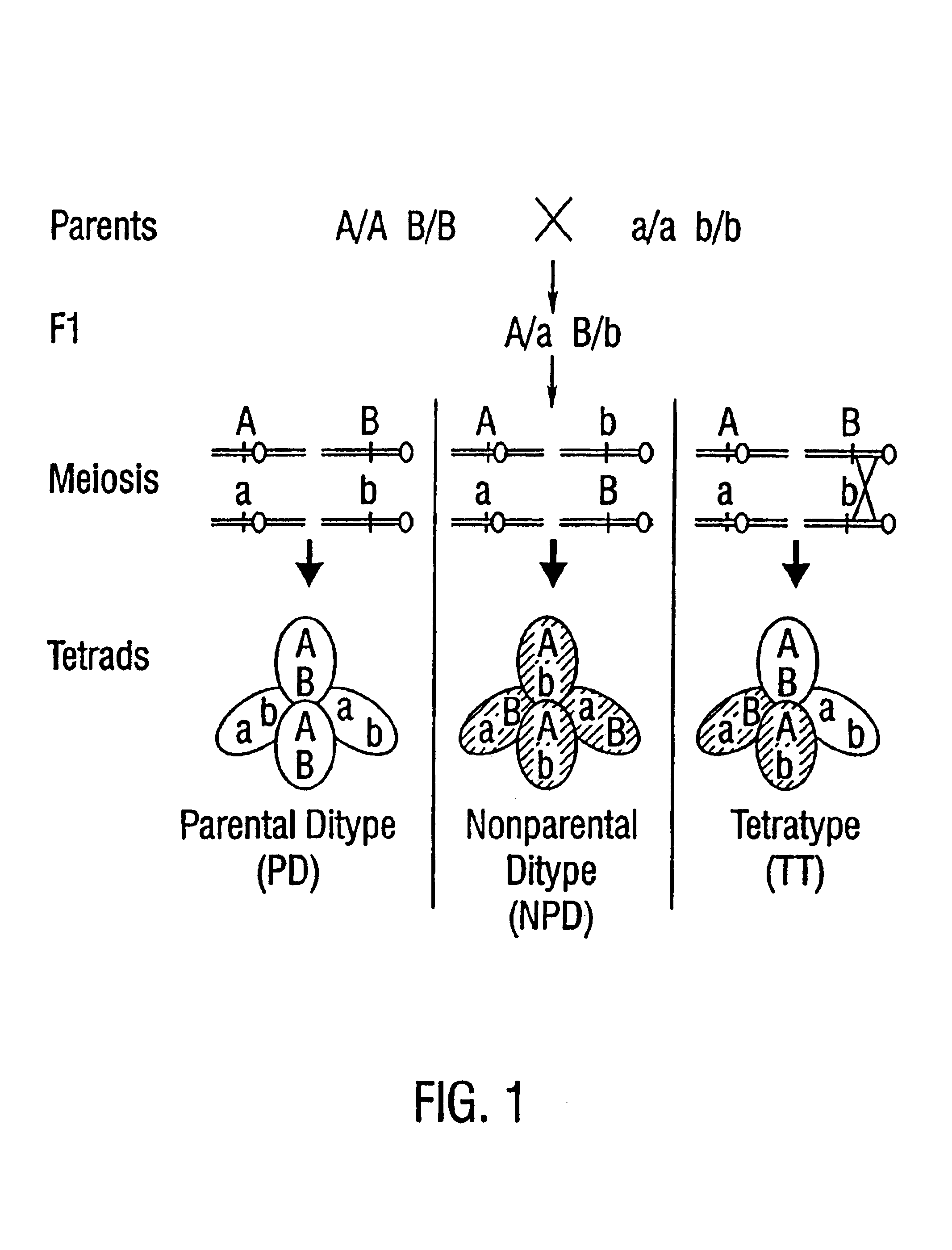
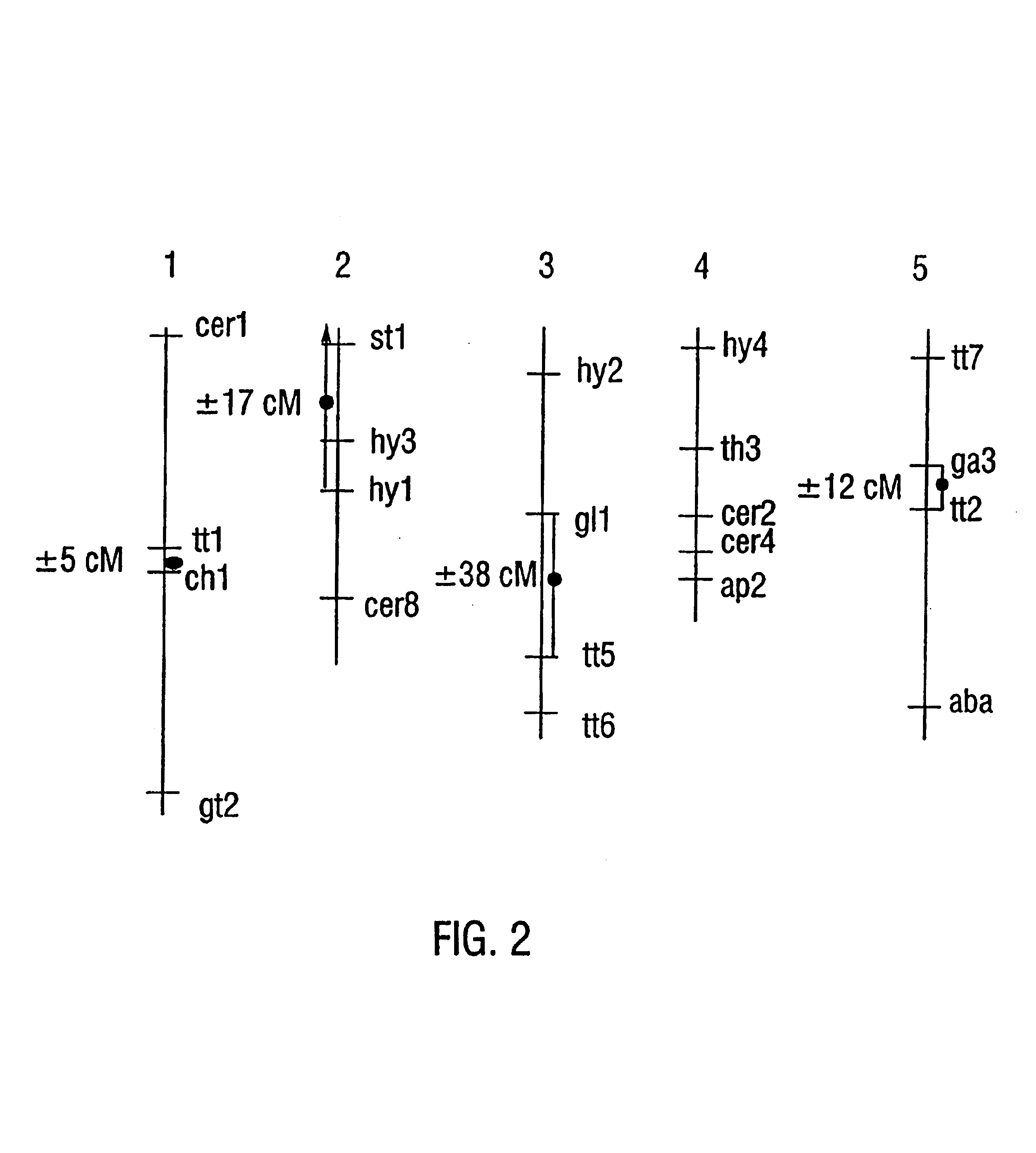
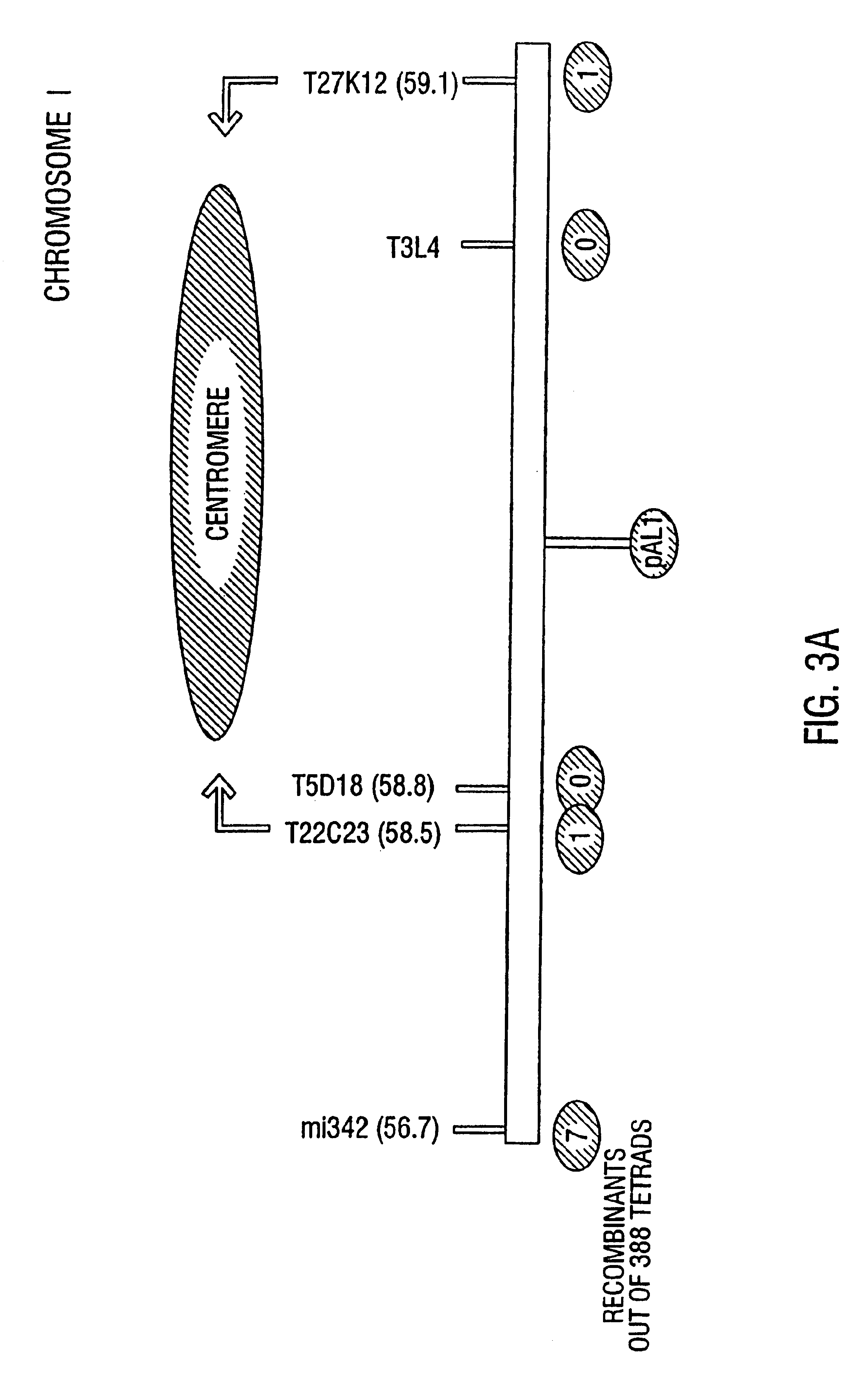
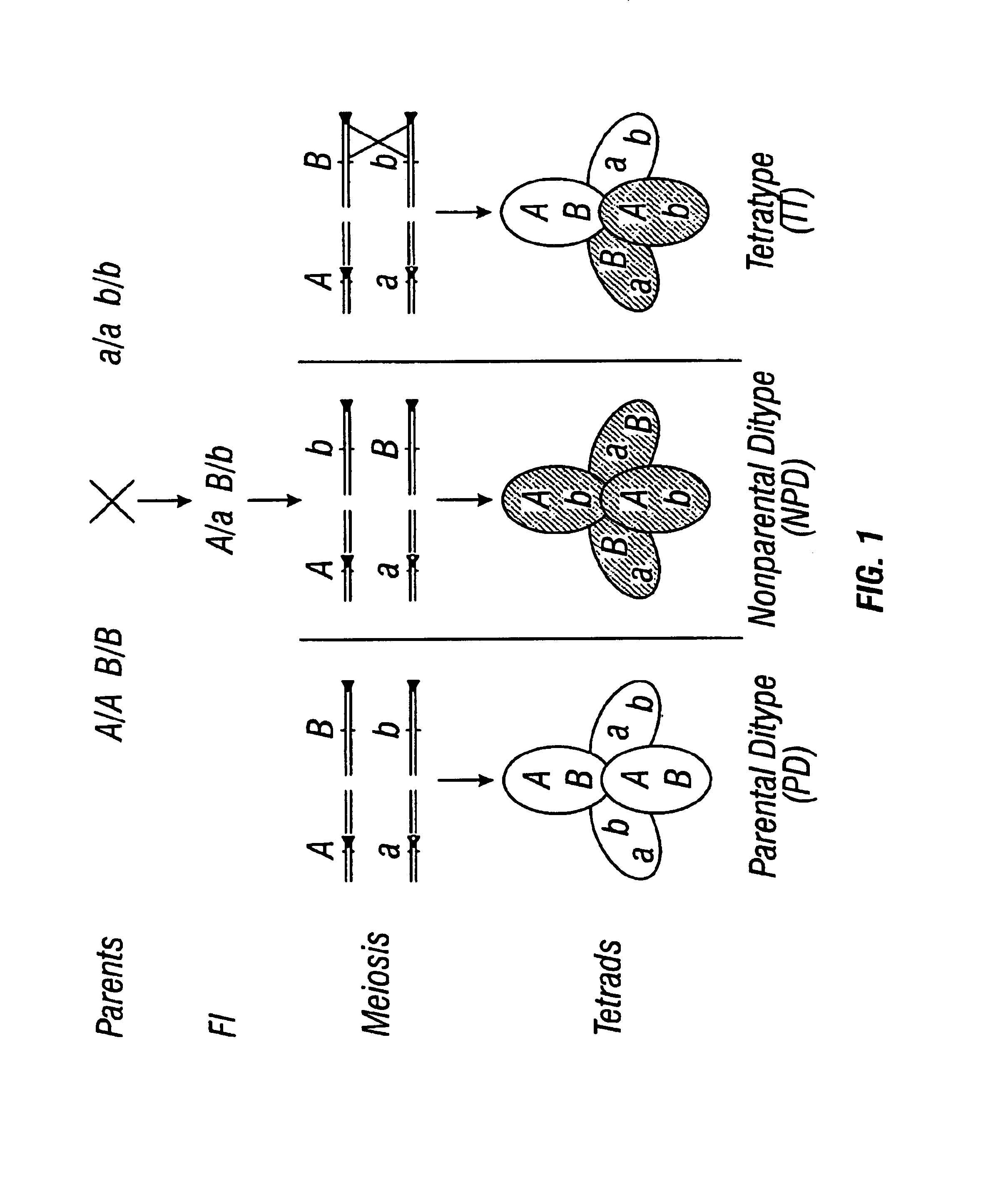
Patents
Literature
118 results about "Centromere" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The centromere is the specialized DNA sequence of a chromosome that links a pair of sister chromatids (a dyad). During mitosis, spindle fibers attach to the centromere via the kinetochore. Centromeres were first thought to be genetic loci that direct the behavior of chromosomes.
Methods for generating or increasing revenues from crops
InactiveUS7193128B2Shorten the timeIncrease incomeData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods of doing business and providing services. For example, methods of increasing the revenue of crops are provided. To this end, the method includes the use of a nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and mini chromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +1
Regulation of epigenetic control of gene expression
Methods are provided for the identification of compounds that selectively modulate epigenetic changes in gene expression. Compounds, compositions, kits or assays devices, and methods are provided for modulating the expression, endogenous levels or the function of small non-coding RNAs cognate to or transcribed by heterochromatic regions subject to epigenetic regulation (i.e., promoters, enhancers, centromeres, telomeres, origins of DNA replication, imprinted loci, or loci marked by dosage-compensation), and for modulating the formation or function of heterochromatin in cells, tissues or animals.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Plant centromere compositions
InactiveUS7235716B2Shorten the timeOvercome limitationsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides for the nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:CHROMATIN
Method for knocking down brewing yeast chromosome
ActiveCN107858346AKnockout simpleKnockout EfficientHydrolasesStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyYeast chromosome
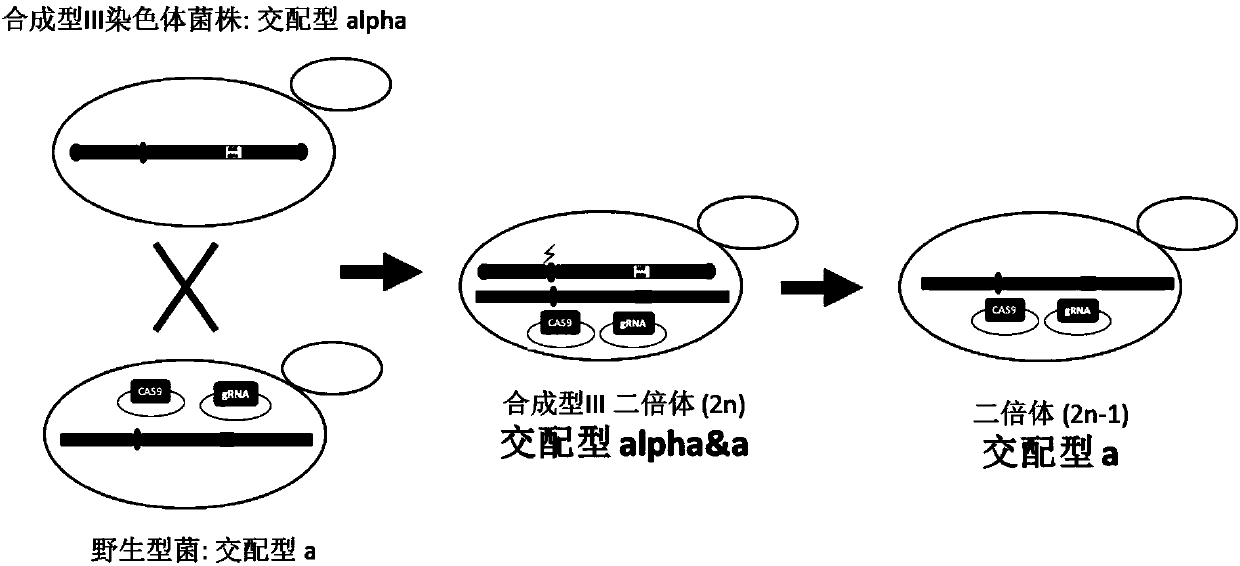
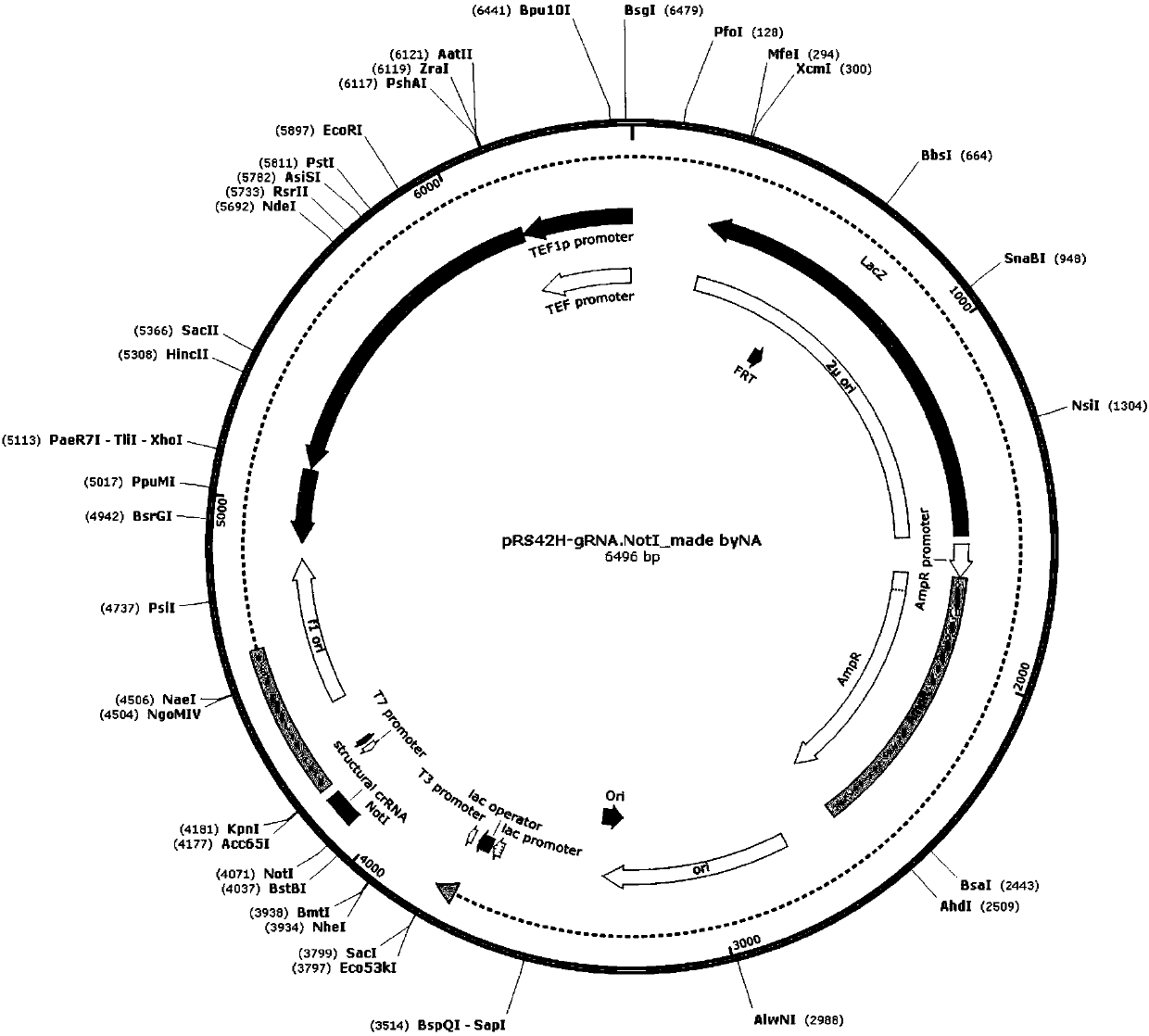
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and specifically discloses a method for knocking down brewing yeast chromosome. The method is characterized in that the complete yeast chromosome is cut according to the CRISPR / Cas9 base technology; a specificity target close to centromere is selected; a corresponding guide RNA is designed to guide Cas9 protein to generate an incision closeto the centromere, thus realizing the knocking down of the whole chromosome. Compared with the conventional method for losing the whole chromosome in manners such as inducing through a Ga1 promoter, and reductional division, the method has the advantages that the brewing yeast chromosome is simply, efficiently and quickly cut; the cross exchange of sister chromatids can be avoided; the chromosome-knocked-down homozygous brewing yeast diploid strain can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Plant centromere compositions
InactiveUS20050268359A1Shorten the timeOvercome limitationsBacteriaVaccinesBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides for the nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF +1
Plant artificial chromosome compositions and methods
InactiveUS6900012B1Confer susceptibilityEnhanced advantageOther printing matterMicrobiological testing/measurementStructure and functionArabidopsis
The present invention provides for the identification and cloning of functional plant centromeres in Arabidopsis. This will permit construction of stably inherited plant artificial chromosomes (PLACs) which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells. In addition, information on the structure and function of these regions will prove valuable in isolating additional centromeric and centromere related genetic elements and polypeptides from other species.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Plant chromosome compositions and methods
The present invention provides for the identification and cloning of functional plant centromeres in Arabidopsis. This will permit construction of stably inherited minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells. In addition, information on the structure and function of these regions will prove valuable in isolating additional centromeric and centromere related genetic elements and polypeptides from other species.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Centromere Detector and Method for Determining Radiation Exposure From Chromosome Abnormalities
ActiveUS20130216118A1Microbiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiation exposureDicentric chromosome
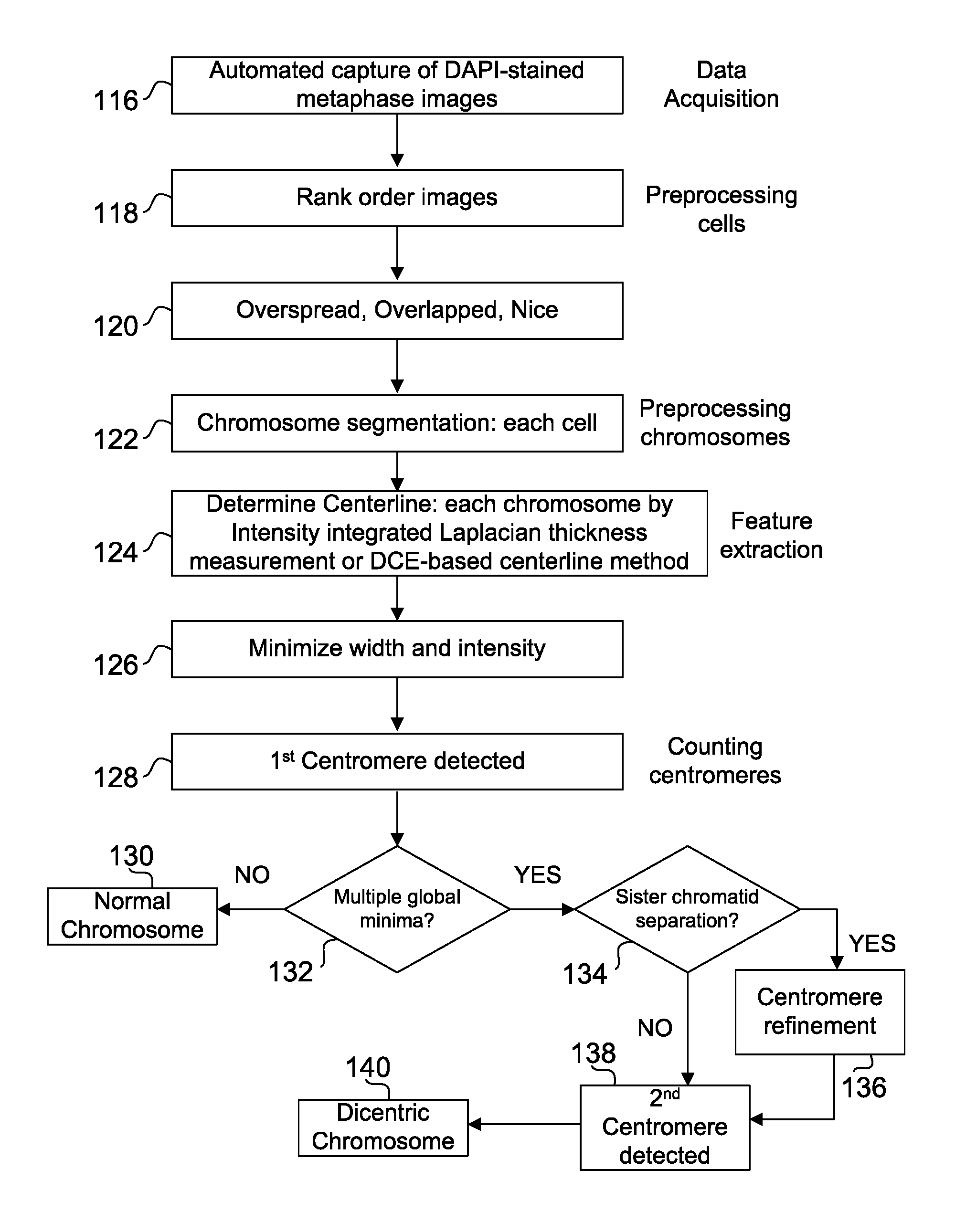
A method for determining radiation exposure from chromosome abnormalities present in a specimen by determining the location or locations of the centromere of each chromosome in a cell in an image of a metaphase cell by segmentation of an accurately drawn chromosome centerline followed by selection of a longitudinal cross-section with the minimum width or intensity or width and intensity; counting the number of centromeres in each chromosome in each cell; computing the frequency of dicentric chromosomes in a population of cells; and determining the radiation dose by comparing the computed frequency of dicentric chromosomes with a previously determined dose-response curve from a calibrated source.
