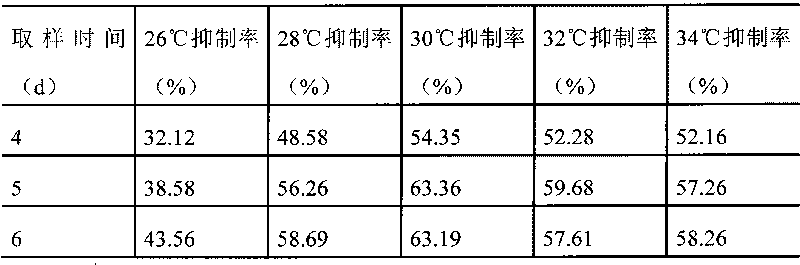
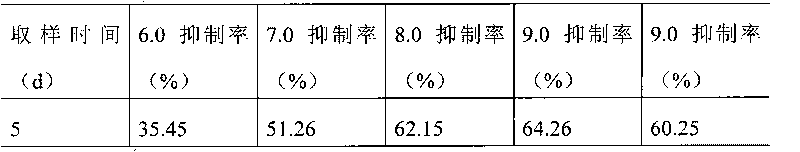
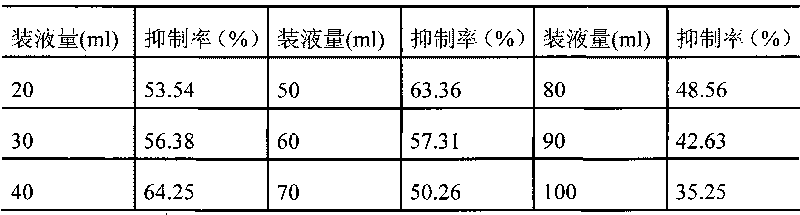
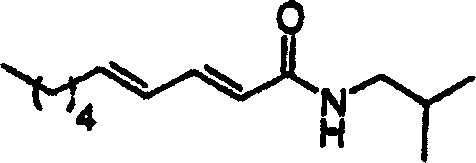
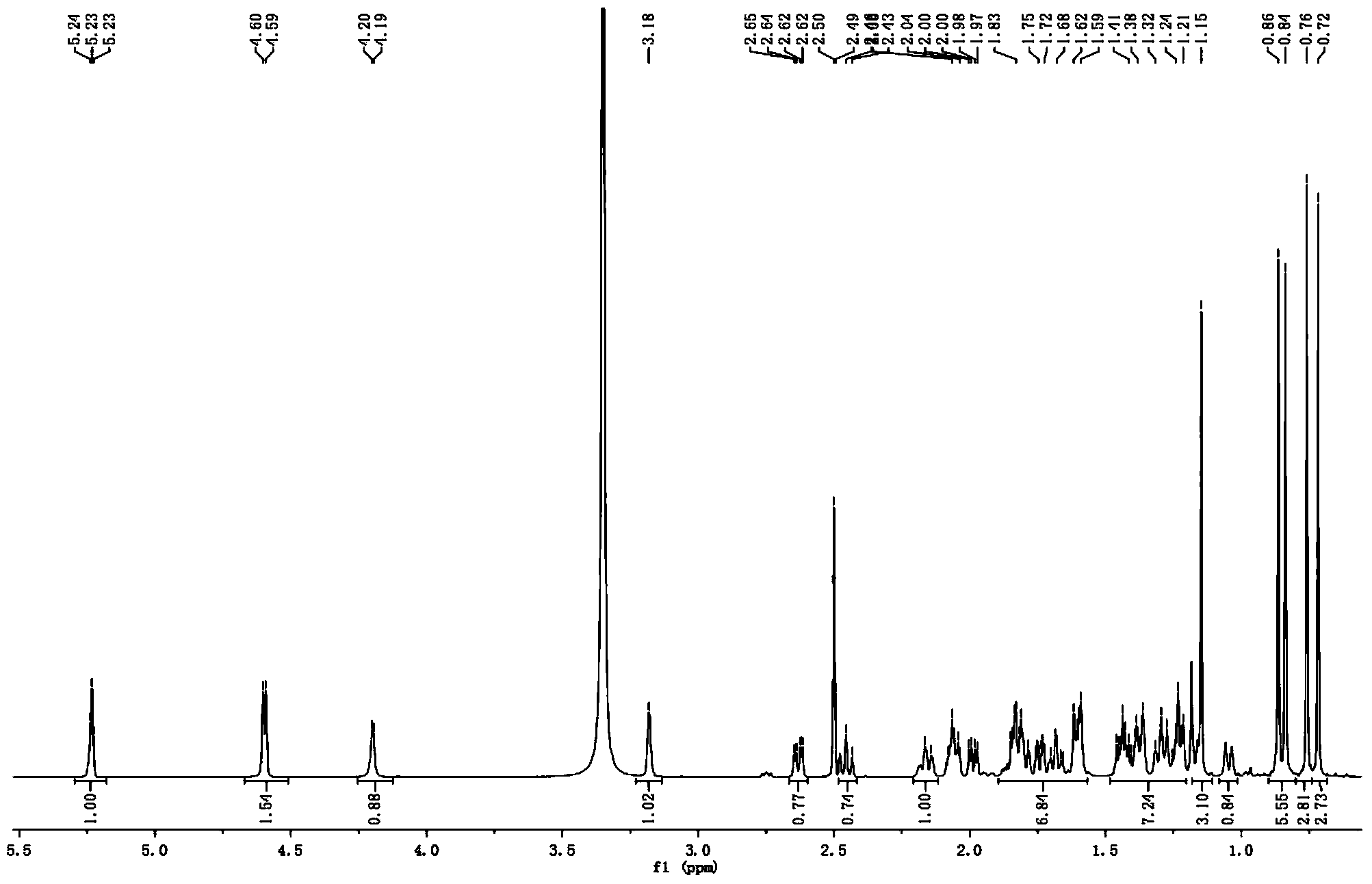
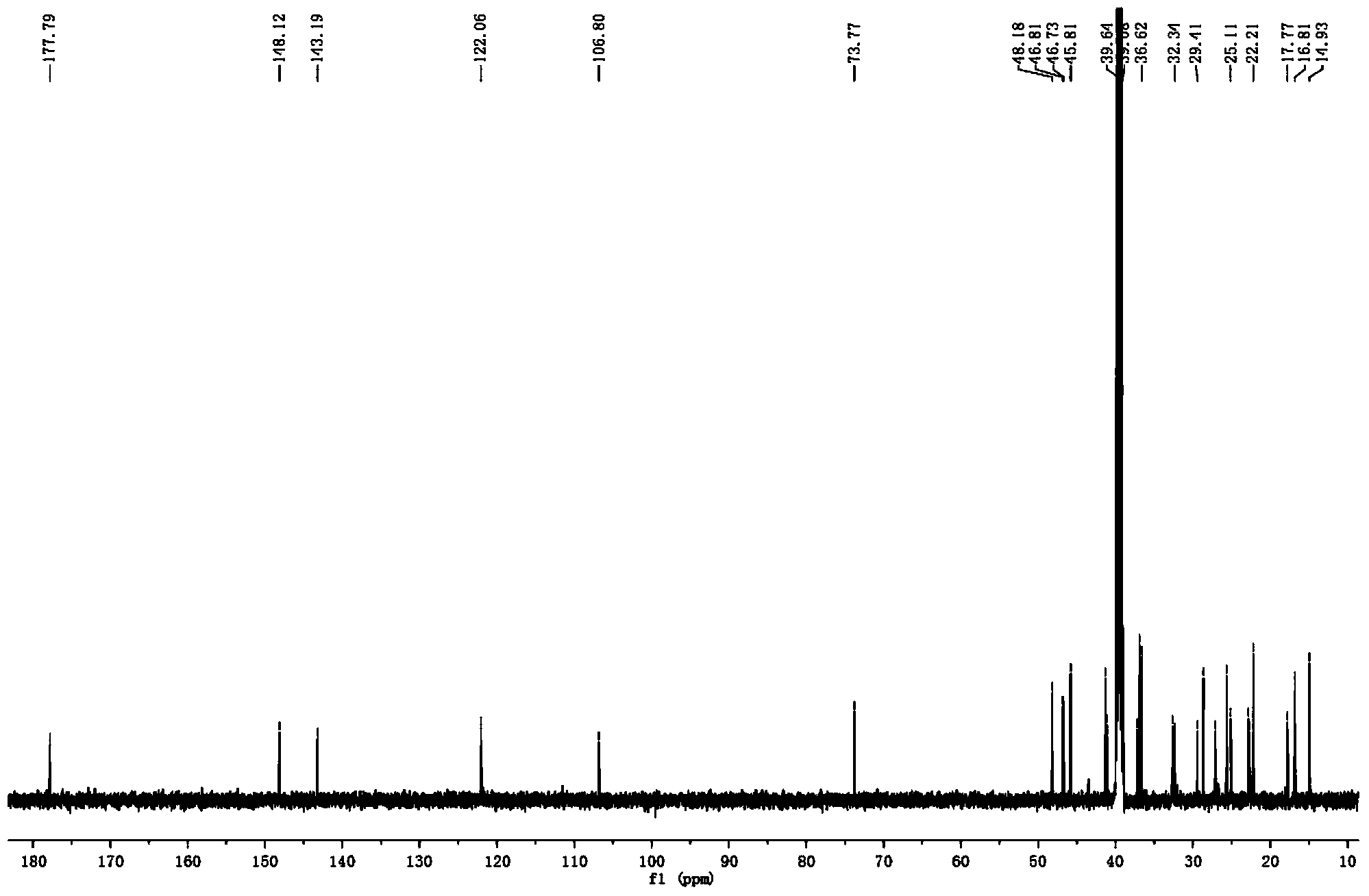
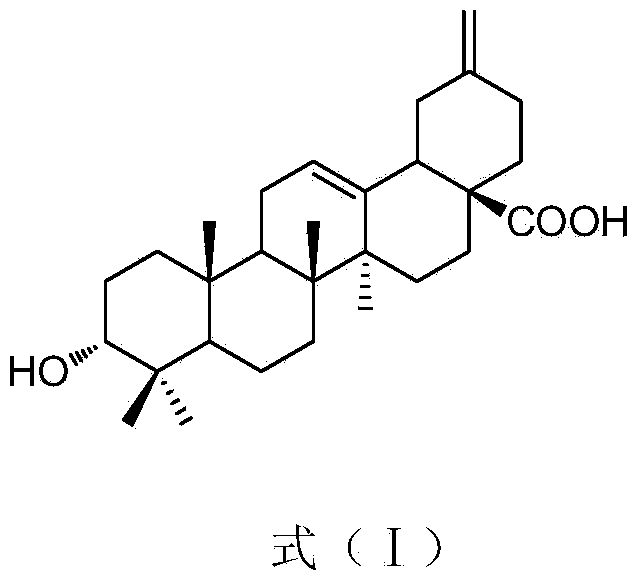
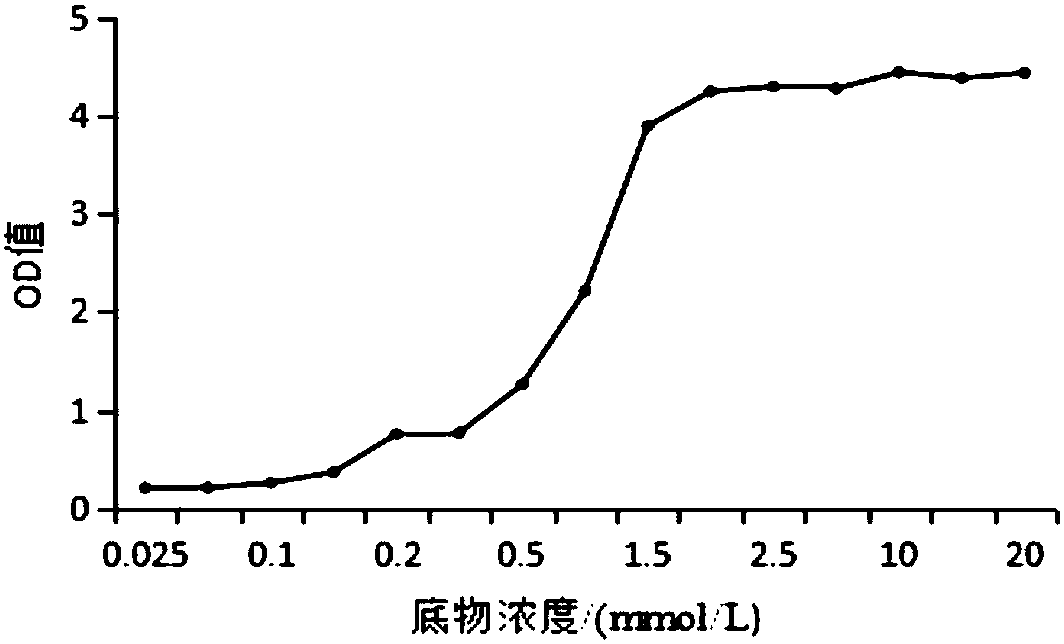
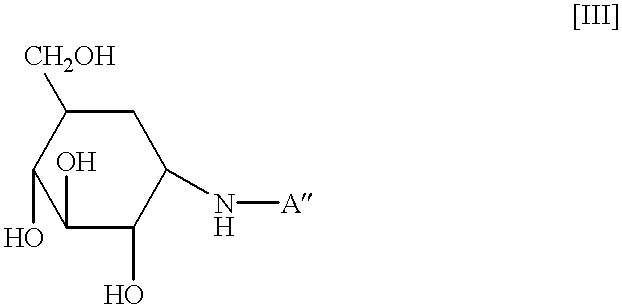Patents
Literature
340 results about "Glucosidase Inhibitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any substance that inhibits glucosidase, specifically alpha-glucosidase in the brush border of the small intestines, an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of carbohydrates to simple sugars. Inhibition of glucosidase reduces and delays the effects of ingested carbohydrates on blood sugar.
