Patents
Literature
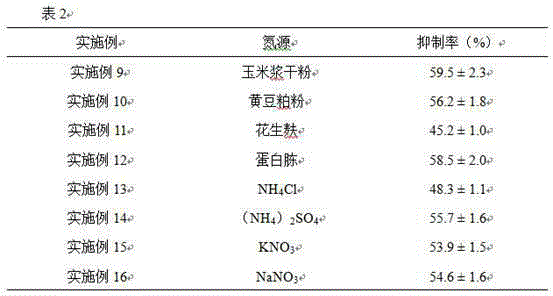
54 results about "Starch corn" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Corn is categorized as a starch or starchy vegetable due to its high starch content. One cup of uncooked corn contains 20.5 grams of starch, 28.2 grams of carbohydrates and 120 calories.
Water-loss reducer using waste pouce or Chinese medicine slag and wastepaper as raw material, and production method thereof
InactiveCN101173157ARich in natural resourcesSolve the problem of poor anti-mold performanceOther chemical processesSlagReaction temperature
The invention relates to a water-retaining agent and a preparation method using discarded flax scraps or traditional Chinese medicine slag and waste paper as raw materials, and relates to a water-retaining agent and a preparation method thereof. It solves the problems that the existing water-retaining agent is difficult to be degraded by soil microorganisms, the cost of using starch and corn as raw materials is high, and the anti-mold performance is poor. The water-retaining agent of the present invention contains 8-17% of cellulose extracted from flax chips, waste paper or traditional Chinese medicine dregs, 0.02-0.18% of initiator, 83-89% of monomer, and 0.06-89% of cross-linking agent according to the percentage by weight. 0.4%. The preparation method is as follows: 1. Separate cellulose from flax scraps or traditional Chinese medicine residue, dry and crush it into cellulose powder; 2. Put the cellulose powder into a four-necked bottle, add water, stir, introduce nitrogen, and exhaust oxygen 1. Control the reaction temperature; 3. Add initiator, monomer and cross-linking agent, and react under nitrogen until the reaction liquid becomes viscous; 4. Dry and pulverize to obtain the water-retaining agent. The present invention has abundant raw material resources, low cost, few types of reagents used in similar synthesis methods, and little environmental pollution.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Lycopene microcapsule granules and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN104431690AImprove liquidityAvoid the problem of exceeding the standardFood preservationFood ingredientsBiotechnologyStarch corn
The invention relates to lycopene microcapsule granules and a preparation process thereof. Lycopene crystal powder, sunflower oil or corn oil, porous starch, oxidized starch, modified cassava starch, corn syrup, trehalose, natural VE oil are used as main raw materials, a process is reasonably improved and optimized to be used for greatly shortening the production time, the entire production process is controlled, the drying is carried out layer by layer and the recycling is carried out step by step. Obtained products are spherical, the surfaces of the products are smooth and trim, the biological activity of the products is kept, the products can be well solved in cold water, the use, storage and transportation are relatively well facilitated, no organic solvent or harmful substance is left, the safety, liquidity, taste and water solubility of the products are greatly improved, and resource waste is reduced. By adopting the process, the yield of the lycopene microcapsule granules is high, and the process is suitable for being used for large scale preparation of the lycopene microcapsule granules, and is used for achieving the continuous mass production and reducing the production cost.
Owner:武汉志邦化学技术有限公司
Additive capable of improving quality of quick-freezing fresh-keeping rice noodles as well as preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN102613488AQuick breaking rateLow sliver breakage rateFood preparationBiotechnologyStarch corn
The invention discloses an additive capable of improving the quality of quick-freezing fresh-keeping rice noodles as well as a preparation method and applications thereof. The proportion of raw materials of the additive of corn modified starch to corn starch calculated by weight parts is 3 to 8. The preparation method comprises the following steps: in preparation, weighing and taking the corn modified starch and the corn starch according to the proportion of raw materials, adding into a stirring machine and stirring, and mixing the raw materials uniformly, thereby obtaining the additive capable of improving the quality of the quick-freezing fresh-keeping rice noodles, wherein the weight proportion of the raw materials of rice to the additive is 100:11. Through adding the additive and the aging treatment before secondary curing, the produced rice noodles are crisp, soft, and elastic and have good toughness, and the rehydration performance, taste, strength, biting, milky soup, easiness in breaking and the like are improved obviously, and especially the phenomenon of easiness in breaking is improved obviously, and the rice noodle breaking ratio is decreased to 10% from 80%.
Owner:张小明
Application of corn ZmWx gene in increase of corn yield and improvement of grain characteristics
InactiveCN105349559AIncreased amylose content in endospermIncrease productionFermentationGlycosyltransferasesStarch cornComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses an application of a corn ZmWx gene in increase of the corn yield and improvement of grain characteristics. A ZmWx gene sequence is cloned in corn endosperm cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid), the ZmWx gene encodes GBSSI (granule-bound starch synthase I), the GBSSI and an endosperm specific promoter form a fusion gene, the fusion gene is recombined in a plant expression carrier with a transgenic technology to transform corn, and corn transgenetic plants with yield increased and grain characteristics improved are obtained; alternatively, GBSSI overexpressed corn and mutant AGPase overexpressed high-starch corn are hybridized, a transgenetic polymer is obtained through screening, and the corn transgenetic plants whose grain yield, starch content and hundred-grain weight are remarkably higher than those of recipient materials are produced. The application provides a basis and a means for development and preparation of high-starch and high-amylose starch corn and also develops a new approach for increase of the corn yield and improvement of the starch quality.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Large chicken cutlet coating flour and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105054103AGolden appearanceCrispy tasteFood ingredientsFood preparationBiotechnologyStarch corn
The invention discloses large chicken cutlet coating flour and a preparation method thereof. The large chicken cutlet coating flour is prepared from wheat flour, wheat starch, corn starch, cassava starch, cassava granulated flour, table salt, white sugar, sodium carbonate, onion powder, garlic powder, baking powder and guar gum. According to the edible characteristics of a large chicken cutlet on a food terminal market, the surface of a large chicken cutlet is coated with flour and the flour-coated large chicken cutlet is fried so that yellow appearance and a crisp taste of the large chicken cutlet are obtained and large chicken cutlet local flavor and taste are improved. Through the standard flour coating production process, large chicken cutlet taste standardization is realized.
