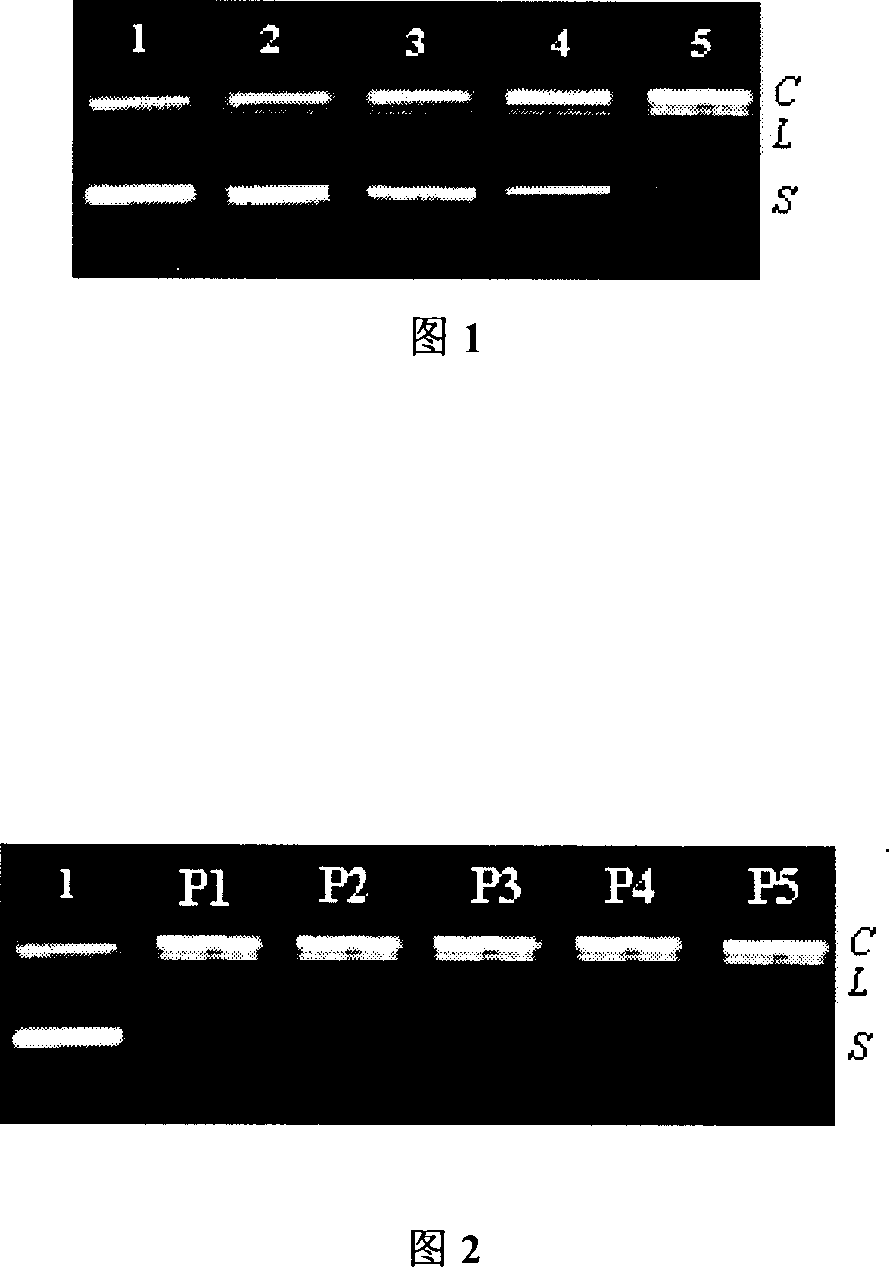
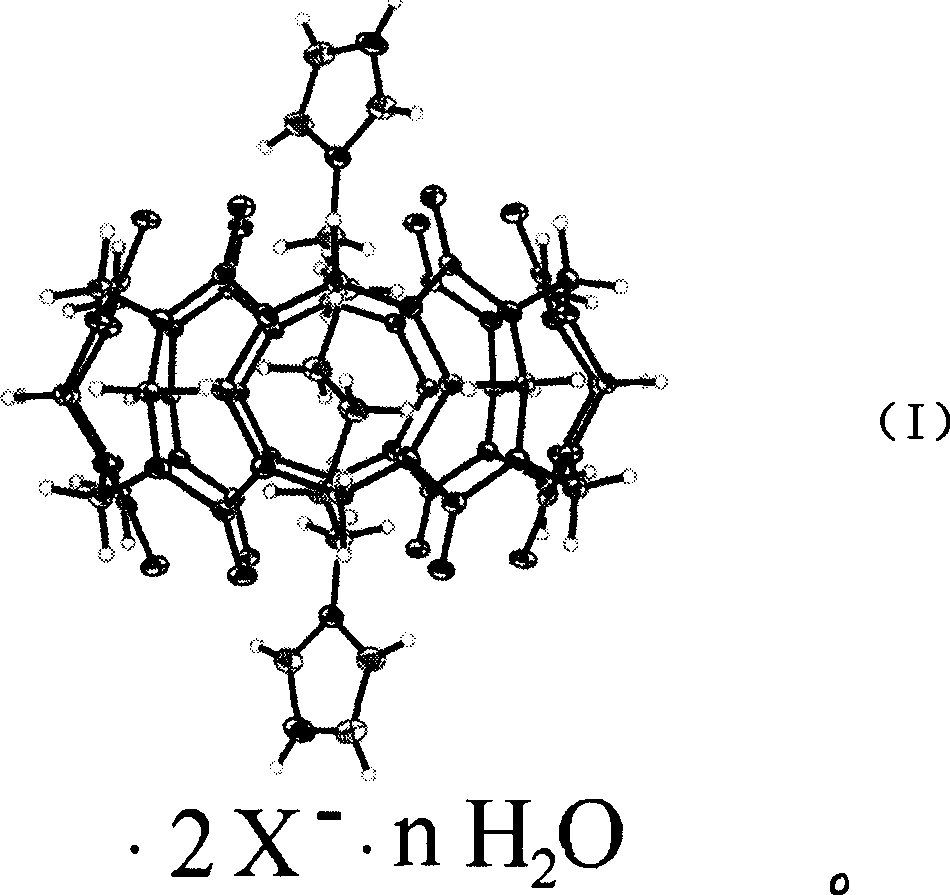
Nucleic acid hydrolysis cutting agent based on cucurbituril
A cutting agent, nucleic acid technology, used in gene therapy, sugar derivatives, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as hindering applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Step 1. Synthesis of the main body cucurbit ring molecule:
[0045] 11.4g glycoluril (80mmol) in 100ml four-neck round bottom flask, add 40ml concentration and be the sulfuric acid H2SO4 solution of 9M (mol / liter), oil bath is warming up to 70 ℃, begins to drop 14ml, 37% formaldehyde aqueous solution, drops When adding, keep the temperature between 70-75°C. After the dropwise addition, keep the temperature at 70-75°C for 24 hours, then raise the temperature to 95-100°C, continue the reaction for 12 hours, cool to room temperature, and pour the reaction solution into 400ml of water , 2 L of acetone was added, and a white solid was precipitated. After standing for 20 min, the obtained solid was collected by suction filtration. The obtained solid was dispersed in 200°C of water, added with 200ml of acetone, stirred for 20min, left to stand, and the white solid obtained by suction filtration was washed three times with 300ml of water at 60°C, rinsed with about 50ml of aceto...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Step 1. Repeat step 1 of Example 1 to obtain the main body melon ring used.
