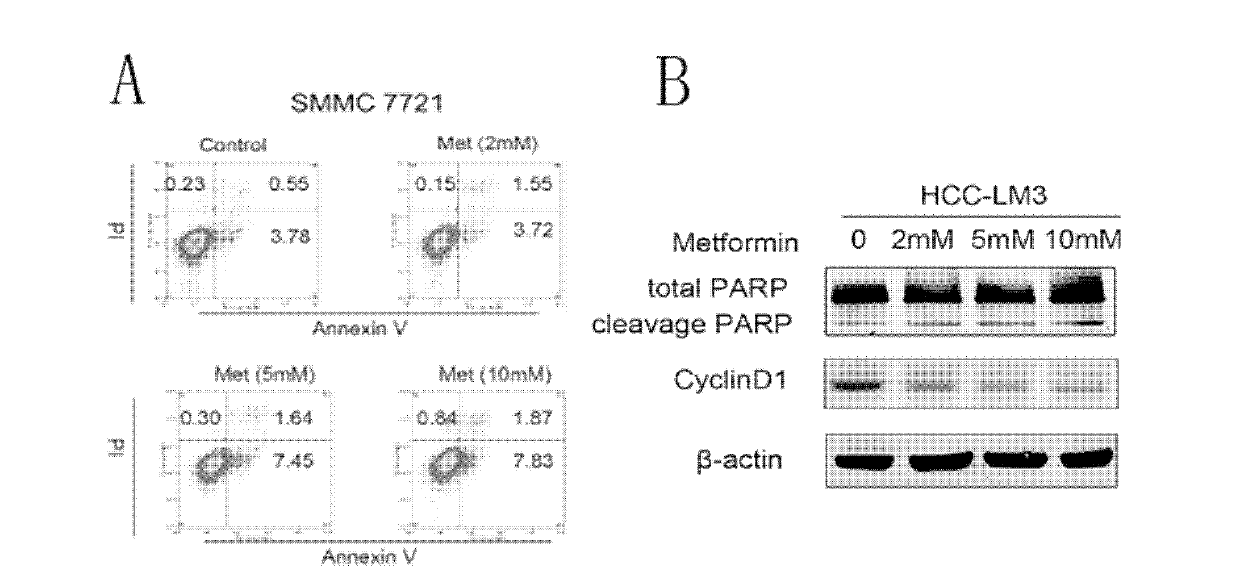
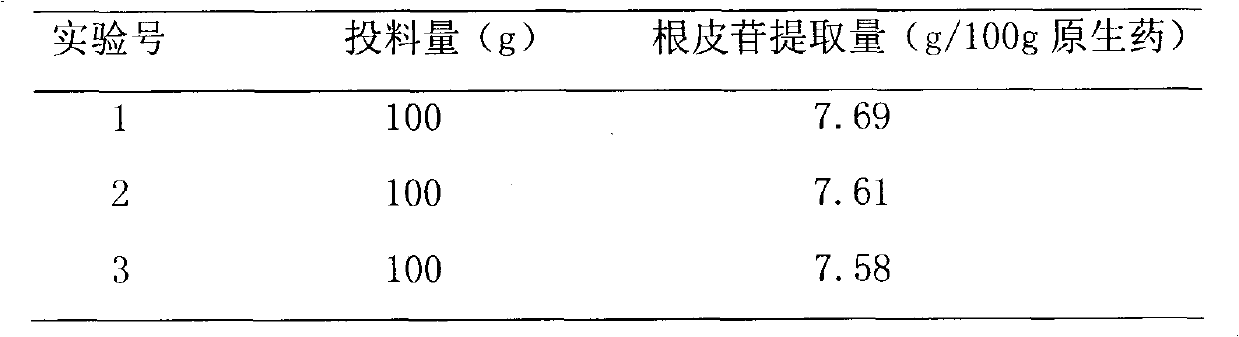
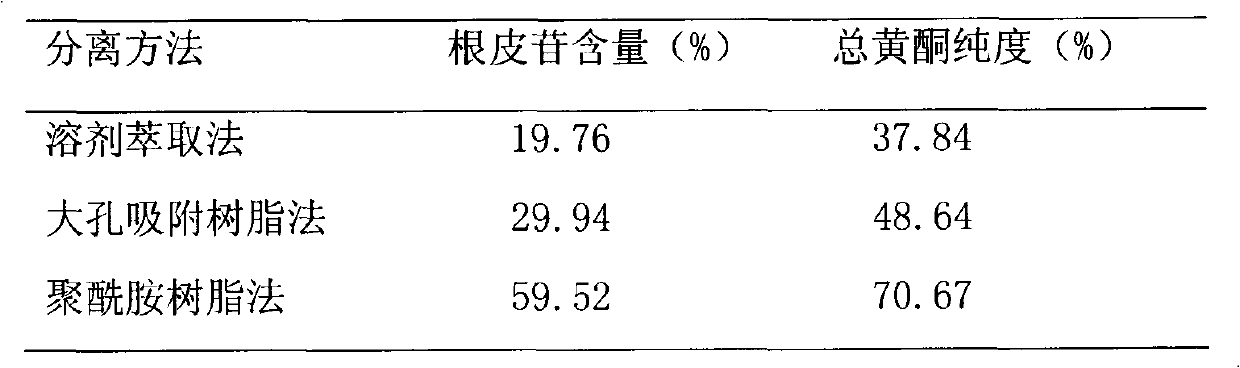
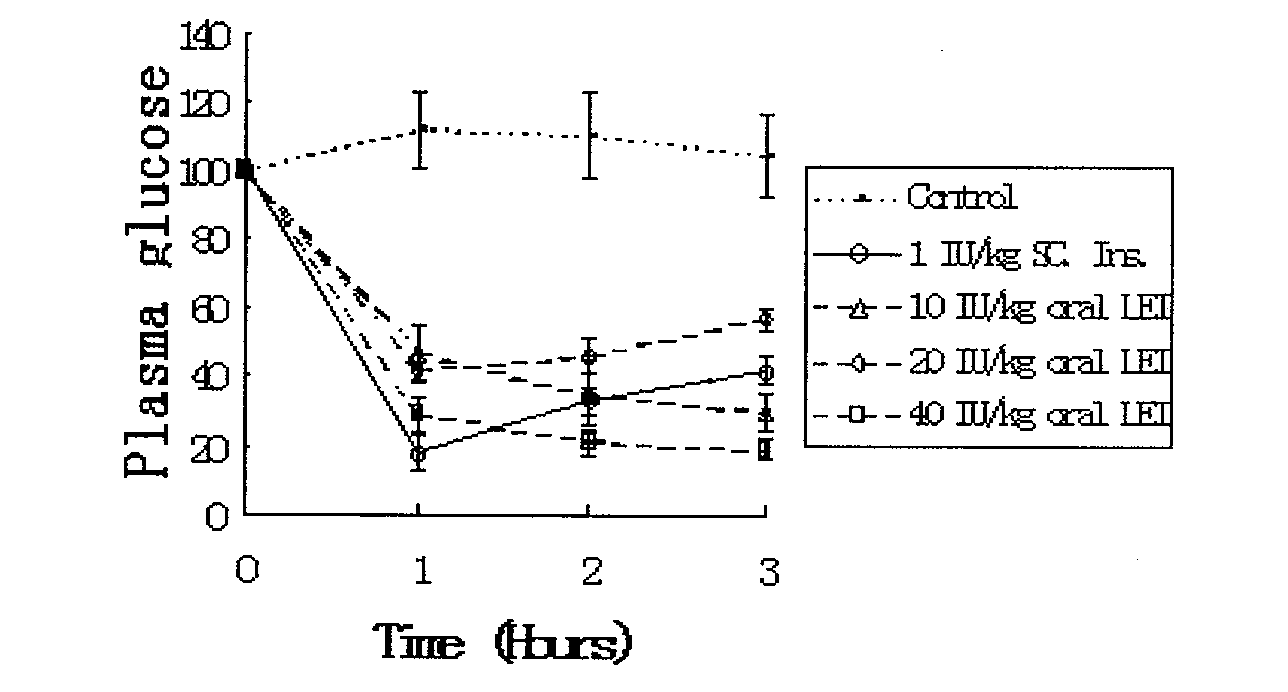
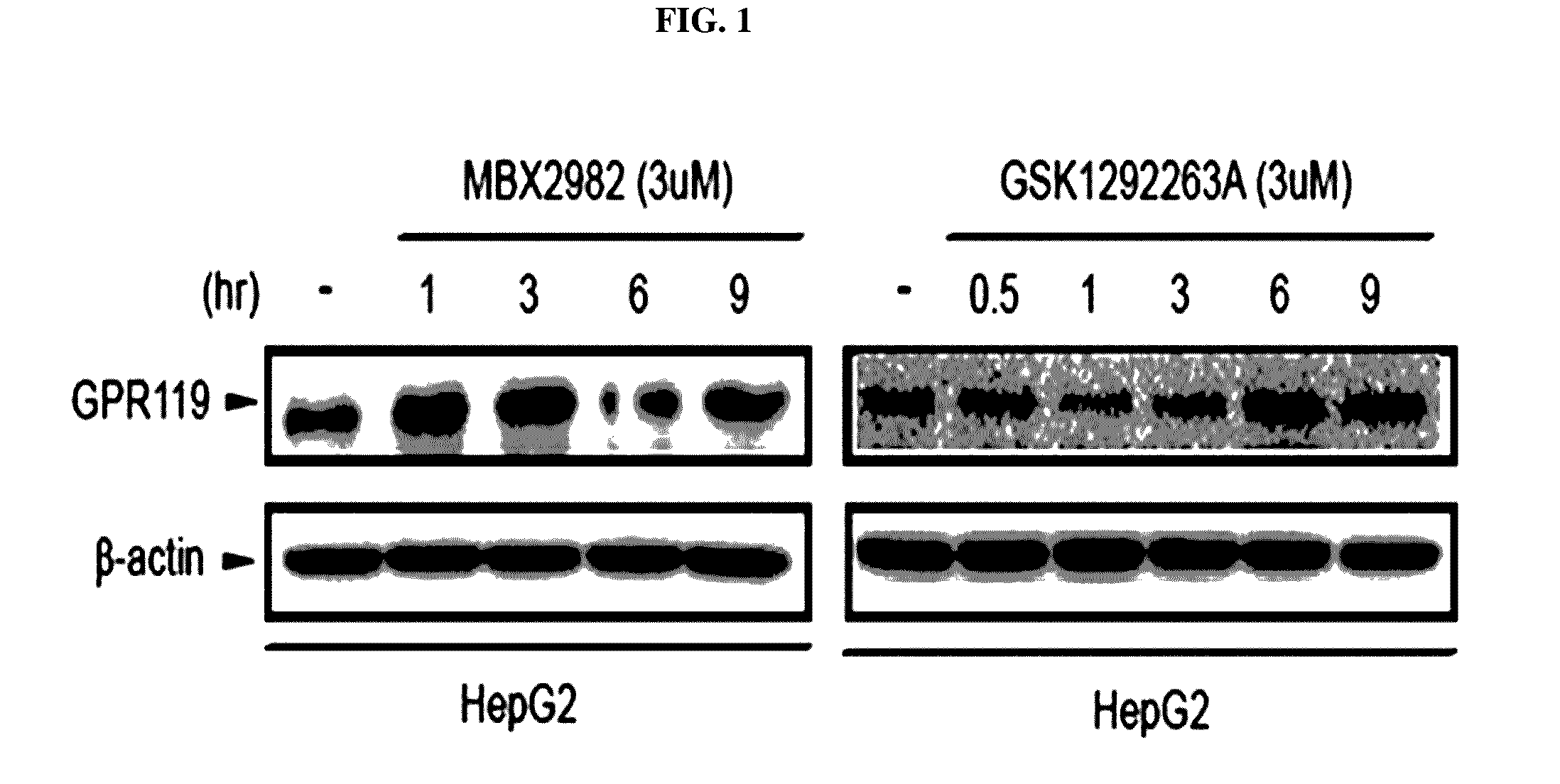
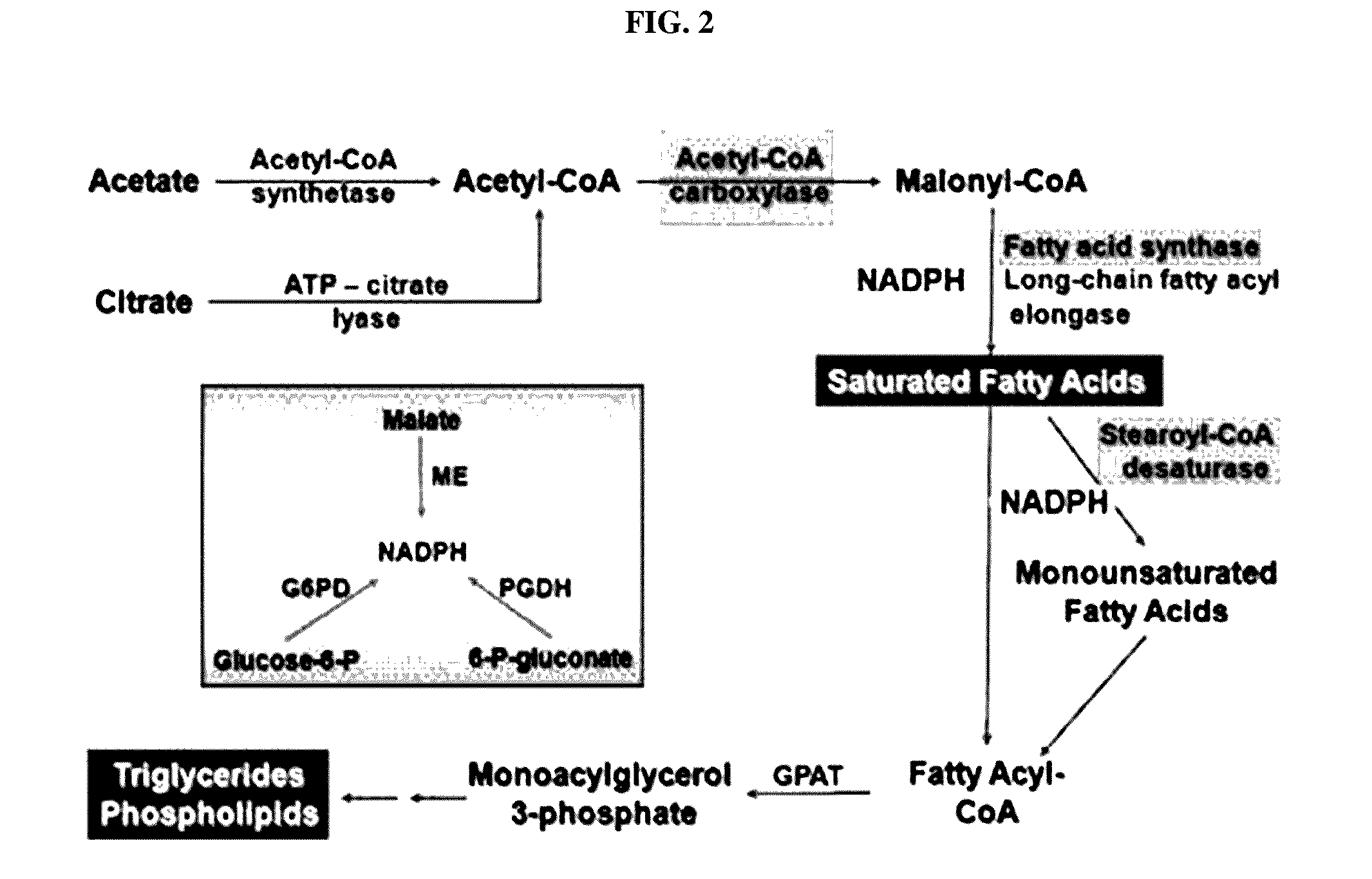
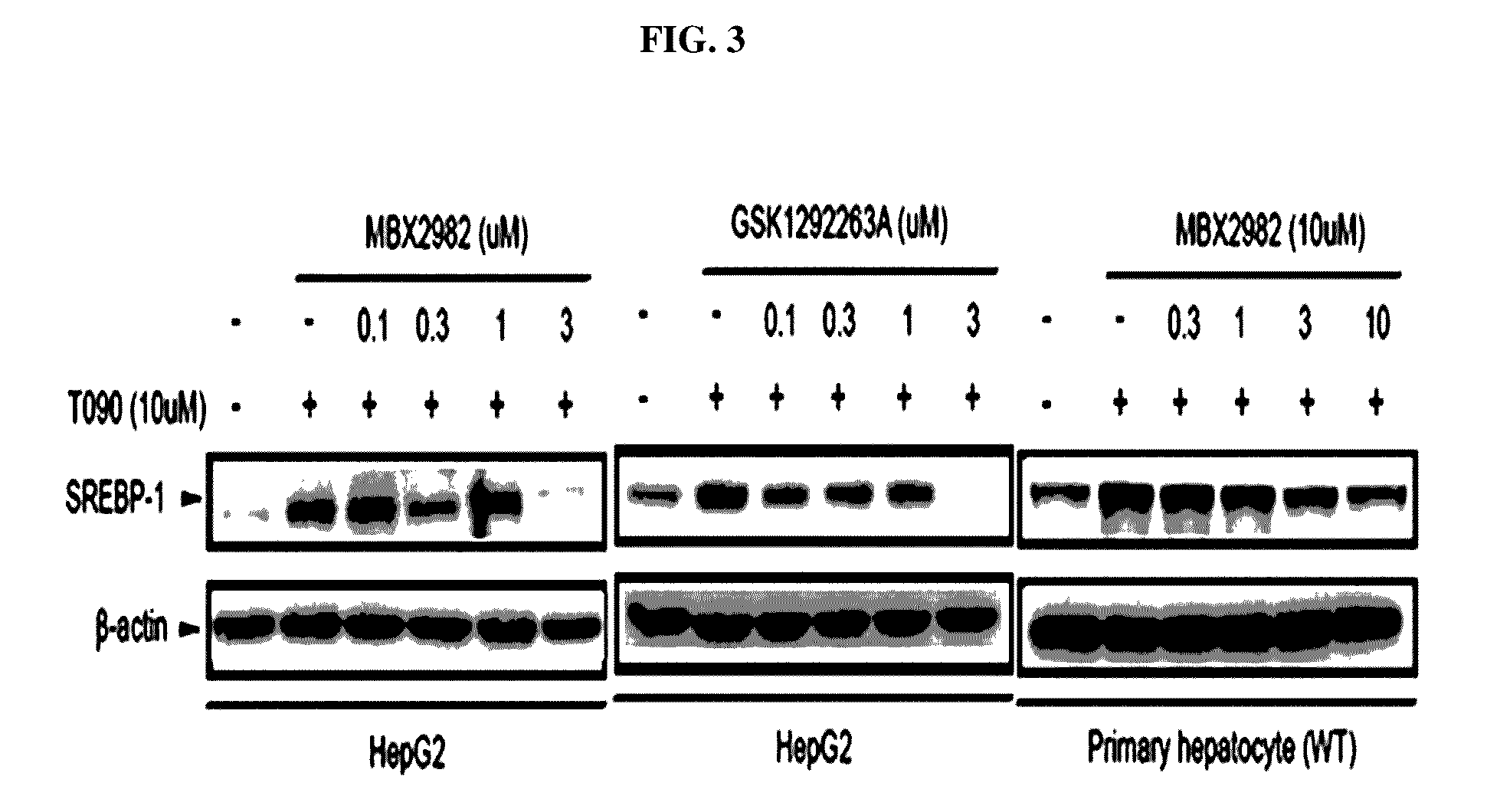
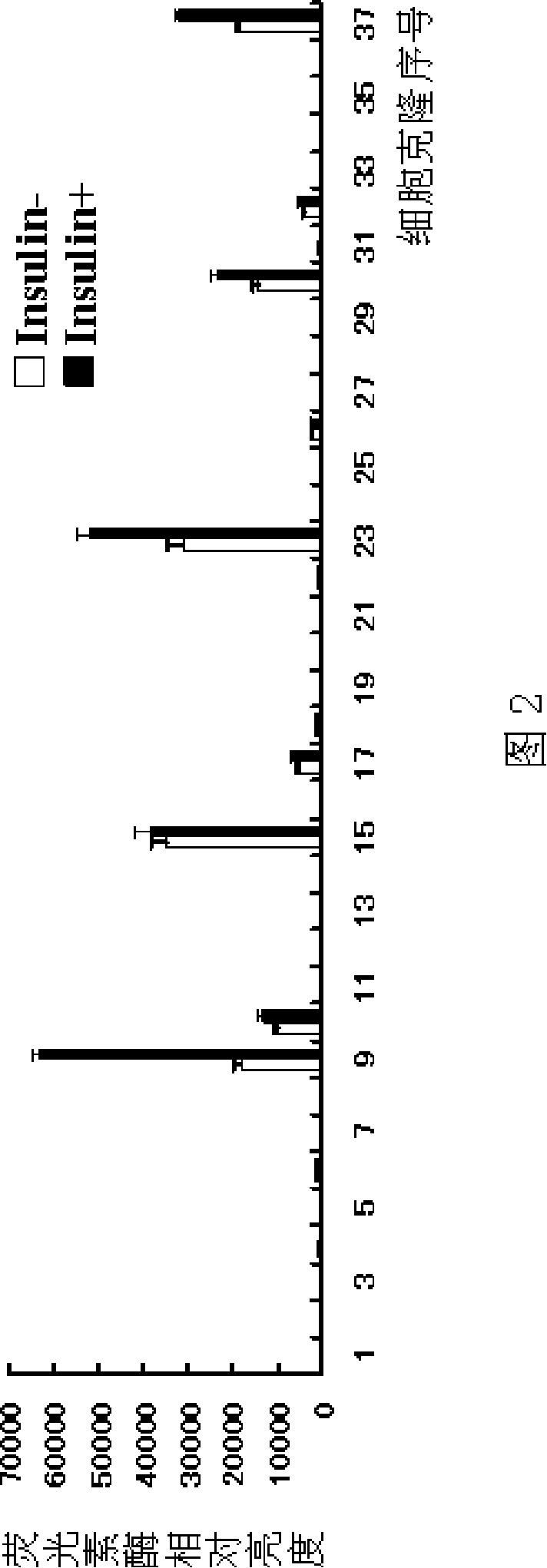
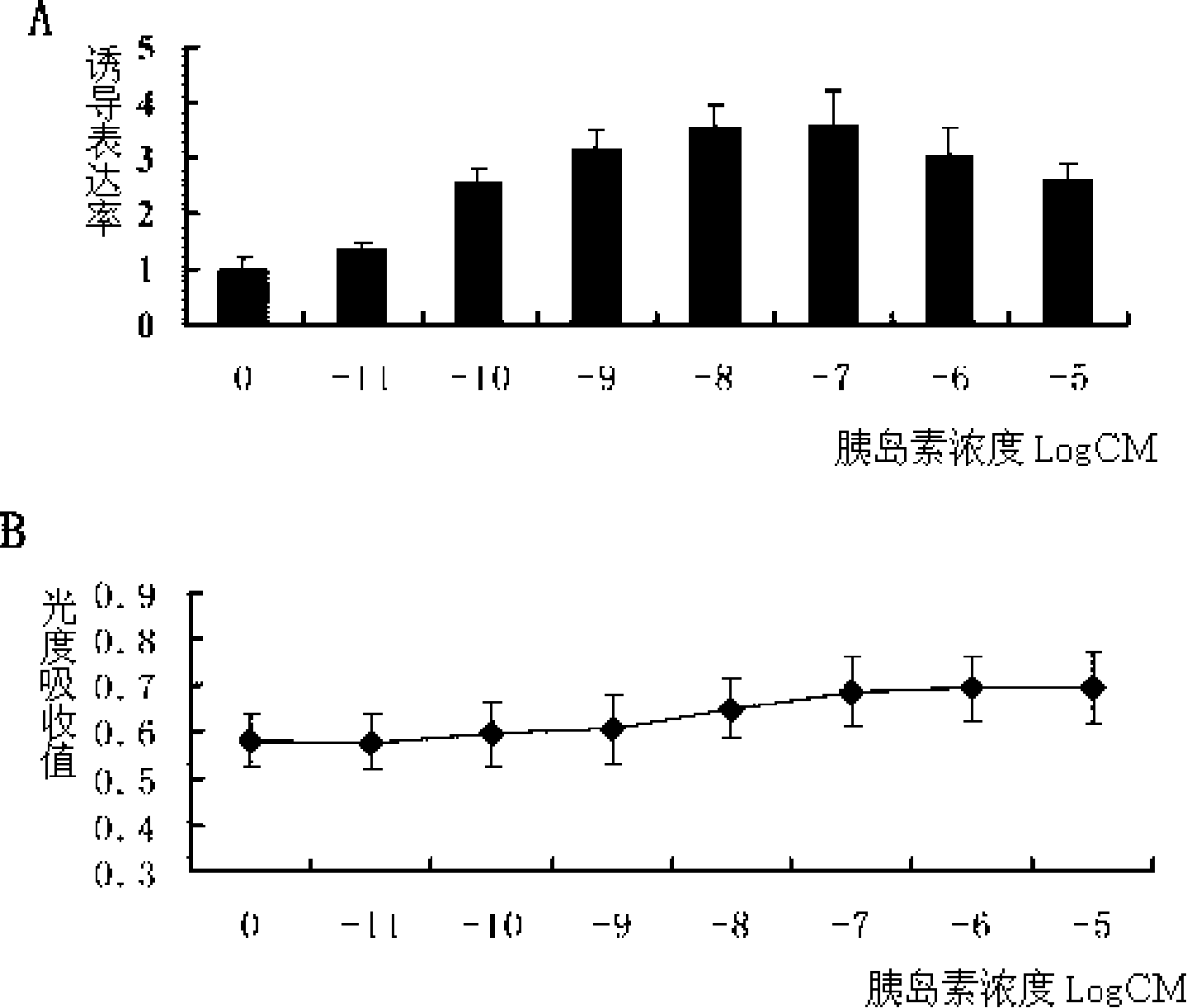
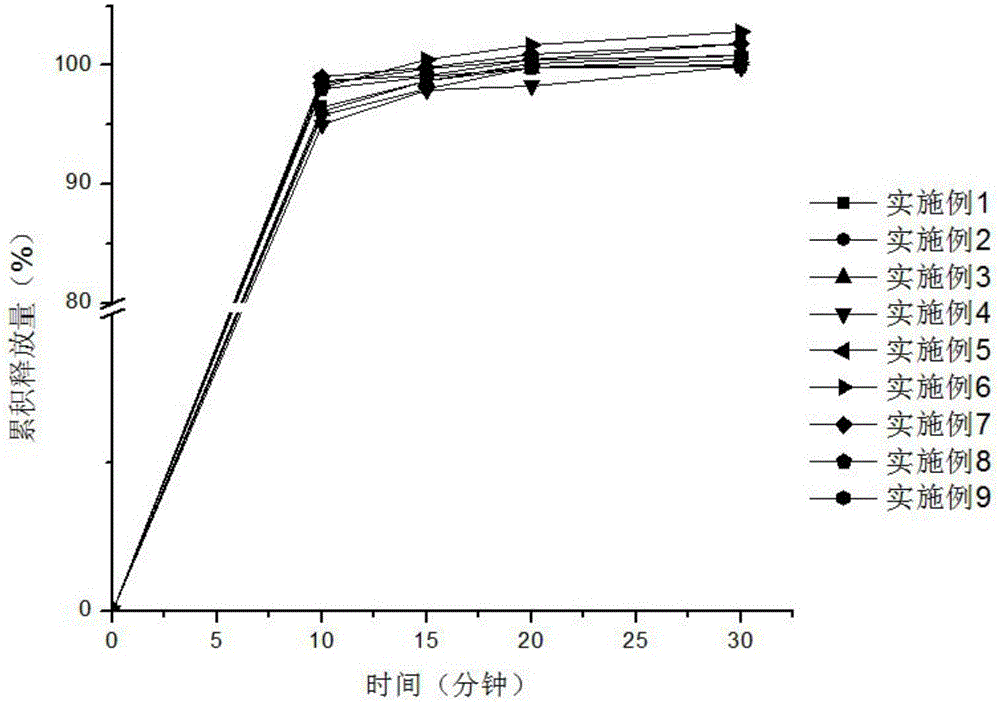
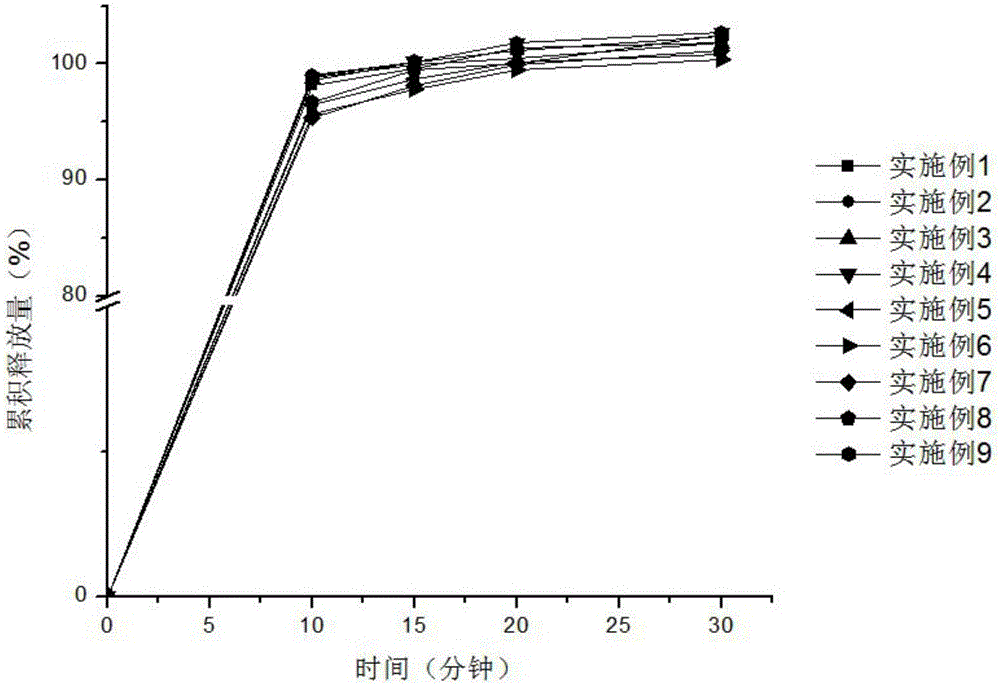
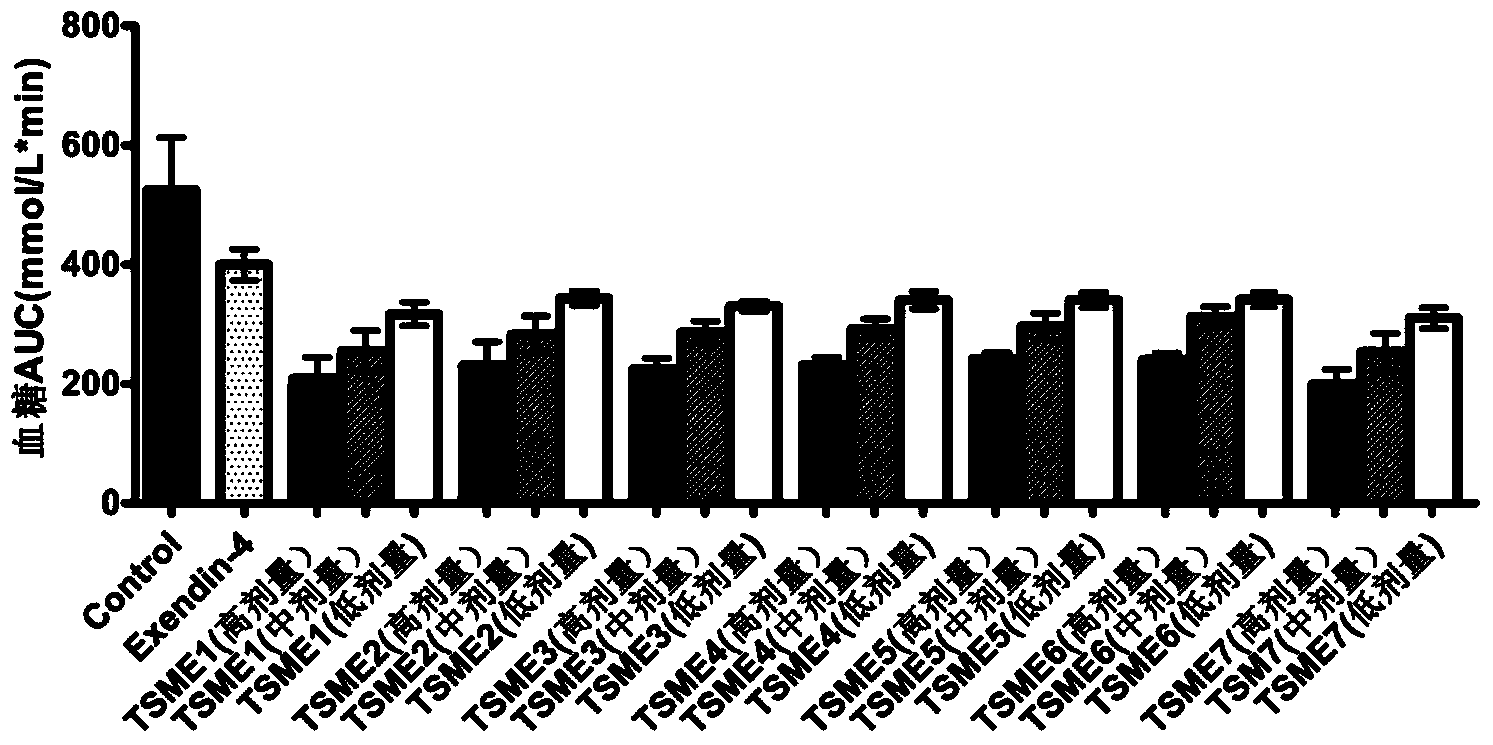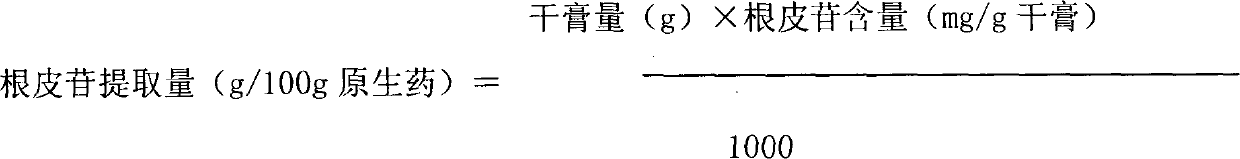Patents
Literature
94 results about "Oral hypoglycemic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
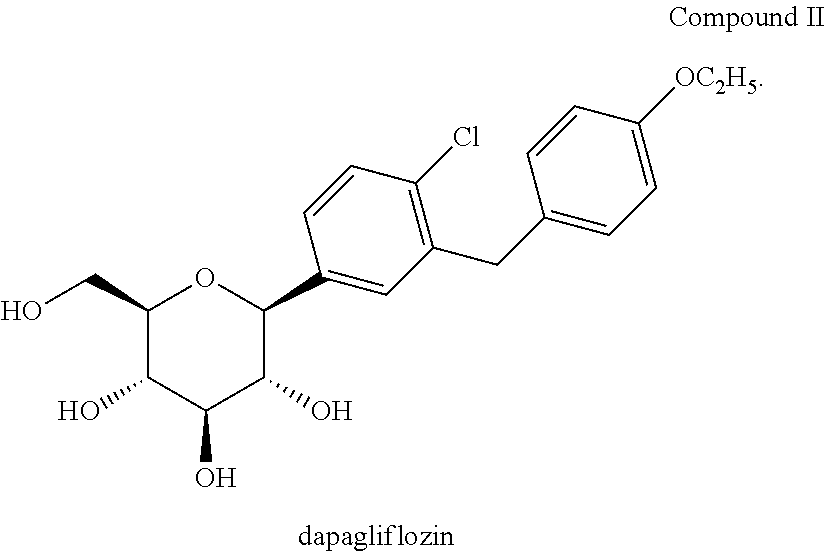
Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by lowering glucose levels in the blood. With the exceptions of Insulin, exenatide, liraglutide and pramlintide, all are administered orally and are thus also called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents.
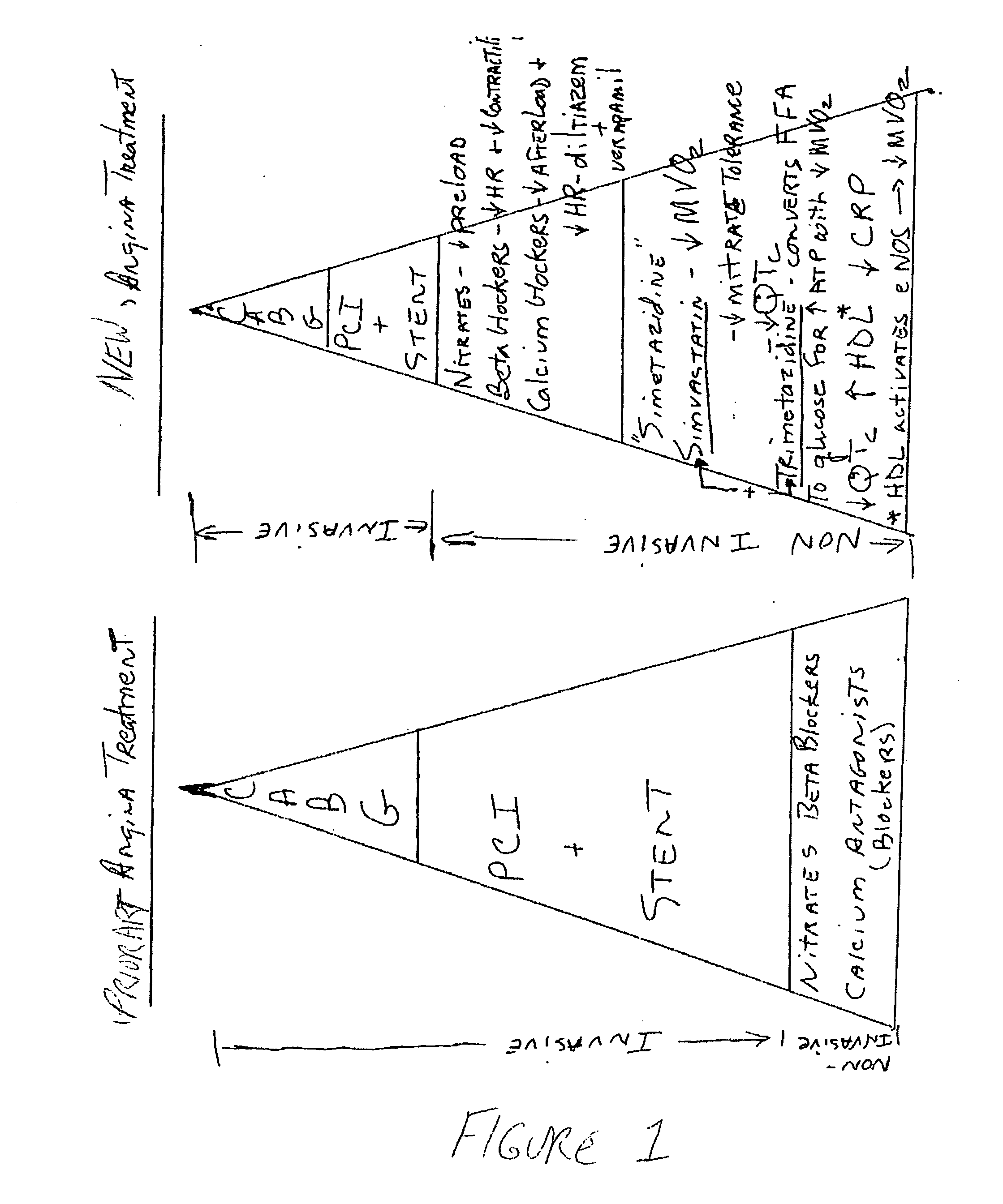
Combination therapy for endothelial dysfunction, angina and diabetes
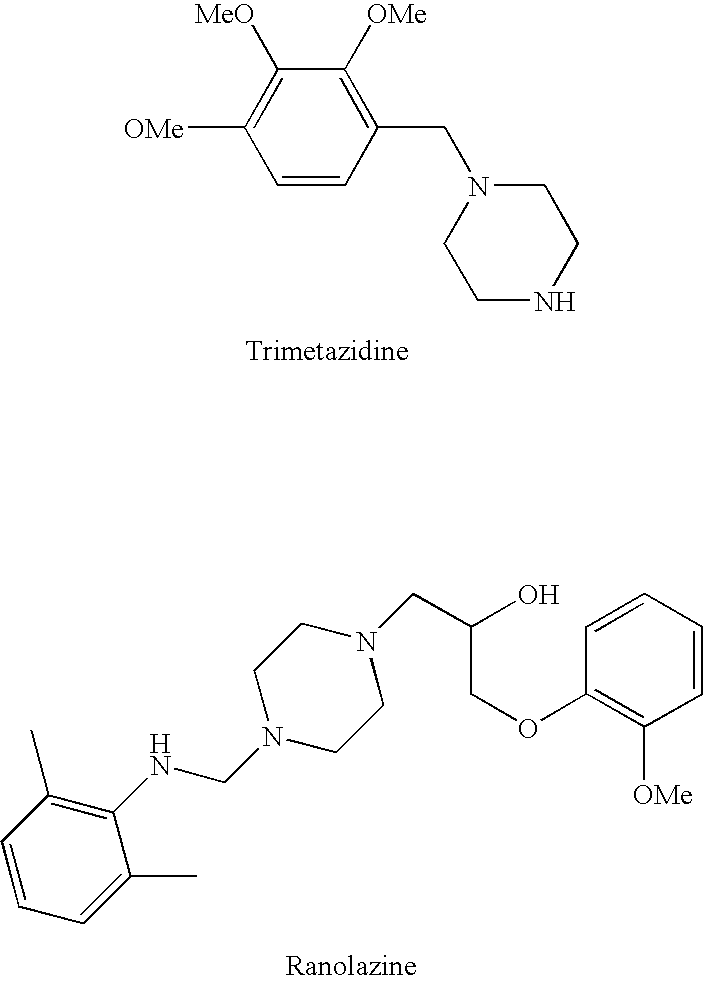
InactiveUS20060205727A1Control blood sugar levelsIncrease productionBiocideMetabolism disorderHMG-CoA reductaseTrimetazidine
The combination of a HMG CoA reductase inhibitor like a statin, such as simvastatin, with a pFox inhibitor such as trimetazidine (“Simetazidine”) is particularly advantageous for treatment of end-stage complications, such as acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and chronic angina, especially in type II diabetics. The combination therapy is also useful in the treatment and / or prevention of chronic heart failure (CHF) and peripheral arterial disease (PAD). The combination of a nitric oxide (NO) mechanism with increased NO production with pFox inhibition simultaneously treats both the effect and the cause of angina. One or more oral hypoglycemic compounds (biguanides, insulin sensitizers, such as thiazolidinediones, α-glucosidase inhibitors, insulin secretagogues, and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors), protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors, and acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors can also be used in combination with the HMG CoA reductase inhibitors and / or pFox inhibitors, especially in type II diabetics, to control glucose levels and treat endothelial dysfunction. The drugs can be given in combination (e.g. a single tablet) or in separate dosage forms, administered simultaneously or sequentially. In the preferred form the statin is given in a dose of between 5 and 80 mg / day in two separate doses, and the pFox inhibitor is administered in a sustained or extended dosage formulation at a dose of 20 mg three times a day or 35 mg two times a day. The dose of the oral hypoglycemic, PKC inhibitor, or acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitor varies with the type of drug used.
