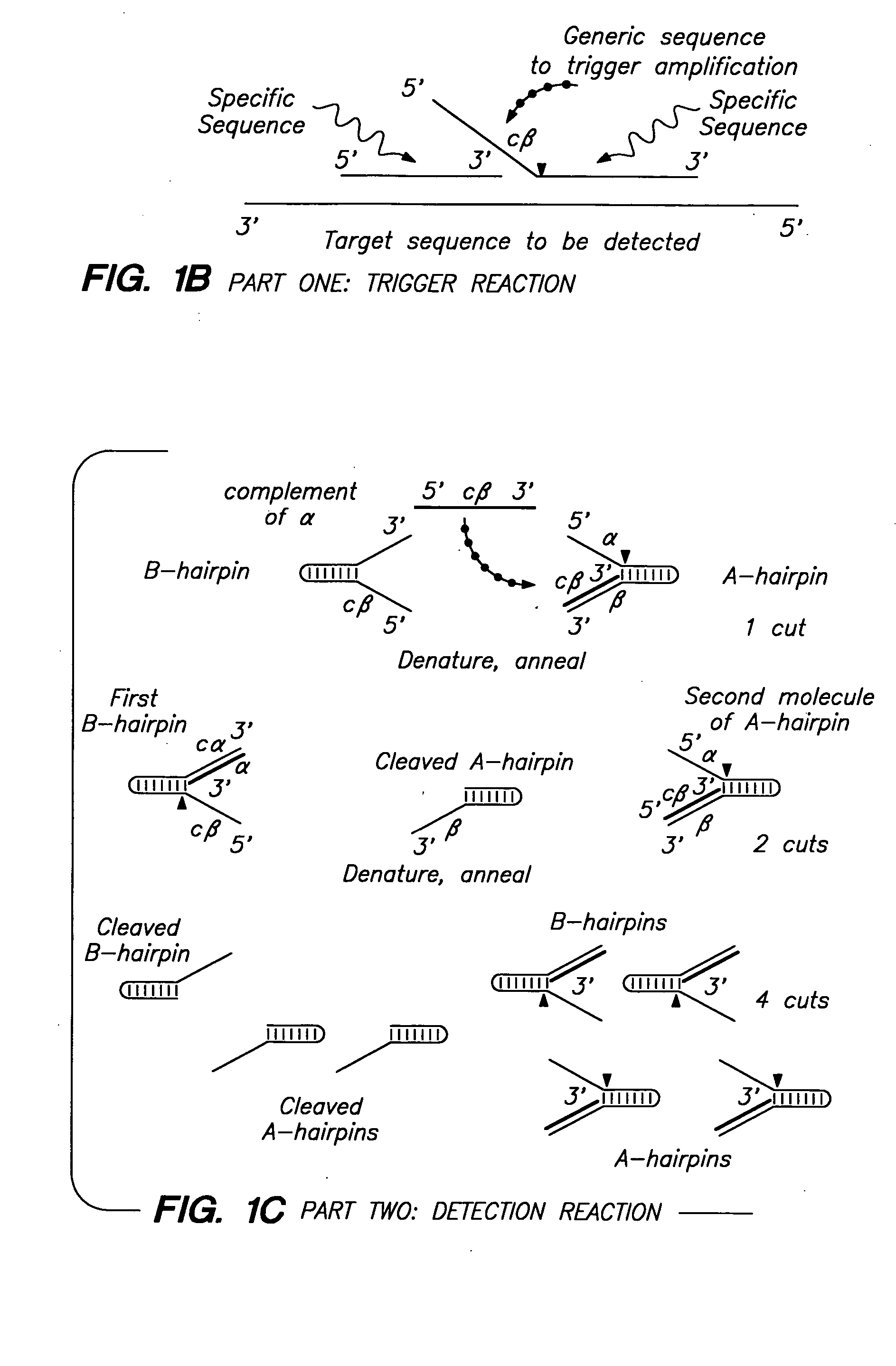
Patents
Literature
171 results about "Exonuclease I" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
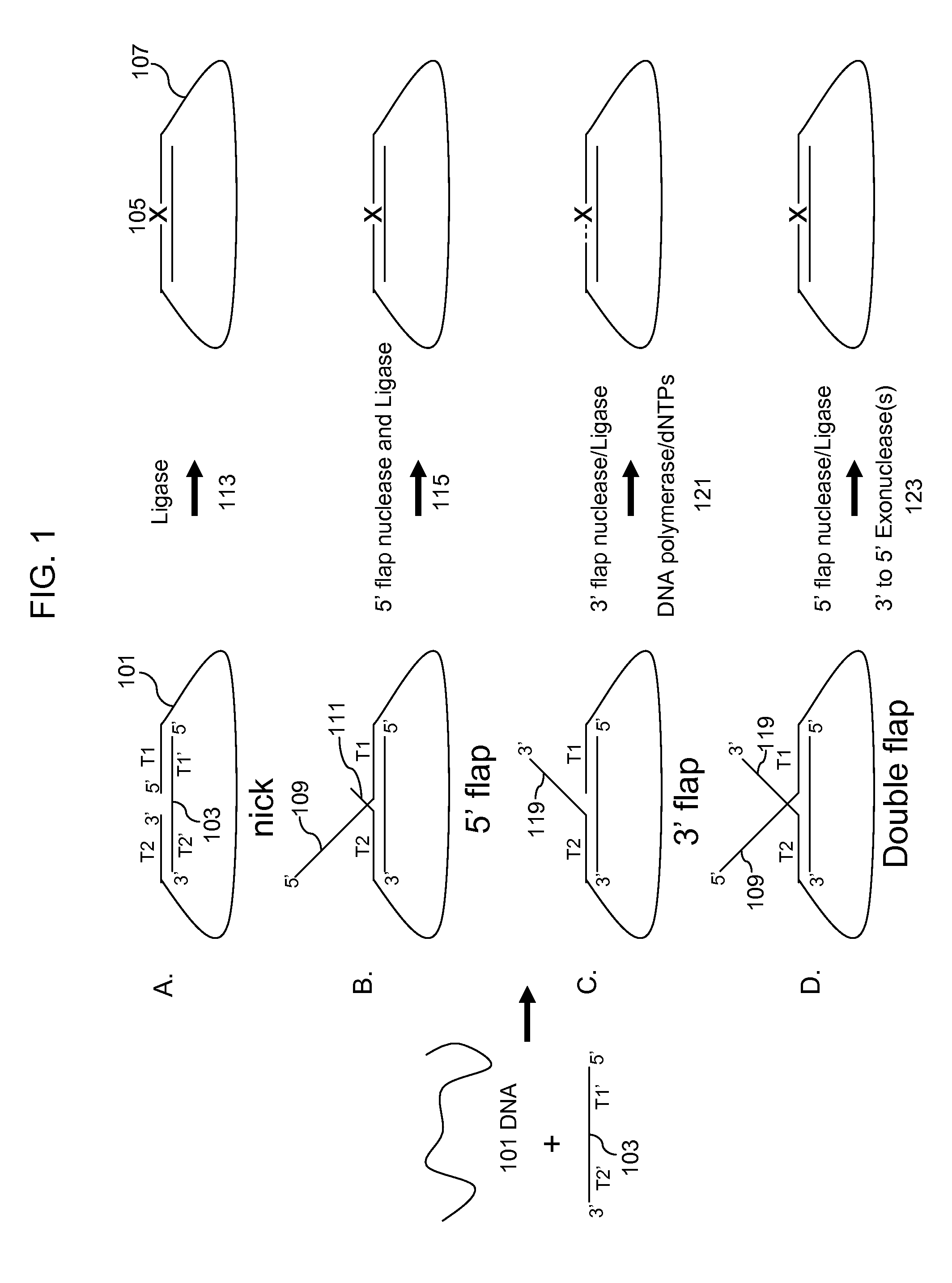
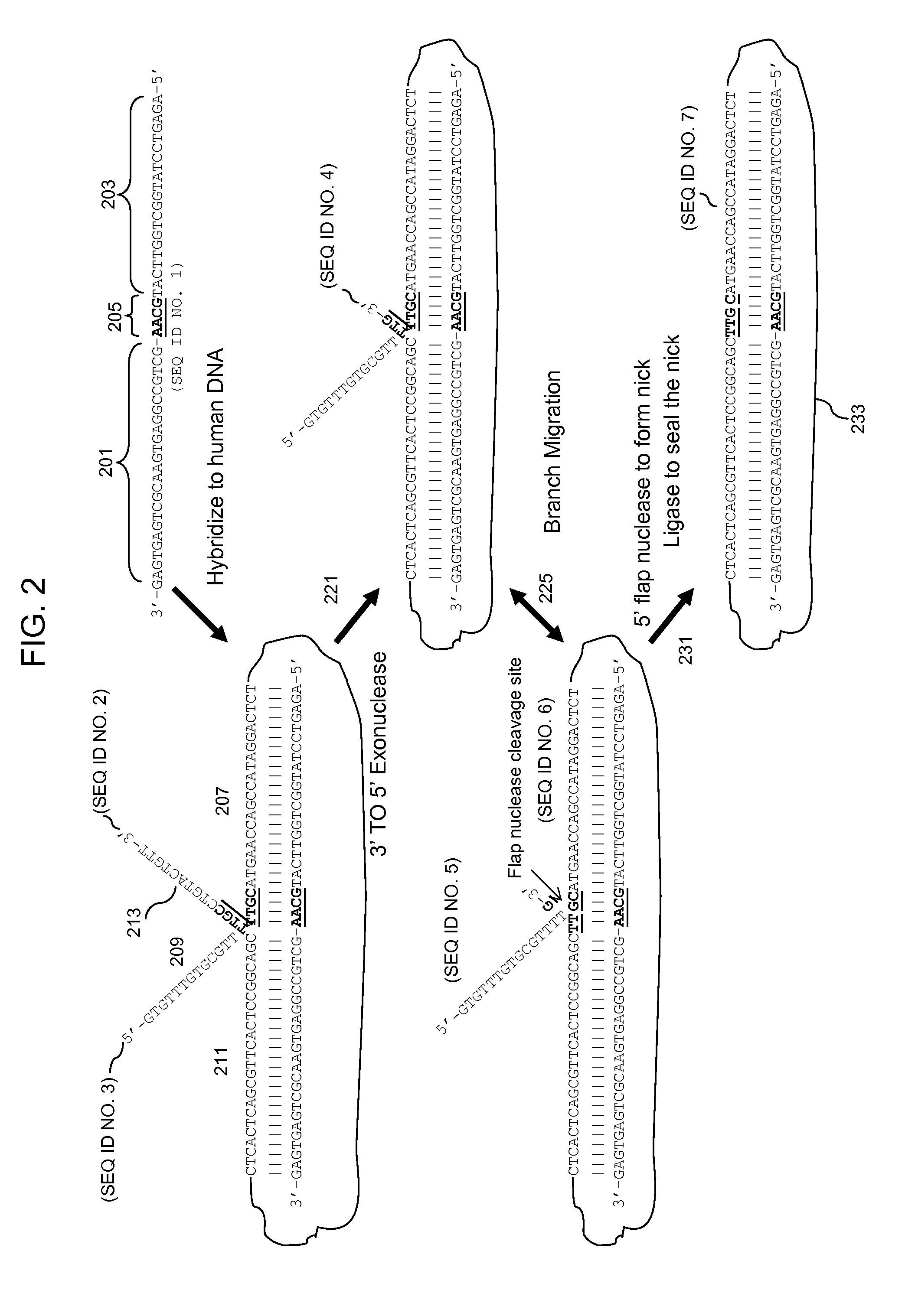
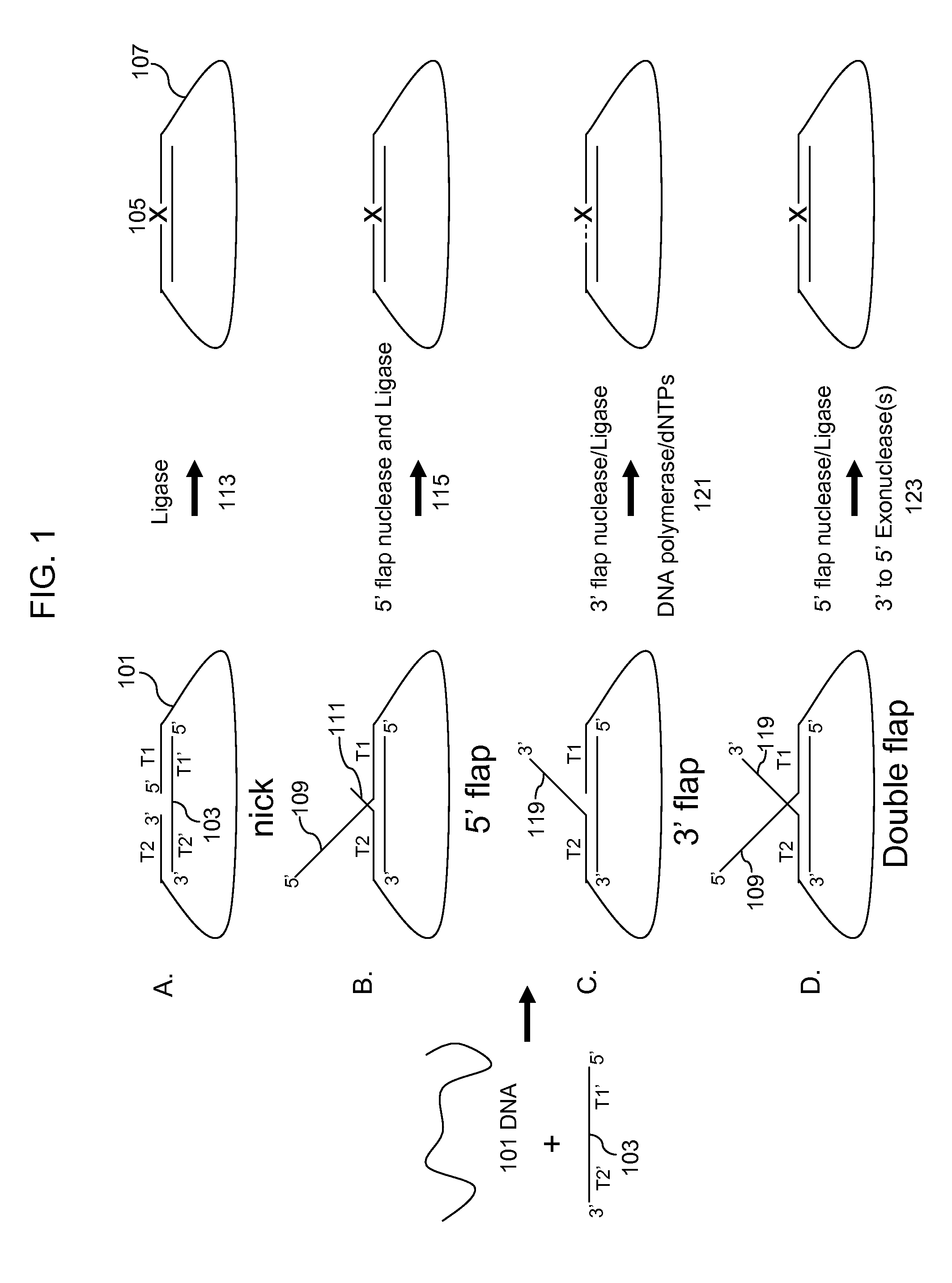
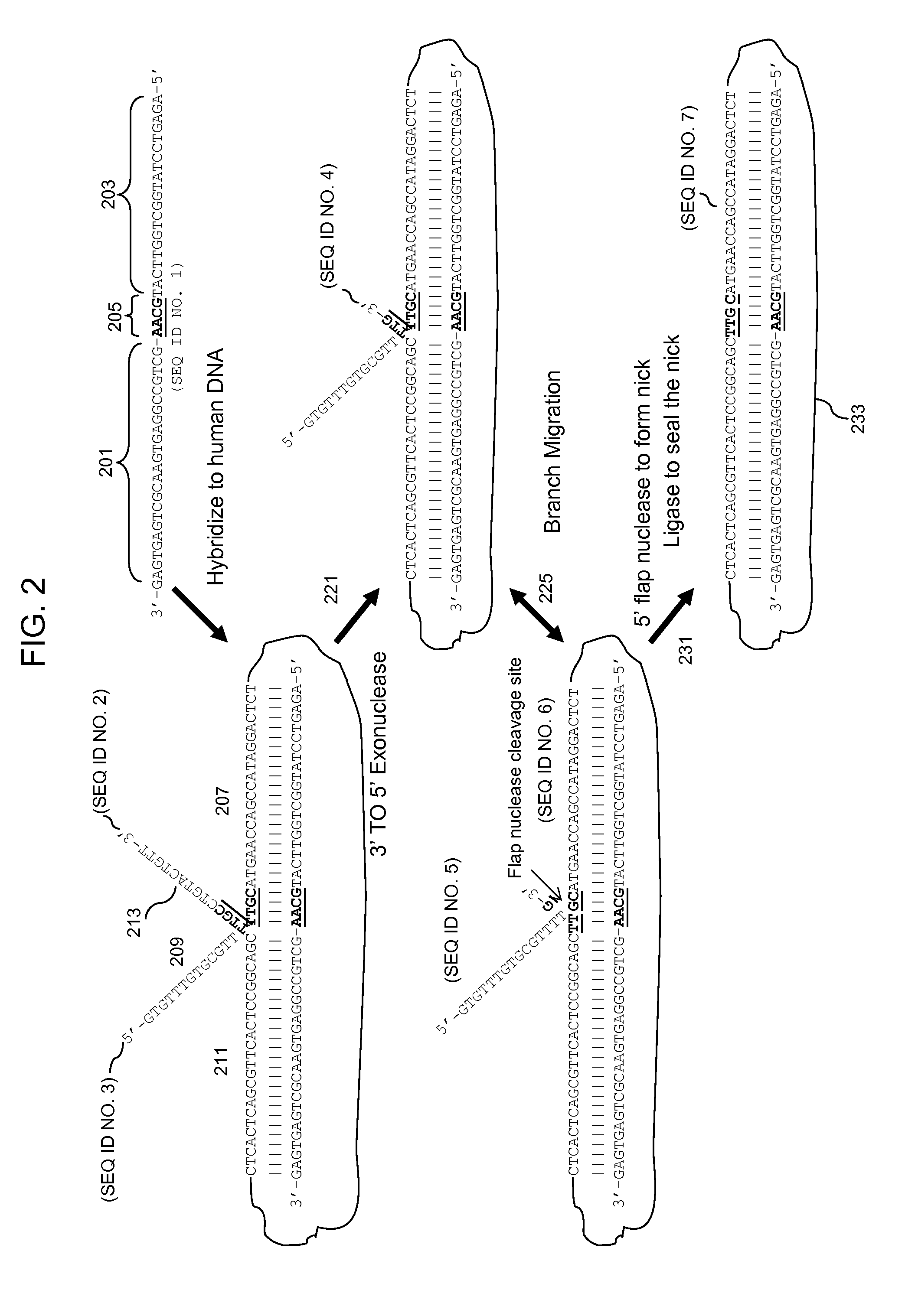
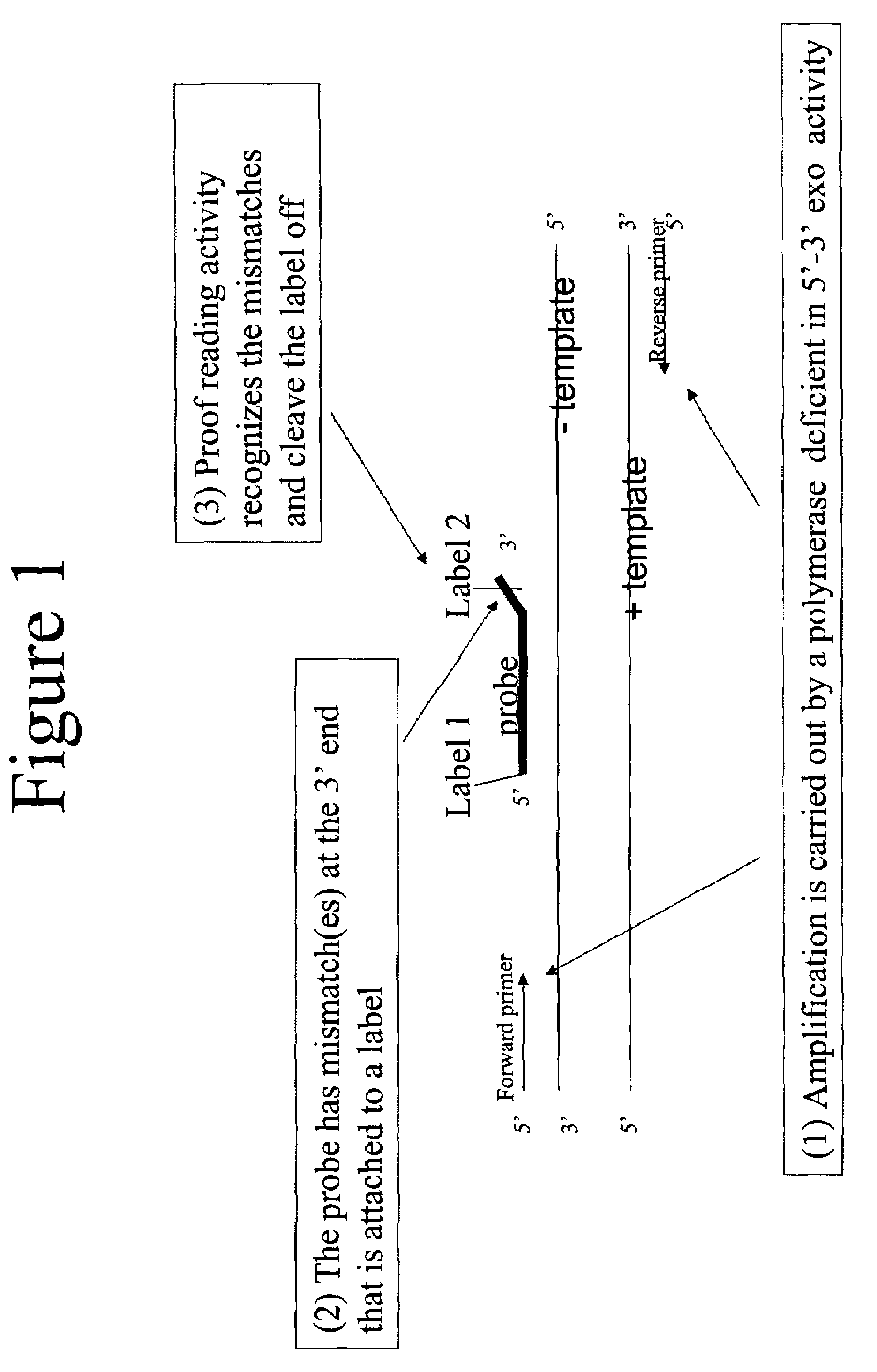
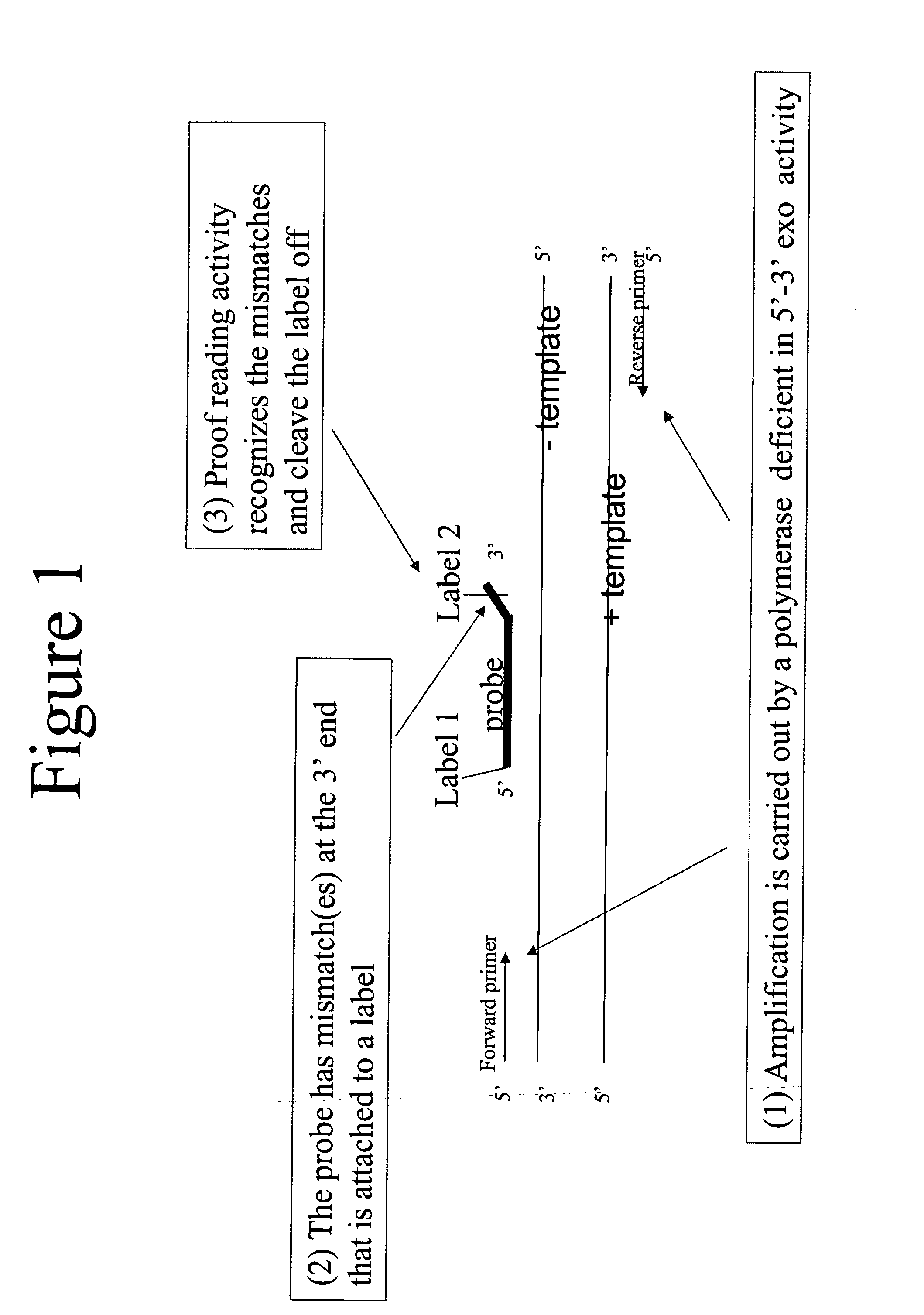
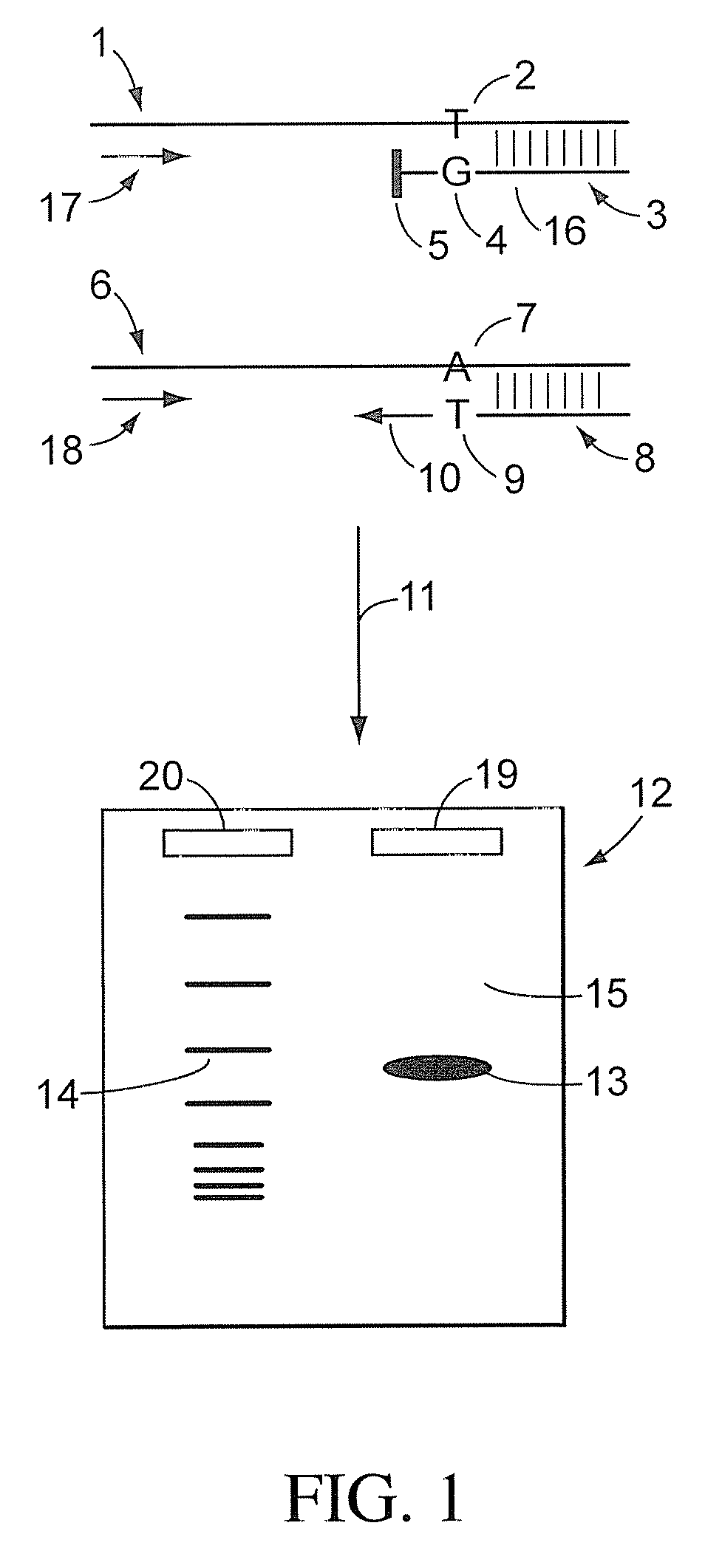
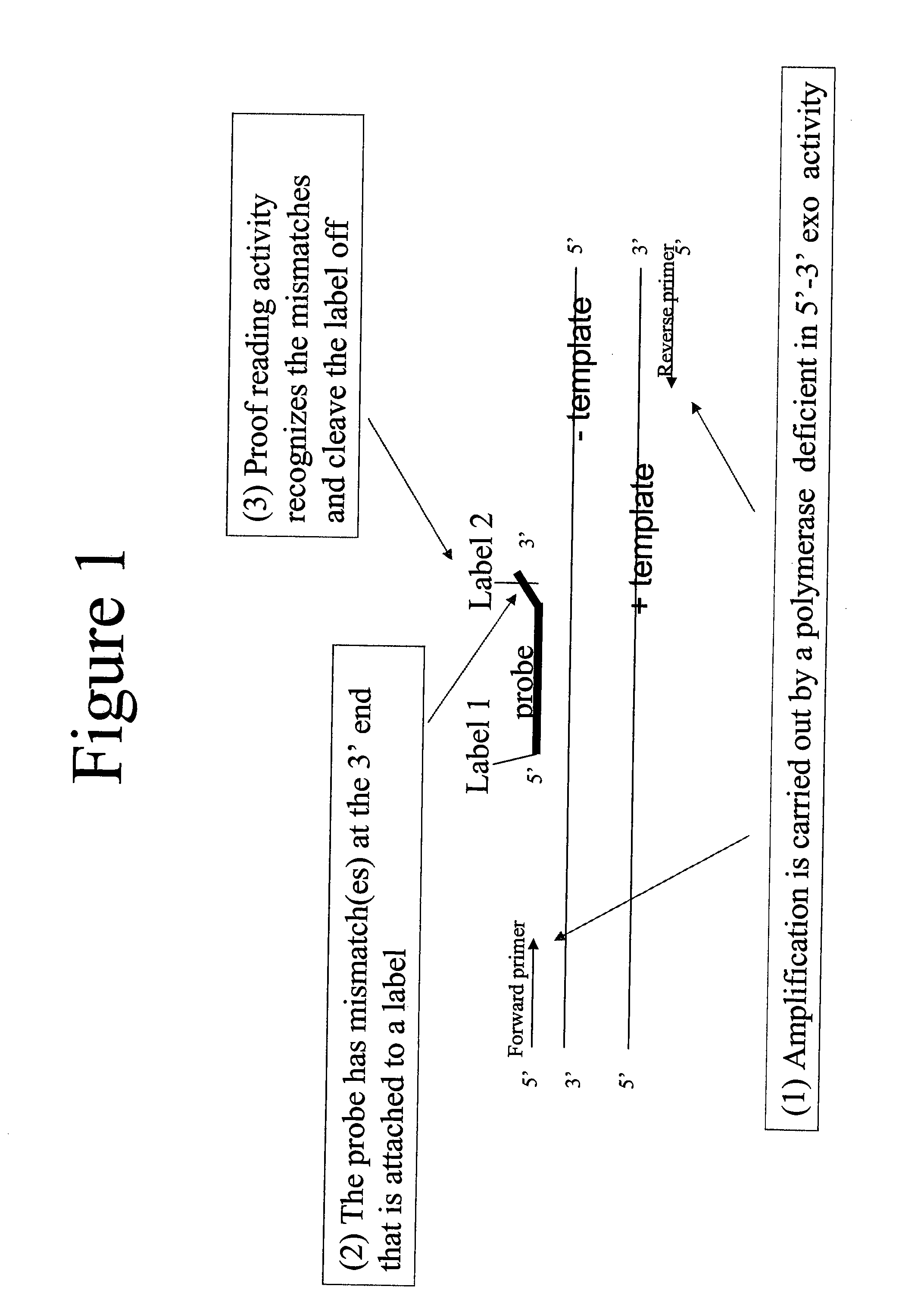
3' to 5' Exonuclease associated with Pol I. Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end (exo) of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3' or the 5' end occurs.
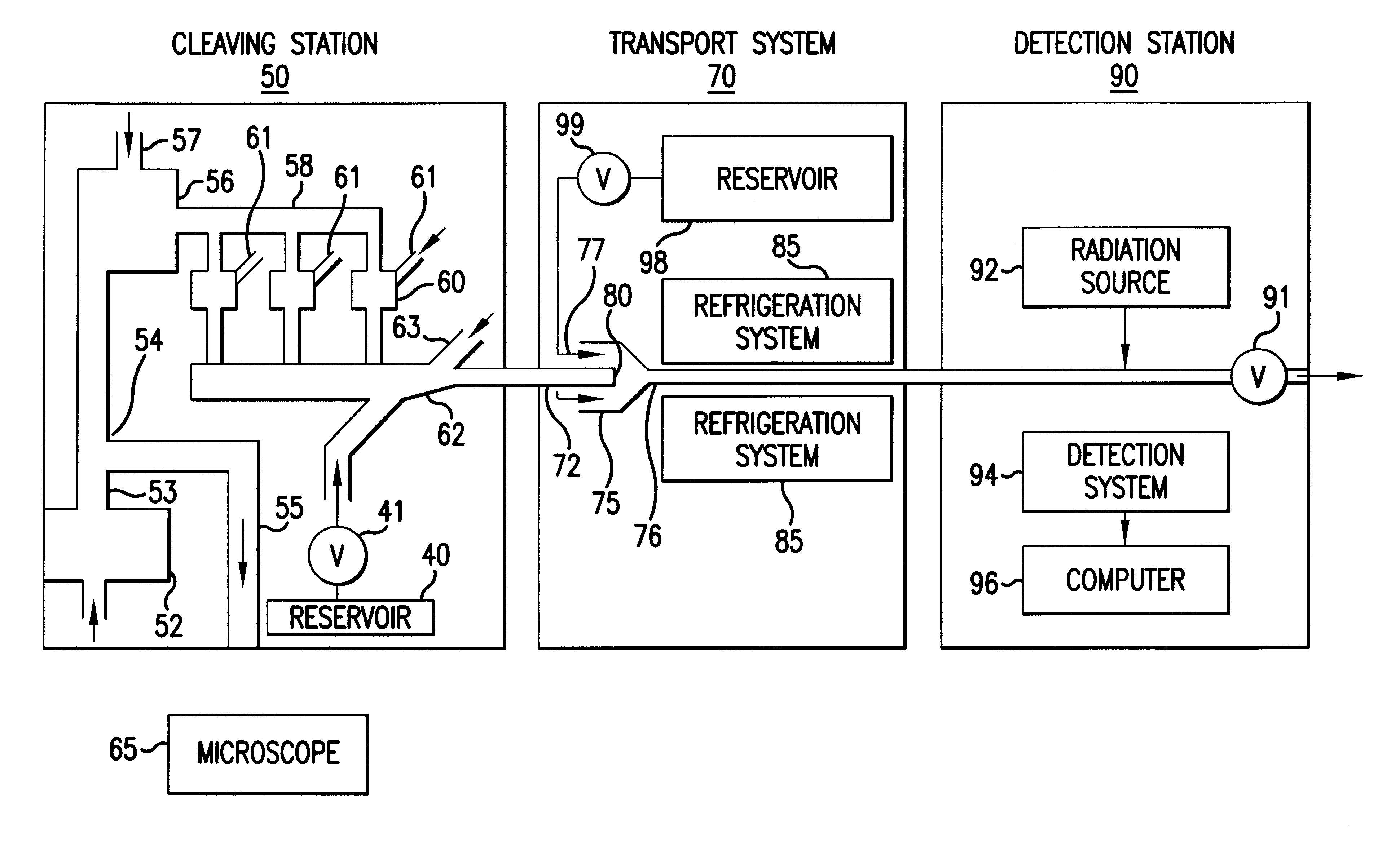
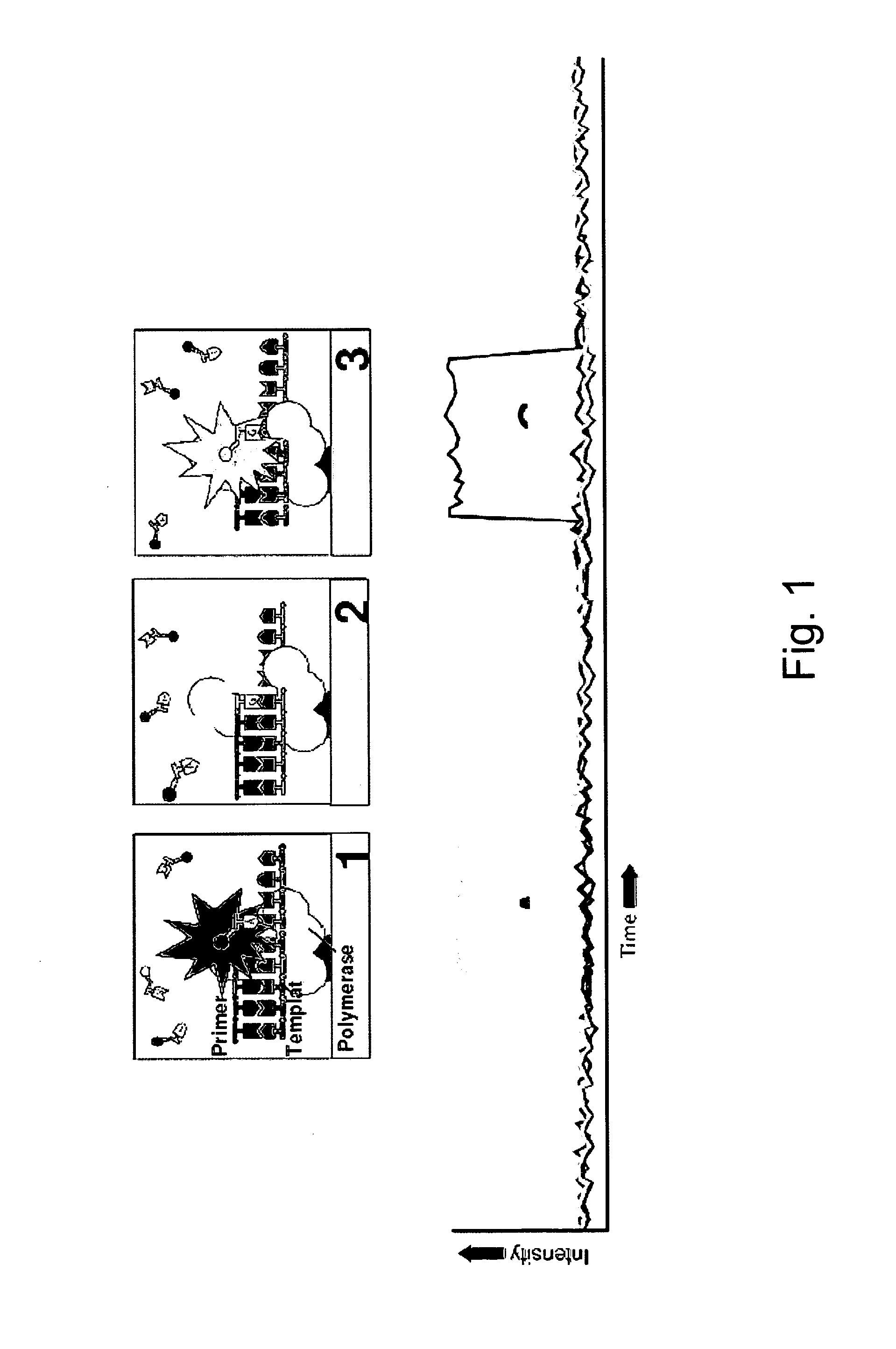
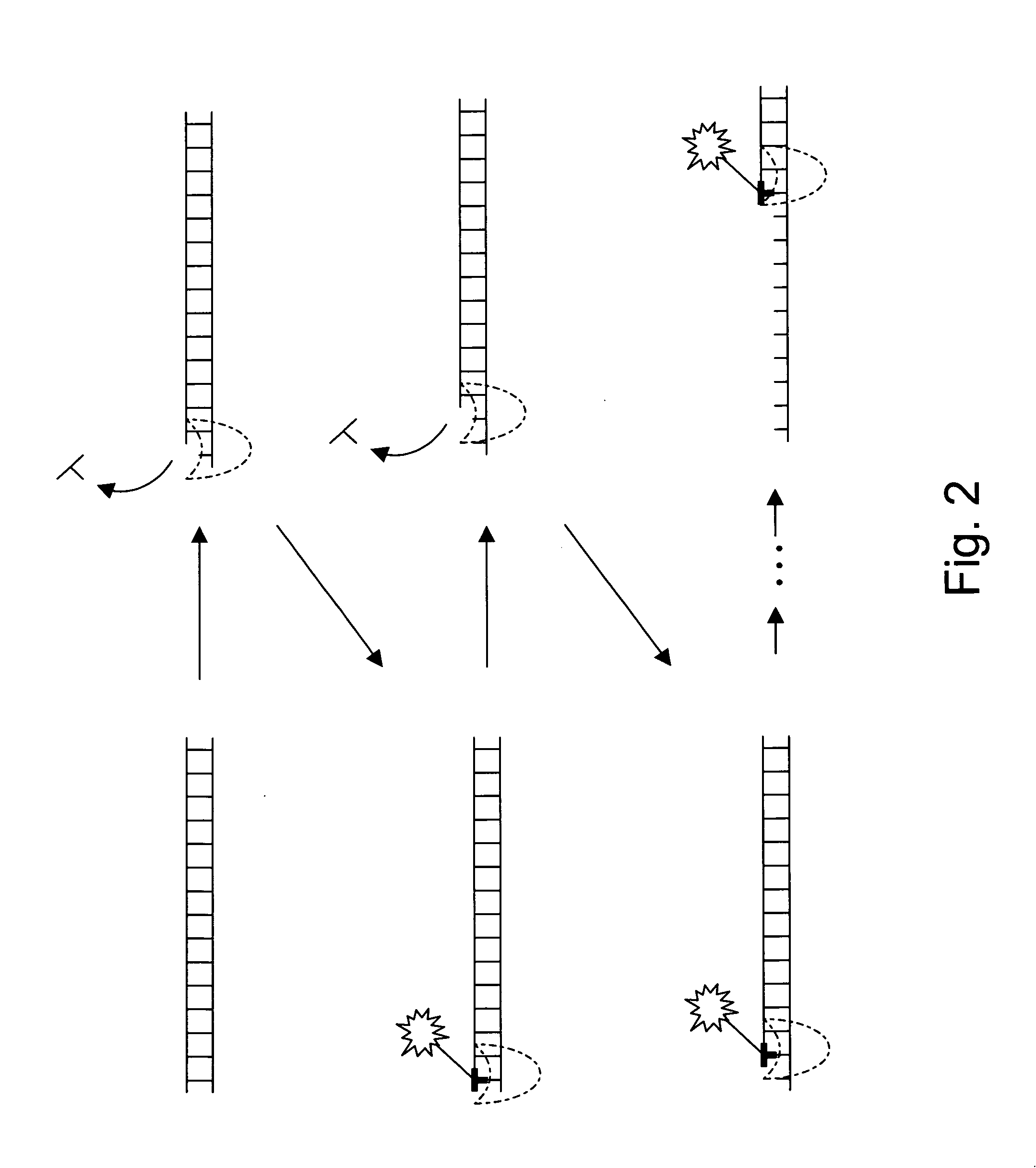
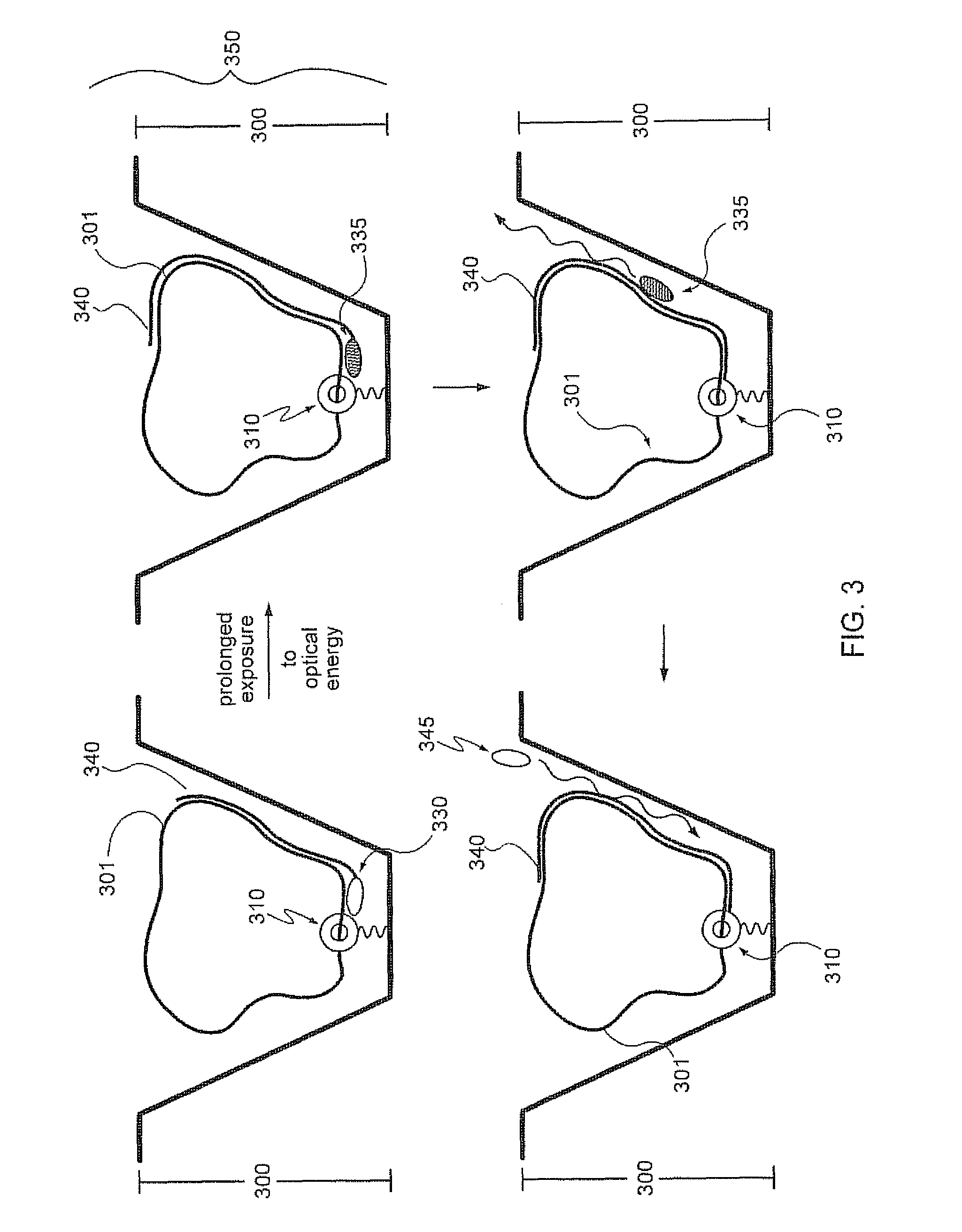
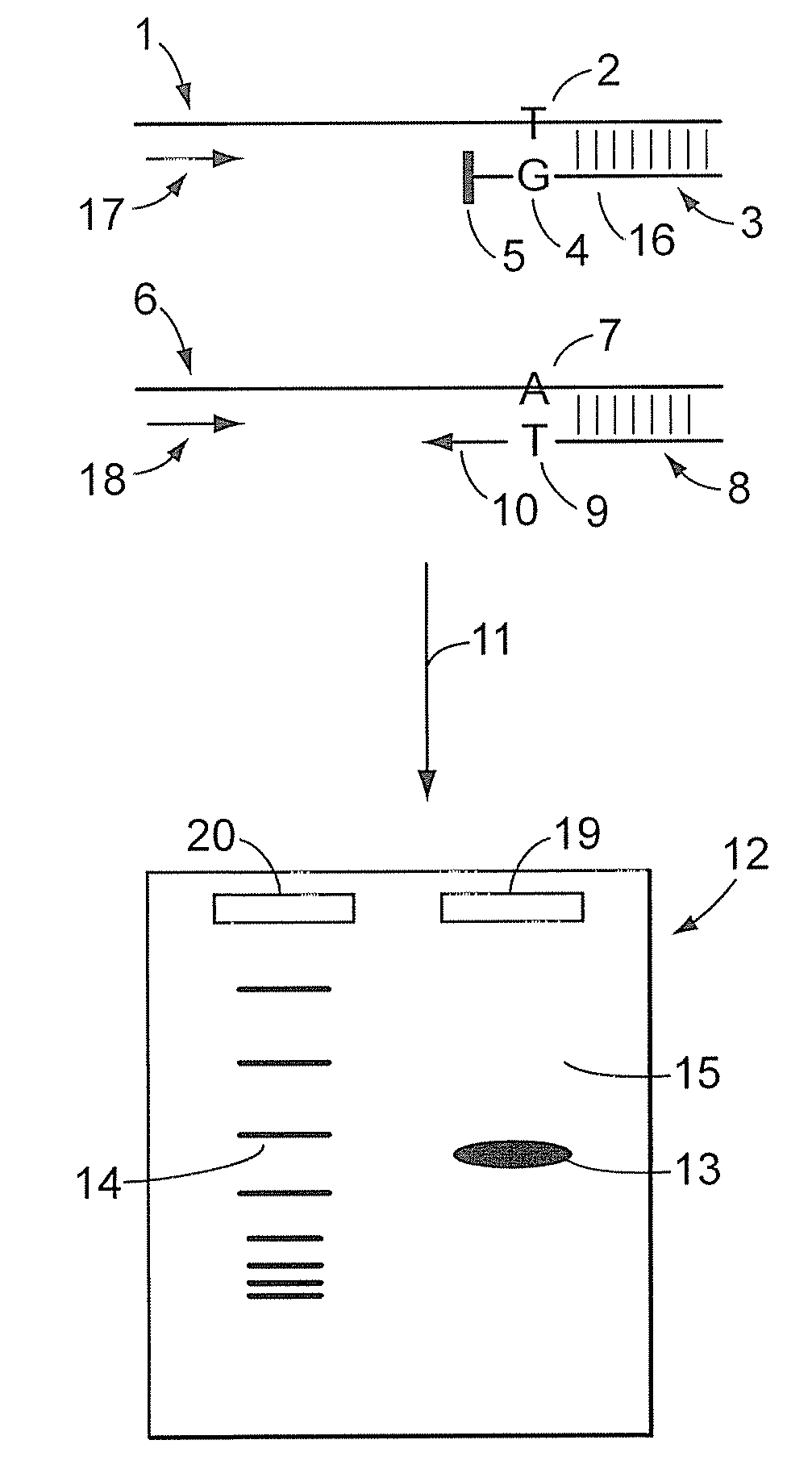
