Physiological microspecies monogenically identifying system for rice blast germ and its construction process
A technology for physiological races and rice blast fungus, which is applied in the fields of plant genetic improvement, botanical equipment and methods, applications, etc., and can solve the problems of lack of true single-gene characteristic verification methods, such as the strength of single-gene system race discrimination.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
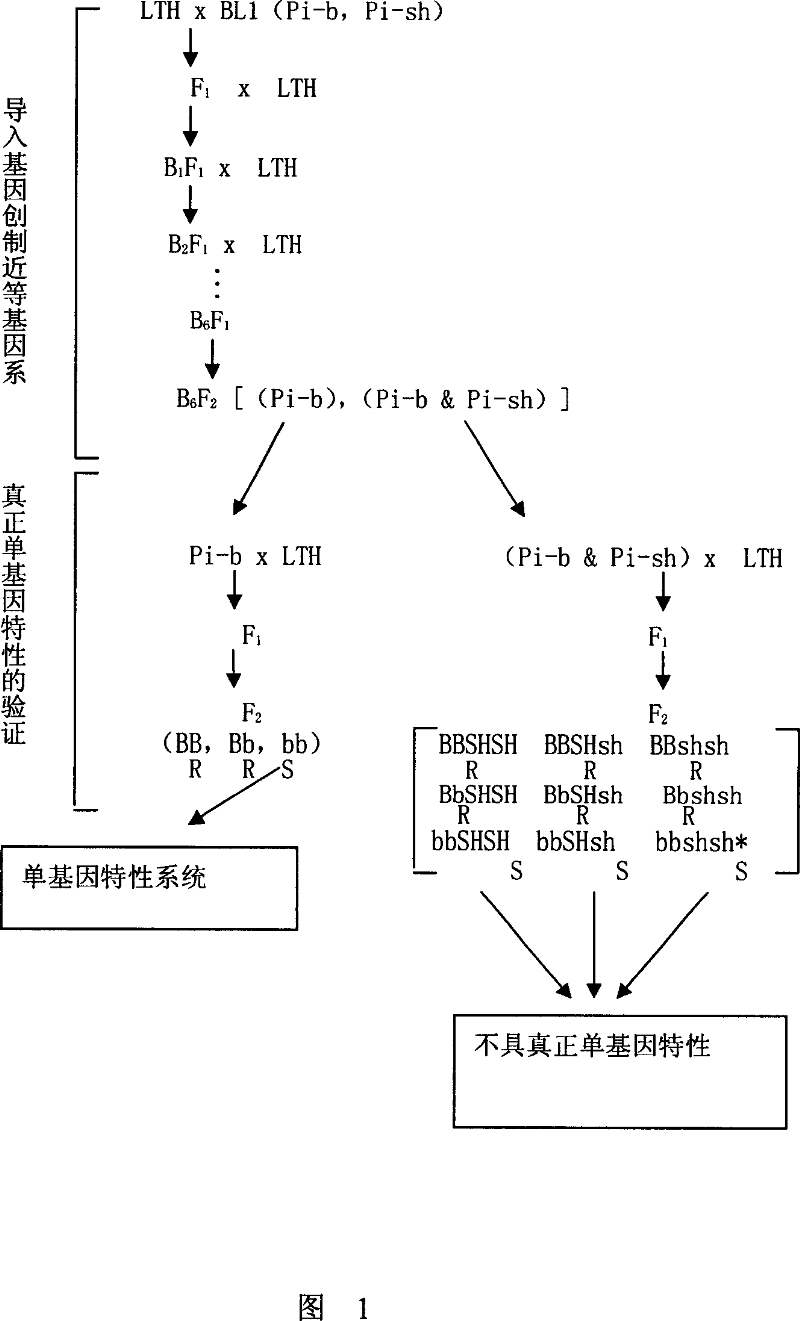
[0036] Embodiment 1: the cultivation of 6 single gene near isogenic lines
[0037] In 1987, LTH was used as the female parent, and the differential varieties Caodi (Pi-k, Pi-sh) and Meiyuming (Pi-k) with known disease resistance genes in Kiyosawa, Japan m , Pi-sh), K1 (Pi-ta, Pi-x), Pi4 (Pi-ta 2 , Pi-sh), K60 (Pi-k p , Pi-sh) and BL1 (Pi-b, Pi-sh) and other donor parents were crossed, and F was obtained in the spring of 1988 1 seed. In the summer of 1988, identification of F 1 Plants, select disease-resistant individuals as female parents, and backcross with LHT to obtain BC 1 f 1 seed. Since the winter of 1988, continuous backcrossing and resistance identification. Received BC in 1991 6 f 1 seed. Inbred in 1992 to obtain BC 6 f 2 seed. Plant BC of each combination in the same year 6 f 2 Seeds, harvested by individual plants BC 6 f 3 . Inoculation identification in 1993, screening out BC 6 f 3 There are 72 disease-resistant strains. In 1994, it was inocula...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: the verification of the gene composition analysis and single gene characteristic of 6 near isogenic lines (NILs) of the present invention
[0039] The resistance of 6 donor parents and 6 near-isogenic lines to Philippine isolates is as follows: 1. The donor parents show disease resistance, and the near-isogenic lines show disease resistance; 2. The donor parents show disease resistance 3. The donor parent showed a susceptible response, and the near-isogenic line showed a susceptible response. In all the combinations, the donor parents were never found to show disease-response, and the near-isogenic line showed disease-resistant response. It can be seen from the results that the six near-isogenic lines in China only express Pi-k, Pi-k m , Pi-ta, Pi-ta 2 、Pi-k p , and Pi-b resistance, while the 6 donor parents also showed the role of Pi-sh, or other disease resistance genes in addition to the role of these genes, so the resistance spectrum of the donor pa...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: Comparison with Donor Discrimination
[0042] Six near-isogenic lines and their six donor parents were inoculated with 42 strains from the Philippines, 25 strains from Japan and 100 strains from the japonica region of northern China. The results of race discrimination comparison are as follows:
[0043] Table 5. Comparison results of race discrimination
[0044] vaccination site
[0045] This result shows that the 6 near-isogenic lines and 6 donor parents of the present invention have the same physiological race discrimination ability for strain division in northern China and Japan. However, the ability of the 6 near-isogenic lines to identify the races of Magnaporthe grisea in the indica region was significantly higher than that of their donor parents.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com