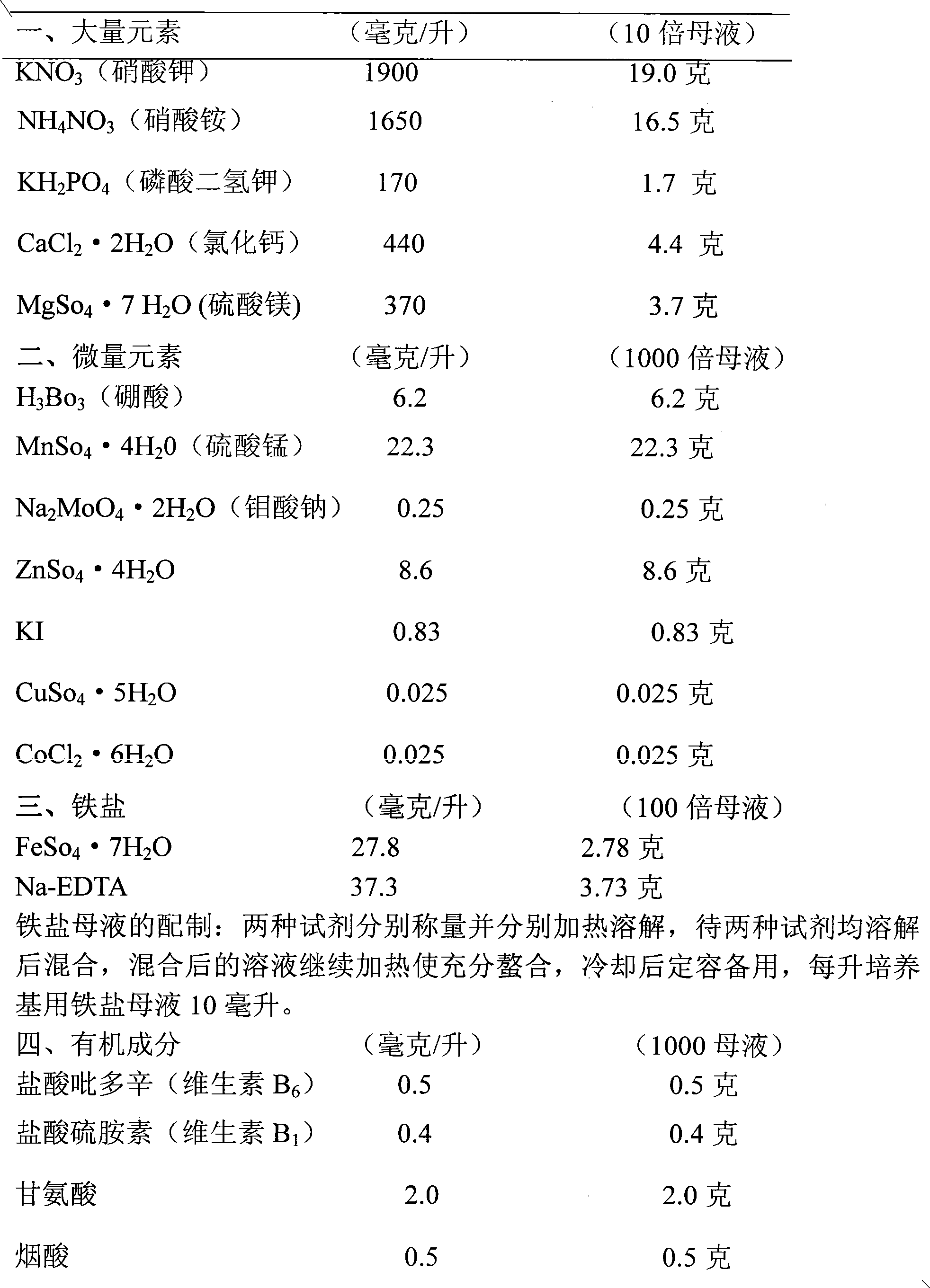
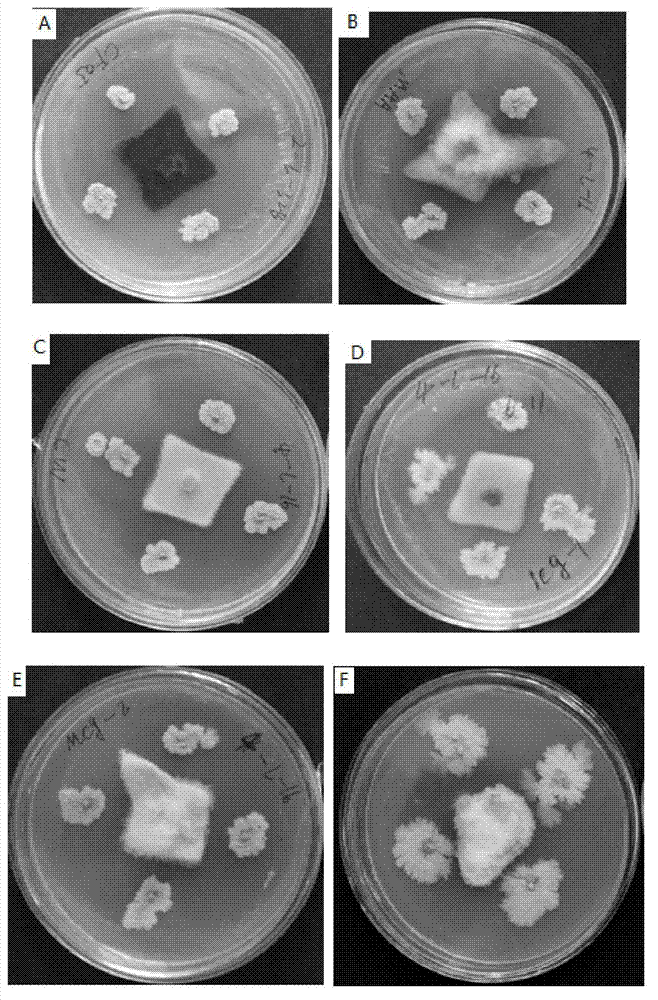
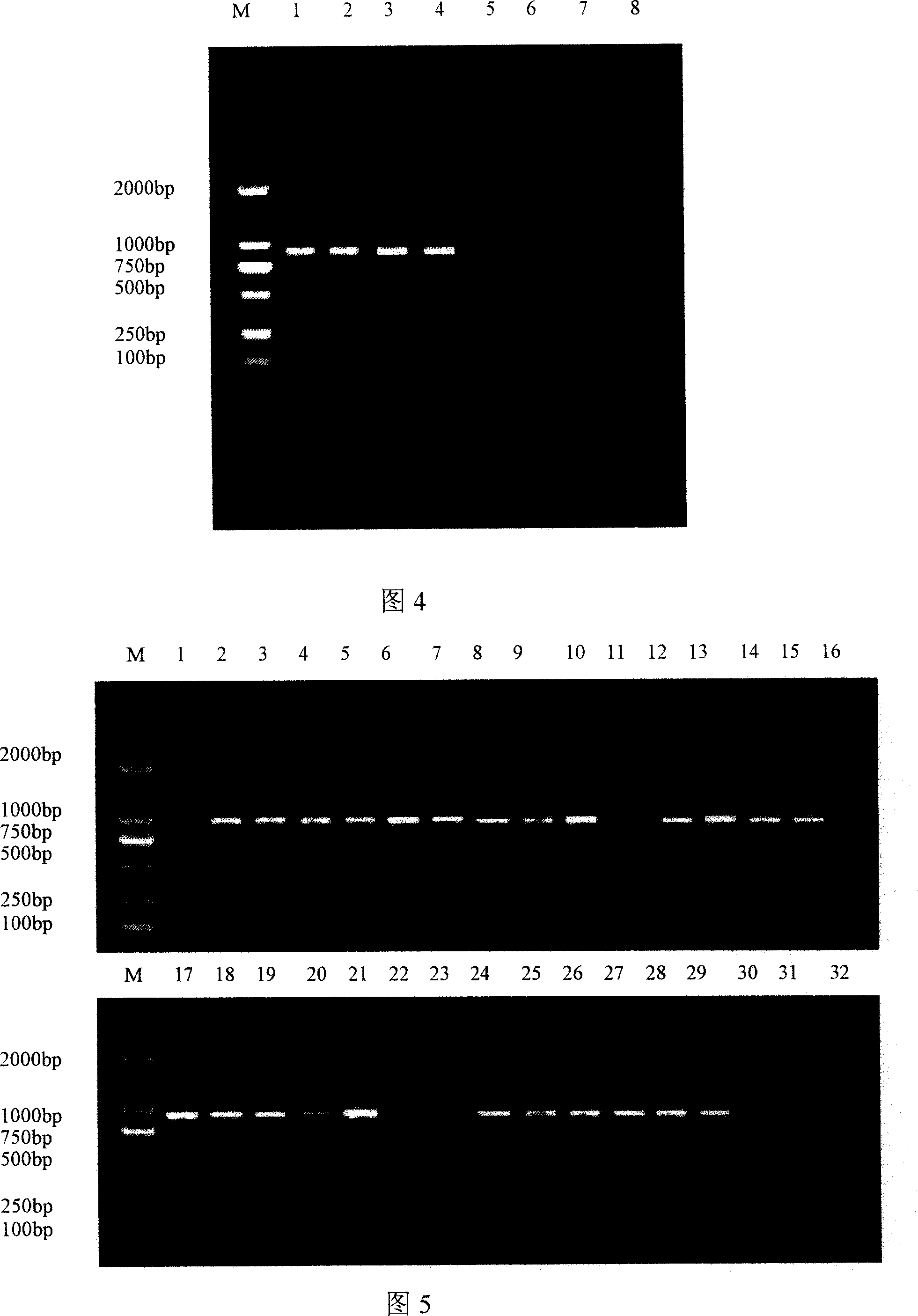
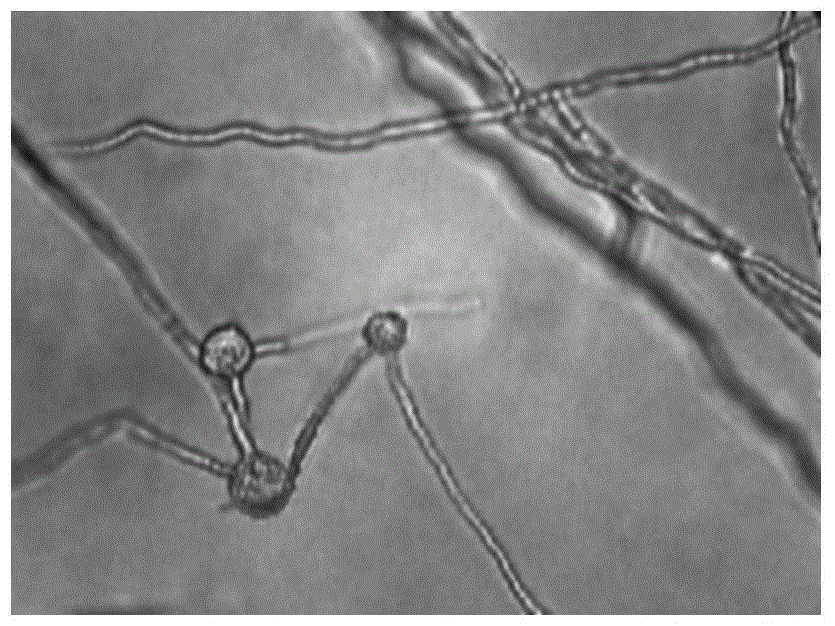
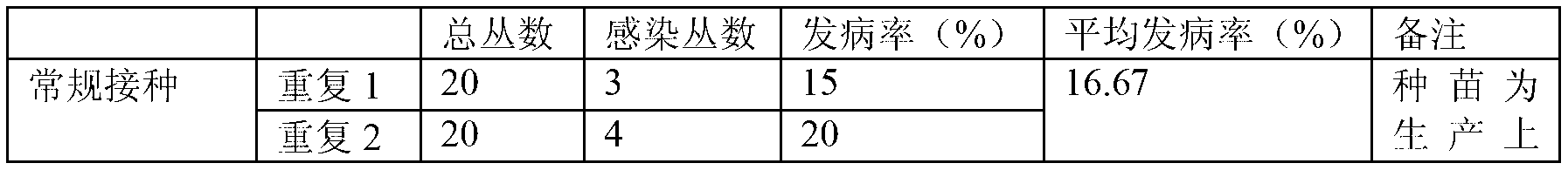
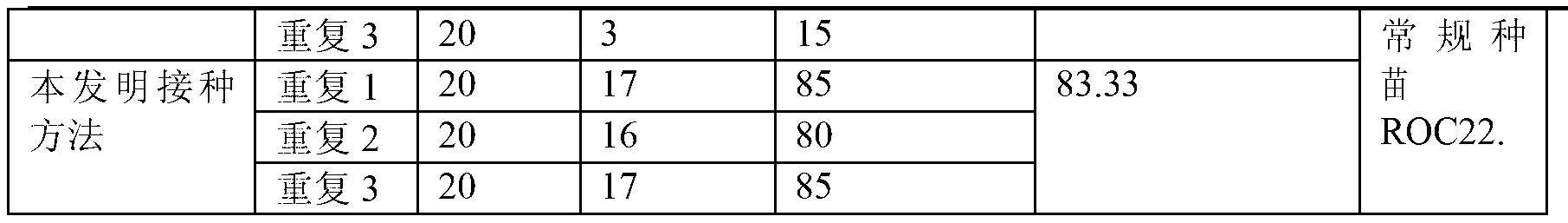
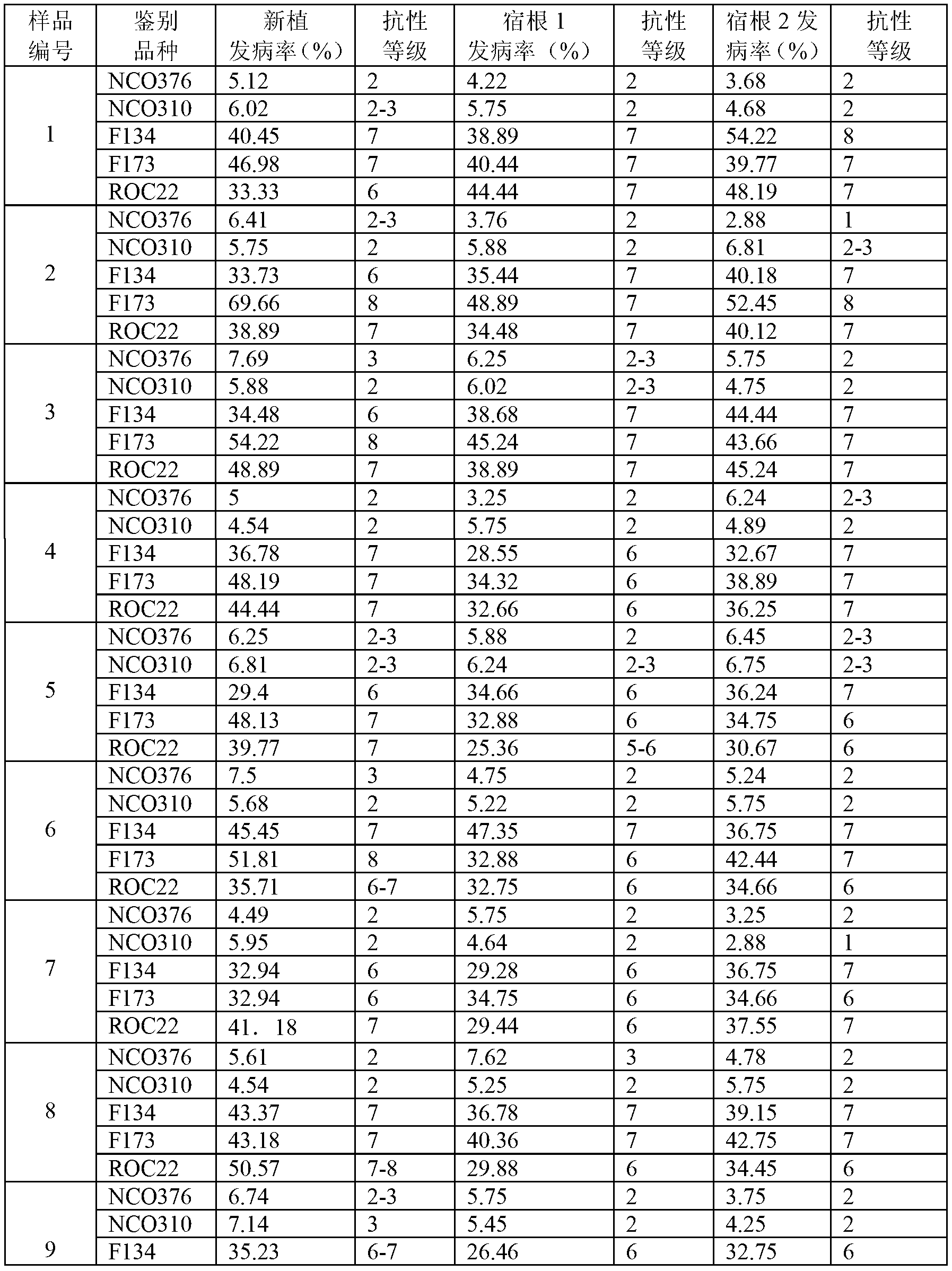
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Lesser florican" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The lesser florican (Sypheotides indicus), also known as the likh or kharmore, is the smallest in bustard family and the only member of the genus Sypheotides. It is endemic to the Indian Subcontinent where it is found in tall grasslands and is best known for the leaping breeding displays made by the males during the Monsoon season. The male has a contrasting black and white breeding plumage and distinctive elongated head feathers that extend behind the neck. These bustards are found mainly in northwestern and central India during the summer but are found more widely distributed across India in winter. The species is highly endangered and has been extirpated in some parts of its range such as Pakistan. It is threatened both by hunting and habitat degradation. The only similar species is the Bengal florican (Houbarobsis bengalensis) which is larger and lacks the white throat, collar and elongated plumes.
Method for breeding minitype potato seeds by directly using potato stem segments
InactiveCN101822214ASimple structureImprove performancePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyLesser florican
The invention provides a production method of minitype potato seeds bred by directly using potato stem segments, relating to the minitype potato seed high power propagation technology. In the invention, potato detoxification test tube tissue culture plantlet stem segments are used as a raw material, and then are directly implanted in an MS liquid or solid induction medium without any plant growth hormone, and the minitype potato seeds capable of sprouting are induced and produced in 6-8 weeks. The tissue culture plantlet stem segments are directly bred without changing the medium, thus obtaining the potato seeds in one step. The method has the advantages of saving time, labor and cost, having simple equipment, less used plantlets, less consumed time, rapid propagation and high efficiency and the like. The breeding period is 1.5-2 months, production can be performed for 5-6 periods each year, and the breeding chamber at unit area can produce 500,000-600,000 minitype potato seeds, thus making full use of the tissue culture chamber production space, greatly improving the output of the detoxification minitype potato seeds at each unit area, and increasing the production efficiency at each unit area by 50-100 times. The method is suitable for large-scale factory production of minitype potato seeds.
