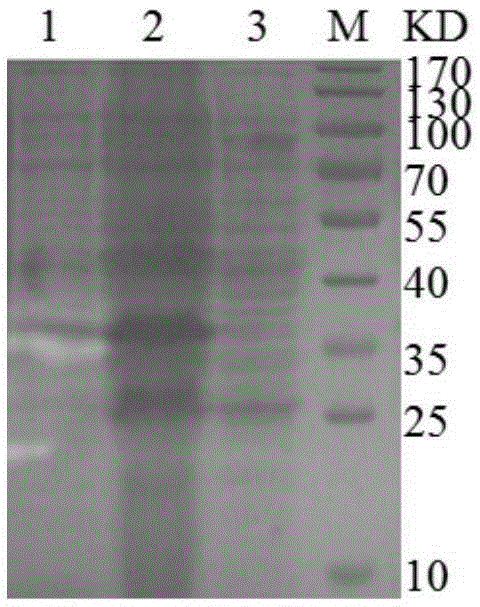
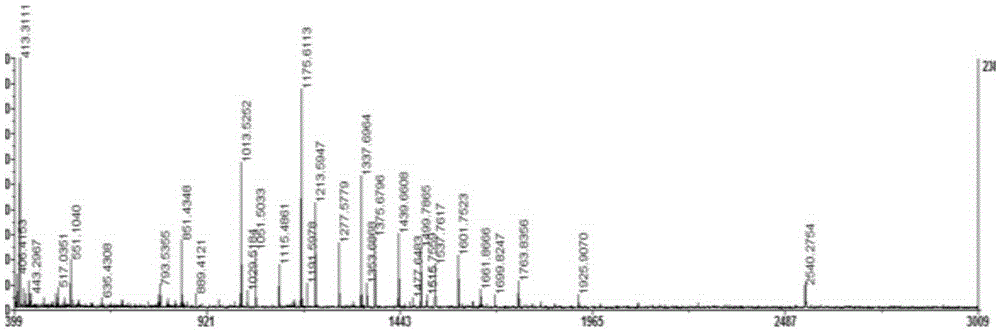
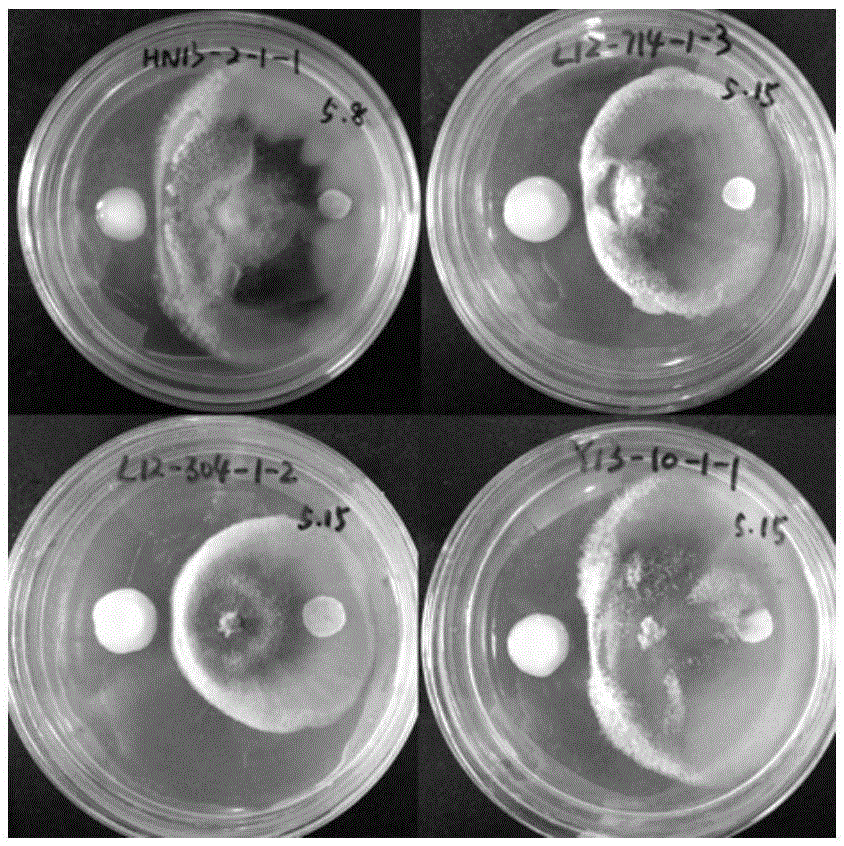
Patents
Literature
127 results about "Magnaporthe grisea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Magnaporthe grisea, also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, and Johnson spot, is a plant-pathogenic fungus that causes a serious disease affecting rice. It is now known that M. grisea consists of a cryptic species complex containing at least two biological species that have clear genetic differences and do not interbreed. Complex members isolated from Digitaria have been more narrowly defined as M. grisea. The remaining members of the complex isolated from rice and a variety of other hosts have been renamed Magnaporthe oryzae. Confusion on which of these two names to use for the rice blast pathogen remains, as both are now used by different authors.
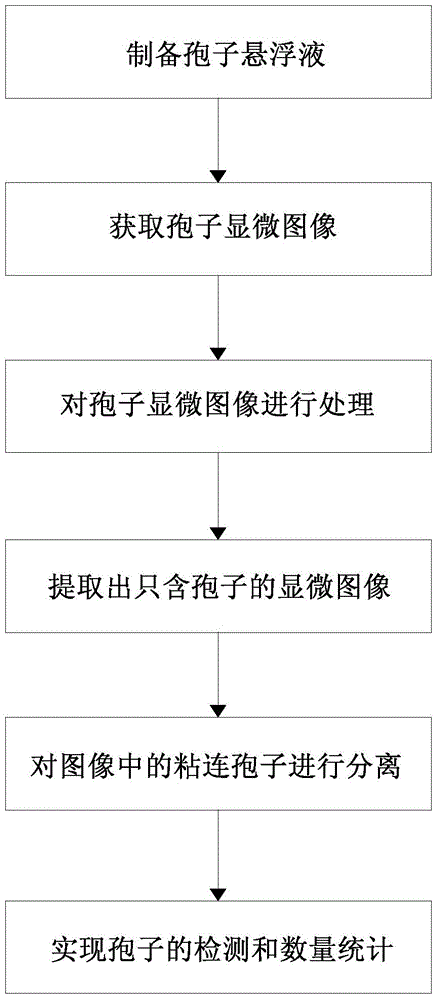
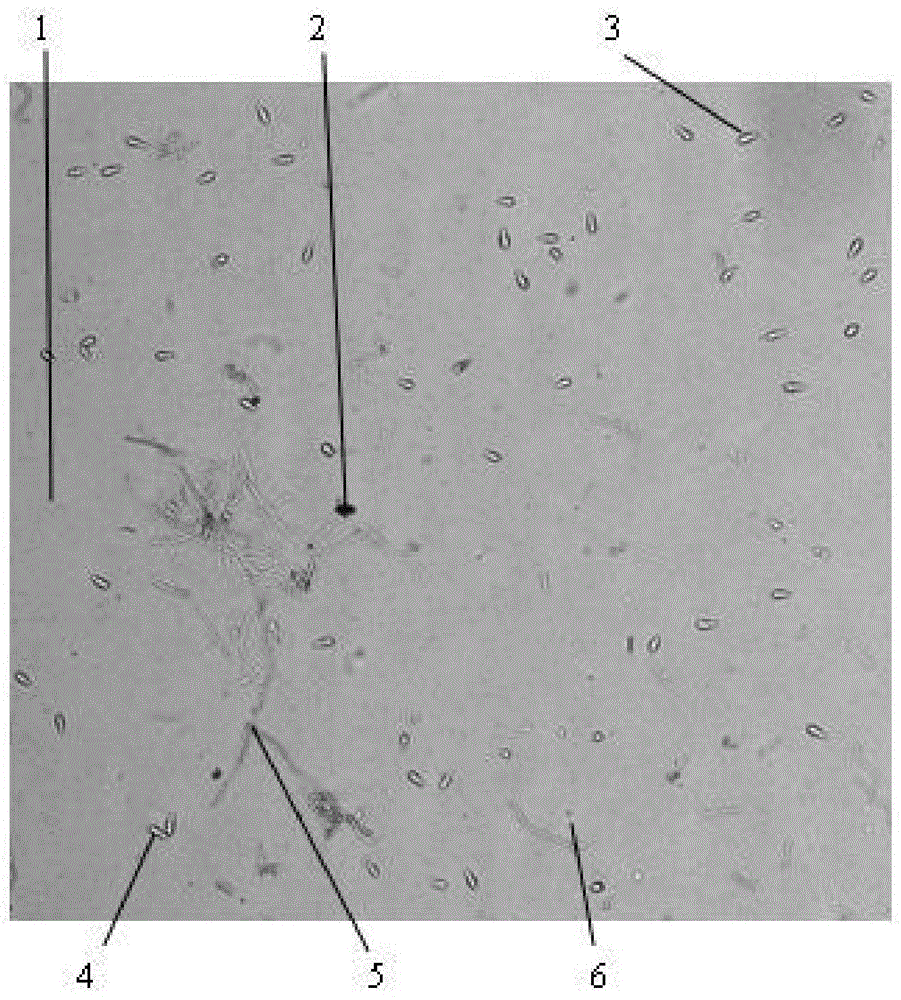
Method for detecting magnaporthe grisea spore based on microscopic image analysis
ActiveCN104651462AEffective segmentationSolve the problem that easily leads to wrong over-segmentationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPattern recognitionMicroscopic image
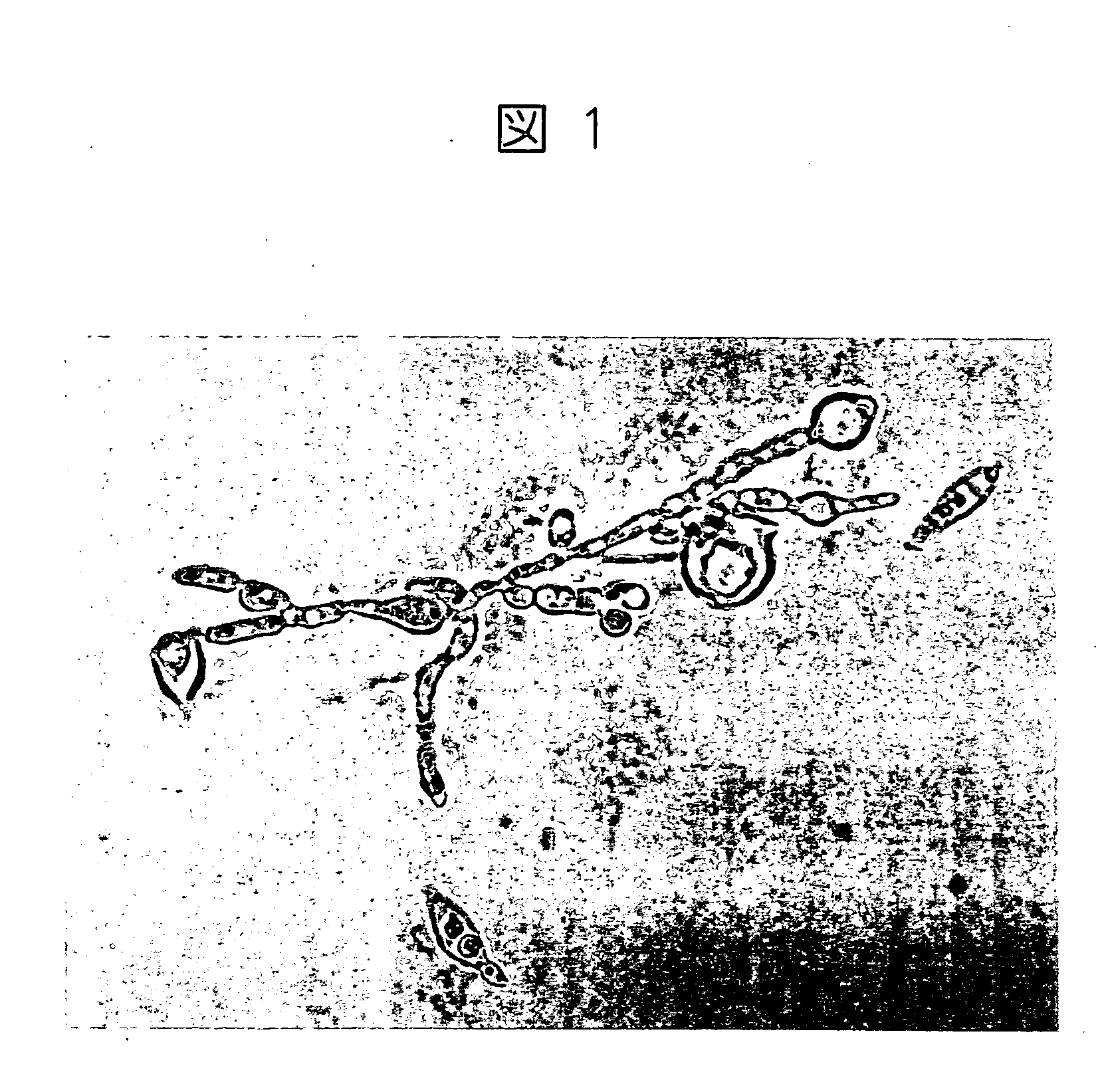
The invention discloses a method for detecting a magnaporthe grisea spore based on microscopic image analysis. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a spore microscopic image in the spore suspension solution by a magnaporthe grisea spore image detecting system; processing the spore microscopic image by using the image illumination adjustment, the median filtering, the edge detection and the morphological algorithm, and extracting a microscopic image containing the spore by combining with the shape characteristic parameters; separating the adhesion spores by using an improved watershed algorithm to realize the spore detection and quantitative statistics in the microscopic image. By adopting the method for detecting the magnaporthe grisea spore, the number of the magnaporthe grisea spore can be rapidly, accurately and automatically detected, the technical assistance for the indoor resistance identification of the magnaporthe grisea is provided and the technical reference for automatically monitoring the magnaporthe grisea in the fields is also provided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
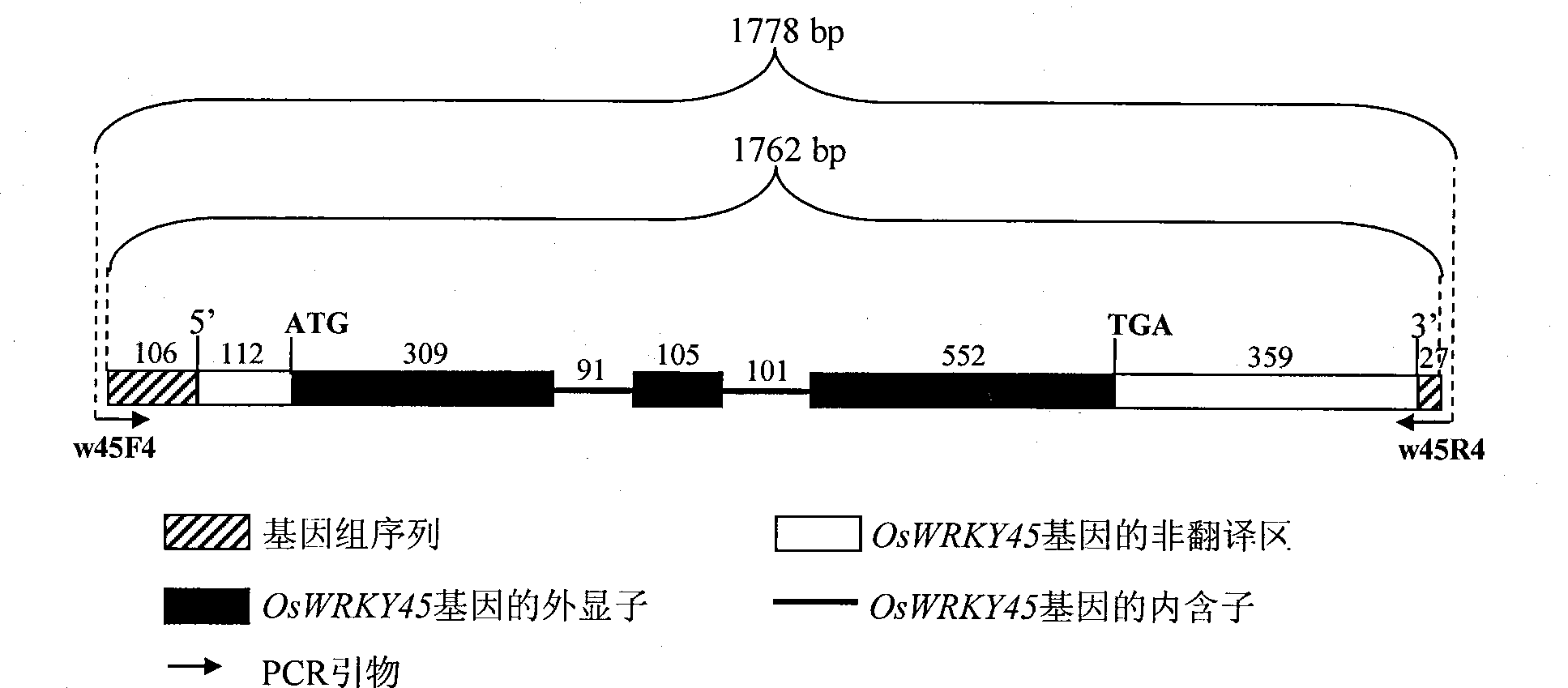
Rice disease resistance relevant gene OsWRKY45-2 and application thereof in improving rice disease resistance
InactiveCN101386856AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified ricePlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, in particular relates to isolating clone and functional verification of a DAN fragment containing a gene OsWRKY45-2 related to rice disease resistance. The gene OsWRKY45-2 codes WRKY proteinoids and can endow rice with resistance to the diseases caused by bacterial pathogenic bacteria, namely the leaf blight bacteria (Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae) and fungal pathogenic bacteria, namely the rice blast bacteria (Magnaporthe grisea). The fragment and the exogenous regulatory sequence thereof are directly transferred into rice, thus the resistance capability of transgenic rice with over-expression OsWRKY45-2 against bacterial blight in and rice blast is improved remarkably.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Application of biopesticide tetramycin in preventing and controlling Magnaporthe grisea
InactiveCN101632367AReduce manufacturing costImprove efficiencyBiocideFungicidesAlbonoursinPositive control
