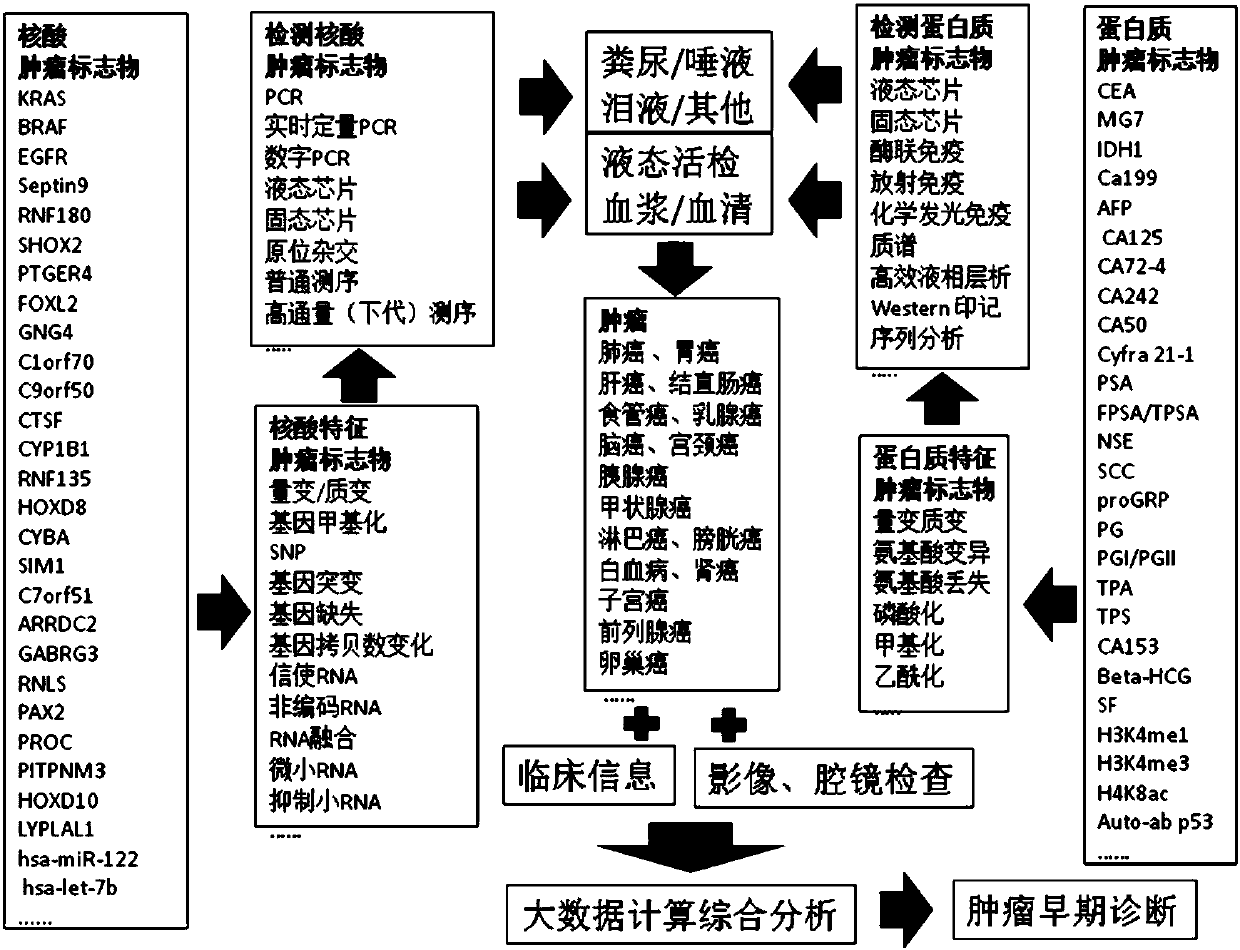
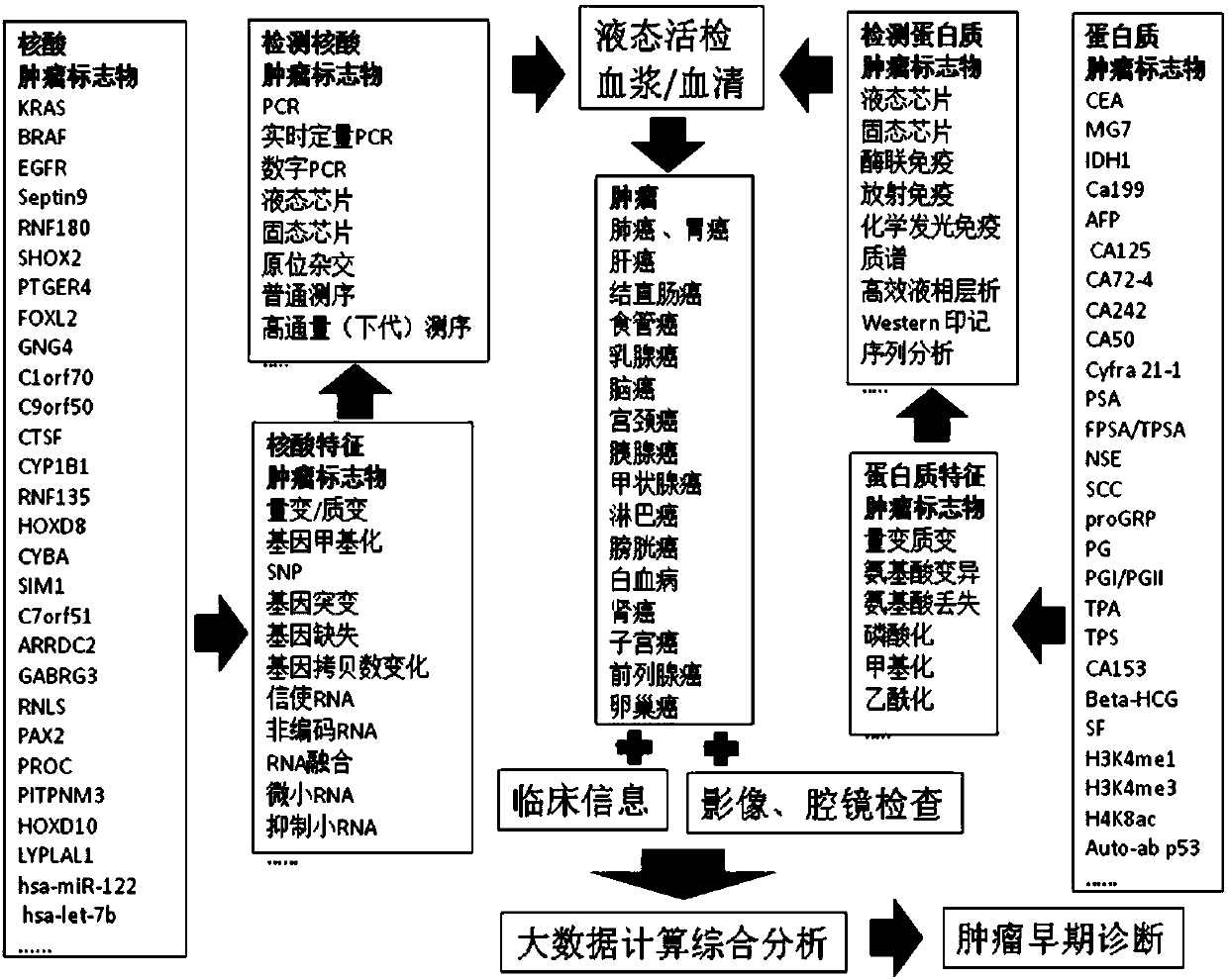
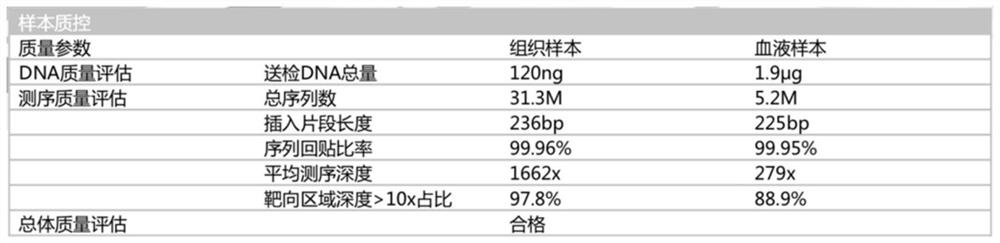
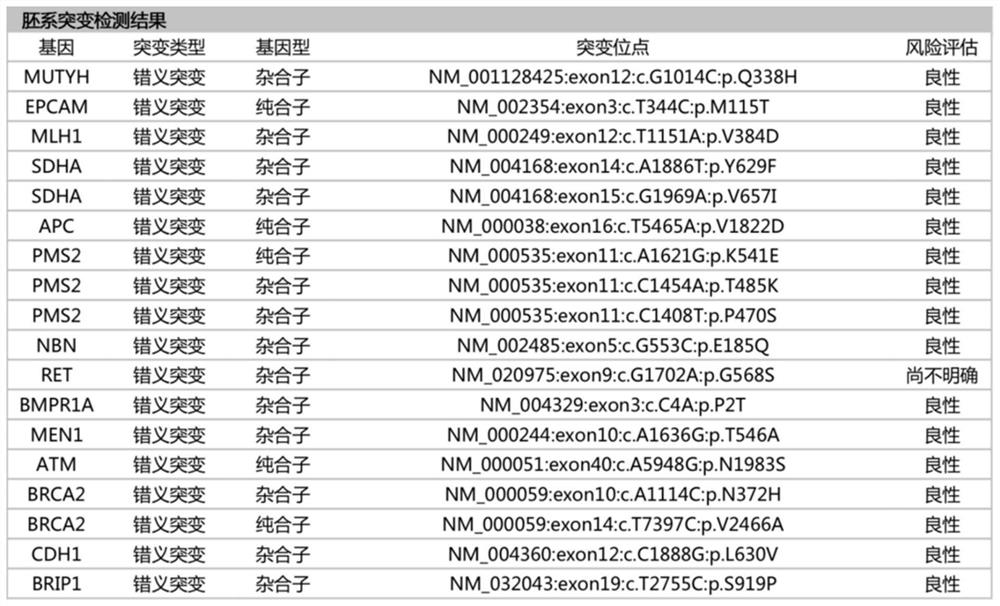
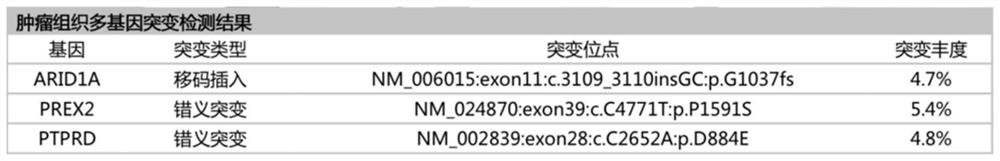
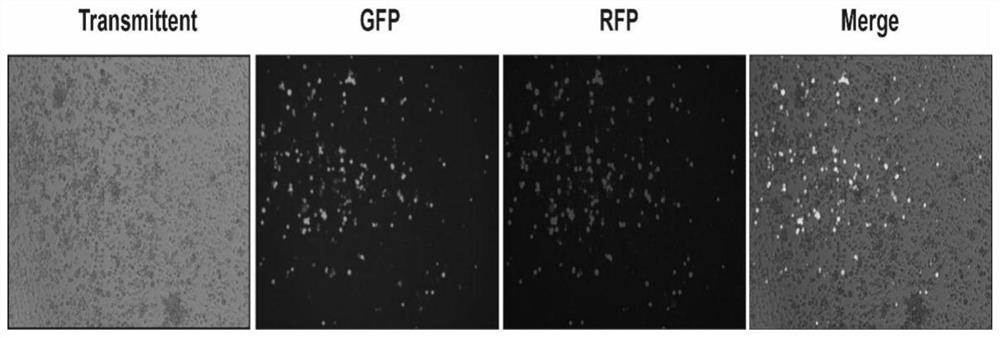
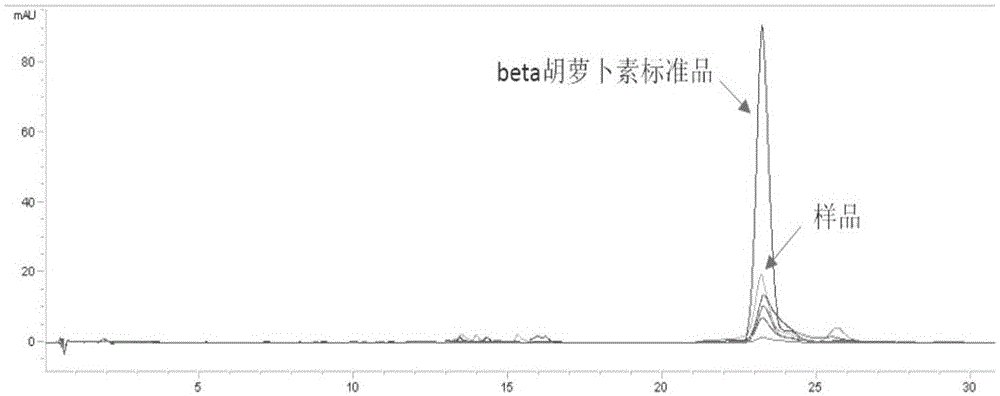
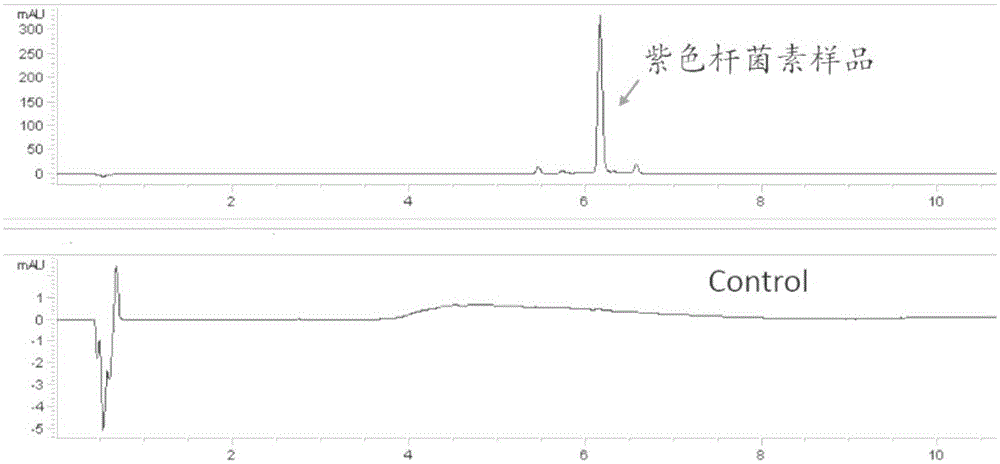
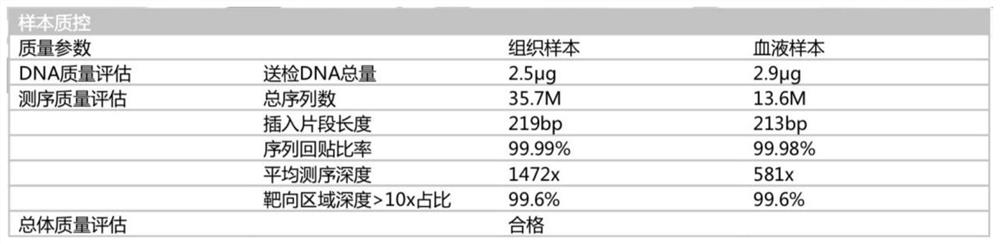
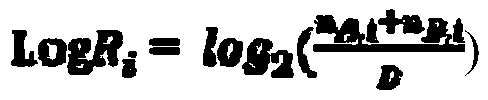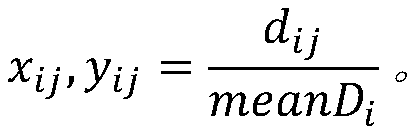Patents
Literature
119 results about "Polygene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A "polygene” or "multiple gene inheritance" is a member of a group of non-epistatic genes that interact additively to influence a phenotypic trait. The term "monozygous" is usually used to refer to a hypothetical gene as it is often difficult to characterise the effect of an individual gene from the effects of other genes and the environment on a particular phenotype. Advances in statistical methodology and high throughput sequencing are, however, allowing researchers to locate candidate genes for the trait. In the case that such a gene is identified, it is referred to as a quantitative trait locus (QTL). These genes are generally pleiotropic as well. The genes that contribute to type 2 diabetes are thought to be mostly polygenes. In July 2016, scientists reported identifying a set of 355 genes from the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) of all organisms living on Earth.
