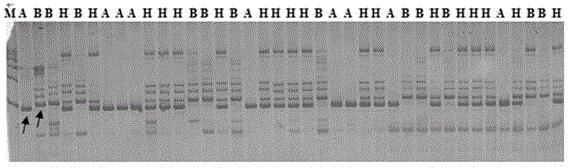
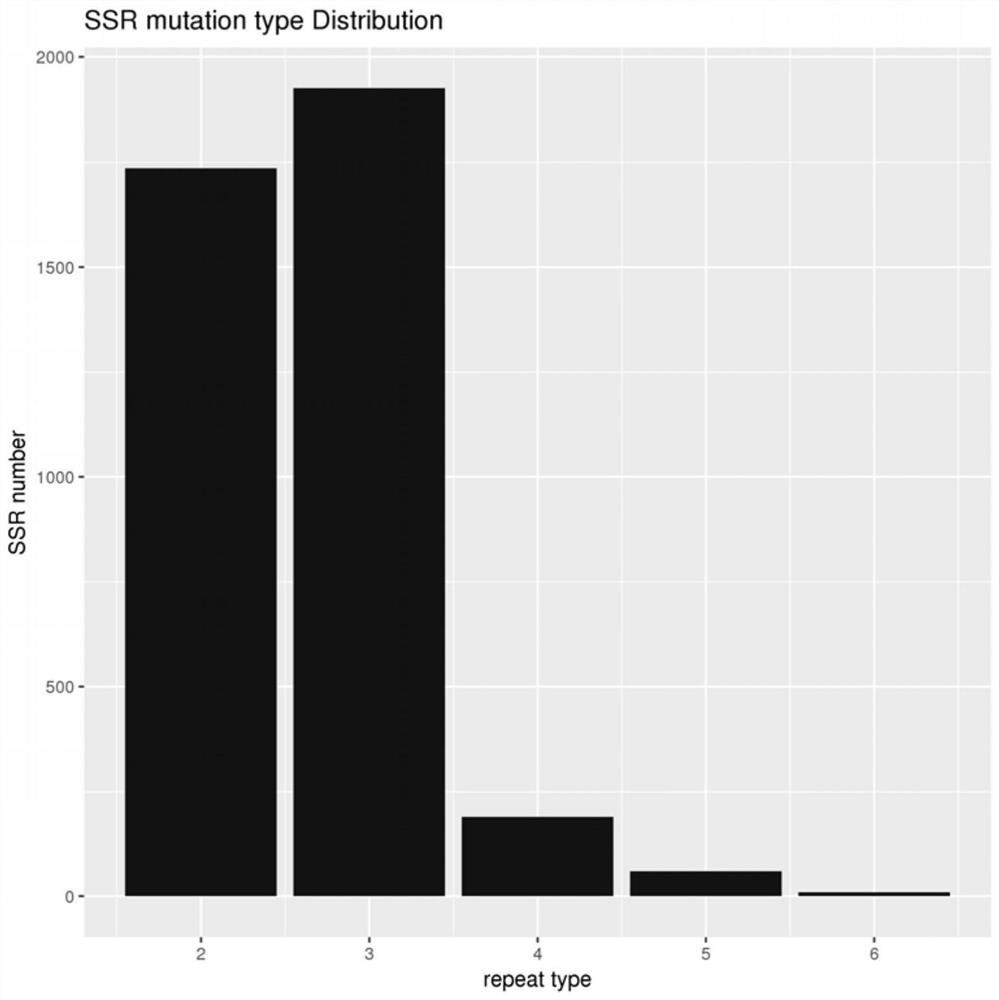
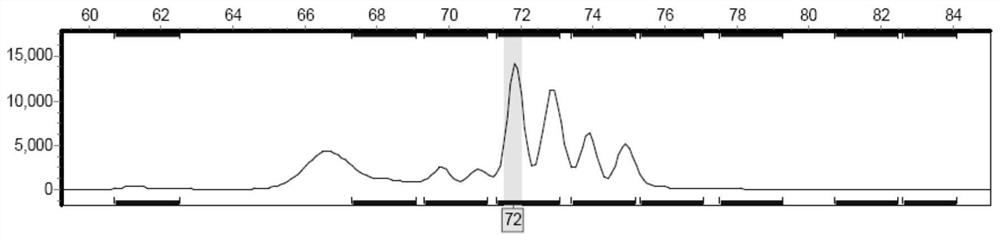
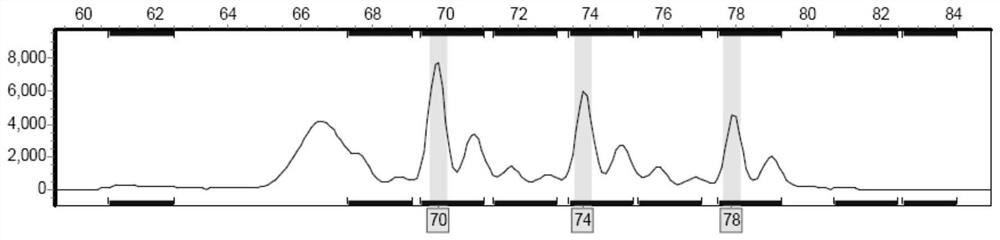
Patents
Literature
48 results about "Qtl analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
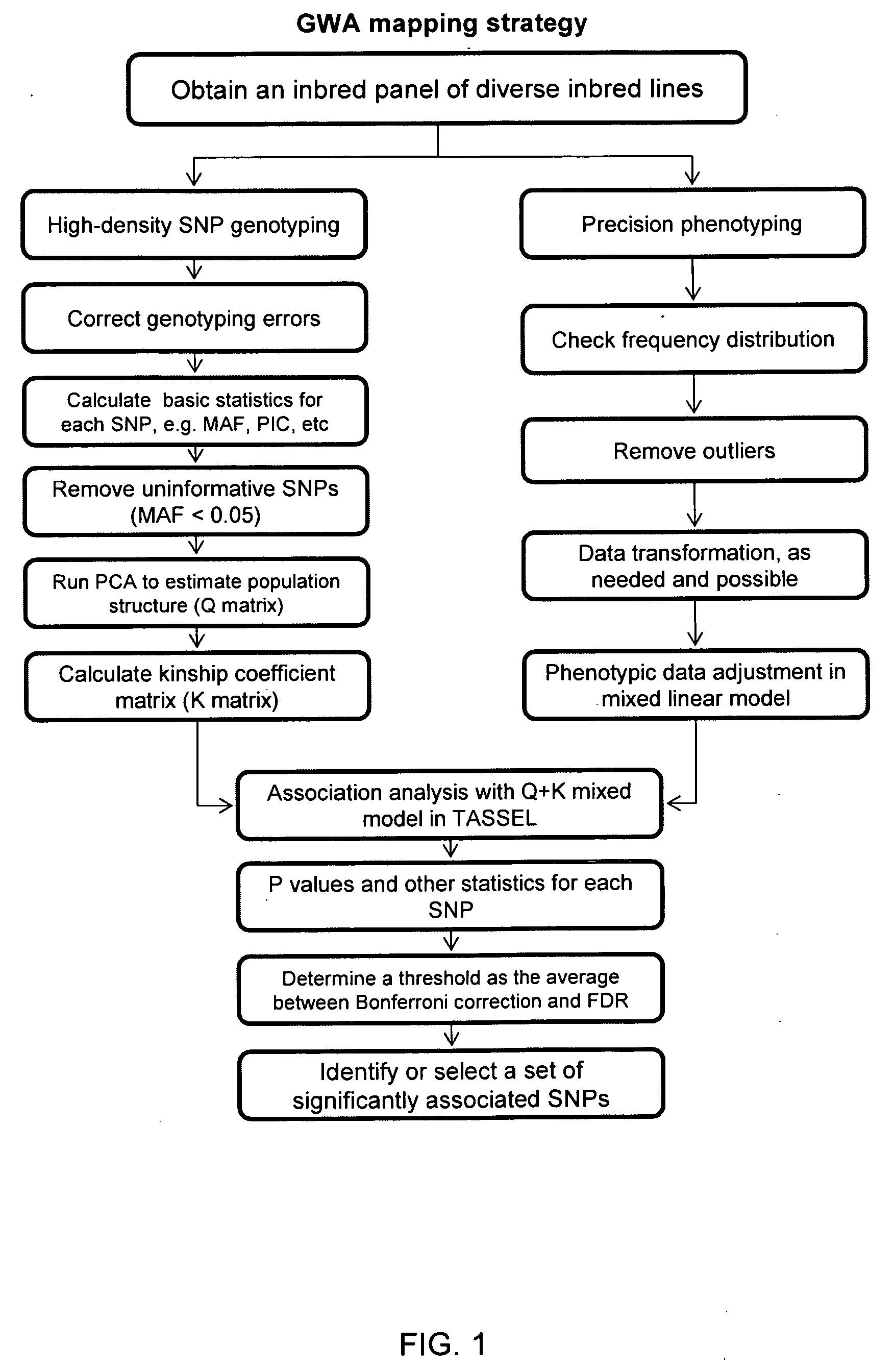
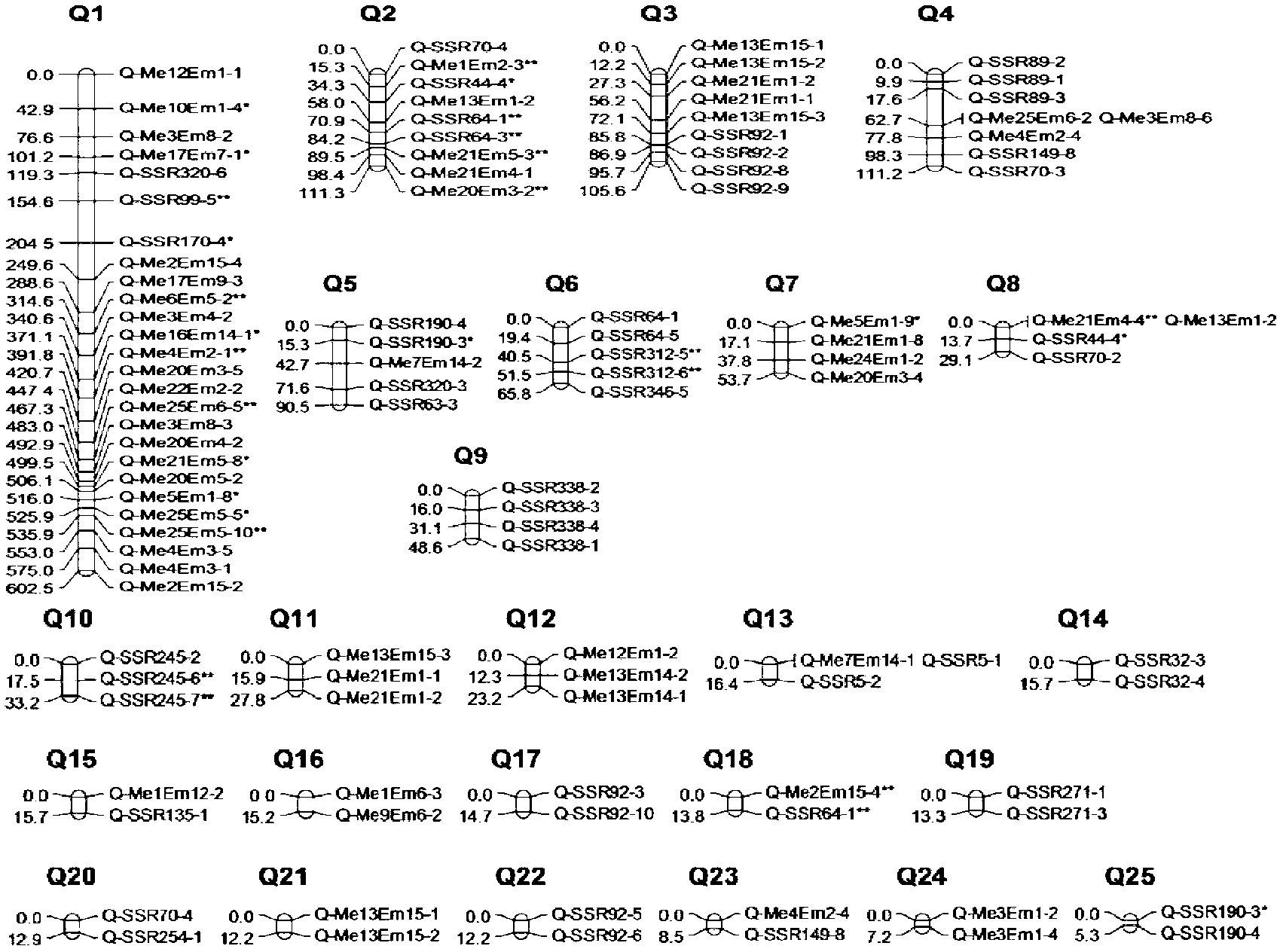
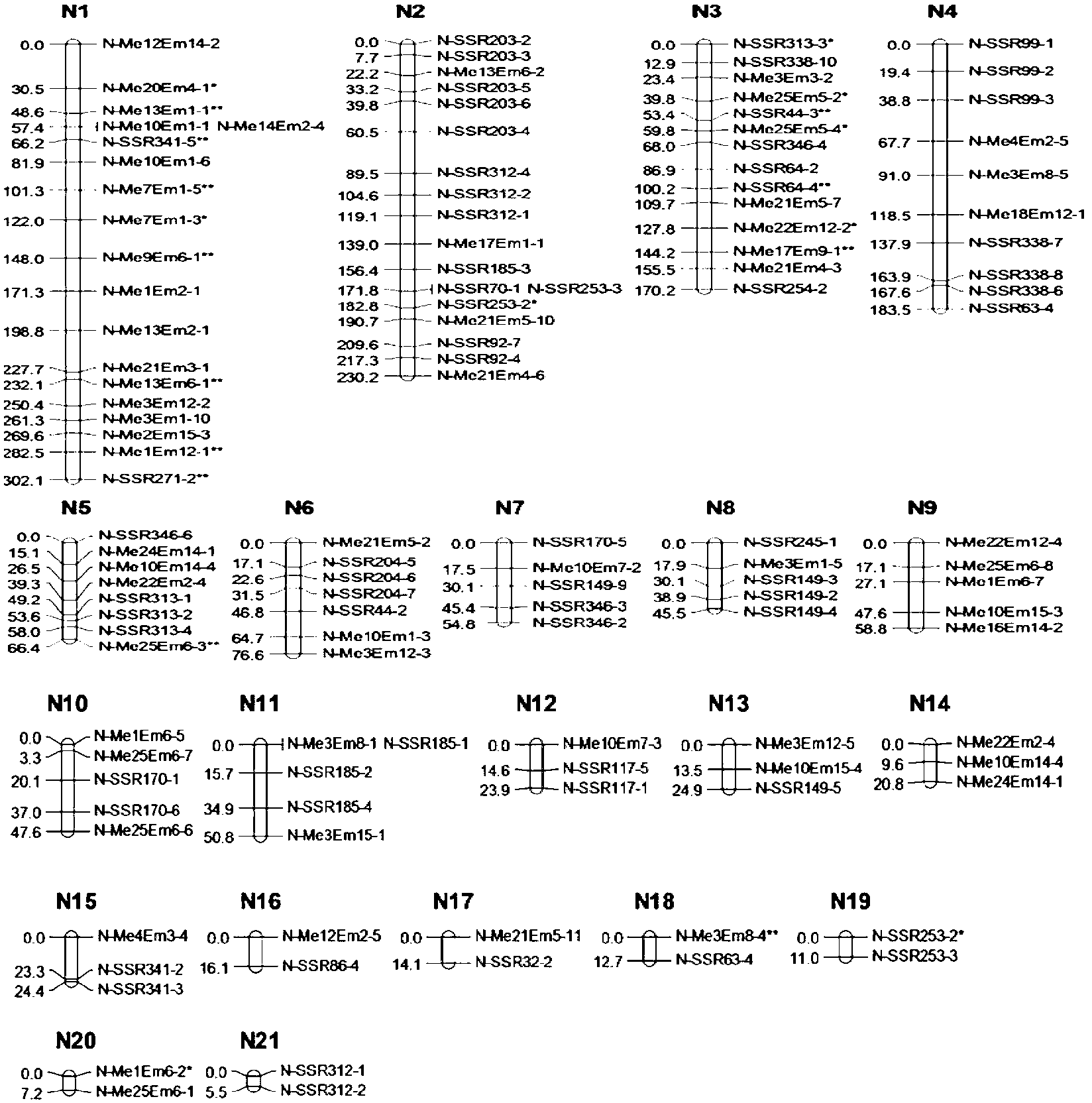