Owner:LELING XISEN POTATO IND GROUP
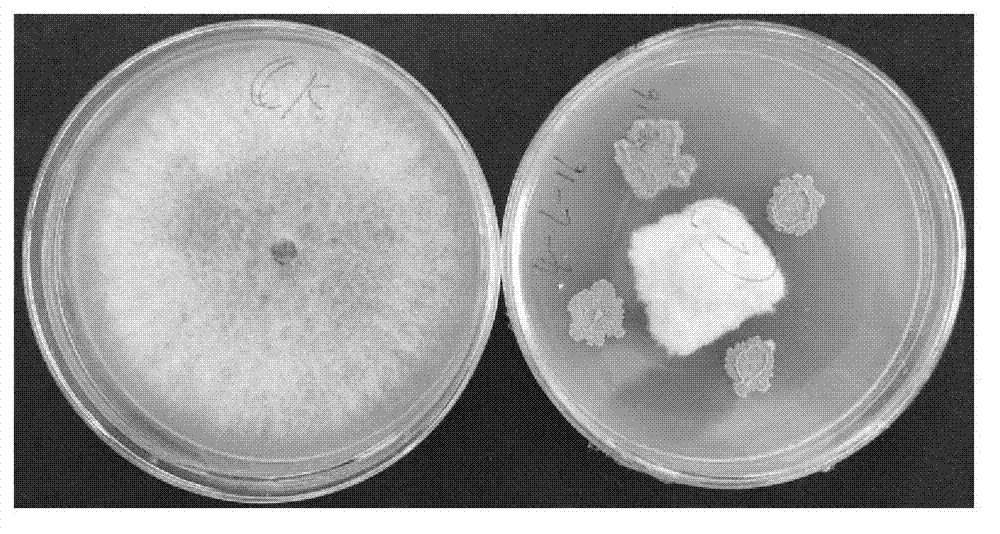
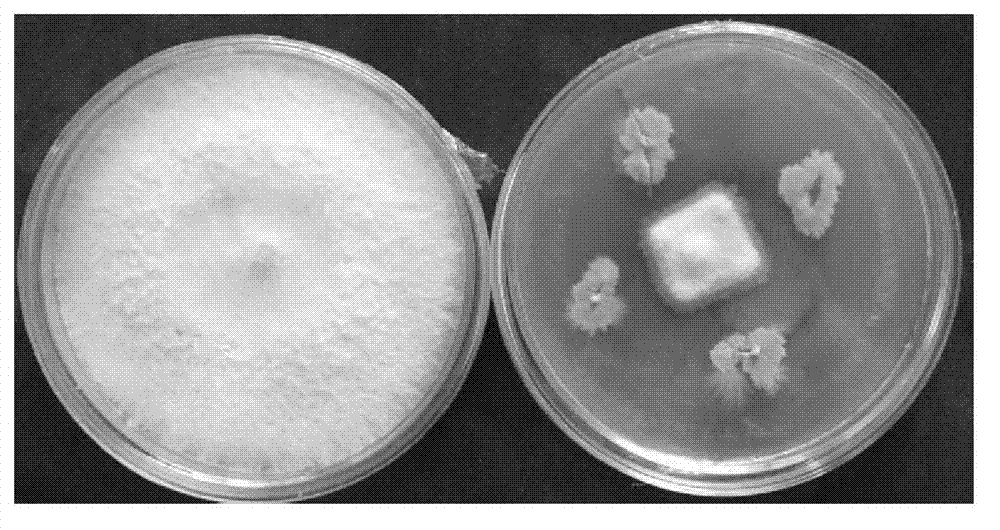
Bacillus methylotrophicus 4-L-16 for prevention and control of banana vascular wilt and its application
ActiveCN102787084AStrong antagonistic effectGrowth inhibitionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsGrowth plantLesser florican
The invention discloses a strain bacillus methylotrophicus 4-L-16 for prevention and control of banana vascular wilt. The strain has a preservation name of bacillus methylotrophicus 4-L-16, and is classified and named as Bacillus methylotrophicus 4-L-16. The preservation organization is China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation date is June 26, 2012, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2012248. The strain has a strong antagonistic effect on No.1 and No.4 physiological races of banana vascular wilt, and other banana common disease categories. The invention also discloses application of the strain in preparation of drugs with a banana vascular wilt prevention and control function, as well as a microbiological preparation containing the strain. The microbiological preparation not only has a better antagonistic effect on a variety of banana pathogenic bacteria, but also has a facilitating effect on plant growth.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Tobacco black shank resistance disease nursery identification method
ActiveCN101491199AConsistent plantingConsistent management levelHorticulture methodsContinuous croppingDisease
The invention relates to a method for identifying tobacco black shank resistance in disease nursery. A continuous cropping tobacco field in a historical high occurrence area of the tobacco black shank disease is selected as a disease nursery; plants are inducted to develop the disease through the improvement of the field humidity, so that the complex operation of strain separated storage and culture is reduced; the strain is sourced from the field; the quantity and variety of the microspecies for inoculation are theoretically unlimited; and the method has better diversity and representativeness, and the inoculation conditions are under the control of nature, so the identification results reflect the local practical situation of the day more correctly. A one-off uprooting investigation method after the collection of the flue-cured tobacco is adopted so as to greatly reduce the workload, save the cost and bring about a correct and reliable result. The method is characterized by low cost and simple and feasible operation. The method is an economical and practical method and has bright market and application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Breeding method of saffron seed ball
ActiveCN106376463AHigh induction rateShorten induction timePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsLesser floricanShoot
A breeding method of saffron seed ball comprises the following steps: selection and disinfection of explants, induction of test tube ball, proliferation of test tube ball, and rooting and transplanting of test tube ball. Small saffron seed balls are taken as the explants. The pollution rate is reduced. The induction rate of test tube ball is increased. The callus phase is not needed, and multiple shoots can be induced out. Multiple shoots can be directly induced to obtain test tube seed balls. The induction time is shortened. The test tube seed balls can be applied to multiplication culture. After proliferation, the test tube balls are subjected to rooting. The saffron test tube ball is converted into saffron seed balls in one step, the time of tissue culture is saved, the operation steps are reduced, the excellent properties of original balls are preserved, and the breeding method can be applied to industrial efficient breeding of saffron. The breeding method provides technical support for the development of saffron industry.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Breeding method for disease-resistant and heat-resistant capsicum annuum L. rootstocks of different physiological races
InactiveCN103843592ASpeed up the process of resistance breedingImprove traitsHorticultureDiseaseAnimal science
The invention discloses a breeding method for disease-resistant and heat-resistant capsicum annuum L. rootstocks of different physiological races. According to the method, the advantages of capsicum annuum L. heterosis breeding and grafting technologies are integrated, and the disease resistance and the heat resistance of varieties with excellent comprehensive characters but poorer disease resistance and heat resistance can be remarkably improved by the bred disease-resistant and heat-resistant capsicum annuum L. rootstocks; the method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, breeding time saving, low breeding cost and the like; by the method for improving the disease resistance and the heat resistance of excellent varieties by breeding the rootstocks, the resistance breeding process of capsicum annuum L. is greatly accelerated.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
SSR markers linked with resistance genes Bs_t of physiological races No. 0 and No. 1 of tobacco black shank and applications thereof
ActiveCN107619881ALow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseBiotechnology
The invention discloses SSR markers linked with resistance genes Bs_t of physiological races No. 0 and No. 1 of tobacco black shank and applications thereof. The SSR markers linked with resistance genes Bs_t of physiological races No. 0 and No. 1 of tobacco black shank are numbered as TM51207 and TM55805, and nucleotide sequences of amplified products of the SSR markers are shown as SEQ ID No. 1,SEQ ID No. 2, SEQ ID No. 3 and SEQ ID No. 4 respectively. The applications refer to applications of the SSR markers linked with resistance genes Bs_t of physiological races No. 0 and No. 1 of tobaccoblack shank in detecting whether resistance genes Bs_t of physiological races No. 0 and No. 1 of tobacco black shank exist in tobacco genomic DNA. The SSR markers disclosed by the invention have the characteristics of being stable, reliable, simple and convenient, rapid and low in cost, and therefore, the molecular markers can be applied as a molecular marker-assisted selection of Bs_t genes in breeding for disease resistance of tobacco black shank (physiological races No. 0 and No. 1).
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Detection primer for banana wilt germina number-four biological strain and method for detecting same
InactiveCN101113467ASpecific detectionSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesLesser floricanBiology
The invention relates to the biological technical field and discloses a detection primer of plant pathogenic fungi and a detection method thereof. The invention adopts a special primer RF4 and optimizes action conditions to invent a PCR detection method for banana fusarium wilt physiological races (Race No. 4). The method can especially, sensitively and effectively detect banana fusarium wilt physiological races (Race No. 4) and mycelium even weighting 0.1 Mug can be detected and pathogen can even be detected from the root and the stem of bananas by adopting the method.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for partitioning germ microspecies of bacterial leaf spot of paddy rice
InactiveCN1695434ASurvey data is accurateSurvey data is reliableRice cultivationDiseaseLesser florican
A method for dividing the bacterial blight strain of rice into microspecies by using the 6 subisopolar gene lines of known disease-resistant genes is disclosed. In the booting stage of rice, the bacterial suspension is inoculated to the leaf on the master stem of rice. The longth of disease spot and the length of whole leaf are respectively measured in 2 weeks and 3 weeks. If the length of disease spot is less than 0.25 times that of whole leaf, it is a disease-resistant plant (R). Otherwise, it is a disease-infectious plant(s). 6 varieties of rice are experimented in the interaction mode of 9 micropecies (R1-R9) to obtain the relative microspecies of bacterial blight strain.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
New wheat stripe rust resisting polygene-polymerized flower-nurture breeding method
InactiveCN101558735AWide resistanceResistance spectrum widthHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureHigh resistanceLesser florican
The invention discloses a new wheat stripe rust resisting polygene-polymerized flower-nurture breeding method. Wheat-breeding parent materials with excellent agronomic characters are selected; 3 major micro-species of puccinia striiformis, which are recently popular, are used to evaluate stripe rust resistance of the wheat-breeding parent materials at seedling stage and adult stage; 3 wheat-breeding parent materials, which have high-resistance immunity to major popular individual micro-species of various puccinia striiformis, are sieved; the 3 wheat-breeding parent materials are hybridized and duplex hybridized to obtain duplex hybridized polygene-polymerized subsequent generation; the duplex hybridized subsequent generation is then cultured and wheat anther tissue is inoculated to one-step seeding culture medium of wheat anther, thereby obtaining complete pollen plant; chromosome doubling liquid with colchicines and dimethyl sulfoxide is injected to tillering node, thereby carrying out pollen plant chromosome doubling to obtain doubly purified individuals of doubled haploid which can be self-hybridized to form a stable doubled haploid system; and stripe rust resisting individual micro-species validation is carried out on the doubled haploid system, so as to obtain a new stripe rust resisting type or species system which is polymerized with 3 stripe rust resisting genes.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Cultivation method for breeding small seed potatoes of virus-free potatoes though areoponics
ActiveCN110463453AGood seedling preservation rateSeedling growth is goodAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserClimate change adaptationLesser floricanNutrient solution
The invention relates to the technical field of soilless cultivation, and in particular to a cultivation method for breeding small seed potatoes of virus-free potatoes though areoponics. According tothe physiological basis of potato cultivation through aeroponic cultivation, the growth can be divided into six stages, and six formulas of suitable nutrient solutions are prepared according to the six growth stages; according to the method and technology involved in the invention, the requirements for external environment conditions of light, temperature, water, fertilizer and air at each growthstage of the potatoes obtained through the aeroponic cultivation are met, three latent traits of the potatoes of stem diversity, bud multiplicity and stem and leaf regeneration are sequentially induced into phenotypic fine traits, stolon promotion, tuber formation, potato pieces swelling and picking are continuous and ceaseless for 100 days or above for growth, 60 to 80 grains of qualified small seed potatoes with a yield of 10 g or above for a single plant are obtained, and the yield per mu of the aeroponic cultivation in a greenhouse is 450000 to 550000 grains; the production cost, storage resistance and preservation property of the potatoes obtained through the aeroponic cultivation are similar to or slightly lower than that of substrate potatoes, and the survival rate of seedlings andthe growth potential at a seedling stage are better than that of the substrate potatoes; the technological achievements of the invention achieve the purposes of the practical promotion and applicationof large-scale production.
Owner:姜润田
Method for identifying phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains
PendingCN105177104ARapid identificationRace rapidMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a method for identifying phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains, and belongs to the technical field of plant pathogen identification. According to the method, a tissue culture vessel method is used for identifying the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains; the environment conditions of culture and impregnation are more stable; the growth of tobacco pathogens is favorably accelerated; the seedling culture period and the dip dyeing period are greatly shortened; meanwhile, the interference of infectious microbes and other physiological strains on the identification result can also be avoided; the flux is high; labor and materials can be saved to the greatest degree; the high-flux, fast and accurate identification on the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains is realized. Compared with a land method and a greenhouse method, the method has the advantages that the identification is fast; the result is more accurate, stable and reliable; higher application values are realized; meanwhile, a thought can also be provided for the identification of physiological strains of other disease pathogenic bacteria of tobaccos.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Crocus sativus production and processing method
ActiveCN109479656AIncrease productionImprove qualitySeed and root treatmentBulb cultivationCold treatmentLesser florican
The invention belongs to the technical field of crocus sativus cultivation and provides a crocus sativus production and processing method. The method is characterized by including steps: S1, selectinghealthy and plump crocus sativus bulbs lighter than 1g in weight, subjecting to cold treatment at 4-10 DEG C for 4-6 weeks, removing integuments, flushing with water for 1-5h, sterilizing, flushing for 3-5 times, and absorbing moisture to dry for standby application; S2, transplanting the crocus sativus bulbs outdoors in November in the last year, burying the bulbs underground by 8-10cm until thebulbs appear in May in the next year, digging out the crocus sativus bulbs, and placing in a shade place for 10 days; S3, from the early June to the late June, sequentially arranging the crocus sativus bulbs on a double-layer net rack according to two grades by a sorting device. The crocus sativus production and processing method has the advantage of high crocus sativus yield.