Owner:HONG KONG NITRIC OXIDE
Cyclohexane analogues as gpr119 agonists
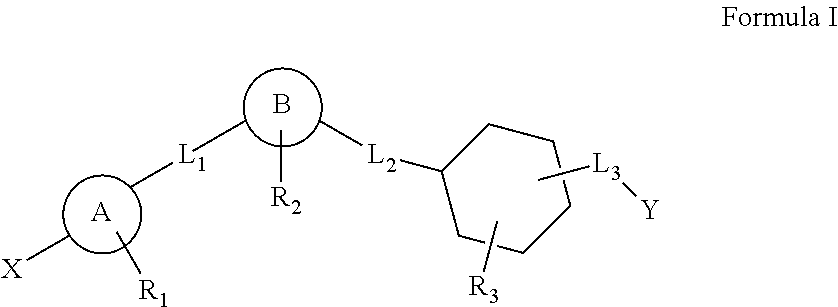
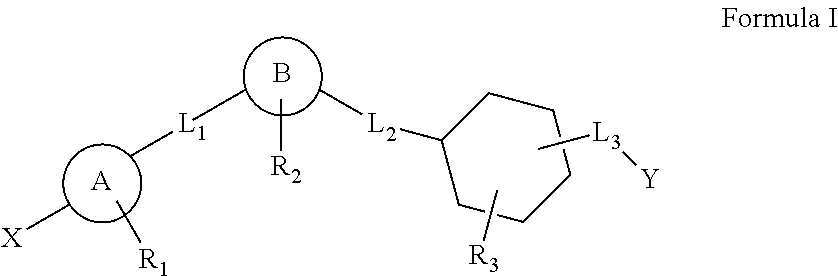
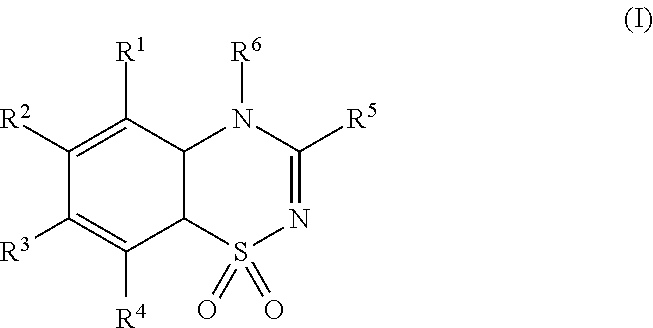
This invention relates to a series of substituted cyclohexane containing analogues which are agonists of GPR119 intended to treat metabolic diseases mediated by GPR119 including Type I & II diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus is an ever-increasing threat to human health causing various complications (blindness, kidney failure, neuropathy, heart attack, stroke, etc.). Recently it was found that activation of GPR119 which is highly expressed in pancreatic beta cells causes glucose dependent insulin secretion and GLP-1 release. Many pharmaceuticals are currently developing GPR119 agonists and herein we disclose alternative GPR119 agonists. Our invention describes GPR119 agonists having structural Formula (I), pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate of Formula (I), isomer or prodrug of Formula (I), and combination therapy of Formula (I) with other anti-diabetic drugs like DPP-IV inhibitors and / or insulin sensitizers.
Owner:THE ASAN FOUND
Oral dosing hypoglycemic polypeptide as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103665148AImprove resistance to enzymatic hydrolysisPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderEnzymatic hydrolysisPharmacology
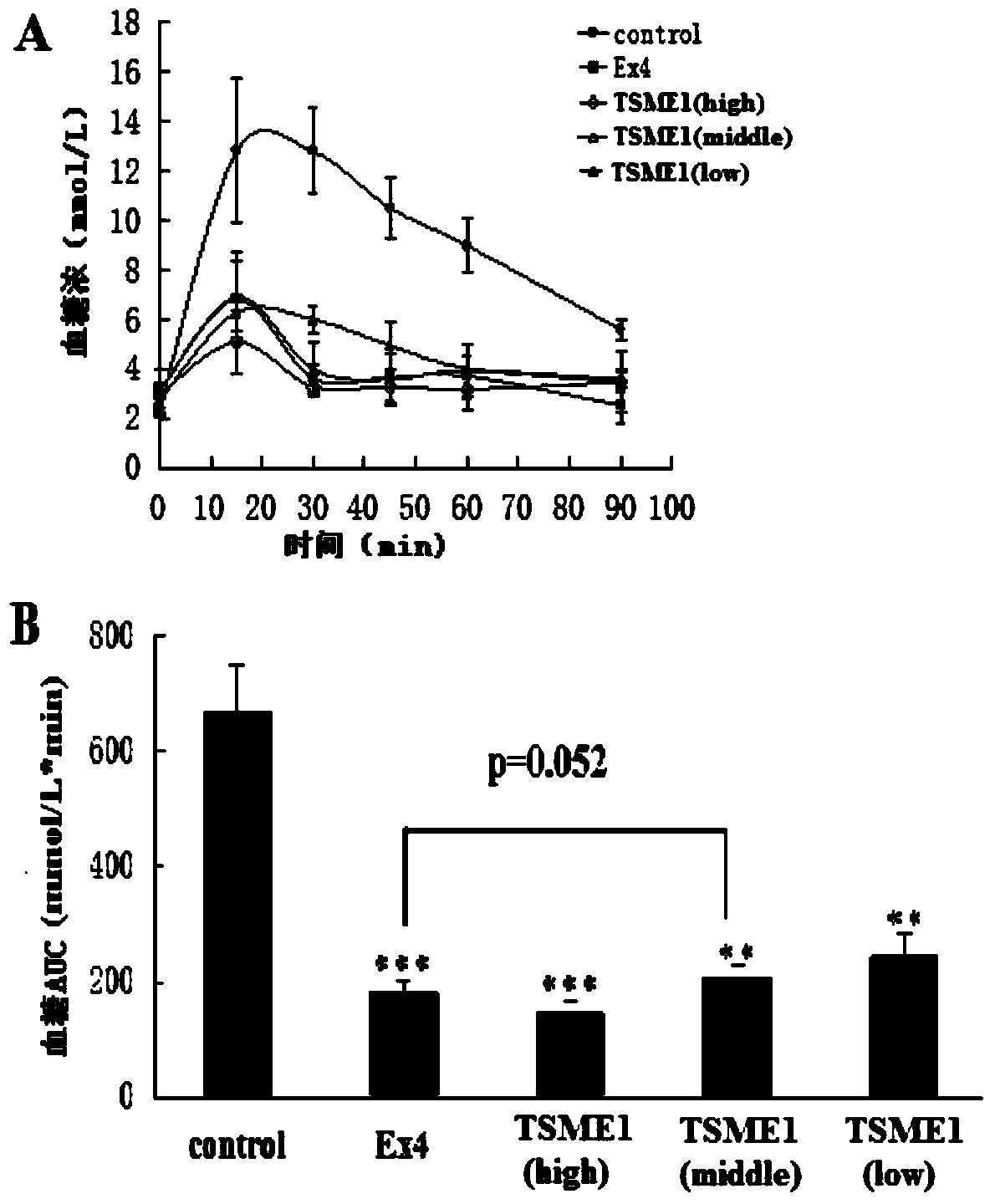
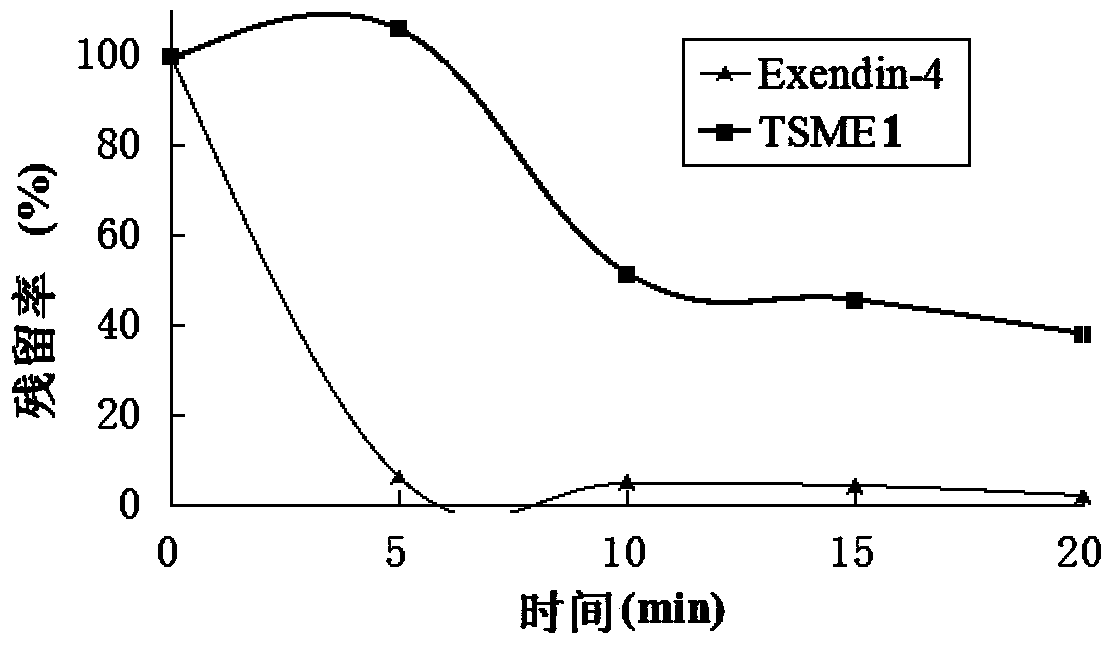
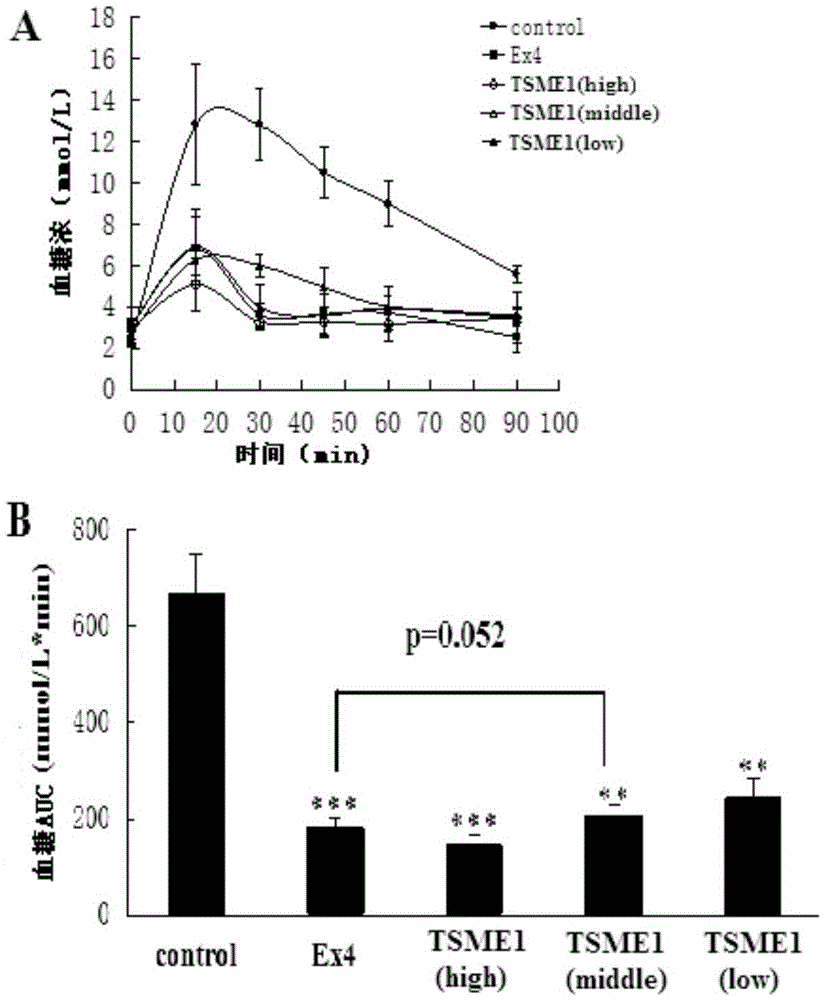
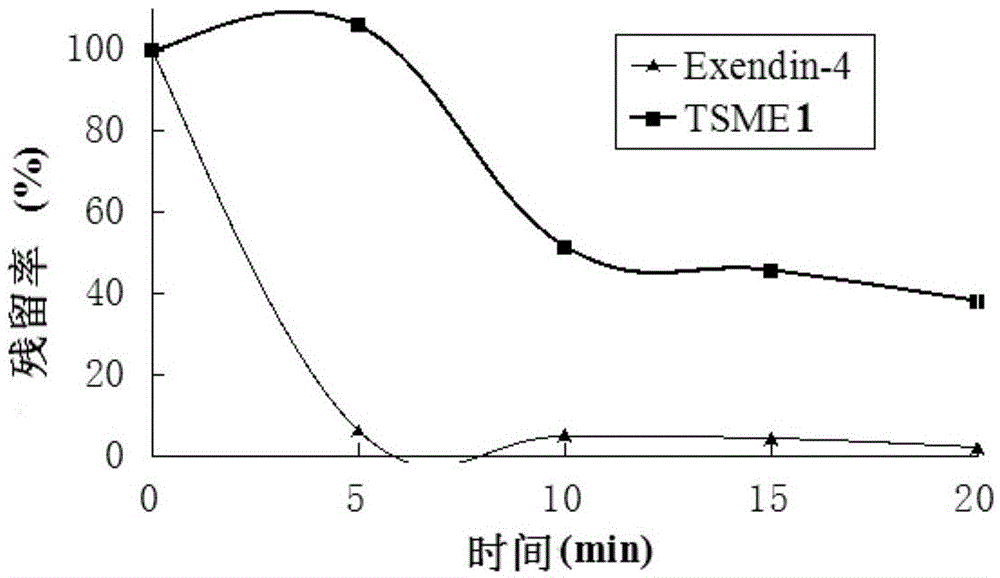
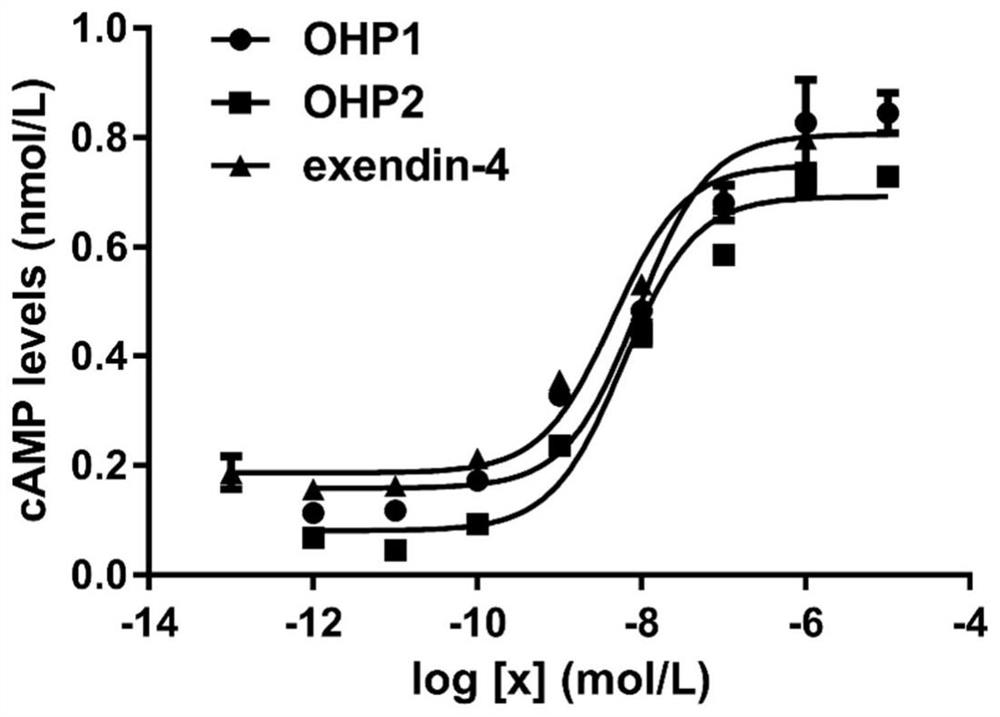
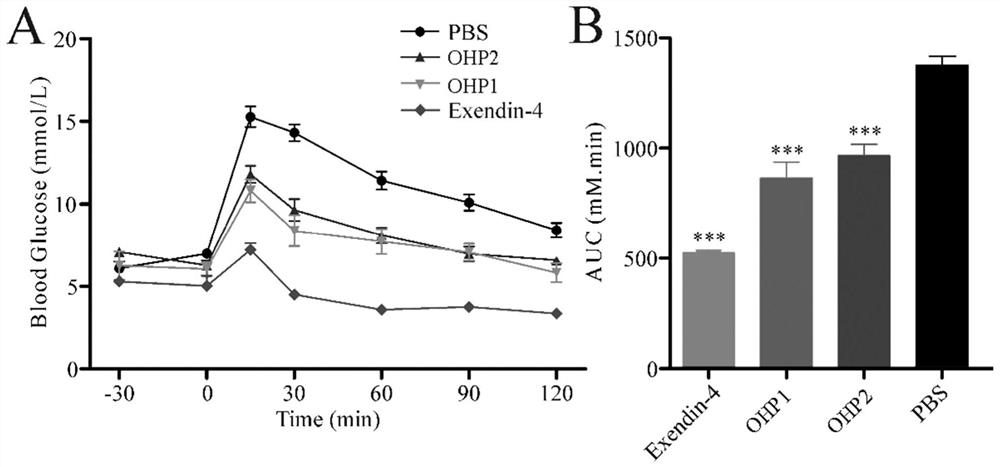
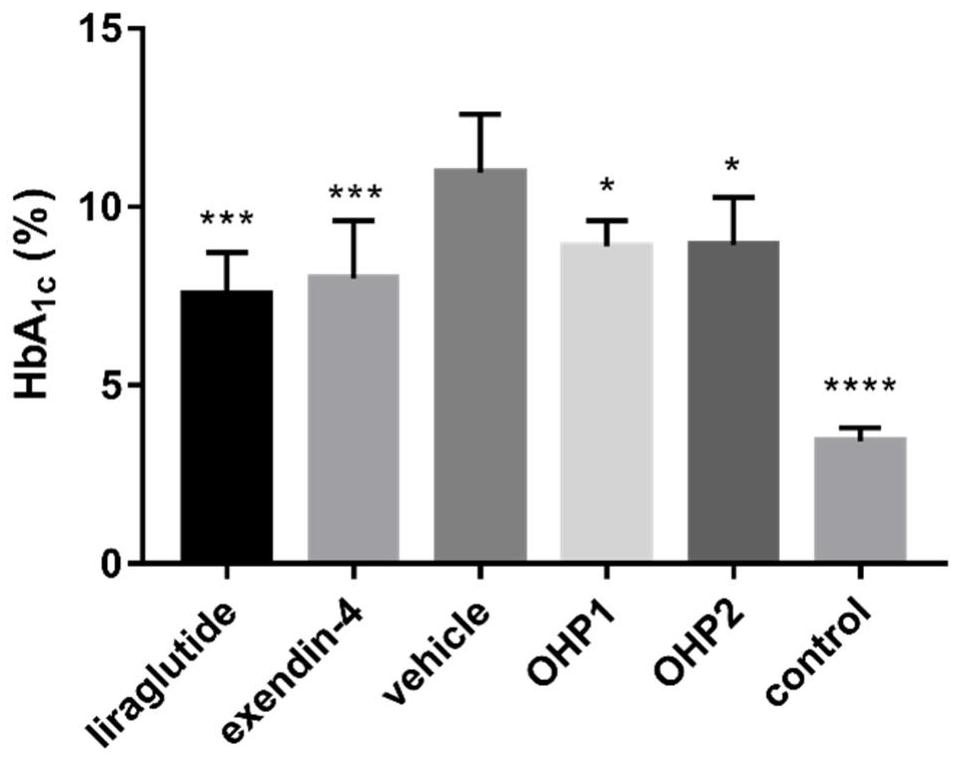
Oral hypoglycemic polypeptide is an Exendin-4 analogue and is obtained by replacing twelfth, twentieth and twenty-seventh amino acids in an amino acid sequence of the Exendin-4 with non basic amino acids. Compared with an Exendin-4 archetype, the enzymatic hydrolysis resistance of the oral hypoglycemic polypeptide is remarkably improved, and the hypoglycemic polypeptide can be orally taken and has a good application prospect in treatment of type II diabetes mellitus.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Peptide
The invention employs GLP-1(7-37), GLP-1(7-36)amide, and certain related compounds in combination with an oral hypoglycaemic agent for treating diabetes mellitus.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Curcumin combination with Anti-type 2 diabetic drugs for prevention and treatment of disease sequelae, drug-related adverse reactions, and improved glycemic control
InactiveUS20120237590A1Reduce incidencePrevention loweringBiocidePowder deliveryAdvanced stageDisease injury
Compositions and methods for treating type 2 diabetes and its sequelae by intravenous or subcutaneous administration of formulations of synthesized curcumin (diferuloylmethane) and concomitantly one or more anti-diabetic agents to human subjects are disclosed herein. The composition of the present invention may be used to: (i) treat patients with diabetes in advanced stages with evidence of any or all encephalopathy, retinopathy, nephropathy, pancreatitis or neoplasias; (ii) treat patients with diabetic disease status without symptomatic or pathologic evidence of associated sequelae but requiring better glycemic control than that offered by standard of care anti-diabetic; and (iii) patients with objective signs or symptoms of sequelae from diabetes of anti-diabetic drugs. One three-drug combination of the present invention includes a slow release PLGA-curcumin and an oral gliptin (DPP-4)-inhibitor or any incretin-mimetic and metformin.
