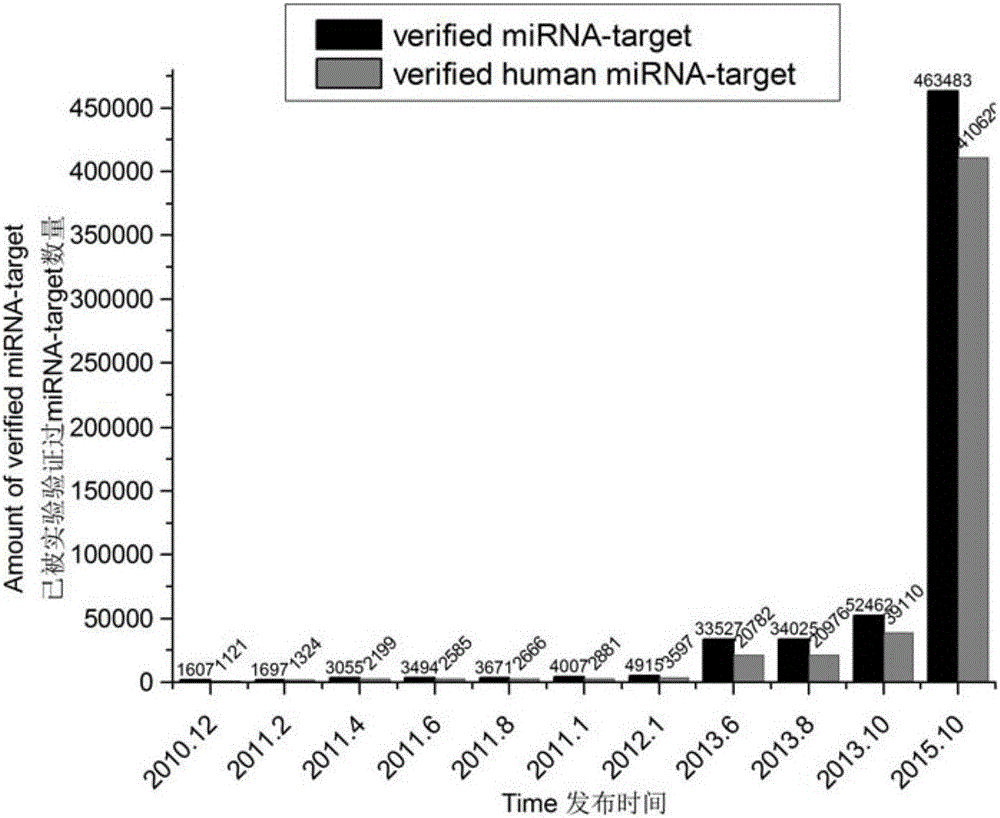
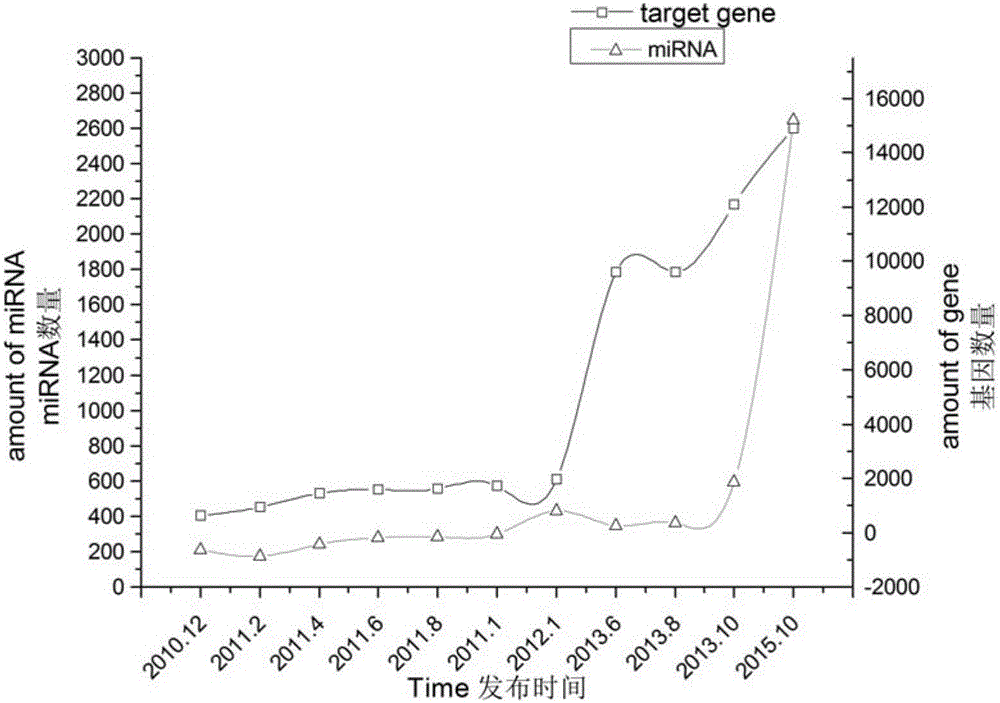
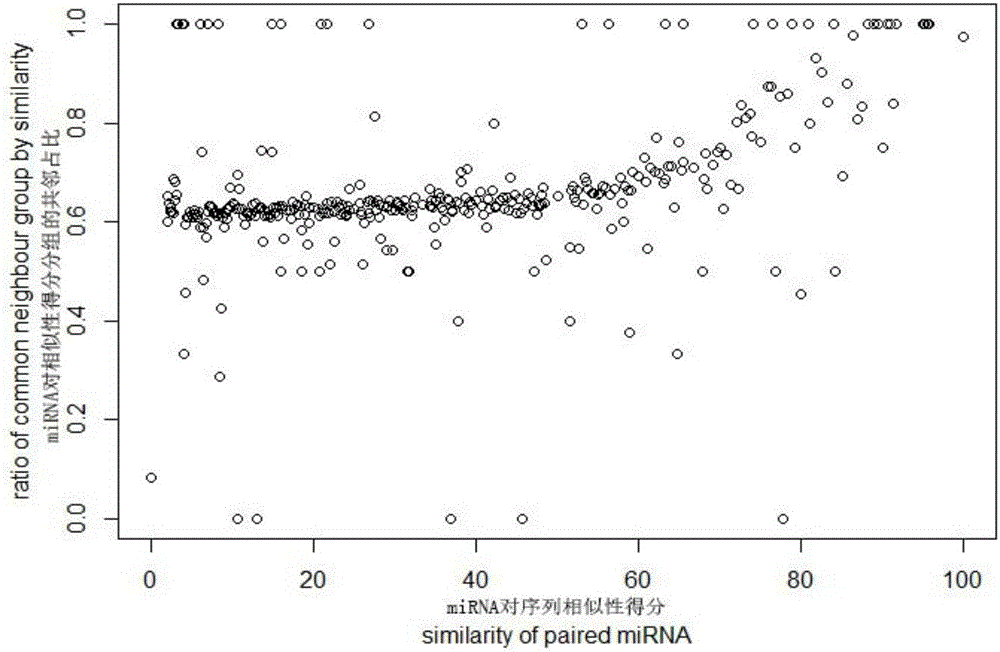
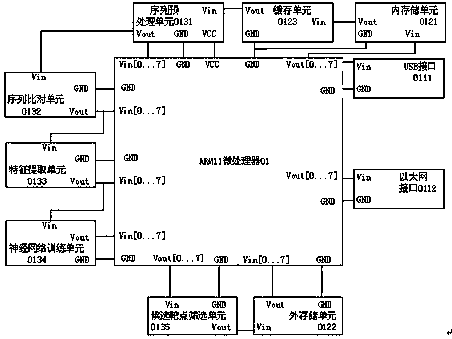
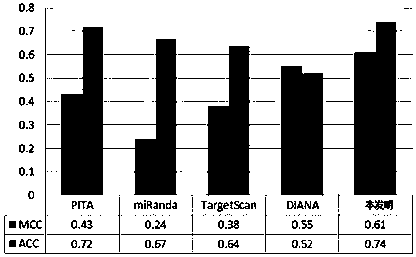
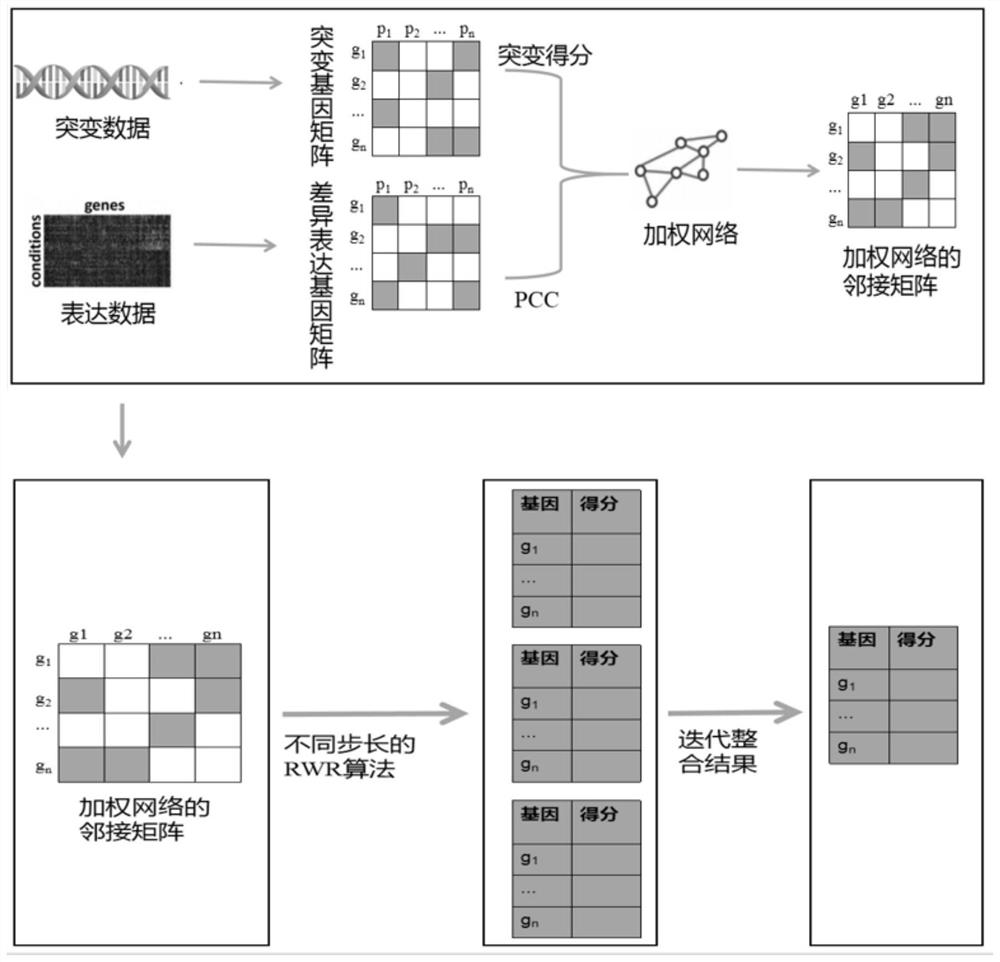
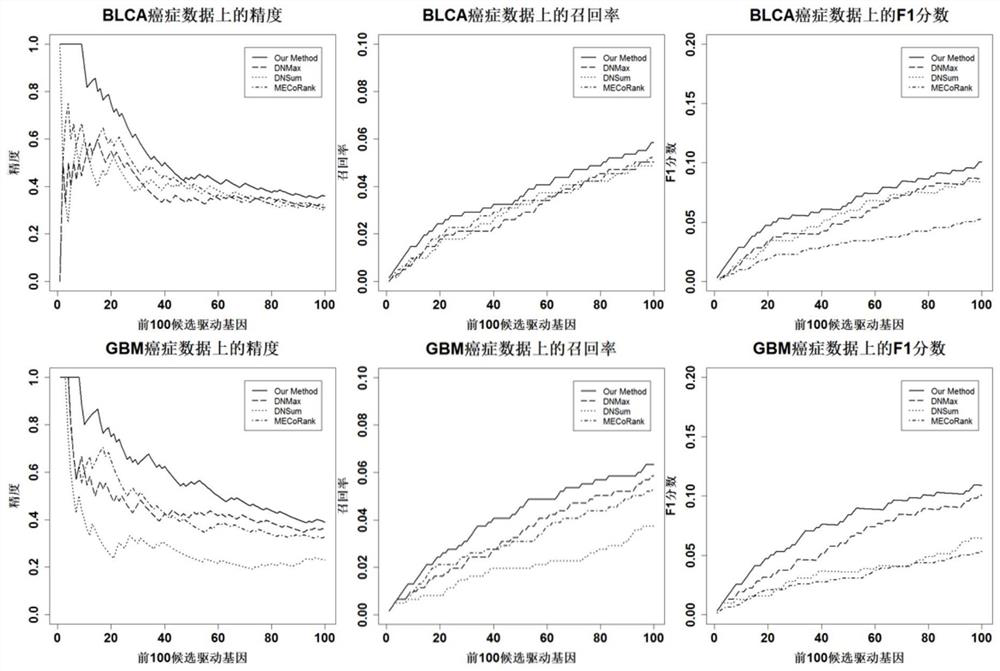
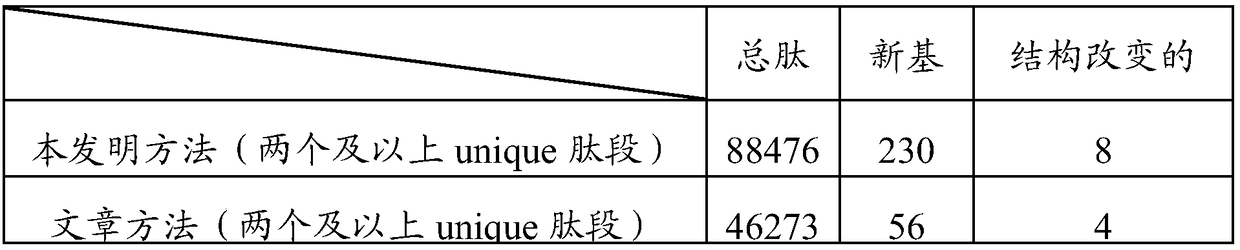
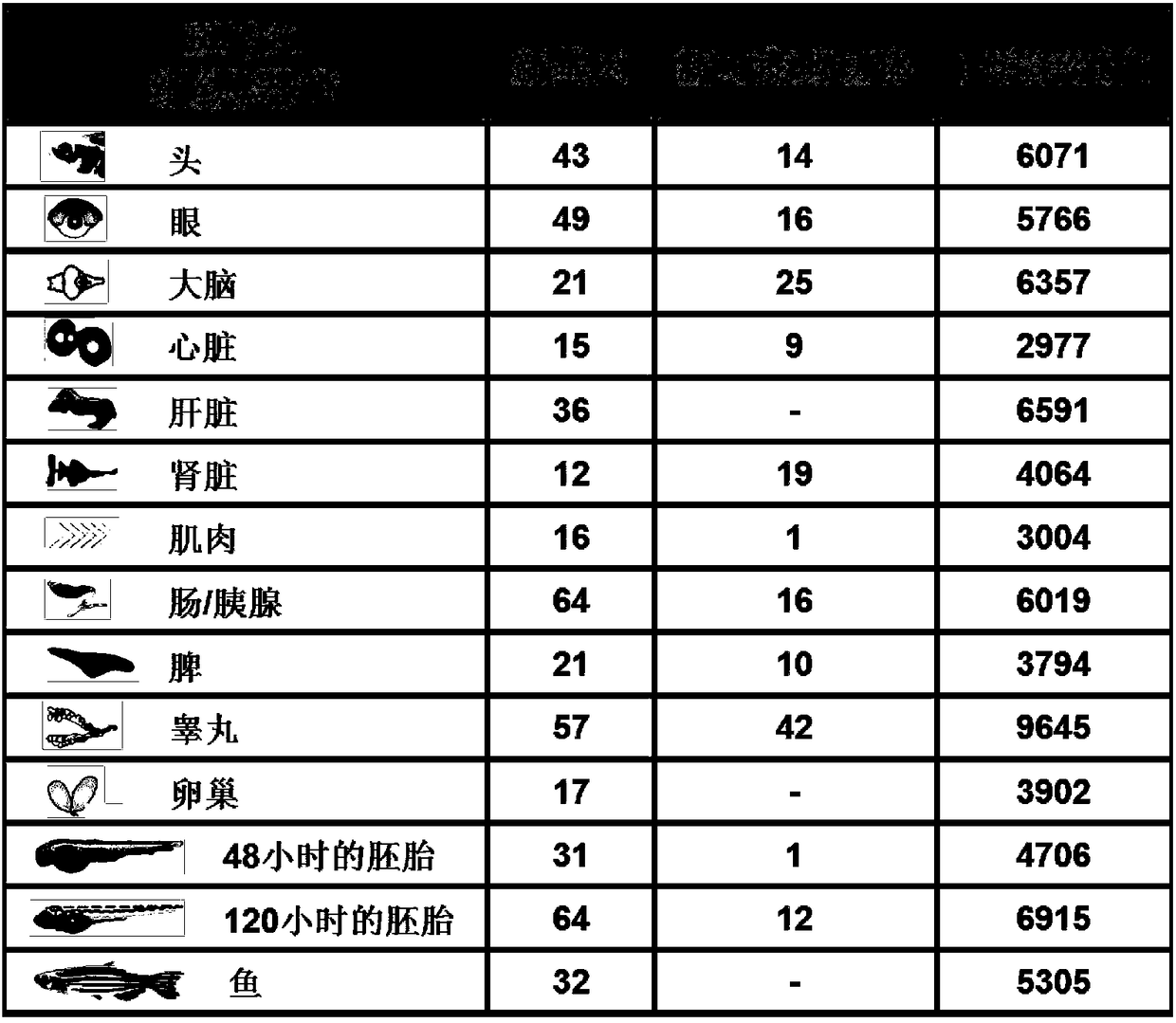
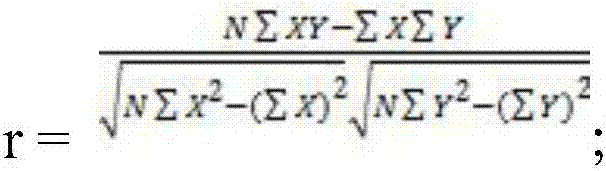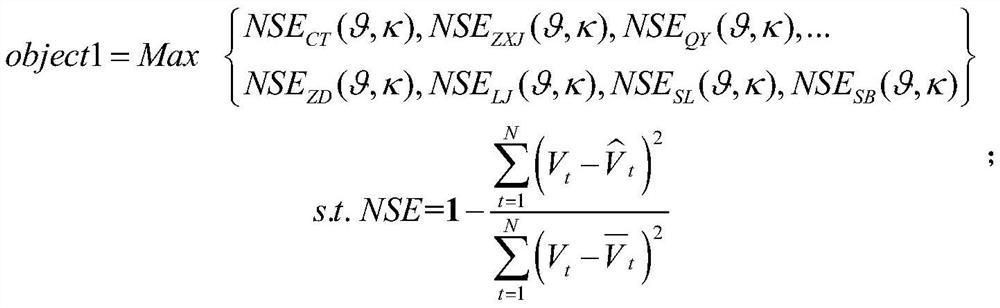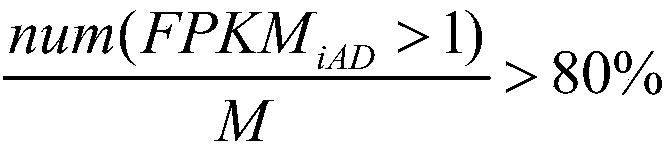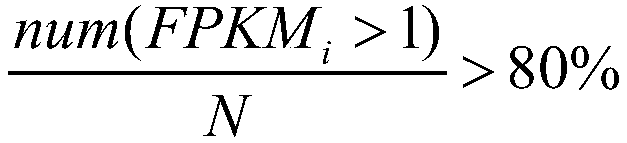Patents
Literature
106 results about "Gene prediction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computational biology, gene prediction or gene finding refers to the process of identifying the regions of genomic DNA that encode genes. This includes protein-coding genes as well as RNA genes, but may also include prediction of other functional elements such as regulatory regions. Gene finding is one of the first and most important steps in understanding the genome of a species once it has been sequenced.