Owner:JIAXING VOCATIONAL TECHN COLLEGE
Rapid breeding method of seed of konjac
ActiveCN109429961ADegradation keepEfficient breedingFertilising methodsRoot crop cultivationApomixisLesser florican
The invention provides a rapid breeding method of the seed of konjac, namely a method for sexual reproduction through apomixis, thus the seed of konjac is a small bulb. The reproduction rate of konjacseed bulbs is not more than 5-7 times in the way of digging big and staying small and large bulb-cutting propagation. According to the rapid breeding method of the seed of konjac, a seed bulb can breed 800-1500 seed bulbs, and the reproduction ratio is close to 1500 times, so that the problem of low breeding coefficient and degradation of seed source in konjac industry is solved. The rapid breeding method of the seed of konjac has the advantages of high breeding efficiency, keeping seed character, preventing and controlling seed source degeneration, fast breeding of konjac bulbs for farmers to grow, thereby producing more konjac bulbs to meet the market needs.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV +1
Yunnan Oryza meyeriana Baill MeXB3 gene and application thereof
PendingCN106480073AIncrease resistanceImprove resistance to bacterial blightLigasesVector-based foreign material introductionDiseaseLesser florican
The invention relates to a Yunnan Oryza meyeriana Baill MeXB3 gene and application thereof to resistance to rice bacterial leaf blight and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. A cDNA sequence of the Yunnan Oryza meyeriana Baill MeXB3 gene is a DNA sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the Yunnan Oryza meyeriana Baill MeXB3 gene is cloned and identified in Yunnan Oryza meyeriana Baill. An encoded Yunnan Oryza meyeriana Baill MeXB3 gene comprises an amino acid sequence shown as EQ ID NO.2. The Yunnan Oryza meyeriana Baill MeXB3 gene and application thereof have the advantages that the Yunnan Oryza meyeriana Baill MeXB3 gene is cloned and identified, and an MeXB3 transgene plant; the Yunnan Oryza meyeriana Baill MeXB3 gene belongs to inducible expression in the Oryza meyeriana Baill; after identification of obtained transgenic materials, it is discovered that the Yunnan Oryza meyeriana Baill MeXB3 gene is capable of improving resistance of rice to part of Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae microspecies, so that resistance to rice bacterial leaf blight is enhanced, gene resources are provided for breeding for disease resistance, and the Yunnan Oryza meyeriana Baill MeXB3 gene is of great theoretical and practical significance to breeding of rice resistant to bacterial leaf blight.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所
Resistance induction method of watermelon fusarium oxysporum physiological race 2
ActiveCN110447413APromote growthPromote accumulationHorticulture methodsPlant protectionLesser floricanSheath blight
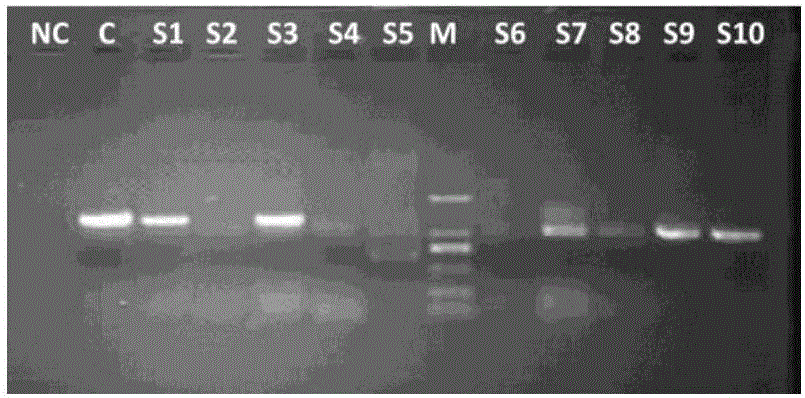
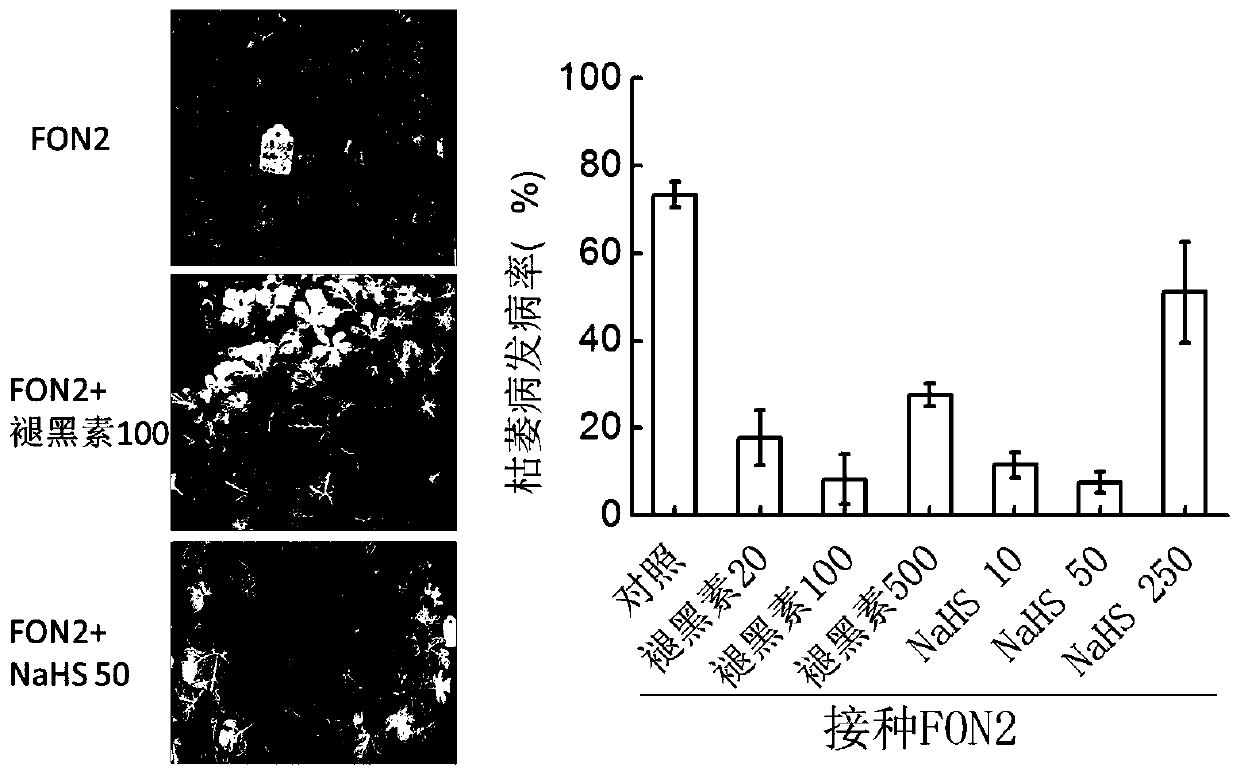
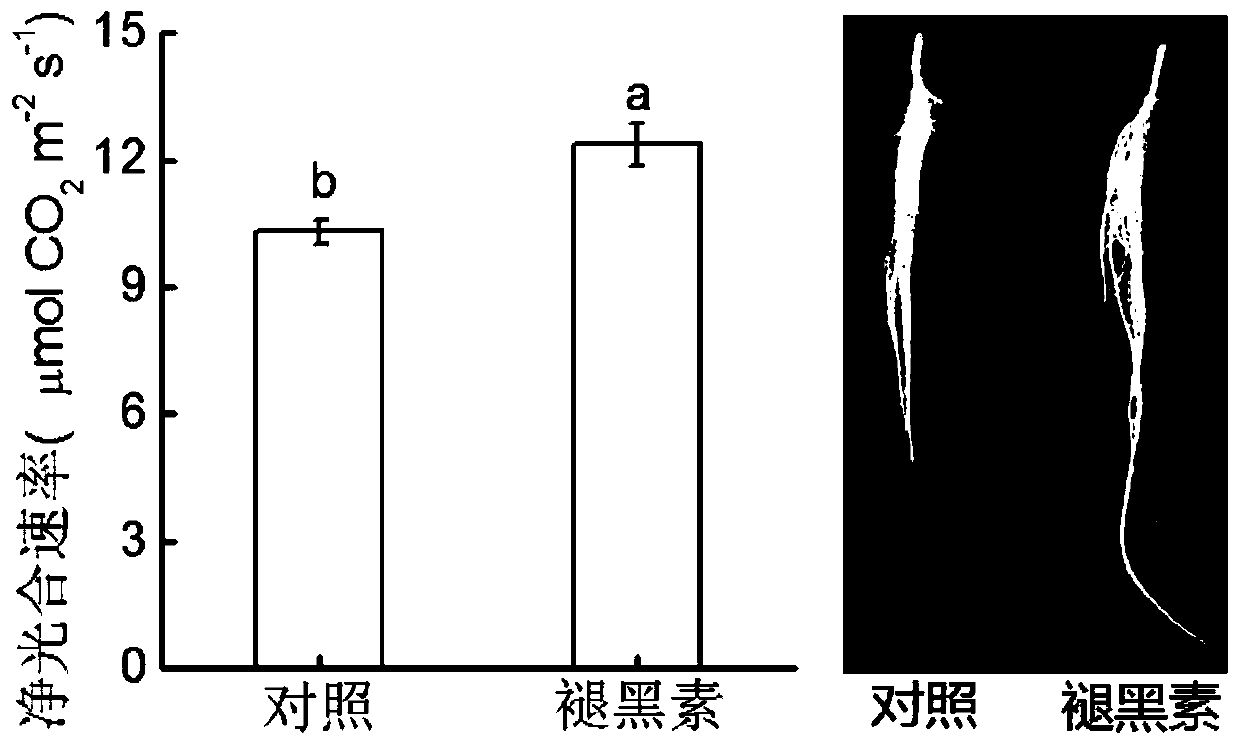
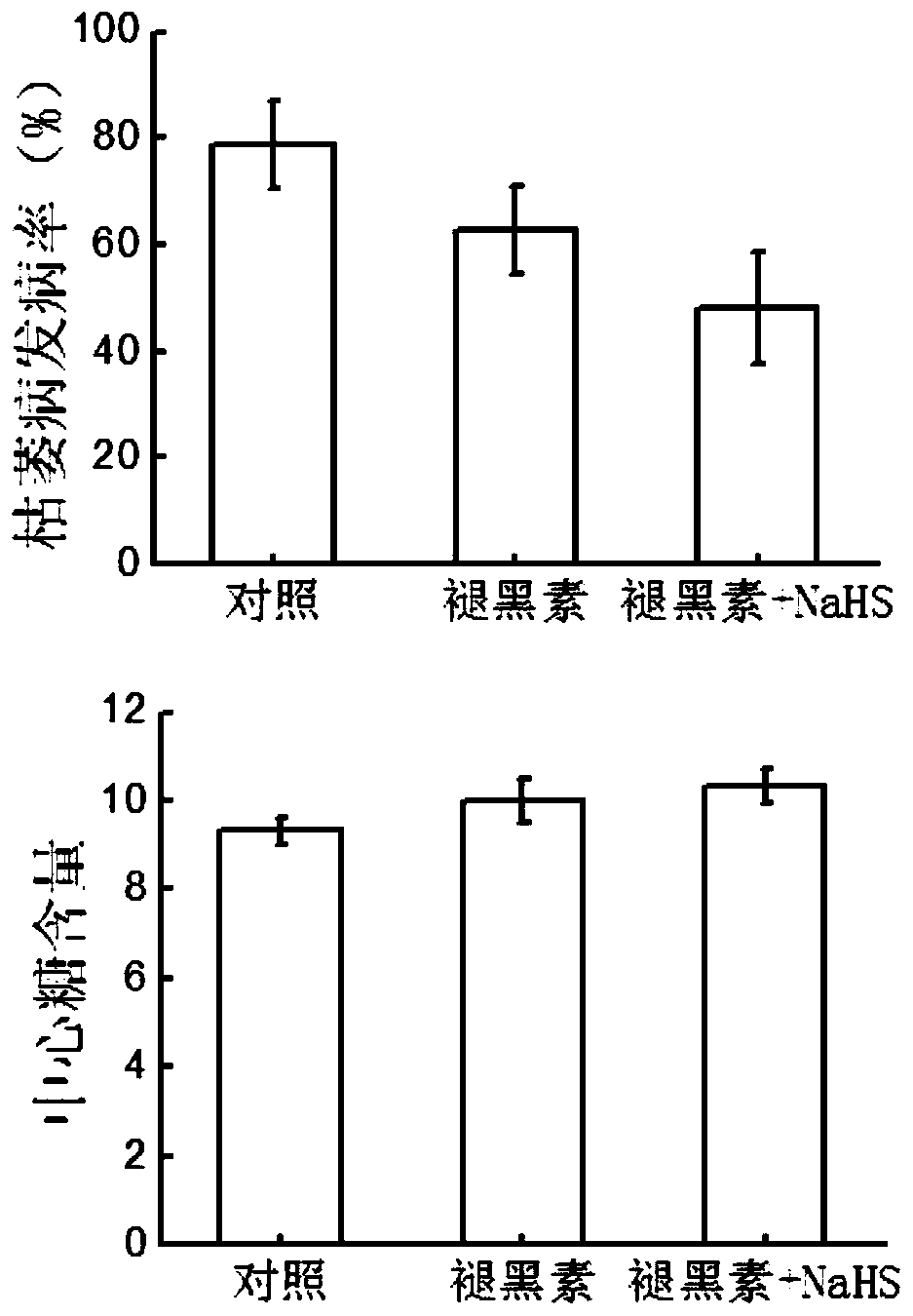
The invention discloses a resistance induction method of a watermelon fusarium oxysporum physiological race 2. According to the technology, a melatonin mixed solution with a proper concentration is mixed with NaHS for treatment and relieving of watermelon fusarium wilt caused by invasion of the watermelon fusarium oxysporum physiological race 2, wherein the treatment concentration of the melatoninmixed solution is 20-500 micromoles per liter, the treatment concentration of NaHS is 10-250 micromoles per liter, 0.3 L of the melatonin mixed solution is used for being sprayed on leaves of each plant, and 1 L of NaHS is applied to each plant for root irrigation. Melatonin can be easily decomposed by strong light, and therefore treatment is carried out at nightfall. According to the treatment time and frequency, treatment is conducted for the first time in