Agent for treating high-risk impaired glucose tolerance
InactiveUS6200958B1Low toxicitySafety managementBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsIGT - Impaired glucose toleranceGlycosidase inhibitor
The present invention discloses an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor for prevention of transition from high-risk IGT to diabetes mellitus, for prophylaxis of diabetes mellitus, as well as for treating high-risk IGT.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Combination therapy for endothelial dysfunction, angina and diabetes
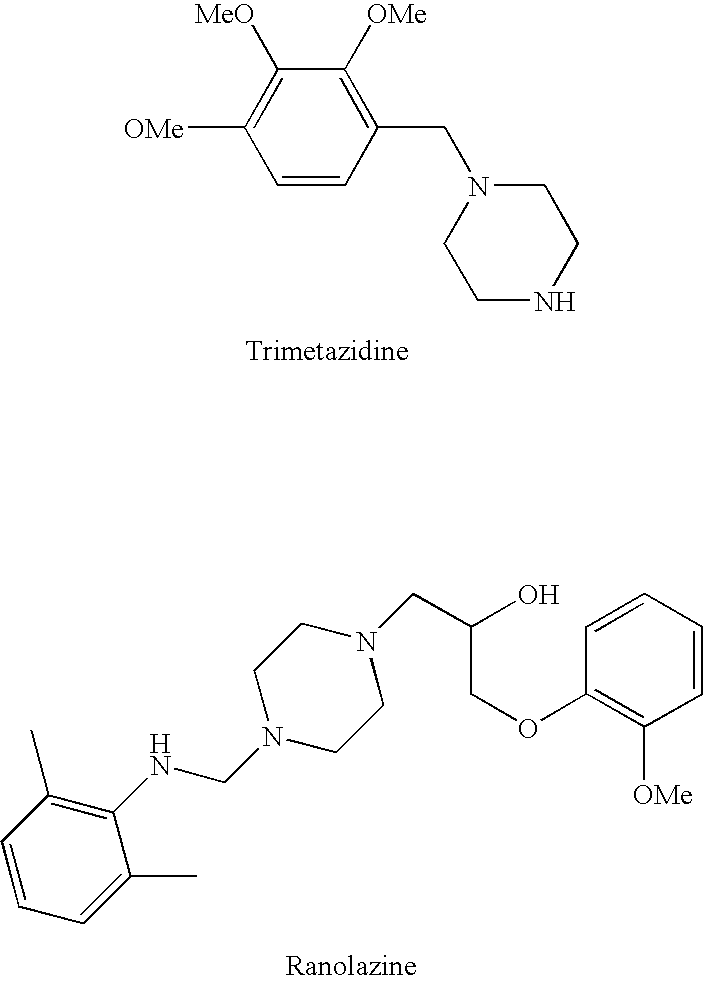
InactiveUS20060205727A1Control blood sugar levelsIncrease productionBiocideMetabolism disorderHMG-CoA reductaseTrimetazidine
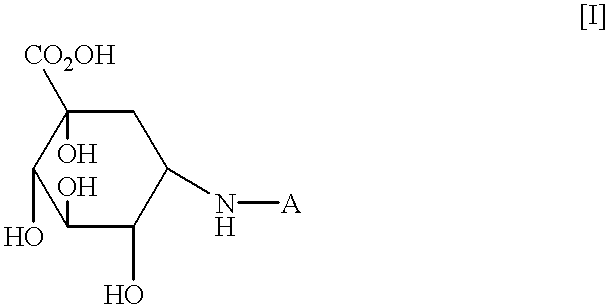
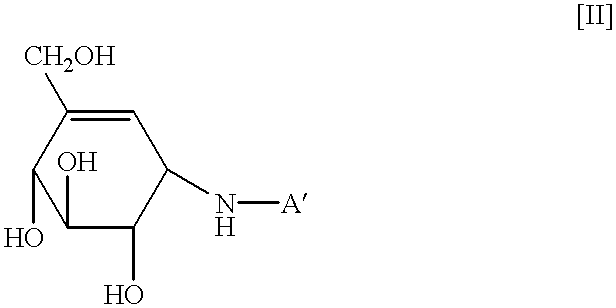
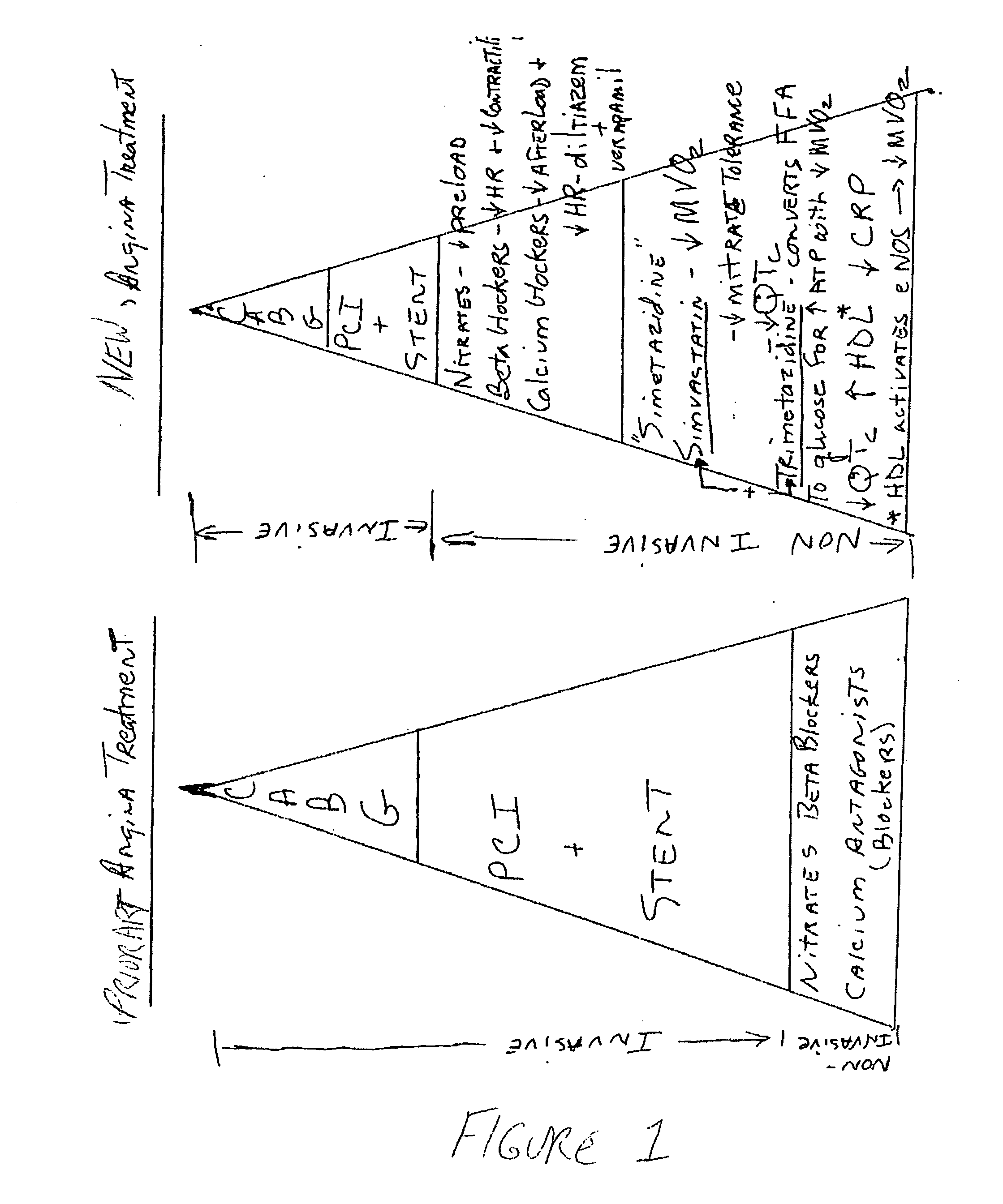
The combination of a HMG CoA reductase inhibitor like a statin, such as simvastatin, with a pFox inhibitor such as trimetazidine (“Simetazidine”) is particularly advantageous for treatment of end-stage complications, such as acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and chronic angina, especially in type II diabetics. The combination therapy is also useful in the treatment and / or prevention of chronic heart failure (CHF) and peripheral arterial disease (PAD). The combination of a nitric oxide (NO) mechanism with increased NO production with pFox inhibition simultaneously treats both the effect and the cause of angina. One or more oral hypoglycemic compounds (biguanides, insulin sensitizers, such as thiazolidinediones, α-glucosidase inhibitors, insulin secretagogues, and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors), protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors, and acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors can also be used in combination with the HMG CoA reductase inhibitors and / or pFox inhibitors, especially in type II diabetics, to control glucose levels and treat endothelial dysfunction. The drugs can be given in combination (e.g. a single tablet) or in separate dosage forms, administered simultaneously or sequentially. In the preferred form the statin is given in a dose of between 5 and 80 mg / day in two separate doses, and the pFox inhibitor is administered in a sustained or extended dosage formulation at a dose of 20 mg three times a day or 35 mg two times a day. The dose of the oral hypoglycemic, PKC inhibitor, or acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitor varies with the type of drug used.
Owner:HONG KONG NITRIC OXIDE
Methods of use and nutritional compositions of touchi extract
InactiveUS20090148545A1Reduce complicationsReduce post-prandial glucose excursionBiocideAntiviralsPhysiologyConstipation
Disclosed is a method and composition for nutritional compositions containing -glucosidase inhibitors, and more specifically Touchi Extract and its uses in the treatment of many disorders. These disorders include diabetes, hyperlipidemia, obesity, Metabolic syndrome / Syndrome X, COPD, malabsorption, Crohn's disease, diarrhea, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, human immunodeficiency virus, cystic fibrosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, polycystic ovarian syndrome including associate infertility, and erectile dysfunction. Further, -glucosidase inhibitors, and more specifically Touchi Extract can be used to aid healing in critical care patients and for general wound healing. Additionally, -glucosidase inhibitors, including Touchi Extract can be used to enhance athletic performance.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Combination therapeutic compositions and method of use
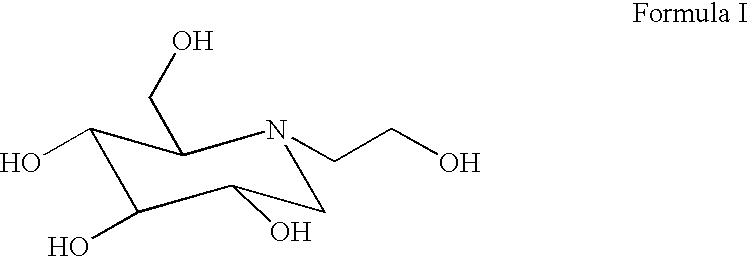
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of diabetes mellitus using combination therapy. The compositions relate to a compound of Formula I selected from one or more of betaines, lipidic betaines, betaine lipids and an antidiabetic agent such as sulfonylureas, biguanides, glitazones, .alpha.-glucosidase inhibitors, potassium channel antagonists, aldose reductase inhibitors, glucagon antagonists, activators of RXR, insulin therapy or other anti-obesity agent. The methods include the administration of the combination of compound of Formula I with antidiabetic agent where the two components are delivered in a simultaneous manner, where the compound of Formula I is administered first, followed by the antidiabetic agent, as well as wherein the antidiabetic agent is delivered first followed by the compound of Formula I.
