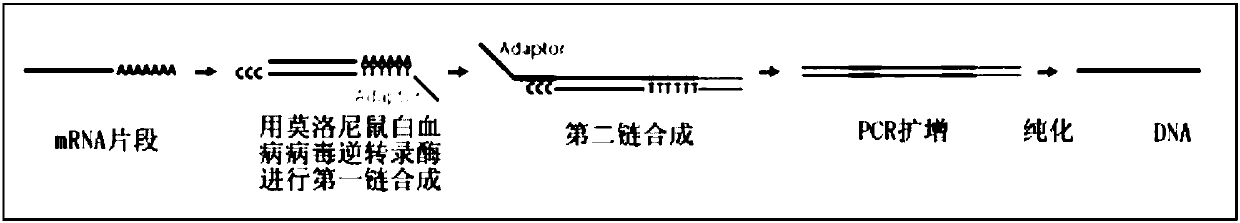
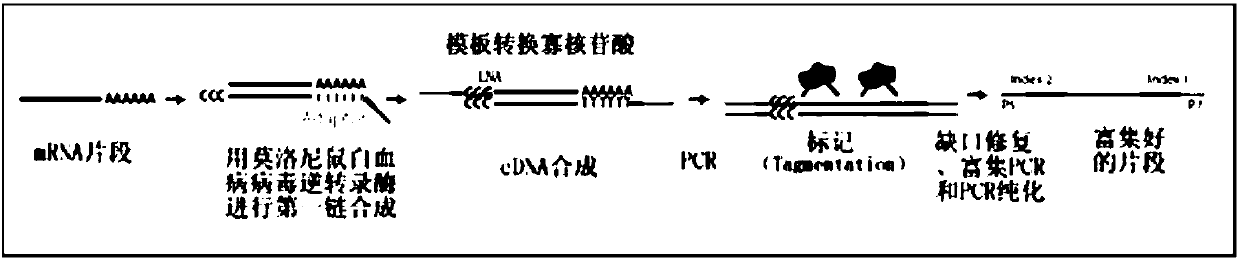
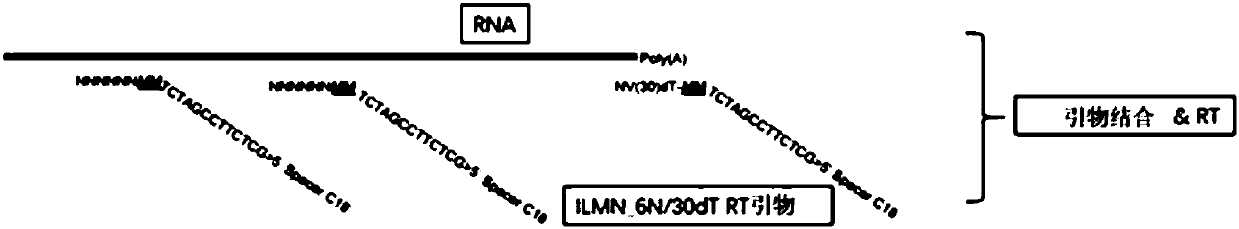
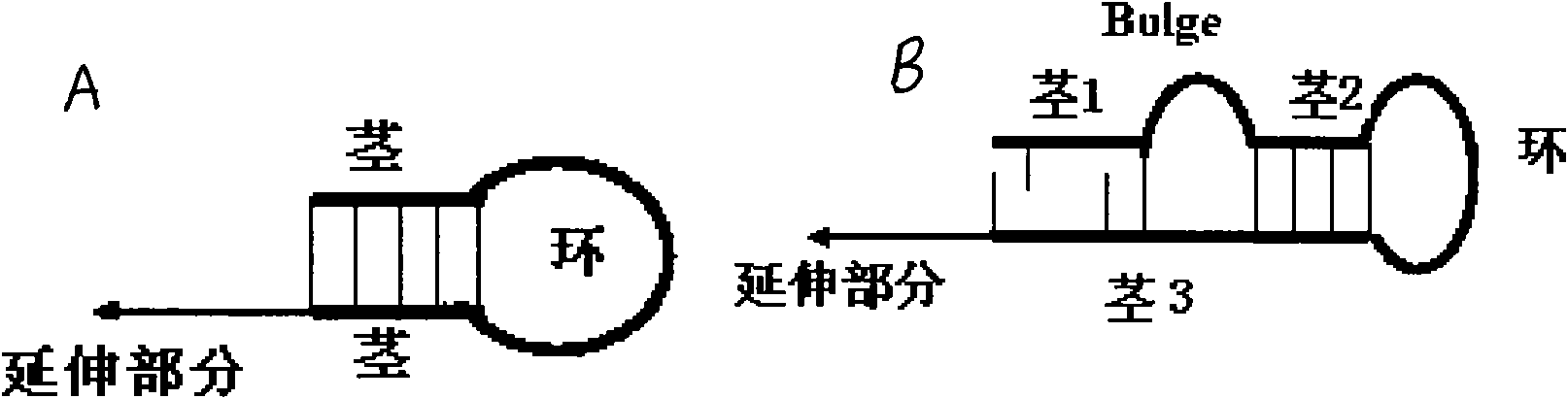
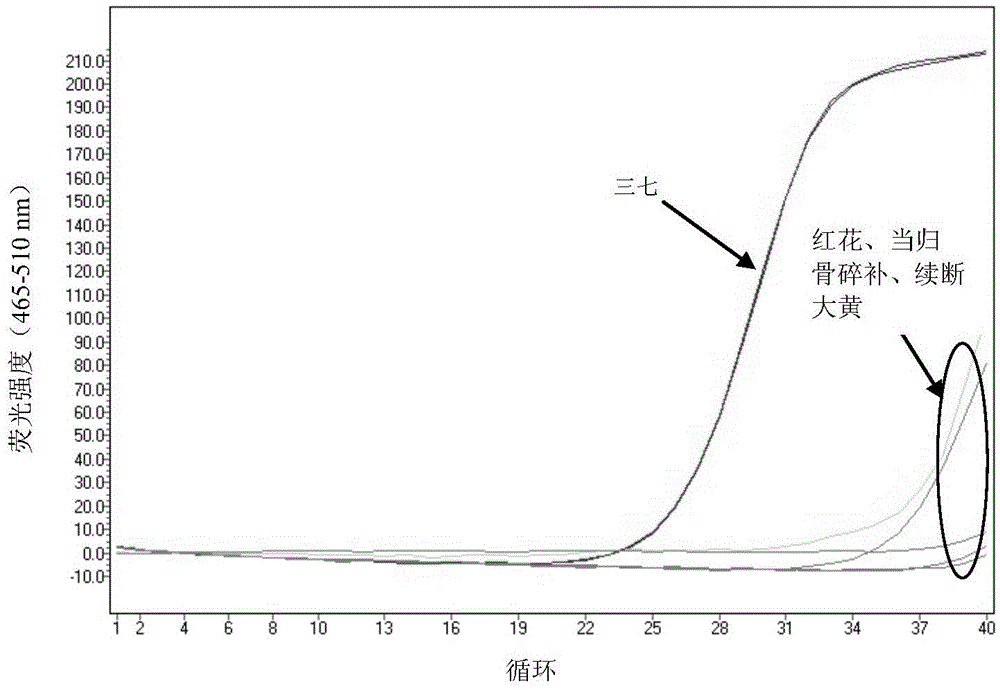
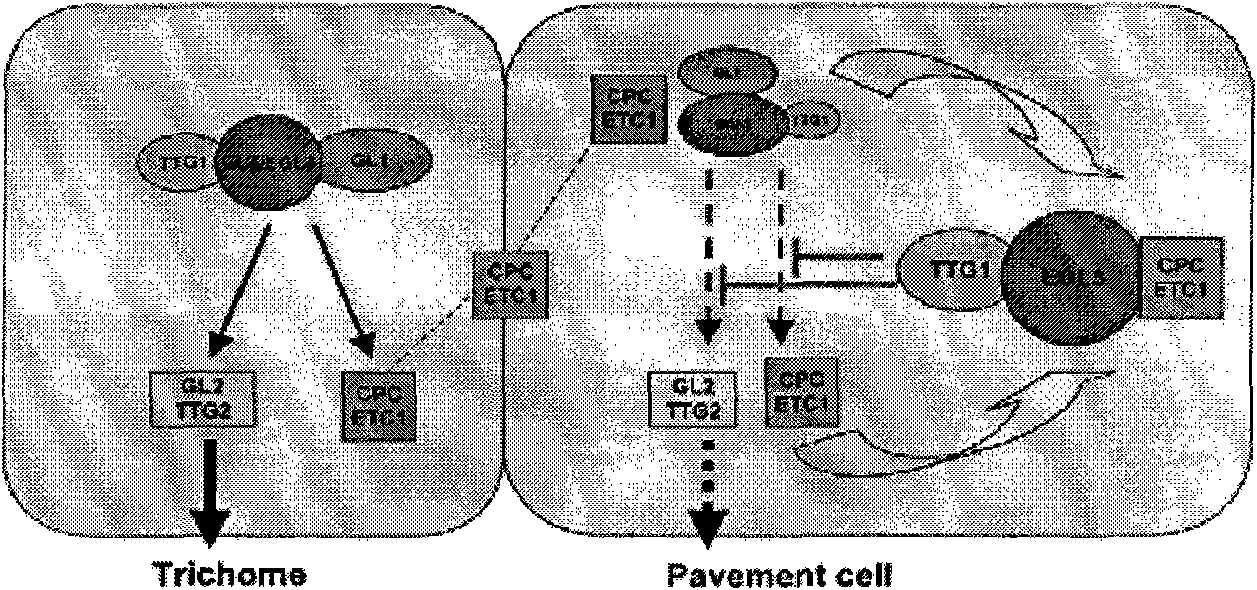
Patents
Literature
604 results about "Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cytochrome P450 dsRNA (double-stranded ribonucleic acid) and application to aphid growth inhibition
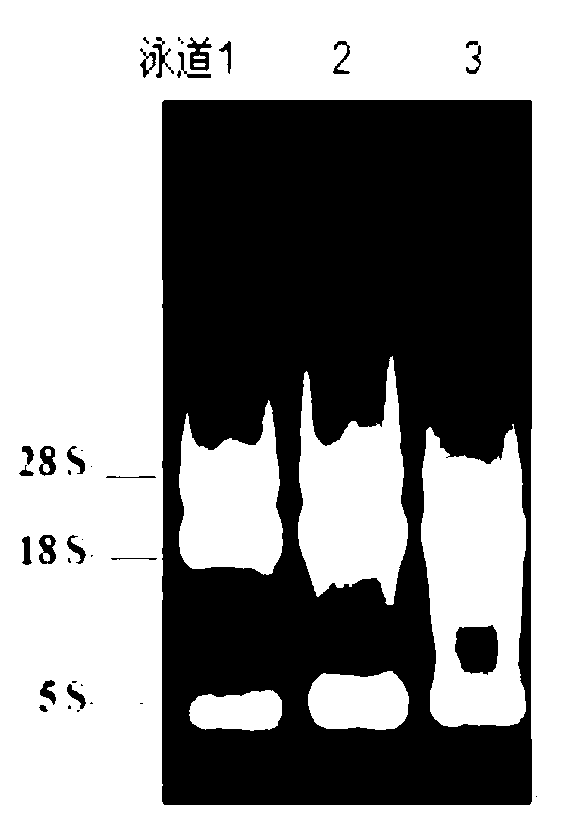
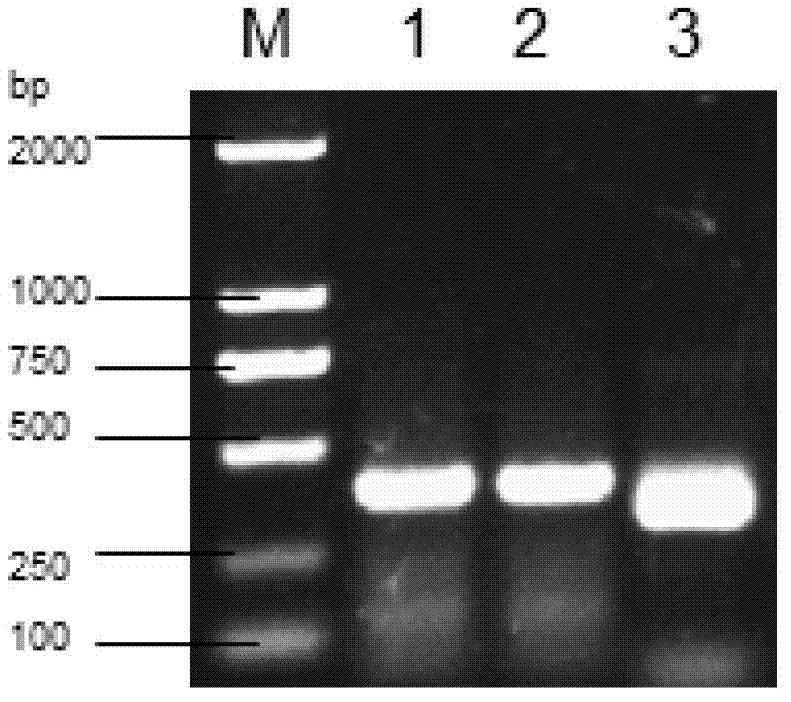
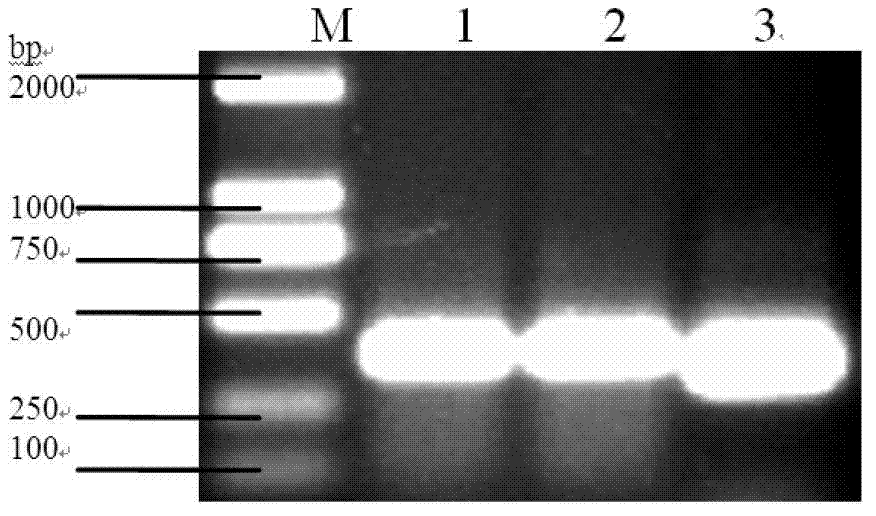
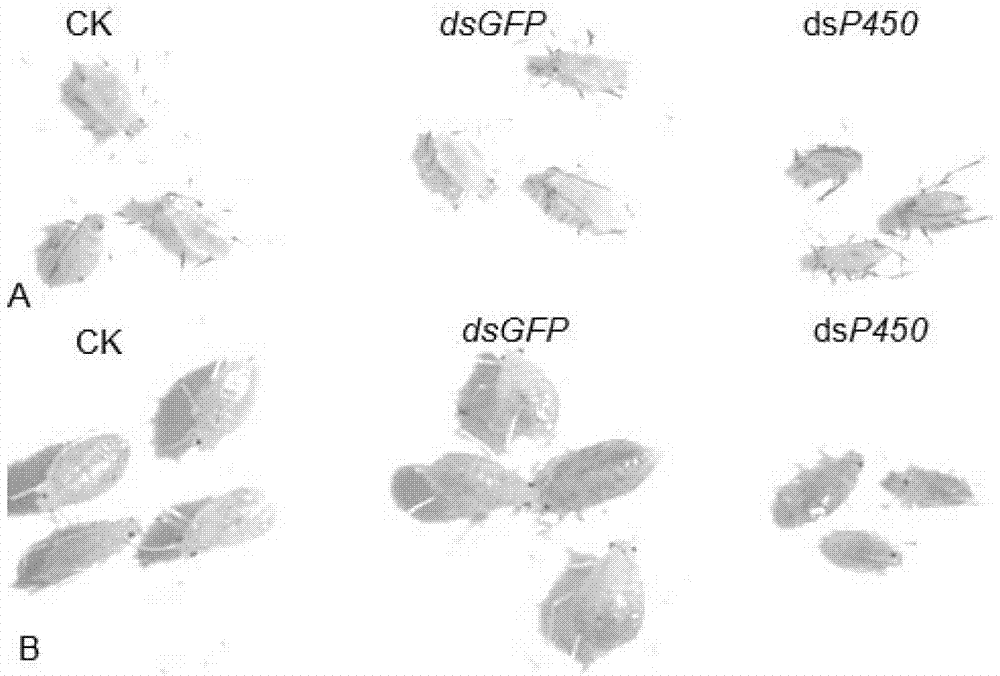
The invention discloses dsRNA (double-stranded ribonucleic acid) and application to aphid growth inhibition. The dsRNA provided by the invention is dsRNA as expressed by 1) or 2) as follows: 1) dsRNA consisting of ribonucleic acid as shown by a sequence 4 in a sequence table and ribonucleic acid as shown by a reverse complementary sequence of the sequence 4; and 2) dsRNA consisting of ribonucleicacid as shown by a sequence 5 in the sequence table and ribonucleic acid as shown by a reverse complementary sequence of the sequence 5. According to experiments, the obtained dsRNA of a conserved sequence of cytochrome P450cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) of English grain aphids and green peach aphids can inhibit growth and development of the English grain aphids and the green peach aphids and can cause a lethal effect by adopting a method of feeding the dsRNA in vitro and using an RNAi (ribonucleic acid interfere) technology to silence the in-vivo cytochrome p450 of the English grain aphids and the green peach aphids.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
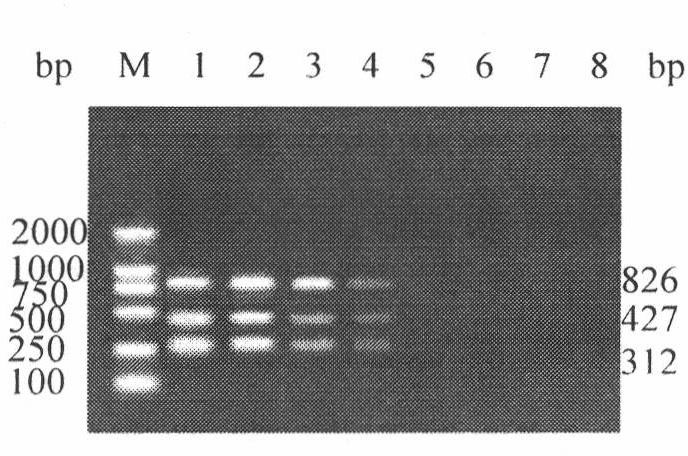
h5, h7, h9 subtype avian influenza virus detection kit
InactiveCN102260749AMicrobiological testing/measurementAvian influenza virusComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
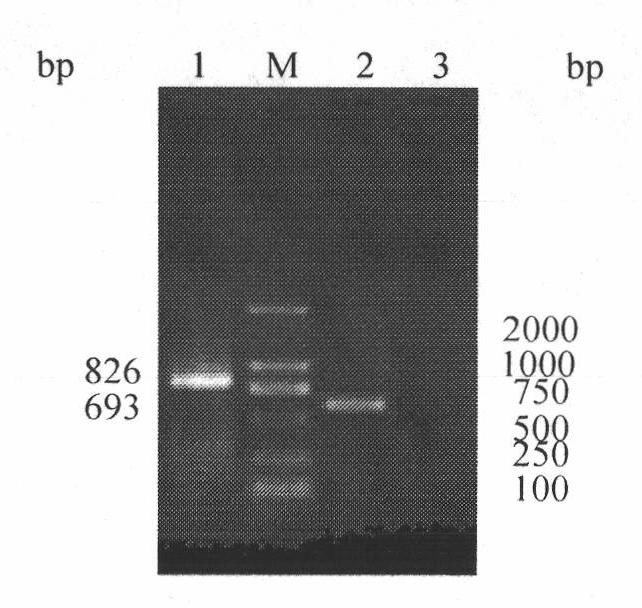
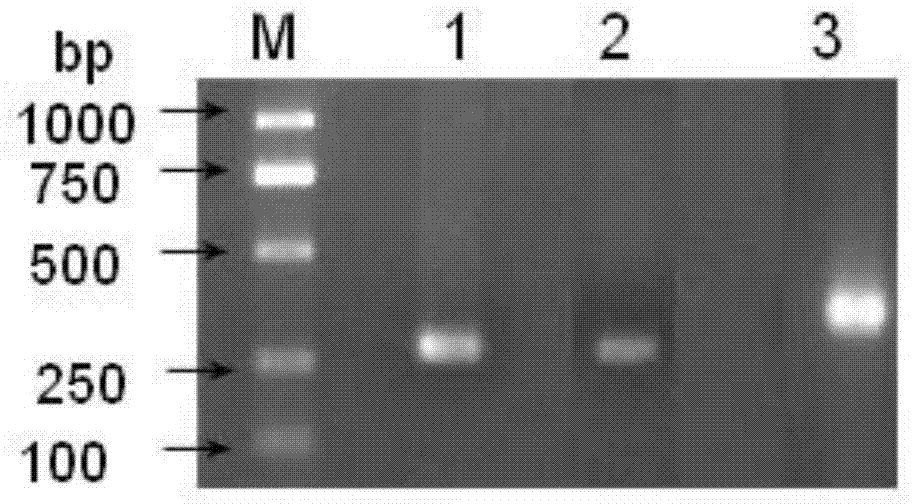
The invention discloses an H5, H7 and H9 subtype avian influenza virus detection kit. In the GenBank, three kinds of subtype HA gene sequences are searched, and specific primers are designed. By many tests and actual detections, three pairs of primers and reaction systems thereof are screened out and optimized, and the sizes of the amplified cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments are respectively 427bp, 312bp and 826bp. The result shows that by optimizing multiple RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) amplification conditions, a multiple RT-PCR detection kit capable of detecting three kinds of subtype avian influenza viruses at the same time is prepared, and the minimum detectable quantity is 10pg. The detection kit does not have cross reaction to various kinds of chicken infectious diseases and normal structures, has strong specificity, and has consistent sensibility to three kinds of subtype detections. The avian influenza can be diagnosed in a shorttime in a primary laboratory and can be positioned in a subtype so as to gain the time for preventing and controlling the avian influenza, thus the spread of the avian influenza can be controlled in a small range as much as possible by adopting measures in time.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Wheat CBL-CIPK (CBL-interacting protein kinase) stress tolerance regulatory factor as well as encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN103555740AImprove salt toleranceStrong drought resistanceTransferasesGenetic engineeringComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidThreonine