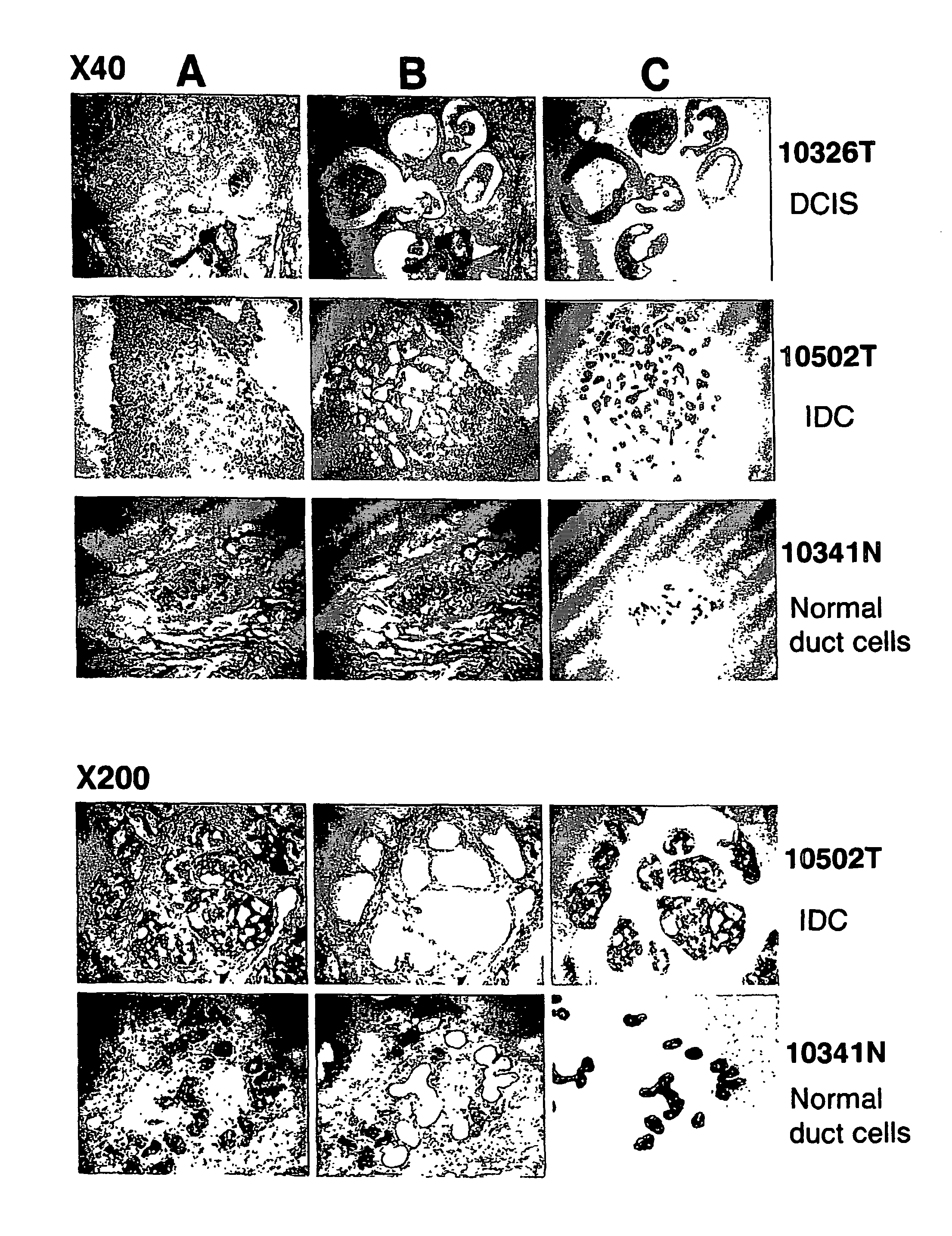
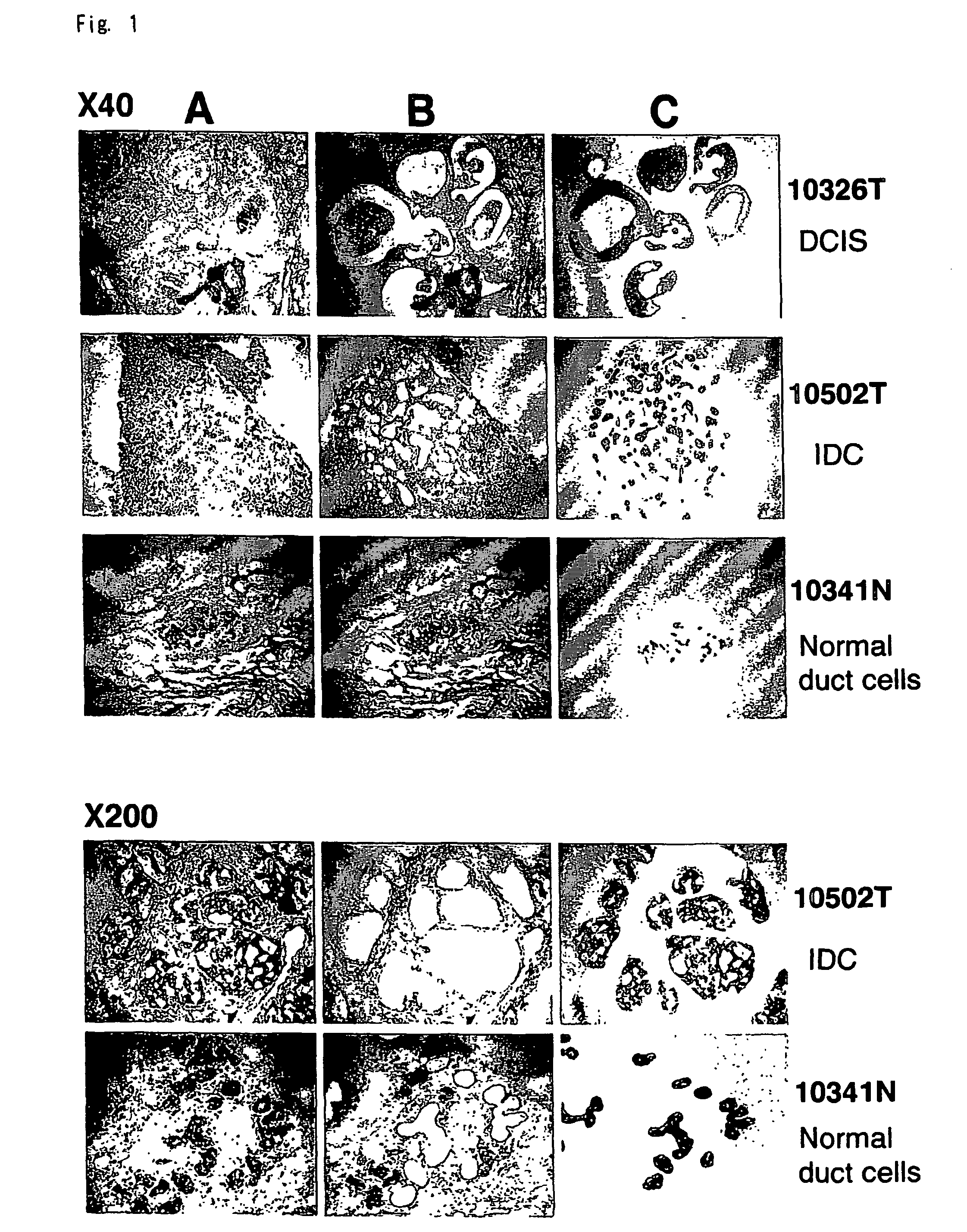
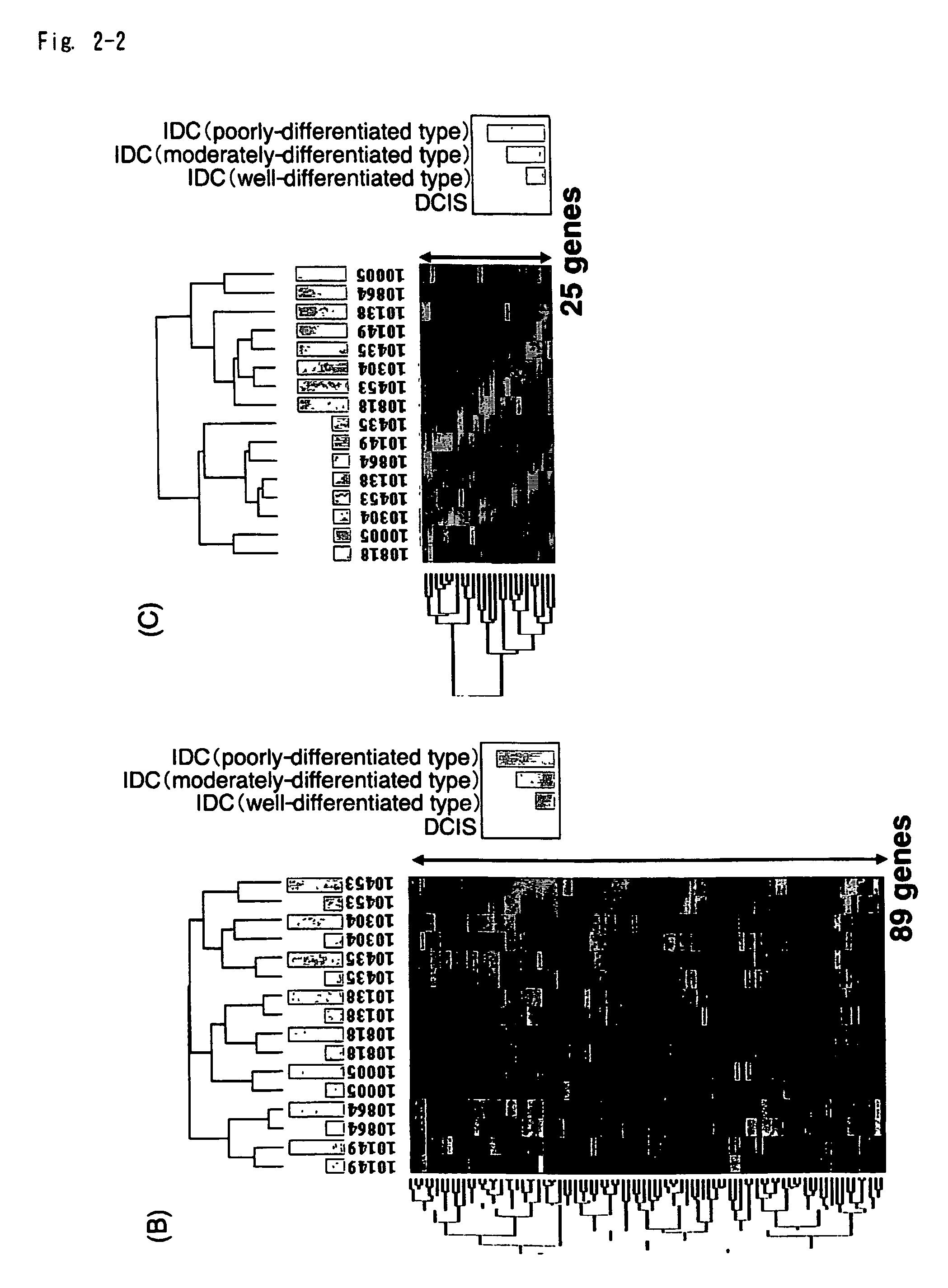
Method of Diagnosing Breast Cancer
InactiveUS20070269432A1Preventing metastasis of breast cancerMetastasis of breast cancer can be treated or preventedOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningBreast cancer metastasisNormal cell
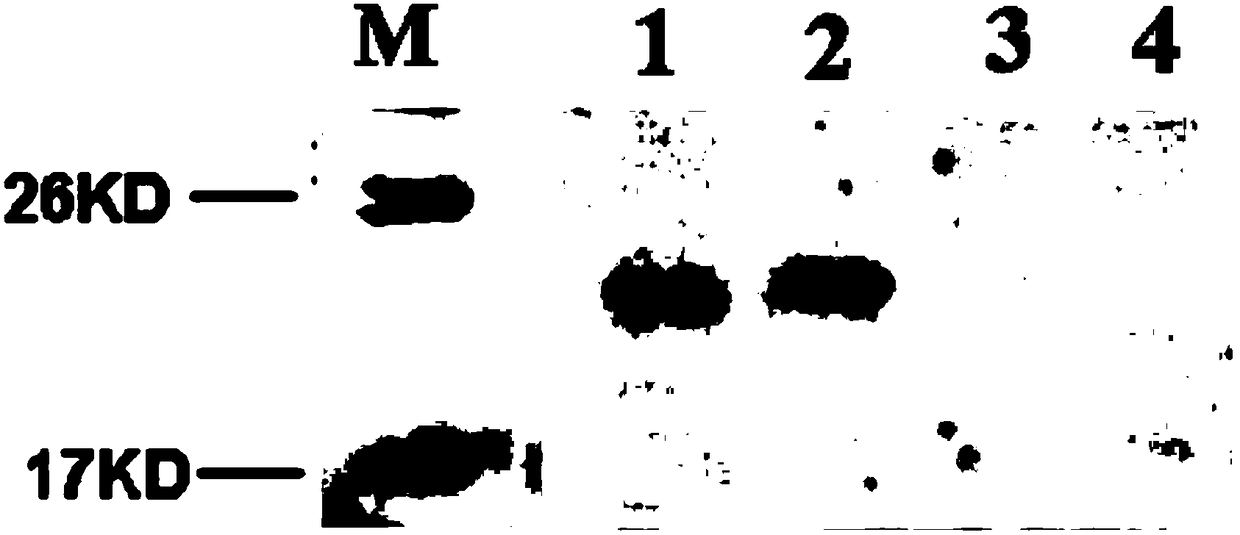
Objective methods for detecting and diagnosing breast cancer (BRC) are described herein. In one embodiment, the diagnostic method involves determining the expression level of a BRC-associated gene that discriminates between BRC cells and normal cells. In another embodiment, the diagnostic method involves determining the expression level of a BRC-associated gene that discriminates among BRC cells, between DCIS and IDC cells. The present invention further provides means for predicting and preventing breast cancer metastasis using BRC-associated genes having unique altered expression patterns in breast cancer cells with lymph-node metastasis. Finally, the present invention provides methods of screening for therapeutic agents useful in the treatment of breast cancer, methods of treating breast cancer and method for vaccinating a subject against breast cancer.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
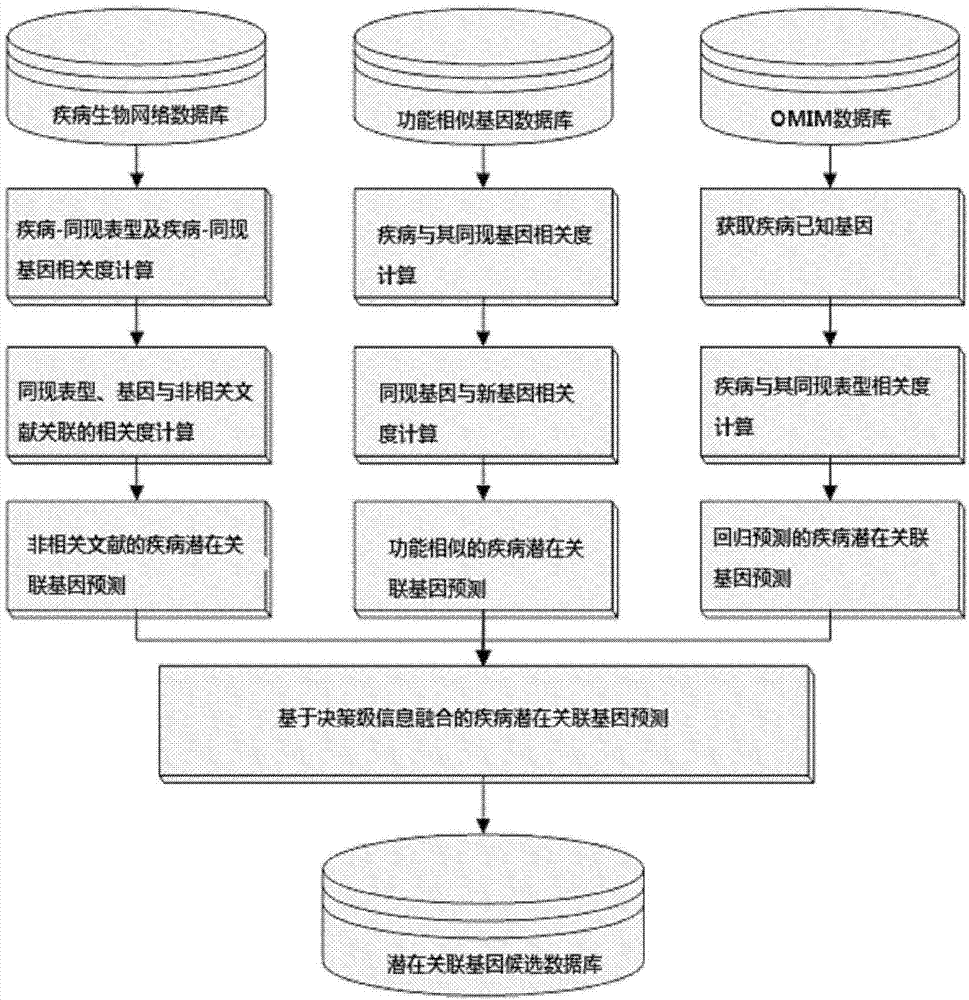
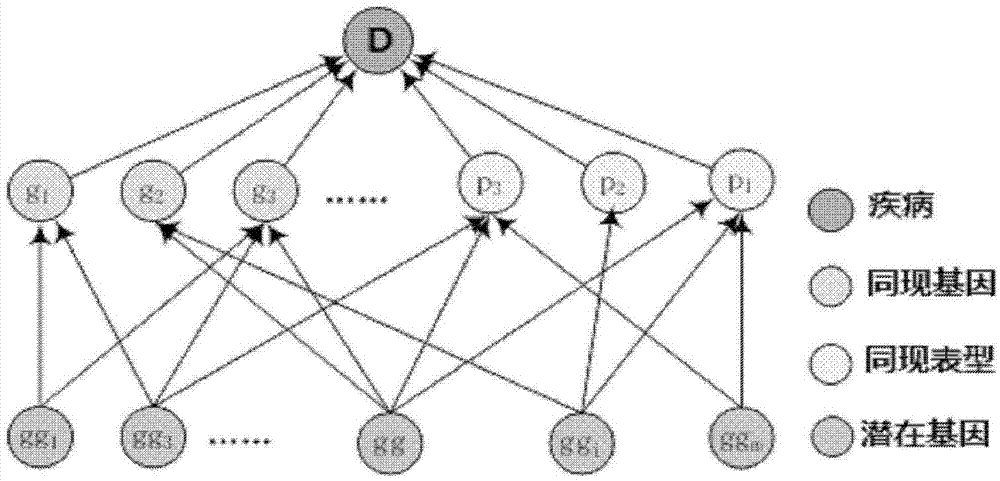
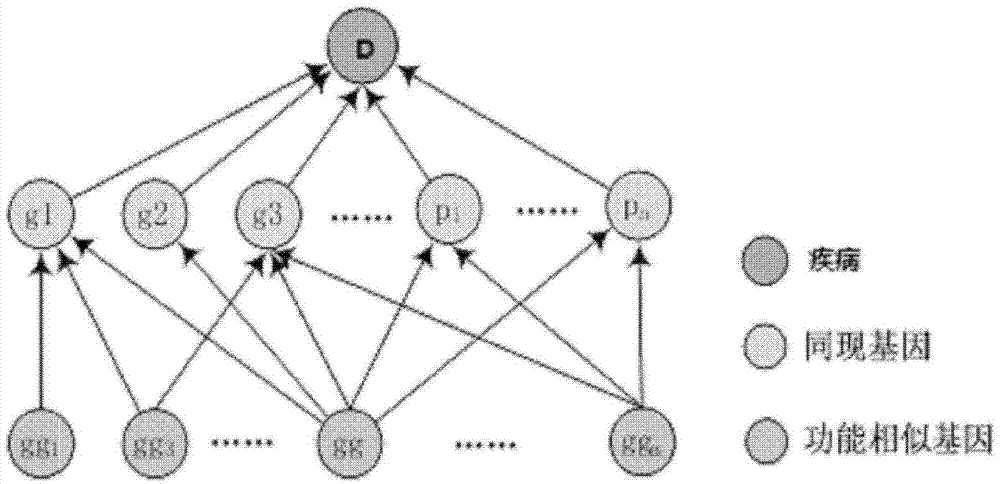
Method for obtaining disease potentially-associated gene based on multi-source information fusion
ActiveCN102855398AOptimal decision resultPromote resultsSpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseGene
The invention discloses a method for obtaining disease potentially-associated genes based on multi-source information fusion. The method comprises the following steps of: predicting disease-associated genes found based on uncorrelated literature knowledge, predicting disease-associated genes based on functional similarity, predicting disease-associated genes based on a regression prediction model, respectively scoring associated genes obtained through prediction of disease-associated genes found based on uncorrelated literature knowledge, prediction of disease-associated genes based on functional similarity and prediction of disease-associated genes based on a regression prediction model, establishing preliminary analysis to the associated genes, and fusing results obtained in all steps to obtain a final judgment result to determine the disease potentially-associated genes.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
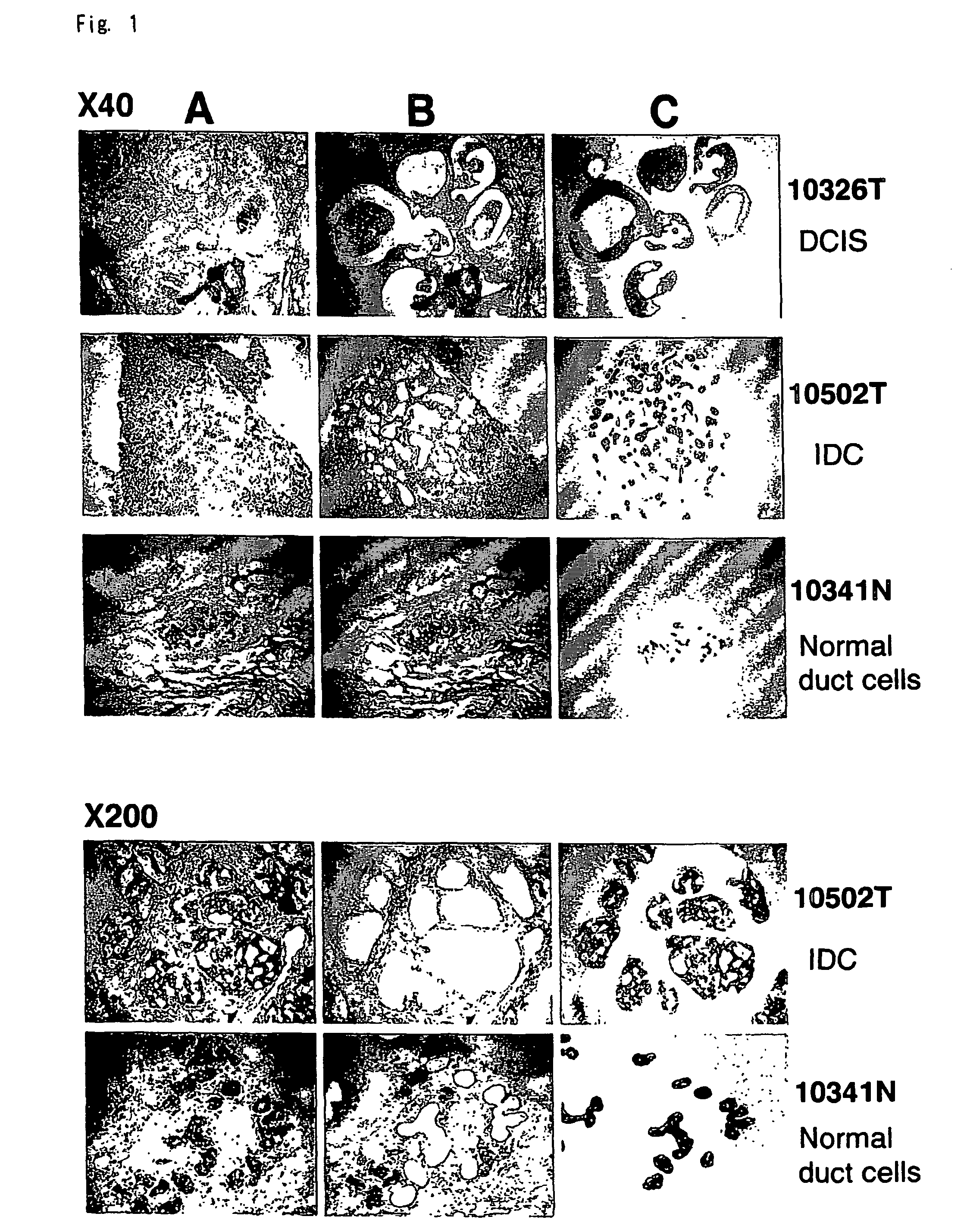
Method of diagnosing breast cancer
InactiveUS7531300B2Preventing metastasis of breast cancerMetastasis of breast cancer can be treated or preventedCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBreast cancer metastasisNormal cell