Pseudorabies virus SA215, pseudorabies virus polygene deletion bacterin and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101186902ALow costConvenient researchViruses/bacteriophagesAntibody medical ingredientsGenetic engineeringPolygene
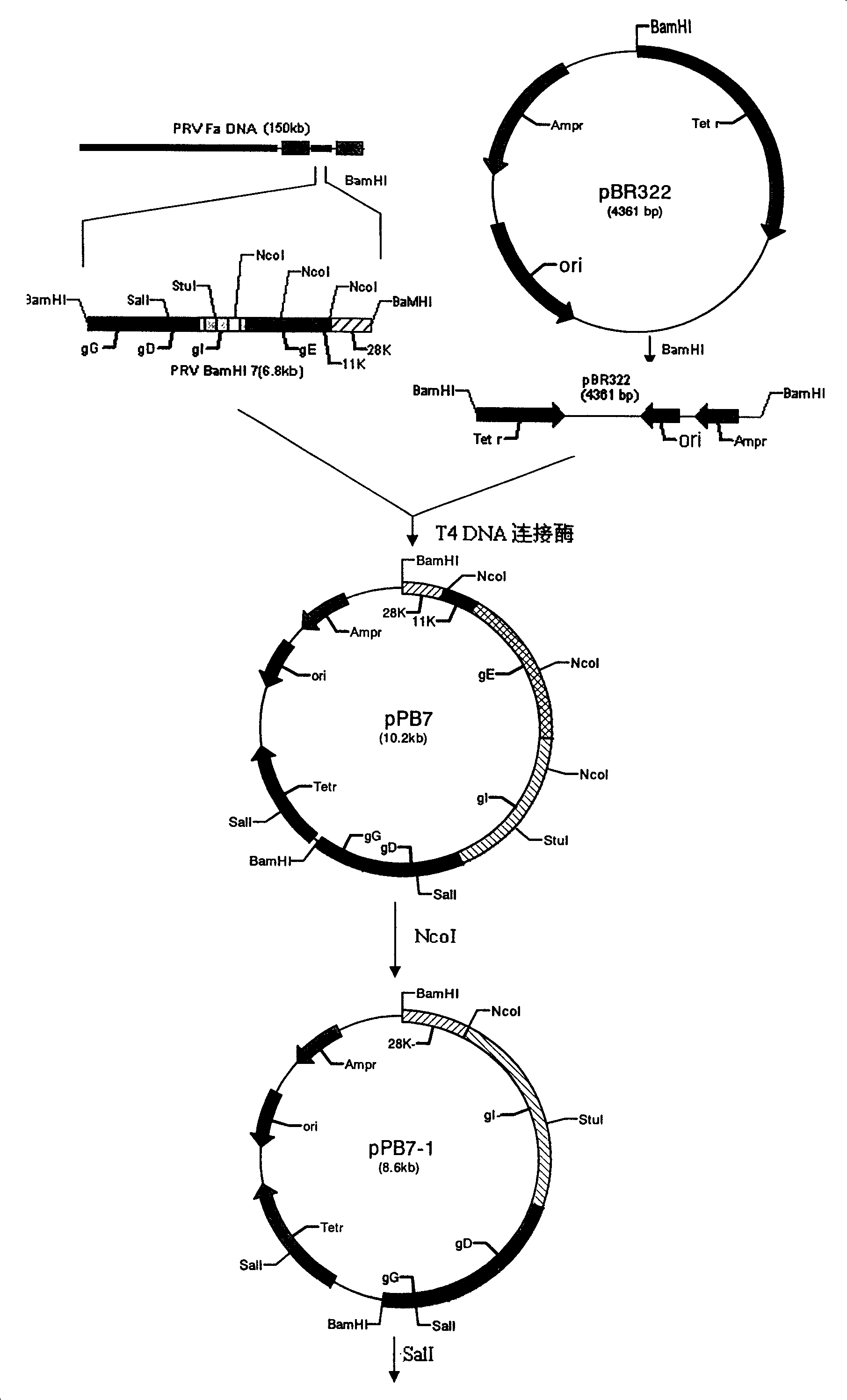
The invention belongs to the technical field of animal virology and genetic engineering, relating to pseudorabies virus which lacks parts of virulence gene of min strain A of pseudorabies virus, and the process for preparing vaccine with the virus. The DNA recombinant technology is employed to artificially remove all or parts of albumen code area of a plurality of genes of TK, gE, gI, 11K, and 28k which are unnecessary genes and duplicate virus of viruses and influence the virulence in the pseudorabies virus, thereby lowering the virulence of the pseudorabies virus, achieving attenuated vaccine strains SA215 of which the attenuation genetic engineering is lack, preparing vaccine with SA215 virus, and immunizing animals to effectively prevent and control the occurrence and prevalence of the pseudorabies.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Primer pair, probe and kit used for noninvasive polygene methylation combination detection for early stage colorectal cancer and applications thereof
ActiveCN108103195AEasy to sampleSampling non-invasiveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA methylationFluorescence
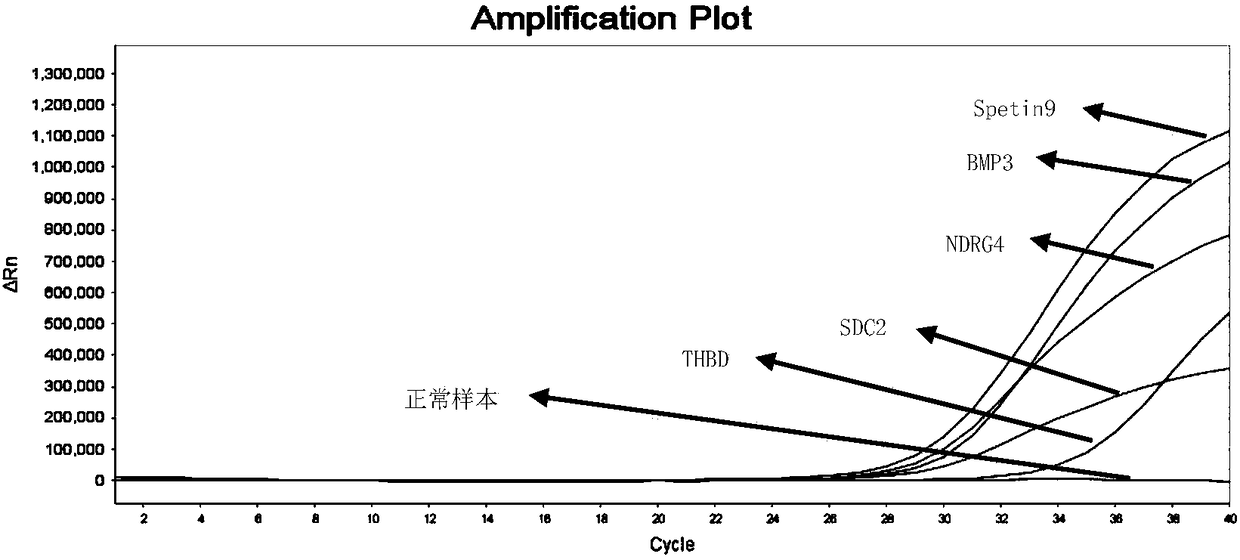
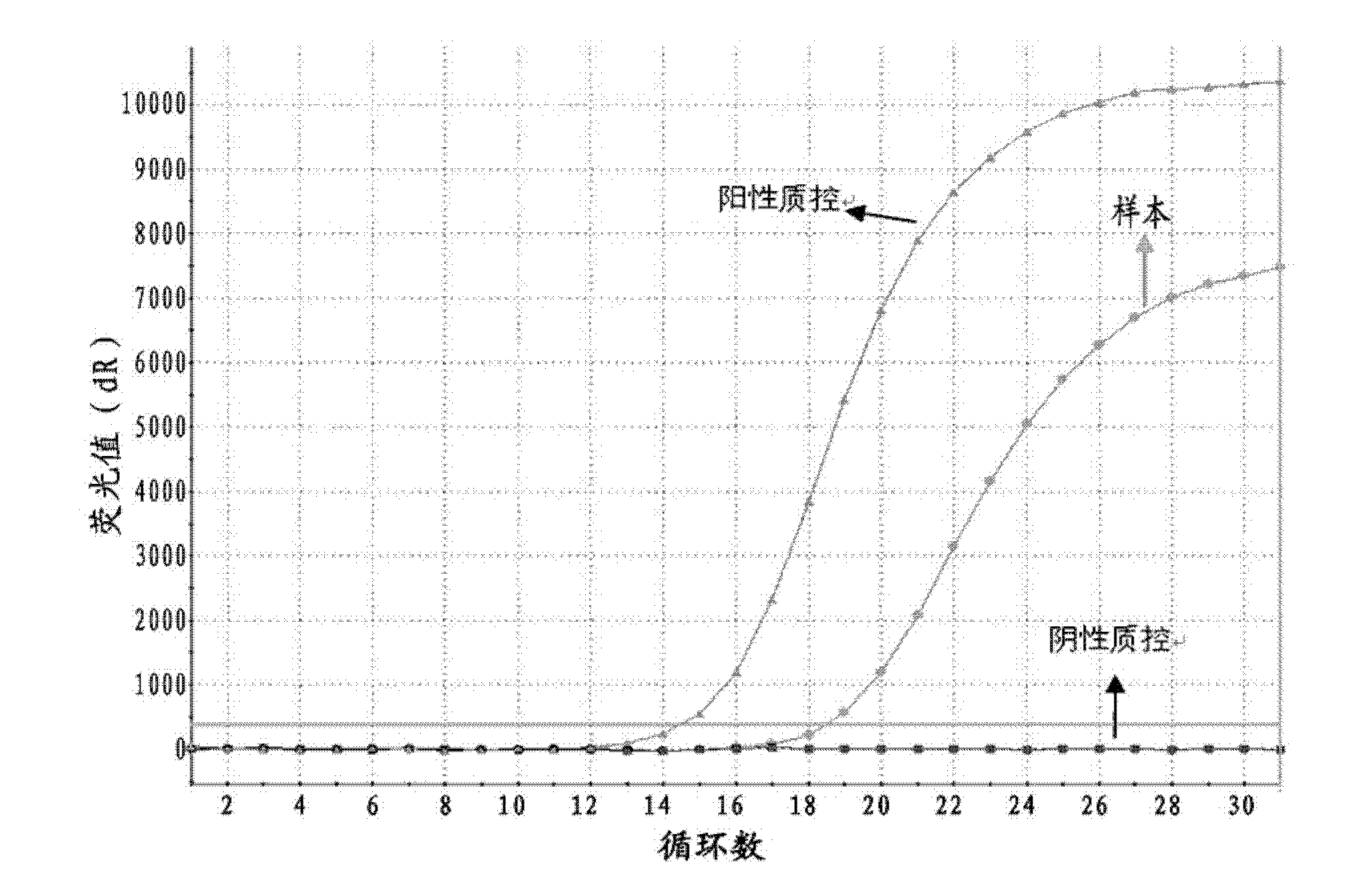
The invention relates to a primer pair and a probe used for noninvasive polygene methylation combination detection for early stage colorectal cancer, and includes the primer pair and the probe used for detecting methylation of genes Spetin9, NDRG4, BMP3, THBD and SDC2 and the primer pair and the probe for internal reference ACTB; the sequences of the primer pair and the probe are represented as the SEQ ID No.1 to the SEQ ID No.18. The invention also provides a kit containing the primer pair and the probe and applications thereof. The application method includes free DNA extraction from a plasma specimen, sulfite conversion, PCR amplification reaction, fluorescent signal detection and result determination. The kit and the method are suitable for methylation detection of the five genes Spetin9, THBD, SDC2, NDRG4 and BMP3 in human peripheral blood; compared with a conventional colorectal cancer diagnosis method, the application method fully utilizes the free DNA extraction from a plasma specimen, the DNA methylation and QPCR associated technologies, thus developing the kit having high sensitivity and specificity. The primer pair, probe and kit are used for performing early stage noninvasive screening to human colorectal cancer.
Owner:上海酷乐生物科技有限公司
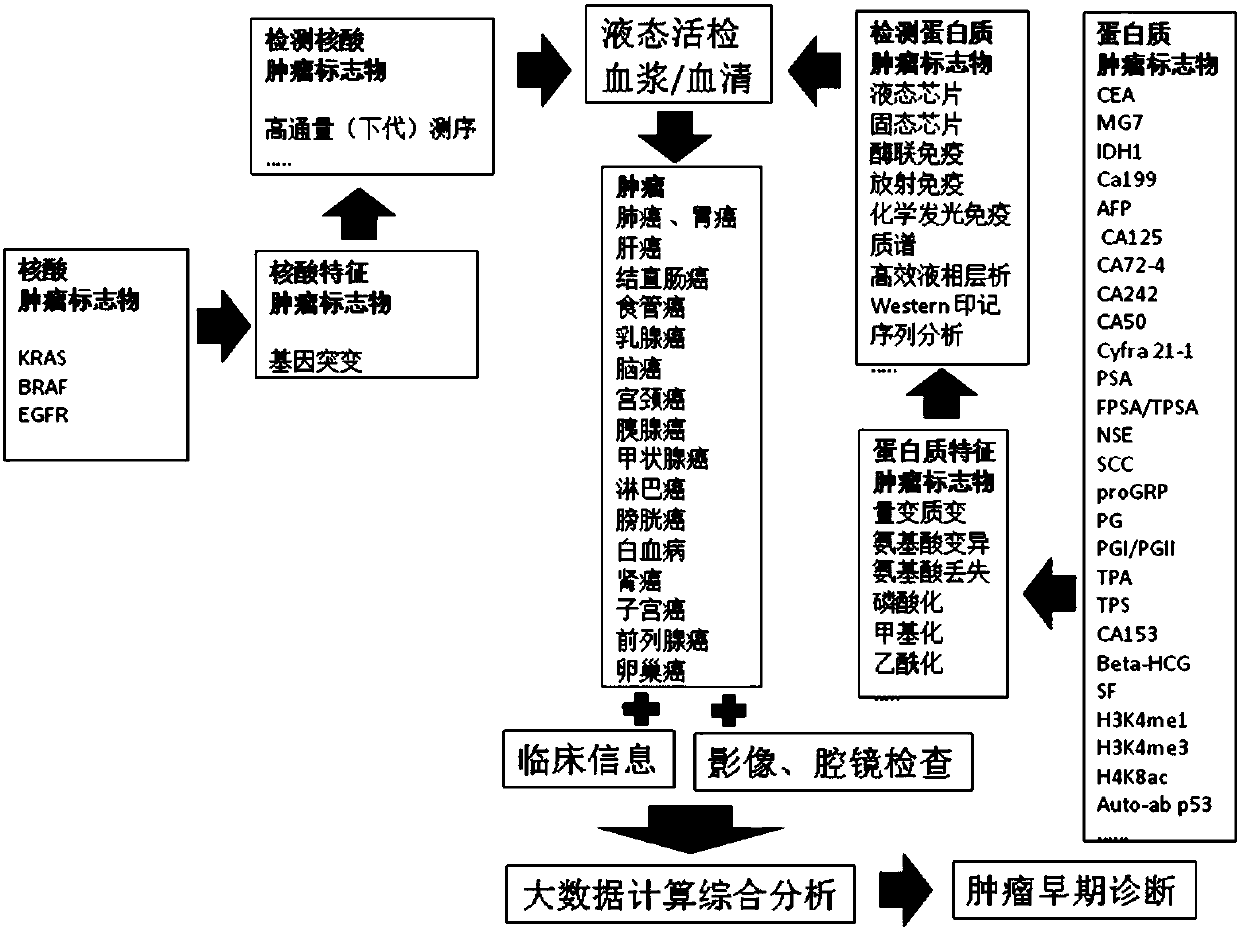
Systemic detection method of tumor marker and application thereof
InactiveCN107727865AReduce the burden onAccurate measurementBiological testingProtein tumor markersNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides a systemic detection method of a tumor marker and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) providing a sample from a checking object, wherein the checking object is a person; 2) detecting the sample of step 1), wherein in the detection step, whether various protein tumor markers exist or not is determined by utilizing high-throughput nucleic acid sequencing and determination comprising polygene mutation, polygene methylation, a plurality of micro RNAs (Ribonucleic Acid) and the like and utilizing a protein chip. According to the systemic detection method of the tumor marker and the application thereof, the different tumor markers are subjected to systemic detection including DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), RNA, protein and the like, so that thesensitivity of early-stage detection of the tumors is improved.
Owner:BIOCHAIN BEIJING SCI & TECH
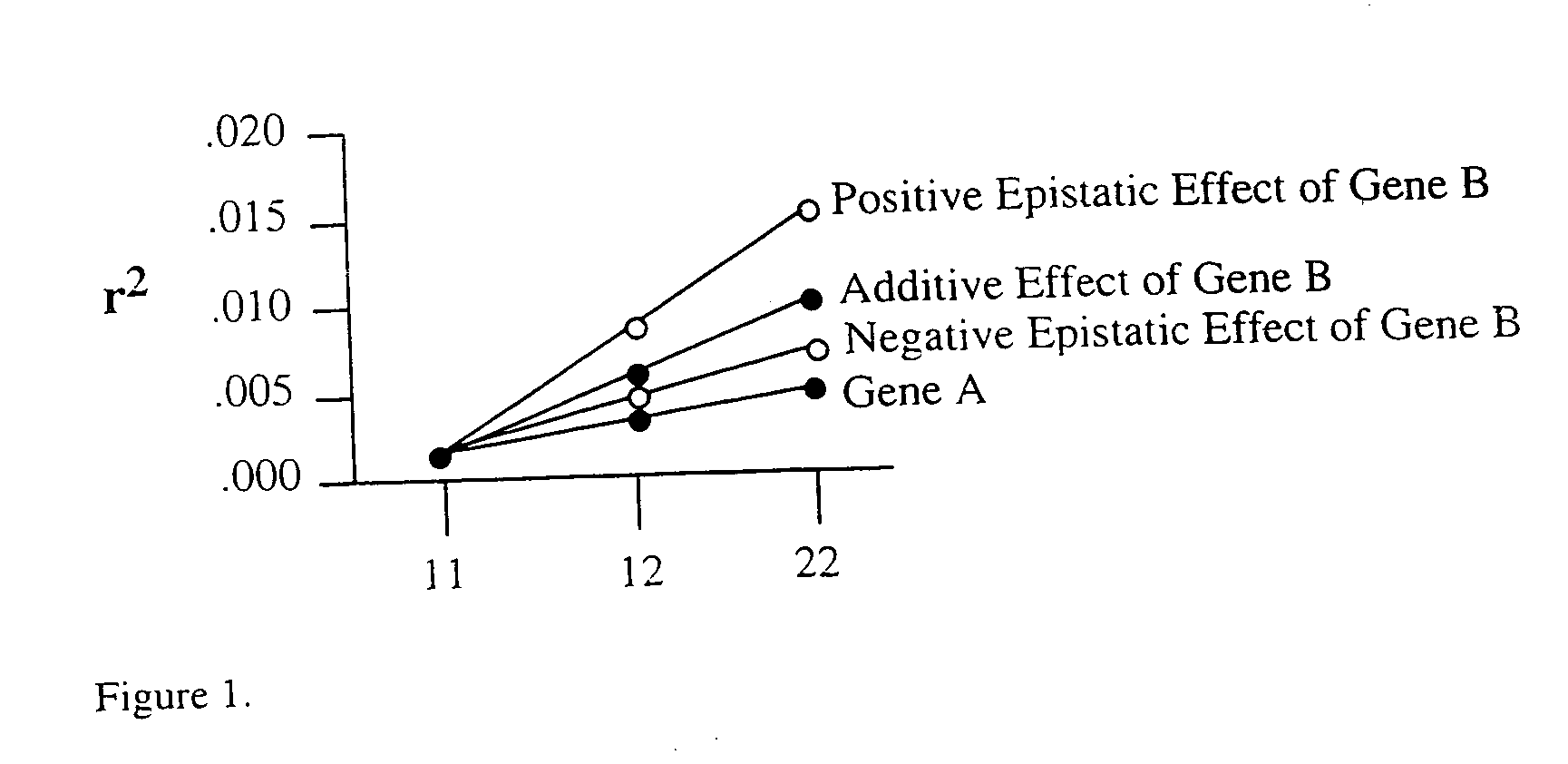
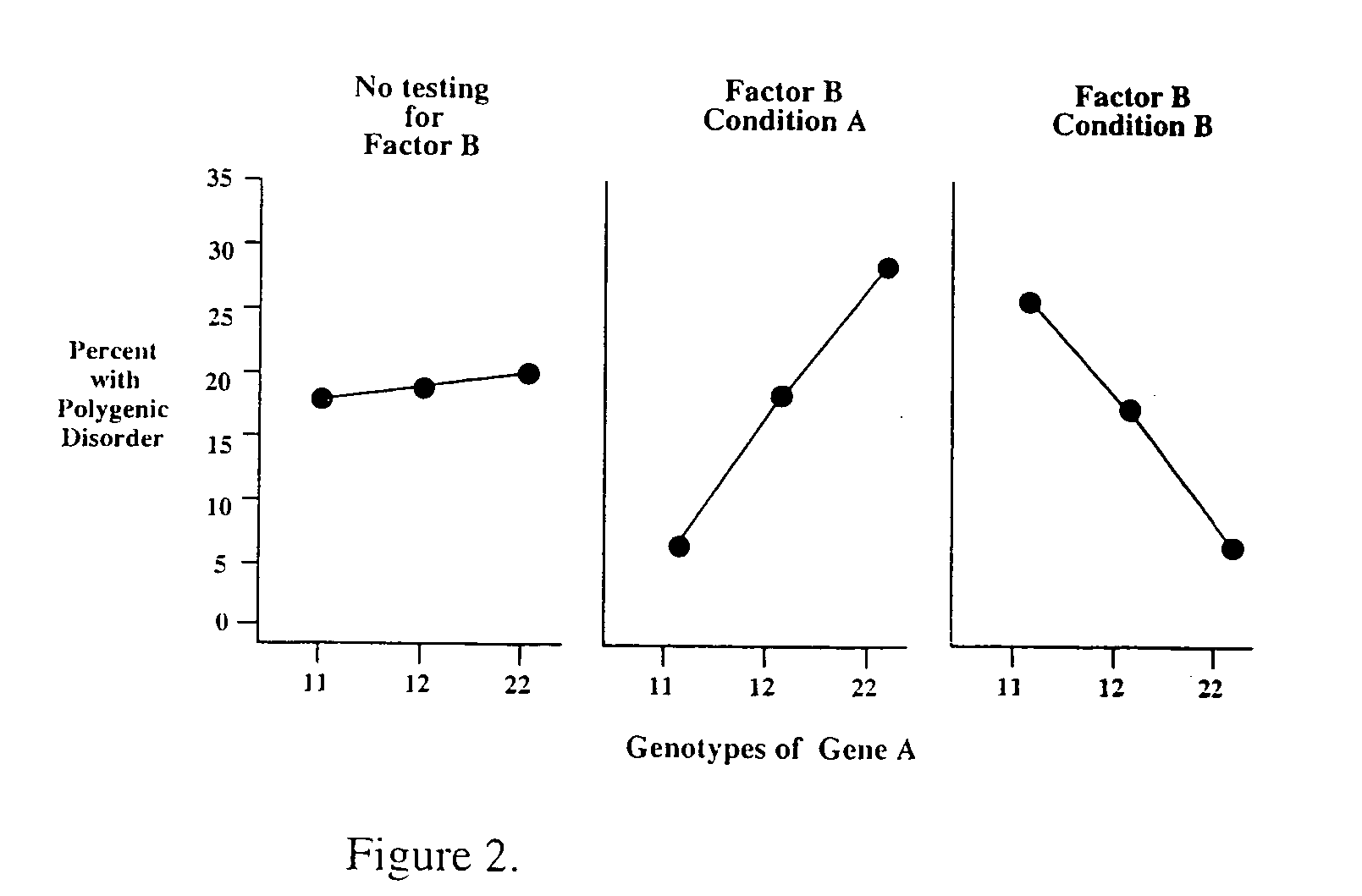
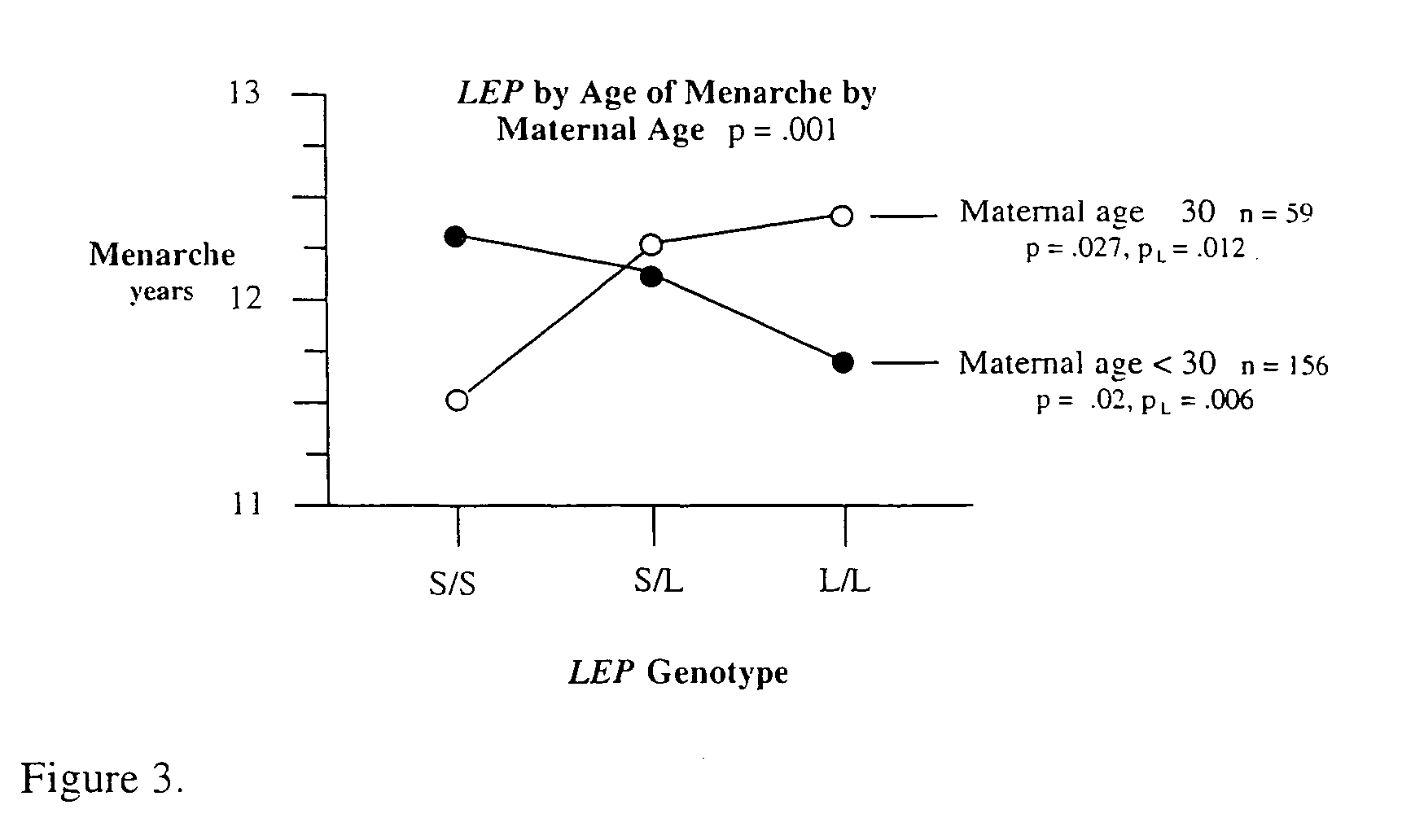
Method for risk assessment for polygenic disorders
InactiveUS20040115701A1Reduce riskIncrease powerMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsPolygenic diseaseGenotype
The present invention is directed to the identification of genostatic factors, methods of determining the association of a plurality of genes with polygenic disorders, and method of assessing the sensitivity and specificity of the risk of polygenic disorders. In particular, the present invention discovers that the association between a polygenic disorder phenotype and polygenes may be masked. Incorporating genostatic factor, such as maternal age, birth disorder, the androgen receptor gene, gender, and age, into the statistical analysis of the association between phenotypes and genotypes reveals statistically significant relationship between the two. Accordingly, the present invention provides novel methods in determining the association of a plurality of genes with a polygenic disease and the likelihood of having the polygenic disease.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Method and device for detecting tumor mutation load based on single sample
ActiveCN111321140AAccurate detectionReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsHuman tumorData set
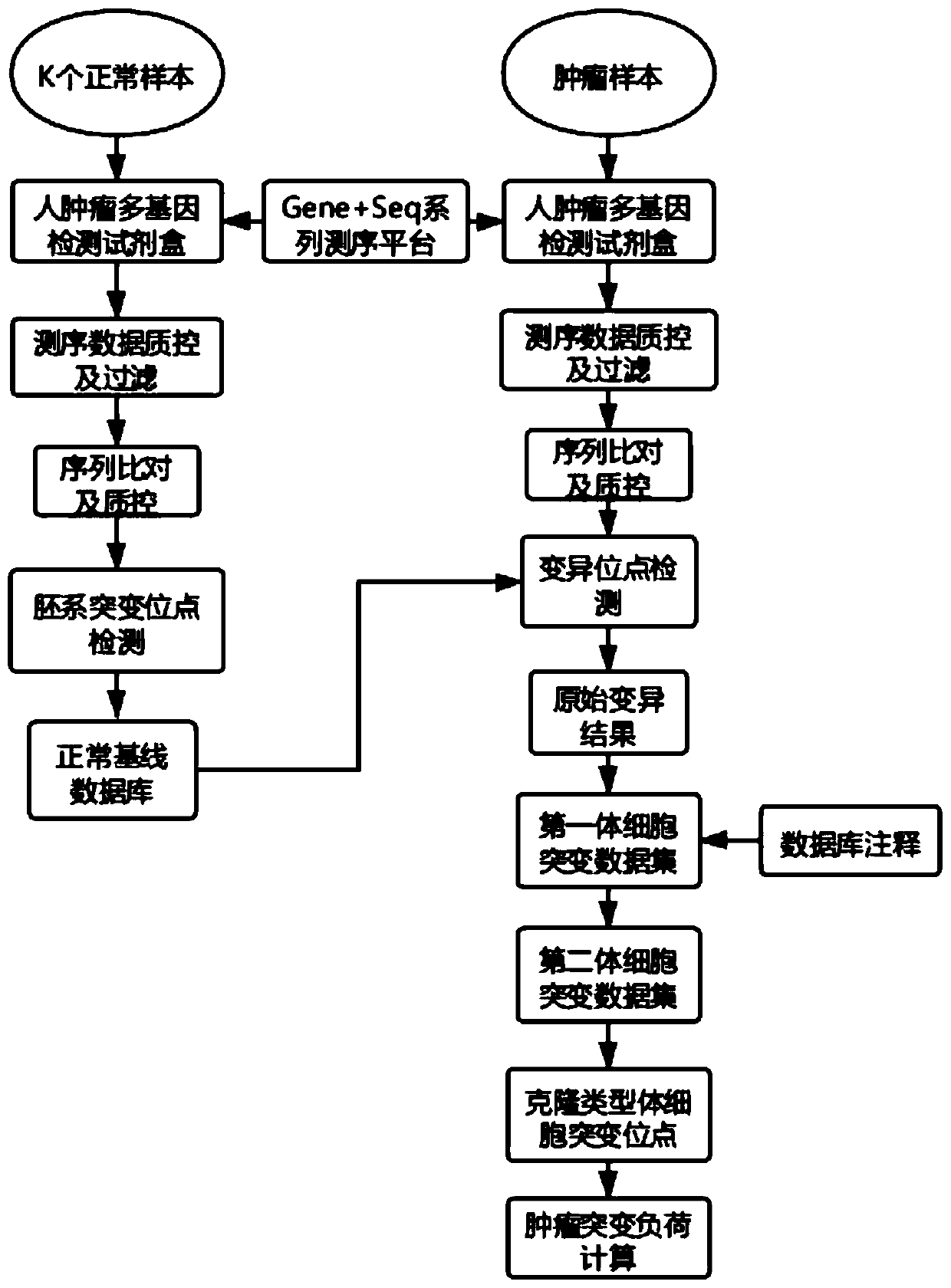
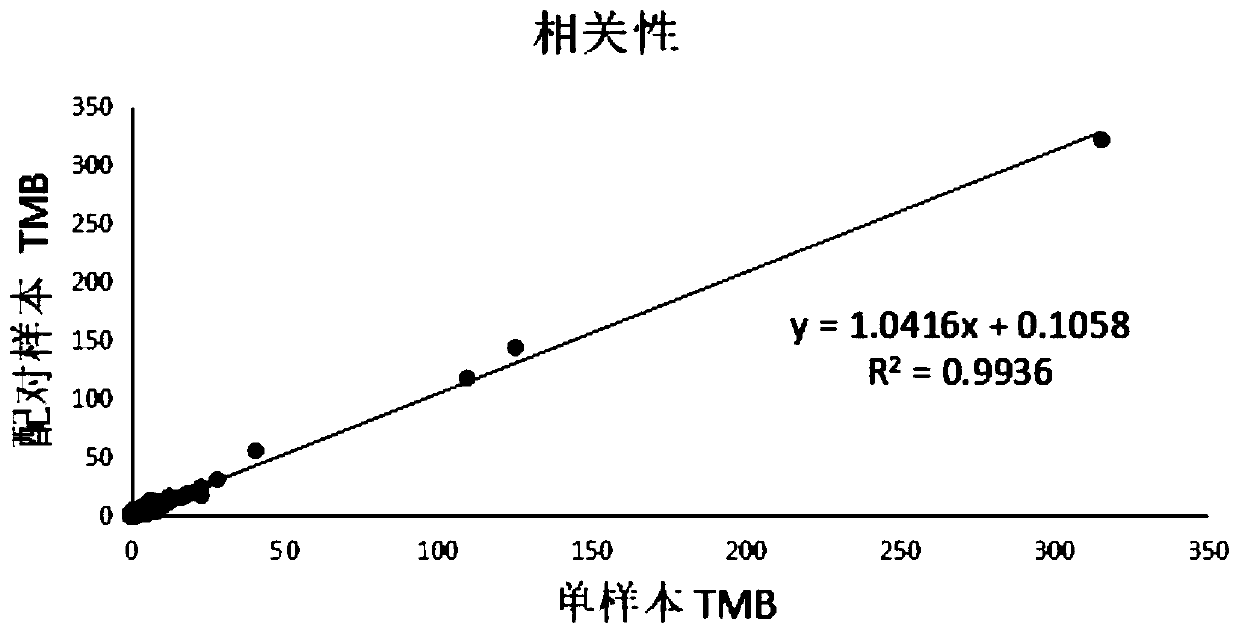