The invention relates to a wheat CBL-CIPK (CBL-interacting protein kinase) stress tolerance regulatory factor as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. According to the wheat CBL-CIPK stress tolerance regulatory factor, protein kinase genes which are consciously induced by salt and drought when being expressed in roots and leaves are selected according to expression profile chip information of salt and drought stress of wheat, and a cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence with a whole-length encoding area is cloned, wherein the nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Analysis shows that the gene can encode CBL-CIPK serine / threonine protein kinase, the amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and is named as TaCIPK33. Transgenic function analysis shows that the gene has the functions of improving plant salt tolerance and drought resistance. Basis is provided for further understanding molecular mechanisms of wheat in responding to drought and saltstress, and meanwhile the gene can be applied to genetic improvement of novel stress tolerance germplasms of crops such as wheat.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Single-cell RNA (ribonucleic acid) reverse transcription and library construction method
ActiveCN108103055AEfficient and uniform transcriptAvoid pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationCDNA libraryTotal rna
The invention belongs to the field of transcriptome analysis and relates to a quick single-cell RNA (ribonucleic acid) reverse transcription and library construction method. According to the method, 20-500ng high-quality full-length double-chain cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) is amplified by taking 1-2000 cells or 10pg-20ng extracted eukaryote total RNA as an initial, and a high-quality cDNA library meeting downstream analysis requirements is obtained. The method effectively avoids 3' preference and genome DNA contamination in a cDNA synthesis process; an expression quantitation molecule label can assist in gene expression quantity calculation; and at the same time, the expression quantitation molecule label can also keep chain source information during complete amplification of RNA sequence information. The method can achieve a reverse transcription and amplification library construction success rate of above 95%; the cDNA library can be connected with an Illumina main stream sequencing platform; lower computer data (5M Reads) can detect gene expression of above 90%; the gene expression consistency exceeds 90%; amplification has no obvious bias; and a required sample input amount is smaller.
Owner:XUKANG MEDICAL SCI & TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
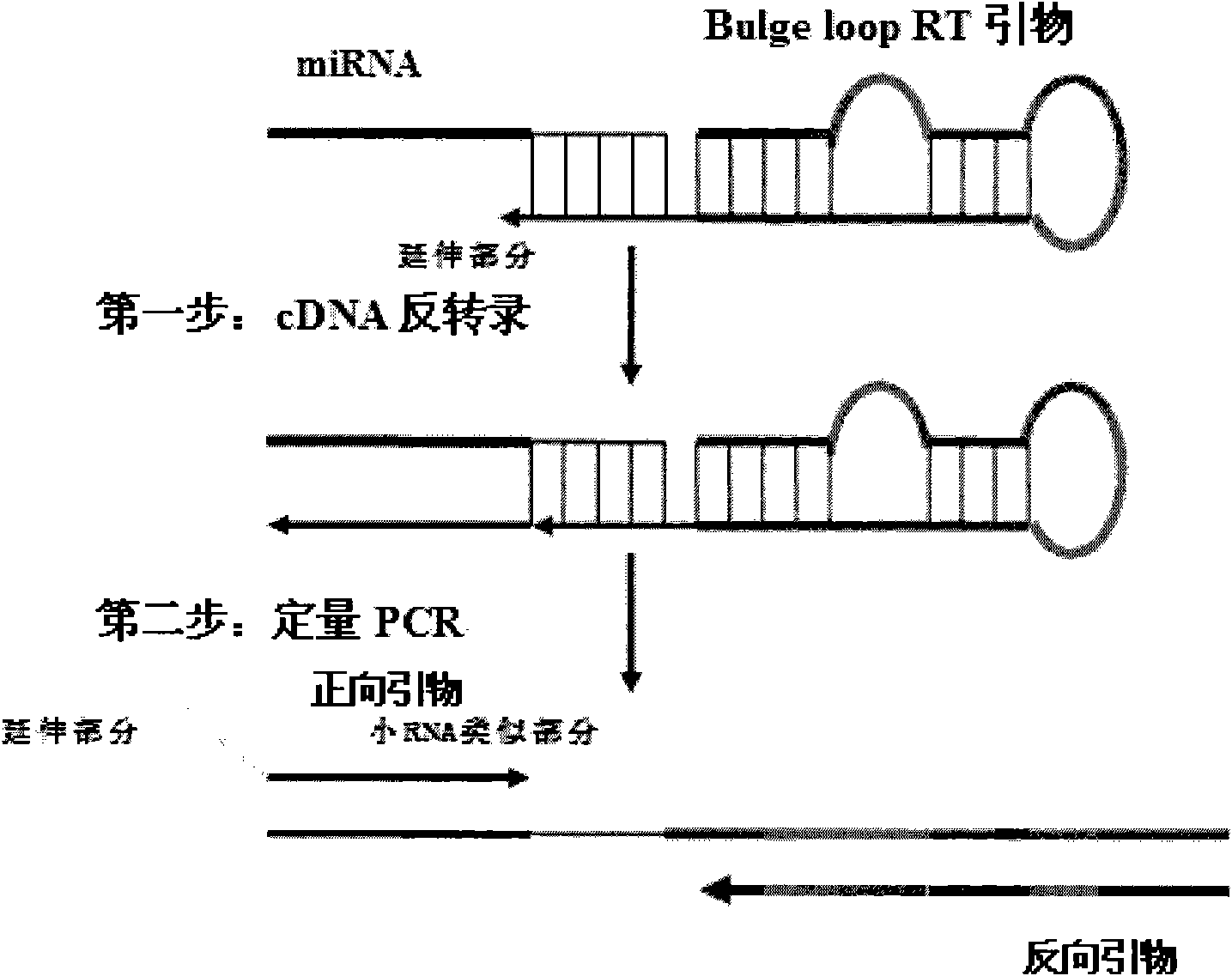
Small RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) quantitative detecting method and reagent kit
ActiveCN101831500AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses a small RNA quantitative detecting method and a reagent kit, which are used for expression analysis of a small RNA, and the method comprises the following steps of: reversely transcribing the small RNA into a cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) through a bulge loop RT (Reverse Transcription) primer, and adding a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) forward primer and a PCR universal reverse primer for quantitative PCR amplification. The small RNA quantitative detecting method and the reagent kit have the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, low price of the reagent kit and the like and can be used for batch detection.