Objective methods for detecting and diagnosing breast cancer (BRC) are described herein. In one embodiment, the diagnostic method involves determining the expression level of a BRC-associated gene that discriminates between BRC cells and normal cells. In another embodiment, the diagnostic method involves determining the expression level of a BRC-associated gene that discriminates among BRC cells, between DCIS and IDC cells. The present invention further provides means for predicting and preventing breast cancer metastasis using BRC-associated genes having unique altered expression patterns in breast cancer cells with lymph-node metastasis. Finally, the present invention provides methods of screening for therapeutic agents useful in the treatment of breast cancer, methods of treating breast cancer and method for vaccinating a subject against breast cancer.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
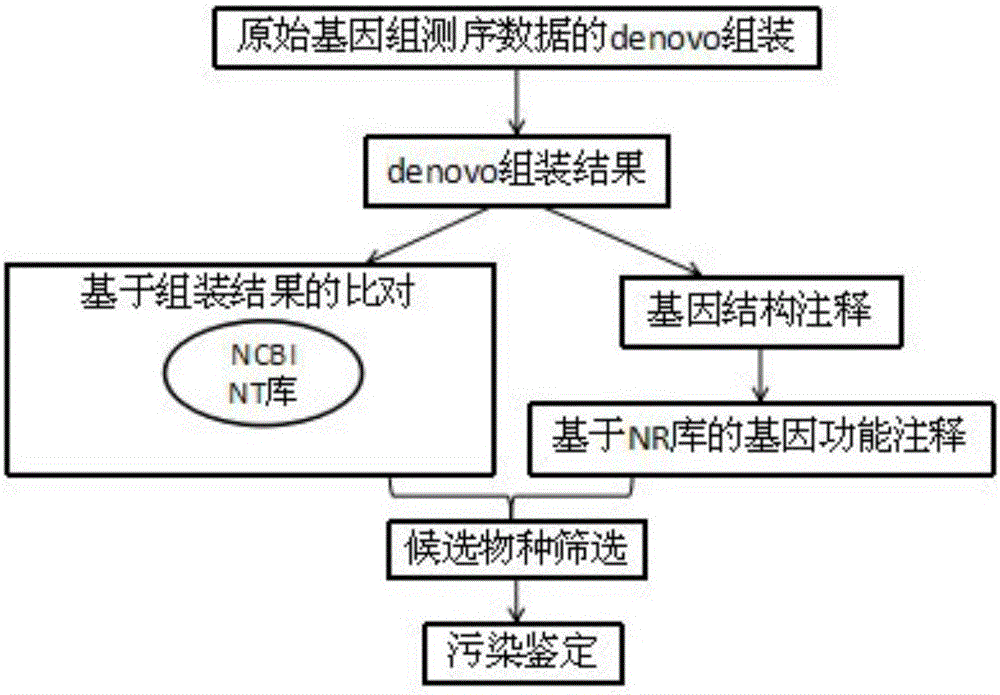
Method for rapidly and accurately identifying high-throughput genome data pollution sources
ActiveCN105740650AOvercome the disadvantage of taking too longFully reflectProteomicsGenomicsInformaticsHomologous Sequences
The invention discloses a method for rapidly and accurately identifying high-throughput genome data pollution sources. The method comprises the steps that original genome sequencing data for denovo sequencing are firstly assembled to obtain assembly results, gene prediction is conducted on the assembly results, amino acid sequences of proteins corresponding to genes are obtained through translation, and blast comparison is conducted on assembled genomic sequences and the amino acid sequences respectively with an NT database and an NR database of the NCBI to obtain homologous sequences serving as original comparison databases; species information corresponding to the sequences is extracted from the original comparison databases and is sequenced, the species corresponding to the sequences are sequenced from most to least, and whether exogenous pollution exists or not is comprehensively judged by combining with gene data results and amino acid data results. The method can reduce high-throughput genome sequencing data pollution and subsequent bioinformatics analysis influence of exogenous pollution sources in a genome denovo project to the most degree and improve pollution source identifying speed and efficiency.
Owner:广西作物遗传改良生物技术重点开放实验室
Genetically predicted life expectancy and life insurance evaluation
The present invention provides a system and methods for using a central database apparatus to evaluate a life insurance policy for a member of a population based on the genetically predicted life expectancy of the member.
Owner:GENOWLEDGE
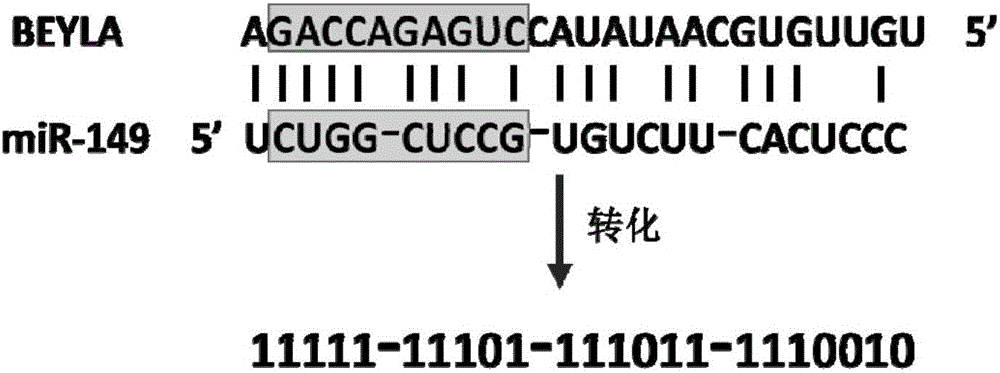
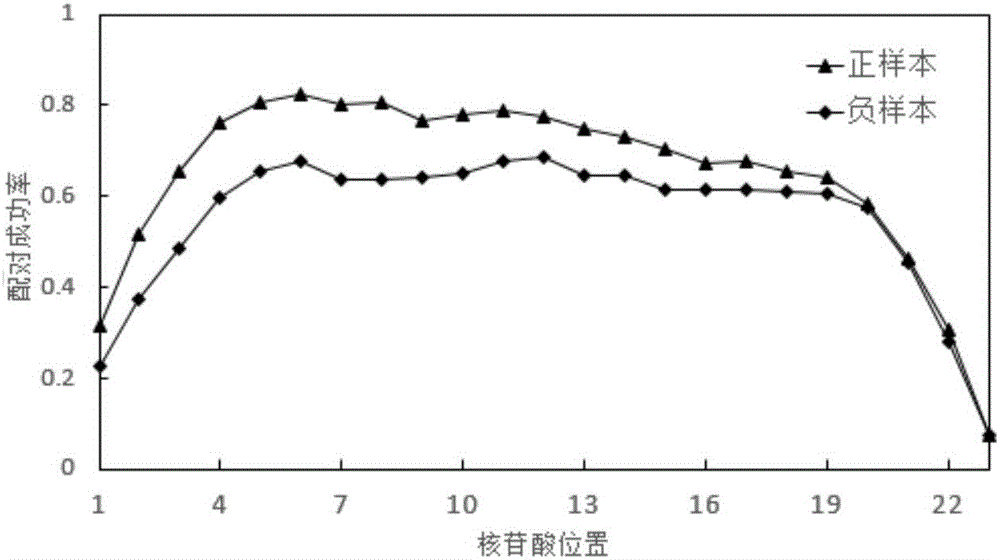
Sequence characteristic analysis method for forecasting miRNA target gene
ActiveCN106599615AMeasuring Binding PossibilitiesBalance differenceBiostatisticsSequence analysisData setRelevant feature
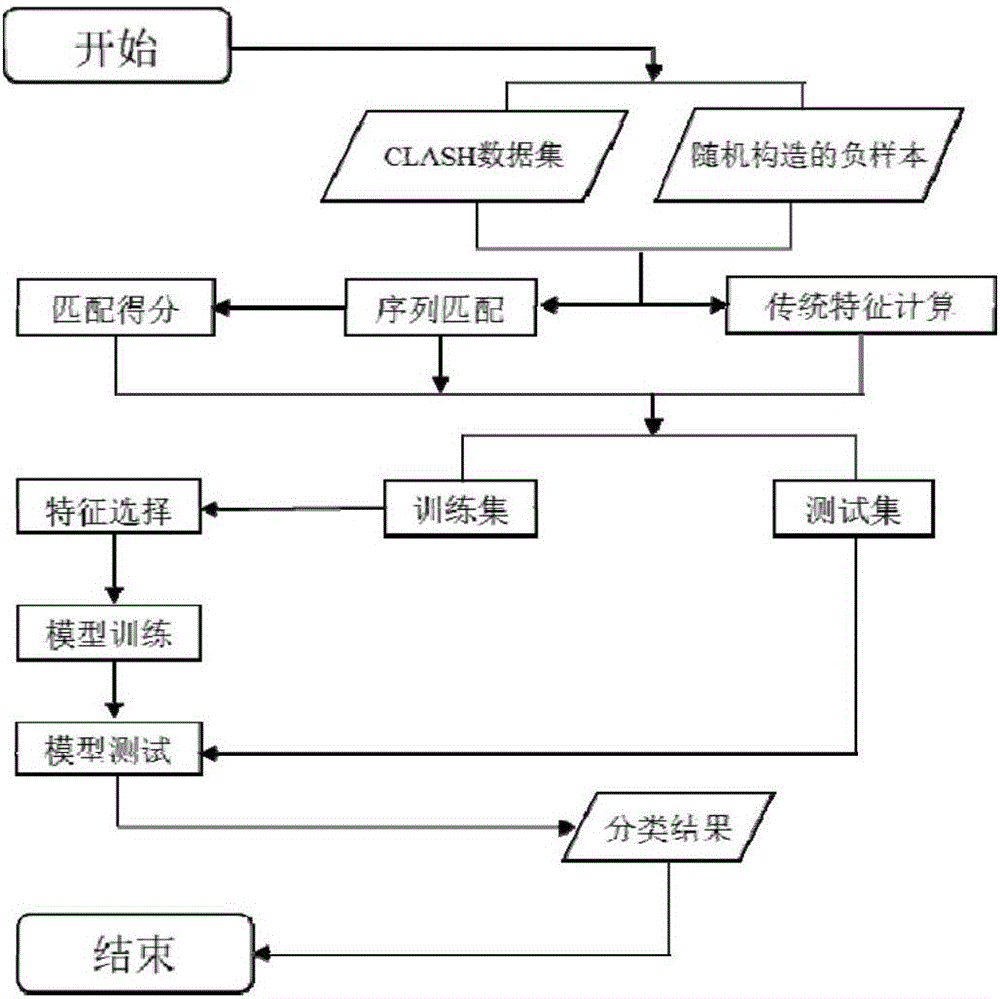
The invention discloses a sequence characteristic analysis method for forecasting a miRNA target gene. The method comprises the steps of constructing related characteristics of 27 miRNA-target point pairing sequences on the basis of a CLASH experiment data set, and forming a characteristic set comprising 84 characteristic values by combining traditional characteristic; and performing machine learning by using a random forest model, and constructing a miRNA target gene forecast model to perform miRNA target gene recognition. The model constructed according to the method has the advantages of high accuracy, sensitivity, specificity and precision, and the miRNA target gene can be relatively and accurately forecasted.