the early stage of outbreak of fusarium wilt in the flowering and fruiting periods of watermelons, treatment is conducted for the secondtime after 5 days, and treatment is conducted for the third time after 12 days. Melatonin is a natural substances existing in plants and free of toxins and pollution, and NaHS releases H2S gas afterdecomposition and is easy to degrade and free of pollution. By mixing melatonin with the proper concentration with NaHS for treatment, the method has the three advantages of preventing watermelon fusarium wilt, promoting plant growth and being environmentally friendly and free of pollution, and is easy to widely use and popularize.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Inoculation method of Ustilago scitaminea
InactiveCN103190303AHigh incidenceEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementHorticulture methodsDiseaseSpore
The invention discloses an inoculation method of Ustilago scitaminea. The method includes the steps of inoculating Ustilago scitaminea spore suspension to the surface of sugarcane buds by spot inoculation and keeping in the wet place for 16-24h. The pore suspension is 106 / ml in concentration. During moisture preservation, the inoculated sugarcane buds are wrapped with humid tissue and are then placed at a shade place after being covered with plastic paper. The inoculation method is convenient to use, incidence rate of susceptible varieties is increased effectively, up to more than 80%, sense resistance of the different sugarcane varieties to Ustilago scitaminea can be distinguished effectively, and accordingly good conditions are created for the intensive study on breeding for disease resistance to Ustilago scitaminea and the study on physiological race differentiation.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
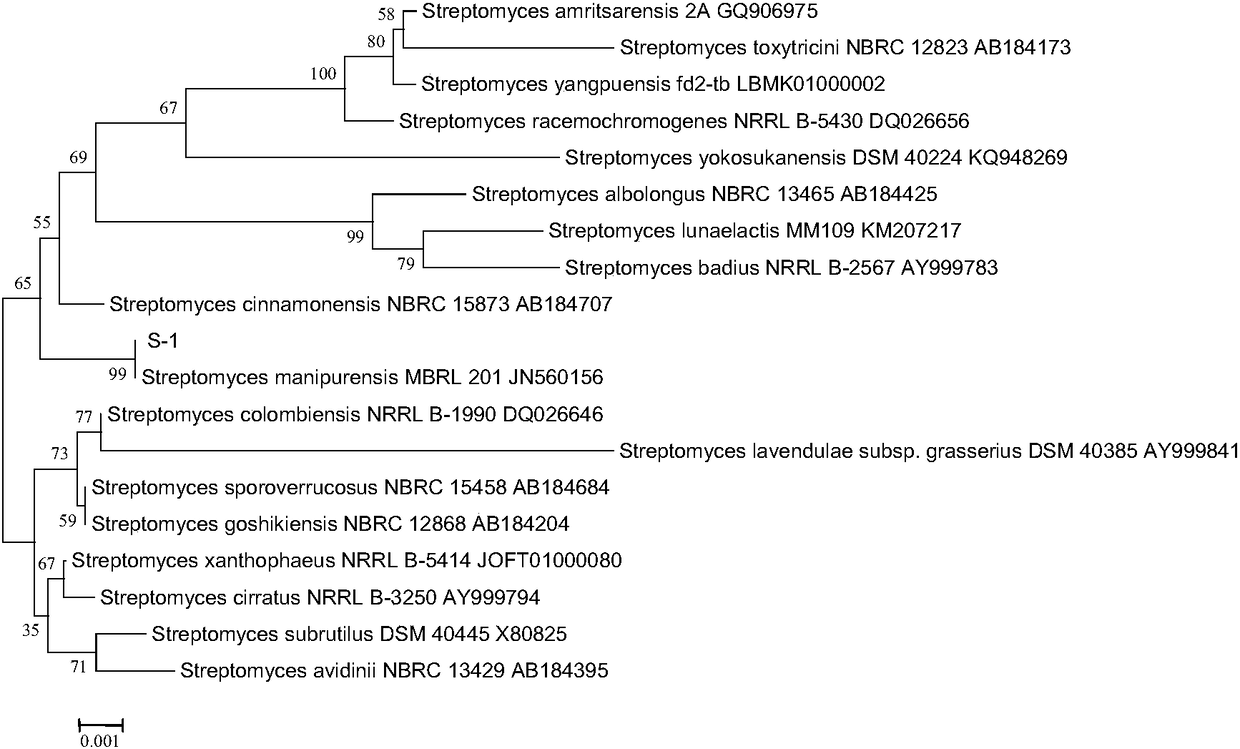
Actinomycetes and application thereof
The invention provides actinomycetes which is streptomyces manipurensis S-1 and is assigned the accession number CCTCC No: M2017261. The streptomyces manipurensis S-1 is 5.0-10.0 in growth pH range, preferably 7.0, and has optimum growth temperature of 28-32 DEG C and cannot grow on a culture medium being more than 3% in content of NaCl. The streptomyces manipurensis S-1 has an antagonism effect against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (FOC) race 1 and 4, and especially has significant antagonism effect against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (FOC) race 4. The streptomyces manipurensis S-1has extensive development space and has great development and application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH SUBTROPICAL CROPS RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Strain of streptomycete for preventing sheath blight of rice
Owner:成都川农邑邦农业发展有限公司
Breeding method for anti-G type orobanche coerulescens sunflower restoring line 1808R
InactiveCN108739354AHigh pathogenicityHigh anti-retinoid propertiesPlant genotype modificationOrobanche coerulescensSunflower material
The invention discloses a breeding method for an anti-G type orobanche coerulescens sunflower restoring line 1808R and relates to the technical field of plant genetic breeding. According to the breeding method disclosed by the invention, an oily sunflower material XR44R of G-type microspecies sunflower orobanche coerulescens and immune G-type orobanche coerulescens is utilized; an existing orobanche coerulescens sunflower material 3603R is improved by methods of hybridization transferring, backcross, selfing, a technology of identifying orobanche coerulescens resistance of sunflower by synchronous tracking and the like, and further a developed orobanche coerulescens-resisting (G-type microspecies) sunflower restoring line 1808R is cultured. The species has a good effect of resisting G-typeorobanche coerulescens and lays solid foundation for orobanche coerulescens-resisting breeding work of sunflowers in China.
