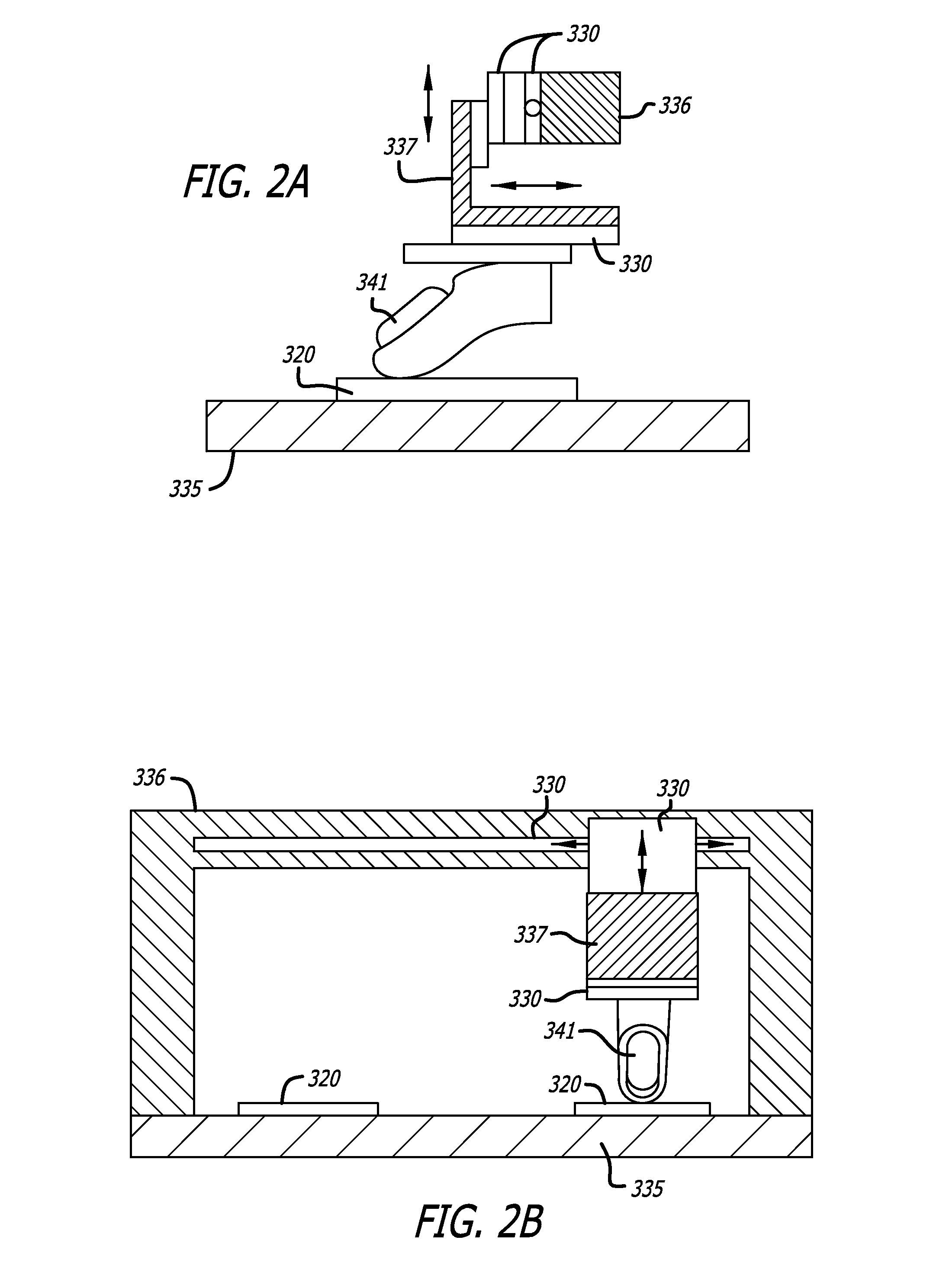
Method and applications for measurement of object tactile properties based on how they likely feel to humans
InactiveUS20160025615A1Special data processing applicationsMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsData setMotion parameter
A system may measure, store, and recall at least one tactile property of multiple objects. The system may include one or more biomimetic tactile sensors that have mechanical properties and sensor modalities that are similar to those of human fingertips. The system may perform at least one exploratory movement on one of the objects by moving the biomimetic tactile sensors over a surface of the object. The at least one exploratory movement may be of a type that a human would normally perform on the object to discern the at least one tactile property and may have one or more movement parameters. Each of the movement parameters may fall within a range of movement parameters that would normally be exhibited if a human performed the exploratory movement for the at least one tactile property. The system may determine and store a value of the at least one tactile property based on information provided by the biomimetic tactile sensors in response to the exploratory movement. The determining may use an analytical function that specifies a mathematical relationship between the value and the information provided by the biomimetic tactile sensors that is based on physical phenomena, rather than extracted from data sets by an adaptive algorithm. The system may repeat the same exploratory movement performance, the same determining the value using the same analytical function, and the same storing the determined value for each of the other objects.
