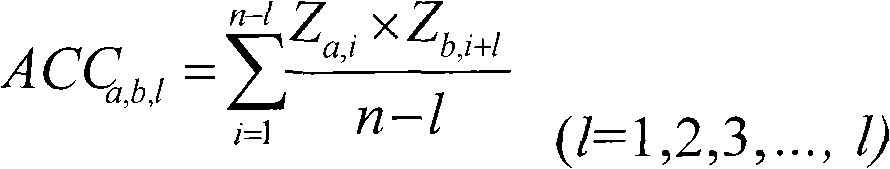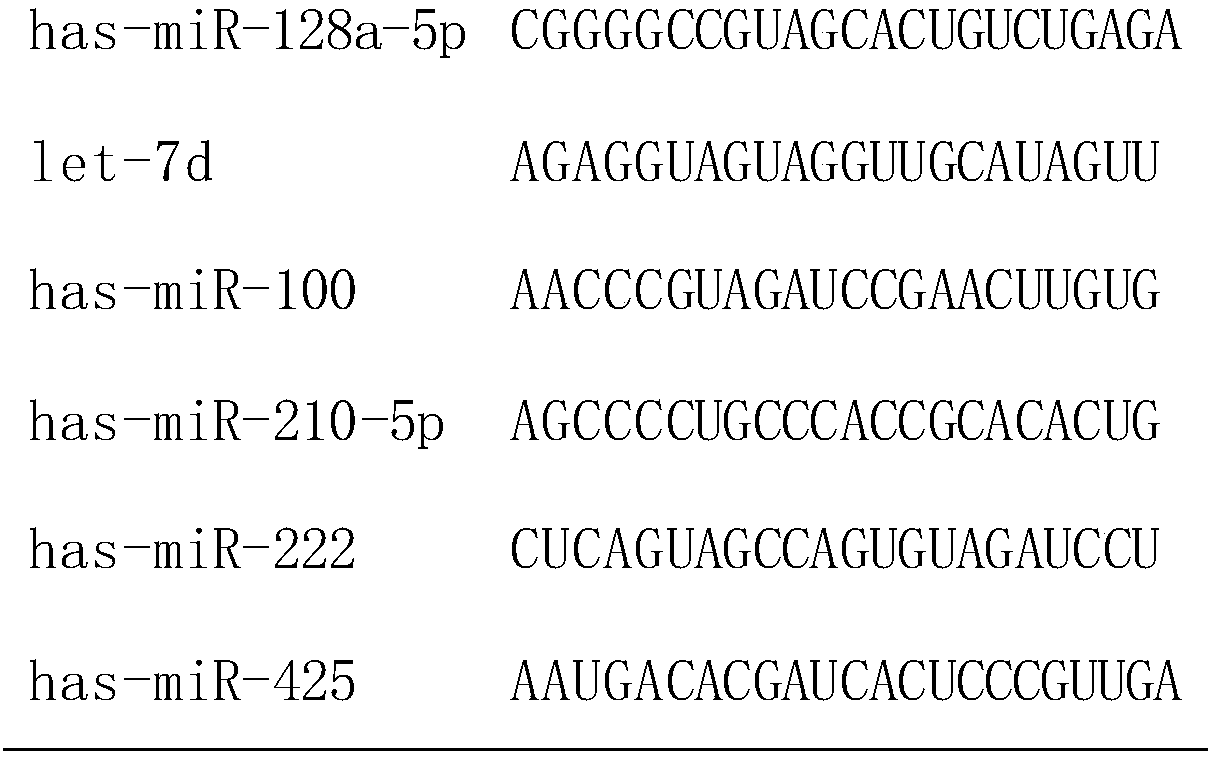Patents
Literature
61 results about "MiRNA Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Novel microarray techniques for nucleic acid expression analyses
ActiveUS20060078925A1Eliminate biasConvenient experimentMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMiRNA GeneExonuclease I
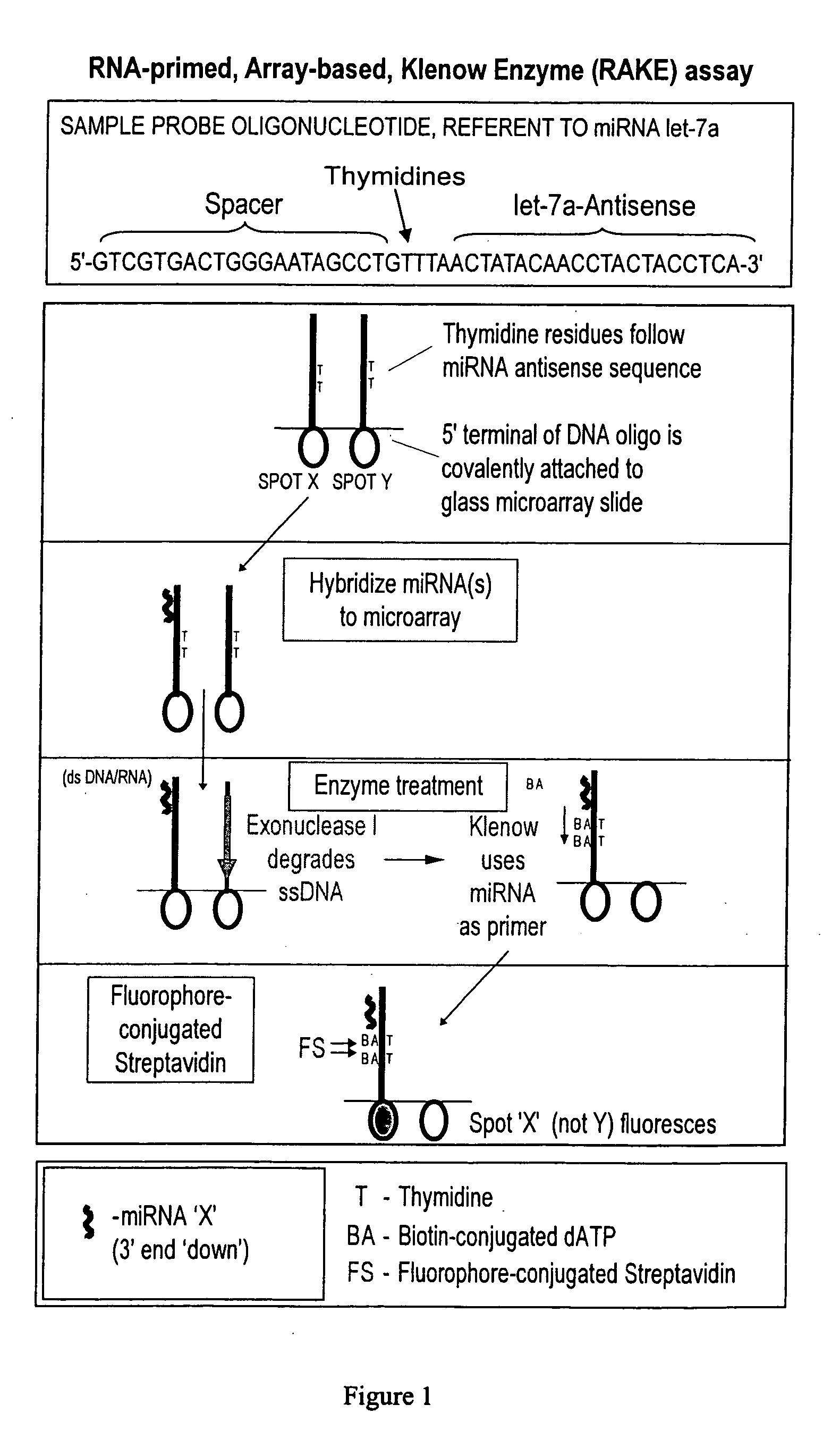
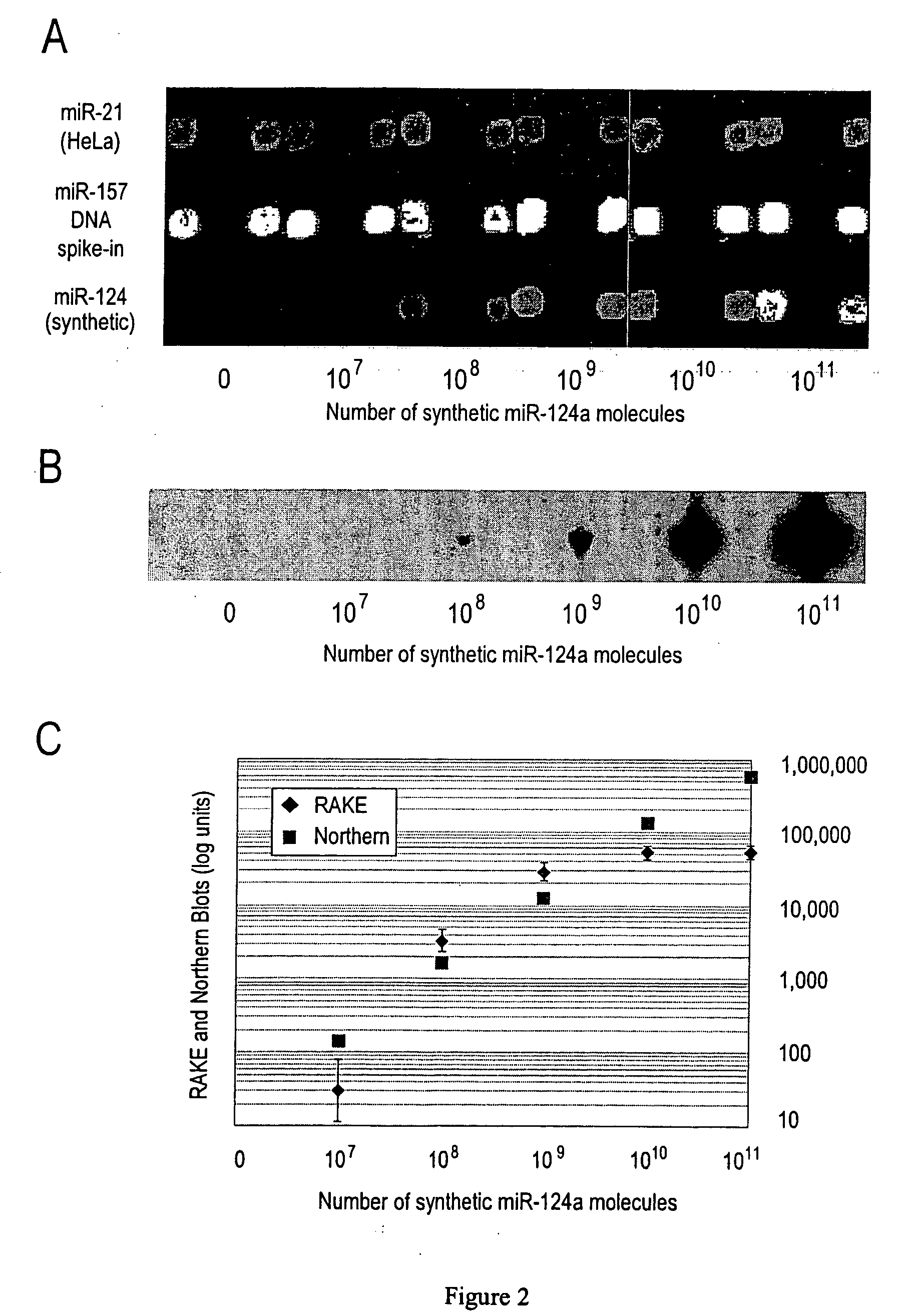
Provided are DNA microarray techniques that allow hybridization without RNA amplification, without using cDNA, and without labeling the nucleic acid prior to hybridization. Referred to as the Double-stranded Exonuclease Protection (DEP) assay, the technique permits the sample RNA to be used directly for hybridization, without manipulation in any way. Further provided is a microarray technique for high-throughput miRNA gene expression analyses, termed the RNA-primed, Array-based, Klenow Enzyme (RAKE) assay. The RAKE assay is a sensitive and specific technique for assessing single-stranded DNA and RNA targets, and offers specific advantages over Northern blots.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Identification method of rice bacterial leaf blight resistance and application of miRNA397a genetic locus
ActiveCN103184286AShort sequenceNot easy to degradeMicrobiological testing/measurementMiRNA GeneResistant genes
The invention discloses an identification method of rice bacterial leaf blight resistance and an application of miRNA397a genetic locus, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The identification method comprises the following steps: inoculating paddy rice to be detected and infected paddy rice; separating miRNA genes of the paddy rice to be detected and the infected paddy rice; detecting the expressions of the miRNA genes; and determining whether the paddy rice to be detected is resistant to bacterial leaf blight. The invention further discloses the application of the miRNA397a genetic locus in identification of rice bacterial leaf bright resistance. The invention uses the transcription of the miRNA397a gene locus to identify whether paddy rice is resistant to bacterial leaf blight, and achieves success. The transcription of the miRNA397a gene locus provided by the invention is detection based on expression level, so as to avoid misjudgment caused by bacterial leaf blight resistance gene silencing; and the identification method provided by the invention does not use the conventional DNA linkage tracer method, so as to avoid misjudgment caused by untightness of DNA linkage, improve the detection accuracy and avoid unnecessary production loss.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
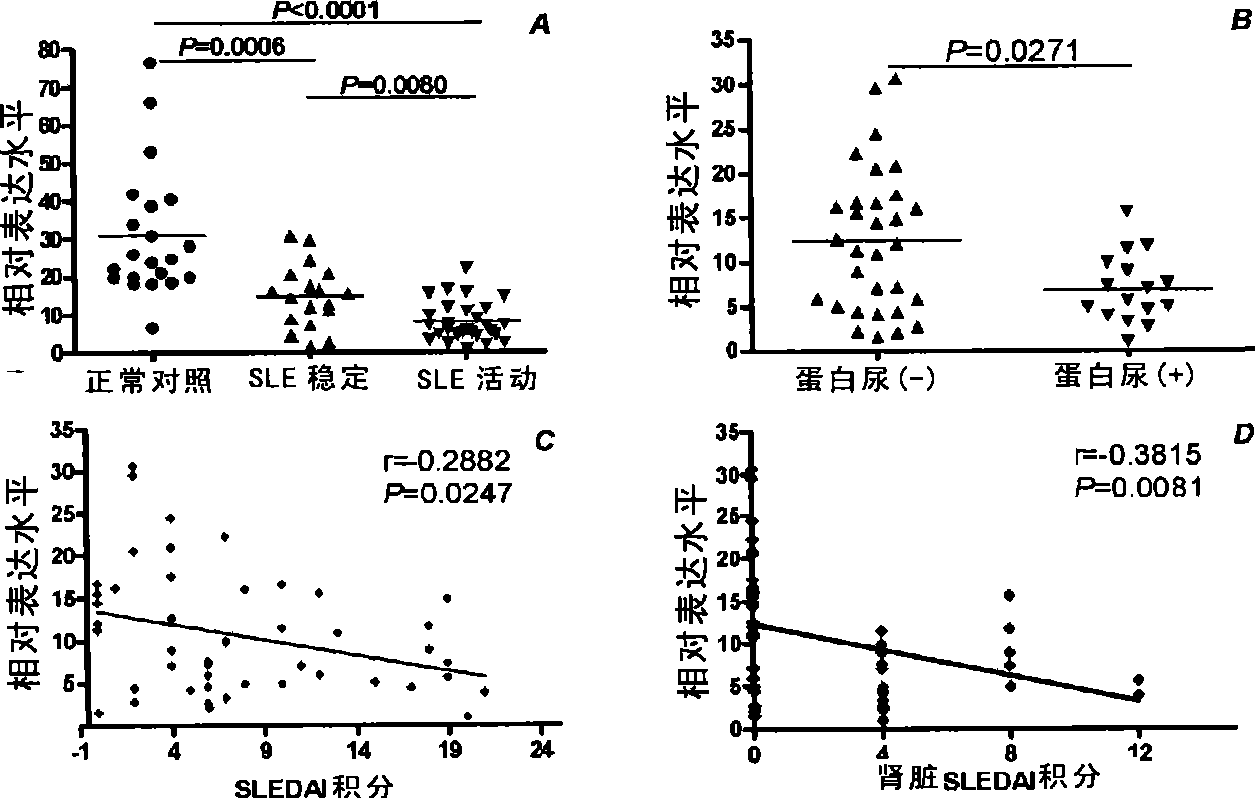
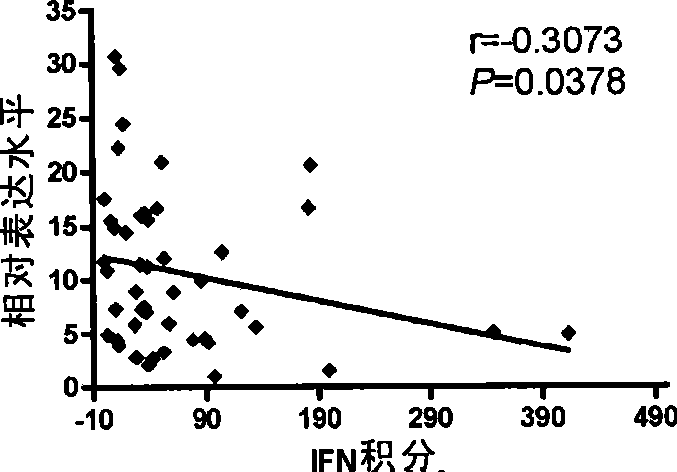
Use of miRNA genes in systemic lupus erythematosus disease diagnose and treatment
ActiveCN101376910AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMiRNA GeneMicroRNA Gene
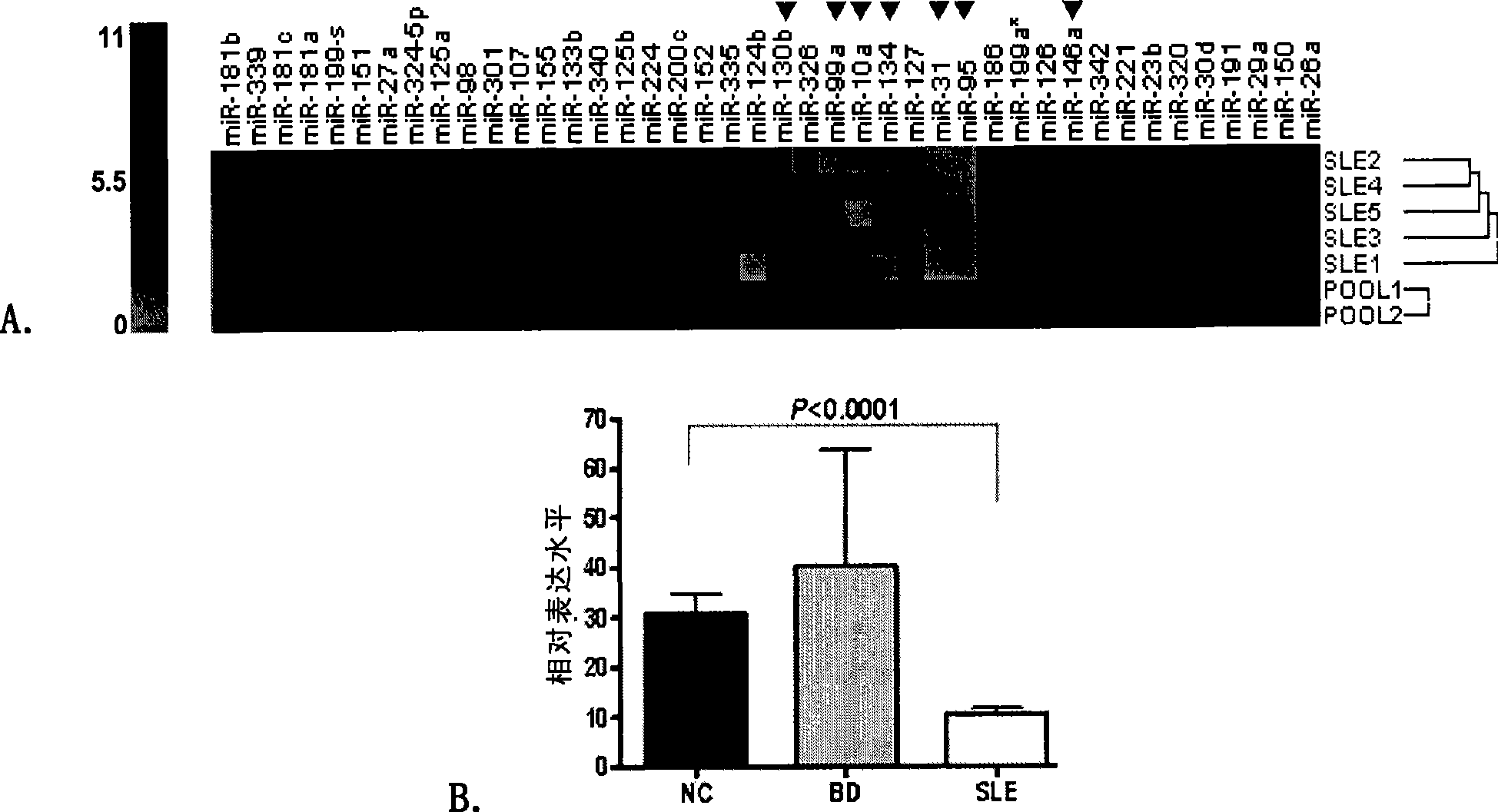
The invention belongs to the biotechnology field and discloses a purpose of small RNA; the small RNA is used to prepare a reagent or a reagent-box of SLE. The invention also discloses a test reagent or a test reagent-box used to test the level of the small RNA, thereby diagnosing the SLE. The invention initially discloses and proves that the small RNA and the SLE are closely related, so as to provide a new drug target for disease prevention; the regulation of the small RNA level is a novel curing means for disease obstruction.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Transgenic regulation and control miRNA (micro ribonucleic acid) gene algae capable of realizing continuous photosynthetic hydrogen production and creation method of gene algae