Owner:CYTOGNOMIX
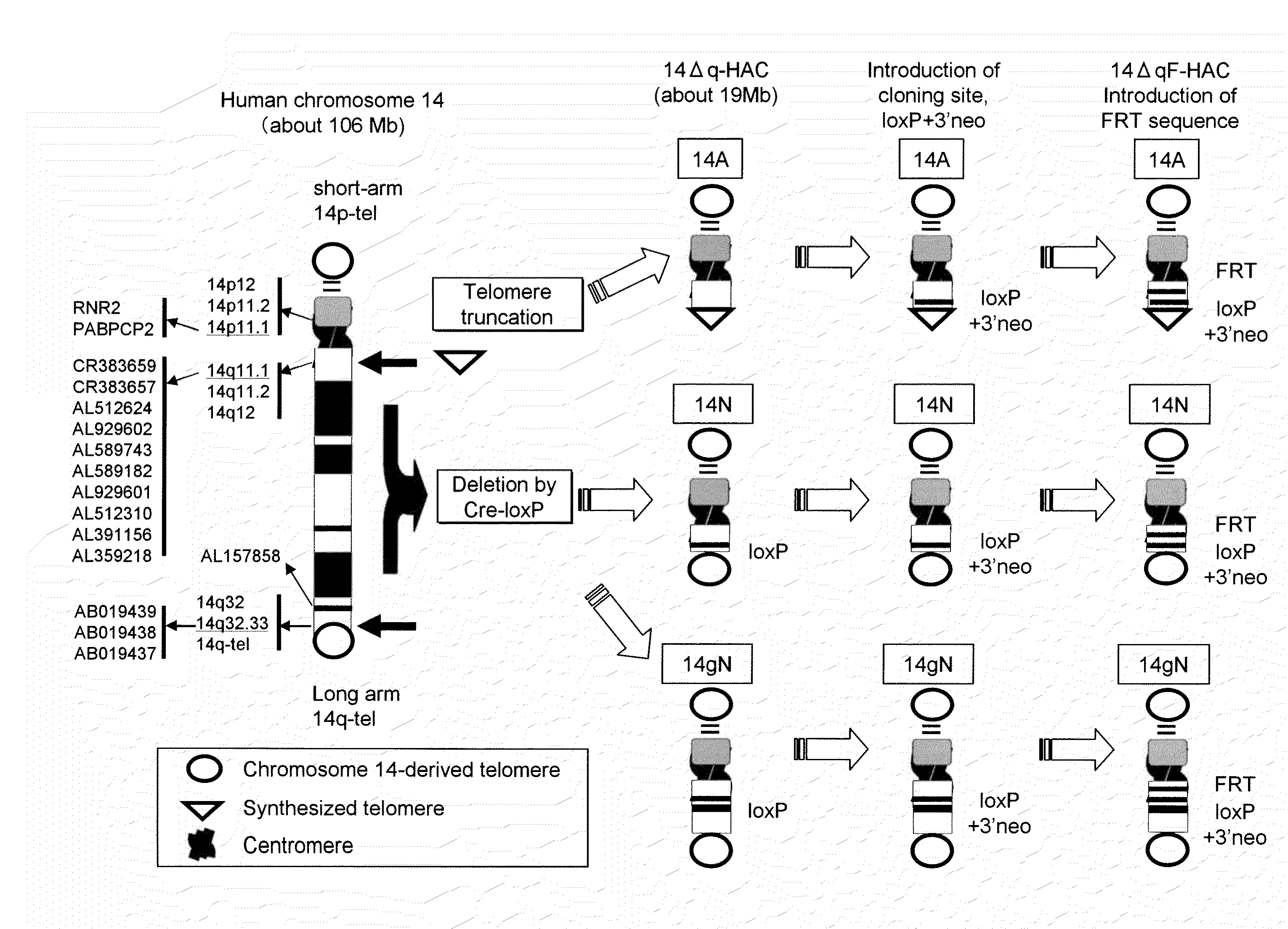
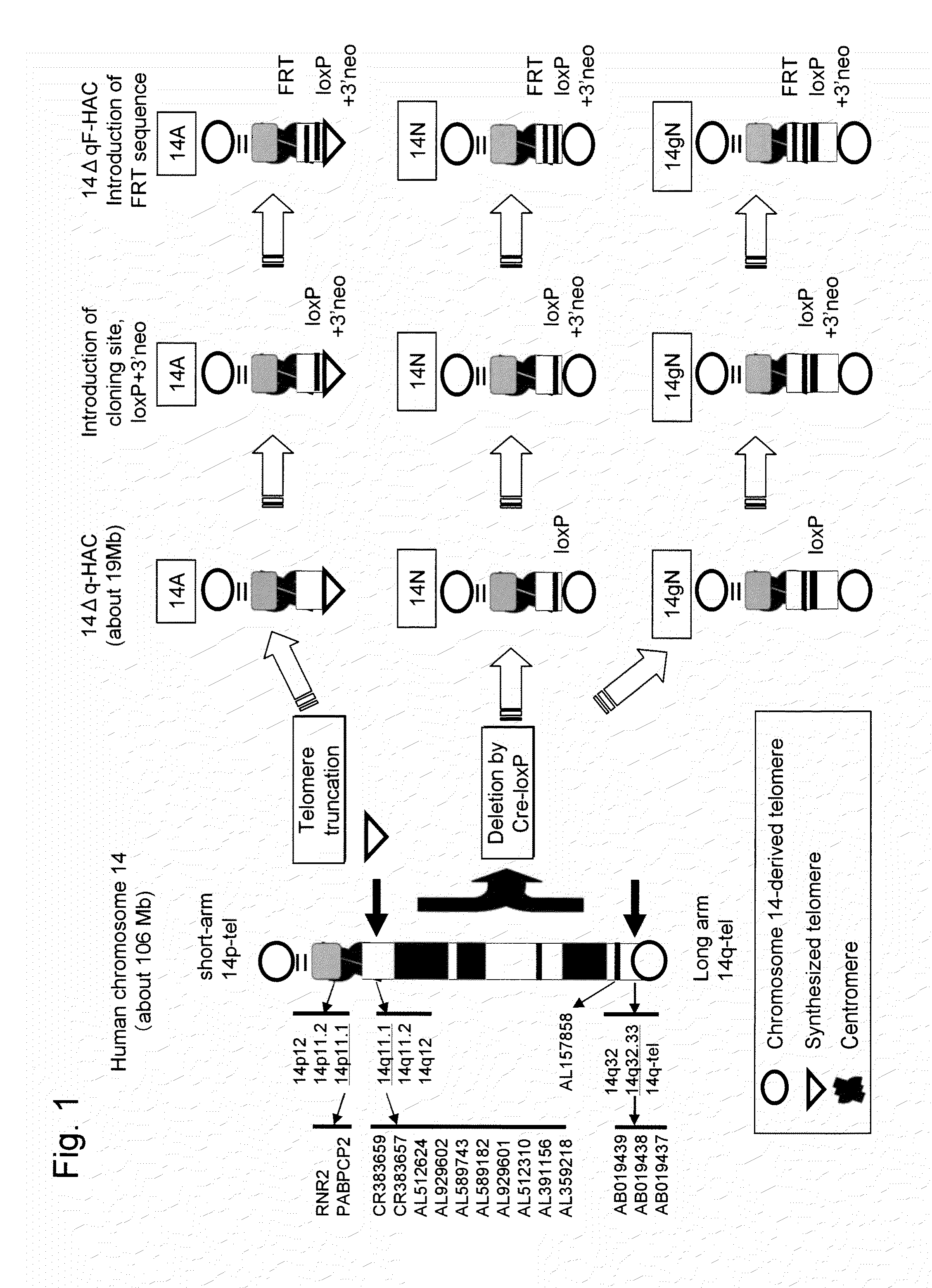
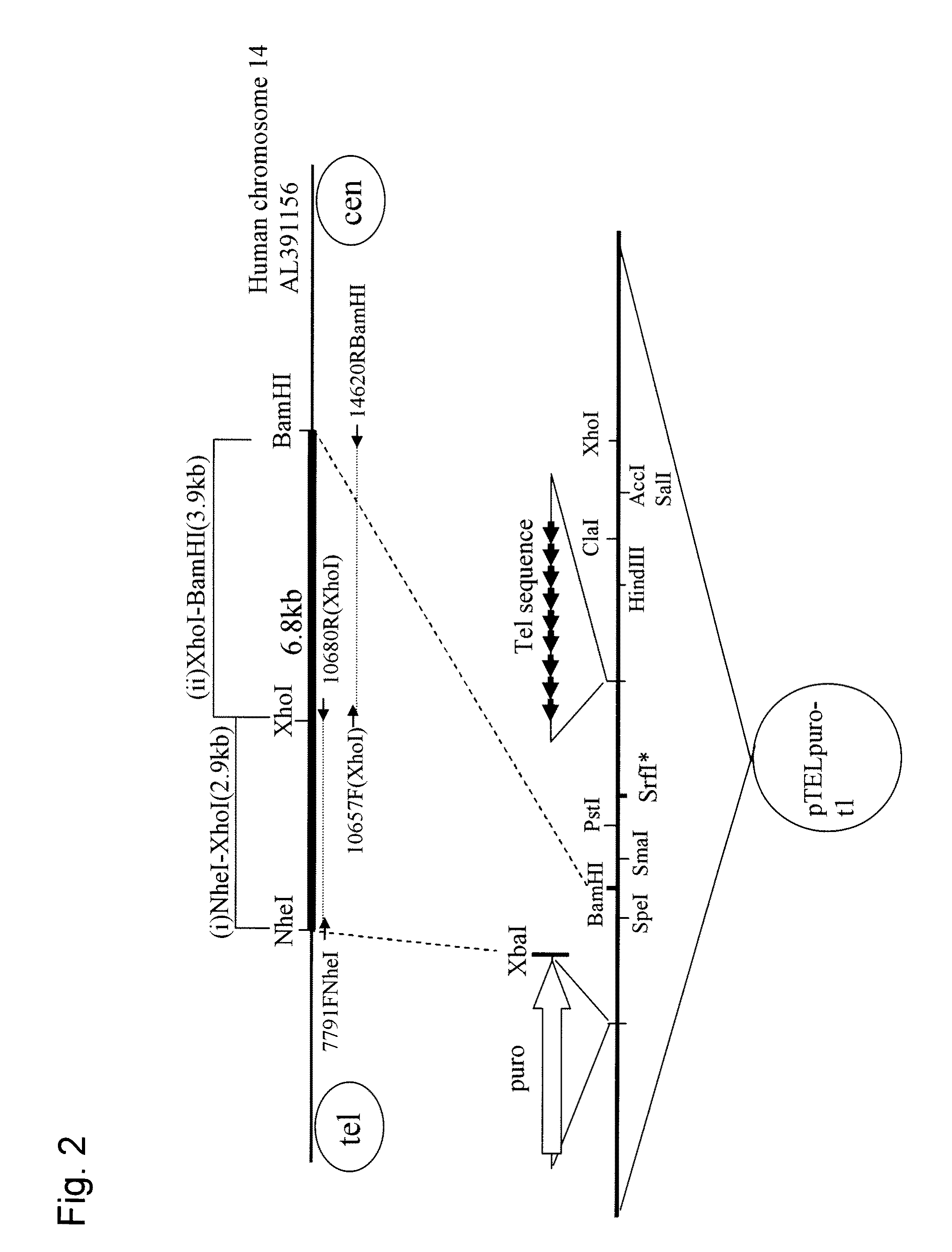
Human artificial chromosome (HAC) vector and human cell medicine comprising same
ActiveUS20100011454A1Improve expression levelPositively affect stable maintenanceBiocideNervous disorderHuman artificial chromosomeTherapeutic protein
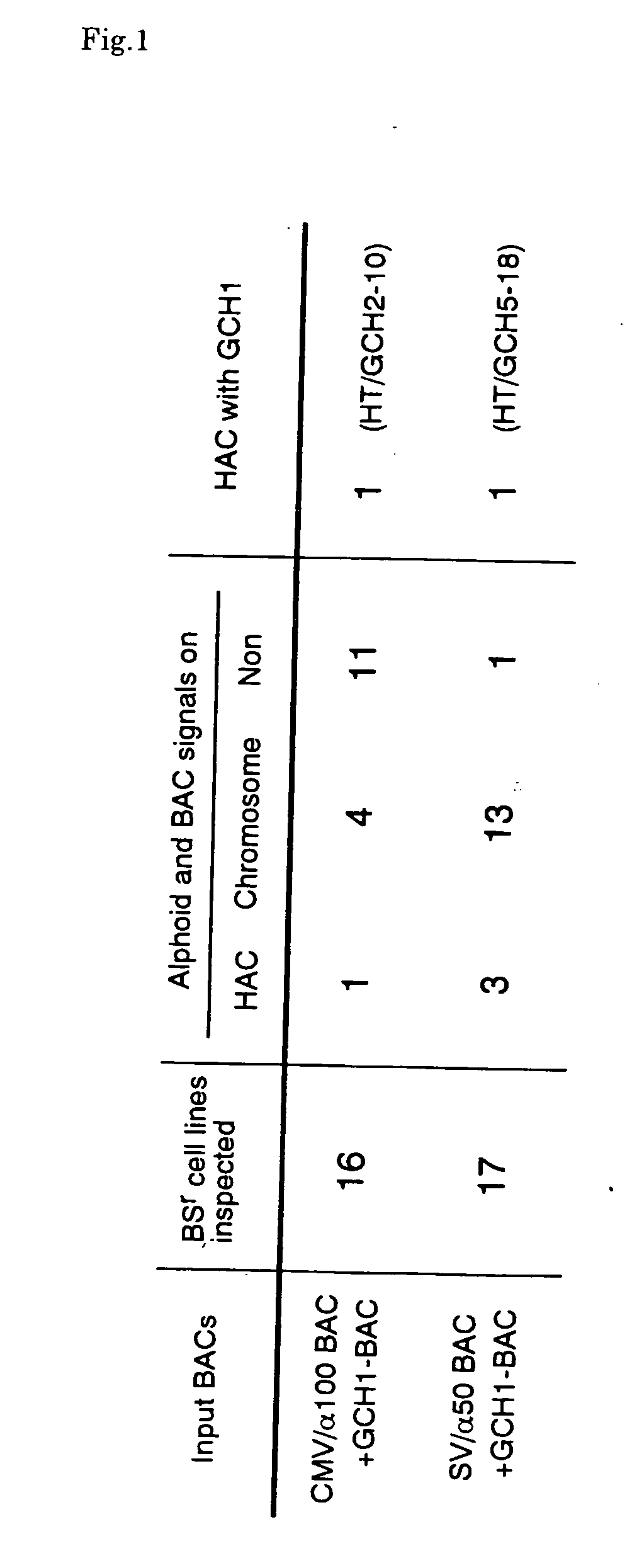
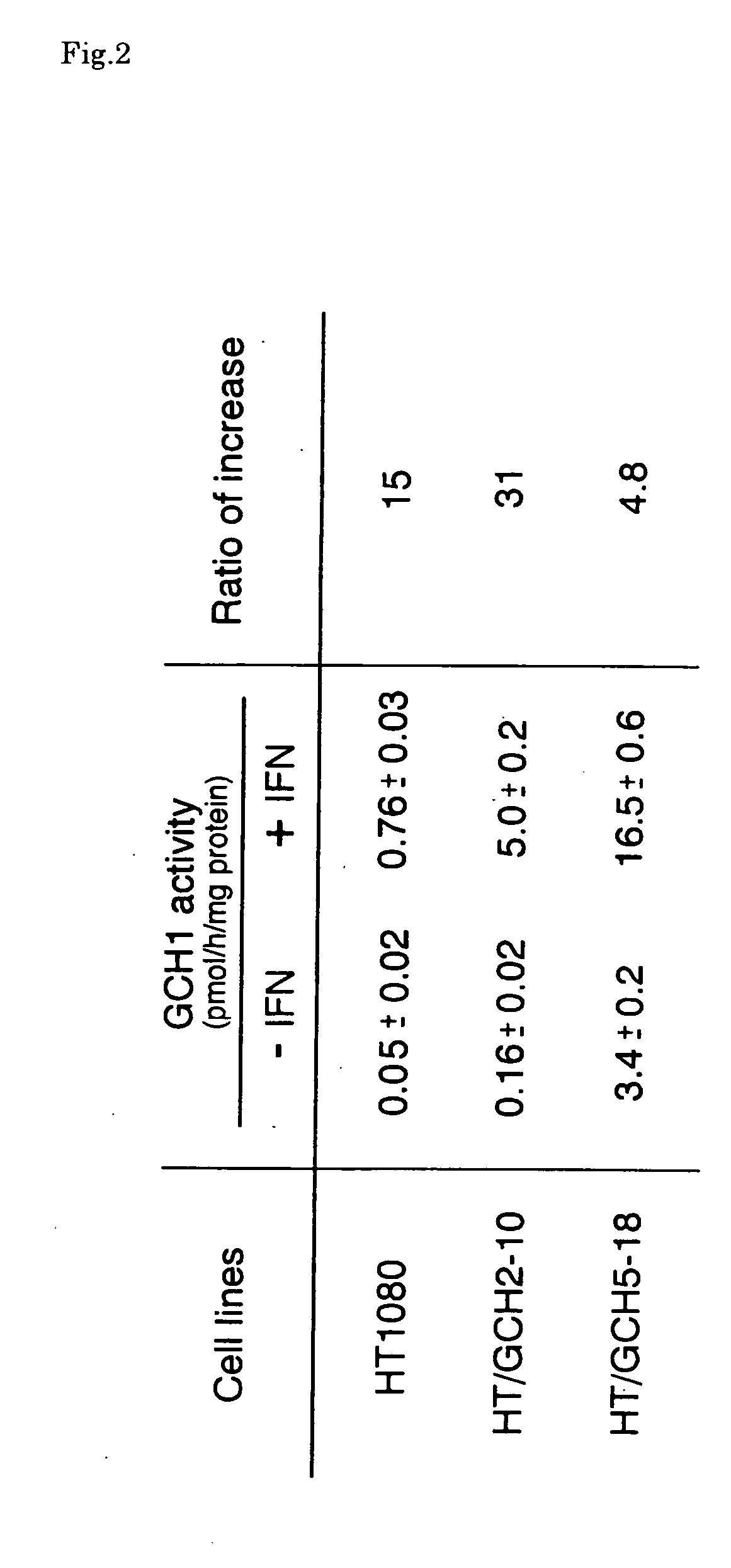
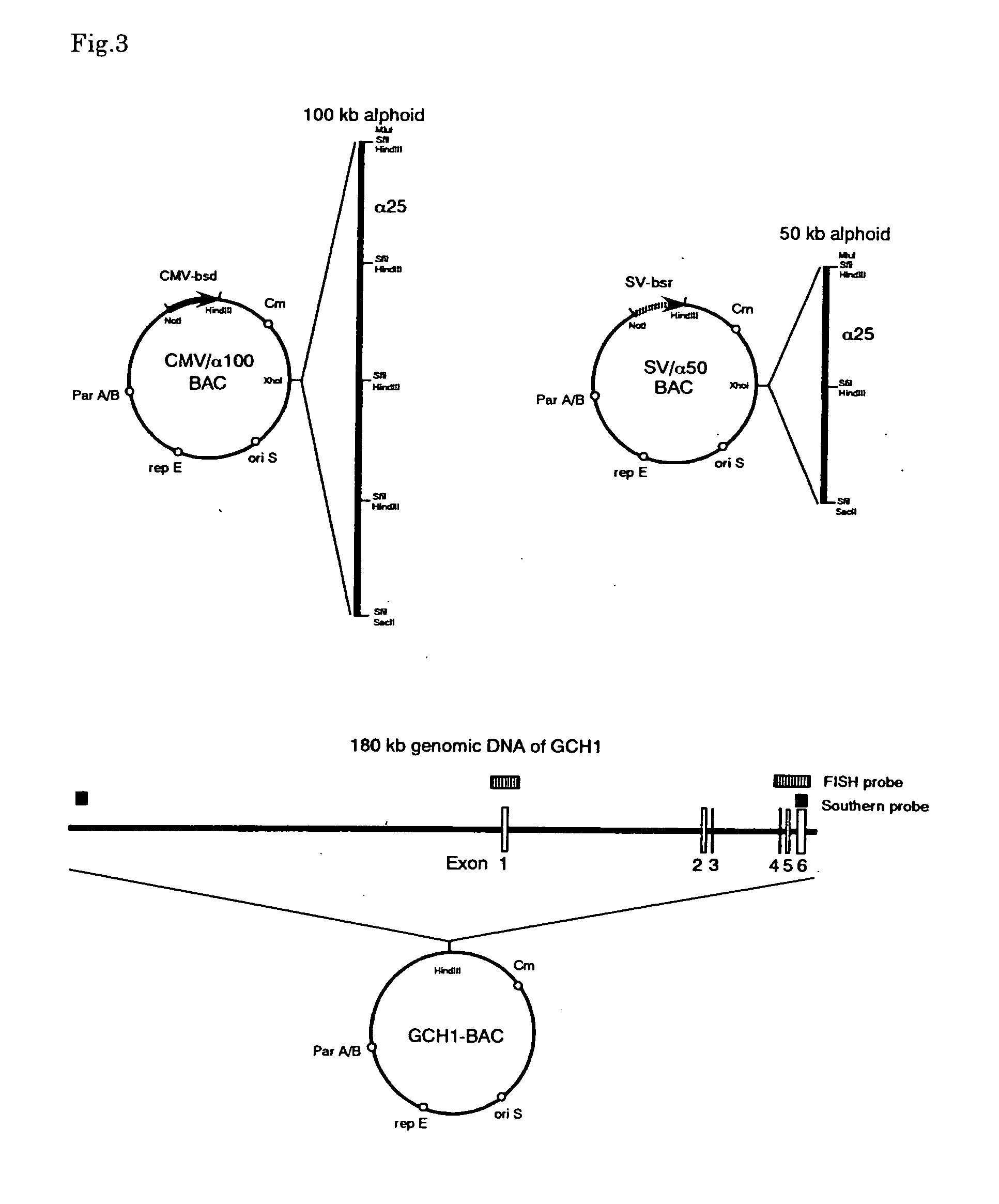
This invention relates to a human artificial chromosome (HAC) vector carrying a human chromosome-derived centromere, a subtelomere sequence, and a telomere sequence, to a human cell medicine or human cells comprising the HAC vector, to methods for preparing the HAC vector and human cells, and to methods for producing a therapeutic protein using the HAC vector.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Use of methylated nucleic acid segments for isolating centromere DNA
InactiveUS7132240B2Reduced viabilityIncreased aneuploidySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyOrganism
The invention provides efficient methods for the isolation of centromeres from potentially any organism. Using the methods of the invention, methylated centromere DNA may be isolated from potentially any centromere in an organism. The technique is amenable to mass screenings employing use of arrays comprising libraries of DNA from a target species.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Donor yeast strain for transfer of genetic material
InactiveUS20060105361A1Reduce needSimple methodFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsBiotechnology
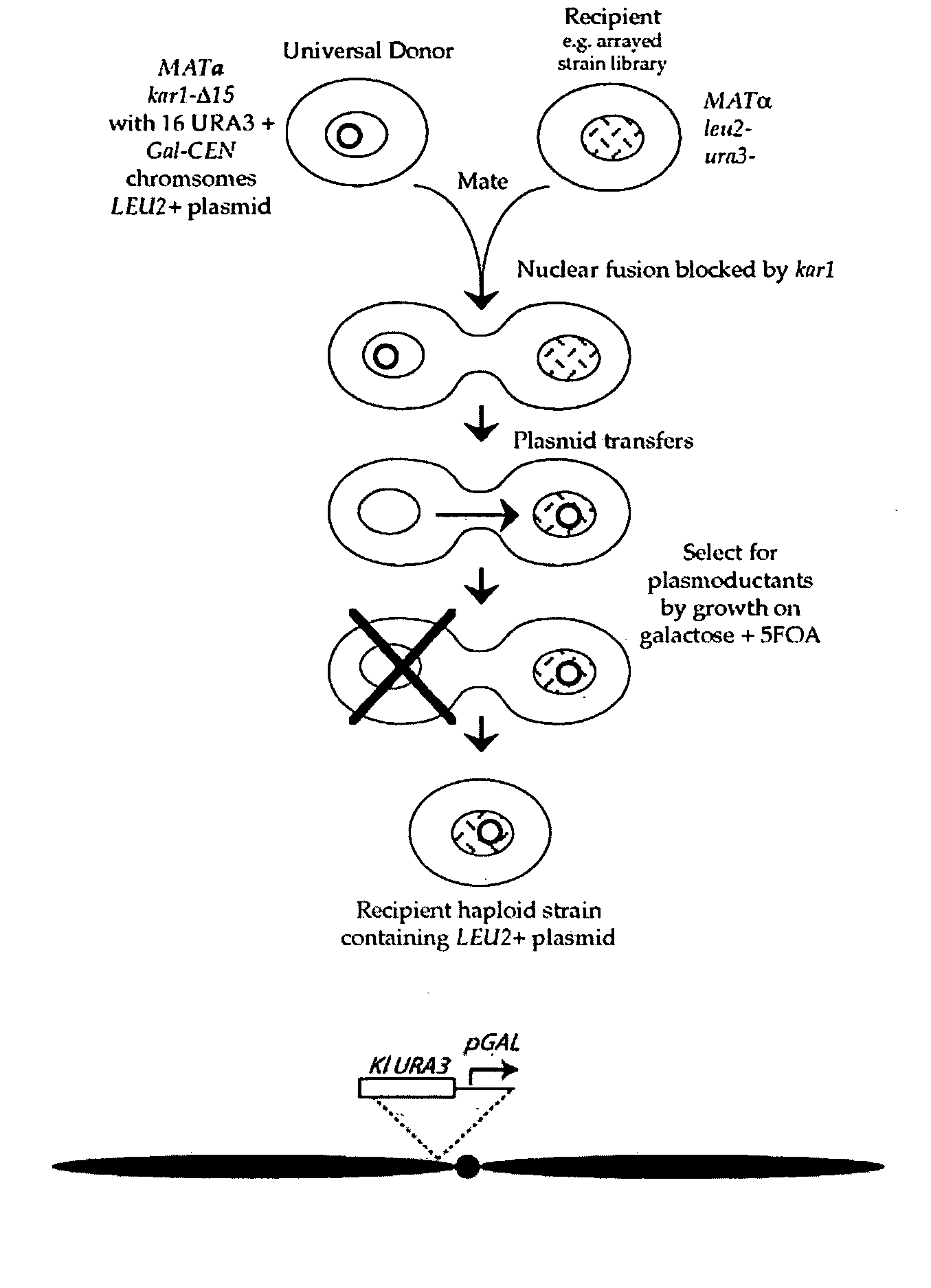
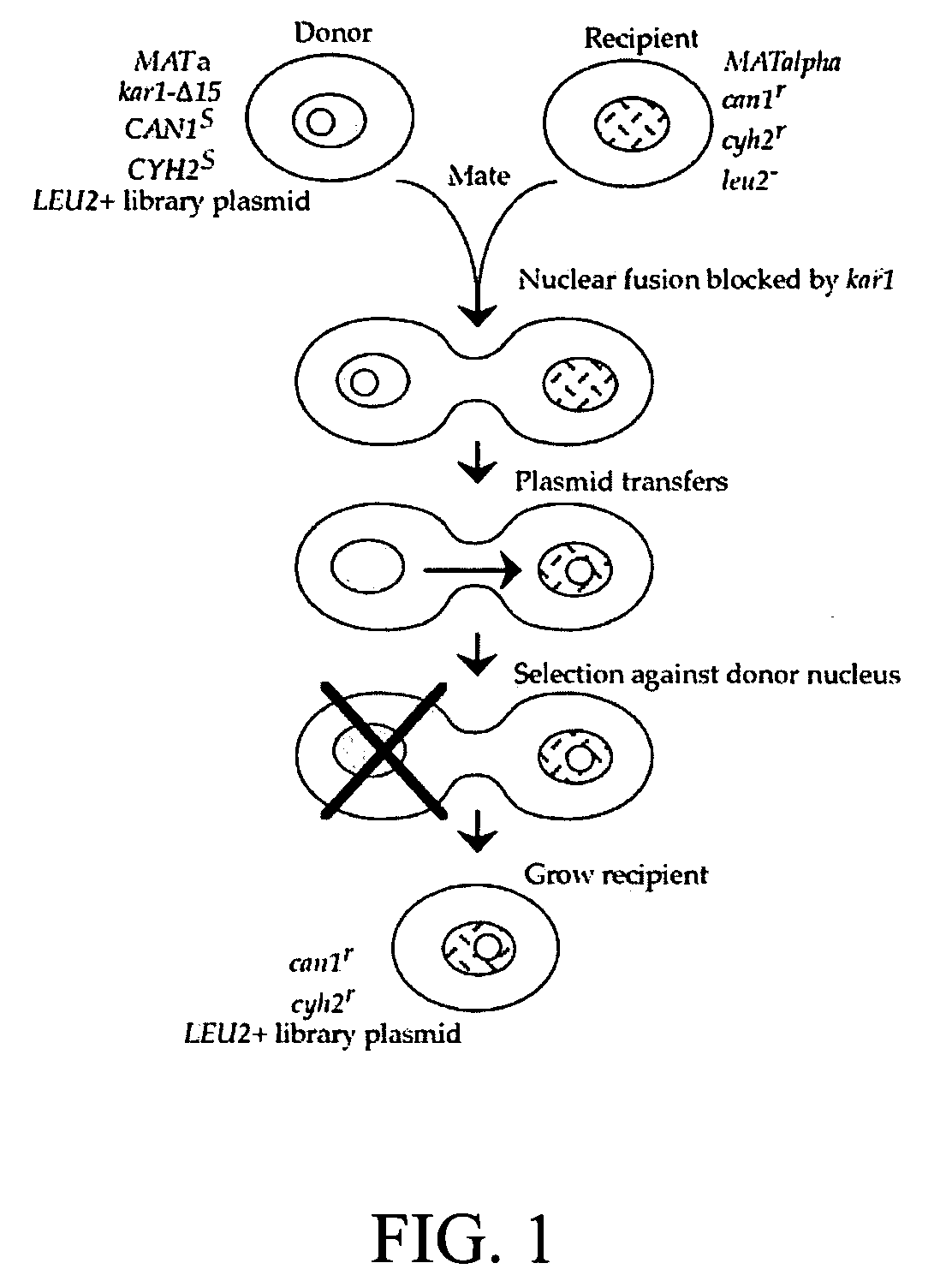
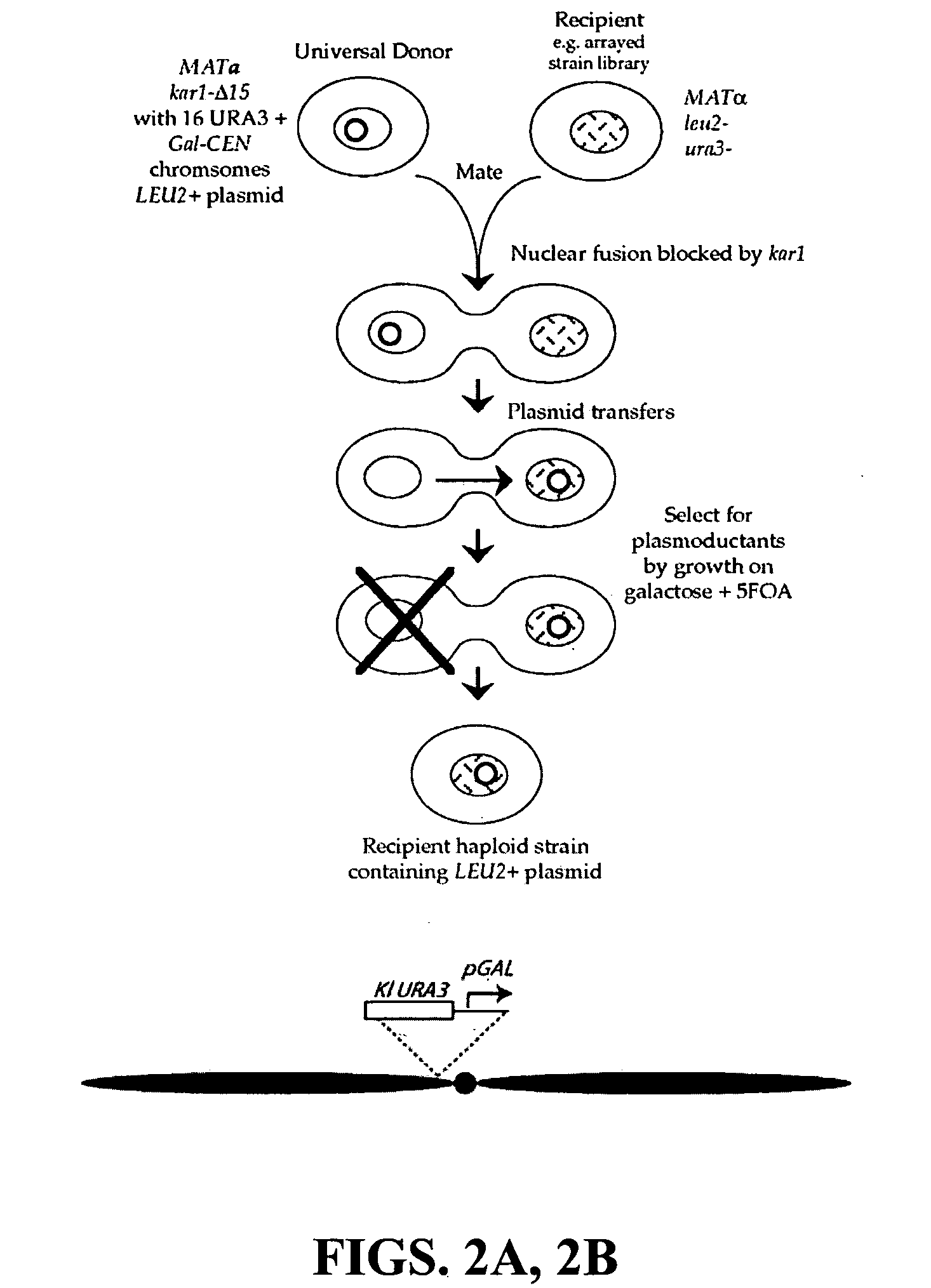
The invention provides a universal yeast donor strain that contains a conditional centromere and a URA3 allele on every chromosome. This strain was constructed in four rounds of crosses of individual conditional chromosome strains using a novel tetrad-based screen to identify segregants in which all marked chromosomes were contained in the same spore. The invention also provides an improved high efficiency method to transfer extrachromosomal genetic material such as plasmid DNA into any Saccharomyces strain for use with the current gene disruption libraries. The method of transfer is mating-based method which uses a kar1 plasmid donor strain that can initiate mating but cannot form a diploid and allows plasmid transfer (plasmoduction) between nuclei in the heterokaryon. kar1 matings have been used to transfer YACs between yeast strains, but previous methods required specialized genetic backgrounds in the recipient strains and suffered from high rates of spurious chromosome transfer (Hugerat, Y., et al. 1994. Genomics 22:108). Plasmoduction with the universal donor strain only requires that the recipient strain be ura3, GAL+ and have another marker available for selection of the transferred plasmid. Counterselection against every donor chromosome also limits the amount of spurious allele transfer. The universal donor strain and the method of the invention are used to screen the yeast gene disruption library with plasmid-based dominant negative alleles of various genes.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Plant centromere compositions
InactiveUS20050241016A1Shorten the timeOvercome limitationsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingRecombinant DNA
The present invention provides for the nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:CHROMATIN
Plant centromere compositions
InactiveUS20050241015A1Shorten the timeOvercome limitationsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingRecombinant DNA
The present invention provides for the nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Plant chromosome compositions and methods
The present invention provides for the identification and cloning of functional plant centromeres in Arabidopsis. This will permit construction of stably inherited minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells. In addition, information on the structure and function of these regions will prove valuable in isolating additional centromeric and centromere related genetic elements and polypeptides from other species.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
HER-2 gene quick FISH detection kit
InactiveCN104195246AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceCentromere
