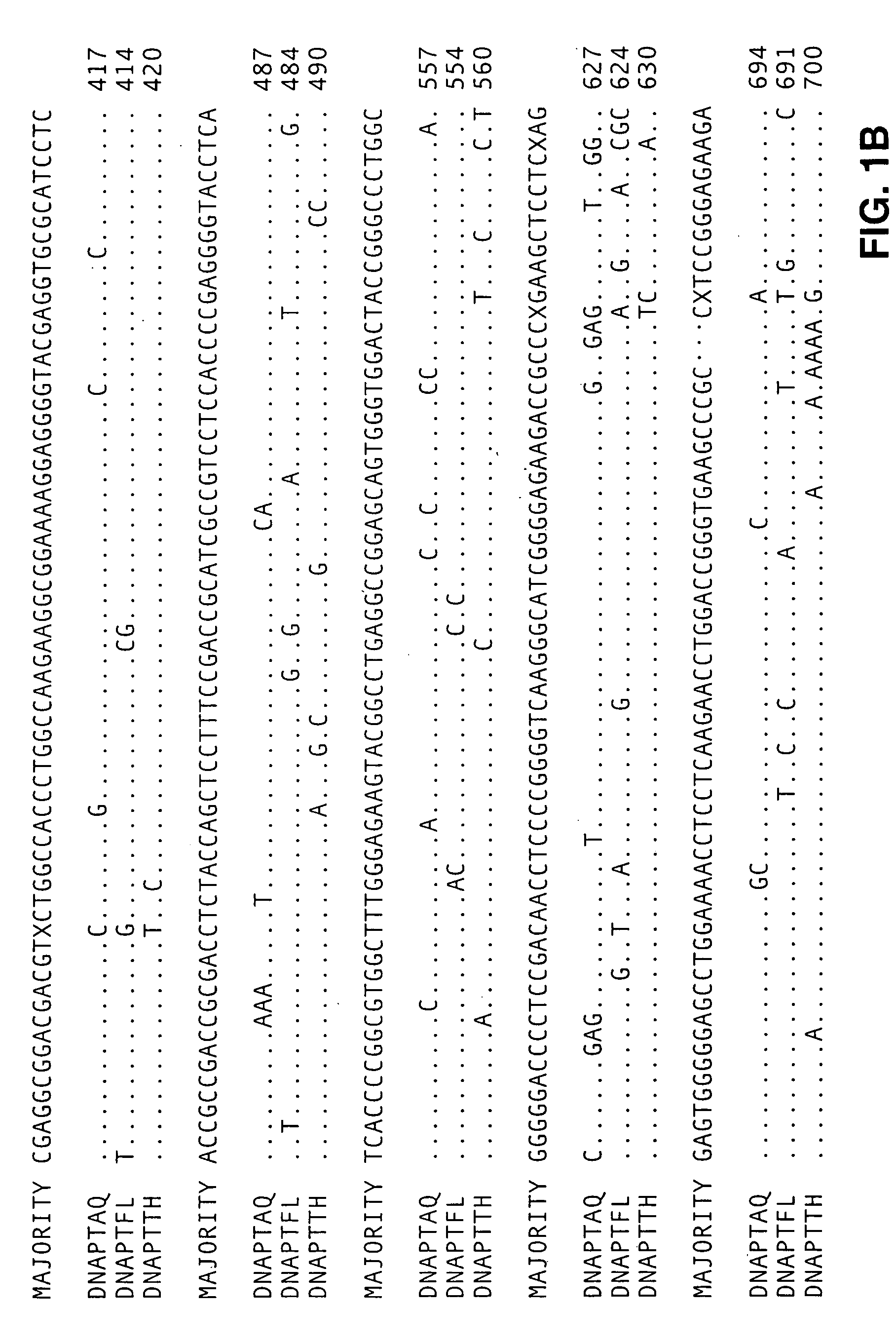
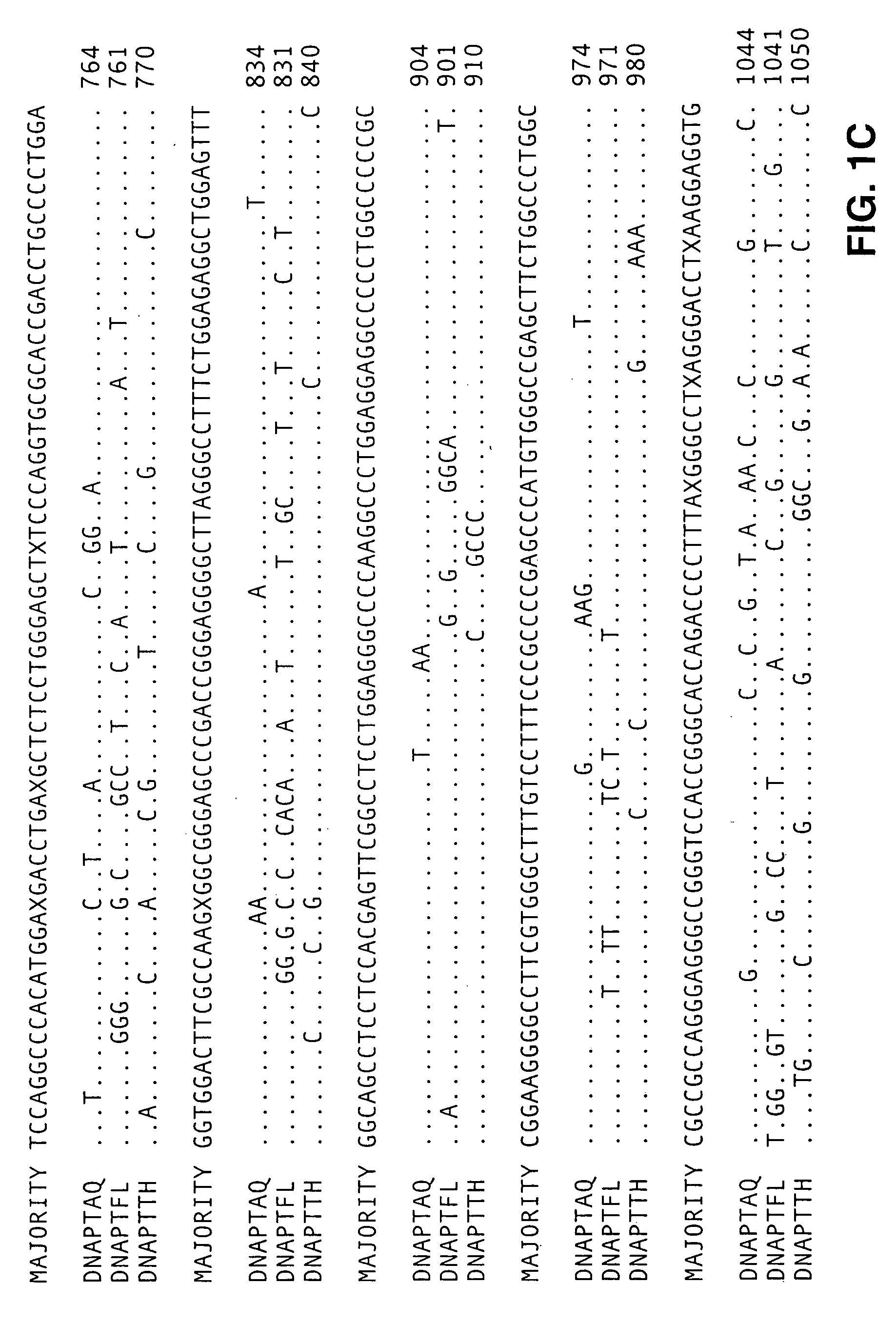
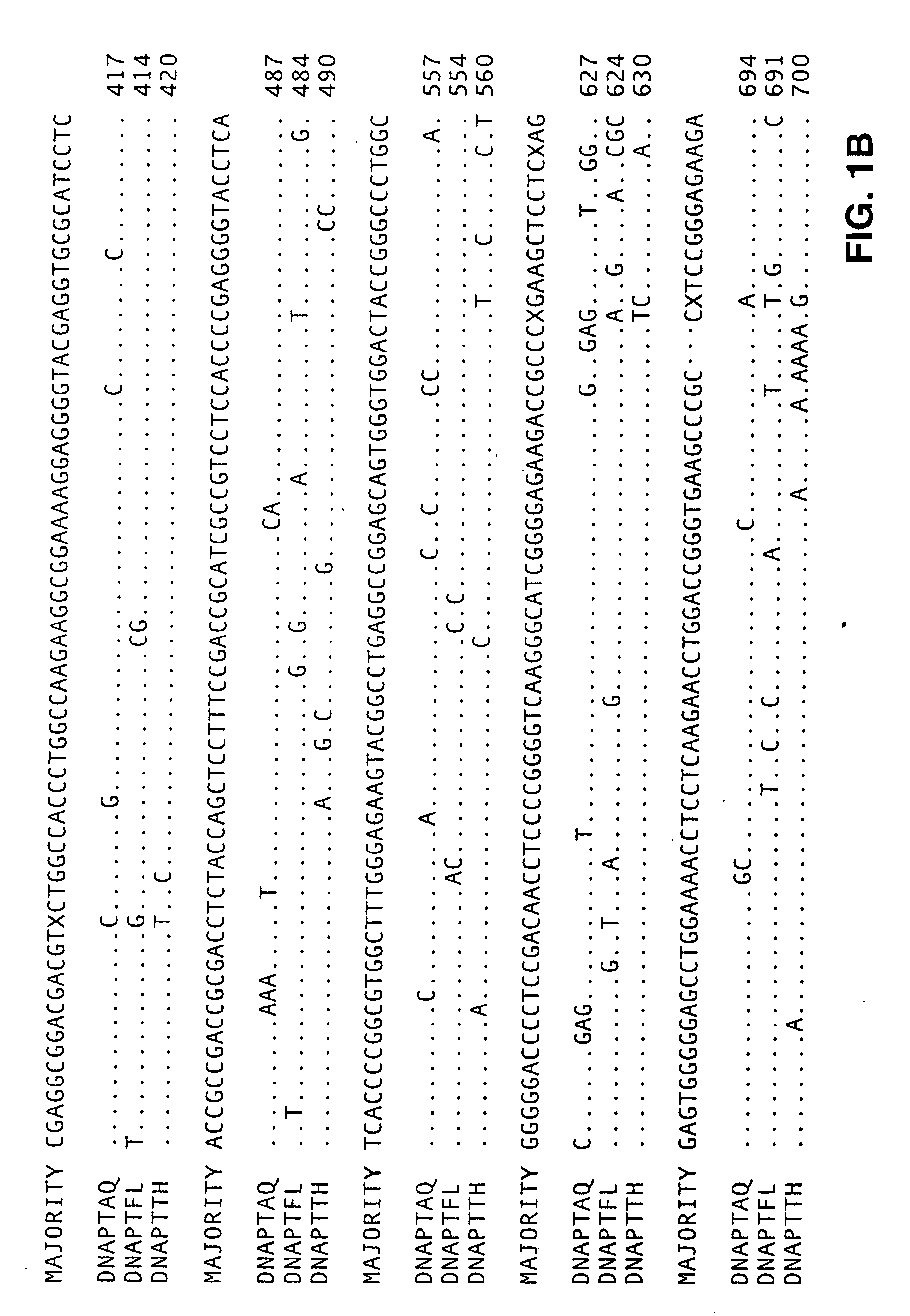
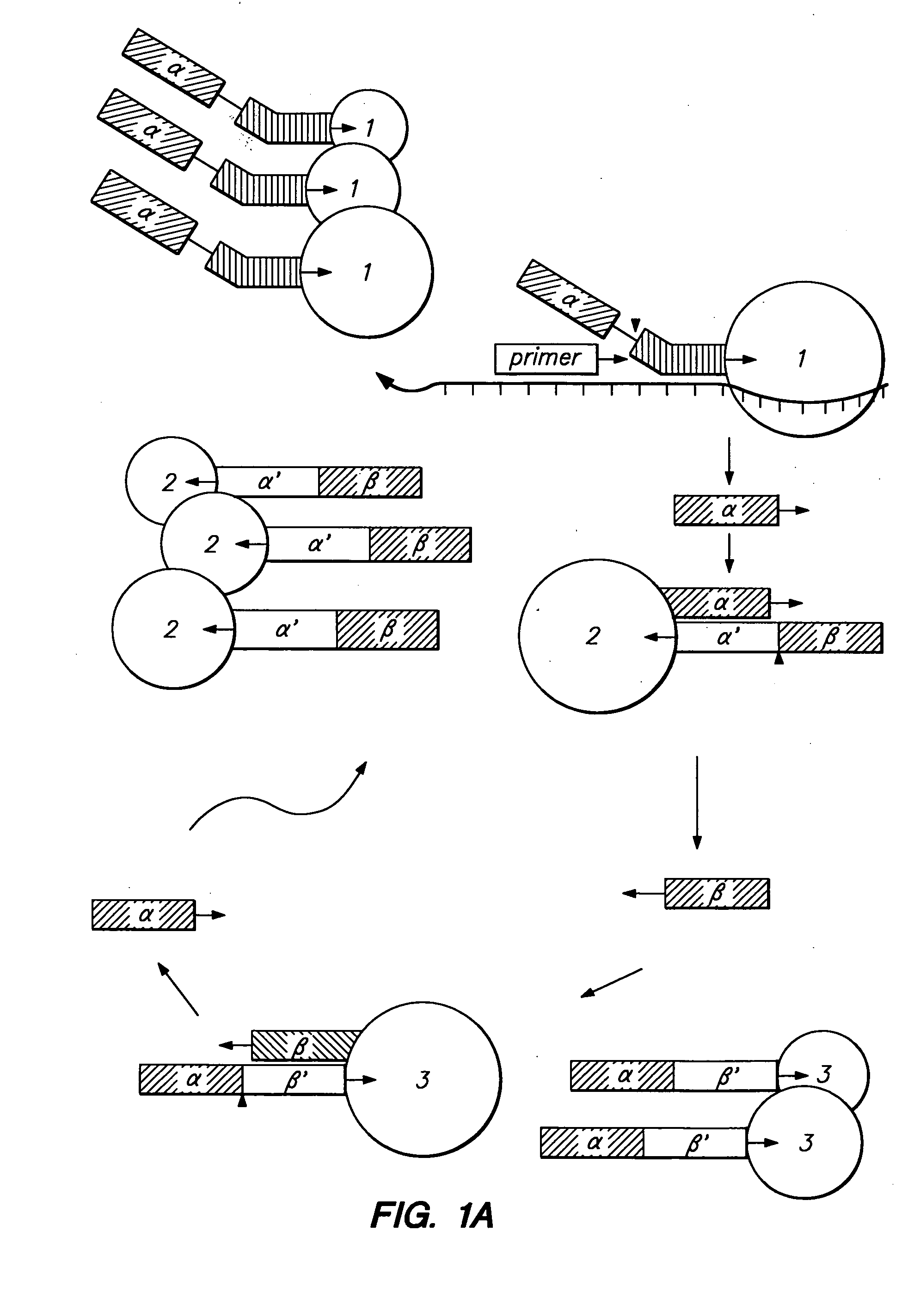
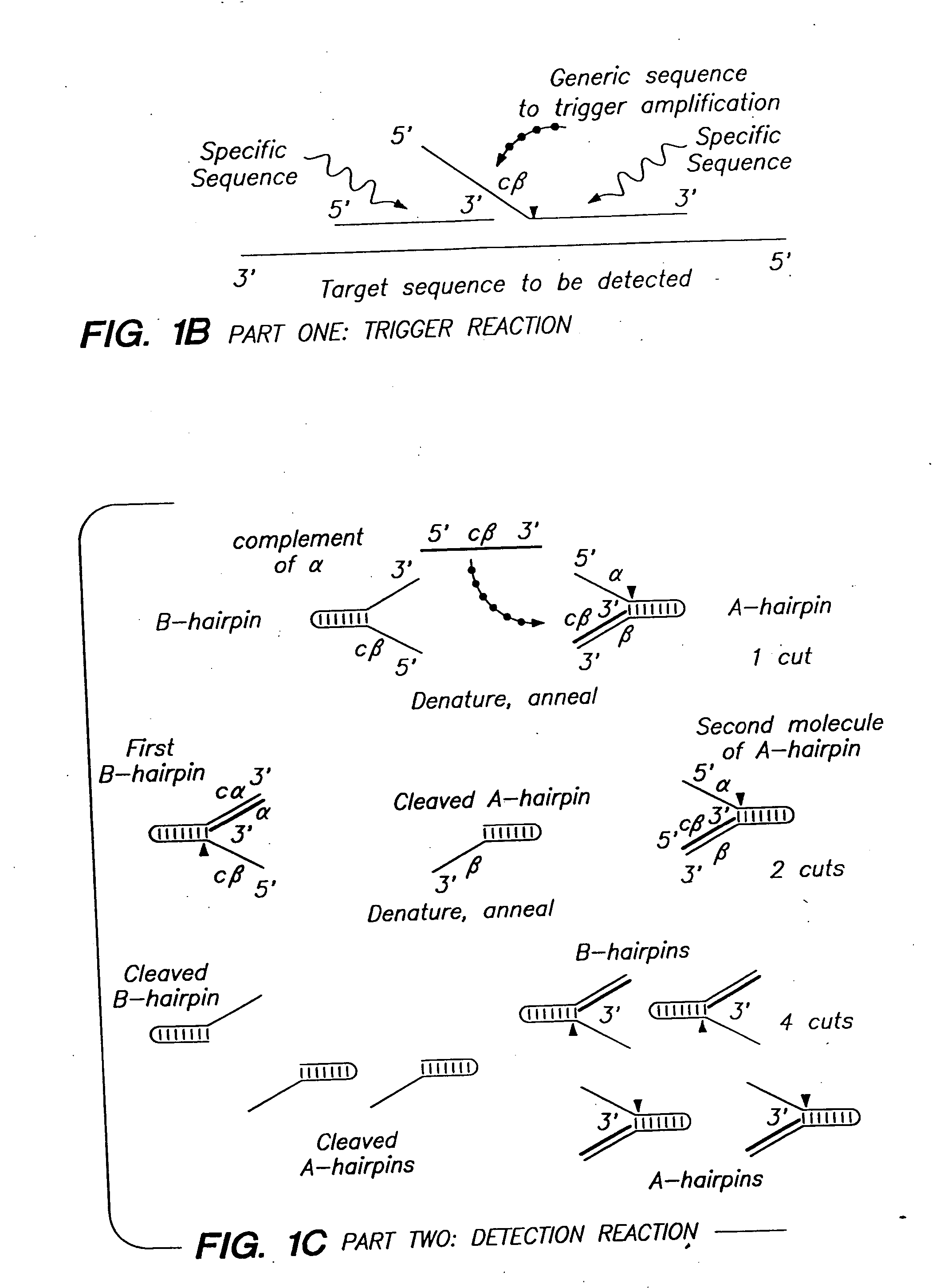
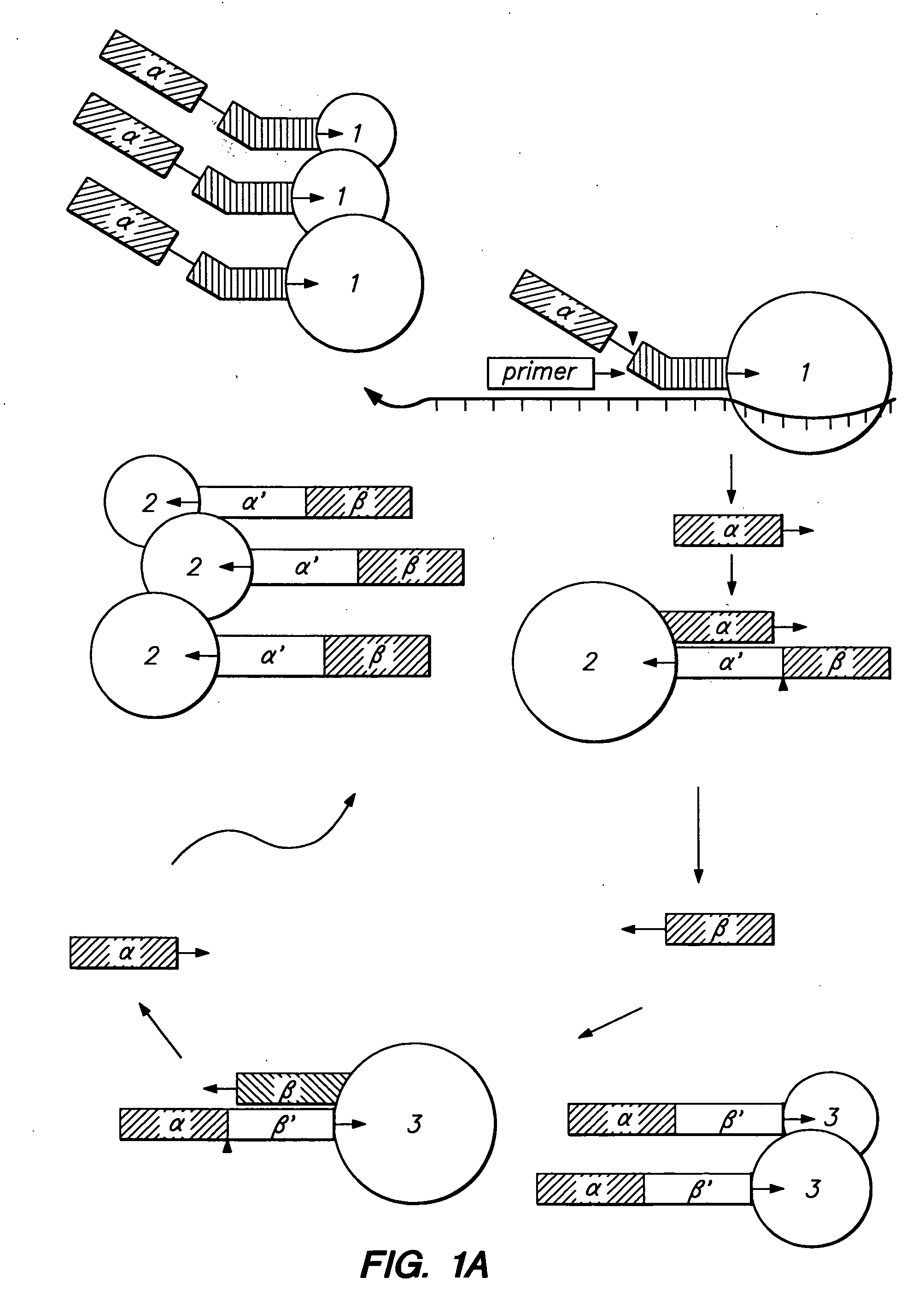
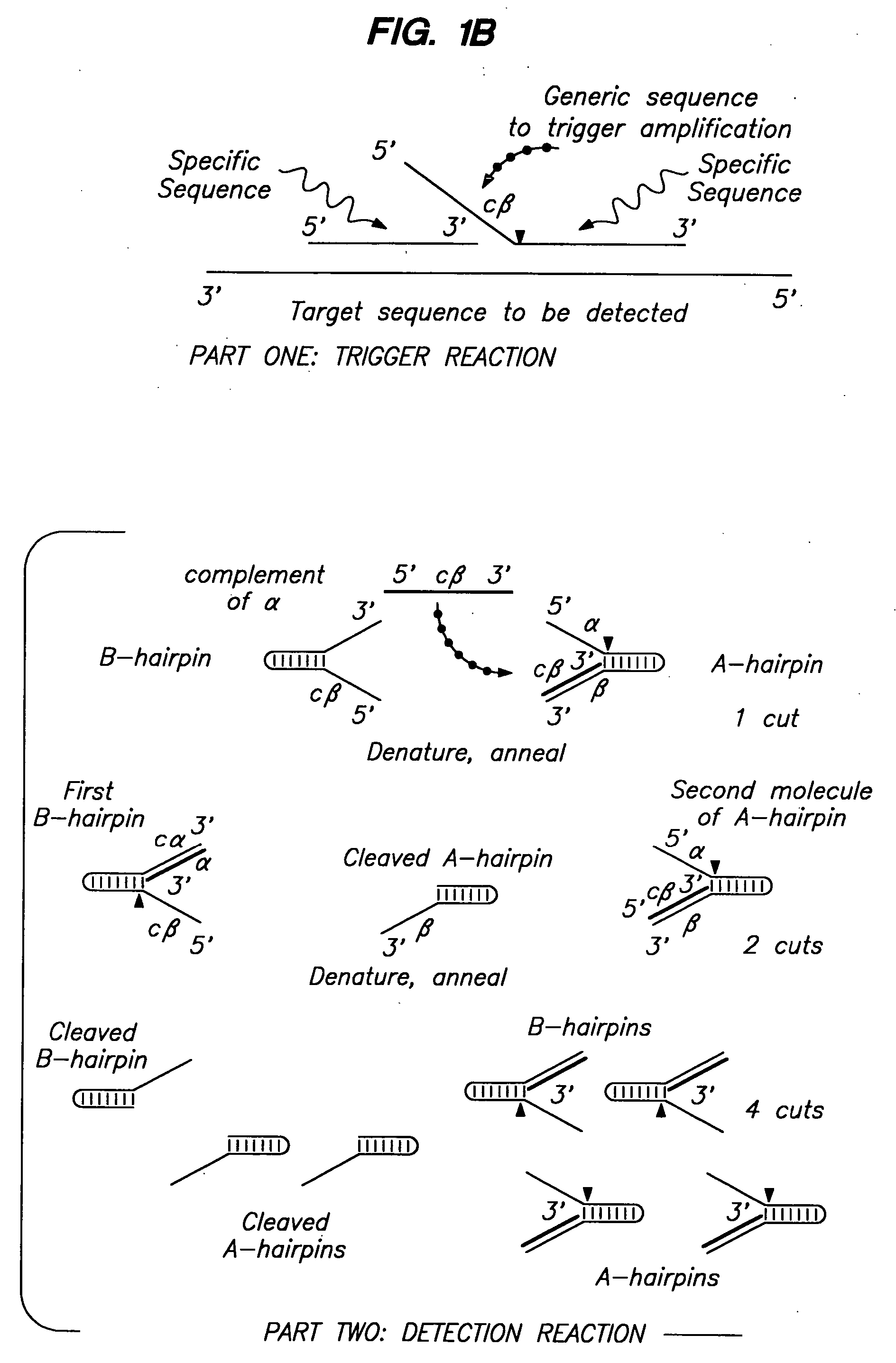
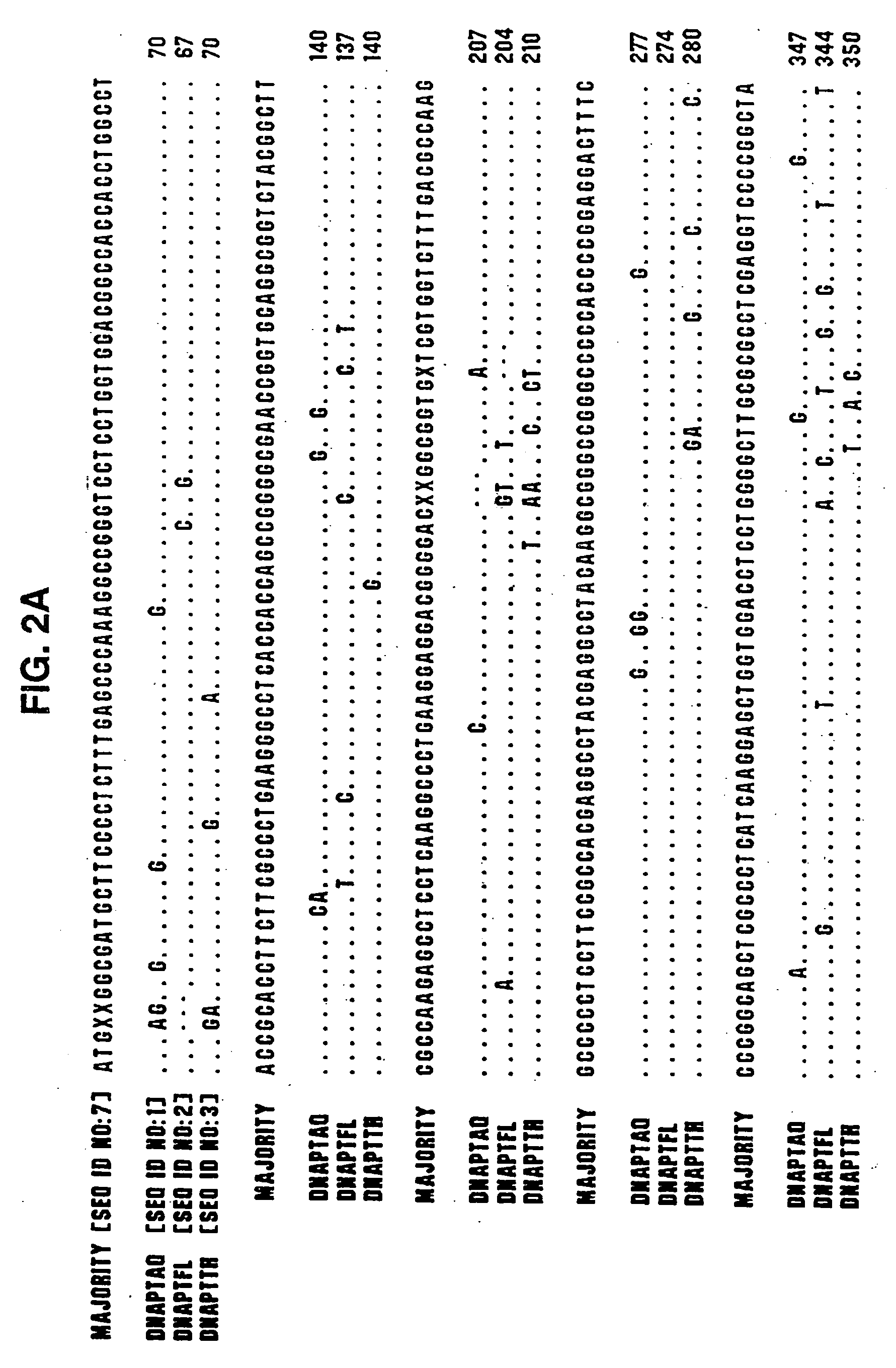
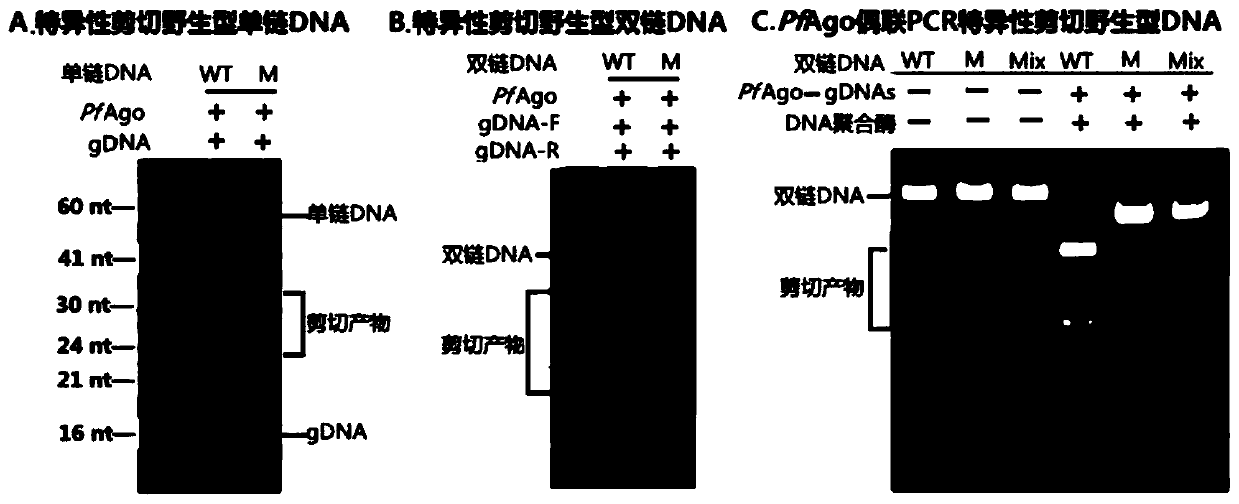
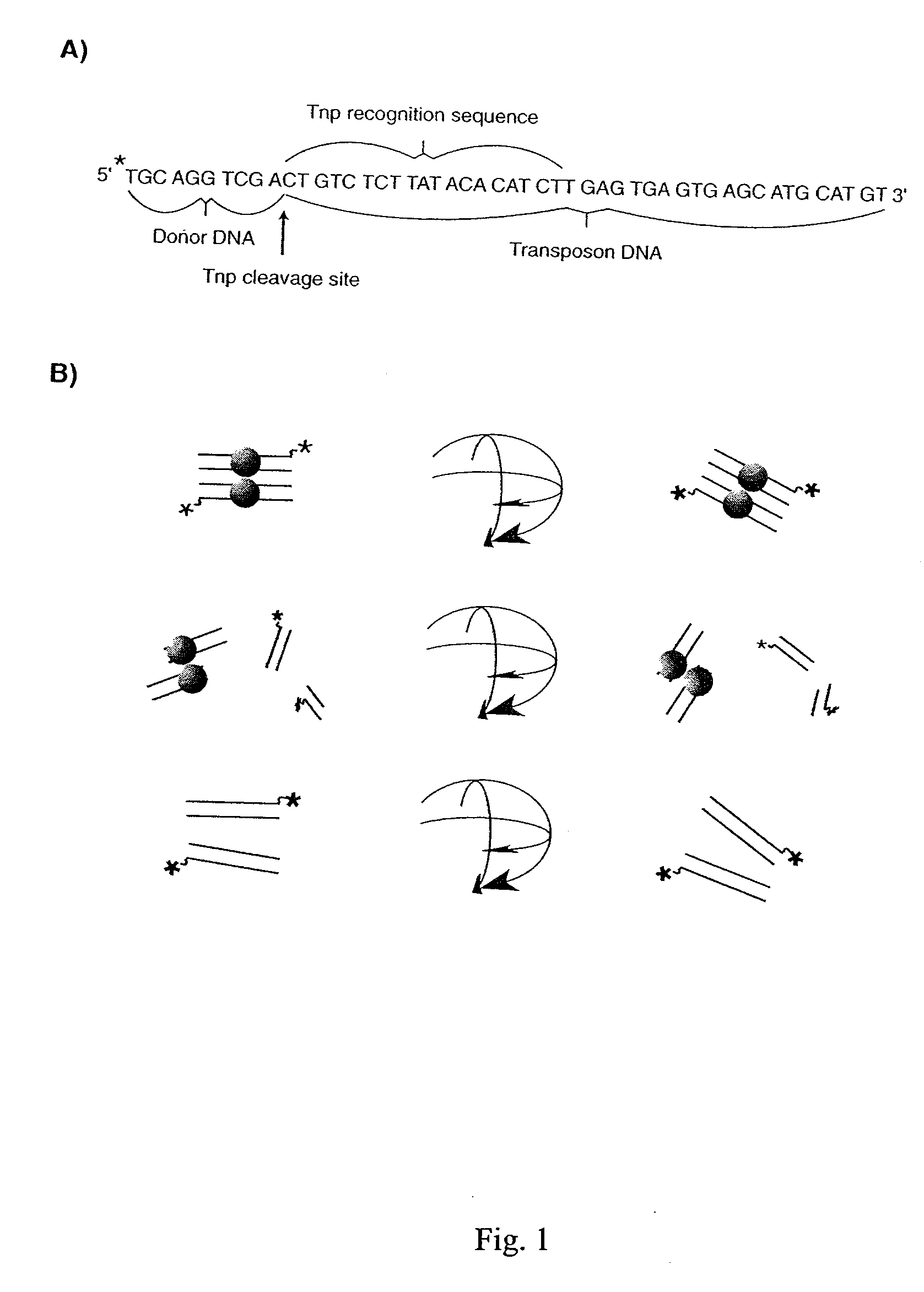Patents
Literature
64 results about "Nucleic acid cleavage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enzymes for the detection of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20030134349A1Simple structureLow detection sensitivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesA-siteA-DNA
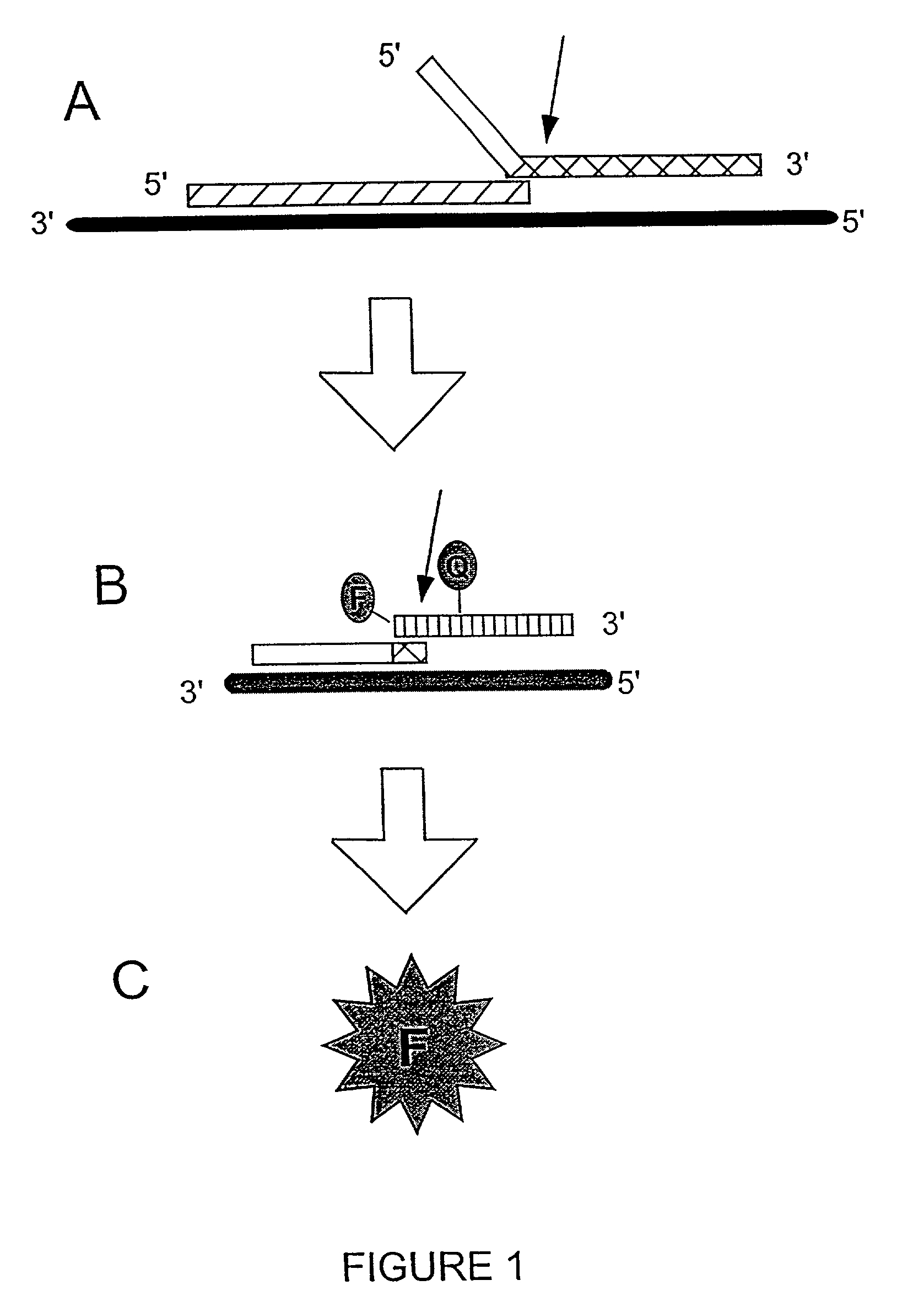
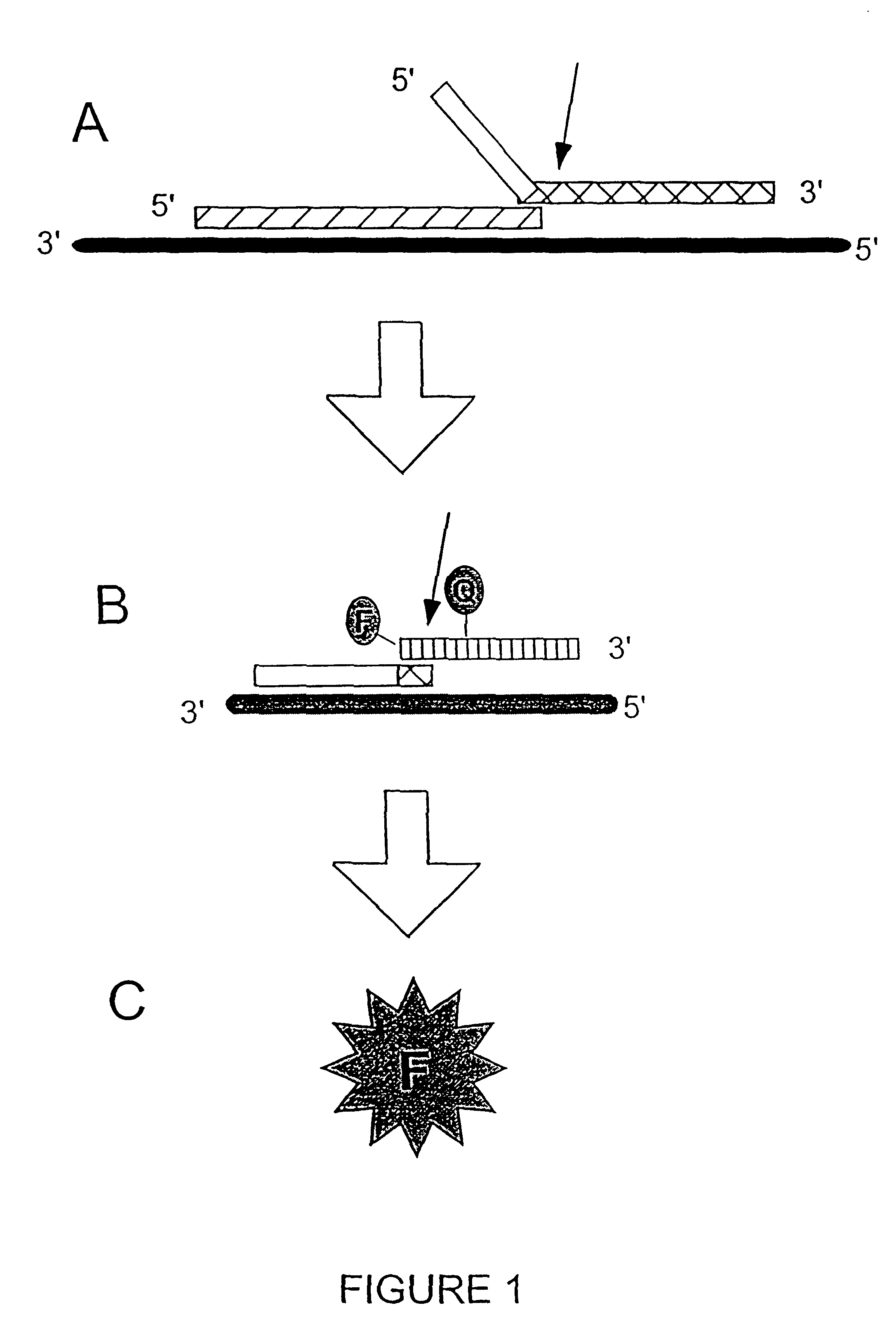
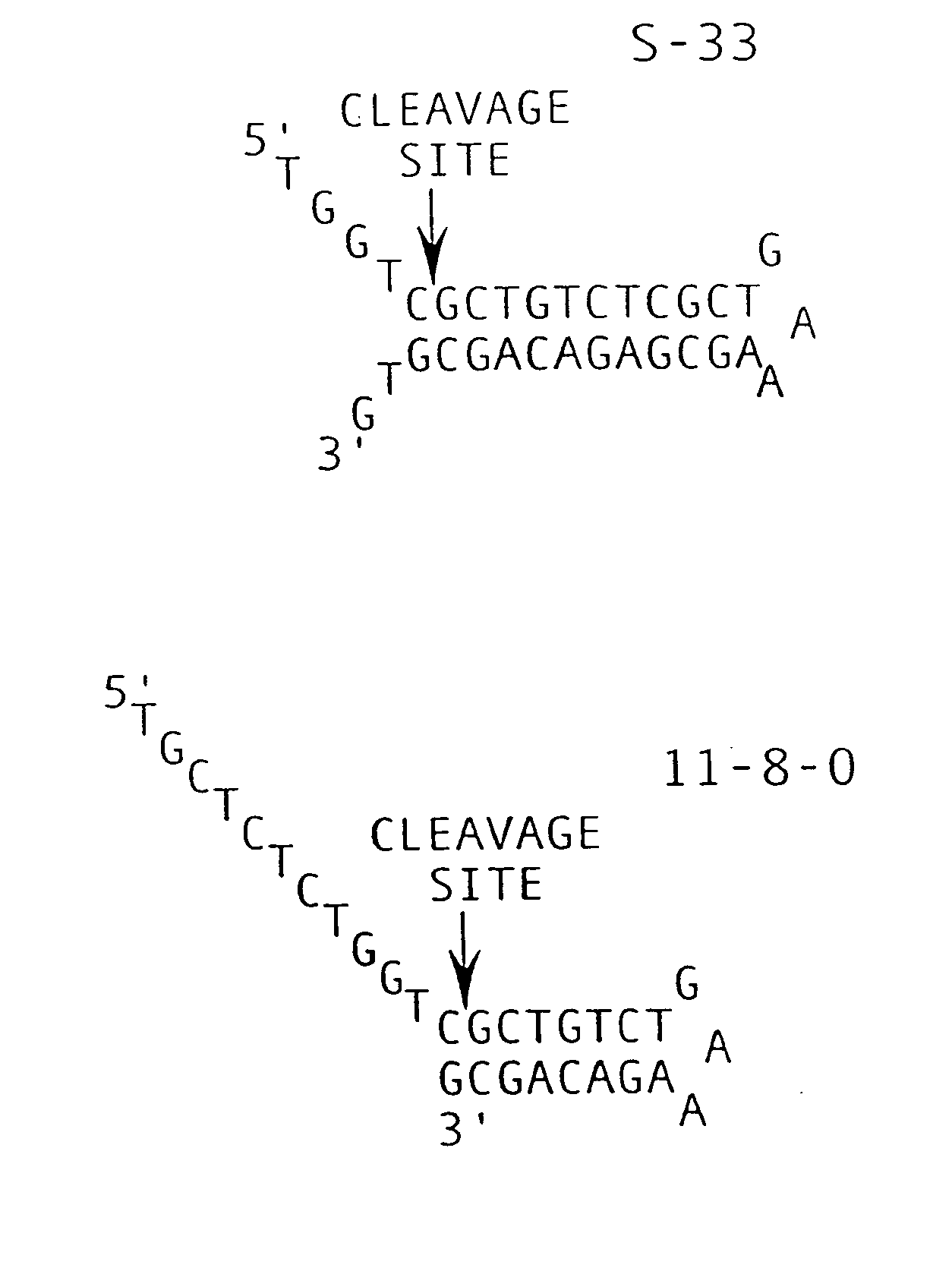
The present invention relates to novel enzymes designed for direct detection, characterization and quantitation of nucleic acids, particularly RNA. The present invention provides enzymes that recognize specific nucleic acid cleavage structures formed on a target RNA sequence and that cleave the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner to produce non-target cleavage products. The present invention provides enzymes having an improved ability to specifically cleave a DNA member of a complex comprising DNA and RNA nucleic acid strands.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Methods and compositions for detecting target sequences
InactiveUS7195871B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid cleavage
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences and variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention relates to methods for forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on a target sequence and cleaving the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. For example, in some embodiments, a 5′ nuclease activity from any of a variety of enzymes is used to cleave the target-dependent cleavage structure, thereby indicating the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences or specific variations thereof.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Enzymes for the detection of nucleic acid sequences
The present invention relates to novel enzymes designed for direct detection, characterization and quantitation of nucleic acids, particularly RNA. The present invention provides enzymes that recognize specific nucleic acid cleavage structures formed on a target RNA sequence and that cleave the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner to produce non-target cleavage products. The present invention provides enzymes having an improved ability to specifically cleave a DNA member of a complex comprising DNA and RNA nucleic acid strands.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
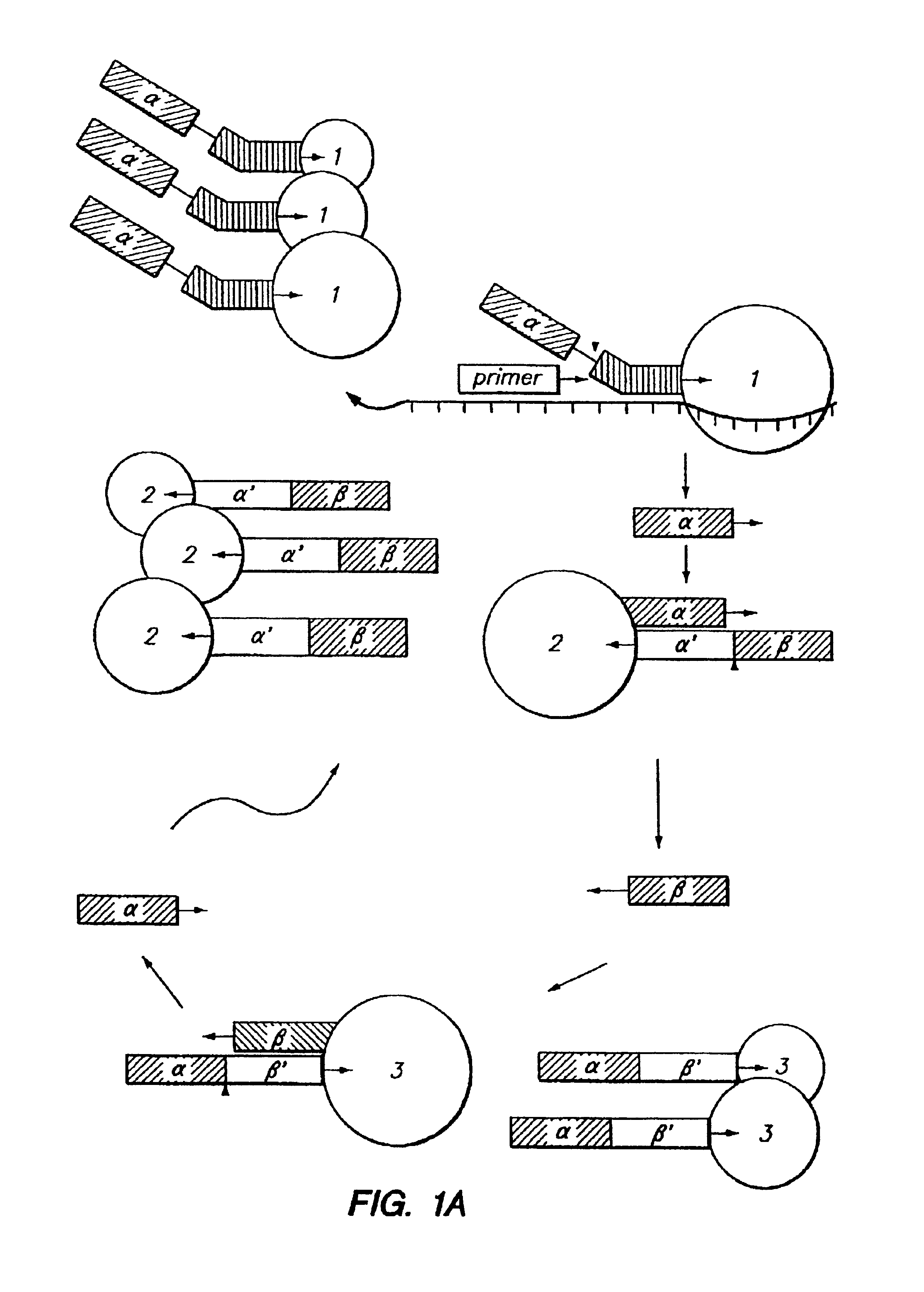
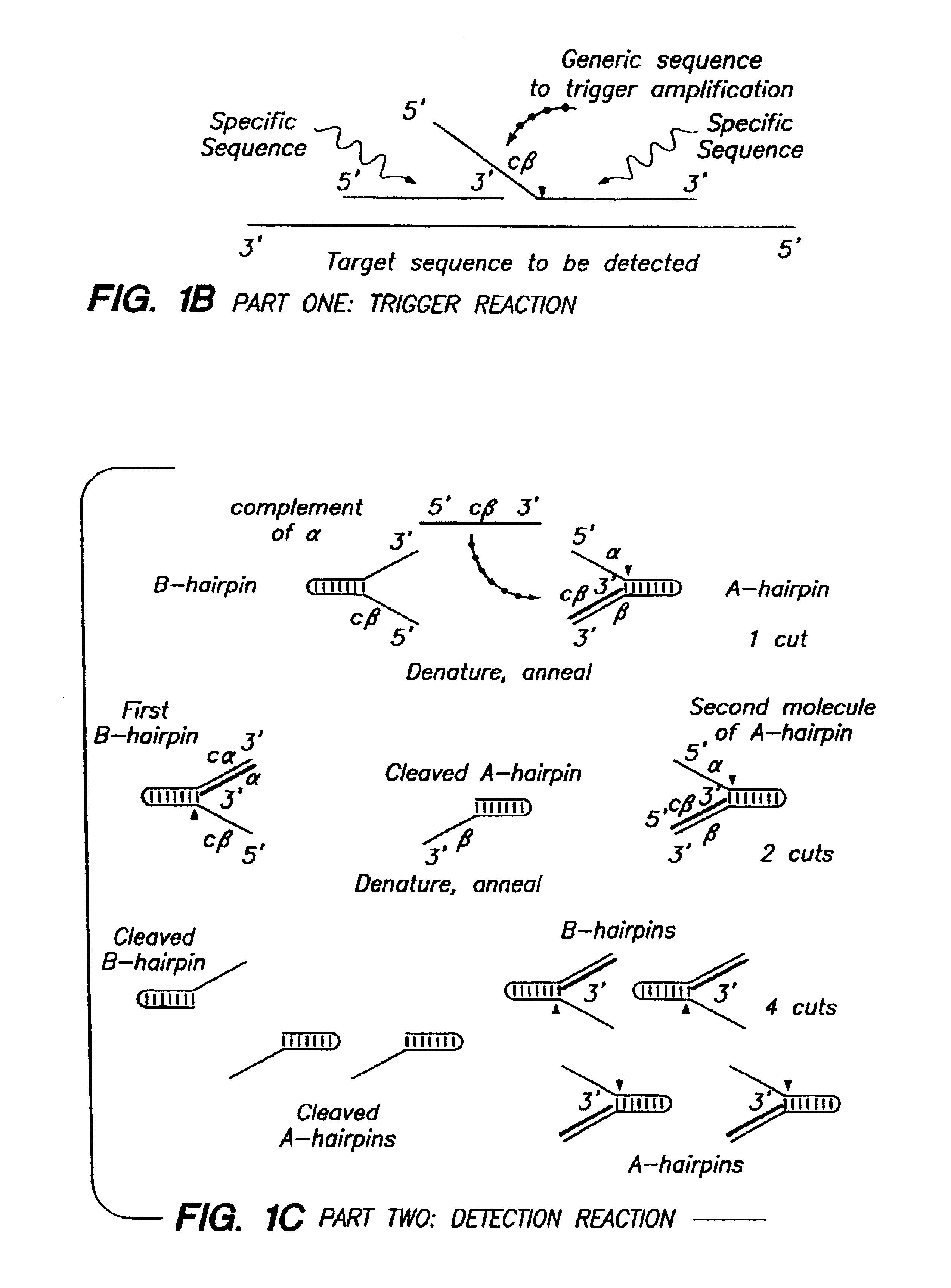