Owner:SHANDONG NEW HOPE LIUHE GROUP
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor pharmaceutical composition, use and preparation method thereof
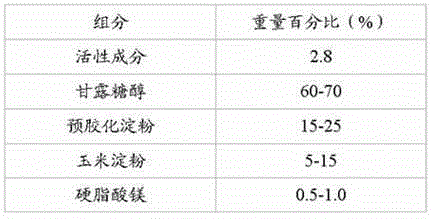
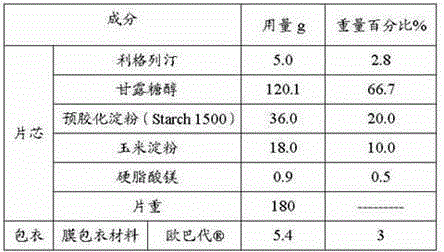
ActiveCN105456270AReduce typesLow costMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsStarch cornMagnesium stearate
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition containing a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor linagliptin, use and preparation method thereof. The linagliptin containing pharmaceutical composition provided by the invention consists of linagliptin or a salt thereof serving as the active ingredient, and pharmaceutical excipients mannitol, pregelatinized starch, corn starch and magnesium stearate. The linagliptin containing pharmaceutical composition provided by the invention reduces the types of excipients, increases the stability of the preparation, reduces the cost of raw materials, and solves the hardness and friability problems of linagliptin tablets by controlling the particle size of the key excipient mannitol. The obtained table has all indicators especially the dissolution rate in line with the drug quality standards, and the process is simple, thus being more suitable for large scale production.
Owner:CSPC ZHONGQI PHARM TECH (SHIJIAZHUANG) CO LTD
Prawn feed
ActiveCN102106478AGuaranteed normal growthImprove survival rateFood processingClimate change adaptationAnimal scienceStarch corn
The invention discloses a prawn feed, which contains fish meal, bean pulp, peanut bran, rape seed dreg, saccharomyces cerevisiae, flour, starch, corn oil, fish oil, K2HPO4 and plantain seed total flavonoids. The prawn feed can remarkably improve the survival rate, weight increment rate and stress resistance of the prawn at the same time of ensuring the growth of the prawn. The consumption of the fish meal is remarkably lower than that of the conventional prawn feed at current markets, so the cost of the feed is greatly reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Clam flavor enhancer and making method thereof
ActiveCN103989135AUmami is deliciousDeliciousFood homogenisationUltra high pressure food processesBiotechnologyMaillard reaction
The invention discloses a clam flavor enhancer and a making method thereof, and the clam flavor enhancer is mainly made from the following raw materials: a clam mixed material, 5-phosphodiesterase and flavor protease. During production, clam edge scraps are crushed and mixed with water for high pressure homogenization, after homogenization, the 5-phosphodiesterase and the flavor protease are added into an enzymolysis tank for hydrolysis, maillard reaction is performed for removing fishy smell and enhancing fragrance, then fresh clam meat powder is obtained by concentrating and spray drying, the fresh clam meat powder is proportionally mixed with starch and corn dextrin, then quantitatively filled into glass bottles, and then sterilizing at high temperature and thermally sealing to obtain the clam flavor enhancer product. The clam edge scraps are scientifically used in the clam processing process, the efficient use of low value shellfish resources can be promoted, nutrition and delicious taste can be obtained, the pollution of the environment is reduced, and the sales value of clam products can be improved.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGSHUN VINEGAR IND
Fast-rehydration-type brewing rice flour and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110663870AImprove water absorption efficiencyShort rehydration timeFood freezingLipidic food ingredientsBiotechnologyStarch corn
The invention relates to the technical field of instant rice flour processing, in particular to fast-rehydration-type brewing rice flour and a preparation method thereof. The fast-rehydration-type brewing rice flour is composed of refined white long-grain-rice, potato modified starch, corn oil and an emulsifier, wherein the emulsifier is sucrose fatty acid ester and / or distilled monoglyceride; andduring a rice flour processing process, the emulsifier and corn oil are added to be combined with starch to form a complex, after vacuum freeze dehydration is carried out, a compound can break through a gelatinized starch layer to form complex pores and channels, the penetration and infiltration of water are facilitated, and the effect of rehydration can be achieved fast. Compared with ordinary rice flour prepared by hot air drying in the market, the rehydration time of the fast-rehydration-type brewing rice flour can be shortened from original 10-15 minutes to about 3 minutes, and the tasteof the rice flour after rehydration is not affected.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Coarse grain total-nutrient formula food for nephritic patients
ActiveCN103478545APromote digestion and absorptionImprove immunityMetabolism disorderUnknown materialsVitamin CPotato starch
The invention discloses coarse grain total-nutrient formula food for nephritic patients and relates to the field of healthcare food. The coarse grain total-nutrient formula food is prepared from the following components by mixing: whey protein, sweet potato starch, corn starch, wheat bran, traditional Chinese medicine powder, vitamin C, calcium gluconate, magnesium oxide, zinc gluconate, stevioside and edible essence. High-quality protein, fortification vitamin and trace elements are adopted in the food, and the traditional Chinese medicine powder is added to not only supplement a large amount of high-quality protein for the nephritic patients, and the traditional Chinese medicine powder, the fortification trace elements and the basic nutrition elements generate a synergistic effect according to the proportion of the food disclosed by the invention, thereby having good auxiliary curative effects on early nephropathy, acme nephropathy, nephritic syndrome, diabetic nephropathy, and the like, and the coarse grain total-nutrient formula food is suitable for early nephritic patients and people with potential nephropathy risk.