The invention discloses a HER-2 gene quick FISH detection kit which comprises FISH fluorescent probes, a hybridization solution and a staining solution, wherein the sequences of the probes are respectively a No.17 chromosome specific probe and a HER-2 gene specific probe. By adopting the optimized short sequence fluorescent probes, the FISH detection time is shortened to 1-2 hours from 16-18 hours, and the kit can quickly and accurately detect the HER-2 gene and is beneficial to early diagnosis and treatment of diseases. By adopting two different types of probes, one probe is combined with the centromere of the No.17 chromosome, and the other probe is combined with the target gene HER-2, thereby better ensuring the reliability of the detection result and reducing the false positive result.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HEAS BIOTECH CO LTD
Plant centromere compositions
InactiveUS20050257282A1Shorten the timeOvercome limitationsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingRecombinant DNA
The present invention provides for the nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:CHROMATIN
Plant Centromere Compositions
InactiveUS20100333235A1Shorten the timeOvercome limitationsSugar derivativesHydrolasesDNA constructNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides for the nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +1
Method for inducing corn haploids
InactiveCN104335889AGood double efficiencyLow doubling efficiencyHybrid peptidesPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceF1 generation
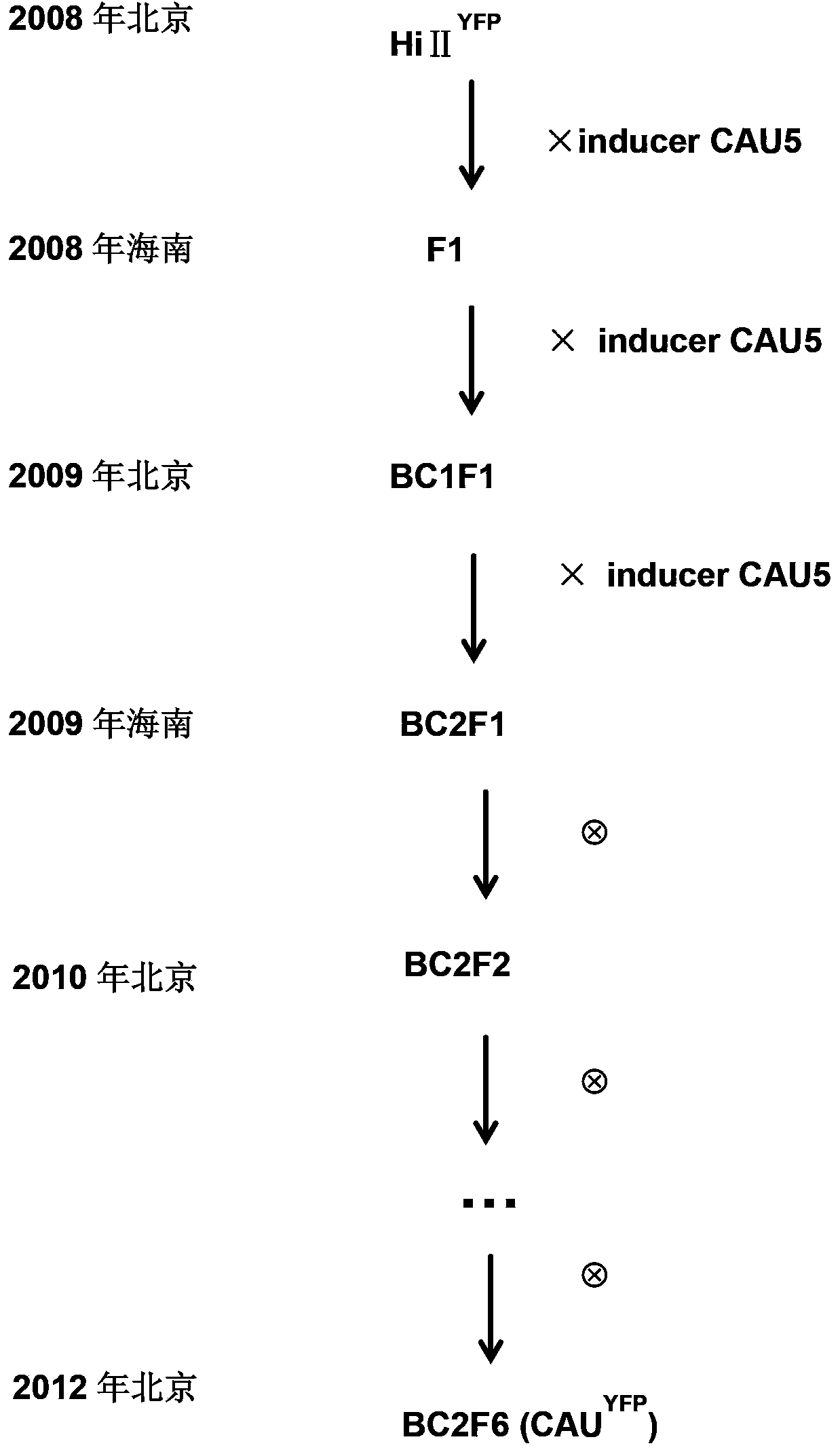
The invention discloses a method for inducing corn haploids. The method comprises the following steps: pollinating a female parent by a male parent corn haploid induction line with a higher corn haploid inductivity than a corn haploid induction line CAU5, and harvesting hybridized F1 generation grains to obtain corn haploids. A method for realizing the corn haploid induction line comprises the following steps: 1, introducing coding gene of a specific centromere histone mutant into a hybrid first generation plant of a corn inbred line HiIIA and a corn inbred line HiIIB to obtain a transgenic corn plant; and 2, hybridizing the specific histone mutant as a female parent with the CAU5 to obtain an F1 generation, hybridizing the F1 generation as a female parent with the CAU5 to obtain a BC1F1 generation, hybridizing the BC1F1 generation as a female parent with the CAU5 to obtain a BC2F1 generation, and continuously selfing the BC2F1 generation at least five generations to obtain the corn haploid induction line.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
Methods for generation or increasing revenues from crops
InactiveUS20080288264A1Shorten the timeIncrease incomeClimate change adaptationVaccinesDNA constructNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods of doing business and providing services. For example, methods of increasing the revenue of crops are provided. To this end, the method includes the use of a nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and mini chromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Plant centromere compositions
InactiveUS7227057B2Shorten the timeOvercome limitationsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA constructNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides for the nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Diagnostic methods for determining prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer
InactiveUS20090258350A1Accurate identificationEnhanced informationMicrobiological testing/measurementFavorable prognosisNucleic Acid Probes
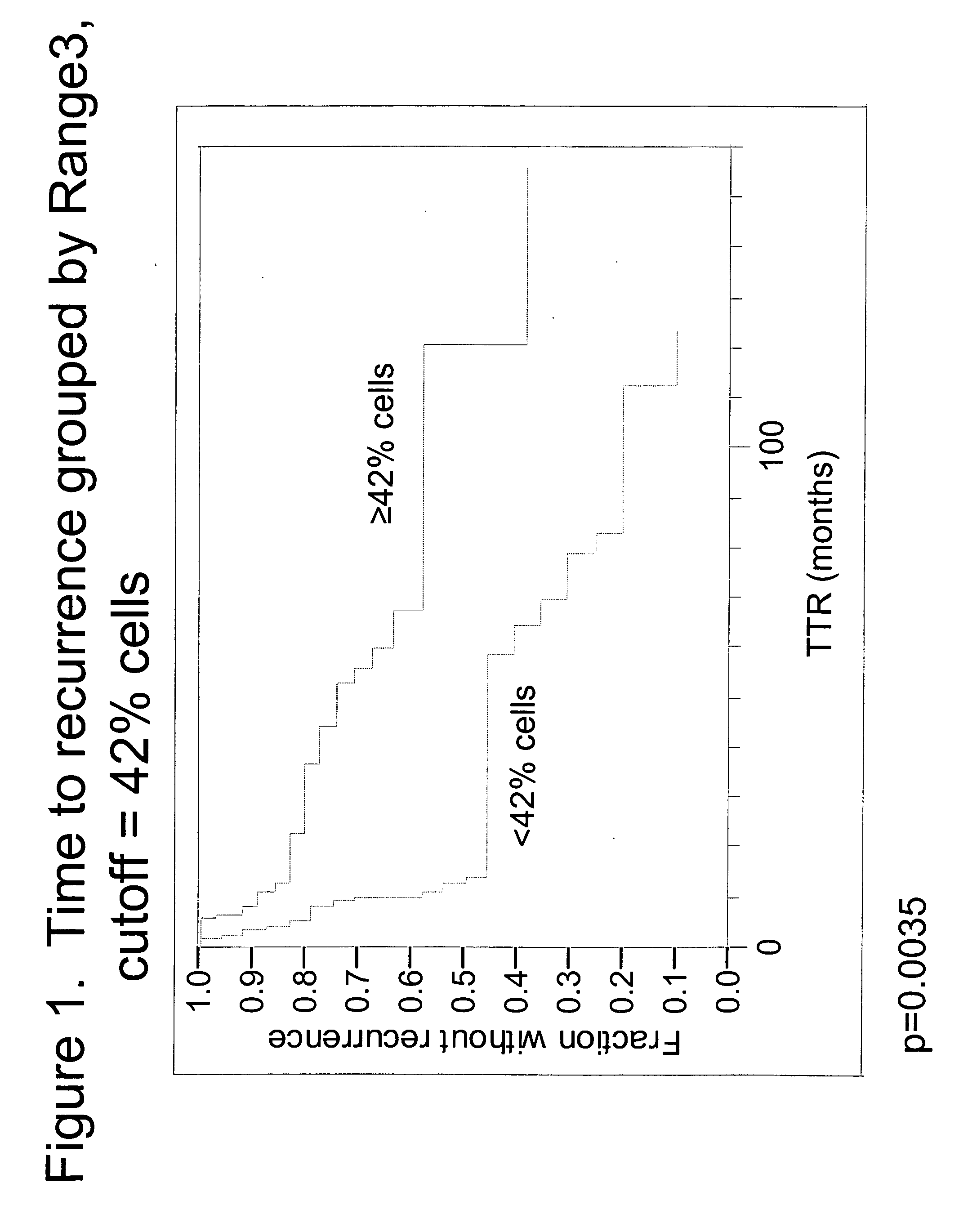
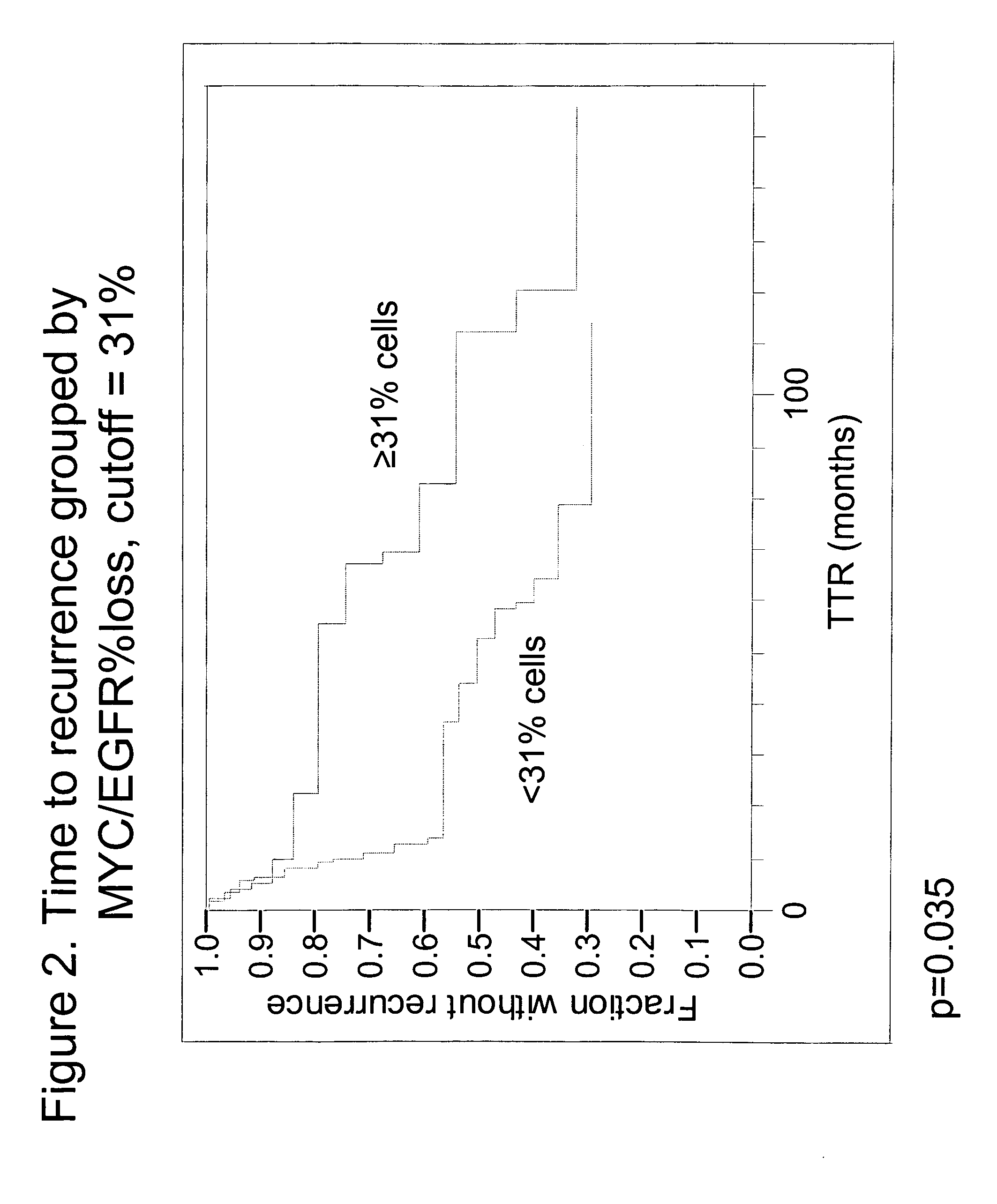
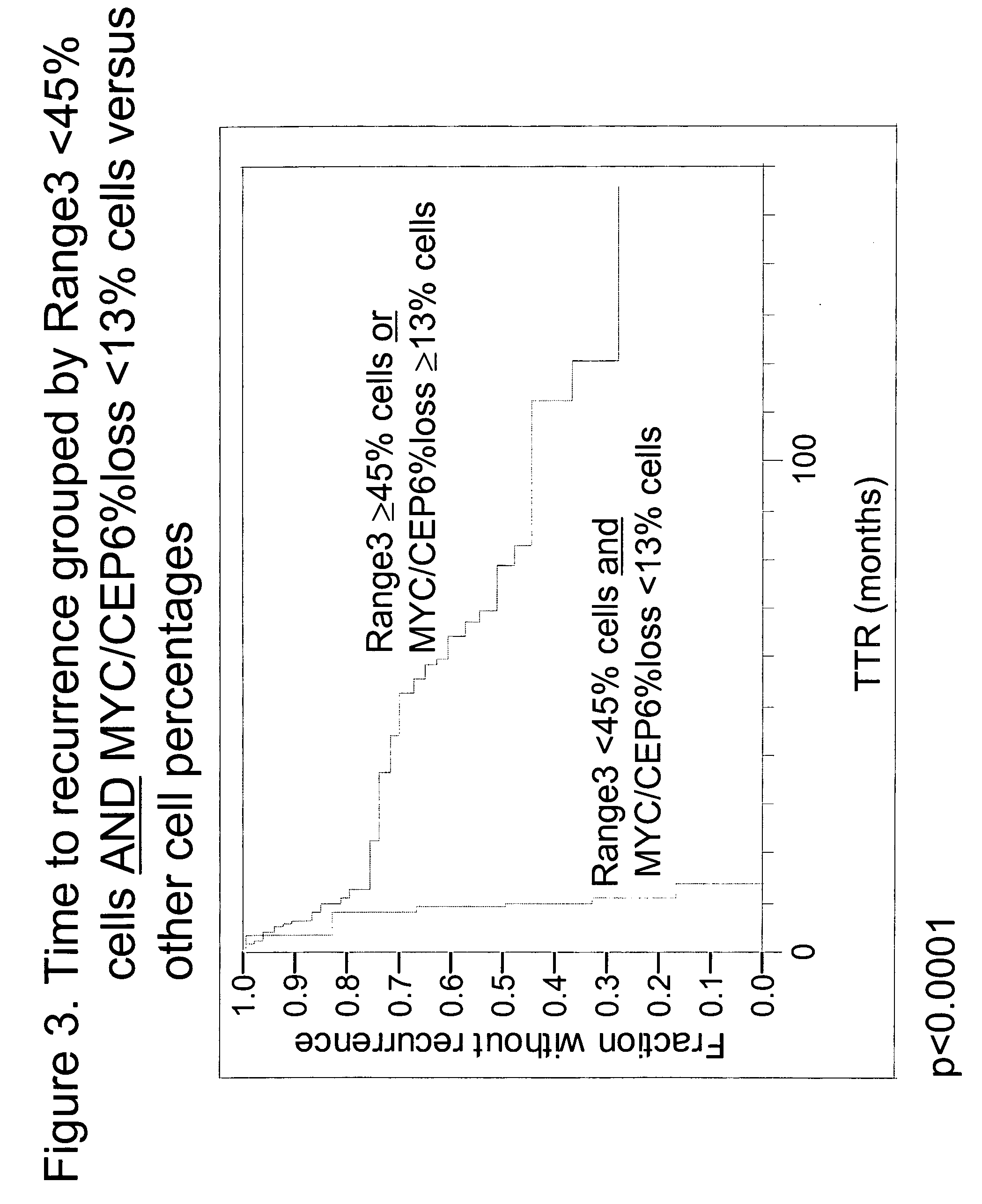