Owner:广州锐博生物技术有限公司
Method for detecting whether Araliaceae plant components exist in sample and whether sample is adulterate
InactiveCN105624291AImprove accuracyQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidOrganism
The invention provides a method for detecting whether Araliaceae plant components exist in a sample and whether the sample is adulterate. The method for detecting whether Araliaceae plant components exist in a sample comprises the following steps: extracting total DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from a sample to be detected; by using the extracted total DNA as a template, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by using a primer pair, wherein the primer pair comprises SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2; and carrying out analytical judgment on the PCR amplification product to identify whether Araliaceae plant components exist in the detected sample. The SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 are designed according to the ITS2 cistron sequence on an eucaryote rDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid). Compared with the ITS2 universal sequence, the SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 can be used for carrying out amplification on the ITS 2 segment sequence of Araliaceae plants and can not be used for amplifying plant drugs of other families. The method can be used for detecting whether Araliaceae plant components exist in the sample, especially ginseng, pseudo-ginseng and / or American ginseng components.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Cloning and function expression method of adversity stress AhMYBL6 gene in peanut
ActiveCN103060340AIncreased transcript levelsImprove stress resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOpen reading frameComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention relates to a cloning and function expression method of an adversity stress AhMYBL6 gene in peanut. The adversity stress AhMYBL6 gene is synthesized by RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) cloning by the steps of preparation and treatment of materials, extraction of RNA (ribonucleic acid) and synthesis of cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid). The open reading frame of the gene is 861bp, and 287 amino acids are coded totally. The homology of the amino acid sequence of the gene with the MYb family proteins GmMYB4, GmMYB29 and GmMYB29A2 of the soybean is higher than 60%. The fluorescent quantitative PCR verifies the expression patterns of the AhMYBL6 under low temperature, salt stress and drought stress; the result indicates that the expression levels of the AhMYBL6 are obviously enhanced after various stress treatment for 1 hour, and kept at high levels all the time thereafter; and the expression level of the AhMYBL6 in the leaf subjected to low-temperature treatment is maximally enhanced by 20 times. After the gene is transferred into peanut by transgenic means, compared with the control, the transgenic plant has obvious characteristics of cold tolerance, salt tolerance and drought tolerance. The AhMYBL6 gene can obviously enhance the stress tolerance of the peanut.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
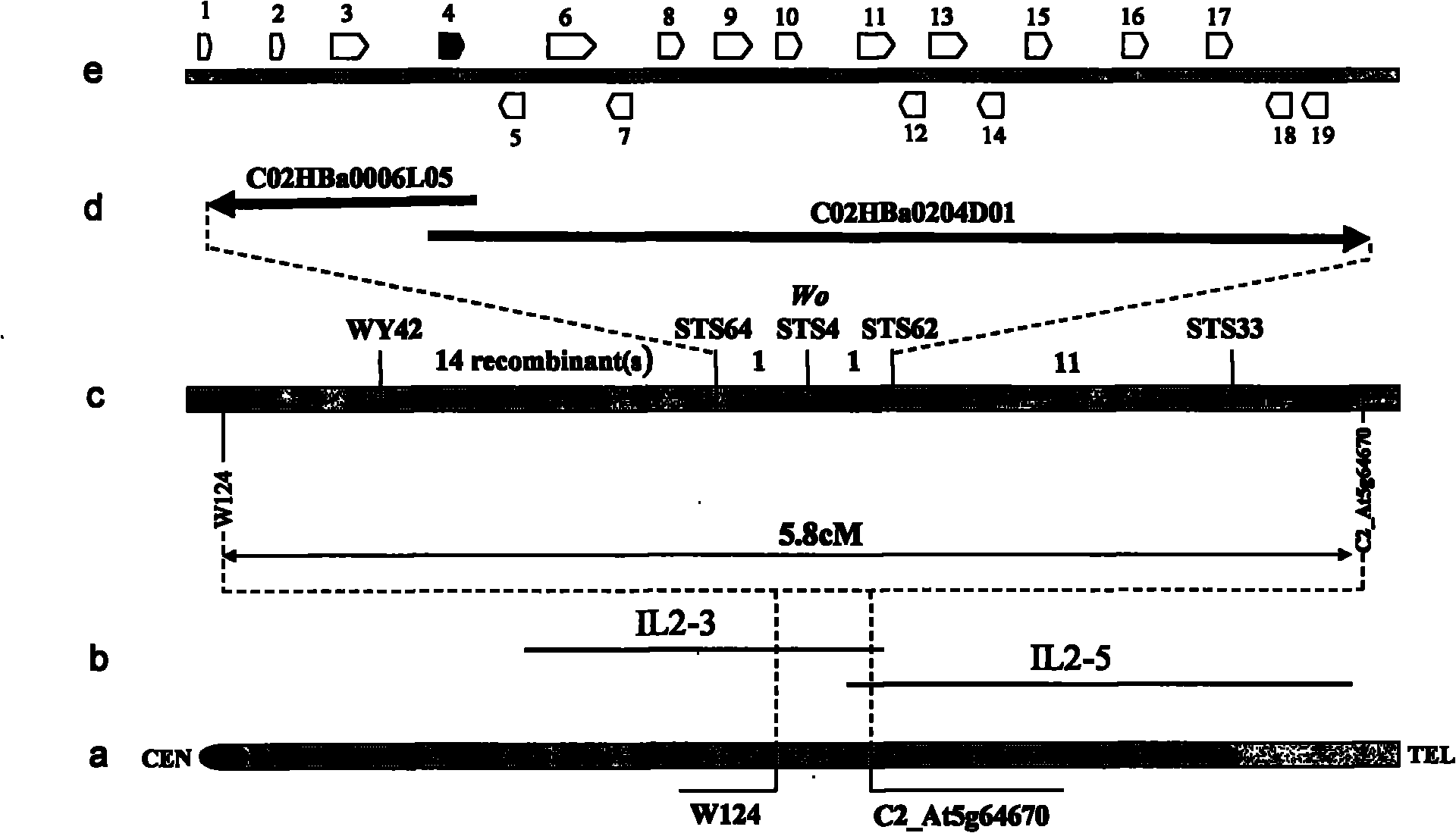
Cloning and application of key gene Wo for controlling tomato hair generation
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and specifically relates to cloning and an application of a Wo gene which is related to tomato hair generation. The cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of the cloned Wo gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1(sequence identity number 1) in a sequence table, the corresponding amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the Wo gene encodes 731 amino acids. The invention further relates to a promoter of the Wo gene and cloning of two allelic genes of the Wo gene. The Wo gene is over-expressed in tomatoes and can improve the amount of epidermal hair of the tomatoes, significantly enhance the insect resistance of the tomatoes and enhance the anti-virus capability.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV) reverse genetic operating system and application thereof
ActiveCN102071218ALow costReduce labor costsInactivation/attenuationVector-based foreign material introductionComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidFull length cdna
The invention relates to a peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV) reverse genetic operating system and an application thereof. The PPRV reverse genetic operating system comprises a transcription plasmid and one or more helper plasmids, wherein the transcription plasmid can express the genome full-length cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of the PPRV; and the helper plasmid(s) can express nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P) and polymerase large protein (L) of the PPRV, and virus replication-permitting host cells of the PPRV. By using the PPRV reverse genetic operating system, the recombined PPRV is successfully saved. The establishment of the PPRV reverse genetic operating technical platform provides an excellent technical platform for the development of PPRV live vector vaccines and the fundamental research related to PPRV.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Efficient virus-induced phytoene desaturase gene silence system for Chinese pink
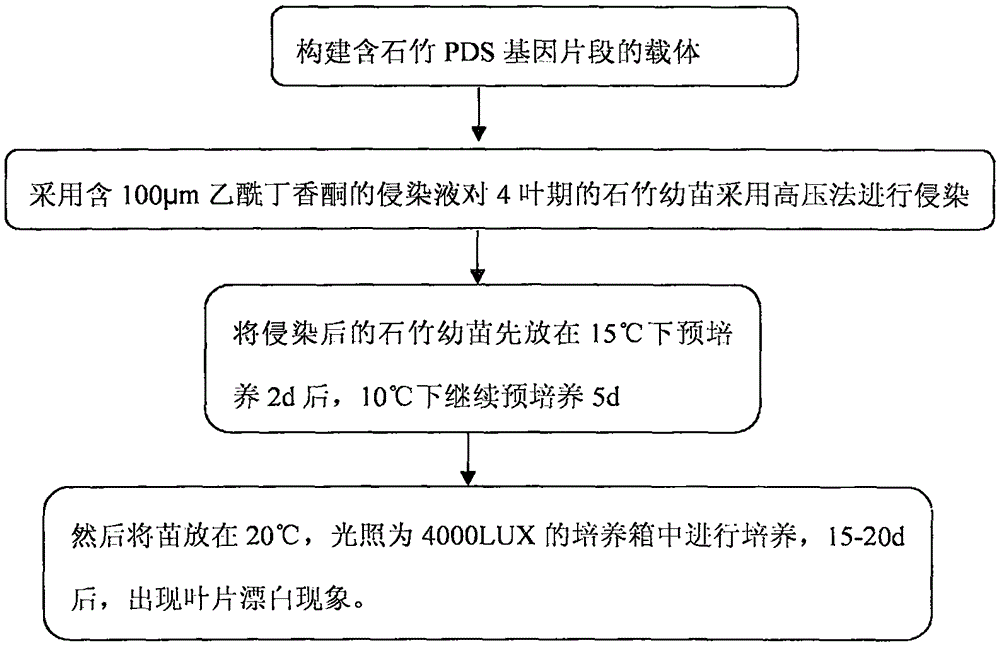
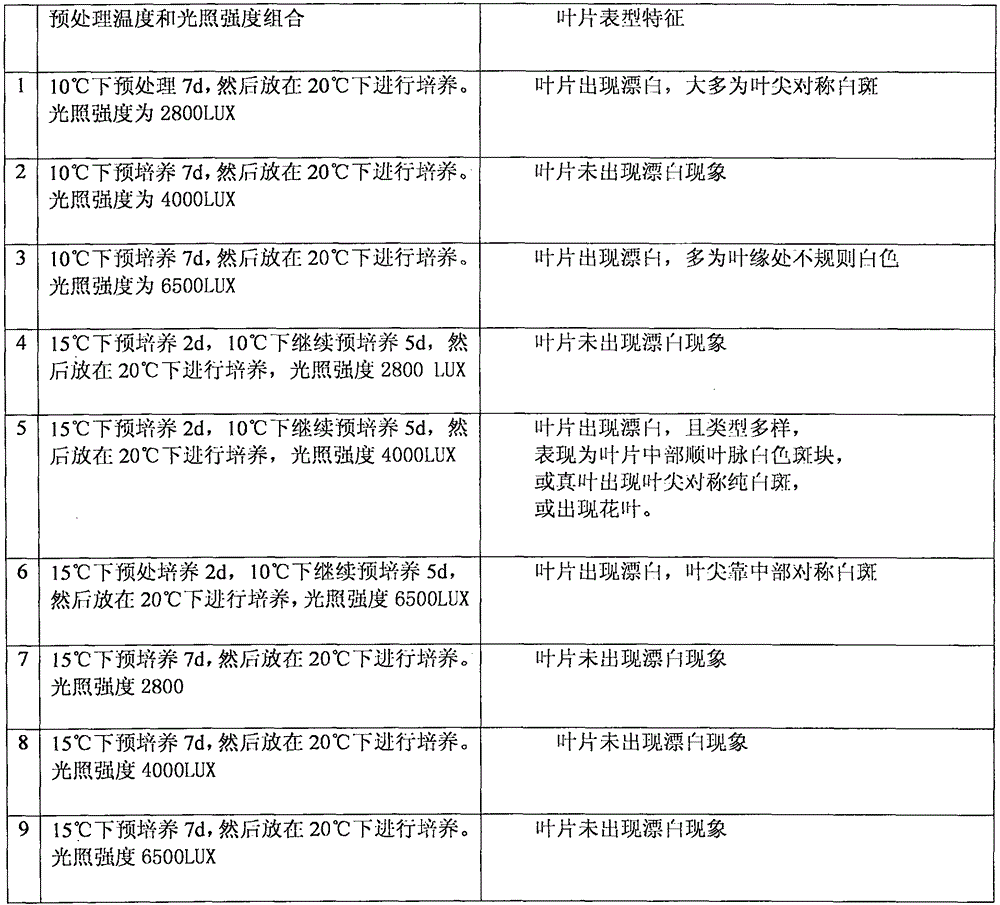
InactiveCN105296535ASolving questions about gene functionGenetic engineeringFermentationComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidMultiplex polymerase chain reaction
The invention discloses an efficient virus-induced phytoene desaturase gene silence system for Chinese pink. A specific primer is designed according to a coding gene sequence of PDS (phytoene desaturase), and about 500bp cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments are amplified in the Chinese pink through RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction). Obtained PDS cDNA fragments are connected to TRV2, and acetosyringone concentration, seedling age and preculture temperature after infection as well as light conditions for plants after preculture are integrated in an assorted manner by optimizing an agrobacterium-mediated virus-induced gene silence system according to photobleaching frequency, bleached leaf area and bleached conditions of the plants, so that the rapid efficient virus-induced silence system is established, virus-induced gene silence character can be obtained, and further, the problem that Chinese pink gene functions are verified effectively is solved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant oral protein TAT-GH of tilapia, preparation method for recombinant oral protein TAT-GH and application of recombinant oral protein TAT-GH
ActiveCN102703483AGuaranteed accuracyIntegrity guaranteedBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses recombinant oral protein TAT-GH of tilapia, a preparation method for the recombinant oral protein TAT-GH and application of the recombinant oral protein TAT-GH. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting total messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) from a pituitary gland of male tilapia, performing reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to obtain complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA), performing PCR amplification to obtain a growth hormone (GH) gene of the tilapia, and amplifying a TAT-GH gene by a PCR overlap extension method; constructing a recombinant plasmid pET-32a(+)-TAT-GH; and transforming Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) by using the recombinant plasmid pET-32a(+)-TAT-GH, efficiently expressing fusion protein TAT-GH in the form of an inclusion body under the induction of isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG), and purifying and renaturing to obtain active protein. The protein can effectively promote the growth and development of fries of the tilapia after being fed to the fries of the tilapia.