Owner:山东卫康生物医药科技有限公司
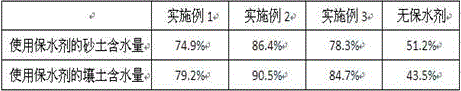
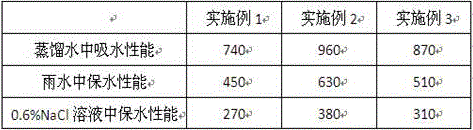
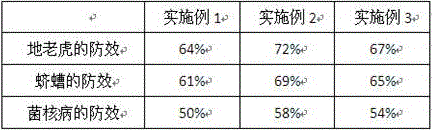
Method for performing natural soil greening on slight alkaline land by using salt-resistant water-retaining agent containing attapulgite
InactiveCN106047357AStrong water absorptionImprove water retentionBiocideDead animal preservationAlkali soilDistilled water
The invention provides a method for performing natural soil greening on slight alkaline land by using a salt-resistant water-retaining agent containing attapulgite. The water-retaining agent comprises attapulgite, acrylic acid, acrylamide, pine needle powder, walnut leaf powder, cassava starch, yam powder, corn stalk powder and bean peel powder. The preparation method comprises leaf powder treatment. The leaf powder treatment comprises a step of monomer solution preparation and a polymerization step. The invention further provides application of the water-retaining agent to trifolium repens plantin in saline-alkali soil. The method has the advantages that the prepared water-retaining agent has high water absorbing capability in distilled water, rainwater, and NaCl solution with a concentration of 0.6%, the capability of water absorption in the distilled water can reach 1030-1300 times the weight of itself, the capability of water absorption in the rainwater can reach 680-820 times the weight of itself, and the capability of water absorption in the NaCl solution with a concentration of 0.6% can reach 390-530 times the weight of itself.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
Cherry tomato edible coating preservative and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104336170AReduce epidermal atrophyControl epidermal atrophyFruits/vegetable preservation by coatingStarch cornGlycerol
The invention relates to a cherry tomato edible coating preservative and a preparation method thereof. The raw material of the preservative is selected from one of potato hydrogen peroxide propyl starch, corn oxidized starch or potato carboxymethyl starch; the edible coating preservative is prepared through adding stearic acid, glycerol monostearate, glycerinum and agar, uniformly mixing the raw materials in proportion, proportioning suspension liquid with certain concentration by deionized water, heating and stirring for a certain time in boiling water bath to gelatinize the liquid into uniform membrane liquid, stirring by a motor stirrer for a certain time, and completely mixing the membrane liquid. The prepared edible coating preservative is easy in obtaining the raw material, low in cost, simple in operation method, free of pollution and easy to realize. The prepared edible coating preservative can effectively control the epidermal atrophy condition of cherry tomato in storage duration; the water loss rate and rot degree can be reduced; the fruit brightness can be kept; the pulp texture can be kept; the refreshing time of the cherry tomato can be obviously prolonged.
Owner:甘肃圣大方舟马铃薯变性淀粉有限公司
Oxidized starch corn biscuit
The invention provides a biscuit which is mainly made of oxidized starch flour and corn sauce. The biscuit is bright yellow in color, crisp in taste and unique in flavor, increases taste varieties and flavors of biscuits and enriches nutrition health-care content. The biscuit is reasonable in cost, bright yellow in appearance, rich in taste and the like.
Owner:张爱标
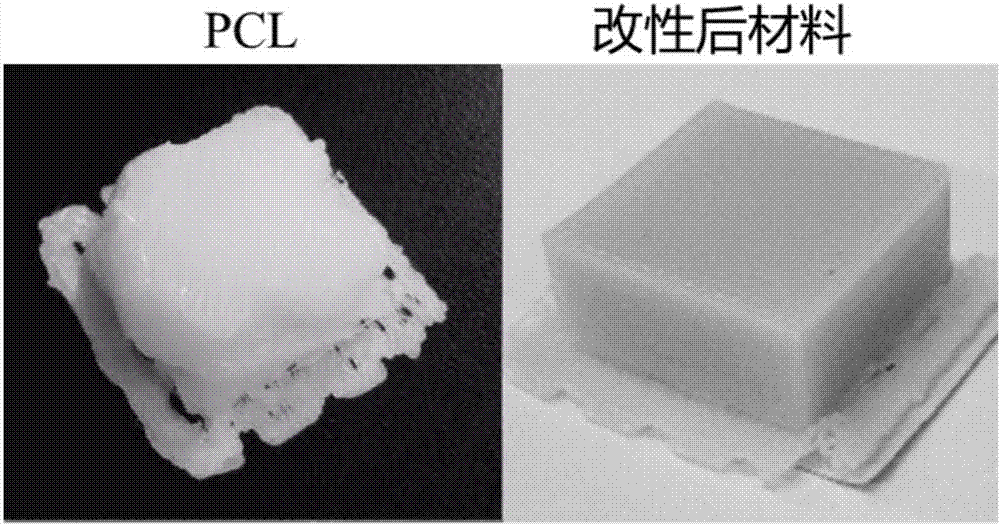
Low-temperature FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) biomedical degradable 3D (three-dimensionally) printing material, preparation and application
InactiveCN107573660ALow print temperatureHigh precisionAdditive manufacturing apparatusWire rodPotato starch
The invention relates to a low-temperature FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) biomedical degradable 3D (three-dimensionally) printing material, preparation and an application, which belong to the field of 3D printing. The material adopts PCL (polycaprolactone), starch (such as potato starch, corn starch or soluble starch), EBS (ethylene bis stearamide), SiO2 and magnesium stearate as materials. The preparation method includes the following steps: after the fillers, such as PCL master batch, starch, EBS, SiO2 and magnesium stearate, are melted and mixed by double screws according to a certain proportion, the mixture is ground, pelletized and extruded out by a single screw, stretched into a line with uniform and appropriate size, and an FDM 3D printer is then used for printing. The process of the invention is simple and easy to implement, the preparation cost is low, and the printing precision is high; moreover, the requirement on 3D printing equipment is low, the selectivity is wide, and an ordinary household FDM 3D printer can be used; furthermore, the material is degradable, a foundation is laid for the development of biomedical FDM 3D printing materials, and great value and significance in the field of 3D printing are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Culture medium for producing staurosporine and method thereof