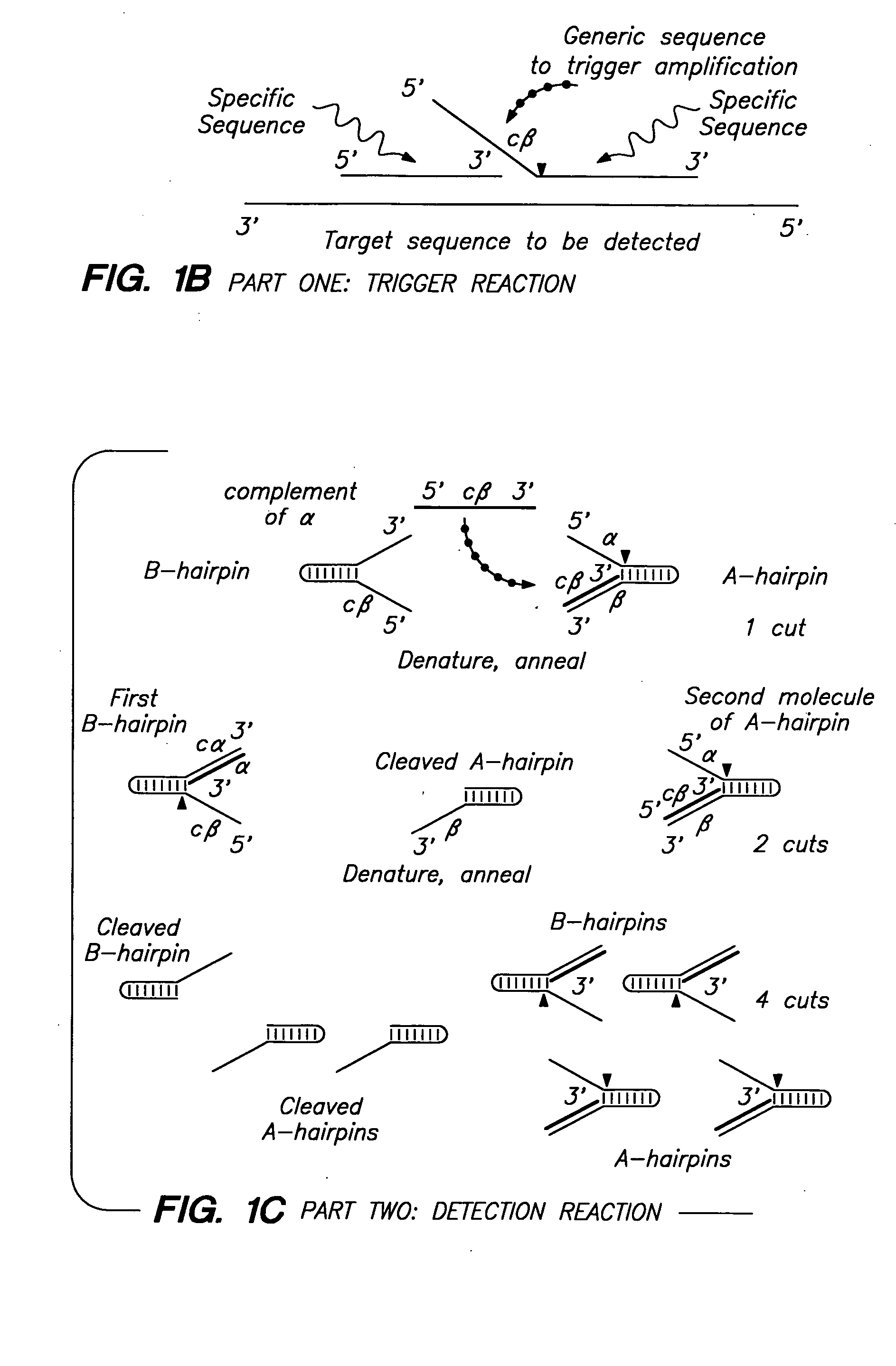
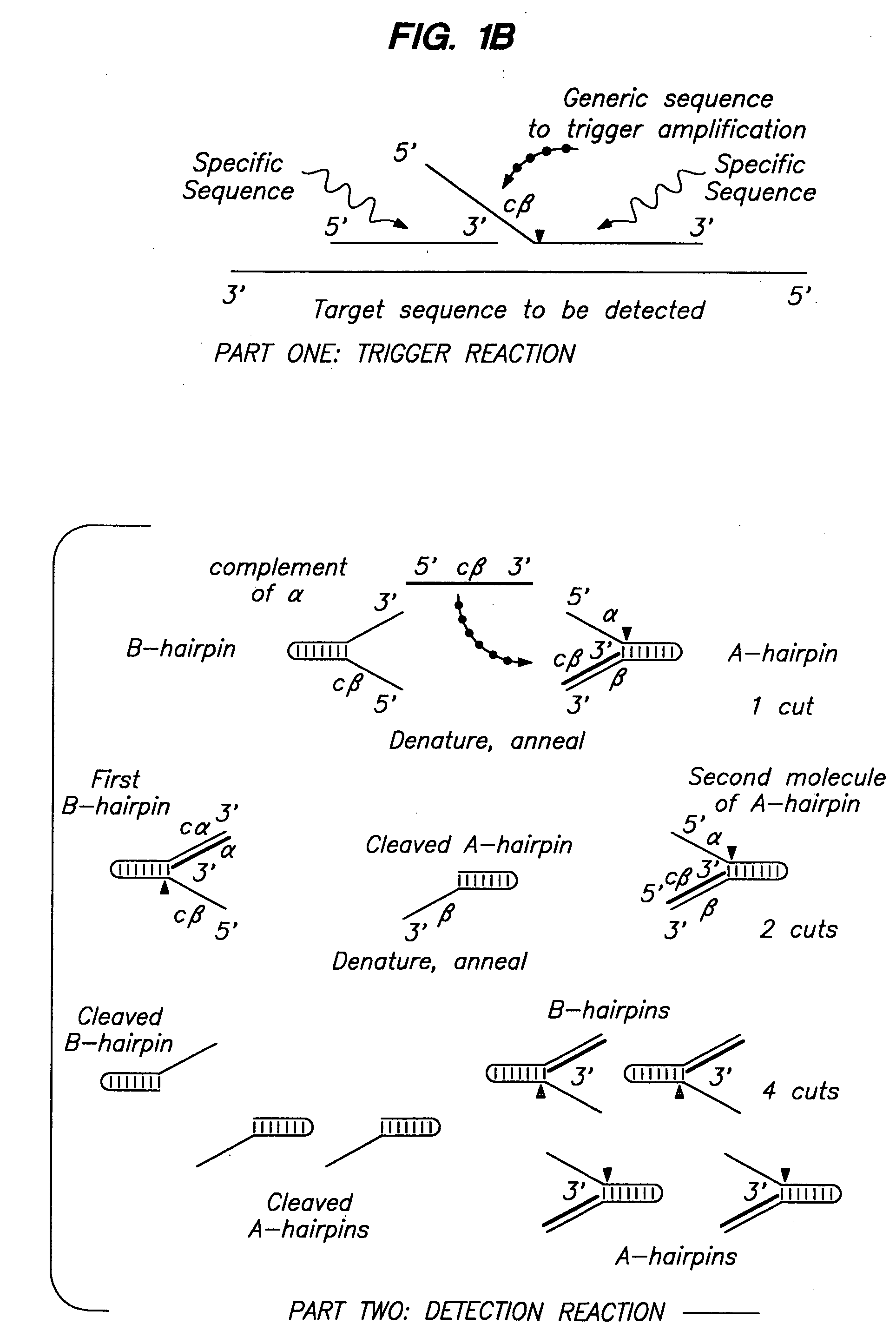
Detection of nucleic acids by multiple sequential invasive cleavages
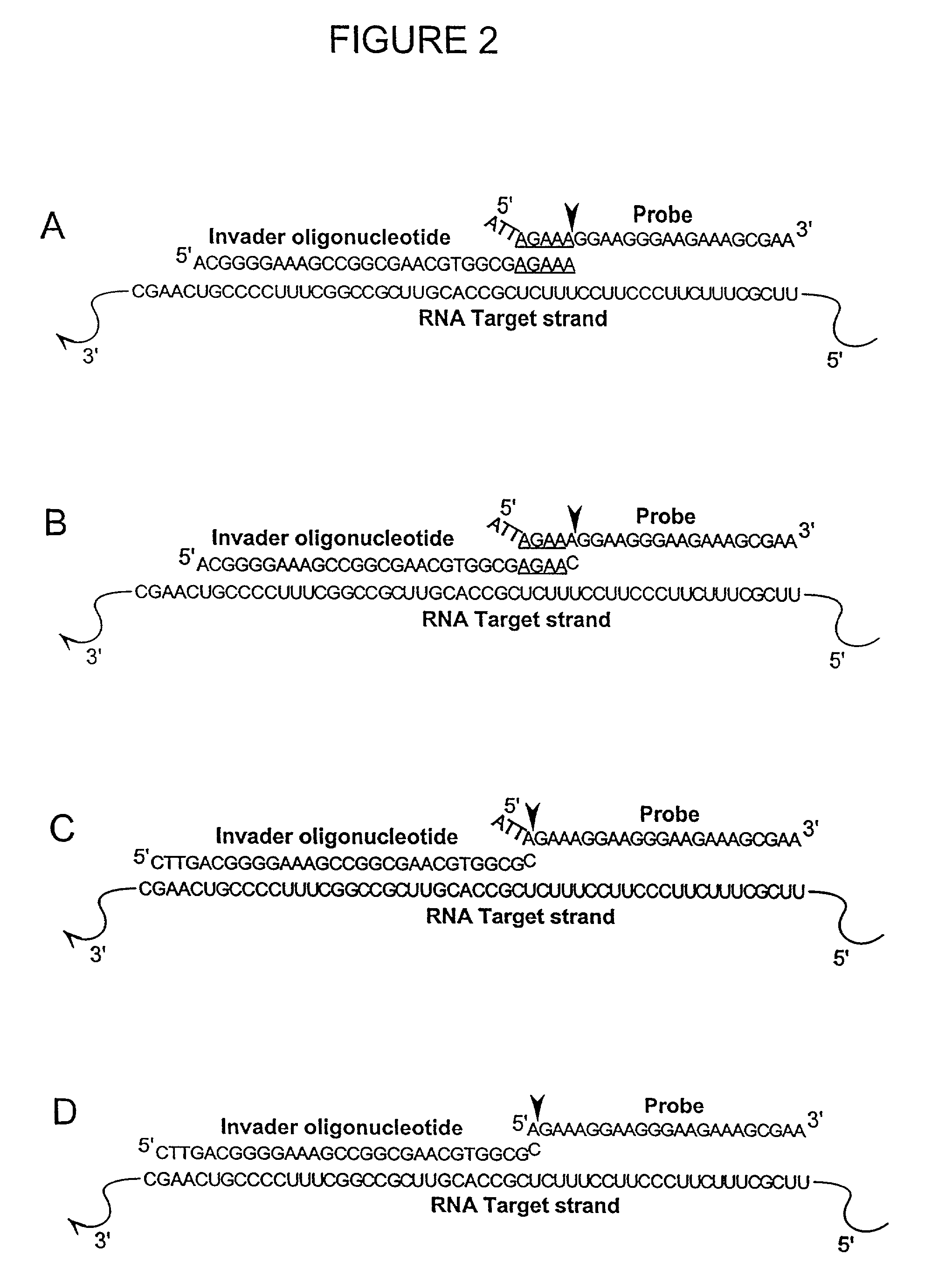
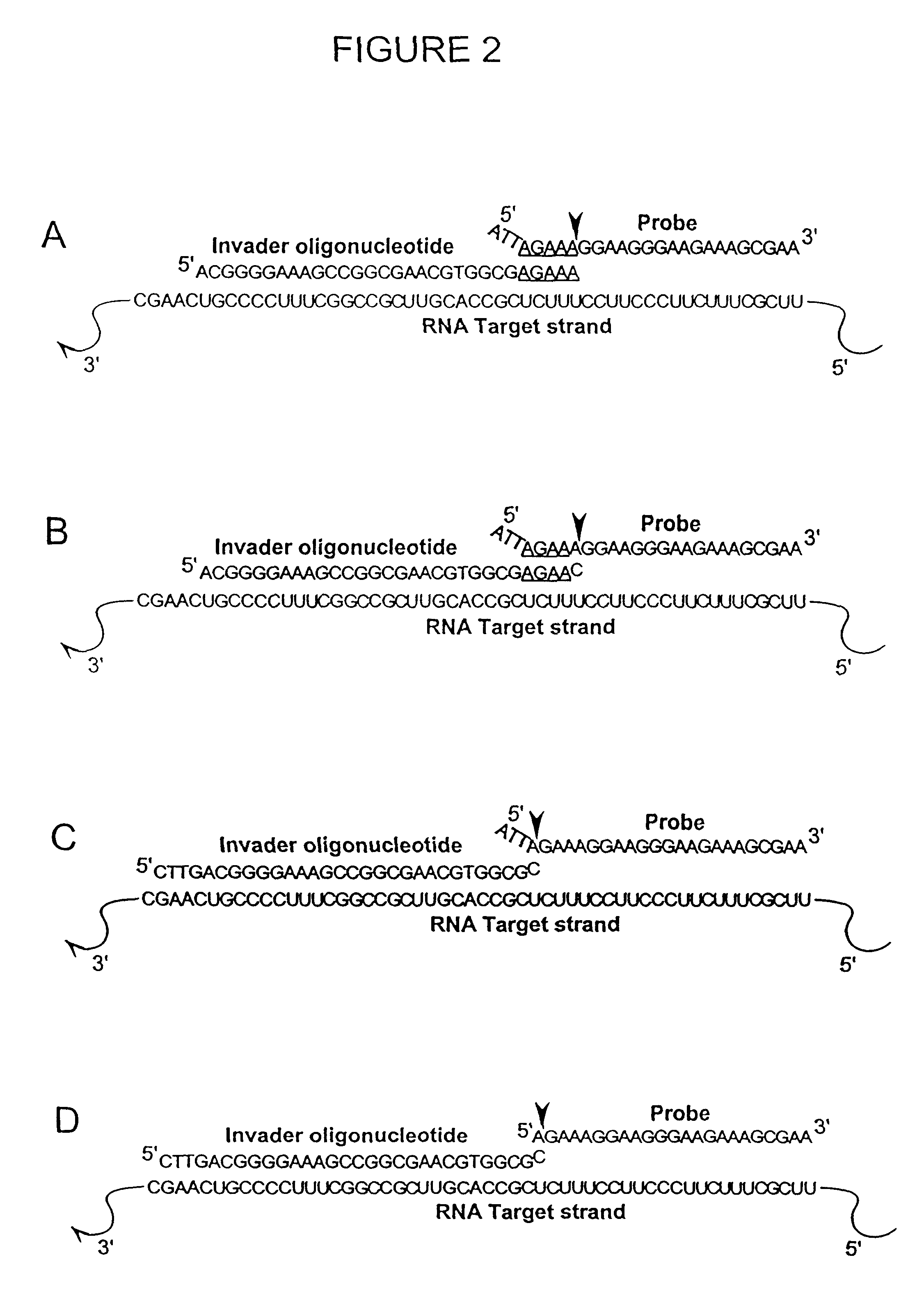
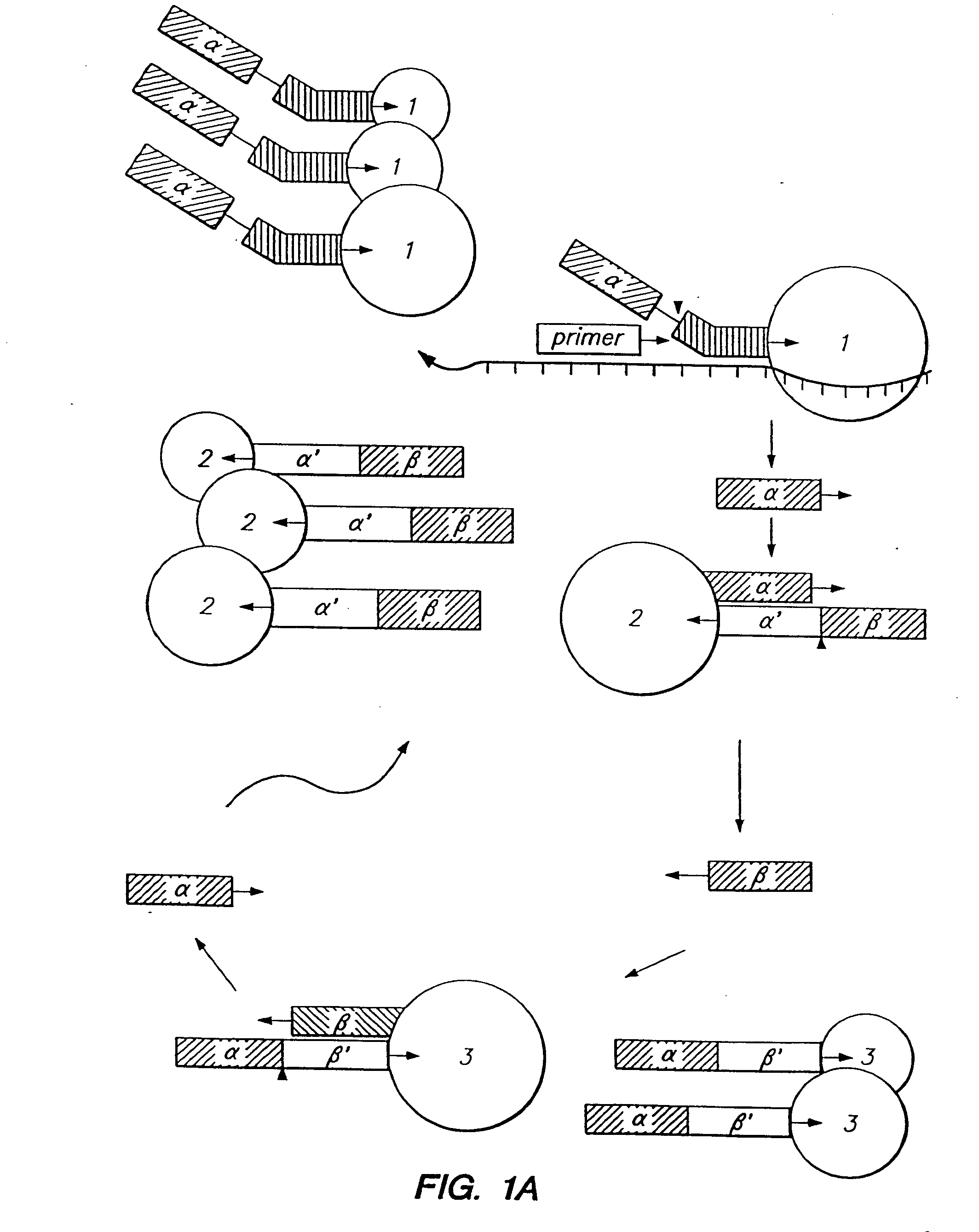
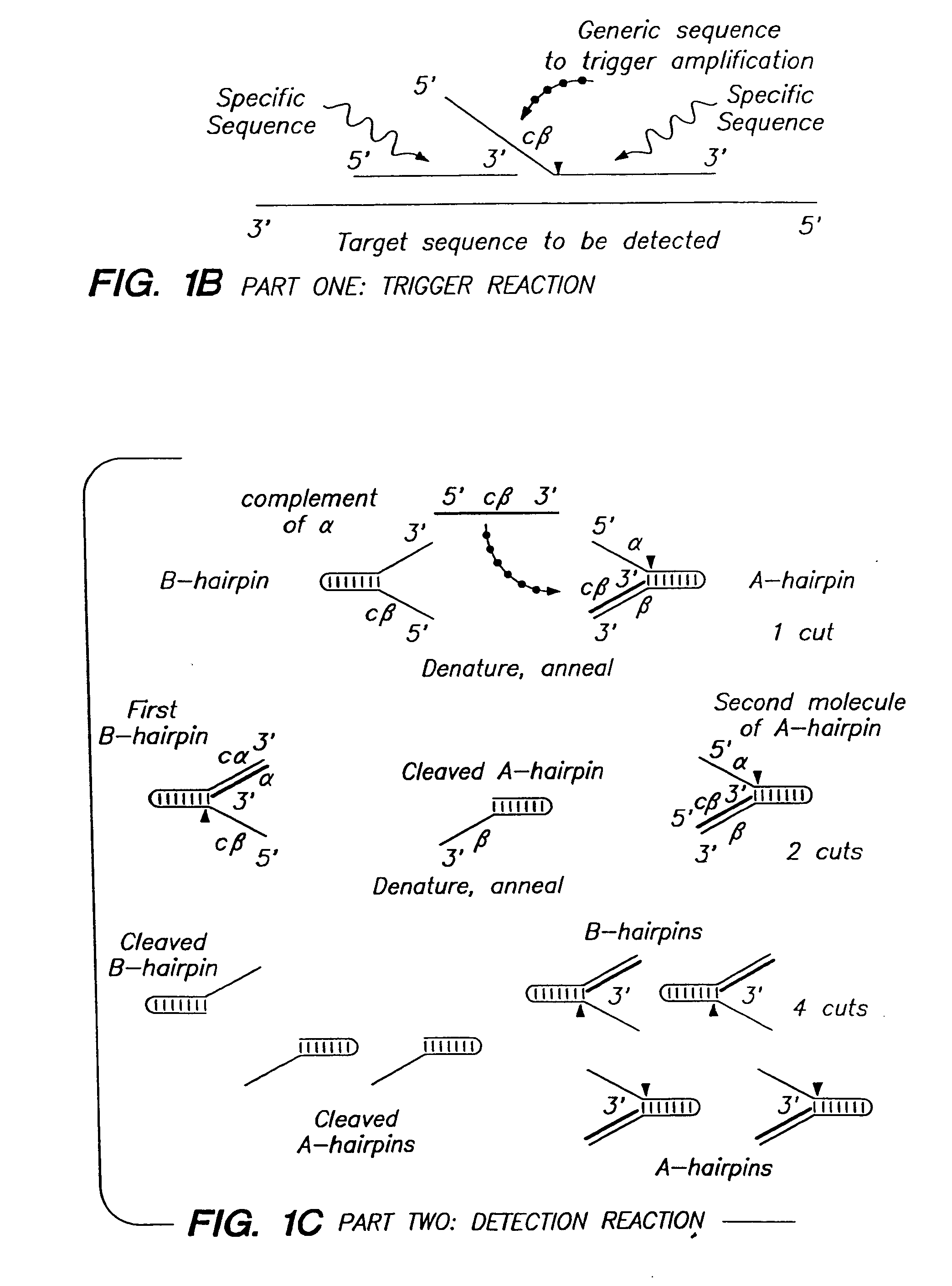
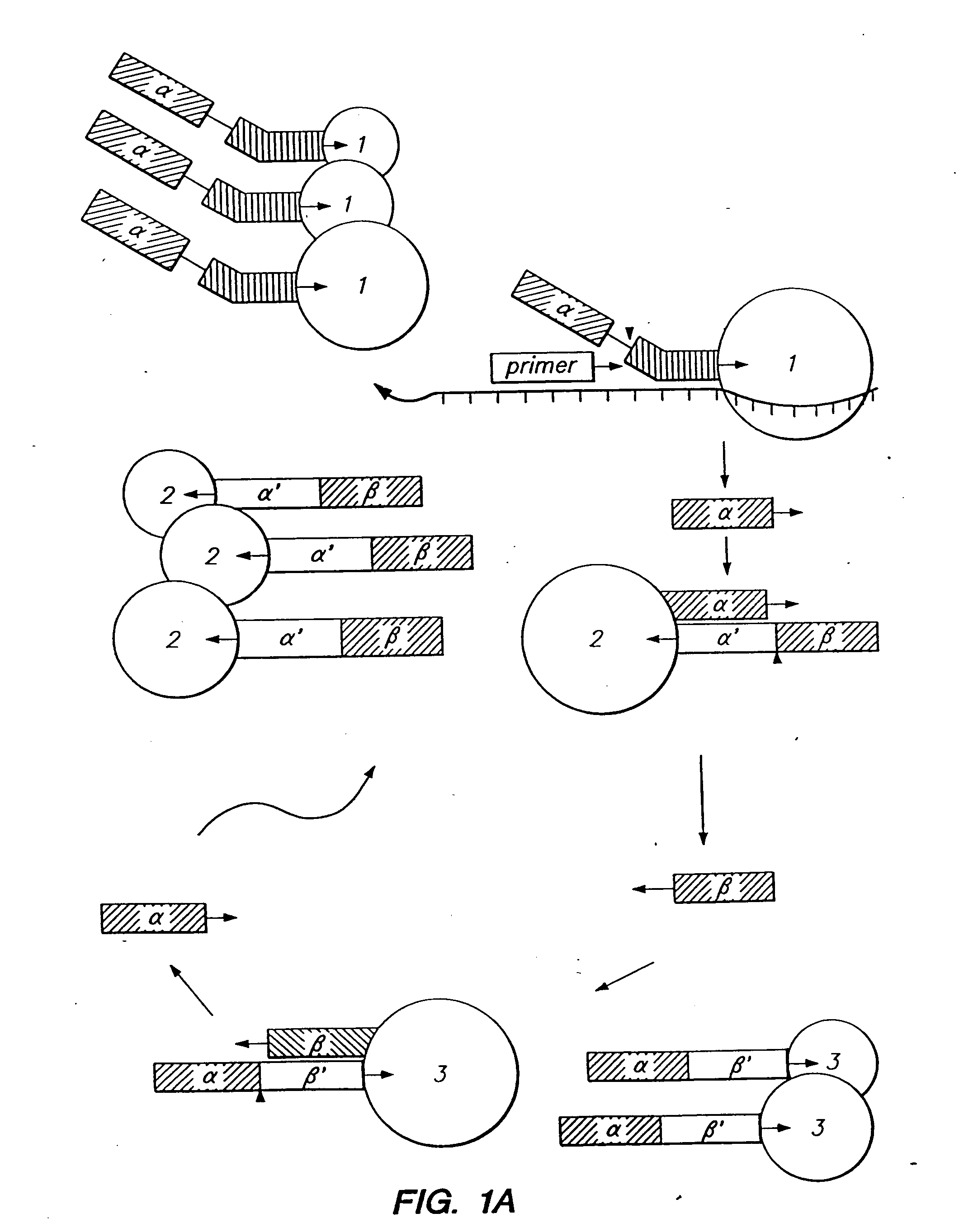
The present invention relates to means for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences, as well as variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention also relates to methods for forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on a target sequence and cleaving the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. The structure-specific nuclease activity of a variety of enzymes is used to cleave the target-dependent cleavage structure, thereby indicating the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences or specific variations thereof. The present invention further relates to methods and devices for the separation of nucleic acid molecules based on charge. The present invention also provides methods for the detection of non-target cleavage products via the formation of a complete and activated protein binding region. The invention further provides sensitive and specific methods for the detection of human cytomegalovirus nucleic acid in a sample.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Systems for the detection of target sequences
InactiveUS7067643B2Rapid detection and identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismExonuclease I
The present invention relates to means for cleaving a nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. Enzymes, including 5′ nucleases and 3′ exonucleases, are used to detect and identify nucleic acids derived from microorganisms. Methods are provided which allow for the detection and identification of bacterial and viral pathogens in a sample.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Methods and compositions for detecting target sequences
InactiveUS7256020B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid cleavage
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences and variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention relates to methods for forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on a target sequence and cleaving the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. For example, in some embodiments, a 5′ nuclease activity from any of a variety of enzymes is used to cleave the target-dependent cleavage structure, thereby indicating the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences or specific variations thereof.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Methods and Compositions for Detecting Target Sequences