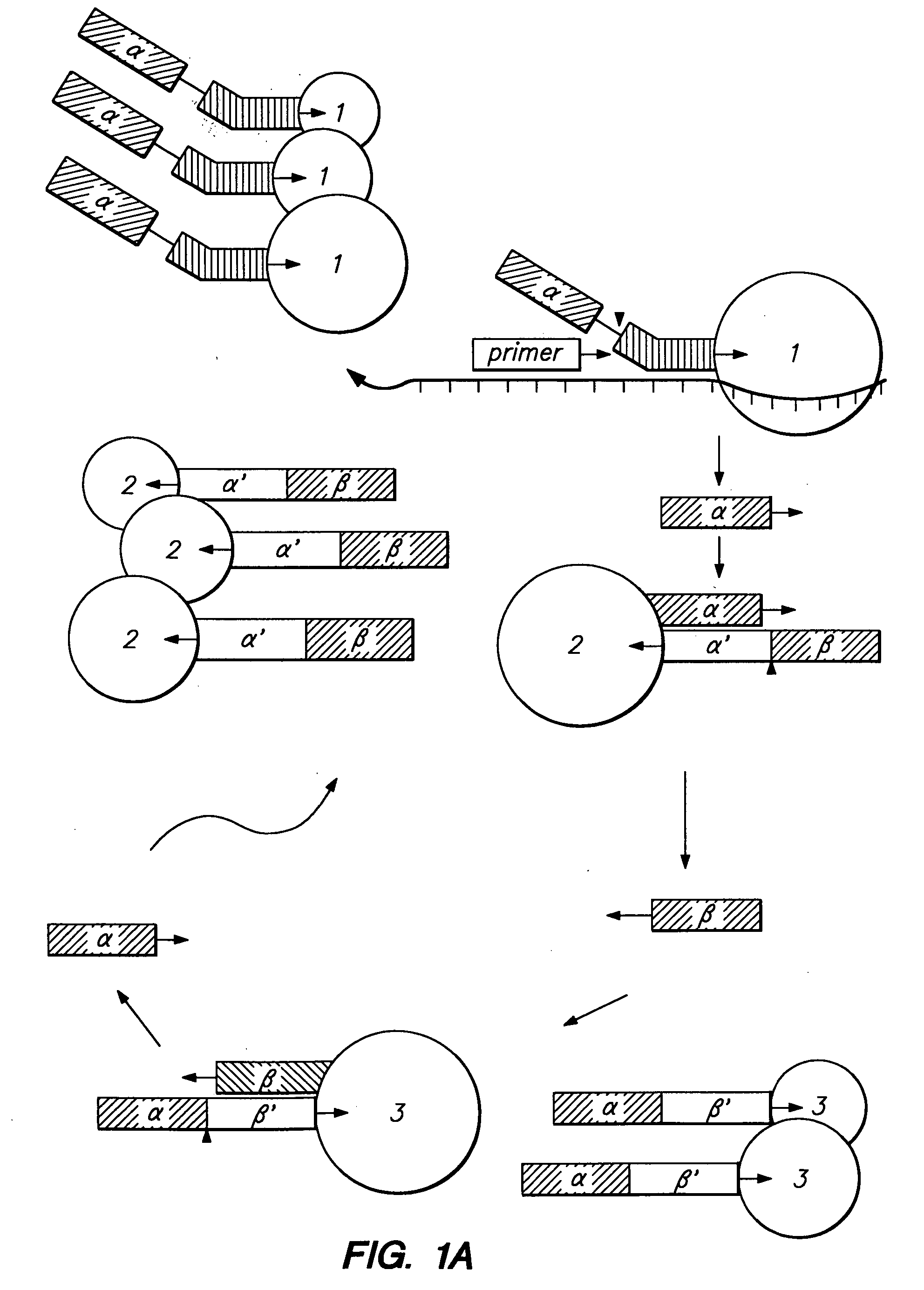
Apparatus for DNA sequencing
InactiveUS6296810B1Enhances natural fluorescent activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsTransport systemNucleotide
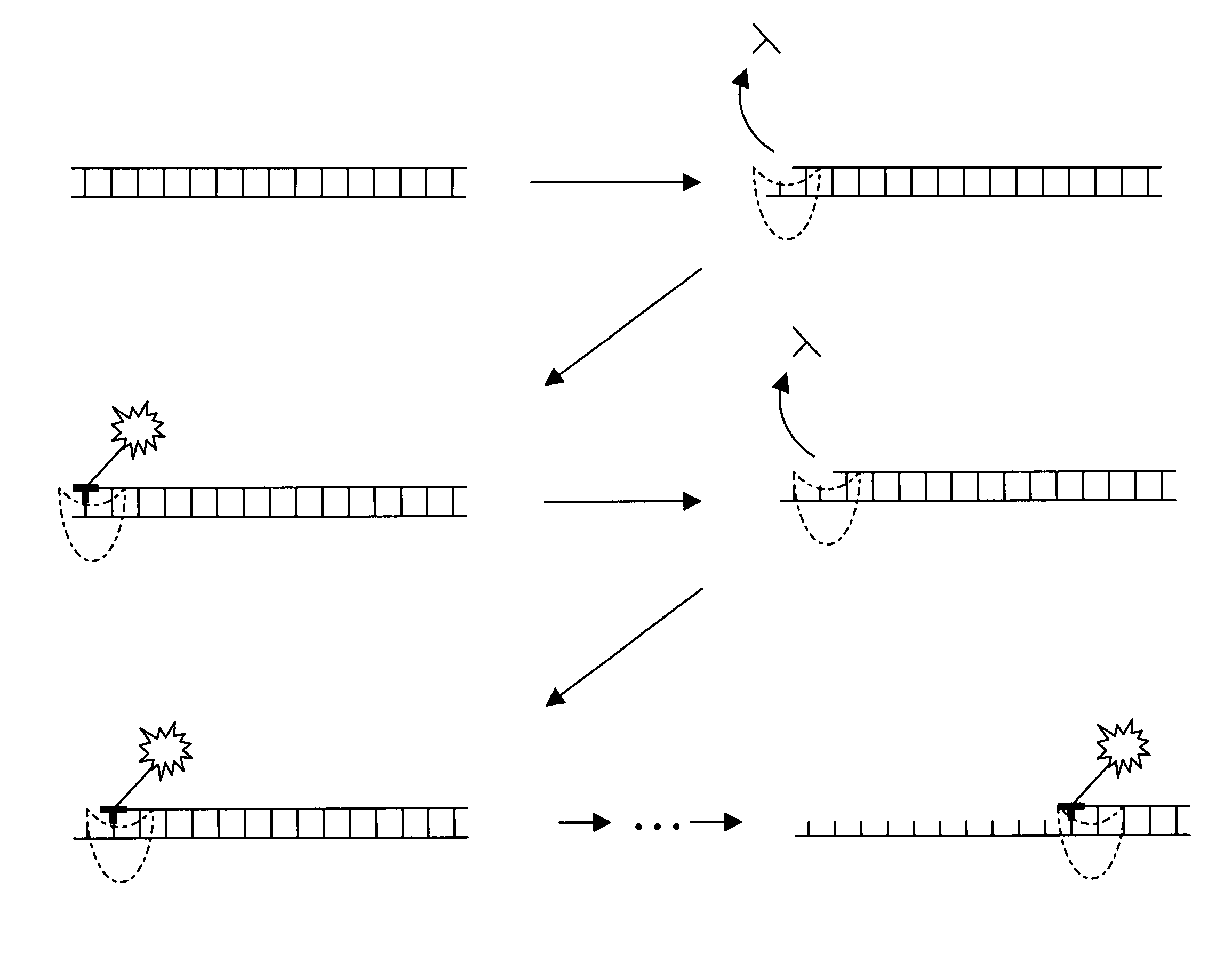
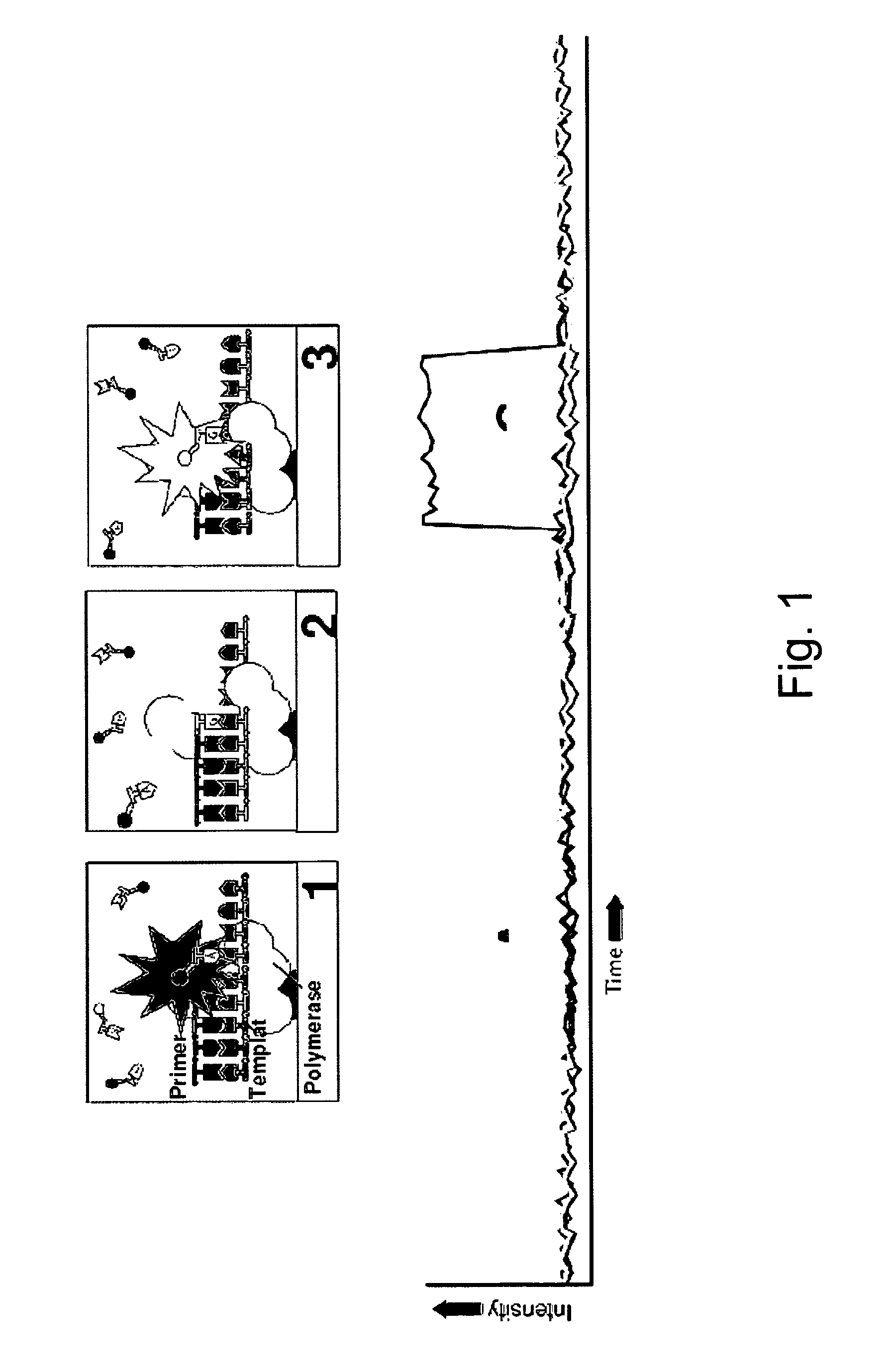
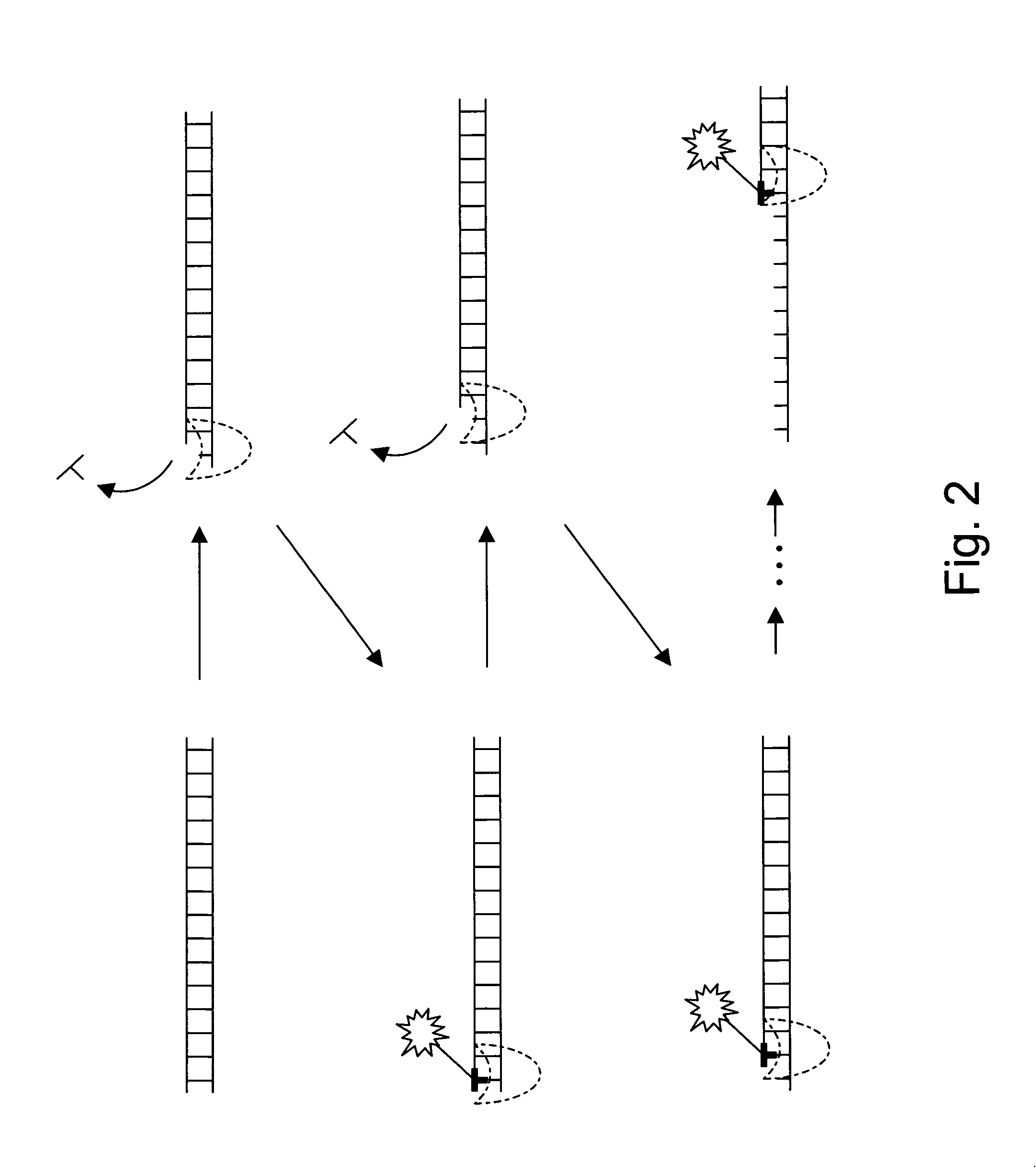
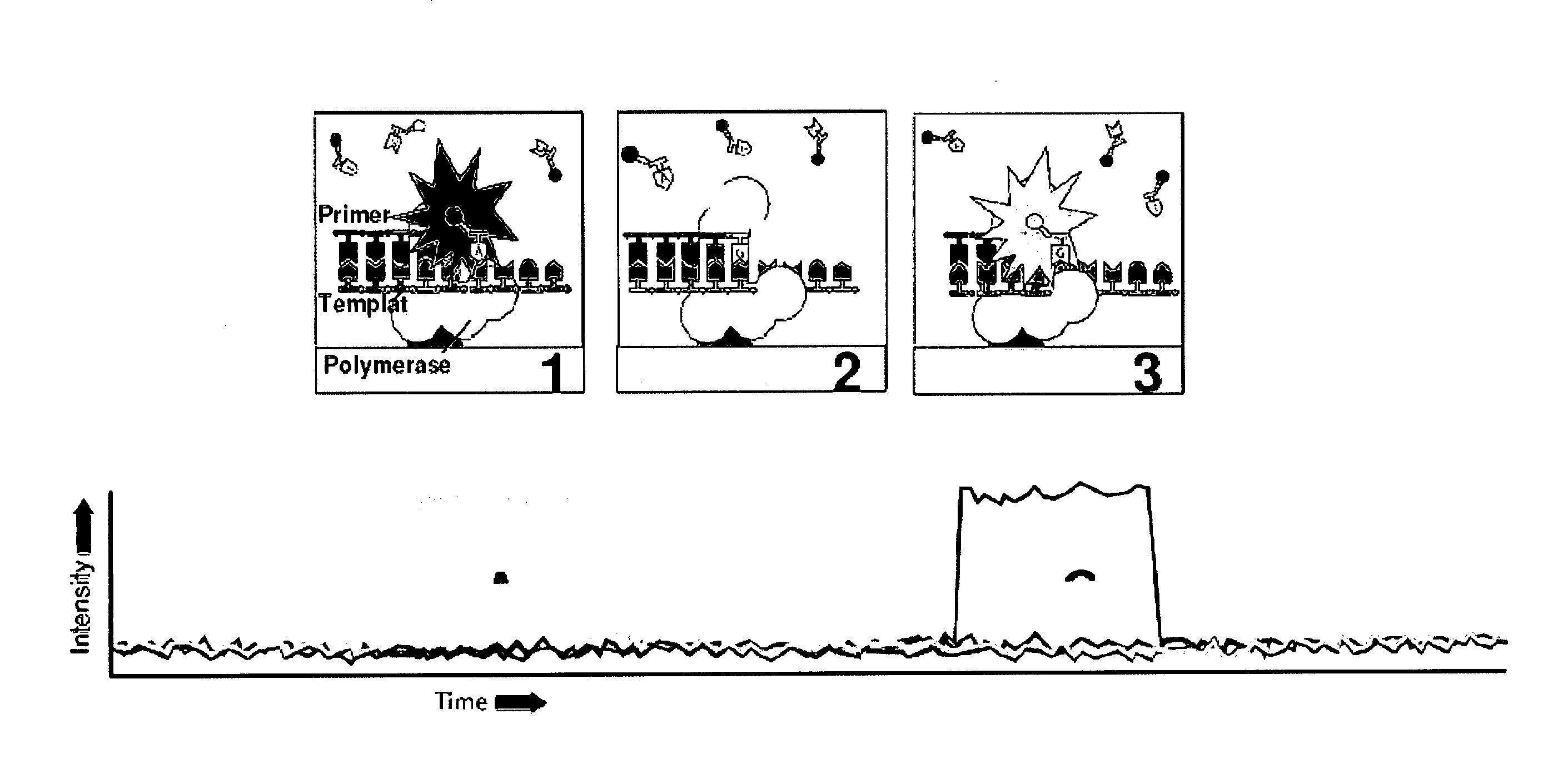
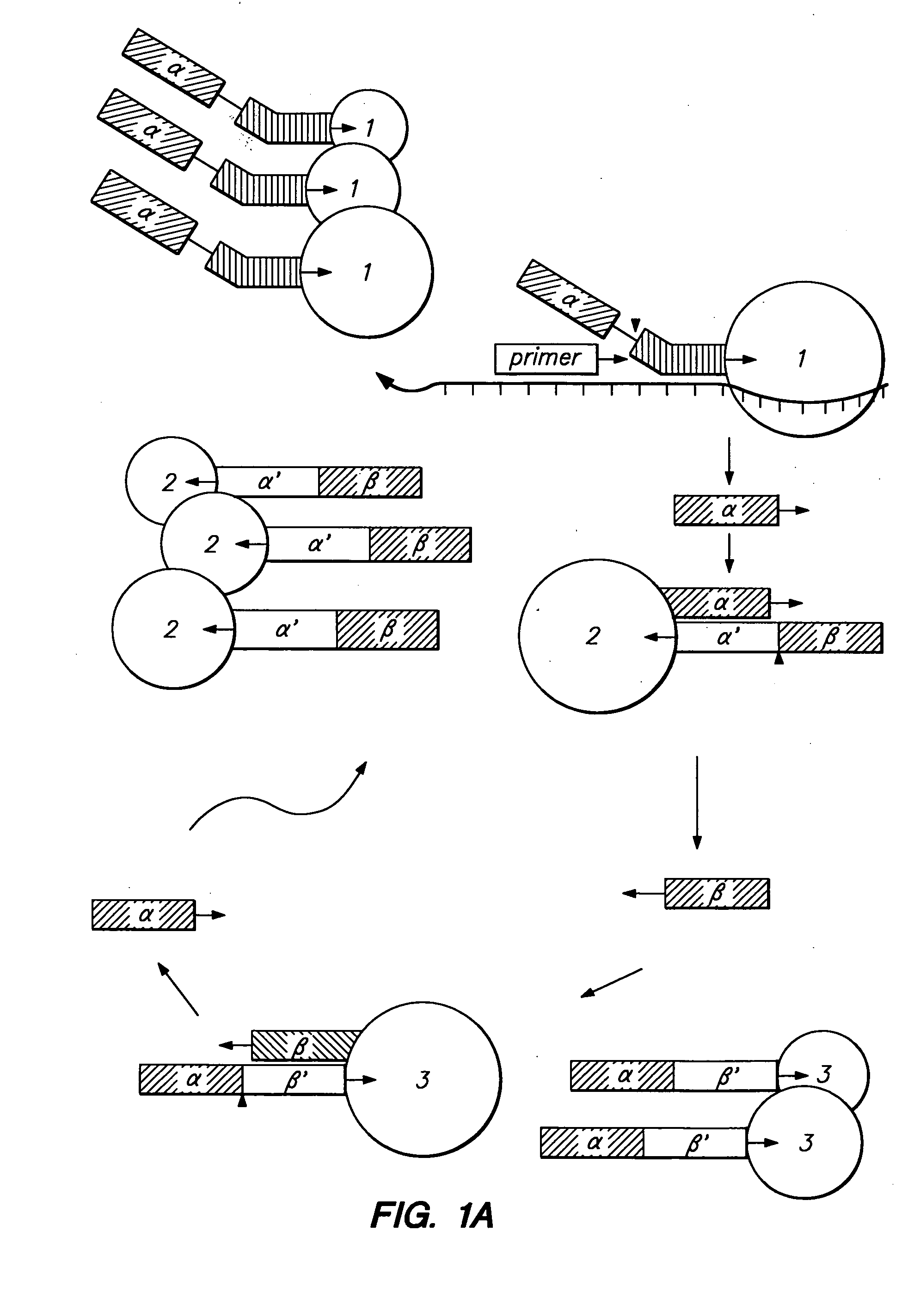
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for automated DNA sequencing. The method of the invention includes the steps of: a) using a processive exonuclease to cleave from a single DNA strand the next available single nucleotide on the strand; b) transporting the single nucleotide away from the DNA strand; c) incorporating the single nucleotide in a fluorescence-enhancing matrix; d) irradiating the single nucleotide to cause it to fluoresce; e) detecting the fluorescence; f) identifying the single nucleotide by its fluorescence; and g) repeating steps a) to f) indefinitely (e.g., until the DNA strand is fully cleaved or until a desired length of the DNA is sequenced). The apparatus of the invention includes a cleaving station for the extraction of DNA from cells and the separation of single nucleotides from the DNA; a transport system to separate the single nucleotide from the DNA and incorporate the single nucleotide in a fluorescence-enhancing matrix; and a detection station for the irradiation, detection and identification of the single nucleotides. The nucleotides are advantageously detected by irradiating the nucleotides with a laser to stimulate their natural fluorescence, detecting the fluorescence spectrum and matching the detected spectrum with that previously recorded for the four nucleotides in order to identify the specific nucleotide.