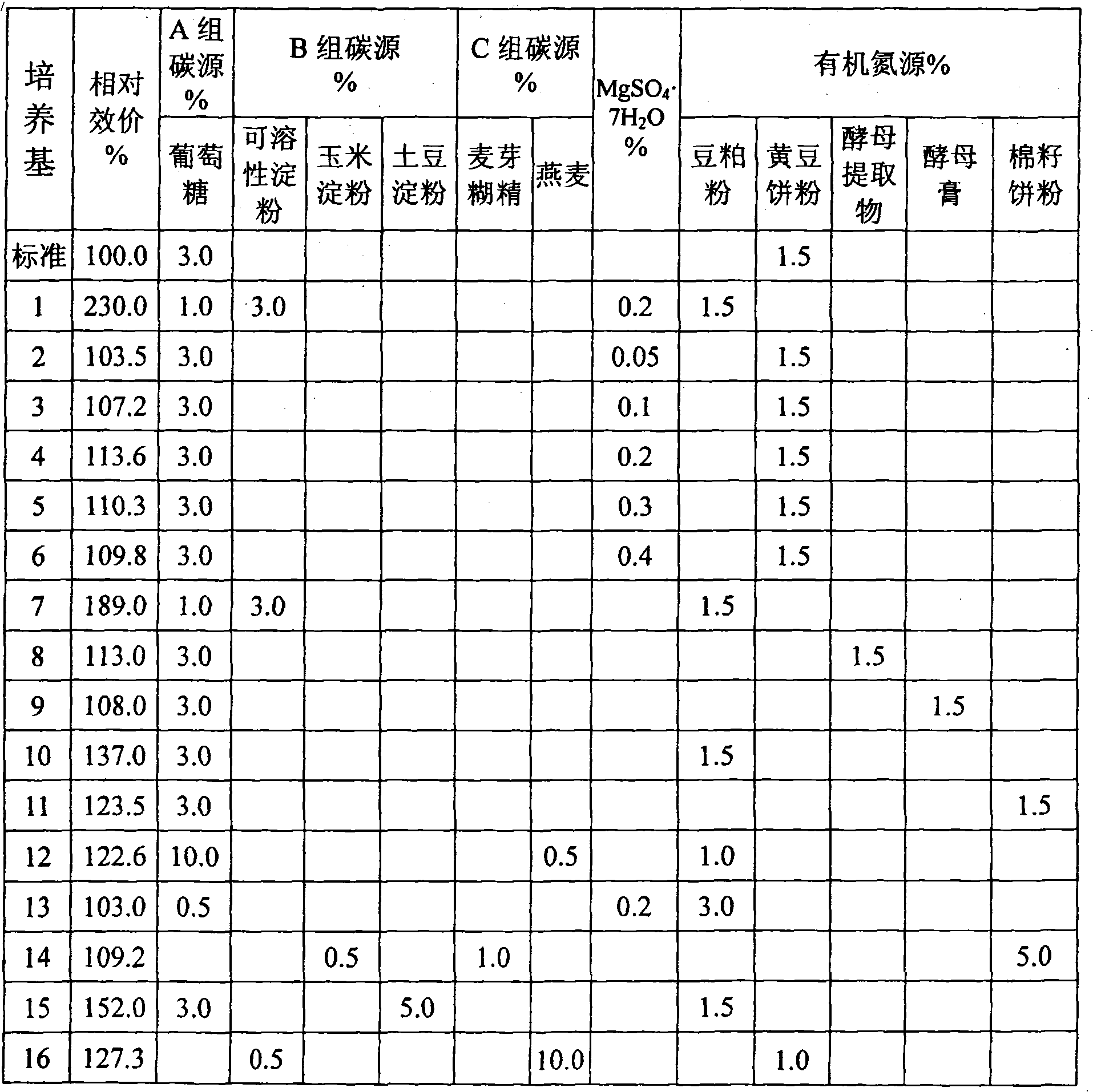
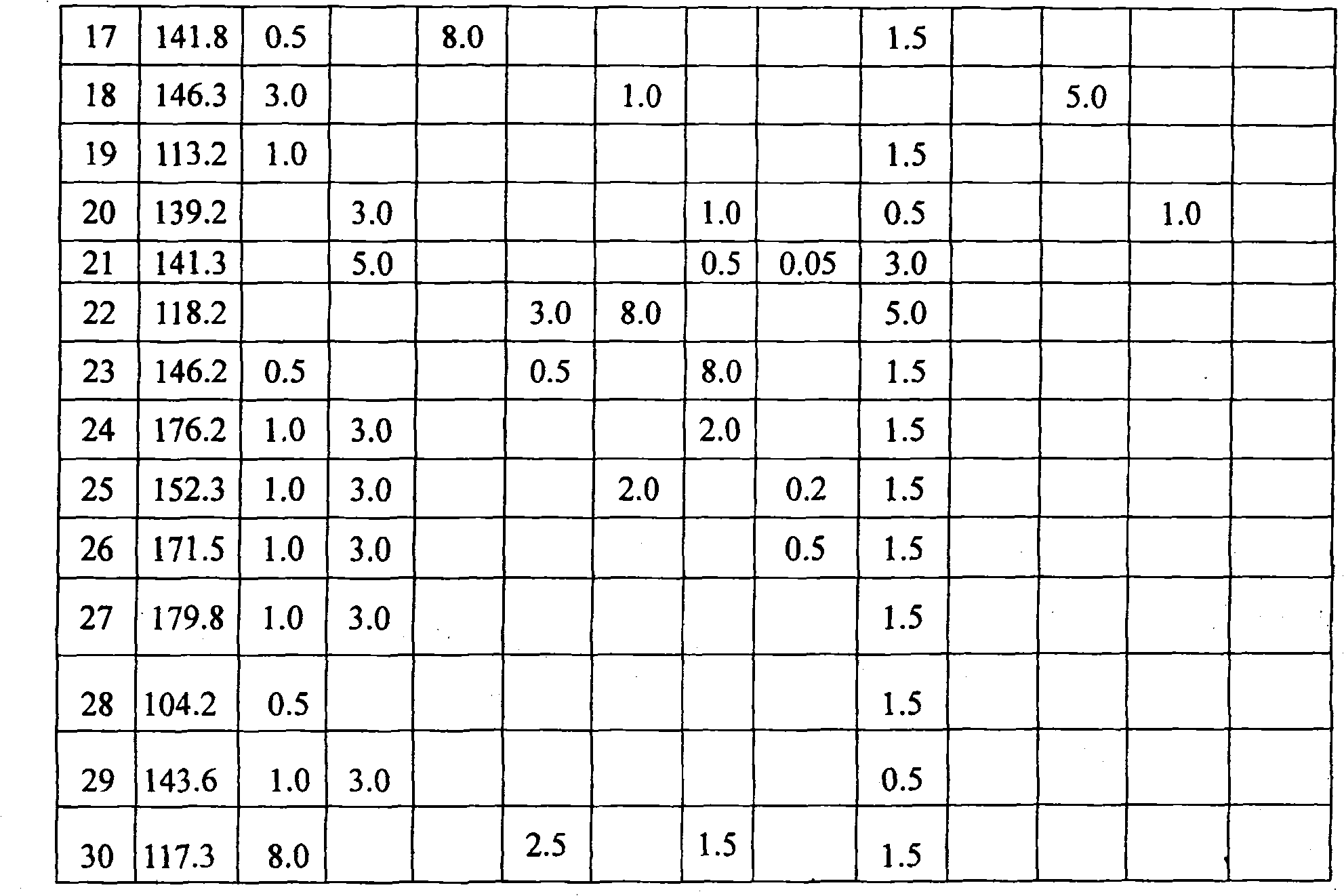
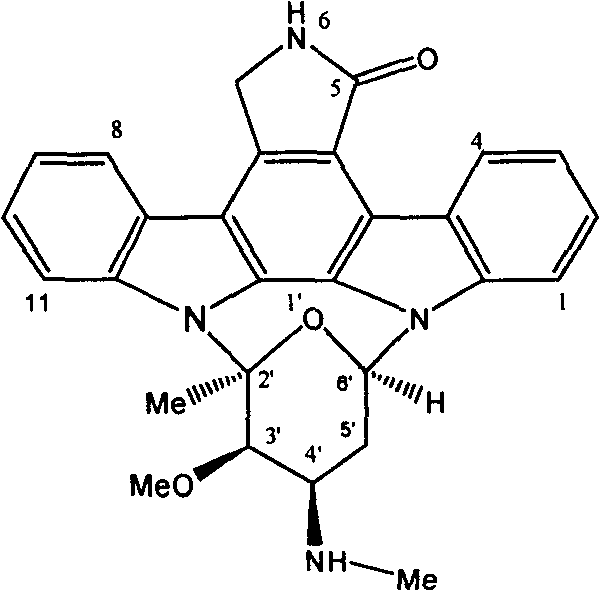
The invention discloses a culture medium which is applicable to culturing staurosporine producing bacteria for producing staurosporine; the culture medium with pH value of 7.0 comprises carbon sources, organic nitrogen sources and inorganic salt, wherein, the inorganic salt comprises calcium salt; the carbon sources are selected from two or more than two of the following three groups of components, namely, A, B and C, wherein, at least two components are selected from different groups, group A: glucose, group B: amidulin, corn starch and potato starch, and group C: oats and maltodextrin; and / or, the organic nitrogen sources are selected from soybean cake powder, yeast extract, yeast cream and kapok meal; and / or, the inorganic salt is also added with magnesium salt. The invention also discloses a method for producing staurosporine from staurosporine producing bacteria by adopting the culture medium. By adopting the fermentation medium for producing staurosporine, the thalli of the staurosporine producing bacteria grows fast, the mycelia are not easy to clot, the yield of fermentation products is high, and the relative potency is optimized 230 percent of a former culture medium.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD
Preparation method of slowly digestible corn starch
The invention belongs to the field of starch preparation, and particularly relates to a preparation method of slowly digestible corn starch. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining corn starch granules; S2, adding the corn starch granules obtained in S1 to a sodium acetate buffer solution with pH of 4-6 and concentration of 0.1-0.3 mol / L to obtain a mixed solution; S3,adding alpha-amylase with enzyme activity content of 40-60 u / mg, beta-amylase with enzyme activity content of 10-30 mu / mg and glucosyltransferase with enzyme activity content of 200,000-400,000 mu / mgto the mixed solution sequentially, performing an oscillation reaction at 40-60 DEG C for 8-12 h, adjusting pH to 9-11, leaving a reaction product for stand for 5-10 min, performing spray drying to obtain the slowly digestible corn starch. The preparation method has the following beneficial effects: 1, the corn starch granules are common raw materials and easy to obtain; 2. by adding mixed enzyme,the method is simple to operate, saves energy cost and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Starch foaming disposable tableware and preparation method of packaging product
The invention discloses starch foamed disposable tableware and a preparation method of a packaging product. The starch foamed disposable tableware comprises the following components in percentage: 45-59% of starch (corn starch or cassava starch), 4%-6% of fibers (various fibers), 3%-5% of bioplastic, 0.5%-2% of zinc stearate, 1%-2% of an accelerant, and 25%-45% of water. The preparation method comprises the following steps: weighing the raw materials in proportion; stirring by a stirrer at low speed and high speed; forming a product by an injection molding machine; drying the product; performing water repelling treatment; and packaging the final product. According to the invention, the starch foamed disposable tableware and the preparation method have the beneficial effects that the starchis adopted as a main preparation component, so that no harm is caused to a human body, environment-friendly treatment is facilitated after the disposable tableware is discarded, and the degradation speed is high.
Owner:北京绿态美景环保科技有限公司
Sesame seed cashew nuts
The invention discloses sesame seed cashew nuts, which comprise cashew nuts, wheat flour, oxidized hydroxypropyl starch, corn starch, white granulated sugar, sesame seeds and salt; and the sesame seed cashew nuts are produced by baking, are crispy, ready-to-eat and very suitable for the taste of the public, and have sesame flavor.
Owner:SUZHOU YOUI FOODS
A kind of ganoderma lucidum liquid strain culture medium and ganoderma lucidum liquid strain cultivation method