InactiveUS20080160524A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesSynthetic DNANucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences and variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention relates to methods for amplifying a synthetic DNA from a target nucleic acid, forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on the synthetic DNA, and detecting cleavage of the nucleic acid cleavage structure as an indicator of the preset of the target nucleic acid.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Kits for detection of nucleic acids by invasive cleavage
InactiveUS7381530B2HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid cleavage
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Methods and Compositions for Detecting Target Sequences
InactiveUS20080220425A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsSynthetic DNANucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences and variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention relates to methods for amplifying a synthetic DNA from a target nucleic acid, forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on the synthetic DNA, and detecting cleavage of the nucleic acid cleavage structure as an indicator of the preset of the target nucleic acid.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Reactions on a solid surface
InactiveUS20050164177A1Improve performanceA large amountBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid cleavage
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences and variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention relates to methods for forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on a solid support and cleaving the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. For example, in some embodiments, a 5′ nuclease activity from any of a variety of enzymes is used to cleave the target-dependent cleavage structure, thereby indicating the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences or specific variations thereof.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Nucleic acid detection kits
InactiveUS20050158716A1Quick checkQuick identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismNucleic acid detection
The present invention relates to means for cleaving a nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. Enzymes, including 5′ nucleases and 3′ exonucleases, are used to detect and identify nucleic acids derived from microorganisms. Methods are provided which allow for the detection and identification of bacterial and viral pathogens in a sample.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
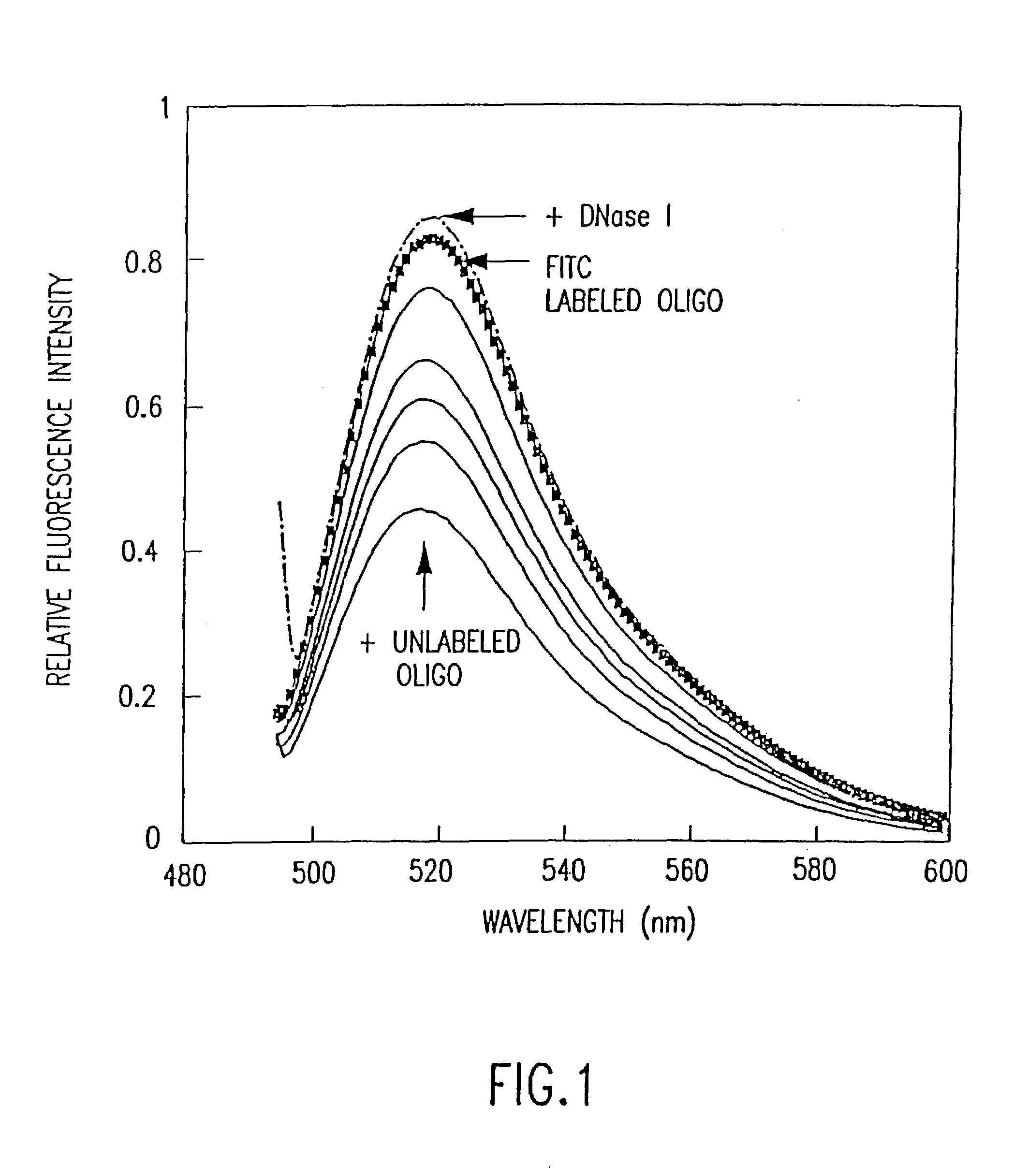
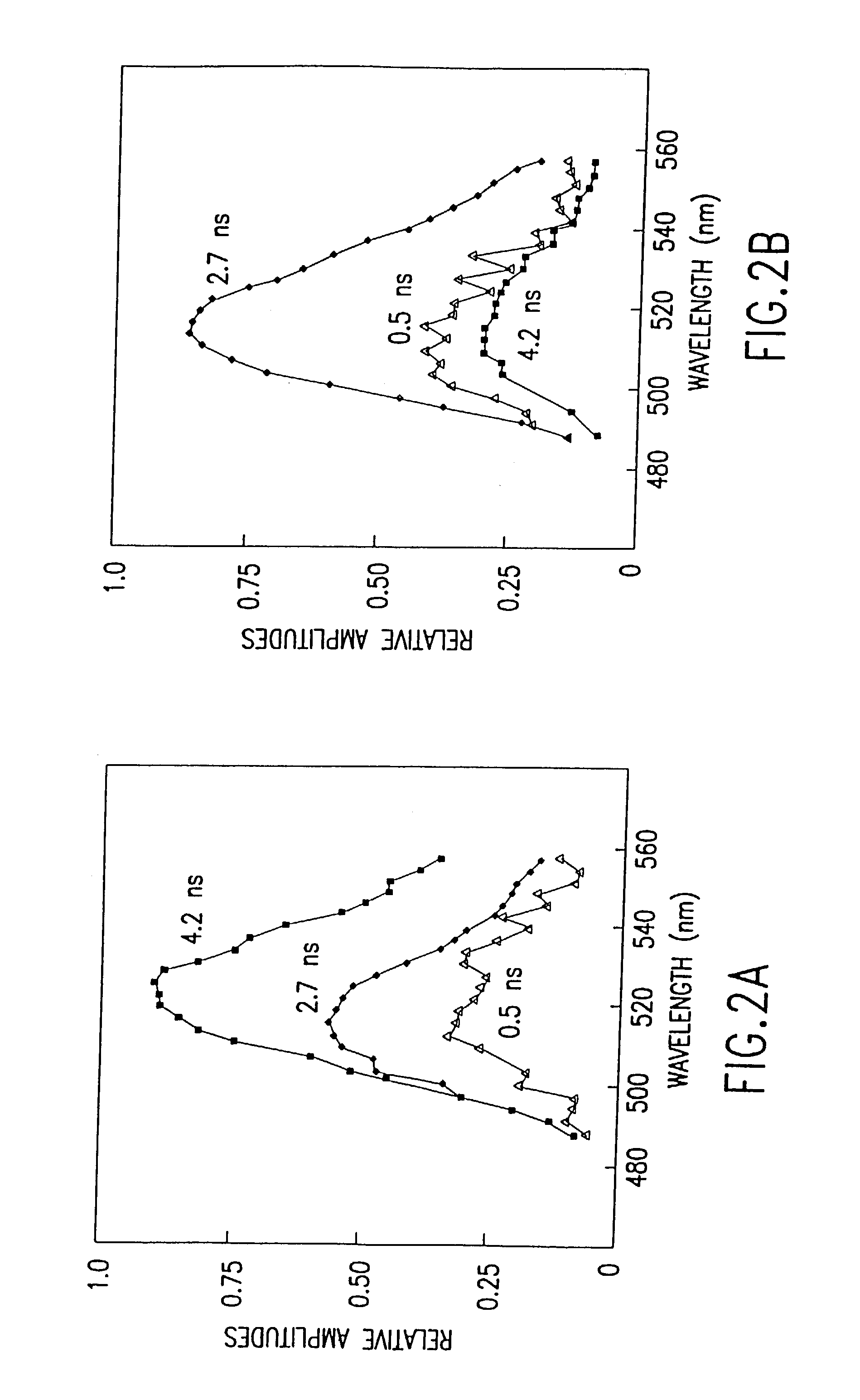
Fluorometric assay for detecting nucleic acid cleavage
A method of detecting an enzyme-mediated DNA cleavage reaction in a fluorometric assay is provided. The method can be used to detect DNA cleavage caused by restriction endonucleases, retroviral integrase enzymes, DNases, RNases, or enzymes utilized in other strand separating processes in molecular biology.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Cleavage of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20060035256A1Rapid detection and identificationHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismNucleic acid cleavage