The invention discloses novel application of biopesticide tetramycin generated by Streptomyces ahygroscopicus subsp.Wuzhouensis n.subsp in preventing and controlling Magnaporthe grisea. The tetramycin is compound agricultural antibiotic, comprises tetramycin A1 and A2, albonoursin and flagecidin, and has a rate of preventing and controlling the apple canker of over 95 percent. Indoor and field experiments prove that tetramycin diluent (the ratio of the tetramycin to water is 1: 999) has better effect of preventing and controlling the Magnaporthe grisea than 4 percent kasugamicin waterable powder, 75 percent tricyclazole waterable powder and 25 percent prochloraz missible oil, and has administration lower than positive control remarkably. The tetramycin used can reduce agricultural production cost, improves prevention effect, can be alternately used with other biopesticides, reduces the generation of resistance, has good effect of preventing and controlling the Magnaporthe grisea, and no problems such as environmental pollution, pesticide residue and the like, belongs to the environment-friendly biopesticide, and has good development and application prospects.
Owner:辽宁省微生物科学研究院
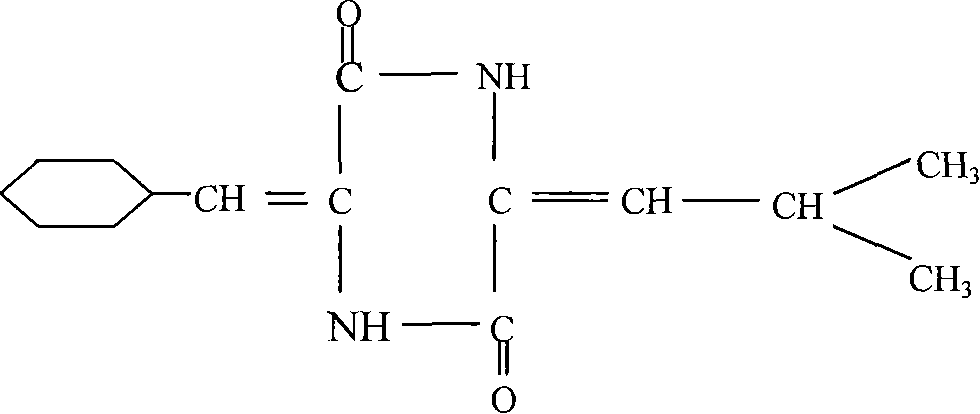
Trichodermin derivant and uses thereof
ActiveCN101429203ABiologically activeHigh activityBiocideOrganic chemistryFusarium oxysporumMagnaporthe grisea
The invention discloses a trichodermin derivative, and a structural general formula of the trichodermin derivative is shown as the right. The trichodermin derivative is used for killing plant pathogenic fungi such as Botrytis cinerea, Pythium ultinum Trow, fusarium, leafmold, Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium oxysporum, Magnaporthe grisea and so on.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DAYANG BIOTECH GROUP
Novel protein, genes encoding the same and method of using the same
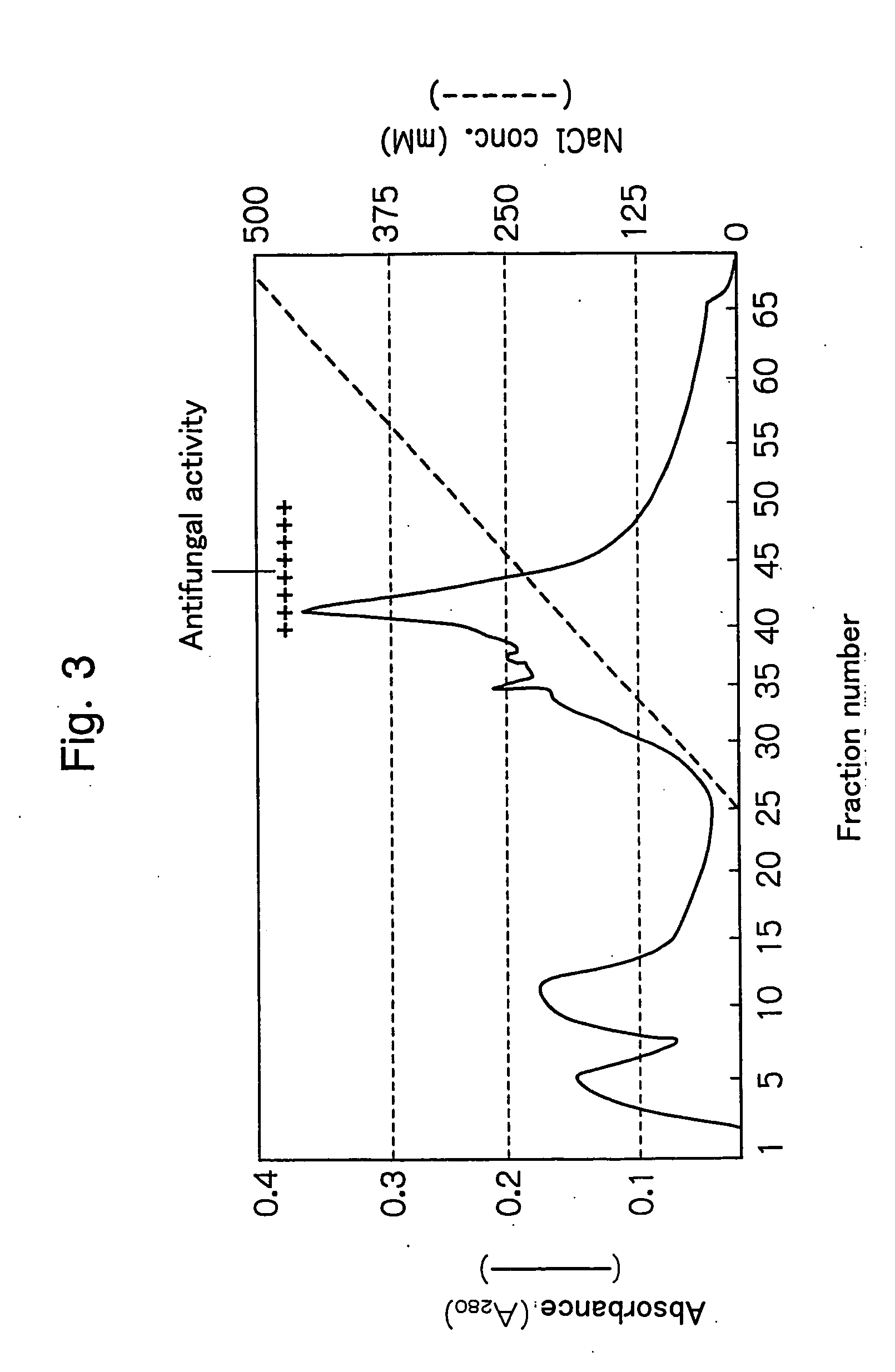
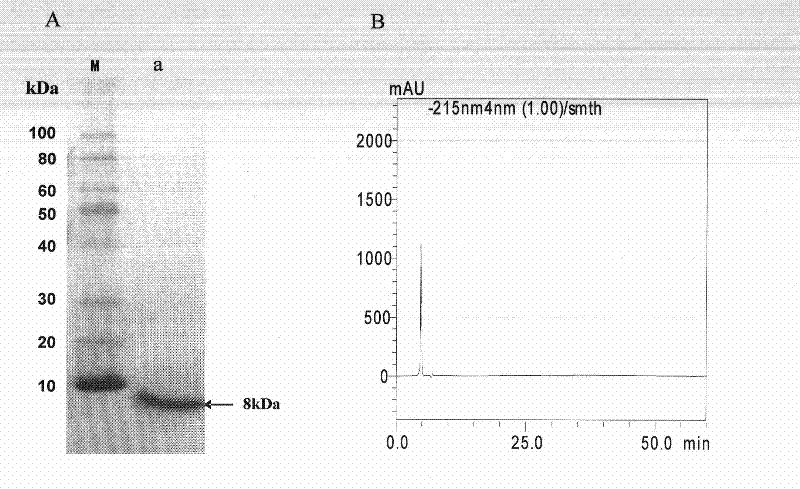
An object of the present invention is to search and identify novel antifungal proteins capable of inhibiting the growth of plant pathogenic microorganisms including Magnaporthe grisea and Rhizoctonia solani causing two major rice diseases at relatively low concentrations, and further to clone a gene for said protein. The present invention provides an antifungal protein which can be obtained from fraction(s) precipitated by ammonium sulfate precipitation using an aqueous extract from Pleurotus cornucopiae, wherein said protein has an antifungal activity against at least rice blast, and exhibits existence of a component having a molecular weight of about 15 kDa as determined by SDS-PAGE method; a gene encoding said protein and uses thereof.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
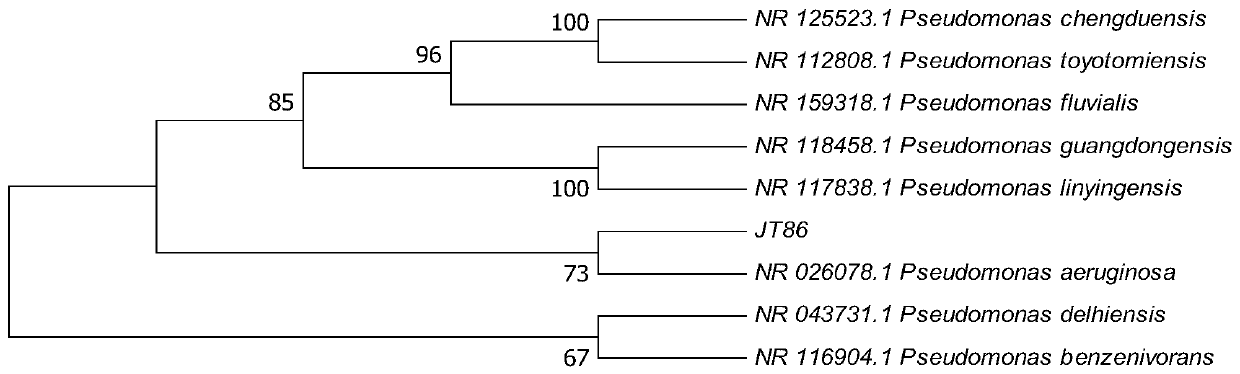
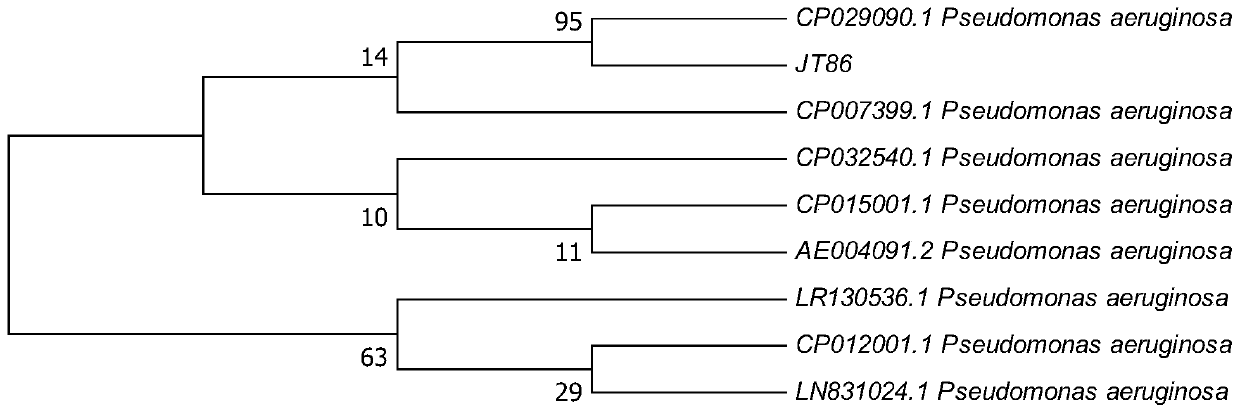
Pseudomonas aeruginosa JT86 and application of pseudomonas aeruginosa JT86 in prevention and treatment of sclerotiniose
The invention discloses pseudomonas aeruginosa JT86 and an application of the pseudomonas aeruginosa JT86 in prevention and treatment of sclerotiniose. The pseudomonas aeruginosa JT86 is screened fromsoil, and the strain is collected in the Guangdong Microbiological Culture Collection Center on September 30, 2019, and has a collection number of GDMCC NO:60799. The strain and a volatile matter thereof can completely inhibit sclerotium germination of rhizoctonia solani, sclerotium rolfsii and sclerotinia sclerotiorum and inhibit growth of sclerotium hyphae, so that the sclerotium hyphae have flakes and wrinkles; the strain also has a good inhibition effect on the rhizoctonia solani, the sclerotium rolfsii, the sclerotinia sclerotiorum, magnaporthe grisea, fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense,brassica parachinensis anthracnose, colletotrichum gloeosporioides and colletotrichum capsici; and therefore, the strain can treat recalcitrant soil-borne pathogenic bacteria in soil in a targeted manner, effectively inhibits the sclerotiniose, and has a good application prospect in preparation of a soil treatment agent for preventing and treating soil-borne fungal diseases.