Owner:SYSU CMU SHUNDE INT JOINT RES INST +2
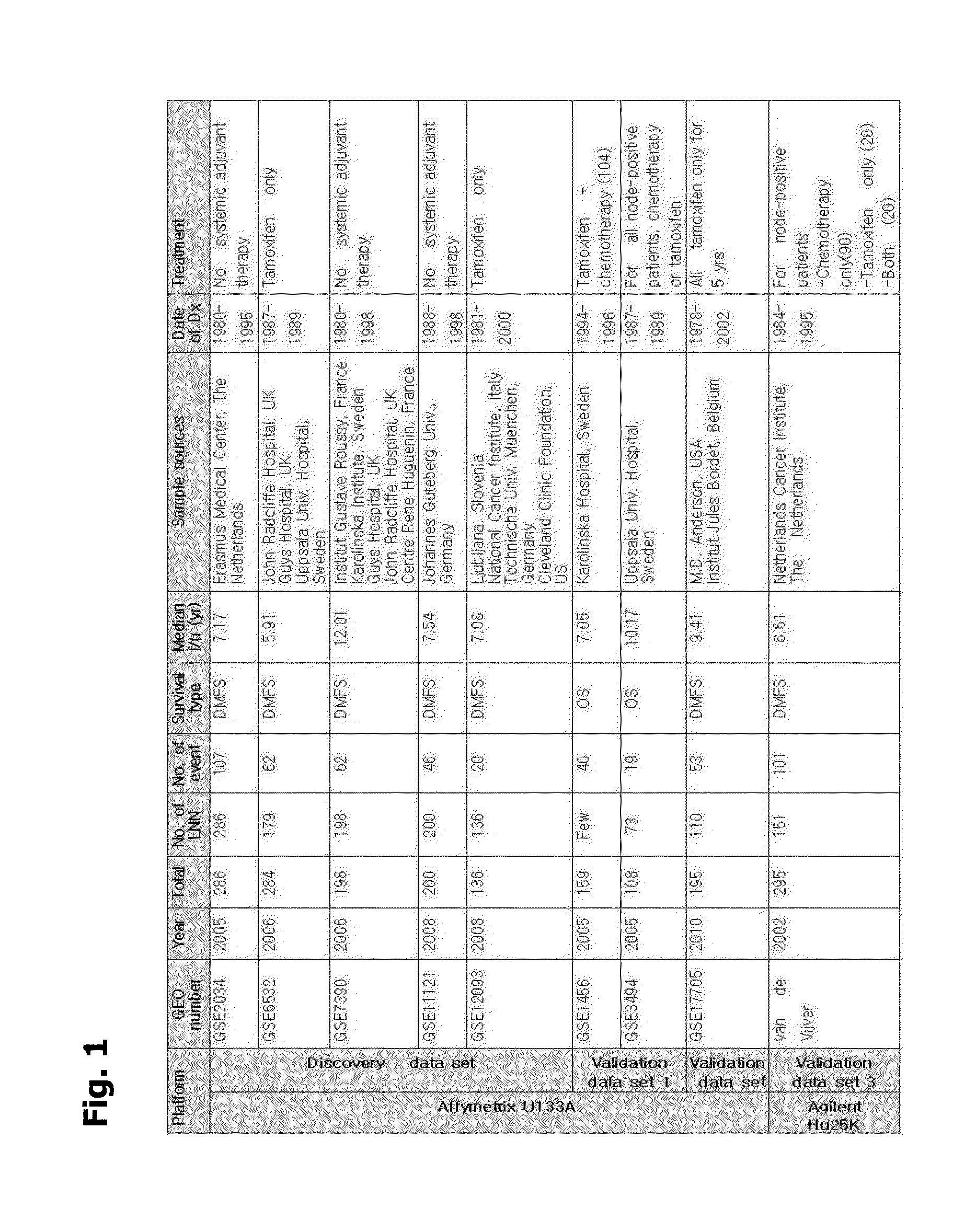
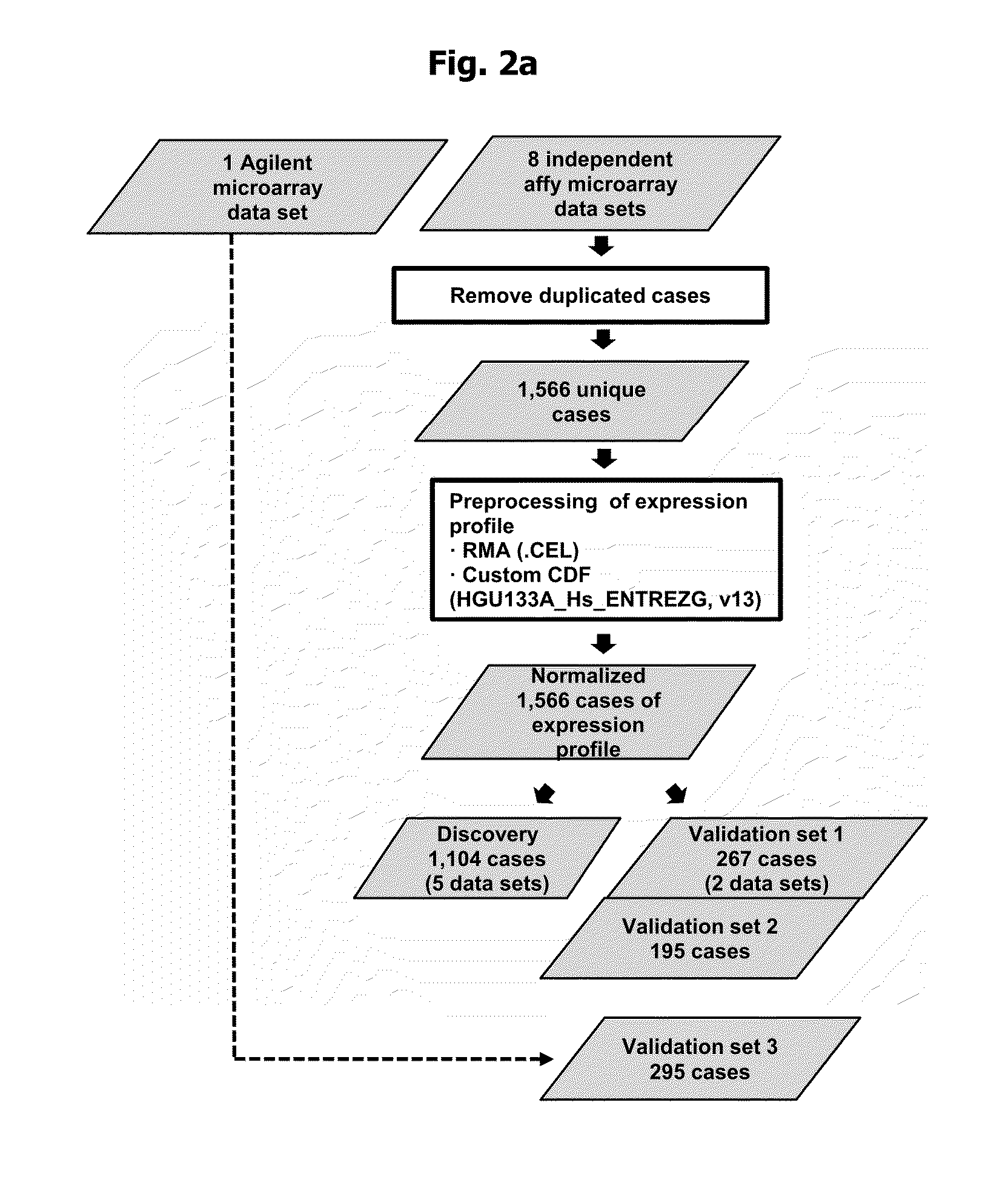
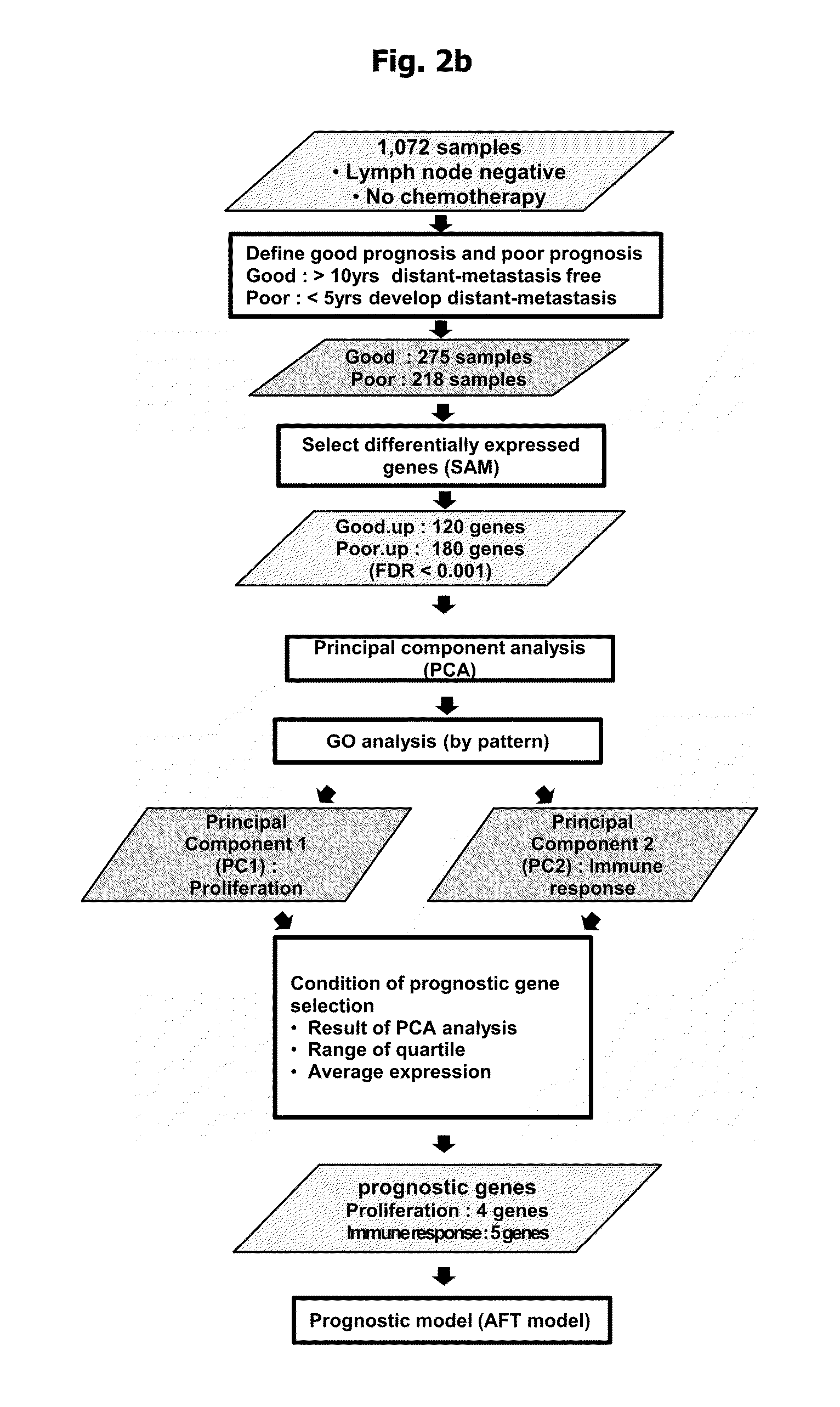
Gene for predicting the prognosis for early-stage breast cancer, and a method for predicting the prognosis for early-stage breast cancer by using the same
InactiveUS20130344482A1Reduce unnecessary anticancer therapySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPredictive methodsOncology
The present invention relates to a method for selecting a gene intended to predict the prognosis for a cancer, to the selected gene for predicting the prognosis of cancer and to a kit for predicting and a method for predicting metastasis in breast-cancer patients by using the same. In the present invention, a straight forward method is used to achieve high-reliability prediction of the patient's prognosis by analysing for the genetic characteristics of early stage breast cancer, and thus the present invention can be used to advantage in prognosis diagnosis which can reduce unnecessary anticancer therapy.
Owner:GENCURIX
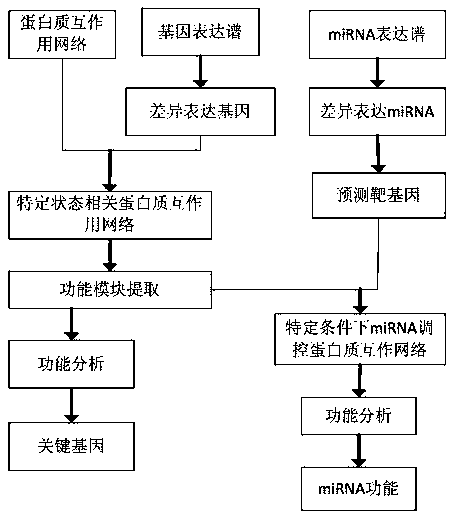
Method of miRNA function recognition based on multi-genomics
The invention relates to a miRNA function recognition method based on multi-genomics, and relates to a miRNA function recognition method based on multi-genome. The present invention aims to solve theproblem of low accuracy of miRNA function recognition in the prior art. The method of the invention comprises: analyzing differentially expressed genes through gene expression profiles; constructing disease-or drug-related protein networks; selecting functional modules of the constructed protein network related to disease or drug; performing enrichment analysis of the selected functional modules to determine the key genes in the functional modules; analyzing differentially expressed miRNAs by miRNA expression profiles to predict the target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs; performing construction of miRNA-regulated disease-or drug-related protein networks; performing functional enrichment analysis on the nodal genes of the constructed miRNA-regulated disease or drug-related proteinnetwork to identify the function of miRNA. The invention is used in the field of bioinformatics.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Recommendation model based miRNA target gene prediction method
ActiveCN105808976AImprove accuracyIncreased sensitivityHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsExperimental validationRecommendation model
The present invention discloses a recommendation model based miRNA target gene prediction method (miRTRS). The method comprises: constructing a bipartite graph of an miRNA and a gene by using experimentally verified miRNA target gene data; on this basis, calculating a possibility that one gene is an miRNA target gene by using a bipartite graph based recommendation algorithm, and introducing biological data, i.e. sequence similarity between miRNAs into the recommendation algorithm; and finally, sorting recommendation values in a descending order, and taking what is ranked at the front as an miRNA target gene relation. The method disclosed by the present invention is simple and easy for use; and compared with the existing miRNA target gene prediction method, the method provided by the present invention is significantly improved on the aspects of accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of prediction, and provides valuable reference information for scientists to perform experiments and further study of miRNA target gene discovery.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
LncRNA (long noncoding ribonucleic acid) excavating method based on gene sequence expression analysis
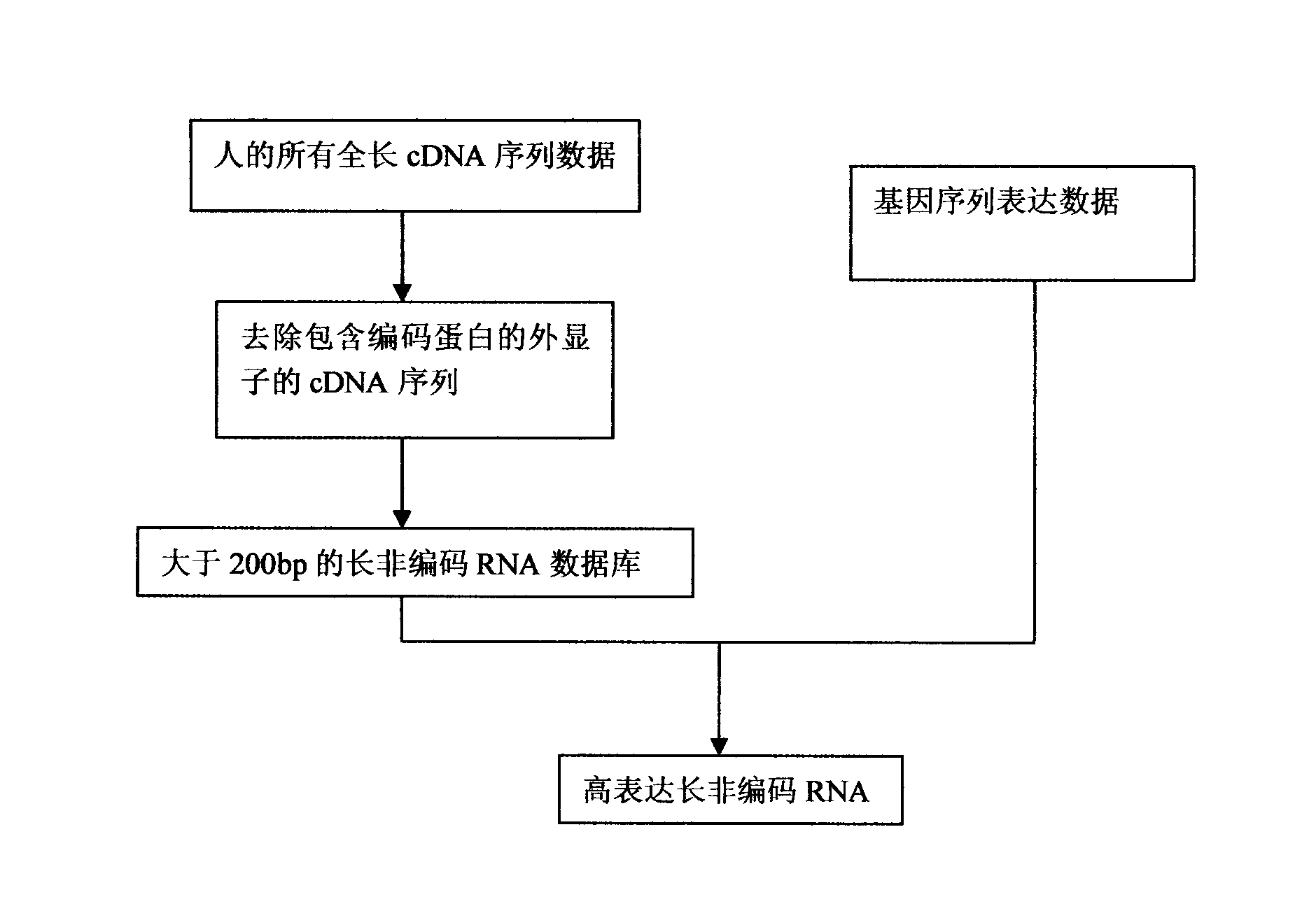
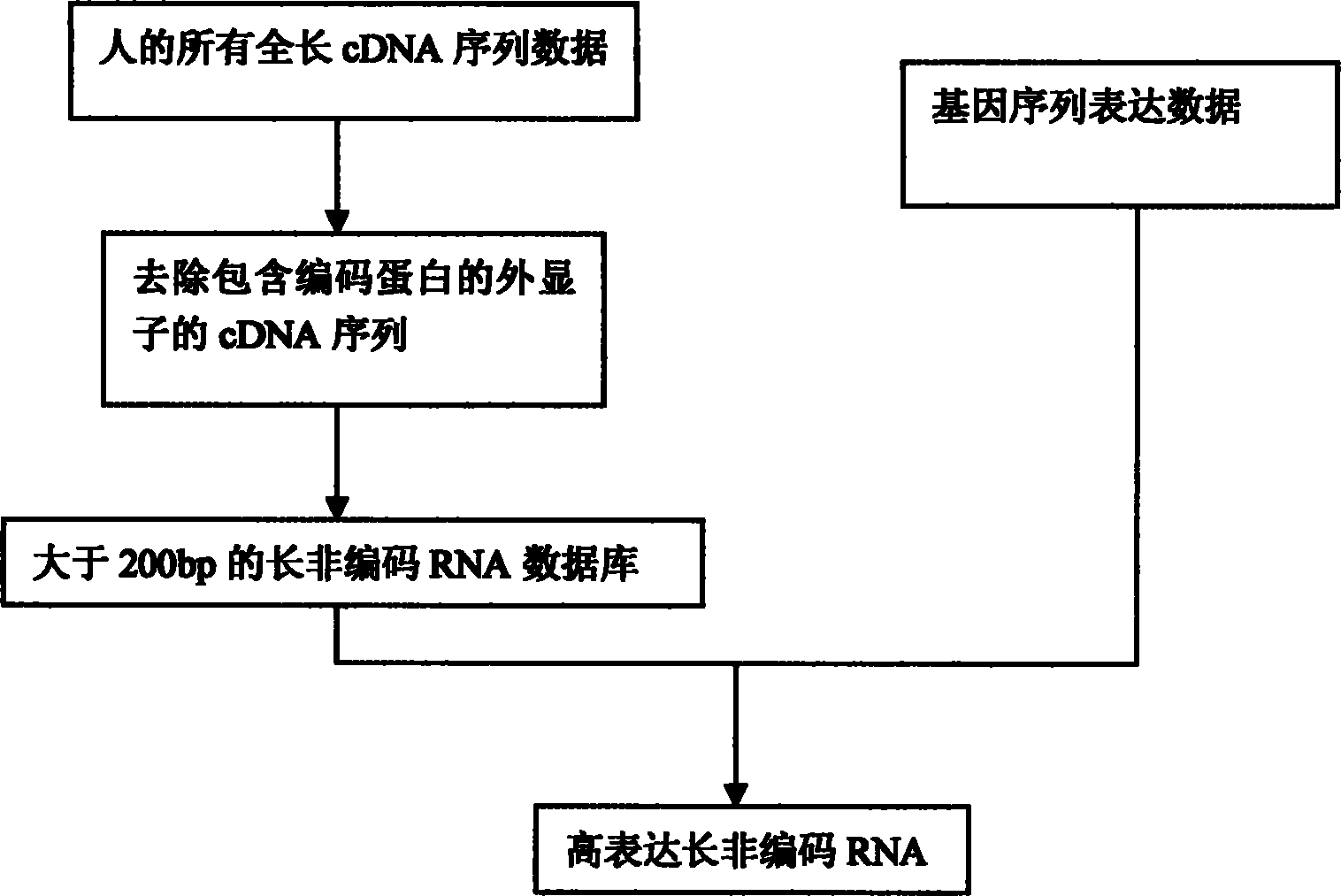
The invention finds a bioinformatics method according to gene sequence expression and gene prediction algorithms, wherein the method can be used for directly predicting and quantifying a long noncoding RNA (ribonucleic acid) and directly locking the LncRNA for further experimental verification. The method disclosed by the invention mainly comprises the following process: step one, collecting all the full-length mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) sequence data of a person; step two, removing the mRNA sequence comprising an extron of a coding protein; step three, forming a retrievable database by using LncRNA more than 200bp, and; step four, searching the existing gene expression sequence analysis data to identify over-expressed LncRNA from the analysis data; and step five, carrying out experimental verification. Thus, the over-expressed LncRNA in a specific cell tissue is predicted finally..