Owner:AMERSHAM BIOSCIENCES KK
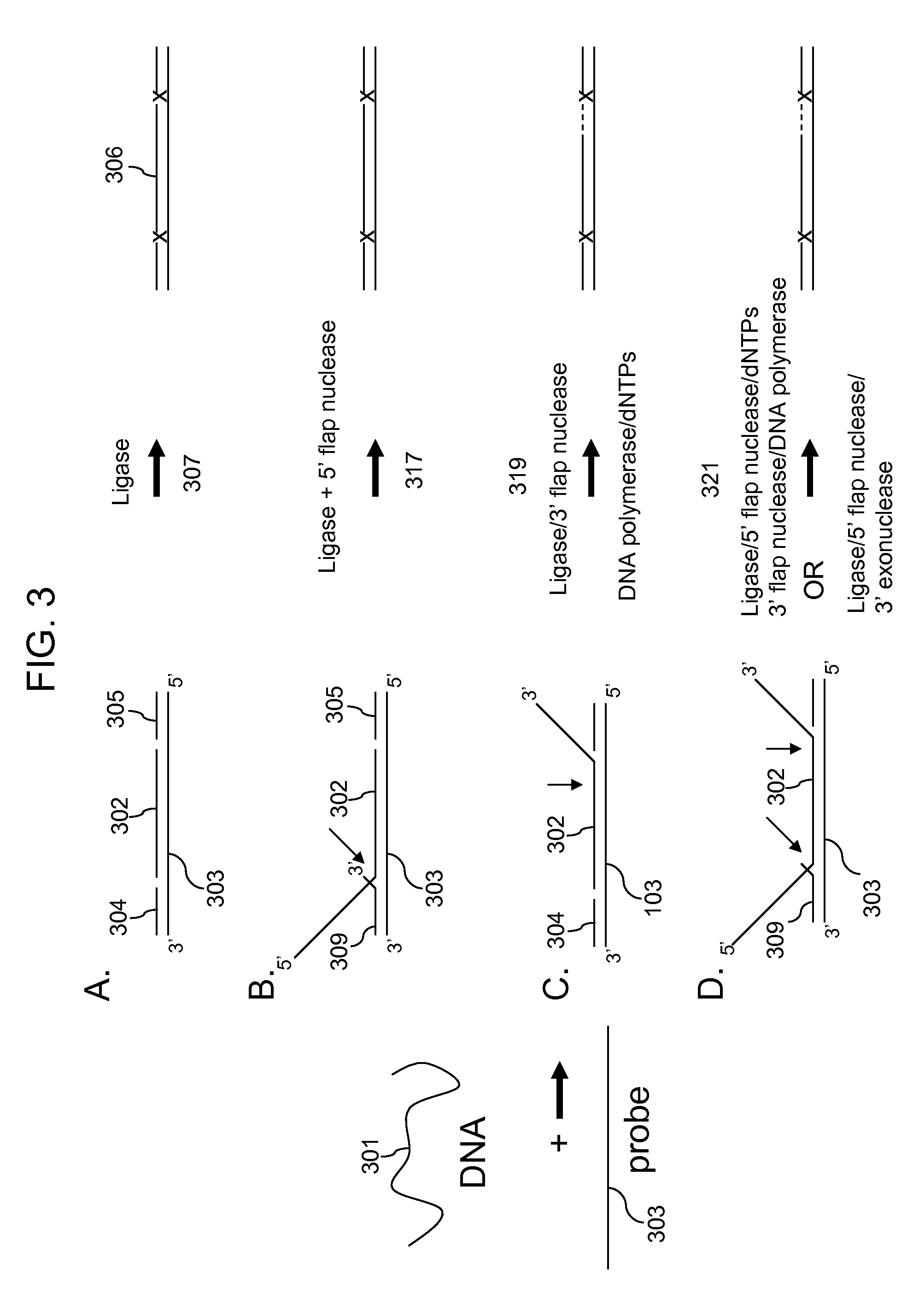
Multiplex targeted amplification using flap nuclease
Methods for multiplex amplification of a plurality of targets of distinct sequence from a complex mixture are disclosed. In one aspect targets are circularized using a single circularization probe that is complementary to two regions in the target that flank a region to be amplified. The targets may hybridize to the circularization probe so that 5′ or 3′ flaps are generated and methods for removing flaps and circularizing the resulting product are disclosed. In another aspect targets are hybridized to dU probes so that 5′ and 3′ flaps are generated. The flaps are cleaved using 5′ or 3′ flap endonucleases or 3′ to 5′ exonucleases. The target sequences are then ligated to common primers, the dU probes digested and the ligated targets amplified.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Chromosome structural abnormality localization with single copy probes
InactiveUS7014997B2Eliminates spurious hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentHybridization probe
Nucleic acid (e.g., DNA) hybridization probes are described which comprise a labeled, single copy nucleic acid which hybridizes to a deduced single copy sequence interval in target nucleic acid of known sequence. The probes, which are essentially free of repetitive sequences, can be used in hybridization analyses without adding repetitive sequence-blocking nucleic acids. This allows rapid and accurate detection of chromosomal abnormalities. The probes are preferably designed by first determining the sequence of at least one single copy interval in a target nucleic acid sequence, and developing corresponding hybridization probes which hybridize to at least a part of the deduced single copy sequence. In practice, the sequences of the target and of known genomic repetitive sequence representatives are compared in order to deduce locations of the single copy sequence intervals. The single copy probes can be developed by any variety of methods, such as PCR amplification, restriction or exonuclease digestion of purified genomic fragments, or direct synthesis of DNA sequences. This is followed by labeling of the probes and hybridization to a target sequence.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
Multiplex targeted amplification using flap nuclease
Methods for multiplex amplification of a plurality of targets of distinct sequence from a complex mixture are disclosed. In one aspect targets are circularized using a single circularization probe that is complementary to two regions in the target that flank a region to be amplified. The targets may hybridize to the circularization probe so that 5′ or 3′ flaps are generated and methods for removing flaps and circularizing the resulting product are disclosed. In another aspect targets are hybridized to dU probes so that 5′ and 3′ flaps are generated. The flaps are cleaved using 5′ or 3′ flap endonucleases or 3′ to 5′ exonucleases. The target sequences are then ligated to common primers, the dU probes digested and the ligated targets amplified.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Nucleic acid sequencing methods and systems
ActiveUS7960116B2Reduced activityHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleobase bindingExonuclease I
Sequencing methods that use an exonuclease that comprises template dependent nucleobase binding activity are provided. Related compositions and sequencing systems are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Nucleic acid sequencing methods and systems
ActiveUS20090087850A1Low polymerization activityEnhanced exonuclease activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleobase bindingExonuclease I
Sequencing methods that use an exonuclease that comprises template dependent nucleobase binding activity are provided. Related compositions and sequencing systems are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Immobilized nucleic acid complexes for sequence analysis
ActiveUS8481264B2Use performanceImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisExonuclease I
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Sequencing library building method and reagent based on molecular inverse probe
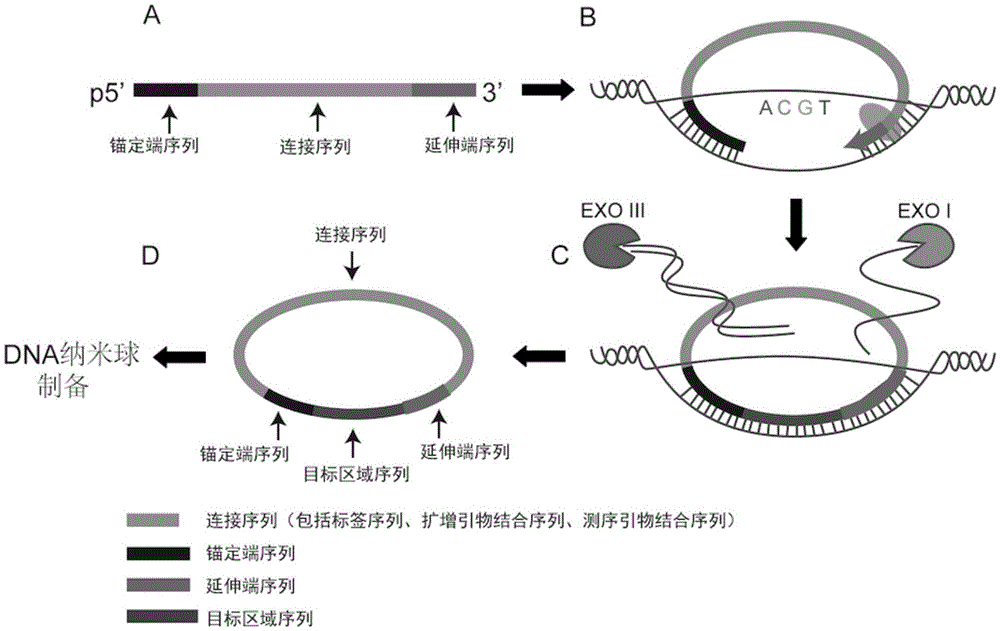
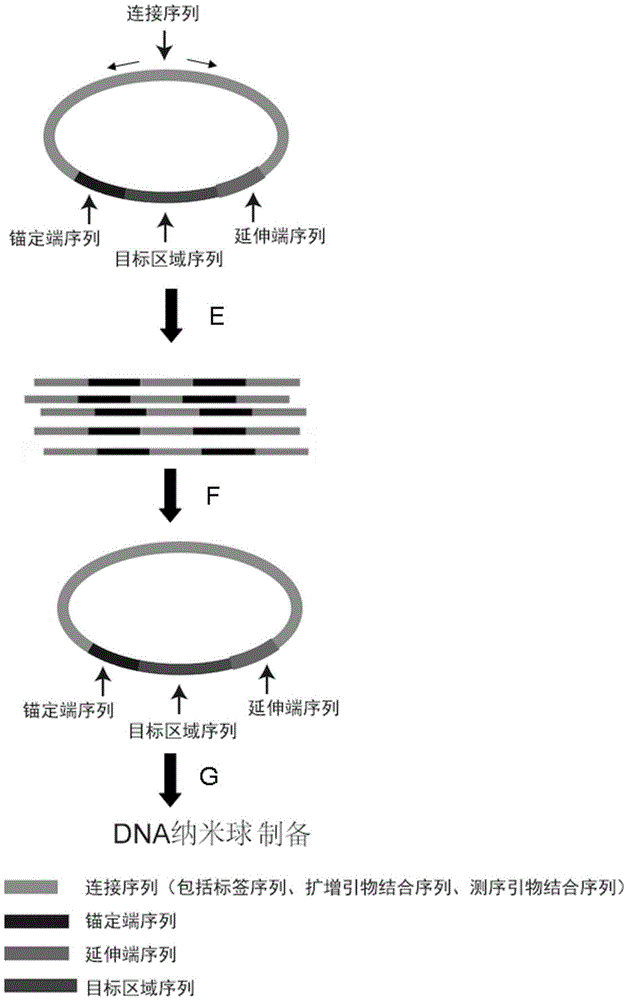
ActiveCN105714383AReduce errorsSimple processMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationExonuclease IReagent
The invention discloses a sequencing library building method and reagent based on a molecular inverse probe. The method includes: using the molecular inverse probe and denatured nucleic acid to perform annealing hybridization, wherein the molecular inverse probe comprises the anchoring sequence of a 5' end, the extension sequence of a 3' end and the sequencing connector sequence between the anchoring sequence and the extension sequence, and the anchoring sequence and the extension sequence are respectively inversely complementary with sequences at two ends of a target area; using the target area as a template, and performing polymerization reaction starting from the extension sequence of the 3' end to generate the supplementary sequence of the target area; connecting the anchoring sequence of the 5' end with the supplementary sequence of the target area to form cyclic annular nucleic acid molecules; using exonuclease to digest non-cyclized linear molecules to obtain single-chain cyclic annular molecules containing the target area; sequencing the obtained single-chain cyclic annular molecules so as to achieve capture sequencing of the target area. The sequencing library building method has the advantages that the building of a single-chain cyclic annular library and target area capture are integrated, and library building process and cycle are shortened greatly.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
