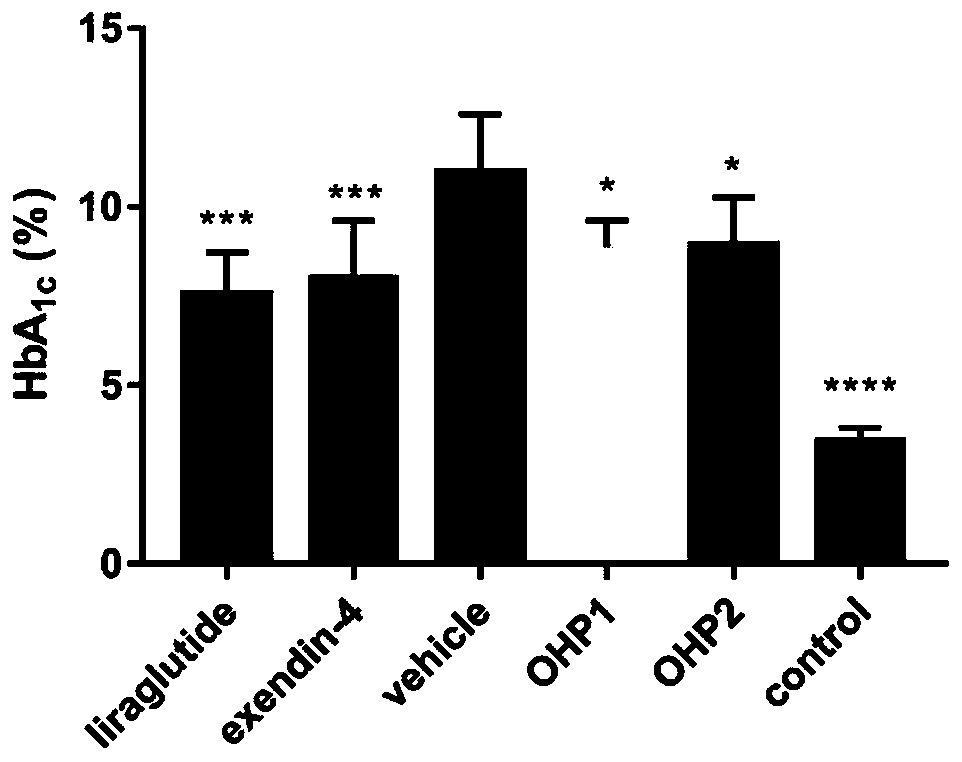
Oral hypoglycemic peptide as well as fatty acid derivative and application thereof
A fatty acid and derivative technology, applied in the field of medicine and biology, can solve problems such as low oral availability, difficulty in absorption, and inability to maintain drug concentration, and achieve the effect of avoiding enzymatic hydrolysis failure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Example 1 Determination of resistance to enzymolysis of OHP1-OHP6
[0070] Step 1: Prepare trypsin, protease, and elastase solutions with a concentration of 0.005 mg / mL, and incubate each protease solution at 37°C for 15 minutes.
[0071] Step 2: Mix 500 μL of 0.5 mg / mL OHPX solution (OHPX is one of OHP1-OHP6, the same below) with an equal volume of protease solution, that is, each protease: OHPX=1:100 (w / w), Incubate at 37°C for 60 min. After the reaction, take out 50 μL of the reaction solution, add 50 μL of 1% (v / v) TFA solution to stop the reaction, centrifuge at room temperature at 12000 rpm for 5 min, collect the supernatant, and use RP-HPLC to analyze the supernatant. detection. At the same time, Exendin-4 (i.e. exenatide), TSME1, and TSME2 were used as control samples, which were treated and detected with the same volume and concentration.
[0072] The third step: use RP-HPLC to detect: the chromatographic column is a Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 reversed-phase chr...
Embodiment 2
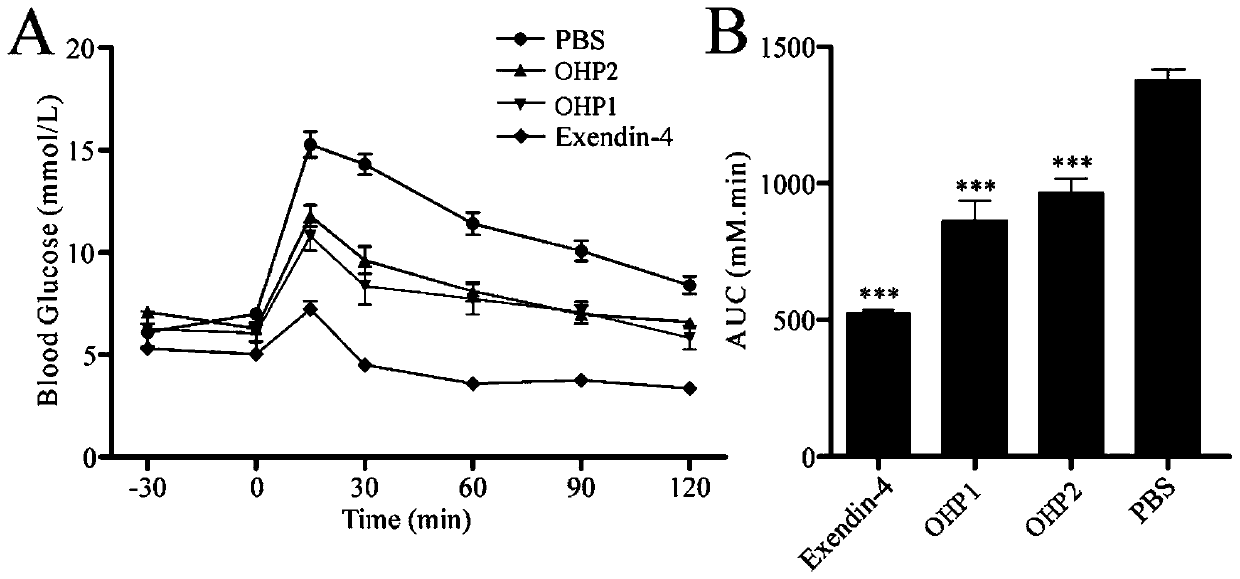
[0079] Example 2 Determination of the ability of OHP1-OHP6 to activate the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
[0080] Step 1: Using the CHO cell line that can stably express the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor on the cell membrane surface and connect the luciferase reporter gene constructed earlier in our laboratory, at 37°C, 5% CO 2 The in vitro activity assay was performed using the luciferase reporter gene method after cultured to the third passage in a cell culture incubator.