Owner:SHANGHAI CLUSTER BIOTECH
Molecule making method for gene locus for preventing mycosphaerella melonis of muskmelon
InactiveCN101173311AClear locationEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementMelon (food)Cultivar
The invention relates to a molecular marker method for a melon blight resistance gene, belonging to the field of biotechnology. There are four AFLP molecular markers that are linked to the gene for resistance to blight blight, the marker EcoRI-TG / MseI-CTC200 is a 200bp band; the marker EcoRI-AT / MseI-CTG90 is a 90bp band; the EcoRI-TC / MseI-CAG60 is a 60bp band band; the marker EcoRI-TG / MseI-CTA70 is a 70bp band; the linkage distances are 2.0, 6.0, 5.4 and 6.0cM, respectively. Detect whether PI 420145 and its derivative varieties (lines) contain the gene through the molecular marker method provided by the present invention, predict its resistance level to vine blight, improve the selection efficiency, and help to accelerate the selection of excellent vine blight-resistant melon varieties in my country It is used in the production process to identify the purity of muskmelon varieties resistant to vine blight.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
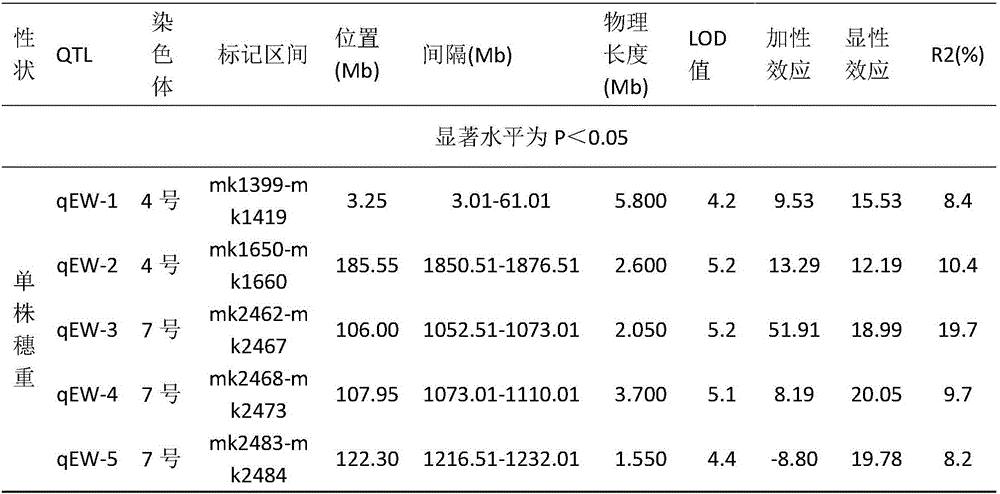
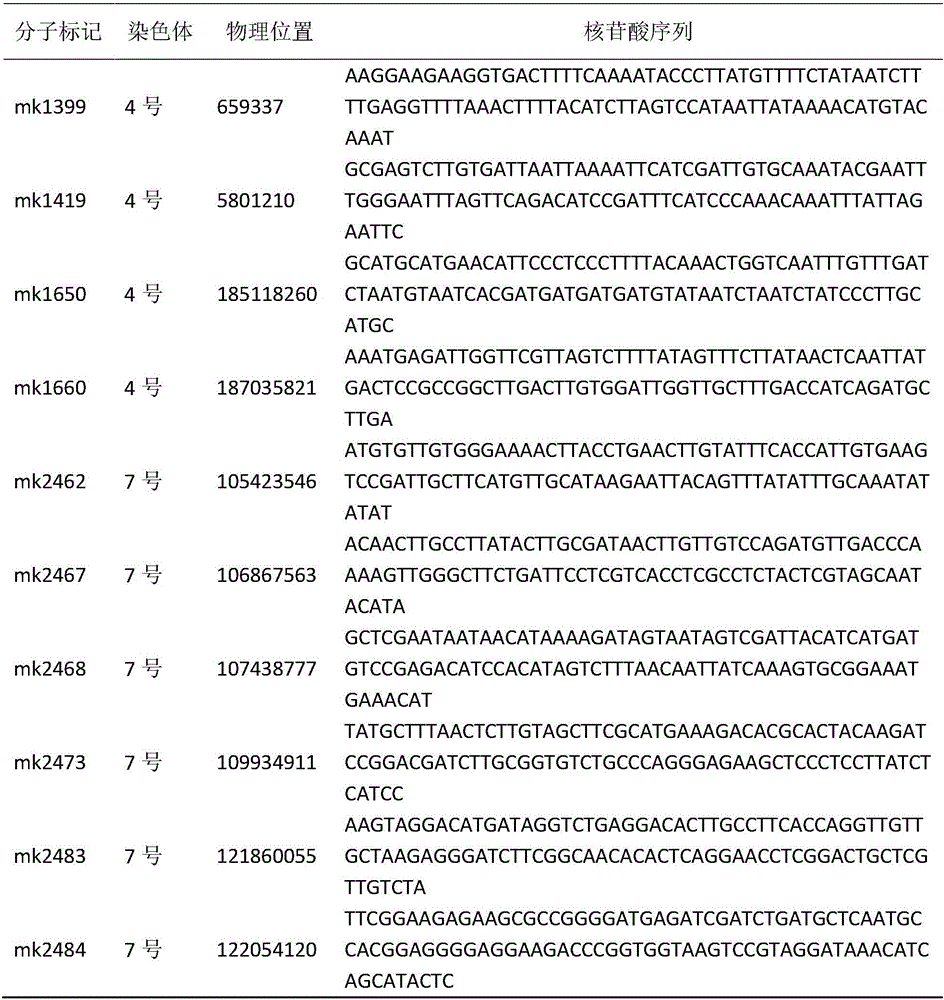
Maize single panicle weight main effect QTL, as well as acquisition method and application thereof
The invention provides a maize single panicle weight main effect QTL, as well as an acquisition method and application thereof. The QTL comprises qEW-1, qEW-2, qEW-3, qEW-4 and qEW-5. The method comprises the following steps: configuring cross combination by taking a high-yield early-maturity maize inbred line SG5 as a female parent and a maize inbred line SG7 with relatively poor yield trait as a male parent, and constructing an F2 genetic group of the cross combination; performing GBS sequencing-basing typing on the F2 genetic group, and performing genotyping by combining differential SNP validated based on SG5 and SG7 parents; investigating the yield trait of single F2 panicle, performing QTL analysis on the F2 single panicle yield trait by utilizing a winQTLcart2.5 software composite interval mapping method, and analyzing the chromosome region of the main effect QTL and the genetic effect. According to the method, a theoretic base is provided to excavating and controlling the maize single panicle weight main effect QTL and linked marker, a molecular marker closely linked with the target QTL is acquired, and foundation is laid to maize single panicle yield trait QTL candidate gene prediction, cloning and molecular mark assisted breeding.
Owner:LIUPANSHUI NORMAL UNIV
Exogenous miRNA regulatory target gene prediction method containing three-dimensional free energy
ActiveCN108090327AImprove accuracyFeature input vector exactSequence analysisHybridisationFree energiesBinding site
The invention discloses an exogenous miRNA regulatory target gene prediction method containing three-dimensional free energy. In order to improve traditional sequence matching characteristics, statistical characteristics of the three-dimensional energy in a seed area and statistical characteristics of a spatial distribution penalty function at binding sites are newly provided, the characteristicsof the seed area binding sites represent the specific matching information of the binding sites, so that a constructed feature input vector is more accurate and more practical, and therefore the accuracy of miRNA target spot prediction is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
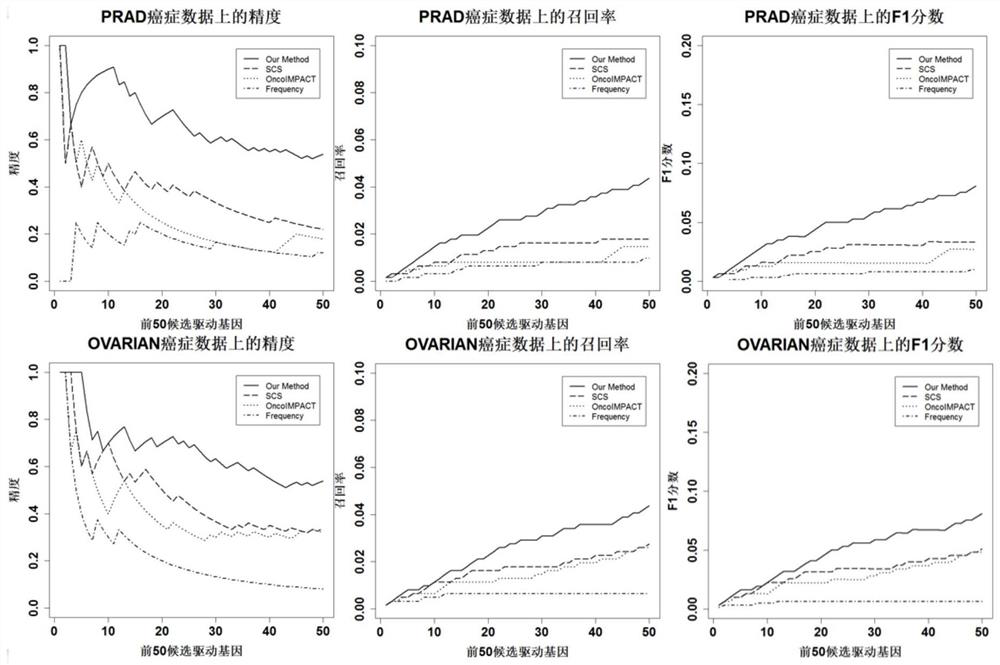
Cancer driver gene prediction method and system based on local and global network centrality analysis
PendingCN113488104AHigh precisionWell representedData visualisationProteomicsCancers diagnosisCancer data
The invention discloses a cancer driver gene prediction method based on local and global network centrality analysis. The method comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out preprocessing of standardized somatic mutation data and gene expression data, and expressing the data into a gene-matrix form; S2, weighting a downloaded PPI network by using the preprocessed data; S3, constructing a model, and analyzing global and local features of the network by using an improved restart random walk algorithm; and S4, predicting a cancer data set by using the constructed model to obtain a ranking vector of a driver gene so as to realize prediction of the cancer driver gene. The invention further discloses a cancer driver gene prediction system based on local and global network centrality analysis. According to the invention, the driver gene can be better identified, the prediction precision of the cancer driver gene is greatly improved, and contributions are made to cancer diagnosis and development of precise medical treatment.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
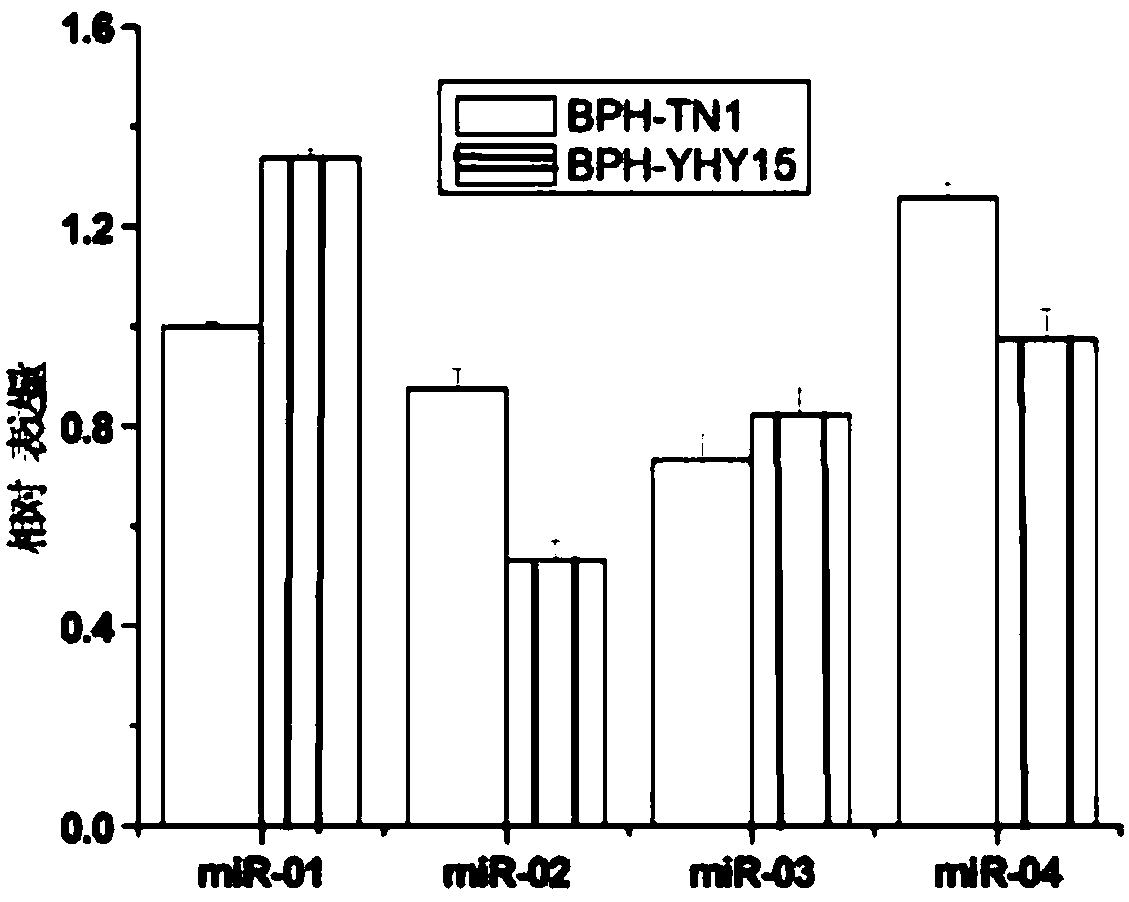
Method for screening MicroRNAs of nilaparvata lugens with effect on oryza sativa resistance adaptability
ActiveCN108504748AMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsBiologyMirna target gene
The invention discloses a method for screening MicroRNAs of nilaparvata lugens with effect on oryza sativa resistance adaptability, and relates to the bioengineering technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) sample collection; (2) sequencing of small RNA; (3) pretreatment of sequencing raw data; (4) sequence alignment; (5) new miRNA prediction; (6) analysis of miRNA differential expression; (7) prediction of differential miRNA target genes; (8) synthesis of miRNA mimic, miRNA inhibitor and control chain; (9) microinjection and artificial feeding of miRNA mimic and miRNA inhibitor to nilaparvata lugens and verification of the function of miRNAs; (10) preliminary study on oryza sativa resistance adaptability change of the nilaparvata lugens after microinjection and artificialfeeding. Small RNAs of two nilaparvata lugens groups are deeply sequenced with a high-throughput sequencing technology, and are analyzed, identified and predicted according to subsequent bioinformatics, differences between the two nilaparvata lugens groups on insect-susceptible oryza sativa TN1 and insect-resistant oryza sativa YHY 15 are compared, the miRNA associated with host resistance adaptability is analyzed, screened and discovered, and the new method is provided for oryza sativa insect-resistant breeding.
Owner:INST OF FOOD CROPS HUBEI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for rapidly identifying cashmere cycle development, molecular target and applications thereof
InactiveCN105648050APlay the role of indicating cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRest periodPhases of clinical research
The invention discloses a method for rapidly identifying cashmere cycle development. The goat miRNA is identified comprehensively, the differential expression profiles of goat skin follicle in different growth periods (growth period, rest period, and regression period) are compared so as to screen out miRNA of differential expression; a technology of fluorescent quantitation is adopted to verify the result; through target gene prediction and transcript profile difference comparison, the gene for modulating follicles is searched, the functions of miRNA is determined; and finally the miRNA-263 is the specific miRNA for cycle development of follicles. Through identifications, people find that the miR-263b is accord with the cashmere cycle development rule; the target gene modulated by miR-263b is part of key gene in the cashmere cycle development pathway; the change of expression of miR-263b can precisely represents the specific periods of cashmere, and thus miR-263b can be used to indicate the periods. So miR-263b has an important value on research and application, and can be used as a novel reference for prognosis judgment of cashmere cycle development.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Gene Predictors of Response to Metastatic Colorectal Chemotherapy
Owner:PFIZER PROD INC
Breast cancer patient recurrence risk 20 gene prediction model based on breast cancer single cell transcriptome sequencing analysis
PendingCN112481378AAccurate judgmentPrecision therapyMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisSingle cell transcriptomeAdjuvant therapy
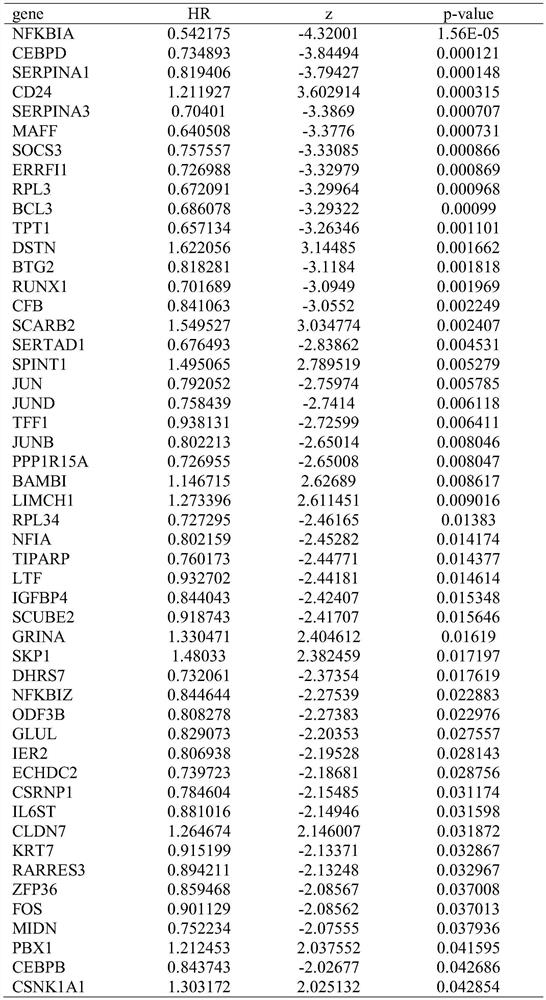
The invention relates to the field of gene detection technologies and biomedicine, in particular to a breast cancer patient recurrence risk 20 gene prediction model based on breast cancer single-celltranscriptome sequencing analysis and an establishment method and application thereof. The model is composed of 20 genes of CEBPD, SERPINA1, CD24, ERRFI1, BCL3, DSTN, BTG2, SERTAD1, SPINT1, BAMBI, LIMCH1, NFIA, SKP1, DHRS7, ODF3B, KRT7, ZFP36, CEBPB, BHLHE40 and UGDH. The breast cancer patient recurrence risk 20 gene prediction model provided by the invention provides more accurate judgment for long-term prognosis of a breast cancer patient, and provides a basis for selection of a postoperative adjuvant therapy scheme of the patient, so that individualized accurate treatment is realized, and meanwhile, a new research perspective is provided for research of breast cancer tumor stem cells.