Owner:海峡两岸农业科技股份有限公司
Primers for molecular detection of nontoxic genes of Magnaporthe grisea and application thereof
InactiveCN102534010AOvercome the disadvantages of laborious and laboriousStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMagnaporthe griseaMeloidogyne oryzae
The invention relates to primers for molecular detection of nontoxic genes of Magnaporthe grisea and a use method thereof, is used for rapid molecular detection of nontoxic genes Avrpik and Avrpizt of Magnaporthe grisea, and belongs to the fields of crop disease control and breeding for disease resistance. According to the invention, two pairs of primers Avrpik-F / R and Avrpizt-F / R are designed, and used for respectively detecting the nontoxic genes Avrpik and Avrpizt of Magnaporthe grisea, wherein the lengths of the specifically amplified DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) fragments are 184 bp and 153 bp respectively. The primers are suitable to be used for analyzing nontoxic gene composition of pure Magnaporthe grisea culture and Magnaporthe grisea colony from disease position.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
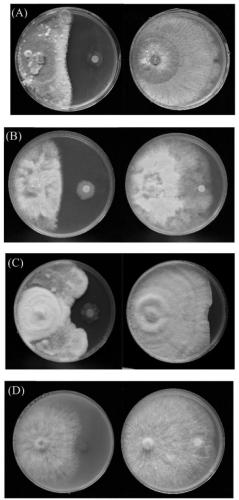
Goffer pseudomonas P94 and application thereof
InactiveCN101012443AIncrease productionGood preventive effectBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesPhospholipase
The invention discloses a new Pseudomonas corrugate strain (P94 GMCC No.1895), which is characterized by the following: manufacturing relative HCN to prevent bacteria, proteinase and phospholipase and IAA; inhibiting partial plant pathogenic fungus (Botrytis cinerea, Ceratocystis fimbriata, Monilinia laxa, Magnaporthe grisea, Pythium aphanidermatum and Phytophthora capsici) and partial pathogenic bacteria (Pseudomonas syringae, Acidovorax avenae and Ralstonia solanacearum); accelerating the growth of tomato and cucumber to improve production by 22%-28%.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
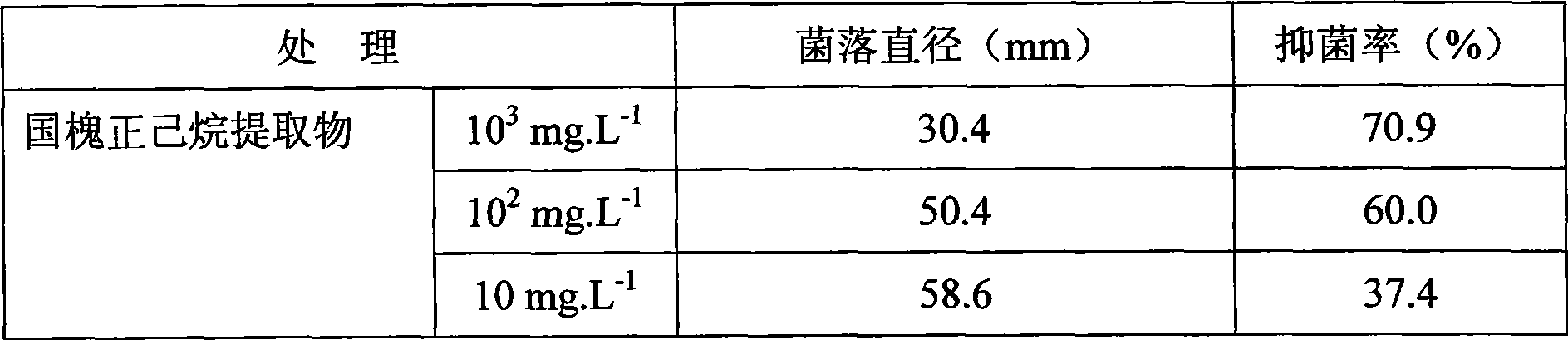
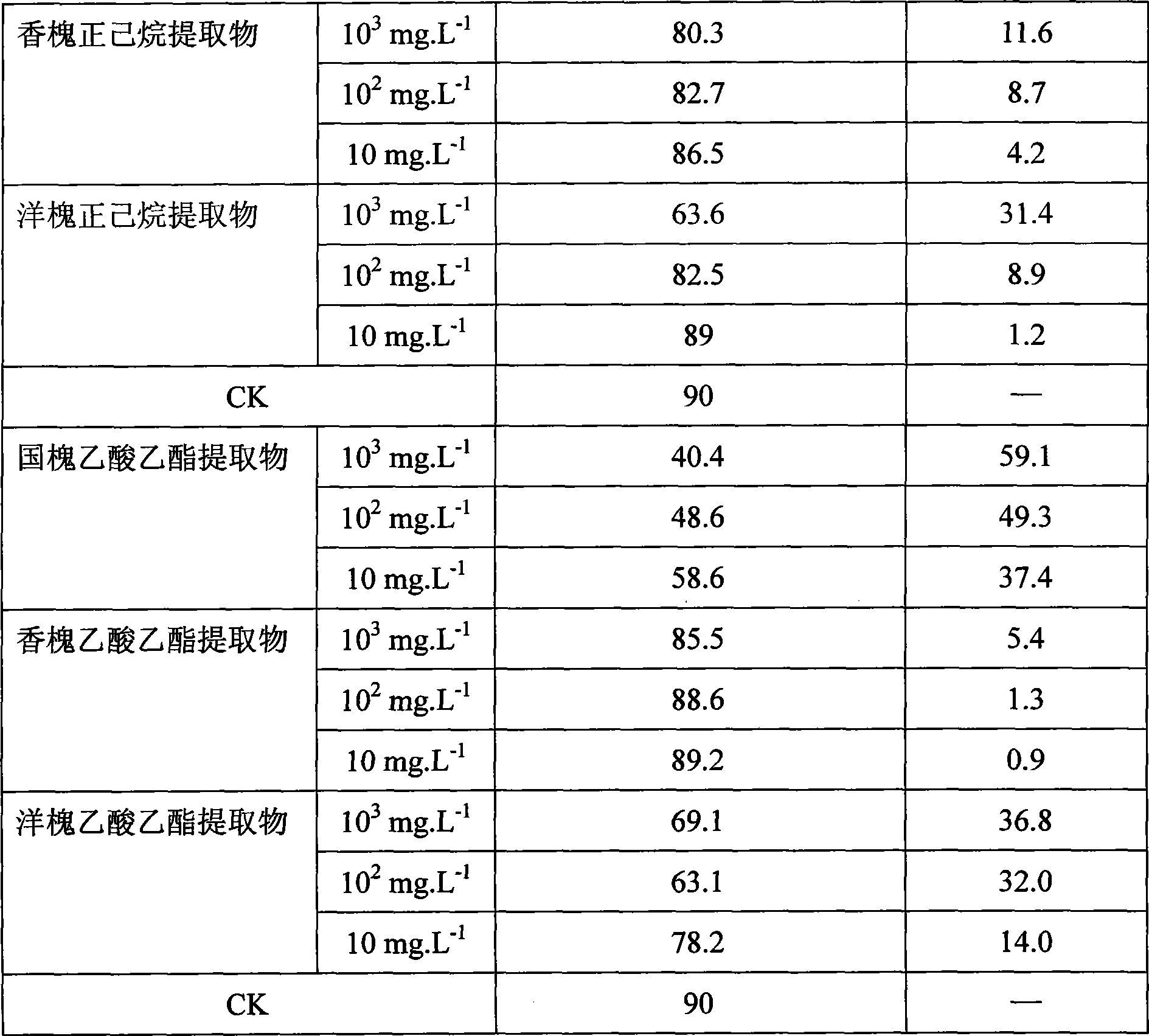
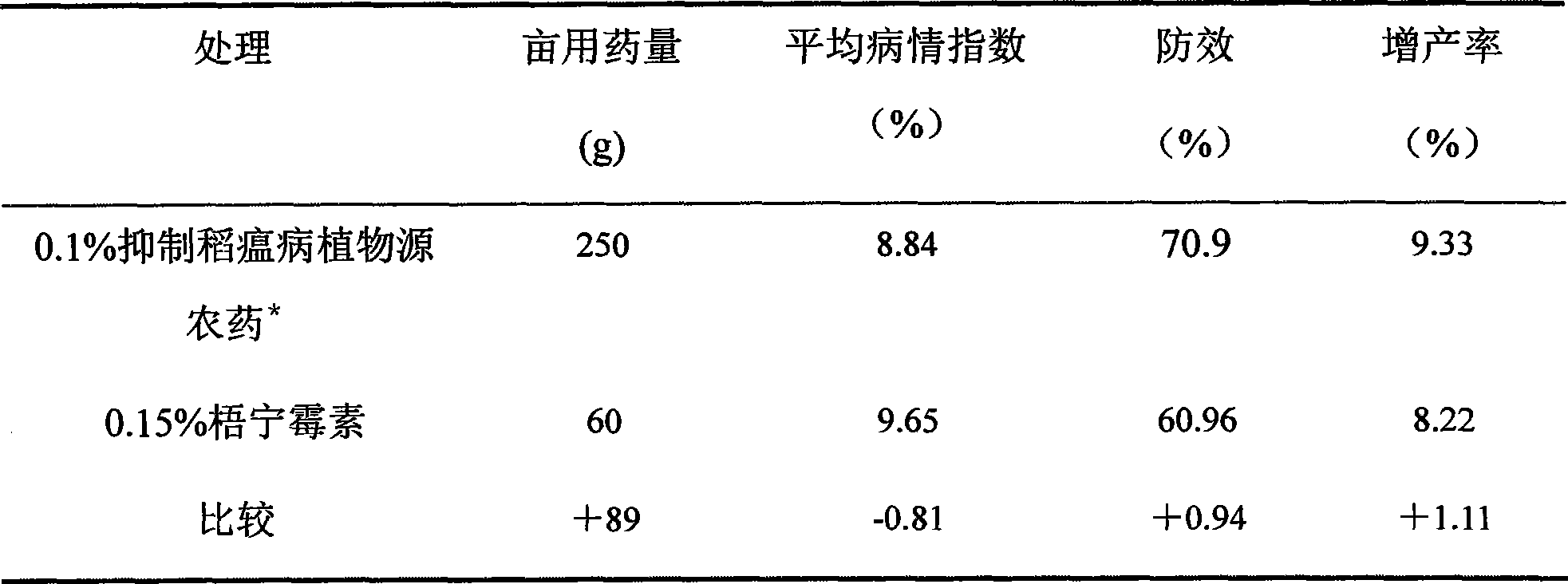
Plant source pesticide for inhibiting rice blast and application thereof in aspect for inhibiting rice blast
InactiveCN101502274ANo residual pollutionAdvancedBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant SourcesBiological product
The present invention discloses a plant pesticide which restrains the rice blast and the application of the plant pesticide for restraining rice blast. The plant pesticide is a low-toxicity and high-efficient novel biological product which is developed by using the plant of Chinese scholar tree as raw material. The pesticide is applied with a mode of foliage spray and can be applied to the agricultural field. The plant pesticide for restraining the rice blast according to the invention is obtained through the following steps: using the Chinese scholar tree as raw material, putting the raw material into an extraction kettle after breaking the tissue of raw material, adding the organic solvent with the weight of 2-3 times of the weight of raw material, immersing and extracting for 12-24 hours in the condition