Owner:ECONOMIC CROPS RES INST XINJIANG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for reducing incidence rate of susceptible varieties by mixed sowing with clubroot-resistant rape varieties
ActiveCN109197428AResistance maintenanceFortified Durable ResistanceLeaf crop cultivationPlant protectionLesser floricanDisease resistant
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural technologies, and specifically relates to a method for reducing the incidence rate of susceptible varieties by mixed sowing with clubroot-resistant rape varieties. The method for reducing the incidence rate of susceptible varieties by mixed sowing with clubroot-resistant rape varieties comprises the step of sowing at least one susceptible rape variety which is susceptible to at least one rape clubroot pathogenic physiological species and at least one clubroot-resistant rape variety which resists at least one rape clubroot pathogenic physiological species in a mixed manner. It is discovered by the inventor that good and bad conditions of various physiological species in the soil can be stabilized by mixed-sowing clubroot-resistant rape varieties and susceptible varieties in proportion, thereby ensuring the durable resistance of the varieties. In addition, the inhibition of the disease-resistant varieties to pathogens is utilized, thereby significantly reducing the incidence rate of the susceptible varieties, and ensuring the planting density of direct-seedling rape so as to stabilize the yield.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A kind of breeding method of heat-resistant capsicum rootstock of different physiological races resistant to blight
InactiveCN103843592BSpeed up the process of resistance breedingImprove traitsHorticultureDiseaseAnimal science
The invention discloses a breeding method for disease-resistant and heat-resistant capsicum annuum L. rootstocks of different physiological races. According to the method, the advantages of capsicum annuum L. heterosis breeding and grafting technologies are integrated, and the disease resistance and the heat resistance of varieties with excellent comprehensive characters but poorer disease resistance and heat resistance can be remarkably improved by the bred disease-resistant and heat-resistant capsicum annuum L. rootstocks; the method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, breeding time saving, low breeding cost and the like; by the method for improving the disease resistance and the heat resistance of excellent varieties by breeding the rootstocks, the resistance breeding process of capsicum annuum L. is greatly accelerated.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for separation and identification of kenaf root knot nematode
InactiveCN105145491AReduce interferenceMaintain wild-type propertiesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAgricultural scienceLesser florican
The invention provides a method for separation and identification of kenaf root knot nematode and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The technical scheme is that (1) classical morphological identification; (2) isozyme analysis and identification; (3) molecular biological identification: the PCR identification is performed through primers 5-GGTCAATGTTCAGAAATTTGTGG-3 and 5-TACCTTTGACCAATCACGCT-3, COll genes and lrRNA genes thereof located in mitochondrion DNAs are amplified, and sequences are subjected to comparative analysis and identification. The physiological race of the root knot nematode is made clear. The method integrates separation, purification and identification, a method of combining morphology, isozyme and molecular biology is adopted for identification and verification, the result shows that the molecular biological identification is high in efficiency and accuracy and suitable for field sampling fast separation, and the biological characteristics of insect body wild type population or the physiological race are identified.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
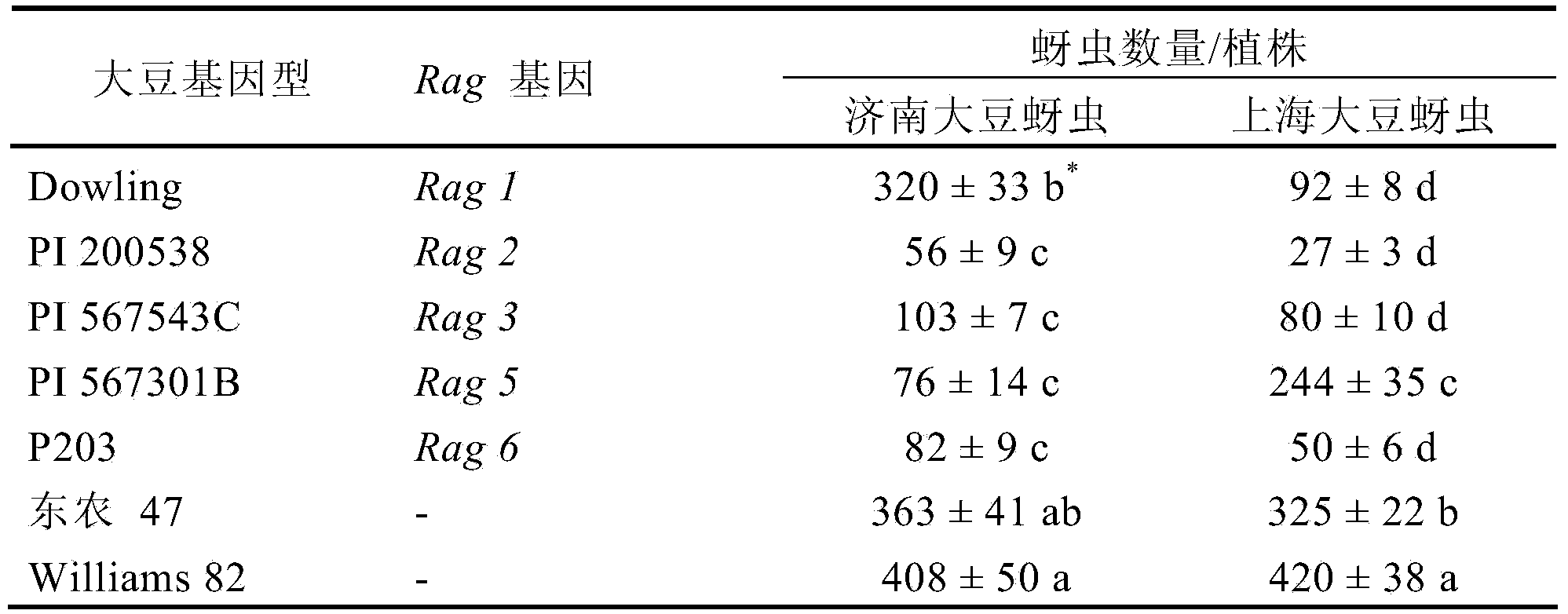
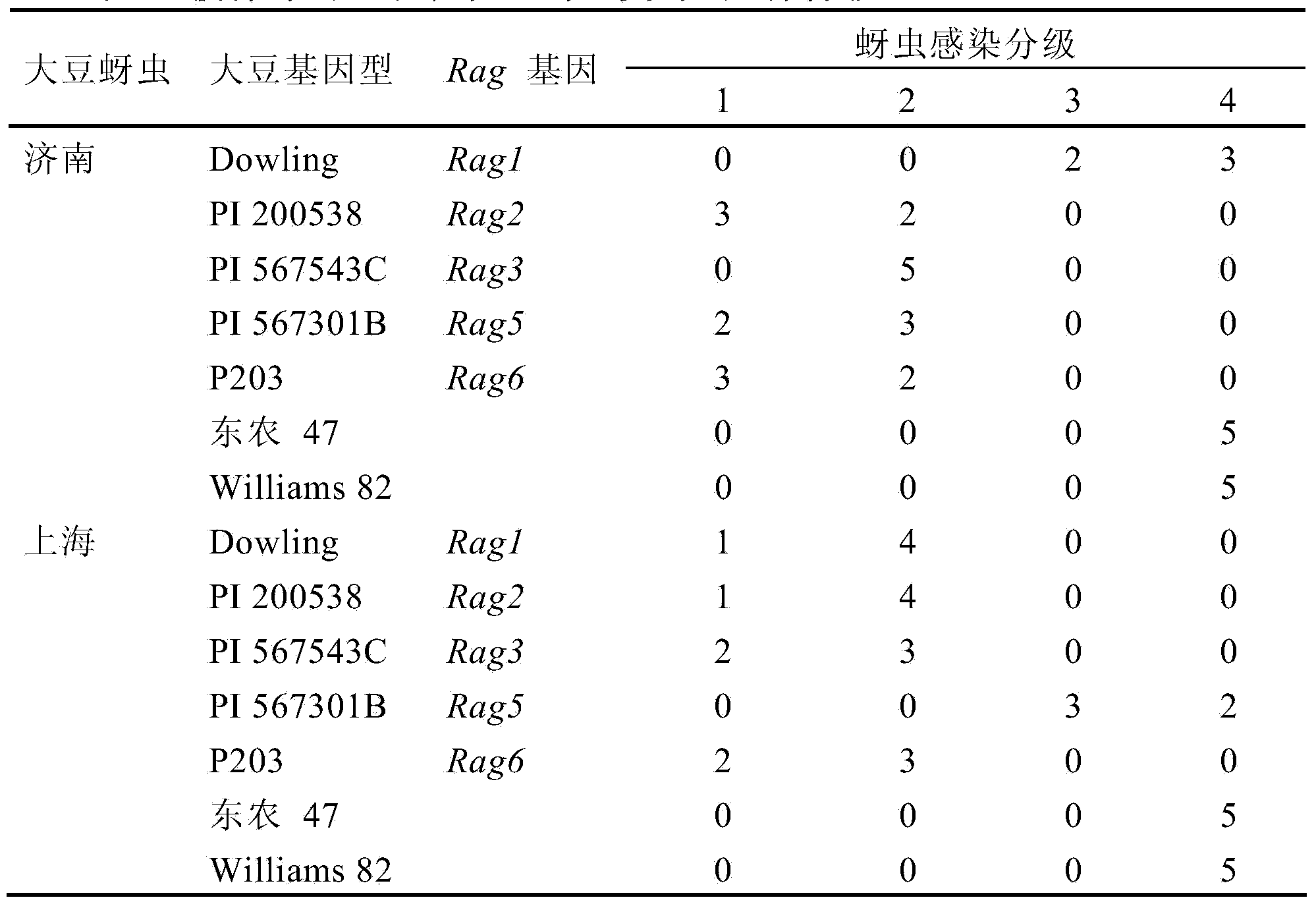
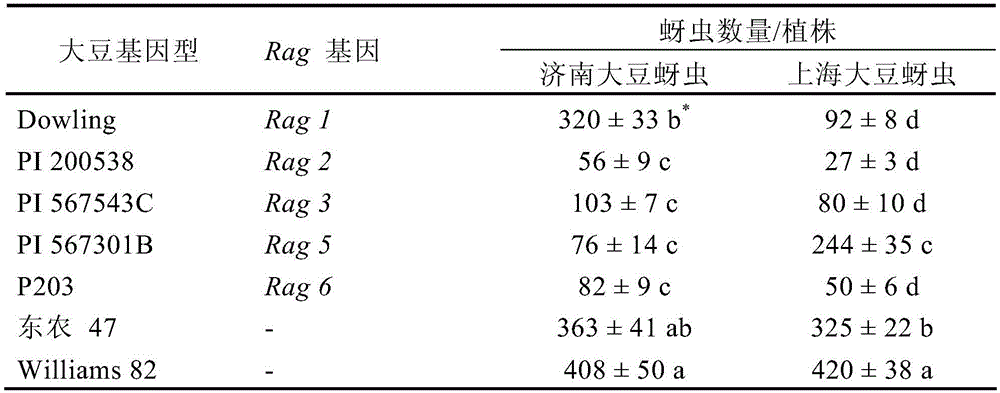
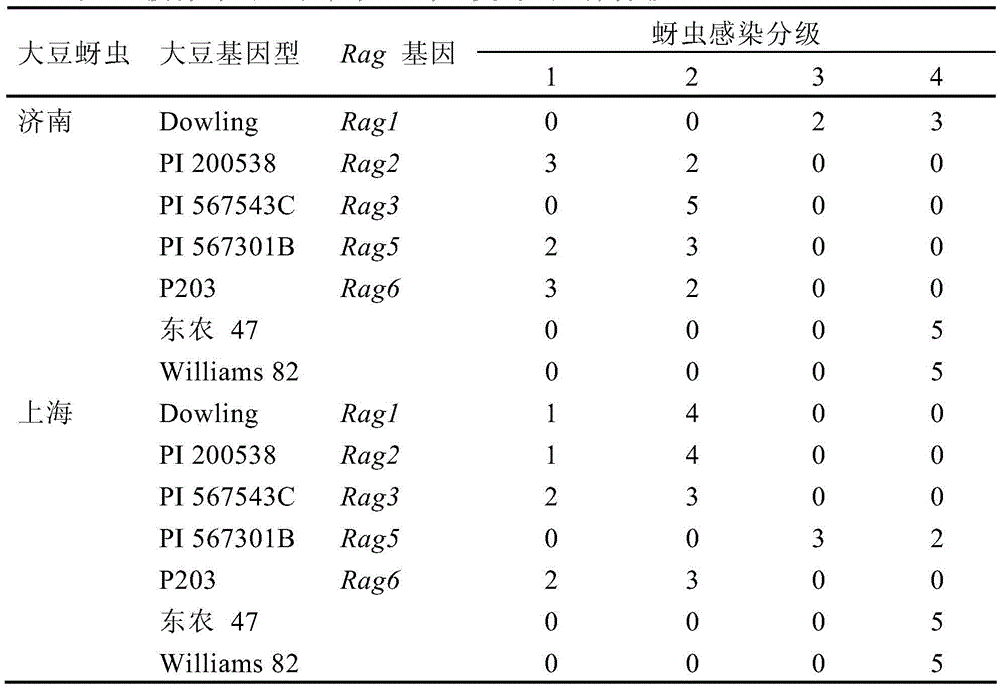
Method for identifying soybean aphid physiological races
InactiveCN103875607AEasy to operateAccurate and reliable identification resultsAnimal husbandryLesser floricanGreenhouse
The invention provides a method for identifying soybean aphid physiological races. The method for combining identification of the number of bred aphids with a differential host under a greenhouse condition and representation of plant diseases is adopted, the soybean aphid physiological races from different sources can be identified fast, targeted soybean aphid race resisting resource screening, new variety breeding and other studies are carried out, bases are provided for determining the target of comprehensive preventing and treating of the soybean aphids and aphid resisting breeding, and the identification method is fast and high in operability, and has good application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for breeding intermediate material with rice blast resistance
InactiveCN110432098AImprove screening efficiencyResourcesRice cultivationHigh resistanceLesser florican
The invention relates to a method for breeding an intermediate material with rice blast resistance. The method belongs to the technical field of rice genetic breeding design, and is characterized by including the following steps: (1) screening a plurality of different physiological races of rice blast in the same region; and (2) preforming gradient selection of rice blast resistance on the same material in different regions. Under the selection pressure of multiple physiological races of Magnaporthe grisea, the breeding intermediate material can obtain broad-spectrum high-resistance breeding material. The tested materials are planted in different regions, and local meteorological data are observed and recorded to screen out rice breeding material that can adapt to different disease pressures. Rice blast resistance screening is carried out by utilizing physiological races of rice blast in different regions and disease pressures in different regions, the efficiency of breeding intermediate material with rice blast resistance by breeders is improved, and the method has the advantages of rapidness, simplicity and economy.