The present invention relates to means for cleaving a nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. Enzymes, including 5′ nucleases and 3′ exonucleases, are used to detect and identify nucleic acids derived from microorganisms. Methods are provided which allow for the detection and identification of bacterial and viral pathogens in a sample.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Nucleic acid detection compositions
The present invention relates to means for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences, as well as variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention also relates to methods for forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on a target sequence and cleaving the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. The structure-specific nuclease activity of a variety of enzymes is used to cleave the target-dependent cleavage structure, thereby indicating the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences or specific variations thereof.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Cleavage of nucleic acids
The present invention relates to means for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences, as well as variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention also relates to methods for forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on a target sequence and cleaving the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. The structure-specific nuclease activity of a variety of enzymes is used to cleave the target-dependent cleavage structure, thereby indicating the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences or specific variations thereof.
Owner:PRUDENT JAMES +4
Cleavage of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20060040299A1Rapid detection and identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesMicroorganismNucleic acid cleavage
The present invention relates to means for cleaving a nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. Enzymes, including 5′ nucleases and 3′ exonucleases, are used to detect and identify nucleic acids derived from microorganisms. Methods are provided which allow for the detection and identification of bacterial and viral pathogens in a sample.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Modulators of enzymatic nucleic acid elements mobilization
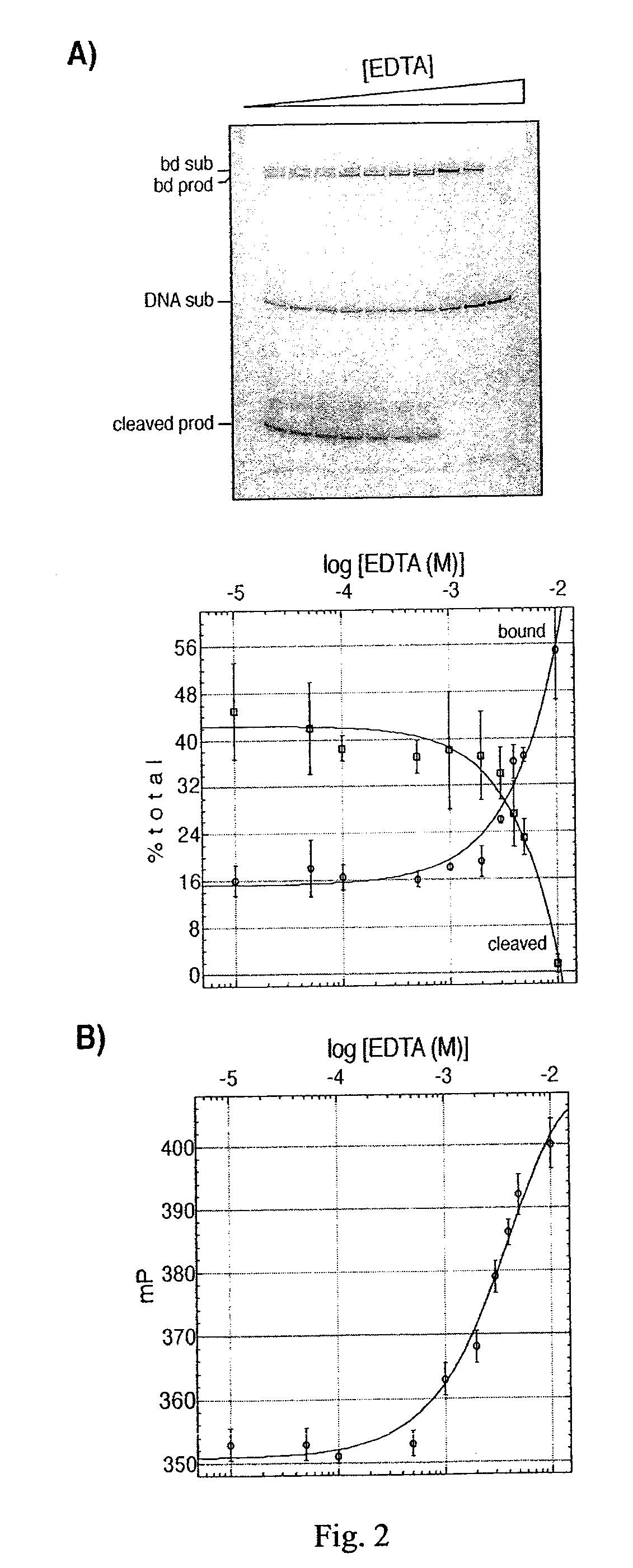
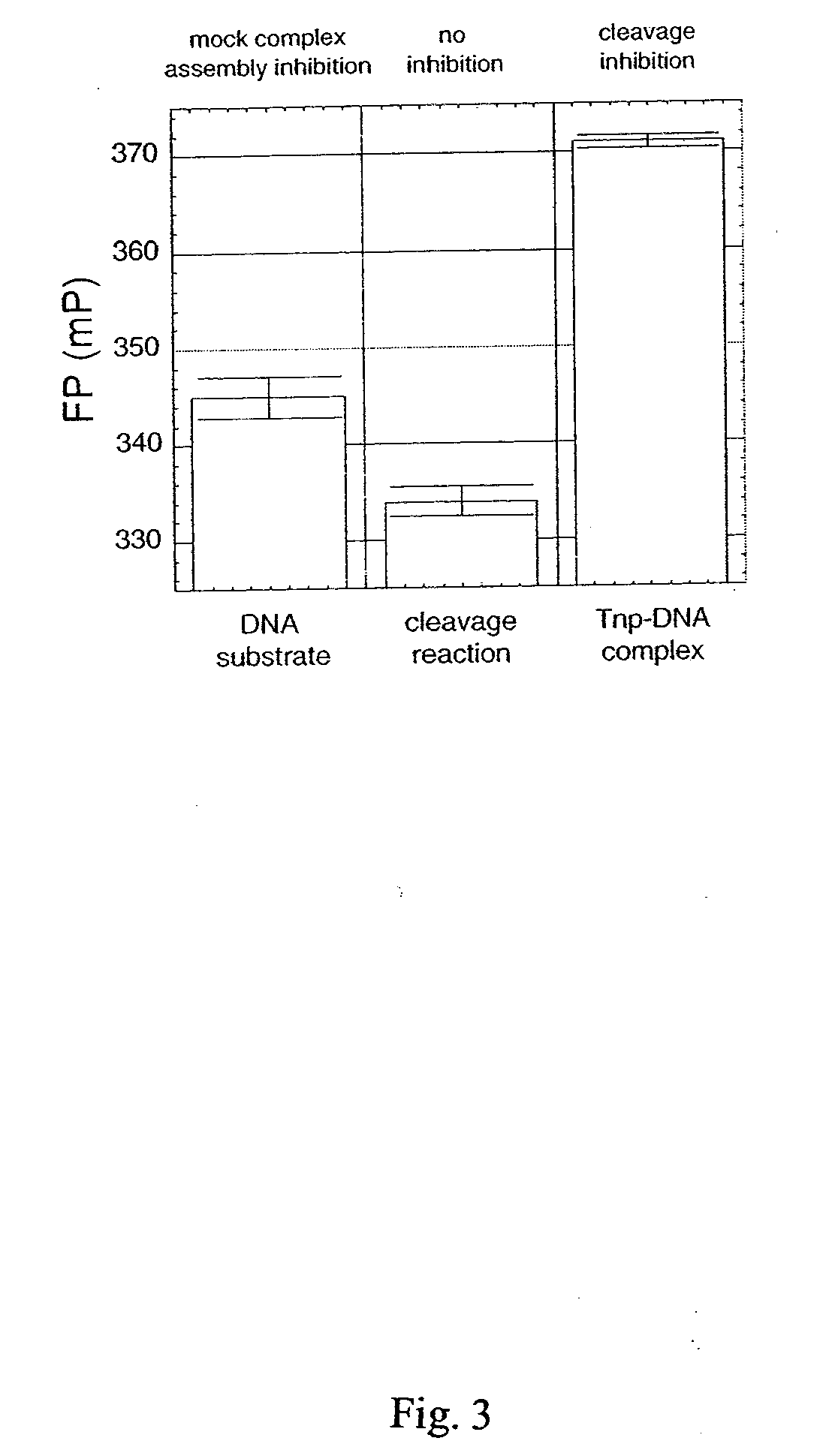