of room temperature, extracting for 2-3 times; condensing the extracted liquid to solid-state concentrate; dissolving the solid-state concentrate into the organic solvent with the weight of 0.5-1.5 times of the weight of solid-state concentrate, adding the emulsifying agent with the weight of 0.1-0.15 times of the weight of solid-state concentrate, sufficiently mixing, adding the water with the weight of 20-40 times of the weight of solid-state concentrate, and the plant pesticide aqueous emulsion for restraining rice blast is prepared. The plant pesticide aqueous emulsion for restraining rice blast can effectively restrain the magnaporthe grisea, increases the quality of arable farming and strengthens the capability of crop for resisting disasters and pests.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
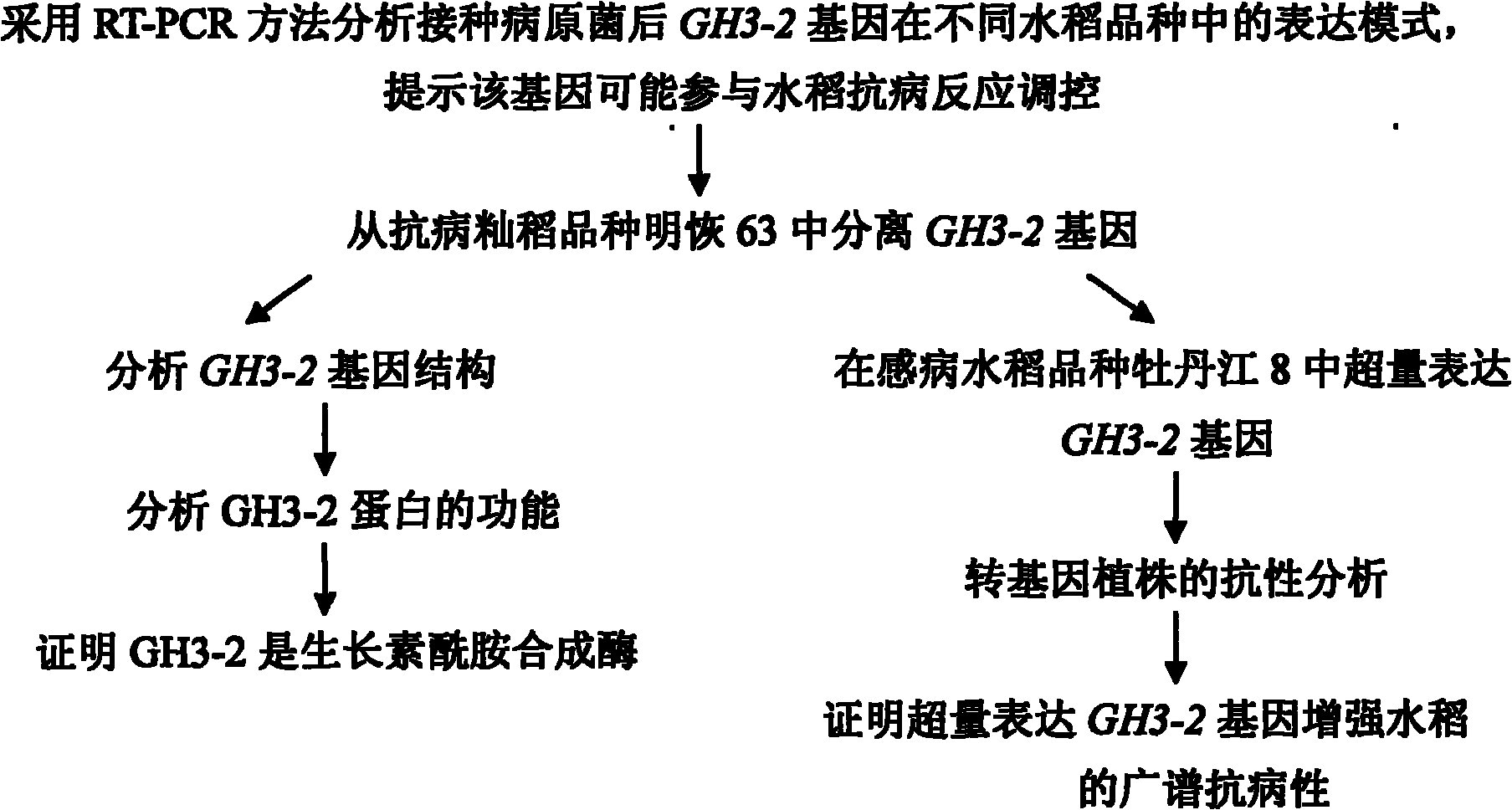
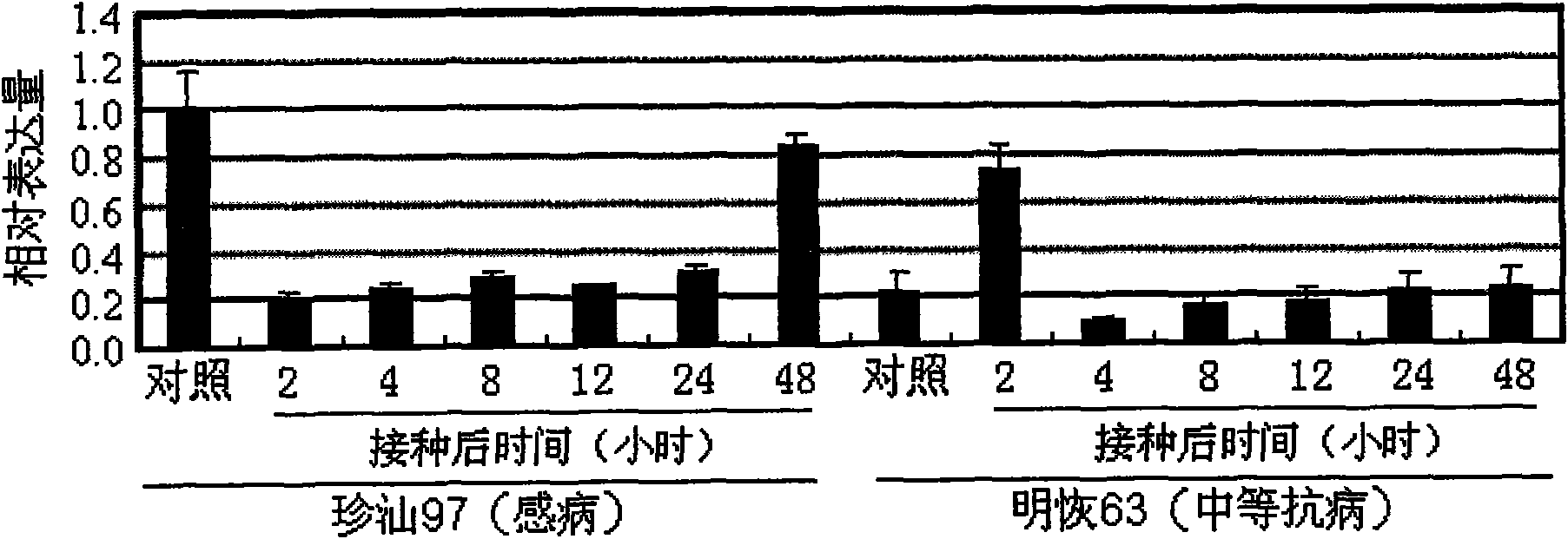
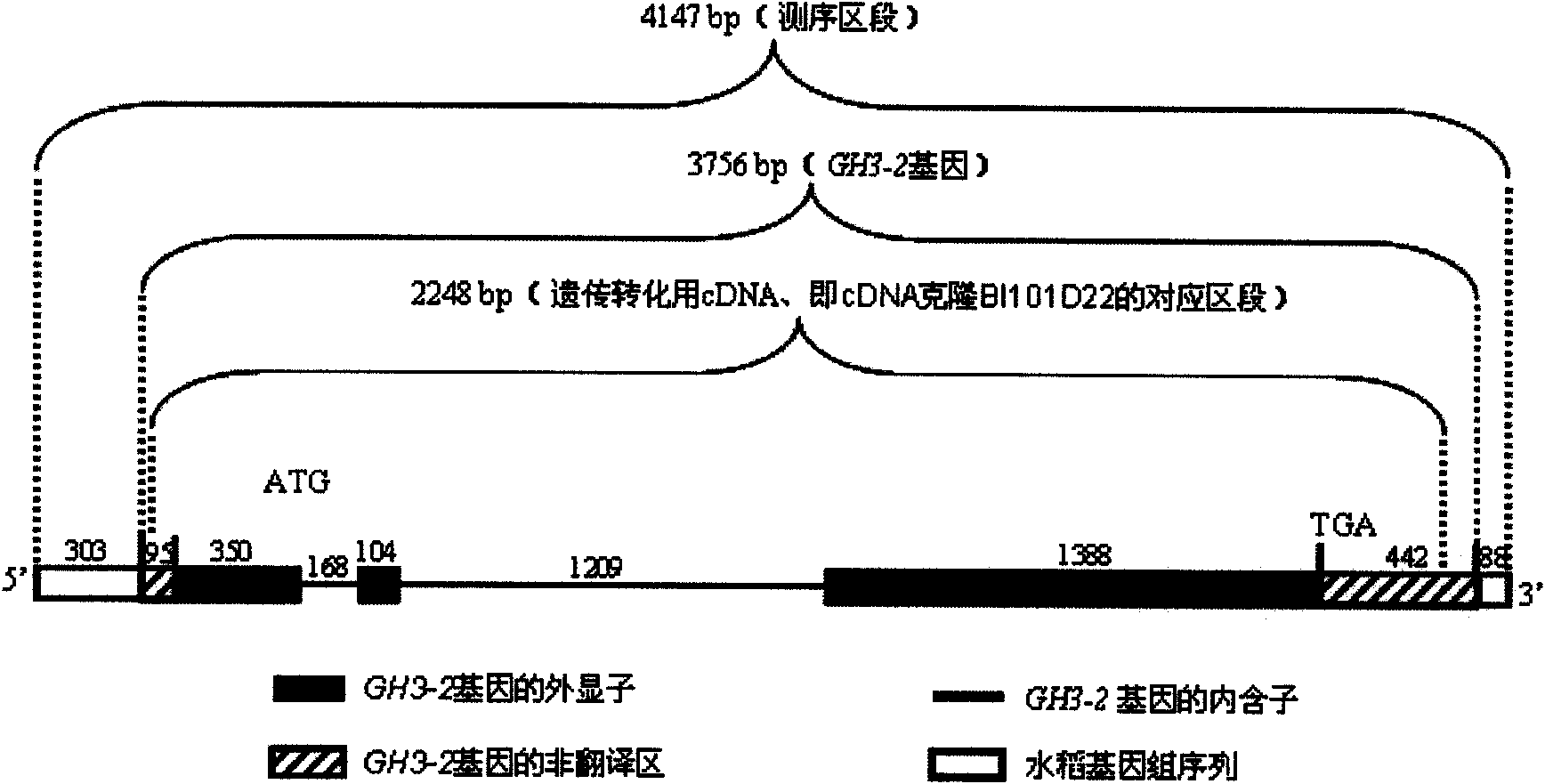
Rice disease resistance related gene GH3-2 and application thereof in breeding of broad spectrum disease-resistant rice
InactiveCN101993880AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseGenetically modified rice
The invention relates to the technical field of plant gene engineering, in particular to separation, cloning and function verification of a DNA fragment containing rice disease resistance related genes GH3-2. The genes GH3-2 code auxin amide synthetase. The genes GH3-2 can endow the rice with function of resisting the diseases caused by bacterial pathogenic bacteria Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, bacterial Xanthomonasoryzae pv. oryzicola and fungal pathogenic bacteria Magnaporthe grisea. The fragment and the exogenous adjusting sequence thereof are directly transferred into the rice, and the transgenic rice for excessively expressing the GH3-2 has the remarkably enhanced resistance to the Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, bacterial Xanthomonasoryzae pv. oryzicola and the Magnaporthe grisea.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
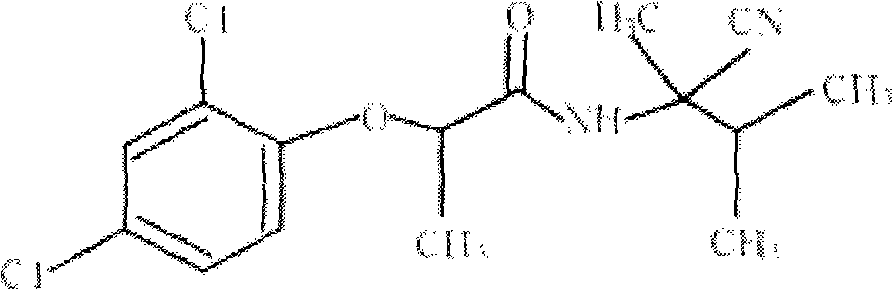
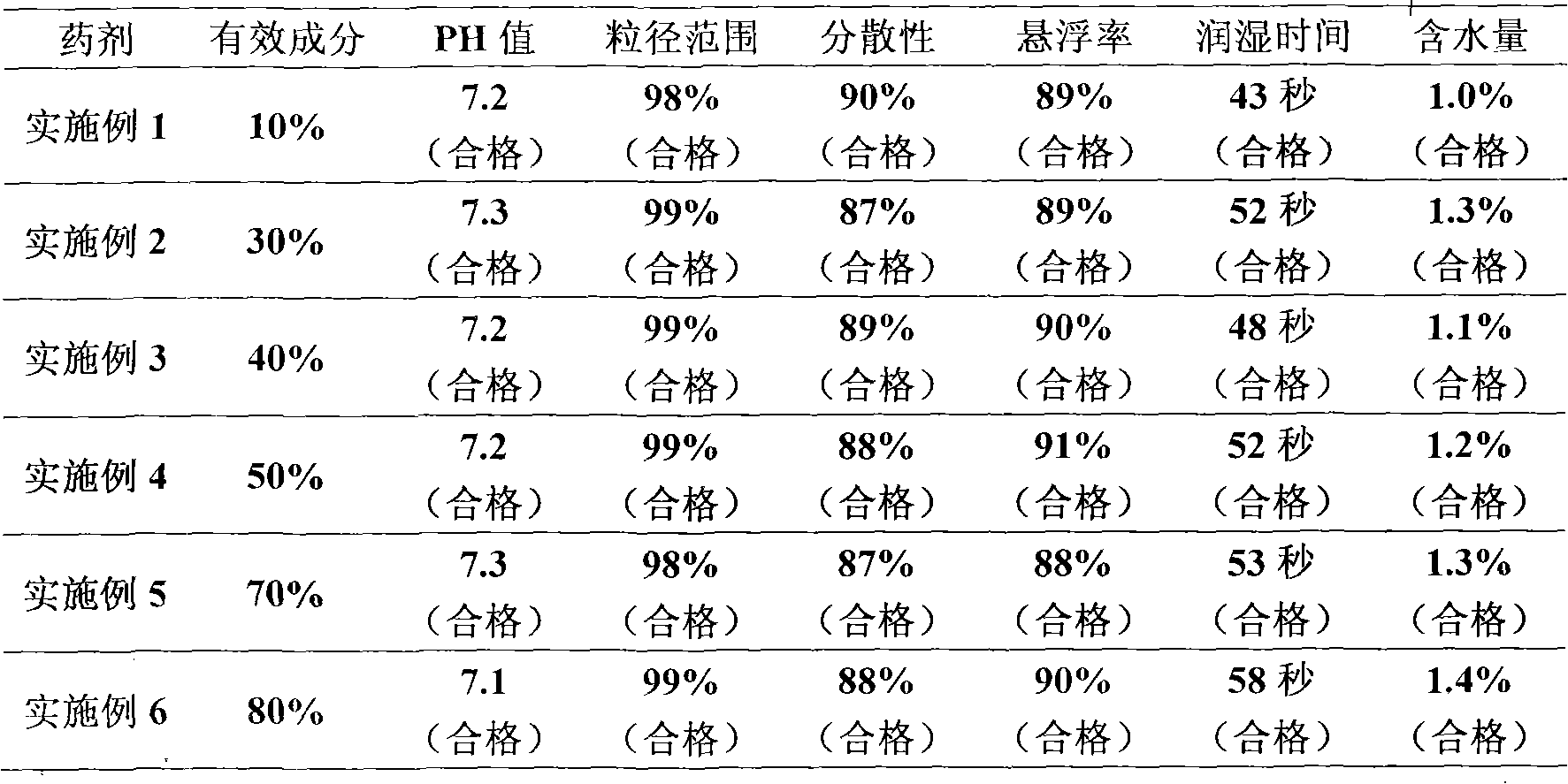
Fenoxanil water dispersible granules
InactiveCN101584317AHealth without harmNo pollution in the processBiocideFungicidesHigh concentrationMagnaporthe grisea
The invention belongs to the technical field of farm chemicals and discloses fenoxanil water dispersible granules, which comprise the following ingredients by mass percentage: 10 to 80 percent of fenoxanil, 3 to 12 percent of wetting agent, 3 to 12 percent of dispersant, 0 to 10 percent of disintegrant, 0.1 to 3 percent of binder and 5 to 84 percent of filler. The ingredients are mixed in proportion, stirred uniformly and crushed to form high concentration dust; the high concentration dust is uniformly mixed with the binder; and the mixture is granulated, and the grains are dried and sieved to obtain the fenoxanil water dispersible granules. The fenoxanil water dispersible granules overcome the drawbacks of suspending agents and wettable powders, reduce environmental pollution and are mainly used for preventing and controlling magnaporthe grisea.