[0052] Step 2. Use concentrated phosphoric acid to replace the concentrated hydrochloric acid used in Step 2 of Example 1 to obtain the guest molecule G2, 1,6-diimidazolylhexane diphosphate. Elemental analysis (calcd.%) for C 12 h 24 N 4 P 2 o 8 : C, 34.78; N, 13.53; H, 5.80. Found: C, 34.91; N, 13.74; H, 5.73.
[0053] Step 3. Substitute the guest molecule G1 with the guest molecule G2, and repeat the step 3 of Example 1 to obtain the quasi-rotaxane compound P2 with a yield of 86%. Elemental analysis (calcd.%) for C 36 h 36 N 24 o 12 ·C 12 h 20 N 4 2H 2 PO 4 12H 2 O: C, 35.42; N, 24.11; H, 5.17. Found: C, 35.59; N, 24.32; H, 5.07.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Step 1. Repeat step 1 of Example 1 to obtain the main body melon ring used.
[0056] Step 2. The concentrated hydrochloric acid used in Step 2 of Example 1 was replaced with concentrated sulfuric acid to obtain the guest molecule G3, 1,6-diimidazolylhexane disulfate. Elemental analysis (calcd.%) for C 12 h 22 N 4 8 2 o 8 : C, 34.78; N, 13.53; H, 5.31.Found: C, 34.78; N, 13.64; H, 5.22.
[0057] Step 3. The guest molecule G1 was replaced by the guest molecule G3, and step 3 of Example 1 was repeated to obtain the quasi-rotaxane compound P2 with a yield of 84%. Elemental analysis (calcd.%) for C 36 h 36 N 24 o 12 ·C 12 h 20 N 4 ·2HSO 4 10H 2O: C, 36.23; N, 24.65; H, 4.91. Found: C, 36.39; N, 24.72; H, 4.88.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com