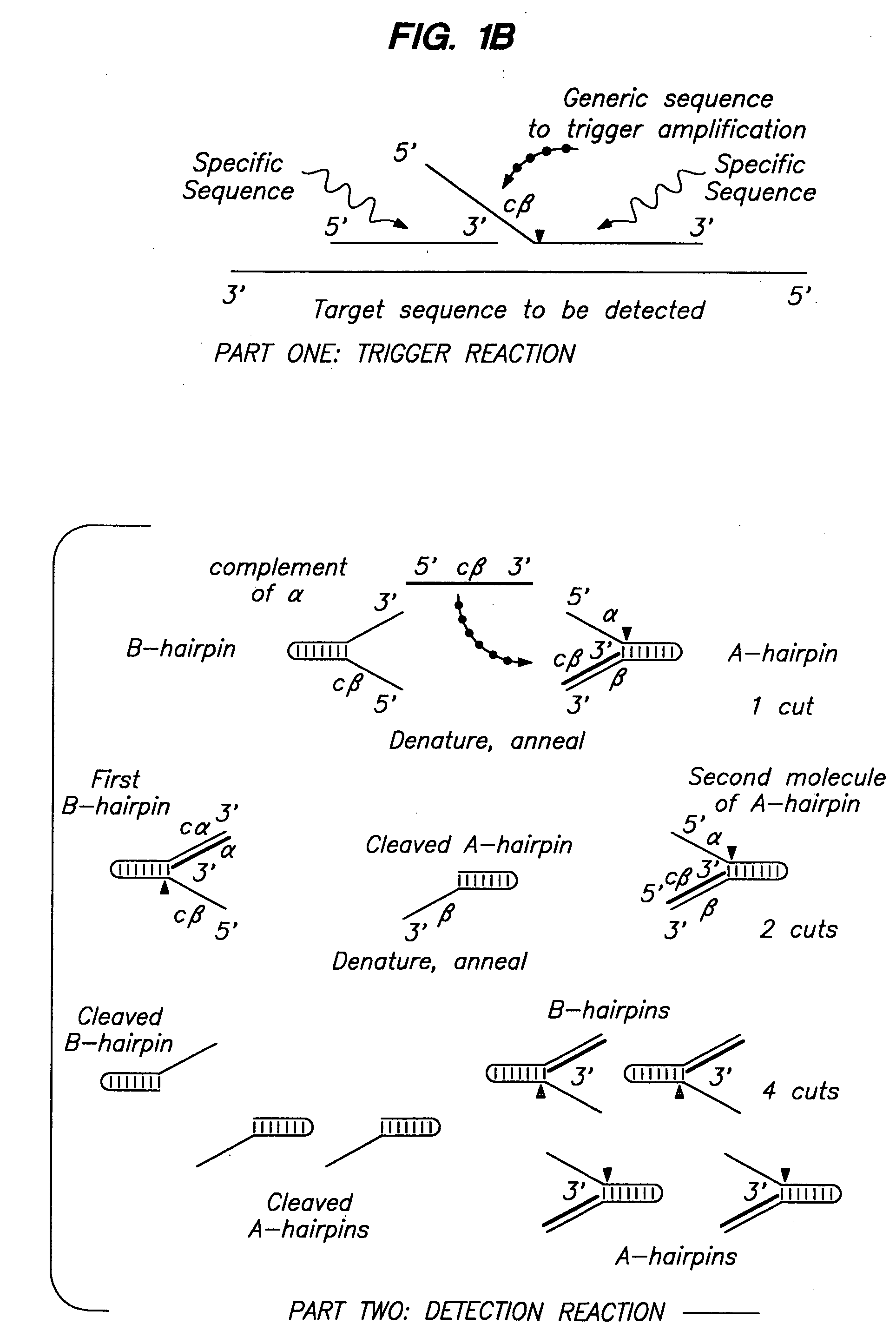
Systems for the detection of target sequences
InactiveUS7067643B2Rapid detection and identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismExonuclease I
The present invention relates to means for cleaving a nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. Enzymes, including 5′ nucleases and 3′ exonucleases, are used to detect and identify nucleic acids derived from microorganisms. Methods are provided which allow for the detection and identification of bacterial and viral pathogens in a sample.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Detection using degradation of a tagged sequence
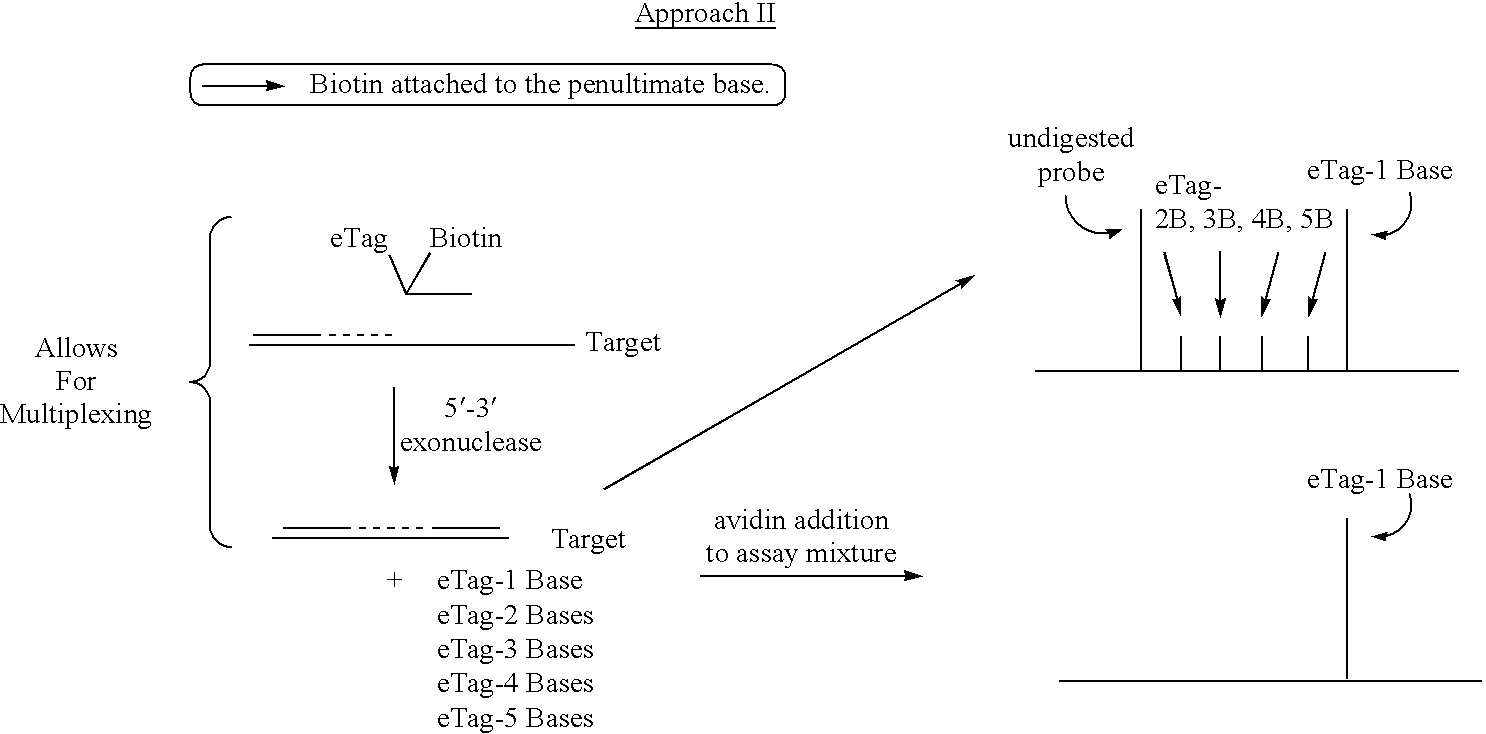
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting DNA sequences, particularly single nucleotide polymorphisms, using a pair of nucleotide sequences, a primer and a snp detection sequence, where the snp detection sequence binds downstream from the primer to the target DNA in the direction of primer extension. The snp detection sequence is characterized by having a nucleotide complementary to the snp and adjacent nucleotides complementary to adjacent nucleotides in the target and an electrophoretic tag bonded to the 5'-nucleotide. The pair of sequences is combined with the target DNA under primer extension conditions, where the polymerase has 5'-3' exonuclease activity. When the snp is present, the electrophoretic tag is released and can be detected by electrophoresis as indicative of the presence of the snp in the target DNA. The sequence containing the snp is exemplary of DNA sequences of interest generally.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
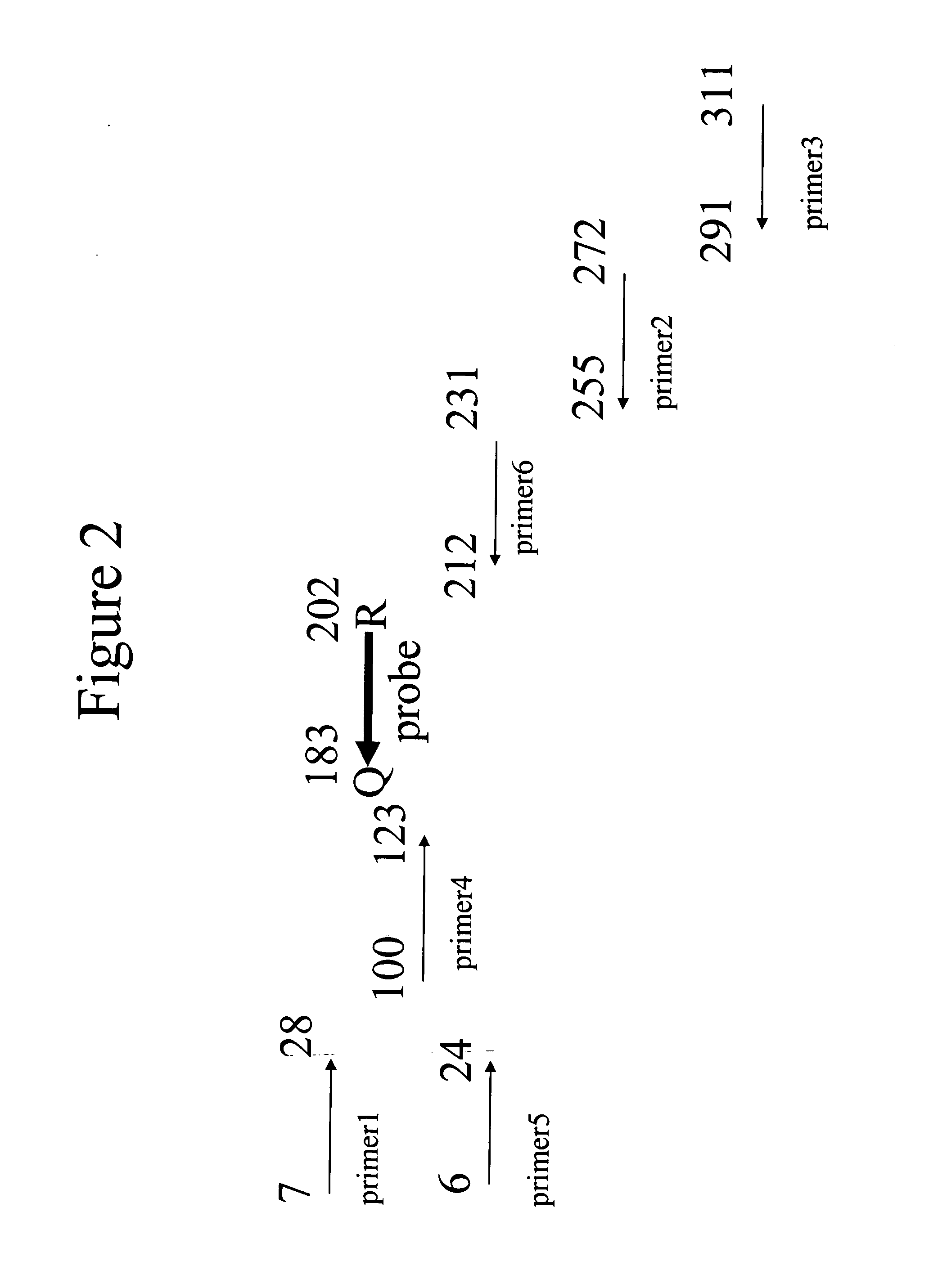
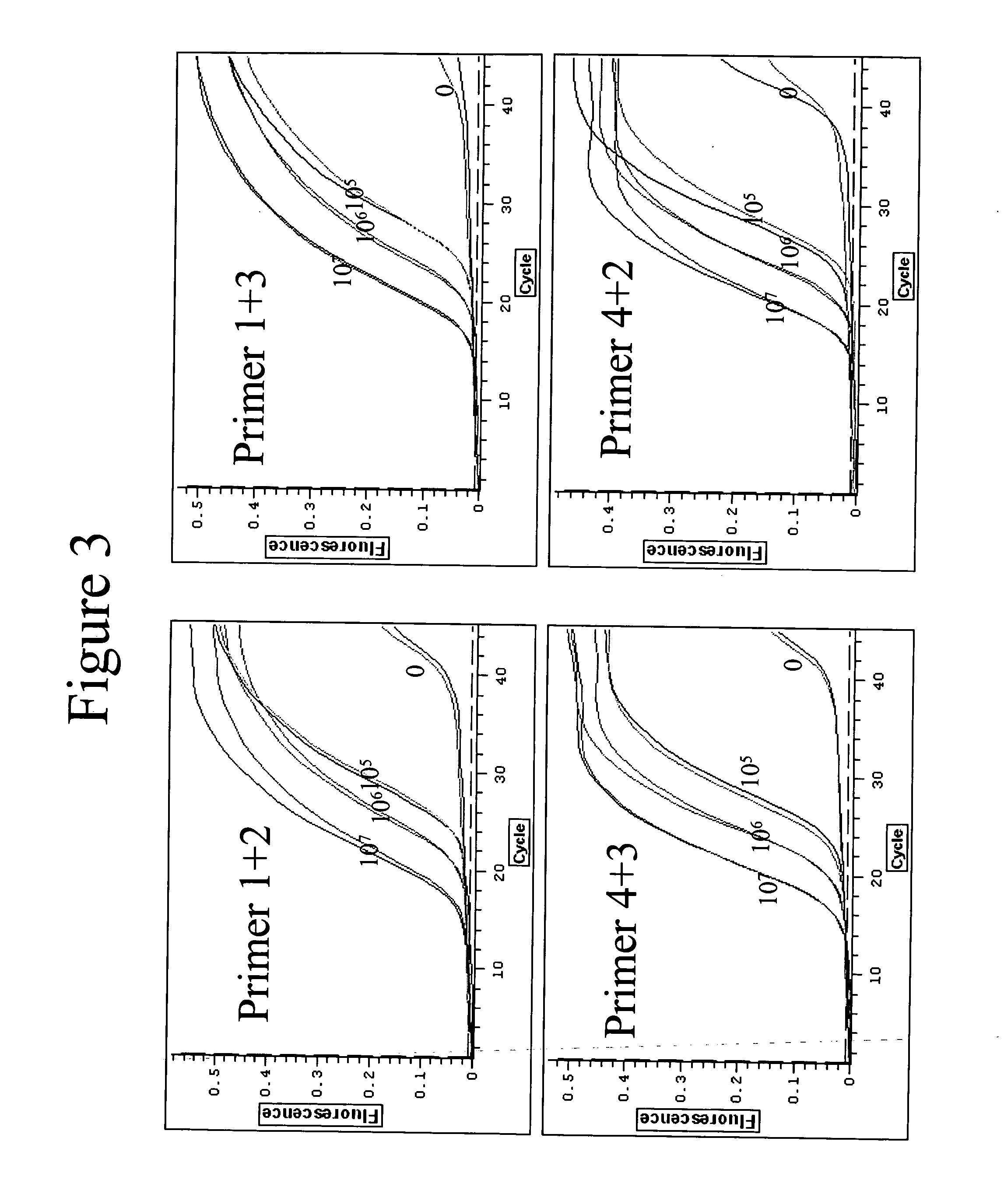
Quantitative amplification with a labeled probe and 3' to 5' exonuclease activity
This invention provides methods and kits for performing a quantitative amplification reaction. The method employs a polymerase enzyme and an enzyme having a 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity that cleaves the 3′ oligonucleotide of the probe.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Quantitative amplification with a labeled probe and 3' to 5' exonuclease activity
This invention provides methods and kits for performing a quantitative amplification reaction. The method employs a polymerase enzyme and an enzyme having a 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity that cleaves the 3′ oligonucleotide of the probe.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Nucleic acid detection kits
InactiveUS20050158716A1Quick checkQuick identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismNucleic acid detection
The present invention relates to means for cleaving a nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. Enzymes, including 5′ nucleases and 3′ exonucleases, are used to detect and identify nucleic acids derived from microorganisms. Methods are provided which allow for the detection and identification of bacterial and viral pathogens in a sample.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Novel microarray techniques for nucleic acid expression analyses
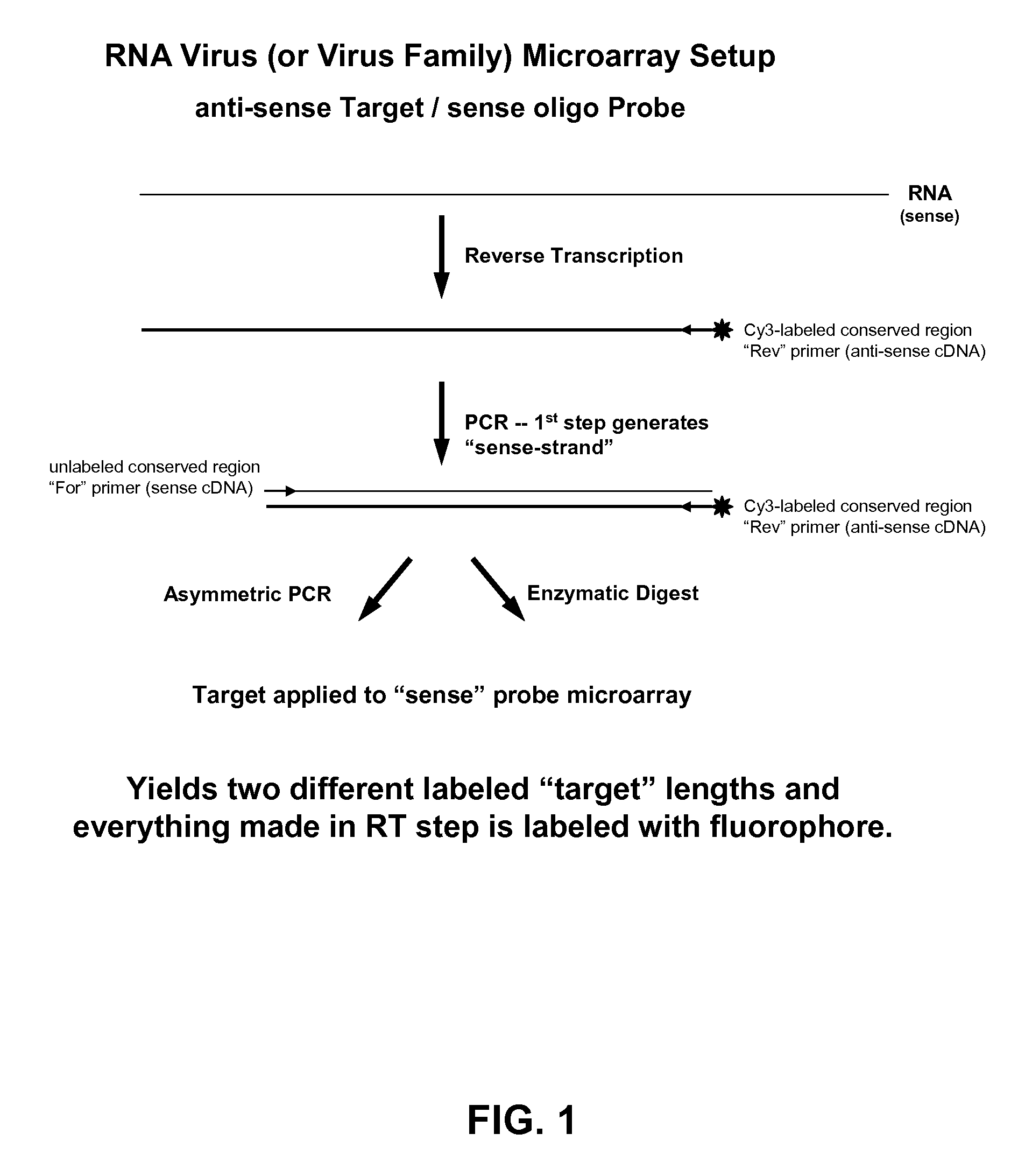
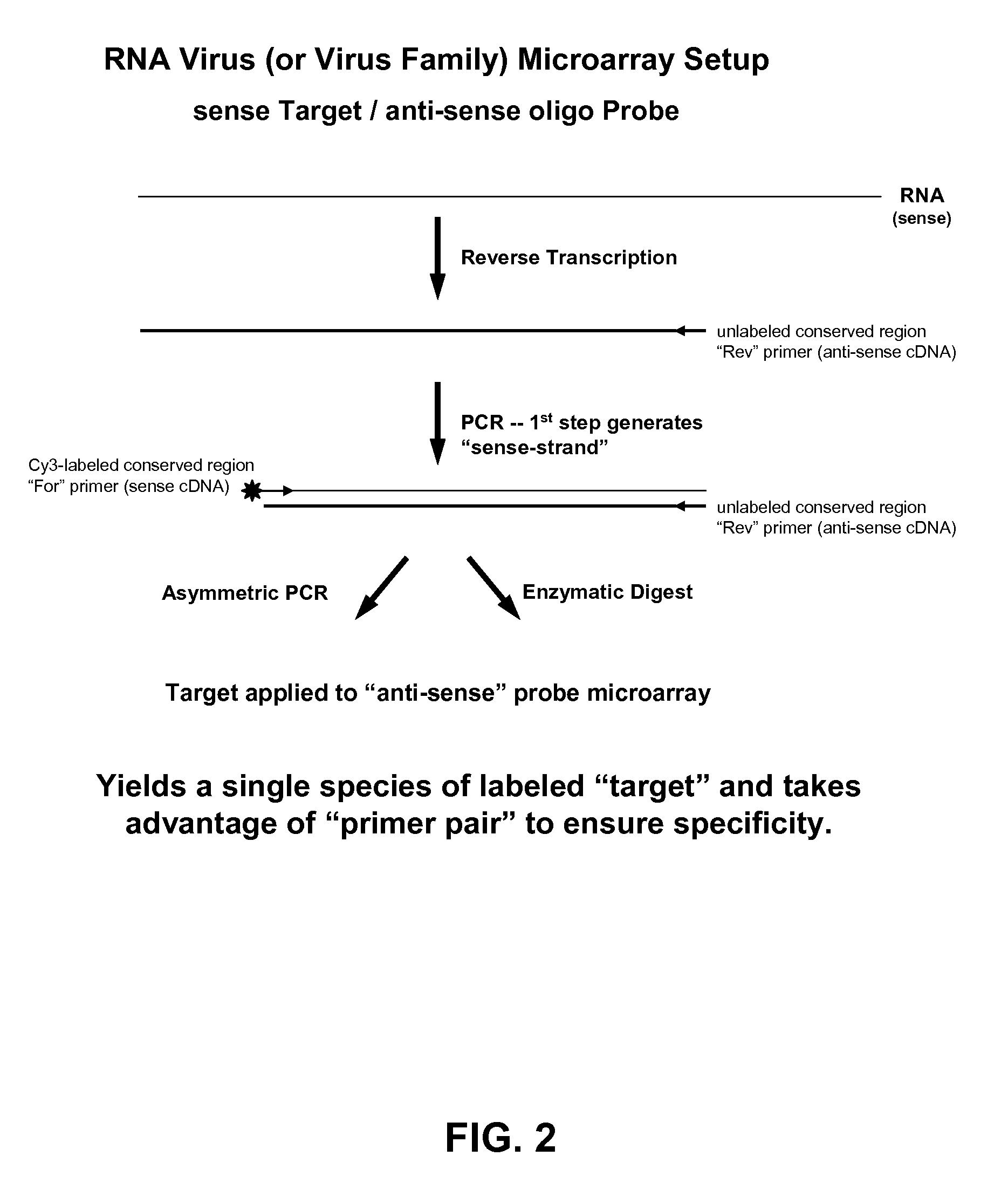
ActiveUS20060078925A1Eliminate biasConvenient experimentMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMiRNA GeneExonuclease I
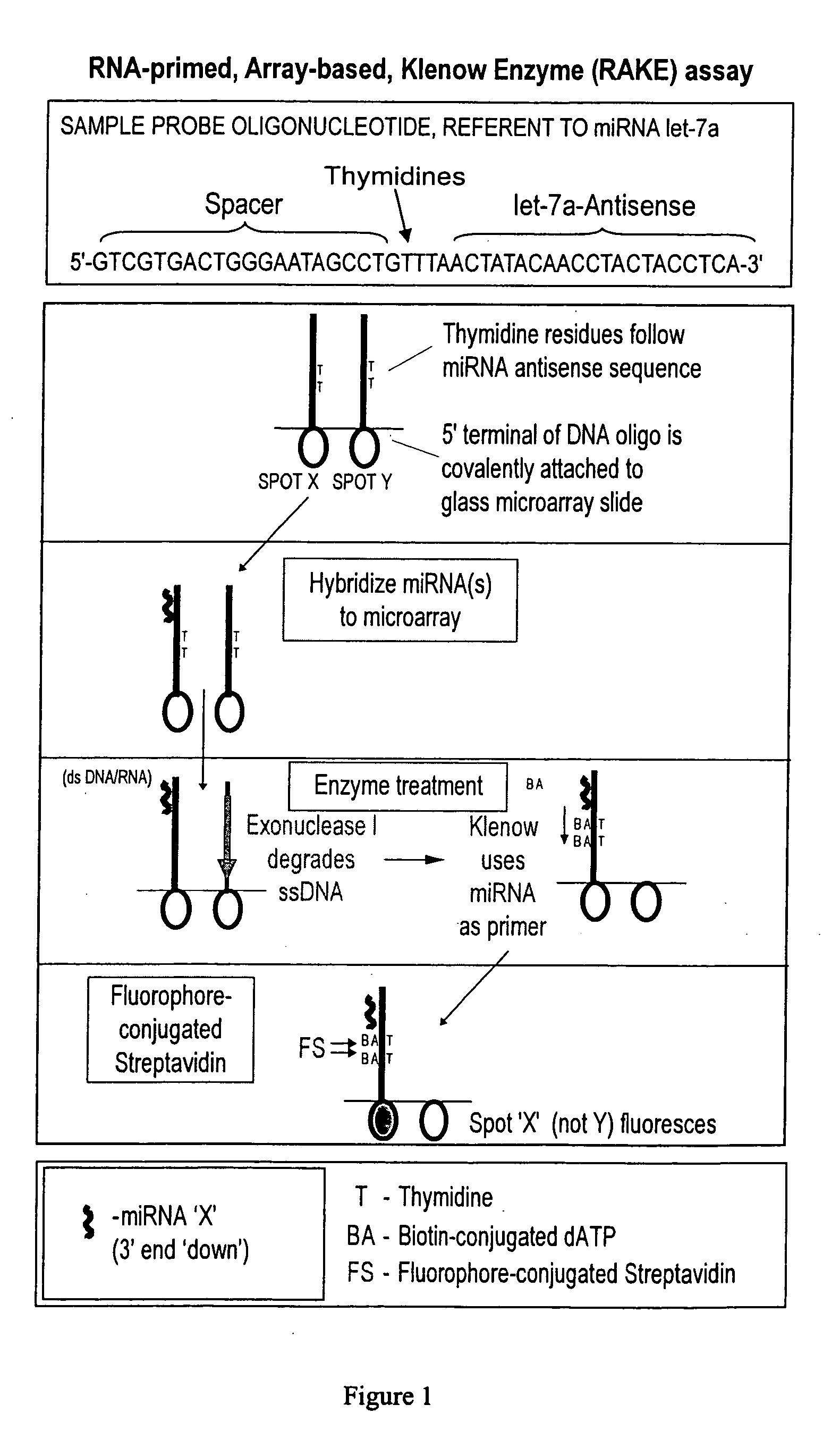
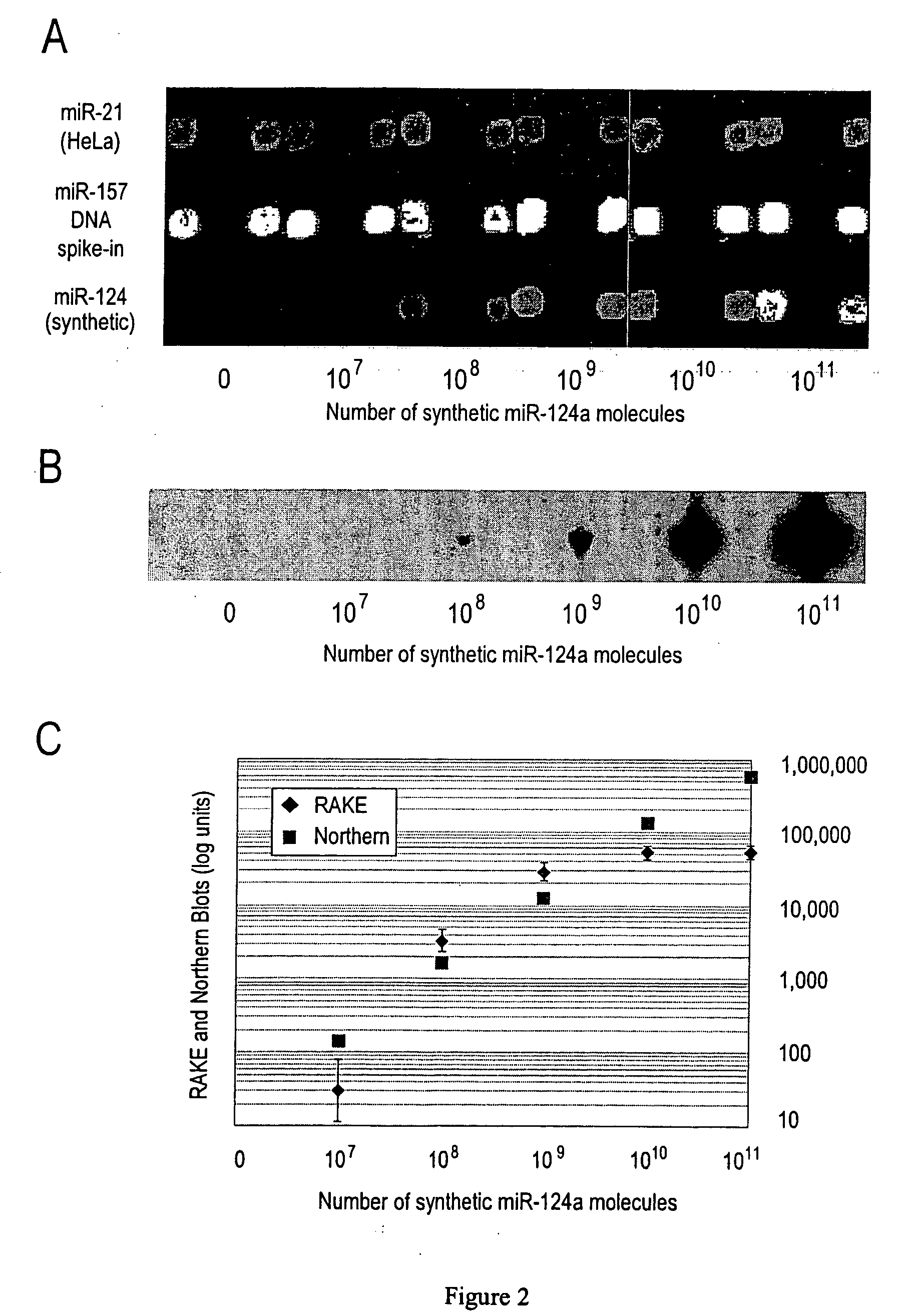
Provided are DNA microarray techniques that allow hybridization without RNA amplification, without using cDNA, and without labeling the nucleic acid prior to hybridization. Referred to as the Double-stranded Exonuclease Protection (DEP) assay, the technique permits the sample RNA to be used directly for hybridization, without manipulation in any way. Further provided is a microarray technique for high-throughput miRNA gene expression analyses, termed the RNA-primed, Array-based, Klenow Enzyme (RAKE) assay. The RAKE assay is a sensitive and specific technique for assessing single-stranded DNA and RNA targets, and offers specific advantages over Northern blots.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Hydrolysis Probes
InactiveUS20130085078A1Increase the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPolymerase LExonuclease I
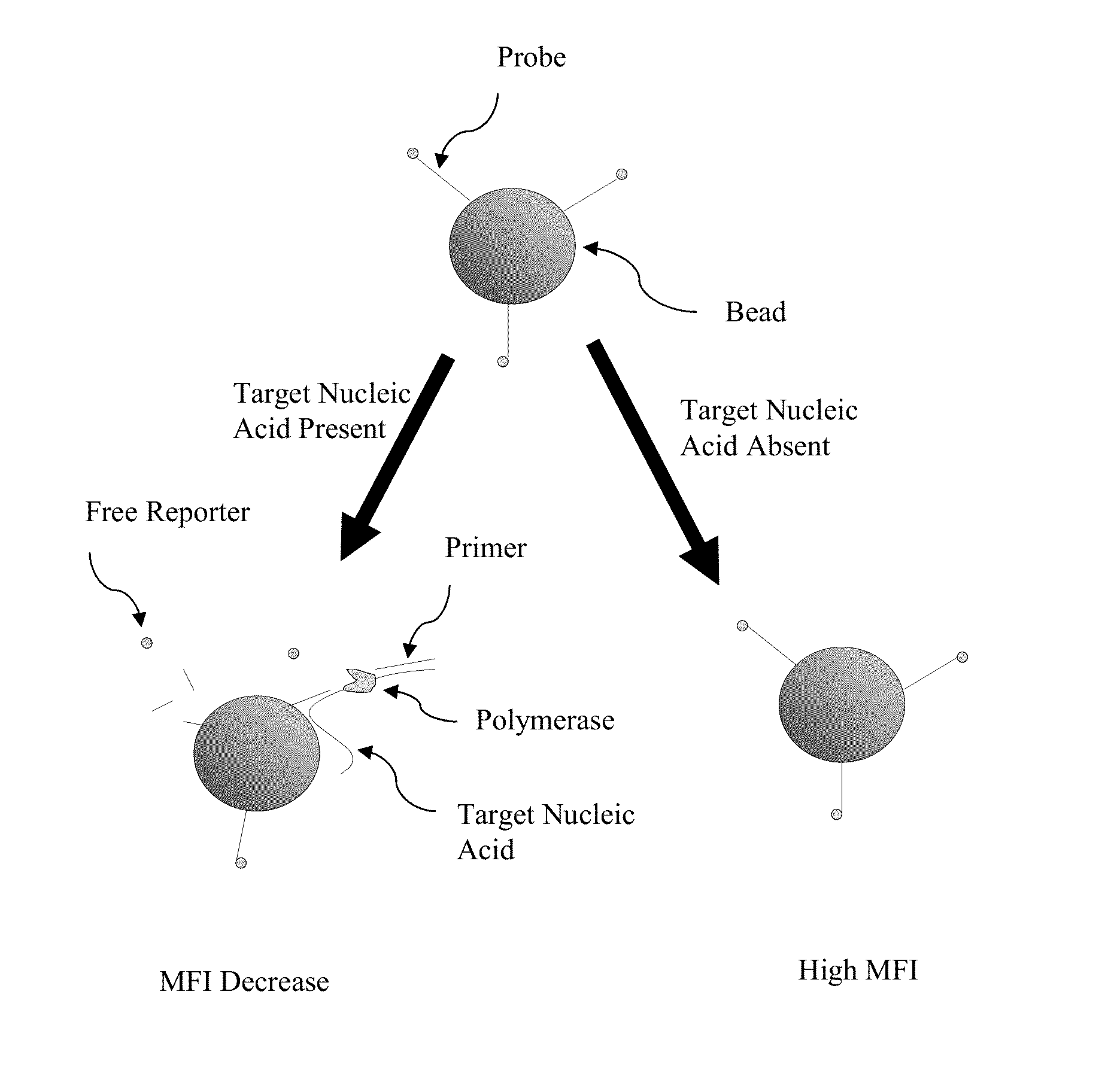
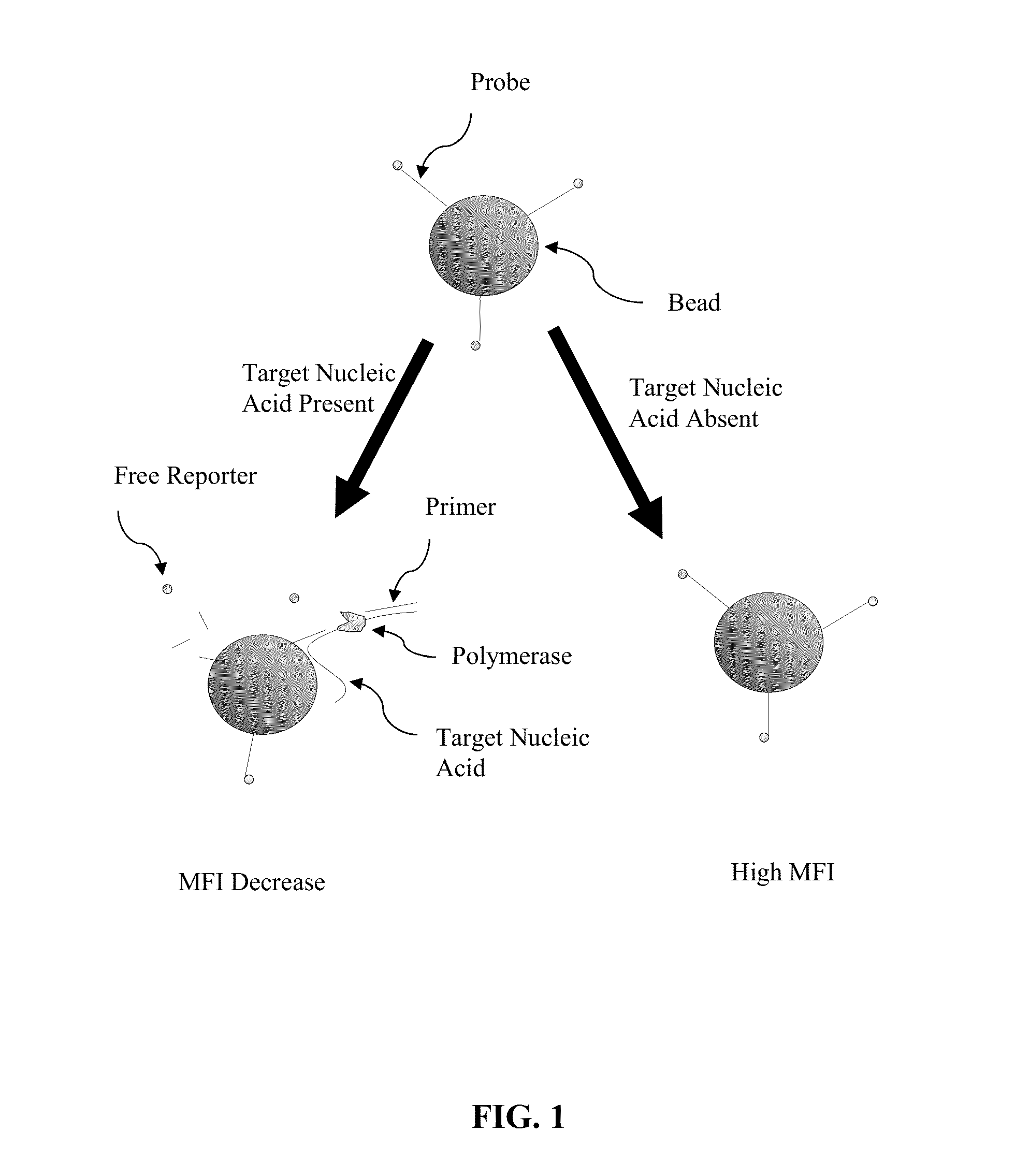
Methods and compositions for the detection and quantification of nucleic acids are provided. In one embodiment, a sample is contacted with a primer complementary to a first region of a target nucleic acid and a probe complementary to a second region of the target nucleic acid downstream of the first region under conditions suitable for hybridization of the target nucleic acid with the primer and the probe. The probe in this embodiment comprises a fluorophore and is attached to a solid support. The hybridized probe is cleaved with a nucleic acid polymerase having exonuclease activity to release the reporter from the solid support. The presence of the target nucleic acid is then detected and optionally quantified by detecting a decrease in signal from the reporter on the solid support.