InactiveCN103571868AContinuous hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesMiRNA GeneFunctional genes
The invention discloses transgenic regulation and control miRNA (micro ribonucleic acid) gene algae capable of realizing continuous photosynthetic hydrogen production. Regulation and control miRNA is screened from a green algae miRNAs library or is designed for a green algae functional gene affecting photosynthetic efficiency, transgenic algae capable of inducing the expression of the regulation and control miRNA through such manners as light intensity or temperature and the like is created, and the activity of a green algae photosynthetic system II is indirectly regulated and controlled by means of inhibition of the miRNAs on a target gene to control the hypoxia environment in algae cells so as to enable the green algae cells to continuously produce hydrogen; a culture medium does not need to be alternately changed in the hydrogen production process of the transgenic regulation and control miRNA gene algae created by the method, and thus the defect that the culture medium needs to be alternately changed to realize the continuous hydrogen production of the existing green algae to cause great reduction on the growth and hydrogen production ability of the culture medium is overcome, and the transgenic regulation and control miRNA gene algae has an industrial application prospect.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
A miRNA barrier technique
InactiveCN101054576AHigh expressionPrevent specific inhibitionRecombinant DNA-technologyMiRNA GeneNucleotide
The present invention relates to miRNA barrier technology, belonging to biological technology. The miRNA technology can be implemented according to the following steps: 1) determining the target gene sequence of combining mRNA 3' UTR and miRNA, 2) synthesizing specific anti-sense oligo-barrier sequence, 3) transducing specific anti-sense oligo-barrier sequence into cell and combining target mRNA to form diploid, which can barrier the target miRNA of mRNA. 5 nucleotides or deoxyadenylic acids positioned at two ends of the specific anti-sense oligo-barrier sequence of the step 2) are locked while ribose ring is bridge-linked by 2' oxygen atom and 4' carbon atom. The inventive method has property of good transduced gene stability, high expression. The present invention proves that it is practical for interfering miRNA function using gene specific mode and provides novel measure for researching miRNA function which enable the selective gene therapy strategy and lay foundation to miRNA gene-specific use.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +1
Rapid construction of Arabidopsis artificial miRNA gene interference vector
InactiveCN102268434AReduce the probability of amplification errorsReduce consumptionMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
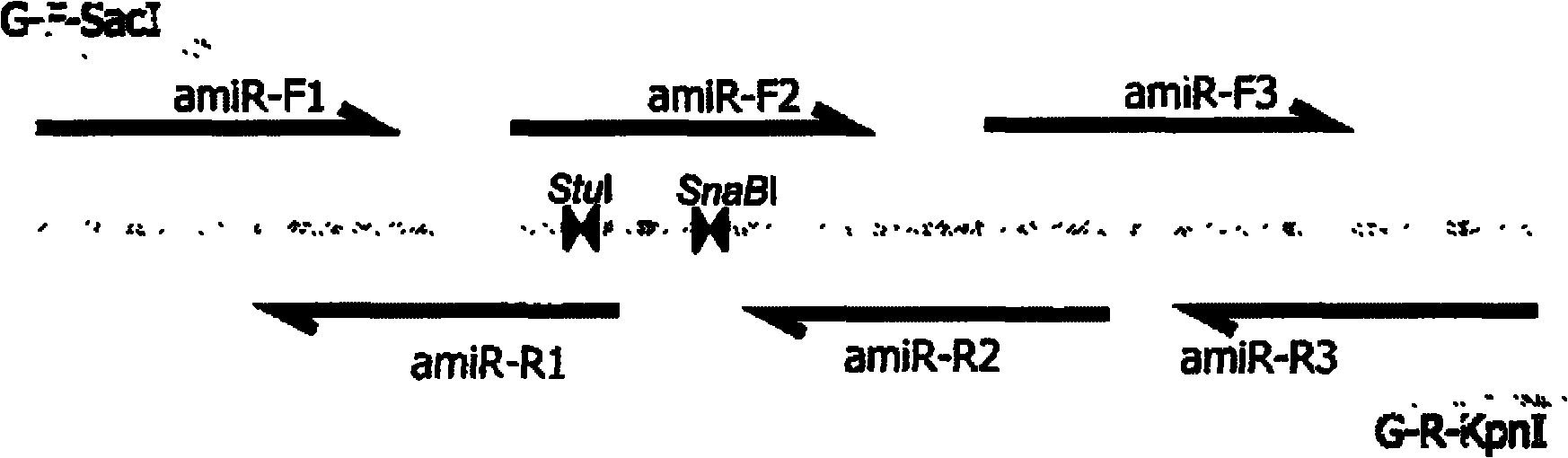