ActiveCN107267398BNo pollution in the processQuality improvementFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyStarch corn
The invention discloses a ganoderma lucidum liquid spawn medium formula which comprises 6g of peptone, 15g of glucose, 0.5g of magnesium sulfate, 0.5g of monopotassium phosphate, 1g of potato starch, 3g of corn, 3g of cassava starch, 10mg of vitamin B1, 1g of agar and 1000ml of purified water. The invention further discloses a ganoderma lucidum liquid spawn culture method. The culture method comprises the following steps: by taking the ganoderma lucidum liquid spawn medium formula as a basis, performing high-temperature sterilization, inoculating into stock culture, and culturing in a shake table, thereby obtaining the ganoderma lucidum liquid spawn. The ganoderma lucidum liquid spawn medium formula and the ganoderma lucidum liquid spawn disclosed by the invention have the advantages that the culture steps are reduced, the fermentation period is shortened, the growth period is shortened, the pollution rate is low, the cost is low, the yield is low, and the culture method is applicable to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:江阴市长泾国民育种场
Superfine stuffing for plastic and its application
The superfine stuffing capable of making plastic degradable and good in machining performance is superfine crushed mixture of starch, corn powder, plant fiber, calcium carbonate, talcum powder and bentonite. The stuffing makes plastic possess certain flowability and lubricity for easy machining and makes plastic become microbe degradable and beneficial to plant and harmless to natural environment.
Owner:北京中宣绿环科技发展有限公司
Method using streptomyces lavendulae fermentation to produce alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
InactiveCN105274147ANo pollution in the processEasy to operateMicroorganism based processesFermentationStarch cornSubmerged fermentation
The invention discloses a method using streptomyces lavendulae fermentation to produce alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. The method is characterized in that strain activation, seed fermentation broth preparation and liquid fermentation are performed on the strains of Streptomyces lavendulae UN-8 with the preservation number being No. M2015512 to obtain fermentation broth rich in alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. The method has the advantages that the method can widely use cheap carbon and nitrogen sources such as soluble starch, cassava starch, corn starch, dried corn steep liquor powder and inorganic ammonium salt; the method adopting liquid-submerged fermentation is convenient to operate and implement, free of pollution, high in production efficiency and capable of satisfying the requirements of industrial production; preliminary identification shows that the alpha-glucosidase inhibitors produced by the method are novel alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, the alpha-glucosidase inhibitors can intensely inhibit alpha-glucosidase, and the IC50 of the alpha-glucosidase inhibitors is 321 times of that of the commercially available alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, namely acarbose; in-vivo experiments show that the alpha-glucosidase inhibitors can evidently improve the formation of postprandial hyperglycemia, the effect of the alpha-glucosidase inhibitors is equivalent to that of the acarbose, and the alpha-glucosidase inhibitors can be used for preventing and treating diabetes.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Solid pharmaceutical composition for treating mental diseases
PendingCN113855640AImprove performanceNervous disorderPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCompulsive disordersStarch corn
The invention relates to a solid pharmaceutical composition for treating mental diseases, in particular to a method for preparing a fluvoxamine maleate tablet. The fluvoxamine maleate tablet is prepared from fluvoxamine maleate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, corn starch, silicon dioxide and sodium stearyl fumarate. The method comprises the following steps that the materials are mixed and granulated, and then pressed into tablets on a tablet press. The invention further relates to the tablets prepared by the method, the coated tablets prepared by taking the tablets as tablet cores, and application of the tablets and the coated tablets in preparation of medicines for treating mental diseases, such as depression and related symptoms, obsessive-compulsive disorder. The tablets have excellent performance.