Owner:MESSADEK JALLAL
Method for preparing timosaponin BIII and uses thereof
InactiveCN101307090AEasy to prepareGood antidiabetic activityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderAlgluceraseMedicine
The invention relates to a method for preparing timosaponin BIII. The method separates an effective constituent of timosaponin BIII from a Chinese traditional medicine anemarrhenae in a chemical way. Simultaneously in-vivo and in-vitro pharmacological tests verify that: as the compound can remarkably inhibit the activity of alpha-glucosaccharase, and effectively reduce animal blood sugar, the compound can be applicable to the preparation of alpha-glucosaccharase inhibitors and medicines for curing diabetes. The method for preparing the timosaponin BIII replaces HPLC preparation with processes such as crystallization with simple operation, thereby facilitating industrialized production more effectively. Simultaneously, the compound displays good anti-diabetes activity in vivo and vitro, thereby not only widening the application field of the compound, but also becoming the effective medicine for curing diabetes in future.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Use of cornel and its extract in preparation alpha-glucosidase inhibitor medicine
InactiveCN1565467ALower postprandial blood sugarControl elevationOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderAdditive ingredientDepressant
The invention provides a dogberry medicament having alpha-glucosaminidase inhibiting activity, and the water or organic solvent extract of dogberry, wherein the dogberry extract comprises total glycosides and poly phenols constitution.
Owner:CHENGDU DIAO PHARMA GROUP
Application of three biflavone monomer components extracted from ginkgo leaves in preparing medicament of alpha-glucosidase inhibitor
The invention provides three biflavone compounds, namely ginkgetin, isoginkgetin and 7-bilobetin from dry leaves of ginkgo biloba L. Pharmacological tests prove that the three biflavone compounds have the activity of inhibiting alpha-glucosidase. The invention discloses novel application of the ginkgetin, the isoginkgetin and the 7-bilobetin in preparing the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, and also discloses a novel method for preparing the three biflavone compounds.
Owner:赵全成
Application of asiatic acid and madecassic acid in preparation of alpha-glucosidase inhibitor drugs
Asiatic acid and madecassic acid are extracted and prepared from Centella asiatica (L.) Urban, and pharmacological experiments prove that the asiatic acid and the madecassic acid have the activity of inhibiting alpha-glucosidase. The invention discloses a new use of the asiatic acid and the madecassic acid in the preparation of alpha-glucosidase inhibitor drugs, and the asiatic acid, the madecassic acid or a composition containing the asiatic acid and the madecassic acid can be used for preparing the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor drugs. The invention simultaneously discloses a new preparation method of the asiatic acid and the madecassic acid.
Owner:赵全成
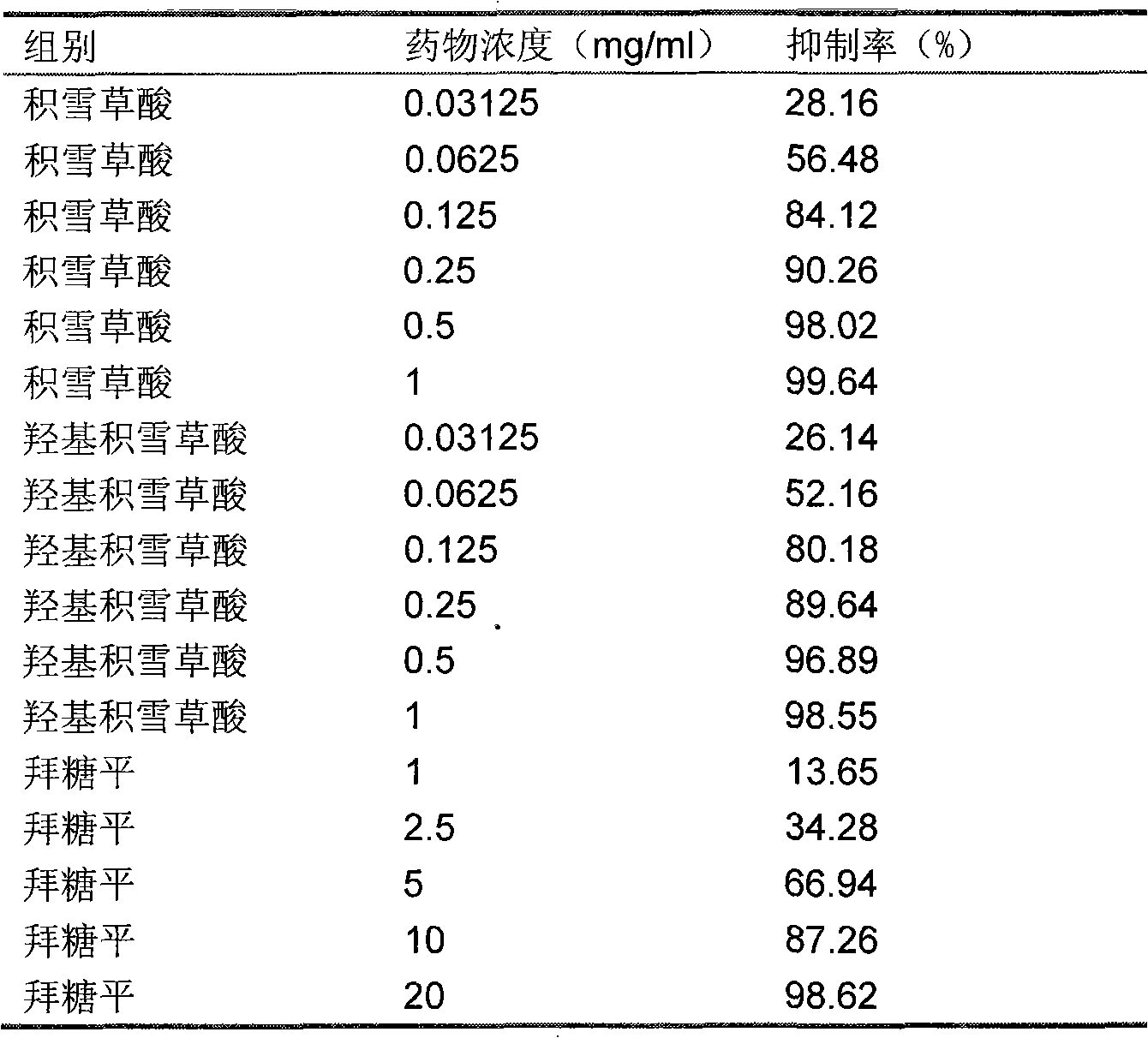
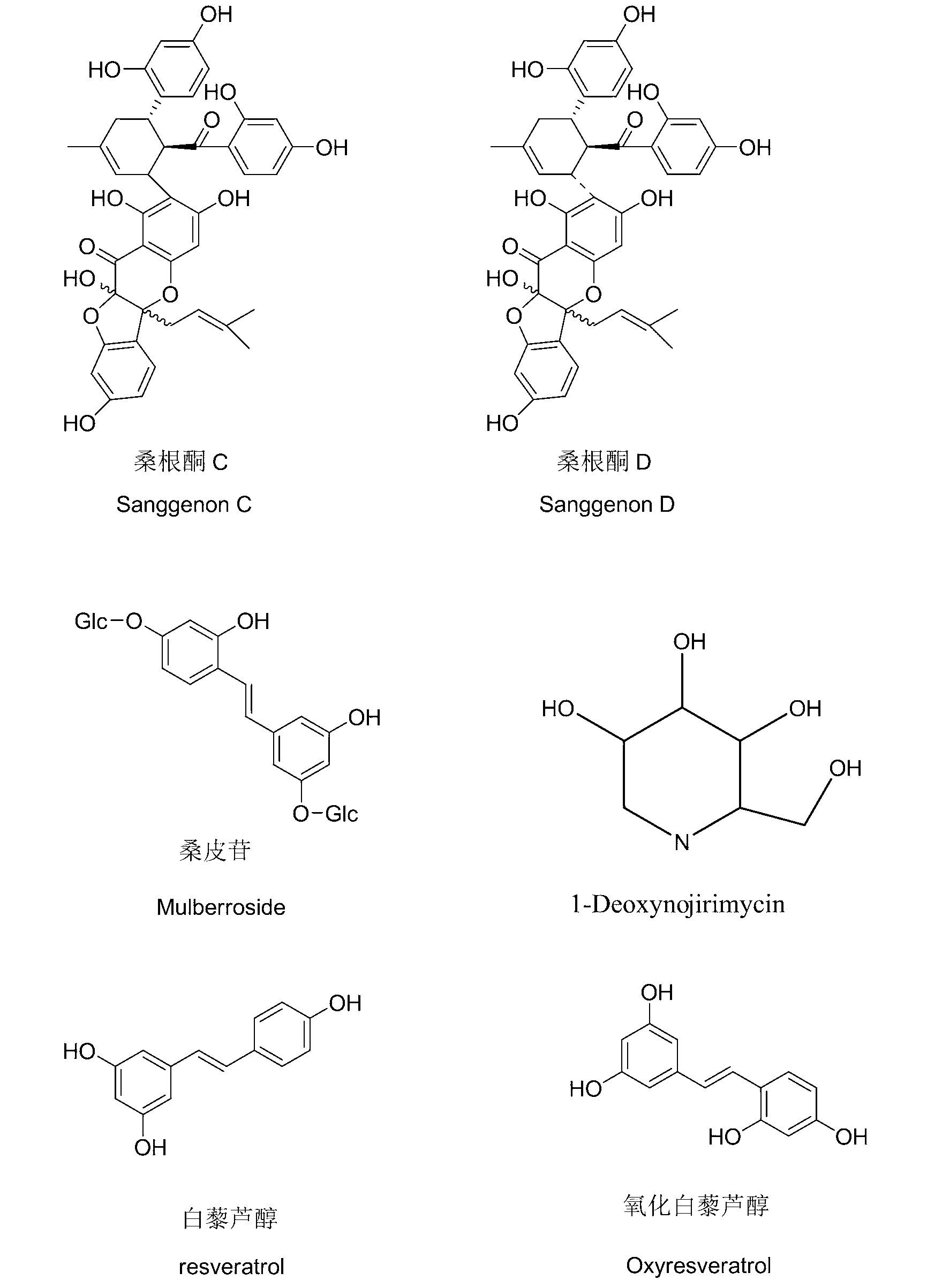
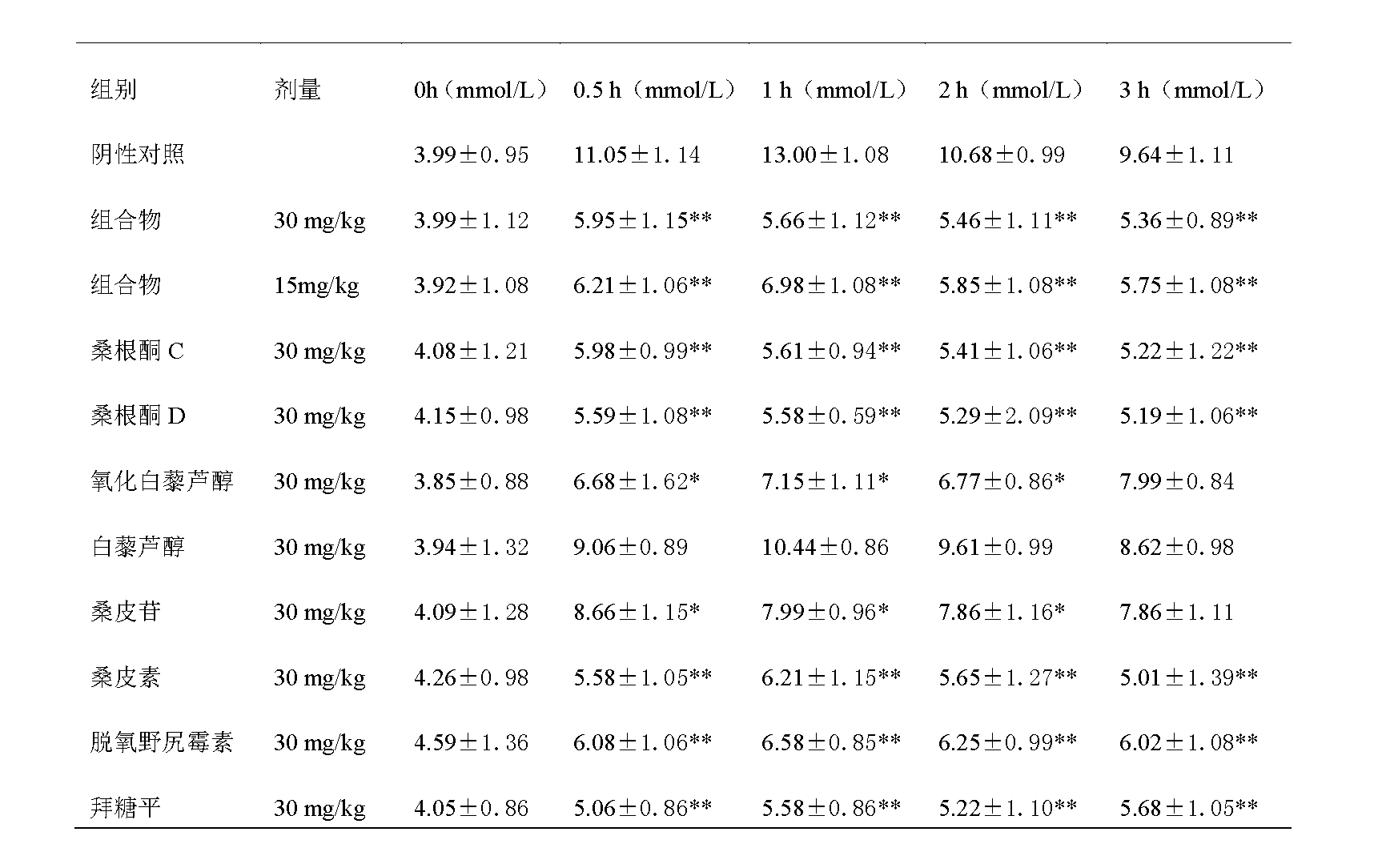
Sanggenone C and sanggenone D extracted from morus plants and new medicine application of composition
The invention discloses sanggenone C and sanggenone D extracted from white mulberry root-barks, mulberry twigs and folium leaves and a new medicine application of a composition comprising the sanggenone C and the sanggenone D which are main ingredients, particularly the application of the single ingredient sanggenone C or sanggenone D and the composition composed of the sanggenone C, the sanggenone D, mulberrin, mulberroside, oxidized resveratrol, resveratrol and deoxynojirimycin in preparation of alpha-glucosidase inhibitor medicines. The composition is prepared by respectively extracting medicinal materials containing the chemical components above and blending according to certain proportions, or using several extraction methods for extracting the medicinal materials simultaneously containing the chemical components above. The white mulberry root-barks, the mulberry twigs and the folium leaves are accidentally found to contain the sanggenone C and the sanggenone D apart from containing alkaloids such as deoxynojirimycin; and the sanggenone C and the sanggenone D have stronger pharmacological activity than the alkaloids such as deoxynojirimycin.
