Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome as well as construction method and application thereof
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and artificial chromosome, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, etc., can solve the problem of small number of genes, low product expression, difficult to meet industrial mass production, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of improving the expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Embodiment 1, the preparation method of yeast chromosome
[0077] 1. Acquisition of yeast strains containing pNEOC14 vector
[0078] 1. Acquisition of pNEOC1 vector
[0079] (1) According to the natural telomere structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a DNA fragment with telomere repeat sequence and Xcore was designed, and the pUC19-F126 vector was synthesized by commercial gene synthesis. The pUC19-F126 vector was double digested with restriction endonucleases BsaI and AgeI, and a 770bp fragment was recovered, which was the DNA fragment of the telomeric repeat sequence and Xcore. The nucleotide sequence of the fragment was shown in the sequence listing Sequence 1 is shown.
[0080] (2) Using pRS414 with the BsaI and BsmBI restriction sites removed as a template, primer 1 (GCACCGGTTTCCCCCGAAAAGTGCCACCT) and primer 2 (TAGGTCTCTTGTGTTTAAACATGTGCGCGGAACCCCTATTT) were used for PCR amplification using pfu enzyme to obtain a PCR amplification product with a size of 4816bp, n...
Embodiment 2
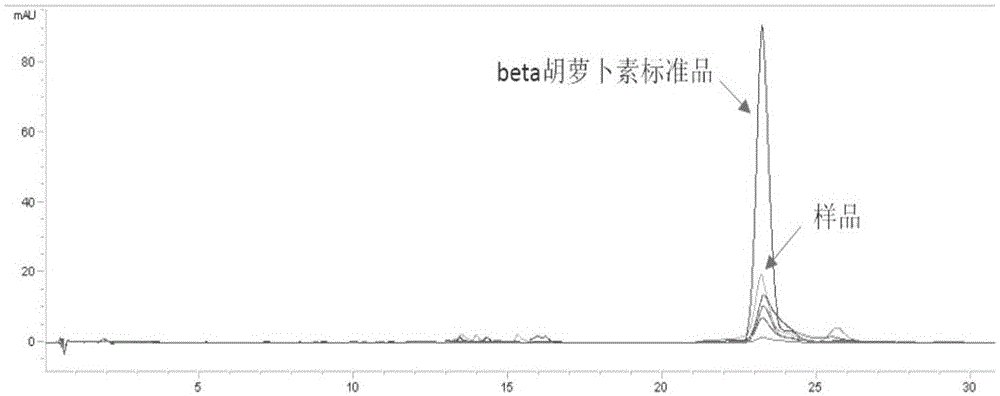
[0132] Embodiment 2, the application of yeast chromosome in the production of beta carotene
[0133] 1. Synthesis of target fragments
[0134]The DNA fragment shown in sequence 17 in the sequence list is artificially synthesized, and the fragment is sequentially terminated by URR1, TDH3 promoter, crtE gene, TEF1 terminator, ADH1 promoter, crtI gene, ADH1 terminator, TEF2 promoter, crtYB gene, and TEF2 Son, LEU2 (screening marker gene) and URR2 composition. All promoters, genes, and terminators are seamlessly connected.
[0135] 2. Conversion
[0136] Transform the DNA fragment shown in sequence 17 in the sequence listing synthesized in step 1 into the yeast strain prepared in Example 1 containing a repeated recombination cassette, and use yeast homologous recombination to obtain a correctly integrated yeast strain. and identified by PCR. The steps of PCR identification are as follows:
[0137] Use the genomic DNA of the transformant as a template, and use PrimerA and Prim...
Embodiment 3
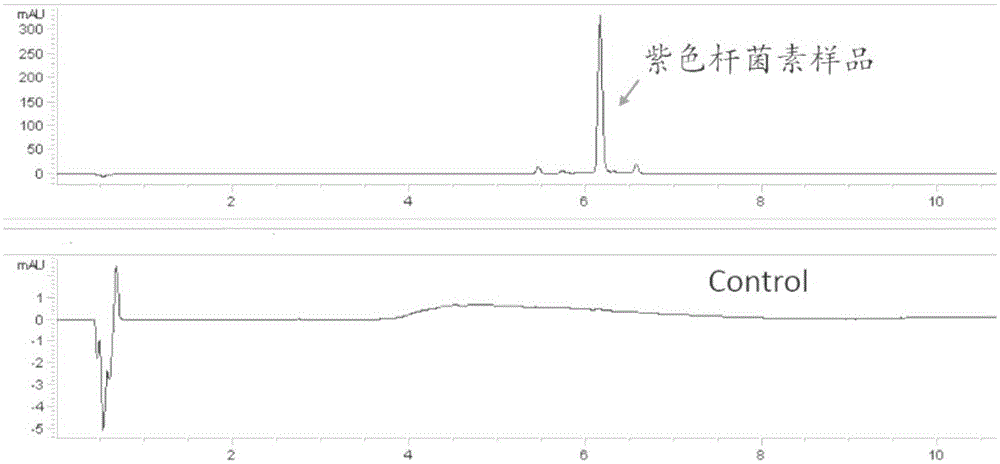
[0155] Example 3, the application of yeast chromosome in the production of violacein
[0156] 1. Synthesis of target fragments
[0157] The DNA fragment shown in sequence 18 in the sequence list is artificially synthesized, and the fragment is sequentially terminated by URR1, TEF2 promoter, vioA gene, ADH1 terminator, TEF2 promoter, vioB gene, ADH1 terminator, TEF2 promoter, vioC gene, and ADH1 promoter, TEF2 promoter, vioD gene, ADH1 terminator, TEF2 promoter, vioE gene, ADH1 terminator, LEU2 (selectable marker gene) and URR2. All promoters, genes, and terminators are seamlessly connected.
[0158] 2. Conversion
[0159] Transform the DNA fragment shown in sequence 18 in the sequence listing synthesized in step 1 into the yeast strain containing the repeated recombination cassette prepared in Example 1, and use yeast homologous recombination to obtain a correctly integrated yeast strain. and identified by PCR. The steps of PCR identification are as follows:
[0160] Use ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com