Owner:SHENGJING HOSPITAL OF CHINA MEDICAL UNIV
Metagenome gene analysis method, device and equipment and storage medium
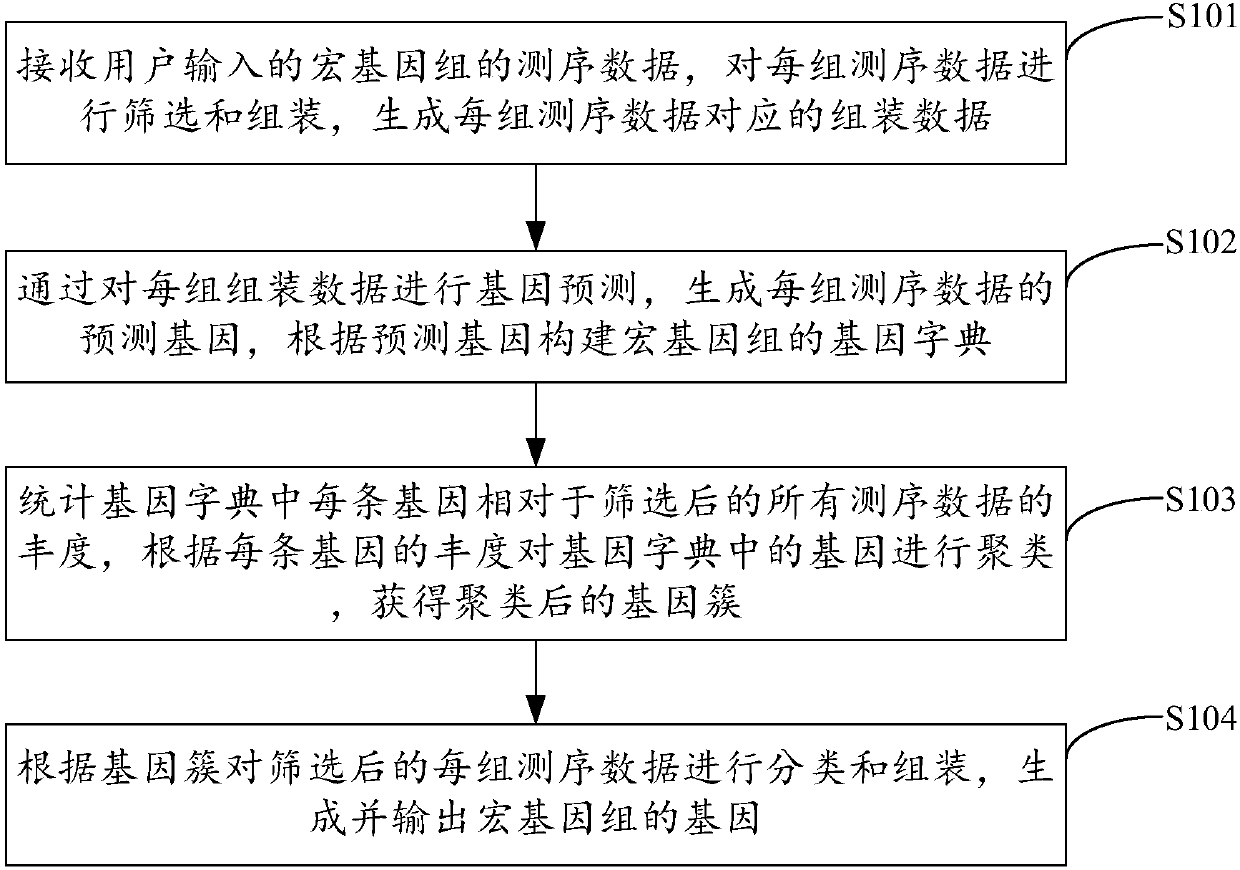
The invention is applicable to the technical field of cross-computer science and bioinformatics, and provides a metagenome gene analysis method, device and equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of screening and assembling each set of received sequencing data, generating assembling data corresponding to the sequencing data, generating predicted genes of each set of sequencing data by performing gene prediction on the assembling data, constructing a gene dictionary according to the predicted genes, clustering the gene dictionary according to the abundance of each gene inthe gene dictionary, classifying and assembling each set of screened sequencing data according to clustered gene clusters, and generating and outputting genes of metagenomes. Accordingly, on the condition that no existing biological gene is adopted as a reference genome, gene analysis of the metagenome is achieved, the limit caused by the reference genome is avoided, and the gene analysis accuracy of the genome is effectively improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Prediction method for target gene of long-fragment non-coding RNA of forest tree
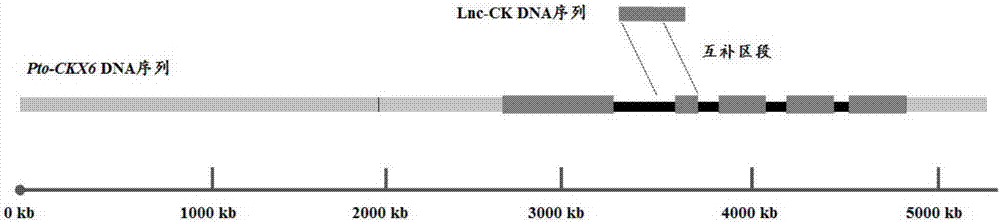
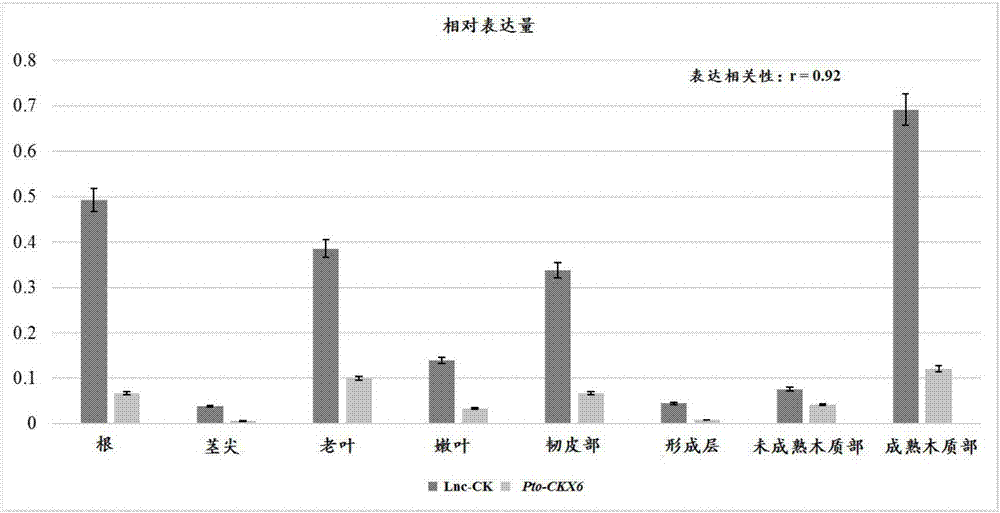
ActiveCN106997429AAchieve forecastImprove accuracySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsNon-coding RNATissue specific
The invention relates to a prediction method for a target gene of long-fragment non-coding RNA of forest tree, and belongs to the technical field of molecular genetics. The prediction method for the target gene of the long-fragment non-coding RNA of the forest tree, provided by the invention, comprises the following steps of 1) obtaining a lncRNA sequence of the forest tree; 2) obtaining a target gene of the lncRNA subjected to preliminary screening by utilizing a blast prediction method; 3) obtaining a target gene of the lncRNA subjected to secondary screening by utilizing an RNAplex prediction method; and 4) detecting tissue specific expression modes of the lncRNA and the target gene of the IncRNA subjected to the secondary screening in the step 3), calculating expression correlation of the lncRNA and the target gene of the lncRNA, and determining an interaction relationship between the lncRNA and the target gene of the lncRNA. According to the prediction method, the action fragments of the lncRNA and the target gene of the lncRNA can be efficiently and stably detected, and the accuracy of predicting the target gene of the lncRNA of the forest tree can be remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
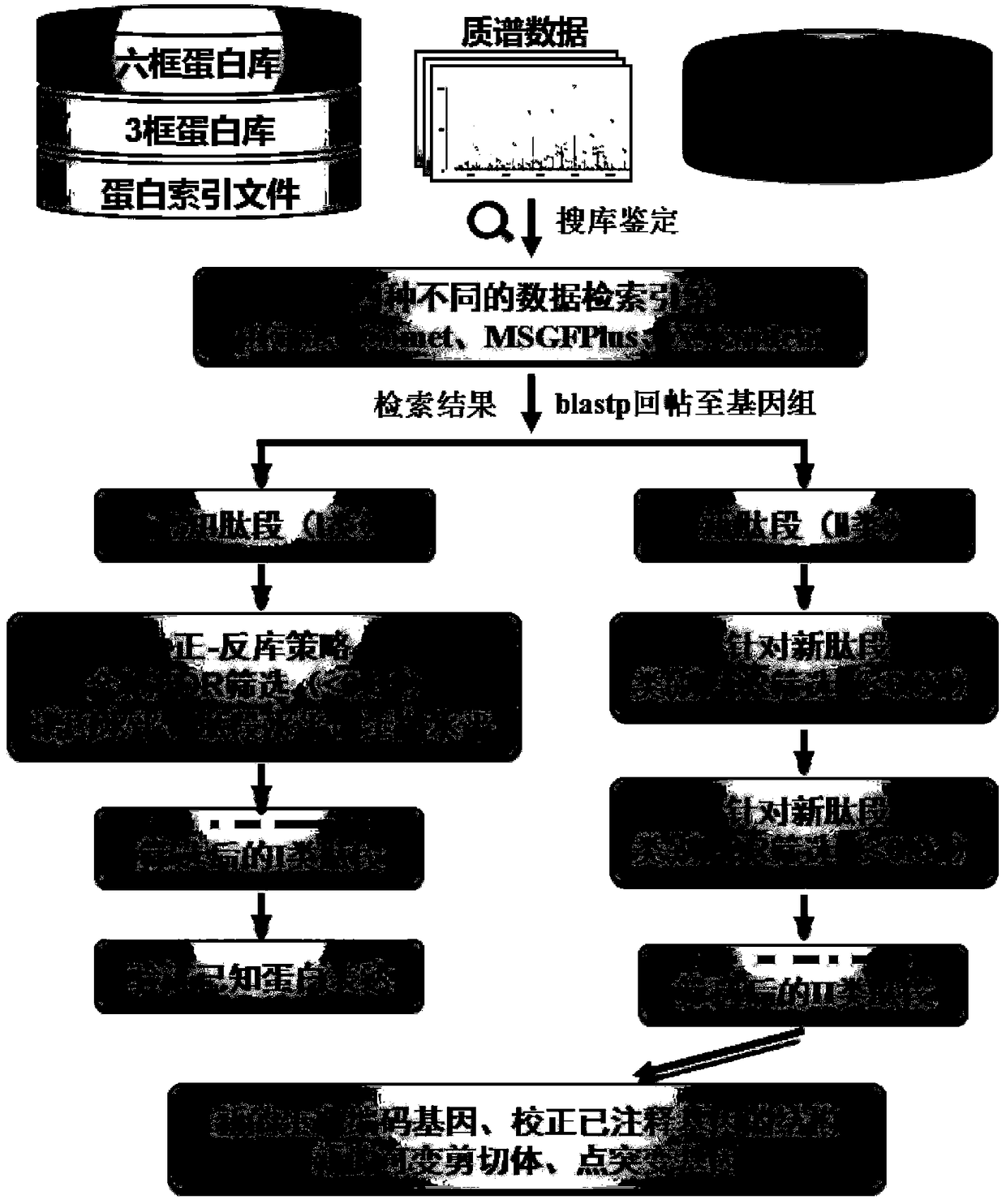
Method for rapidly analyzing eukaryotic protein genomic data
ActiveCN108920898ARapid Identification AnalysisIncrease coverageSpecial data processing applicationsPositive controlScreening method
The invention provides a method for rapidly analyzing eukaryotic protein genomic data, and belongs to the technical field of protein genomic data analysis methods. According to the method for rapidlyanalyzing eukaryotic protein genomic data, II-type credible peptide fragments are obtained by adoption of a prokaryote multi-group data arrangement method and a screening method; and three different genome replying methods for the aims of predicting new genes, variant spliceosomes and point mutation genes and correcting structures of annotated genes are designed. The method provided by the invention is suitable for any sequenced eukaryon, and through a variant spliceosome and point mutation gene prediction method, the coverage degree of authentication is improved; by adoption of different relatively strict false positive control strategies, the credibility of the authentication is improved; and through predicting and correcting original mass spectrometric data, final new genes, variant spliceosome and point mutation genes, annotated gene structure series are analyzed, so that rapid authentication and analysis of eukaryotic mass spectrometric data are really realized.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
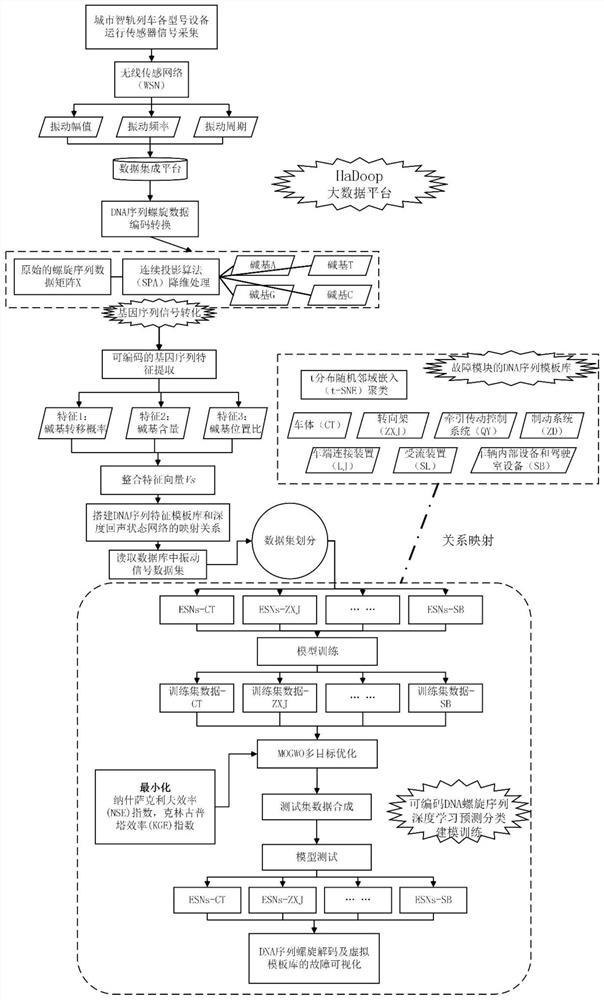
Smart city intelligent rail vehicle fault gene prediction method and system
PendingCN112734094AQuick identificationAccurate directionForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionEcho state networkSmart city
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
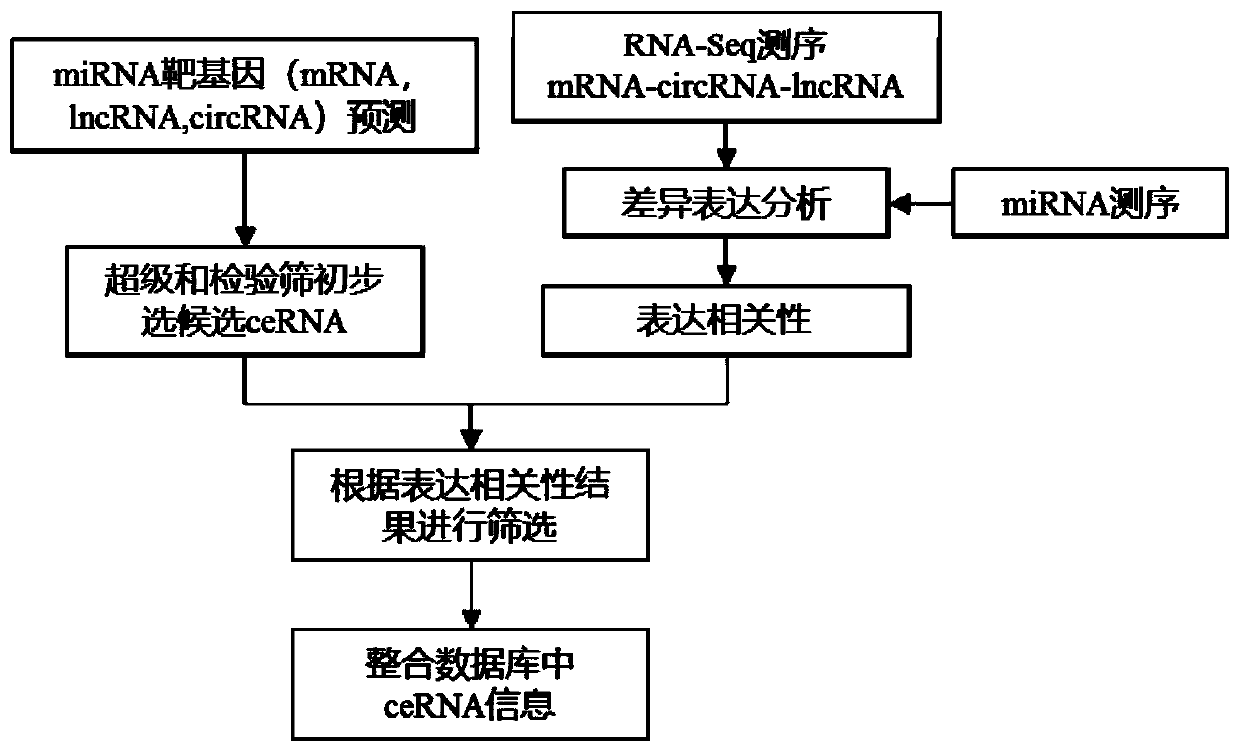
Method for carrying out ceRNA prediction based on miRNA target gene prediction and related expression analysis
The invention discloses a method for carrying out ceRNA prediction based on miRNA target gene prediction and related expression analysis. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps:carrying out correlation analysis on a ceRNA action pair; screening potential ceRNA relationship pairs according to the number of common MERs; evaluating the regulation and control function of the miRNA on a pair of competitive lncRNA-mRNA by adopting two scoring modes according to the expression correlation of the miRNA and the ceRNA to the three; and obtaining results of statistical test significance, and sorting the results according to scores. The method for carrying out ceRNA prediction based on miRNA target gene prediction and related expression analysis has the advantages that after the ceRNA is preliminarily analyzed, the inter-gene expression correlation is analyzed according to an actual sequencing result, and the result is screened; different target gene prediction methods areadopted for animals and plants, so that ceRNA prediction analysis can be performed; and information in a common database is integrated, and the reliability of an analysis result is improved.