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine, in particular to a method and a device for detecting tumor mutation load based on a single sample. According to the device, a probe combination comprises probes that capture the exon region of a gene shown in Table 1, an intron promoter fusion breakpoint region of a gene shown in Table 2, and a coding region region of a gene shown in Table 3. A human tumor polygene detection kit comprises the probe combination. The TMB detection method based on the single sample comprises the following steps: access to target area of the tumor samples under test sequencing data, with the reference genome comparison, based on comparing the results obtained, detecting mutation loci, filtering original variable results with normal sample normal baseline database coincidence loci, filtering the high frequency reproductive mutation locus of a first cell mutation data set, screening the clonal somatic cell mutation locus of a second somatic cell mutation data set and calculating TMB. This method can accurately detect TMB of tumor samples without pairing samples.
Owner:苏州吉因加生物医学工程有限公司 +1
Breeding method and application of new recessive dwarf rape
ActiveCN105475118ASolve the problem of lodging and production reductionHigh yieldPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyBrassica
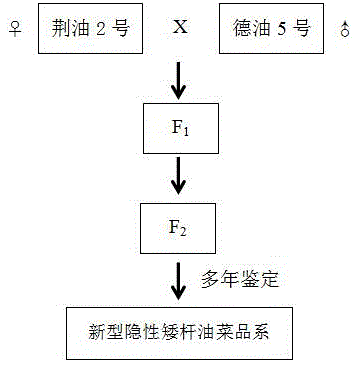
The present invention discloses a method breeding and application of a new recessive dwarf rape. Brassica napus L variety Jinzhou rape No.2 and de nong zheng cheng company-rape No.5 are used as parents for hybridization to obtain F1, F1 is bagged for selfing breeding to obtain segregating populations. By many years of in-field phenotypic characterization of the segregating populations, a dwarf single plant with excellent comprehensive agronomic traits and quality is selected for continuous selfing breeding for many years to breed a dwarf strain with stable dwarf trait. The dwarf material is used for hybridization with a high material, multi-generation joint analysis finds that the dwarf trait of the rape are controlled by two pairs of additive-dominance-epistatic main gene and additive-dominance-epistatic polygene, and the dwarf trait is recessive. The new dwarf material is used for hybridization with the high material to breed a semi-dwarf anti-lodging new rape variety, and the yield per unit can be significantly improved.
Owner:贵州省油菜研究所
Blood plasma cfDNA detection technology-based noninvasive pancreas cancer polygene detection method and kit
InactiveCN106065414AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPancreas CancersMutation frequency
The invention belongs to the field of medicines and biology, and relates to a blood plasma cfDNA detection technology-based noninvasive pancreas cancer polygene detection method and kit. The blood plasma cfDNA detection technology-based noninvasive pancreas cancer polygene detection method comprises the following steps: collecting blood, separating blood plasma, and purifying cfDNA; designing the panel of a pancreas cancer characteristic hotspot mutation region; and carrying out PCR primer amplification, constructing a library, and carrying out high-flux next generation sequencing and data analysis. The dynamic change of the mutation type and the mutation frequency of pancreas cancer characteristics in the blood plasma cfDNA is detected according to the treatment process and the pathogenesis development of every individual, so information is provided for pathogenesis monitoring and resistance drugs of the pancreas cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
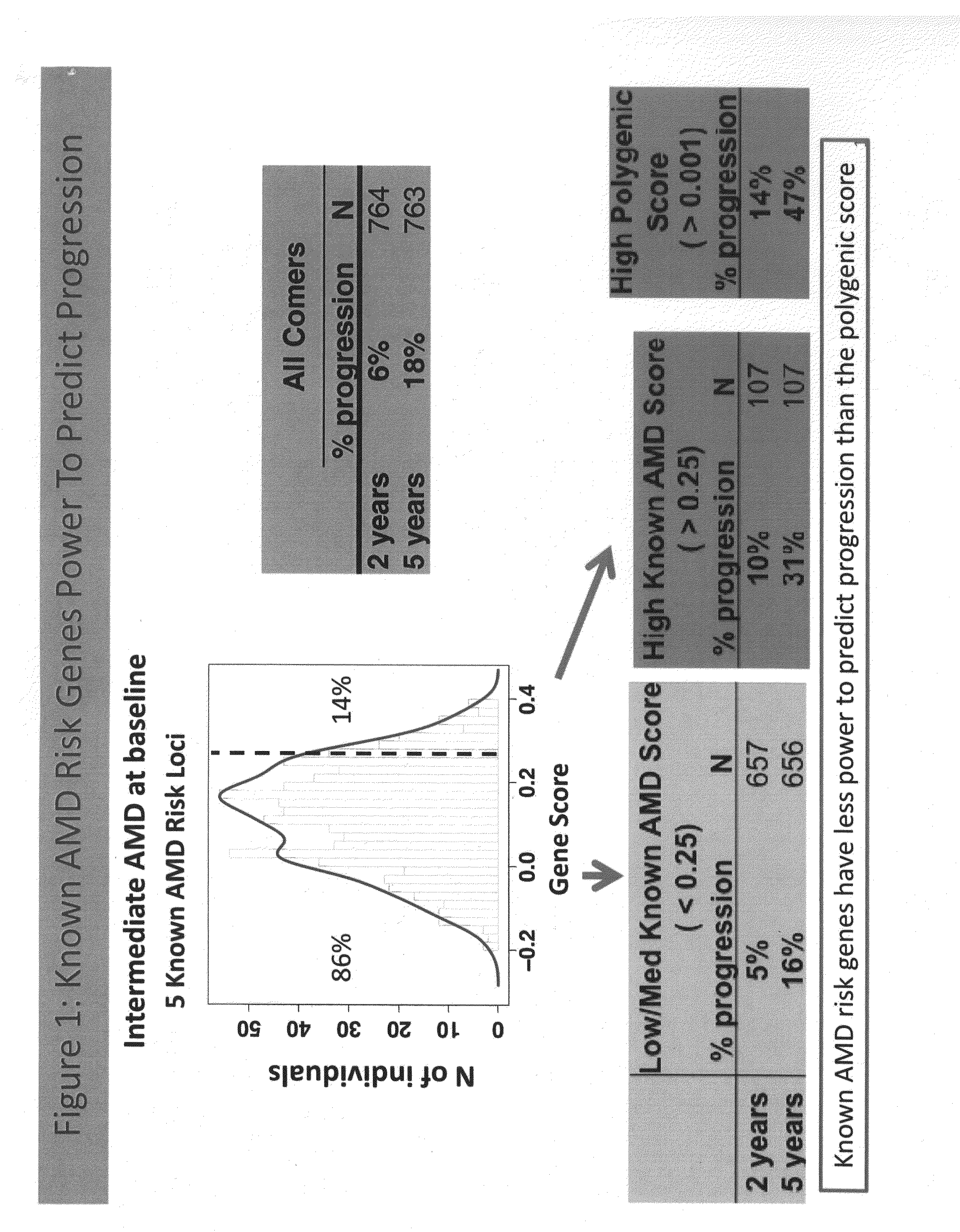
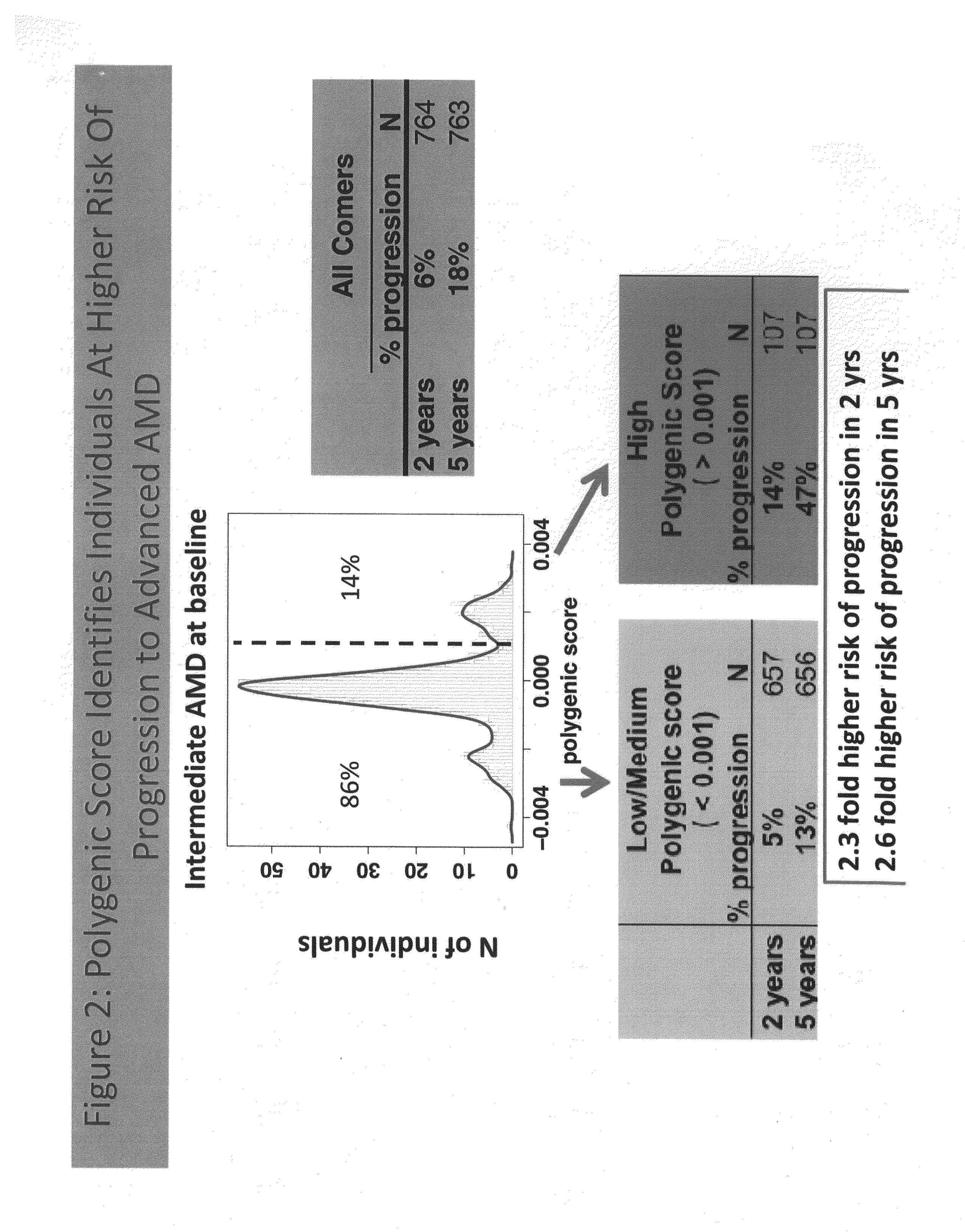
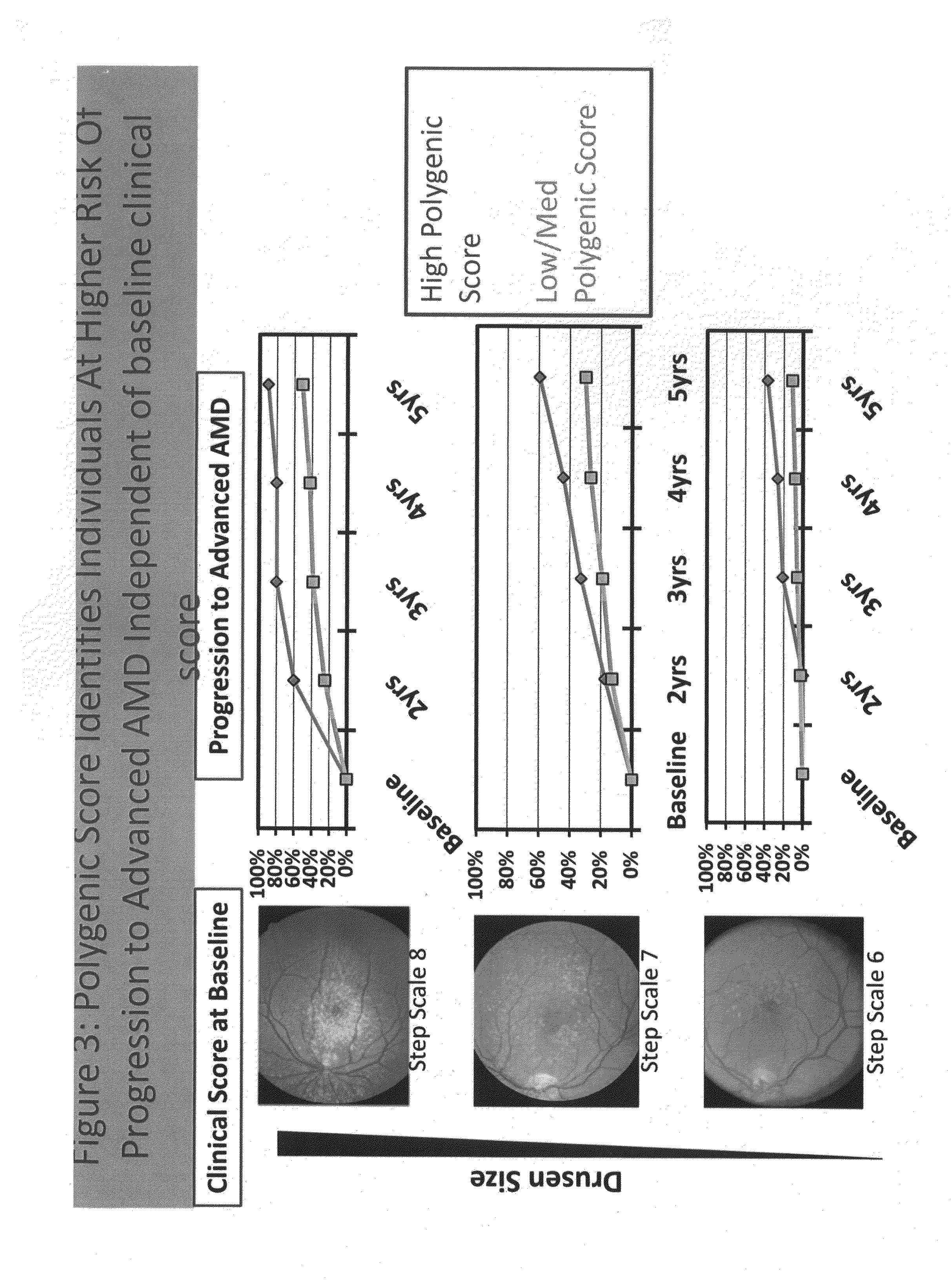
Predicting progression to advanced age-related macular degeneration using a polygenic score
The present invention relates to methods for identifying individuals with intermediate age-related macular degeneration (AMD) who possess a greater risk of progression to advanced AMD, using a polygenic score calculated based on the results of genome-wide gene association studies, using thousands of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Composition and reagent kit for early cervical cancer detection
ActiveCN110564857AIncrease coverageHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCervical cancer screeningNon invasive
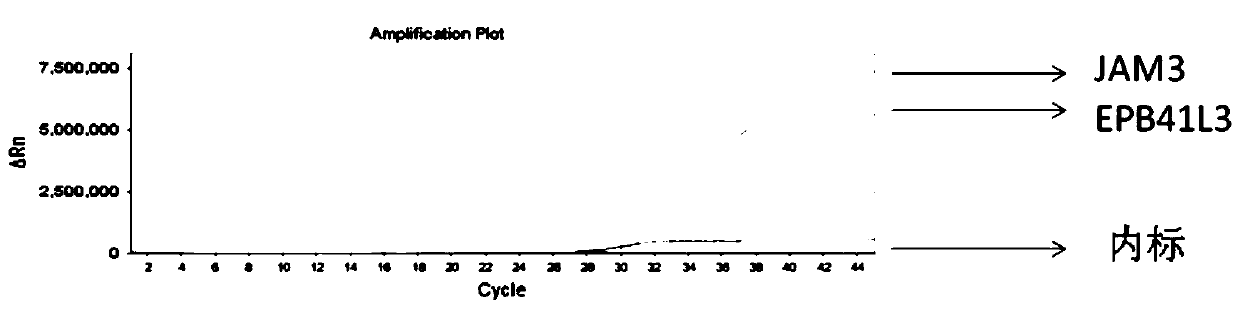
The invention discloses a composition and reagent kit for early cervical cancer detection. The composition comprises 3 CpG island regions subjected to high methylation in an EPB41L3 gene and 3 CpG island region amplifying primers subjected to high methylation in a JAM3 gene, 98% or above of different types of cervical cancer can be covered, and detection of polygene polymethylation regions can berealized through a one-pipe reaction and detection. A specific MGB probe and a degenerate closed primer are preferably selected for cooperation, so that sensitivity and accuracy are further increased.The whole detection process is free from wounds, simple and convenient to operate and easy to interpret, universal qPCR equipment can meet detection, a wholly-closed form is adopted in the PCR process, and the possibility of cross-contamination can be avoided; besides, three segments of two markers are detected at the same time, so that the result is more accurate; and all the factors are integrated, so that the composition disclosed by the invention has social promotion properties. Due to high sensitivity of detection, the composition is suitable for non-invasive early cervical cancer screening.