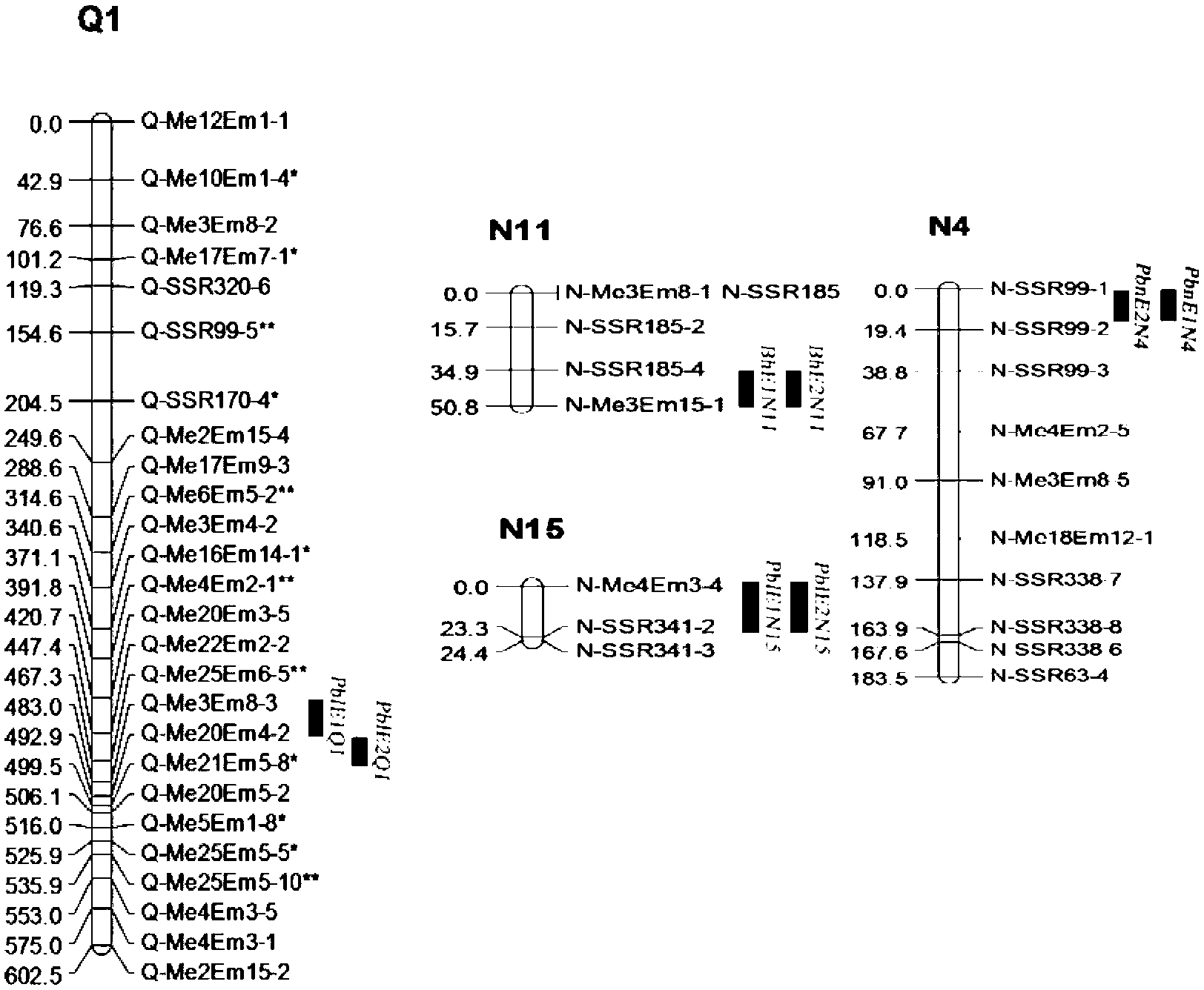
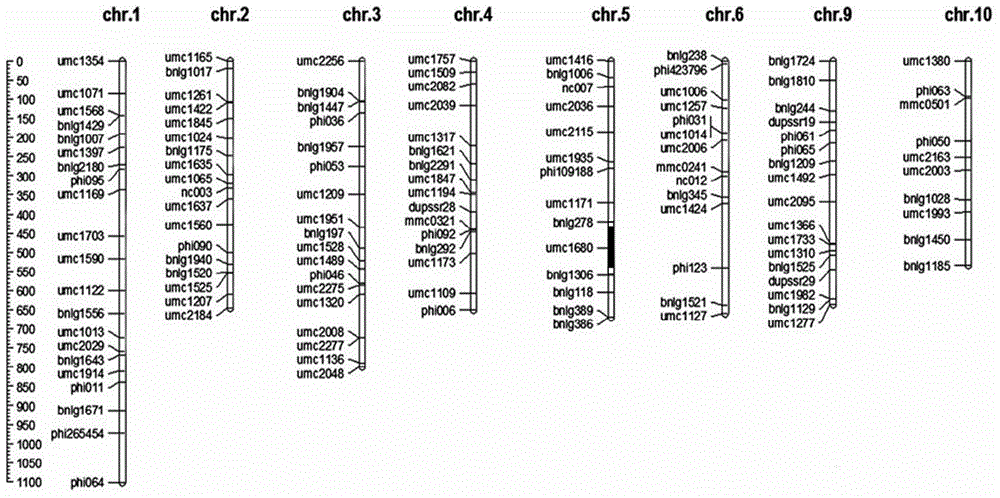
QTL analysis. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis is a statistical method which links the phenotypic data (trait measurements) to genotypic data (usually molecular markers) to explain the genetic basis of variation underlying complex traits (Miles and Wayne, 2008).