Owner:SIGNPATH PHARMA INC
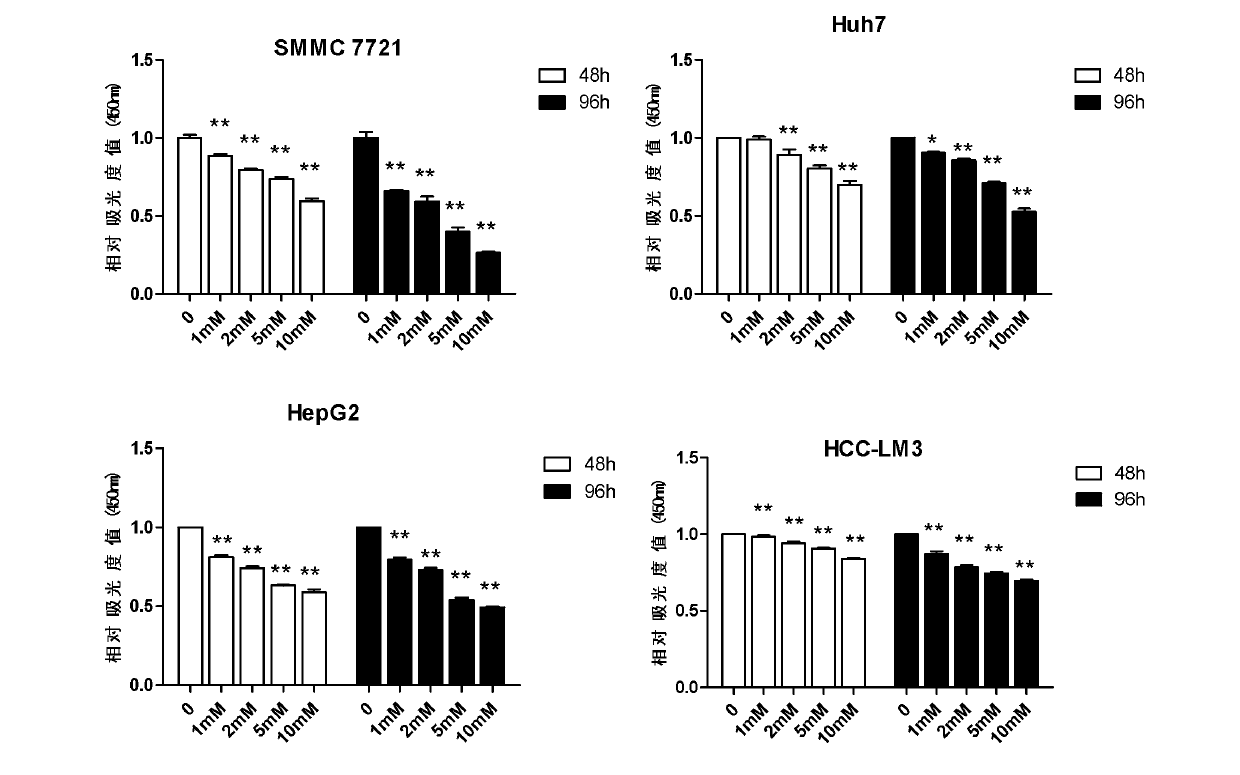
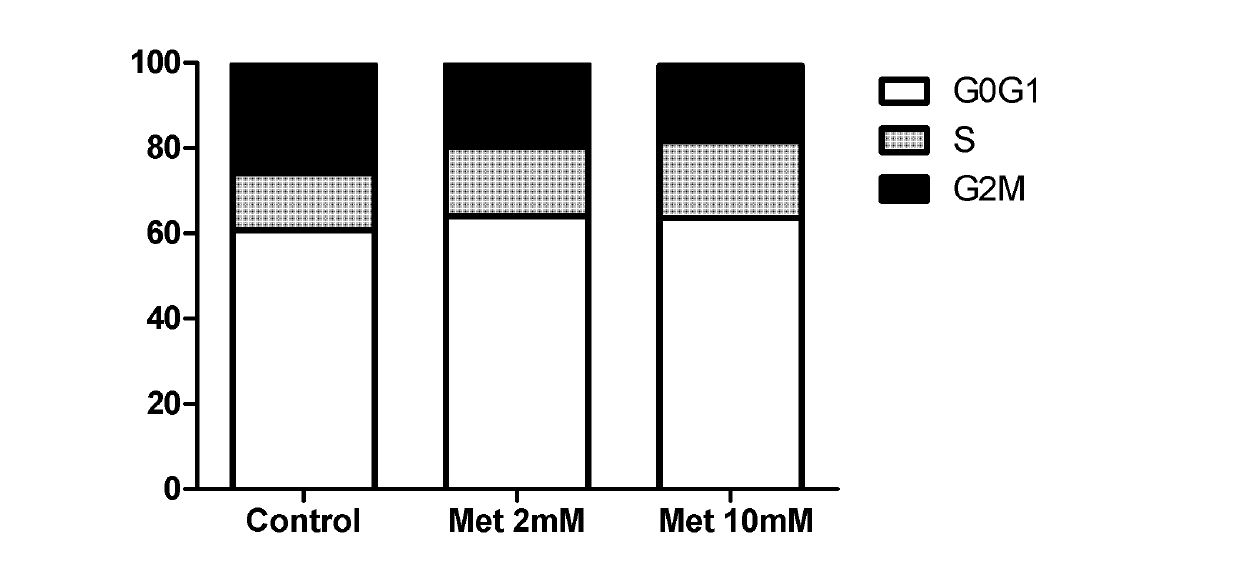
Application of dimethyldiguanide in preparation of medicaments for preventing or treating hepatocellular carcinoma
The invention relates to the technical field of medicaments. Dimethyldiguanide belongs to a biguanides oral hypoglycemic medicament and is widely applied to pharmaceutical therapy of type 2 diabetes. The invention aims at providing a novel application of the dimethyldiguanide and particularly an application of the dimethyldiguanide in preparation of medicaments for preventing or treating the hepatocellular carcinoma. According to the application disclosed by the invention, the restriction effect of the dimethyldiguanide on the hepatocellular carcinoma is found by research from two aspects, namely, cell culture in vitro and animal experiment in vivo. Experiments find that the dimethyldiguanide has the capabilities of restricting proliferation and clone formation of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line and causing the cell cycle arrest and apoptosis increase of the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, and also has the capability of enhancing the hepatocellular carcinoma resisting effect of chemotherapeutics when combined with the chemotherapeutics, such as cis-platinum, doxorubicin and the like. The invention provides the novel application of the dimethyldiguanide and also provides a novel concept for prevention and treatment of the hepatocellular carcinoma.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Preparation method of lithocarpus litseifolius total flavone
InactiveCN101904882AImprove solubilityLow toxicityMetabolism disorderFood preparationEnergy consumptionFlavones
The invention discloses lithocarpus litseifolius total flavone extracted by using plant lithocarpus litseifolius as a raw material to develop a new hypoglycemic medicament, and provides a method for preparing the lithocarpus litseifolius total flavone. The purity of the lithocarpus litseifolius total flavone prepared by the method can reach over 80 percent, the phloridzin content reaches over 65 percent, the process is simple and has low energy consumption, and the technological condition is reasonable, stable and feasible. A hypoglycemic capsule developed by using the lithocarpus litseifolius total flavone can provide a convenient, acceptant and long-term taking oral hypoglycemic preparation for diabetics.
Owner:GUANGXI INST OF CHINESE MEDICINE & PHARMA SCI
Health care tea capable of reducing blood sugar and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103005057AGood hypoglycemic effectLower blood sugarPre-extraction tea treatmentMetabolism disorderBiotechnologyTraditional medicine
The invention relates to a health care tea capable of reducing blood sugar and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of natural plant processing. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: cleaning fresh sweet potato leaves, mulberry leaves and tea leaves, soaking with electrolysed water, removing green, and then drying; and mixing in proportion, carrying out coarse crushing, and drying, so that the health care tea capable of reducing blood sugar is prepared. Clinical verifications show that the conventional oral blood sugar reducing medicine and the health care tea capable of reducing blood sugar provided by the invention can enhance the blood sugar reducing effect of a blood sugar reducing medicine and also obviously relieve symptoms such as swirl, thirst, fatigue, soreness of waist and leg weakness, and the total effective rate is 89%. The health care tea provided by the invention is unique in taste and has good blood sugar reducing health care function.
Owner:邓东
Compound having alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity in lotus leaves and application
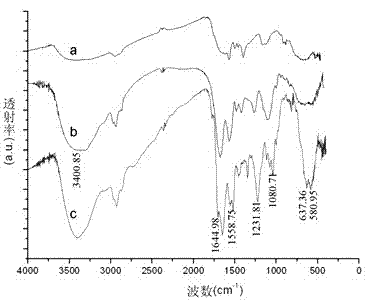
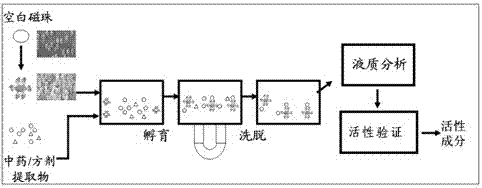
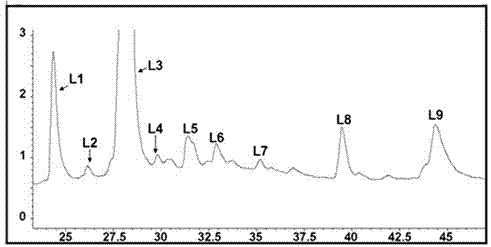
InactiveCN102827221AReduce blindnessImprove screening efficiencySugar derivativesMetabolism disorderAlglucerasePrimary screening
The invention provides a compound having an alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity in lotus leaves. Nine compounds having the alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity are screened from the lotus leaves through magnetic bead separation and liquid chromatogram-mass spectrometry analysis, and the obtained compounds are confirmed to have the alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity through a verification of the alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity. Compared with tradition methods, separated compounds are not needed to prepare during a primary screening, thereby substantially improving screening efficiency and shortening screening time. Due to changing a traditional activity-screening mode which separates firstly and screens secondly to a novel activity-screening mode which screens firstly and separates secondly, blindness of preparing and separating compounds is greatly reduced. The method can be popularized and applied to quick screening of compounds having the alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity from natural medicines or herbal mixtures. The obtained compounds can be used for preparing anti-diabetic drugs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Combination therapeutic compositions
InactiveUS7939551B2Good curative effectReduce doseBiocideMetabolism disorderSulfonylureaAldose reductase inhibitor
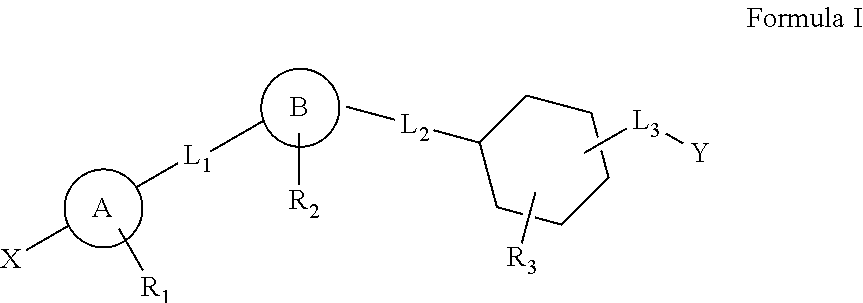
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of diabetes mellitus using combination therapy. The compositions relate to a compound of Formula I and an antidiabetic agent such as sulfonylureas, biguanides, glitazones, α-glucosidase inhibitors, potassium channel antagonists, aldose reductase inhibitors, glucagon antagonists, activators of RXR, insulin therapy or other anti-obesity agent. The methods include the administration of the combination of compound of Formula I with antidiabetic agent where the two components are delivered in a simultaneous manner, where the compound of Formula I is administered first, followed by the antidiabetic agent, as well as wherein the antidiabetic agent is delivered first followed by the compound of Formula I.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Oral hypoglycemic peptide as well as fatty acid derivative and application thereof
ActiveCN110437329AAvoid enzymatic failurePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderProteinase activityProtease
The invention relates to oral hypoglycemic peptide as well as a fatty acid derivative and application thereof. The sequence of the polypeptide is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The polypeptide or the fatty acid derivative can be used for preparing a drug or a drug composition for preventing or treating diabetes or preparing a hypoglycemic drug or drug composition. Compared with the prior art, the polypeptide can well prevent enzymolysis ineffectiveness in gastrointestinal tracts for enzymolysis resistance of protease and is more suitable to be used as an oral hypoglycemic drug.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Novel compositions and uses of metformin agents
InactiveUS20180064662A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce deliveryImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAbnormal tissue growthCell-Extracellular Matrix
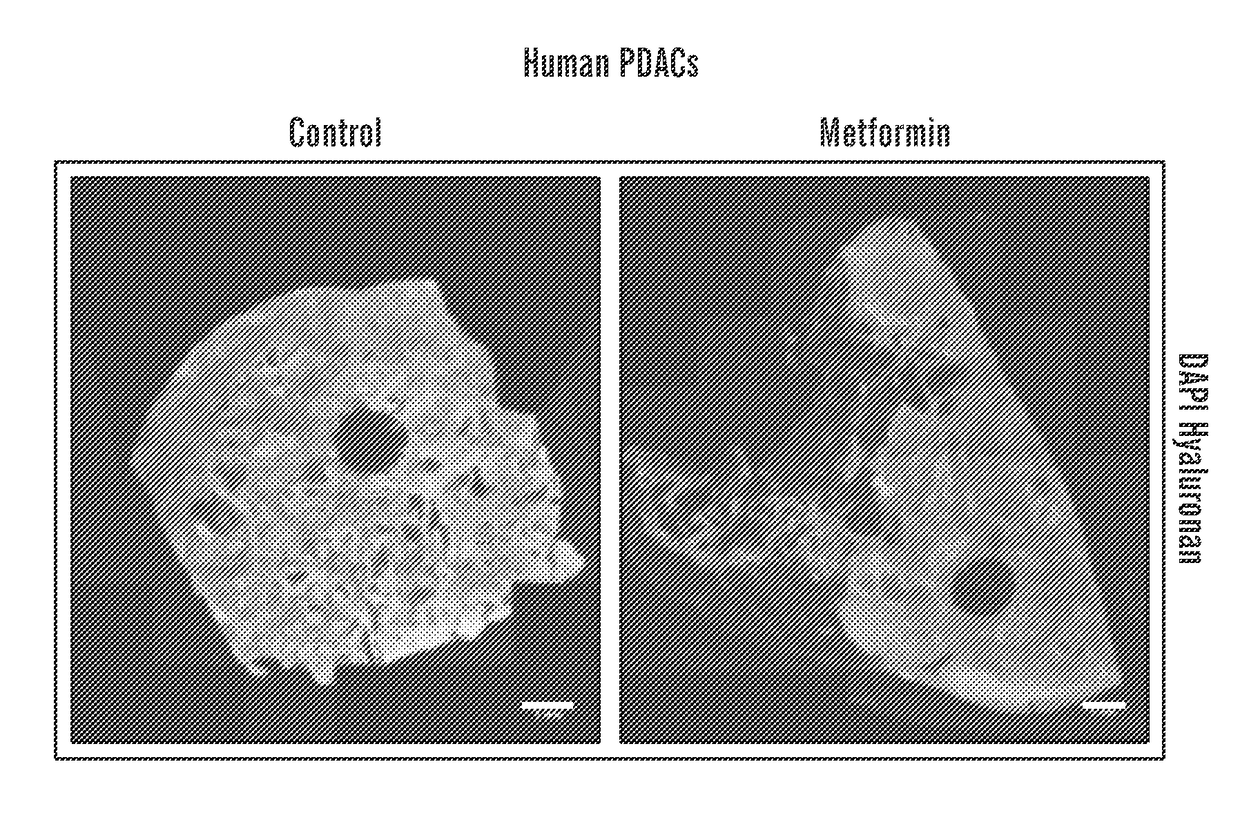
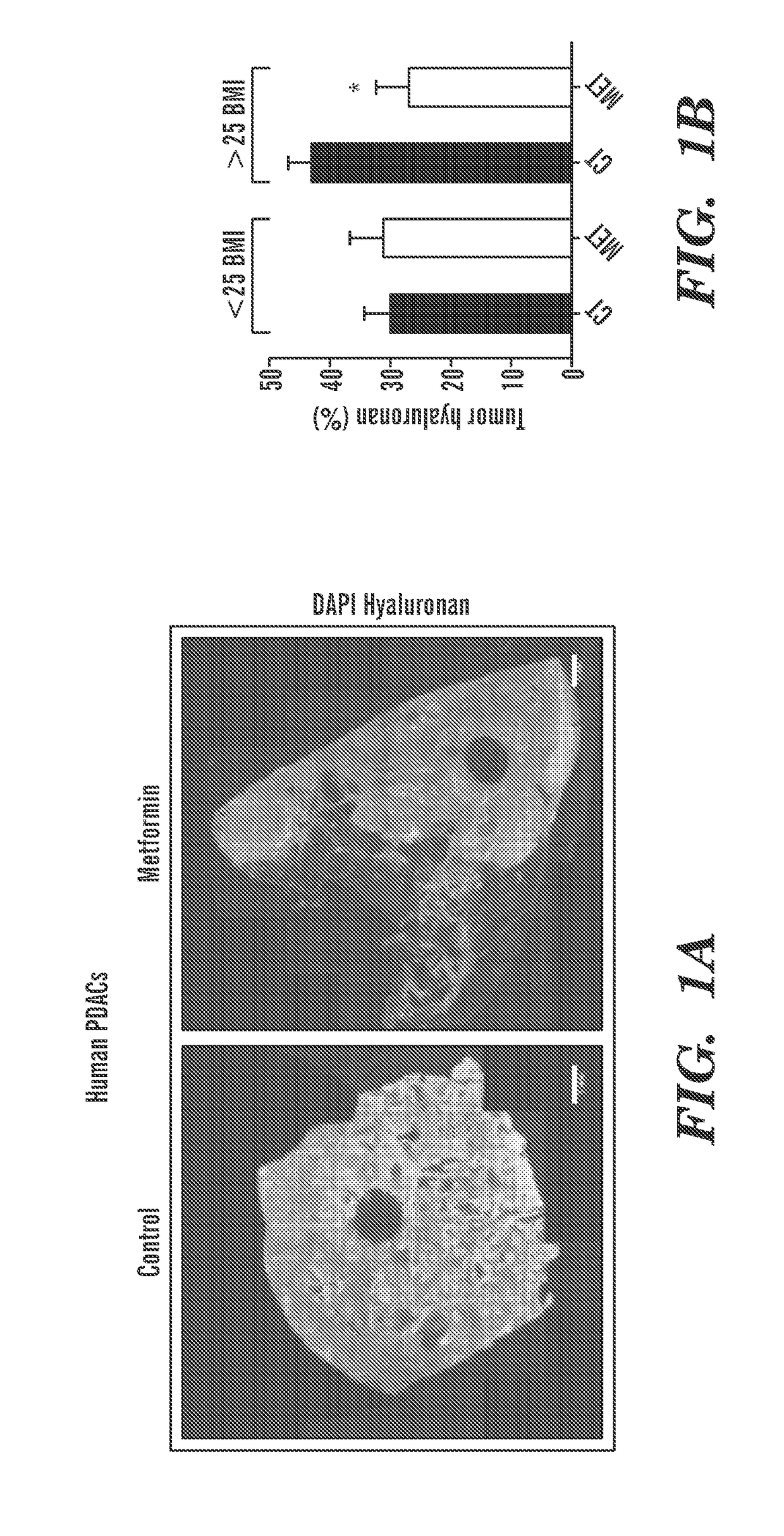
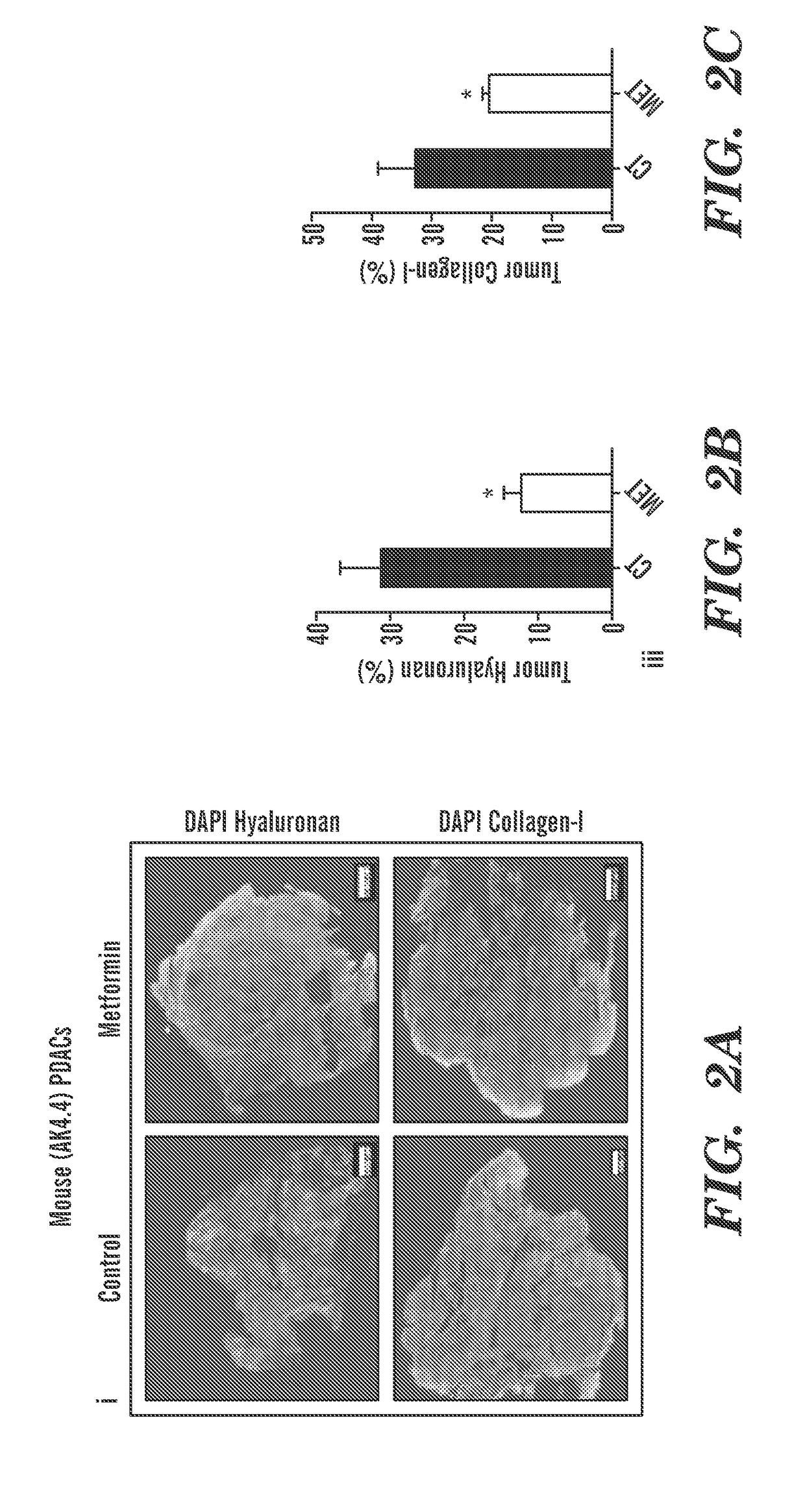
Methods and compositions for improving the delivery and / or efficacy of a therapy (e.g., an anti-cancer, anti-fibrotic or anti-inflammatory therapy) are disclosed. The invention is based, at least in part, on the discovery that metformin, a widely prescribed anti-diabetic drug, can affect the tumor microenvironment (e.g., directly, i.e., independent of its effects on cancer cells themselves or tumor metabolism). In embodiments described herein, metformin has been shown to reduce the amount of extracellular matrix, including collagen 1 and hyaluronan, in the fibro-inflammatory tumor microenvironment in a subject (e.g., a subject with a desmoplastic tumor).