Owner:LUMINEX
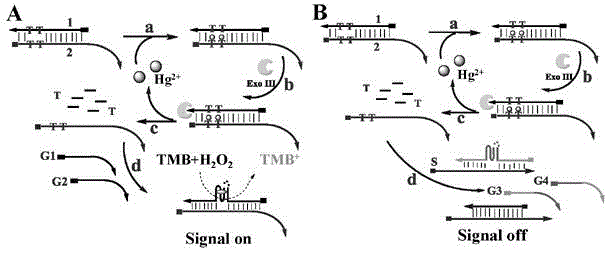
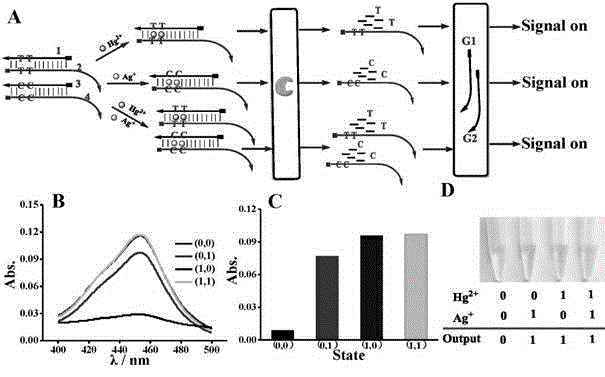
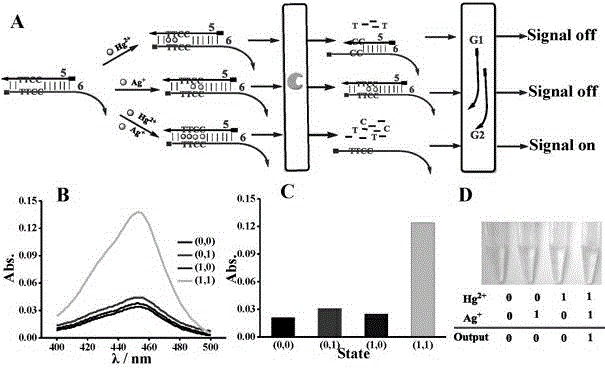
DNA colorimetric logic gate construction method based on metal ion regulation and control of exonuclease III shearing action
The invention discloses a DNA colorimetric logic gate construction method based on metal ion regulation and control of exonuclease III shearing action and belongs to the technical field of molecular computer. Double-stranded DNA containing T-T or C-C mismatched base cannot be sheared by exonuclease III. When there exists Hg<2+> or Ag<+>, 3' end completely matched double-stranded DNA formed by action of T-Hg<2+>-T or C-Ag<+>-C can be sheared by exonuclease III, and released single-stranded DNA hybridizes with a DNA signal probe 1 or DNA signal probe 2, thus leading to formation or disintegration of a G-quadruplex structure. Hereby, Hg<2+> and Ag<+> are used as input signals, and logic operation is carried out through the DNA signal probe so as to construct multiple DNA colorimetric logic gates.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Isothermal SNP Detection Method
In some embodiments, the present teachings provide a method for detecting a nucleotide of interest comprising; forming an amplification reaction mixture comprising a mismatched primer, a target polynucleotide, a strand-displacing polymerase lacking 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity, a recombinase, and a single-stranded DNA binding protein; hybridizing a mismatched primer to the target polynucleotide to form a primer-target complex; and, detecting the nucleotide of interest by the absence of a primer extension product. In some embodiments, control reactions are performed in which a control polynucleotide is exponentially amplified. Additional methods, as well as reaction mixtures and kits, are also provided.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Composition and method for hot start nucleic acid amplification
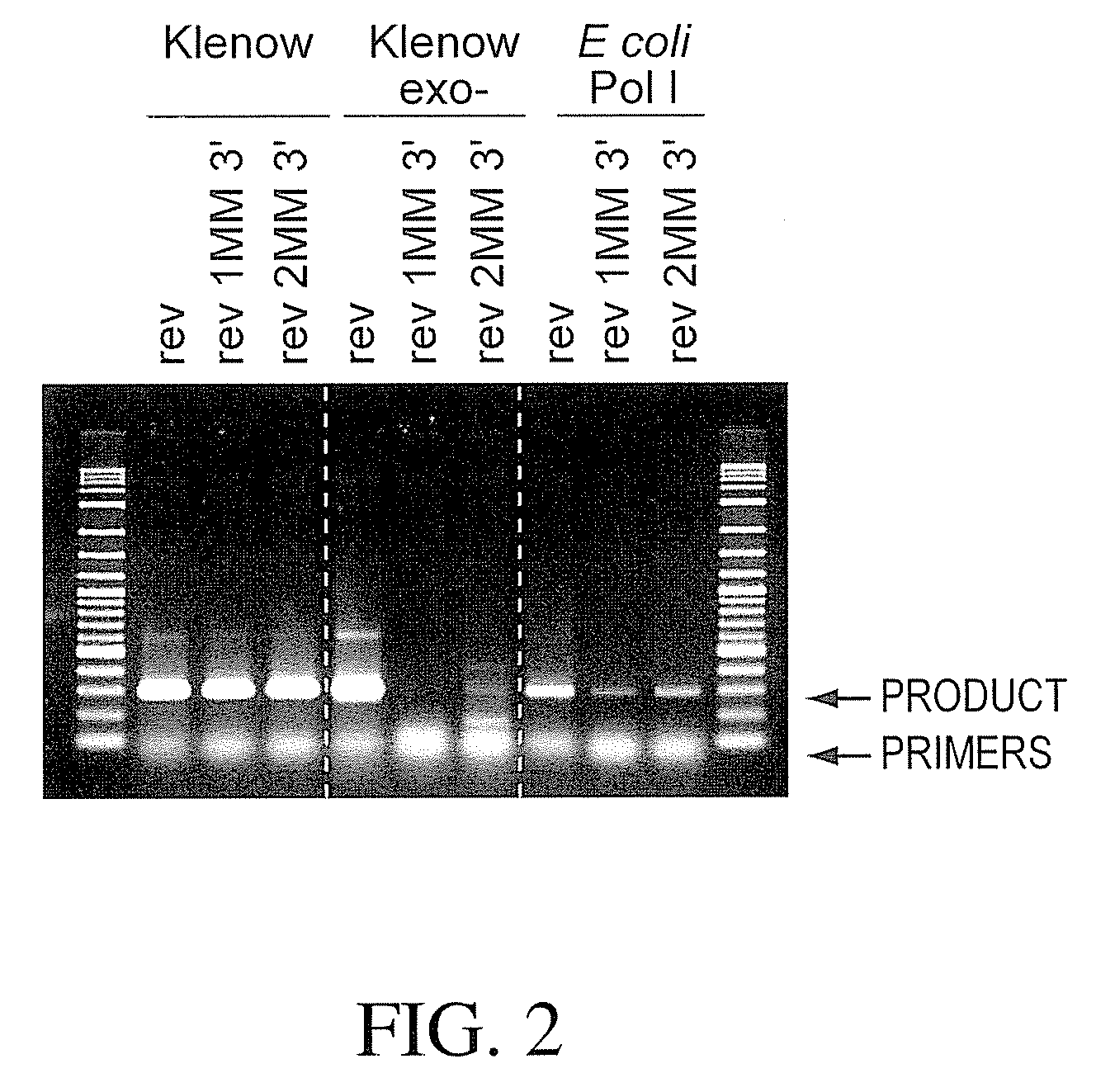
InactiveUS7122355B2Good choiceIncrease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyBiotechnologyExonuclease I
The present invention is directed to a new composition for performing a nucleic acid amplification reaction comprising (i) a thermostable DNA-Polymerase, (ii) a thermostable 3′-5′ Exonuclease, and (iii) at least one primer for nucleic acid amplification with a modified 3′ terminal residue which is not elongated by said thermostable DNA-Polymerase as well as methods for performing a PCR reaction using this composition. Furthermore, the method is directed to kits comprising such a composition.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
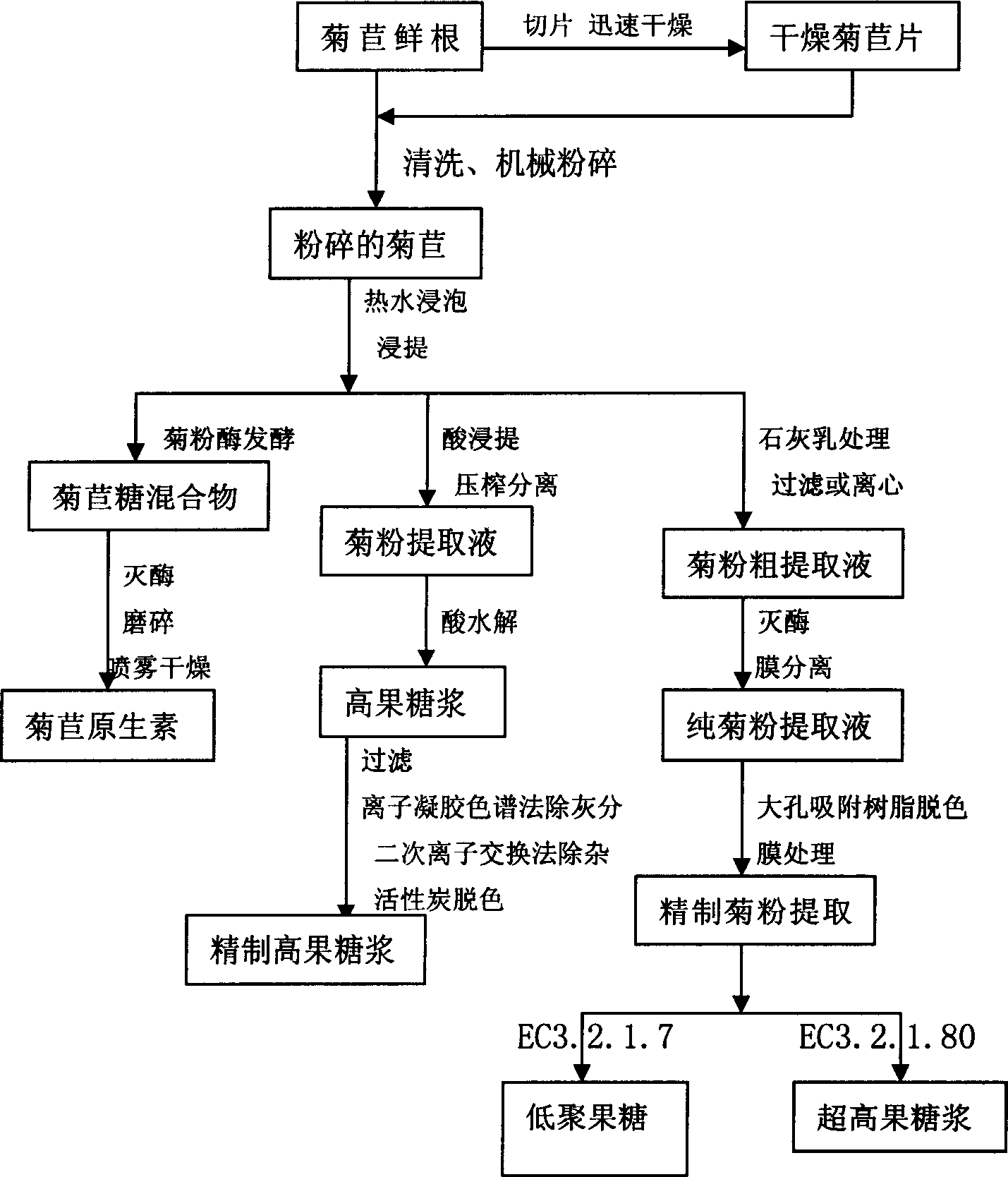
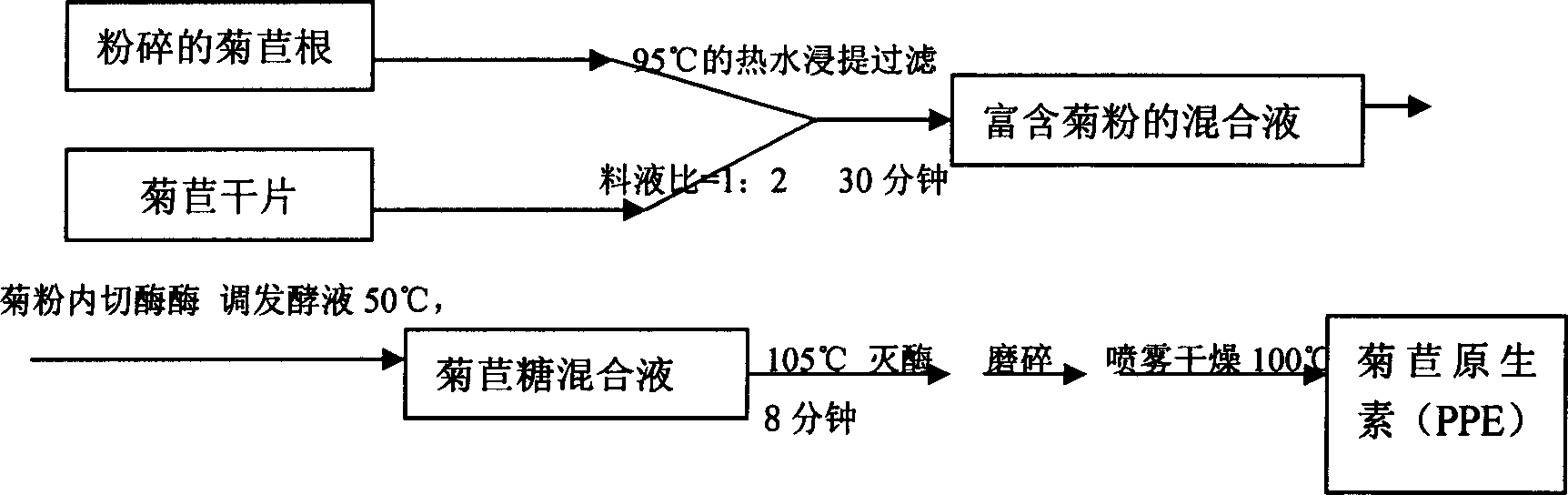
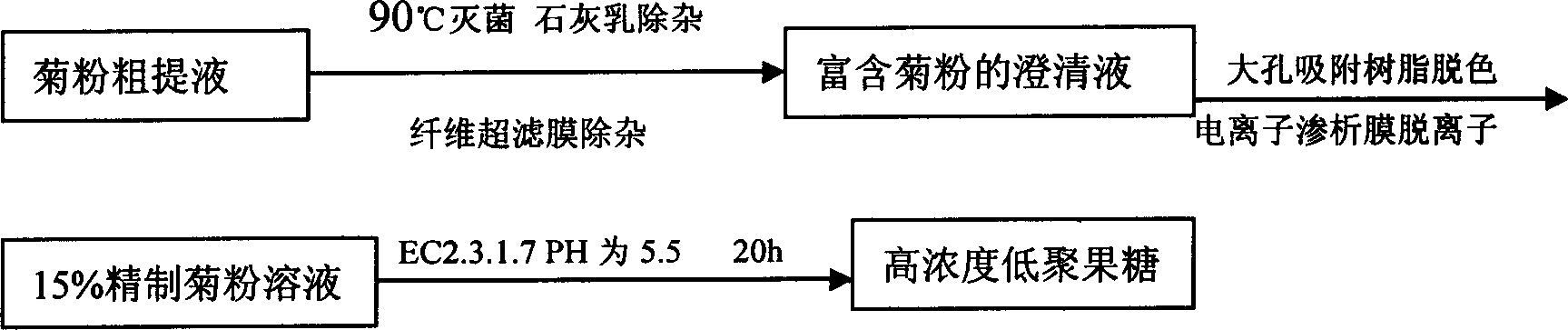
Technique for producing fruit sugar by using chicory to carry out hydrolysis
InactiveCN1661027AReduce manufacturing costImprove product qualityFructose productionFermentationFructoseCichorium
A process for preparing pectose from witloof by hydrolysis features that the acidolsis is used to prepare the high-pectose syrup, the inulase is used to prepare chicorose mixture (PPE), the inulin endonuclease is used to prepare oligopectose by fermenting, and the inulin exonuclease is used to prepare the ultrahigh-pectose syrup by fermentation.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Cleavage of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20060035257A1Quick checkQuick identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismExonuclease I
The present invention relates to means for cleaving a nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. Enzymes, including 5′ nucleases and 3′ exonucleases, are used to detect and identify nucleic acids derived from microorganisms. Methods are provided which allow for the detection and identification of bacterial and viral pathogens in a sample.