Owner:HUBEI TAIYANGHONG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for preventing and treating bemisa babaci by utilizing RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) interference technology
InactiveCN102212522AEasy to controlIn line with habitsVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsInhibitor of apoptosisComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention provides a method for preventing and treating bemisa babaci by utilizing an RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) interference (RNAi) technology, belonging to the technical field of agriculture and biology. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting a target sequence IAP (Inhibitor Of Apoptosis Protein) gene of RNAi according to a gene sequence of the bemisa babaci and designing a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification primer of the target sequence; (2) extracting the RNA of the bemisa babaci and carrying out transcription to obtain a cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid); then carrying out PCR amplification on the cDNA and purifying to prepare a target gene; (3) inserting the target gene into an expression vector to prepare the expression vector containing the target gene; (4) and transforming the expression vector containing the target gene into a crop to obtain a transgenic crop for preventing and treating bemisa babaci; and planting the crop. The method provided by the invention has important guiding value and theoretical significance on researching the gene function of the bemisa babaci by utilizing the RNAi technology, preventing and treating the bemisa babaci by utilizing the RNAi technology, and preventing and treating the bemisa babaci by utilizing the transgenic crop.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
New botrytis cinerea gene related to pathogenicity and application of new botrytis cinerea gene
InactiveCN102965382ABiocideMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention relates to a new botrytis cinerea gene which is named as Bcdp1. The gene contains three exons and two introns, the total length of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is 1608bp, the total length of cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) is 597bp, and 198 amino acids are encoded. The invention also relates to an expression vector and a host containing the gene, and application of the gene in the prevention and control of plant diseases (especially botrytis) and application of the gene used as a target of a pesticide for preventing and controlling the plant diseases.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Receptor protein kinase gene and expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN102586291AIncrease resistanceScab resistantTransferasesFermentationDiseaseComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
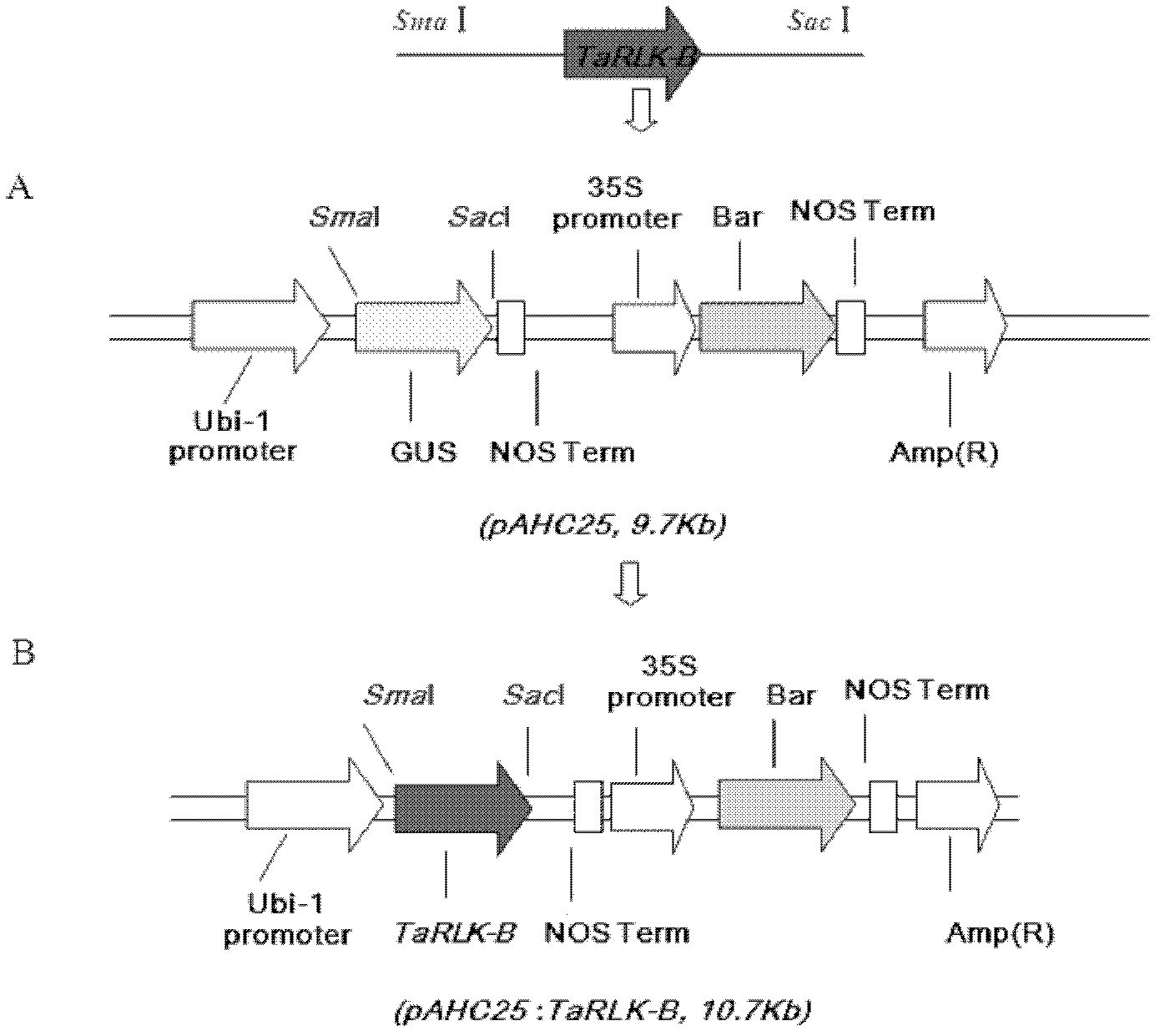
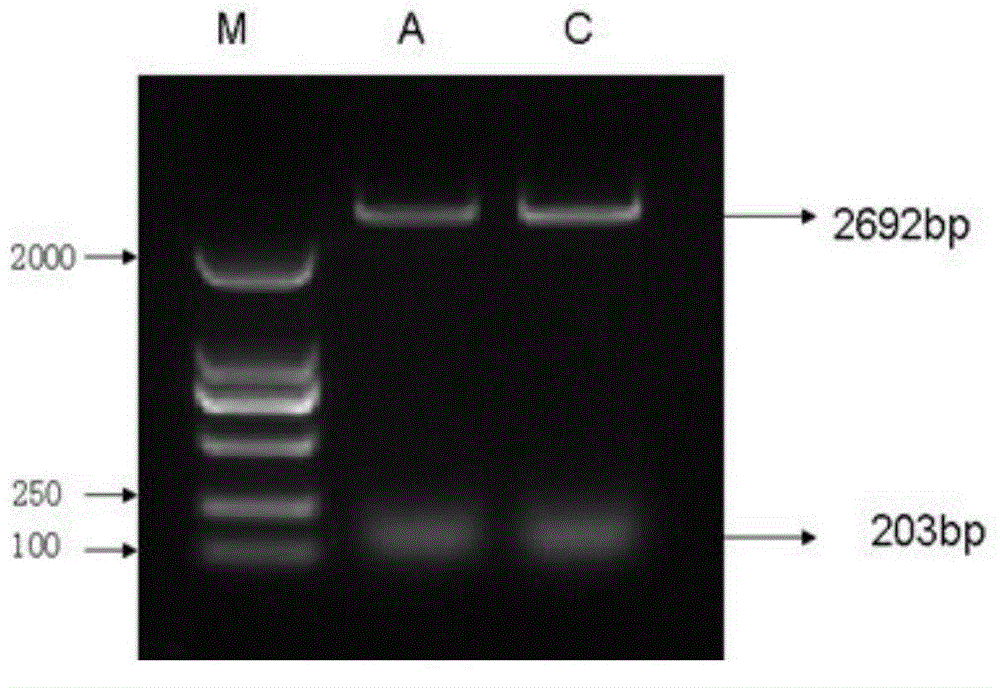
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a receptor protein kinase gene and an expression vector and application thereof. The complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequence of the receptor protein kinase gene TaRLK-B is a sequence identifier number 1 (SEQ ID N0.1), and the coded amino acid sequence of the receptor protein kinase gene TaRLK-B is an SEQ ID NO.2. The gene is from a wanghuibai variety of common wheat (Triticum asetivumL.), and is reported in the wheat for the first time. The TaRLK-B is induced by a gibberellic disease in wanghuibai one variety of the wheat capable of resisting the gibberellic disease to be enhanced in expression, and the expression level of the TaRLK-B is much higher than that in Alondra's one variety of the susceptible wheat. The gene is inserted in pAHC25 to obtain an overexpression vector to convert yang wheat 158 one variety of the wheat affected by the gibberellic disease. After identification of T0-generation gibberellic disease resistance, results show that overexpression of the TaRLK-B can improve resistance of varieties of wheat affected by the gibberellic disease on the gibberellic disease.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
DHAV (duck hepatitis A virus) typing detection method based on fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) melting curve method
InactiveCN104789700AEasy to identifyRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDuck hepatitis A virusComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses a DHAV (duck hepatitis A virus) typing detection method based on a fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) melting curve method. The DHAV typing detection method comprises steps as follows: virus RNA (ribonucleic acid) extraction and cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) synthesis; preparation of positive standard forms; establishment of the DHAV typing detection method based on the fluorescent quantitative PCR melting curve method; method validation adopting a specificity test, a sensitivity test and a reproducibility test. According to the DHAV typing detection method, all that is required is to add a pair of primers, A and C gene types are detected by single tube, the method is simple and feasible, and time consumption is low; the whole amplification and detection process adopts closed tube operation, so that pollution of PCR amplification products is avoided, and false positive results are reduced; amplified fragments are short, higher annealing temperature is adopted, and amplification specificity is guaranteed. The fast DHAV typing detection method is established, great convenience is provided for correct diagnosis and control of the DHAV, and economic benefits of agricultural production are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