The invention relates to a method for quickly constructing an Arabidopsis thaliana artificial miRNA gene interference vector, which completes the construction of the Arabidopsis thaliana silencing vector, mainly for modifying the silencing segment for different genes, and the other parts are the same, expanding the unchanged DNA on the target carrier In the interval, the invariant regions at both ends of the silencing-related fragments are put into the transgenic target vector in advance, and then the core silencing fragments are connected into the transformed vector to directly complete the vector construction. When selecting the head and tail fragments, the DNA sequence was analyzed, so that after the head and tail fragments were connected by a bridge fragment, a StuI restriction site and a SnaBI restriction site could be obtained. After transforming E. coli, the vector could be prepared in large quantities and used with StuI and The SnaBI enzyme endonuclease linearizes it, and directly connects the core silencing fragment synthesized by this patent method to complete the construction of the Arabidopsis thaliana silencing vector. The beneficial effects of the present invention are: simple and easy to operate, convenient operation, high benefit, can greatly shorten the experiment time, and reduce the transformation cost of a single silencing carrier.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
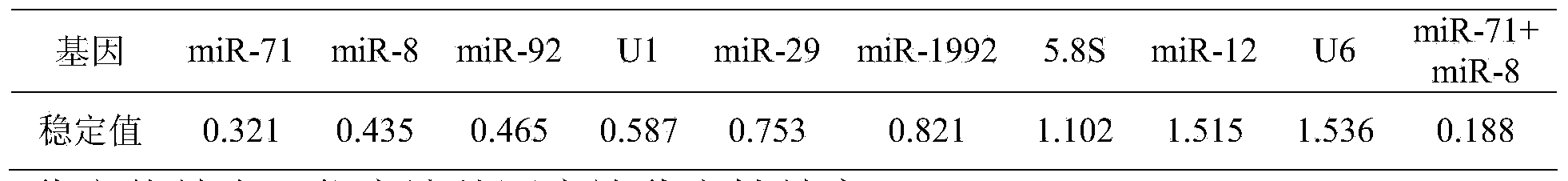
Dual-gene micro RNA fluorescent quantitative internal reference and application of primer in shellfish development samples
ActiveCN103710457AEasy to operateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationScreening proceduresReference genes
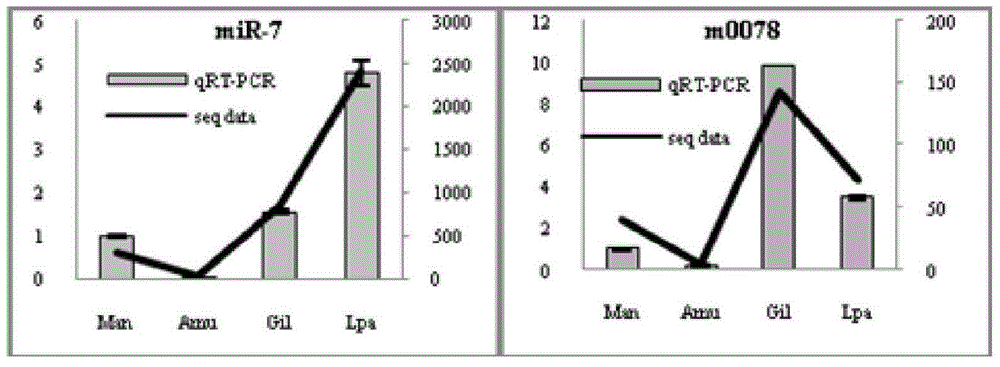
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, in particular to a dual-gene micro RNA (miRNA) fluorescent quantitative internal reference and application of a primer in shellfish development samples. The two genes (miR-71 and miR-8) are selected by the strict internal reference screening procedure and are the most stable miRNA genes in different development stages of shellfish miRNA, the expression stability of the two genes in different development stages is superior to that of common miRNA internal reference genes snRNA U6, snRNA U1 and 5.8S RNA. Two miRNAs are selected randomly, the dual-gene miRNA is used as the internal reference for carrying out fluorescent quantitative analysis in development samples, the expression results are highly accordance with the miRNA sequencing expression profile, and the reliability and the stability of the dual-gene internal reference are proved.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
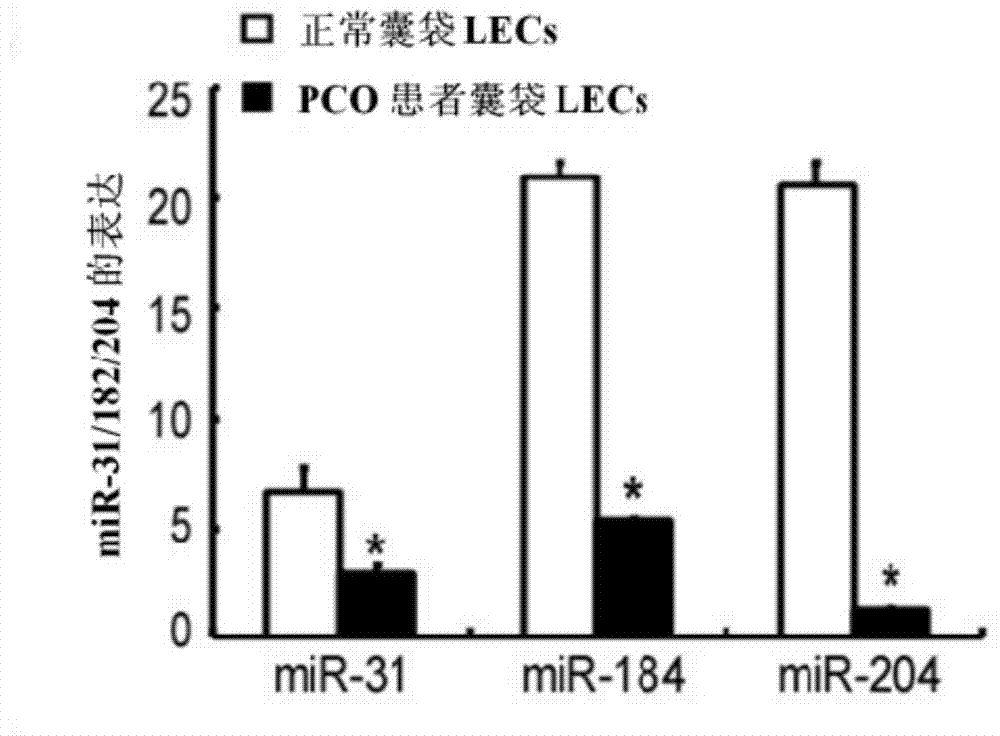
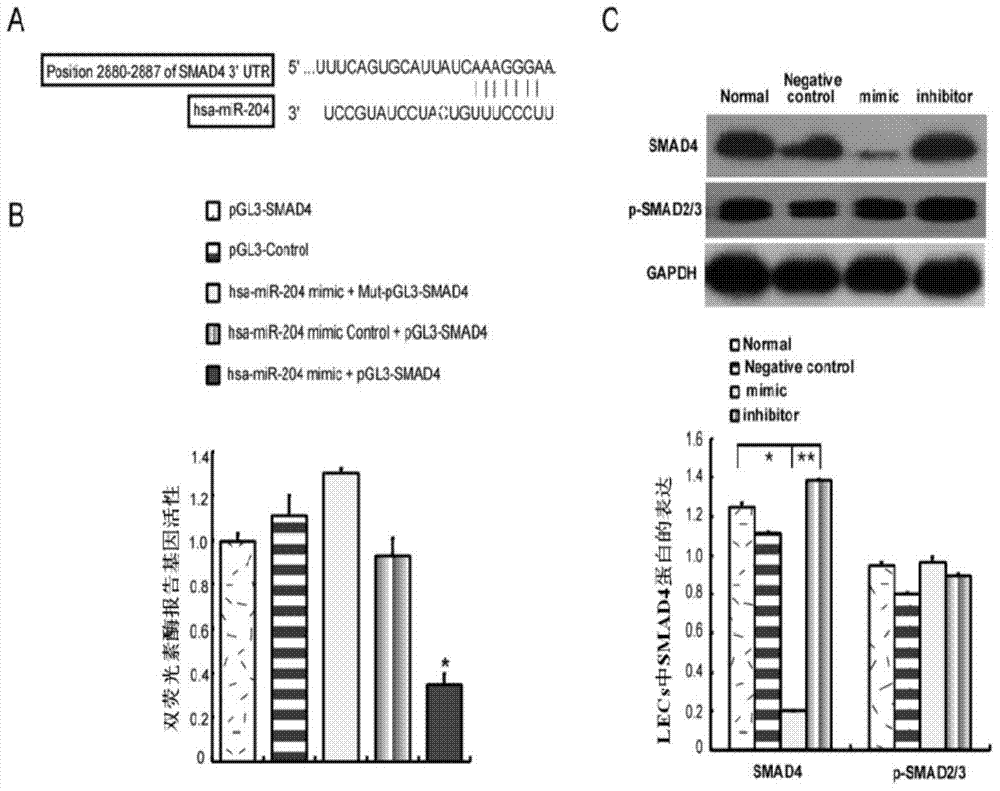
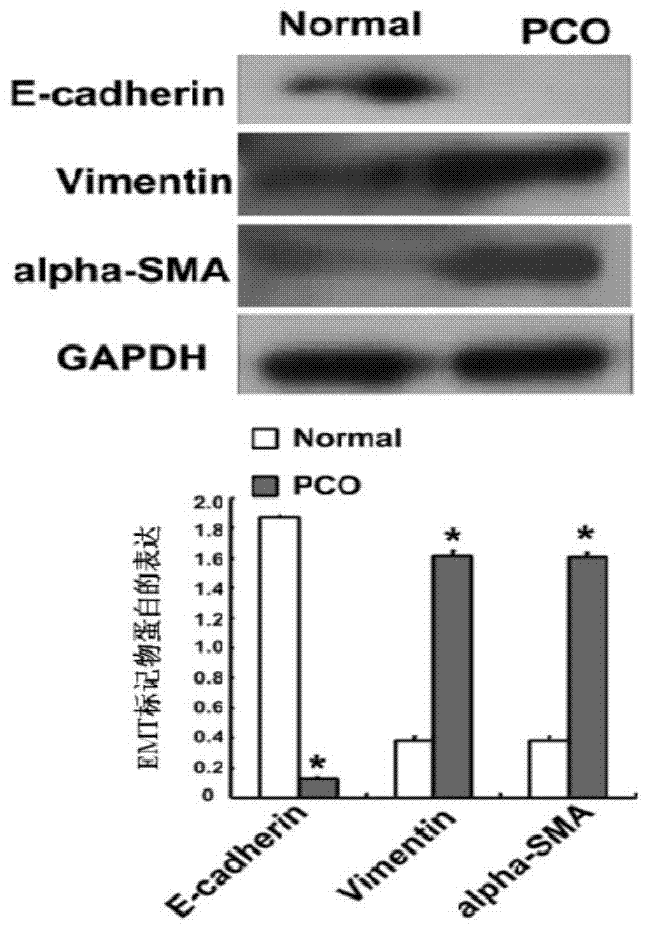
miRNA and application of miRNA in preparation of product for diagnosing and treating posterior capsule opacification
InactiveCN103773764ARegulate expressionInhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transitionSenses disorderGenetic material ingredientsPosterior capsule opacificationMiRNA Gene
The invention aims to provide a miRNA and an application of miRNA in preparation of a product for diagnosing and treating posterior capsule opacification. The miRNA is miR-204-5p and the RNA sequence is SEQ ID NO:1. A miRNA gene product can be used for adjusting the expression of an SMAD4 gene, blocking a TGF (Transforming Growth Factor)-beta / Smads signal channel and inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and has the potential of preparing the diagnosing and treating product for the posterior capsule opacification PCO.