Owner:DAHLBERG JAMES +2
Methods for identification of alleles
ActiveUS20100041563A1Low homologyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPolymerase LGenomic DNA
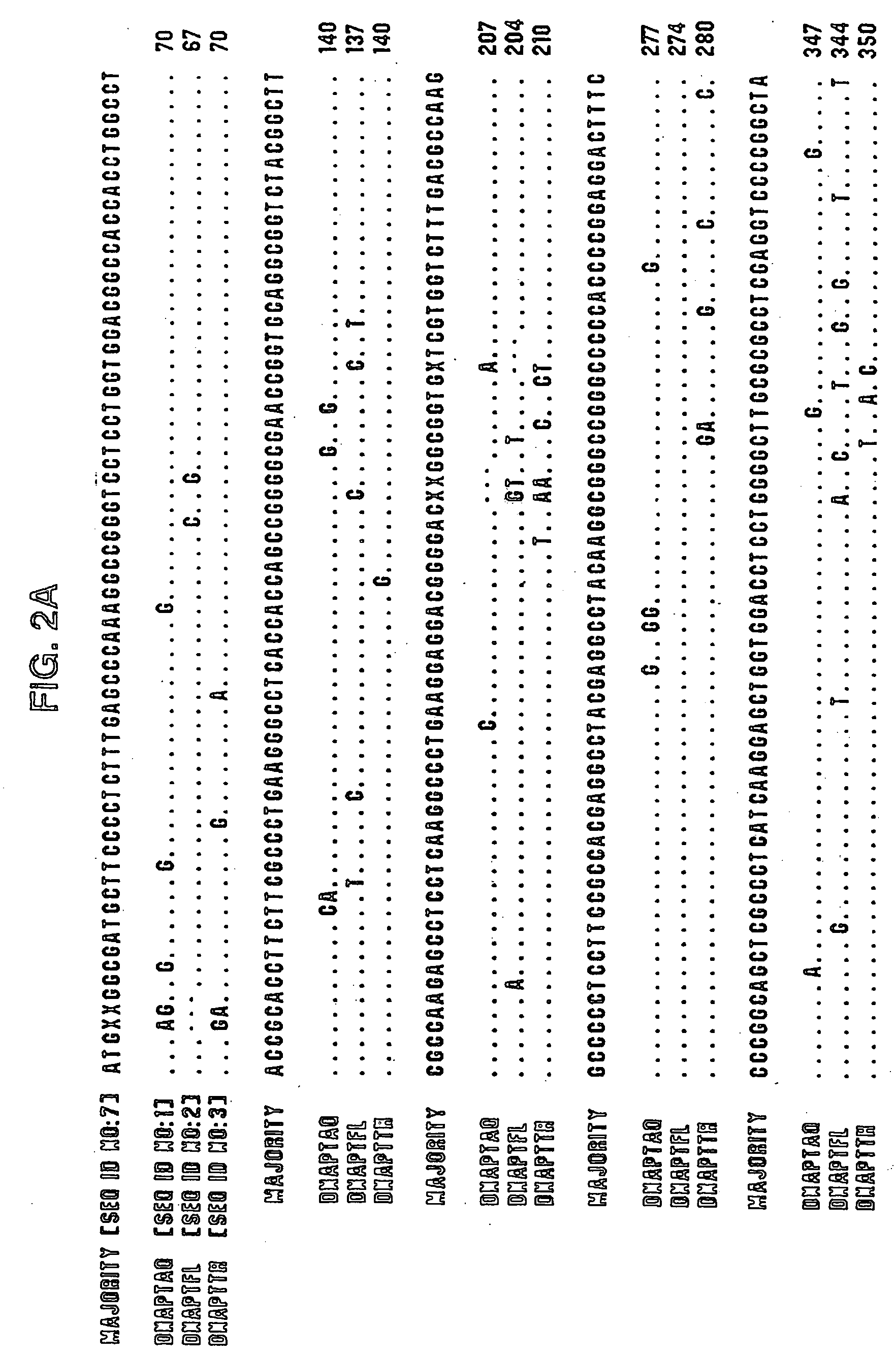
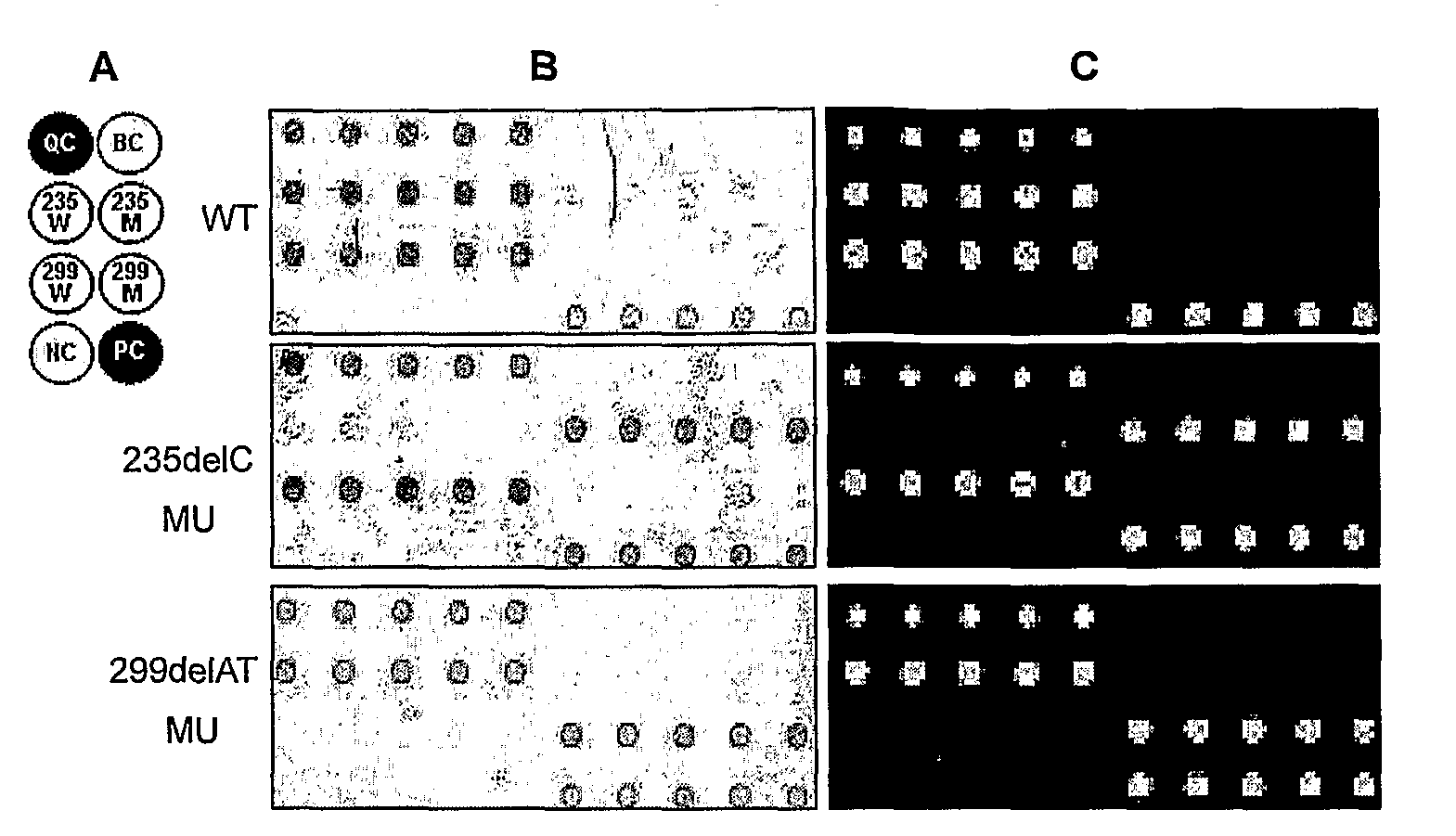
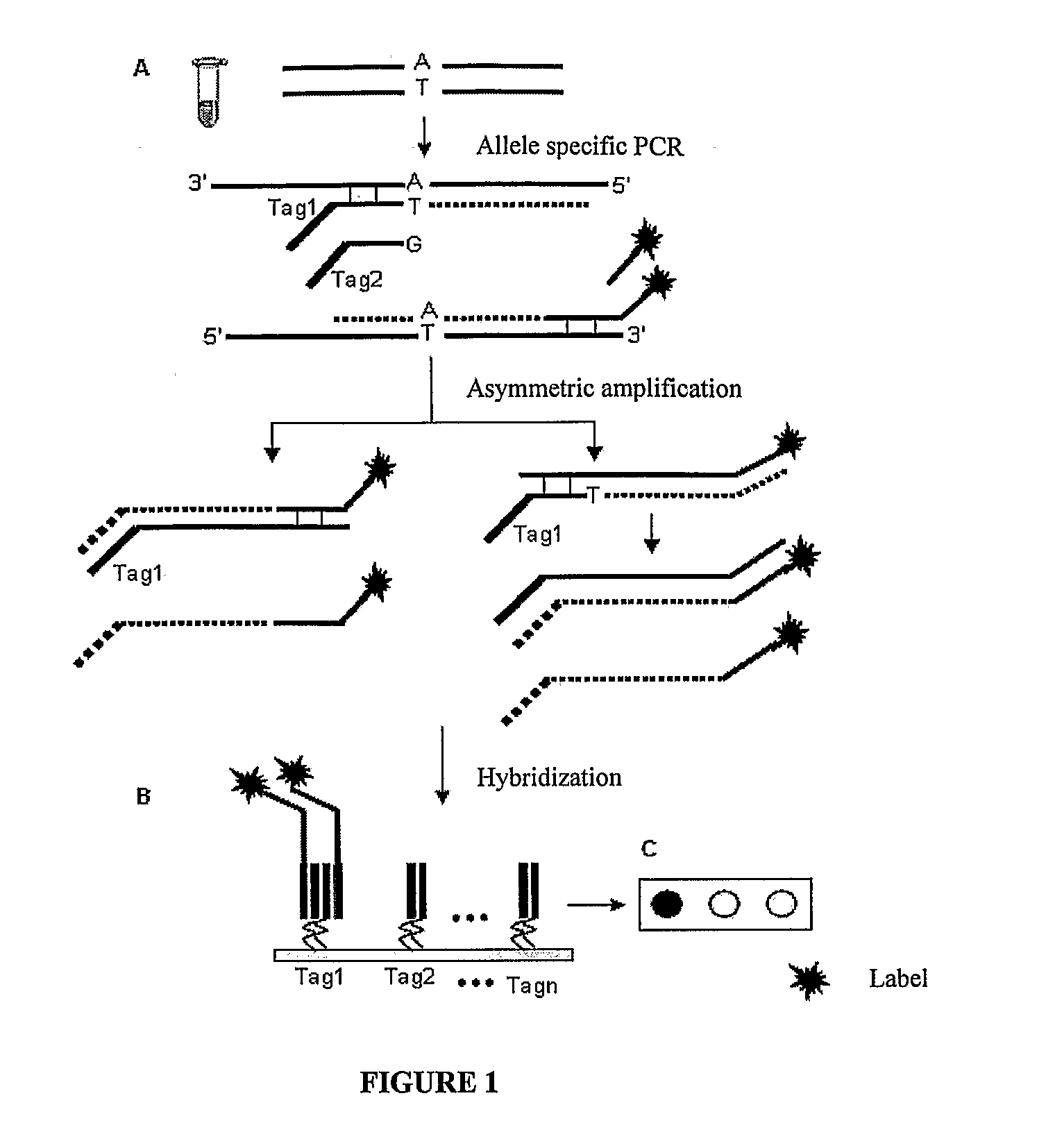
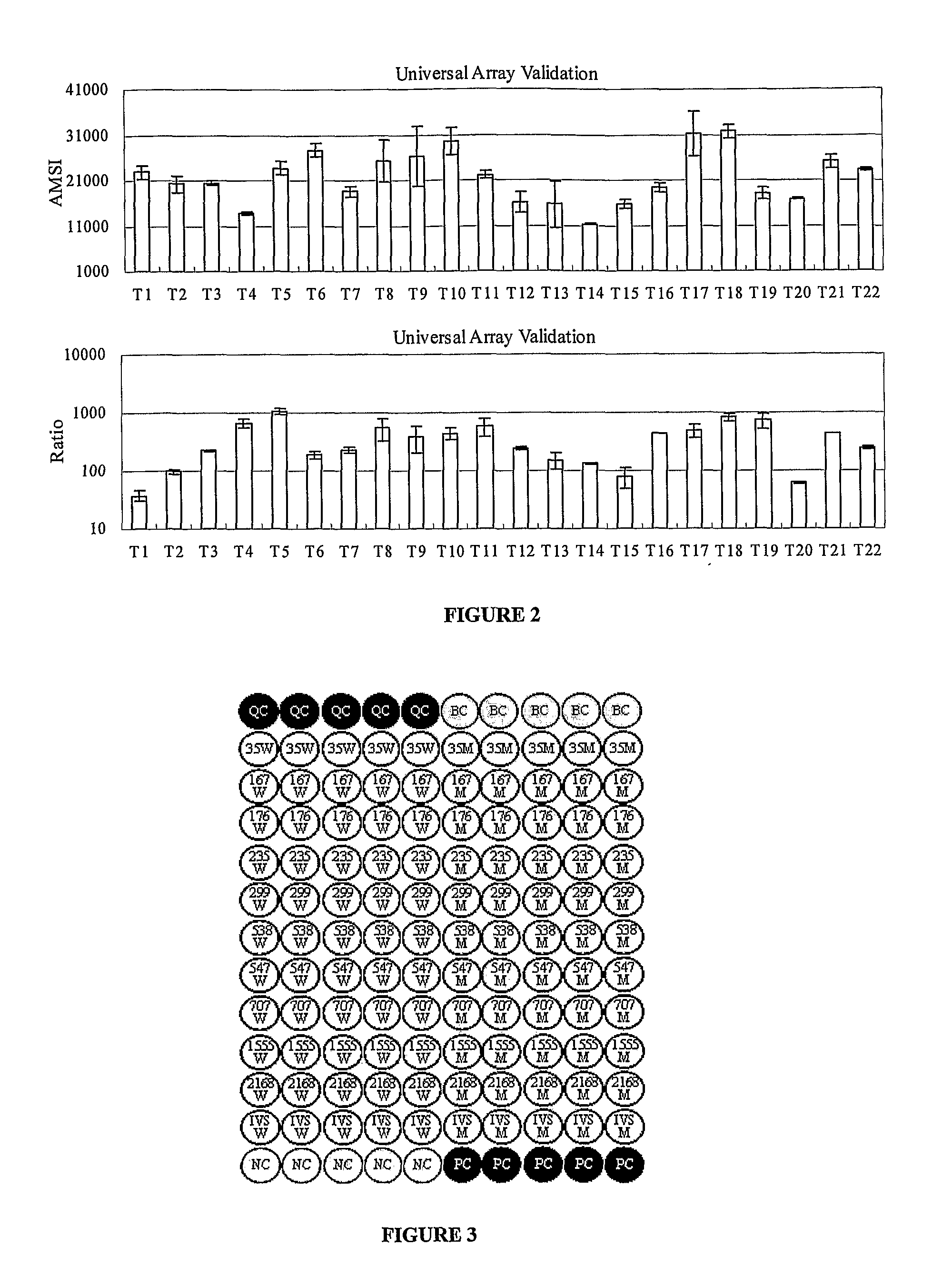
The invention provides a method for identification of alleles. In this method, genomic DNA is used as target. Multiple allele-specific PCR amplification are carried out with a group of primers comprising one or more allele-specific primers for a target gene, a universal primer, and a common primer; and a DNA polymerase without 5′ to 3′ exonuclease activity. The PCR products are hybridized with tag probes immobilized on a DNA chip. Results are determined based on the signal intensity and the position of the probe immobilized on the array. Each allele-specific primer comprises a unique tag sequence at the 5′ end. Each tag probe immobilized on the DNA chip comprises a sequence identical to its corresponding tag sequence; and each tag probe hybridizes only with the complementary sequence in the PCR amplification product.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +1
Microarray system with improved sequence specificity
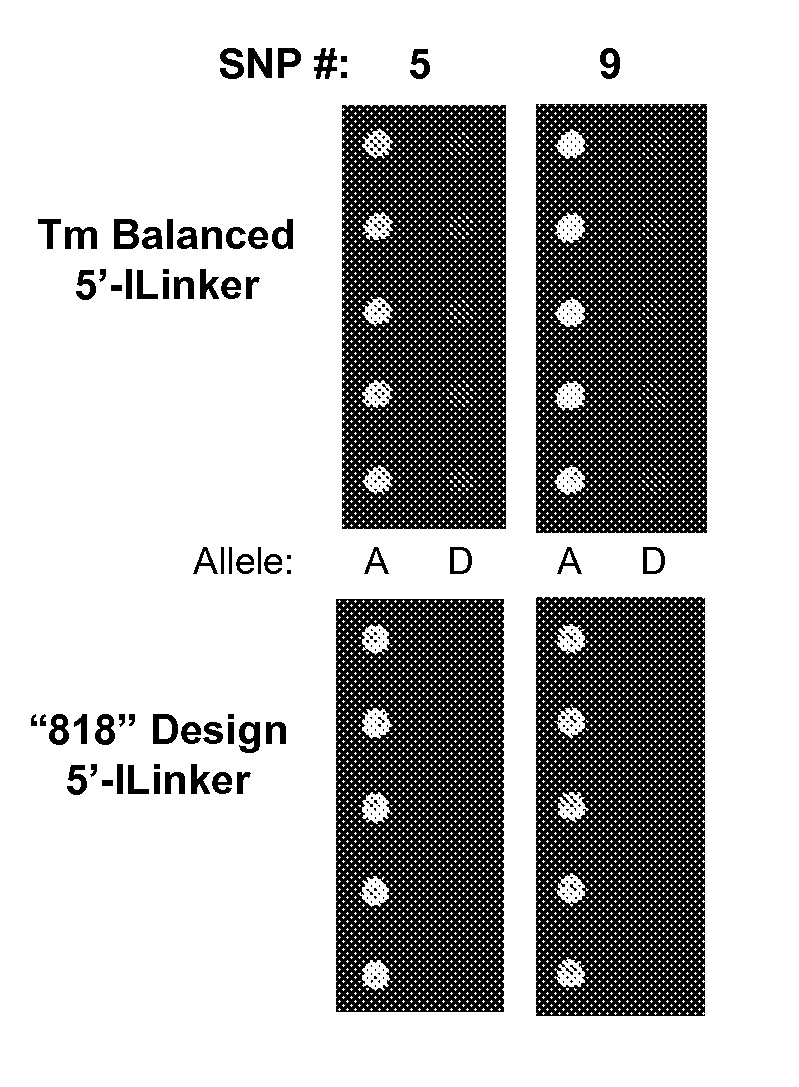
InactiveUS20090143243A1High stringency conditionSequential/parallel process reactionsSugar derivativesNucleic acid sequencingExonuclease I
The invention provides a novel array method for nucleic acid sequence detection with improved specificity which allows for detection of genetic variation, from simple SNPs (where the variation occurs at a fixed position and is of limited allelic number) to more complex sequence variation patterns (such as with multigene families or multiple genetic strains of an organism where the sequence variation between the individual members is neither fixed nor consistent). The array is comprised of short, synthetic oligonucleotide probes attached to a solid surface which are hybridized to single-stranded targets. Single stranded targets can be produced using a method that employs primers modified on the 5′ end to prohibit degradation by a 5′-exonuclease that is introduced to degrade the unprotected strand. The invention further provides for printing buffers / solutions for the immobilization of oligonucleotide probes to an array surface. The invention also provides hybridization and wash buffers and conditions to maximize hybridization specificity and signal intensity, and reduce hybridization times.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
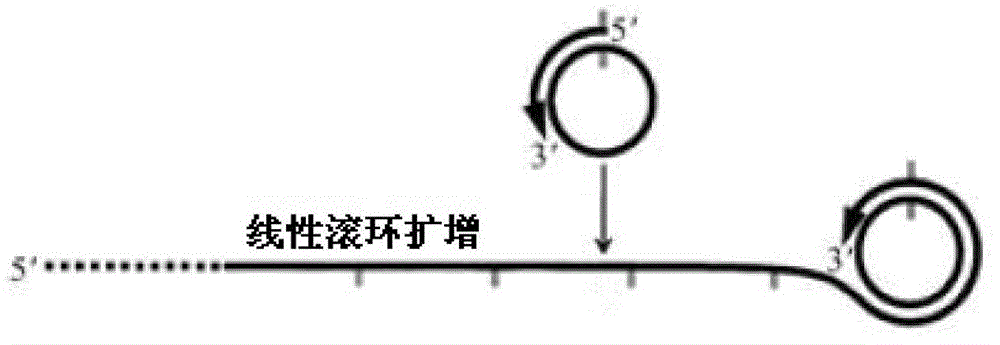
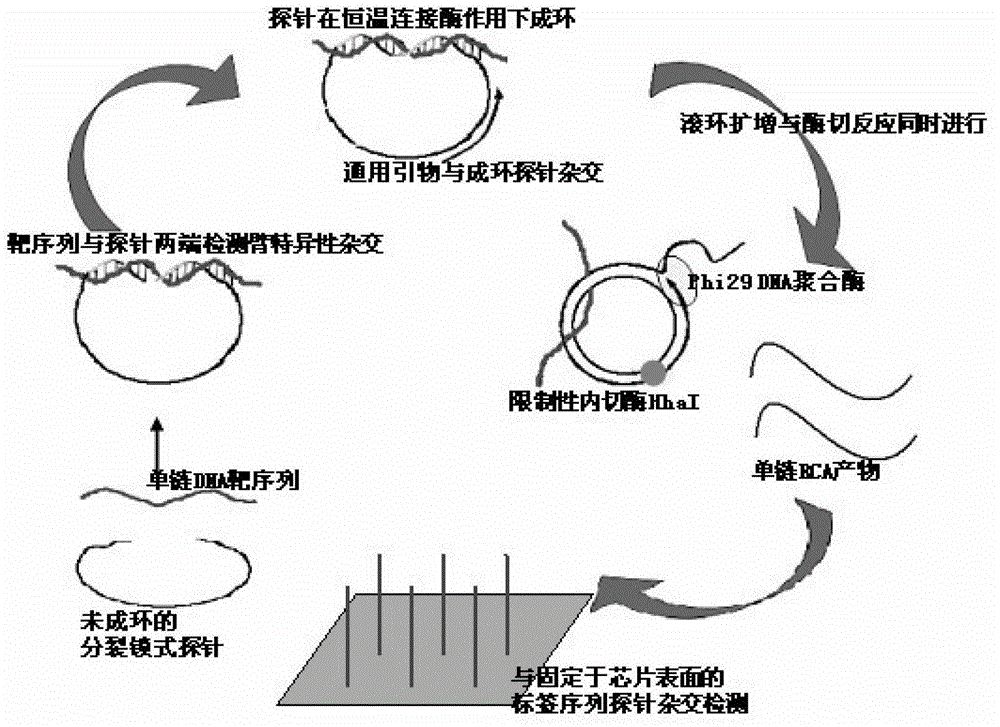
Multi-RCA (rolling circle amplification) method based on split padlock probes
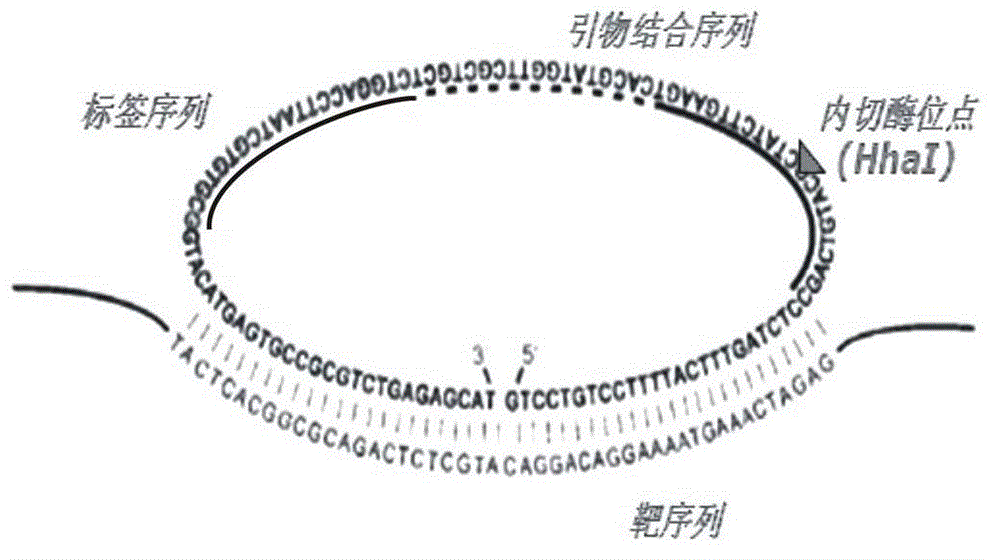
InactiveCN102719550AEasy to operateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LExonuclease I
The invention discloses a multi-RCA (rolling circle amplification) method based on split padlock probes. Each novel split padlock probe is about 90bp in length and comprises four parts, namely a detection arm, a universal primer area, an HhaI endonuclease site and a tag sequence area, wherein an amplification system is composed of a connection system and an RCA system. The concrete detection method comprises the steps of: firstly, carrying out coupled reaction, mixing a target sequence DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segment and four split padlock probes of which the final concentration is 1mol / L, hybridizing for 15 minutes after boiling and degenerating, adding T4DNA ligase and T4DNA ligase buffer solution, supplying 10 muL of reaction system; carrying out exonuclease I and exonuclease III exterior contact for 45 minutes at 37 DEG C, preparing an annular template and then carrying out RCA reaction; mixing, boiling and degenerating 10 muL of connection product and universal primer, respectively adding dNTP, phi29DNA polymerase, HhaI restriction enzyme and buffer solution to form 20 muL of reaction system, stewing for 60 minutes at 37 DEG C; finally detecting single-chain DNA product of RCA with a specific tag sequence, thus obtaining a corresponding test conclusion according to the result.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Kit for detecting 7 hot mutant sites of phenylketonuria PAH gene and PCR amplification method thereof
ActiveCN101899518AStrong specificityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceFluorescence
The invention relates to a kit for detecting 7 hot mutant sites of a phenylketonuria PAH gene and a PCR amplification method thereof. The invention is characterized in that in the PCR reaction in which high-fidelity DNA polymerase participates, the product of a mutation detection primer which is modified in a 3'-5' exonuclease digestion resistance way, has very high specificity, and people can directly observe the existence of the strips obtained by gel electrophoresis to judge the genotype of the corresponding mutant sites of the PAH gene. The invention has the advantages of simple operation and economical performance, does not need sequencing, and can be operated in a common molecular biology laboratory. The method of the invention is combined with the fluorescence quantitative PCR technology, and can realize automation and high flux of clinic detection of the biological sample, thereby greatly enhancing the detection accuracy and efficiency.