Owner:赵全成
Benzimidazole chiral heterocyclic compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109336887AHigh enantioselectivityImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryAntipyreticEnzyme inhibitionAmination
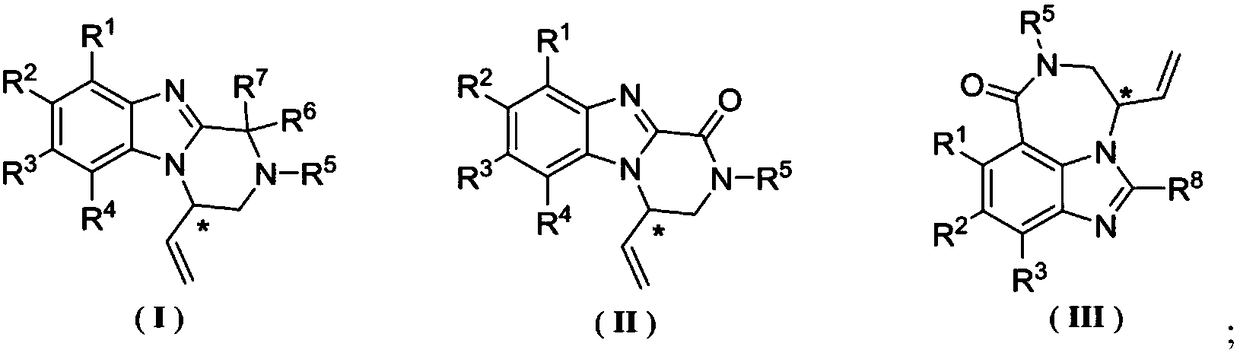
The invention discloses a benzimidazole chiral heterocyclic compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structure formula of the benzimidazole chiral heterocyclic compound isshown in formula I, formula II or formula III in the description. The benzimidazole chiral heterocyclic compound is prepared by treating an iridium complex which is prepared through a metal iridium compound and a phosphoramidite ligand as a catalyst, performing intra-molecular allyl amination on allyl substrate, and then synthesizing with high efficiency and high enantioselectivity. The method has the advantages of being high in catalytic reaction activity, mild in reaction conditions, high in enantioselectivity, wide in substrate applicable scope, and environmentally friendly; the primary in-vitro enzyme inhibition activity test shows that the compound is high in alpha-glucosidase inhibiting activity and can be used as an alpha-glucosidase inhibiting agent, and the compound can also be used as a further modified drug intermediate; the compound has a potential application value in preventing or treating II-diabetes, obesity and complication medicines thereof and pilot compounds thereof.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Pharmaceutical composition having alpha-glucosidase inhibition activity, and applications thereof