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Glucokinase Activator Compositions for the Treatment of Diabetes
ActiveUS20140066372A1Improve glucose toleranceIncrease secretionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSitagliptinAcetic acid
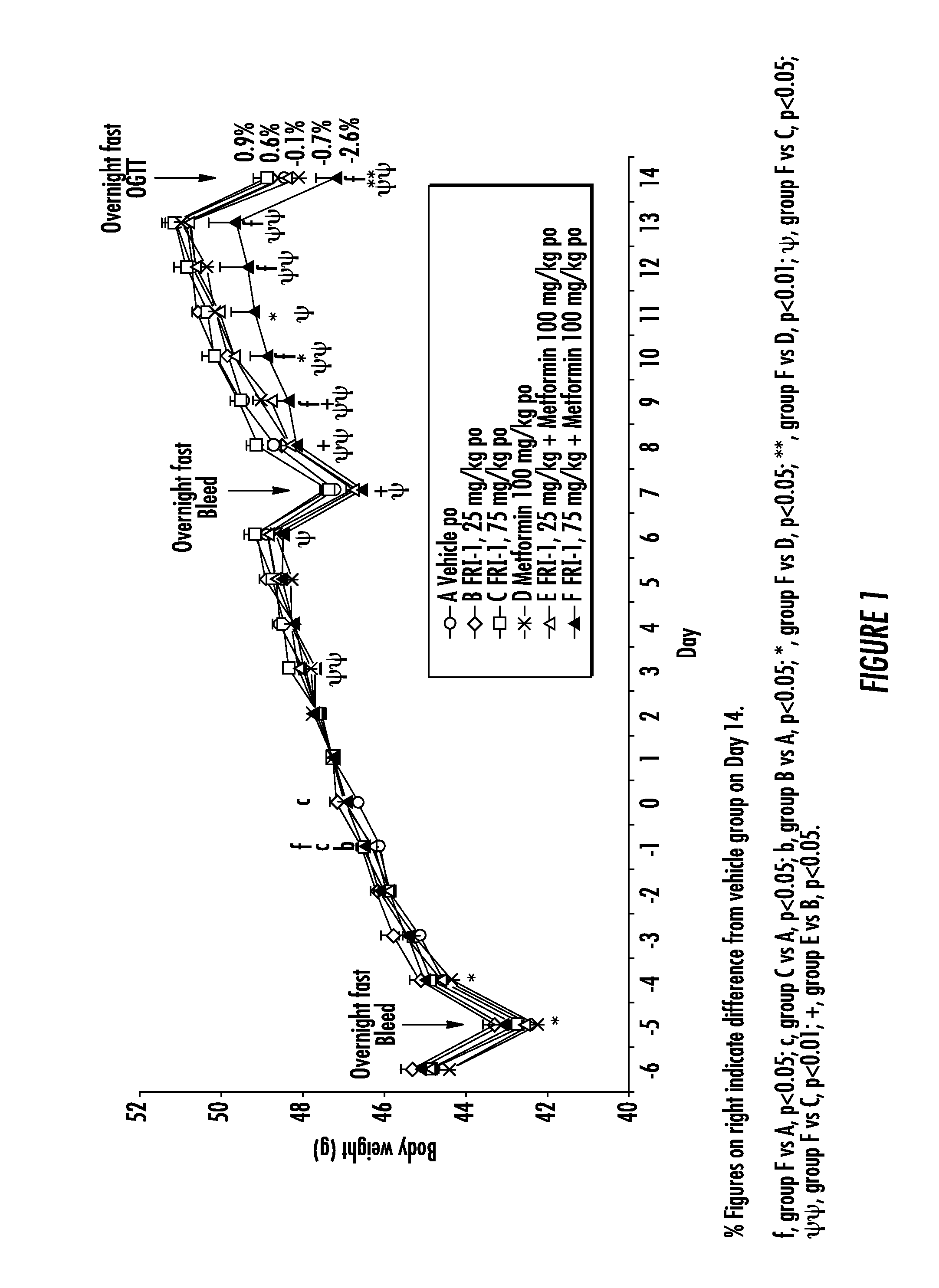
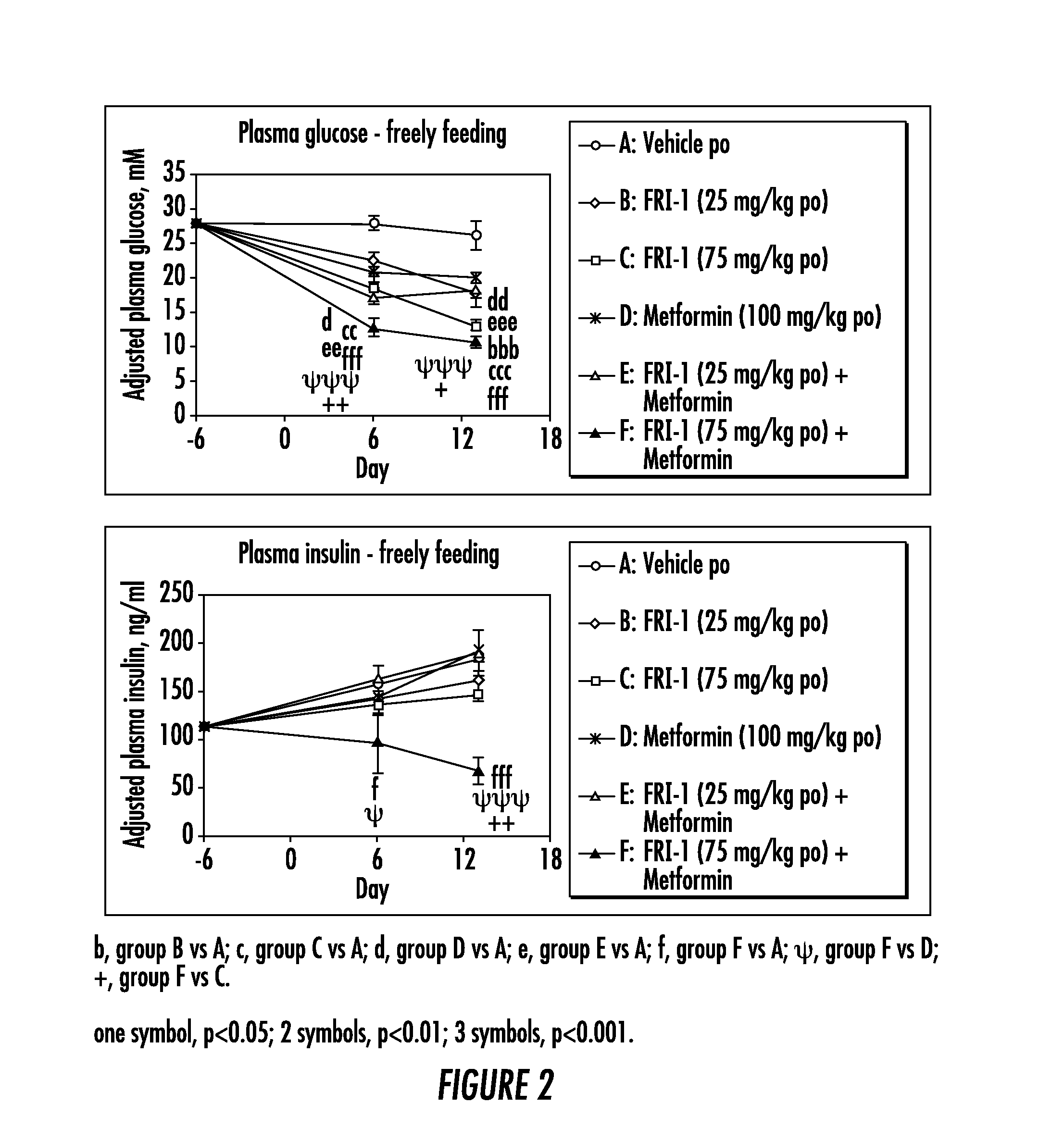
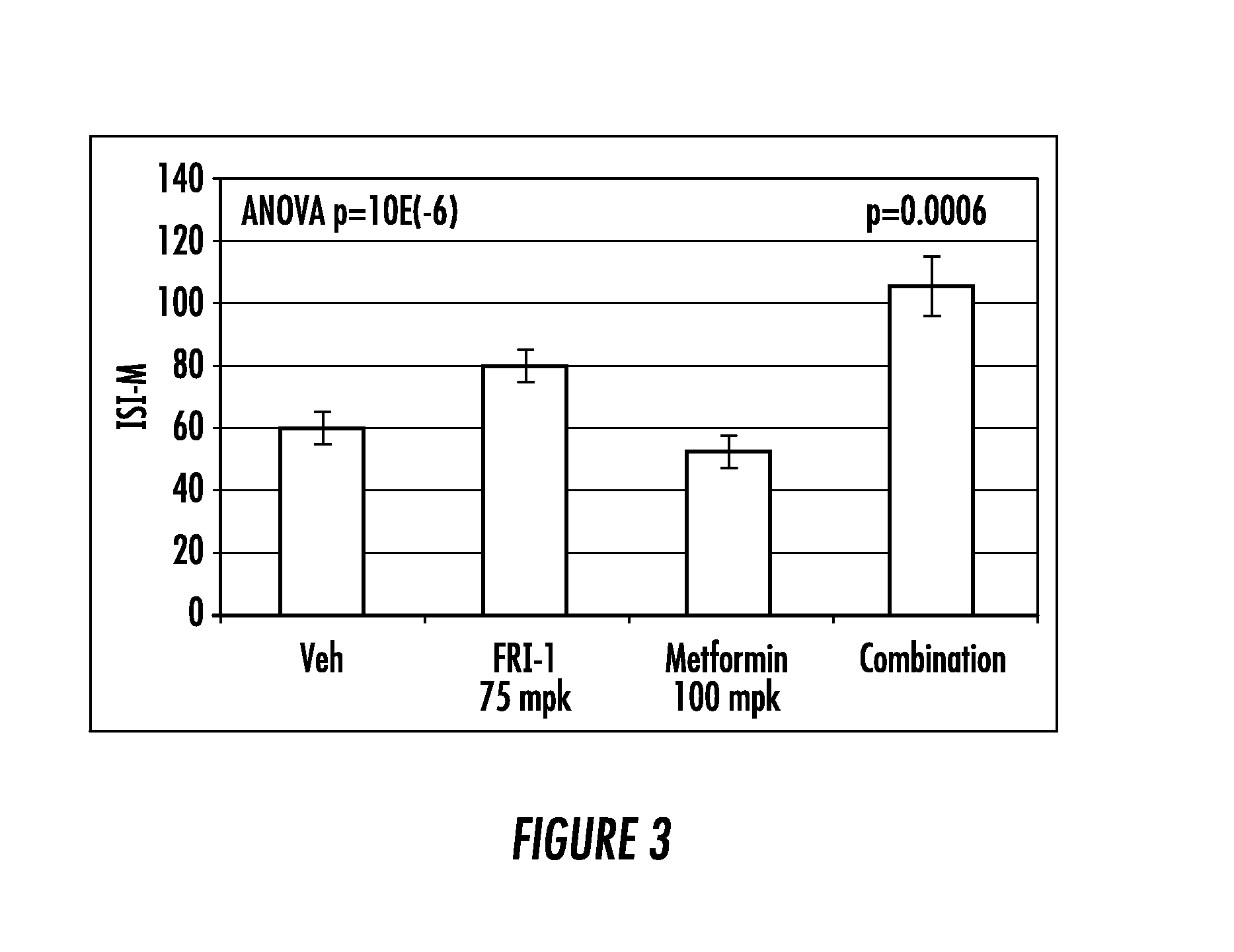
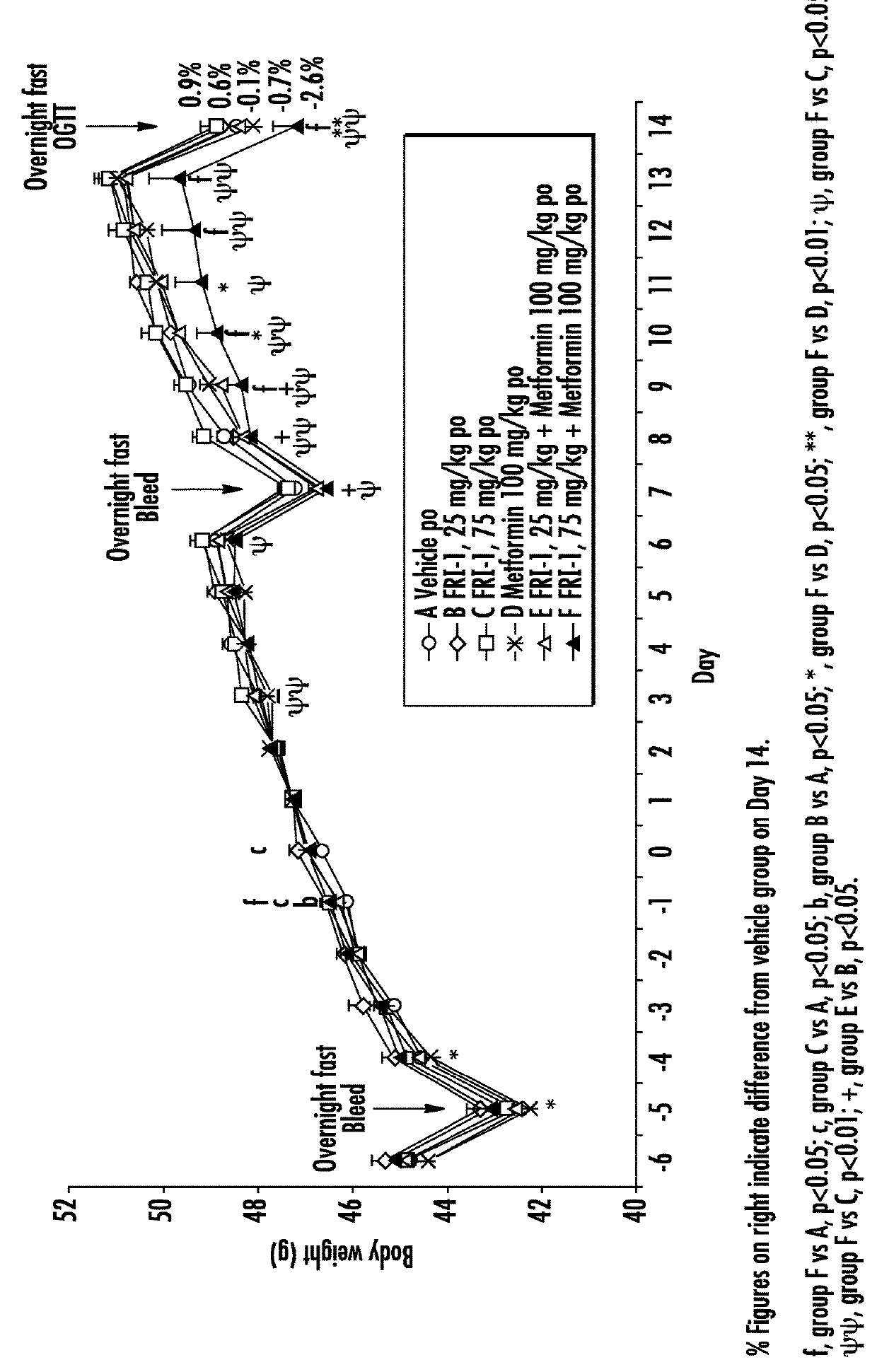
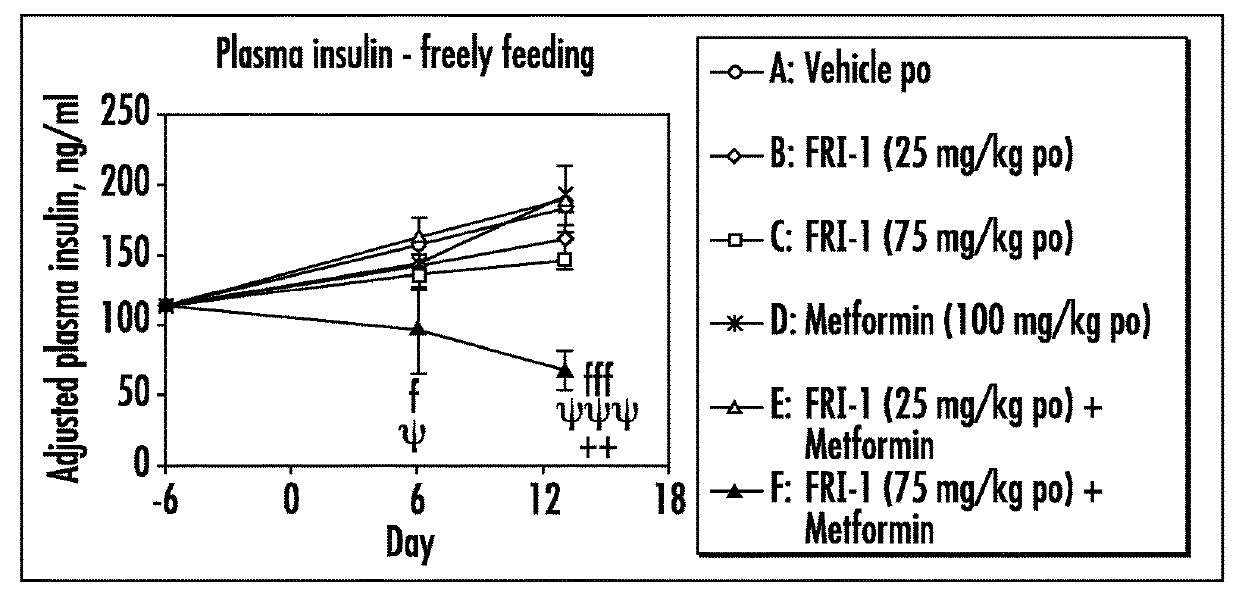
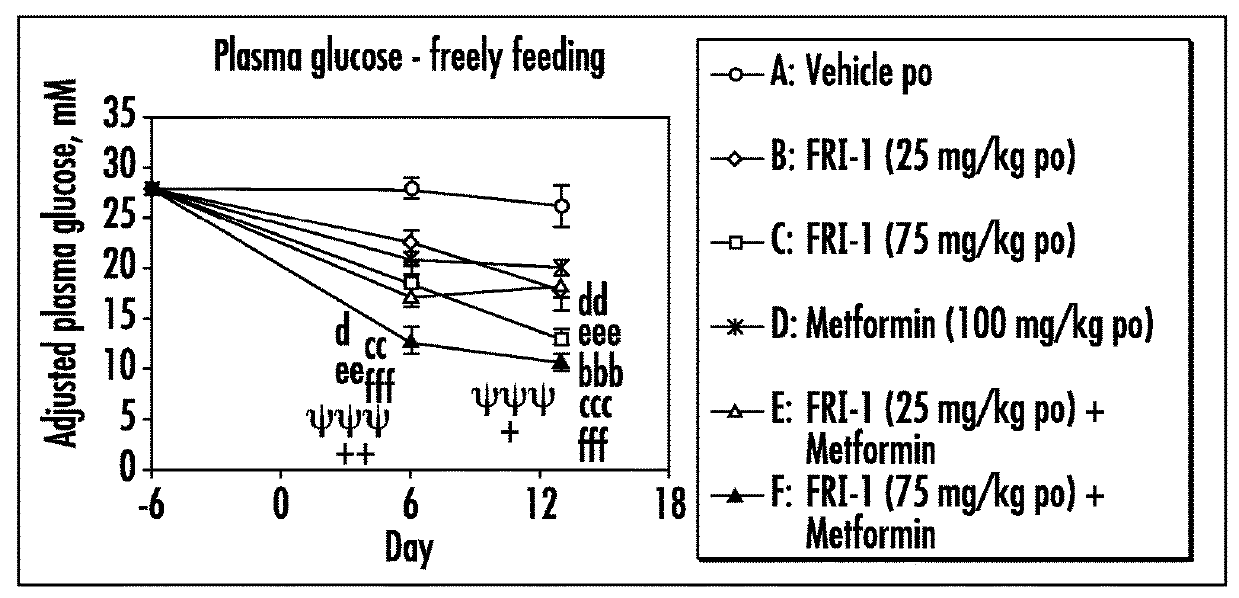
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising {2-[3-cyclohexyl-3-(trans-4-propoxy-cyclohexyl)-ureido]-thiazol-5-ylsulfanyl}-acetic acid (FRI-1) in combination with an anti-diabetic drug selected from the group consisting of metformin, sitagliptin or exenatide. The present invention also relates to the use of the pharmaceutical compositions in restoring insulin sensitivity and treating type II diabetes, including reducing body weight in subjects undergoing type II diabetes treatment.