[0081] Step 2: For experimental determination, the cells were first digested with 0.25% trypsin, and then the complete medium containing 0.25% fetal bovine serum was added. Take 2×10 5 Inoculate the cell solution in a 96-well plate at a concentration of 1 cell / mL, inoculate 100 μL per well, and inoculate at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in a cell culture incubator for 4 h.
[0082] Step 3: Take out the 96-well plate, and add 20 μL of OHPX solution, TSME1 solution, TSME2 solution, or Exendin-4 positive con...
Embodiment 3
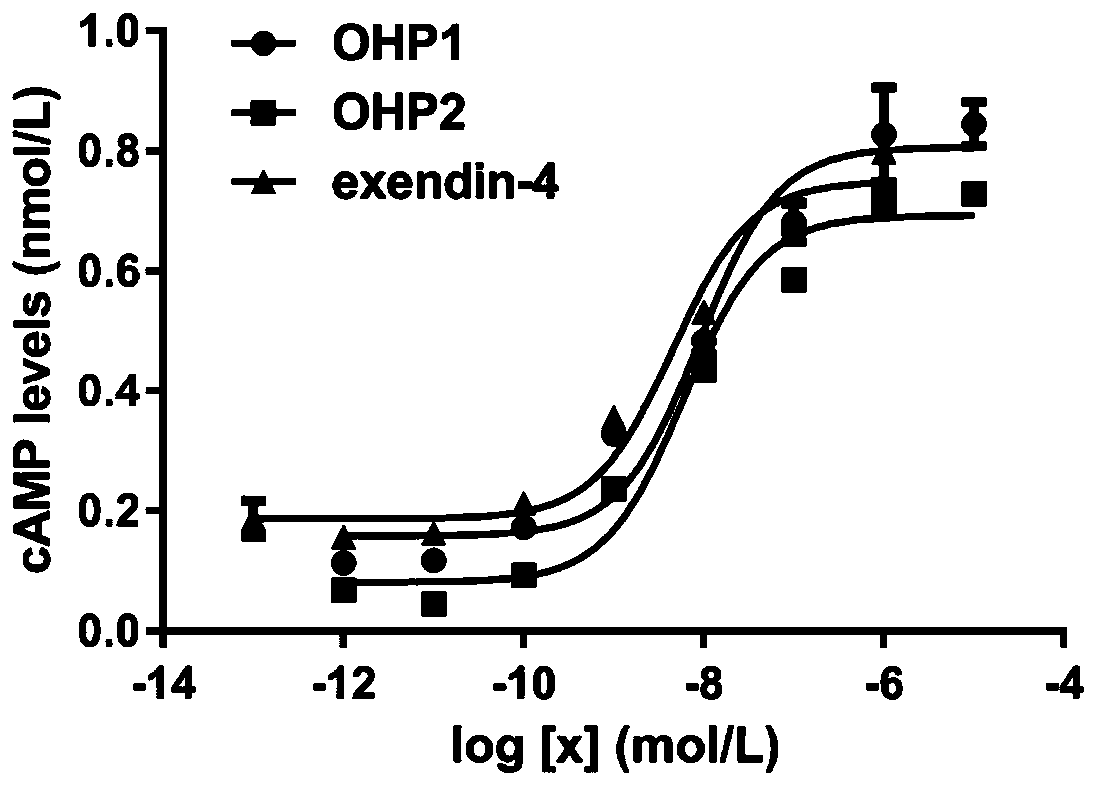
[0091] Example 3 OHP1 and OHP2 activate the content of the second messenger cAMP downstream of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
[0092] The first step: use the CHO cell line constructed in our laboratory that can stably express the GLP-1 receptor on the cell membrane surface and connect the luciferase reporter gene to carry out the second messenger molecule cAMP downstream of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor Determination of activation content, cell culture conditions as previously described.
[0093] Step 2: For experimental determination, the cells were first digested with 0.25% trypsin, and then a complete medium containing 0.25% fetal bovine serum and 0.5mmol / L IBMX was added. Take 2×10 5 Inoculate the cell solution in a 96-well plate at a concentration of 1 cell / mL, inoculate 100 μL per well, and inoculate at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in a cell culture incubator for 4 h.
[0094] Step 3: Take out the 96-well plate, and add a certain amount of OHP1 / OHP2 solution o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com