ActiveCN104984346AGood hypoglycemic effectHypoglycemic effect achievedOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderSide effectHypoglycemia
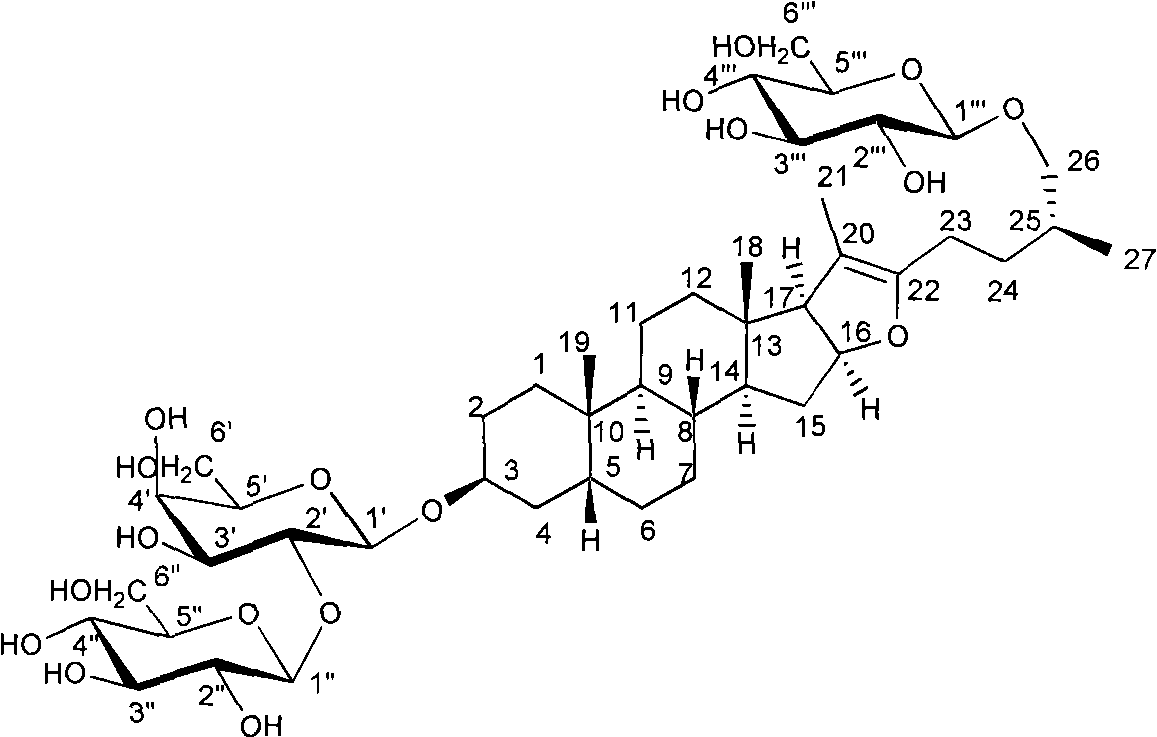
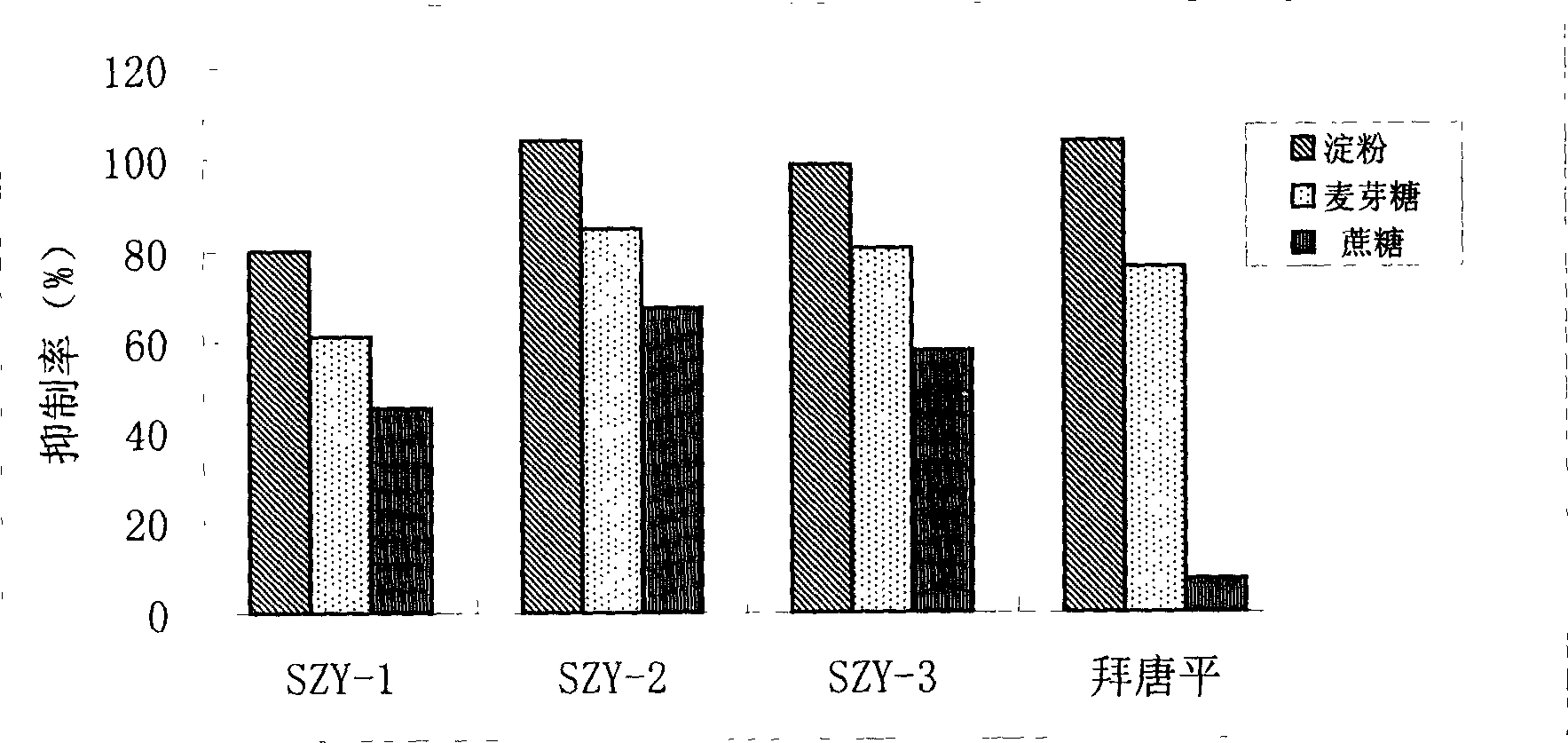
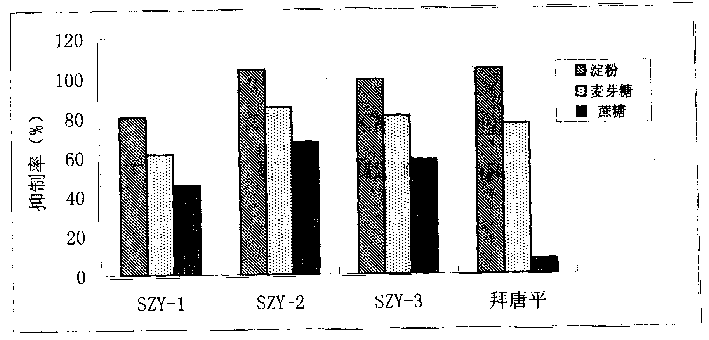
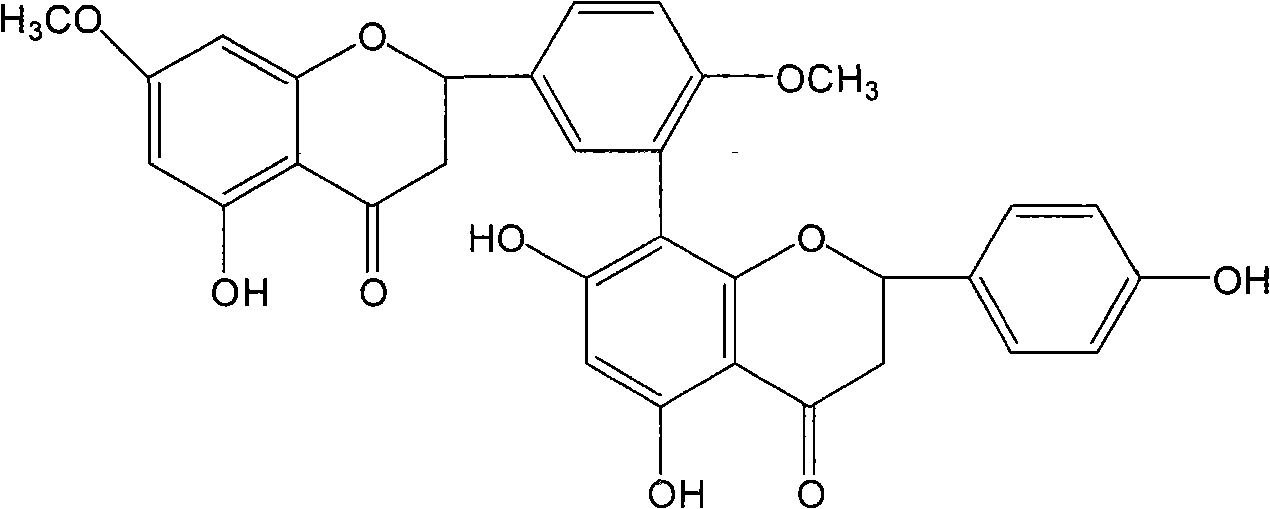
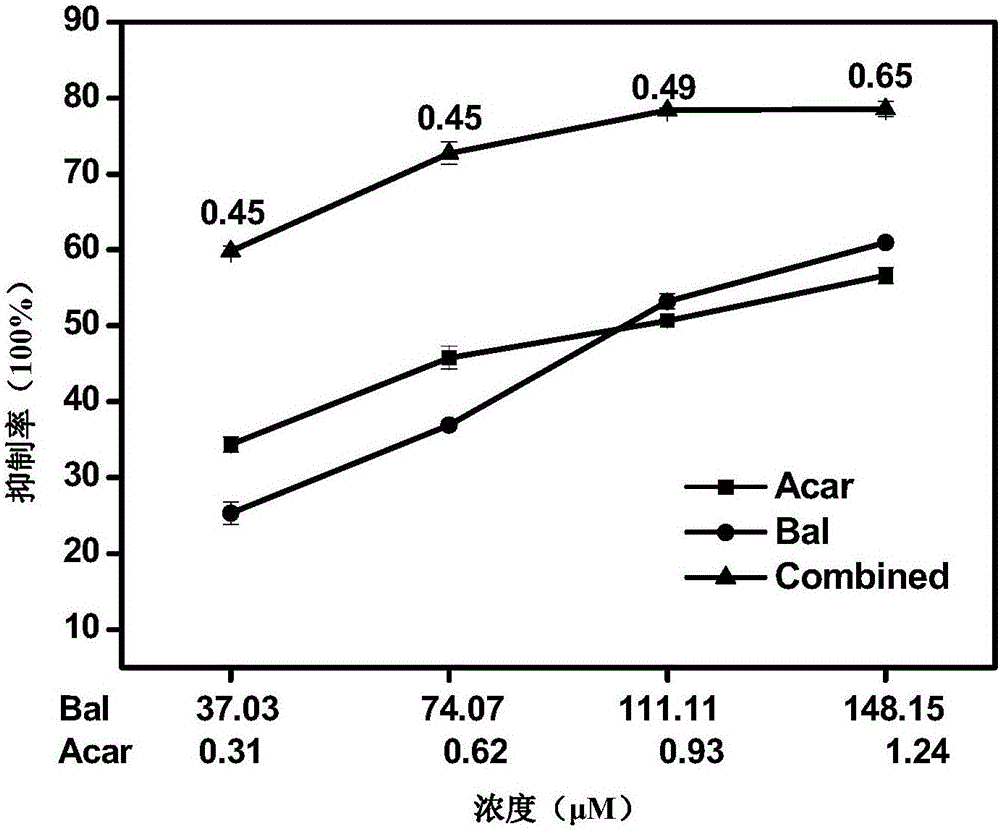
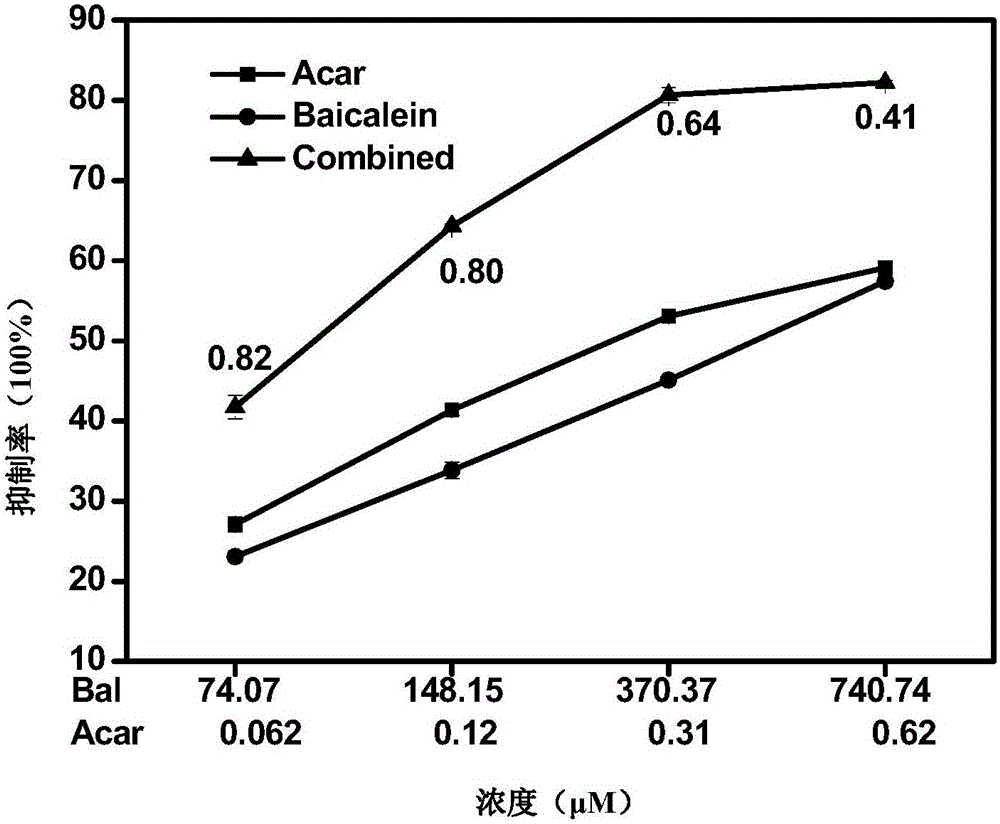
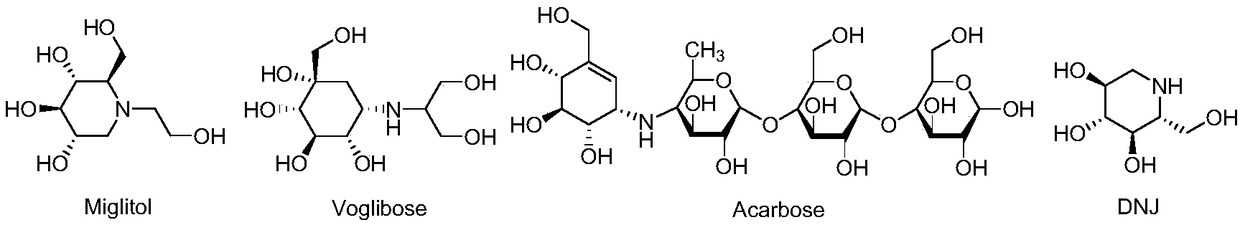
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition having alpha-glucosidase inhibition activity, wherein the pharmaceutical composition comprises a flavone compound and an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, the flavone compound is at least one selected from a monomer such as baicalein, quercetin, luteolin, baicalein-7-O-glucoside and catechin, an organic salt of the monomer, and an inorganic salt of the monomer, and the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor is at least one selected from a monomer such as acarbose, voglibose and miglitol, an organic salt of the monomer, and an inorganic salt of the monomer. According to the present invention, the pharmaceutical composition can effectively reduce postprandial blood glucose, can inhibit the activity of alpha-glucosidase adopting starch, maltose and sucrose as substrates, and less uses the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, such that the efficacy can be improved, the side effect of the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor can be effectively reduced, and hypoglycemia and other problems easily caused by drug combination are effectively solved.