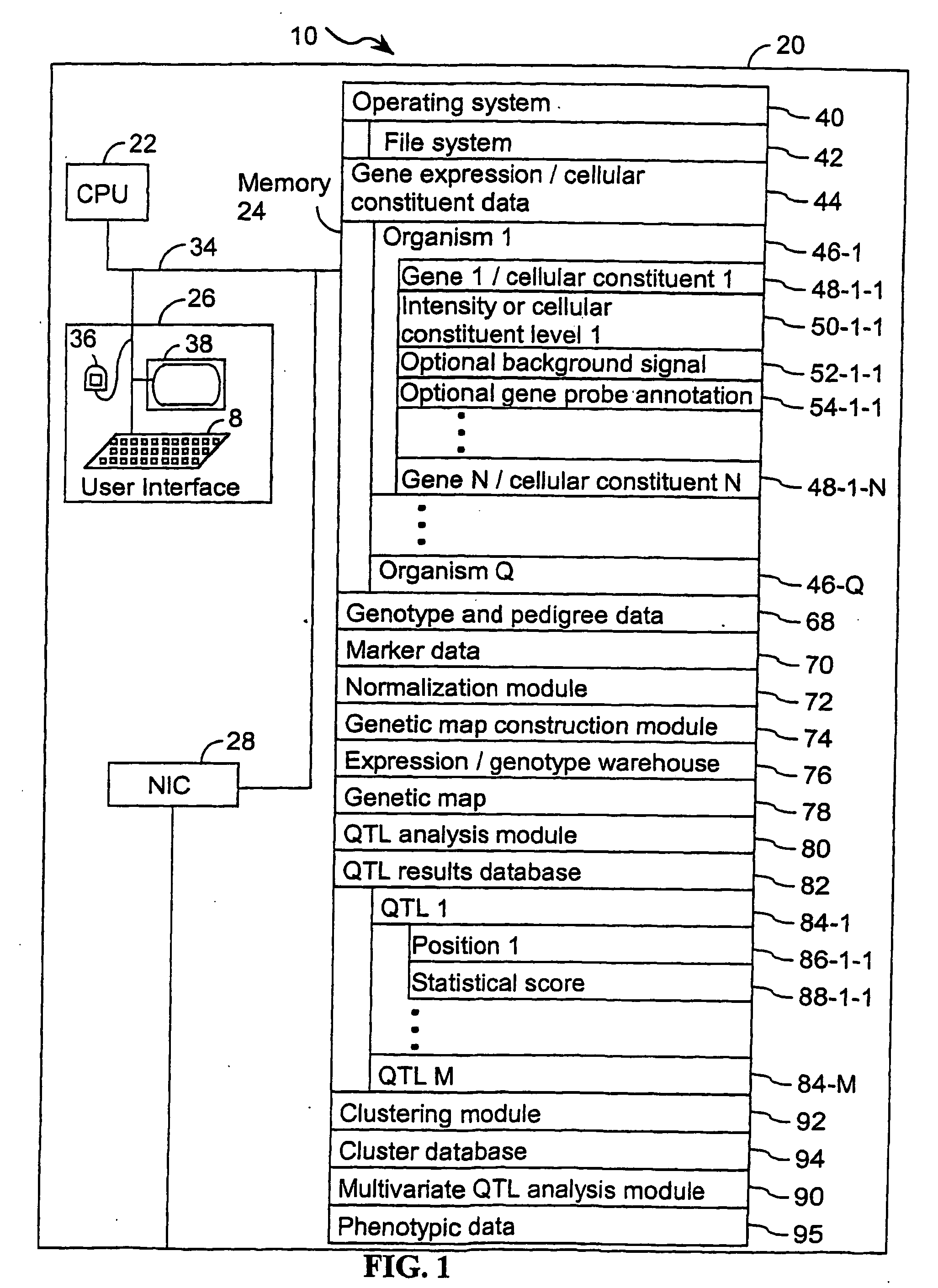
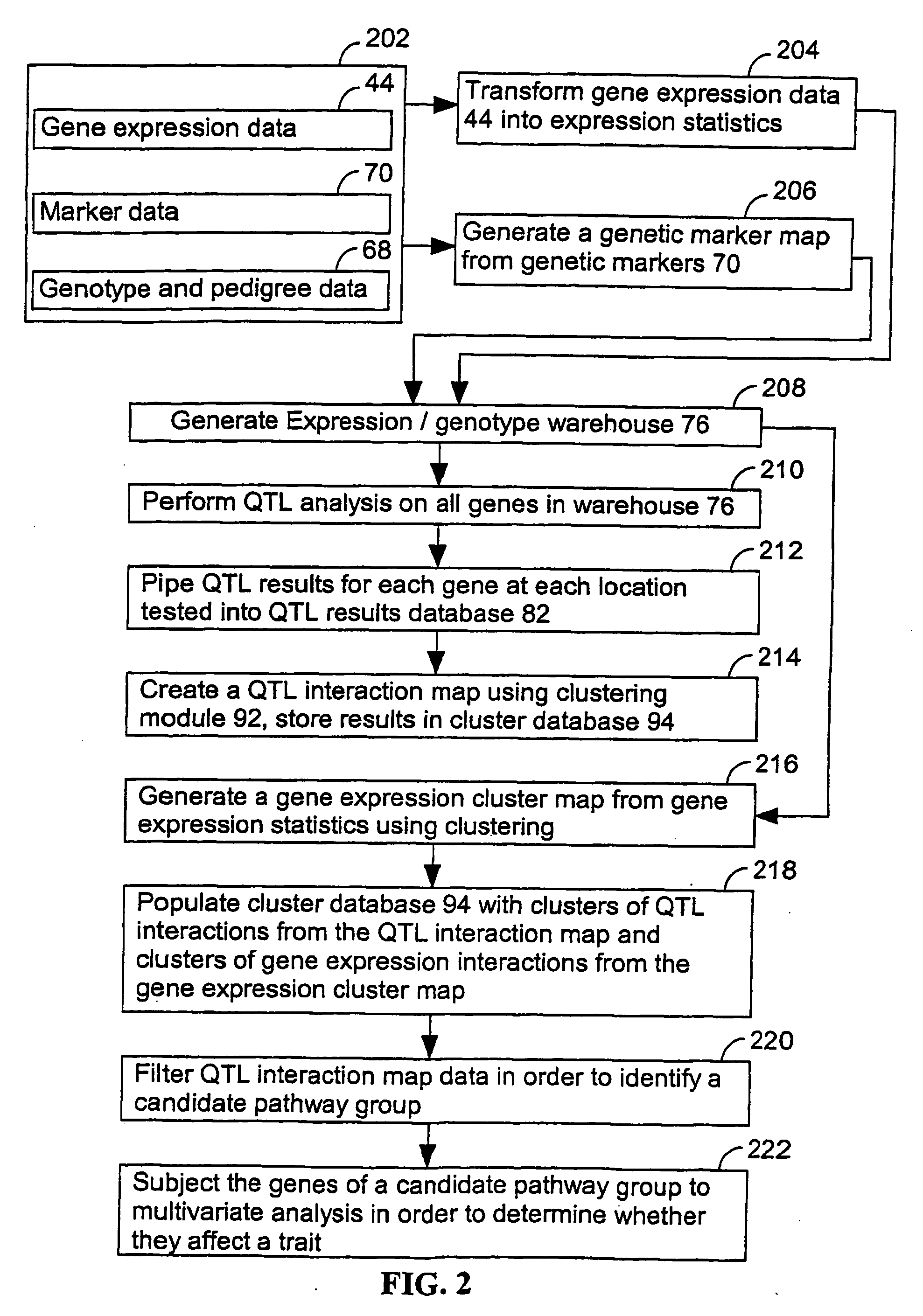
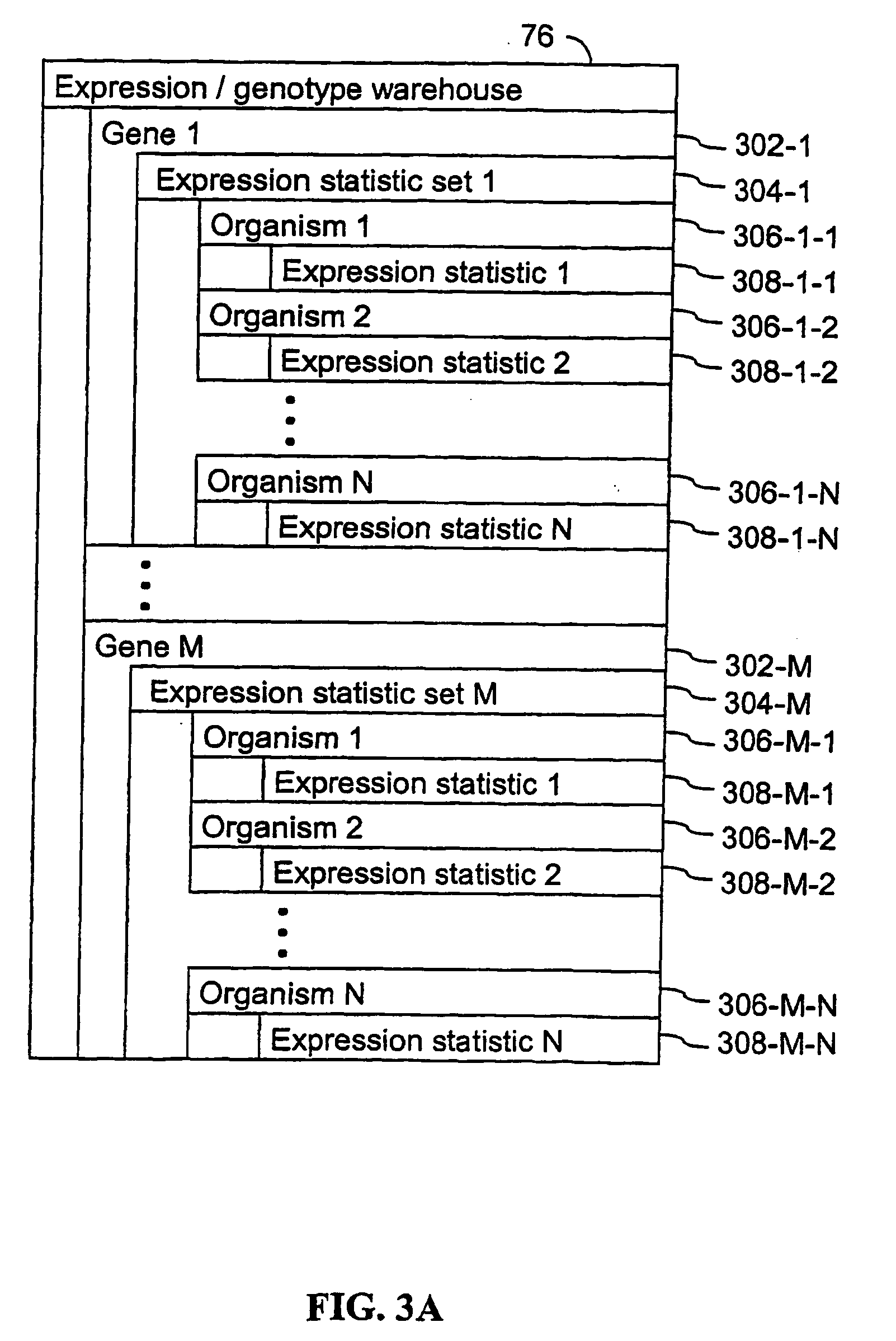
Computer systems and methods that use clinical and expression quantitative trait loci to associate genes with traits
A method for associating a gene G in the genome of a species with a clinical trait T exhibited by one or more organisms in a plurality of organisms of the species. An expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) is identified for the gene G using a first quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis. The first QTL analysis uses a plurality of expression statistics for gene G as a quantitative trait. Each expression statistic in the plurality of expression statistics represents an expression value for gene G in an organism in the plurality of organisms. A clinical quantitative trait loci (cQTL) that is linked to the clinical trait T is identified using a second QTL analysis. The second QTL analysis uses a plurality of phenotypic values as a quantitative trait. Each phenotypic value in the plurality of phenotypic values represents a phenotypic value for the clinical trait T in an organism in the plurality of organisms. When the eQTL and the cQTL colocalize to the same locus, the gene G is associated with clinical trait T.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Method for selecting statistically validated candidate genes