The present invention discloses a nucleic acid cleavage assay for members of the transposase / integrase superfamily. A method of using the assay to screen for modulators of the nucleic acid cleavage activity is also disclosed. The present invention further provides a method for screening for modulators of binding of a transposase / integrase to its corresponding recognition sequence. In addition, the present invention provides a method of identifying a modulator for a particular transposase / integrase such as HIV integrase based on modulators of other members of the transposase / integrase superfamily. Also disclosed are Tn5 transposase inhibitors and HIV integration inhibitors.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cleavage of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20060035257A1Quick checkQuick identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismExonuclease I
The present invention relates to means for cleaving a nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. Enzymes, including 5′ nucleases and 3′ exonucleases, are used to detect and identify nucleic acids derived from microorganisms. Methods are provided which allow for the detection and identification of bacterial and viral pathogens in a sample.
Owner:DAHLBERG JAMES +2
A method for fast nucleic acid extraction
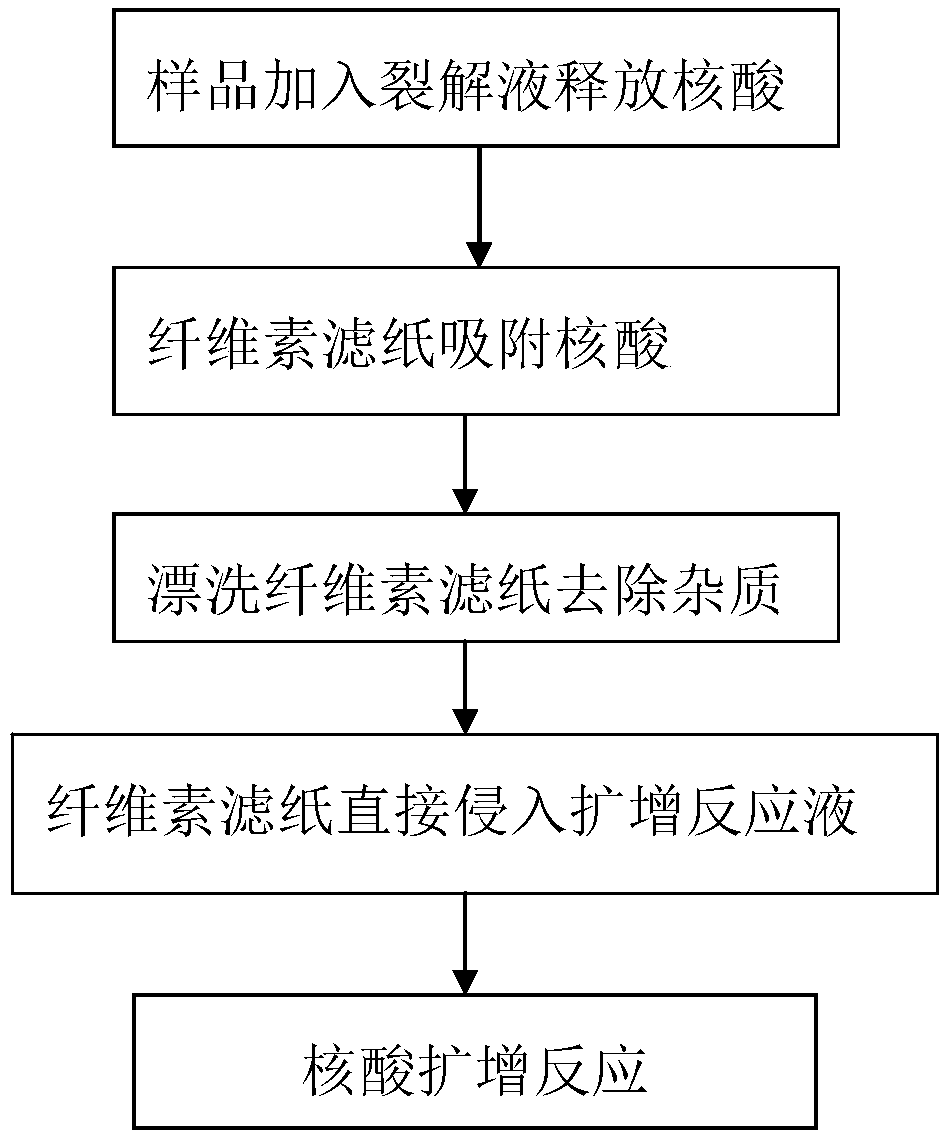
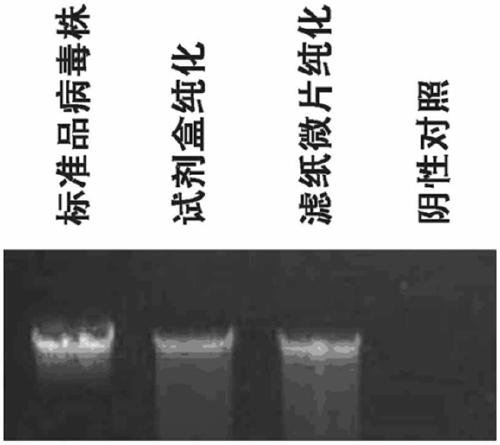
InactiveCN109207475AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationCelluloseNucleic acid amplification technique
A method for extract nucleic acid includes such step as cracking nucleic acid sample, adding sample containing nucleic acid to cracking solution to form nucleic acid cracking solution, cracking nucleic acid sample to form nucleic acid cracking solution, cracking nucleic acid sample to obtain nucleic acid sample, cracking nucleic acid sample to obtain nucleic acid sample, cracking nucleic acid sample to obtain nucleic acid sample, cracking nucleic acid sample to obtain nucleic acid sample, cracking nucleic acid sample to obtain nucleic acid sample, cracking nucleic acid sample to obtain nucleicacid sample. 2, adsorb nucleic acid: adding that carry into the nucleic acid cleavage solution to obtain a carrier for adsorbing nucleic acid; 3, remove impurities: rin that carrier adsorbed with nucleic acid in a rinsing solution to remove impurities other than nucleic acid; 4, amplification reaction, wherein that rinse carrier adsorb with nucleic acid is directly added into a nucleic acid amplification system for amplification reaction. The carrier is cellulose filter paper; a simple, a method for extract nucleic acid based on cellulose filt paper is disclosed. Applicable to polymerase chain reaction amplification and recombinase polymerase isothermal amplification and other nucleic acid amplification technology, suitable for operating at room temperature, suitable for biological samples from various sources, can be loaded with nucleic acid cellulose filter paper directly into the nucleic acid amplification system for amplification reaction, the whole process is less time-consuming.