Owner:JIANGSU COASTAL AREA AGRI SCI RES INST
Method for cultivating watermelon variety with high resistance to fusarium wilt
PendingCN110622852AStrong disease resistanceImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationHigh resistanceDisease
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a watermelon variety with high resistance to fusarium wilt. The method comprises the following steps: taking a breeding material A of a physiological race 1 with high resistance to fusarium wilt of watermelons as a donor parent, taking a breeding material B of a disease-sensitive high-quality material as a recurrent parent for hybridization, continuously backcrossing for 4 generations, then carrying out selfing, and selecting homozygous disease-resistant genotype plants for keeping selfing until homozygous disease-resistant genotype inbred linesare obtained. DNA is extracted from each backcross generation and self-bred offspring at one-leaf and one-core stage of a seedling, screening is carried out by using an Indell-fon1 marker, hybrid disease-resistant genotype plants are selected and planted in a fusarium wilt disease nursery for disease nursery screening, and single plant seed collection of plants with good growth state and agronomic characters close to recurrent parents is selected. According to the method disclosed by the invention, 'nursery-separation double-selection' is adopted, double screening is carried out by a method of combining molecular markers with disease nursery screening, the breeding material obtained by the method is reliable, the incidence rate of the fusarium wilt of the breeding material can be controlled at 20% or below, and accurate breeding of the watermelon variety resistant to the fusarium wilt is realized.
Owner:黑龙江省农业科学院园艺分院
A method for identifying physiological races of soybean aphids
InactiveCN103875607BEasy to operateAccurate and reliable identification resultsAnimal husbandryLesser floricanGreenhouse
The invention provides a method for identifying soybean aphid physiological races. The method for combining identification of the number of bred aphids with a differential host under a greenhouse condition and representation of plant diseases is adopted, the soybean aphid physiological races from different sources can be identified fast, targeted soybean aphid race resisting resource screening, new variety breeding and other studies are carried out, bases are provided for determining the target of comprehensive preventing and treating of the soybean aphids and aphid resisting breeding, and the identification method is fast and high in operability, and has good application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Detection primer for banana wilt germina number-four biological strain and method for detecting same
InactiveCN100588716CSpecific detectionSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesLesser floricanBiology
The invention relates to the biological technical field and discloses a detection primer of plant pathogenic fungi and a detection method thereof. The invention adopts a special primer RF4 and optimizes action conditions to invent a PCR detection method for banana fusarium wilt physiological races (Race No. 4). The method can especially, sensitively and effectively detect banana fusarium wilt physiological races (Race No. 4) and mycelium even weighting 0.1 Mug can be detected and pathogen can even be detected from the root and the stem of bananas by adopting the method.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for Quantitative Detection of Banana Fusarium wilt Race 4 from Soil
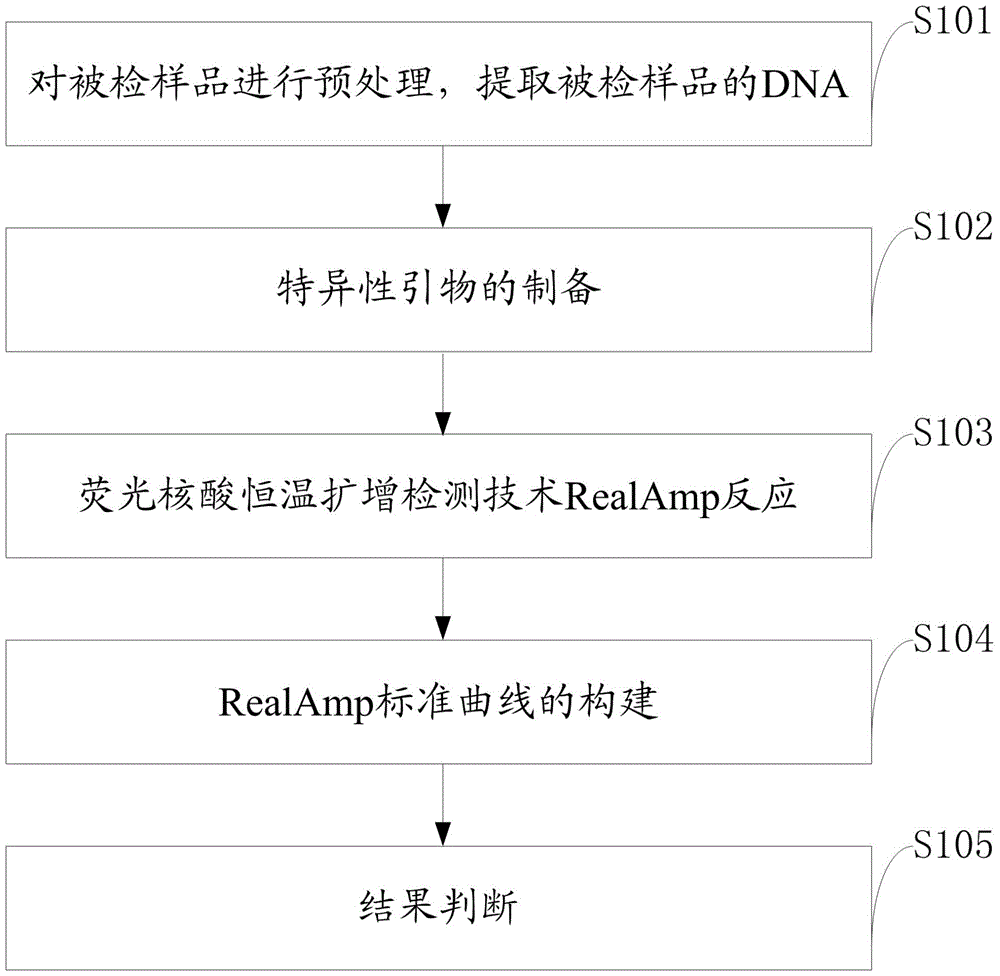
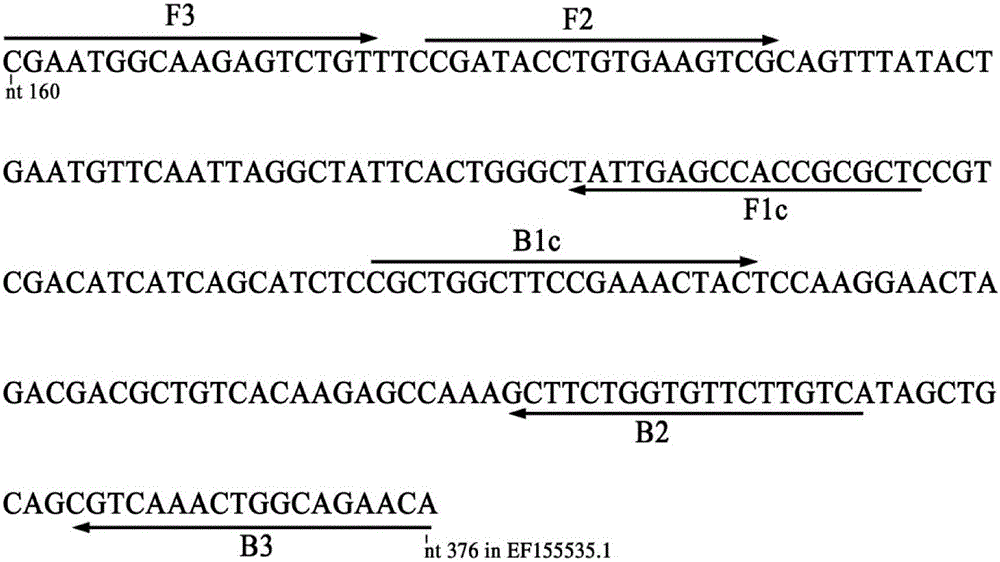
InactiveCN103757093BImprove toleranceCapable of chain displacementMicrobiological testing/measurementLesser floricanFluorescence