Owner:SHAANXI MEIBANG PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Biocontrol pseudomonas sp. and application thereof
ActiveCN111187741AEnhanced inhibitory effectConducive to green and pollution-free productionBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMagnaporthe grisea
The invention relates to a biocontrol pseudomonas sp. and an application thereof, specifically to a biocontrol strain GZ9 with a preservation number of CCTCC M 20191037. The strain has a significant inhibition effect on botrytis cinerea, and shows a good inhibition effect on phytophthora capsici, magnaporthe grisea and gibberella zeae. The fermentation liquor of the strain has a good control effect on tomato gray mold, and can reach a control effect of 78.66%. Thus, the strain has good biocontrol application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
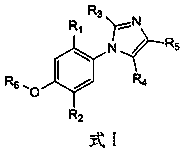
Phenylimidazole derivative, synthesis method of phenylimidazole derivative and application of phenylimidazole derivative to pesticide
ActiveCN109810062ASimple structureNovel structureOrganic chemistryFungicidesSynthesis methodsAlternaria tomato
The invention relates to a phenylimidazole derivative, a synthesis method of the phenylimidazole derivative and application of the phenylimidazole derivative to pesticide, particularly application tothe fungicide pesticide aspect, and belongs to the technical field of pesticide. In order to solve the technical problems, the invention provides a novel phenylimidazole derivative, a synthesis methodof the novel phenylimidazole derivative and application of the novel phenylimidazole derivative to the pesticide. The structure of the compound is shown as a formula I. The compound structure is simple and novel; the synthesis is easy; meanwhile, the fungicidal activity is realized; a better bacteriostasis or sterilization effect is achieved on important plant pathogenic fungi such as tomato early blight, tomato botrytis cinereal, cucumber fusarium oxysporum, magnaporthe grisea and rice rhizoctonia solani.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting magnaporthe grisea genes for enhancing magnaporthe grisea strain pathogenicity
InactiveCN105177145AIncrease infectivityOvercoming the disadvantages of understanding the infectivity of germsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyReal-Time PCRs
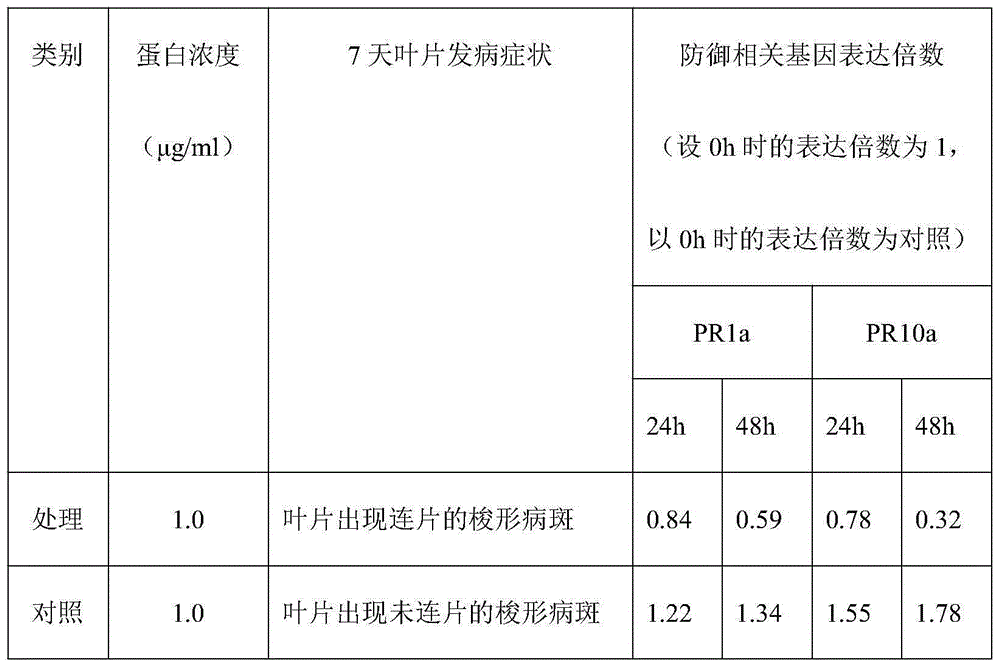
The invention discloses a method for detecting magnaporthe grisea genes for enhancing magnaporthe grisea strain pathogenicity, and relates to the field of plant protection and biological technology. The method comprises the steps that a reaction of resistance or susceptibility and a real-time RT-PCR are inspected for analyzing defense related gene expression of rice early stage response and a qPCR is adopted for detecting the relative fungus growth amount of disease spots; a prokaryotic expression product of the genes is sprayed to leaves for 24 h on the basis of the concentration being 1.0 microgram / ml-6.0 microgram / ml, and then strong / weak pathogenic strains are inoculated; the reaction of resistance or susceptibility and the real-time RT-PCR are inspected for analyzing rice defense related gene expression; overexpression strains of the genes are utilized for being inoculated on rice blades in an in-vitro mode, and the reaction of resistance or susceptibility and the real-time RT-PCR are inspected for analyzing the rice defense related gene expression and the qPCR is inspected for analyzing relative fungus growth amount on disease spots. The method can comprehensively and accurately clear pathogen effect protein genes and improve the pathogen infective ability, and the accurate and comprehensive method is provided for determining the pathogen effect protein for improving the pathogen infective ability in the future.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Magnaporthe grisea MoLON1 gene function and application thereof
The Magnaporthe grisea MoLON1 gene function and application thereof belong to the field of bioengineering technology, and the invention relates to the function in the pathogenic processes of Magnaporthe grisea MoLON1 gene and purification and purpose of coding proteins thereof. The gene and the ATP-dependent protease Lon1 in yeast, Escherichia coli and other organisms have high homology, and the gene codes 1119 amino acids and contains one intron and two exons. The knockout of MoLON1 gene leads to minimizing of Magnaporthe grisea aerial hyphae quantity, reduction of conidiospore output, basic deprivation of expansion capability of infective hyphae in the paddy rice leaf cells, and improvement of sensitivity to a plurality of adverse conditions; the invention also relates to expression and purification of proteins coded by the MoLON1 gene, and gene can be used as a candidate target for designing and screening anti-Magnaporthe grisea novel medicament.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for in vitro detection of transport of Magnaporthe grisea effector proteins in root tissues of rice
InactiveCN102749308ASimple methodAccurate methodAnalysis by material excitationMagnaporthe griseaMeloidogyne oryzae
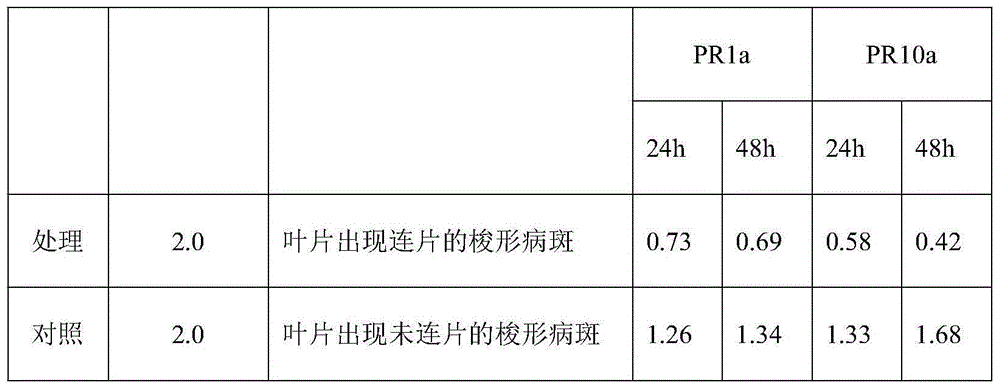
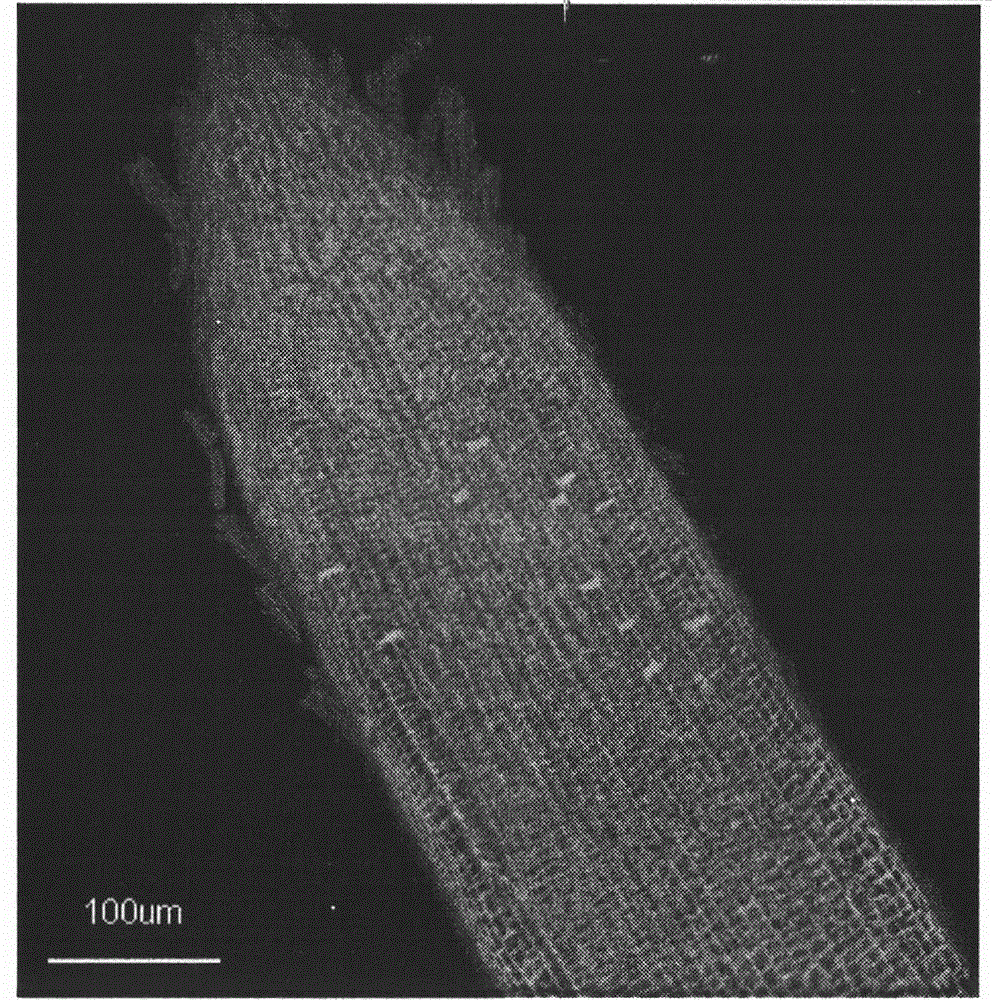
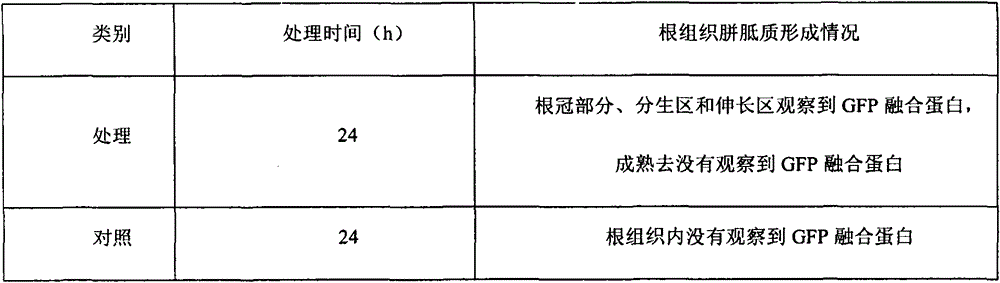
The invention discloses a method for in vitro detection of the transport of Magnaporthe grisea effector proteins in root tissues of rice. The transport of GFP fused proteins in the root tissues of rice is directly observed through a confocal microscope after disease-resistant rice cultivar Lijiangxintuanheigu root tips of 0.5cm are processed with 5.0mg / ml of prokaryotic expression products of Magnaporthe grisea effector proteins fusing GFP for 12-72h. The method is simple, accurate and rapid.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rice blast resistance gene RMg4 or RMg5 or RMg6 and application thereof
InactiveCN103060337AOvercoming the Difficulty of Distant HybridizationShorten the breeding cycleBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and specifically relates to a rice blast resistance gene RMg4 or RMg5 or RMg6 and an application thereof. The invention discloses a nucleotide sequence of the rice blast resistance gene RMg4 or RMg5 or RMg6 and an encoded amino acid polypeptide sequence thereof. The three genes belong to members of an NBS-LRR (nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich-repeat) type anti-disease gene family. The three blast resistant genes disclosed by the invention are cloned from a rice line expressing high resistance to magnaporthe grisea and converted to a magnaporthe grisea-susceptible variety, a magnaporthe grisea infection method is utilized for assessing the resistance against diseases of the genes, and then the three genes can be finally determined to have the resistance to rice blast.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Pathogenicity gene MoSNT2 from magnaporthe oryzae and application thereof
PendingCN107200773AControl pathogenicityEpidemic controlMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesAntifungalProtein target
The invention discloses a pathogenic protein MoSNT2 derived from Magnaporthe grisea, the protein is composed of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 1; the invention also discloses the gene MoSNT2 encoding the pathogenic protein, the gene It consists of the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No:2. The invention also discloses the use of the above-mentioned gene or protein as a target for designing or screening antifungal drugs. The invention provides an important target gene or target protein for the control of rice blast. The drug developed by using the gene or protein as a target can destroy the gene expression or protein function of the rice blast fungus, and can effectively control the pathogenicity and prevalence of the rice blast fungus.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase LPMO M1 encoding gene and enzyme thereof, and preparation method and application