dsRNA (double-strand ribonucleic acid) and application of combination thereof to control aphid damage
ActiveCN103571844AImprove aphid resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses a dsRNA (double-strand ribonucleic acid) and an application of combinations thereof to control aphid damage. The dsRNA consists of (1) a nucleotide shown as a sequence 4 in a sequence table and a nucleotide shown as a reversely complementary sequence of the sequence 4; (2) a nucleotide shown in a sequence 5 in the sequence table and a nucleotide shown as a reversely complementary sequence of the sequence 5; or (3) a dsRNA shown by (1) and a dsRNA shown by (2). Experiments show that effects of inhibiting the growth and development of sitobion avenae and causing the death of the sitobion avenae are achieved by feeding the dsRNA for growth and development related genes 8273 and 22544 cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) of the sitobion avenae in vitro and silencing the growth and development related genes 8273 and 22544 of the sitobion avenae by utilizing an RNAi (RNA interference) technology.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Neurons directly induced from human skin cells and preparation method for neurons
InactiveCN102796696AHigh biosecurityImprove motor functionNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsASCL1SOX2
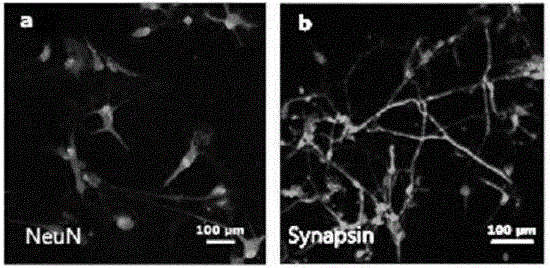
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine and relates to neurons directly induced from human skin cells and a preparation method for the neurons. By the method, induced human neurons which can perform stable passage are directly prepared by importing complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) containing reprogramming transcription factors, namely Sox2, Ascl1 and Myt1l into isolated adult skin cells, screening cells which express a human neuron marker and cloning the cells which express the human neuron marker. The invention is characterized in that (1) the neurons express human neuron-specific marker protein in vitro; and (2) the neurons can survive in vivo and exert functions. The human neurons with the functions are obtained without the process of multipotential stem cells, so that the technology is relatively simple and effective; a heterologous feeder layer is avoided, so that the neutrons have a good clinical application prospect; and the report related to the tumorigenesis is not known about the adopted transcription factors, so the neurons have relatively high biosafety.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Soybean cyst nematode resistance gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102206651AEffective guidanceEffectively guide conventional breedingFungiBacteriaGlycineAgricultural science
The invention relates to a soybean cyst nematode resistance gene and application thereof. The cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment (SRC-J-6) provided by the invention is derived from soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill.) variety L-10, and has a nucleotide sequence shown in 1) a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1; 2) a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule capable of hybridizingwith the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and being expressed under strict conditions; 3) an mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) molecule, which has homology of more than 90% with the nucleotide sequence shown in 1) and can be expressed; or 4) a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule, which has homology of more than 90% with the nucleotide sequence shown in 1) and can be expressed. After theplant tissues are transformed by the gene disclosed by the invention, the resistance to cyst nematode of the transgenic soybean is significantly improved. The soybean cyst nematode resistance gene provided by the invention has important significance, not only can effectively guide conventional breeding, can also provide excellent genetic resources for the transgenic breeding of soybean and has broad application prospects in the soybean production.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Cloning, expression and application of alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene
InactiveCN106191084AReduce manufacturing costIncreased substrate specificityFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisRapid amplification of cDNA ends
The invention discloses cloning, expression and application of an alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene. A coding gene is obtained from aspergillus tubingensis and is expressed in pichia pastoris GS115; specifically, total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of the aspergillus tubingensis is used as a template and cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of alpha-L-rhamnosidase is cloned through RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) and RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) technologies; pPIC9k is used as an expression vector and is subjected to secreting expression in the pichia pastoris GS115. The alpha-L-rhamnosidase can be used for efficiently hydrolyzing naringin; when the naringin is used as a substrate, Km and Vmax values respectively are 1.27mu.mol / mL and 3445mu.M min<-1>; the thermal stability at 60 DEG C is good and the alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene has a good application prospect in food and biopharmaceutical industries.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Primers, probes and detection kit for detecting human HCC (Hepatocellular Carcinoma) marker