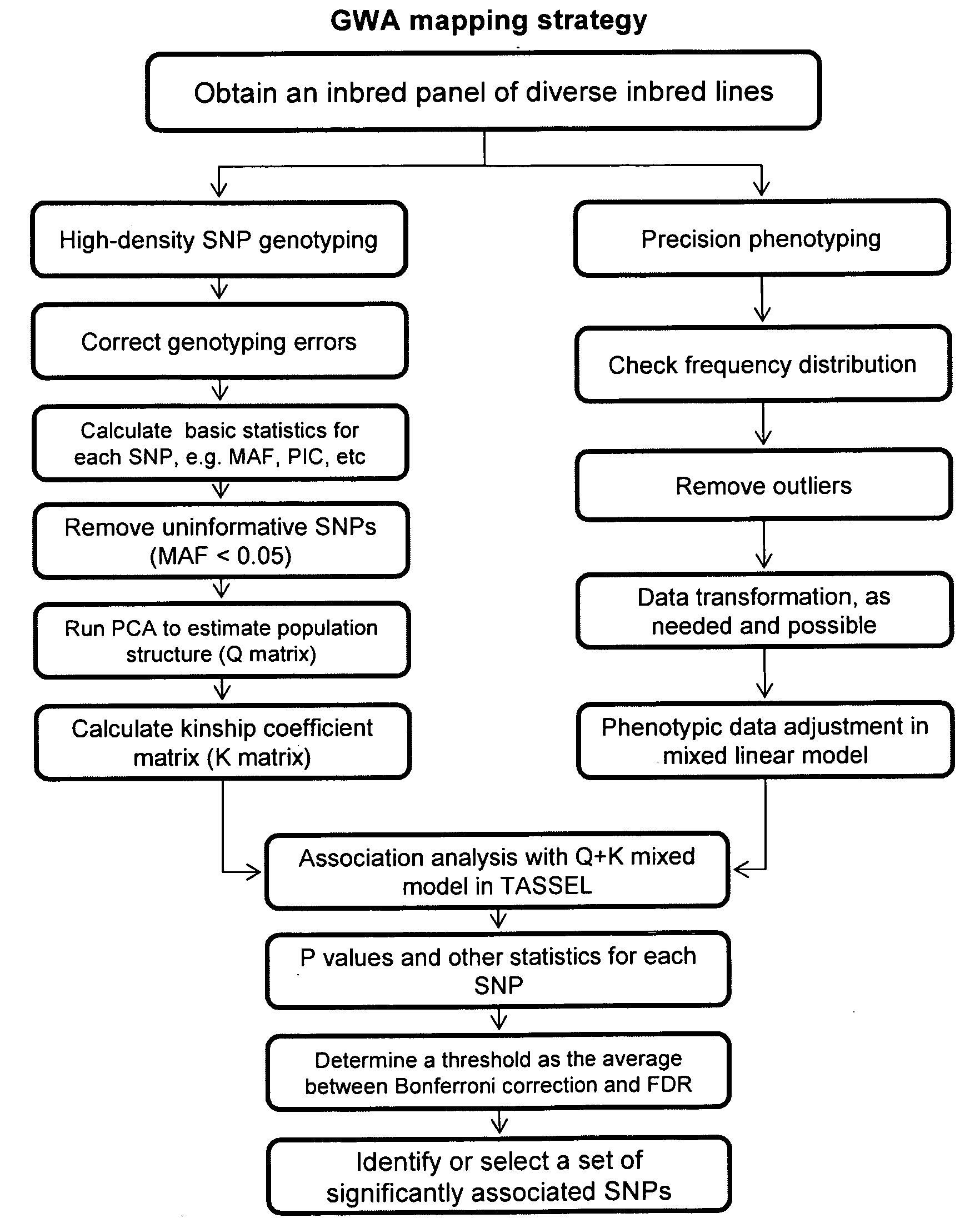
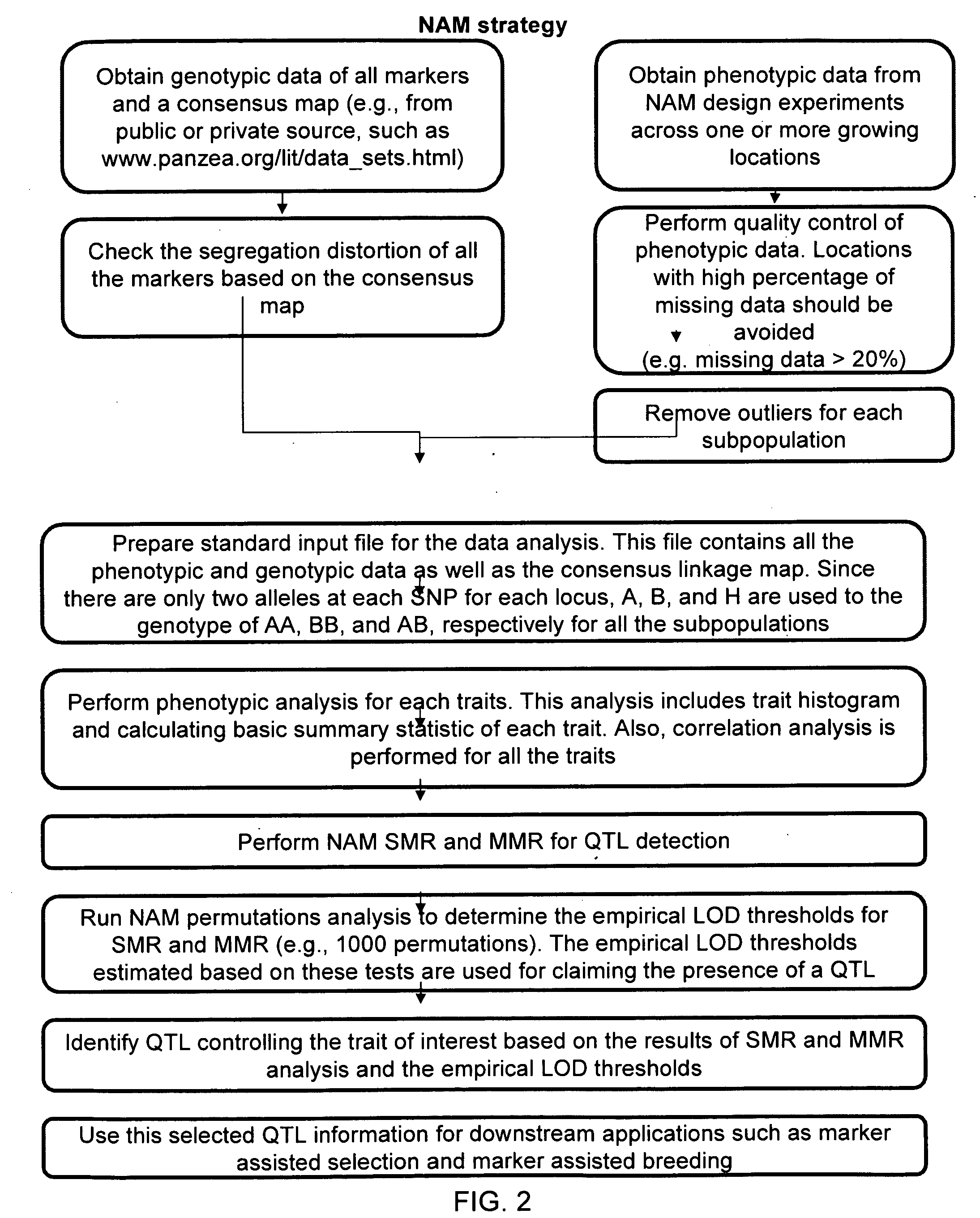
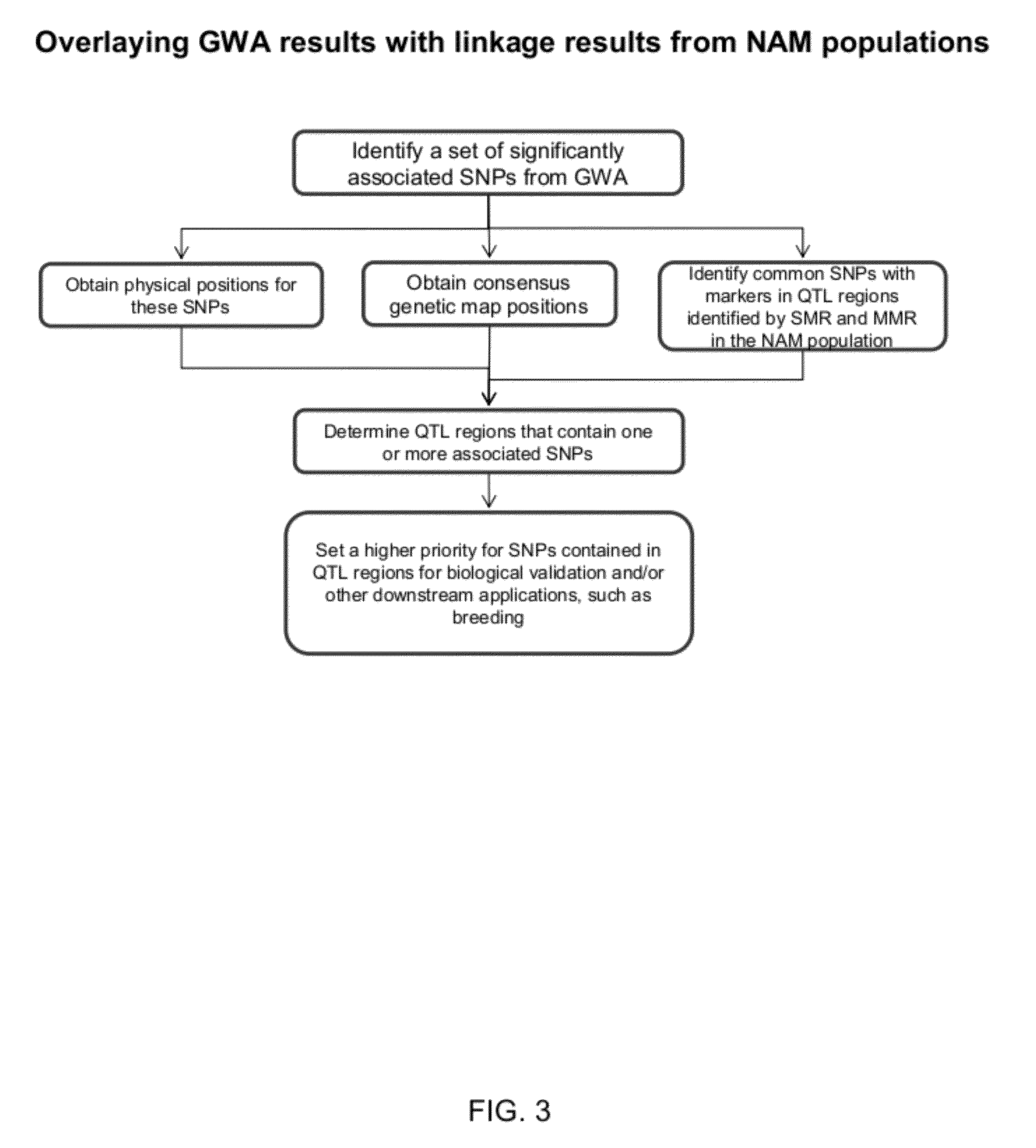
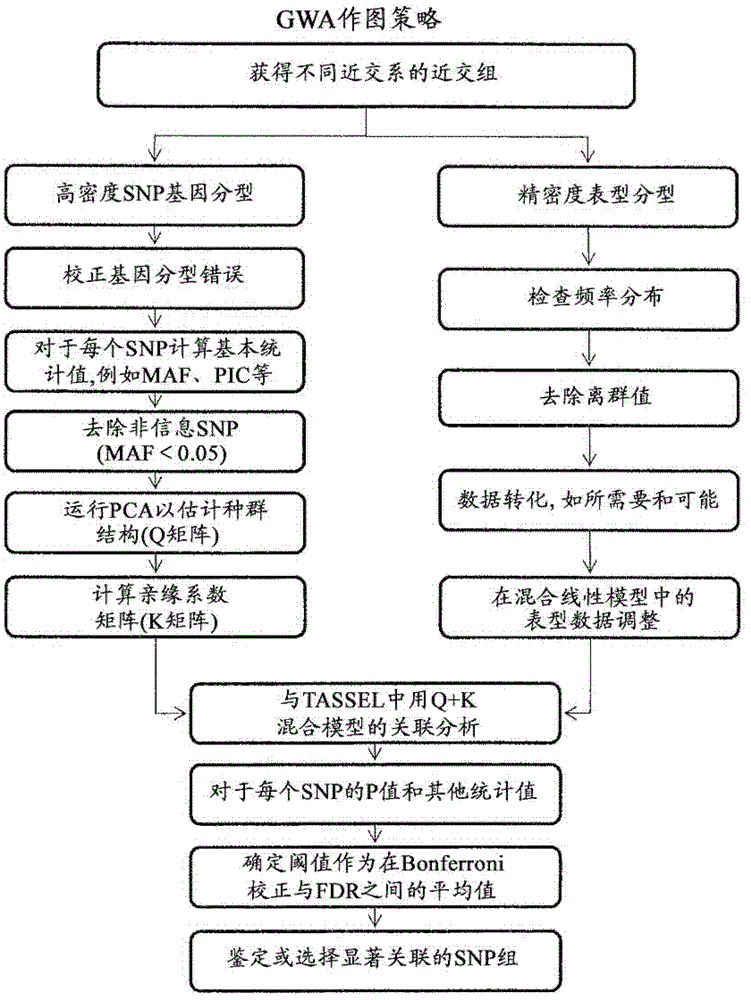
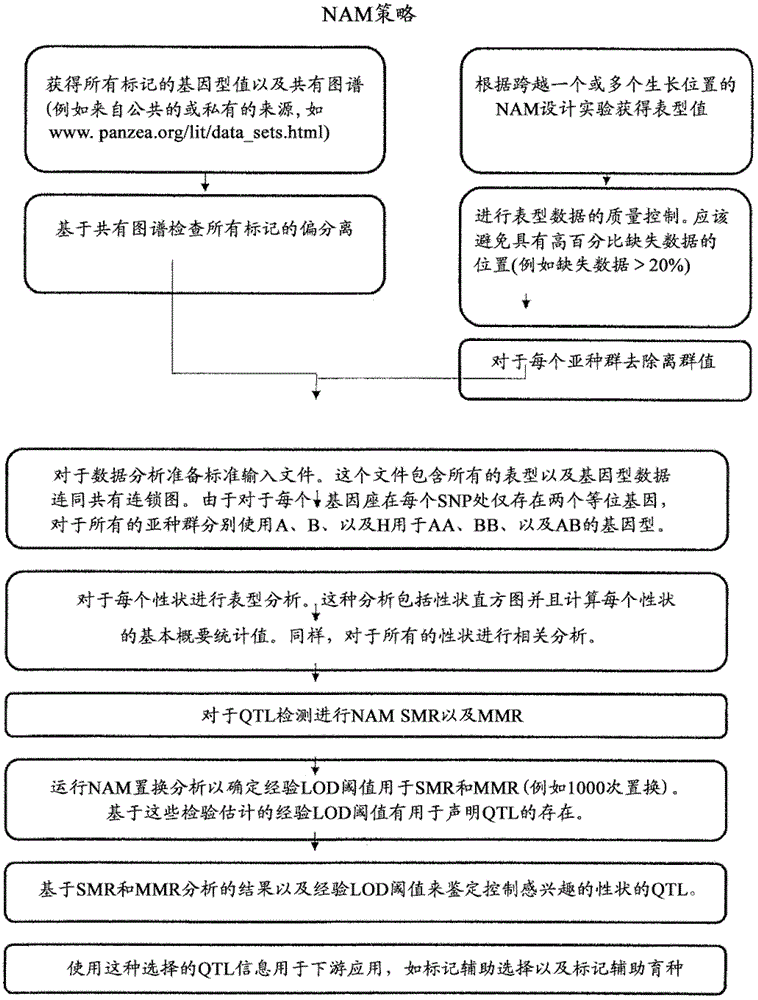
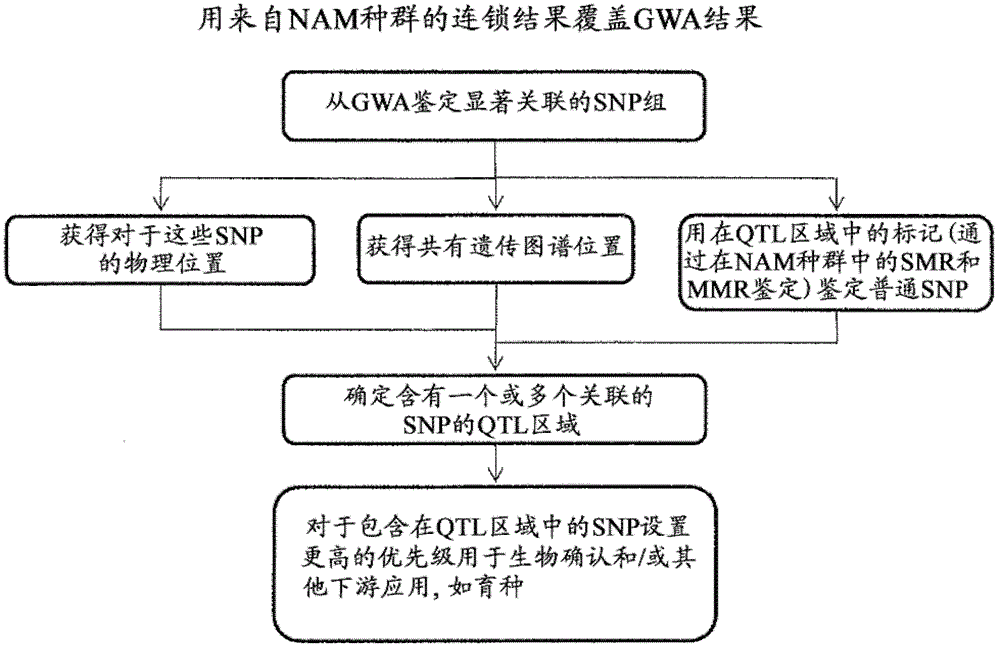
Provided herein are methods for evaluating associations between candidate genes and a trait of interest in a population. The methods include a combination of genome-wide association analysis and one or more of nested association mapping (NAM), expression QTL analysis (eQTL), and allele epistastic analysis (AEA). Markers are selected or prioritized if they are shown to be positively-correlated with a trait of interest using GWA and a combination of one or both of NAM and eQTL. Also provided are models for evaluating the association between a candidate marker and a trait in a nested population of organisms. These methods include single marker regression and multiple marker regression models. Markers identified using the methods of the invention can be used in marker assisted breeding and selection, as genetic markers for constructing linkage maps, for gene discovery, for identifying genes contributing to a trait of interest, and for generating transgenic organisms having a desired trait.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
SSR molecular marker in linkage with radish clubroot-resisting QTL and applications of SSR molecular marker
InactiveCN109280716ANo pollution in the processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerGenomic sequencing
The invention discloses an SSR molecular marker in linkage with radish clubroot-resisting QTL. The radish clubroot-resisting QTL has 5 sites, respectively RsCr1, RsCr2, RsCr3, RsCr4 and RsCr5. The sequences of a forward primer and a reverse primer of the molecular marker are SEQ ID NO.1 and 2. The invention further discloses an acquiring method of the SSR molecular marker. The method comprises thefollowing steps: simplifying genomic sequencing, constructing a radish high-density SNP genetic map, carrying out phenotype identification on the clubroot resistance of the radish F3 family, carryingout radish clubroot-resisting QTL analysis, and developing and screening the SSR molecular marker. The SSR molecular marker provided by the invention can be directly utilized for identifying the clubroot resistance of radish and molecular marker assistant breeding, and has great significance in prevention and treatment research of radish clubroot.