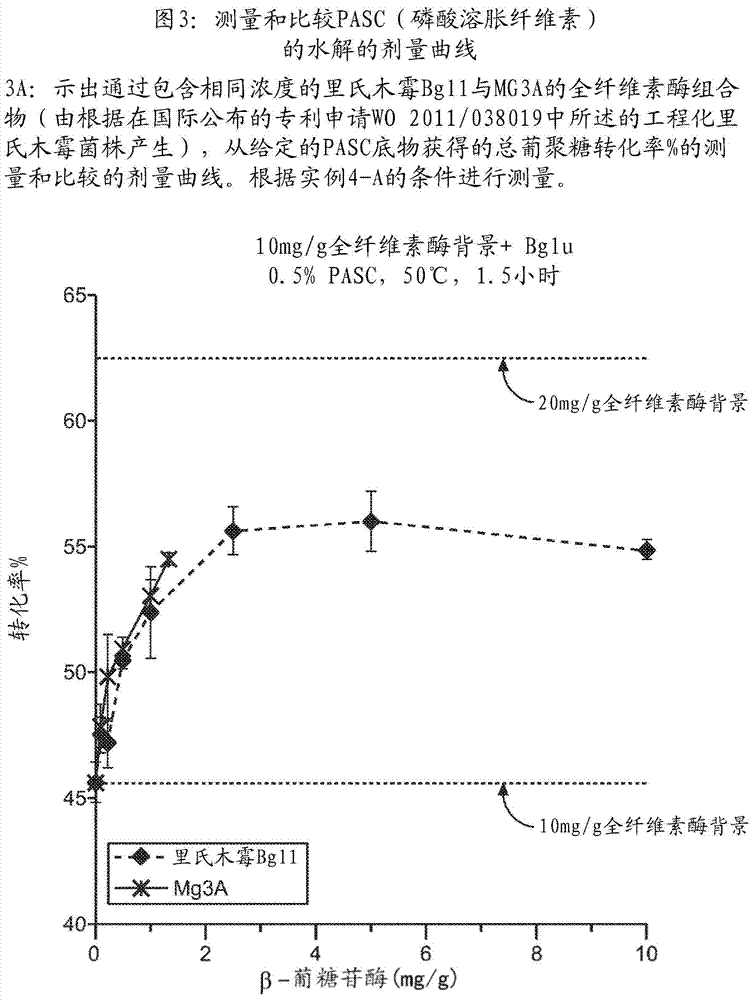
The invention discloses a lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase (LPMO) M1 encoding gene coming from magnaporthe grisea, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase LPMO M1 is sourced from the magnaporthegrisea 70-15, which is a pathogenic bacterium of paddy rice. The invention also provides a method of producing the novel LPMO, wherein by means of genetic engineering technical methods, the gene of the novel LPMO is cloned onto an escherichia coli expression vector to obtain an escherichia coli recombination strain that can heterologously express the enzyme. The LPMO M1 prepared through the heterologous expression by the strain can degrade PASC (microcrystalline cellulose processed by phosphoric acid) to generate cello-oligosaccharide and cello-oligosaccharide acid. The LPMO M1 can be widely applied in the fields of chemical engineering, agriculture, feed additives, medicines and the like, and has huge production potential and economic value.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for separating and screening out antagonistic bacterium from lycoris aurea bulb
PendingCN105524871AShorten the growth cycleLow environmental requirementsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMeloidogyne oryzae
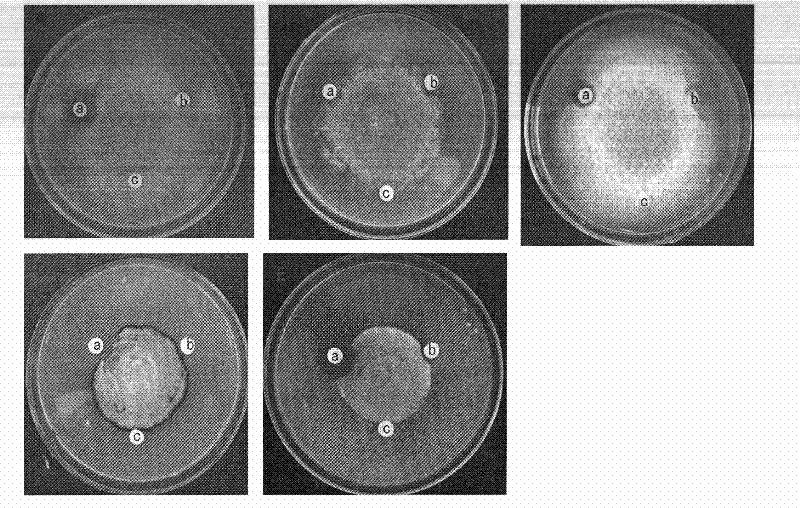
The invention relates to a method for separating and screening out an antagonistic endophytic bacterium from a lycoris aurea bulb. According to the method, by using an endophyte separation method, an endophytic bacterium is obtained by separating the endophytic bacterium from the lycoris aurea bulb; an improved confrontation culture method is adopted, test magnaporthe grisea is dripped in the center of a flat plate, and is cultured for 2-3 days; four crosswise corners around the magnaporthe grisea are inoculated with four bacterial strains respectively, and culture is carried out for 5-6 days; through observation, a bacterium having a bacteriostatic effect is the antagonistic bacterium obtained through screening. The antagonistic bacterium having an obvious inhibiting effect on magnaporthe grisea of rice is obtained; an antimicrobial spectrum experiment proves that the antagonistic bacterium also has an inhibiting effect on fusarium graminearum, aspergillus fumigatus and candida albicans. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the screening efficiency can be remarkably improved, and the antagonistic bacterium obtained by separation can be used as a biocontrol bacterium for being prepared into a microbial preparation, thus providing a basis for biological control over diseases.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A kind of camel velvet transfer protein and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102286085AGood antifungal activityEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationAntifungal
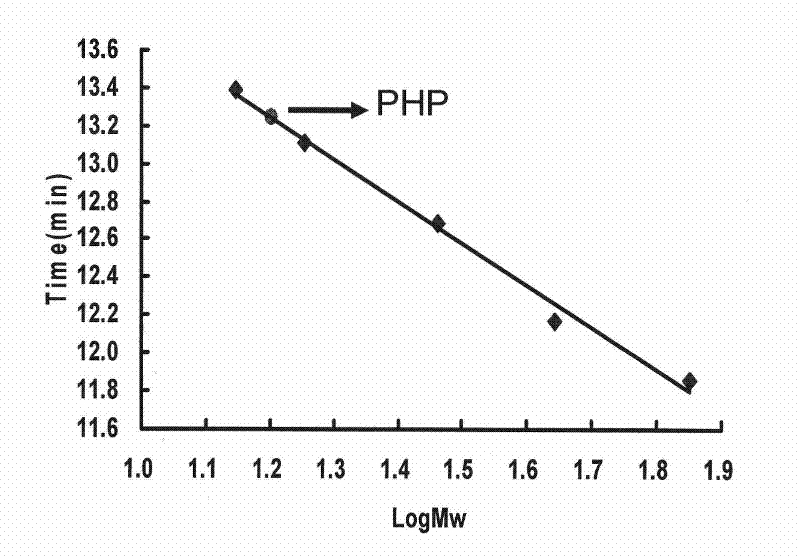
The invention discloses a peganum harmala lipid transfer protein (PHP) and relates to the preparation and use of new protein with antifungal, anticancer and antivirus activities. The method uses seeds of a peganum harmala plant as raw materials and comprises the following steps: preparing a coarse product, performing cationic exchange chromatographic separation and purifying by using a molecular sieve; and gradually separating and collecting a purified component having antibacterial activity, dialyzing, desalting, freeze-drying and thus, obtaining purified PHP. In the invention, a filter paper disc agar diffusion method is adopted, and researches prove the protein has growth inhibiting effect on five plant pathogenic fungi, namely alternaria alternate, penicillium degitatum, rhizopus stuolonifer, magnaporthe grisea and penicillium italicum. An 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) method proves that the protein has inhibiting effect on proliferation of human esophageal carcinoma cell Eca109, human cervical cancer cells HeLa, human stomach cancer cells MGC-7, mouse melanoma cells B16 and the like. The protein can inhibit the activity of human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase. The protein can be used for developing medicines for resisting agricultural pathogenic fungi, tumors and viruses.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of fertilizer for preventing and controlling rice blast
InactiveCN108101625AIncrease contentIncrease speedCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersActinidiaPesticide residue
The invention discloses a preparation method of a fertilizer for preventing and controlling rice blast, and belongs to the field of fertilizers. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, brassinolide is compounded with diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate, and the main effects are as follows that on one hand, the carbon and nitrogen metabolism of plants are promoted, so that the vigorand the development of rice are improved; on the other hand, the crop yield is improved, and the crop quality is improved. According to the preparation method, a penetration enhancer is penetrated into the roots of the rice, the enzyme activation and the photosynthesis are promoted through the brassinolide and the diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate; then the activity of separately cultivated strains isgreatly increased under the action of the enzyme activation, so that the capability of resisting the invasion of magnaporthe grisea is promoted; and on the other hand, the active substances of the stems and leaves of kiwifruits are added, the propagation and the growth of the magnaporthe grisea in rice are inhibited, and the rice blast is controlled. The preparation method solves the problem thatsterilization agents are adopted to prevent and control the rice blast in the prior art, a large amount of manpower and material resources are wasted, and unnecessary pollution is caused to the environment, and unnecessary pesticide residue is generated in the rice.
Owner:芮志行
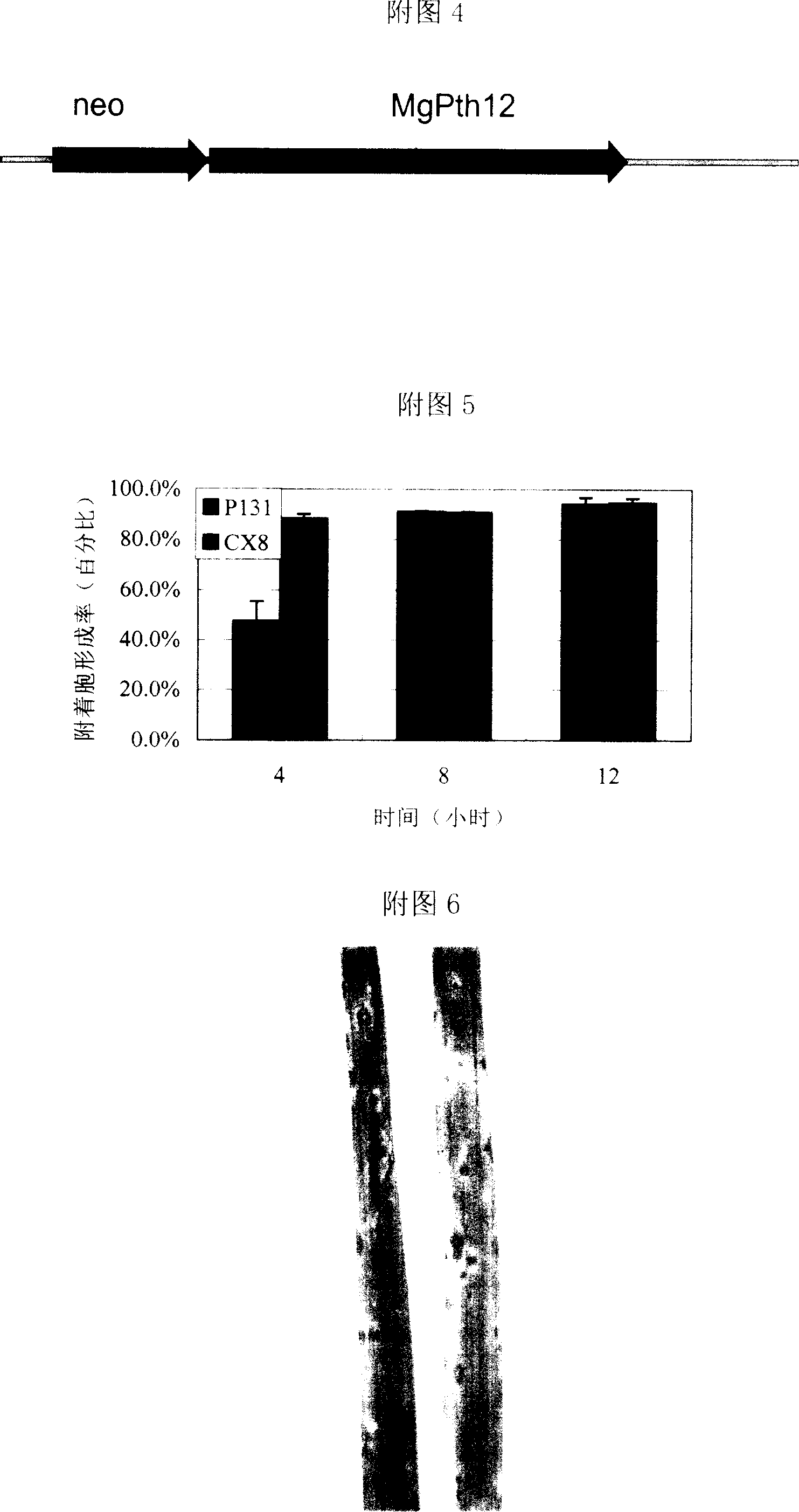
Gene MgPTH12 for controlling mature and pathogenicity of fungi appressorium derived from Magnaporthe grisea and its uses
The invention discloses a new necessary MgPTH12 gene and utility to make pear spore bacterium attach to mature and lead to disease, which is characterized by the following: the gene and its cDNA and coding product possess the sequence in the SEQ ID No.:1, No.:2 and No.:3; the protein of coded gene possesses homeo structural region, which is not similar to known functional protein; the gene removes abnormal and matured attaching cell, which reduces forming frequency of infecting tin and extending infecting hypha without pathogenic ability for rice; the homologous gene of gene lies in the plant pathogenic bacteria widely, which can be applied to design and sieve new drug to prevent fungus.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Agricultural bactericide containing azoxystrobin
The invention belongs to the technical field of pesticide and relates to a broad spectrum fungicide, in particular to a farming fungicide comprising Azoxystrobin. The invention consists of the original pesticide of the Azoxystrobin, an accessory ingredient and an excipient; and microemulsion and missible oil are manufactured by a normal production technique. The Azoxystrobin is a methoxy acrylate fungicide developed by Syngenta Company, is used for controlling powdery mildew, rust disease, glume blight, scab, downy mildew and Magnaporthe grisea on cereal crops, fruit trees and vegetables, and has specific effects on powdery mildew of cucumber, downy mildew of grape and apple scab.