Owner:博迪泰(厦门)生物科技有限公司
Detection of nuceic acids by multiple sequential invasive cleavages
InactiveUS20080268455A1Easy to quantifyLeast riskSugar derivativesBacteriaNucleic acid sequencingHuman cytomegalovirus
The present invention relates to means for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences, as well as variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention also relates to methods for forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on a target sequence and cleaving the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. The structure-specific nuclease activity of a variety of enzymes is used to cleave the target-dependent cleavage structure, thereby indicating the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences or specific variations thereof. The present invention further relates to methods and devices for the separation of nucleic acid molecules based on charge. The present invention also provides methods for the detection of non-target cleavage products via the formation of a complete and activated protein binding region. The invention further provides sensitive and specific methods for the detection of human cytomegalovirus nucleic acid in a sample.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Detection technical system for enriching low-abundance DNA mutation based on nuclease-coupled PCR principle and application thereof
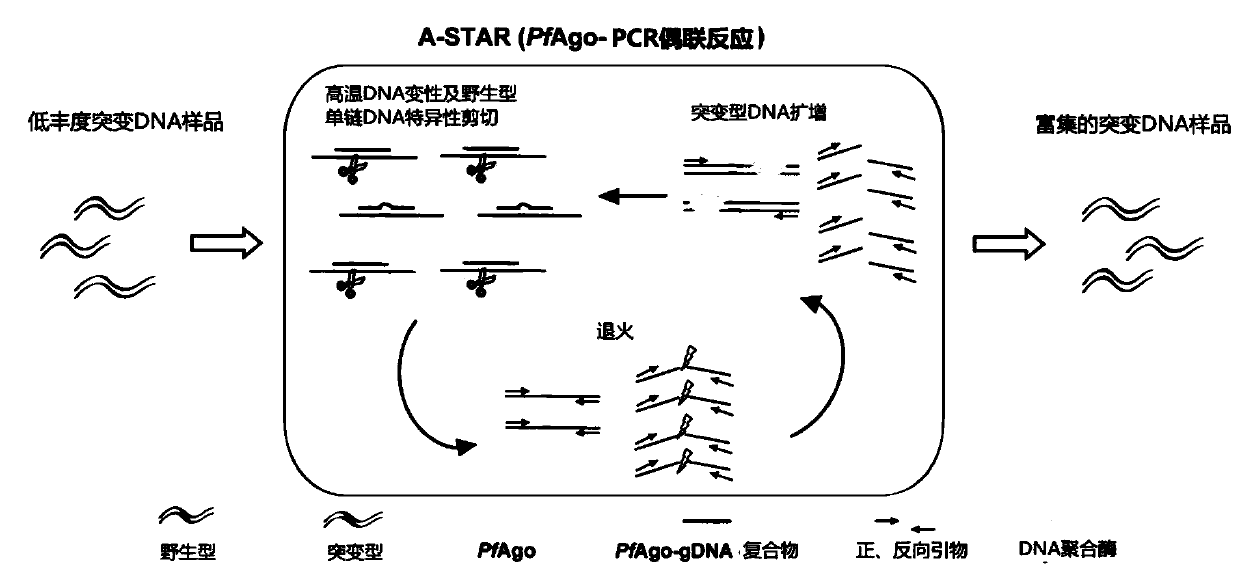
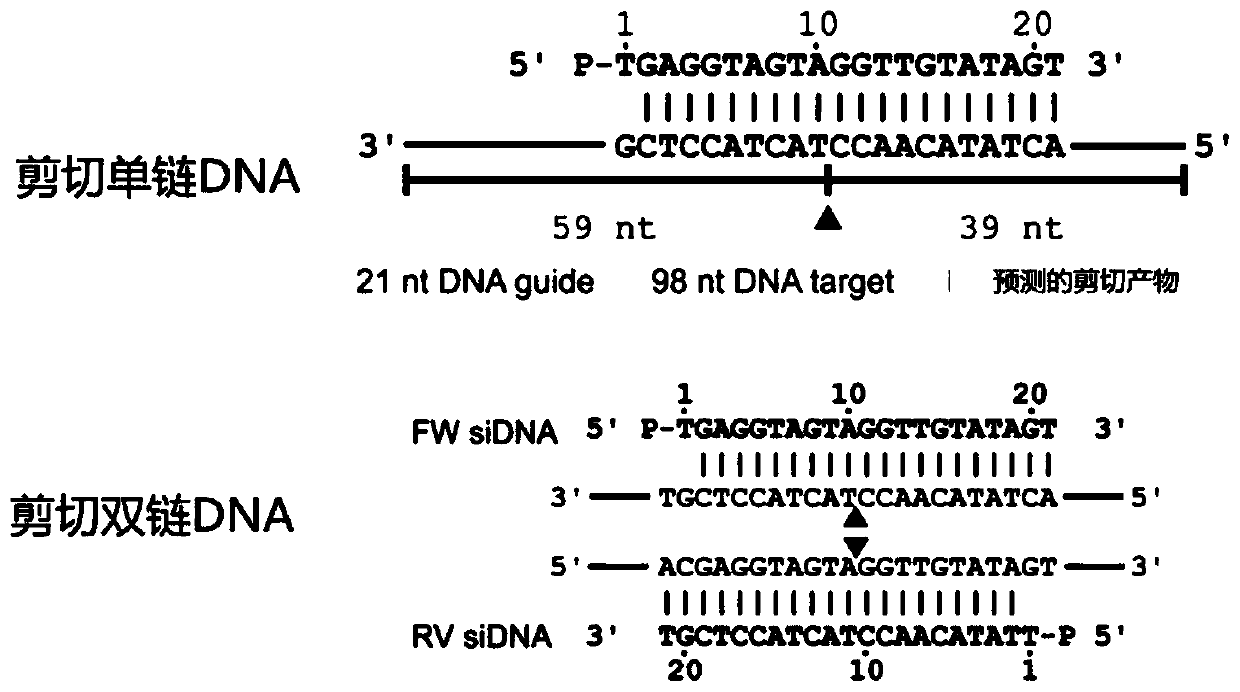
The invention provides a detection system for enriching low-abundance mononucleotide mutant genes based on a nuclease-coupled PCR principle. The invention particularly provides a method for increasingthe relative abundance of a target nucleic acid, which comprises the following steps: (a) providing a nucleic acid sample containing a target nucleic acid and a non-target nucleic acid, wherein the abundance of the target nucleic acid in the nucleic acid sample is F1a; (b) using the nucleic acid in the nucleic acid sample as a template, performing PCR and nucleic acid cleavage reaction in the amplification-cleavage reaction system to obtain amplification-cleavage reaction product; the target nucleic acid is amplified the abundance of the amplification-cleavage reaction product is F1b, and theratio of F1b / F1a is more than or equal to 10. The detection system has the advantages of non-invasion, easy operation, high speed and the like, the sensitivity can reach 0.01%, and the DNA quantity of the sample can be reduced to aM grade.
Owner:JIAOHONG BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
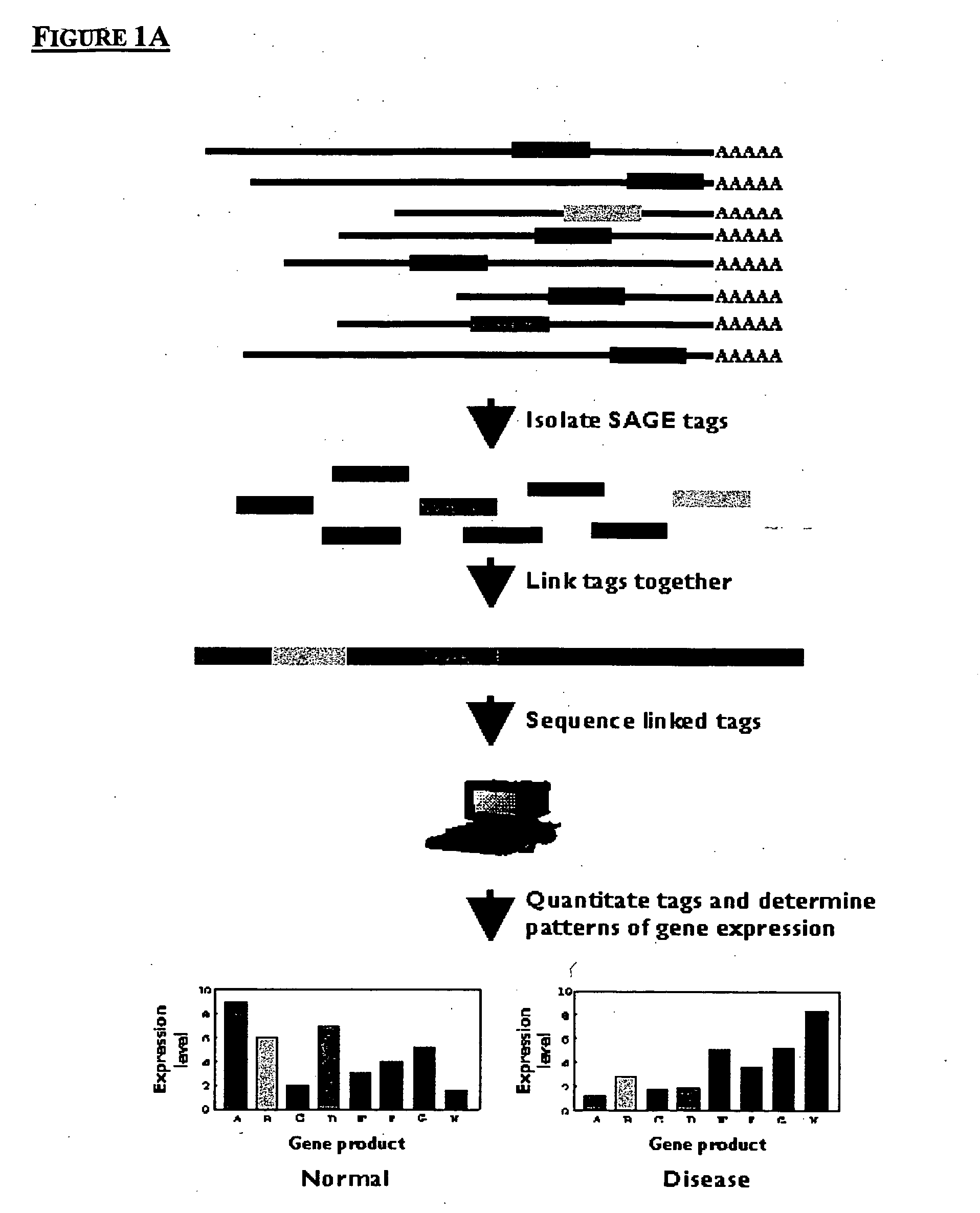
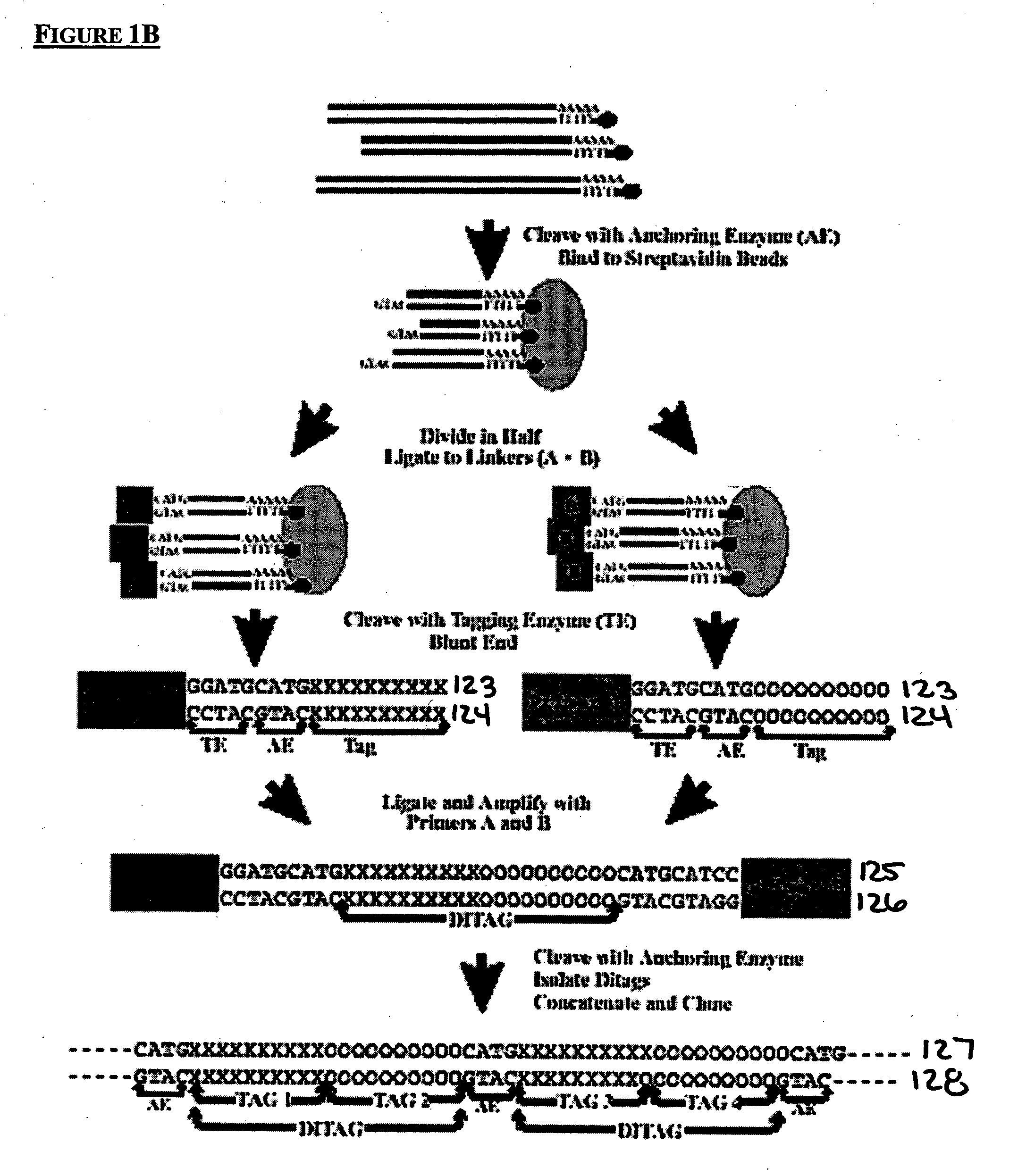
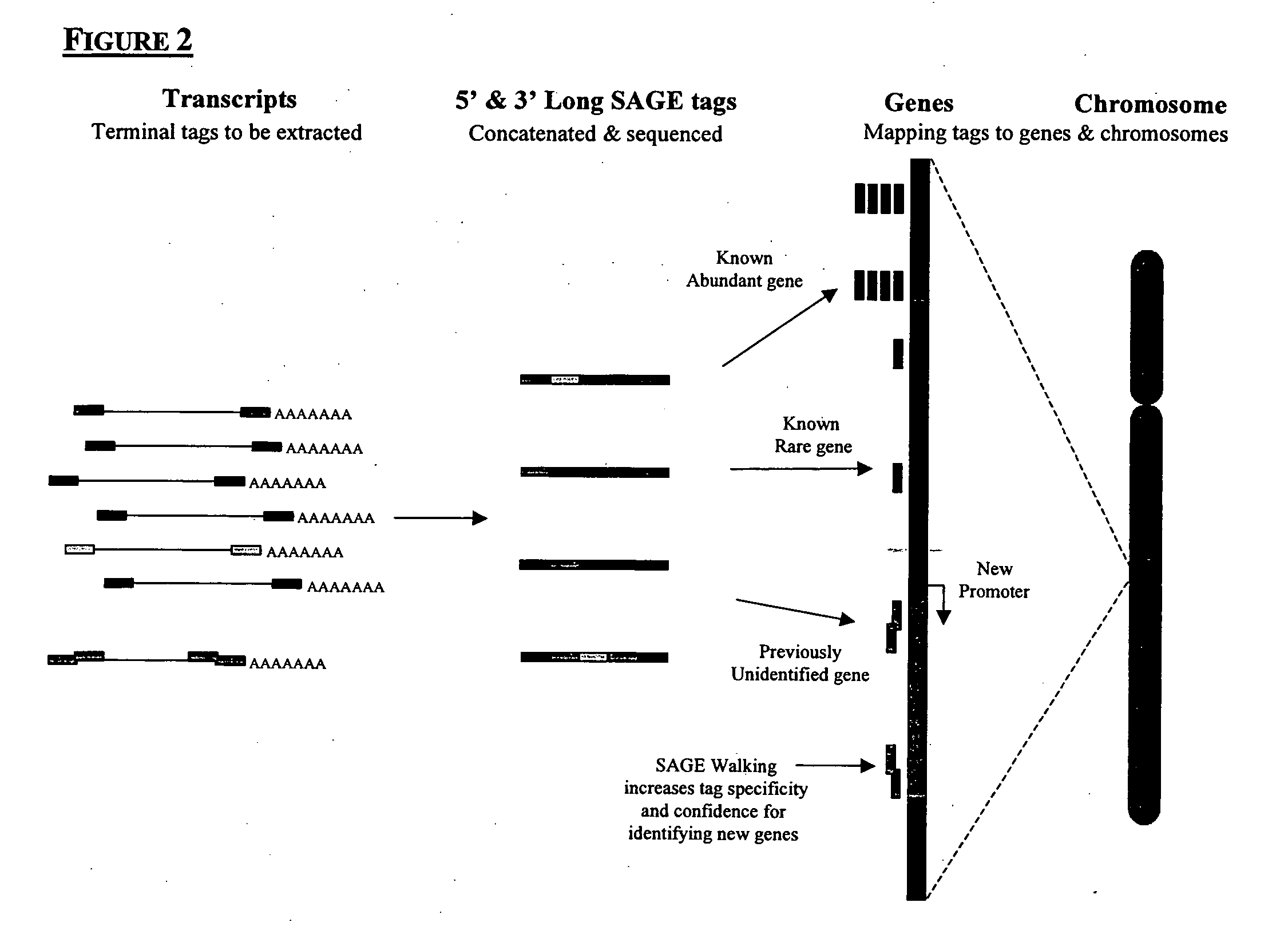
Method to generate or determine nucleic acid tags corresponding to the terminal ends of DNA molecules using sequences analysis of gene expression (terminal SAGE)
A method of providing an indication of an instance of expression of a gene is described herein, the method which may comprise the steps of: (a) providing a complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) having a terminus comprising a terminal transcribed sequence of a gene; (b) linking the cDNA to an linker sequence thereby forming a linked nucleic acid, in which the linker sequence comprises a first recognition site for a first nucleic acid cleavage enzyme, preferably a restriction endonuclease, that allows nucleic acid cleavage at a site distant from the first recognition site; and (c) cleaving the linked nucleic acid with the first nucleic acid cleavage enzyme to provide a linked tag, in which the linked tag comprises a nucleotide sequence tag representative of a terminal transcribed sequence of the gene; and (d) detecting the presence or identity of the linked tag or the nucleotide sequence tag to provide an indication of an instance of gene expression.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for concurrent amplification and real time detection of polymorphic nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20030165898A1Improve reliabilityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid cleavage