Owner:北京鑫诺美迪基因检测技术有限公司
Principle of quantitative trait locus (QTL) positioning
The invention relates to a principle of quantitative trait locus (QTL) positioning. The QTL refers to the position of a gene for controlling quantitative traits in a genome; A polygenic system for controlling the quantitative trait is used as integration for research on the basis of classical quantitative genetics of polygene hypothesis by several genetic designs and statistical models; and the genetic characteristics of the quantitative traits are described by genetic parameters, such as hereditary capacity and genetic variance.
Owner:李祥
Polygene assembling carrier system and its polygene assembling method
ActiveCN107177616AQuick assemblyEasy to buildNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEngineeringCarrier system
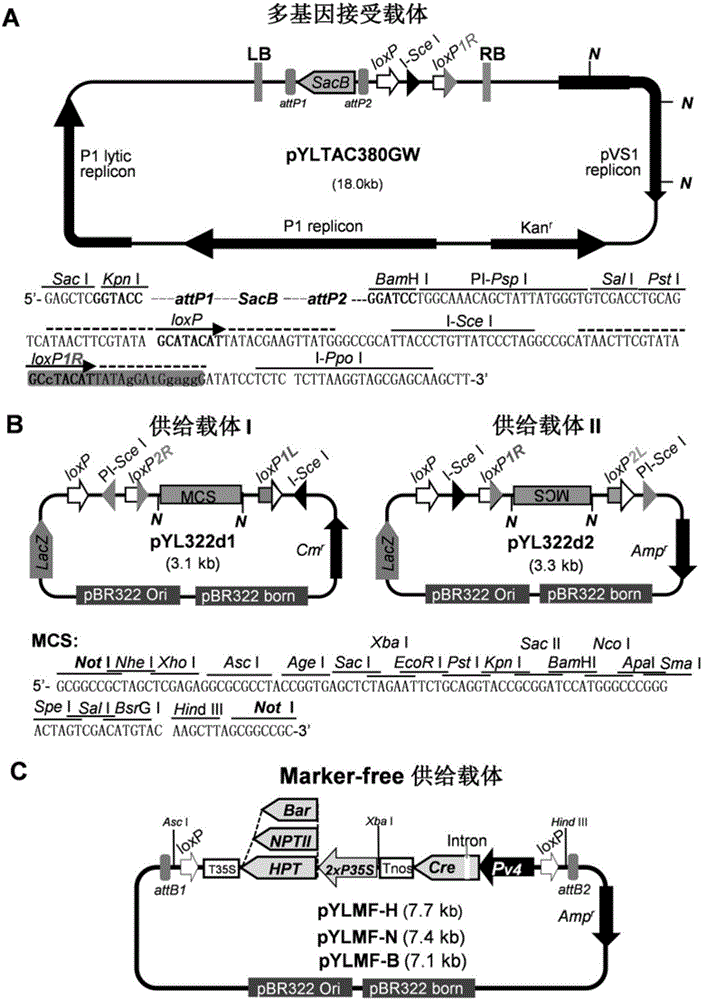
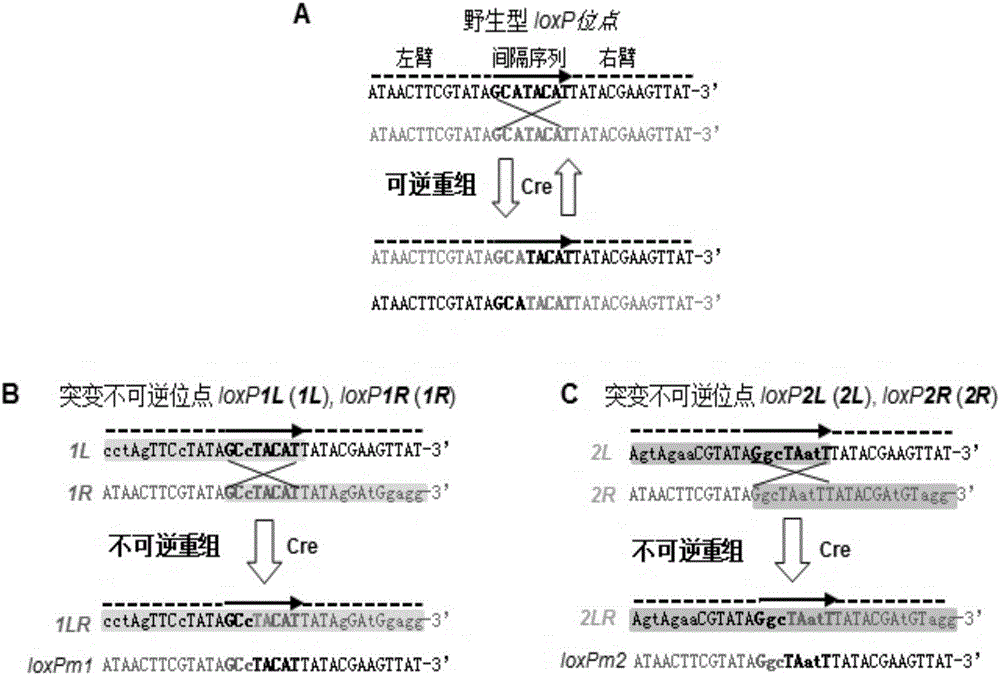
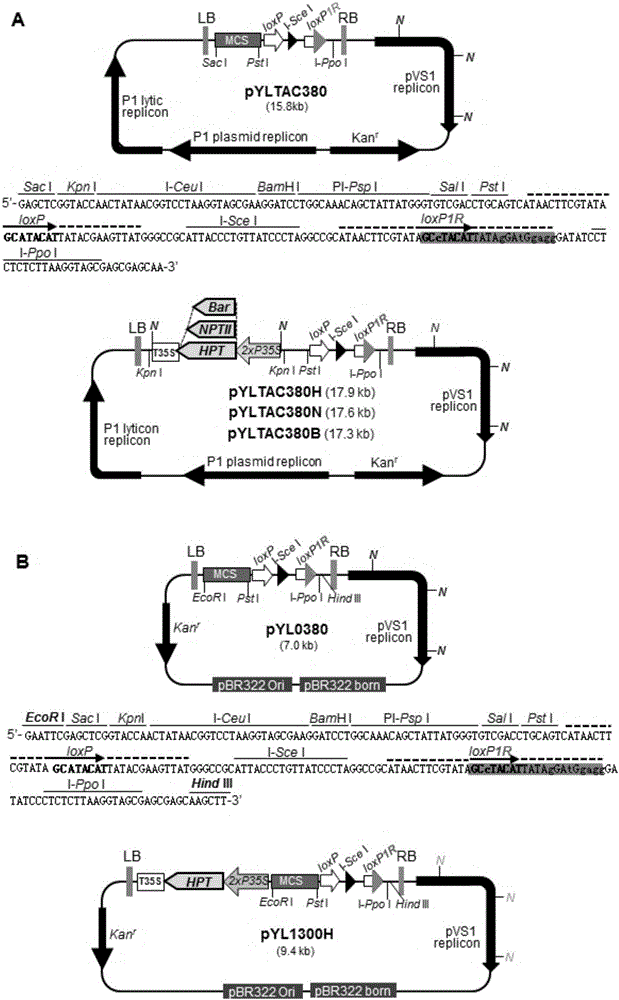
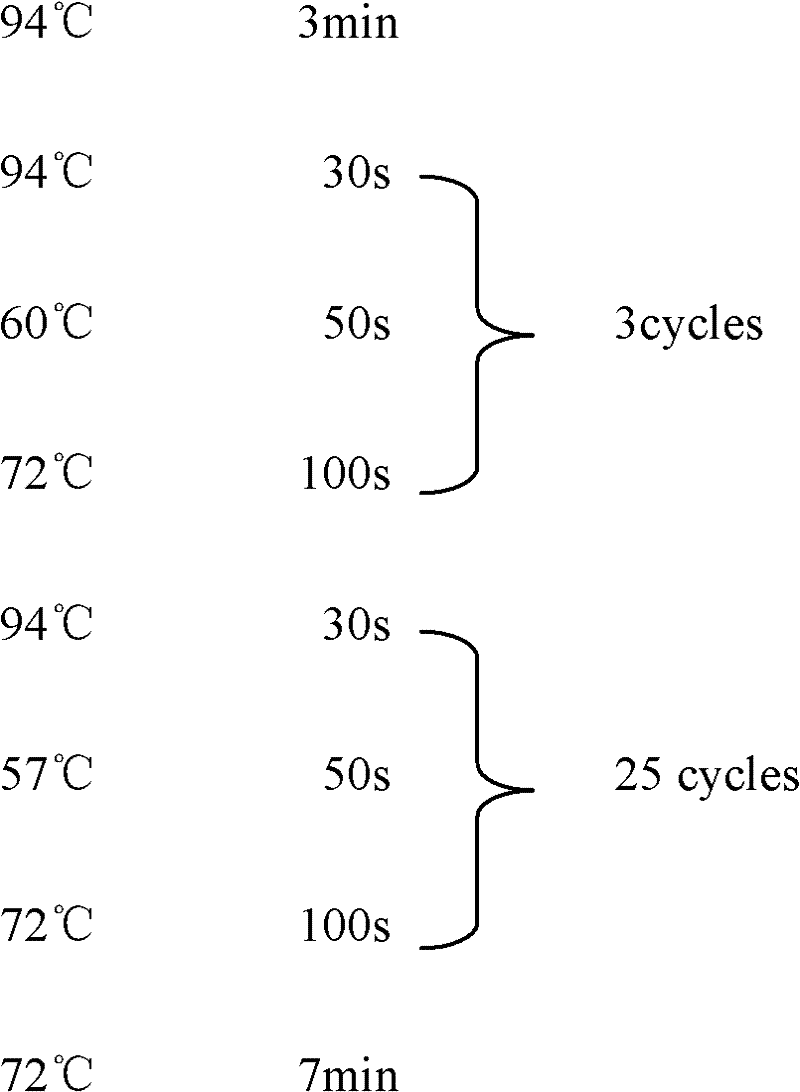
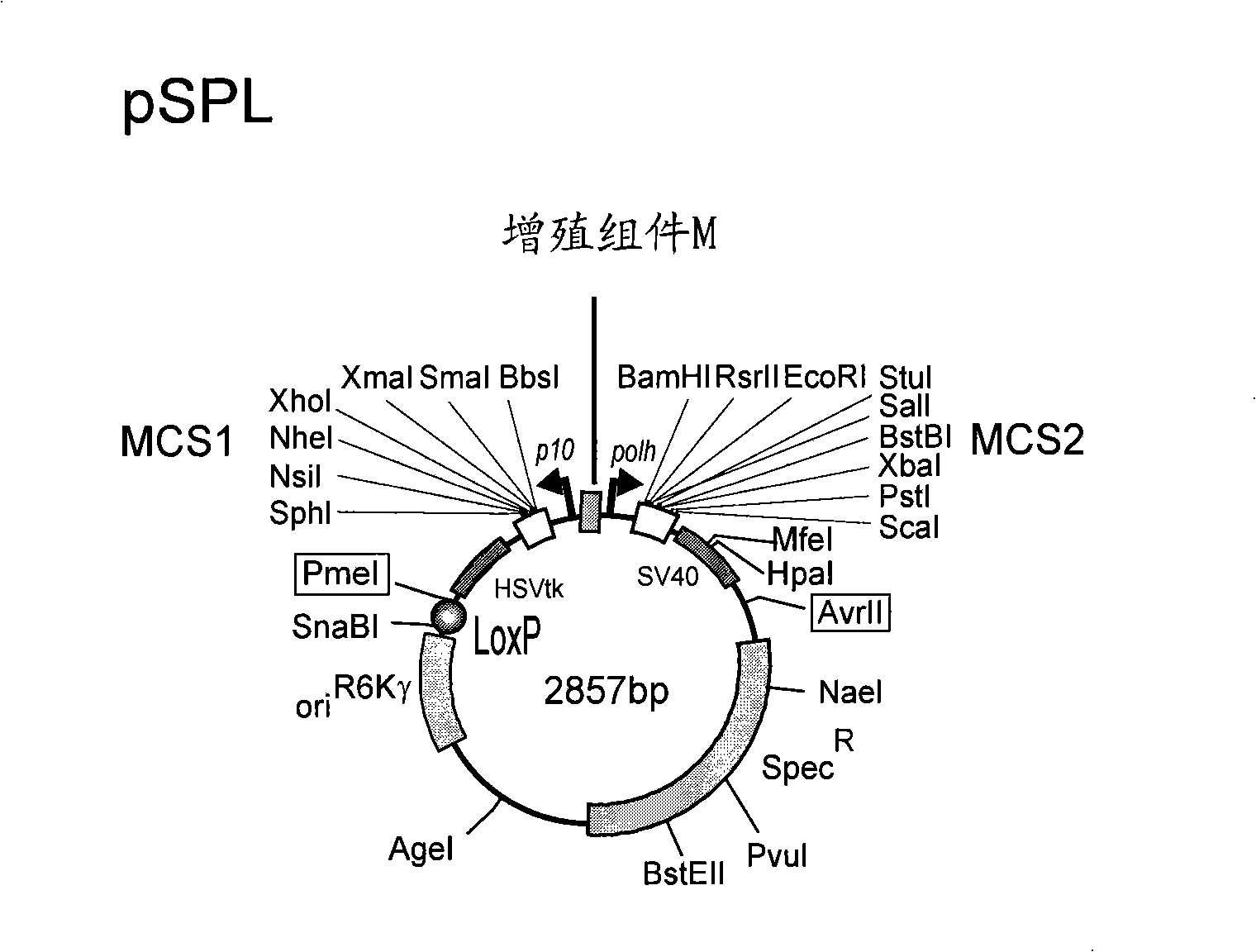
The invention discloses a polygene assembling carrier system and its polygene assembling method. The system comprises a 1-type accepting carrier, a 2-type supply carrier, and a supply plasmid capable of being selectively used and generating self-deletion of a selection marker. The system applies a Cre / loxP recombination system and irreversible recombination sites of two groups of mutant type loxP; under the function of Cre enzyme, the supply carrier is integrated to the accepting carrier through the recombination of a wild loxP site; then a framework of the supply carrier is automatically deleted through the irreversible recombination of one group of mutant type loxP, and only the target gene is left on the accepting carrier; by repeating the alternation of the 2-type supply carrier and the assembly of the accepting carrier, the rapid assembly of the polygene can be realized. The invention is the simplest and most high-efficient polygene carrier system at present. Therefore, the polygene assembling carrier system provides an operable technology platform for important and complex biosynthetic pathways and important agronomic trait polygenic inheritance engineering; the polygene assembling carrier system is of important application value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
High-throughput method for segregating quantitative character regulatory gene
InactiveCN101544974AAvoid false positivesImprove screening efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationTotal rnaCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention discloses a high-throughput method for segregating a quantitative character regulatory gene, which comprises the following steps of: 1) construction of a target character segregation population, in which the population is a population in two parent hybridization progenies (F2 and F3), a DH system and a RIL; 2) mixing of extreme samples and segregation of total RNA in the population, in which a progeny segregation population is divided into three categories according to character phenotype; 3) gene expression analysis, in which the difference and sameness of gene expressions between two extreme mixed samples are compared by utilizing a gene expression analysis method, namely one of chip, EST sequencing, subtraction, cDNA-AFLP, and the like; and 4) acquisition and verification of a candidate gene, in which a differential expression gene between the two extreme mixed samples is found and is a candidate regulatory gene related to target character, and the function of the gene is verified through transgene, gene expression, molecular marker correlation and a contribution rate analysis method to obtain a target gene with regulatory character phenotype. The method is suitable for the segregation of a certain quantitative character regulatory gene controlled by multigene of all organisms, and is a simple, quick, high-throughput and economical gene segregation method.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Process for structuring carrier of expressing seven exogenous geng at same time in chloroplast