Owner:SYNTOUCH
Mobile sensory device
InactiveUS20120268268A1Devices with GPS signal receiverDevices with sensorHuman–machine interfaceTransceiver
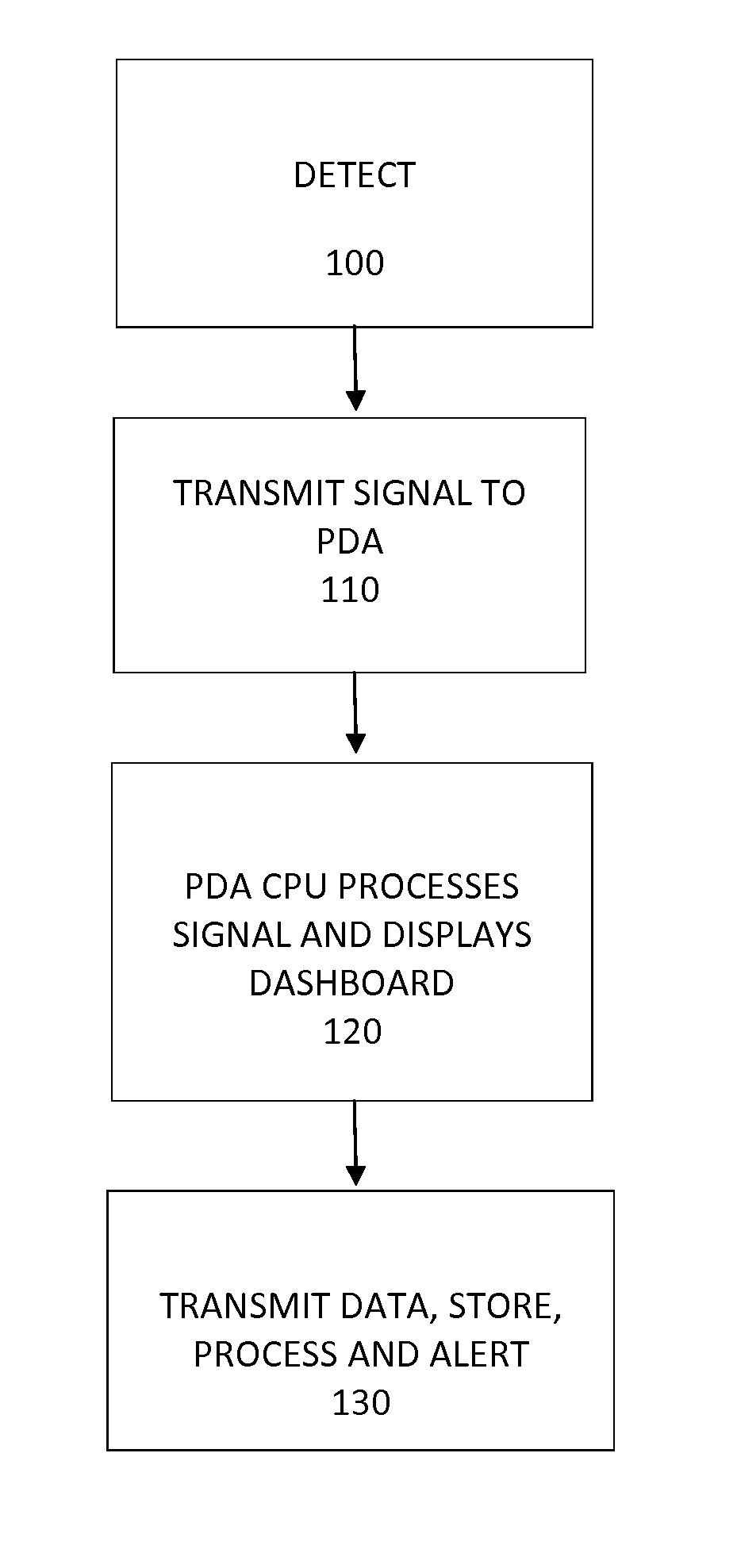
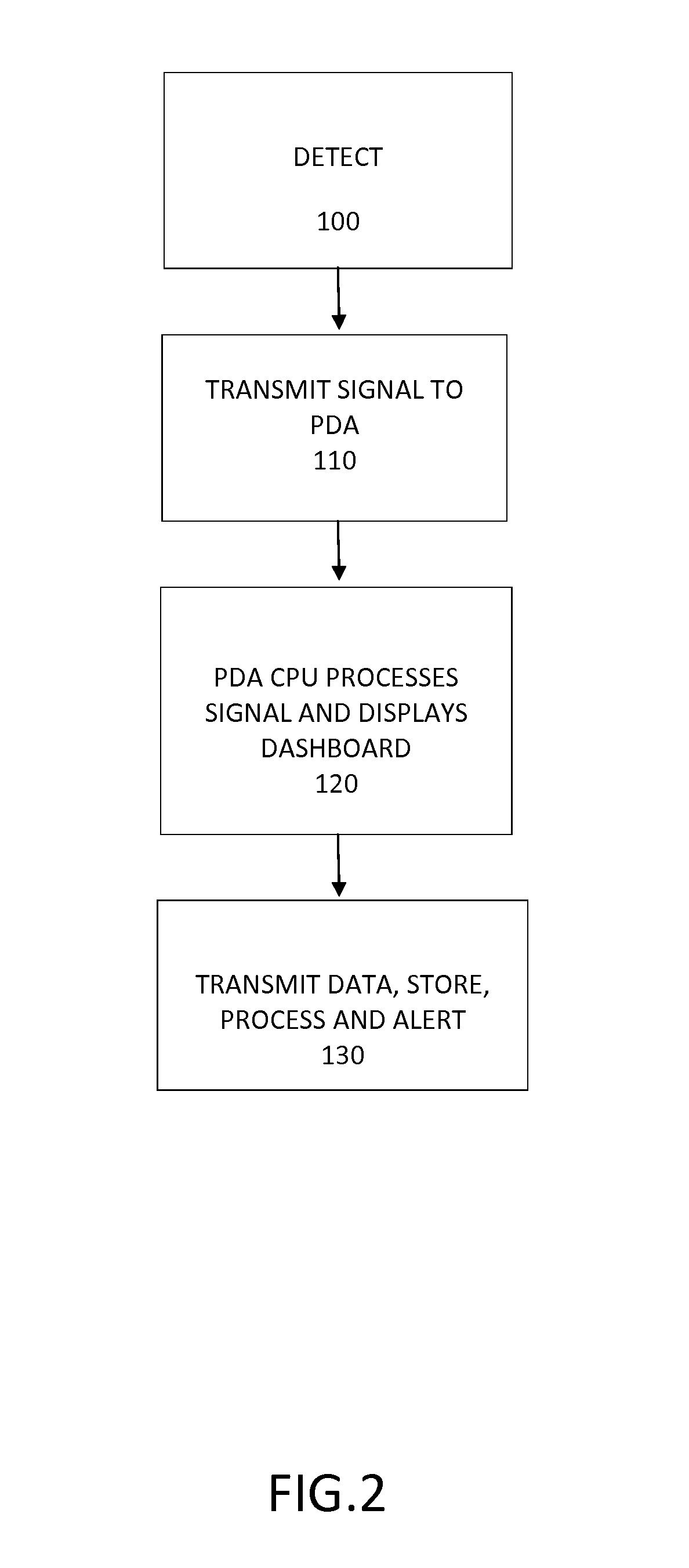
A remote sensory device used in conjunction with a handheld device , such as a PDA (Personal Data Assistant) that utilizes its various computational and telephonic properties as well as other features such as its; short-wave transceiver, display and human interface, electrical power, texting, internet and web browsing capabilities The sensory device utilizes a variety of sensors both individually and in combination to detect physical phenomenon, such as temperature, humidity, gases, radiation, sounds, light, object proximity ,and the like and convert them into an electronic signal that can be interpreted, analyzed, stored and transmitted by the hand-held device and presented to the user. The remote sensory device may be stand alone or imbedded into a case suitable for the PDA and may transfer the data either through a radio means or through a direct electrical connection.