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
An orally administrable hypoglycemic polypeptide and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN103665148BImprove resistance to enzymatic hydrolysisPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderEnzymatic hydrolysisPharmacology
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Oral suspension of liposome-encapsulated insulin lyophilized preparation and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN102144968AMaintain a healthy weightGood comprehensive curative effectPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderOral suspensionsLiver functions
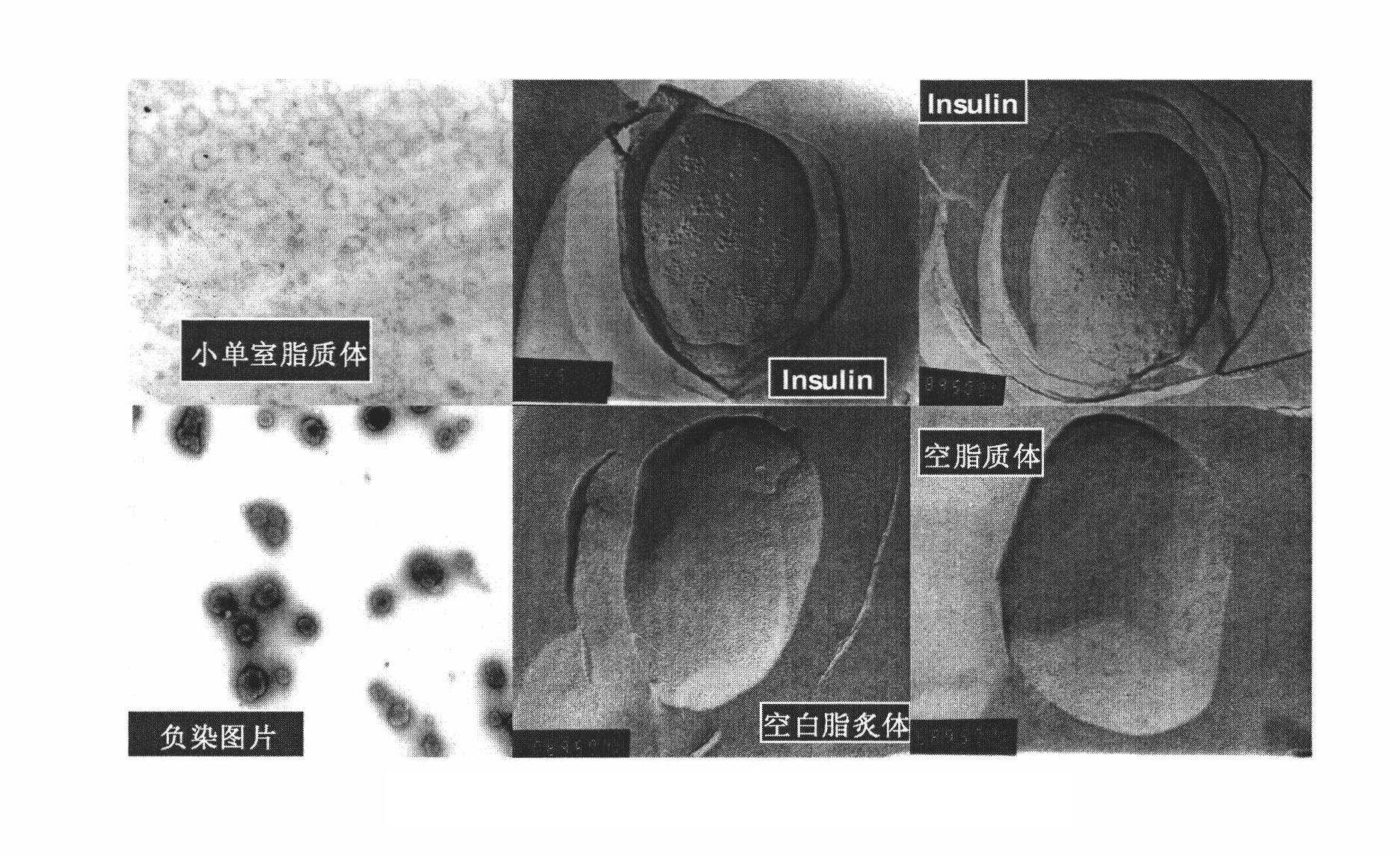
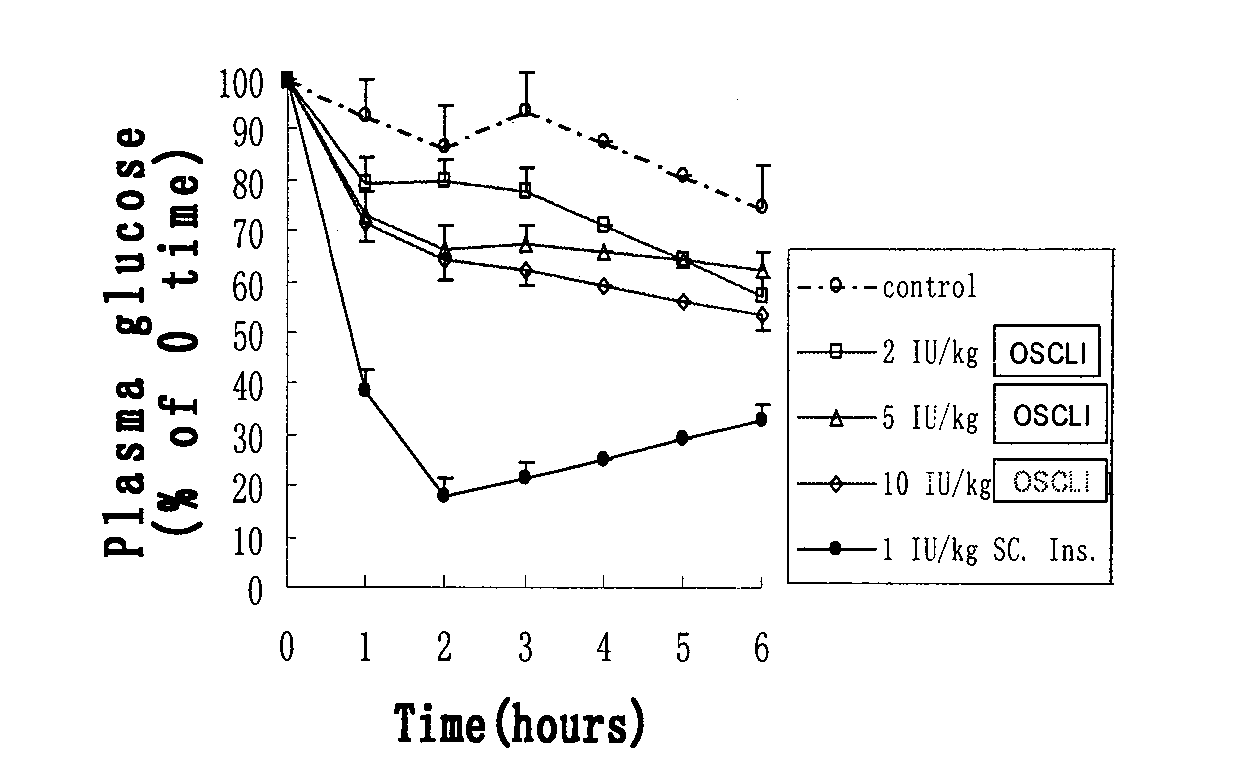
The invention relates to an oral suspension of a liposome-encapsulated insulin lyophilized preparation, named as O-SCULI. The O-SCULI contains lecithin, cholesterol, polyglycol aliphatic acid ester, vitamin E, insulin, water, sodium chloride and phosphate buffer. The invention also provides a two-step process of the O-SCULI, comprising (1) a dewatering / moistening control process: preparing a liposome-encapsulated insulin lyophilized preparation and SCLI so that the encapsulation rate of the insulin is increased to 80 percent by liposome amalgamation; and (2) a respective constant volume / stepped liquefaction process: preparing the SCLI into an O-SCULI oral suspension, preventing the SCLI liposome from leaking and keeping the constant encapsulation rate of the insulin. After a patient acutely takes the O-SCULI, the liposome insulin effectively enters the intestine-hepatic portal vein, the liver and the blood circulation to reduce blood sugar, blood fatty acids and blood ketone with high utilization degree. After a patient continuously orallly takes the oral suspension, the saccharification of hematoglobin, triglyceride and, aminotransferase and the oxidative stress are reduced, the structural damage of liver cells is recovered, and the comprehensive curative effects of diabetes treatment by using various liver functions are improved. The invention also opens up a new path for non-injection administration of active polypeptide protein, such as cytochrome C, albumin, interferon, and the like.
Owner:刘树森
Pharmaceutical composition containing gpr119 ligand as active ingredient for preventing or treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
InactiveUS20170049773A1High expressionInhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemGPR119Diabrezide
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing a G protein coupled receptor 119 (GPR119) ligand as an active ingredient for preventing or treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. More particularly, it was confirmed that the GPR119 ligand, which has been developed as only an anti-diabetic drug, exhibits superior effects on the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver and the signal pathways in hepatocytes therefor differ from the signal pathways in the small intestine and the pancreas exhibiting anti-diabetic effects, whereby the GPR119 ligand can be useful to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver.
Owner:PHARMEDIX CO LTD
Use of a combination of diazoxide and metformin for treating obesity or obesity related disorders
InactiveUS20120053172A1Metabolism disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsPotassiumDiabrezide
The present invention relates to a method for suppressing the fasting plasma insulin level and / or postabsorptive insulin level in a mammal in need thereof, said method comprising administering to said mammal a pharmaceutically effective amount of a combination of a potassium channel activator and an anti-diabetic drug. The present invention also relates to a method for treating or preventing obesity, obesity related disorders and conditions and other disorders and conditions related to weight gain in a mammal in need thereof, said method comprising administering to said mammal a pharmaceutically effective amount of a combination of a potassium channel activator and an anti-diabetic drug.
Owner:COOP MIRZORG U A ARNHEM
Methods for treating extreme insulin resistance in patients resistant to previous treatment with other anti-diabetic drugs employing an SGLT2 inhibitor and compositions thereof
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Use of szechuan melandium root pentacyclic triterpenoid saponin compound in preparation of drug for reducing blood sugar
ActiveCN103599117AGood antidiabetic activityLower blood sugarOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineBlood sugar
The invention relates to a use of a szechuan melandium root pentacyclic triterpenoid saponin compound in preparation of a drug for reducing blood sugar. Through massive screening and research, the inventor first finds the szechuan melandium root pentacyclic triterpenoid saponin compound extracted from a caryophyllaceae plant szechuan melandium root, purifies it and especially finds that a composition of a compound with sinocrassuloside as a mother nucleus and the szechuan melandium root pentacyclic triterpenoid saponin compound has strong blood sugar-reduction effects and can be used for preparation of anti-diabetic drugs.
Owner:王学勇 +1
Composite dietary fiber and preparation method
InactiveCN103504315AImprove glucose toleranceEnhanced interactionNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsDiseaseIsomalt
Owner:中美御康生物科技(北京)有限公司
Pharmaceutical dosage forms of biguanide-sulfonylurea combinations
The present invention relates to orally administered pharmaceutical compositions that include a combination of antidiabetic agents wherein one agent is present in an extended release form and the other agent is present in an immediate release form. For example, in one embodiment the dosage form includes an extended release layer that includes a biguanide; and an immediate release layer that includes a sulfonylurea.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Method for constructing related intestinal canal-pancreatic islet regulation axis function evaluation model and application of model
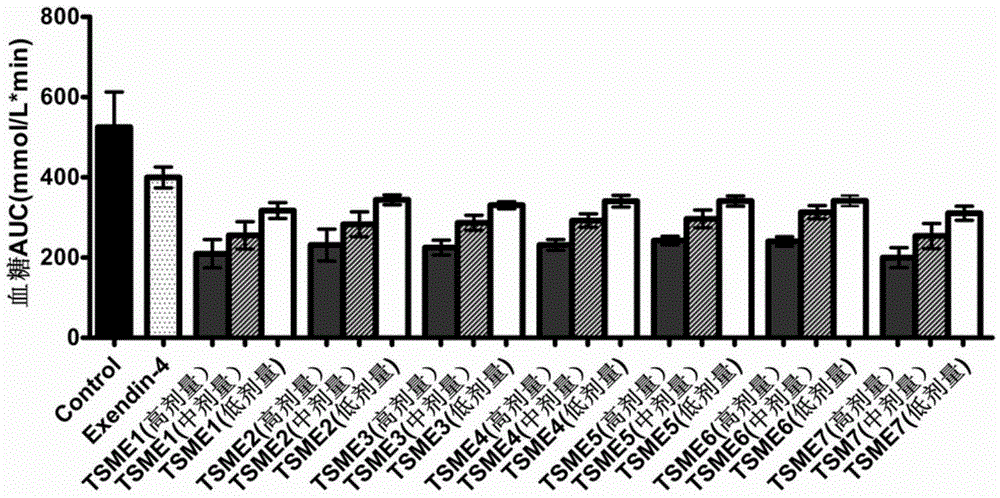
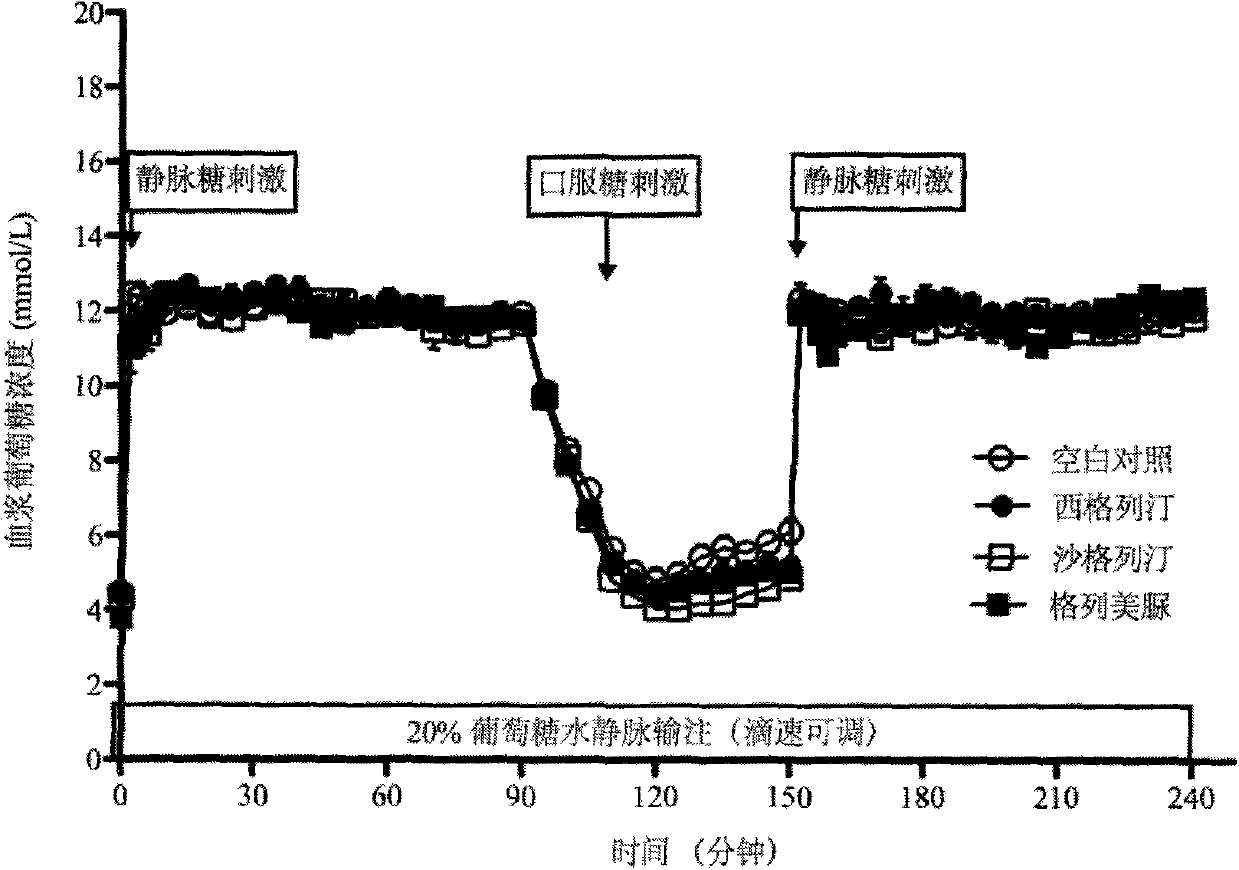
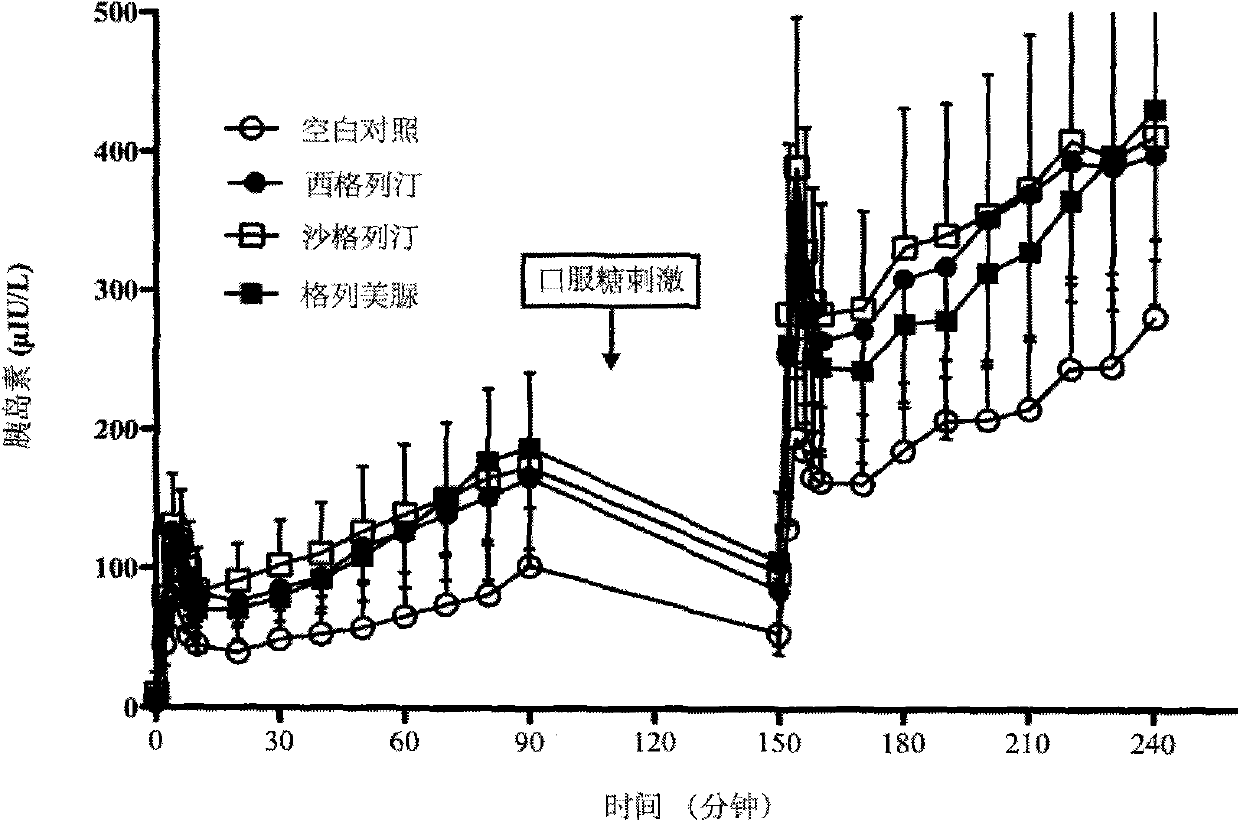
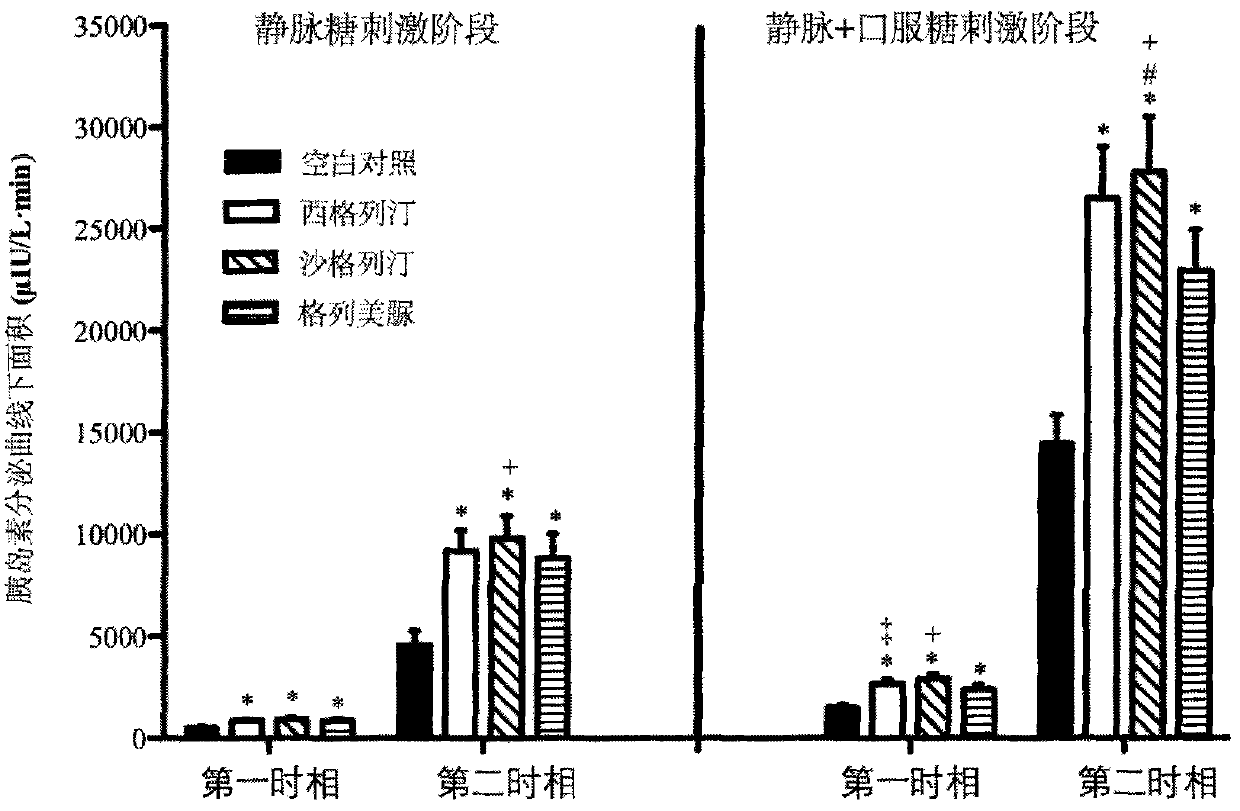
The invention provides a method for constructing a related intestinal canal-pancreatic islet regulation axis function evaluation model. The method includes: allowing a subject to take different oral hypoglycemic drugs or blank control in different stages, then performing intravenous-oral dual hyperglycemic clamp tests on the subject in each stage, drawing an area under the curve for a serum insulin value, a C-peptide value, a plasma glucagon value and an active glucagon-like polypeptide-1 (GLP-1) value acquired through the dual hyperglycemic clamp tests in each stage, and applying Metlab to perform 3D (three-dimensional surface fitting on the areas under the curve in one-to-one correspondence to obtain the related intestine-pancreas axis function evaluation model. By the method, two-phase insulin secretion patterns in intravenous-oral glucose stimulation states can be evaluated and compared accurately, besides, intestinal canal hormone effect and insulin-glucagon secretion can be related quantitatively, and accordingly an accurate intestine-pancreas axis effect model evaluation system is obtained.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Orally-administered hypoglycemic sweet potato leaf single prescription traditional Chinese medicine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101167781AClear functionLasting effectMetabolism disorderPlant ingredientsInsulin dependent diabetesSide effect
The invention discloses a simple oral hypoglycemic traditional Chinese medicine of sweat potato leaf and process for preparation. Plant of sweat potato leaf is refluxed, extracted and concentrated through ethanol and ethanol extract is obtained. The ethanol extract after being absorbed through macroreticular absorbing resin is respectively eluted through distilled water, 10-20% ethanol and 40-60% ethanol, and the eluent liquid is concentrated and then is extracted through acetic ether. The extracting liquid is recycled and concentrated and extractum is obtained. The extractum is dried and the effective component of the sweat potato leaf--sweat potato leaf flavone is obtained. Tested by pharmacological experiment, sweat potato leaf flavone without toxic and side effects has the effect of reducing blood glucose and action time is lasting, thereby the invention can be used for curing type II diabetes and complication and provides a natural hypoglycemic medicament for non- insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM).