ActiveCN103540679AThe detection method is simpleFast detection methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSpecific detectionFluorescence
The invention provides primers and probes for specifically detecting human HCC (Hepatocellular Carcinoma) marker, including a primer and a probe (Seq ID No.1-3) for detecting glypican cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) and a primer and a probe (Seq ID No.4-6) used for detecting alpha fetoprotein cDNA. The invention also provides a detection kit containing the primers and the probes and used for detecting the marker of human HCC by multiplex real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction). According to the invention, by virtue of the multiplex real-time fluorescence quantification PCR, alpha fetoprotein messenger RNA (AFP mRNA) and glypican messenger RNA (GPC3 mRNA) in human HCC at the mRNA level can be detected; the detection method is simple, quick, high in sensitivity and strong in specificity; the whole detection reaction only lasts for 100min. An important technical support is provided for the specific detection of canceration of human HCC.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Application of corn ZmWx gene in increase of corn yield and improvement of grain characteristics
InactiveCN105349559AIncreased amylose content in endospermIncrease productionFermentationGlycosyltransferasesStarch cornComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses an application of a corn ZmWx gene in increase of the corn yield and improvement of grain characteristics. A ZmWx gene sequence is cloned in corn endosperm cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid), the ZmWx gene encodes GBSSI (granule-bound starch synthase I), the GBSSI and an endosperm specific promoter form a fusion gene, the fusion gene is recombined in a plant expression carrier with a transgenic technology to transform corn, and corn transgenetic plants with yield increased and grain characteristics improved are obtained; alternatively, GBSSI overexpressed corn and mutant AGPase overexpressed high-starch corn are hybridized, a transgenetic polymer is obtained through screening, and the corn transgenetic plants whose grain yield, starch content and hundred-grain weight are remarkably higher than those of recipient materials are produced. The application provides a basis and a means for development and preparation of high-starch and high-amylose starch corn and also develops a new approach for increase of the corn yield and improvement of the starch quality.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
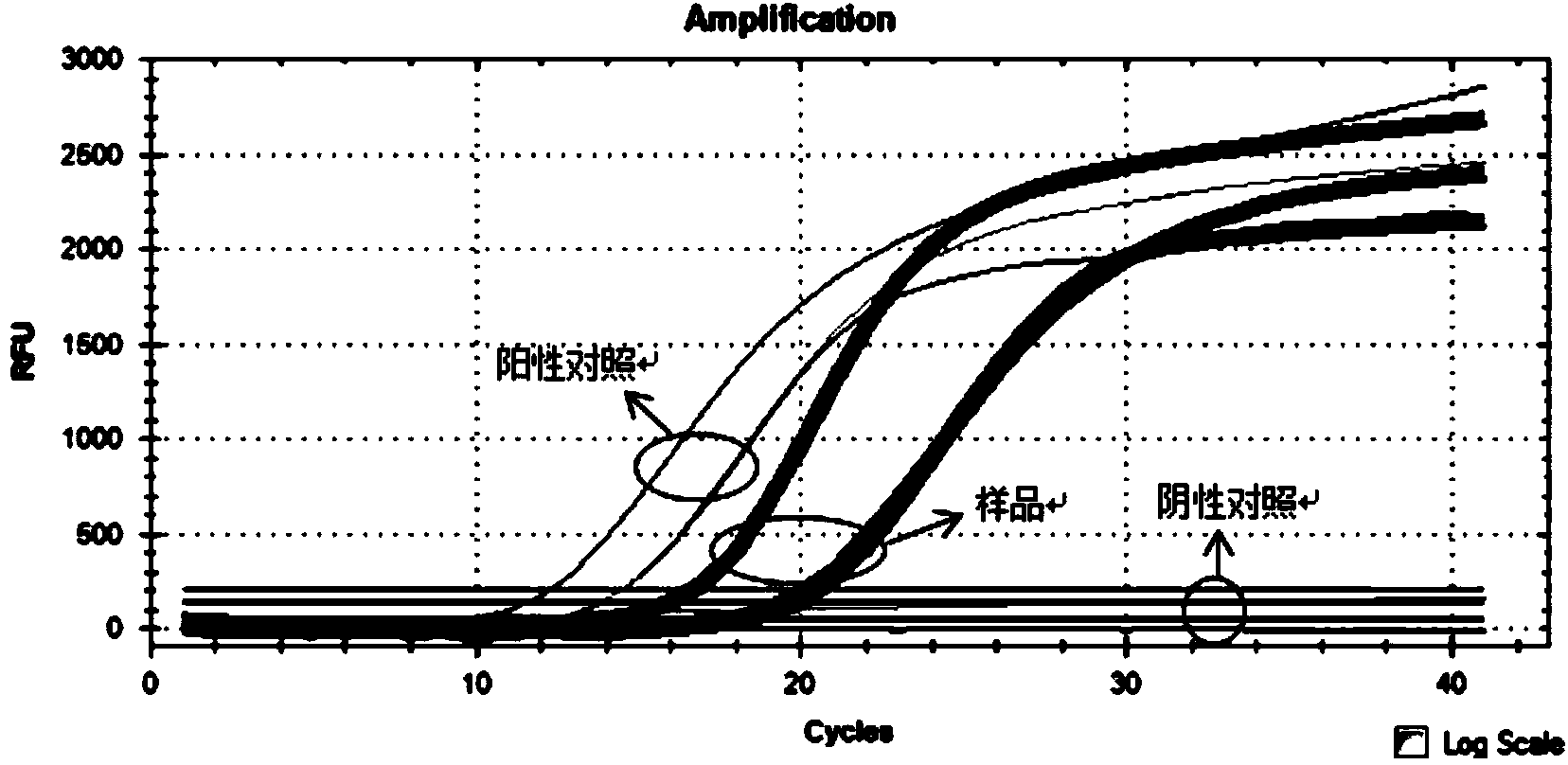
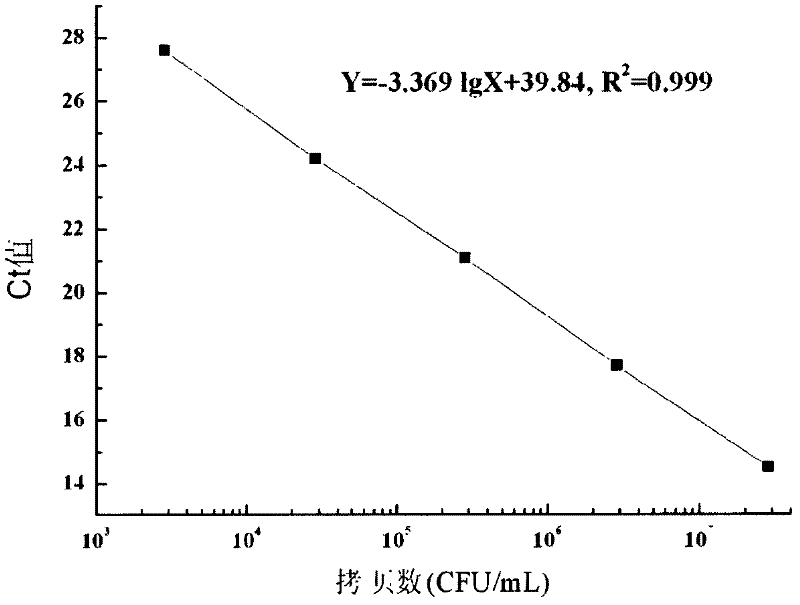
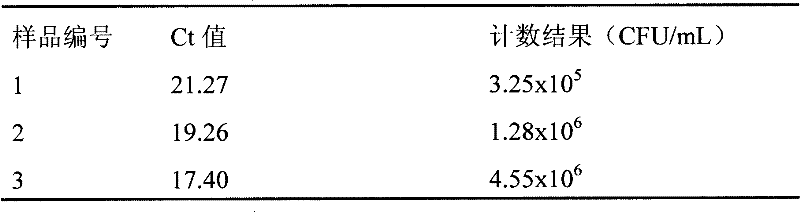
Method and kit for quickly and quantificationally detecting lactobacillus plantarum ST-III
ActiveCN102453767AThe detection process is fastStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceTotal rnaComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses a method and a kit for quickly and quantificationally detecting lactobacillus plantarum ST-III. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) extracting total RNA (ribonucleic acid) of a sample to be detected; 2) carrying out inverse transcription on the total RNA extracted in the step 1) to obtain cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid); 3) carrying out fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification detection by utilizing a primer pair of specifically amplified lactobacillus plantarum ST-III and taking the cDNA obtained in the step 2) as atemplate; and 4) comparing the circulation thresholds of the sample to be detected and a quantitative external standard product to quantify the actual number of copies in the sample to be detected. The method and the kit can quickly detect the quantity of lactobacillus plantarum ST-III in a detected sample and have fast speed, strong specificity and high sensitivity, and the limit of detection can be up to 2.85*10<3>CFU / mL.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
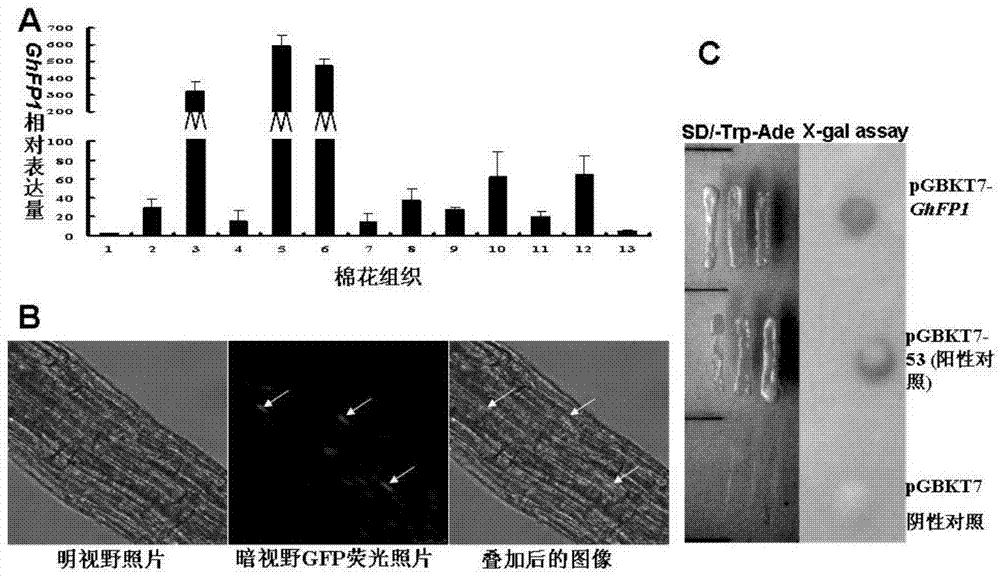
Identification and application of cotton bHLH transcription factor gene GhFP1 and promoter thereof
ActiveCN104711266AHigh specific expression activityHigh elongationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesAgricultural sciencePromoter activity
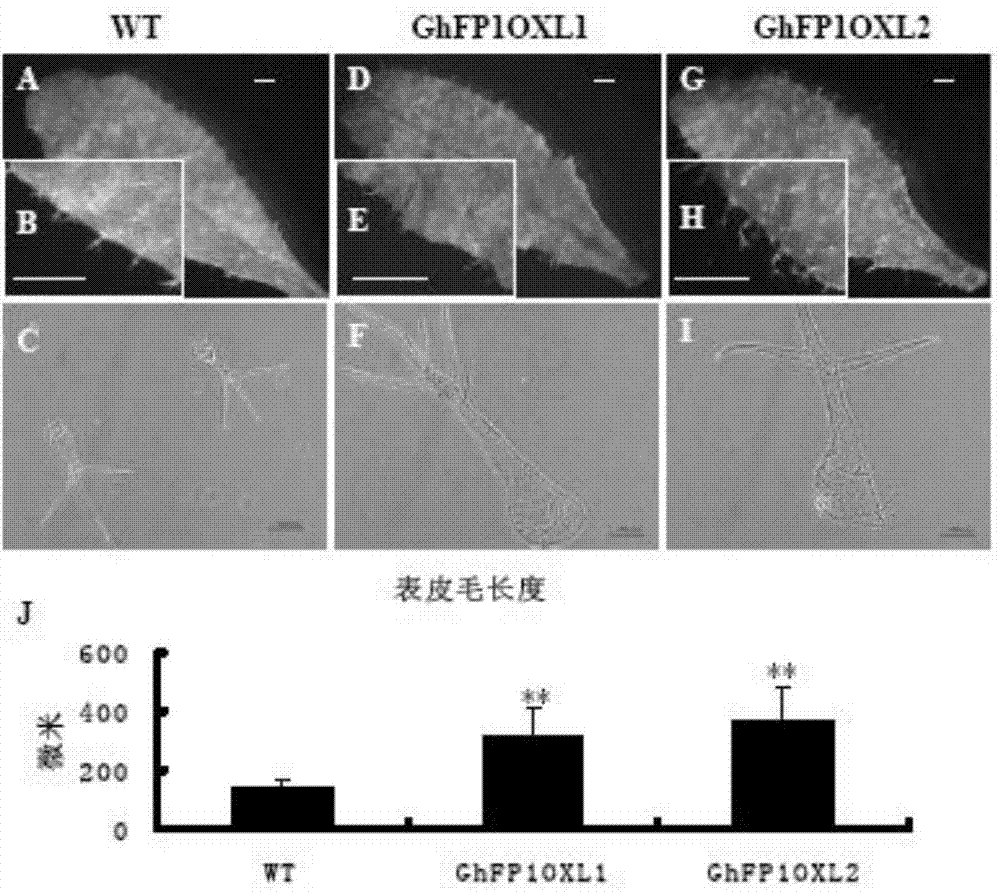
The invention relates to a cotton GhFP1 gene which belongs to a member of a bHLH transcription factor gene family, the cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) full length is 1262bp, and the cotton GhFP1 gene can code a bHLH protein containing 355 amino acids. GhFP1 is respectively expressed in various tissues of cotton, and is highly expressed in the fiber development premetaphase. The GhFP1 promoter segment with the length of 1061bp is separated and cloned. The analysis on the activity of the promoter by using the GUS report gene indicates that the promoter has higher specific expression activity in cotton fibers. The experiment indicates that the overexpression of GhFP1 in Arabidopsis thaliana results in increase of leaf epidermal hair; and the overexpression of GhFP1 in cotton results in enhancement of expression of related genes of cotton fibrocyte brassinolide and increase of ripe cotton fiber length. The result proves that the GhFP1 protein performs positive regulating actions and promotes elongation of fibrocytes in the cotton fiber elongation process, and thus, possibly has important application value in improving the cotton fiber quality and increasing the cotton yield.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