InactiveCN1793377AOvercoming key shortcomings of polygenic manipulation techniquesHigh practical application valueVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention relates to a chloroplast simultaneity expression seven exogenous genes vector forming method. It belongs to genetic engineering technique field. It includes the following steps: forming a chloroplast expression vector containing faeC, faeD, faeE, faeF, faeG, faeH, and faeI seven gene orders which form K88ac flagellin gene cluster; extracting coding K88ac wild bacterium C83907 plasmid; using primer 1 whose nucleotide sequence is same with SEQ ID NO: 1 and primer 2 whose same with SEQ ID NO: 2 to process PCR amplification; nucleotide sequence 3018bp is same with SEQ ID NO.5; using primer 3 whose same with SEQ ID NO:3 and primer 4 whose same with SEQ ID NO:4 to process PCR amplification; the nucleotide sequence is same with SEQ ID NO.6; connecting with pMD18-T vector; transforming to escherichia coli DH5 alpha; and gaining escherichia coli clone pTEI with faeCD sequence. The invention overcomes the key defect of polygene technique of plant genetic improvement, and offers a good method of producing effective antibody plant bacterin for baby pig.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for preparing shikimic acid using biosynthesis technology and engineered bacteria
InactiveCN101085998AThe operation method is simple and preciseEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
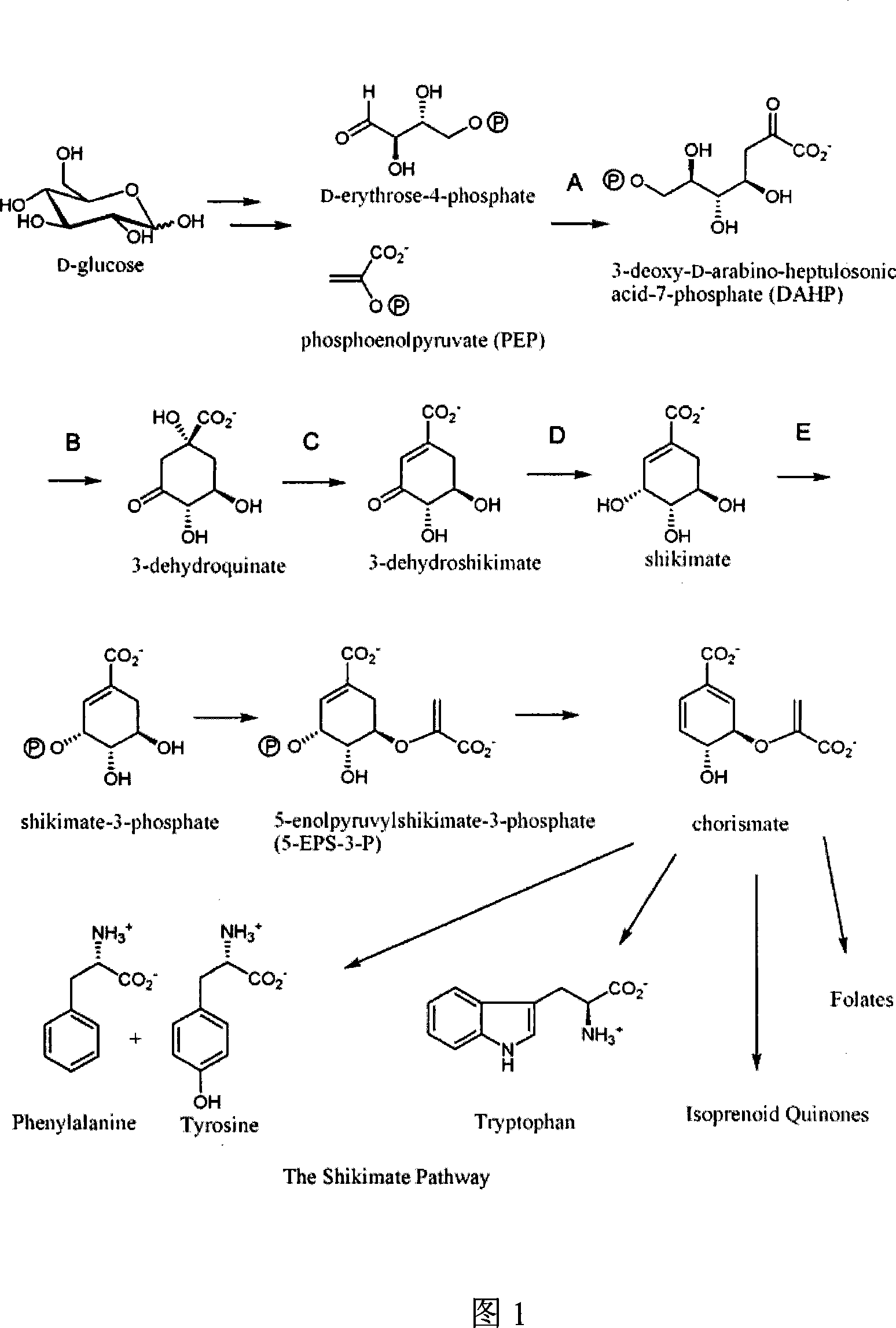
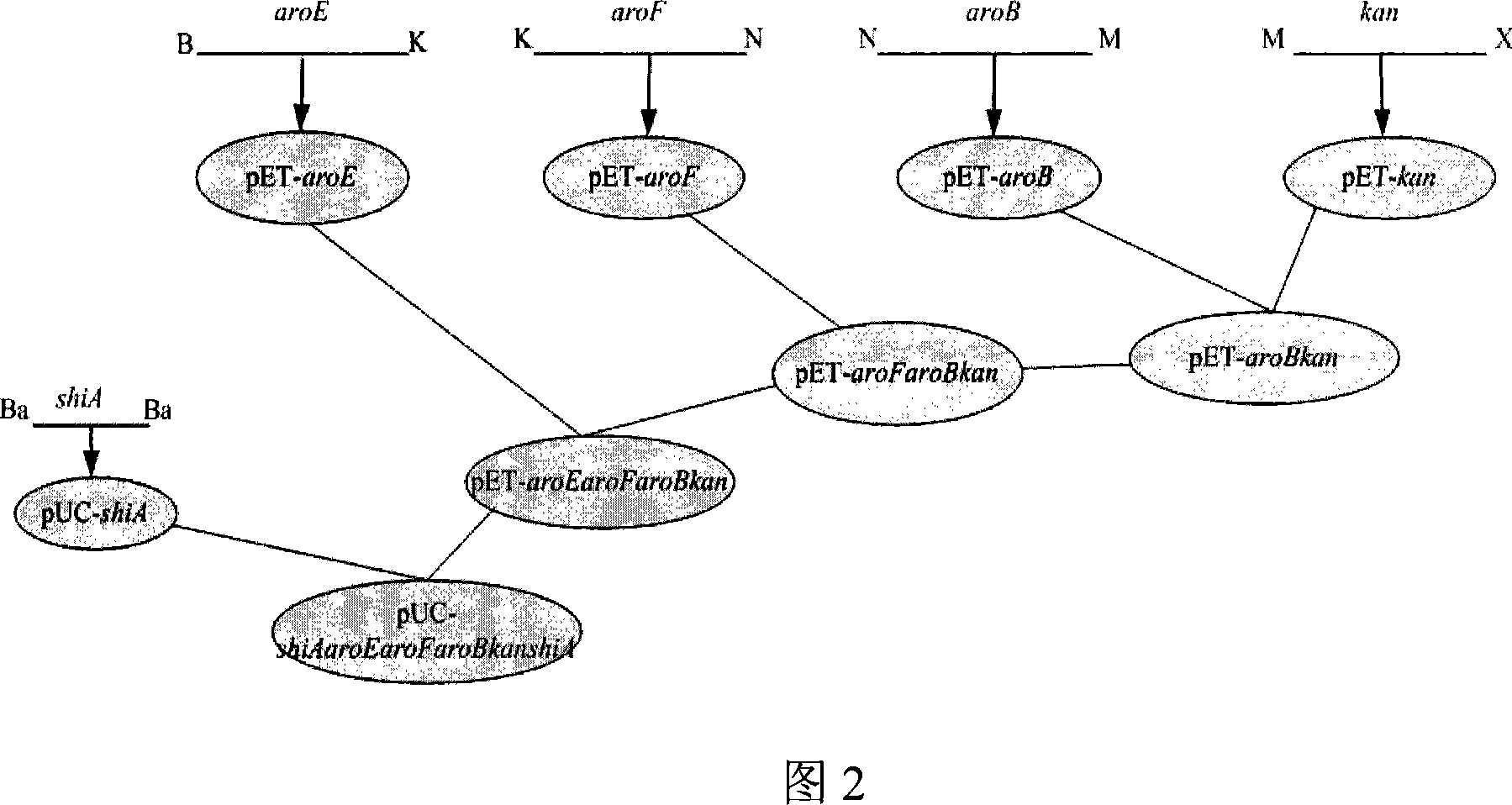
The invention discloses a method for preparing shikimic acid by using biological synthesis technique, and the employed recombined bacillus coli. The method comprises following steps: constructing carrier for speed- limit enzyme polygene box containing shikimic acid metabolic pathway; repalcing shiA gene with polygene box; removing shikimic acid kinase- mb in bacteria by using Red recombinant system; fermenting recombinant engineering bacteria and getting shikimic acid and purifying shikimic acid. The invention can increase expression amount for shikimic acid, reduces production cost and provides raw material for preparing medicine Duffy that can prevent influenza.
Owner:汪莉
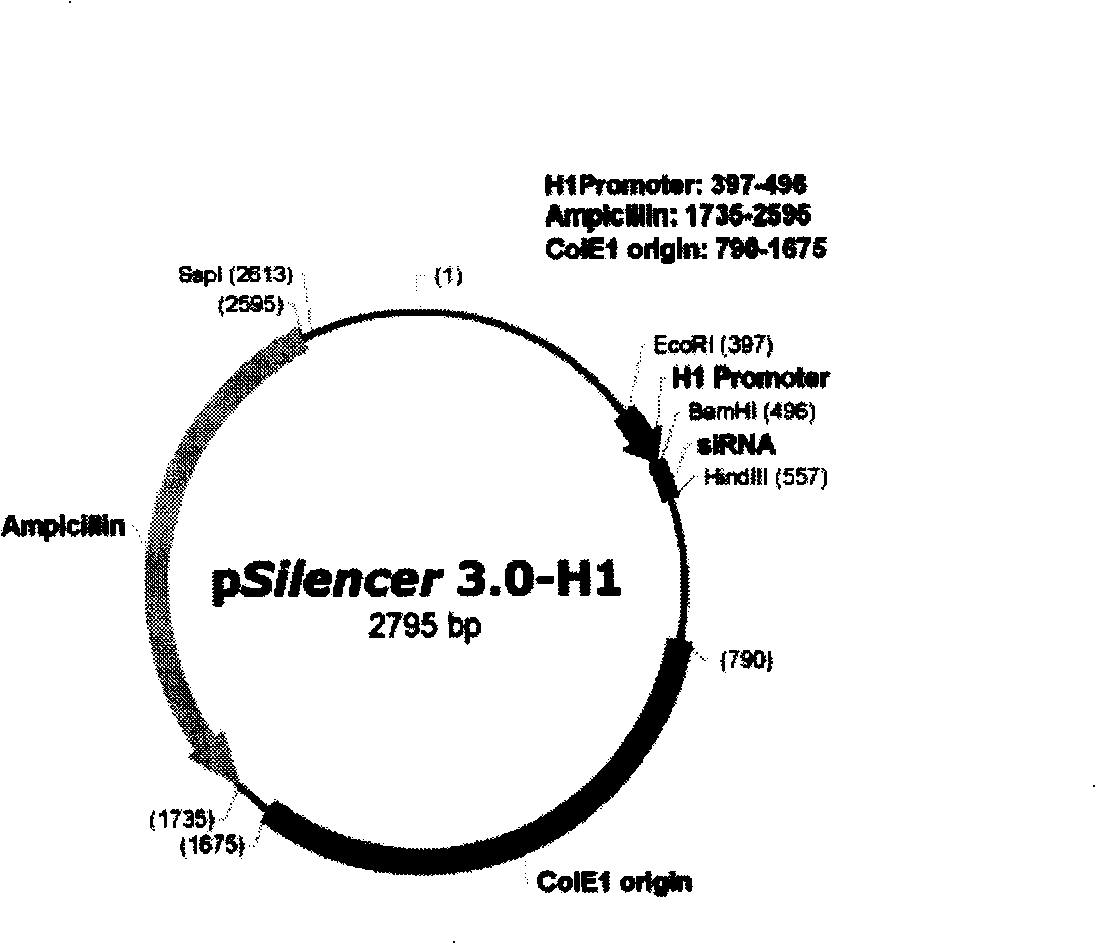
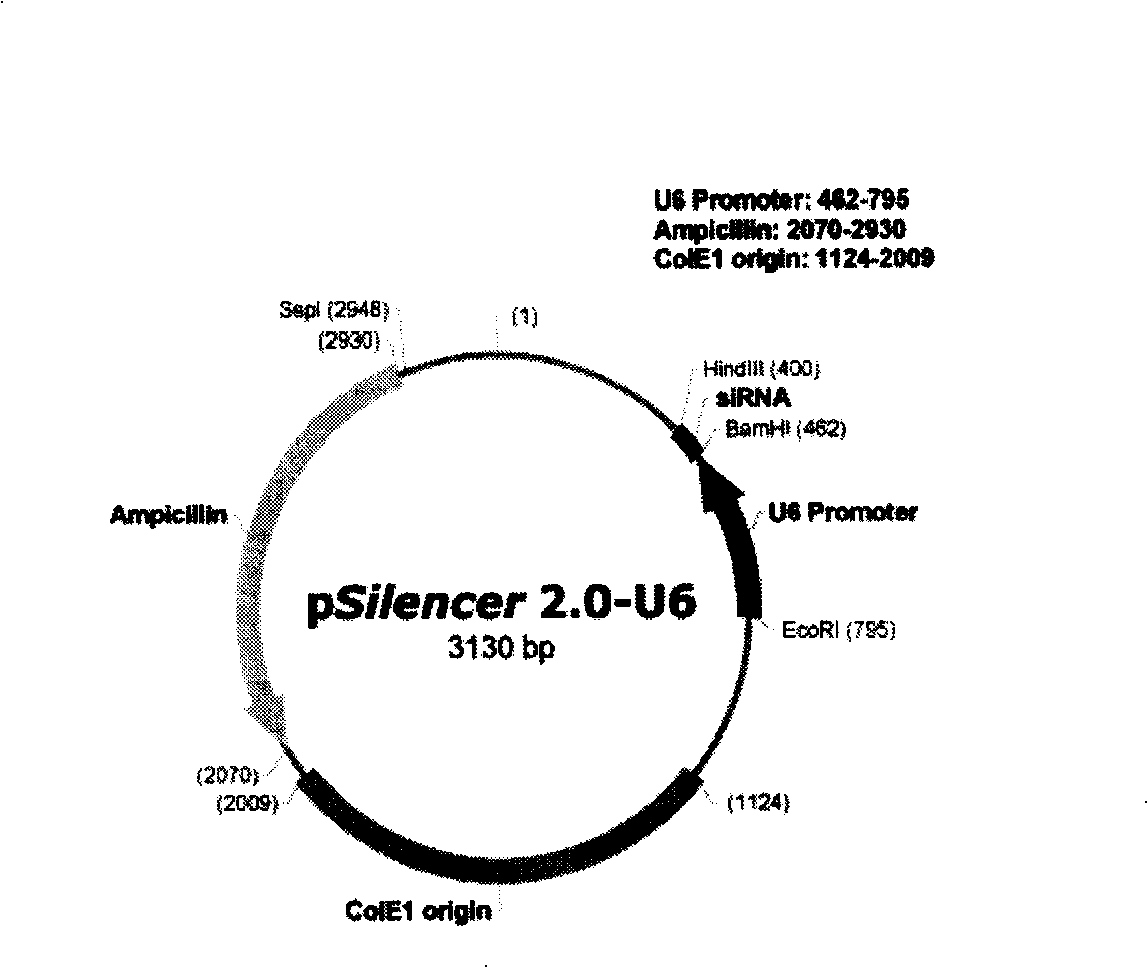
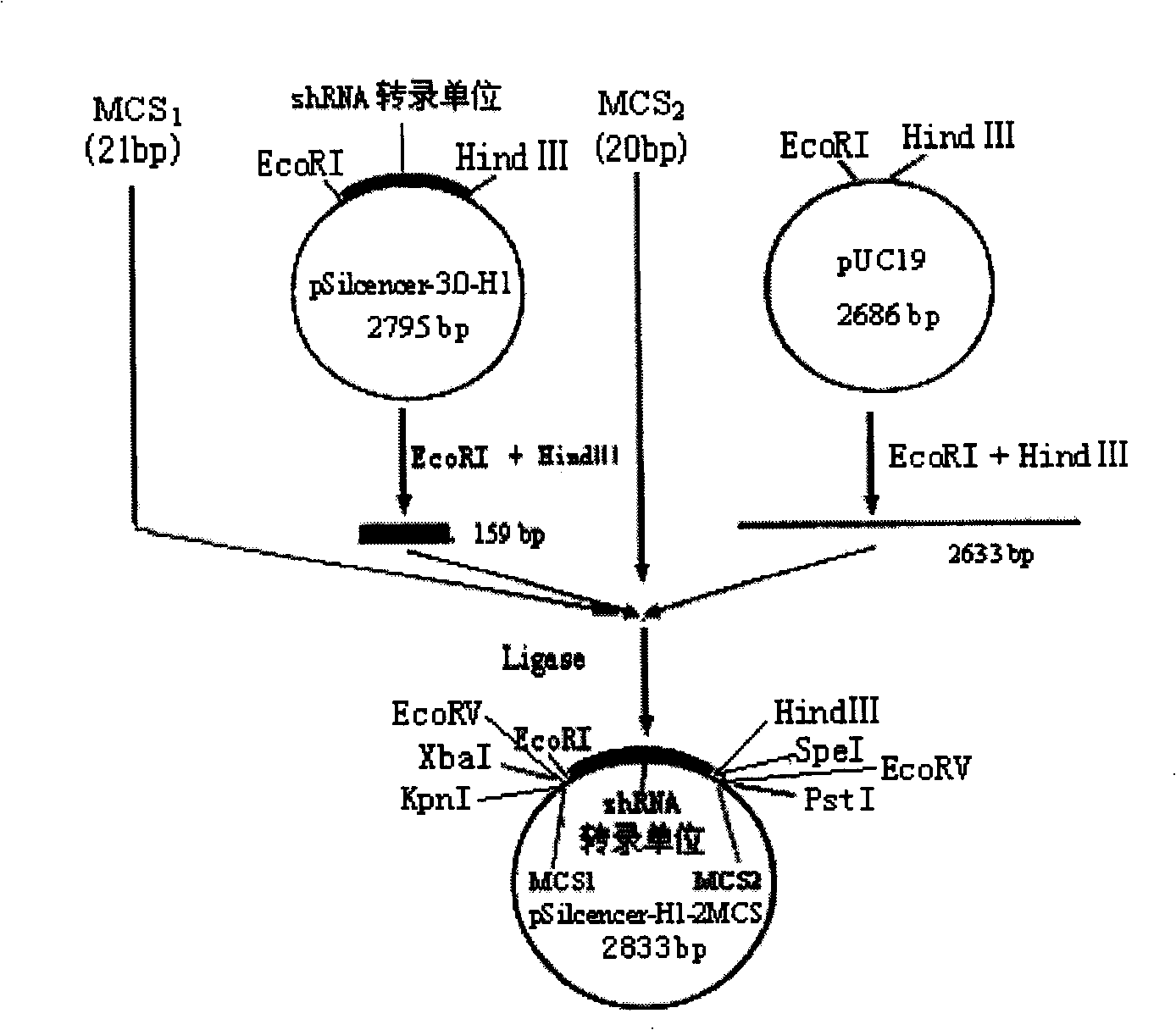
Polygene interferential shRNA plasmid expression vector, construction method and application
InactiveCN101245352AExpression effect is stableEasy to operateGenetic material ingredientsGene therapyPlasmid VectorMultiple cloning site
The invention discloses a plasmid vector pSilencer-U6 / H1-(shRNA)n which can be used for simultaneously expressing a plurality of shRNA, a construction method and application thereof. The vector is composed of two groups of sequences of multiple cloning sites (MCS), a plurality of target gene shRNA transcription units and plasmid sequences. The shRNA transcription units of a plurality of different or same target genes can be connected in series between the two groups of the sequences of the multiple cloning sites of the vector, a plurality of shRNA transcription units thereon can express one target gene for many times or express a plurality of different sites of one target gene or express different target genes after the transcription of cells or animals, so as to specifically inhibit the expressions of two or more target genes. The vector can be easily used in the gene function research and the research and development of the gene therapeutic drugs for diseases.