Owner:INST OF ECONOMIC CROP HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Chrysanthemum-branching-trait-related molecular marker acquisition method
InactiveCN103232996AGood polymorphismGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationQtl analysisMolecular genetics
The invention relates to a chrysanthemum-branching-trait-related molecular marker acquisition method, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the steps that: a, a testing material and phenotypic data thereof are obtained; b, a chrysanthemum linkage map is established; c, chrysanthemum branching trait QTL analysis is carried out according to the phenotypic data and a molecular genetic map; and d, chrysanthemum-branching-trait-related molecular markers are determined. According to the invention, 'QX-145' (P1) is adopted as a female parent, NanNongYinShan is adopted as a male parent (P2), and 92 F1 segregating populations obtained by hybridization are adopted as the testing material; and a plurality of molecular markers substantially related to chrysanthemum branching traits are obtained. The molecular markers can be used in chrysanthemum branching trait good gene fine positioning and cloning, such that selection efficiency can be greatly improved, and breeding process can be accelerated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
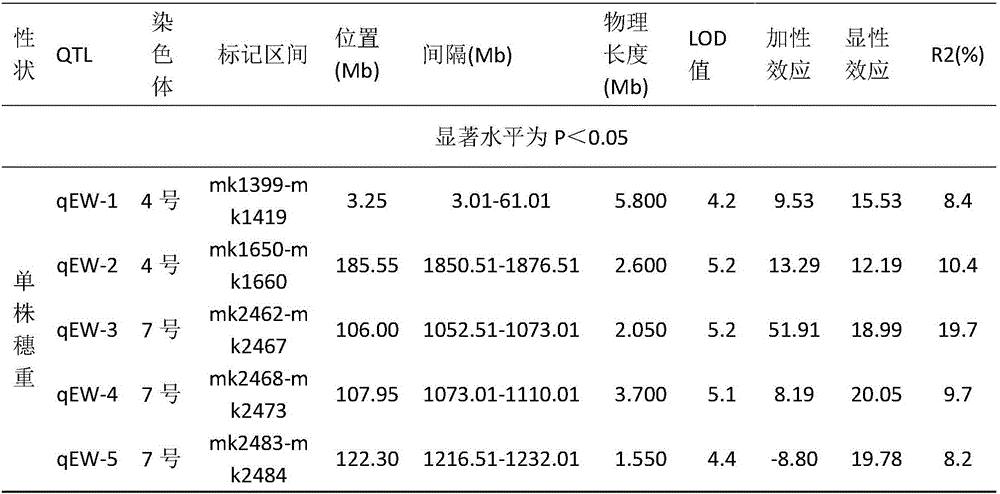
Maize single panicle weight main effect QTL, as well as acquisition method and application thereof
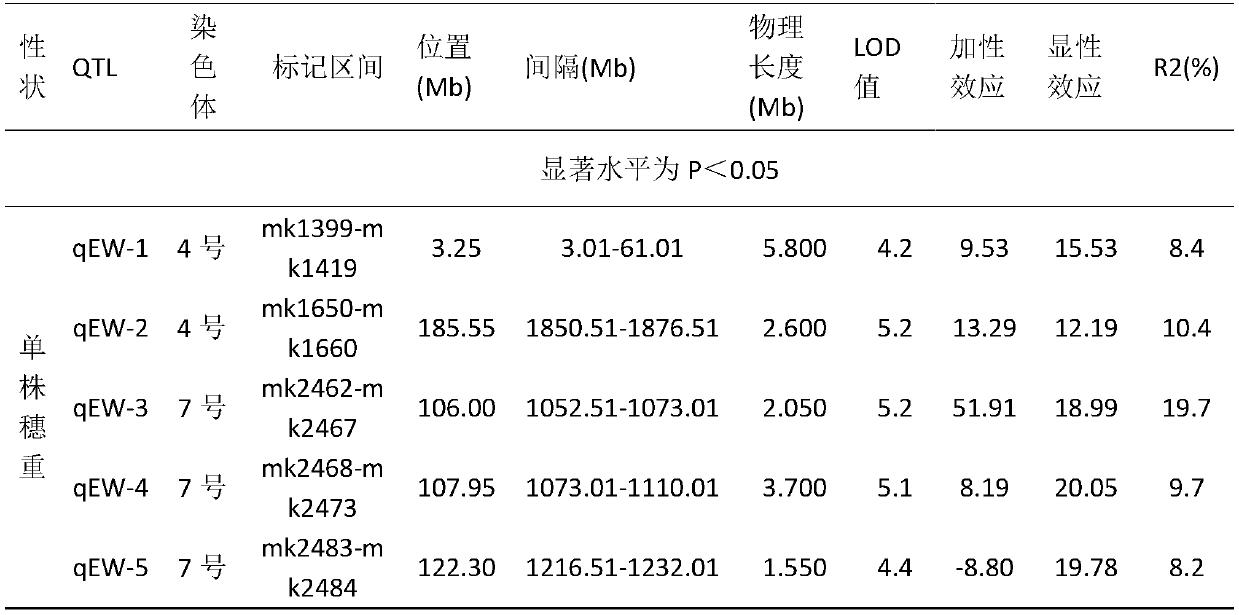
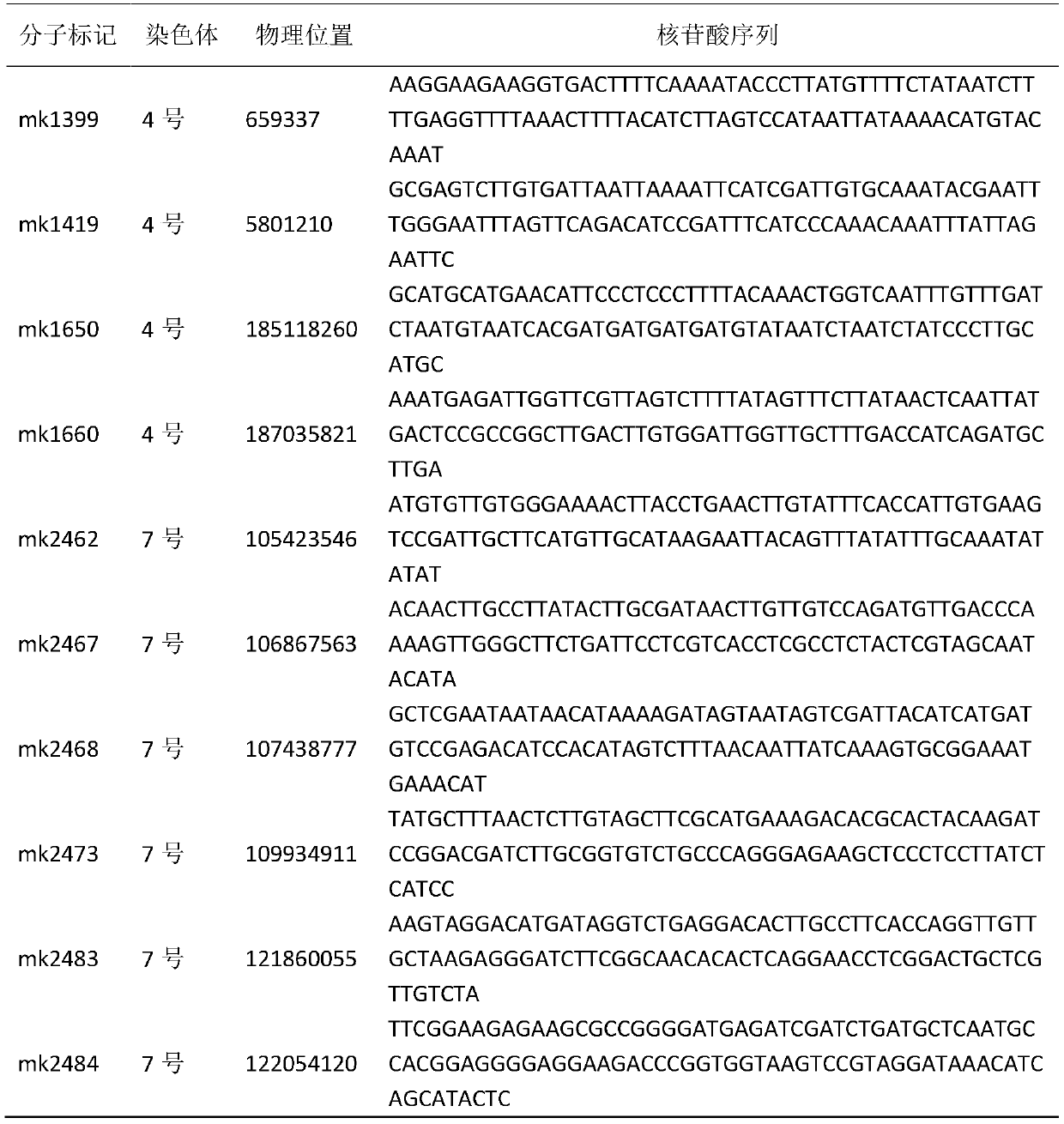
The invention provides a maize single panicle weight main effect QTL, as well as an acquisition method and application thereof. The QTL comprises qEW-1, qEW-2, qEW-3, qEW-4 and qEW-5. The method comprises the following steps: configuring cross combination by taking a high-yield early-maturity maize inbred line SG5 as a female parent and a maize inbred line SG7 with relatively poor yield trait as a male parent, and constructing an F2 genetic group of the cross combination; performing GBS sequencing-basing typing on the F2 genetic group, and performing genotyping by combining differential SNP validated based on SG5 and SG7 parents; investigating the yield trait of single F2 panicle, performing QTL analysis on the F2 single panicle yield trait by utilizing a winQTLcart2.5 software composite interval mapping method, and analyzing the chromosome region of the main effect QTL and the genetic effect. According to the method, a theoretic base is provided to excavating and controlling the maize single panicle weight main effect QTL and linked marker, a molecular marker closely linked with the target QTL is acquired, and foundation is laid to maize single panicle yield trait QTL candidate gene prediction, cloning and molecular mark assisted breeding.