The invention discloses a quantitative detection method for FOC (Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (E.F. Smith) Snyd. & Hans.) race 4 from the soil. The method comprises the following steps: pretreating a sample to be detected and extracting DNA of the sample to be detected; preparing specific primers; conducting fluorescent nucleic acid isothermal amplification detection technique RealAmp reaction; constructing a RealAmp standard curve; and determining the result. The real-time fluorescent nucleic acid isothermal amplification detection technology provided by the invention is a novel nucleic acid detection technology combining a new generation of isothermal nucleic acid amplification technology with the real-time fluorescent detection technology, and has the advantages of high sensitivity, high specificity, low pollution and stable reaction. RealAmp can quantitatively detect pathogens; because of the characteristics of LAMP, Bst DNA polymerase has chain exchange capacity and good tolerance of inhibiting substances contained in the soil DNA extracts; the method carries out detection work on the soil, avoids cover opening and influence by contaminants and conducts on-site soil sample detection; the method for analysis and determination of reaction products is very simple; therefore, the method is suitable for wide application.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method for microbe gene clone
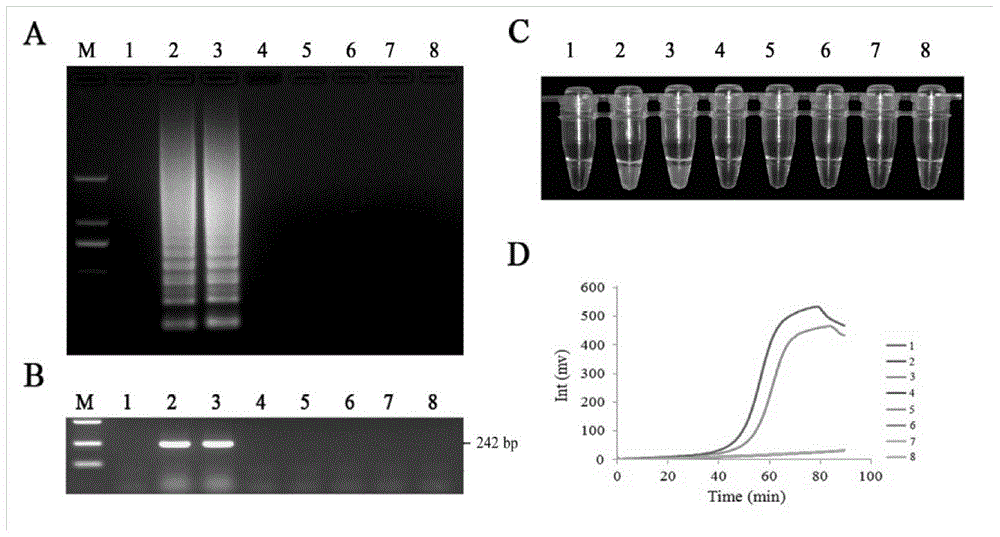
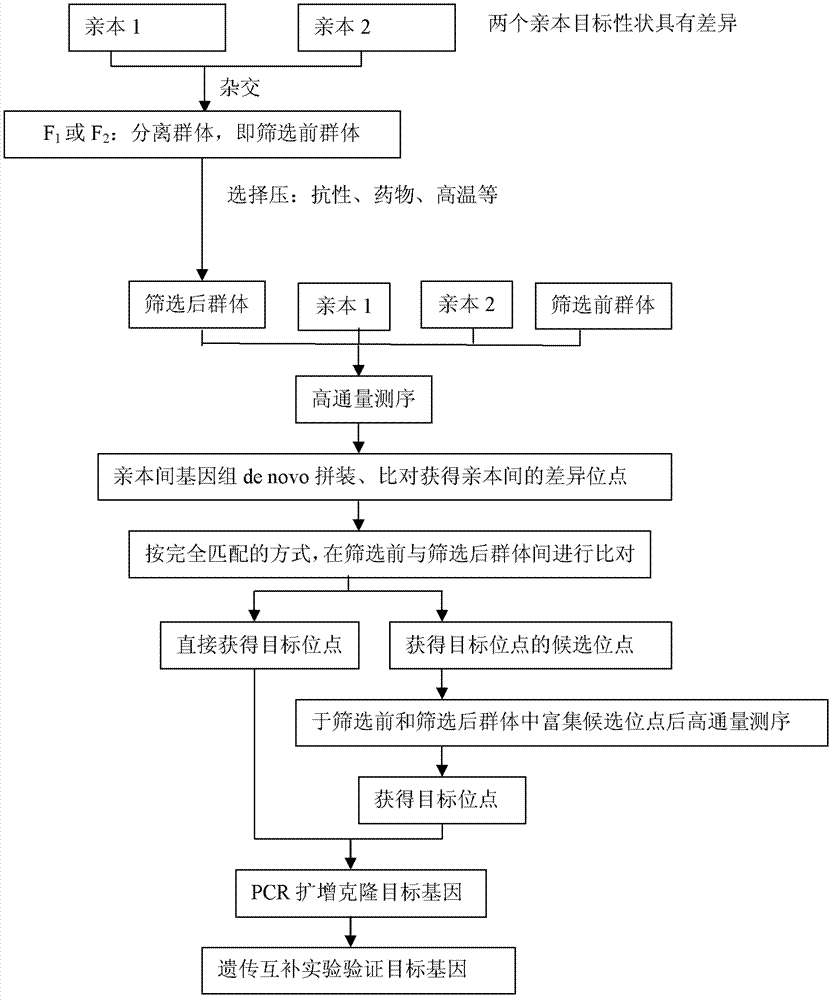
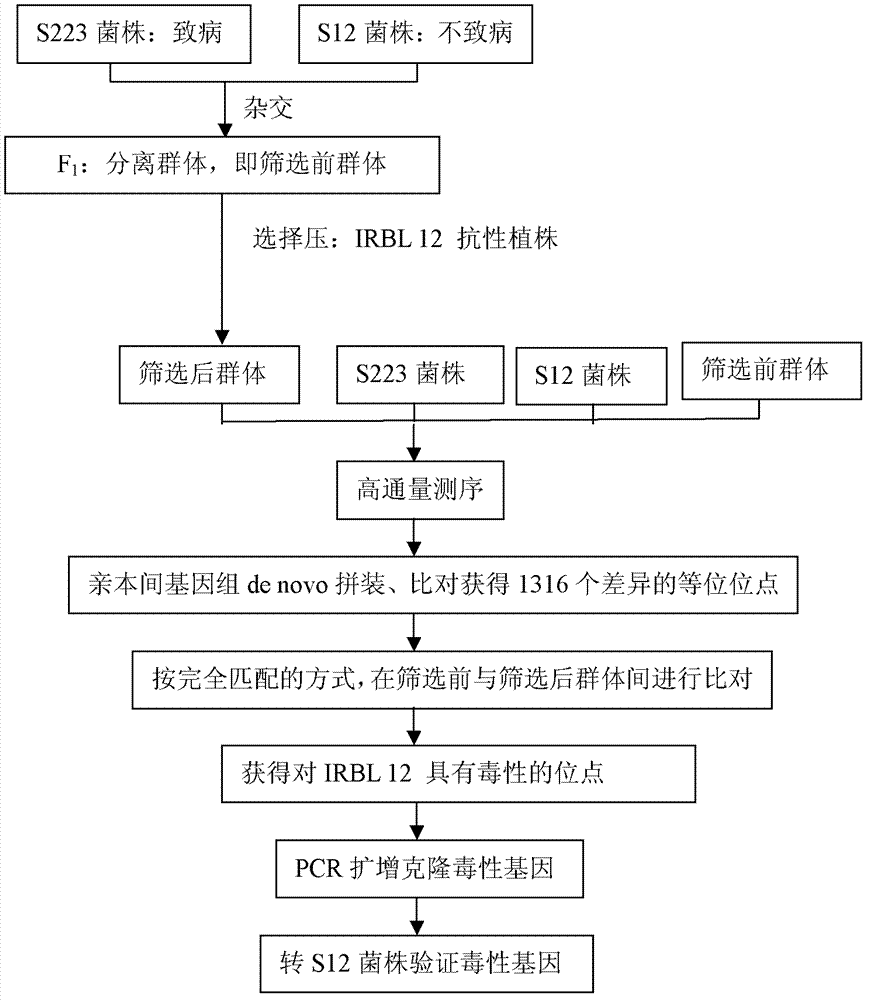
InactiveCN102899313AAvoid separabilityAvoid normal workMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationLesser floricanLower risk
The invention discloses a method for microbe gene clone. The method comprises the steps of constructing segregation populations by hybridizing parents having target character differences; automatically screening the segregation populations by setting a selection pressure to obtain screened populations; high-throughput genome sequencing of the two parents, populations before screening and populations after screening; obtaining specific loci of the parents by preliminary direct assembly and comparison; comparing the specific loci of the parents with the genomes of the populations before screening and the populations after screening in a completely matching mode; looking for loci which exists in the parents and the populations before screening but disappears in the populations after screening, wherein the loci are candidate gene loci for controlling target characters; obtain full-length sequence of the genes by comparing with the genomes of the parents; cloning target genes via PCR amplification; and verifying functions of the cloned target genes via genetic complementary experiments. The method directly clones genes themselves, and reduces a lot of microspecies isolation and identification work of the microbes. The method has little workload, fast speed and low risk.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
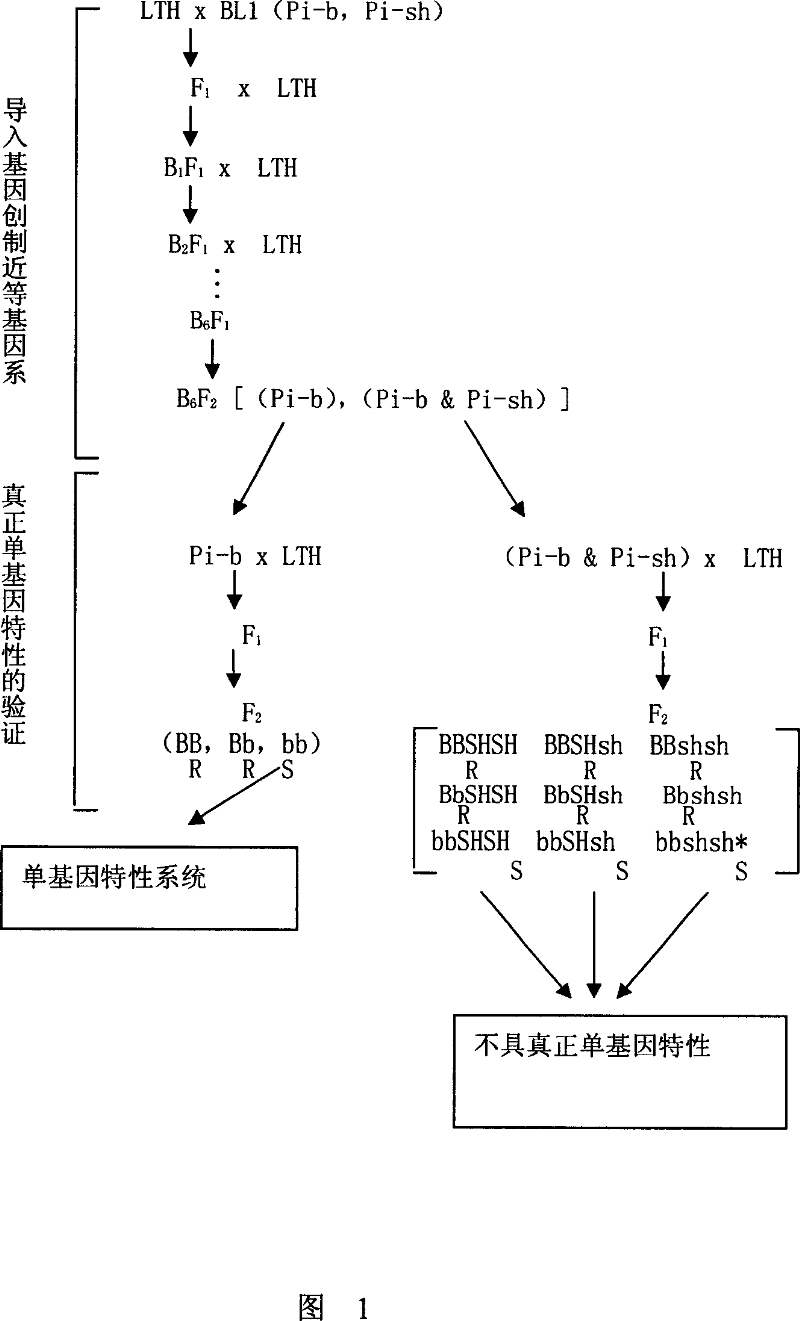
Physiological microspecies monogenically identifying system for rice blast germ and its construction process
InactiveCN100353832CAvoid interactionGuaranteed true monogenic propertiesPlant genotype modificationLesser floricanAgricultural science
The present invention aims at provides one kind of physiological microspecies monogenically identifying system for rice blast germ with high identification capacity and wide applicable range and its culture method. The system is one monogenic near isogenic line cross bred with LTH as one local japonica rice variety without major disease resistant gene as recurrent parent and through cross breeding and backcross to introduce known disease resistant gene into LTH. The system constituting process includes cross breeding and backcross with LTH as recurrent parent to introduce known disease resistant gene into LTH and to obtain the near isogenic line; identifying and confirming the monogenic characteristic of the near isogenic line; and deciding the physiological microspecies discriminability of the near isogenic line and constituting new discrimination system. The monogenic near isogenic line is suitable for various rice producing areas in the world.
Owner:CROP BREEDING & CULTIVATING INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com