Owner:马义才
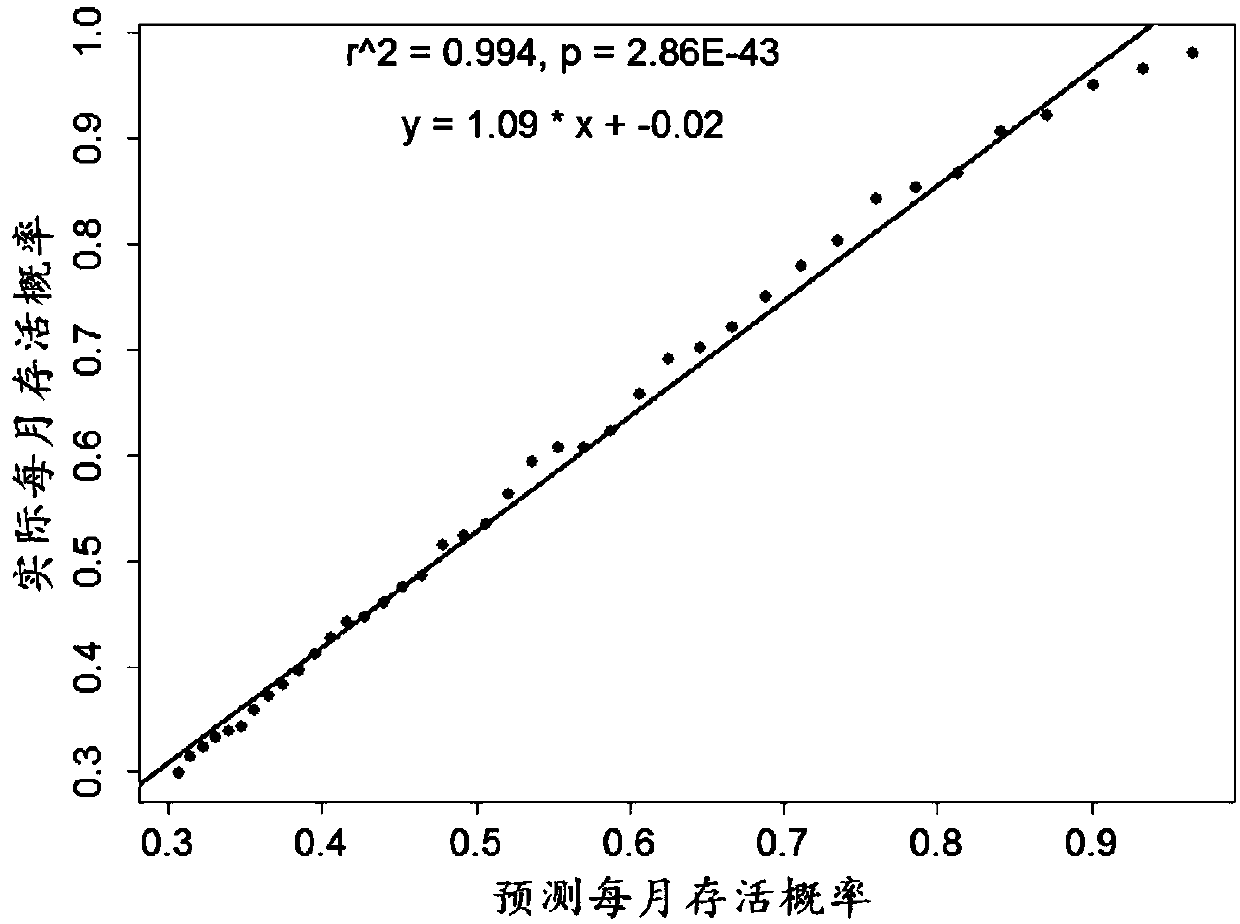
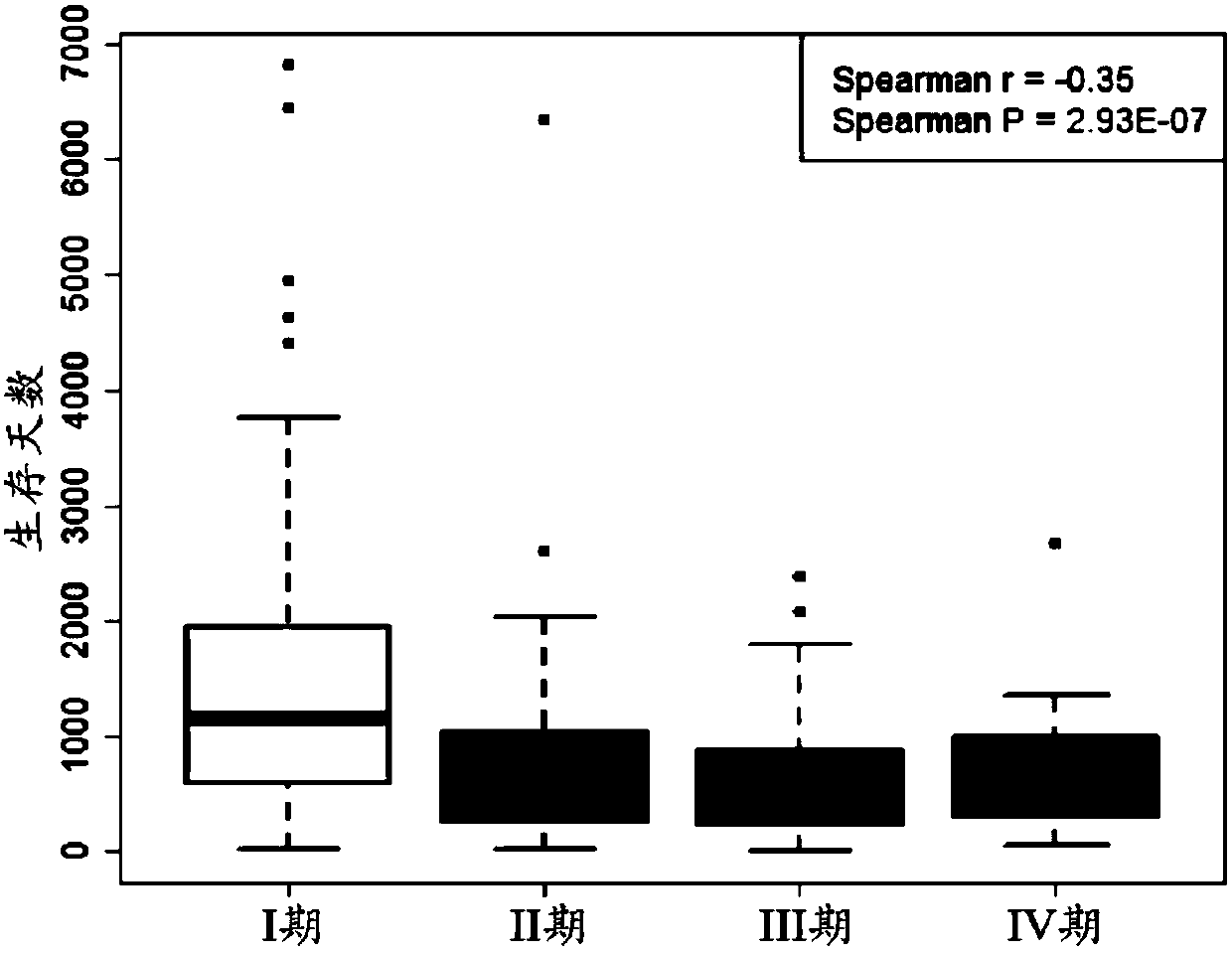
Lung adenocarcinoma individuation prognosis evaluation method based on polygene expression characteristic spectrum
ActiveCN108363907APrecise Survival StatusReflect the state of existenceHealth-index calculationHybridisationLinear correlationCvd risk
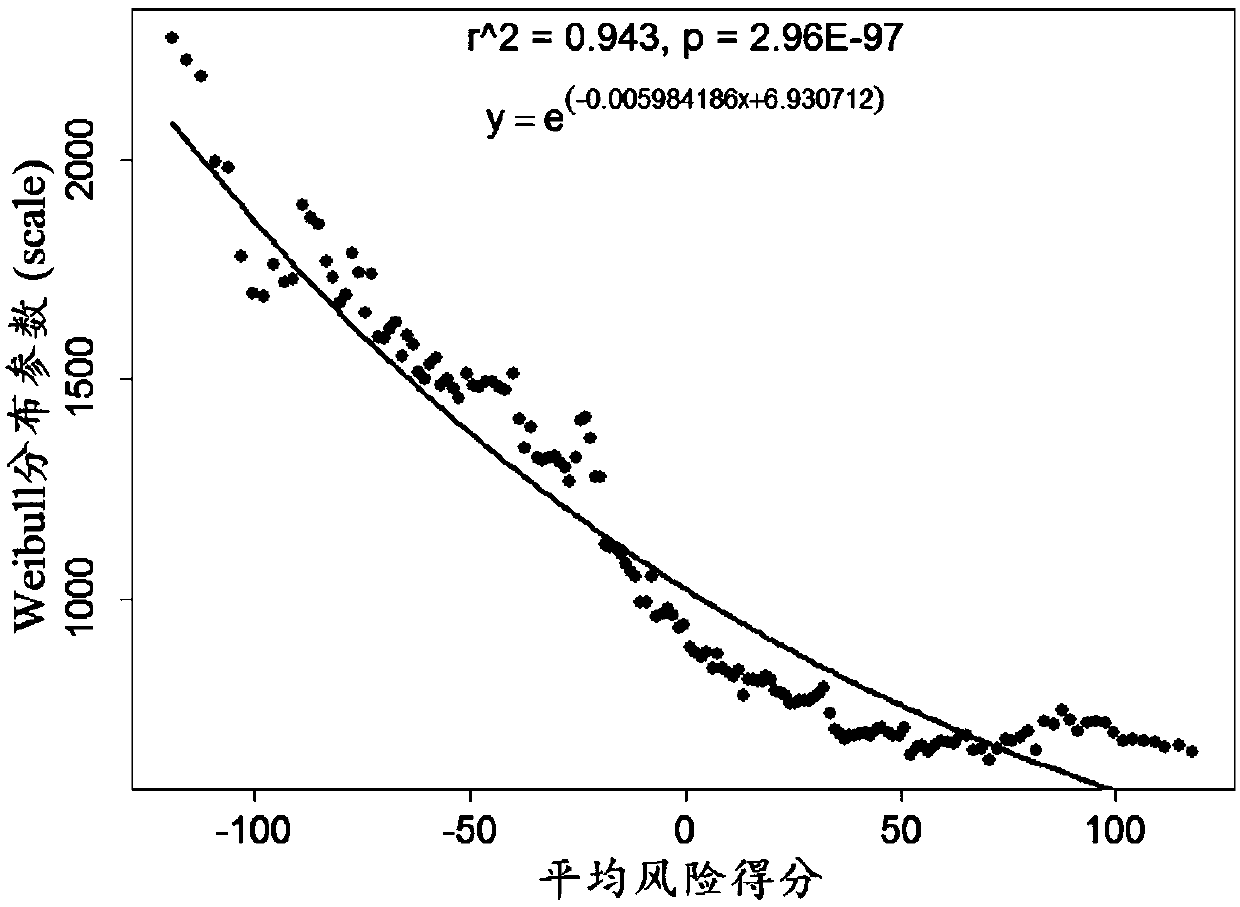
The invention discloses a lung adenocarcinoma individuation prognosis evaluation method based on a polygene expression characteristic spectrum. The method comprises the following steps that a lung adenocarcinoma prognosis risk gene list and weight are acquired; a prognosis evaluation model is established by using a tumor tissue transcriptome and survival data of a patient with lung adenocarcinoma;a risk score of the patient is calculated according to a gene expression spectrum of the tumor tissue of the patient with lung adenocarcinoma; the annual survival probability of the patient is calculated according to the risk score of the patient. According to the method, the annual survival probability of the patient with lung adenocarcinoma and the actual annual survival probability are highlyidentical, the linear correlation R2 is equal to 0.994, and the P value is equal to 2.86E-43. It is proved that the method has high prediction accuracy, and the state is highly identical to the actualsurvival state. Meanwhile, for each patient with lung adenocarcinoma, the method can provide a specific survival probability curve of the patient.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Solid tumor polygene detection gene chip and preparation method and detection device thereof
ActiveCN110387419AAccurately reflects point mutationsAccurately reflects indelsMicrobiological testing/measurementICT adaptationMicrosatelliteWilms' tumor
The invention provides a solid tumor polygene detection gene chip and a preparation method and a detection device thereof. The solid tumor polygene detection gene chip comprises a probe sequence of agene area used for detecting tumor mutational load and targeted pharmacy related mutation sites shown in a list 1 and a probe sequence used for detecting unstable position sites of a microsatellite shown in a list 2. According to the solid tumor polygene detection gene chip, the gene area of the 859 tumor mutational loads and the targeted pharmacy related mutation sites and the 250 unstable sitesof the microsatellites, the gene areas can truly reflect a change trend of tumor mutational loads and a microsatellite unstable state of a human whole-genome, the areas cover common targeted pharmacyrelated mutation sites, and the solid tumor polygene detection gene chip can be simultaneously used for detecting various tumor molecular markers.
Owner:裕策医疗器械江苏有限公司
Gastric cancer detection panel based on next-generation sequencing technology and application of gastric cancer detection panel
PendingCN111996257ALow costAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenes mutationExon
The invention belongs to the technical field of polygene detection of gastric cancer, and discloses a gastric cancer detection panel based on a next-generation sequencing technology. According to theinvention, important exon regions and a part of intron regions of 557 genes are enriched by using a gene probe hybridization method, and high-depth sequencing is carried out, so events such as gene mutation, copy number variation and the like having clear clinical correlation with the gastric cancer can be accurately detected; and a multi-gene screening list is made into a probe, and high-risk genes are detected in a targeted mode through DNA sequencing, so gene mutation with guiding significance for diagnosis and treatment can be detected more efficiently, accurate typing of tumor patients are realized, and meanwhile, a plurality of tumor patients can be helped to participate in clinical tests.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
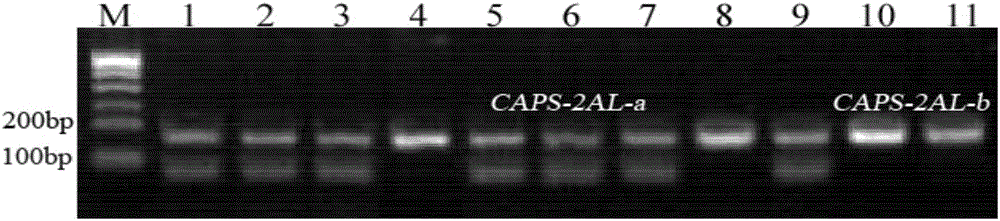
Wheat seed dormancy persistence-substantially related SNP label and its CAPS label and use
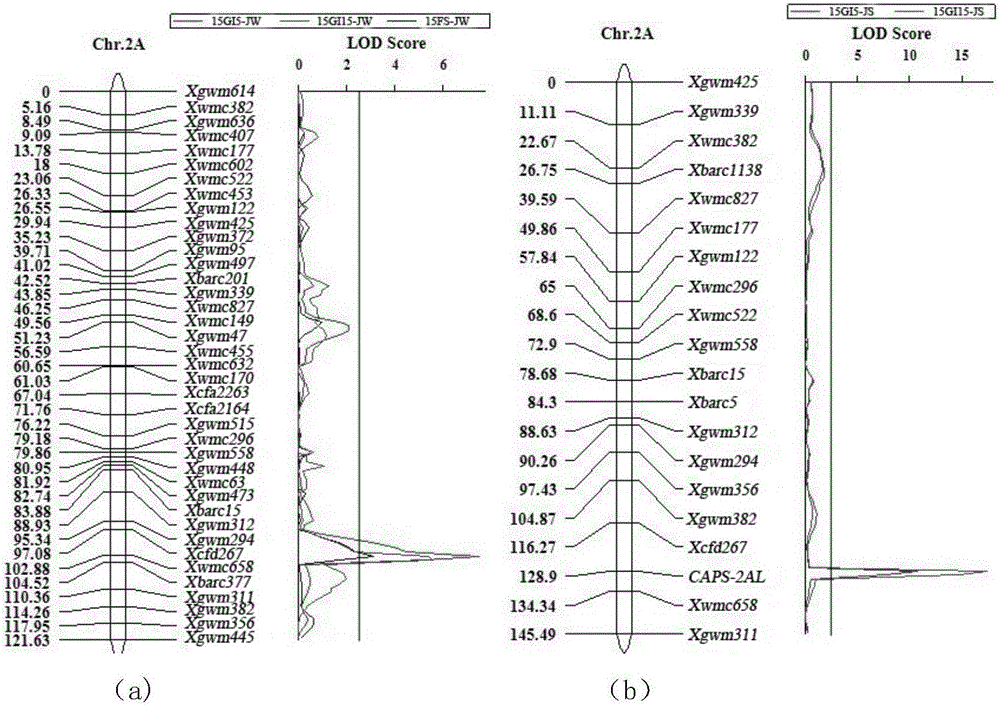
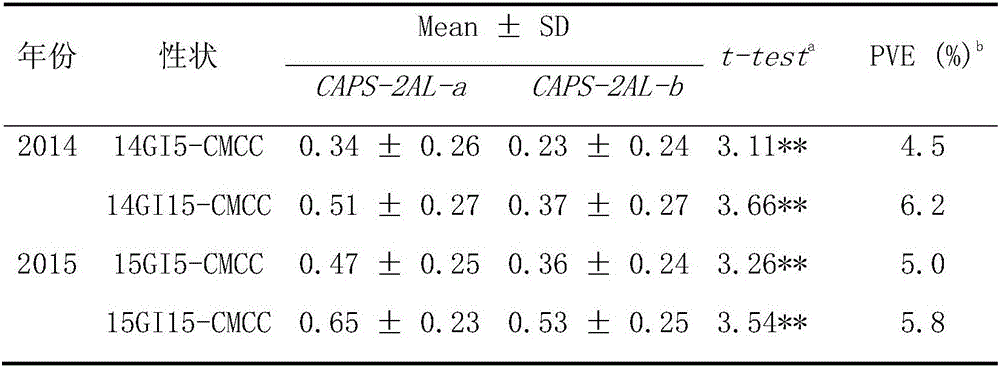
ActiveCN106048056AContribute to polygenic aggregation breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSeed dormancyAgricultural science
The invention discloses a wheat seed dormancy persistence-substantially related SNP label and its CAPS label and use. The SNP is located at a wheat 2AL chromosome, is tightly linked to a SSR label Xwmc658 in a genetic map and is a novel seed dormancy persistence main-effect site. The CAPS label developed on this basis provides a novel method for wheat preharvest sprouting resistance molecular marker-assistant breeding, lays the foundation for cultivation of a wheat specie with good preharvest sprouting resistance persistence, fills in the blank of continuous seed dormancy / preharvest sprouting resistance identification and is conducive to wheat preharvest sprouting resistance polygene polymerization breeding.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Polygene multi-target enrichment method
The invention discloses a polygene multi-target enrichment method. A capture probe library is designed, and target gene sequences are enriched in a probe capture way at a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) level, so that detection on all variation types, such as mutation, deletion, insertion, fusion and copy number amplification, of target genes is realized, and the defect that presently the target gene sequences are enriched by a PCR method at the DNA level, only mutation and deletion of the target genes can be detected, and the fusion cannot be detected is overcome.