Owner:LIUPANSHUI NORMAL UNIV
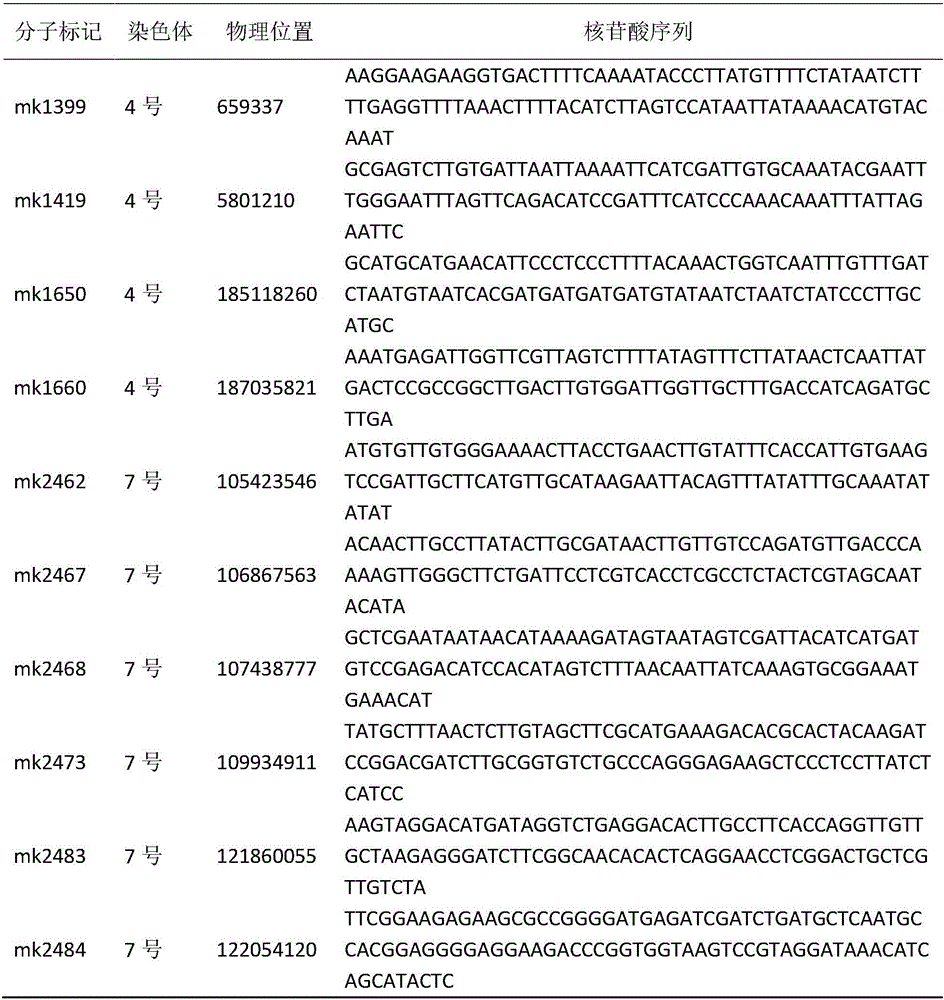
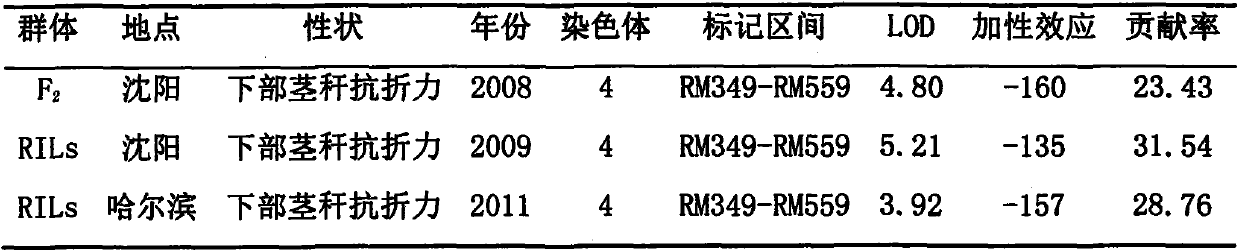
Molecular marker of paddy-rice stalk-strengthening lodging-resistant gene prl4 and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN104087575AEasy wayMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVascular bundleResistant genes
The invention relates to a molecular marker of paddy-rice stalk-strengthening lodging-resistant gene prl4 and application of the molecular marker. QTL (quantitative trait loci) analysis is performed on F2 and RILs crowds of lodging-resistant correlated character of japonica type super rice Shennong 265 and Yunnan local japonica rice variety Lijiangxintuanheigu, so that major QTL is identified, which is stably expressed in different crowd type (F2 and RILs), at different years (2008, 2009 and 2011) at different place (Shenyang and Haerbin), and a synergistic allelomorphic gene of major QTL comes from Yunnan local japonica rice variety Lijiangxintuanheigu. Further analysis shows that the major QTL simultaneously controls push-resistant strength of the lower part of a plant, breaking-resistant strength of a stem, stem wall thickness, area of larger vascular bundle and smaller vascular bundle, and xylem area of larger vascular bundle and smaller vascular bundle. The major QTL is named as prl4 (pushing resistance of the lower part 4). The invention also discloses a molecular marker of prl4. The molecular marker is closely linked with prl4, and is separated with prl4 in a plant later generation, so that a molecular-marker assistant means is applicable to selectively culture paddy rice varieties possessing both high-yield property and lodging resistance.
Owner:FARMING & CULTIVATION RES INST OF HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
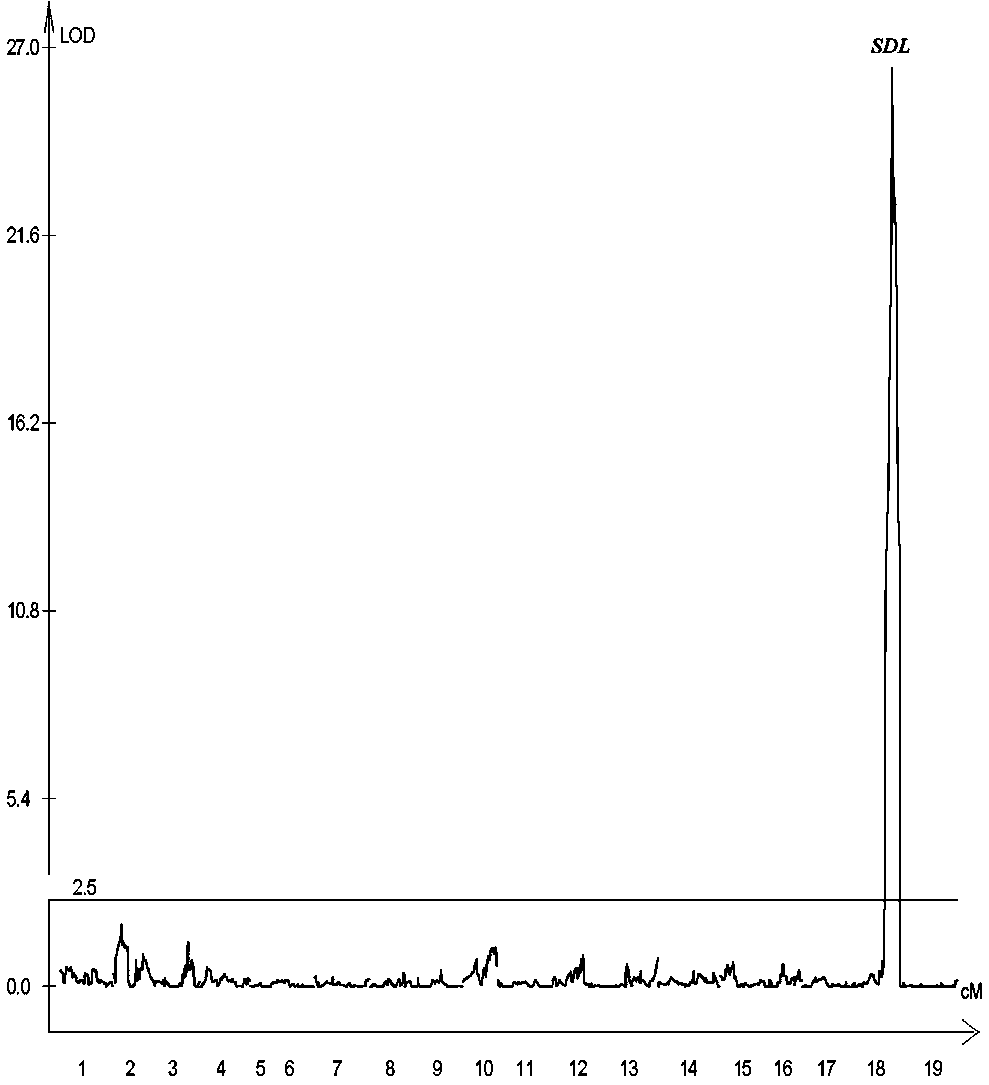
SNP molecular marker for grape fruit seedless major QTL site SDL and application
ActiveCN107723378AGuaranteed accuracyEasy to separateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVitis viniferaAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the field of grape molecular breeding, and particularly provides a molecular marker for a grape fruit seedless major QTL site and an application. An RAD-seq method is utilizedfor sequencing and constructing a joint genetic linkage map of a female parent 'Red Globe' and a male parent 'Centenial Seedless', identification is carried out in combination with a grape fruit phenotype, and an interval mapping method is utilized for QTL analysis, then the presence of the major QTL site (i)SDL( / i) is detected in combination with a 18th linkage group in the genetic linkage map,a contribution rate of the major QTL site is 77.9%, and two SNP markers closely linked to the site are SDL1 and SDL2, with a genetic distance of 124kb. The SNP molecular marker for the grape fruit seedless major QTL site obtained in the invention can be used for early screening of grape fruit seedless traits, and has important theoretical and practical guiding significance for improving the breeding efficiency.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU FRUIT RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
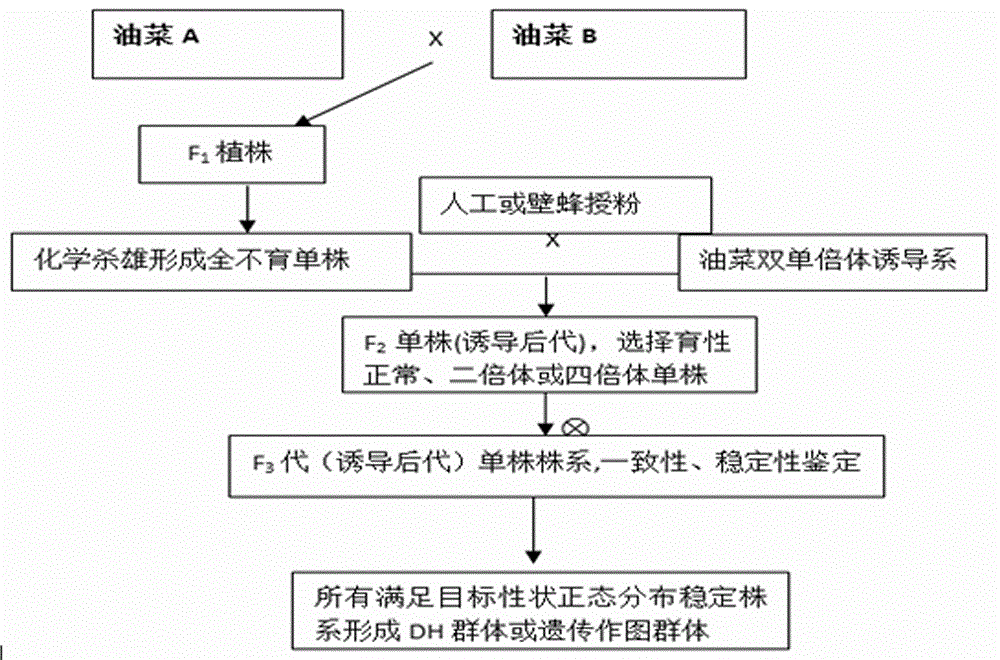
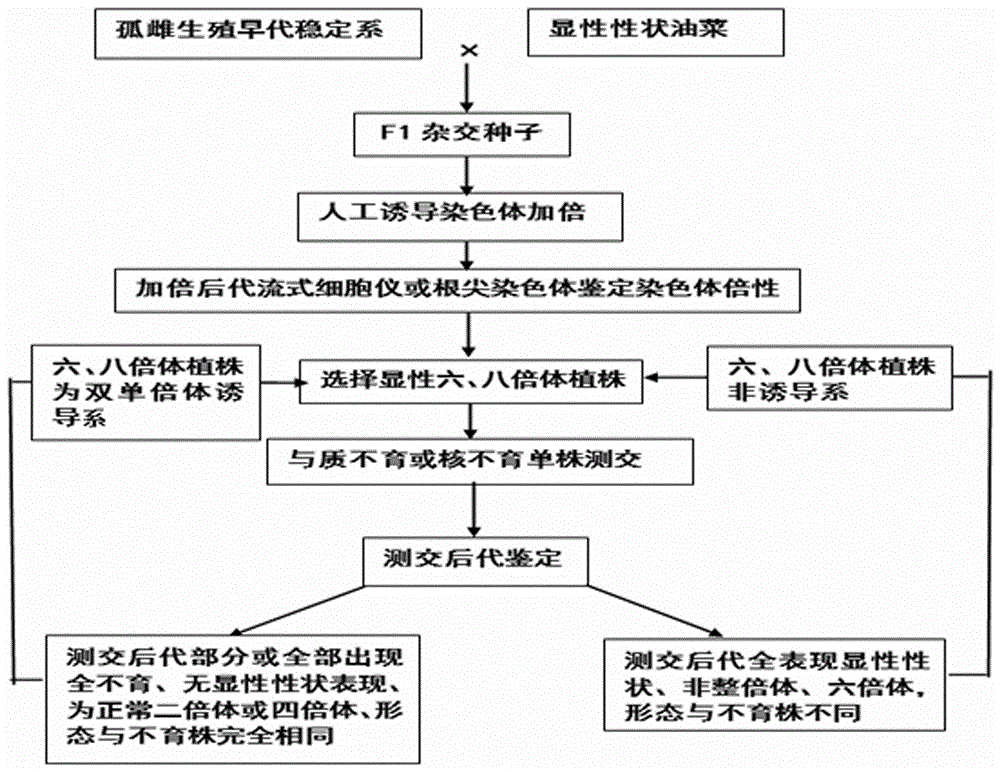
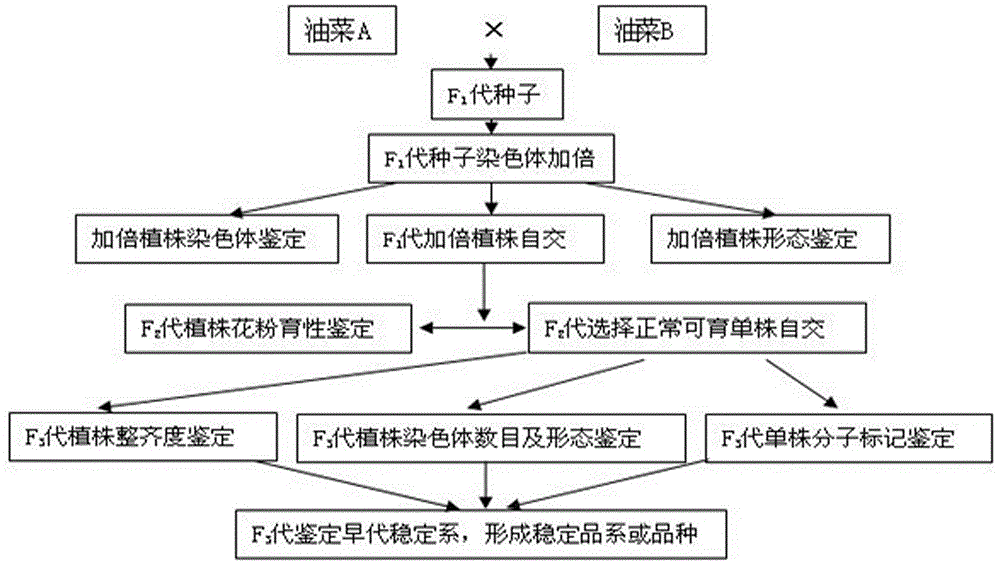
Method for creating rape genetic-stability group through rape doubled haploid inducible system in large scale
ActiveCN106069719ASimple methodEasy to masterMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissue cultureGene mappingF1 generation