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Glucokinase activator compositions for the treatment of diabetes
ActiveUS10004782B2Normalizing or lowering blood glucoseLowering of food intakeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSitagliptinAcetic acid
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising {2-[3-cyclohexyl-3-(trans-4-propoxy-cyclohexyl)-ureido]-thiazol-5-ylsulfanyl}-acetic acid (FRI-1) in combination with an anti-diabetic drug selected from the group consisting of metformin, sitagliptin or exenatide. The present invention also relates to the use of the pharmaceutical compositions in restoring insulin sensitivity and treating type II diabetes, including reducing body weight in subjects undergoing type II diabetes treatment.
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
Radix pseudostellariae homogeneous polysaccharide for promoting insulin secretion of islet cells and use thereof
ActiveCN106519054APromote secretionOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderElemental compositionIslet cells
The invention discloses a radix pseudostellariae homogeneous polysaccharide for promoting insulin secretion of islet cells and use thereof. The radix pseudostellariae homogeneous polysaccharide provided by the invention is acidic polysaccharide, has a molecular weight of 4.8*10<4> Da and specific rotation [alpha] of D<25>+174.5DEG (c 0.485, H2O); the molecular formula consists of three elements: C, H, O, and C, H and O are in a ratio of 1:2.1:1.4. The radix pseudostellariae homogeneous polysaccharide is composed of monosaccharide galacturonic acid, rhamnose, galactose and arabinose, galactose uronic acid is a main monosaccharide component of polysaccharide, alpha-1, 4- connected galacturonic acid constitutes a main chain of polysaccharide. Part of galacturonic acid C6-OH undergoes methyl esterification, the hydroxyl on C2 and C3 are partly acetylized, a small amount of rhamnose exists on the main chain, and 1, 5- connected arabinose composes a branched chain. The radix pseudostellariae homogeneous polysaccharide can promote insulin secretion of Ins-1 cells, and provides the basis for application in development of anti-diabetic drugs, health care products and other fields in the future.
Owner:福建省中医药科学院
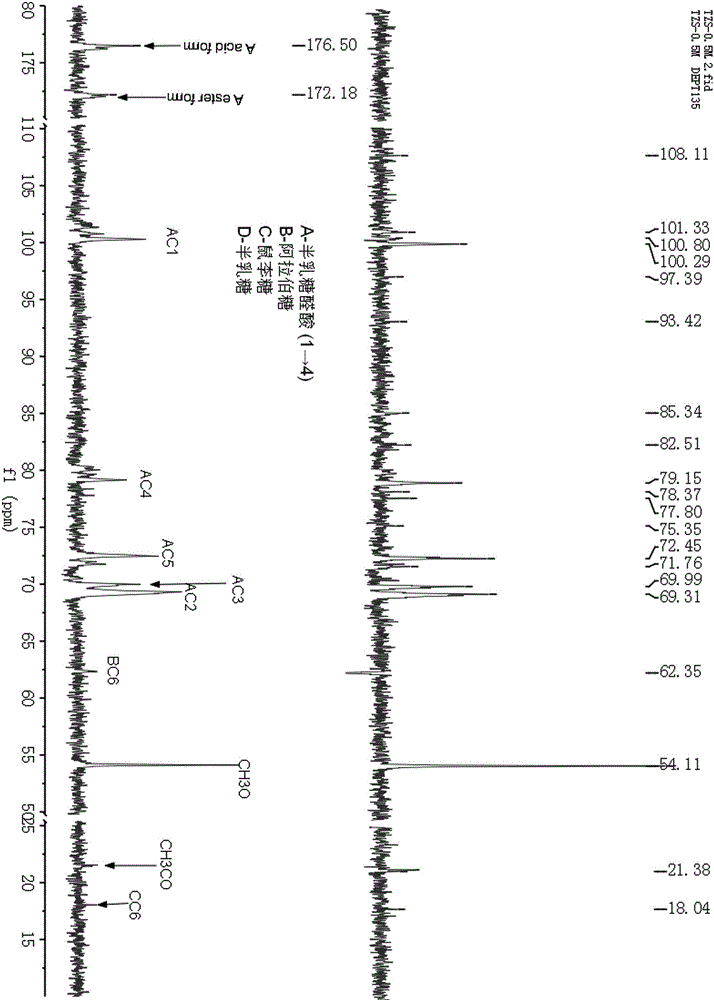
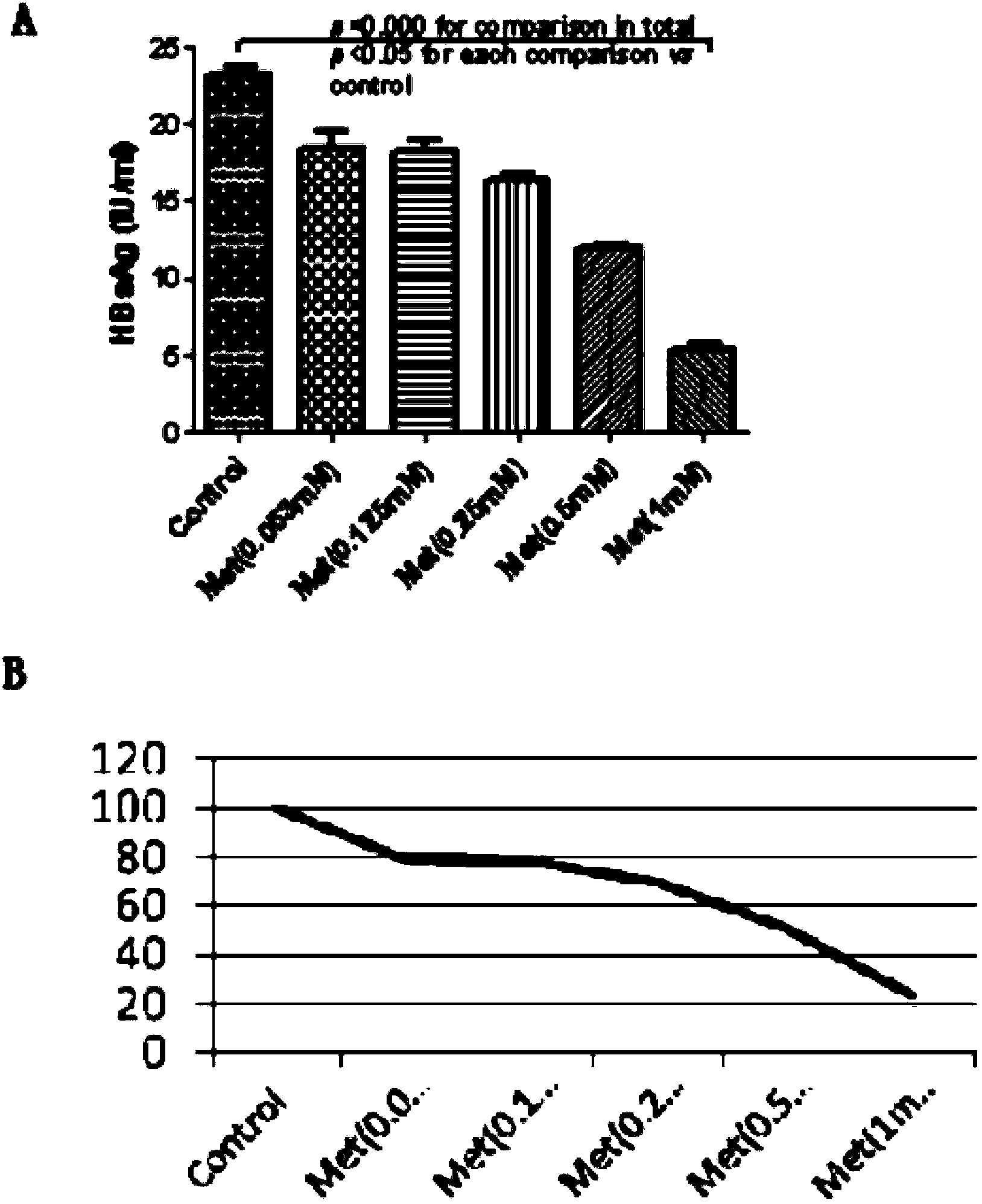
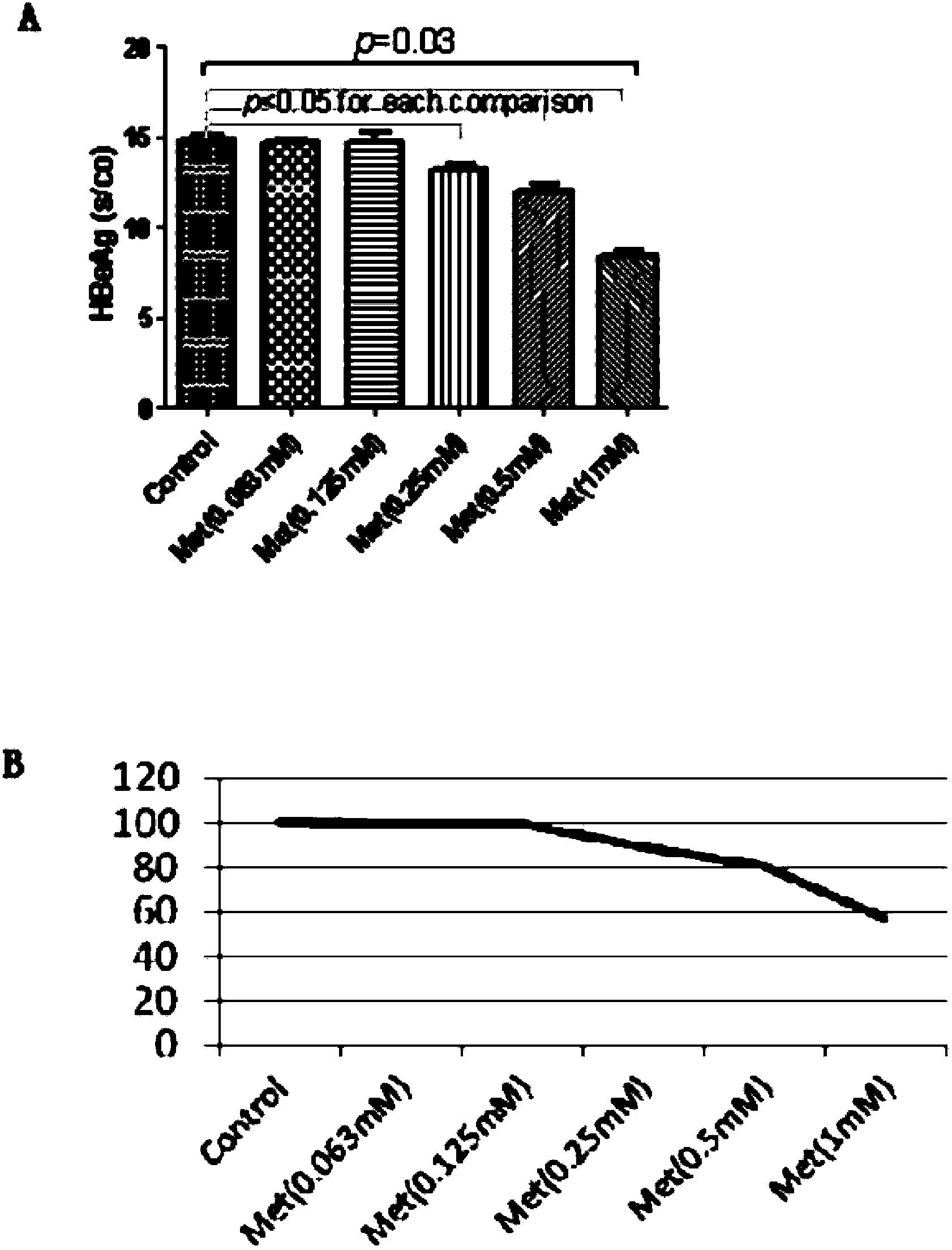
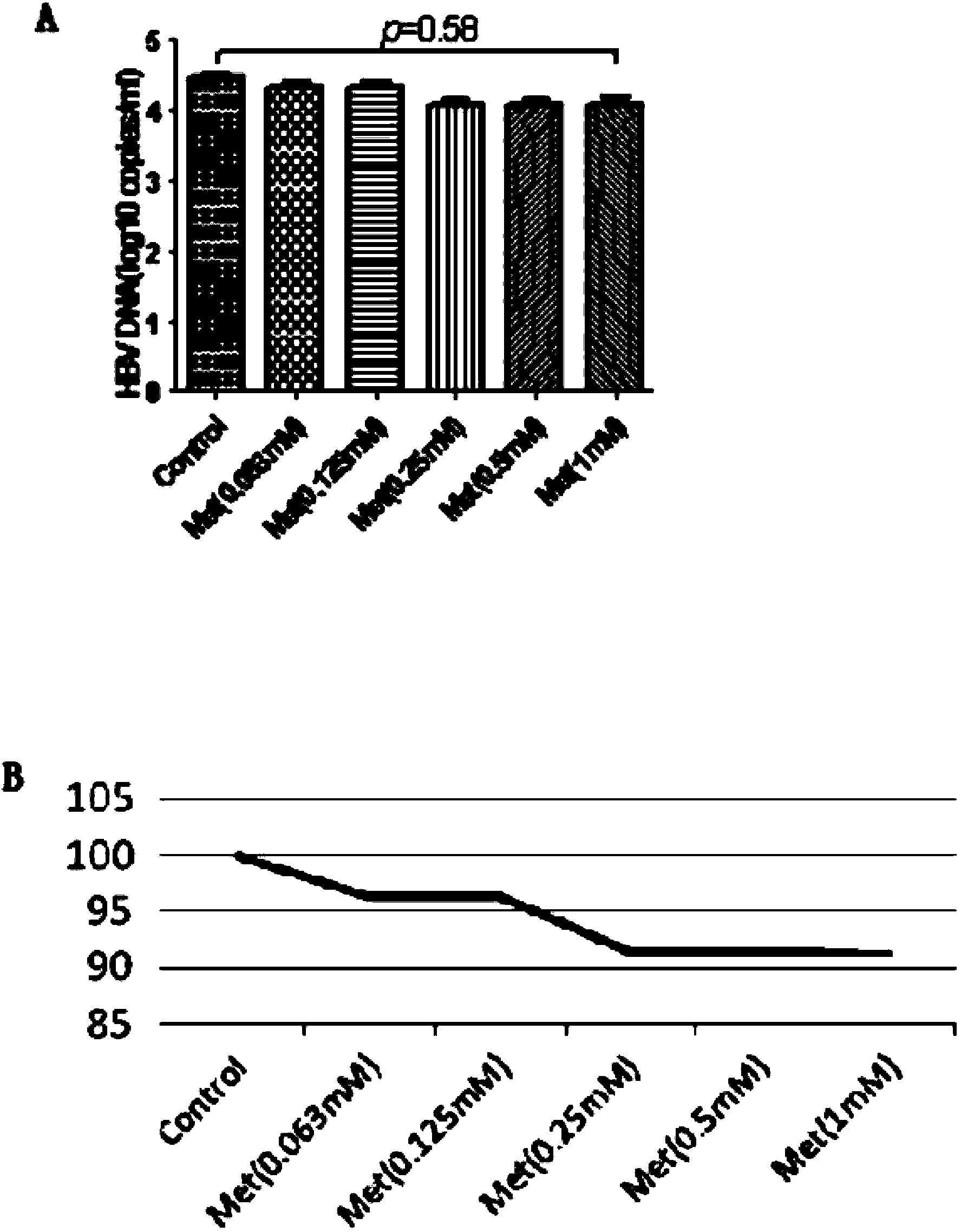
Application of metformin on preparation drugs for reducing surface antigen level of hepatitis B virus
InactiveCN103446080AReduce or eliminate serum surface antigensOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemCell culture supernatantHbv replication
The invention belongs to the field of medicine, and relates to a pharmaceutical application of an oral hypoglycemic drug metformin, and especially relates to an application of metformin on preparation drugs for reducing surface antigen level of hepatitis B virus. The results of in-vitro cell culture tests and drug intervention tests show that metformin can prominently reduce HBsAg titer of stable cell line HepG 2.2.15 and HBeAg titer of cell culture supernatant, and has an inhibition tendency on HBV-DNA of HepG 2.2.15 cell culture supernatant and HBV replication intermediates in cells. The metformin can be used to prepare drugs for inhibiting HBsAg, and furthermore, can be used to prepare drugs for reducing or eliminating serum surface antigen of hepatitis B virus chronic infection patients, drugs for reducing or inhibiting core antigen of hepatitis B virus, and drugs for inhibiting DNA and virus replication intermediates of hepatitis B virus.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV +1
Oral hypoglycemic peptide, its fatty acid derivatives and uses
ActiveCN110437329BAvoid enzymatic failurePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical drugGlycopeptide