Owner:TIANJIN TUMOR HOSPITAL +1
Single-gene or polygene copy number detection system and method based on next generation sequencing technology
ActiveCN109887546AEasy to correctSolve the strong batch effectBiostatisticsSequence analysisAlgorithmLinear regression
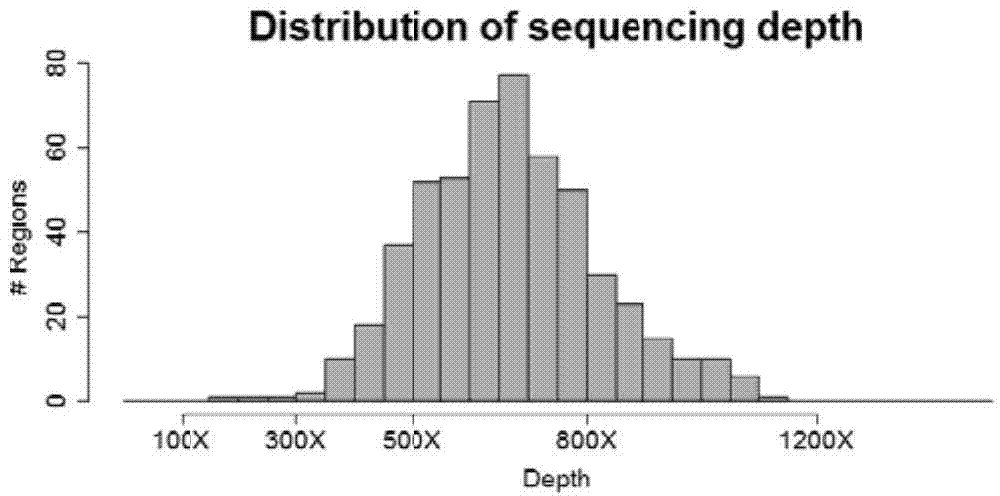
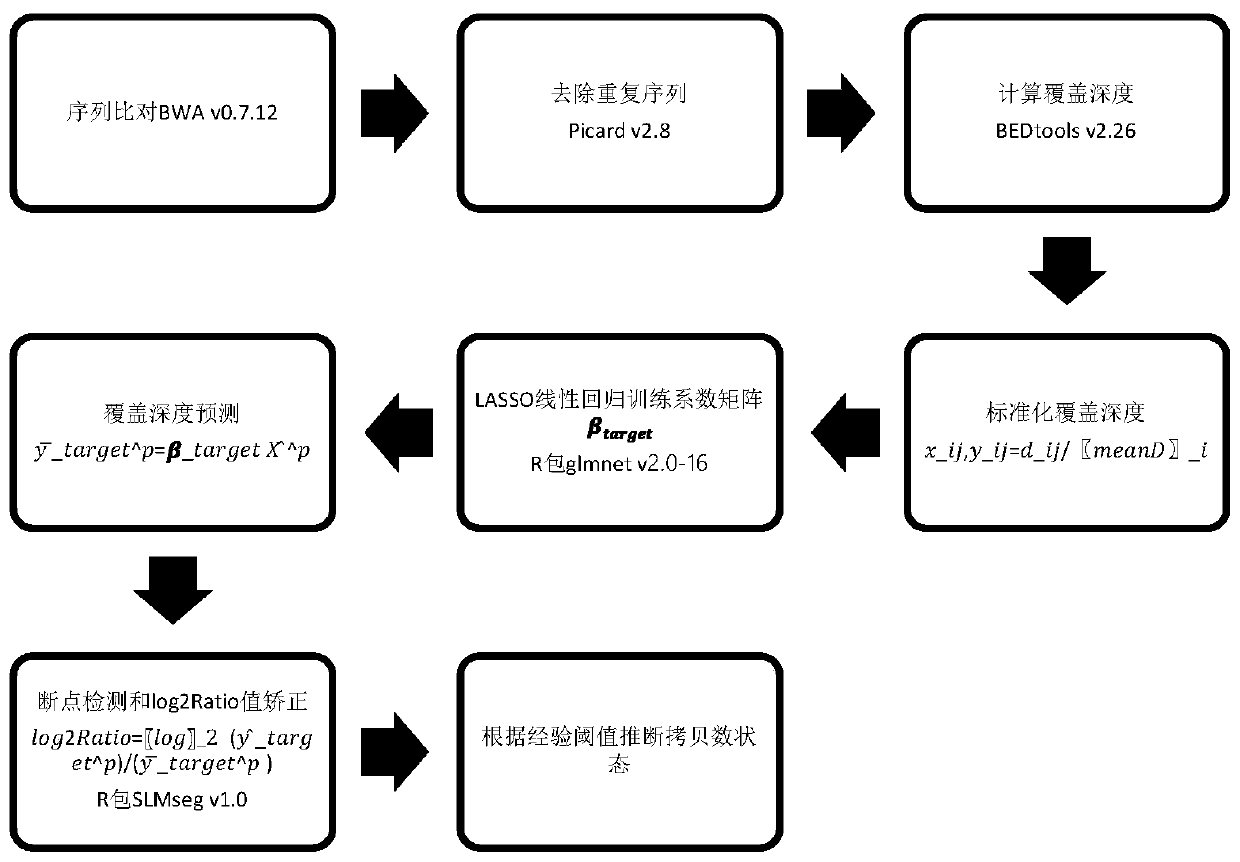
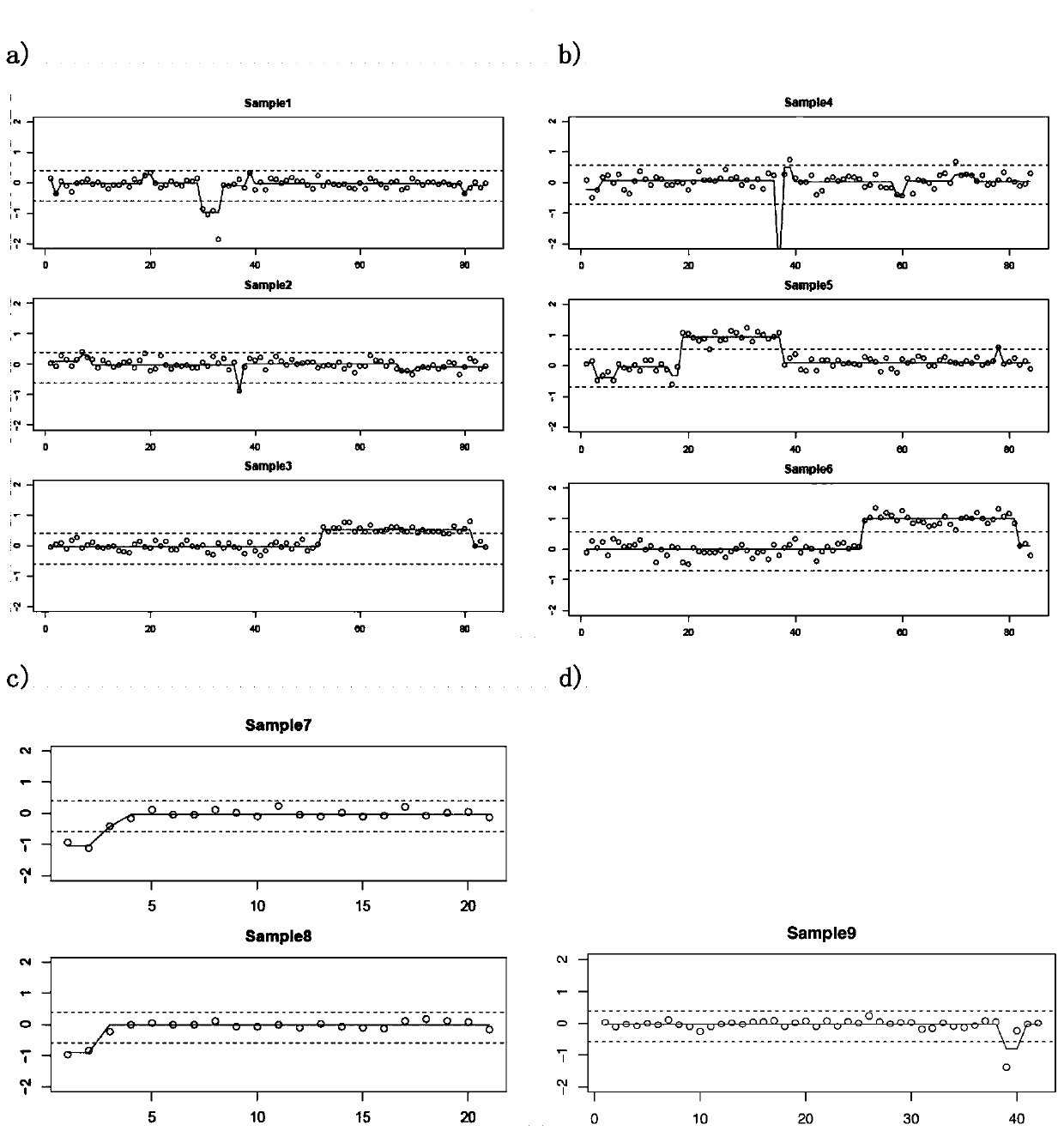
The invention discloses a single-gene or polygene copy number detection system and method based on a next generation sequencing technology. The single-gene or polygene copy number detection system uses a machine learning algorithm based on a regularized linear regression model (LASSO) and shifting level models to infer copy number variation of single-gene or polygene exons, and includes successively connected sequence alignment module, repeat sequence removal module, calculation coverage depth module, standardized coverage depth module, regularized linear regression training module (LASSO linear regression training module), coverage depth prediction module, breakpoint detection and log2Ratio value correction module, and copy number state inference module. The single-gene or polygene copy number detection system and method based on a next generation sequencing technology utilize the machine learning method to train large-scale next-generation targeted capture sequencing data, and combine the shifting level models to reduce technical and biological errors caused by batch effects, thereby achieving better copy number detection accuracy and precision.
Owner:上海序祯达生物科技有限公司
Hansenula polymorpha with double selection marker and application thereof
InactiveCN102226154AMaintain physiological and biochemical characteristicsHigh copy numberFungiMicroorganism based processesGenomicsHigh level expression
The invention discloses hansenula polymorpha with a double selection marker and an application thereof. The hansenula polymorpha with a double selection marker provided by the invention is uracil-synthesized and tryptophan-synthesized double-deficient hansenula polymorpha HUT-31 with a preservation number of CGMCC No.4778. The strain has a uracil and tryptophan double-auxotrophic selection marker, maintains the physiological biochemical characteristics of wild-type strains, facilitates the culture of recombinant strains and the high-level expression of heterologous protein; not only recombinant strains can be selected easily and rapidly, but also the double selection marker can increase the copy number of target genes integrated on a chromosome, can increase the expression level of targetprotein, and has important industrial application value. Meanwhile, the double selection marker is also applicable to the polygene genetic modification of hansenula polymorpha in functional genomics,synthetic biology, and metabolic engineering.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
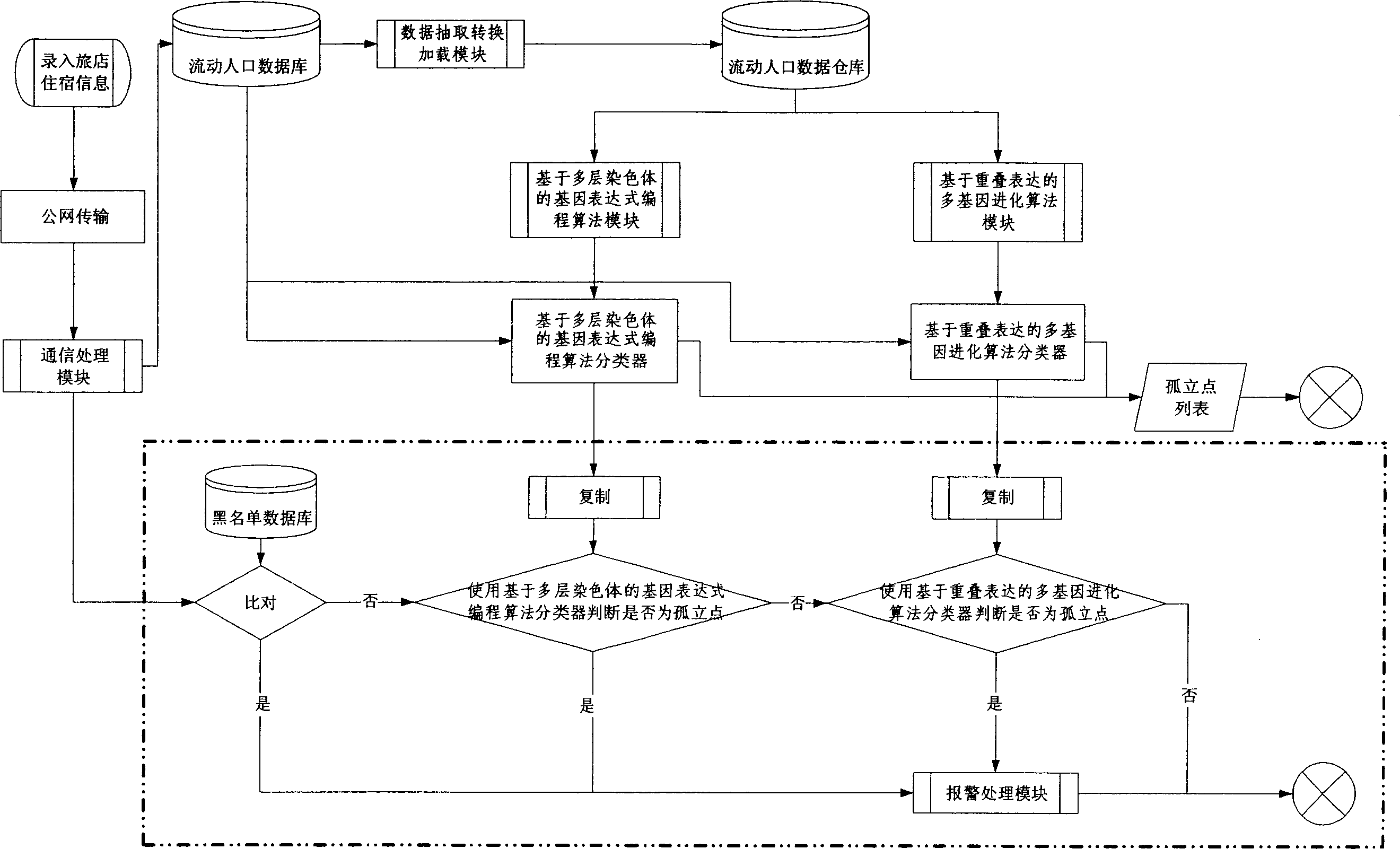
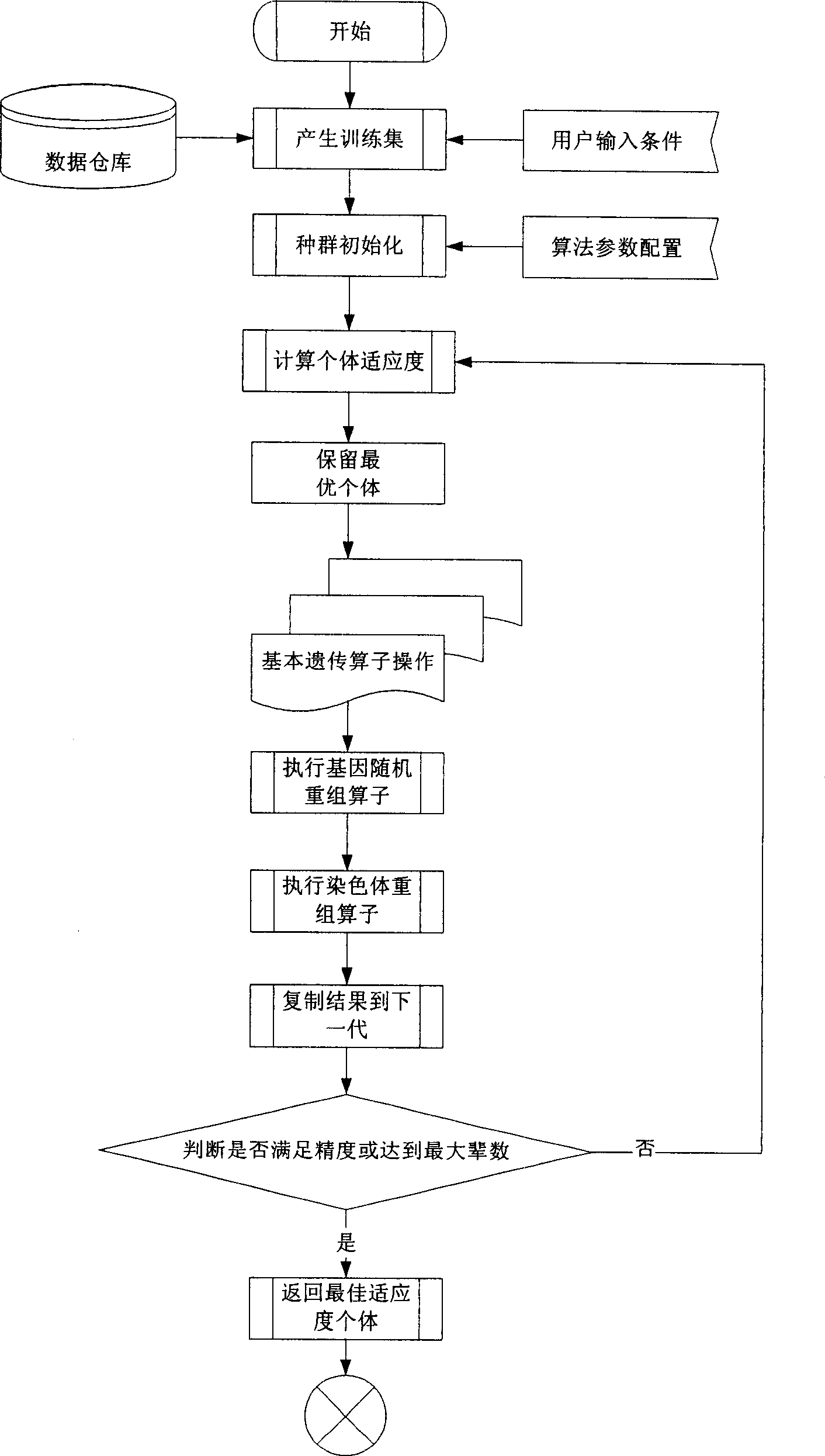
Biologic heuristic calculation based floating population information analysis and alert and alarm method
InactiveCN1808483AFill real-timeFill in the gaps in the alarmGenetic modelsResourcesInformation analysisData stream
The invention provides a floating population information analysis and warning and alarming method based on biological instructive calculation. Wherein, with current floating population information system from department of public safety, extracting need information to calculate floating population data with the multilayer chromosome gene expression programming algorithm and overlap-expressive polygene evolution algorithm in biological instructive calculation filed; and completing data mine and classification and isolated-point analysis to realize the warning and alarm. This invention can take deep analysis to trace and trend of abnormal floating population and different criminal feature, builds a intelligent analysis platform, and can also provide useful information for local peace.