Owner:BARGERO JOHN EUGENE
Superconducting coil quench detection method
InactiveCN101126787AImprove reliabilityThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectrical testingHigh-temperature superconductivityThermodynamics
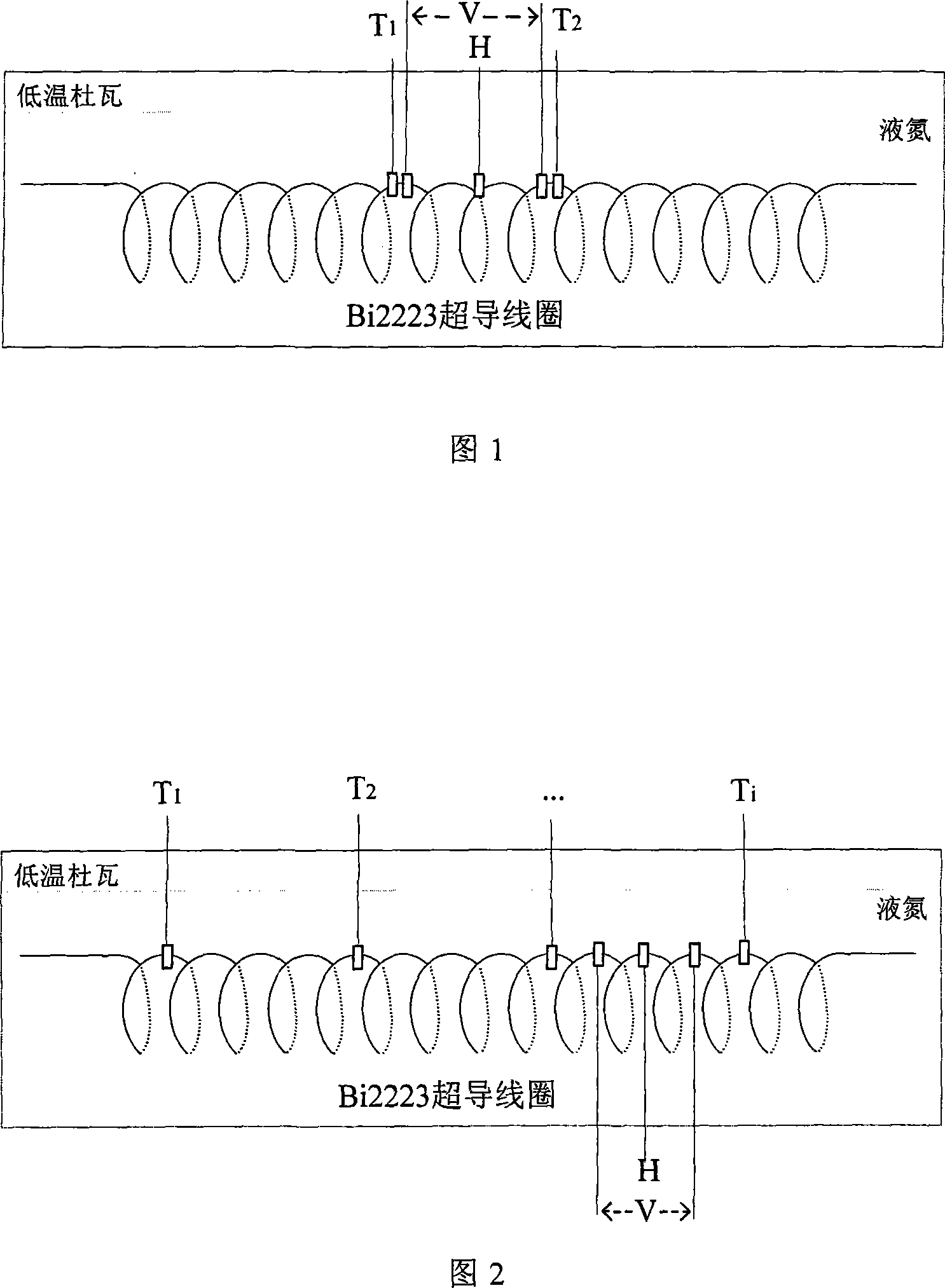
The utility model relates to a quench detecting method of superconducting coils, which is characterized in detecting the temperature of superconducting coil winding at real time; a quench detecting value (temperature rising rate) is acquired by the means that the difference value on adjacent temperature in time is divided by time interval of temperature detection. By comparing the temperature rising rate with the threshold value of the temperature rising rate, the coil quench can be judged if the temperature rising rate exceeds the threshold valve. The determination method on the threshold value of the temperature rising rate is to detect the voltage and the temperature near the quench point at the same time in the process of detecting quench on the superconducting coil and to transform the temperature into the temperature rising rate. When the voltage rises to 1MuV / cm, coil quenches and the mean value of the temperature rising rate on both side of quench point is the threshold value of the temperature rising rate. The utility model is closer to the essence of physical phenomenon and has the advantages of fast detecting speed and high sensitivity. The utility model is applicable for low temperature superconducting (NbTi, Nb3Sn, MgB2) coils and high temperature superconducting (Bi2223, YBCO) coils.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of operating a self-powered home automation sensor device for detecting the existence of and/or for measuring the intensity of a physical phenomenon
ActiveUS20080017726A1Easy to manageGood anticipationLight dependant control systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsOperation modeEngineering
The method of operation applies to a self-powered home automation sensor device for detecting the existence of and / or for measuring the intensity of a first physical phenomenon, comprising a means of converting an effect of a second physical phenomenon into electrical energy and a means of determining the instantaneous power of this second physical phenomenon that can be converted into electrical energy, wherein a normal, first mode of operation of the device or an energy-saving second mode of operation of the device is activated according to a value defined on the basis of the determination of the instantaneous power that can be converted into electrical energy.
Owner:SOMFY ACTIVITES SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com