Owner:HUNAN DONGTING PHARMA
Lipid-lowering wrapping deep-frying powder of curry flavor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103976195ACrispy tasteNice appearanceNatural extract food ingredientsFood preparationBiotechnologyMonosodium glutamate
The invention provides a lipid-lowering wrapping deep-frying powder of curry flavor. The powder is prepared by mixing the following components by weight: modified starch, corn starch, konjac starch, glutinous rice powder, hawthorn powder, cooked sesame powder, salt, monosodium glutamate, low gluten flour, pectin, licorice powder, oenanthe stolonifera, dateplum persimmon, ginkgo biloba, peanut leaf, gynostemma pentaphyllum, lotus leaf, root of kudzu vine, hyacinth bean vine, a garlic powder, a cinnamon powder, a crispy agent, a baking powder, vitamin C, and a curry powder. According to the lipid-lowering wrapping deep-frying powder provided by the invention, the formula is added with Chinese herbal medicine extracts for clearing heat and lowering lipid, so as to effectively overcome the shortcoming of high blood lipid generation due to inner heat caused by existing deep-fried food; and the fried meat product can maintain the crisp taste and keep the appearance after standing at room temperature for a long time.
Owner:快乐蜂食品(安徽)有限公司
Wrapped meat balls and making method thereof
InactiveCN108094910APure colorCreamy tasteFood coatingFood ingredient functionsMonosodium glutamateLean meat
The invention relates to the technical field of deep processing of meat, in particular to wrapped meat balls and a making method thereof. The wrapped meat balls comprise main materials, ingredients and seasonings, wherein the seasonings consist of edible salt, white granulated sugar, scallion powder, ginger powder, monosodium glutamate, a soy sauce, baking soda, composite phosphate, carrageenin, five spice powder and white pepper powder; the main materials comprise fresh chicken breast, pig tenderloin fat, refined lean meat of pig rear legs, and white radishes; and the ingredients comprise icewater, soy protein isolate powder, potato starch, corn starch, pig bone soup and water. The wrapped meat balls are made through the steps of making wrapper materials through combining minced chickenbreast, minced pig tenderloin fat, diced white radishes, the seasonings and the ingredients; making filling materials through combining minced refined lean meat of pig rear legs, minced pig tenderloinfat, the seasonings and the ingredients; and wrapping the filling materials with the wrapper materials. The making method of the wrapped meat balls is simple and convenient, and the wrapped meat balls are fresh, tender and delicious, rich in nutrition, and rich in various elements, and have the efficacy of strengthening bodies; and besides, the raw materials of the wrapped meat balls are purely natural and do not contain preservatives, so that the wrapped meat balls can be frozen and kept fresh for a time, the wrapped meat balls can be cooked before being eaten, the wrapped meat balls can cater to market requirements, and industrialized production is realized.
Owner:江苏百斯特农业发展有限公司
Prawn feed
ActiveCN102106478BGuaranteed normal growthImprove survival rateFood processingClimate change adaptationAnimal scienceStarch corn
The invention discloses a prawn feed, which contains fish meal, bean pulp, peanut bran, rape seed dreg, saccharomyces cerevisiae, flour, starch, corn oil, fish oil, K2HPO4 and plantain seed total flavonoids. The prawn feed can remarkably improve the survival rate, weight increment rate and stress resistance of the prawn at the same time of ensuring the growth of the prawn. The consumption of the fish meal is remarkably lower than that of the conventional prawn feed at current markets, so the cost of the feed is greatly reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Purple sweet potato sheet jelly and manufacture technology thereof
InactiveCN106107925AImprove toughnessGreat tasteClimate change adaptationFood ingredientsBiotechnologyStarch corn
The present invention discloses purple sweet potato sheet jelly and a manufacture technology thereof. The purple sweet potato sheet jelly comprises the following raw materials in weight percentages: 70-85% of purple sweet potato starch, 5-15% of corn starch and 5-15% of tapioca starch. By adding the corn starch and the tapioca starch into the purple sweet potato starch, the manufacture technology can increase the toughness of the sheet jelly and enhance the taste. The purple sweet potato sheet jelly is strong in the cooking resistance, not stick or thick and chewy and tasty. But the addition of the corn starch and tapioca starch cannot be added too much, which leads to the too hard sheet jelly and affects the taste.
Owner:叙永县鸿艺粉业有限公司
Method for continuously culturing bacillus subtilis and special fermenting system
ActiveCN106635890AStable and uniform qualityUniform and stable qualityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological activationPollution
The invention belongs to the field of microbes, and particularly relates to a method for continuously culturing bacillus subtilis and a special fermenting system. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) transferring stored bacillus subtilis strain to a test tube agarslantculture-medium, performing strain activation, and then, transferring the strain into a triangular flask and a seeding tank for culturing in sequence to prepare a bacillus subtilis seed; (2) taking culture materials including starch, corn powder, soya bean meal, peptone, NaCl, CaCl2, MgSO4.7H2O, KH2PO4, K2HPO4, MnSO4, a defoaming agent and water; (3) after the culture materials in the step (2) are subjected to sterilizing treatment, inoculating the activated and cultured bacillus subtilis seed, and performing three-stage continuous culturing to obtain a fermenting liquid. The bacillus subtilis cultured with the method provided by the invention is stable and uniform in quality; neither mixed fungi pollution nor strain mutation is easily caused; the service life of various detectors is prolonged; the time is reduced; the yield and the production efficiency are improved; the concentration and the spore rate of thalli of the bacillus subtilis are improved.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Processing method of deep-fried crispy sweet potato strips
InactiveCN112220013ATight bondIncrease productivityFood freezingSugar food ingredientsSodium bicarbonateStarch corn
The invention discloses a processing method of deep-fried crispy sweet potato strips. The deep-fried crispy sweet potato strips produced by the method are prepared from the following raw materials ofsweet potato strips, coating flour and coating pulp. The coating flour is prepared from wheat flour, modified starch, corn starch, granulated sugar, edible salt, glucose, disodium dihydrogen pyrophosphate, sodium bicarbonate and other raw materials; and the coating pulp is prepared from wheat flour, corn flour, modified starch, granulated sugar, edible salt, glucose, disodium dihydrogen pyrophosphate, sodium bicarbonate, lemon yellow, sunset yellow, ice water and the like. The process for processing the deep-fried crispy sweet potato strips comprises the following steps of cleaning fresh sweetpotatoes, peeling the fresh sweet potatoes, cutting the fresh sweet potatoes into the strips, and performing flour coating, pulp coating, deep-frying, quick-freezing and packaging. The deep-fried crispy sweet potato strips processed by the processing method are golden yellow in color and luster, soft and dense in inner-layer taste, crispy in outer-coating-layer taste, uniform in flour coating, stable in product quality and relatively high in economic value, and coating layers are not separated from the sweet potato strips.