The invention provides methods for identifying early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients who will have a favorable prognosis for the recurrence of lung cancer after surgical resection. The invention is based on the discovery that assessment of chromosomal copy number abnormalities at two or more of chromosome 5p15, 7p12, 8q24 and centromere 6 can be used for prognostic classification. The invention preferably uses fluorescence in situ hybridization with fluorescently labeled nucleic acid probes to hybridize to patient samples to quantify the chromosomal copy number of the these genetic loci. Assessment of the copy number abnormality patterns using four classifiers produced statistically significant prognostic classification for NSCLC: (i) the Range3 pattern of cells showing a difference on a cell by cell basis, of at least three FISH probe signals between the FISH signals at the chromosomal locus with the largest number of FISH signals minus the FISH signals at the chromosomal locus with the lowest number of FISH signals; (ii) the MYC / EGFR % loss pattern assessing the percentage of cells showing fewer MYC FISH probe signals than EGFR FISH probe signals; (iii) a combination of the Range3 pattern and the MYC / CEP6 ratio pattern of a percentage of cells showing a relative loss of MYC FISH probe signals to the FISH probe signal for CEP6; (iv) the combination of the MYC / 5p15 ratio pattern showing the relative ratio of MYC and 5p15 locus signals of ≧0.80 and the 5p15 / CEP6 ratio pattern assessing percentage of cells having a relative ratio of 5p15 FISH probe signals to CEP6 FISH probe signals ≧1.1 versus MYC / 5p15 ratio of <0.80 or 5p15 / CEP6<1.1; and (v) a combination of the average range of probe signal differences of equal to or greater than about 2.5 with the Range3 pattern in a percentage of the cells. The invention can be used to identify those early stage NSCLC patients at higher risk of recurrence who should be treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy before surgery or with adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery.
Owner:ABBOTT MOLECULAR INC
Plant centromere compositions
InactiveUS7989202B1Shorten the timeOvercome limitationsBryophytesSugar derivativesBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides for the nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:CHROMATIN
Reagent for detecting copy number of EGFR gene and ploidy of chromosome 7
ActiveCN101899504AHelps with sensitivityAids in prognostic judgmentMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceTyrosine-kinase inhibitorPloidy
The invention discloses a reagent for detecting a copy number of an EGFR gene and the ploidy of a chromosome 7. The reagent comprises a fluorescence probe RP11-339F13 used for detecting the copy number of the EGFR gene and a fluorescence probe RP11-144H20 used for detecting the ploidy of the chromosome 7, wherein the RP11-339F13 is cloned by BAC, which covers the whole EGFR gene, and marked with rhodamine fluorescein; and RP11-144H20 is cloned by specific BAC of the centromere of the chromosome 7 and marked with fluorescein isothiocyanate. The reagent can quickly, simply and conveniently detect the copy number of the EGFR gene and the ploidy of the chromosome 7, contributes to the judgment of medicament susceptibility and prognostic judgment, and has great significance for the guidance of use of molecular targeted medicament tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) of tumors, such as non-small cell lung cancer and the like.
Owner:合肥艾迪康医学检验实验室有限公司
Prognostic test for early stage non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
InactiveUS20100120027A1Accurate identificationEnhanced informationMicrobiological testing/measurementFavorable prognosisFluorescence
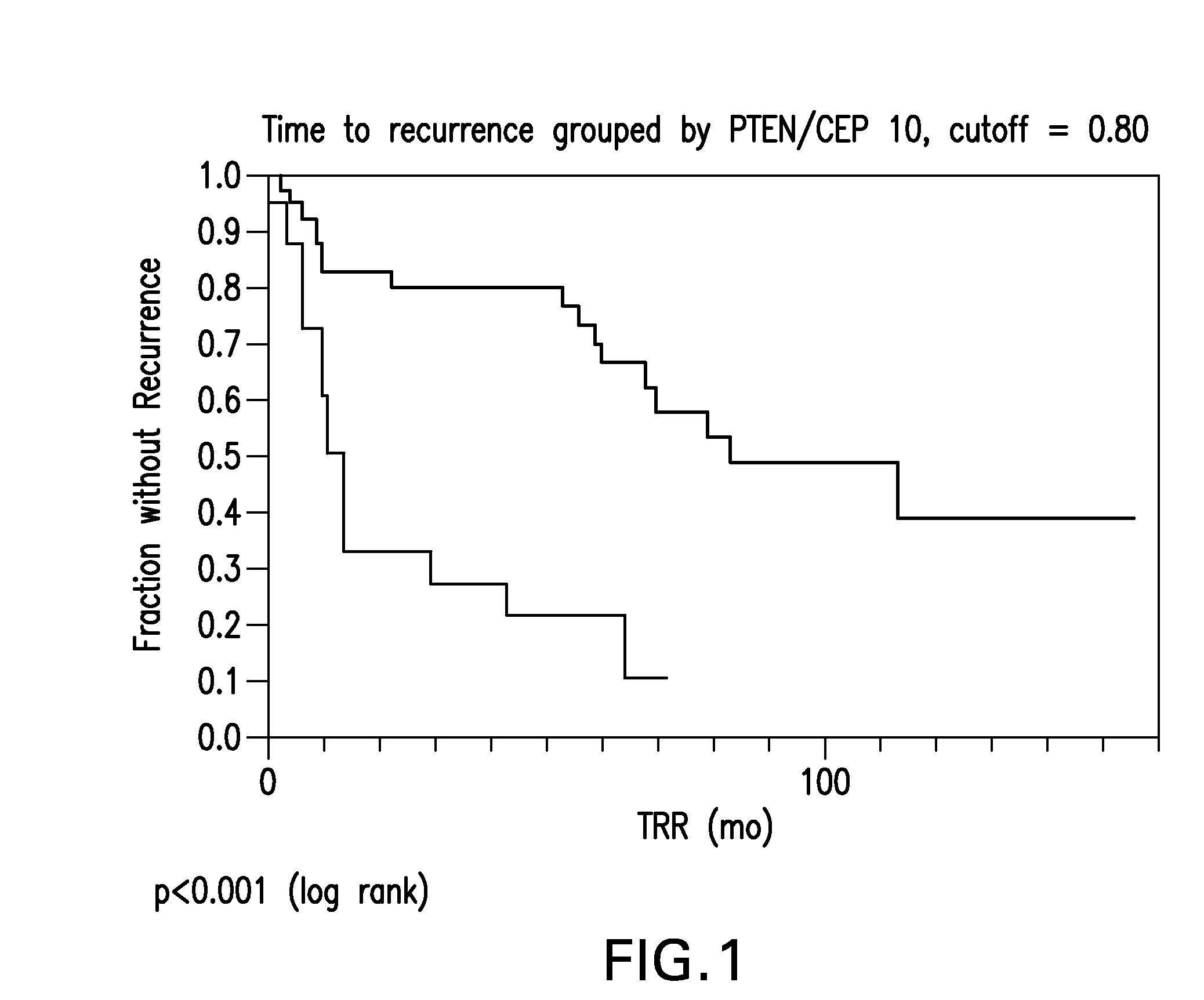
The invention provides methods for identifying early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients who will have a favorable prognosis for the recurrence of lung cancer after surgical resection. The invention is based on the discovery that assessment of chromosomal copy number abnormalities at chromosome 10q23.3 and centromere 10 can be used for prognostic classification. The invention preferably uses fluorescence in situ hybridization with fluorescently labeled nucleic acid probes to hybridize to patient samples to quantify the chromosomal copy number of the these genetic loci. The chromosome copy number can also be determined using, for example, PCR or array CGH. Assessment of the copy number abnormality patterns with a classifier based on the relative loss of 10q23.3 signals compared to the centromere 10 signals produced statistically significant prognostic classification for NSCLC. The ratio of PTEN / CEP 10 signals, using a cutoff of 0.80, was capable of dividing patients into a group of 41 (≧0.80) in which 33 (80.5%) had the favorable prognosis, and a group of 18 (<0.80) in which 6 (33.3%) had the favorable prognosis (p=0.0008). Median times to recurrence in the former and latter groups were 83.0 and 13.0 months, respectively (p<0.0001).