The present invention provides a method of detecting a genetic polymorphism in an individual or between individuals. The method comprises the following steps, (1) obtaining a sample containing nucleic acid from an individual; (2) contacting the sample, under conditions which permit primer-initiated nucleic acid amplification and nucleic acid cleavage, with (i) a primer suitable for initiating amplification, (ii) an indicator system which provides a signal proportional to the amount of amplification product, and (iii) a sequence specific nucleic acid cleavage agent; and (3) measuring the signal produced by the indicator system against time. Cleavage of the amplification product by the cleavage agent results in an inhibition of the rate of accumulation of amplification product comprising the sequence recognised by the cleavage agent relative to the rate of accumulation of amplification product not comprising the sequence recognised by the cleavage agent.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON RES PTY LTD
Novel DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) nucleic acid cleaving enzyme and application thereof
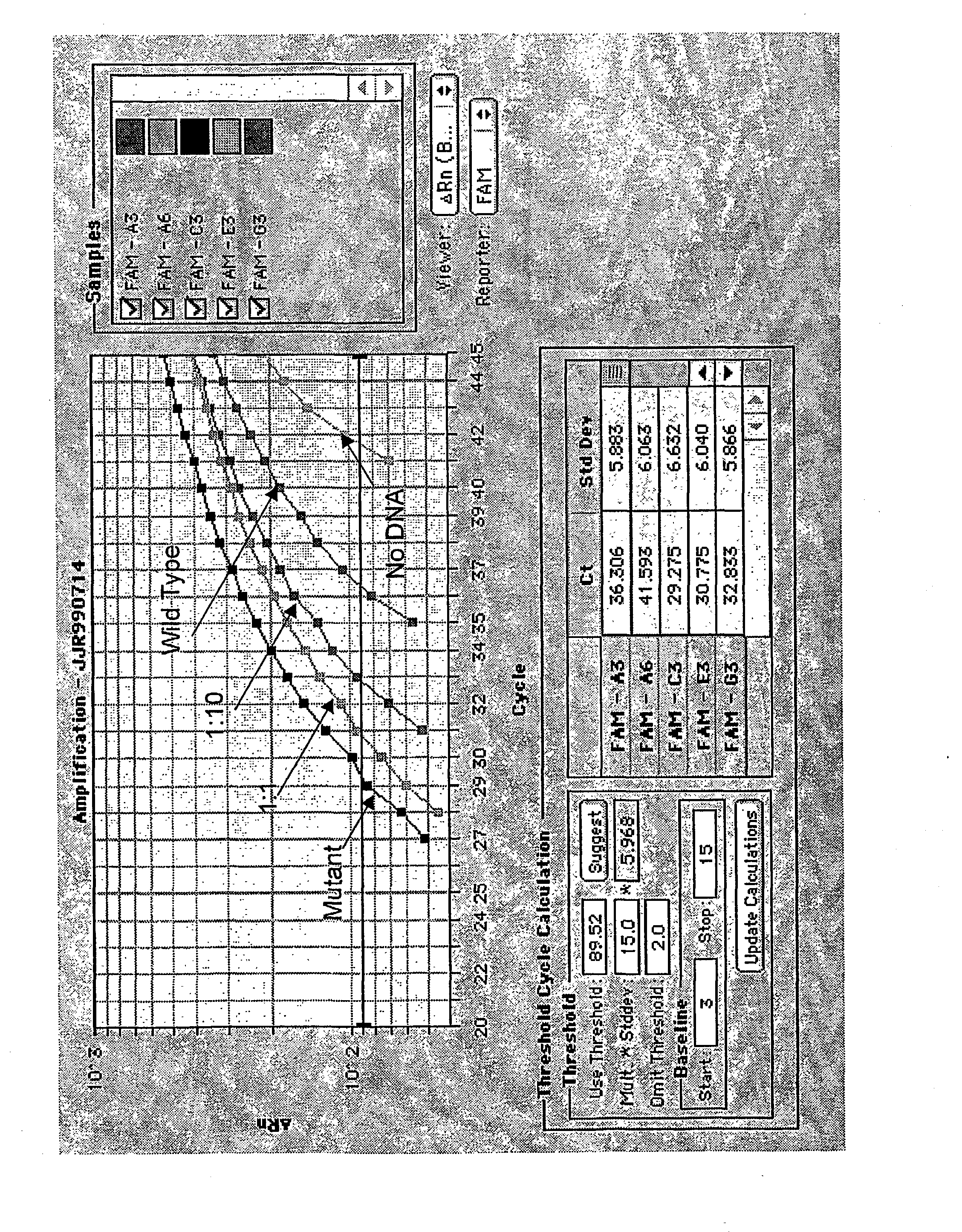
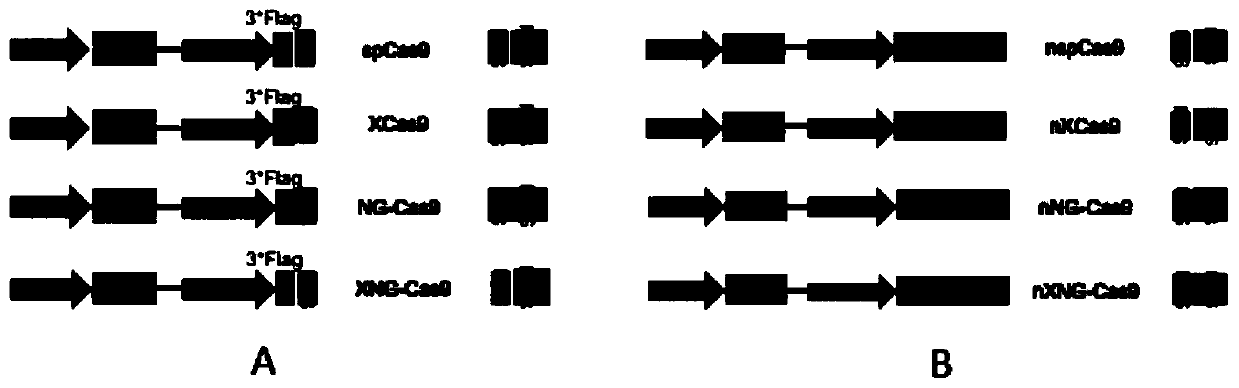
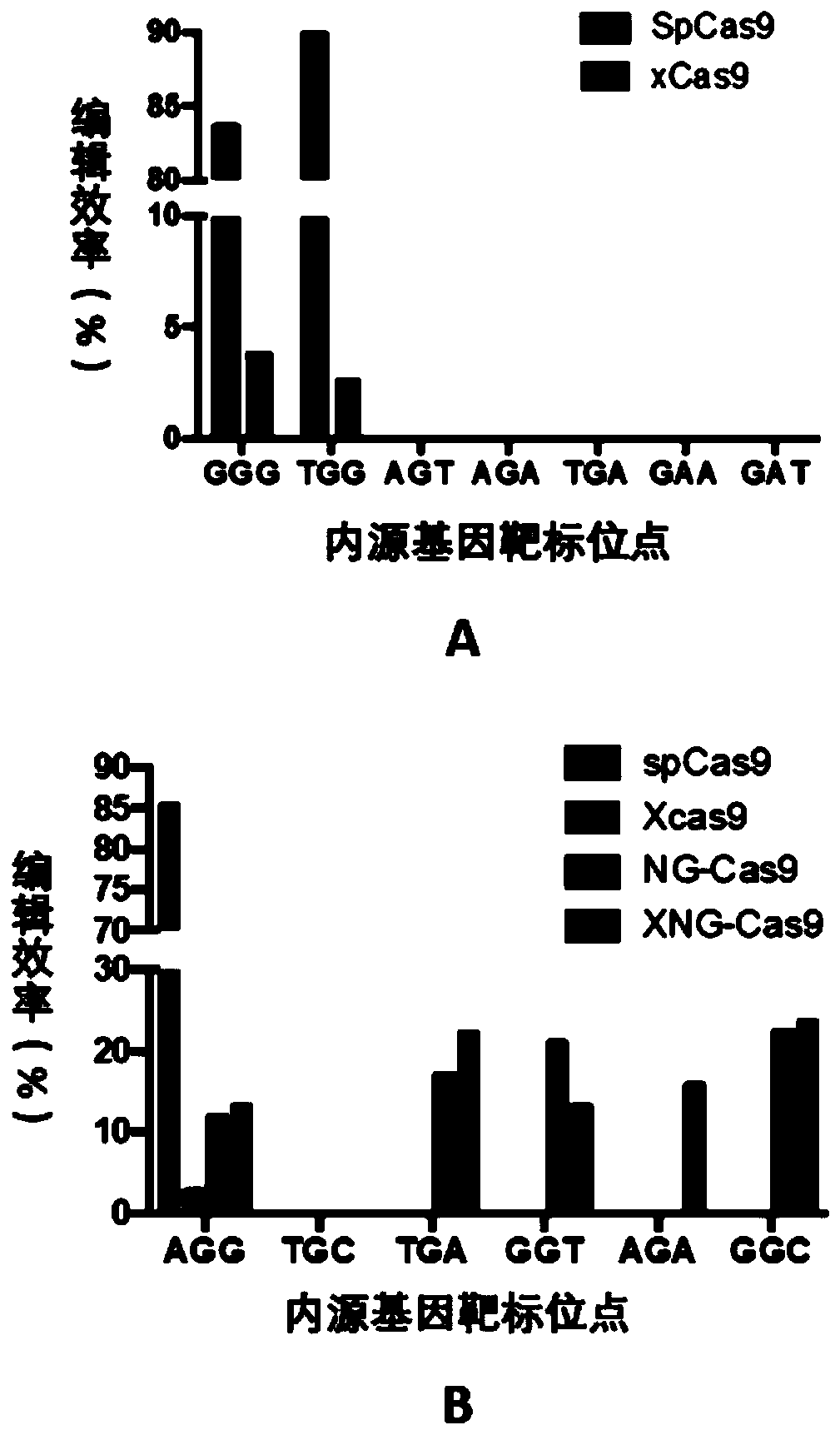
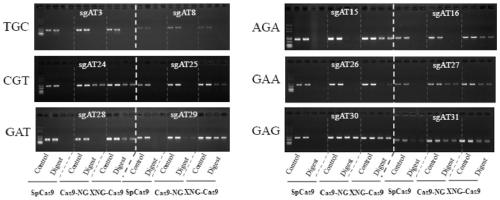
The invention relates to a novel DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) nucleic acid cleaving enzyme and application thereof, and particularly relates to a mutant gene editing protein and a fusion protein containing the mutant gene editing protein. The mutant gene editing protein and the fusion protein can identify more types of PAM (polyacrylamide) sequences, so that the gene editing range is expanded, theediting efficiency can be improved, and mutation of a target site can be accurately mediated. The mutant gene editing protein and the fusion protein can be widely applied to animal and plant cells.
Owner:SHANDONG SHUNFENG BIOTECH CO LTD
Detection of nuceic acids by multiple sequential invasive cleavages
InactiveUS20050003432A1Reduce interactionHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNon targeted
The present invention relates to means for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences, as well as variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention also relates to methods for forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on a target sequence and cleaving the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. The structure-specific nuclease activity of a variety of enzymes is used to cleave the target-dependent cleavage structure, thereby indicating the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences or specific variations thereof. The present invention further relates to methods and devices for the separation of nucleic acid molecules based on charge. The present invention also provides methods for the detection of non-target cleavage products via the formation of a complete and activated protein binding region. The invention further provides sensitive and specific methods for the detection of nucleic acid from various viruses in a sample.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Modulators of enzymatic nucleic acid elements mobilization