Owner:SHANDONG EYE INST
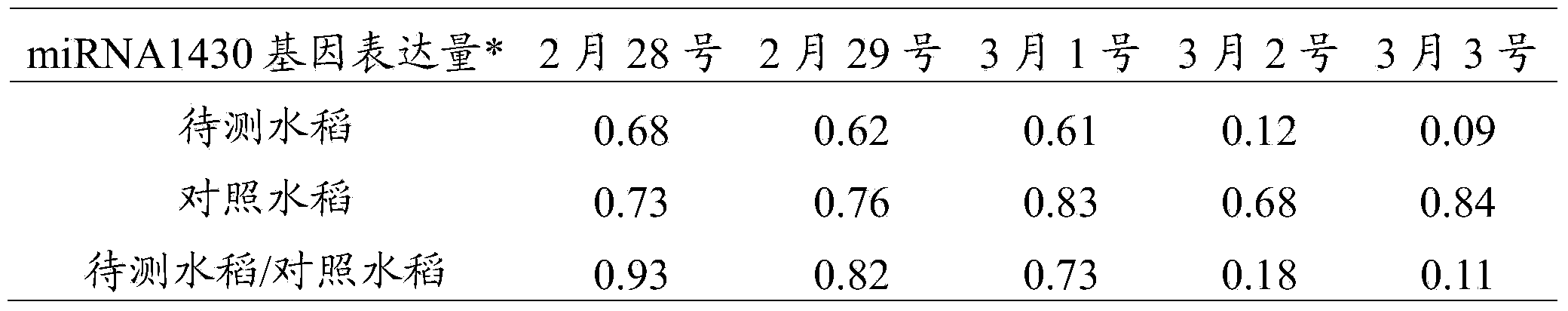
Method for predicting bacterial blight of rice by utilizing miRNA 1430 genes
ActiveCN104141004AAvoid ambiguityEarly forecastMicrobiological testing/measurementMiRNA GeneOryza sativa
The invention discloses a method for predicting bacterial blight of rice by utilizing miRNA 1430 genes, belonging to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting rice to be detected and control rice, wherein the selected control rice is not infected with the bacterial blight but is cultivated with the rice to be detected under the same conditions; respectively separating total miRNA genes in the rice to be detected and the control rice; respectively detecting the expression quantities of the miRNA1430 genes in the total miRNA genes in the rice to be detected and the control rice, wherein the sequences of the miRNA1430 genes are shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table; and judging whether the experiments are successful according to the expression quantities of the miRNA1430 genes in the rice to be detected and the control rice and further judging whether a plant to be detected is infected with the bacterial blight if the experiments are successful. The prediction method disclosed by the invention achieves success, can achieve accurate prediction a few days before the bacterial blight of rice appears and has the effects of gaining time for early prevention and treatment and reducing the rice loss caused by the bacterial blight.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Identification method of rice bacterial leaf blight resistance and application of miRNA1425 genetic locus
ActiveCN103184285AShort sequenceEasy to degradeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMiRNA Gene
The invention discloses an identification method of rice bacterial leaf blight resistance and an application of miRNA1425 genetic locus, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The identification method comprises the following steps: inoculating paddy rice to be detected and infected paddy rice; separating miRNA genes of the paddy rice to be detected and the infected paddy rice; detecting the expressions of the miRNA genes; and determining whether the paddy rice to be detected is resistant to bacterial leaf blight. The invention further discloses the application of the miRNA1425 genetic locus in identification of rice bacterial leaf bright resistance. The invention uses the transcription of the miRNA1425 gene locus to identify whether paddy rice is resistant to bacterial leaf blight, and achieves success. The transcription of the miRNA1425 gene locus provided by the invention is detection based on expression level, so as to avoid misjudgment caused by bacterial leaf blight resistance gene silencing; and the identification method provided by the invention does not use the conventional DNA linkage tracer method, so as to avoid misjudgment caused by untightness of DNA linkage, improve the detection accuracy and avoid unnecessary production loss.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
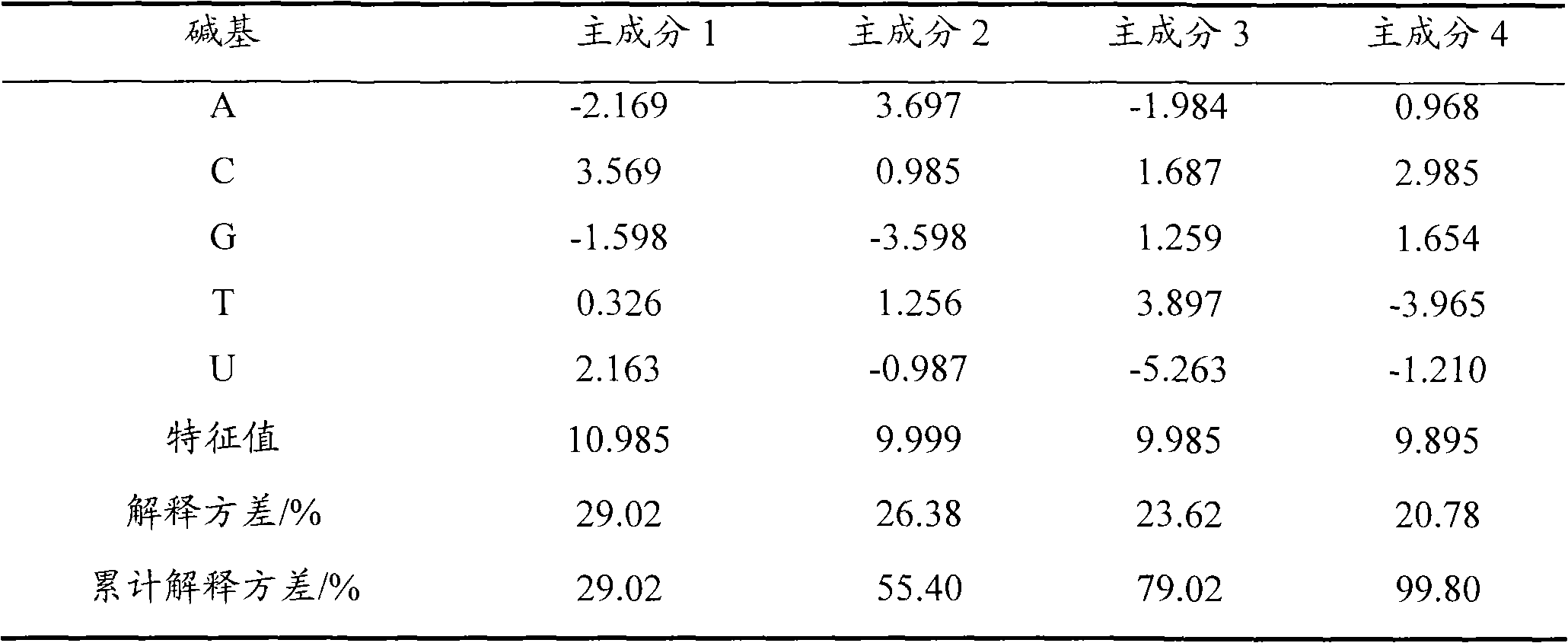
miRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid) forecasting method
InactiveCN101845485AEfficient forecastingLarge amount of informationMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsMiRNA GenePrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses an miRNA forecasting method, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (a) according to a principal component analysis method, establishing a new nucleotide sequence structure characterization method to obtain base two-dimensional characteristic scores; (b) characterizing the structures of the miRNAs and the non-miRNAs of human genes by the base two-dimensional characteristic scores; (c) carrying out normalization processing on the characterization variables of each miRNA and each non-miRNA by using a self-cross covariance method; (d) selecting parameters closely related with the miRNA structural characteristics by using a step-by-step method and establishing an miRNA forecasting model by a linear discriminatory analysis method; and (e) verifying the forecasting ability of the forecasting method by respectively adopting self-substitute verification, 1 / 5 reserving method cross verification and external verification. The miRNA forecasting method can be used for miRNA forecasting to discover new unknown miRNA genes.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for predicting bacterial blight of rice by utilizing miRNA 5794 genes
ActiveCN104141003AAvoid ambiguityEarly forecastMicrobiological testing/measurementMiRNA GeneOryza sativa
The invention discloses a method for predicting bacterial blight of rice by utilizing miRNA 5794 genes, belonging to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting rice to be detected and control rice, wherein the selected control rice is not infected with the bacterial blight but is cultivated with the rice to be detected under the same conditions; respectively separating total miRNA genes in the rice to be detected and the control rice; respectively detecting the expression quantities of the miRNA5794 genes in the total miRNA genes in the rice to be detected and the control rice, wherein the sequences of the miRNA5794 genes are shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table; and judging whether the experiments are successful according to the expression quantities of the miRNA5794 genes in the rice to be detected and the control rice and further judging whether a plant to be detected is infected with the bacterial blight if the experiments are successful. The prediction method disclosed by the invention achieves success, can achieve accurate prediction a few days before the bacterial blight of rice appears and has the effects of gaining time for early prevention and treatment and reducing the rice loss caused by the bacterial blight.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