Owner:上海皋鱼医药科技有限公司
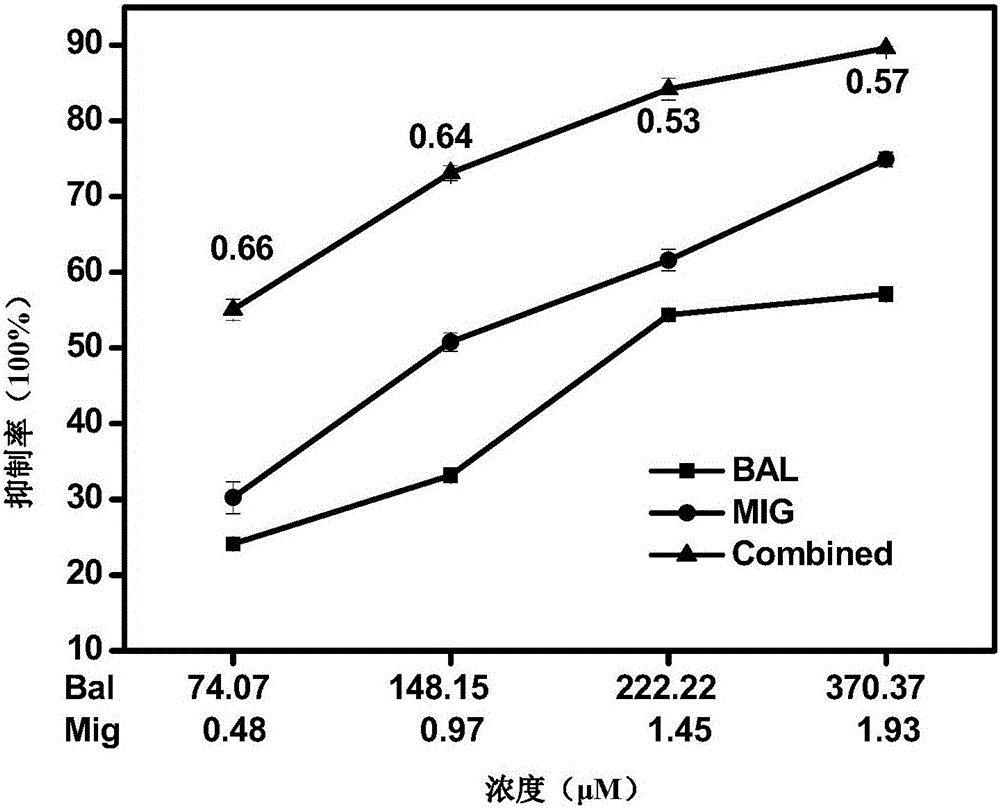
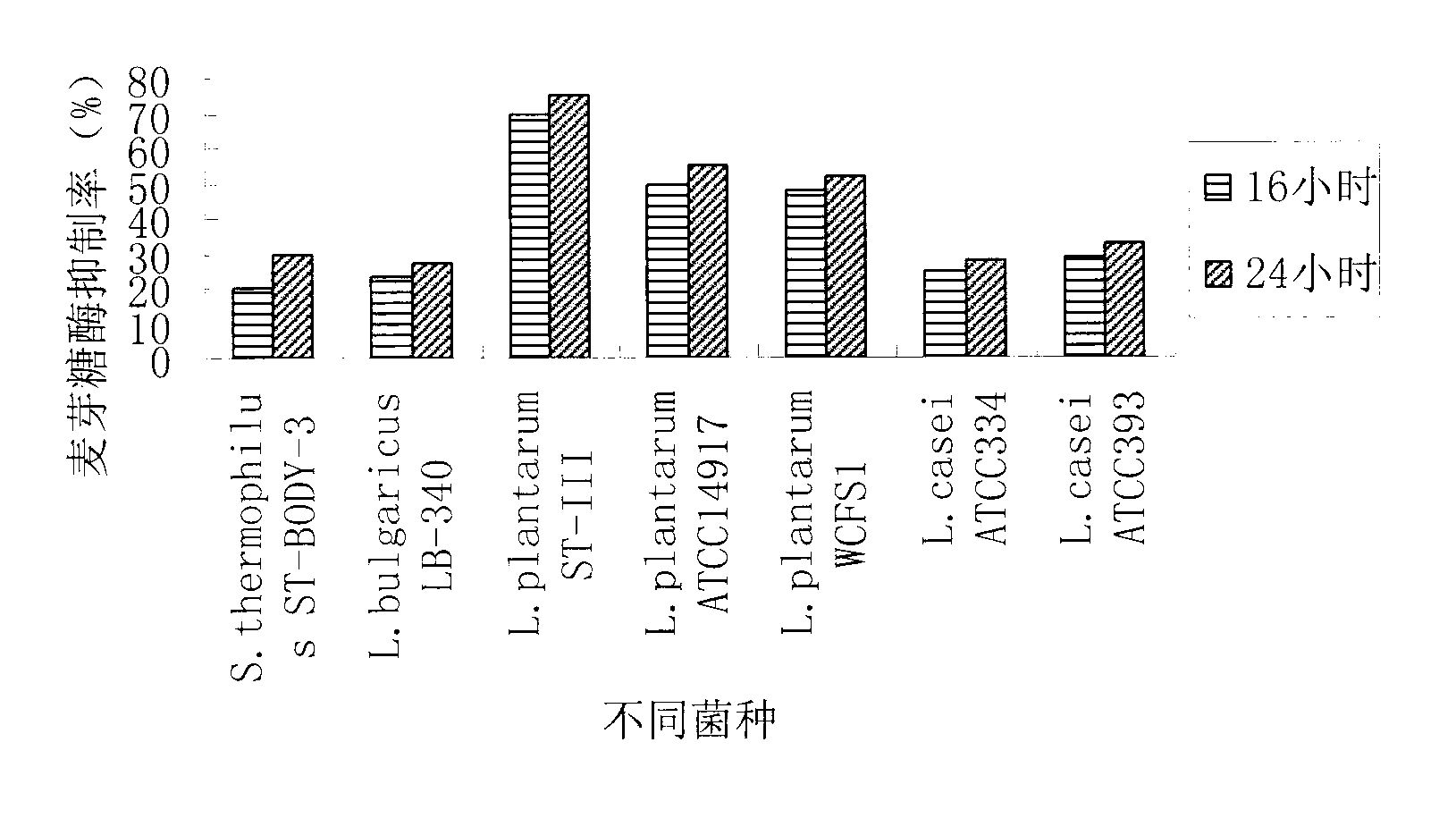
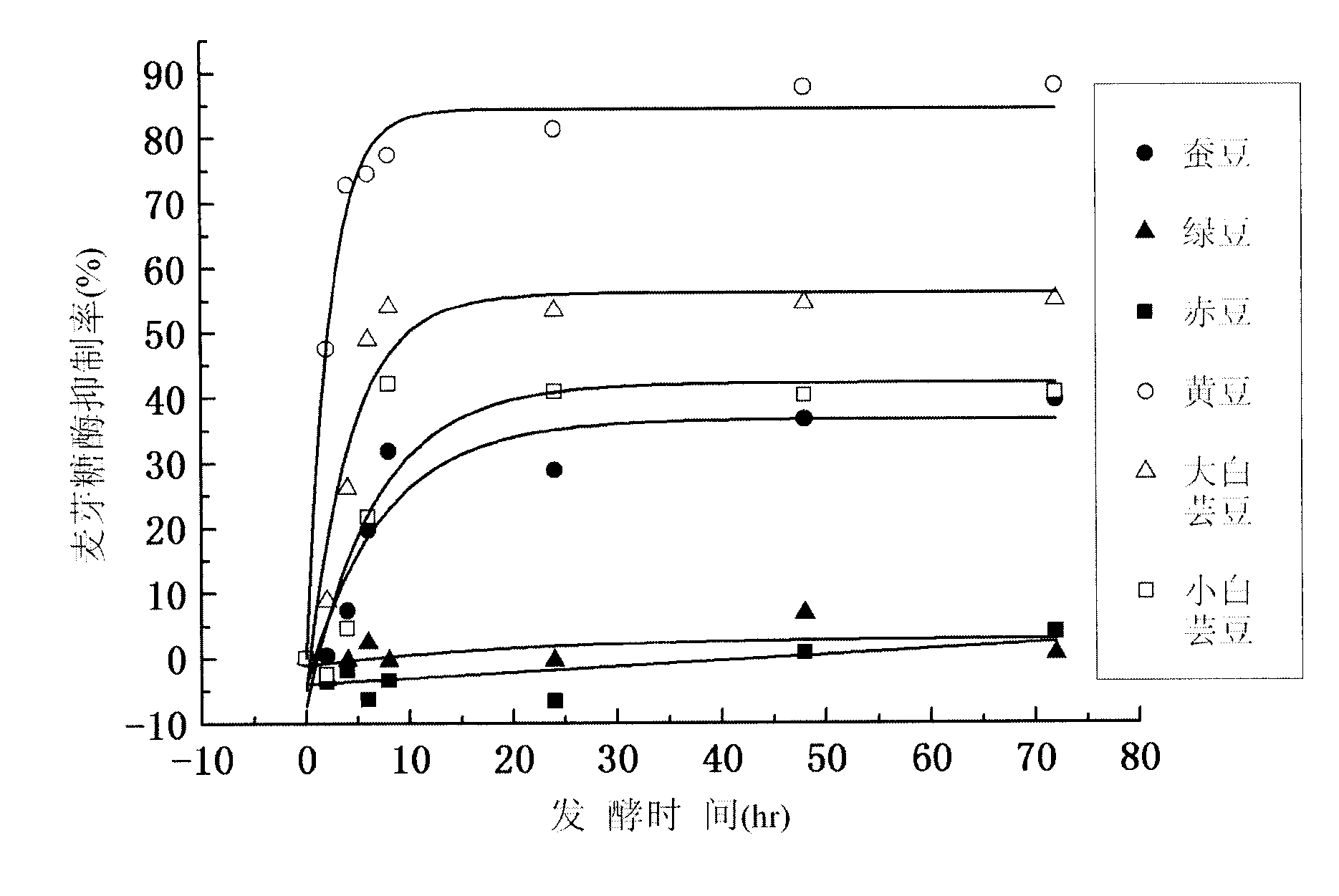
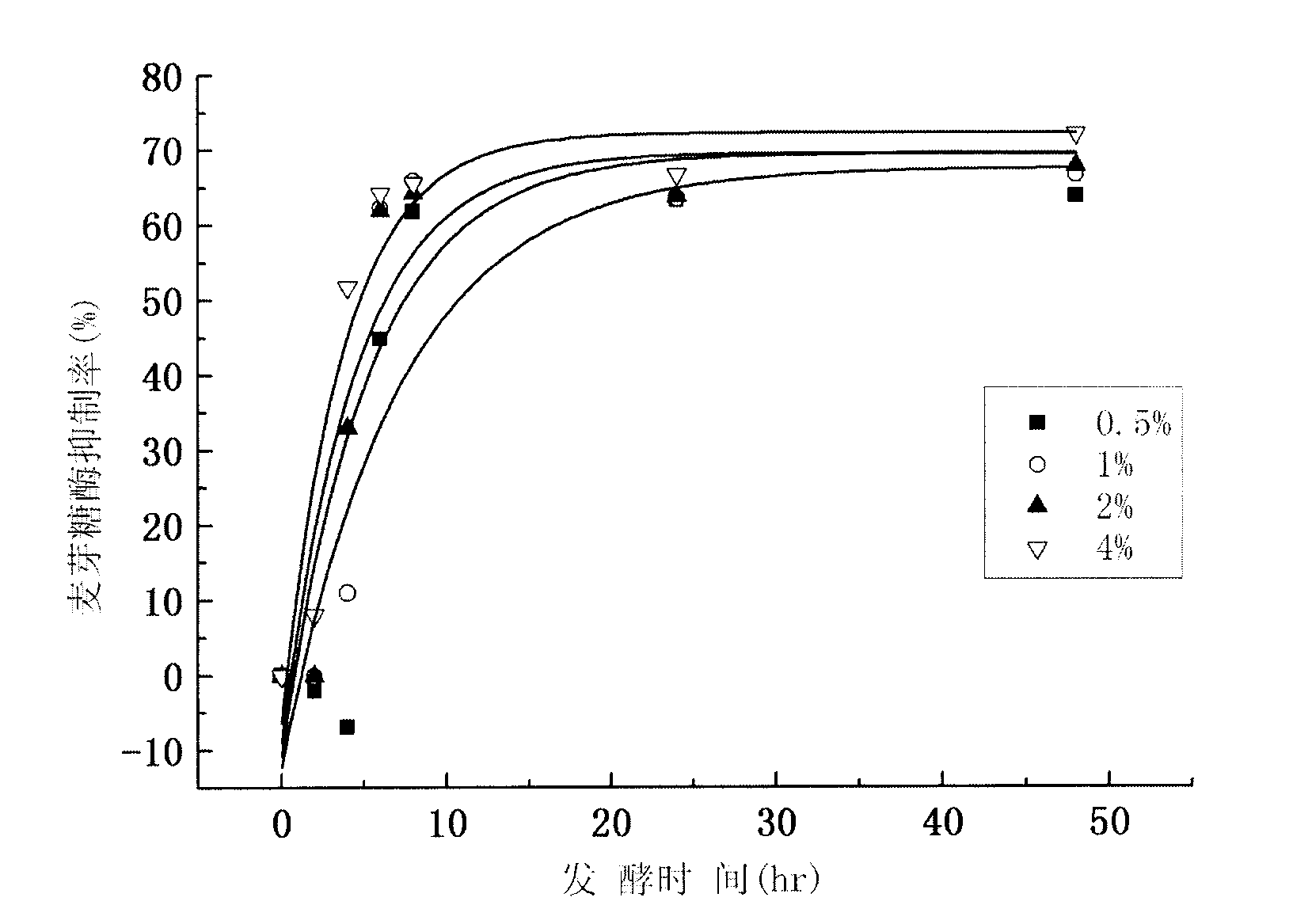
Fermented bean product fermented by lactobacillus plantarum ST-III and alpha-glucosidase inhibitor
ActiveCN103169075AClear compositionShorten fermentation timeMetabolism disorderBacteria material medical ingredientsOral glucoseGlucose fluctuations
The invention discloses a use of lactobacillus plantarum ST-III in preparation of an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor or the preparation of a fermented bean product with alpha-glucosidase inhibition activity. The invention further discloses fermented soymilk or fermented beans with the alpha-glucosidase inhibition activity, which can be obtained by inoculating the lactobacillus plantarum ST-III into sterile soymilk or cooked soymilk and fermenting at the temperature of 25-40 DEG C. Water is added into the fermented beans for homogenizing, the pH value is regulated to 6.5-7.5, the boiling is performed for 10-60 minutes, cooling is performed, then solid-liquid separation is performed, and a liquid phase is taken so as to get a water-soluble extract of the fermented soymilk. The lactobacillus plantarum ST-III has high alpha-glucosidase inhibition activity and can be used in glucose-reducing foods, health care products or medicaments. As the oral glucose-reducing foods, the health care products or the medicaments, the high postprandial blood glucose of patients with diabetes can be reduced and the postprandial blood glucose fluctuation can be regulated.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
Compounds Affecting Glycemic Index
Compounds of formula I are disclosed which are useful as glycemic index lowering agents and / or, as α-amylase and / or α-glucosidase inhibitors. Also disclosed are nutritional and / or pharmaceutical compositions and supplements comprising one or more of these compounds. The compounds will be beneficial to patients who require stabilization of their postprandial glucose levels.