The present invention discloses a nucleic acid cleavage assay for members of the transposase / integrase superfamily. A method of using the assay to screen for modulators of the nucleic acid cleavage activity is also disclosed. The present invention further provides a method for screening for modulators of binding of a transposase / integrase to its corresponding recognition sequence. In addition, the present invention provides a method of identifying a modulator for a particular transposase / integrase such as HIV integrase based on modulators of other members of the transposase / integrase superfamily. Also disclosed are Tn5 transposase inhibitors and HIV integration inhibitors.
Owner:ASON BRANDON L +3
Purification of biomolecules from contaminating intact nucleic acids
InactiveUS20060068430A1Microbiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionNucleic acid cleavageSmall molecule
The present invention provides methods for the removal, destruction or inactivation of intact nucleic acids contaminating desired biomolecules by the use of small molecule nucleic acid cleavage agents.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
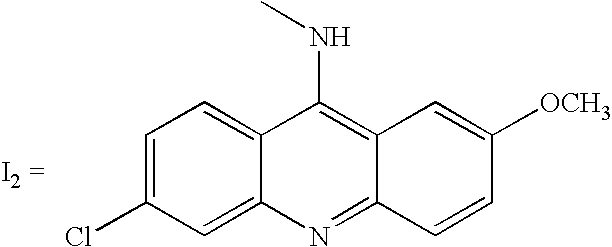
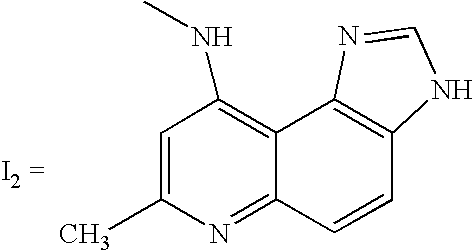
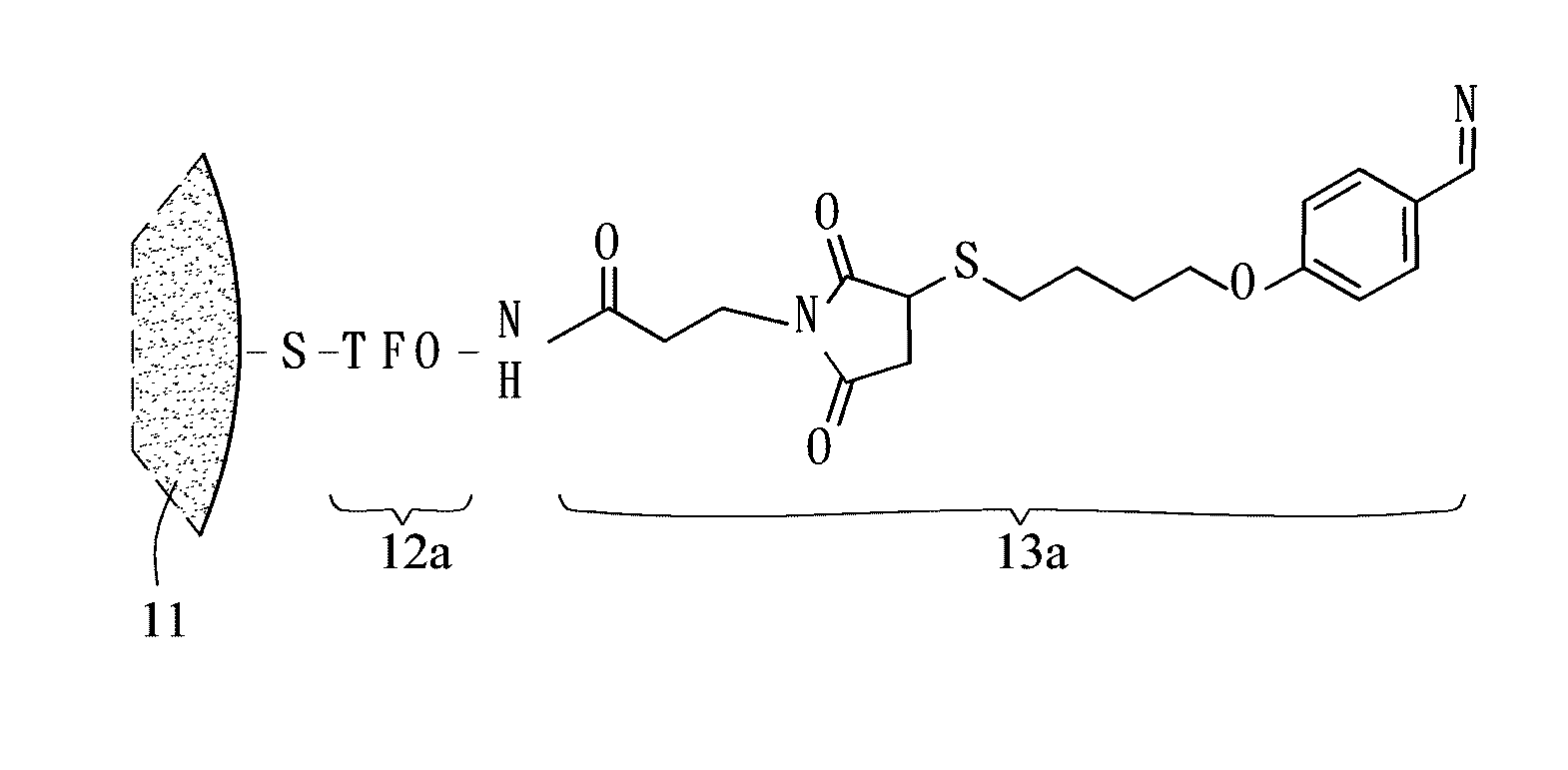
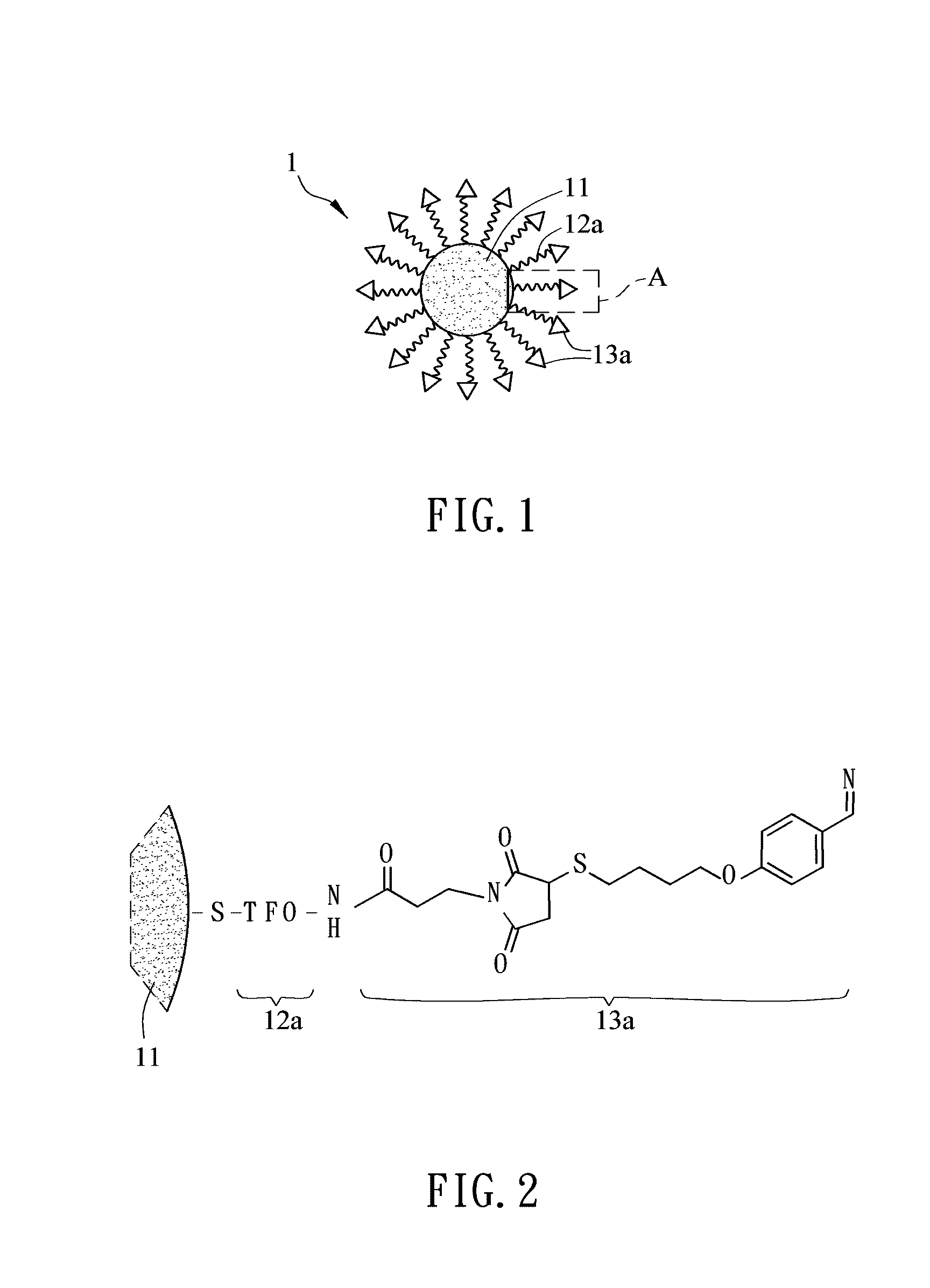
Cleavage kit, and gene therapy by using the same and nucleic acid cleavage detection apparatus
ActiveUS20110014293A1High sequence specificityEliminate side effectsPowder deliveryBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFhit geneNucleic acid cleavage
A nucleic acid cleavage kit is used to cleave a target nucleic acid. The nucleic acid cleavage kit includes a carrier, an oligonucleotide, and a nucleic acid cleavage agent. The oligonucleotide recognizes at least partial sequence of the target nucleic acid. Then, the nucleic acid cleavage agent cleaves the target nucleic acid. A nucleic acid cleavage detection apparatus including the nucleic acid cleaving kit and a gene therapy by administering the nucleic acid cleavage kit are also disclosed.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Nucleic acid hydrolysis cutting agent based on cucurbituril
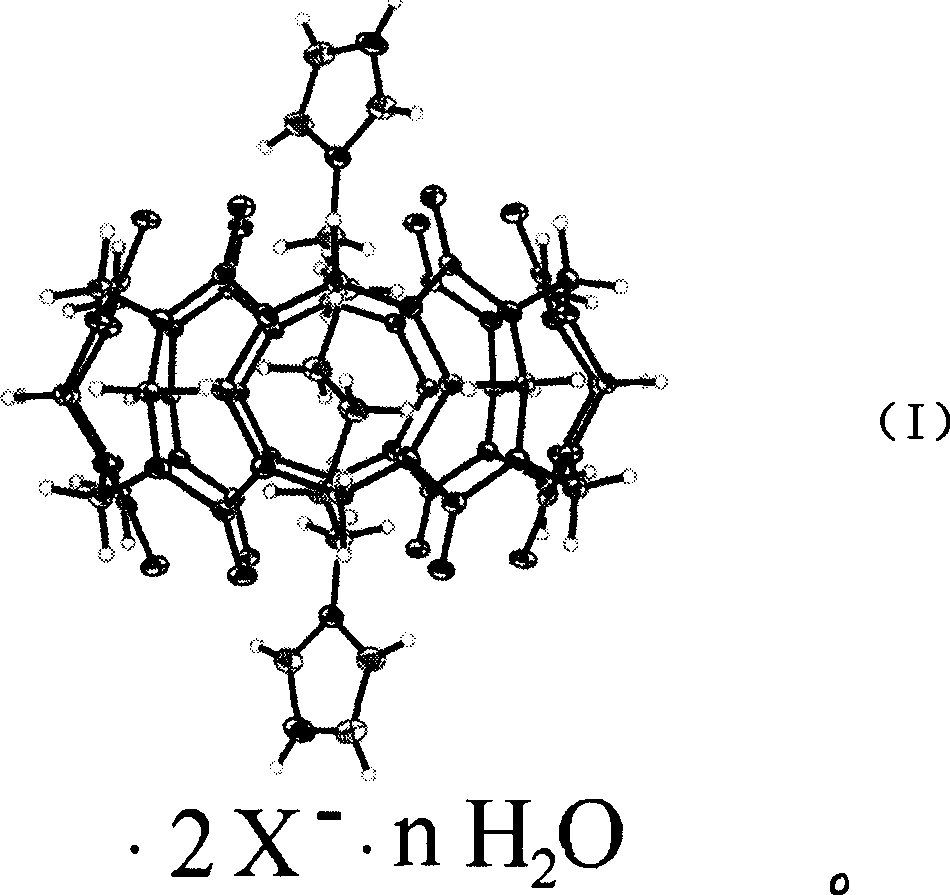
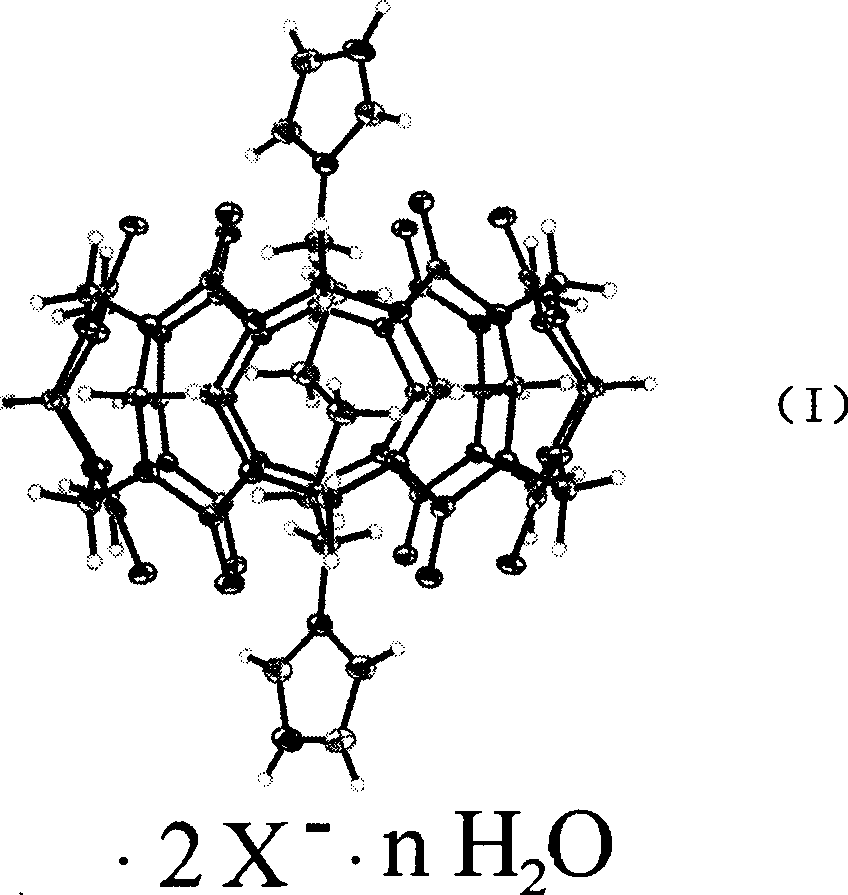
InactiveCN1935829AAchieve reductionSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsVolumetric Mass DensityCucurbituril
The invention relates to pseudorotaxane molecular compound produced by cucurbit[6]uril and 1, 6-di-imidazole group di-acid salt whose chemical molecular formula is C36H36N24O12*C12H20N4*2X*nH2O whose X equals to Cl, H2PO4, HSO4, NO3, Br; n is not less than 1. The compound can be used in nucleic acid cutting whose condition is that the cutting reagent is dissolved in buffer system solution with given pH value, then mixed with cutting substrate; their final density is kept in given range; and their temperature is also kept in given range. The cutting reagent can be used to cut nucleic acid in short time at physiology condition, further study the application in gene therapy medicine preparation to develop into gene therapy medicine.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
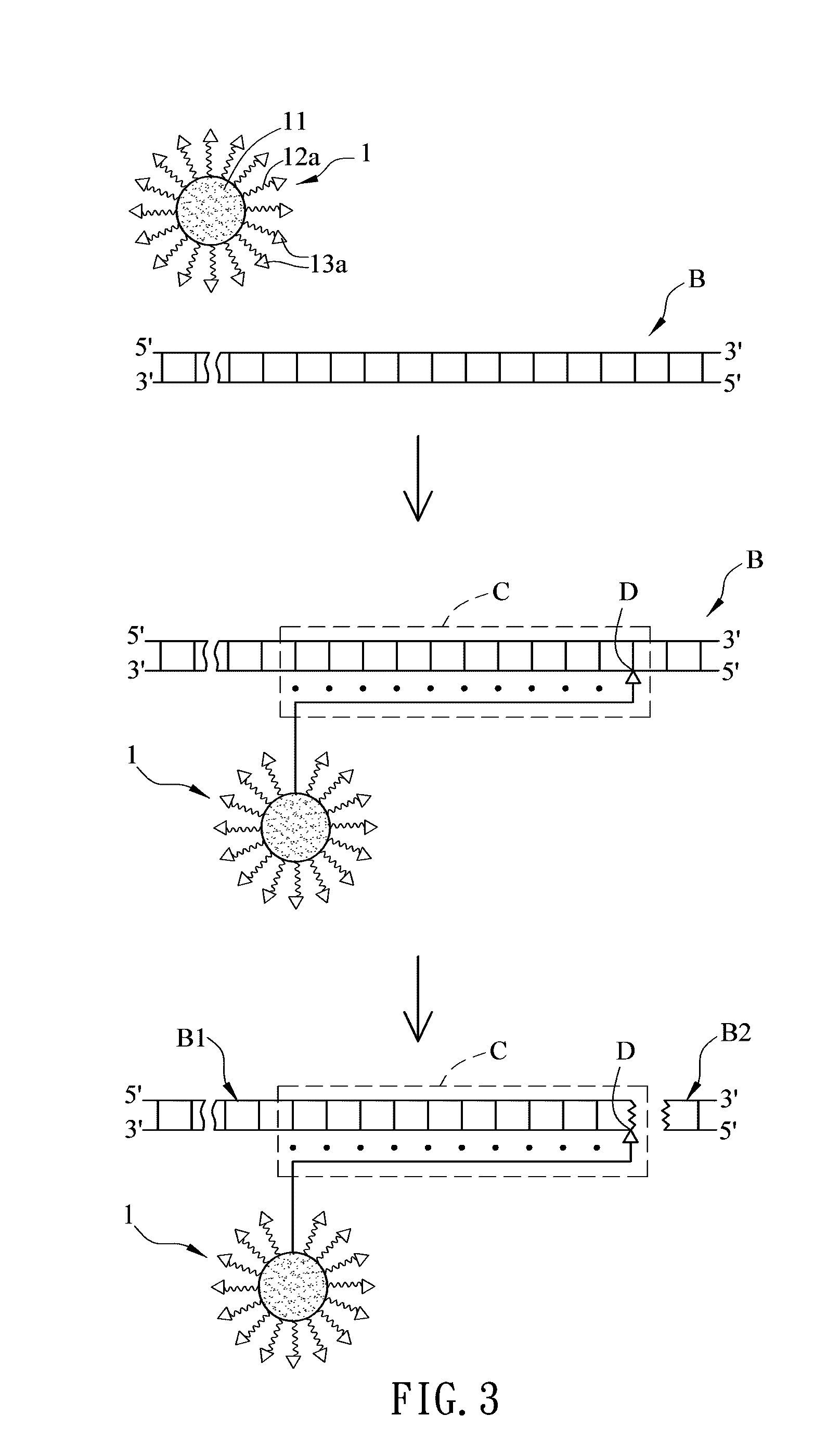
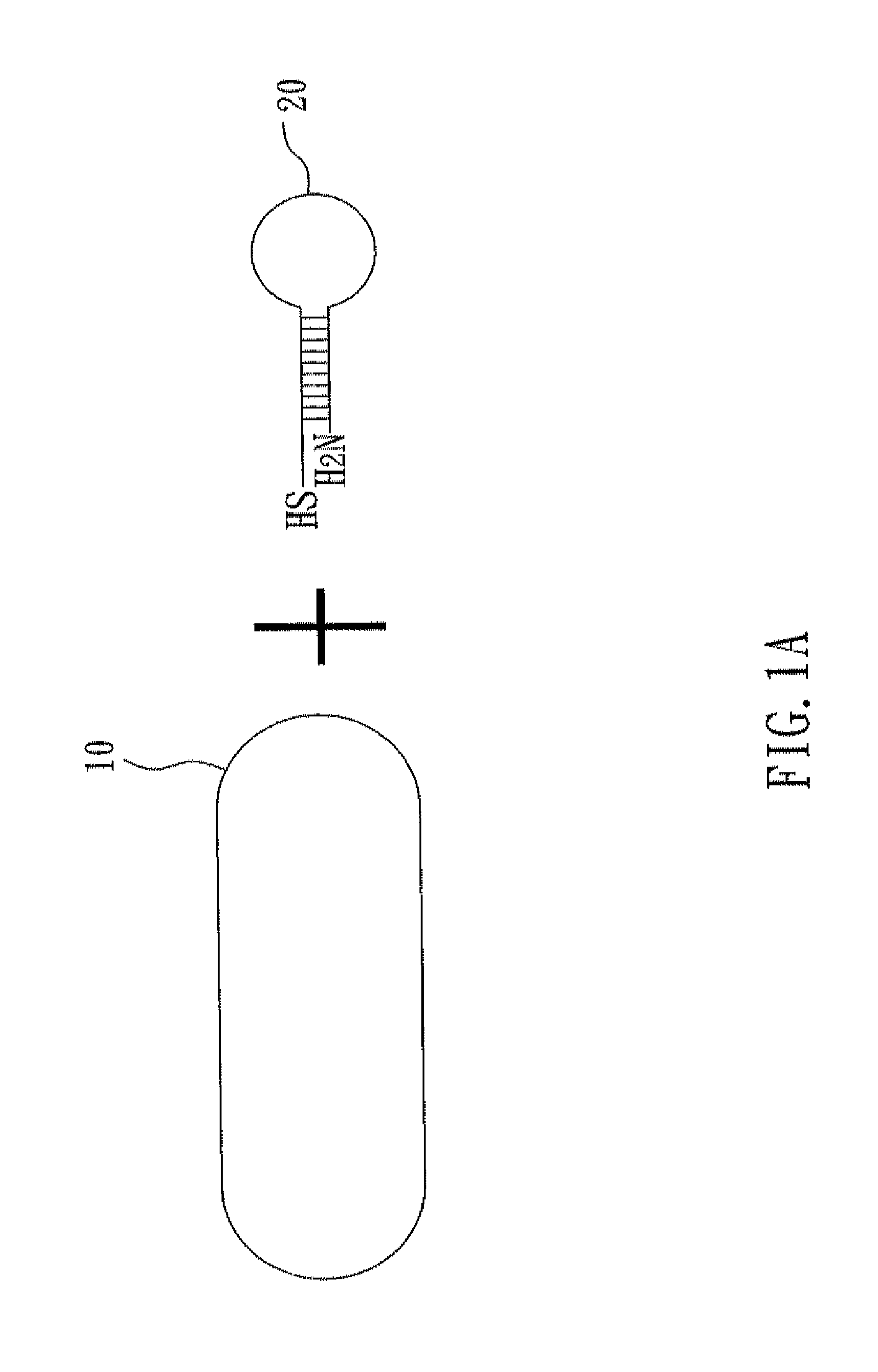
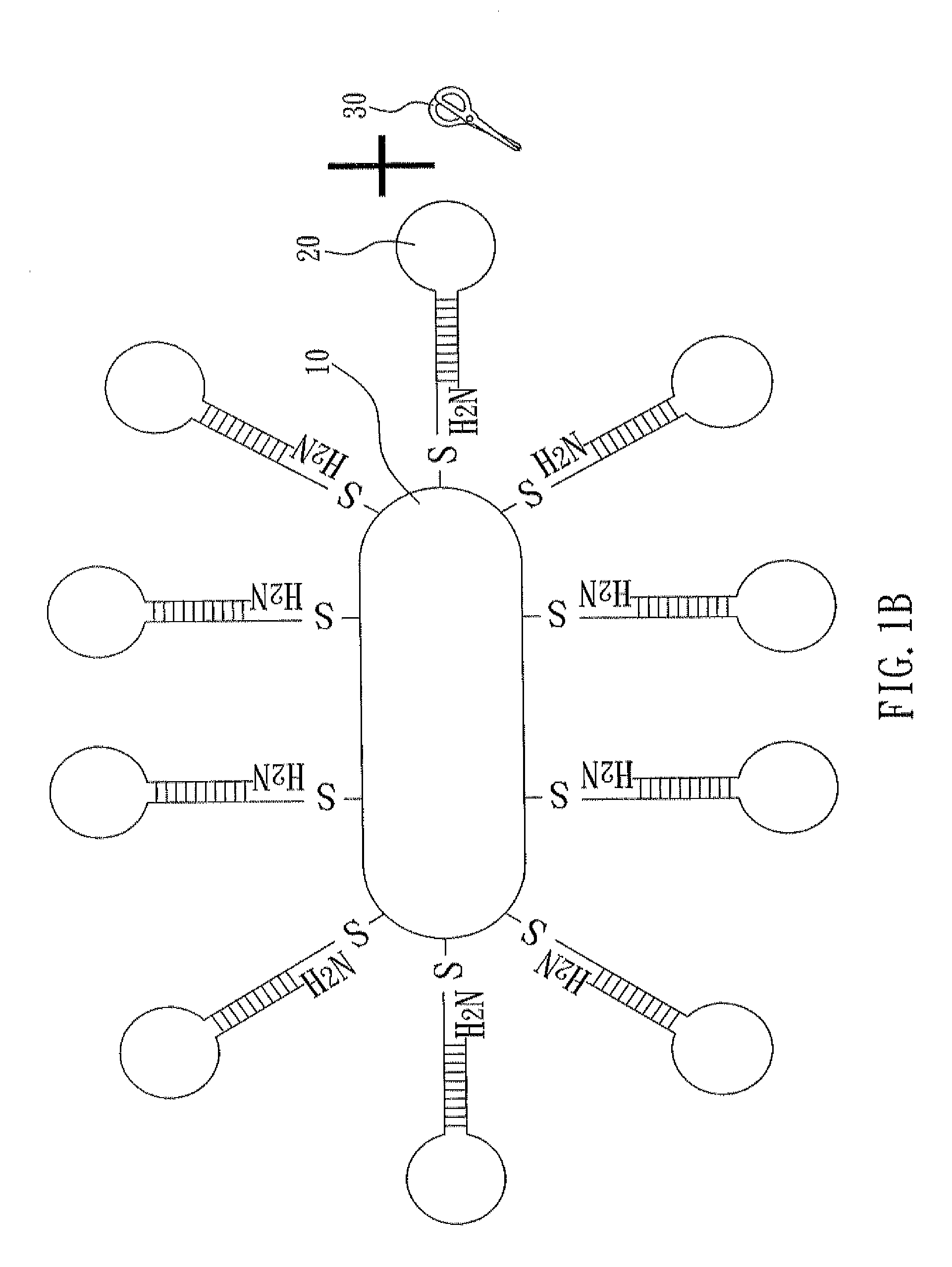
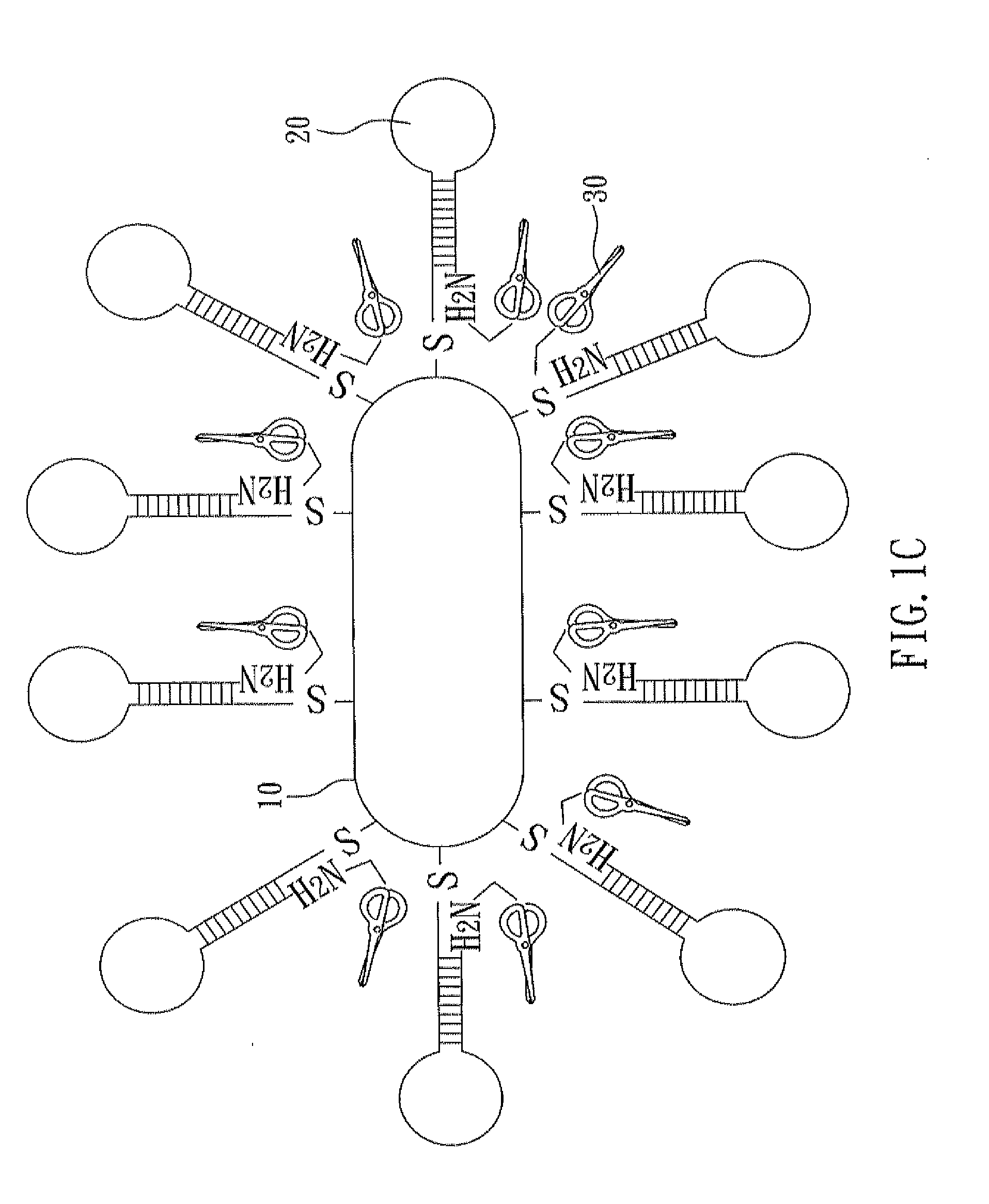
Nucleic acid cleavage complex and method for using the same
ActiveUS20120123107A1Not to damageEasily exposedSugar derivativesOther chemical processesNanoparticlePolynucleotide
A nucleic acid cleavage complex is disclosed, which includes: a nanoparticle, a nucleic acid cleavage reagent, and a polynucleotide chain specifically recognizing a sequence of a target nucleic acid and having a first terminal and a second terminal opposite to the first terminal, wherein the first terminal is connected to the nanoparticle, the second terminal is connected to the nucleic acid cleavage reagent, and the first terminal sequence and the second terminal sequence are base-paired to make the polynucleotide chain form a hairpin. Also, a method for using the nucleic acid cleavage complex is also disclosed.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com