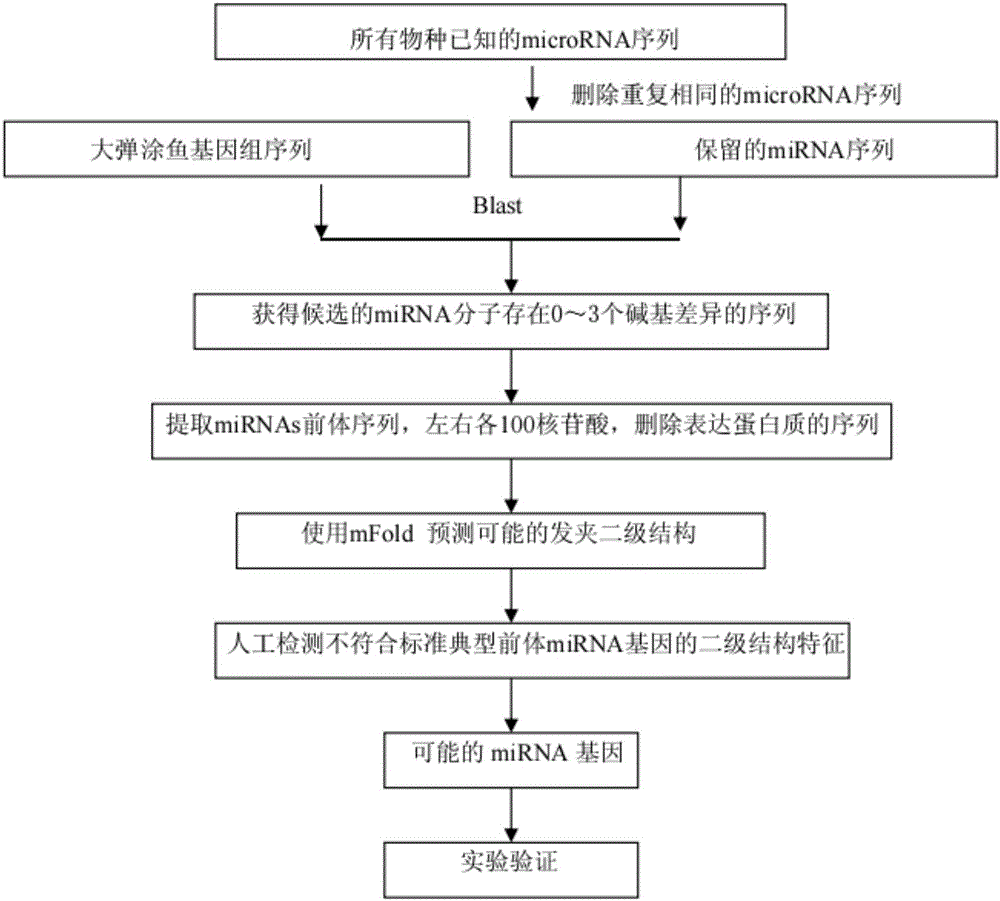
Biological genome sequence-based microRNA predicting method
InactiveCN107523631AFast wayEfficient methodMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisMiRNA GeneAnimal genome
The invention discloses a biological genome sequence-based microRNA predicting method. According to the invention, a method for predicting microRNA in an animal genome sequence is designed and experimental verification is performed. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, downloading genome sequences and mature miRNAs sequences of biological species from a website; secondly, removing the sequences with inconsistent number of matched bases by performing genome balst comparison by utilizing downloaded miRNAs of other species, and extracting a precursor sequence of the microRNA for performing stem-and-loop structure predicting; thirdly, deleting predicted stem-and-loop sequences which contain encoding protein from the genome; fourthly, screening and deleting the sequences which have inappropriate AU content and are not accordance with typical structural characteristics of the precursor miRNA; fifthly, acquiring possible miRNAs genes; sixthly, verifying the predicted microRNA by utilizing a stem-loop RT-PCR experiment.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
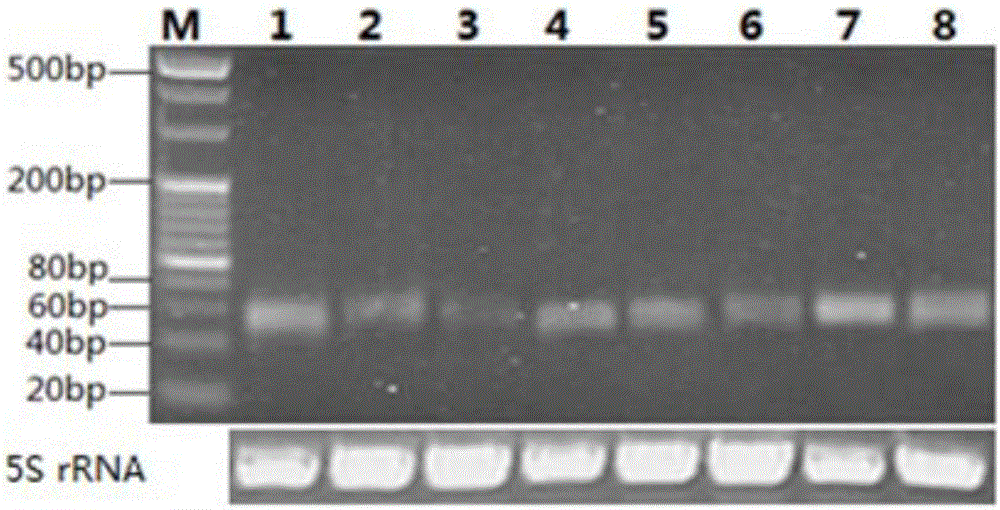
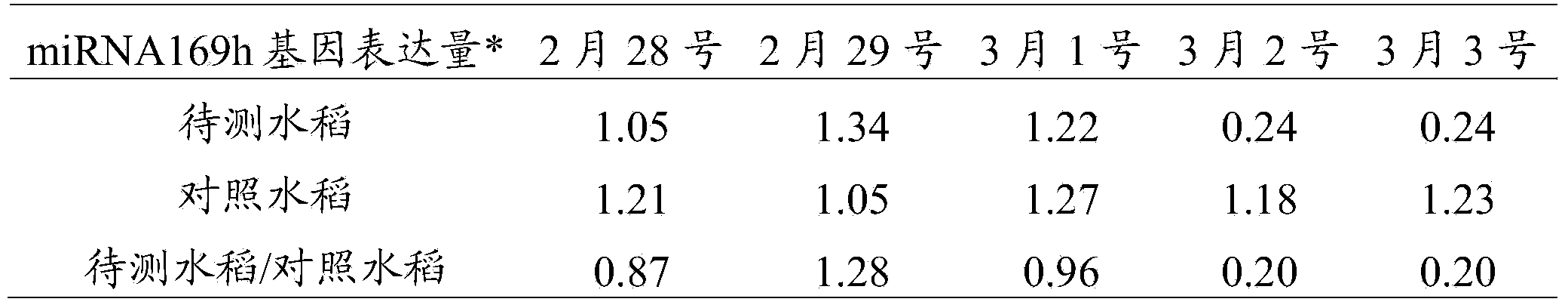
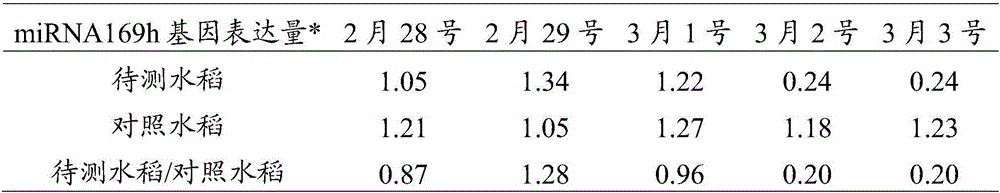
Method for predicting bacterial blight of rice by utilizing miRNA169h genes
ActiveCN104141008AAvoid ambiguityEarly forecastMicrobiological testing/measurementMiRNA GeneOryza sativa
The invention discloses a method for predicting bacterial blight of rice by utilizing miRNA 169h genes, belonging to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting rice to be detected and control rice, wherein the selected control rice is not infected with the bacterial blight but is cultivated with the rice to be detected under the same conditions; respectively separating total miRNA genes in the rice to be detected and the control rice; respectively detecting the expression quantities of the miRNA169h genes in the total miRNA genes in the rice to be detected and the control rice, wherein the sequences of the miRNA169h genes are shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table; and judging whether the experiments are successful according to the expression quantities of the miRNA169h genes in the rice to be detected and the control rice and further judging whether a plant to be detected is infected with the bacterial blight if the experiments are successful. The prediction method disclosed by the invention achieves success, can achieve accurate prediction a few days before the bacterial blight of rice appears and has the effects of gaining time for early prevention and treatment and reducing the rice loss caused by the bacterial blight.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
FISH probe composition and kit for detecting miRNA gene related to esophagus cancer and use method of kit
InactiveCN103866040ATraumatic NoneEasy to collectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMiRNA GeneFluorescence
The invention relates to a FISH probe composition for detecting a miRNA gene related to esophagus cancer. The probe composition contains a FISH probe for detecting the miRNA gene related to esophagus cancer. The invention further provides a FISH kit for detecting the miRNA gene related to esophagus cancer. The FISH kit comprises the FISH probe composition according to claims 1-5. In addition, the invention further discloses a use method of the FISH kit for detecting the miRNA gene related to esophagus cancer. According to the technical scheme, various miRNA genes related to esophagus cancer in saliva can be detected by directly adopting the fluorescence in situ hybridization technology, so that not only is a sample directly in-situ quantified, but also noninvasive diagnosis and screening of early esophageal cancer can be realized.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIOSENSE BIOSCI
Osteosarcoma miRNA detection reference gene identification method
ActiveCN108085386AAids in clinical translationIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMiRNA GeneBiology
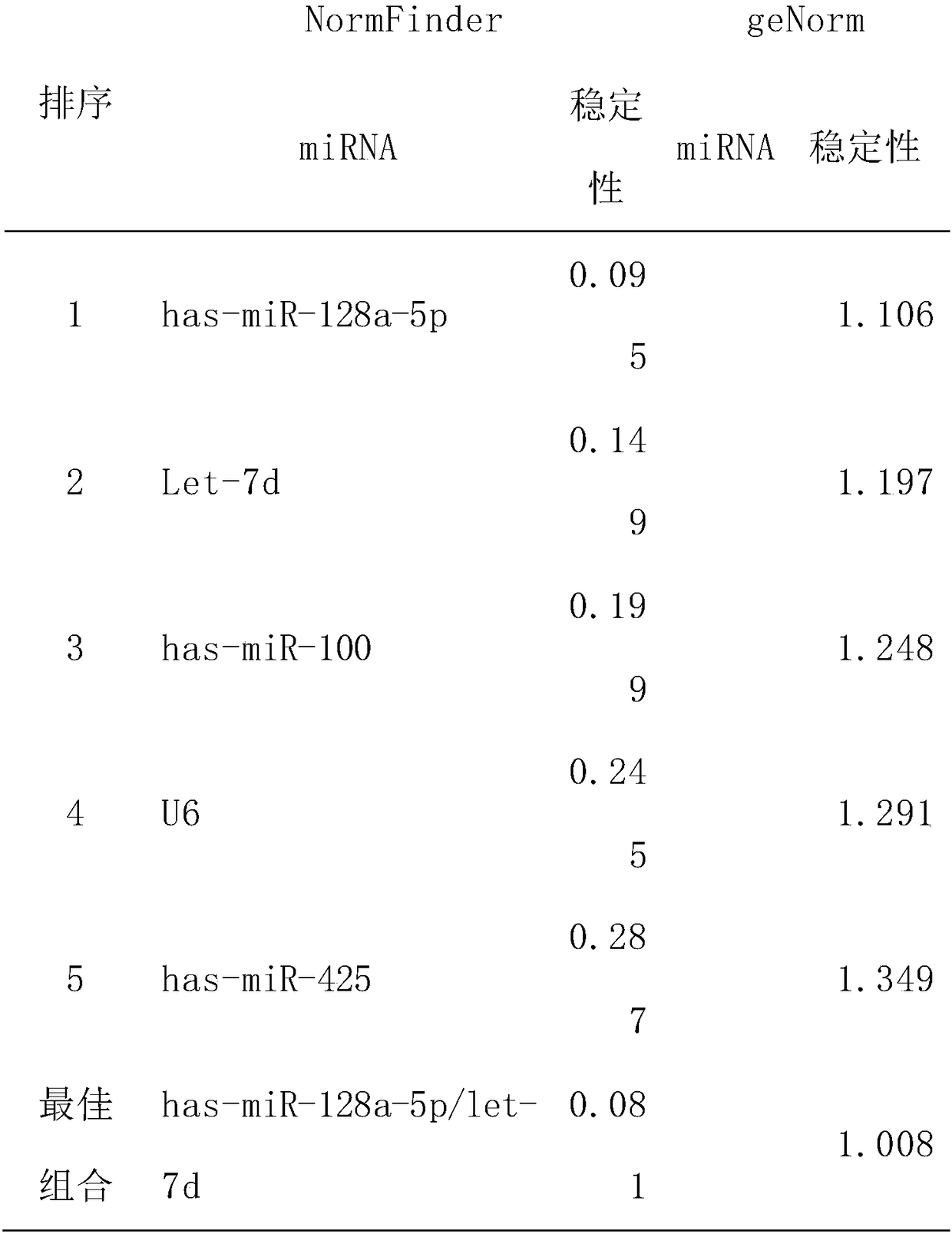
The invention discloses a reference miRNA gene stably expressed in an osteosarcoma patient. The reference miRNA gene comprises an hsa-miR-128a-5p or combination of hsa-miR-128a-5p and let-7d. The reference gene can be used for standardizing a target gene in osteosarcoma patient miRNA detection, research results of different laboratories can be compared, and normalization processing of experimentalresults is promoted.