Owner:SACRON INNOVATIONS
Methods of use and nutritional compositions of Touchi Extract
InactiveUS8815312B2Improve blood sugar controlDelaying the appearance of glucose in the bloodBiocideAntiviralsPhysiologyConstipation
Disclosed is a method and composition for nutritional compositions containing glucosidase inhibitors, and more specifically Touchi Extract and its uses in the treatment of many disorders. These disorders include diabetes, hyperlipidemia, obesity, Metabolic syndrome / Syndrome X, COPD, malabsorption, Crohn's disease, diarrhea, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, human immunodeficiency virus, cystic fibrosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, polycystic ovarian syndrome including associate infertility, and erectile dysfunction. Further, glucosidase inhibitors, and more specifically Touchi Extract can be used to aid healing in critical care patients and for general wound healing. Additionally, glucosidase inhibitors, including Touchi Extract can be used to enhance athletic performance.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Virtual screening method of alpha-glucosidase inhibitor
ActiveCN108830041AReduce in quantityAvoid blindnessSpecial data processing applicationsVirtual screenIn vivo
The invention aims at disclosing a virtual screening method of an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, the virtual screening method and the application of screened compounds in pharmaceutical preparations forpreventing and / or treating 2-type diabetes. The method comprises the steps of 1, the obtaining, analyzing and treating of the three-dimensional structure of a large molecular protein; 2, the construction of a traditional Chinese medicine natural product library and the preparation of a small molecular compound; 3, the calibration of the prediction capability of a virtual screen model and the establishment of the screen model; 4, the virtual screening of the natural product library and the analyzing of a mutual impacting mechanism; 5, in vivo and in vitro biological activity verification of ascreening result. The method is used for screening and can be used for the discussing of a structure-activity relationship of compounds of the type, and the further modification of a structure based on a biological compound is guided.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
Glycosidase inhibitors
ActiveCN105143222AGood for healthEffective treatmentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGlycosidase inhibitorDisease cause
Compounds of formula (I) wherein X1, X2, W, R1 to R5, L and m have the meaning according to the claims, are glucosidase inhibitors, and can be employed, inter alia, for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitor and preparation method thereof
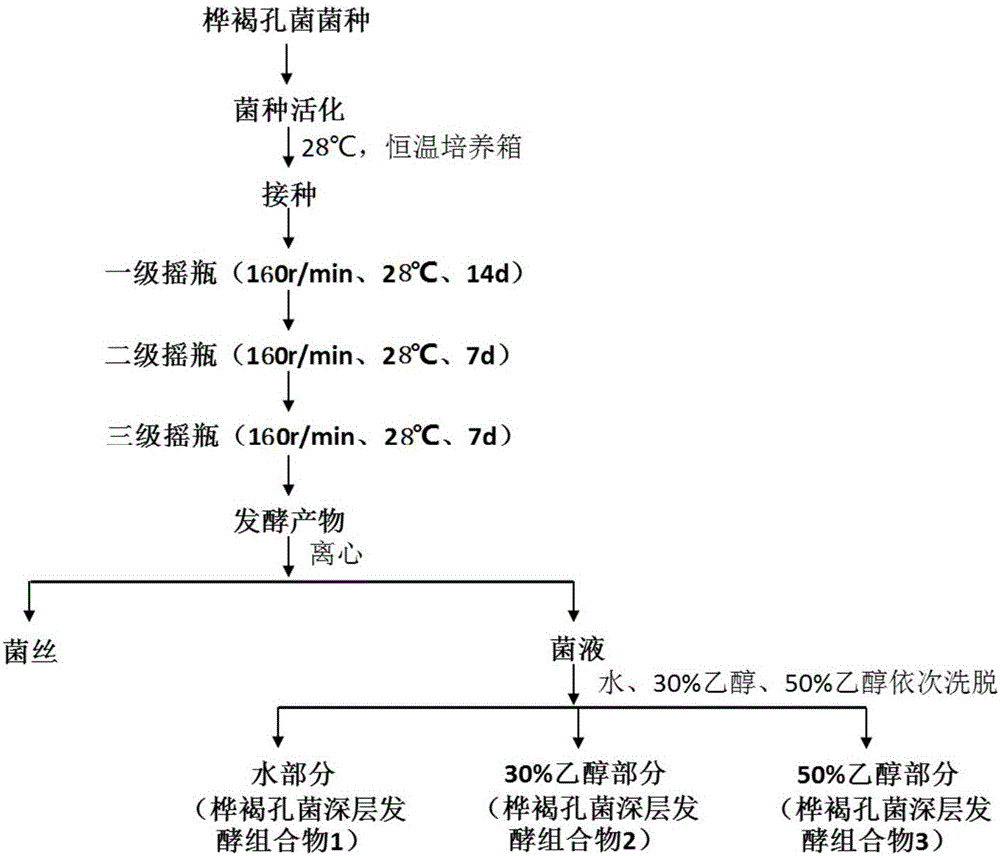
InactiveCN101724015AStrong inhibition rateFast production and reproductionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: culturing and activating a strain; culturing seeds; inoculating the stain into a shake flask for fermentation culture; collecting fermentation liquor; and performing separation and purification to obtain the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor. In the invention, the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor is obtained by microbial fermentation and can be used for developing hypoglycemic medicaments and provide a new tool for further research on active site of enzymes such as the alpha-glucosidase.
Owner:GUANGXI NANNING ZHITIAN BIOTECH +1
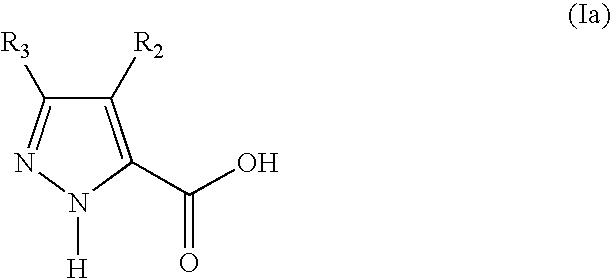
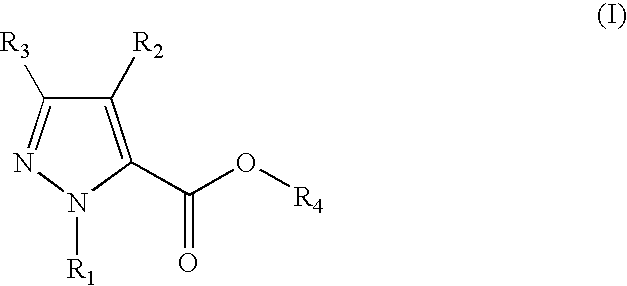
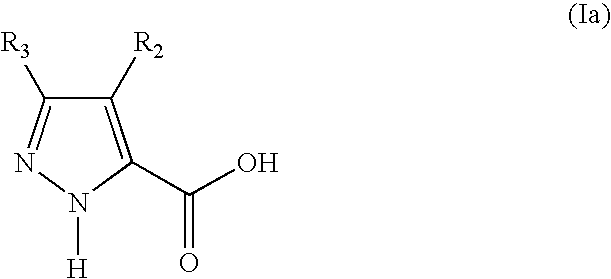
5-substituted 2h-pyrazone-3-carbixylic acid derivatives as antilipolytic agents for the treatment of metabolic-related disorders such as dyslipidemia
The present invention relates to certain pyrazole carboxylic acid derivatives of Formula (Ia), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, as antilipolytic agents and against for the receptor RUP25, wherein: R2 is H, halogen, C1-12 alkyl or C1-12 haloalkyl; and R3 is C3-6 cycloalkyl, C1-12 alkyl, C1-12 haloalkyl, C3-6 cycloalkyl-C1-4-alkylene, aryl-C1-4-alkylene or heteroaryl-C1-4-alkylene, wherein said aryl-C1-4-alkylene and heteroaryl-C1-4-alkylene can be optionally substituted 1 to 5 substituents selected from the substituents listed in the claims. Also provided by the present invention are pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds of the invention, and methods of using the compounds and compositions of the invention in the treatment of metabolic-related disorders, including dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, Syndrome-X and the like. In addition, the present invention also provides for pharmaceutical compositions in combination with other active agents, for example, those agents belonging to the class of α-glucosidase inhibitors, aldose reductase inhibitors, biguanides, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, squalene synthesis inhibitors, fibrates, LDL catabolism enhancers, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, insulin secretion enhancers, thiazolidinedione and the like.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
New alpha-glucosidase inhibitors from a natural source
The present invention relates to a method for providing alpha -glucosidase inhibition to a subject by administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a alpha -glucosidase inhibitory agent selected from pipataline (formula 1a), sesamin (formula 1b), pellitorine (Formula 1c), guineensine (Formula 1d) and brachystamide-B (formula 1e) having therapeutic application for diabetes mellitus, cancer, viral diseases such as hepatitis B and C, HIV, AIDS etc; also the invention provides a process for the isolation of said alpha -glucosidase inhibitory agent from the plant source Piper longum in significant yields.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Hypoglycemic drug composition and application of hypoglycemic drug composition
ActiveCN102698271AReduce usageSmall toxicityMetabolism disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsLow glucoseHypoglycemia
The invention relates to a hypoglycemic drug composition, which contains alpha-glucosaccharase inhibitor and Indian Trumetflower Seed extract, wherein the Indian Trumetflower Seed extract is prepared by the processes of extracting the Indian Trumetflower Seed with aqueous solution of organic solvent, filtering, re-extracting, separating and drying. The drug composition prepared from the Indian Trumetflower Seed extract and alpha-glucosaccharase inhibitor lower than normal dosage has excellent hypoglycemic effect. The hypoglycemic drug composition has the main advantages that postprandial blood glucose can be reduced faster and more efficiently, and less alpha-glucosaccharase inhibitor is used, so the drug effect can be improved, the toxic and side effects of the alpha-glucosaccharase inhibitor are effectively reduced, and the problems of hypoglycemia and the like easily caused by drug combination are also effectively solved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Combination therapeutic compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20060035928A1Good curative effectReduce doseBiocideMetabolism disorderAldose reductase inhibitorCombination therapy
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of diabetes mellitus using combination therapy. The compositions relate to a compound of Formula I and an antidiabetic agent such as sulfonylureas, biguanides, glitazones, α-glucosidase inhibitors, potassium channel antagonists, aldose reductase inhibitors, glucagon antagonists, activators of RXR, insulin therapy or other anti-obesity agent. The methods include the administration of the combination of compound of Formula I with antidiabetic agent where the two components are delivered in a simultaneous manner, where the compound of Formula I is administered first, followed by the antidiabetic agent, as well as wherein the antidiabetic agent is delivered first followed by the compound of Formula I.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Method for extracting alpha- glucosidase inhibitor from traditional Chinese cinnamomum cassia
InactiveCN1839939ANo pollution in the processSimple processMetabolism disorderPlant ingredientsAlgluceraseAlcohol
The invention relates to a process for preparing alpha- glucosidase depressant from Cinnamomum cassia, which comprises removing low-polarity constituents with no inhibiting activity to alpha-glucosidase from Cinnamomum cassia by means of fluid extraction technique, and carrying out solid-liquid oscillation extraction to the residual of extracting with anhydrous alcohol. The extracted effective portion has rather strong inhibiting activity to alpha-glucosidase.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Marine fungus-derived polyketone compound and application thereof in treatment of type 2 diabetes
ActiveCN104987316ASimple extraction and separation methodLow costOrganic chemistryMetabolism disorderDrug compoundMicrobiology
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal compounds, and concretely discloses a marine fungus-derived polyketone compound, a preparation method thereof, and an application thereof in treatment of type 2 diabetes. The structure of the polyketone compound is represented by formula (I). The compound can substantially inhibit the activity of alpha-glucosidase, and the IC50 value of the compound is (9.05+ / -0.60)[mu]M. Enzyme kinetic researches show that the compound is a typical noncompetitive inhibitor. The compound can be used for preparing alpha-glucosidase inhibitor medicines in order to prevent and treat the type 2 diabetes.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Modulators of the gpr119 receptor and the treatment of disorders related thereto
InactiveUS20130023494A1Increase secretionIncreasing blood incretin levelBiocideNervous disorderBiguanideSGLT2 Inhibitor
The present invention relates to compounds of Formula (Ia) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, and hydrates thereof, that are useful as a single agent or in combination with one or more additional pharmaceutical agents, such as, an inhibitor of DPP-IV, a biguanide, an SGLT2 inhibitor, or an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, in the treatment of, for example, a disorder selected from: a GPR119-receptor-related disorder; a condition ameliorated by increasing a blood incretin level; a metabolic-related disorder; type 2 diabetes; obesity; and complications related thereto.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
Use of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors to treat alphavirus infections
The present invention provides methods for treating a flavivirus infection, including hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, in an individual suffering from a flavivirus infection. In some embodiments, the methods involve administering to an individual in need thereof an effective amount of an agent that inhibits enzymatic activity of a membrane-bound α-glucosidase inhibitor. In other embodiments, the methods involve administering to an individual in need thereof effective amounts of an α-glucosidase inhibitor and at least one additional therapeutic agent.