Owner:彭京
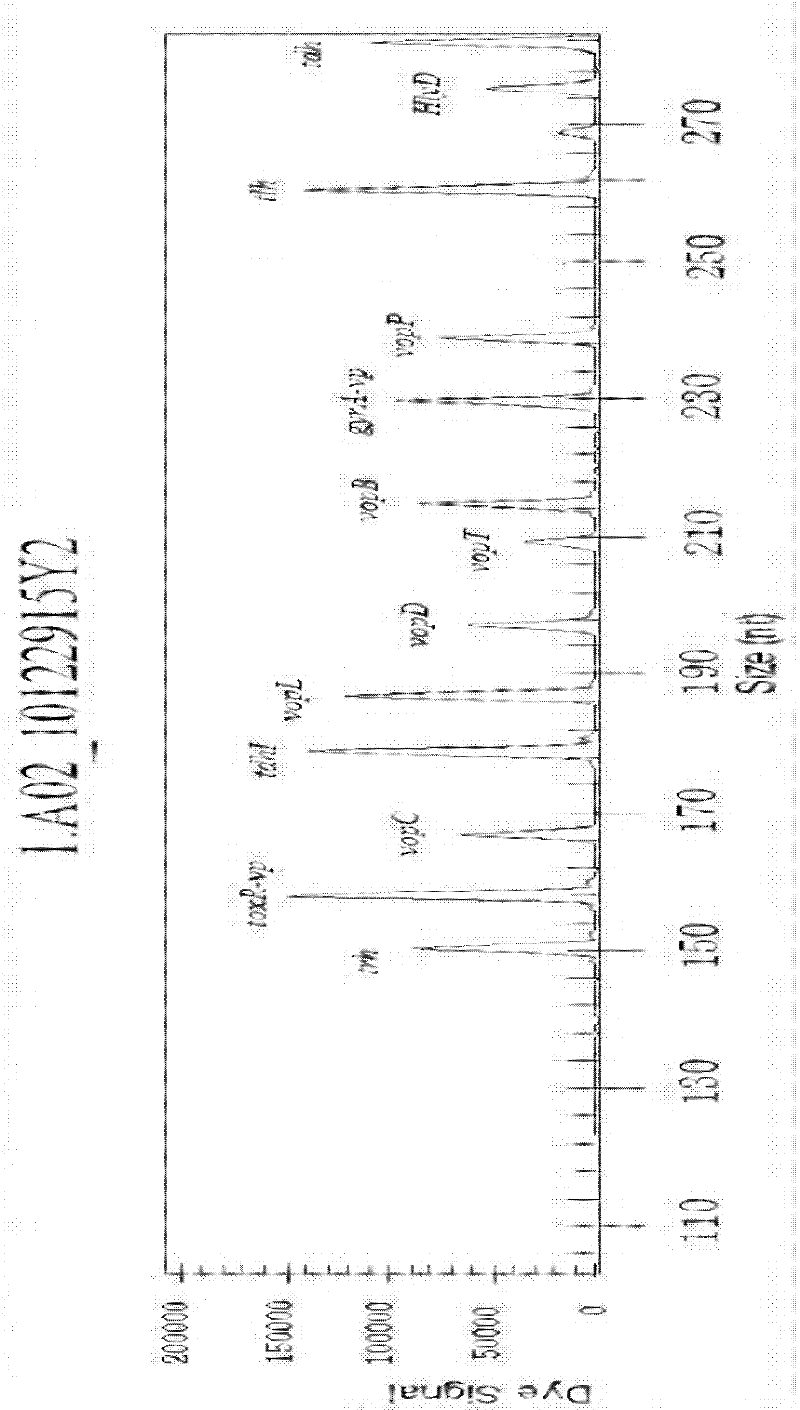
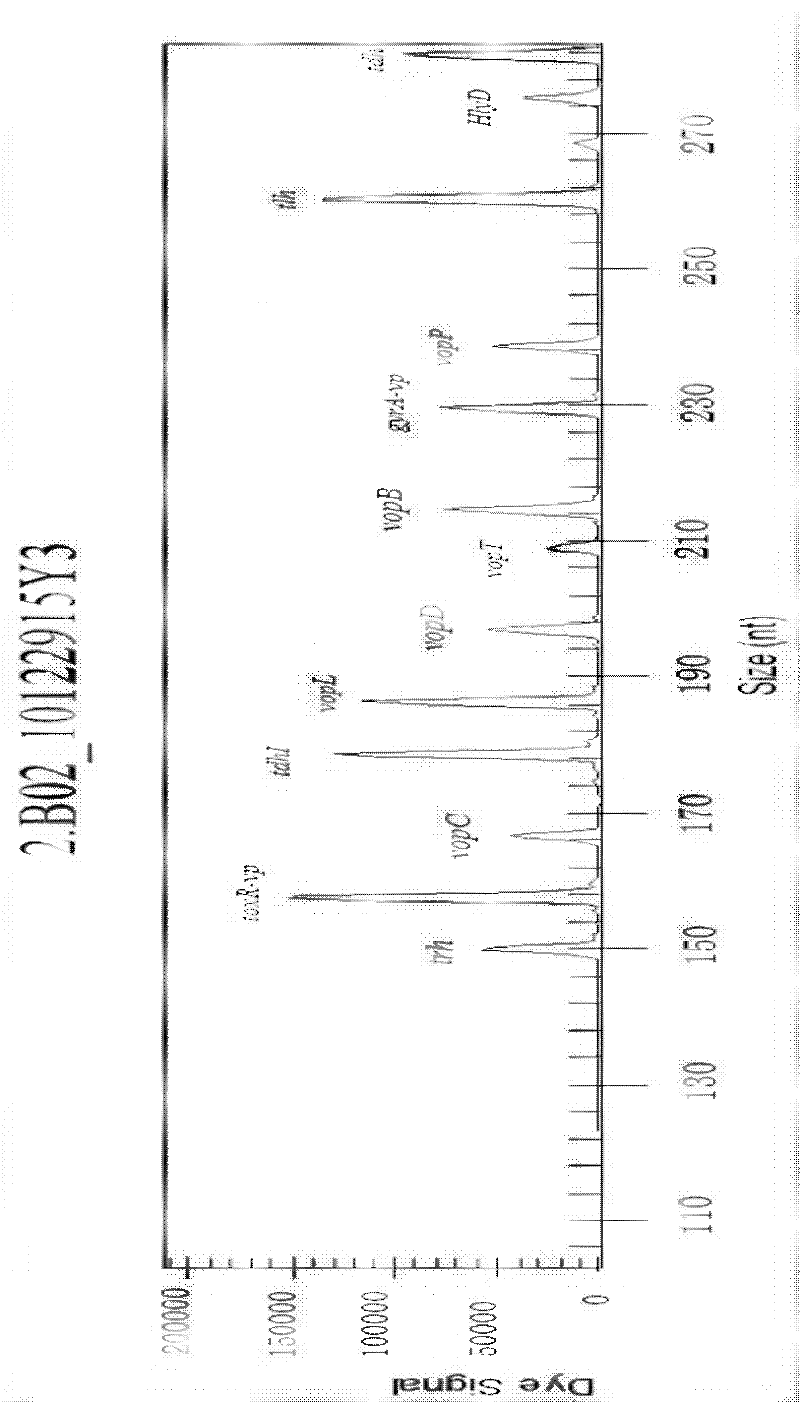
Rapid detection kit and detection method for v.parahaemolyticus multiple virulence factor GeXP
ActiveCN102559889AImprove accuracyEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesVibrio parahaemolyticusEpidemiologic survey
The invention discloses a rapid detection kit and a detection method of a v.parahaemolyticus multiple virulence factor GeXP. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting a genome DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of the v.parahaemolyticus; performing multiple PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on 13 pairs of polygene PCR primers and a pair of general primers by taking the genome DNA as a template to obtain a multiple PCR reaction product; and detecting and analyzing by using a GenomeLab Gexp genetic analysis system. In the invention, a specific primer is designed specific to 13 kinds of known virulence genes of v.parahaemolyticus, and 13 kinds of genes are detected rapidly and efficiently at one time through a single-tube reaction to detect whether a sample contains v.parahaemolyticus which carries virulence genes and has potential pathogenic ability can be known, so that the detection coverage is wide, the accuracy of pathogenicity evaluation of v.parahaemolyticus can be greatly increased, and a more effective detection measure is provided for pathogenicity evaluation of v.parahaemolyticus. The method has important application prospects on the aspects of aquaculture disease detection, epidemiological investigation, pathogenic bacterium detection in foods, aquatic product import and export detection, hospital infection monitoring, and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant expression of multiprotein complexes using polygenes
InactiveCN101356275AWith medical useFusion with DNA-binding domainGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideMultiprotein complex
The present invention relates to a recombinant polynucleotide encoding a polygene coding for at least three polypeptides wherein at least one of the genes constituting the polygene is of non-viral origin, at least two of the polypeptides encoded by the genes constituting the polygene are each capable of at least transiently interacting with at least one other polypeptide encoded by a gene of said polygene, and the genes constituting the polygene are each connected to one another by a sequence coding for at least one protease cleavage site. The present invention also relates to polyproteins encoded by the polygene. Further embodiments of the present invention are a vector containing the recombinant polypeptide, a host cell containing the recombinant polypeptide and / or the vector and a non-human transgenic animal transformed with the recombinant polypeptide and / or the vector. The present invention also relates to methods for the production of the polynucleotide and for the manufacture of multiprotein complexes. The embodiments of the present invention are particularly useful in gene therapy, drug candidate screening, vaccine production and crystallisation of multiprotein complexes for structural investigations.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Polygene joint detection probe for early diagnosis of tumour, primer and kit
InactiveCN102628077AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationKRASWild type
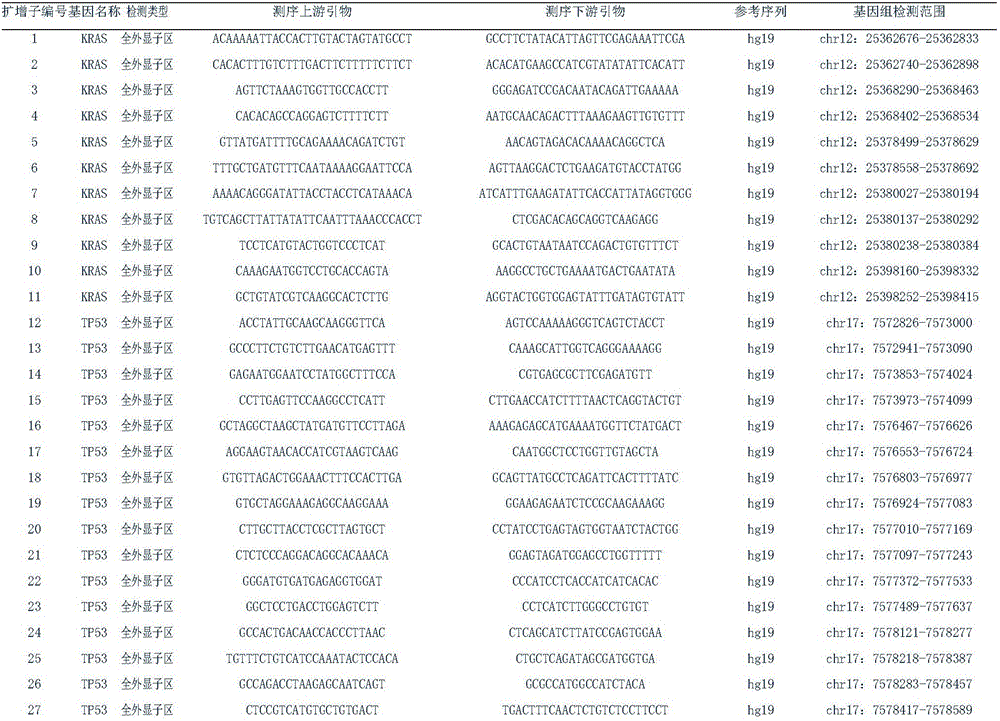
The invention discloses a polygene joint detection probe for early diagnosis of tumour, a primer and a kit. The probe and the primer contain SEQ ID NO: 1-SEQ ID NO: 91, can be used for joint detection of p53, KRAS, EGFR, BRAF, PIK3CA and MEK1 genes; can be used to simultaneously detect a plurality of driving abrupt changes in one PCR reaction tube; has high sensitivity and can be used to detect 5-10 copy abrupt change; has strong singularity without generation of non-specificity signals from 10 ng of wild type genome DNA; and has advantages of rapid detection speed, easy operation and low cost.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Construction of African swine fever attenuated strain with polygene joint deletion and application of African swine fever attenuated strain with polygene joint deletion, as vaccine
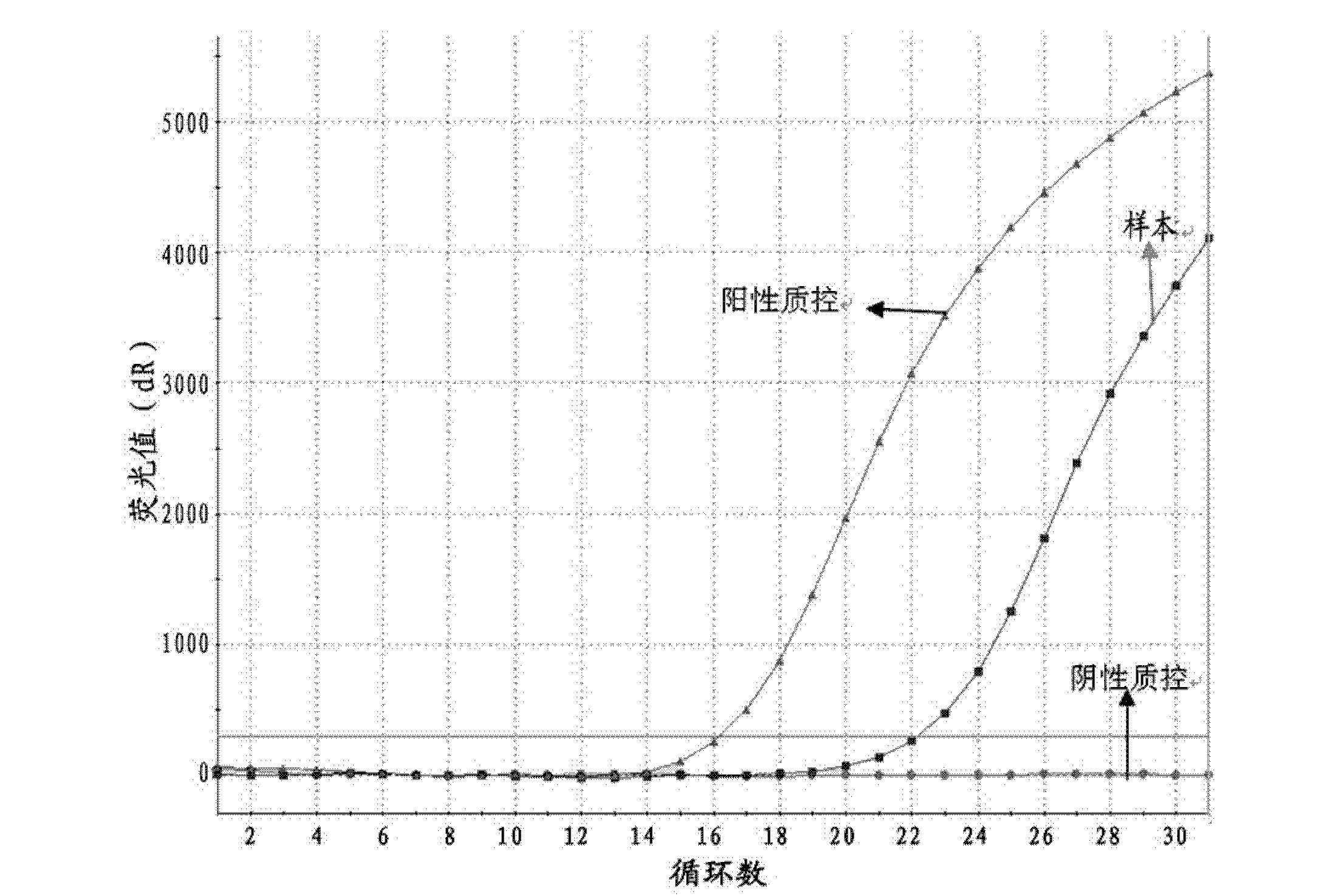
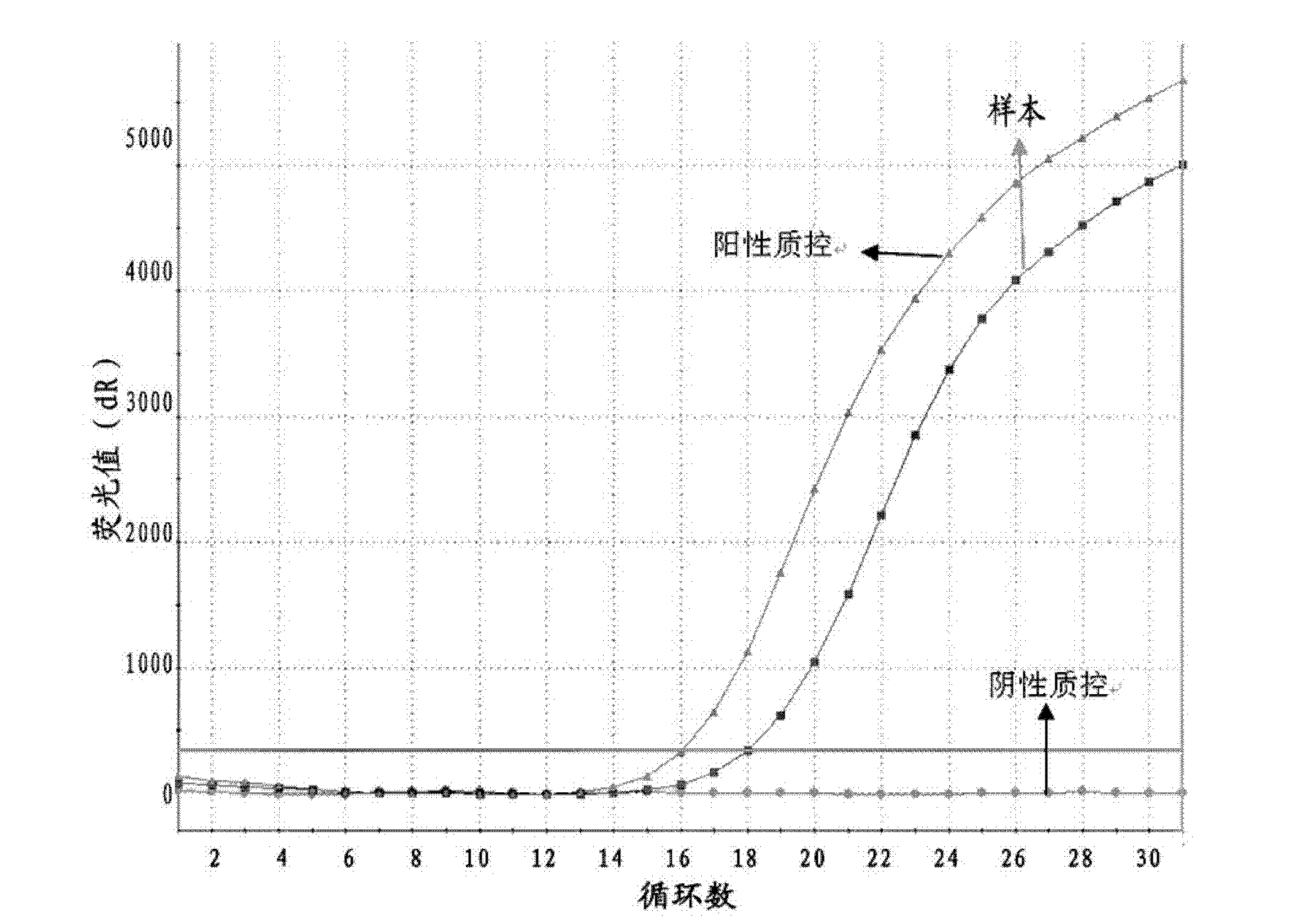
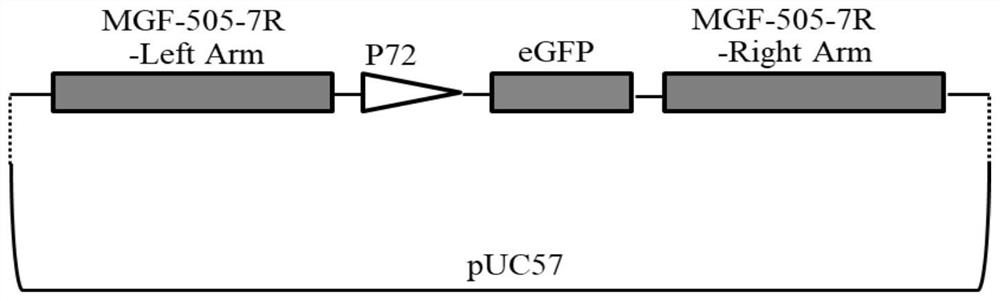
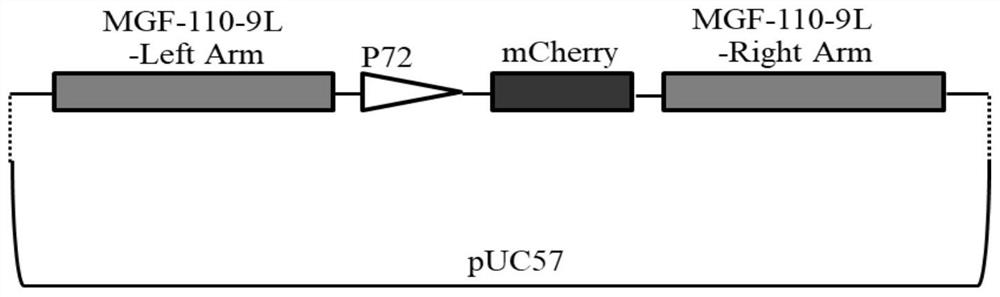
ActiveCN113215109AAttenuated virulenceImprove securityViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesAfrican swine feverGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to an attenuated African swine fever virus with immunosuppressive gene deletion, and a vaccine. According to the invention, an ASFV MGF-110-9L gene and an ASFV MGF-505-7R gene are found to have a relatively strong immunosuppression effect, the virulence of the African swine fever virus can be weakened by knocking out the genes from the African swine fever virus, and the genes are new target genes for preparing attenuated swine fever vaccines. The functions of ASFV G-ACD-00190 gene coding proteins, ASFV MGF-110-9L gene coding proteins, ASFV G-ACD-00210 gene coding proteins and ASFV MGF-505-7R gene coding proteins are deleted in an African swine fever parent strain ASFV CN / GS / 2018 in a combined manner by adopting a genetic engineering means, so that the toxicity of the parent strain is reduced, and the attenuated African swine fever candidate vaccine strain with high safety is obtained. The attenuated African swine fever candidate vaccine strain is completely attenuated after immunizing a pig, the immunized pig is healthy, 100% immune protection can be provided for attacking (100HAD50 dosage) of ASFV CN / GS / 2018 virulent strain, and the attenuated African swine fever candidate vaccine strain can be used as a safe and effective candidate vaccine for preventing and controlling the African swine fever epidemic situation and has great social value.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
New wheat stripe rust resisting polygene-polymerized flower-nurture breeding method
InactiveCN101558735AWide resistanceResistance spectrum widthHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureHigh resistanceLesser florican
The invention discloses a new wheat stripe rust resisting polygene-polymerized flower-nurture breeding method. Wheat-breeding parent materials with excellent agronomic characters are selected; 3 major micro-species of puccinia striiformis, which are recently popular, are used to evaluate stripe rust resistance of the wheat-breeding parent materials at seedling stage and adult stage; 3 wheat-breeding parent materials, which have high-resistance immunity to major popular individual micro-species of various puccinia striiformis, are sieved; the 3 wheat-breeding parent materials are hybridized and duplex hybridized to obtain duplex hybridized polygene-polymerized subsequent generation; the duplex hybridized subsequent generation is then cultured and wheat anther tissue is inoculated to one-step seeding culture medium of wheat anther, thereby obtaining complete pollen plant; chromosome doubling liquid with colchicines and dimethyl sulfoxide is injected to tillering node, thereby carrying out pollen plant chromosome doubling to obtain doubly purified individuals of doubled haploid which can be self-hybridized to form a stable doubled haploid system; and stripe rust resisting individual micro-species validation is carried out on the doubled haploid system, so as to obtain a new stripe rust resisting type or species system which is polymerized with 3 stripe rust resisting genes.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105087632AHigh expressionImprove stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome as well as a construction method and application thereof. The saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome comprises two telomeric repeat sequences, two insulator sequences, a centromere-autonomously replicating sequence, a po130 gene and n repeated recombination boxes. Experiment results prove that auxotrophic marker genes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome are few, normal and stable growth in the situation that screening is not carried out can be realized, the expression quantity and copy number of exogenous genes in yeast are increased, the stability of exogenous genes in yeast is improved, genes integrated into a genome can be increased or reduced, and even expanded into new polygene clusters, and the rapid exogenous expression of beta carotene and violacein is successfully realized in yeast, so that a rapid feasible method is provided for yeast heterogeneous production of various exogenous approaches, and the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome can meet the application requirements of fields of gene engineering, metabolic engineering and synthetic biology.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Liver cancer detection panel based on next-generation sequencing technology, kit and application of panel
The invention belongs to the technical field of liver cancer polygene detection, and discloses a liver cancer detection panel based on a next-generation sequencing technology. Important exon regions and partial intron regions of 557 genes are enriched by using a gene probe hybridization method, and high-depth sequencing is carried out, so that events such as gene mutation and copy number variation which have clear clinical correlation with liver cancer are accurately detected; and a polygene screening list is made into a probe, and high-risk genes are detected in a targeted mode through DNA sequencing, so that gene mutation with guiding significance for diagnosis and treatment can be detected more efficiently, and important guiding significance is achieved for clinical diagnosis and discovery of targets of targeted therapy.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com