Owner:苏州闻达食品配料有限公司
AGEs feed for SPF-level experimental rats and mice and preparation and content determination method of AGEs feed
PendingCN114711329AEasy to manufactureEasy to measureComponent separationFood processingBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention provides an AGEs feed for SPF-grade experimental rats and mice, and a preparation method and a content determination method of the AGEs feed. The AGEs feed is obtained by the following method: uniformly mixing casein, corn starch, corn dextrin, sugar, cellulose, soybean oil, cystine, vitamins, S10022M mixed mineral powder and choline bitartrate, flatly paving, and uniformly heating; cooling and grinding the substance obtained by heating, and supplementing vitamins and minerals; pressing and shaping the obtained mixture, and performing vacuum packaging; and carrying out sterilization treatment on the packaged product, so as to obtain the AGEs feed. The method also comprises a detection method for testing the content of each nutrient component in the high AGEs feed, and combines a fluorescence and surface fluorescence method and a reverse high performance liquid chromatography method, so that the determination accuracy of the content of AGEs can be improved, and the content of original nutrients in the feed can be evaluated at the same time.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
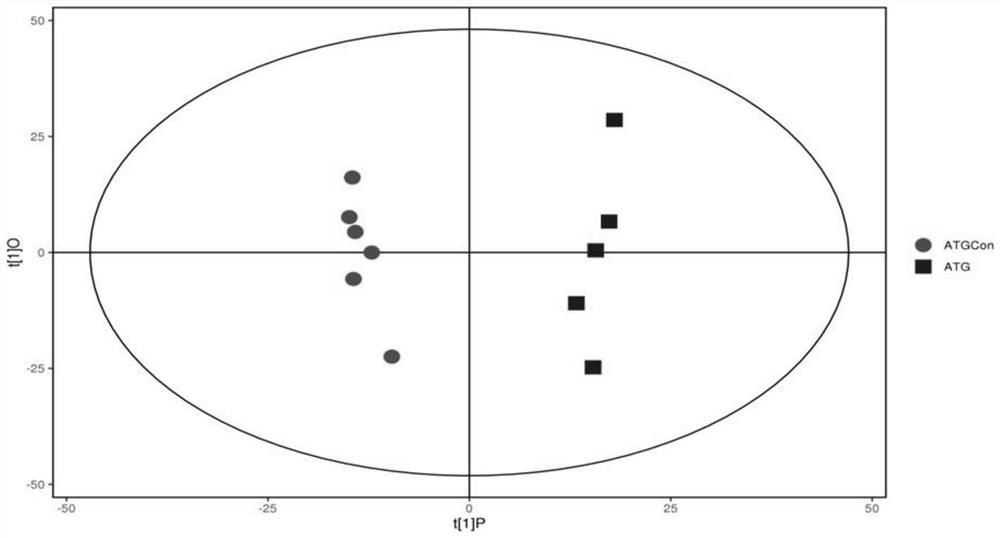
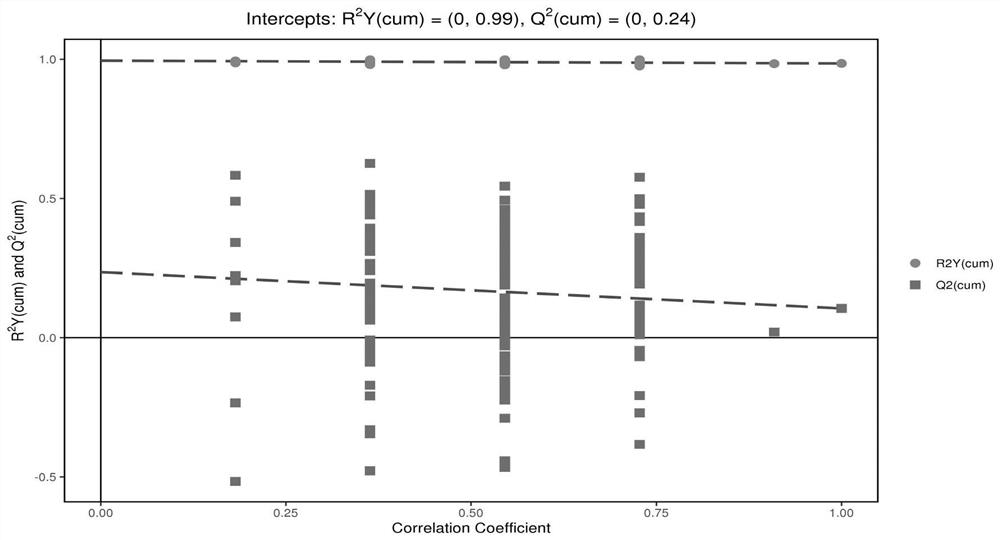
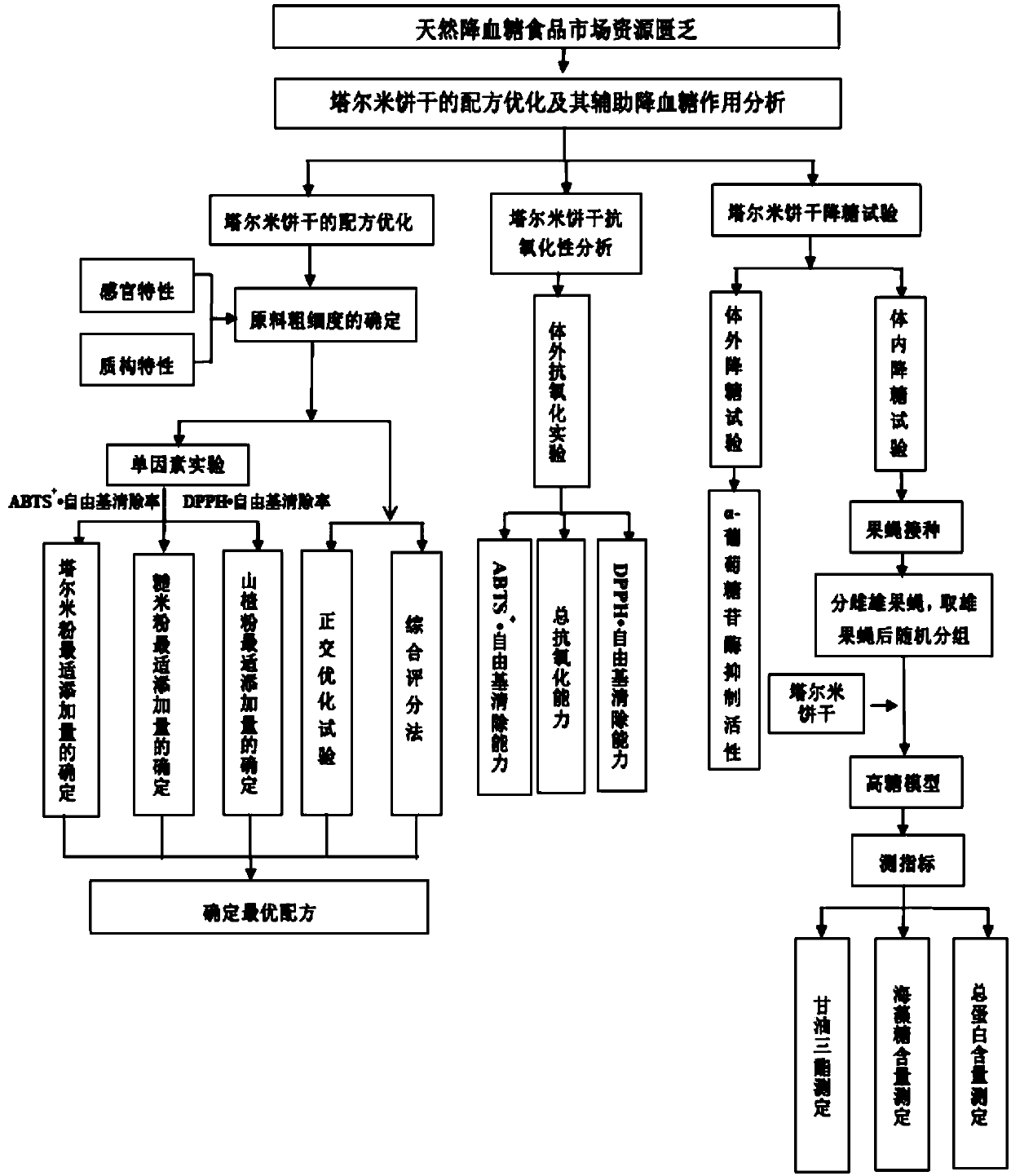
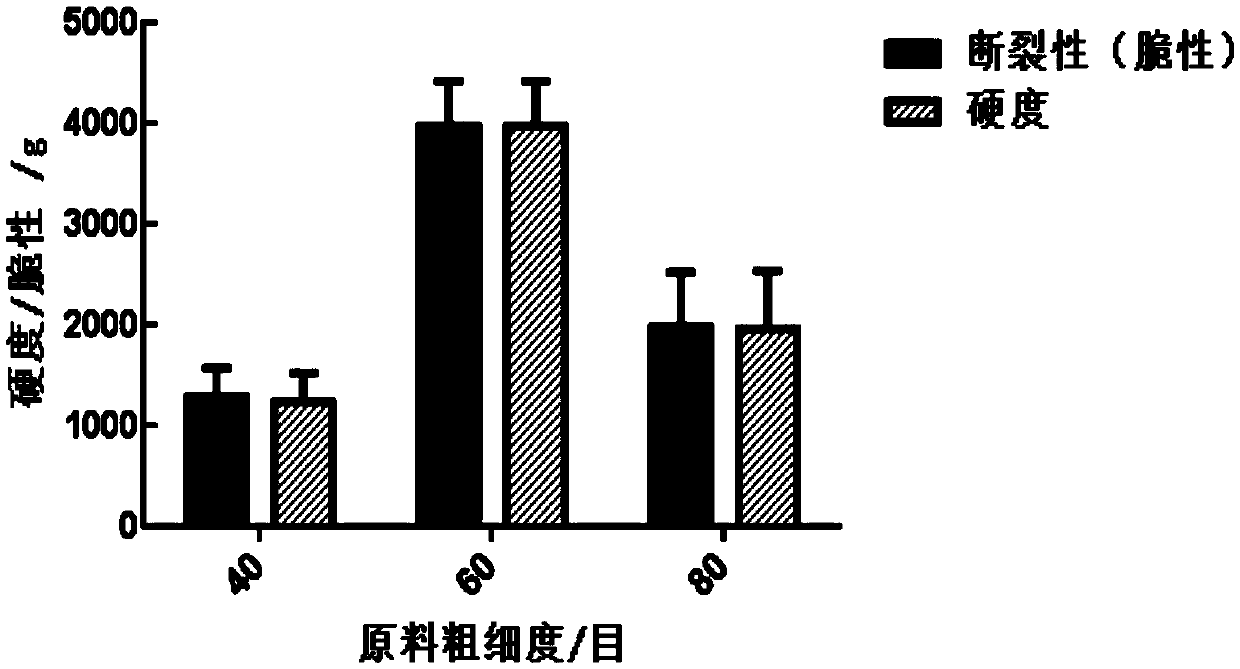
Panicum miliaceum L. biscuit for assisting blood sugar reduction, and preparation method thereof
PendingCN109527025AUniform colorComplete shapeDough treatmentBakery productsSodium bicarbonateStarch corn
The invention provides a Panicum miliaceum L. biscuit for assisting blood sugar reduction. The Panicum miliaceum L. biscuit is prepared from, by weight, 500-650 parts of Panicum miliaceum L. four, 350-500 parts of wheat flour, 60-100 parts of hawthorn powder, 60-100 parts of brown rice flour, 100 parts of inulin, 100 parts of plant oil, 30 parts of starch corn, 5 parts of edible salt, 8 parts of sodium bicarbonate and 4 parts of ammonium bicarbonate. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the Panicum miliaceum L. biscuit. The Panicum miliaceum L. biscuit has a blood sugar reduction effect, can realize the assisted treatment of diabetes caused by high blood sugar, has free radical removal and anti-oxidation capability, and can be eaten to promote the body health and delay ageing. The product added values of the Xinjiang characteristic edible plant resource Panicum miliaceum L. are effectively increased.
Owner:SHAOGUAN COLLEGE
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com