Provided are an oral hypoglycemic peptide, and a fatty acid derivative and use thereof. The sequence of the polypeptide is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The polypeptide or fatty acid derivative thereof may be used to prepare drugs or pharmaceutical compositions for preventing or treating diabetes, or may be used to prepare drugs or pharmaceutical compositions for lowering blood sugar. The polypeptide possesses enzymolysis resistance against a variety of proteases, may prevent failures caused by enzymolysis in the gastrointestinal tract, and is suitable as an oral hypoglycemic drug.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Cell model for sifting anti-diabetic drugs
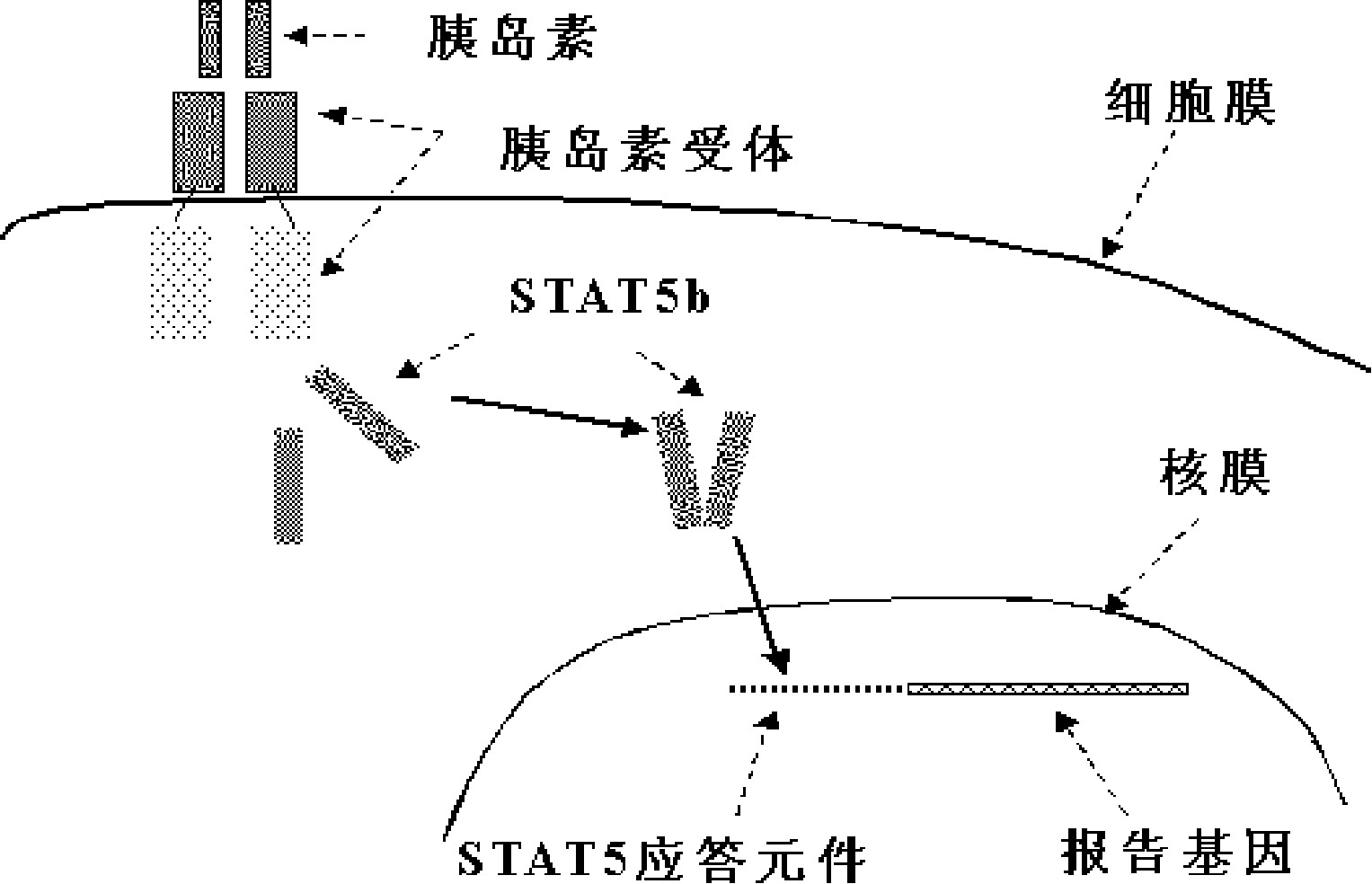
InactiveCN101200707AThe preparation method is simple and controllableLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementFused cellsFiltrationMammal
The present invention relates to a cell model for sieving diabetes resistant medicine and a preparation method thereof. A technical problem for solving is to provide a medicine sieving cell model which is provided with definite medicine effect mechanism and direct, prompt, simple and convenient medicine filtration and is fit for high-throughput medicine sieving and a corresponding sieving method. The cell model of the present invention is mammalian cell which clones the coding sequence of IR gene, the coding sequence of STAT5B gene and the coding sequence of reporter gene which is regulated by STAT5B responsive element. The present invention can indirectly monitor IRTK activity by inspecting reporter gene expression level in the cell model to exactly sieve the diabetes resistant medicine with the high-throughput of the cell level.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
Composition of anti-diabetic drugs
InactiveCN105030724AAvoid contactTo avoidOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderFiller ExcipientAdhesive
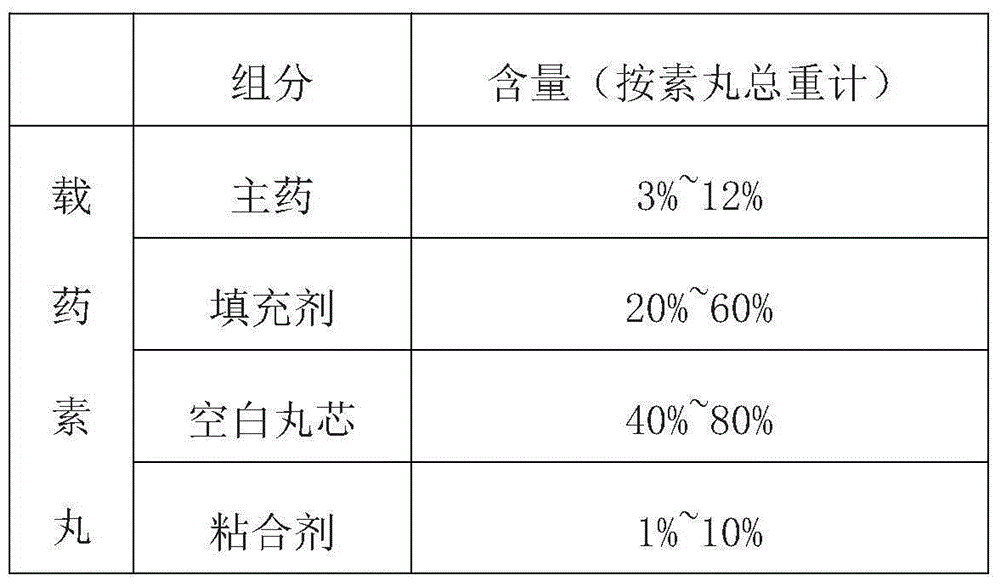
The invention provides a composition of anti-diabetic drugs. The composition comprises alogliptin coated pellets, pioglitazone coated pellets and a gelatin capsule shell and is used for treating type II diabetes, wherein blank pellets comprise main drugs, filling agents and adhesives; in the total blank pellets, the main drugs account for 3-12wt%, the filling agents account for 20-60wt%, blank pellet cores account for 40-80wt% and the adhesives account for 1-10wt%; the weights gained by coating layers are about 2-10% of the weights of the drug-loaded blank pellets. Alogliptin and pioglitazone pellets with different coating colors are preferentially prepared. The composition has the advantages of simple and reliable production process, low loss, good product stability and few by-products, so that the composition is beneficial to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:杭州成邦医药科技有限公司
Application of oral hypoglycemic peptide to preparation of medicine for treating or preventing diabetes complicated with cardiovascular diseases
ActiveCN111905097AImproves oxidative stressReduce contentPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderFibrosisGlycopeptide
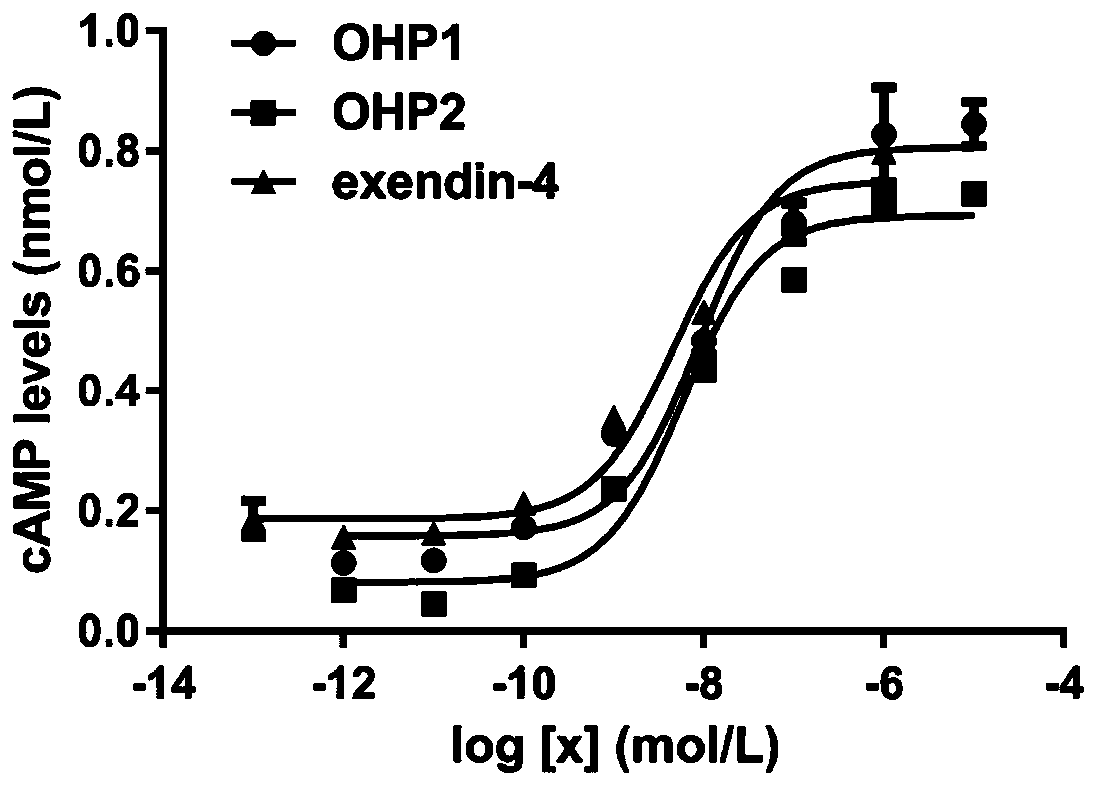
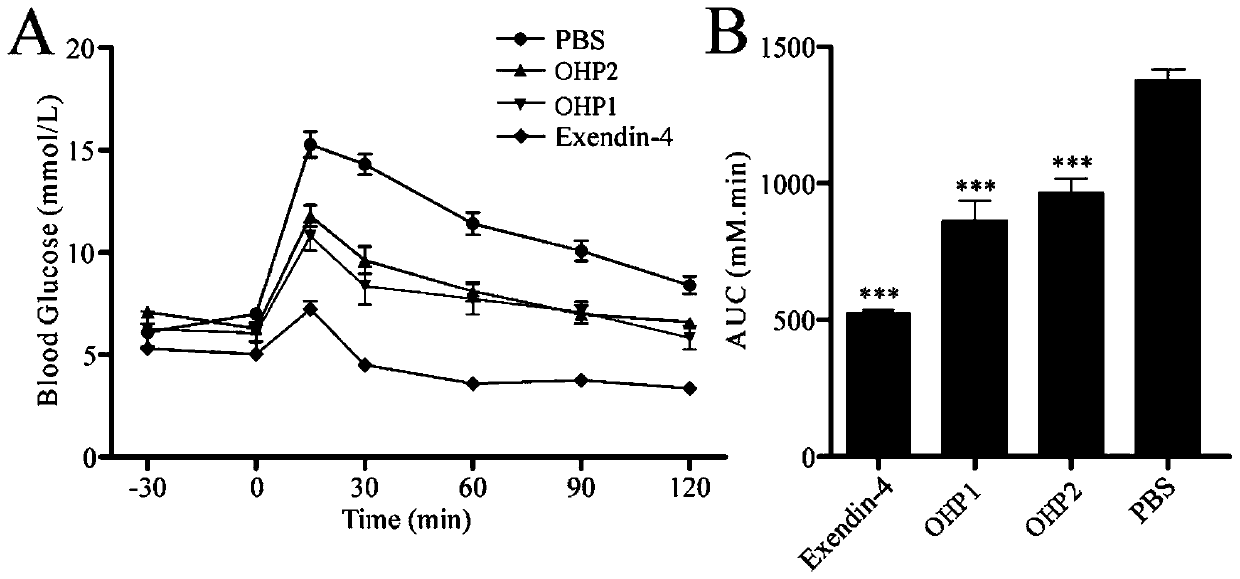
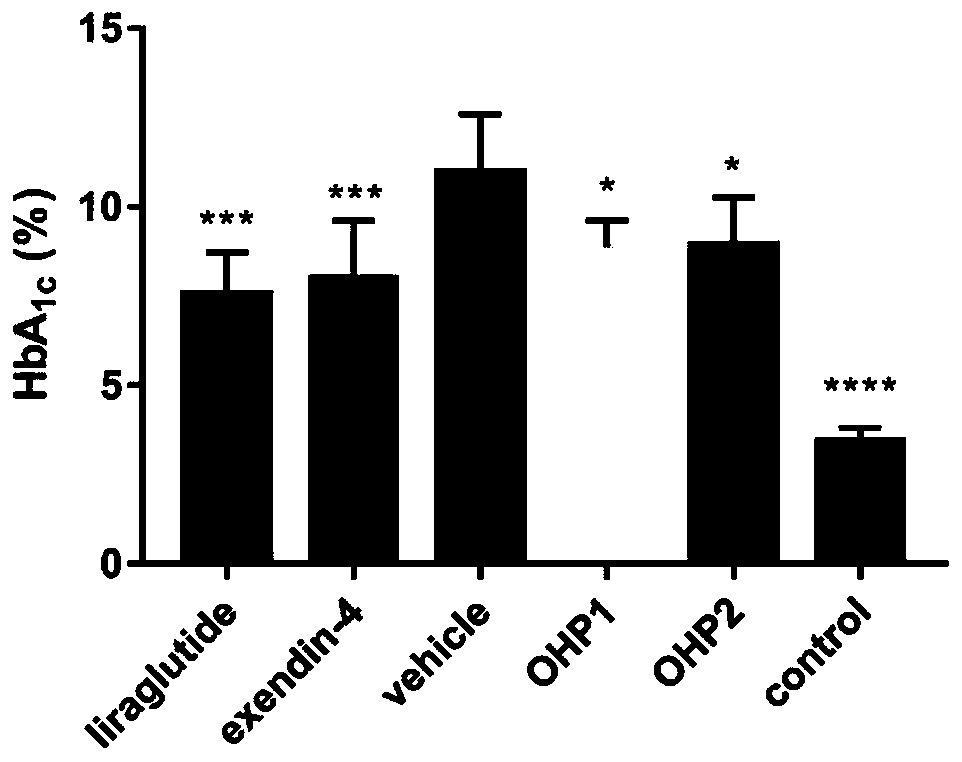
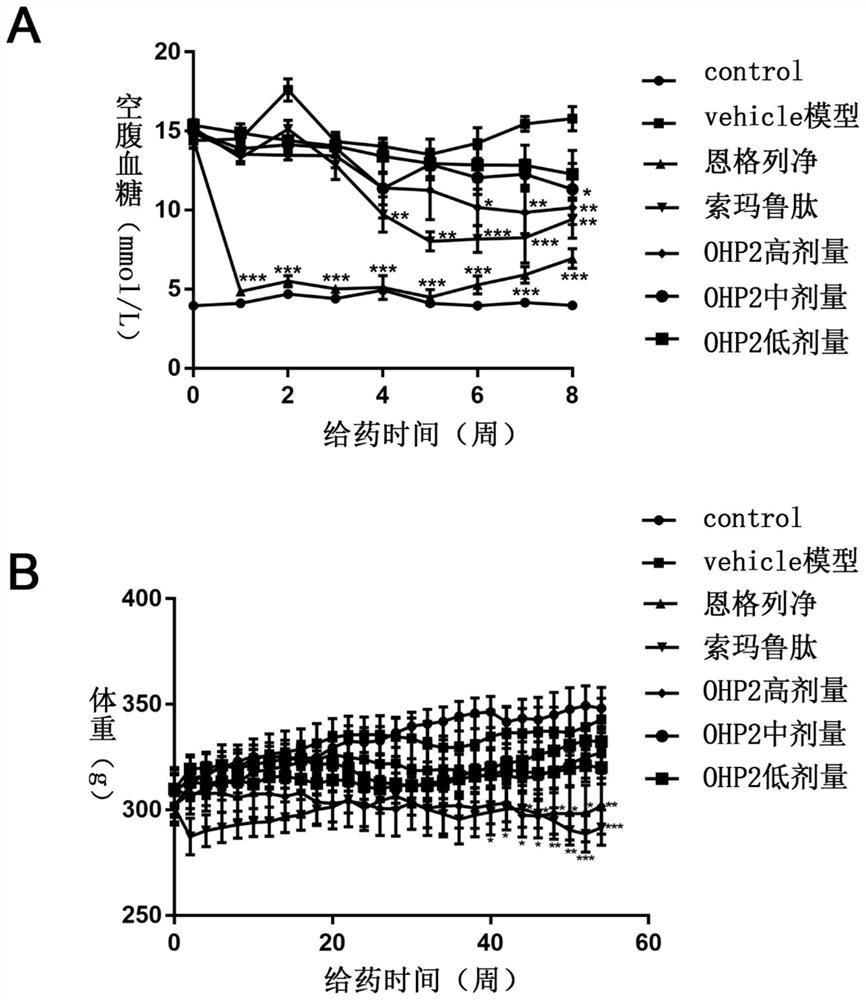
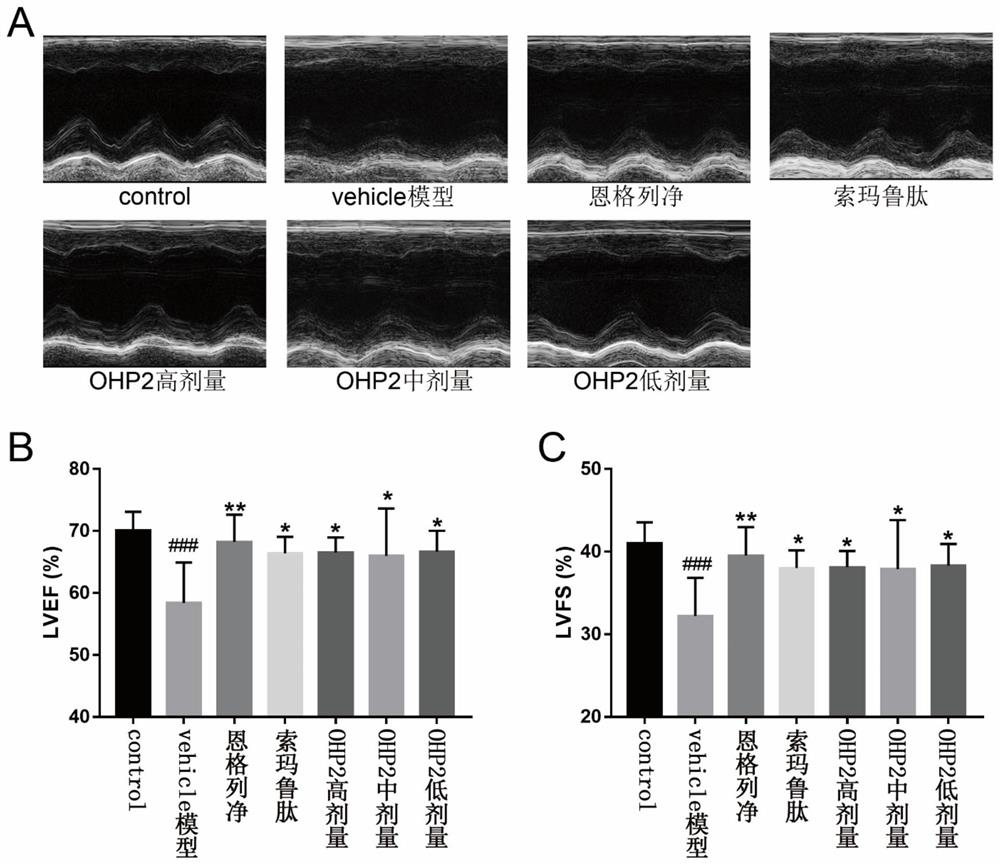
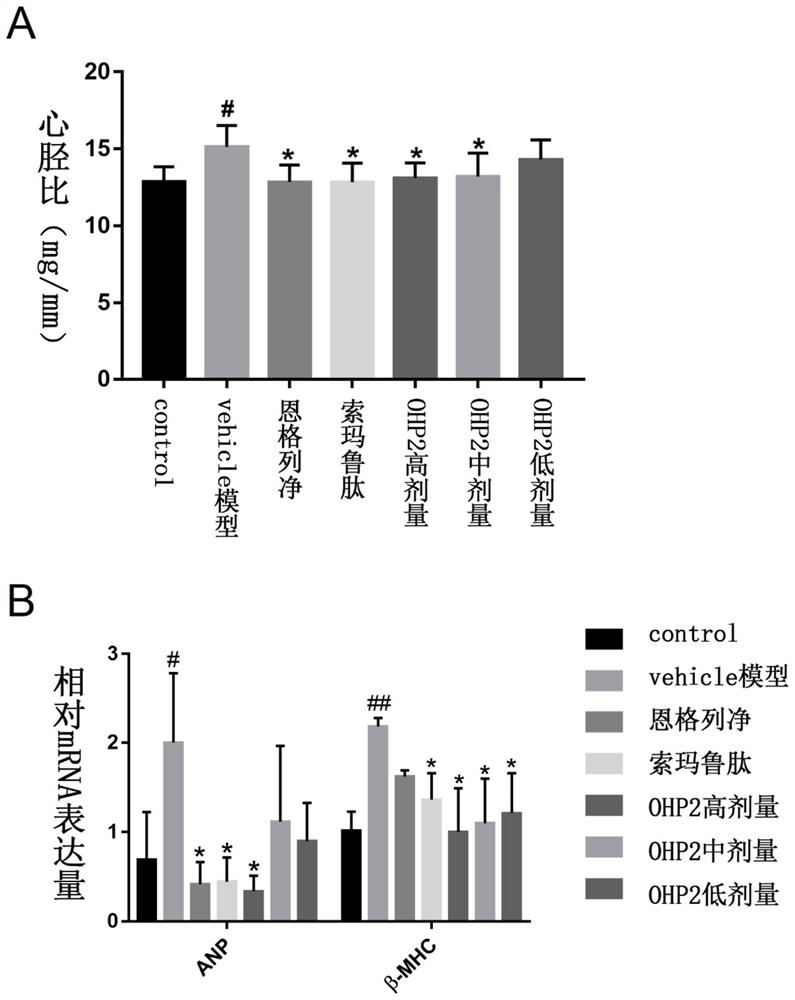
The invention relates to application of an oral hypoglycemic peptide. The application is used for preparing a medicine or a medicine composition for treating or preventing diabetes complicated with cardiovascular diseases. The oral hypoglycemic peptide is polypeptide OHP2. The polypeptide can effectively improve myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis damage caused by the diabetes, reduce the contentof related myocardial enzymes, adjust the lipid metabolism level and improve myocardial cell oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage, so that the effect of protecting the heart is achieved; and therefore, the polypeptide can be used as a candidate molecule for treating or preventing the diabetes complicated with the cardiovascular diseases (especially diabetic cardiomyopathy), and has a good application prospect.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com