Owner:ABBOTT MOLECULAR INC
Population genetic evolution map and construction method thereof
ActiveCN110910959AGenetic relationship is clearBuild accuratelySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsCold spotGenetics
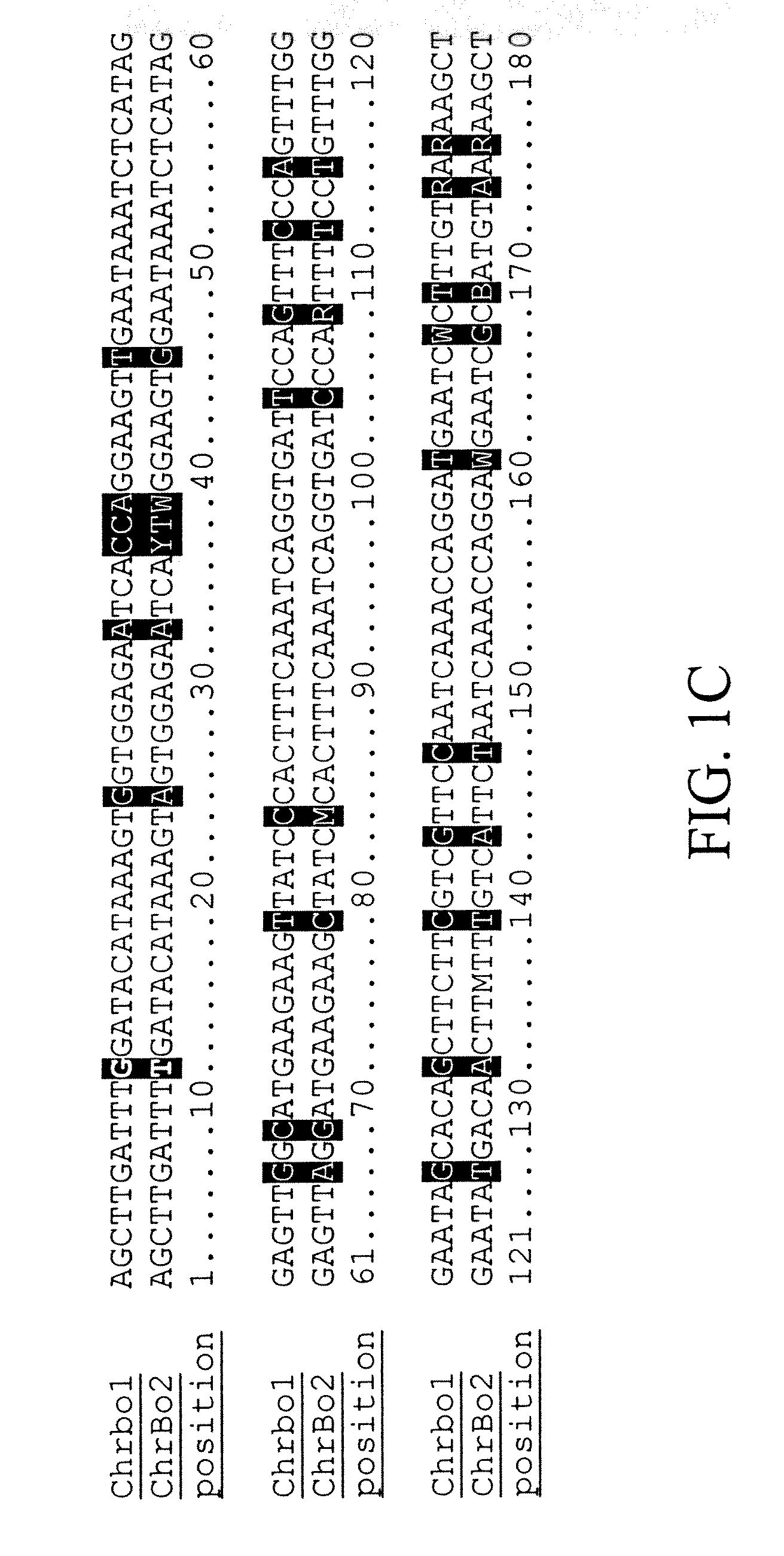
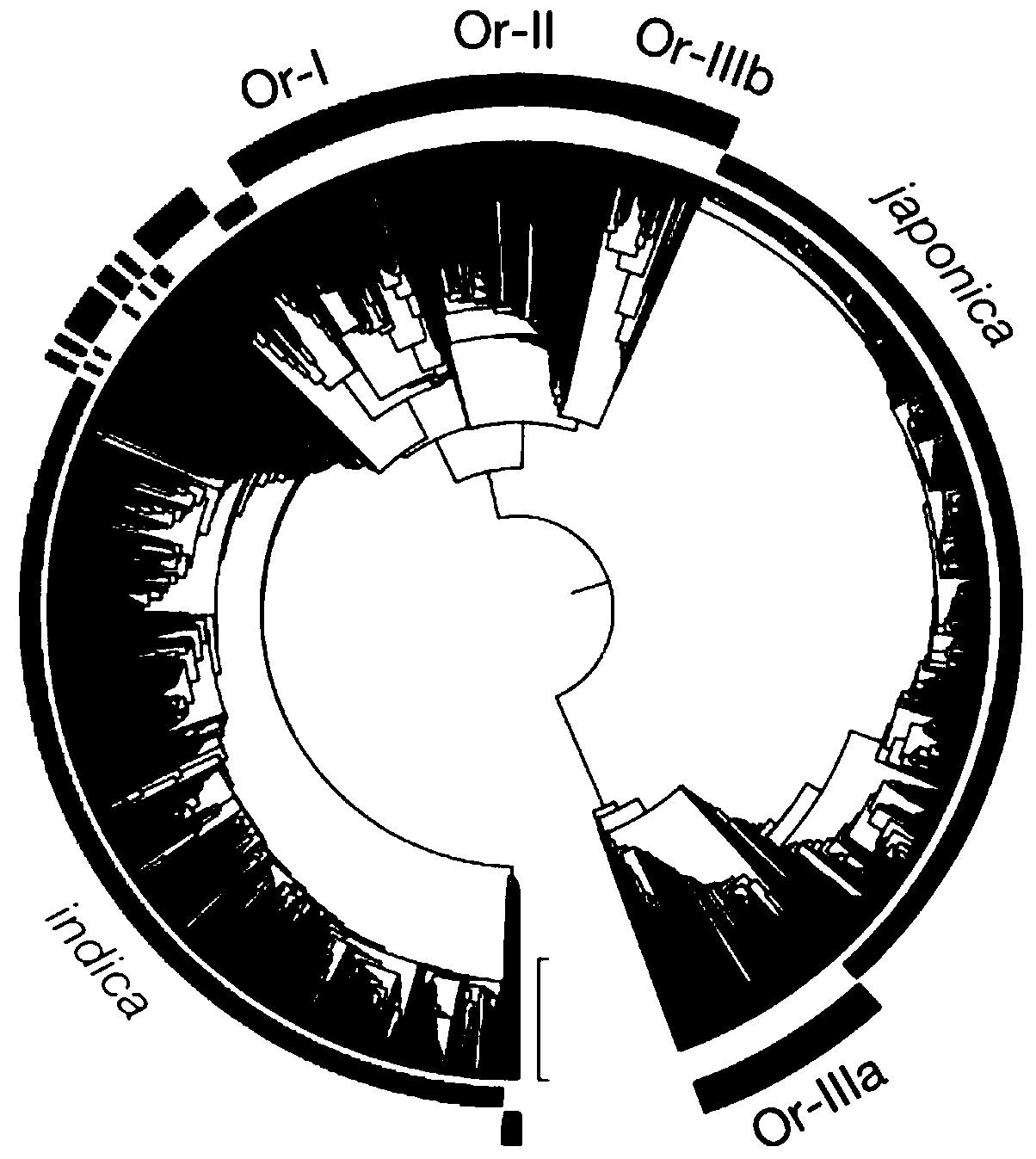
The invention provides a population genetic evolution map and a construction method thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: selecting a recombined cold spot region; constructing a phylogenetic tree by utilizing the SNP sites of the recombined cold spot region; performing clustering analysis on the phylogenetic tree, and determining an evolution relationship between speciesso as to obtain a population genetic evolution map. According to the method, the phylogenetic tree is constructed by selecting SNP sites of the recombined cold spot region (such as a centromere region); on one hand, due to low recombination occurrence rate and stable inheritance between parents and filial generations, the genetic evolution relationship is clear, the constructed phylogenetic tree is more accurate, and on the other hand, the number of SNP sites in the selected sequence is smaller than that of whole genome sequences and is more and more comprehensive than that of SNP sites in a haplotype analysis method. Therefore, the phylogenetic tree can be quickly and accurately constructed.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Artificial mammalian chromosome
InactiveUS20070004002A1Stable expressionEfficient expressionGenetic material ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsMammalDividing cell
It is intended to provide an artificial mammalian chromosome which is stably held in mammalian cells and allows efficient expression of a target gene carried thereby. Namely, a first cyclic vector containing a mammalian centromere sequence and a selection marker gene and a second cyclic vector containing a functional sequence are transferred into mammalian host cells. Then transformed cells are selected by using the above-described selection marker gene and cells holding an artificial mammalian chromosome are selected from among the transformed cells thus selected. Thus, it is possible to construct an artificial mammalian chromosome which has a mammalian replication origin, the mammalian centromere sequence and the functional sequence, is in a cyclic form, can be replicated in mammalian cells, extrachromosomally held in the host cells and transferred to daughter cells in cell division.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method and system for automatically identifying microscopic image of metaphase splitting phase of chromosome
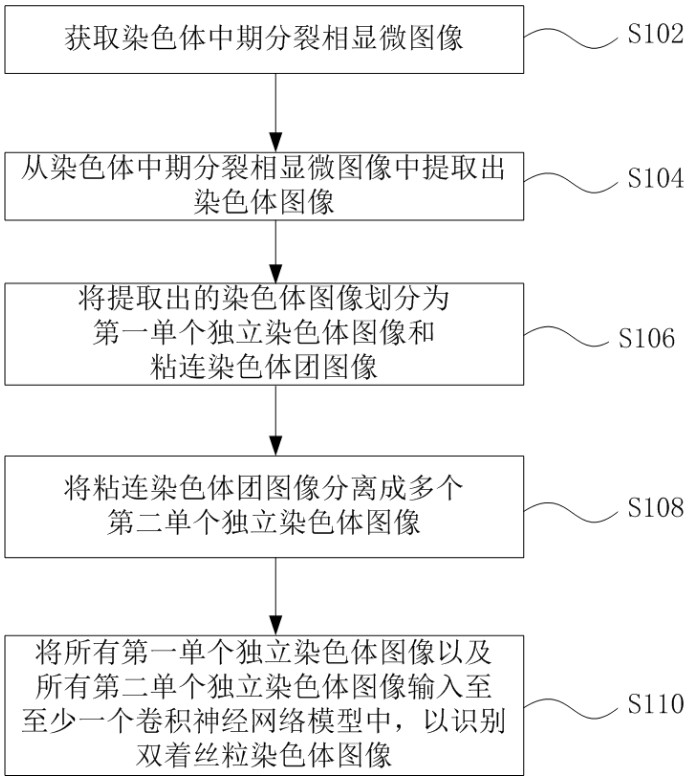
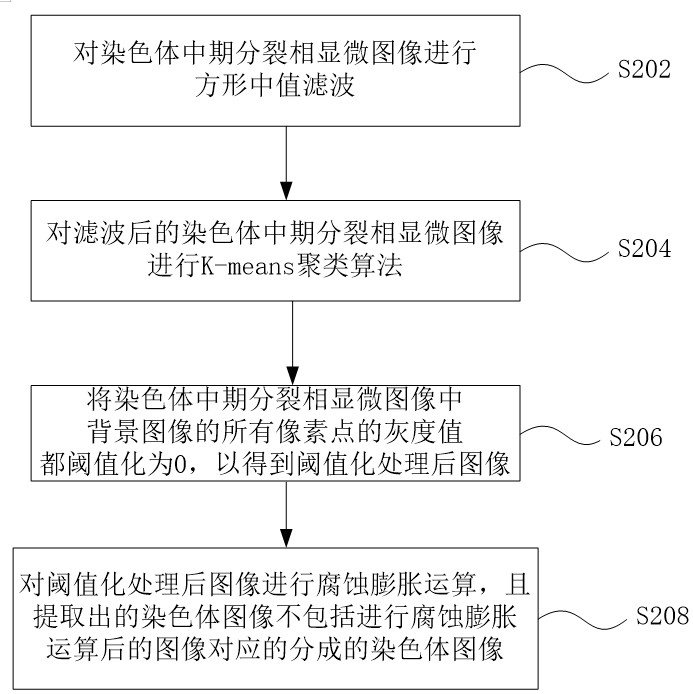
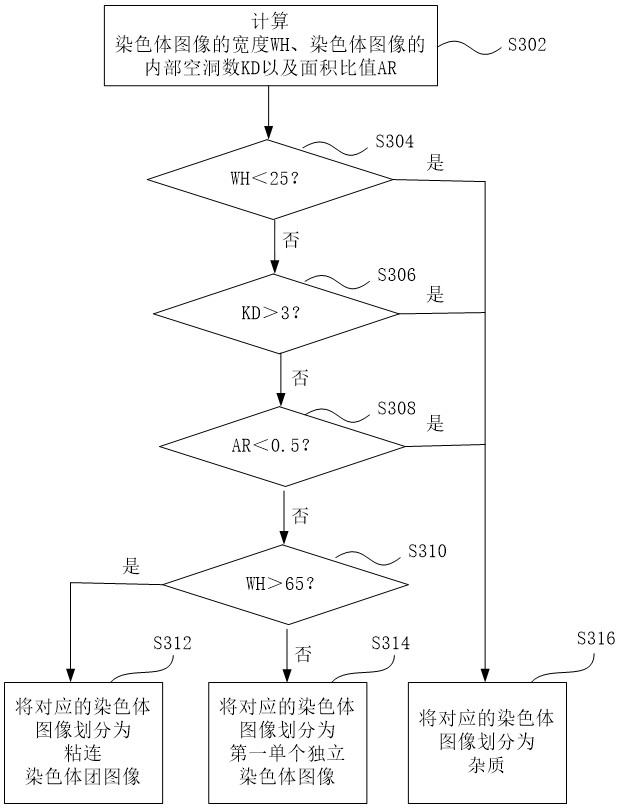
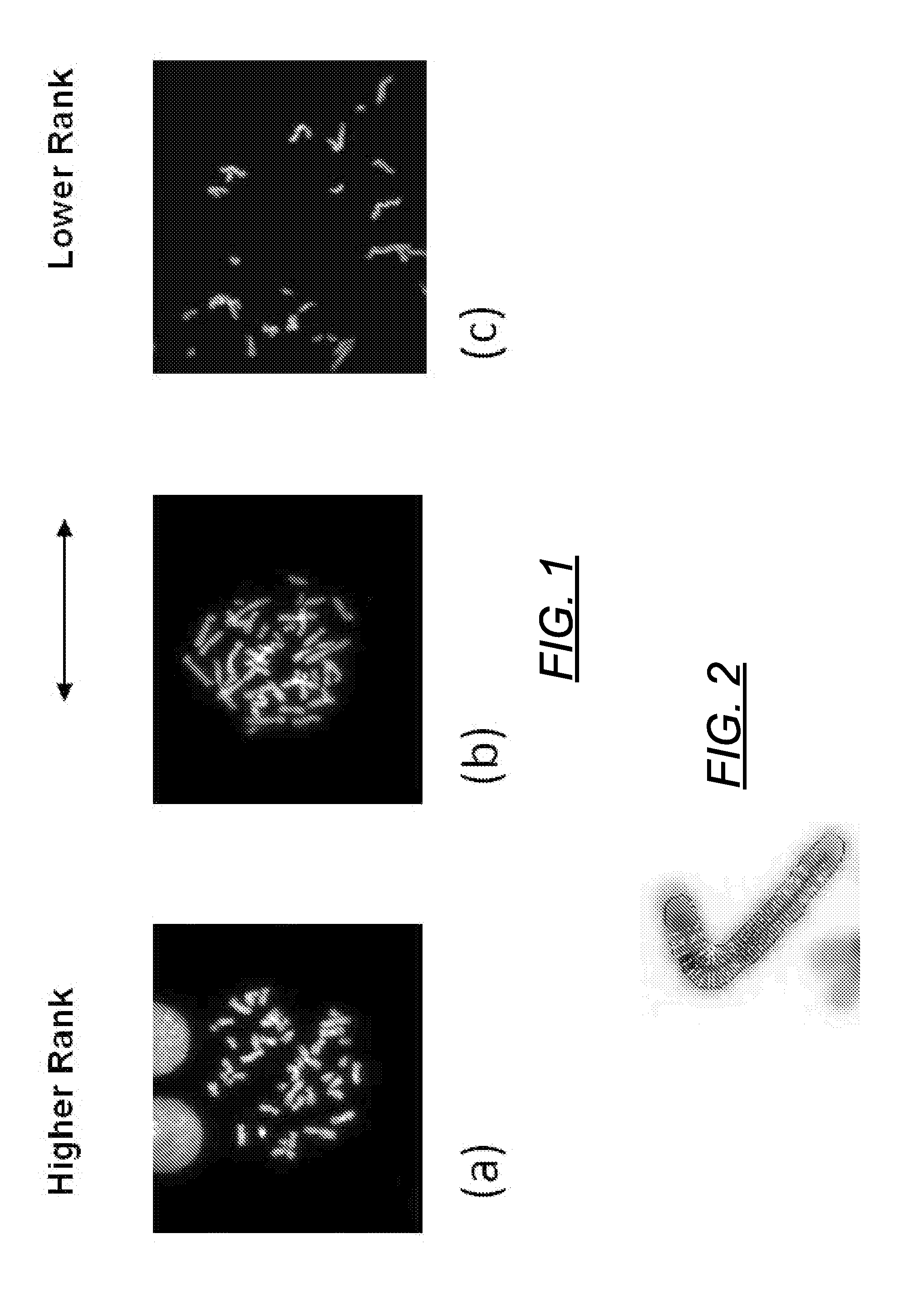
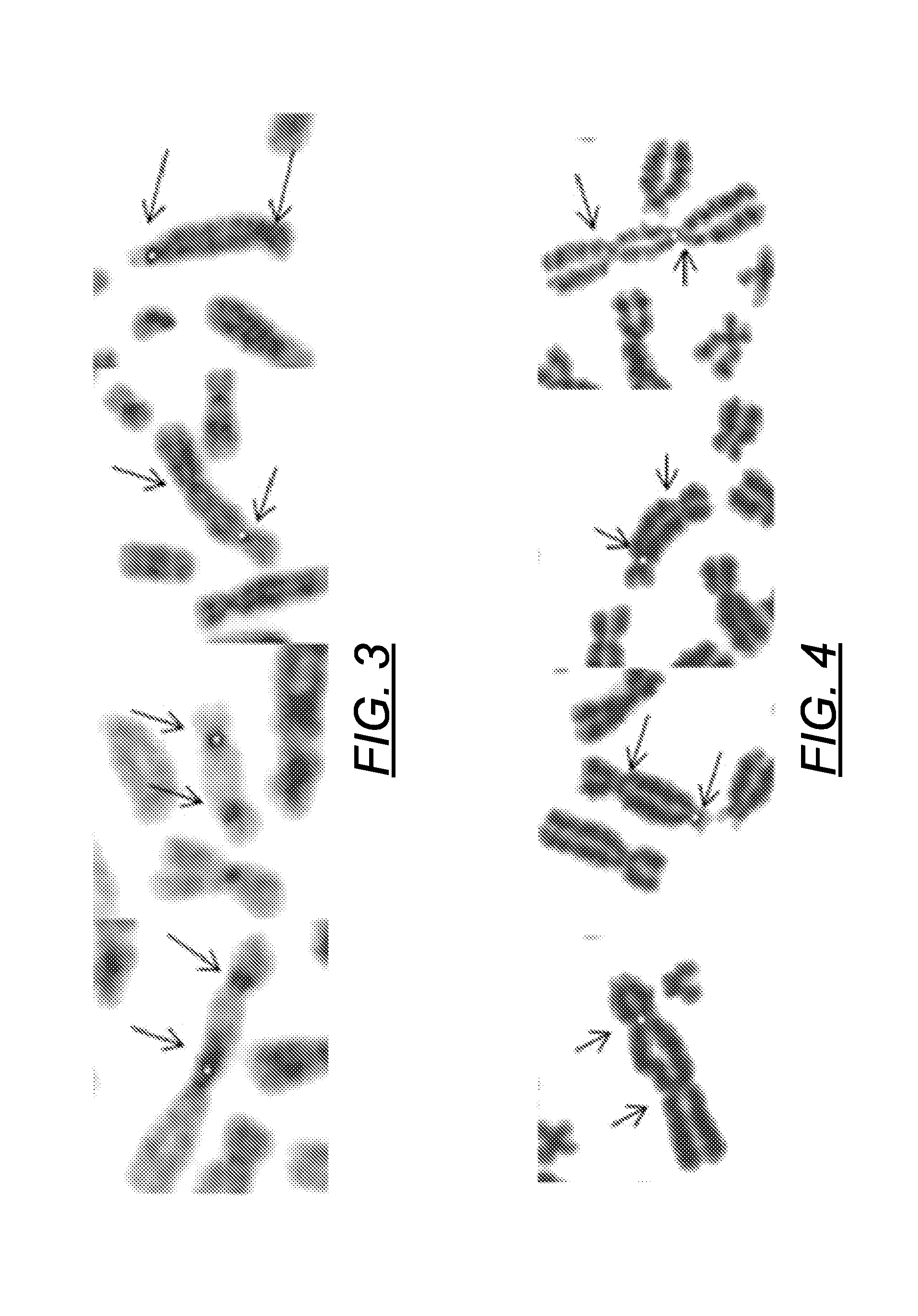
ActiveCN113537182AFully automatedRecognition speed is fastImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageChromosome metaphase
The invention discloses an automatic identification method and system for a chromosome metaphase splitting phase microscopic image based on a convolutional neural network. The automatic identification method comprises the following steps: acquiring the chromosome metaphasesplitting phase microscopic image; extracting a chromosome image from the chromosome metaphase splitting phase microscopic image; dividing the extracted chromosome image into a first single independent chromosome image and an adhesion chromosome group image; separating the adhesion chromosome group image into a plurality of second single independent chromosome images; and inputting all the first single independent chromosome images and all the second single independent chromosome images into at least one convolutional neural network model to identify a double centromere chromosome image. The double-centromere chromosome image is identified through the convolutional neural network model, so that automation in the identification process of the double-centromere chromosome is realized.