Owner:南京派森诺基因科技有限公司
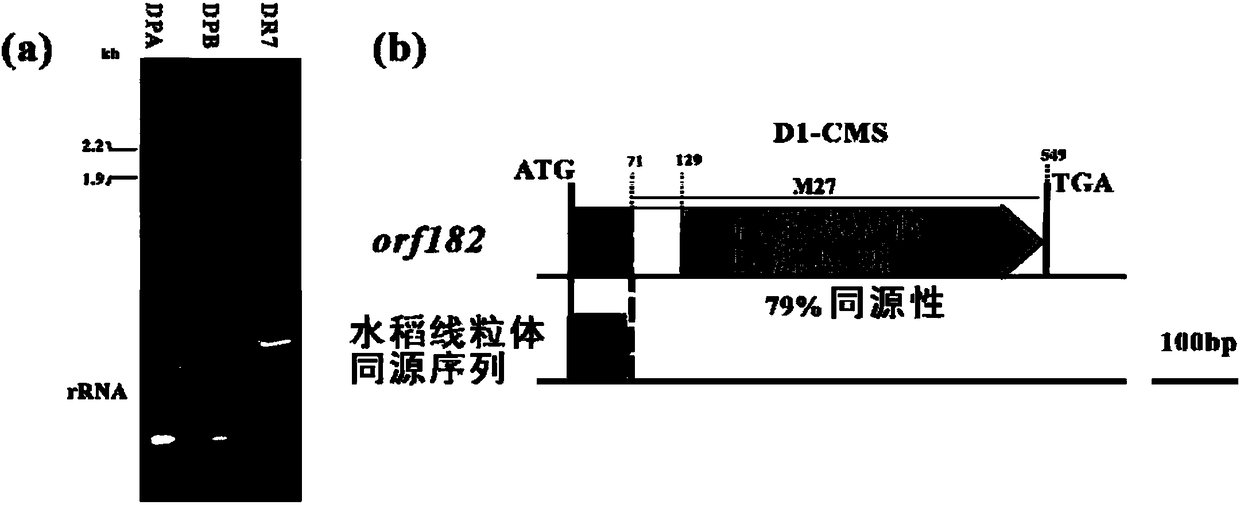
Rice mitochondria sterility gene and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of rice breeding, and specifically relates to a rice mitochondria sterility gene and the application thereof. The invention discloses a rice mitochondria sterility gene and a coding sequence thereof, and D1 type cytoplasm can be quickly and efficiently screened and authenticated from wild rice for cultivation of a D1 type cytoplasm sterile line by designing a specific molecular marker through the gene sequence. A mitochondrial genome specific sequence of the D1 type cytoplasm sterile is authenticated through comparative genomics, sterility related ORFs are authenticated through gene predication and differential expression analysis, and a plant transformation vecter is constructed for transforming maintenance line verification and sterility function.
Owner:JIANGXI SUPER RICE RES & DEV CENT (HAINAN RICE BREEDING CENT OF JIANGXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI) +1
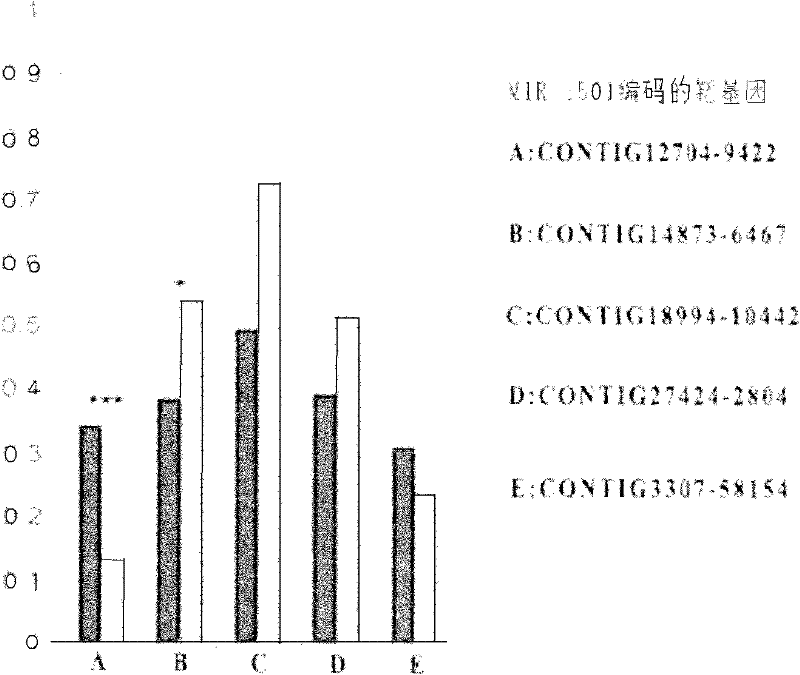
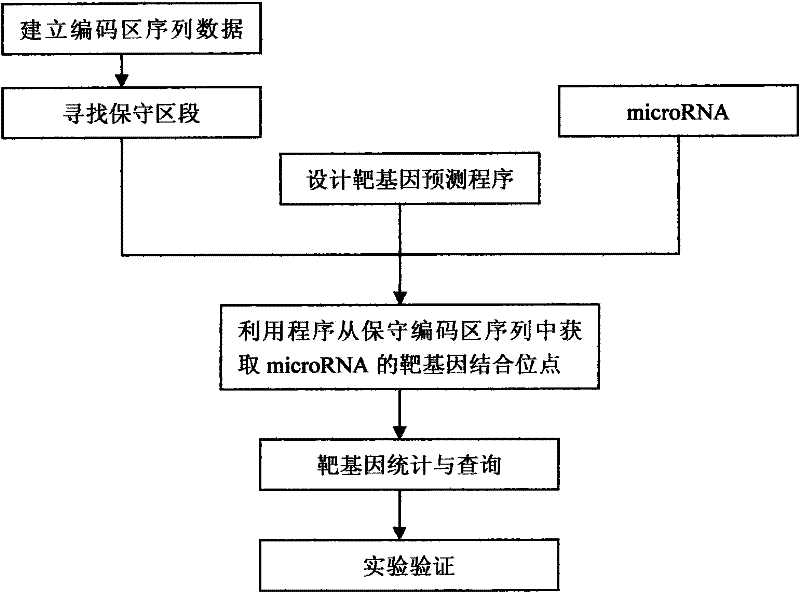
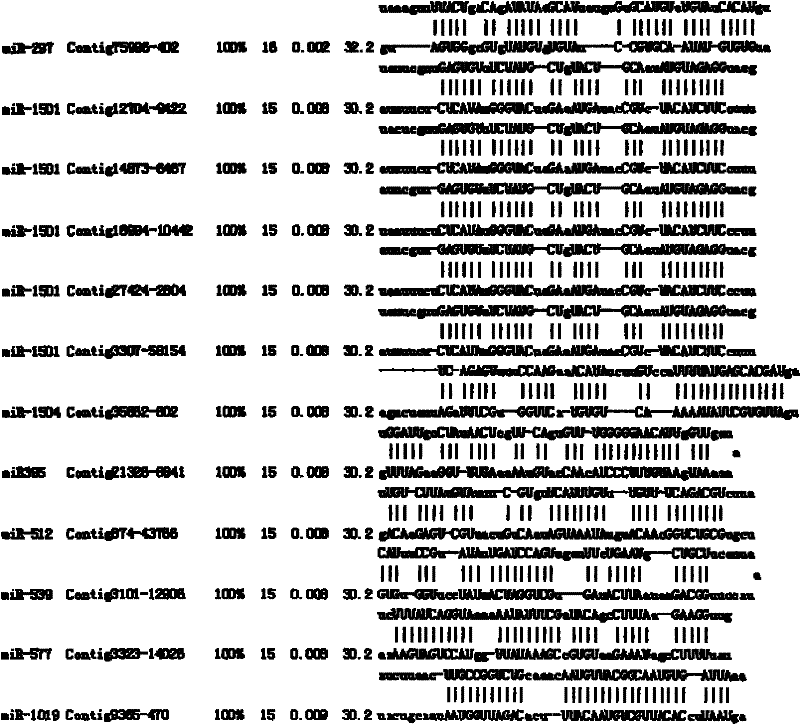
A method for target gene prediction in microRNA coding region
InactiveCN102270282AMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsConserved sequenceBinding site
The invention relates to a method for predicting a microRNA target gene, which is suitable for predicting the target gene of the microRNA located in the gene coding region. The present invention includes the following procedures: step 1, establishing the coding region sequence database of the organism to be studied; step 2, performing sequence comparison with the coding region sequences of other species to find conserved segments; step 3, designing a target gene prediction program and compiling and debugging; step 4, for each microRNA, scan the coding regions of all genes, and obtain binding sites from conserved sequences; step 5, statistics and query of target genes; step 6, experimental verification. The method has the advantages of simple implementation, high reliability of results, and can meet the needs of prediction of target genes in most microRNA coding regions.
Owner:SHANGHAI CLUSTER BIOTECH
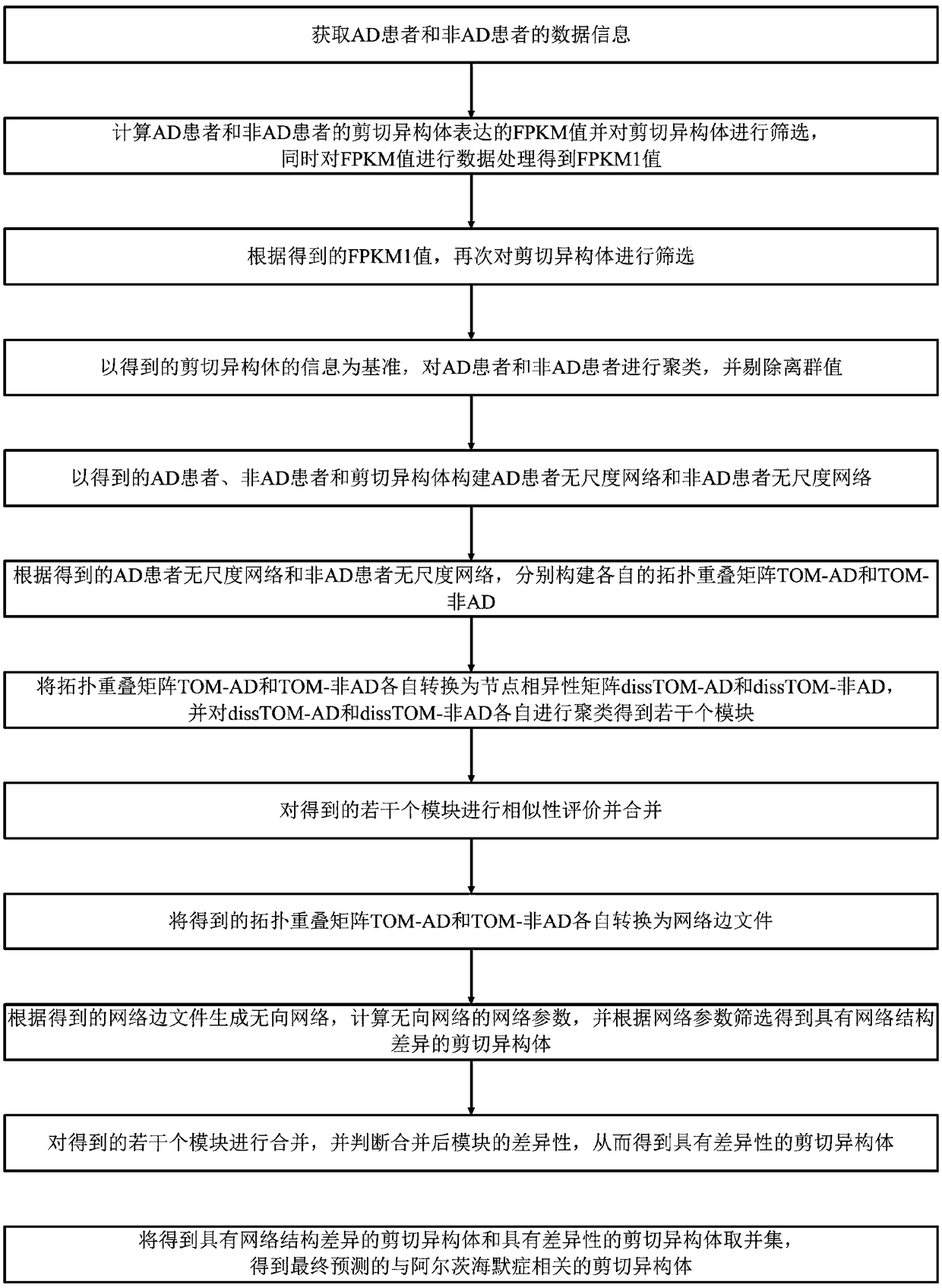
Alzheimer's disease related gene prediction method
The invention discloses an Alzheimer's disease related gene prediction method. The method includes the following steps that: data information is obtained; FPKM values expressed by splicing isoforms are calculated, the splicing isoforms are screened, so that FPKM1 values are obtained; the splicing isoforms are screened; samples are clustered, and outliers are eliminated; the scale-free networks, topology overlap matrixes and node dissimilarity matrixes of the samples are constructed, and clustering and merging are performed; a network edge file is generated through transformation; an undirectednetwork is generated, screening is performed, so that splicing isoforms with network structure differences are obtained; modules are merged, the differences of the modules are judged, splicing isoforms with differences are obtained; and the union of the splicing isoforms with network structure differences and the splicing isoforms with differences is obtained, and a final result is obtained. Withthe method of the invention adopted, the related genes and splicing isoforms of the Alzheimer's disease can be predicted, and data support and theoretical basis can be provided for subsequent work.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
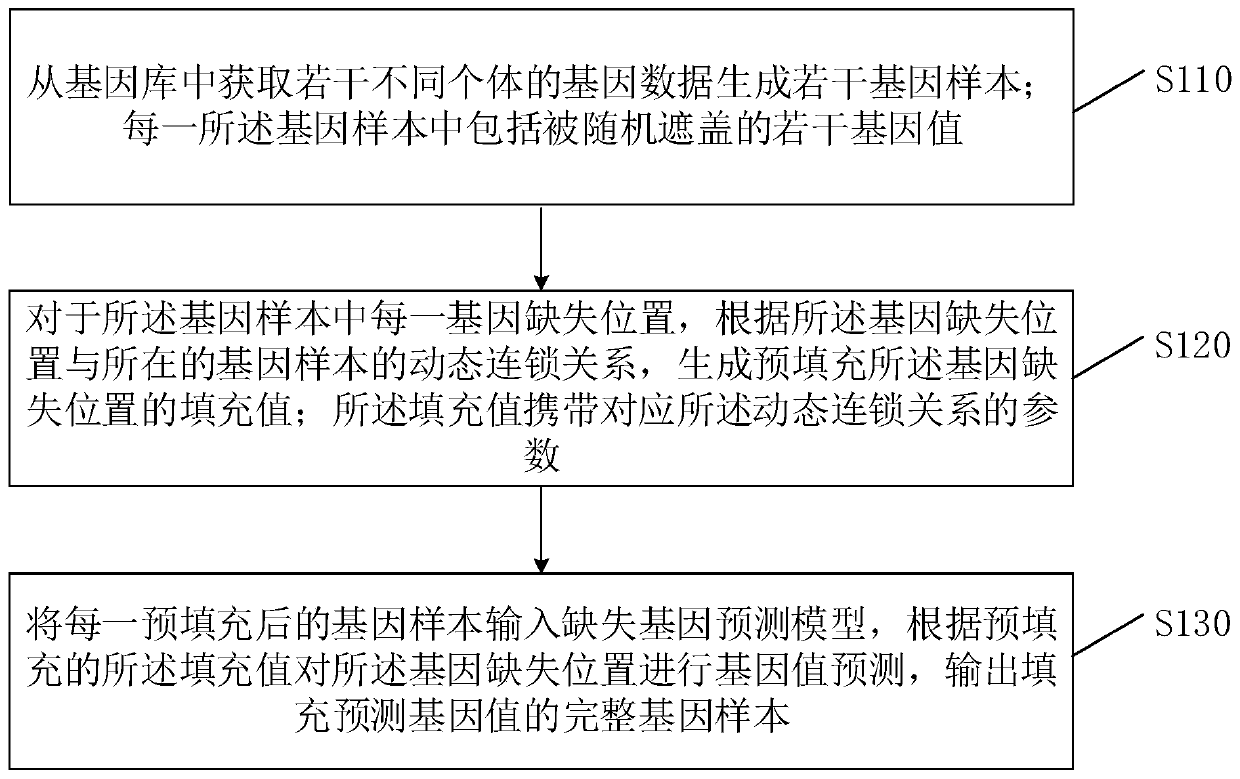
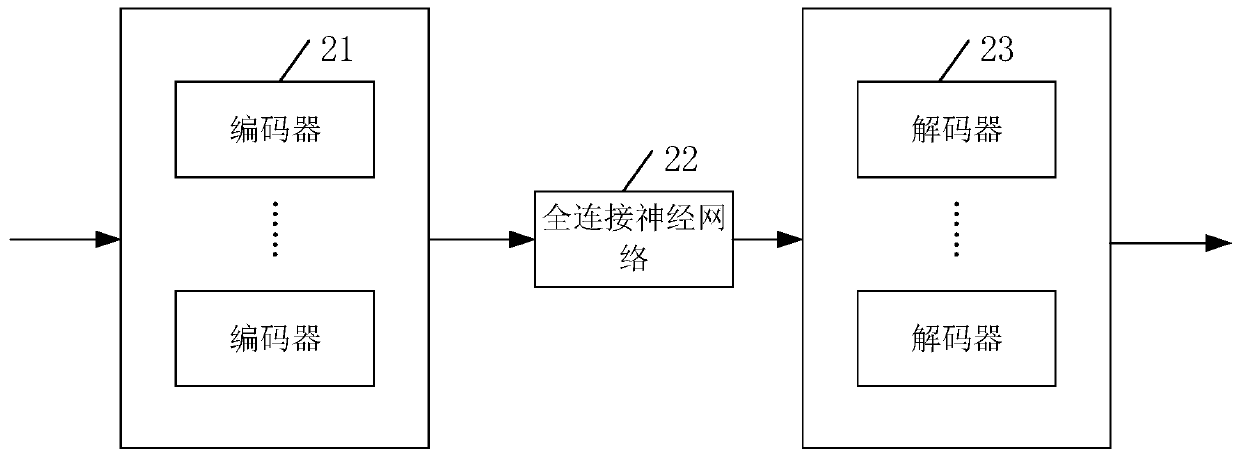
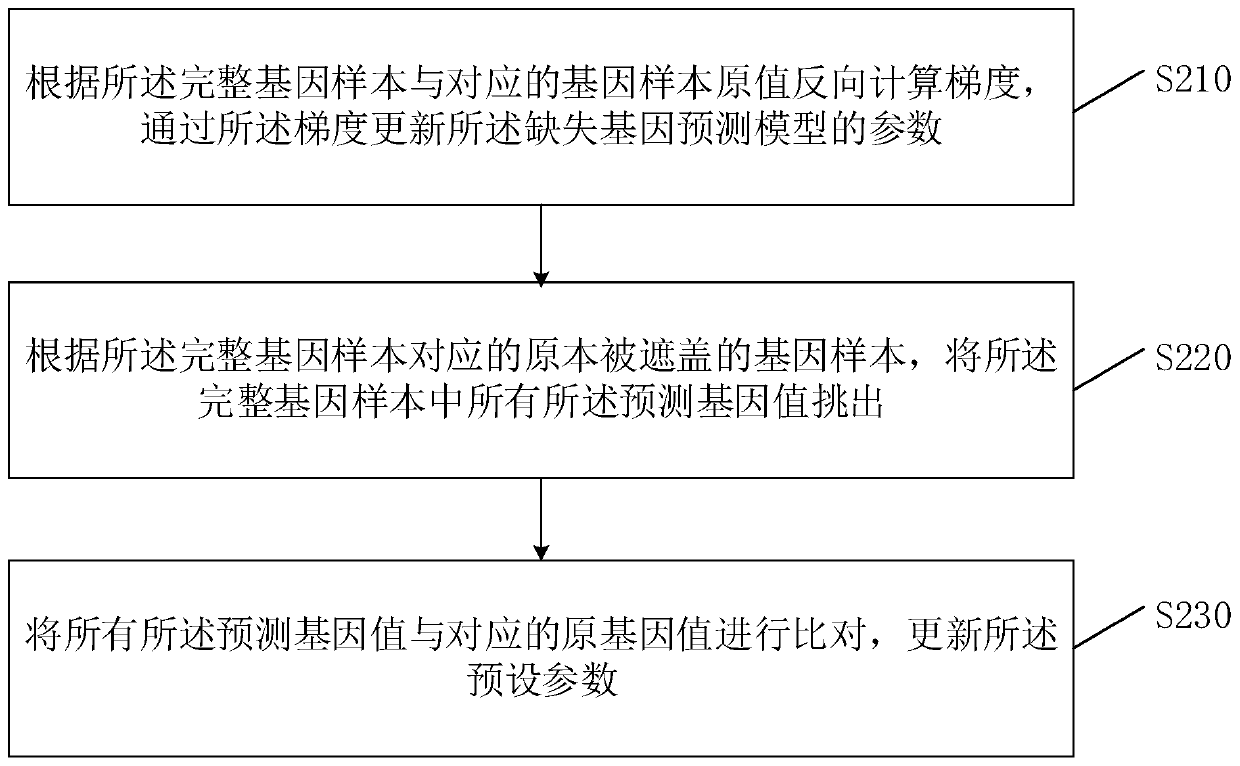
Filling method and device for genotype data missing and server
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene prediction, and provides a filling method and device for genotype data missing and a serve. The method comprises the steps: obtaining gene data ofa plurality of different individuals from a gene pool, and generating a plurality of gene samples; for each gene deletion position in the gene sample, generating a filling value for pre-filling the gene deletion position according to a dynamic linkage relationship between the gene deletion position and the gene sample where the gene deletion position is located;; and inputting each pre-filled genesample into a missing gene prediction model, carrying out gene value prediction on the gene missing position according to the pre-filled filling value, and outputting a complete gene sample filled with the predicted gene value. Each gene sample comprising a plurality of gene values which are randomly covered; and the filling value carries a parameter corresponding to the dynamic linkage relationship. According to the embodiment of the invention, the problems of low filling efficiency and high error rate of the predicted gene filling value are solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
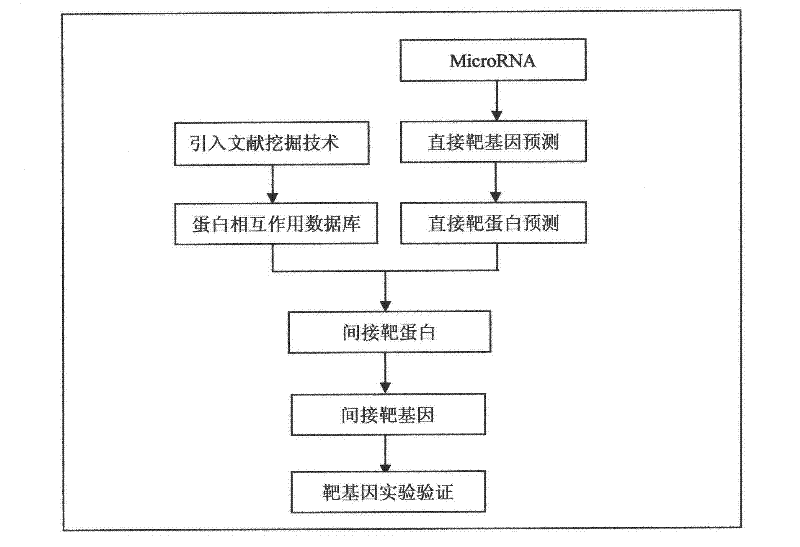
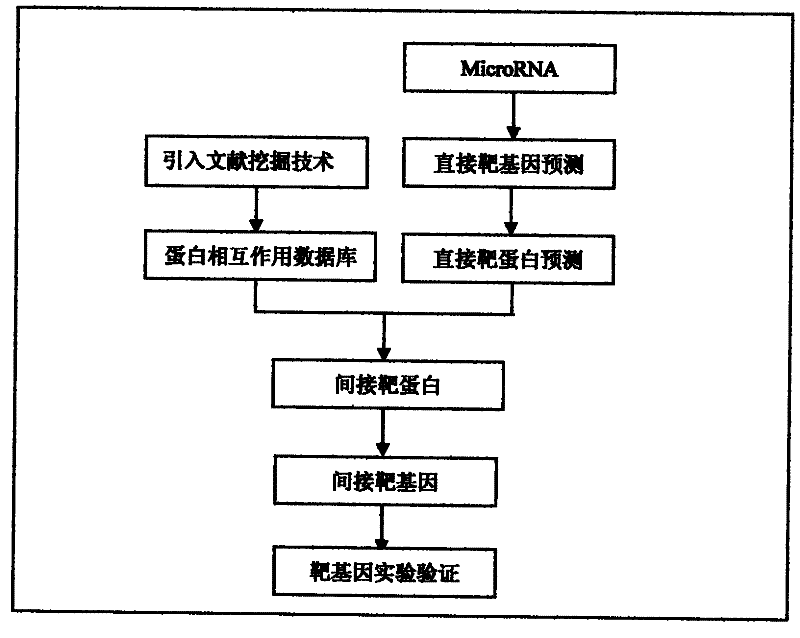
A method for predicting indirect target genes of microRNAs using literature mining
InactiveCN102268473AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPresent methodProtein target
The present invention designs a method for using literature mining technology to study the relationship between virus and human protein expression regulation, including the following main steps: step 1, predicting the direct target gene from microRNA; step 2, predicting the direct target protein from the above target gene; Step 3, use literature mining technology to construct a protein-protein interaction database; Step 4, use the constructed protein interaction database to screen out the indirect target protein and indirect target gene of microRNA from the direct target protein; Step 5, through the experiment Validation of indirect target genes of microRNAs. The feature of this method is that an "indirect" target gene model is proposed, and the literature mining technology is introduced to screen out the real microRNA target genes that are difficult to detect by conventional methods.