Owner:陕西亿田丰作物科技有限公司
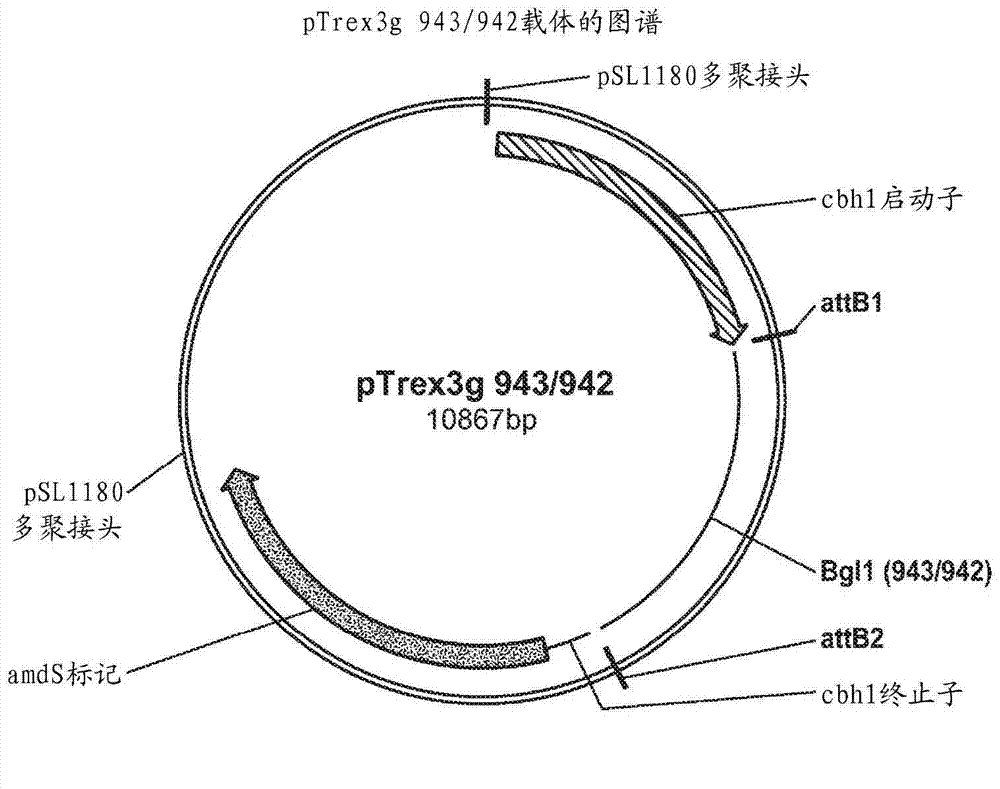
Beta-glucosidase from magnaporthe grisea
The present compositions and methods relate to a beta-glucosidase from Magnaporthe grisea, polynucleotides encoding the beta-glucosidase, and methods of make and / or use thereof. Formulations containing the beta-glucosidase are suitable for use in hydrolyzing lignocellulosic biomass substrates.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Novel gene necessary for production of conidium from Magnaporthe grisea and its uses
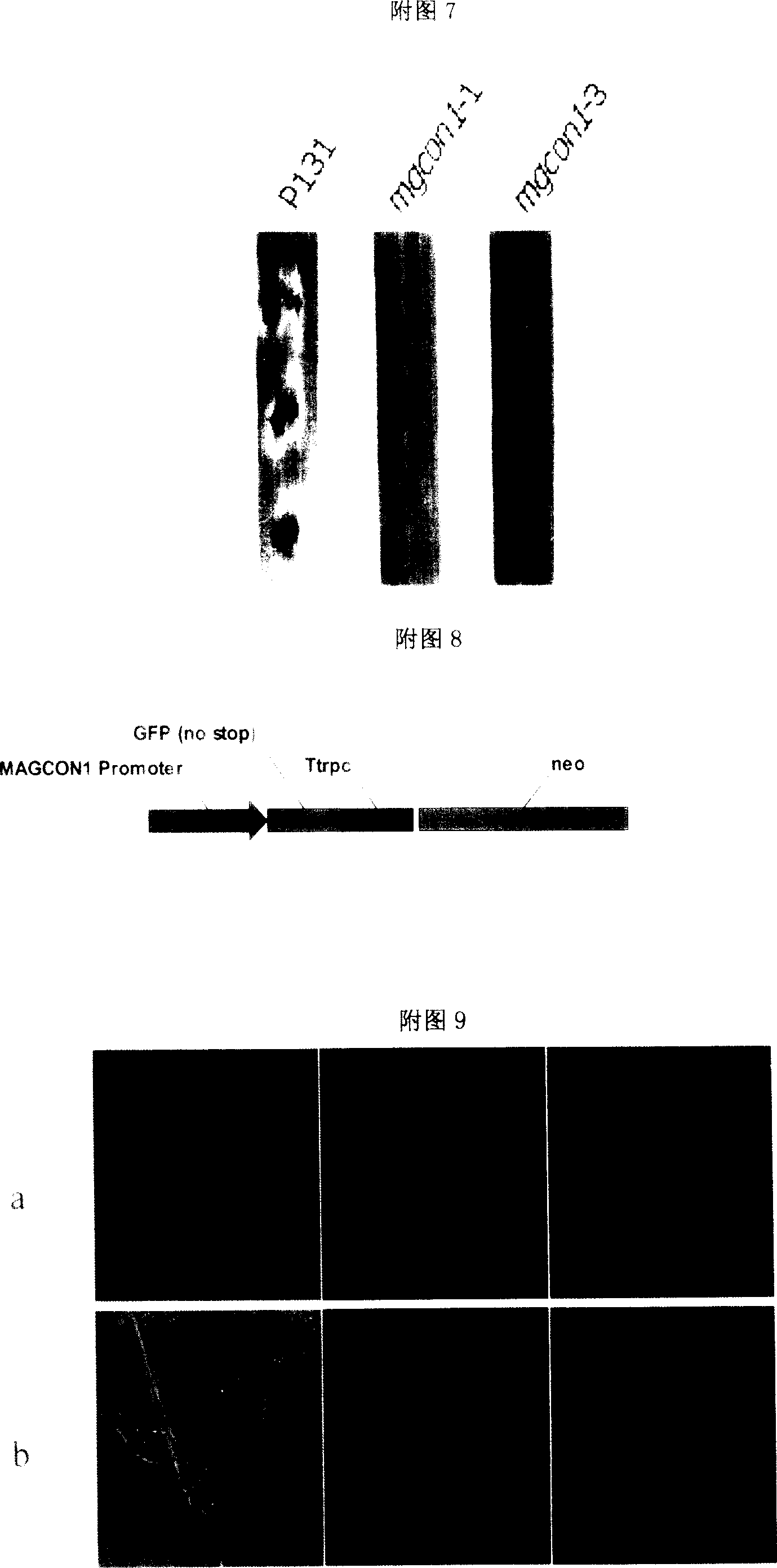
The invention discloses a new necessary MgCON1 gene and utility generated by pear spore bacterium, which is characterized by the following: the gene and its cDNA and coding product possess the sequence in the SEQ ID No.:1, No.:2 and No.:3; the protein of coded gene possesses homeo structural region, which is not similar to known functional protein; the gene removes abnormal and matured attaching cell, which reduces forming frequency of infecting tin and extending infecting hypha without pathogenic ability for rice; the MgCON1 can be important candidate target, which can be applied to design and sieve new drug to prevent fungus.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
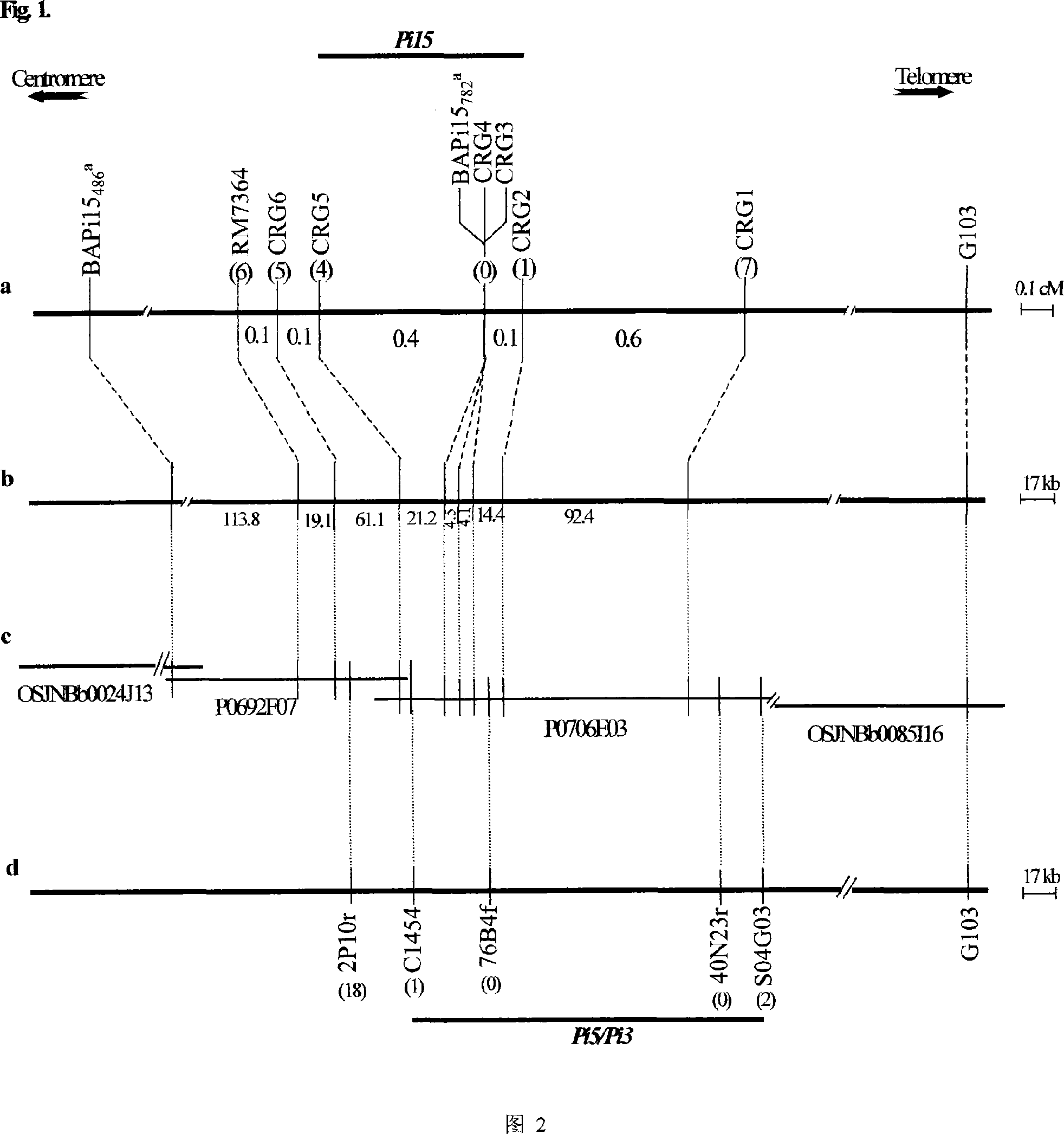
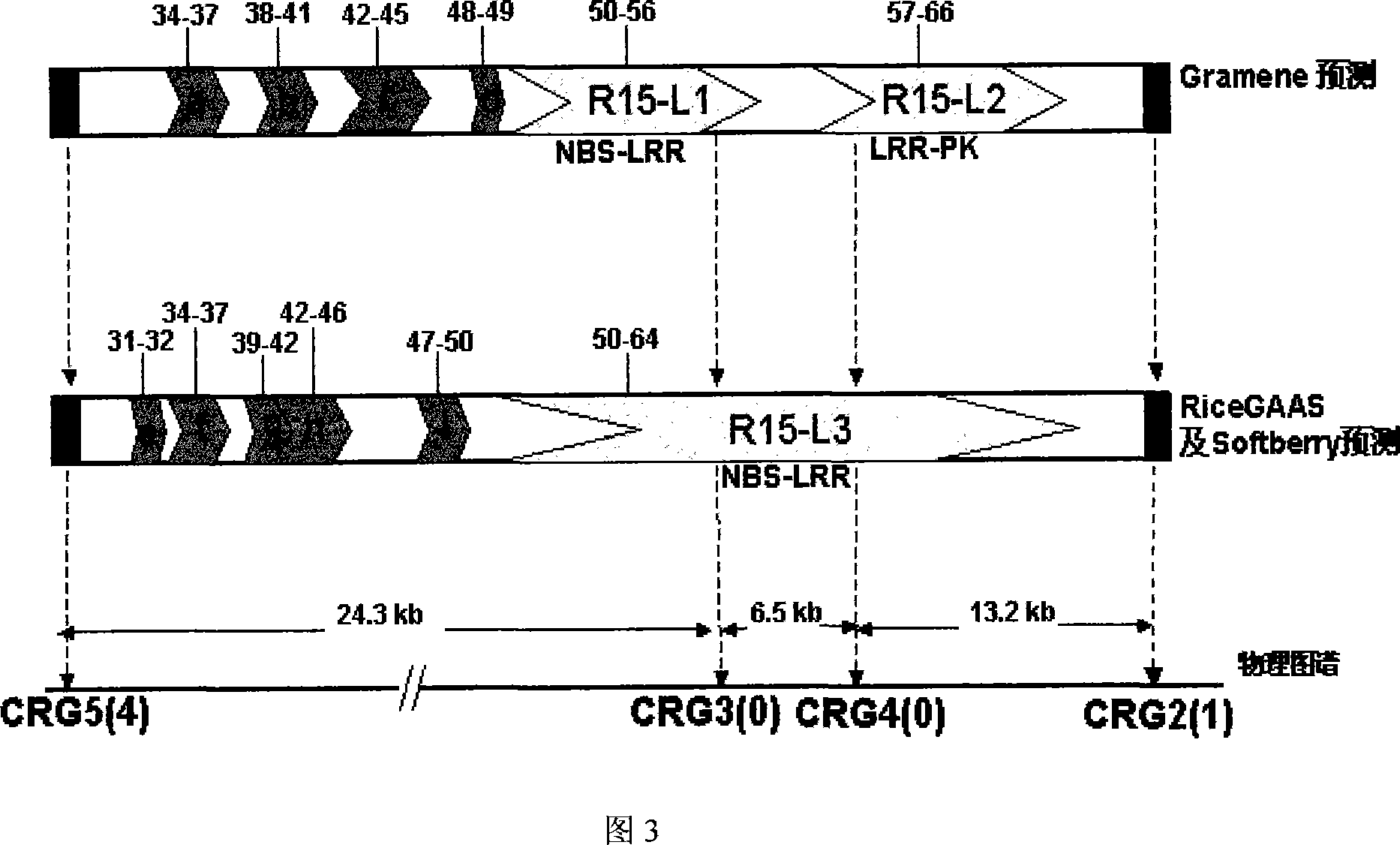
Pi15 resistance gene of rice blast, and application
InactiveCN101050232ADoes not create linkage problems with bad genesNo cascading problemsPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceMagnaporthe grisea
This invention discloses rice Magnaporthe grisea resistance gene Pi15 nucleotide sequence; amino acid polypeptide sequence coded by rice Magnaporthe grisea resistance gene Pi15, and its application. Magnaporthe grisea resistance gene Pi15 is a member of resistance gene family nonTIR-NBS-LRR, and is a constitutive expression gene. Magnaporthe grisea resistance gene Pi15 can be used to breed disease-resistant rice or plants through genetic transformation, or used as a molecular marker in plant breeding.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Rice induced disease-resistant gene OsAAA1 and application thereof
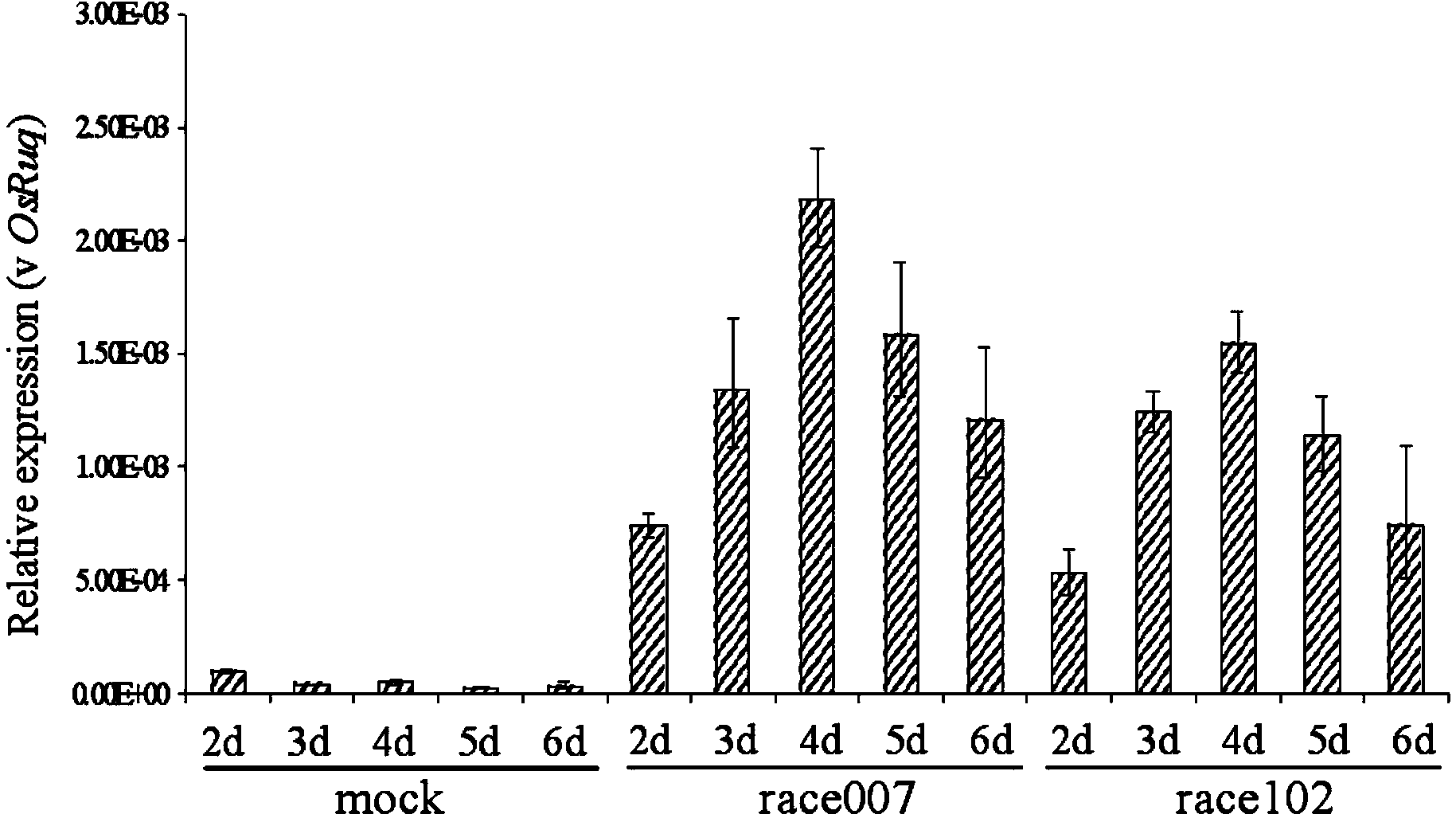
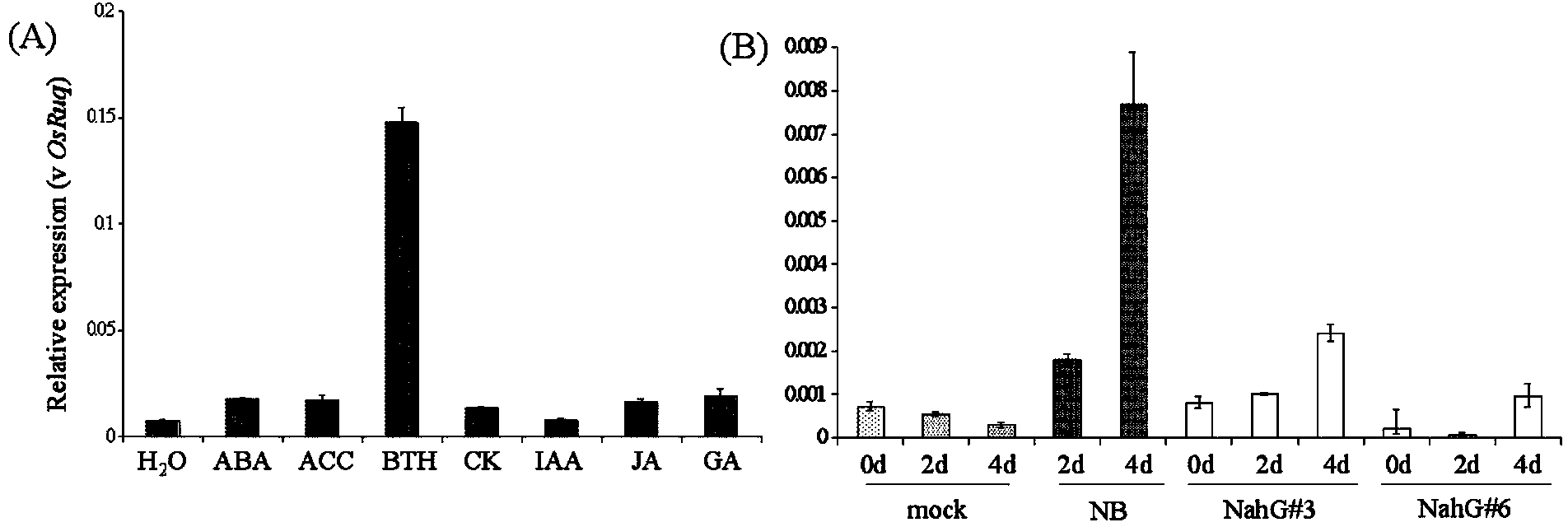
The invention provides a rice induced disease-resistant gene OsAAA1 which is doubly induced by salicylic acid and magnaporthe grisea. The nucleotide sequence of the rice induced disease-resistant gene OsAAA1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The amino acid sequence of a rice disease-resistant protein coded by the rice induced disease-resistant gene OsAAA1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The rice induced disease-resistant gene OsAAA1 provided by the invention can be applied to breeding of a rice variety with resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight. A specific application mode is as follows: an excessive expression vector is constructed according to the rice induced disease-resistant gene OsAAA1 provided by the invention; the excessive expression vector is transferred into a receptor variety by utilizing agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation. The variety shows the antibacterial property for magnaporthe grisea and xanthomonas oryzae under the induction of salicylic acid.