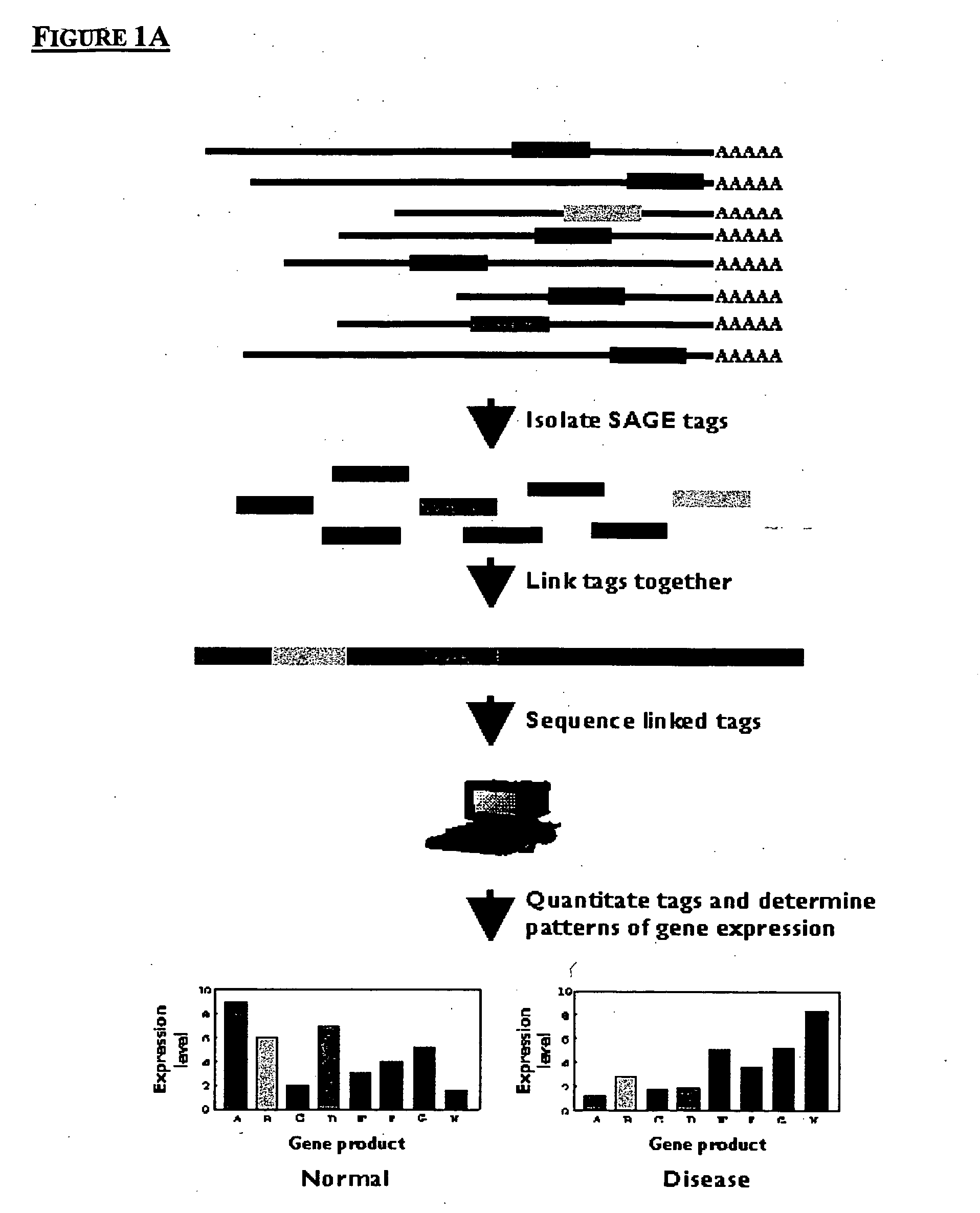
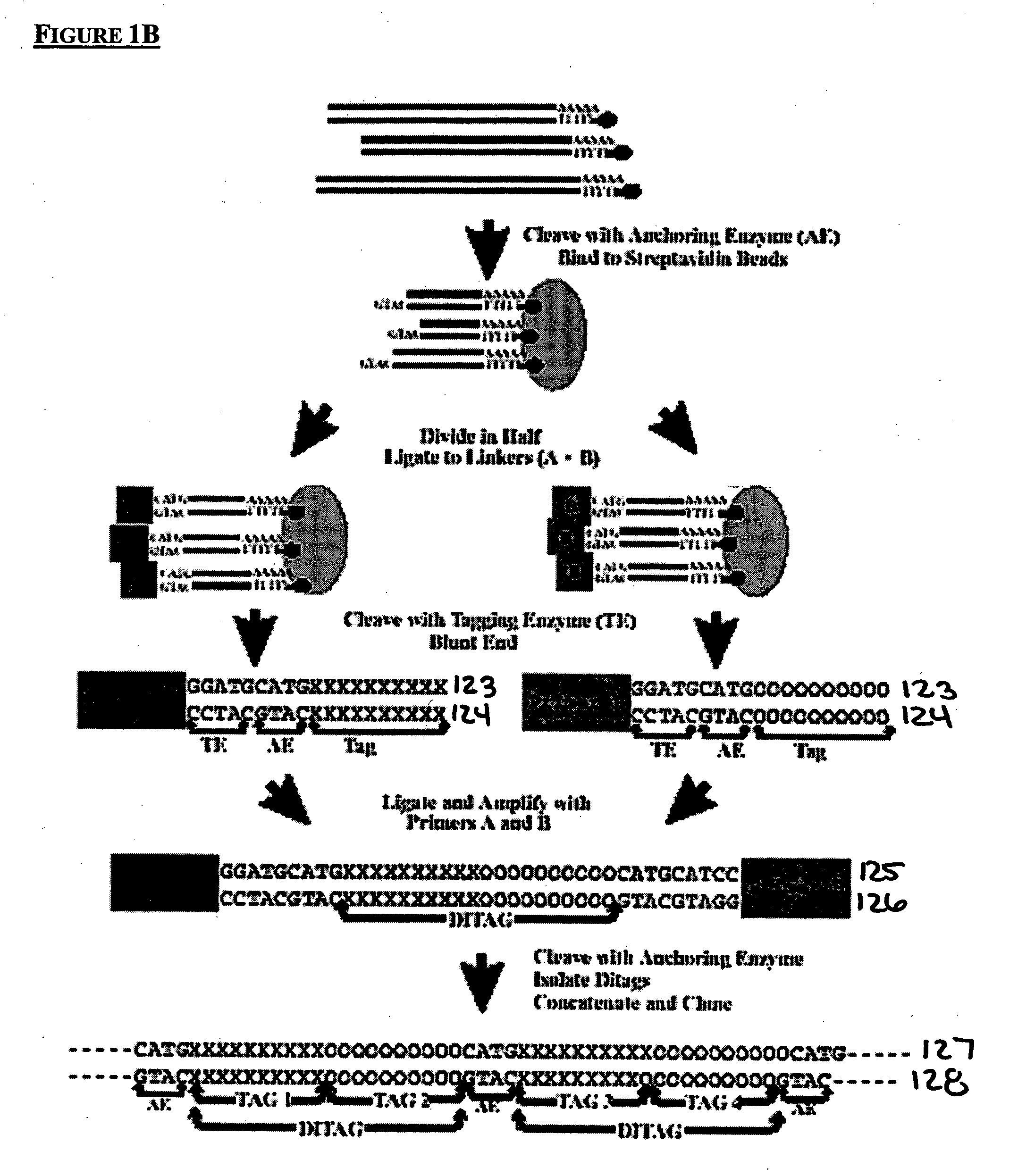
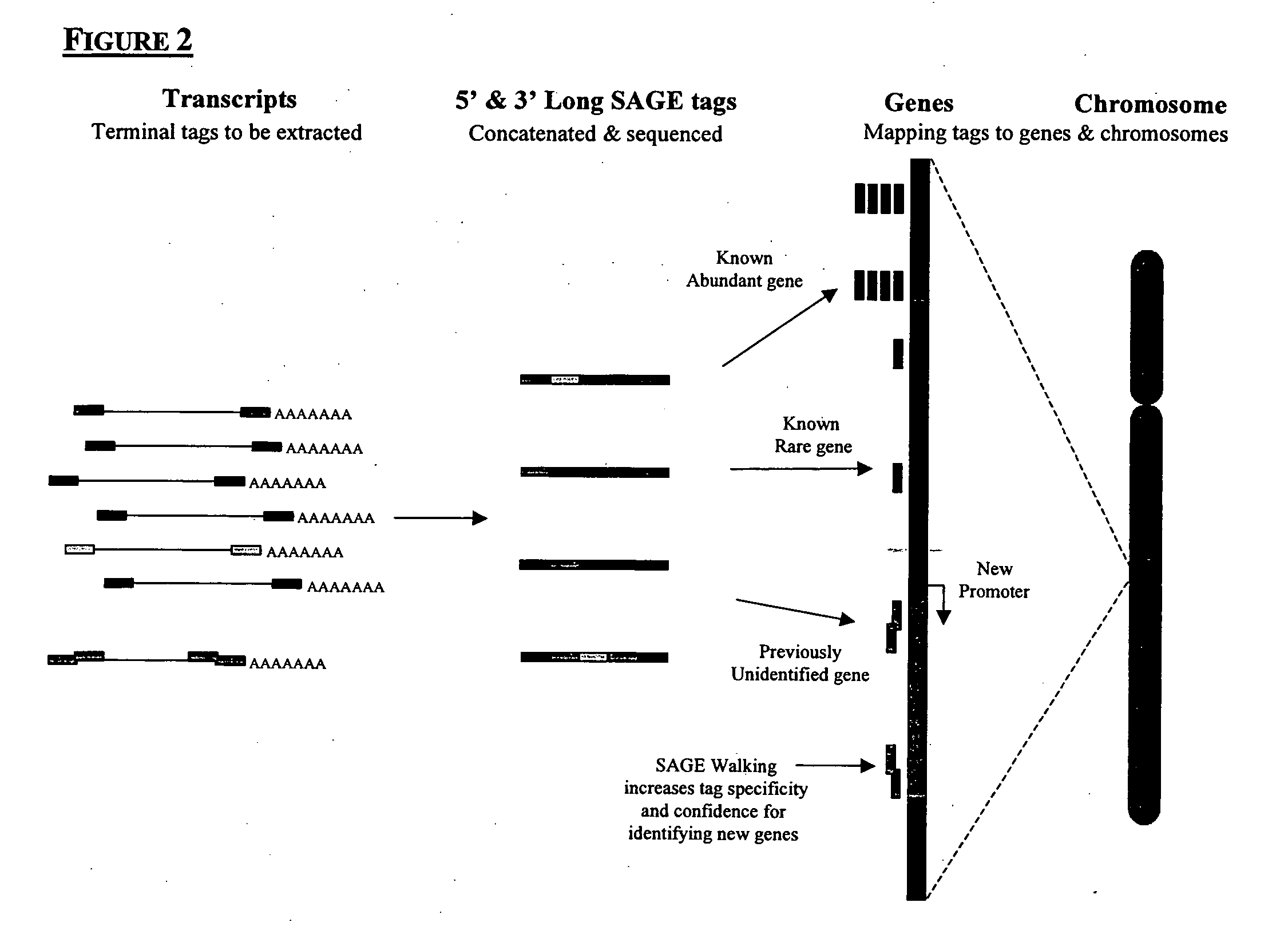
Method to generate or determine nucleic acid tags corresponding to the terminal ends of DNA molecules using sequences analysis of gene expression (terminal SAGE)
A method of providing an indication of an instance of expression of a gene is described herein, the method which may comprise the steps of: (a) providing a complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) having a terminus comprising a terminal transcribed sequence of a gene; (b) linking the cDNA to an linker sequence thereby forming a linked nucleic acid, in which the linker sequence comprises a first recognition site for a first nucleic acid cleavage enzyme, preferably a restriction endonuclease, that allows nucleic acid cleavage at a site distant from the first recognition site; and (c) cleaving the linked nucleic acid with the first nucleic acid cleavage enzyme to provide a linked tag, in which the linked tag comprises a nucleotide sequence tag representative of a terminal transcribed sequence of the gene; and (d) detecting the presence or identity of the linked tag or the nucleotide sequence tag to provide an indication of an instance of gene expression.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Fish natural killer (NK)-lysin effective factors and application method thereof
InactiveCN103145822AImprove anti-virusImprove the ability to resist bacterial infectionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEffective factorLysin
The invention relates to the filed of molecular biology, in particular to cynoglossus semilaevis natural killer (NK)-lysin and application method of the cynoglossus semilaevis NK-lysin. NK-lysin is as the display of an amino acid sequence in sequencer (SEQ) ID No.1. The application method is that the cynoglossus semilaevis complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (c DNA) serves as a template, and a primer F1 and a primer R1 are utilized to carry out polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification. After a PCR product is connected with an expressive vector, plasmids (p CNK1) are obtained, the plasmids (p CNK1) are injected into fishes and the antiviral capacity and the antibacterial capacity of the fishes can be obviously intensified.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant carp Nrf2 (NF-E2-related factor 2) gene, protein, preparation and detection methods and application of recombinant carp Nrf2 gene
InactiveCN103074348AImprove culture survivalImprove antioxidant capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideCarp
The invention discloses a recombinant carp Nrf2 (NF-E2-related factor 2) gene, a recombinant carp Nrf2 protein, preparation and detection methods and application of the recombinant carp Nrf2 gene. The recombinant carp Nrf2 gene has a sequence shown by SEQIDNO:1, and the recombinant carp Nrf2 protein has a sequence shown by the SEQIDNO:2. By the nucleotide sequence of the carp Nrf2 gene complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) disclosed by the invention, the tissue specific expression of the Nrf2 gene can be further detected through a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or hybridization method, and the full-length cDNA of the carp Nrf2 gene can be further cloned. The complete Nrf2 protein may be expressed through recombining the cDNA of the recombinant carp Nrf2 gene onto an expression vector, so that the Nrf2 protein can be used for producing antibodies, and the Nrf2 gene expression states of cells, tissues, early embryos and individuals of carps under different states are detected.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Antimicrobial peptide as well as preparation method and application thereof
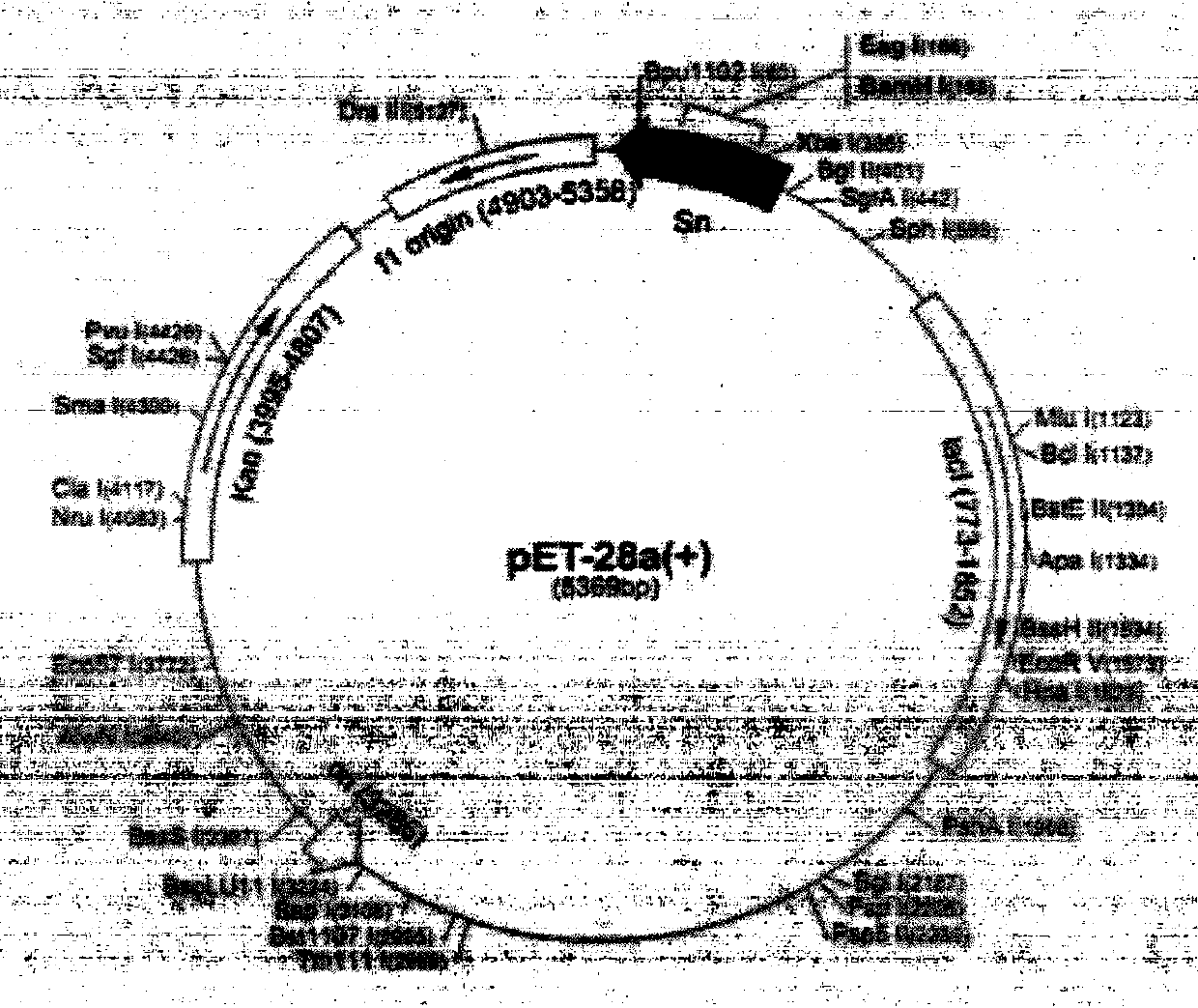
InactiveCN103436538ASignificantly kills root-knot nematode incognitaBiocidePlant peptidesEscherichia coliAntimikrobielle peptide
The invention discloses an antimicrobial peptide. The gene sequence of the antimicrobial peptide is a gene code sequence of a no-signal peptide of an antimicrobial peptide Snakin. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the antimicrobial peptide. The method comprises the following steps of (1) extracting the total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of capsicum leaf tissue, thereby obtaining a first chain cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) for standby by adopting a reverse transcriptase; (2) carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) cloning to obtain the gene code sequence, denoted by an Sn gene sequence, of the no-signal peptide of the antimicrobial peptide Snakin; (3) forming recombination plasmids; (4) screening successfully-recombined plasmids denoted by pET-Sn; (5) transforming the successfully-recombined plasmids into competent cells BL21 (DE3) of Escherichia coli, carrying out induced expression by adopting IPTG, and meanwhile, secreting proteins; (6) carrying out ultrasonic-wave crushing on the competent cells which secrete the proteins in the step (5), carrying out centrifugation, and then, collecting the antimicrobial peptide from an supernatant. The method has the advantages that the antimicrobial peptide which does not contain signal peptides is obtained and has a killing effect on meloidogyne incognita chitwood.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