Owner:SUZHOU KUANGYUAN MOLECULAR BIOTECH
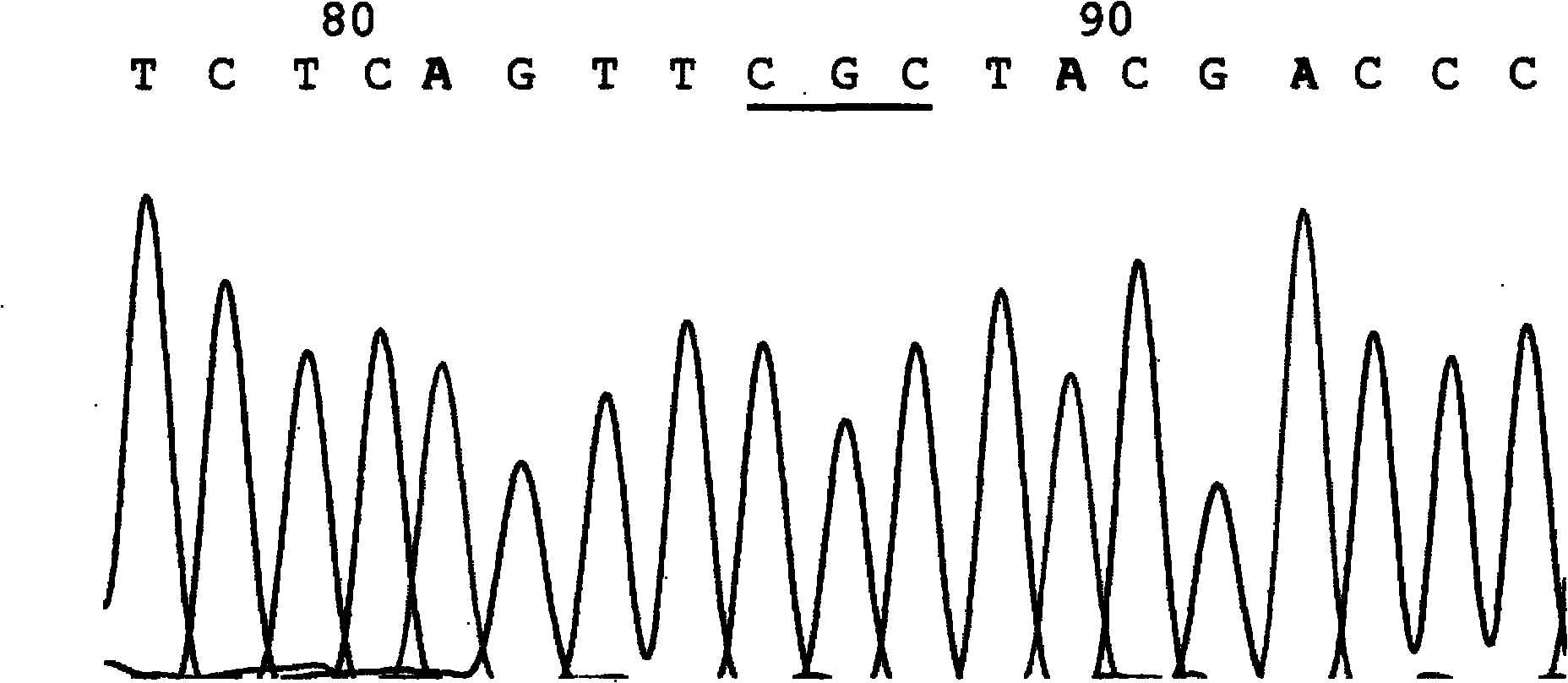
African swine fever virus fluorescent type RAA detecting kit
PendingCN110358867ARealize detectionEfficient amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDecompositionSwine Fever Virus
The invention discloses an African swine fever virus fluorescent type RAA detecting kit which comprises specific primers ASFV-F and ASFV-R and an RAA-exo probe ASFV-P. The basic groups in a target amplification subsequence are substituted by tetrahydrofuran (THF residues), dT-fluorophore and dT-quenching groups, a marked reported fluorescent dye is FAM, a fluorescent quenching group is BHQ-1, splitting decomposition can be conducted on the probe at the THF site by exonuclease in an agent, the fluorescent group can be separated from the quenching groups, and fluorescent signals are generated. By means of the kit, at the constant temperature of 37-42 DEG C, the African swine fever virus is detected within 20 minutes, the specificity is 100%, and the detection sensitivity is 10 copies per microliter. Thus, the kit has the advantages of being simple, rapid and sensitive in operation and provides effective technological means for on-site rapid detecting and screening of the African swine fever virus.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU ZHONGDAO BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +2
Quantitative amplification with a labeled probe and 3' to 5' exonuclease activity
This invention provides methods and kits for performing a quantitative amplification reaction. The method employs a polymerase enzyme and an enzyme having a 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity that cleaves the 3′ oligonucleotide of the probe.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
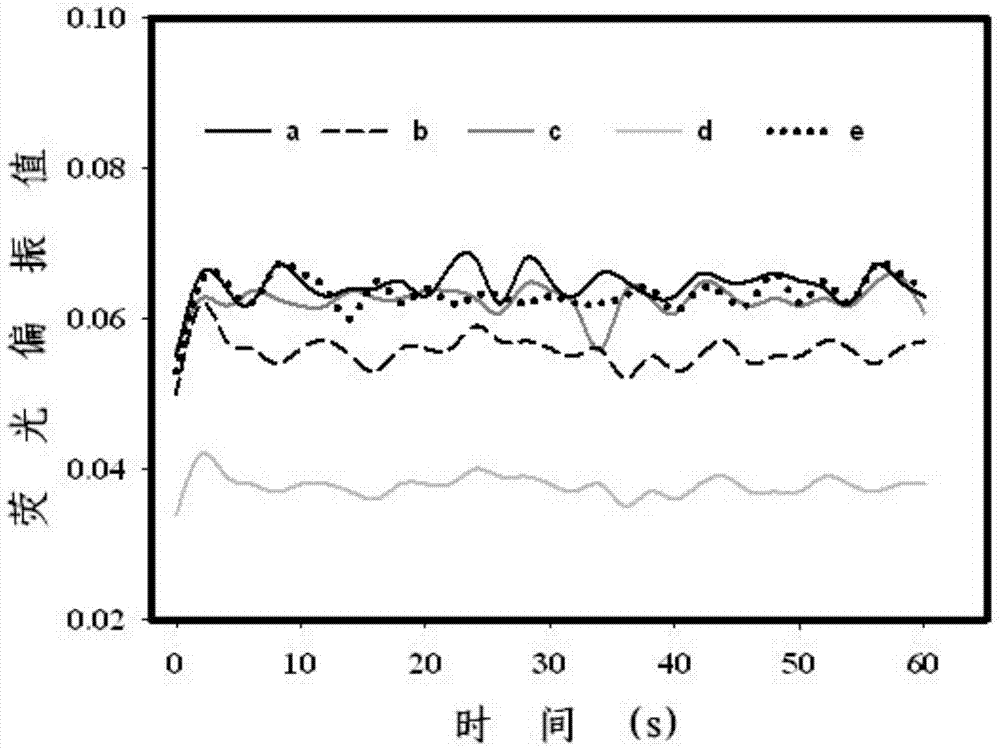
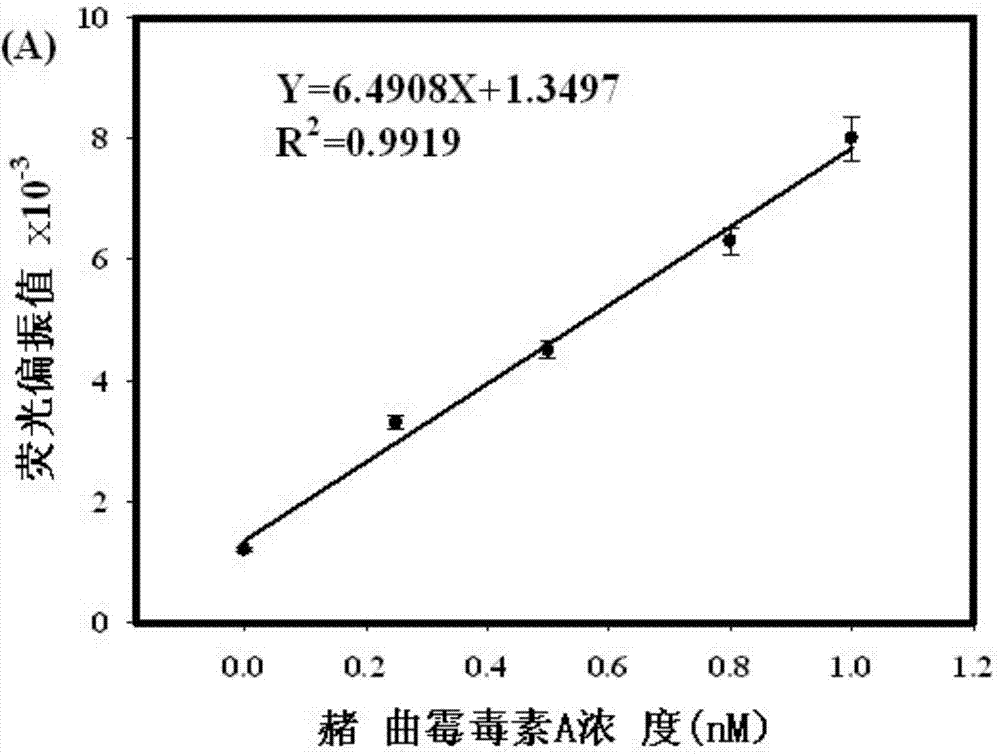
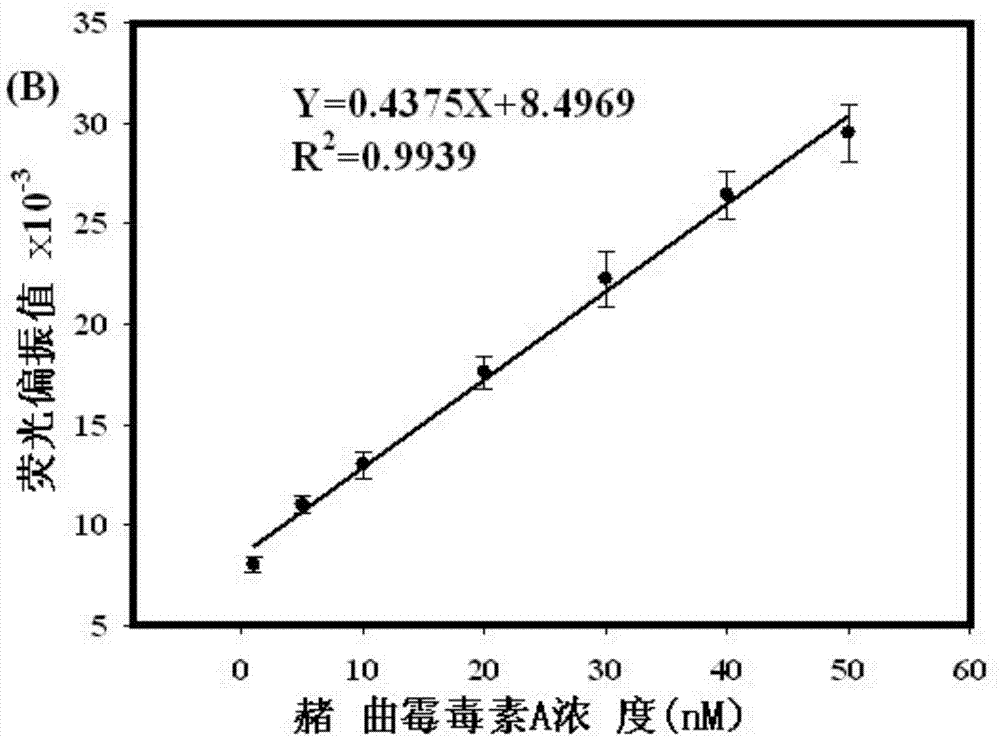
Rapid detection method of ochratoxin A by fluorescence polarization based on exonuclease I circular enzyme digestion and amplification
InactiveCN103926397AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityPolarisation-affecting propertiesColor/spectral properties measurementsAptamerEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a rapid detection method of ochratoxin A (OTA) by fluorescence polarization based on exonuclease I (ExoI) circular enzyme digestion and amplification. According to the method, hybridization between an aptamer and a single-stranded fluorescent labeled oligonucleotide probe is performed to form a double-stranded complex; a specific strand displacement reaction between the complex and OTA can be carried out and a fluorescent labeled probe and OTA-aptamer complex is released so as to trigger an enzyme digestion reaction of ExoI to the single-stranded fluorescent labeled oligonucleotide probe and the OTA-aptamer complex to release OTA; and the released OTA can trigger next strand displacement reaction and enzyme digestion reaction, followed by recycling so as to realize signal amplification. The defect that a present antibody dependent OTA rapid detection method easily causes a cross reaction, has low sensitivity, is complicated to operate and has too high costs is solved by the method provided by the invention. The method provided by the invention is simple to operate and is convenient and fast. By the method, it only takes 15 min to realize rapid detection of OTA, and sensitivity can reach 0.5nM.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Isothermal Amplification of Nucleic Acids
InactiveUS20080286835A1Easy to disassembleFluorescence enhancementSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementExonuclease IStrand invasion
A process of amplifying a nucleic acid template dependent on partial destruction of primer molecules which have extended onto the template molecule followed by strand invasion of the partially destroyed primer template by a replacement primer. The destruction of the primer molecule may be performed by either endonuclease or exonuclease digestion. A signal generation from the amplified products may be obtained by the use of adaptors capable of binding probe molecules as well as the amplified product.
Owner:AVACTA GROUP
Method for plasmid preparation by conversion of open circular plasmid
InactiveUS20040191871A1Increase percentageFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotidePhosphoric acid
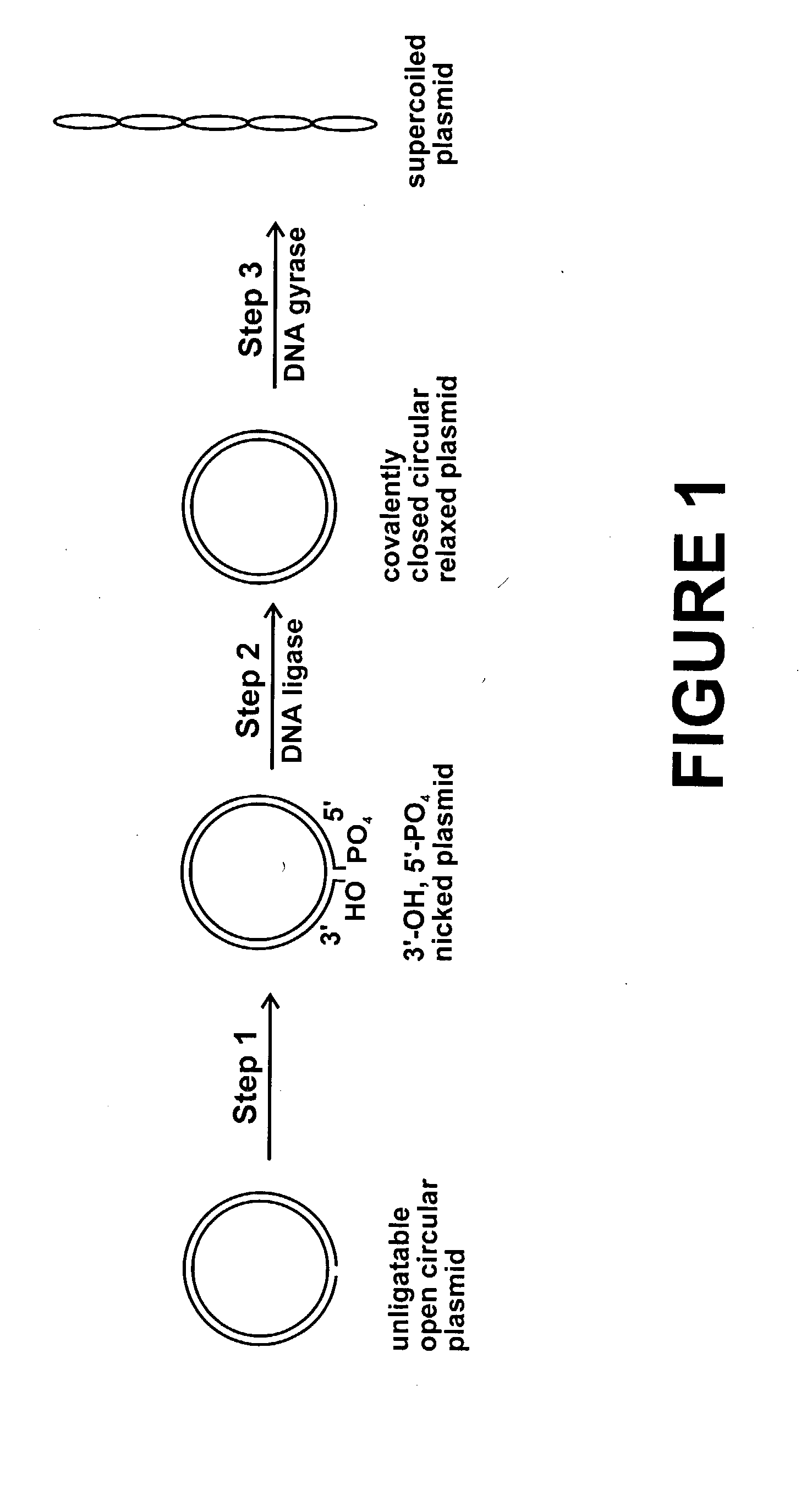
In accordance with the invention, there is provided a method for preparing plasmid from host cells which contain the plasmid, comprising the steps: (a) preparing a cleared lysate of the host cells, wherein the cleared lysate comprises unligatable open circular plasmid, wherein the open circular plasmid is not 3'-hydroxyl, 5-phosphate nicked plasmid; (b) incubating the unligatable open circular plasmid with one or more enzymes in the presence of their appropriate nucleotide cofactors, whereby the unligatable open circular plasmid is converted to 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid; (c) incubating the 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid with DNA ligase in the presence of DNA ligase nucleotide cofactor, whereby 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid is converted to relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid; and (d) incubating the relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid with DNA gyrase in the presence of DNA gyrase nucleotide cofactor, whereby relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid is converted to negatively supercoiled plasmid. Preferably, the enzymatic steps (b), (c), and (d) are performed in a single step using an enzyme mixture comprising DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, and DNA gyrase. Preferably, the mixture further comprises a 3' terminus deblocking enzyme, such as exonuclease III or 3'-phosphatase. Preferably, the mixture further comprises one or more regenerating enzymes and a high energy phosphate donor, whereby the nucleotide by-products of the nucleotide cofactors generated by DNA ligase and DNA gyrase are converted to back to nucleotide cofactor. Preferably, the enzyme mixture further comprises one or more exonucleases, such as ATP dependent exonuclease, whereby linear chromosomal DNA is selectively degraded.
Owner:HYMAN EDWARD DAVID
Multicolor fluorescence composite detection method and kit of 44 SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) loci
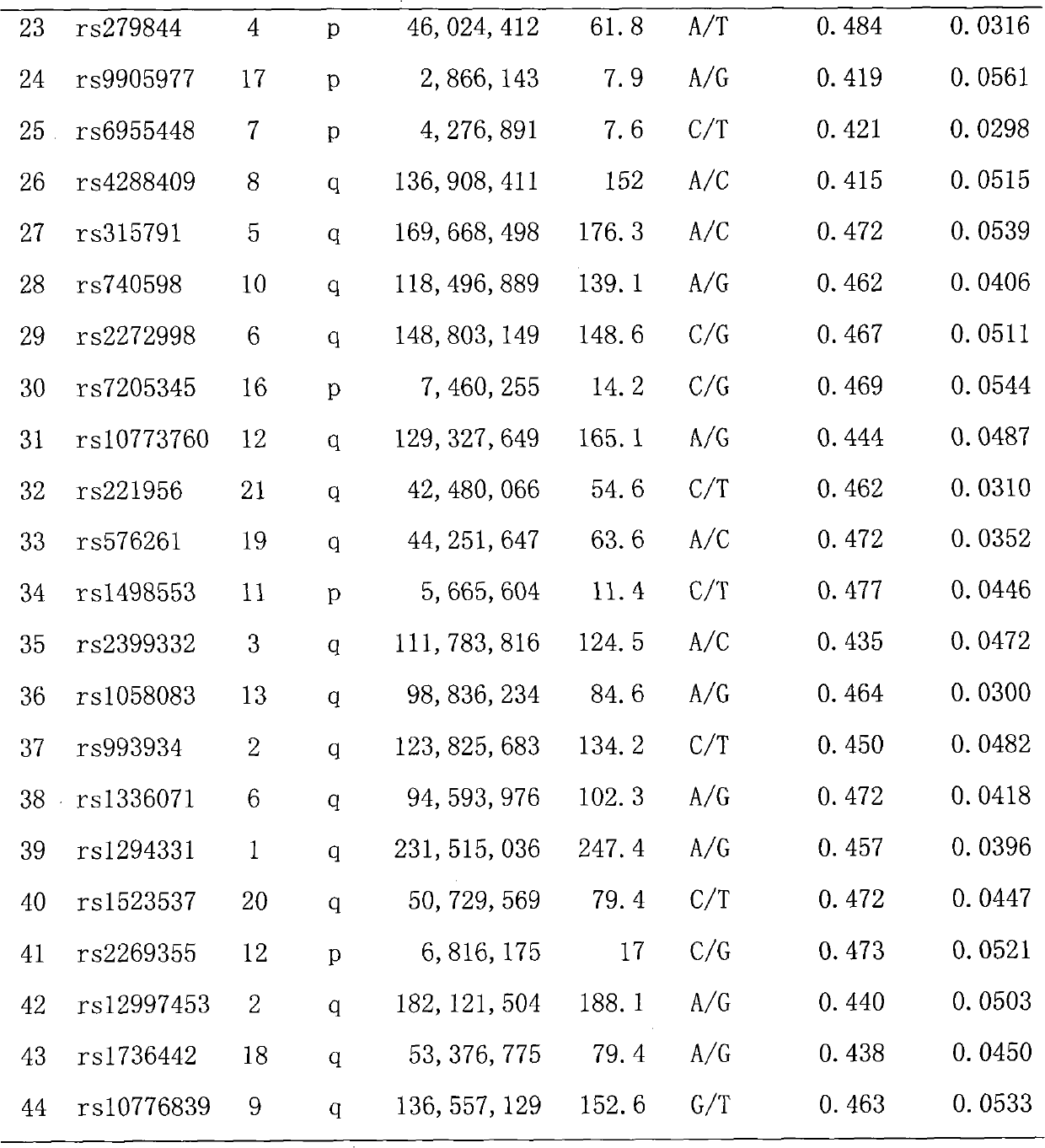
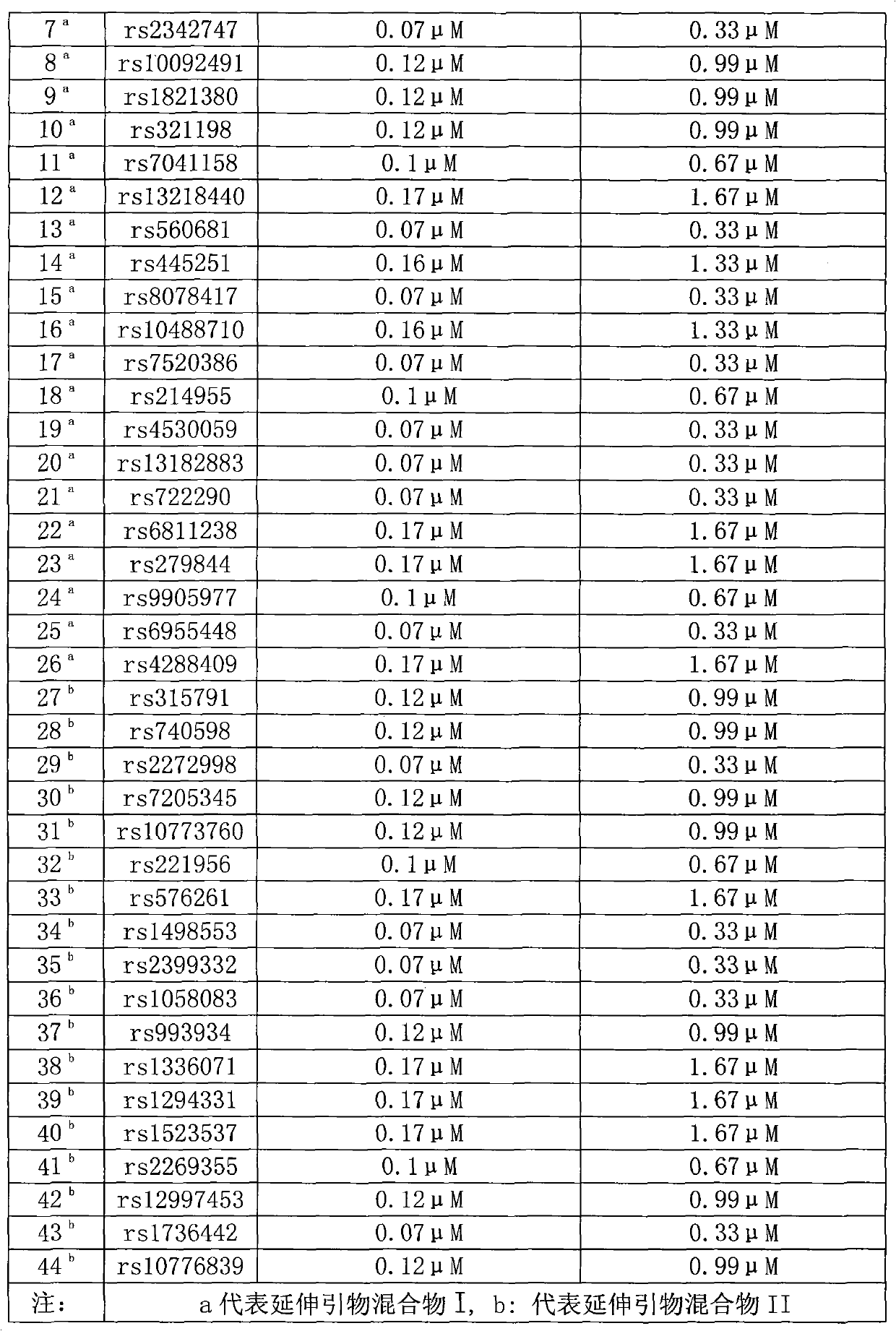
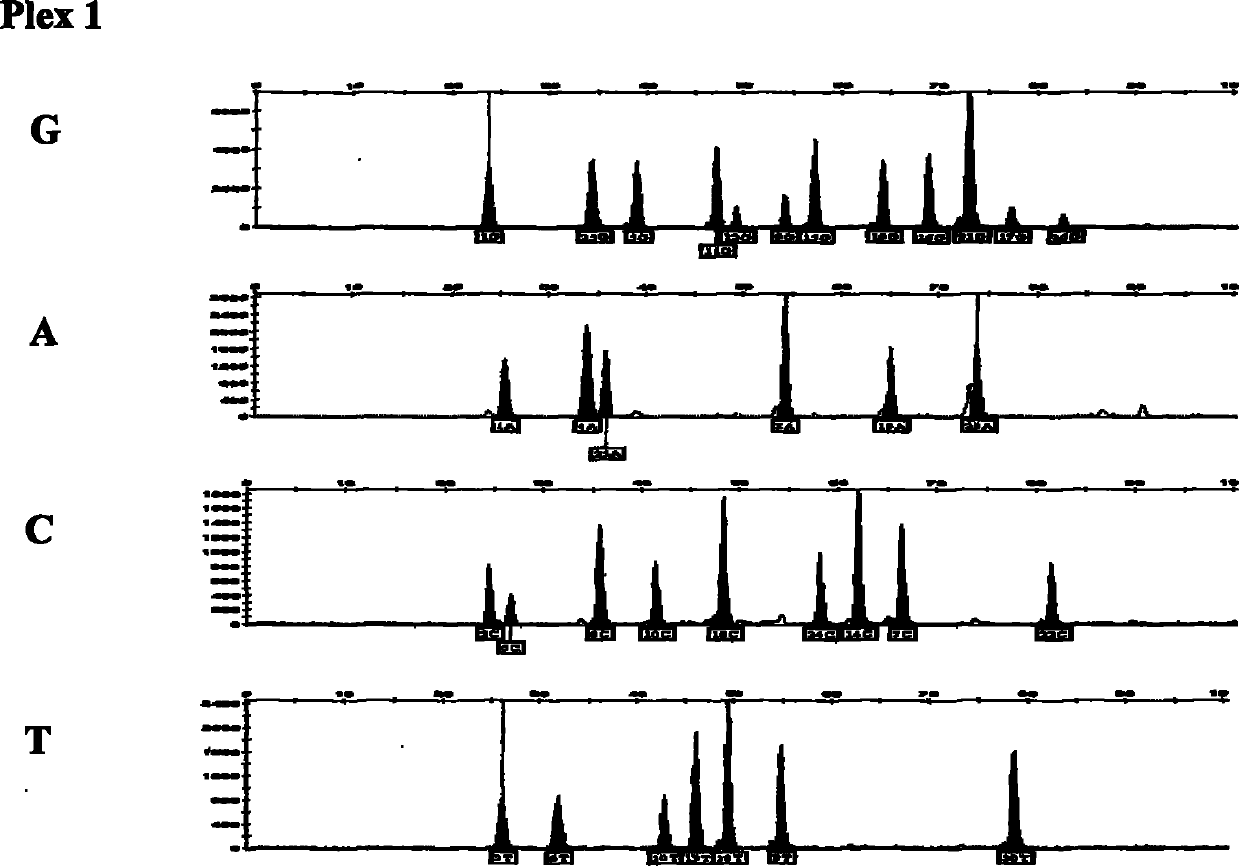
ActiveCN101921860AAccurate genotypingMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceExonuclease I
The invention discloses a multicolor fluorescence composite detection kit and detection method of 44 SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) loci, which is used for individual recognition. The kit comprises a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer, a DNA polymerase, a PCR buffer solution, an exonuclease I, a shrimp alkaline phosphatase, an extended primer and a SNaPshot reaction mixed solution; thePCR primer and the extended primer consist of primers containing 44 SNP gene loci and respectively aim to DNA fragments containing the 44 SNP loci. By adopting the invention, the genotyping of the 44SNP loci can be obtained quickly and accurately, and the individual recognition is carried out on human biological samples through detection and analysis of a fluorescence automatic typing apparatus.
Owner:HEBEI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com