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Method for treating paddy rice tissues by using prokaryotic expression product and inducing generation of callose
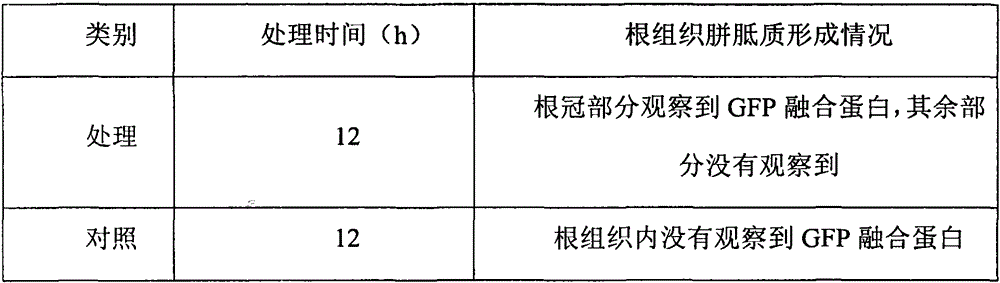
The invention relates to a method for treating paddy rice tissues by using a prokaryotic expression product of a magnaporthe grisea effect protein gene and inducing generation of callose, belonging to the technical field of plant protection and biology. The method is an improvement on the prior art, comprises a prokaryotic expression technology which is the same as that of the conventional method, a protein purifying technology, the wavelength ranges of exciting light and emitted light of a used fluorescence microscope and an aniline blue dyeing method, and is characterized by comprising the following steps of: treating the root tissues of Nipponbare serving as a disease-resistant paddy rice variety with the prokaryotic expression product which is 1.0-10.0 mg / ml in concentration of the magnaporthe grisea effect protein gene is used for treating the root tissues for 12 hours; performing aniline blue dyeing; and directly observing the formation of callose under the fluorescence microscope. The method is easy, convenience, accurate and rapid; and a large amount of spontaneous fluorescence interference can be avoided effectively, and the situation of basic defense reaction of paddy rice can be obtained directly and qualitatively.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
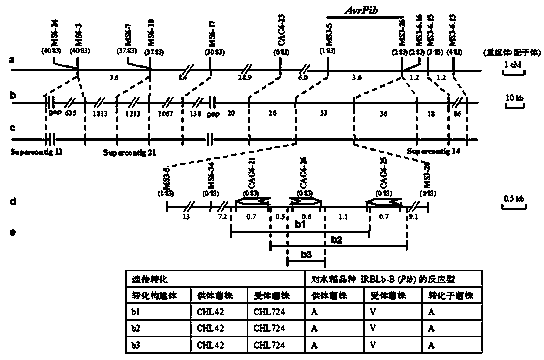
Magnaporthe oryzae avirulence gene AvrPib and application thereof
ActiveCN104356213AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly discloses magnaporthe oryzae avirulence gene AvrPib and application thereof. The avirulence gene comprises a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence, with a promoter, as shown in SEQIDNO:1 or a cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence as shown in SEQIDNO:2. Molecular targets of a novel pesticide can be designed on the basis of the structure of the gene and application test results thereof; by covalently introducing the gene and relevant anti-disease genes into host plants, such as rice, new disease-resistant varieties can be bred; specific molecular markers produced according to the gene sequence can be applied to monitoring field magnaporthe grisea groups; monitoring results obtained can be used for guiding the reasonable layout of the disease-resistant varieties; the gene has a wide application value, and has great significance in rice production and breeding research.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com