Owner:SHANGHAI CLUSTER BIOTECH
Cancer driver gene prediction method
ActiveCN113517021APromote the development of pre-diagnosisImprove forecast accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionProteomicsData setData mining
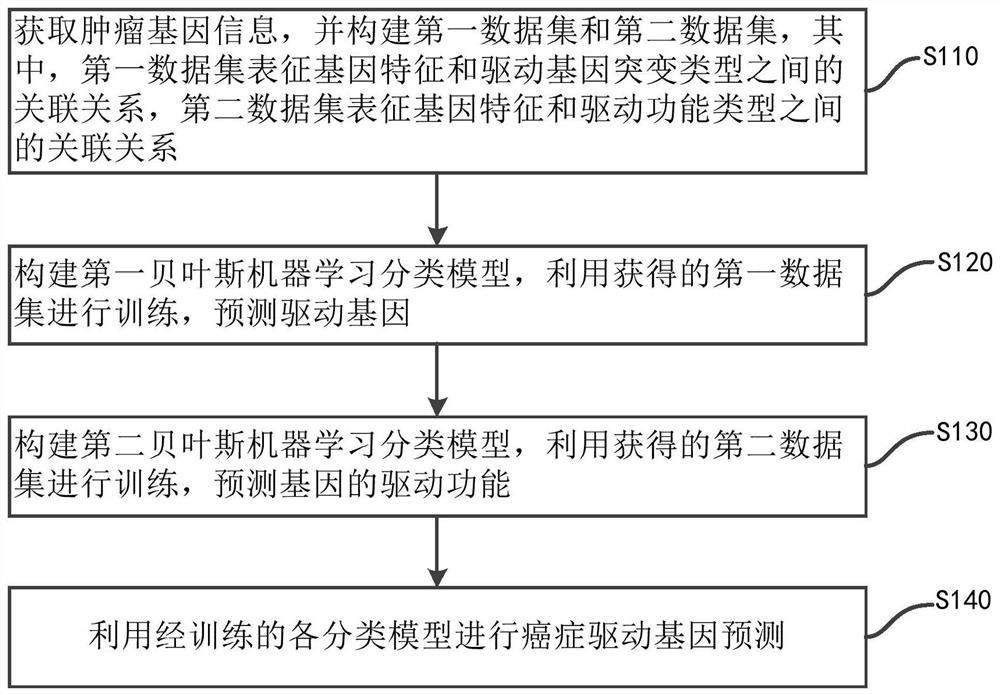
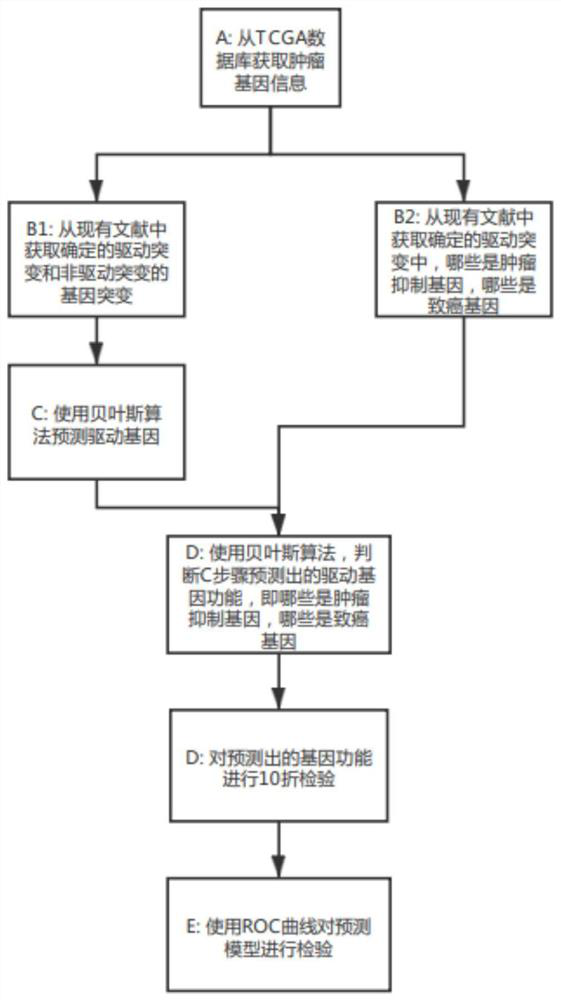
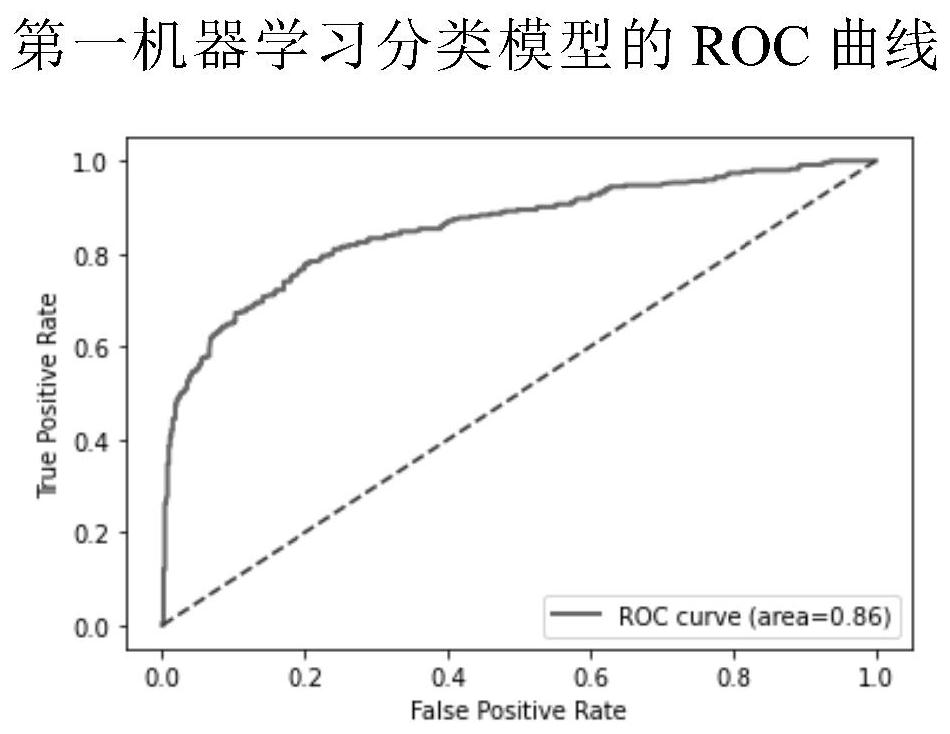
The invention discloses a cancer driver gene prediction method. The method comprises the steps: constructing a first data set and a second data set, wherein the first data set represents the incidence relation between gene features and driving gene mutation types, and the second data set represents the incidence relation between the gene features and driving function types; training a first machine learning classification model by using the first data set, and predicting a new driver gene; confirming data corresponding to the new driver gene predicted by the first machine learning classification model as a second prediction data set; training a second machine learning classification model by using the second data set, and predicting the second prediction data set by using the trained second machine learning classification model to predict the driving function of the new driver gene. According to the invention, the prediction accuracy and the generalization ability of model application can be effectively improved.
Owner:海南精准医疗科技有限公司
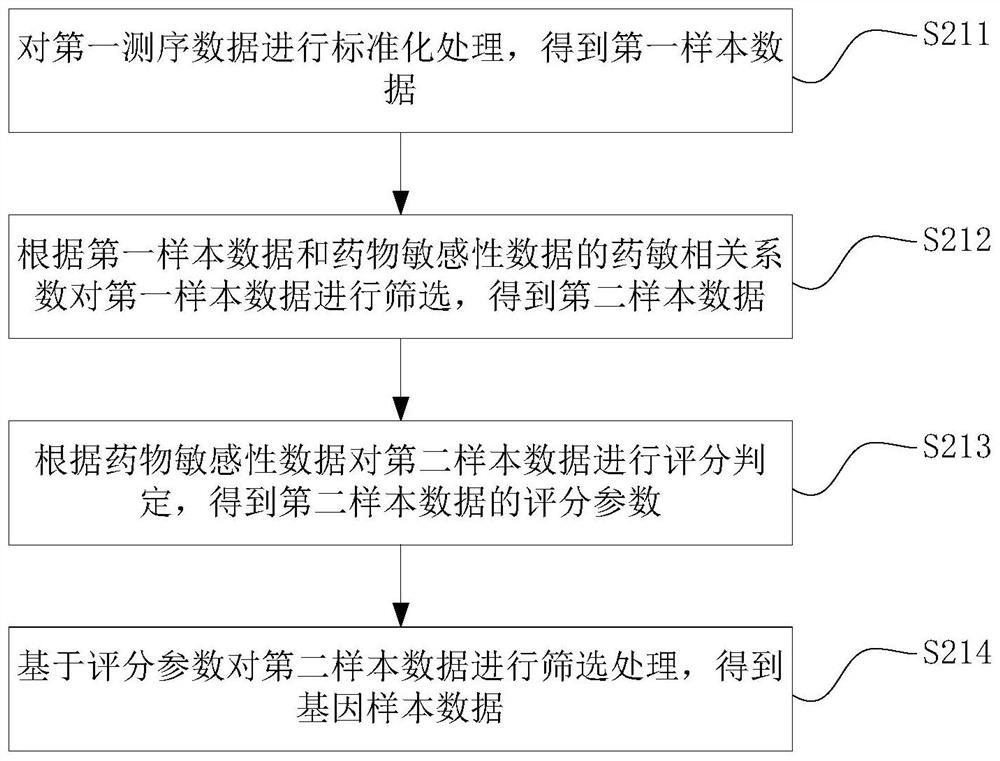
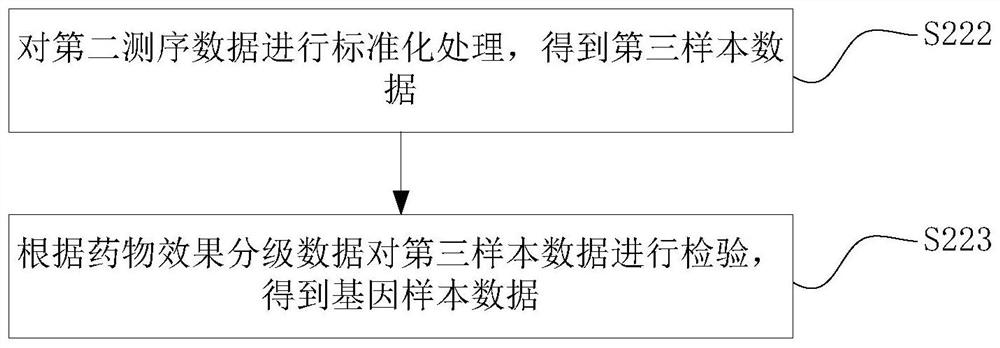
Drug sensitivity prediction method, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN112951327AEnabling Drug Response PredictionLow costDrug and medicationsProteomicsCancer cellEfficacy
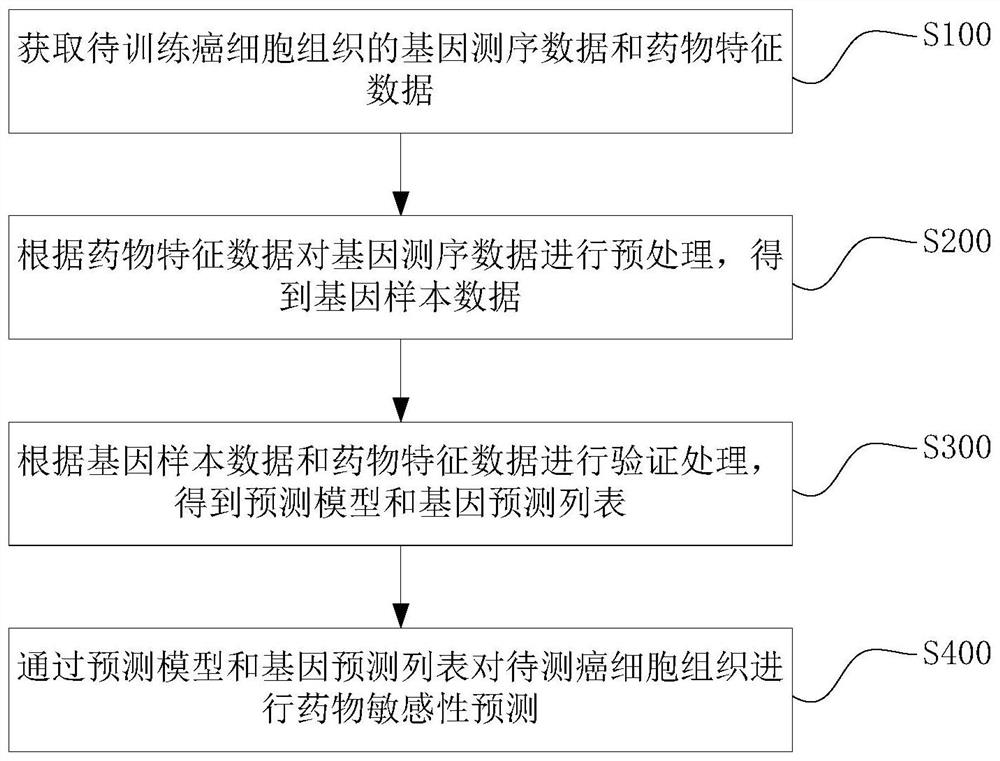
The invention discloses a drug sensitivity prediction method, electronic equipment and a computer readable storage medium, and relates to the technical field of drug detection. The method comprises the steps: acquiring gene sequencing data and drug feature data of cancer cell tissue to be trained, pre-processing the gene sequencing data according to the drug feature data to obtain gene sample data, performing verification processing according to the gene sample data and the drug characteristic data to obtain a prediction model and a gene prediction list, and performing drug sensitivity prediction on the cancer cell tissues to be detected through the gene prediction list and the prediction model. Therefore, drug reactivity prediction on clinical patients can be quickly and accurately realized, the prediction cost and the time cost are reduced, the prediction efficiency is improved. and the efficacy prediction efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com