Owner:NANJING NOVOACINE BIO-TECH CO LTD
Method for predicting potential association between miRNA and disease based on constrained probability matrix decomposition
The invention relates to data mining in bioinformatics, and particularly to mining of disease bioinformatics data and miRNA gene data. Specifically, the invention relates to prediction of the potential association between miRNA and a disease through data mining of miRNA and disease biological information. The method provided by the invention comprises the steps of processing of miRNA and disease-related data; analysis of disease similarity; analysis of miRNA similarity; learning of domain-based miRNA and the disease; constraint probability matrix decomposition of disease-related miRNA; and prediction of potential association between miRNA of the disease. The method provided by the invention can be used for predicting the potential association between miRNA and the disease, and can detect potential miRNA associated with the disease.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
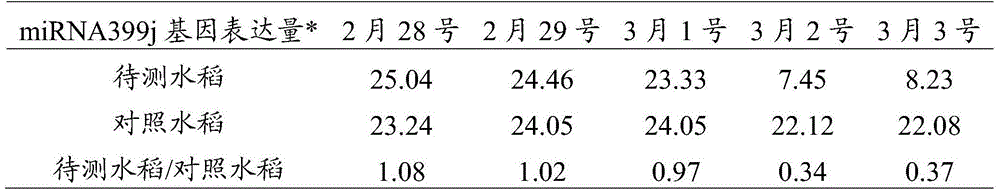
Method using miRNA399j gene for prediction of bacterial leaf blight of rice
The invention discloses a method using miRNA399j gene for prediction of bacterial leaf blight of rice, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps: rice to be measured and control rice are selected, the selected the control rice is not infected with the bacterial leaf blight and is cultivated in the same condition with the rice to be measured; total miRNA genes in the rice to be measured and the control rice are separated respectively; the expression amounts of the miRNA399j gene in the total miRNA genes in the rice to be measured and the control rice are detected respectively; the miRNA399j gene sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table; and according to the expression amounts of the miRNA399j gene in the total miRNA genes in the rice to be measured and the control rice, whether the experiment is successful is judged, and if the experiment is successful, whether the plant to be measured is infected with the bacterial leaf blight is further determined. The prediction method achieves a success, can accurately predict a few days before the bacterial leaf blight of rice, wins time for the early prevention and treatment, and reduces the loss caused by the bacterial leaf blight of rice.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
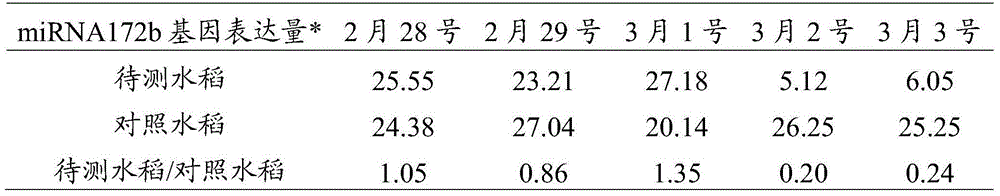
Method for forecasting bacterial leaf blight of paddy rice by utilizing miRNA172b gene
ActiveCN104131081AAvoid ambiguityEarly forecastMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceMiRNA Gene
The invention discloses a method for forecasting bacterial leaf blight of paddy rice by utilizing miRNA172b gene, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting to-be tested paddy rice and control paddy rice, wherein the selected control paddy rice is paddy rice which is not infected by bacterial leaf blight and is cultivated under same conditions with the to-be tested paddy rice; respectively separating total miRNA gene of the to-be tested paddy rice and the control paddy rice; respectively detecting the expression level of miRNA172b gene in the total miRNA gene of the to-be tested paddy rice and the control paddy rice, wherein the sequence of the miRNA172b gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1; and determining whether the experiment is successful according to the expression level of miRNA172b gene in the to-be tested paddy rice and the control paddy rice, if successful, further determining whether the to-be tested plant is infected by bacterial leaf blight. The provided prediction method is successful, is capable of accurately performing forecast several days before paddy rice has symptoms of bacterial leaf blight, wins time for early prevention and early controlling, and helps to reduce loss of paddy rice caused by bacterial leaf blight.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
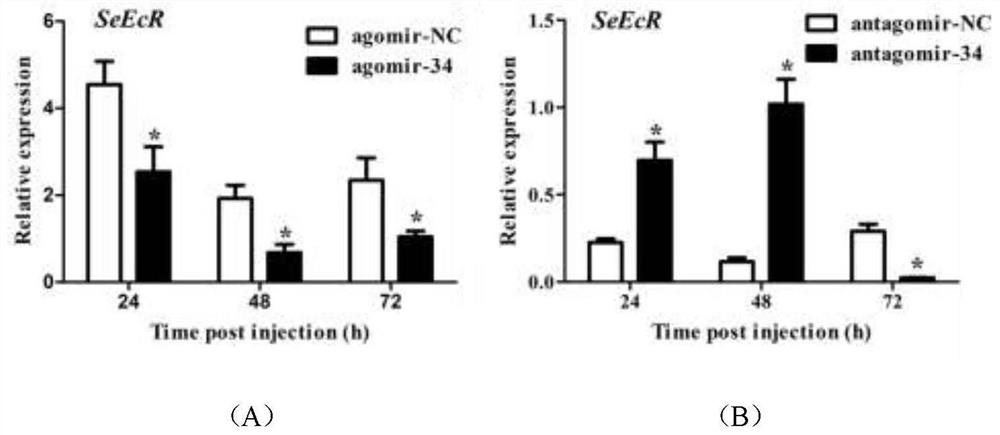
MiRNA for regulating lepidoptera pest death, analogue and inhibitor and application thereof
PendingCN113106100AInhibition of growth and developmentPromote growthBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyMiRNA Gene
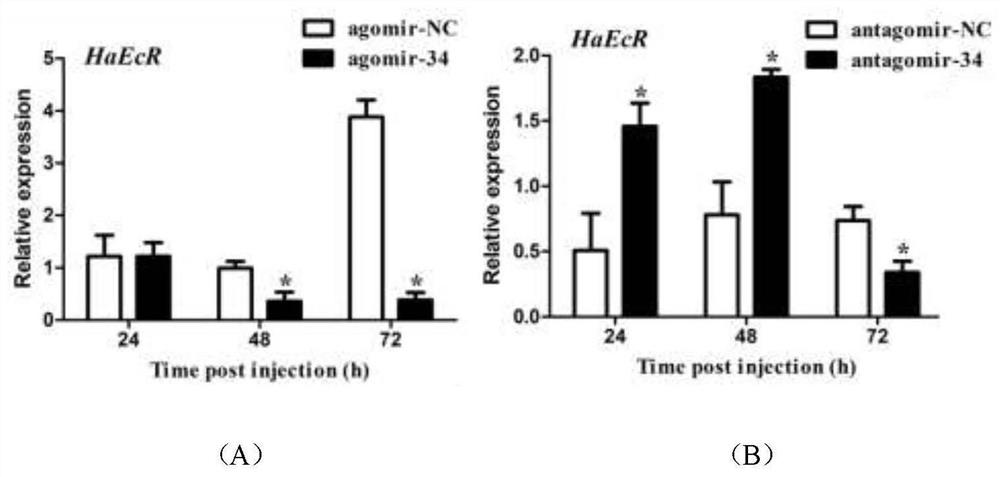
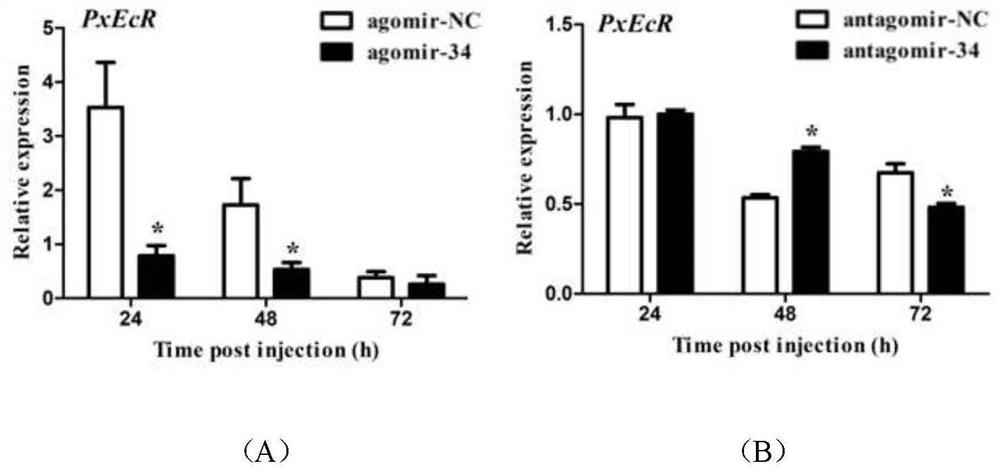
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural biology, particularly relates to miRNA capable of regulating lepidoptera pest death and delaying growth and development of lepidoptera pests as well as an analogue and an inhibitor of the miRNA, and further discloses application of the miRNA to preparation of medicaments for preventing and treating lepidoptera pests. According to the present invention, the sequence of a lepidoptera insect miRNA gene family is analyzed to obtain the lepidoptera insect plutella xylostella miRNA, i.e., pxy-miR-34-5p, and the mature body sequence of the pxy-miR-34-5p is further labeled and chemically modified so as to synthesize the corresponding miRNA analogue agomiR-34 and the inhibitor anti-agomiR-34 in vitro. A microinjection method is used for researching and finding that the analogue agomiR-34 and the inhibitor agomiR-34 of the pxy-miR-34-5p can delay the growth and development of lepidoptera pests or reduce the survival rate of lepidoptera pests by regulating and controlling the EcR of lepidoptera pests, and theoretical guidance is provided for establishing a new strategy for controlling lepidoptera pests based on the miRNA interference technology.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