Owner:BEIJING HUIRONGHE TECH
Centromere detector and method for determining radiation exposure from chromosome abnormalities
ActiveUS8605981B2Microbiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiation exposureDicentric chromosome
A method for determining radiation exposure from chromosome abnormalities present in a specimen by determining the location or locations of the centromere of each chromosome in a cell in an image of a metaphase cell by segmentation of an accurately drawn chromosome centerline followed by selection of a longitudinal cross-section with the minimum width or intensity or width and intensity; counting the number of centromeres in each chromosome in each cell; computing the frequency of dicentric chromosomes in a population of cells; and determining the radiation dose by comparing the computed frequency of dicentric chromosomes with a previously determined dose-response curve from a calibrated source.
Owner:CYTOGNOMIX
Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105087632AHigh expressionImprove stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome as well as a construction method and application thereof. The saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome comprises two telomeric repeat sequences, two insulator sequences, a centromere-autonomously replicating sequence, a po130 gene and n repeated recombination boxes. Experiment results prove that auxotrophic marker genes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome are few, normal and stable growth in the situation that screening is not carried out can be realized, the expression quantity and copy number of exogenous genes in yeast are increased, the stability of exogenous genes in yeast is improved, genes integrated into a genome can be increased or reduced, and even expanded into new polygene clusters, and the rapid exogenous expression of beta carotene and violacein is successfully realized in yeast, so that a rapid feasible method is provided for yeast heterogeneous production of various exogenous approaches, and the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome can meet the application requirements of fields of gene engineering, metabolic engineering and synthetic biology.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
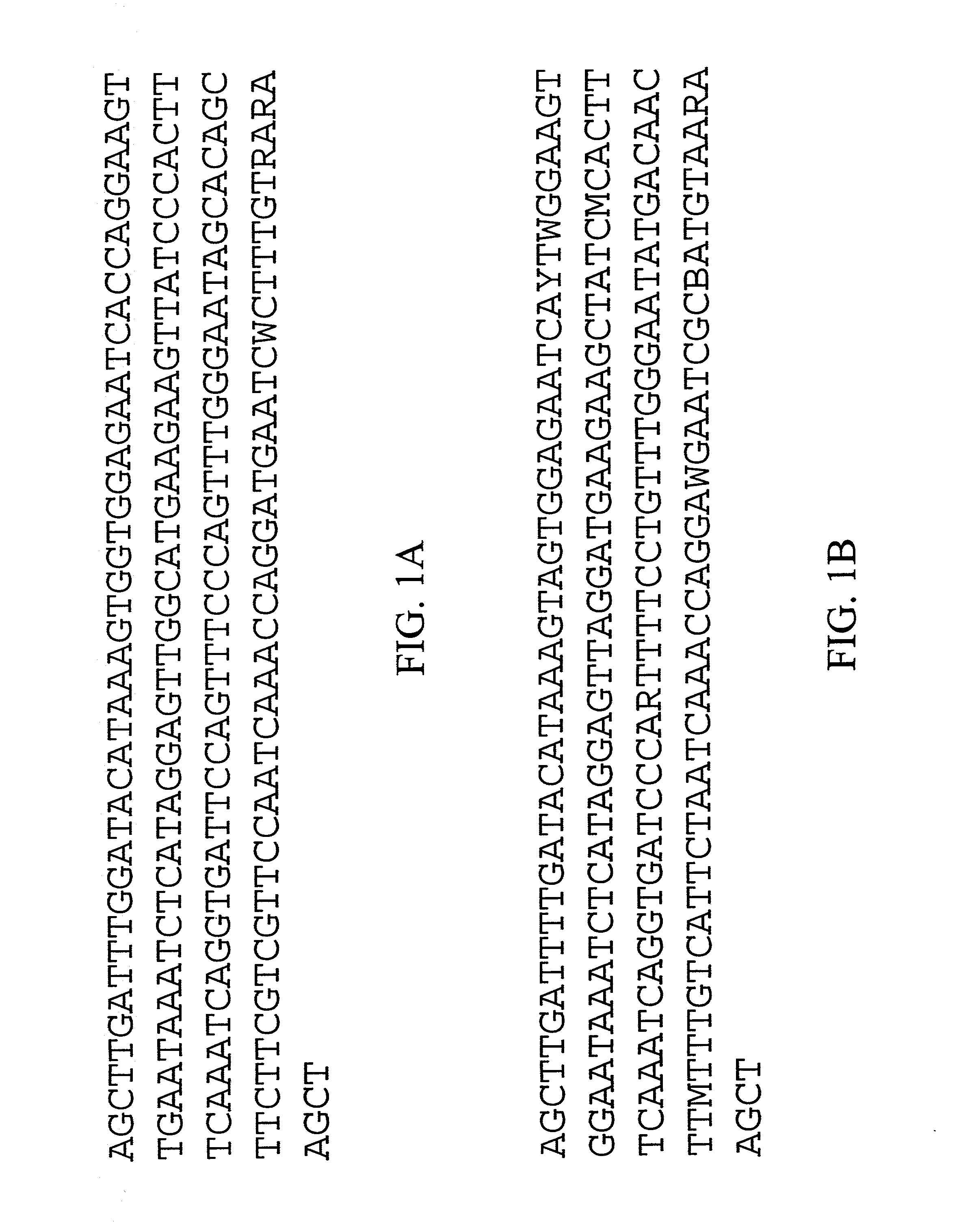
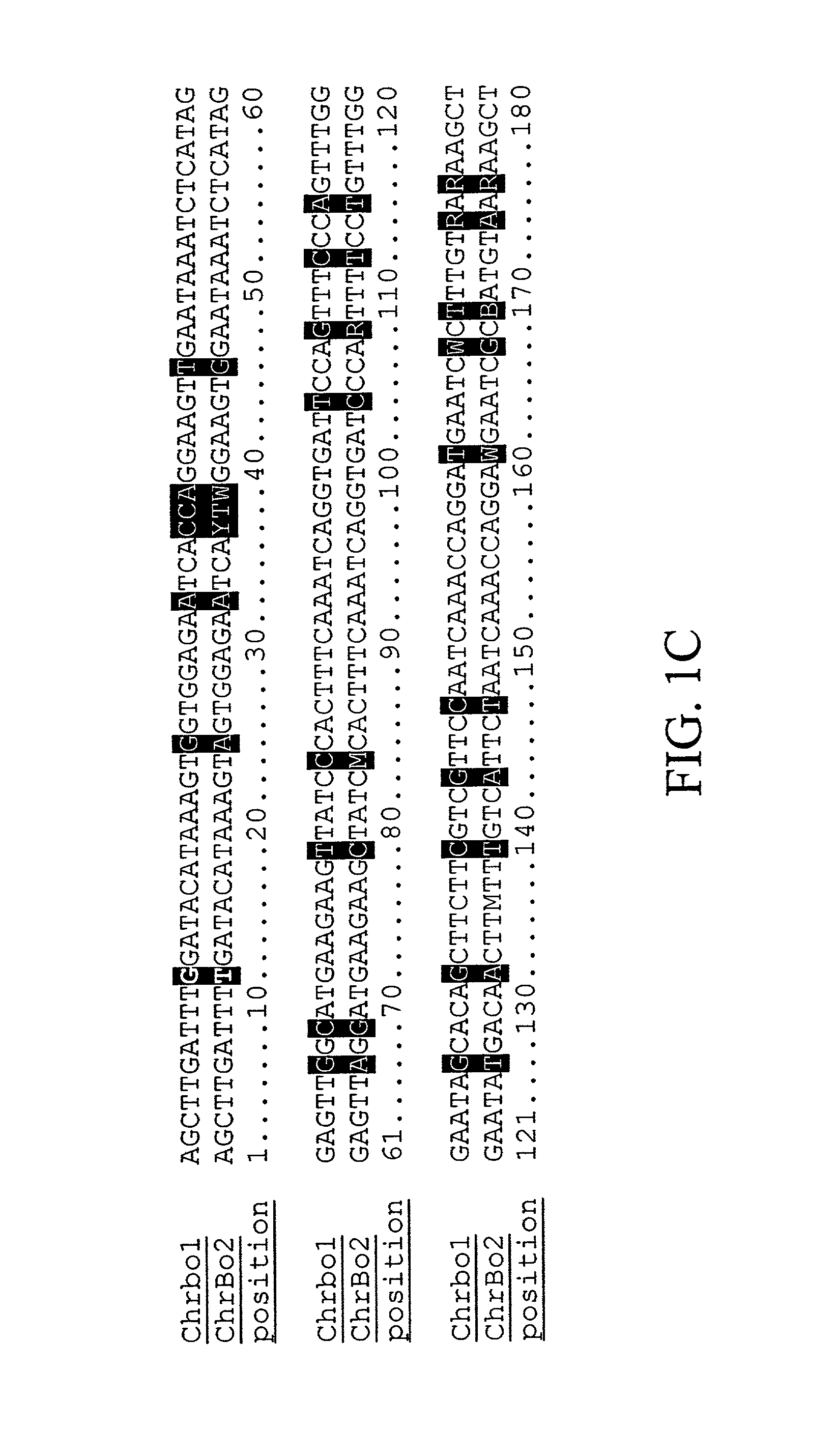
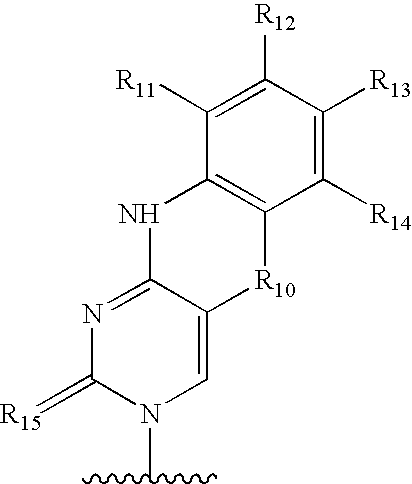
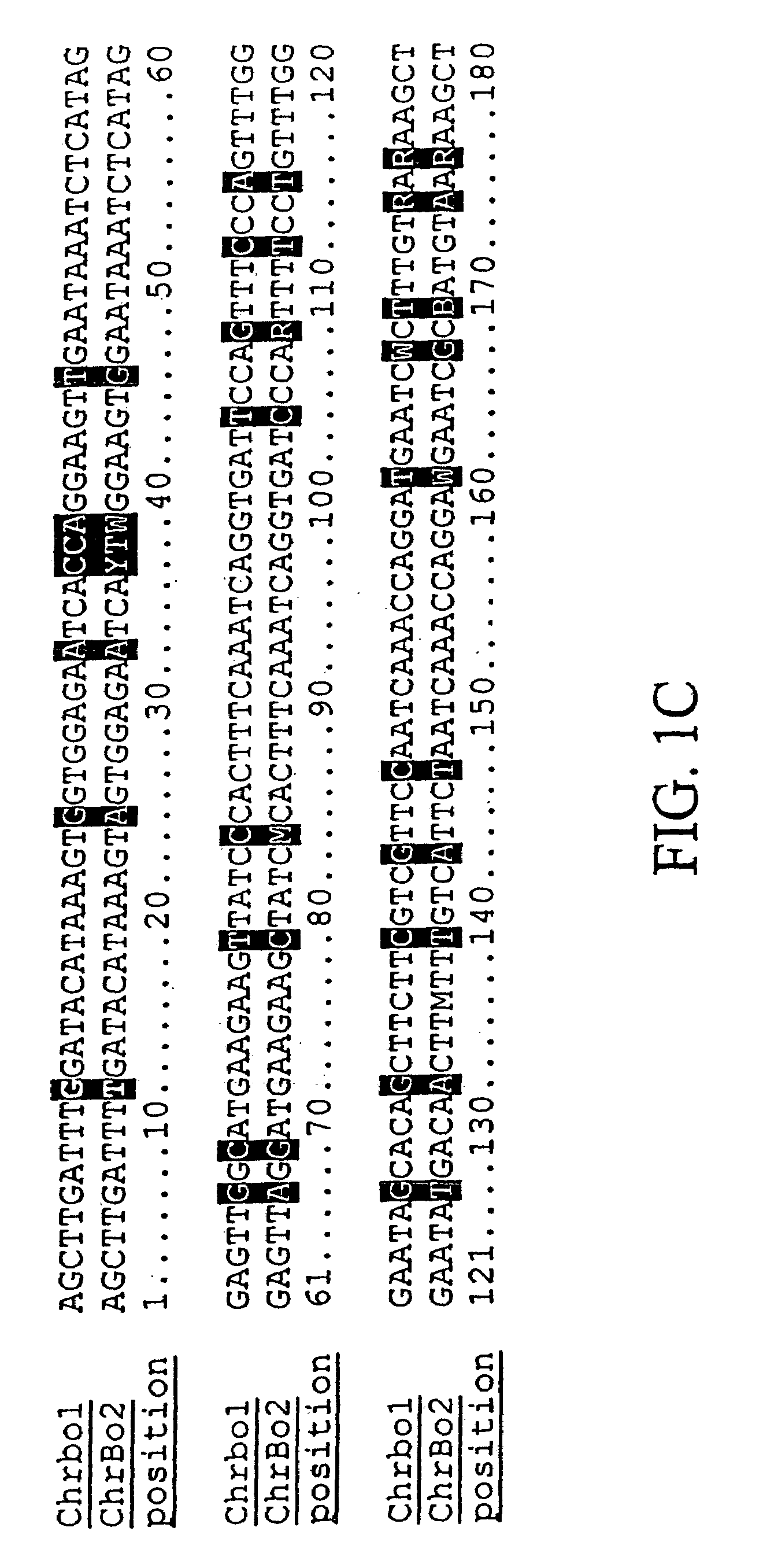
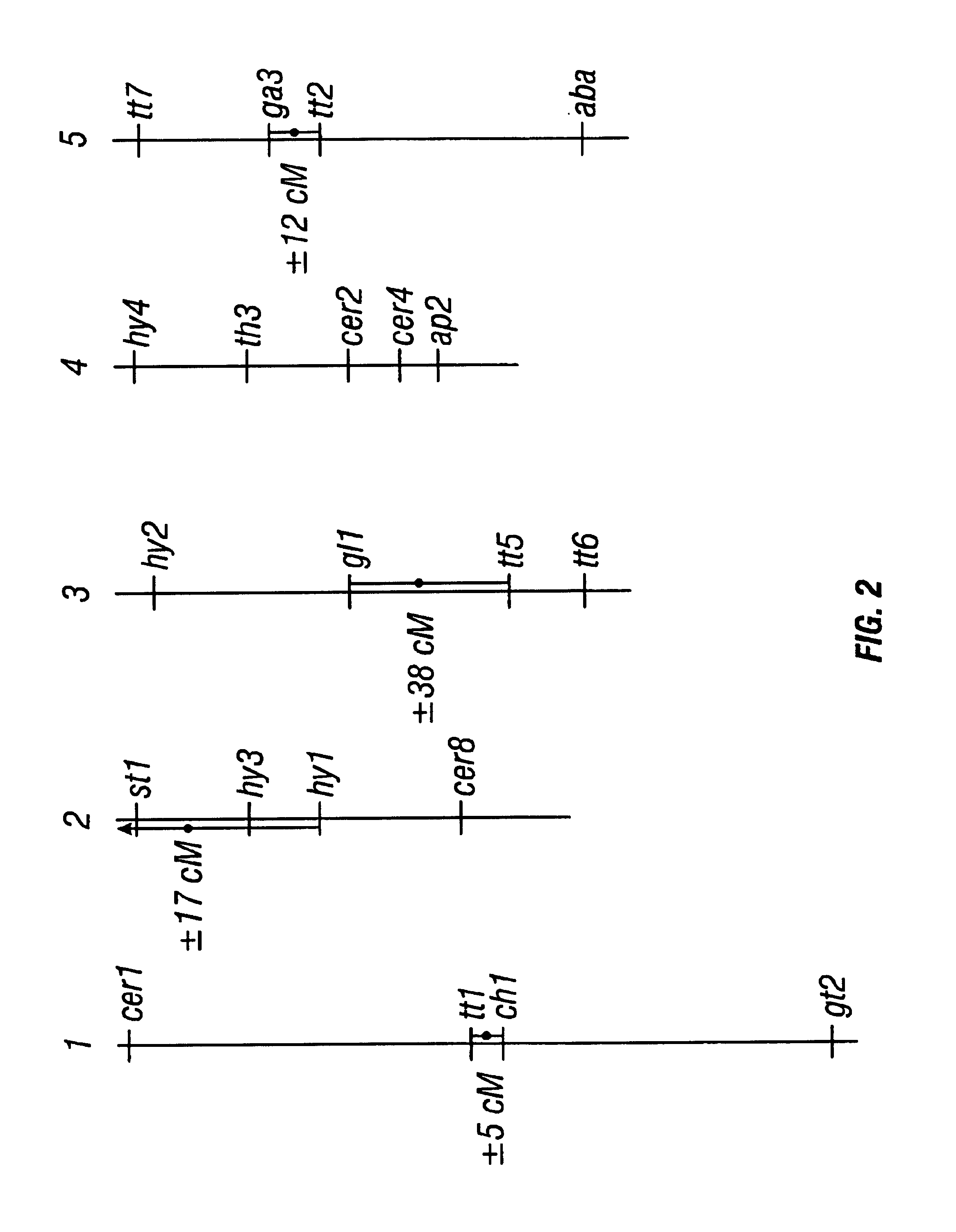