Owner:INTERMUNE INC
Inonotus obliquus submerged fermentation product and application
InactiveCN106434755AImprove adsorption capacityReduce loss rateMetabolism disorderMicroorganismsGlycosidase inhibitorSubmerged fermentation
The invention discloses an inonotus obliquus submerged fermentation product and application. The inonotus obliquus submerged fermentation product comprises a composition A, a composition B and a composition C. By the utilization of a biological fermentation technology, inonotus obliquus strains are fermented to obtain the new composition, and the composition belongs to a natural alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, and is low in price and environmentally friendly; the preparation technology is easy to industrialize. The inonotus obliquus submerged fermentation product is suitable for a broad crowd of people, convenient to eat and capable of serving as a daily drink to be drunk by people with diabetes, will not generate adverse reactions such as abdominal discomfort, flatulence and exsufflation, and can achieve a health-care effect after being drunk by average persons.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for compound 3 alpha-Akebonolic acid and application of compound to preparation of glycosidase inhibitor drug
InactiveCN103622972ARich sourcesHigh alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderAlgluceraseGlycosidase inhibitor
The invention discloses a preparation method for a compound 3 alpha-Akebonolic acid and the application of the compound in the preparation of a glycosidase inhibitor drug. According to the invention, an alpha-glucosaccharase inhibitor is extracted and separated from akebia plants; the source of the plant material is abundant, the extraction and preparation method is easy to operate, and the plants can be utilized for a long term without being damaged through adopting fruits for extraction, so that the economic benefit can be improved, and the monomeric compound is environmentally friendly, stable, and easy to store. Pharmacology experiments show that the activity of the alpha-glucosaccharase inhibitor of the compound 3 alpha-Akebonolic acid is higher than that of the first-line diabetes drug acarbose, so that the compound 3 alpha-Akebonolic acid is expected to be developed into a drug for preventing and treating type 2 diabetes mellitus, and has excellent application and development prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Space lactobacillus plantarum SS18-37 capable of reducing activity of alpha-glucosaccharase and application of space lactobacillus plantarum SS18-37
ActiveCN108018236AStrong ability to tolerate gastrointestinal adverse environmentSmooth passage through the gastrointestinal tract to exert health benefitsBacteriaMetabolism disorderDiabetes mellitusGenetics
The invention discloses space lactobacillus plantarum SS18-37 capable of reducing activity of alpha-glucosaccharase and an application of the space lactobacillus plantarum SS18-37. The lactobacillus plantarum Fullarton-SS18-37 is provided and has the collection number of CGMCC NO.14918. Ground original lactobacillus plantarum GS18 is taken as a control, the space lactobacillus plantarum Fullarton-SS18-37 with higher inhibition on activity of alpha-glucosaccharase is screened out, and the space lactobacillus plantarum Fullarton-SS18-37 has higher tolerance capability for the inverse environmentof the gastrointestinal tract, can smoothly have healthcare efficacy through the gastrointestinal tract and can be the most potential strain for controlling DM (diabetes mellitus).
Owner:FULLARTON BIOENG TECH BEIJING CO LTD
Mangnolia officinalis alkaloid, extraction method and applications thereof
InactiveCN101966228ASimple extraction and preparation processEasy to operateMetabolism disorderAntiviralsStrong acidsOfficinalis
The invention belongs to the organic chemistry technical field, relating to an extraction method of mangnolia officinalis active constituent alkaloid and applications thereof used as alpha-glucuroide inhibitor. The mangnolia officinalis alkaloid of the invention comprises magnoflorine, liriodenine, anonaine, roemerine and total alkaloids of lysicamine, and mangnolia officinalis bark is taken as a raw material and then is extracted with acid aqueous solution at normal temperature or by heating; the extracting solution passes through strong-acid-type cation exchange resin or weak-acid-type cation exchange resin; and the active component is adsorbed on the resin; the resin column is washed by water, is eluted with ammonia water or alcoholic solution, and the obtained product is concentrated and dried to obtain total mangnolia officinalis alkaloids. The invention has the advantages of simple extraction and preparation process, easy operation and low cost and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Application of radix acanthopanacis trifoliate extract in inhibiting alpha-glucosidase
ActiveCN104922173AInhibitory activityHigh activityMetabolism disorderPlant ingredientsPL ExtractEthyl acetate
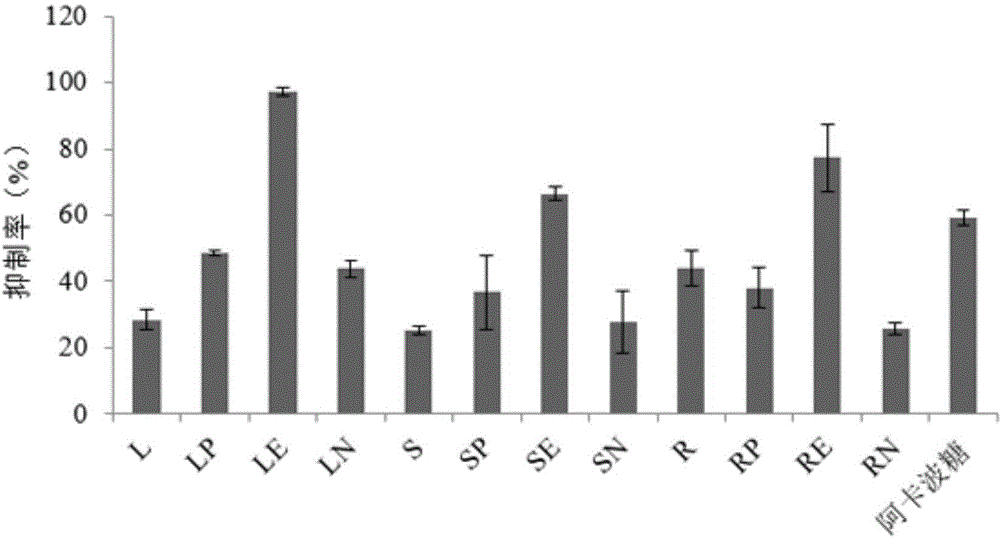
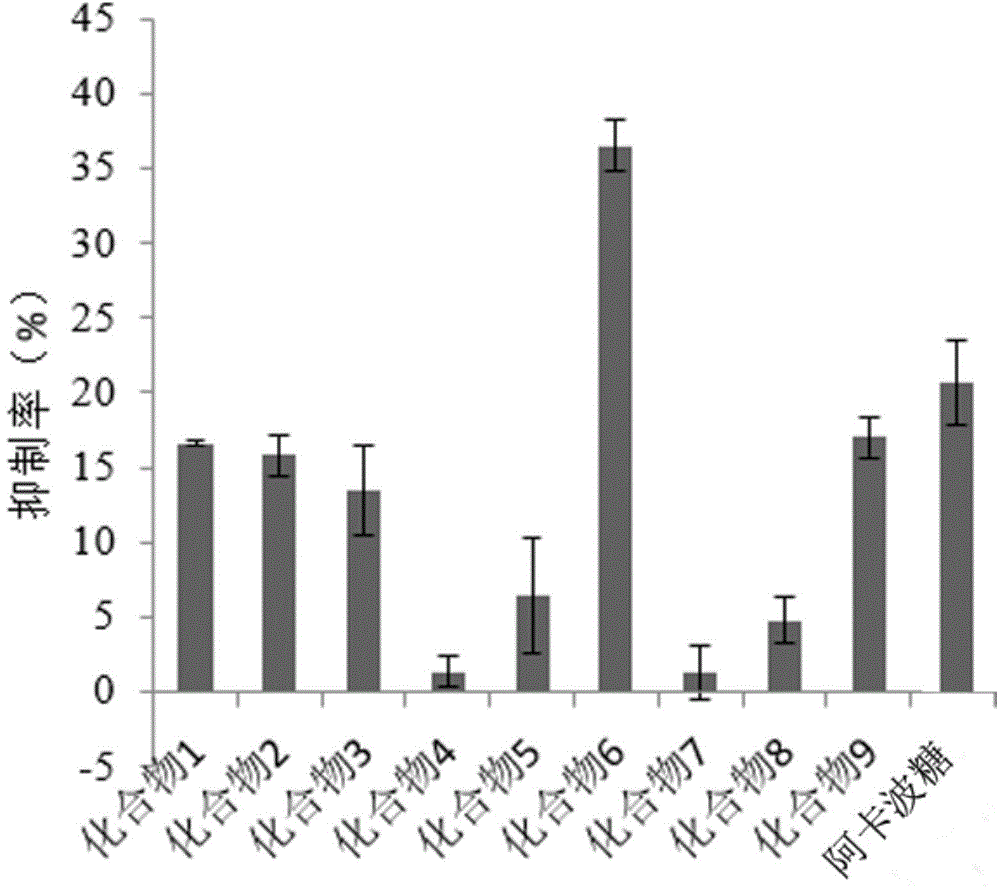
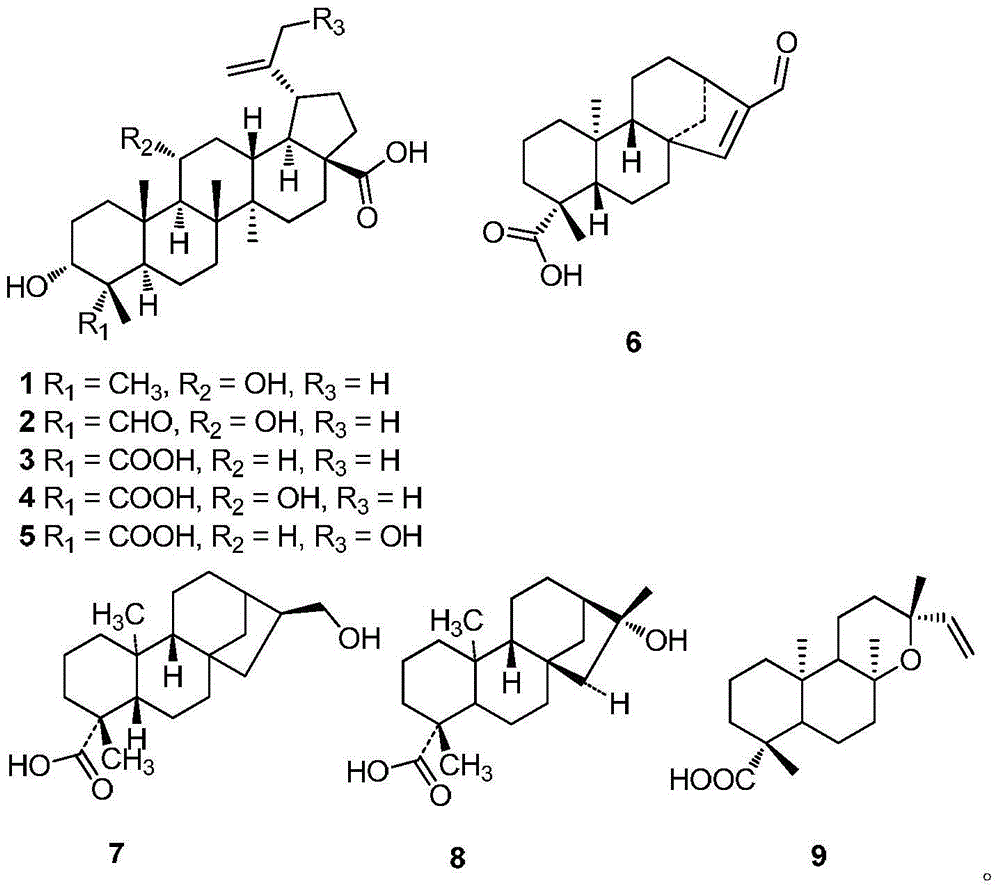
The invention discloses an application of radix acanthopanacis trifoliate extract in inhibiting alpha-glucosidase. The radix acanthopanacis trifoliate extract is extracted and concentrated by ethanol and then extracted respectively by petroleum ether, ethylacetate and normal butanol. The radix acanthopanacis trifoliate extract is identified to have 9 terpenoids. The invention also discloses an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, and the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor comprises radix acanthopanacis trifoliate extract as well as one or more additives acceptable on the medicine. The experiment shows that the extract of radix acanthopanacis trifoliate leaves, stalks and roots has inhibitory activity for the alpha-glucosidase; in 9 terpenoids of the radix acanthopanacis trifoliate extract, the compound 6 has best activity for inhibiting the alpha-glucosidase, which is far higher than a reference product acarbose.
Owner:WUYI UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com