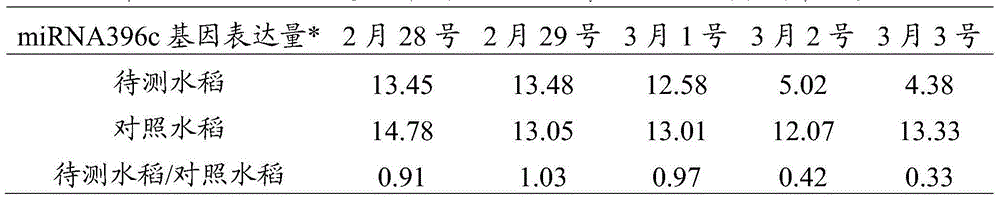
Method for forecasting bacterial leaf blight of paddy rice by utilizing miRNA396c gene
ActiveCN104131080AAvoid ambiguityEarly forecastMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceMiRNA Gene
The invention discloses a method for forecasting bacterial leaf blight of paddy rice by utilizing miRNA396c gene at early stage, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting to-be tested paddy rice and control paddy rice, wherein the selected control paddy rice is paddy rice which is not infected by bacterial leaf blight and is cultivated under same conditions with the to-be tested paddy rice; respectively separating total miRNA gene of the to-be tested paddy rice and the control paddy rice; respectively detecting the expression level of miRNA396c gene in the total miRNA gene of the to-be tested paddy rice and the control paddy rice, wherein the sequence of the miRNA396c gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1; and determining whether the experiment is successful according to the expression level of miRNA396c gene in the to-be tested paddy rice and the control paddy rice, if successful, further determining whether the to-be tested plant is infected by bacterial leaf blight. The provided prediction method is successful, is capable of accurately performing forecast several days before paddy rice has symptoms of bacterial leaf blight, wins time for early prevention and early controlling, and helps to reduce loss of paddy rice caused by bacterial leaf blight.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Medulloblastoma genes as targets for diagnosis and therapeutics
ActiveUS9695479B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingHigh-Density MicroarrayHistone methylation
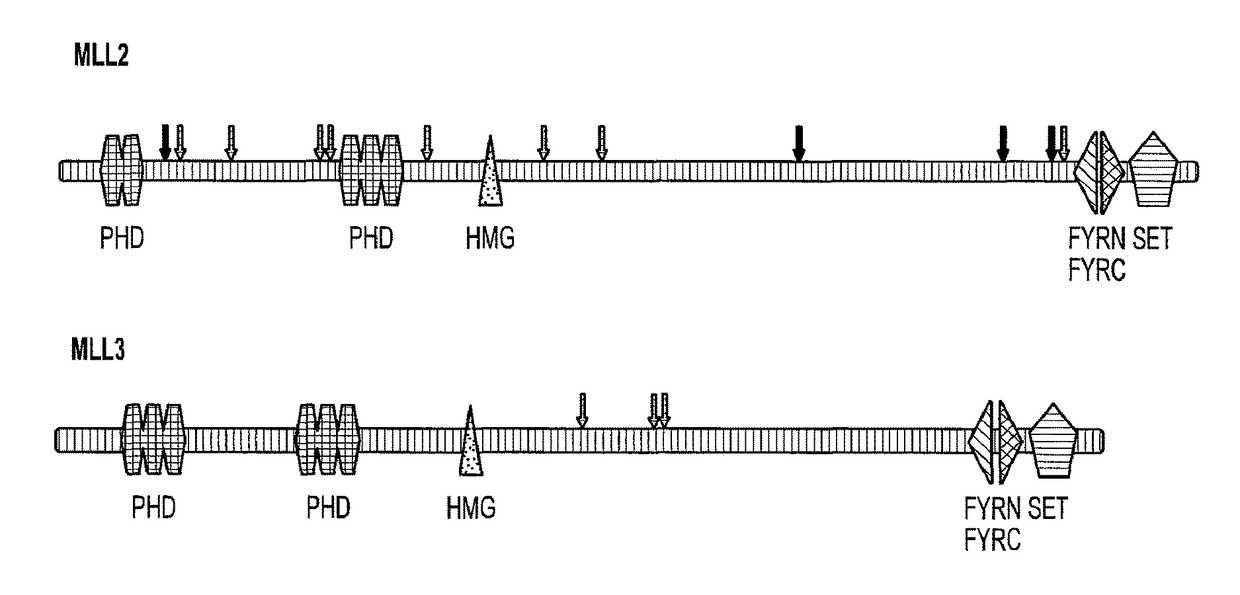
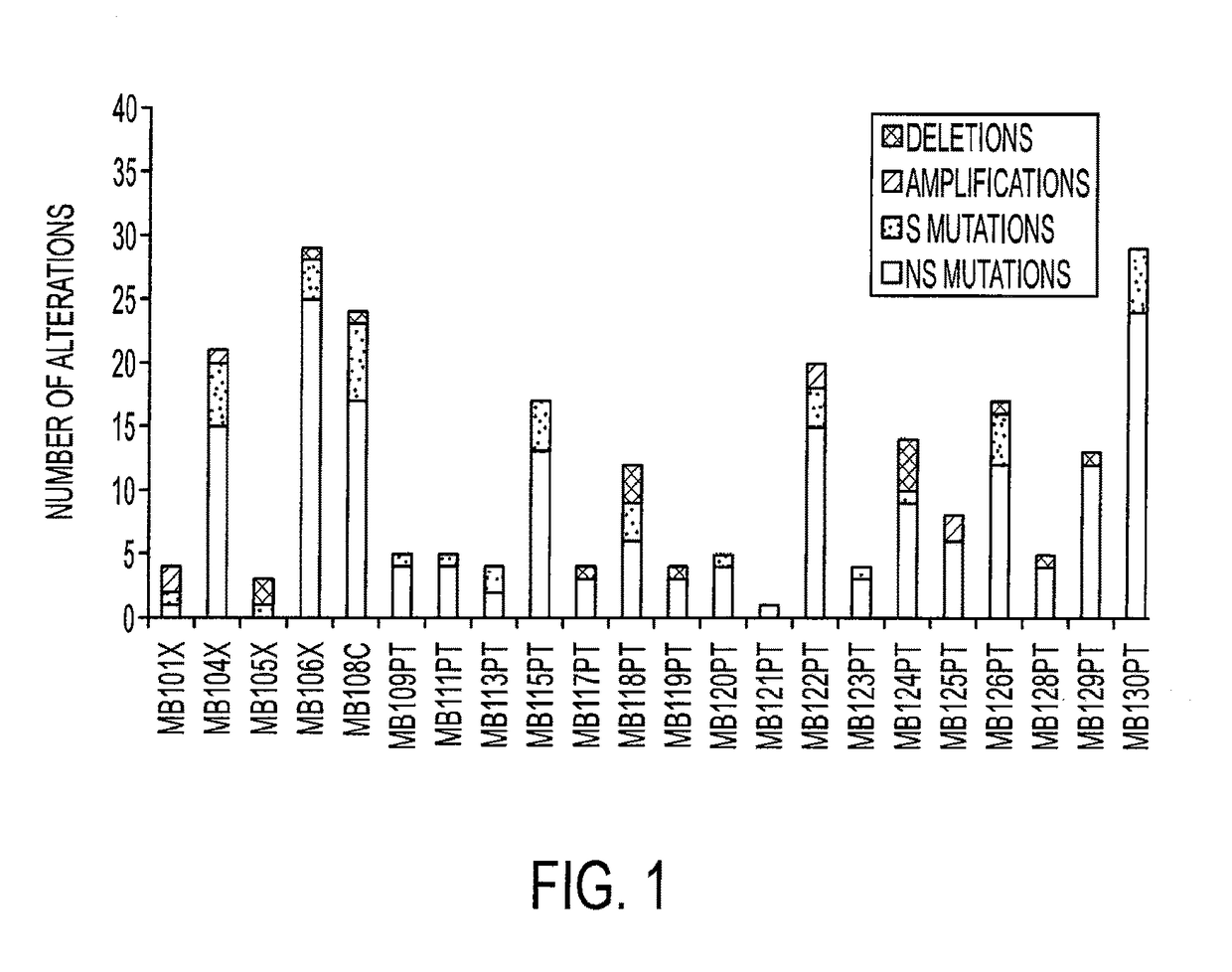
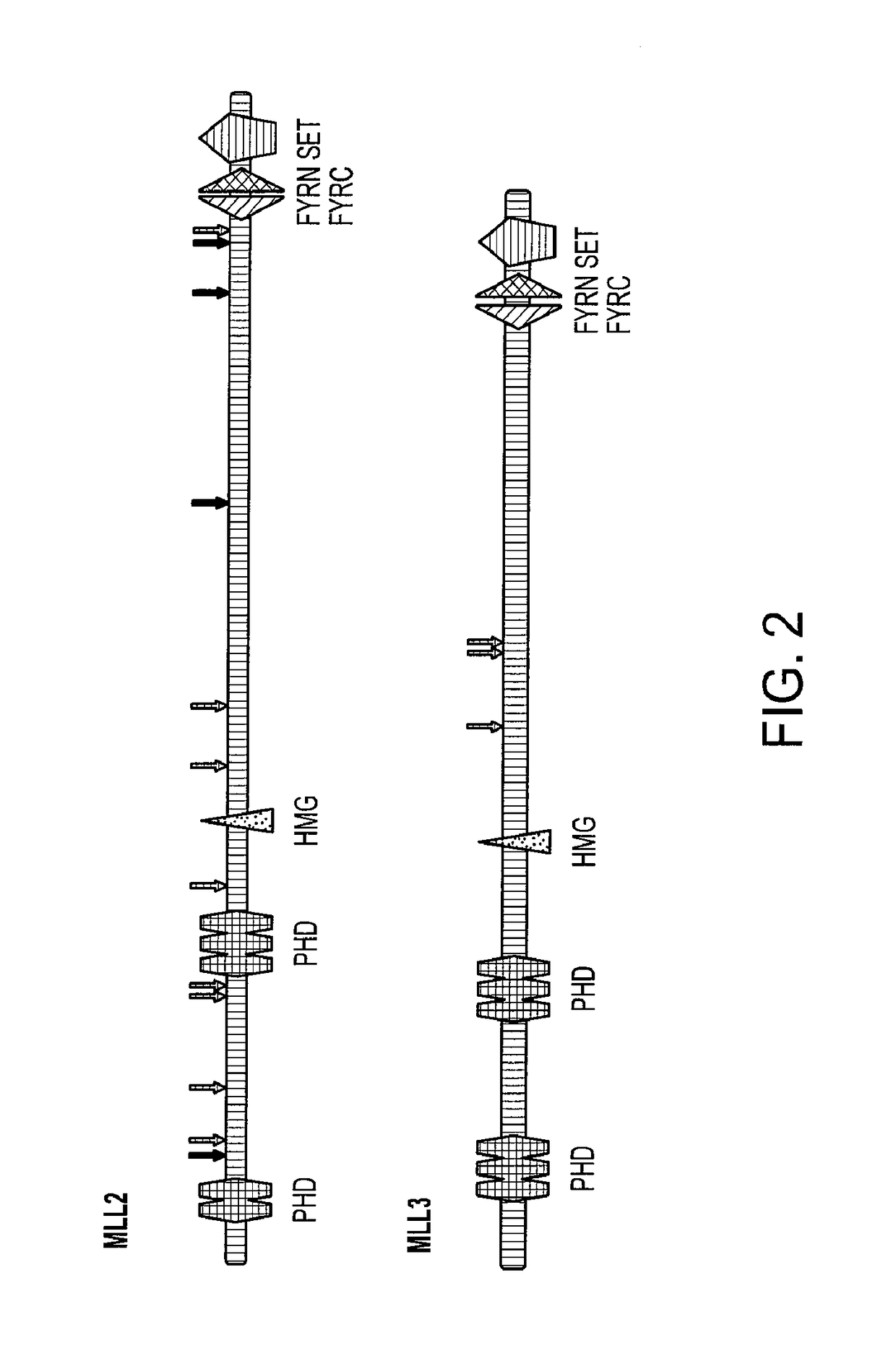
Medulloblastoma (MB) is the most common malignant brain tumor of children. To identify the genetic alterations in this tumor type, we searched for copy number alterations using high density microarrays and sequenced all known protein-coding genes and miRNA genes using Sanger sequencing. We found that, on average, each tumor had 11 gene alterations, markedly fewer than in common adult cancers. In addition to alterations in the Hedgehog and Wnt pathways, our analysis led to the discovery of genes not previously known to be altered in MBs. Most notably, inactivating mutations of the histone H3K4 trimethylase genes MLL2 or MLL3 were identified in 16% of MB patients. These results demonstrate key differences between the genetic landscapes of adult and childhood cancers, highlight dysregulation of developmental pathways as an important mechanism underlying MBs, and identify a role for a specific type of histone methylation in human tumorigenesis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Identification method of rice bacterial leaf blight resistance and application of miRNA1318 genetic locus
ActiveCN103184288BShort sequenceNot easy to degradeMicrobiological testing/measurementMiRNA GeneAgricultural science
Owner:海南广陵高科实业有限公司 +1
Application of a dual-gene microRNA fluorescence quantitative internal reference and its primers in shellfish tissue samples
ActiveCN103740823BEasy to operateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesMiRNA Gene
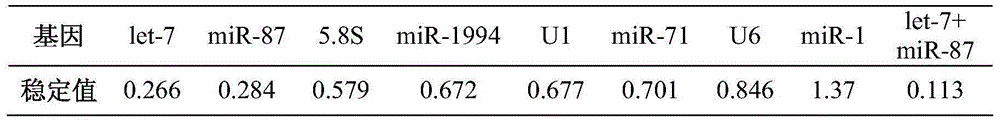
The invention relates to the field of biology, and particularly relates to application of dual-genetic microRNA (miRNA) fluorescent quantitative internal references and a primer thereof in shellfish tissue samples. Two genes (let-7 and miR-87) selected by the invention are selected according a strict internal reference screening process, and are miRNA genes with the most stable expression in the shellfish microRNA in different tissues; the expression stability of the genes in the tissue is superior to the common miRNA internal reference genes snRNA U6, snRNA U1 and 5.8S RNA. Two miRNAs are selected at random, and the dual-genetic miRNAs are taken as internal references to carry out fluorescence quantitative analysis in the tissue samples; the obtained expression result is highly identical to miRNA sequencing expression profile; the reliability and the stability of the dual genetic internal reference are proved.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
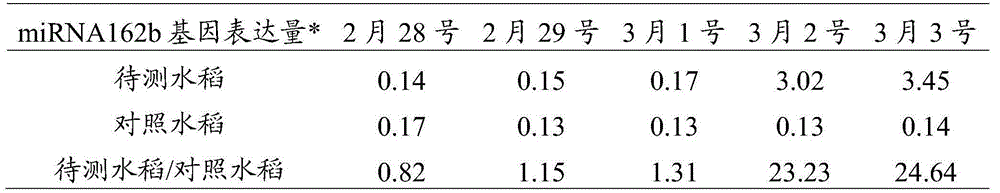
A method for early and accurate prediction of rice bacterial blight by using mirna162b gene
ActiveCN104131083BAvoid ambiguityEarly forecastMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceMiRNA Gene