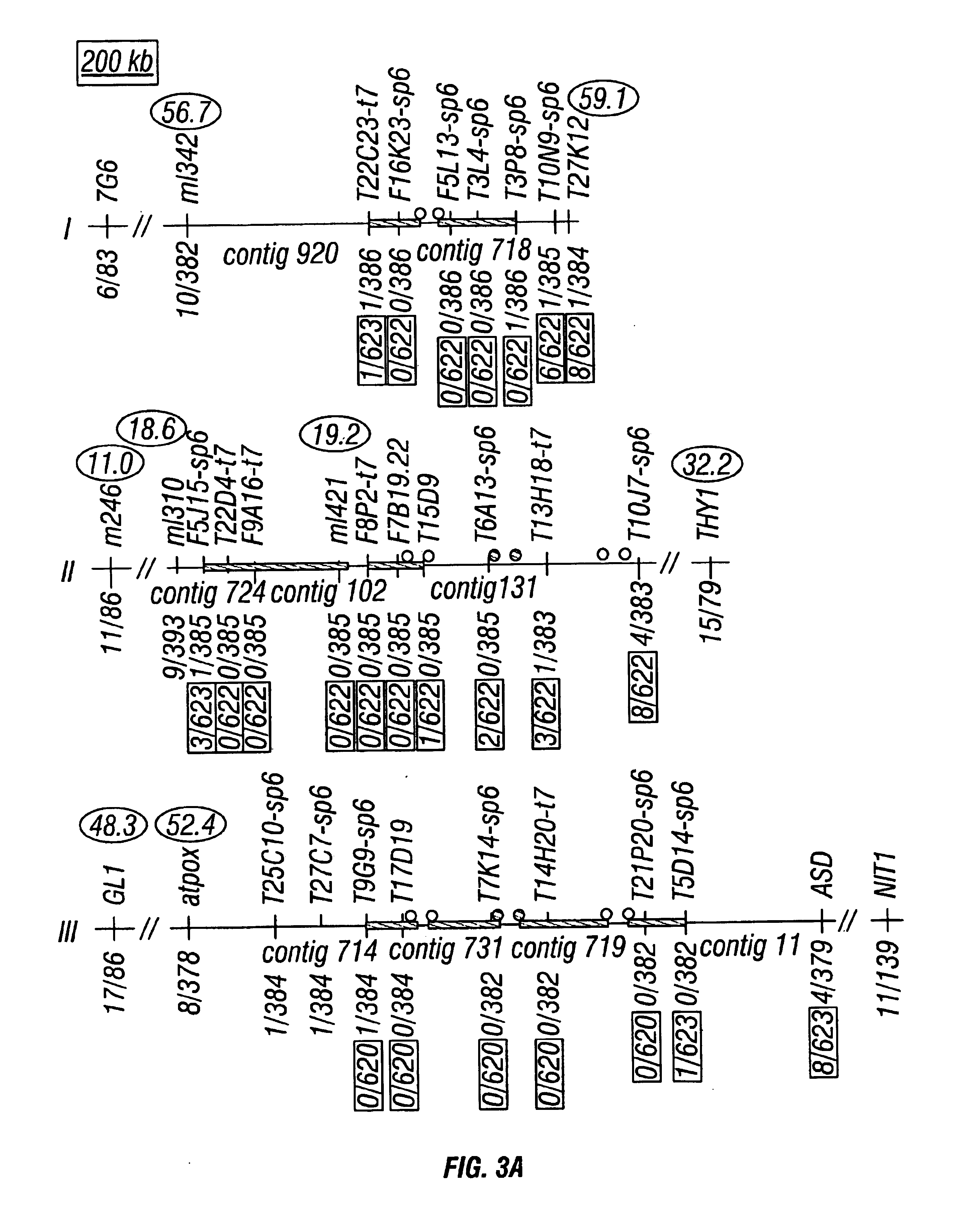
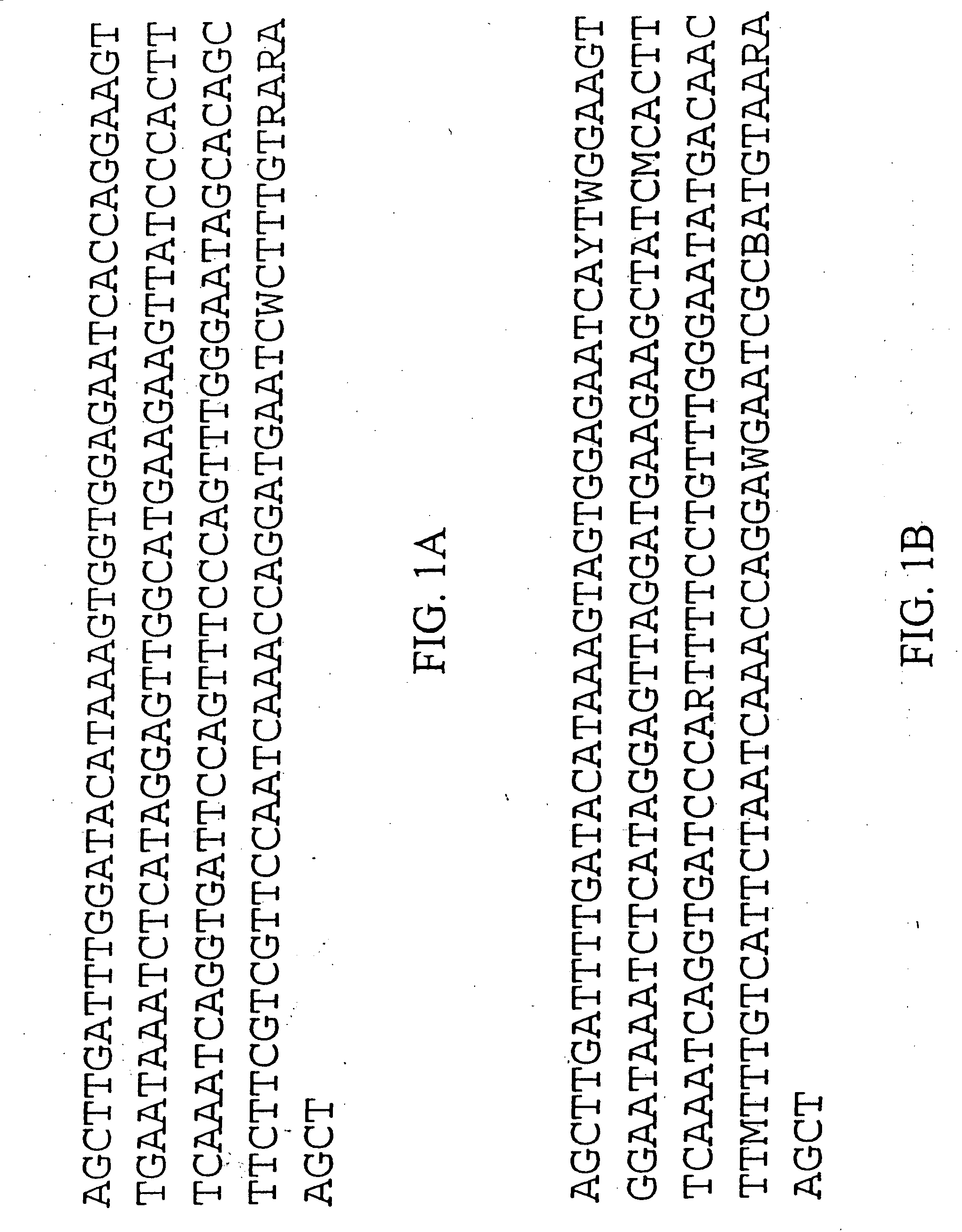
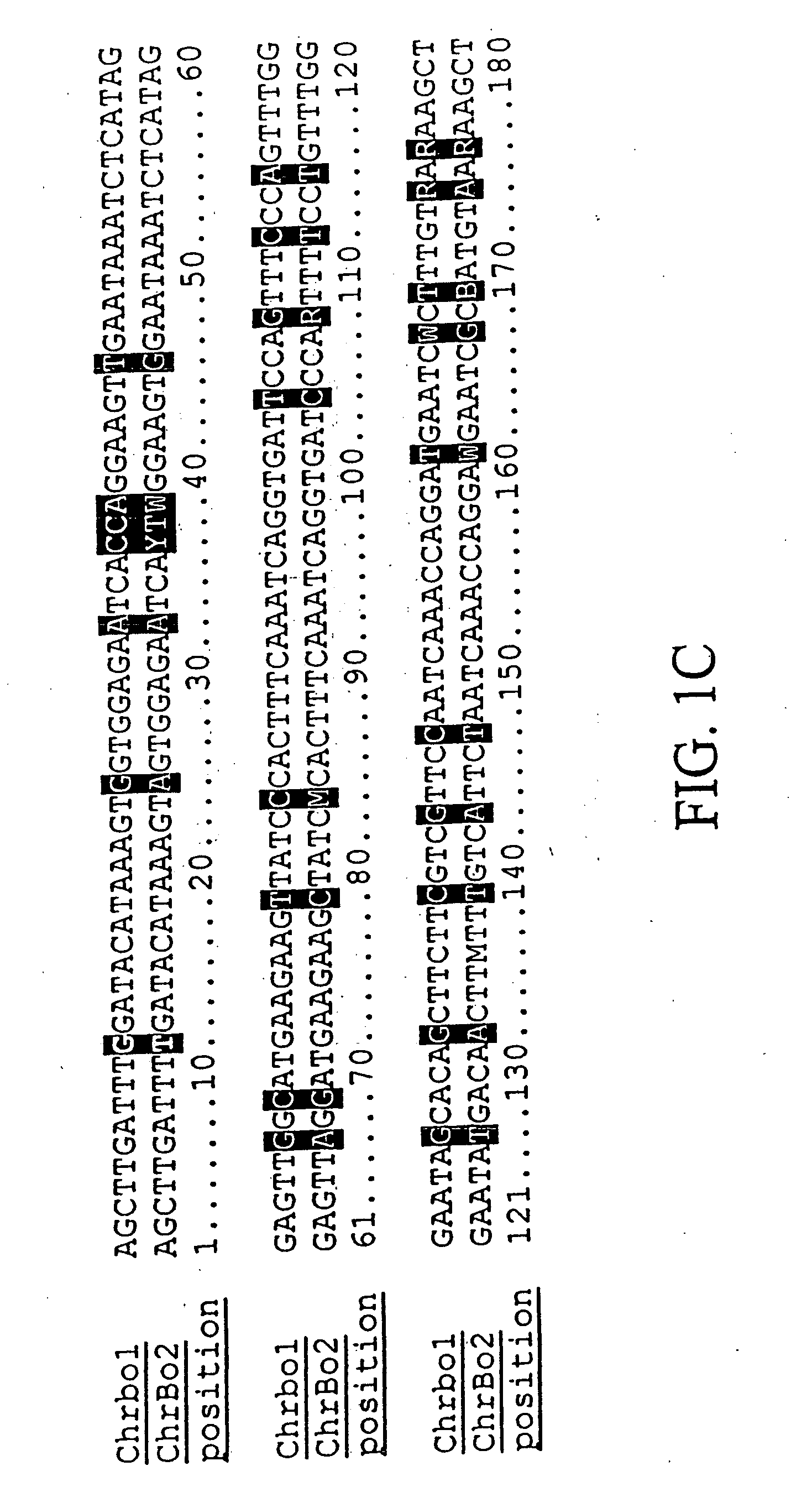
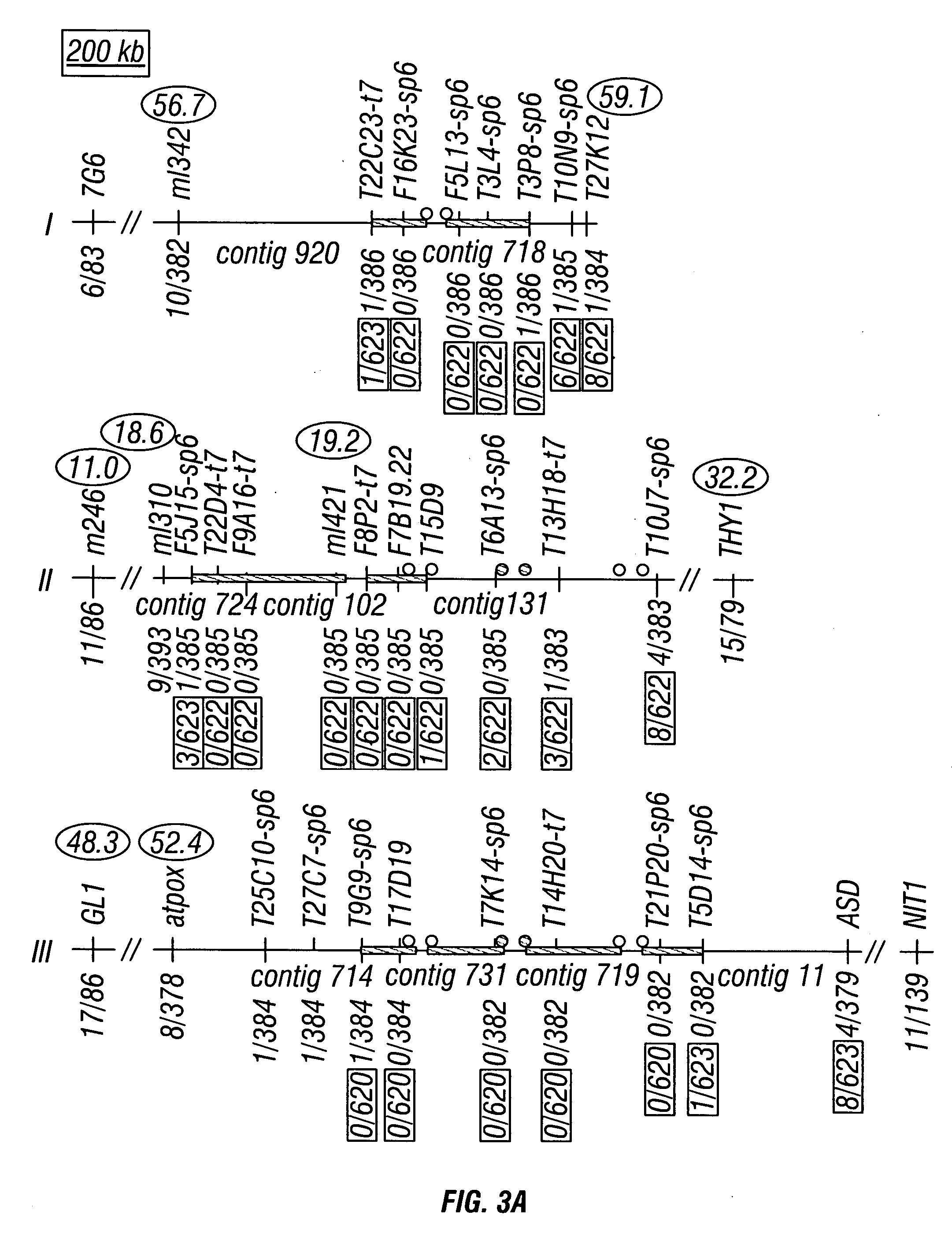
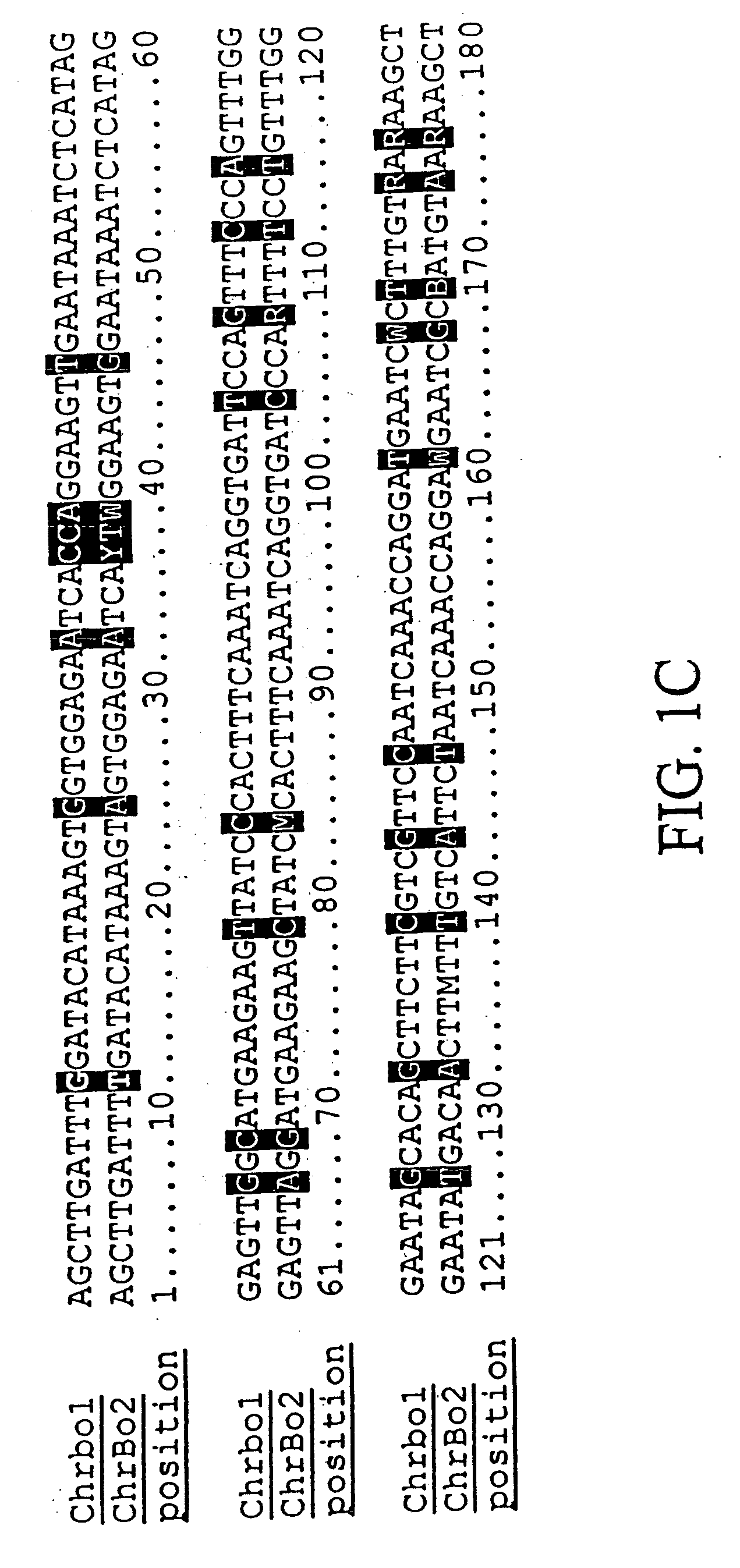
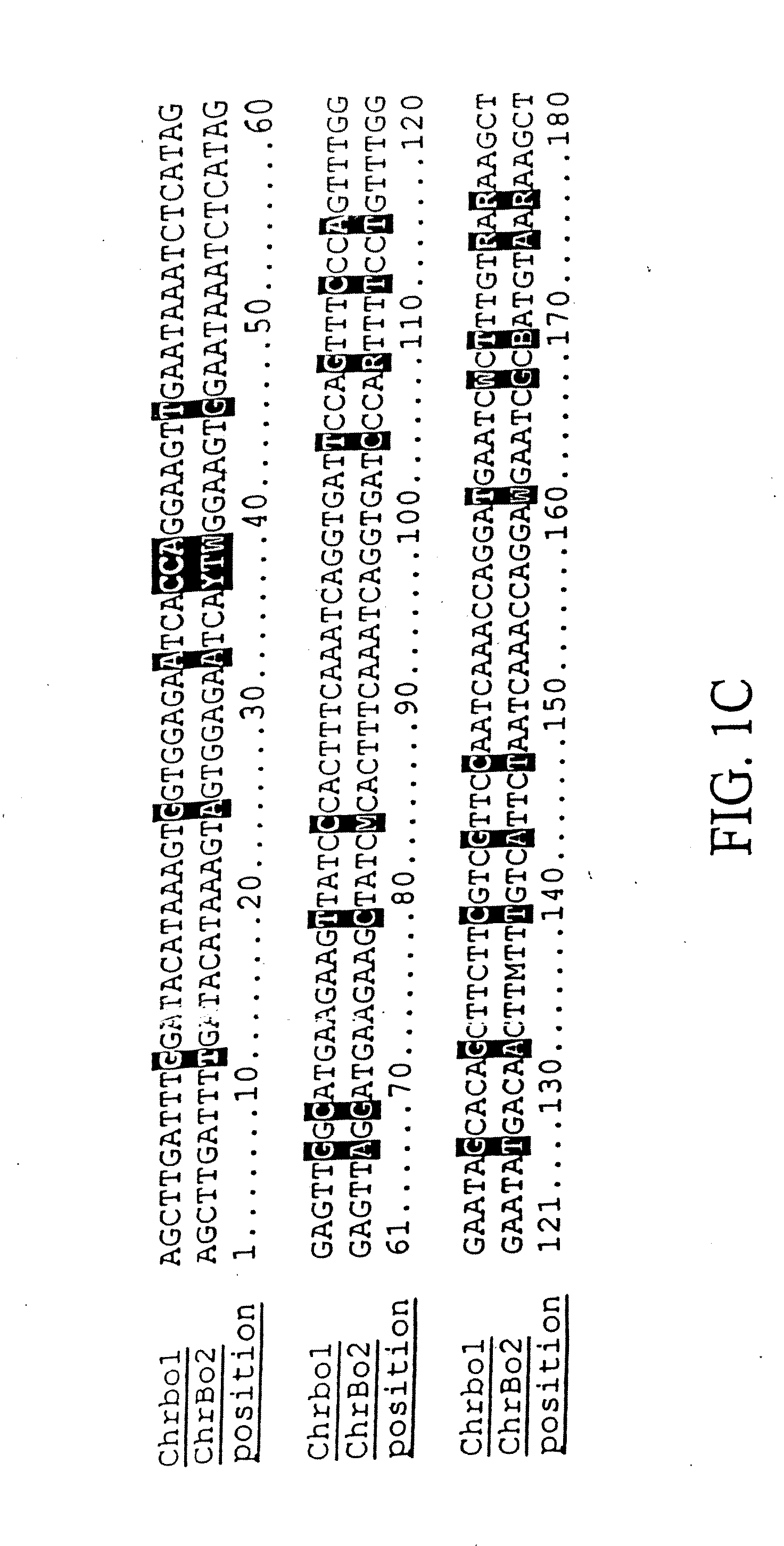
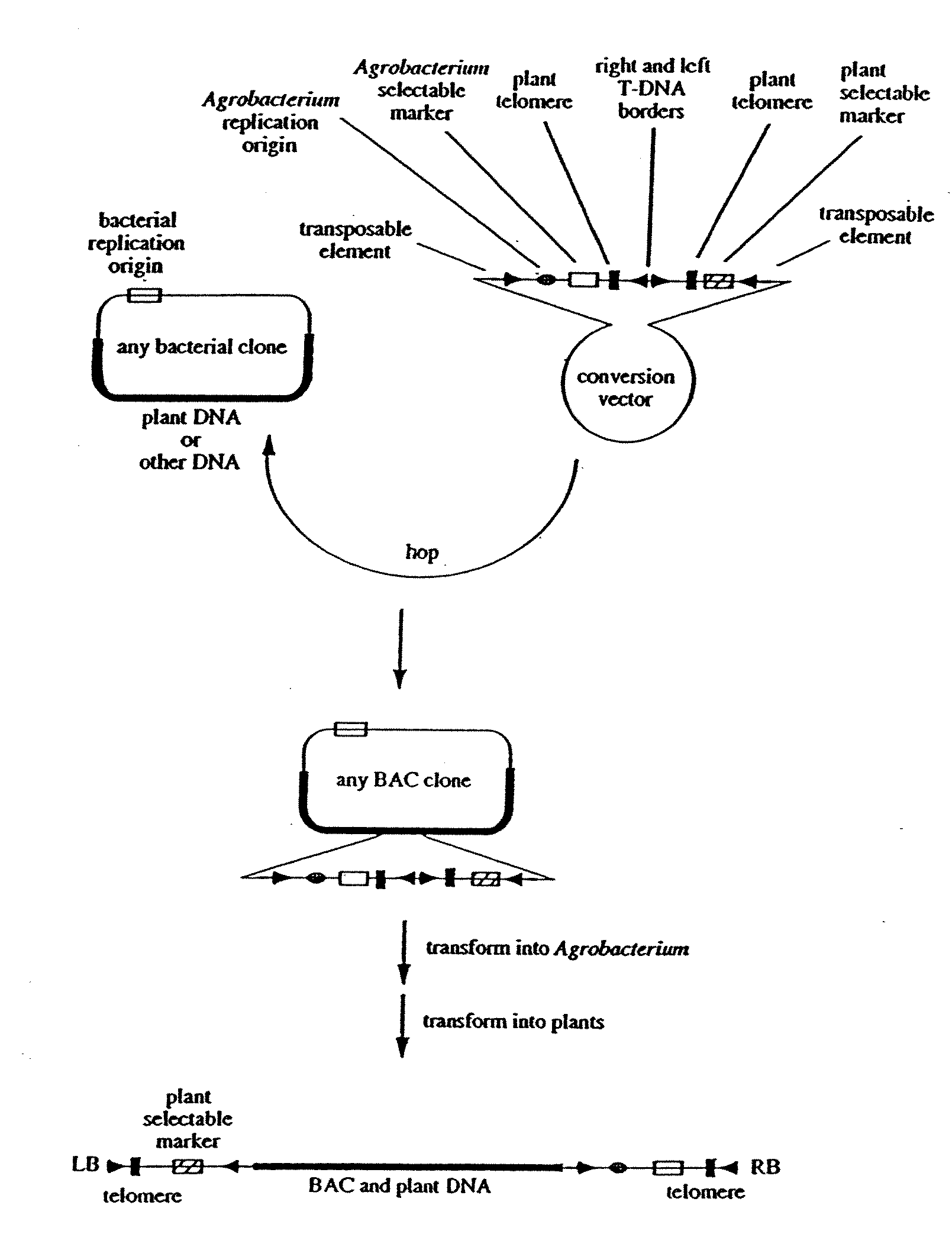
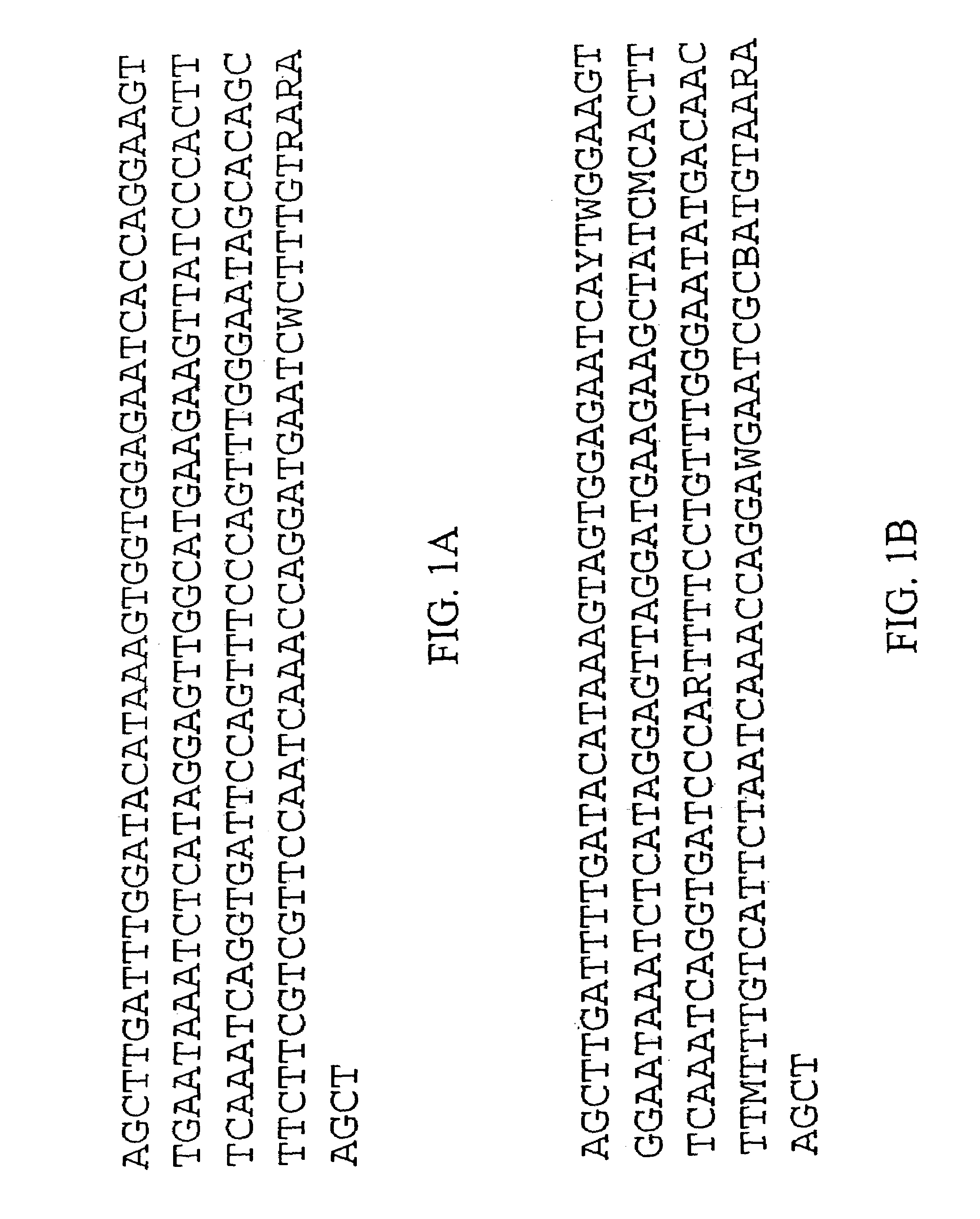
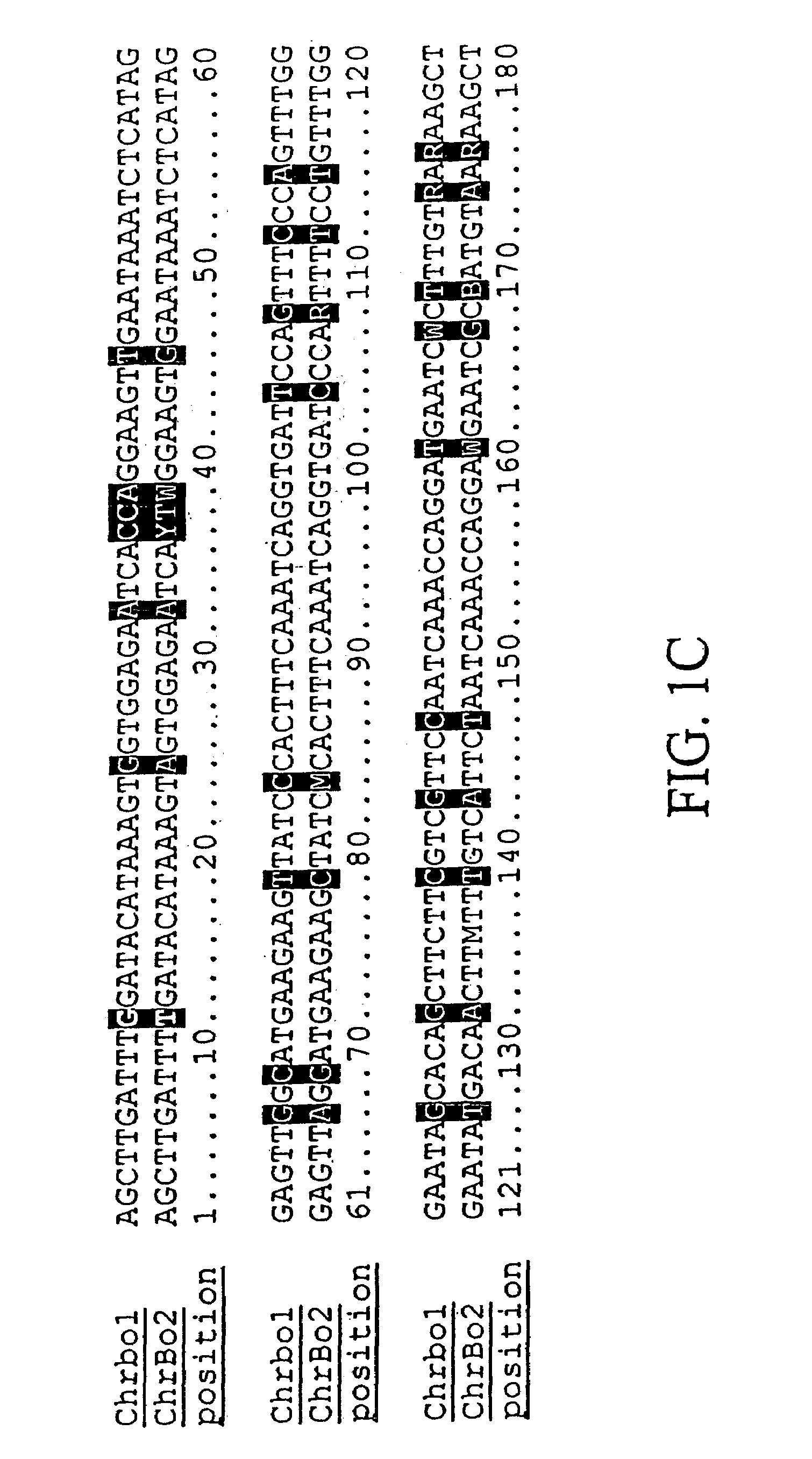
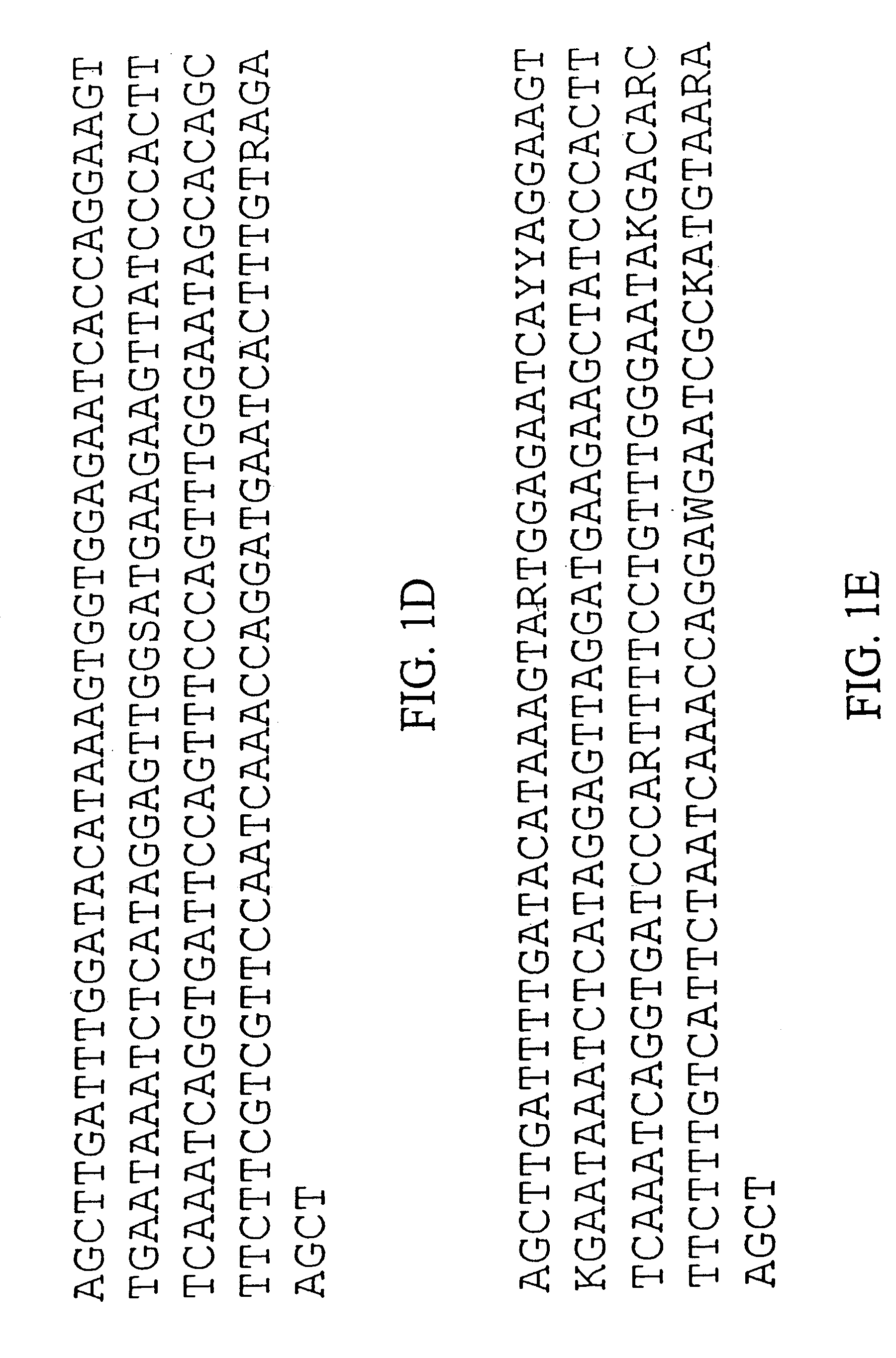
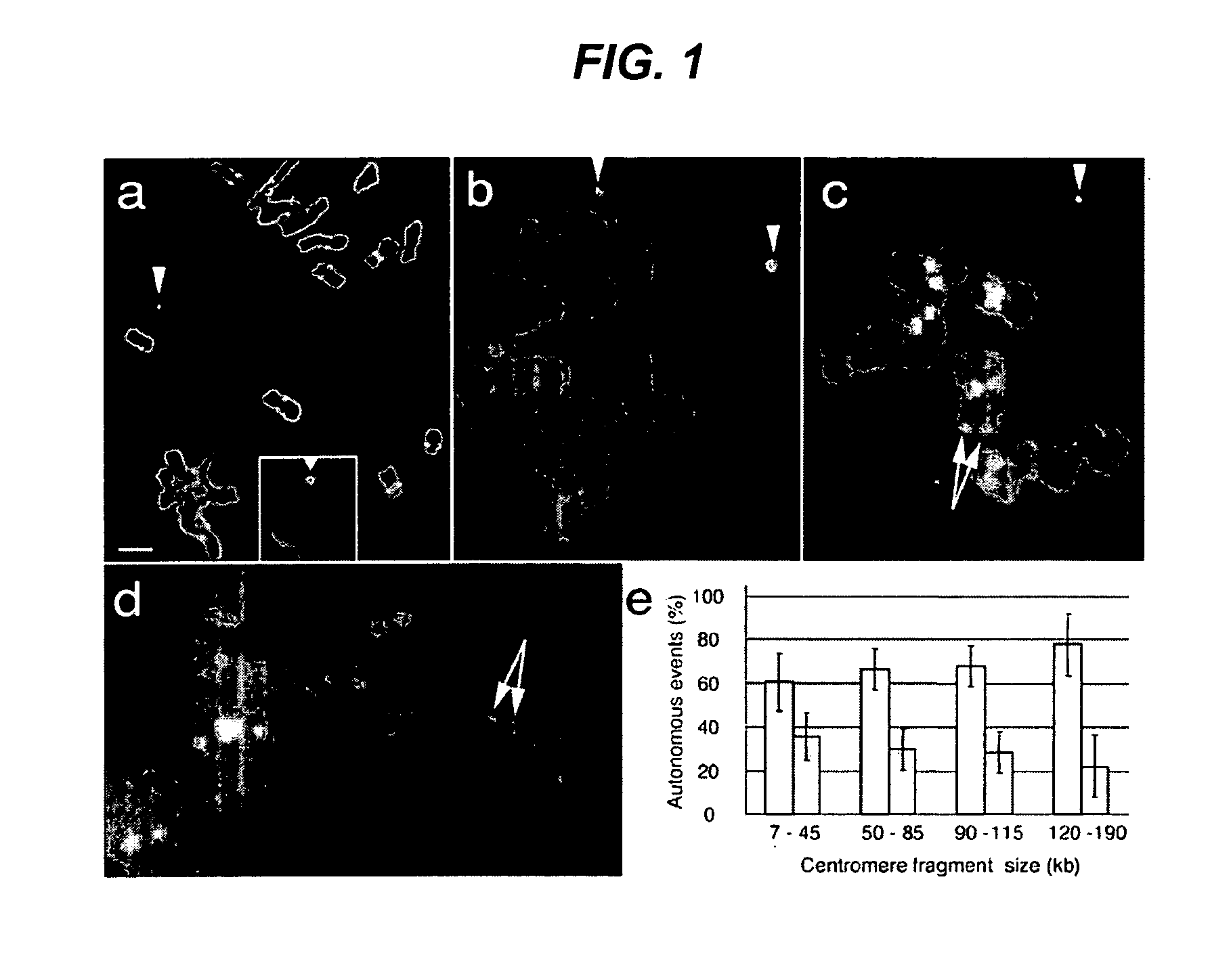
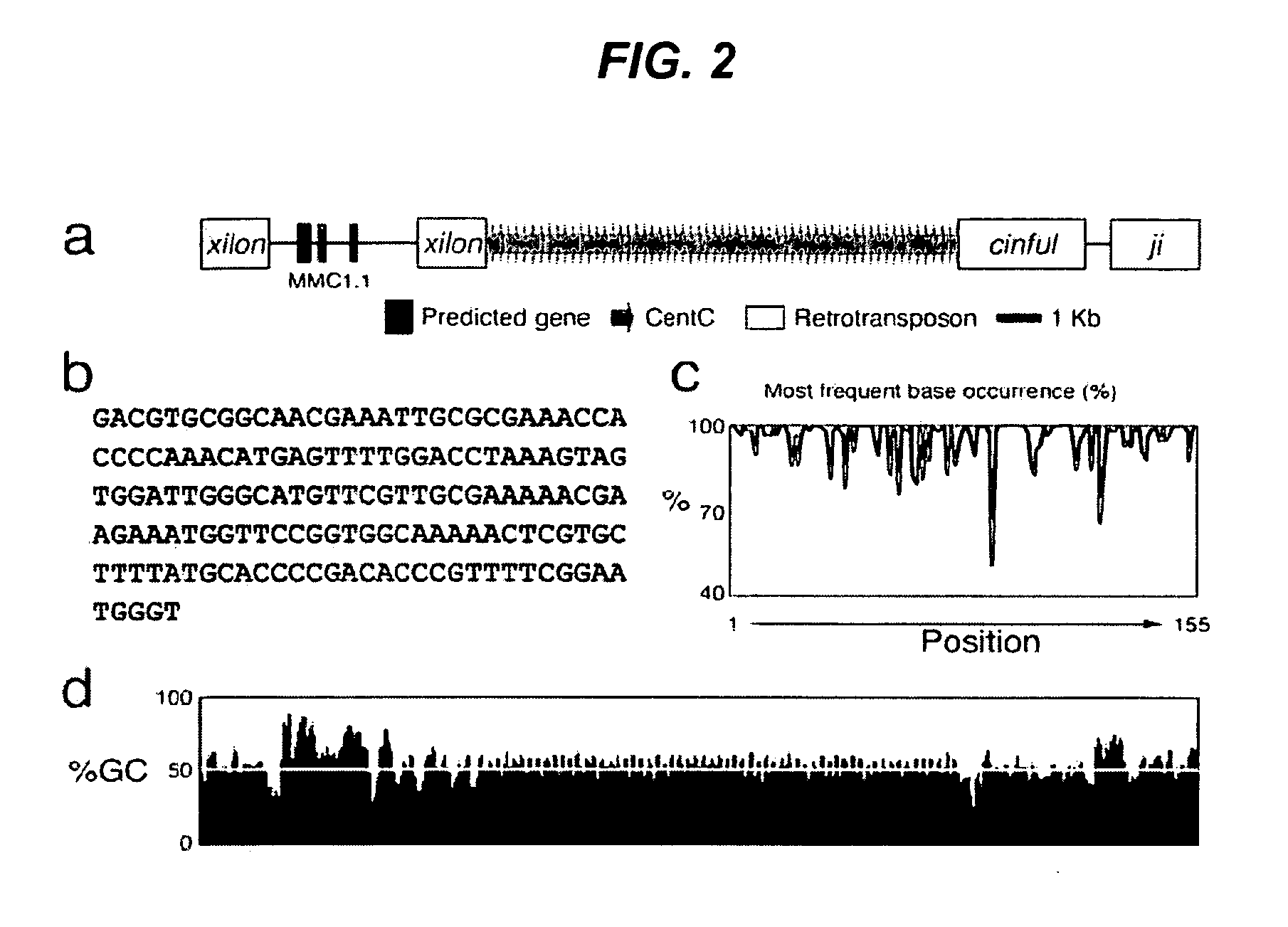
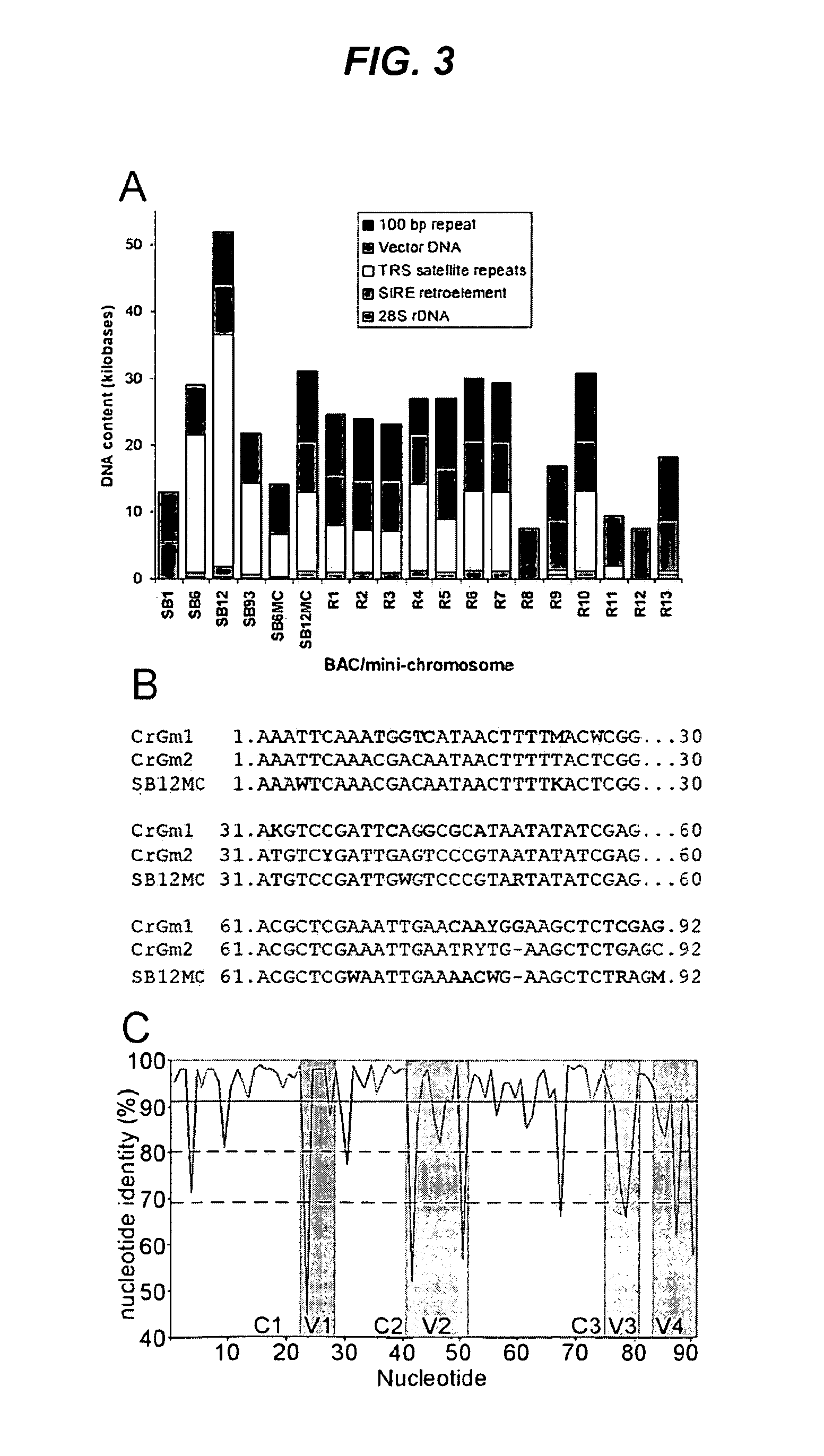
Centromere sequences and minichromosomes
The invention is generally related to methods of generating plants transformed with novel autonomous mini-chromosomes. Mini-chromosomes with novel compositions and structures are used to transform plants cells which are in turn used to generate the plant. Methods for generating the plant include methods for delivering the mini-chromosome into plant cell to transform the cell, methods for selecting the transformed cell, and methods for isolating plants transformed with the mini-chromosome. Plants generated in the present invention contain novel genes introduced into their genome by integration into existing chromosomes.
Owner:CHROMATIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com