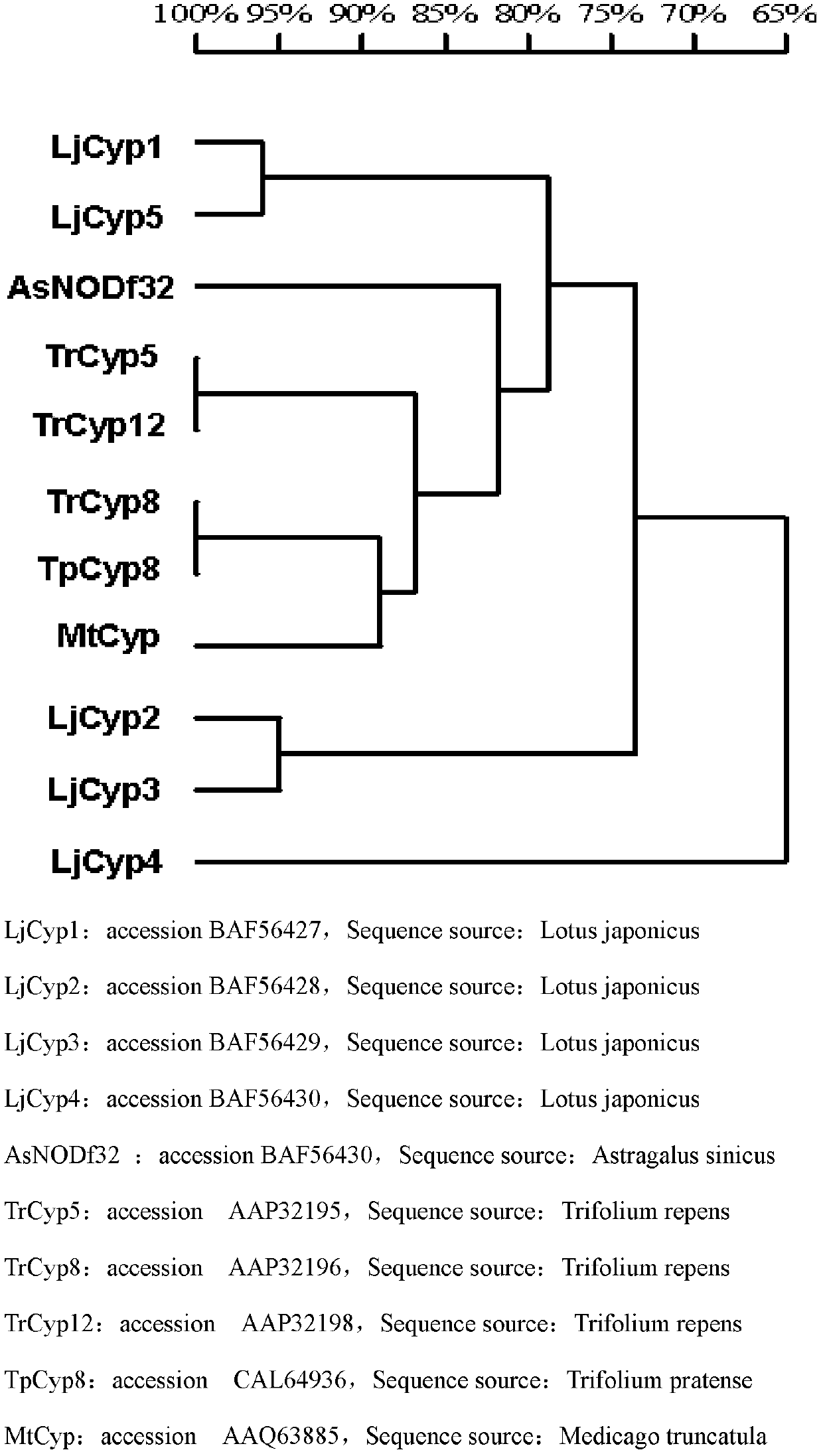
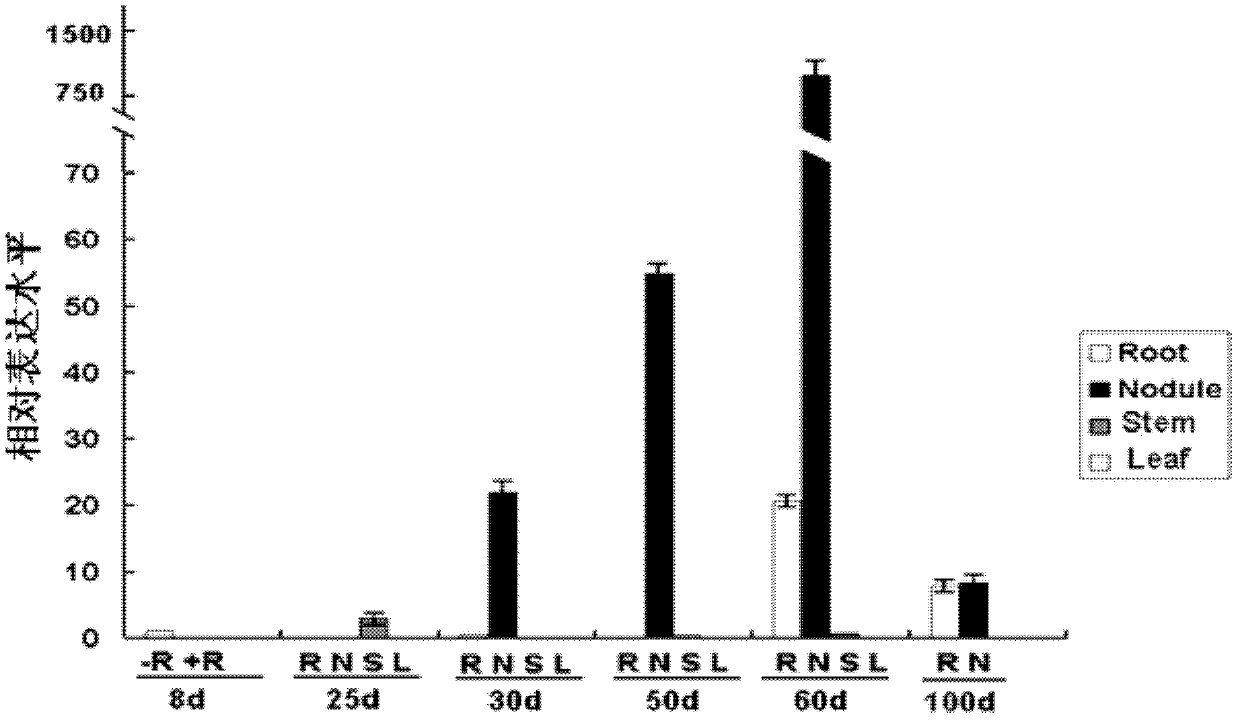
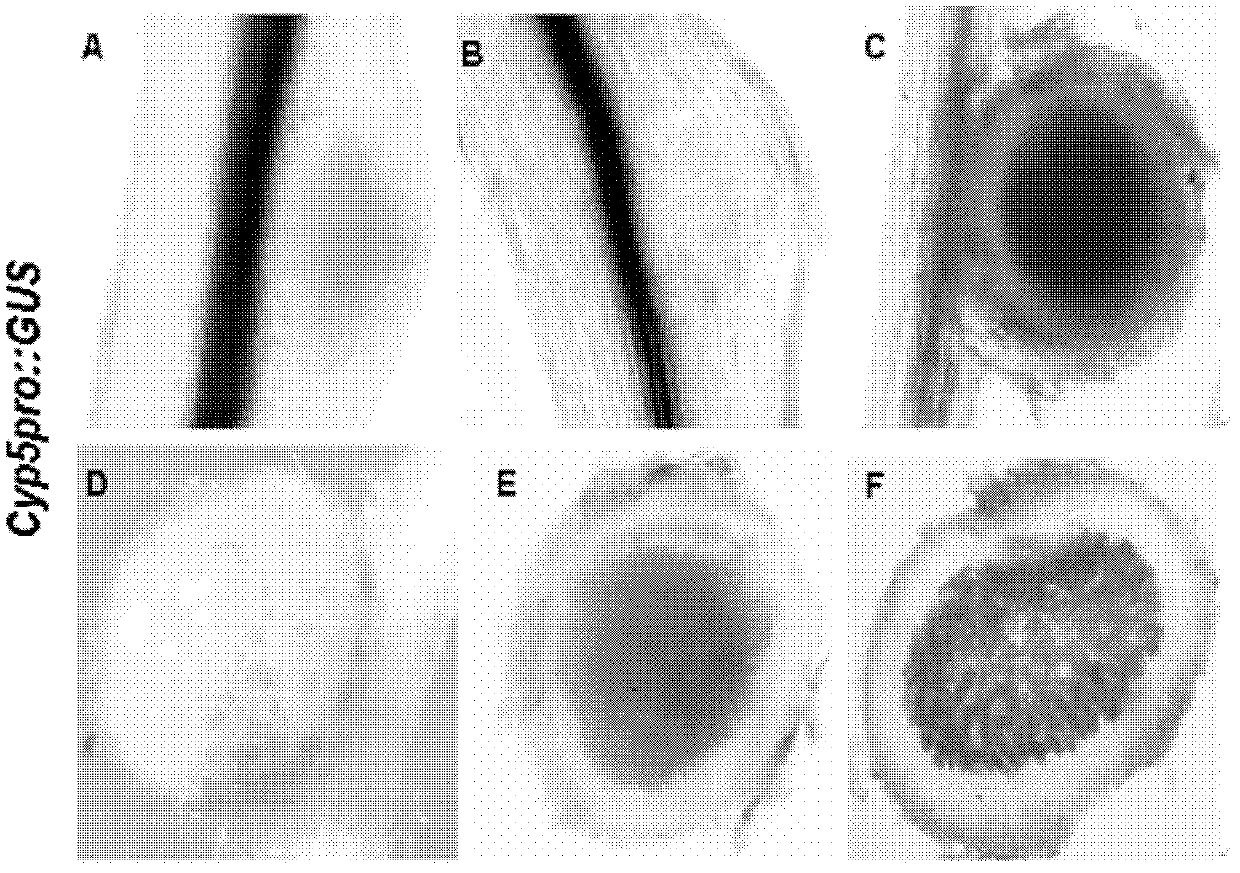
Cysteine protease gene for regulating and controlling root nodule senescence, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103290040ARegulation of agingShort lifeHydrolasesFermentationSequence analysisPlant nodule
The invention discloses a cysteine protease gene for regulating and controlling root nodule senescence, and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, a Japan lotaustralin genomic sequence library is compared by utilizing the known cysteine protease gene of astragalus smicus; after the Japan lotaustralin genomic sequence library is analyzed and compared on the internet in a detailed manner, a primer having strong specificity is designed to carry out gene cloning by taking initiation codon as the starting point and termination codon as the finishing point; in addition, due to sequencing analysis and comparing analysis, a cloned fragment proves that the cysteine protease gene for regulating and controlling root nodule senescence is successfully cloned from the lotaustralin genomic sequence and cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid). The invention discloses application of the cysteine protease gene on leguminous plants; the expression mode of a gene promoter and the functions of the gene in the root nodule senescence process are researched by utilizing a histochemical localization technology. Compared with contrast plants, the results show that the root nodule of an RNAi (ribonucleic acid interference) plant is enlarged; the nitrogen fixation enzyme activity is increased; senescence of the root nodule is delayed; the effective nitrogen fixation time of the root nodule is prolonged; growth of the plant is more vigorous; the cysteine protease gene disclosed by the invention has application prospect on leguminous crops.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Whole blood immune repertoire detection method based on high-flux sequencing technology
ActiveCN104263818ALow costReduce sequencing timeMicrobiological testing/measurementComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidT cell
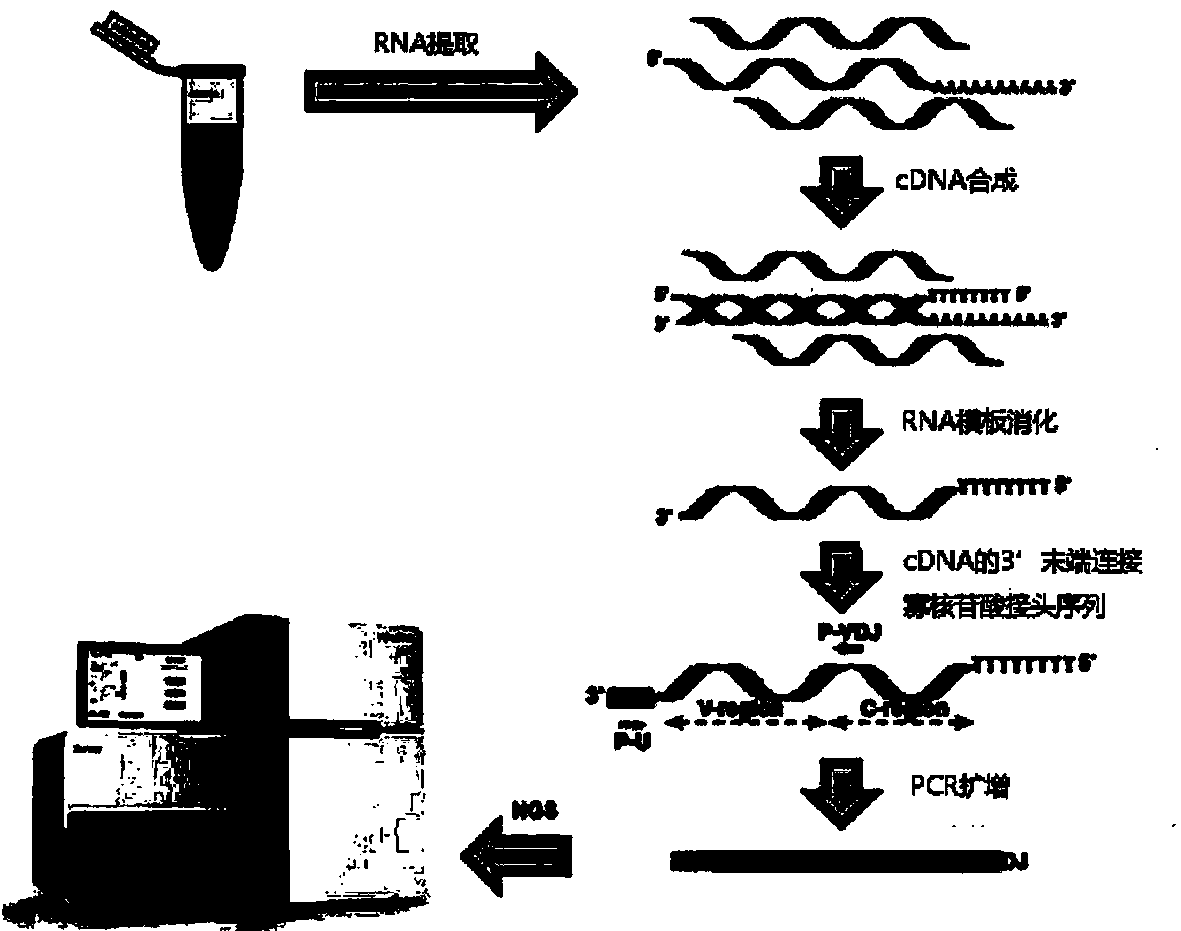
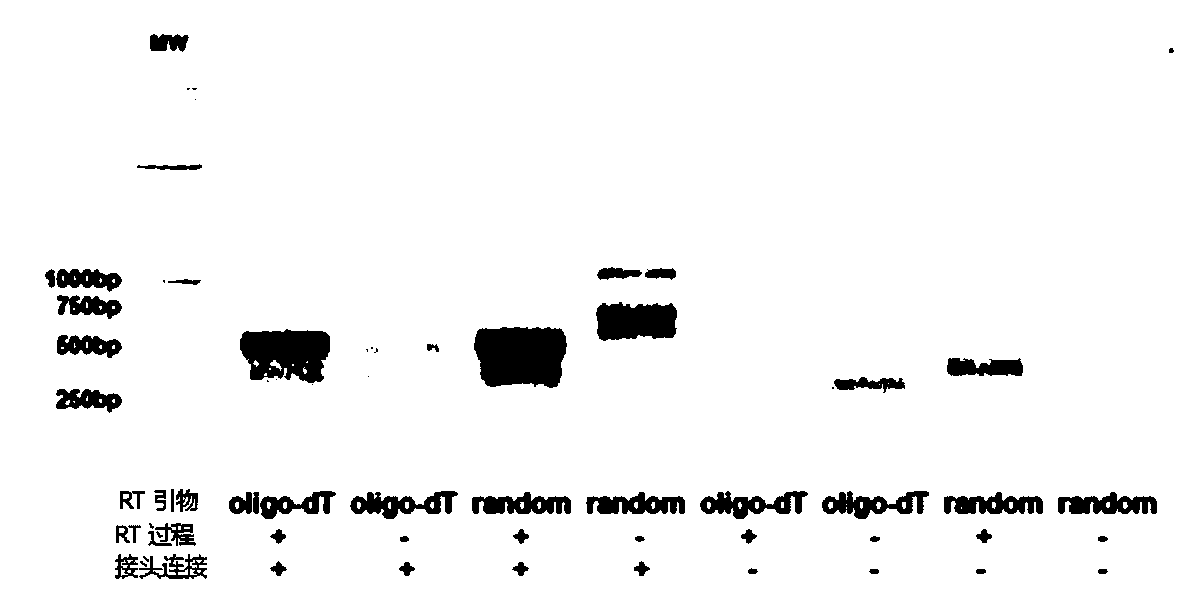
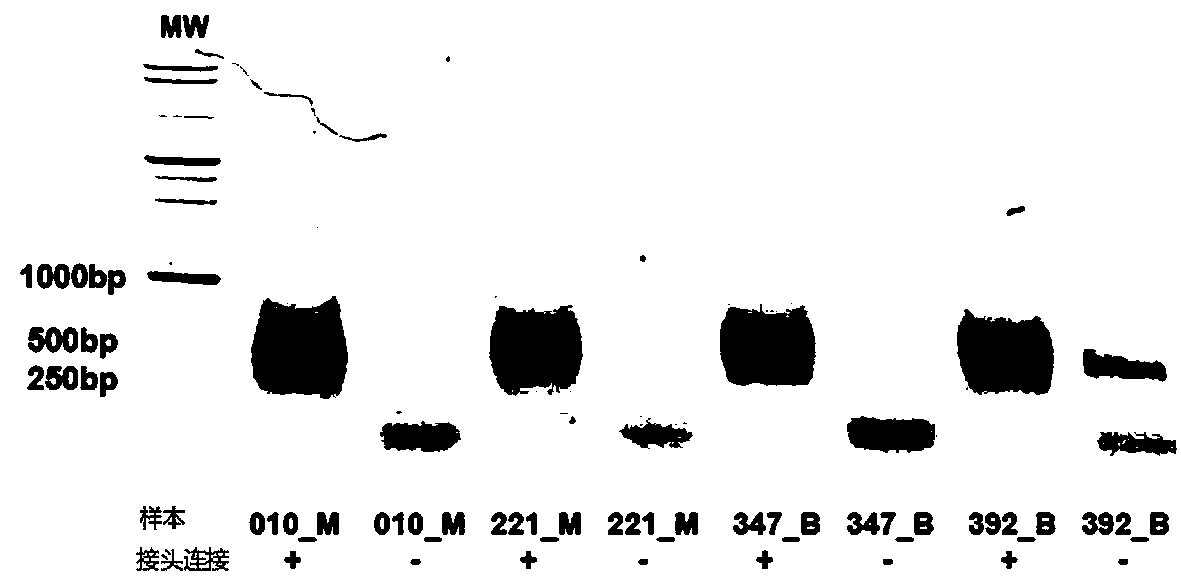
The invention provides a whole blood immune repertoire detection method based on high-flux sequencing technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) directly extracting RNA (ribonucleic acid) from a whole blood sample; (2) carrying out reverse transcription on the RNA to generate single chain cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid), connecting an oligonucleotide joint sequence to the tail end of the single chain cDNA, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) reaction on the single chain cDNA subjected to oligonucleotide joint sequence connection by using a universal primer and a special targeted primer P-VDJ (of which the sequence is GAC CTC GGG TGG GAA CAC) as a special primer pair for PCR reaction, and amplifying the immune receptor genome; and (3) carrying out high-flux sequencing. The method of directly extracting the RNA from the whole blood sample is more suitable for clinic; the single target specific primer is utilized to uniformly amplify the variable region of the subtype T cell receptor gene; and a Hi-SEQ 2500 of the Illumina corporation and a bar code are utilized for sequencing, thereby ensuring the lower cost, the sequencing time of less than 48 hours and favorable sequencing depth.
Owner:武汉希望组生物科技有限公司
BVDV (bovine viral diarrhea virus) internal control typing fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit and preparation thereof
InactiveCN103725796AShort detection timeShorten detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceBovine Viral Diarrhea VirusesComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses a BVDV (bovine viral diarrhea virus) internal control typing fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit and a preparation thereof. By means of the primer design, a BVDV I, a BVDV II and a PCR template for monitoring internal control are obtained through single PCR amplification, a BVDV internal control typing fluorescent PCR detection system is established through the primer design, PCR amplification and optimization of reaction conditions, the BVDV I and the BVDV II can be independently detected or synchronously detected, and quality monitoring can be performed on the detection result. The prepared kit comprises two parts of a cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) synthesis system and an SYBR fluorescent PCR amplification system. The minimum detection limit of the kit to three types of genes is 102 copy, the kit has better specificity and repeatability, the detection quality is ensured, and the kit has a better application value.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com