The invention discloses a method for early and accurate prediction of rice bacterial blight by using miRNA162b gene, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting the rice to be tested and the control rice, wherein the selected control rice is not infected with bacterial blight but cultivated under the same conditions as the rice to be tested; isolating the rice to be tested and the rice to be tested respectively The total miRNA gene in the control rice; respectively detect the expression level of the miRNA162b gene in the total miRNA gene in the rice to be tested and the control rice, the sequence of the miRNA162b gene is as SEQ? ID? Shown in NO: 1; According to the expression levels of the miRNA162b gene in the rice to be tested and the control rice, judge whether the experiment is successful, and if successful, further determine whether the plant to be tested is infected with bacterial blight. The prediction method provided by the invention is successful, and can realize accurate forecast several days before the rice bacterial blight occurs, gaining time for early prevention and early treatment, and reducing the loss caused by the bacterial blight to rice.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Identification method of rice bacterial blight resistance and application of miRNA172a
InactiveCN103184287BShort sequenceNot easy to degradeMicrobiological testing/measurementMiRNA GeneMicrobiology
The invention discloses an identification method of rice bacterial leaf blight resistance and an application of miRNA172a genetic locus, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The identification method comprises the following steps: inoculating paddy rice to be detected and infected paddy rice; separating miRNA genes of the paddy rice to be detected and the infected paddy rice; detecting the expressions of the miRNA genes; and determining whether the paddy rice to be detected is resistant to bacterial leaf blight. The invention further discloses the application of the miRNA172a genetic locus in identification of rice bacterial leaf bright resistance. The invention uses the transcription of the miRNA172a gene locus to identify whether paddy rice is resistant to bacterial leaf blight, and achieves success. The transcription of the miRNA172a gene locus provided by the invention is detection based on expression level, so as to avoid misjudgment caused by bacterial leaf blight resistance gene silencing; and the identification method provided by the invention does not use the conventional DNA linkage tracer method, so as to avoid misjudgment caused by untightness of DNA linkage, improve the detection accuracy and avoid unnecessary production loss.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
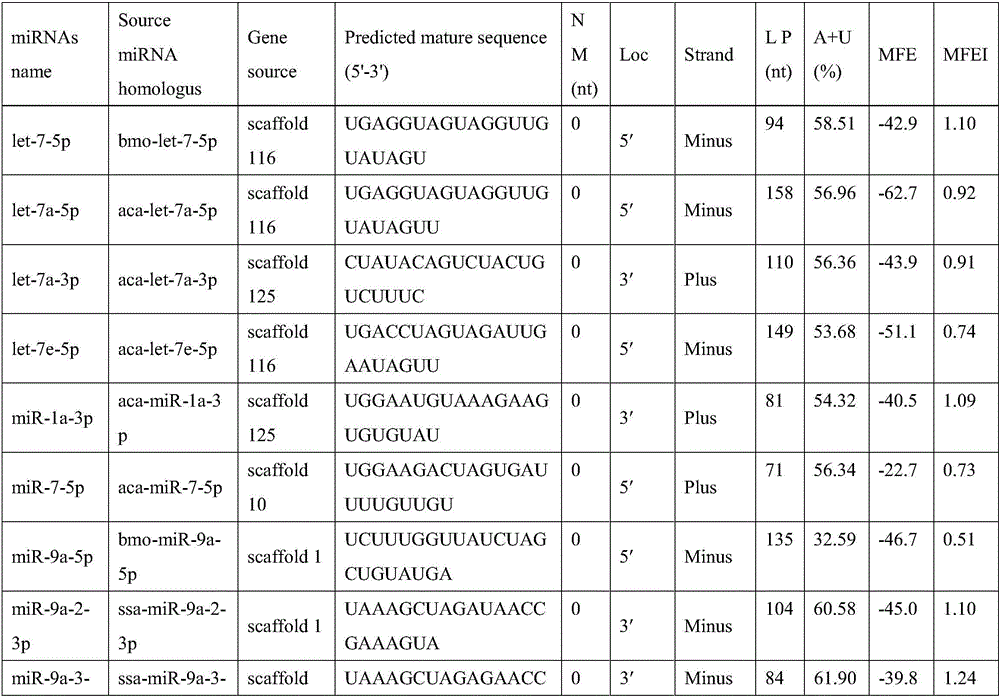
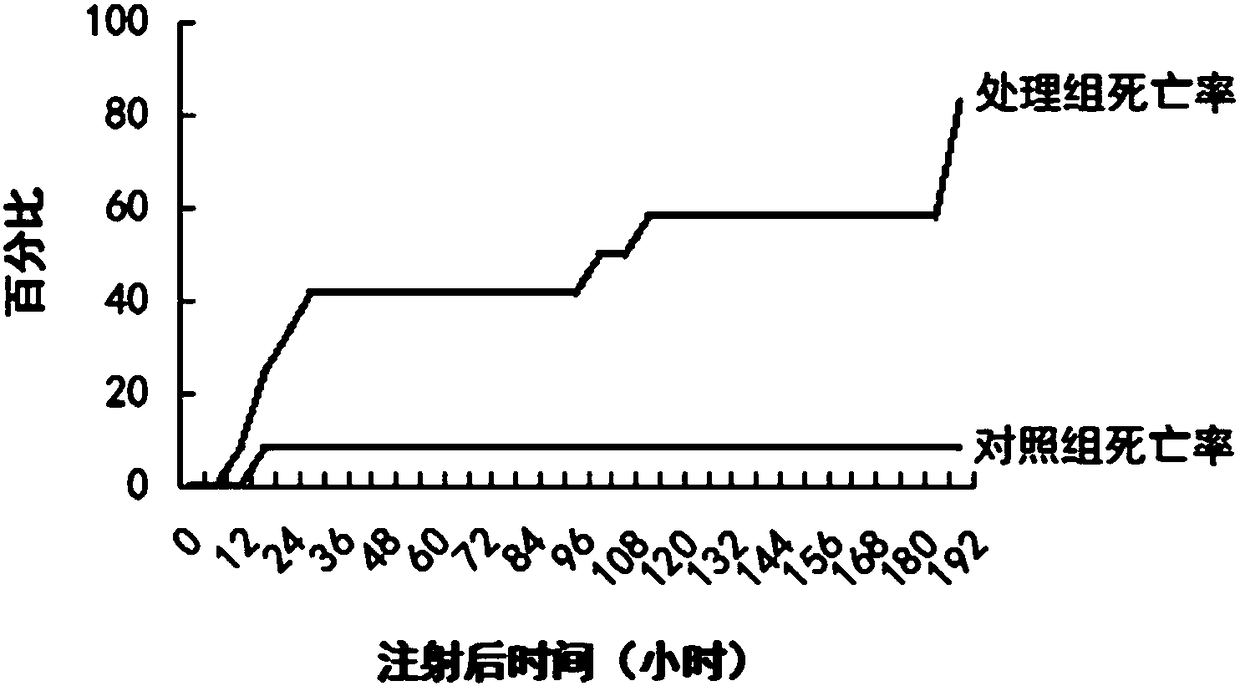
The lethal gene csu-mir-9b of Chilo suppressalis and its application
ActiveCN105238786BSignificant lethal effectResistance to degradationBiocideAnimal repellantsMiRNA GeneSmall RNA
The invention discloses the lethal gene csu-miR-9b of Chilo suppressalis and its application. The lethal gene csu-miR-9b of C. suppressalis borer, the sequence is 5'-UCUUUGGUUAUCUAGCUGUAUGA-3'. The application of the csu-miR-9b of the present invention in the preparation of an insecticidal agent for Chilo suppressalis. The present invention uses complete miRNA bioinformatics analysis to search for an effective miRNA—csu-miR-9b from a large amount of small RNA library data. Injection of C. suppressalis with csu-miR-9b synthesized in vitro has obvious lethal effect on C. suppressalis, indicating that the miRNA gene can be used as an effective interferer of important genes in C. suppressalis.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A method for predicting rice bacterial blight with miRNA169h gene
ActiveCN104141008BAvoid ambiguityEarly forecastMicrobiological testing/measurementMiRNA GeneGene prediction
The invention discloses a method for predicting rice bacterial blight with miRNA169h gene, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting the rice to be tested and the control rice, wherein the selected control rice is not infected with bacterial blight but cultivated under the same conditions as the rice to be tested; isolating the rice to be tested and the rice to be tested respectively The total miRNA gene in the control rice; respectively detect the expression level of the miRNA169h gene in the total miRNA gene in the rice to be tested and the control rice, the sequence of the miRNA169h gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in the sequence table According to the expression levels of the miRNA169h gene in the rice to be tested and the control rice, judge whether the experiment is successful, and if successful, further determine whether the plant to be tested is infected with bacterial blight. The prediction method provided by the invention is successful, and can realize accurate forecast several days before the rice bacterial blight occurs, gaining time for early prevention and early treatment, and reducing the loss caused by the bacterial blight to rice.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Identification method of rice bacterial leaf blight resistance
ActiveCN103184285BShort sequenceNot easy to degradeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMiRNA Gene
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
A miRNA that Regulates the Expression of the Anti-rust Fungus Infection Gene in Populus nigra
InactiveCN104059910BMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMiRNA GeneNucleotide sequencing
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com