The invention provides a method for creating a rape genetic-stability group through a rape doubled haploid inducible system in large scale. The method comprises the steps: 1), according to research requirements, selecting and breeding an objective trait; 2), according to the objective trait, selecting and breeding two parent materials with relatively large objective trait difference; 3), enabling the two parent materials to be hybridized; 4), pollinating parent hybridized F1 generation by using the rape doubled haploid inducible system; 5), discriminating induced progeny genetic stability; 6), performing induced progeny objective trait research to form the genetic-stability group. The method provided by the invention can be applied to three cultivated species of rapes, including cabbage type rapes (2n=38), turnip type rapes (2n=20) and mustard type rapes (2n=36), can obtain rapid (three-generation) large-scale genetic-stability DH (double haploid) groups, has a remarkable facilitation function to rape fundamental research, particularly application of genetic mapping groups to gene mapping, gene fine mapping and QTL analysis, shortens the cycle of rape fundamental research, and reduces the labor and material investments.
Owner:CHENGDU ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
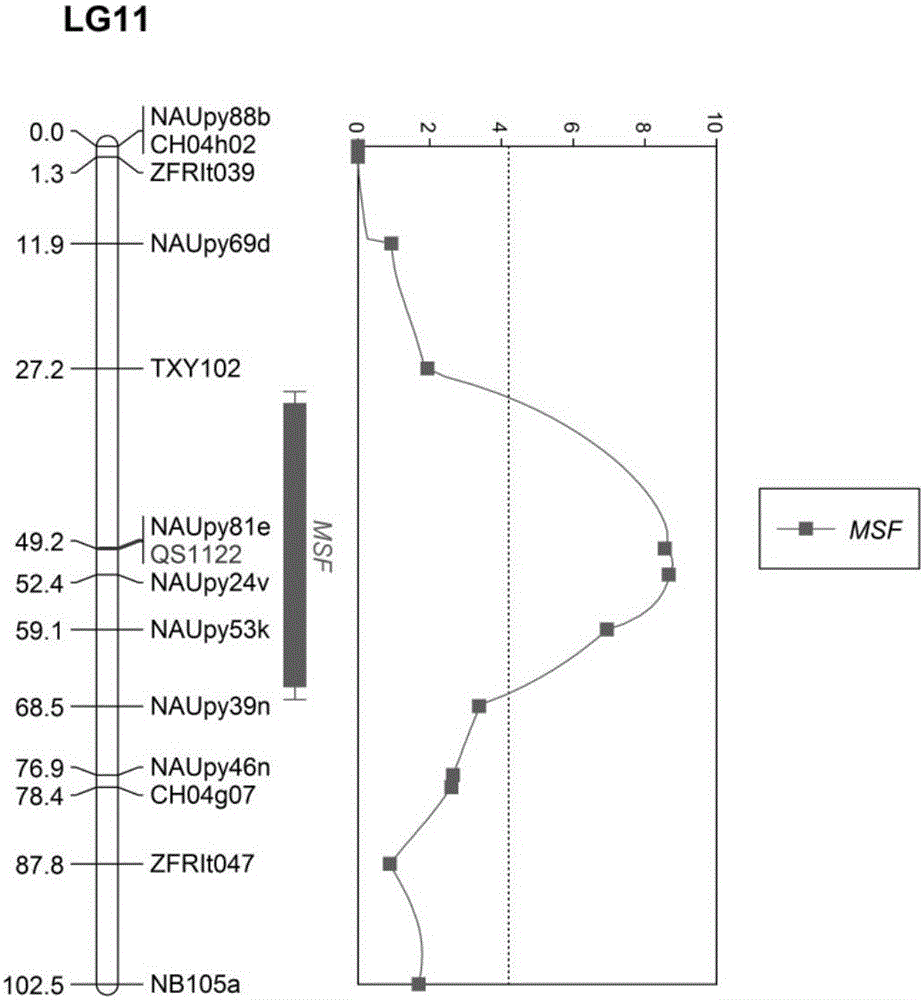
Molecular marker of pear fruit single fruit weight main-effect QTL (quantitative trait loci) site MSF, and application thereof
InactiveCN105803083AEasy to separateGuaranteed accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPEARAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the field of pear molecule breeding, and provides a molecular marker of a pear fruit single fruit weight main-effect QTL (quantitative trait loci) site, and application thereof. A starkrimson and Wanxiu pear combined genetic linkage map is built by SSR (simple sequence repeat) marker; the pear fruit single fruit weight phenotype identification is combined; in addition, an interval mapping method is used for QTL analysis; the existence of the main-effect QTL site is detected at the eleventh linkage group of the combined linkage map; the contribution rate of the main-effect QTL site is 51.9 percent. The SSR marker tightly linked with the main-effect QTL site is QS1122-135, and the genetic distance is 4.37cm. The obtained pear fruit single fruit weight main-effect QTL molecular marker can be used for early selection on the basis of fruit characters of single fruit weight; the important theoretical and practice guidance significance is realized for improving the breeding efficiency.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU FRUIT RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Genetic marker linked to gene locus involved in barley resistance to yellow mosaic disease and use thereof
InactiveCN1934254AShorten the breeding periodReduce laborMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyDiseaseQtl analysis
Through creation of a detailed linkage map of barley and QTL analysis thereof, there have been found five genetic markers linked to gene locus involved in barley resistance to yellow mosaic disease and situated on barley 1H chromosome, two genetic markers linked to gene locus involved in barley resistance to yellow mosaic disease and situated on barley 2H chromosome barley resistance to yellow mosaic disease, five genetic markers linked to gene locus involved in barley resistance to yellow mosaic disease and situated on barley 3H chromosome, four genetic markers linked to gene locus involved in barley resistance to yellow mosaic disease and situated on barley 4H chromosome, and two genetic markers linked to gene locus involved in barley resistance to yellow mosaic disease and situated on barley 5H chromosome.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Plant having increased resistance or susceptibility to 4-hppd inhibitor
ActiveUS20150047066A1Efficient productionIncrease resistanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementInhibitor resistanceQtl analysis
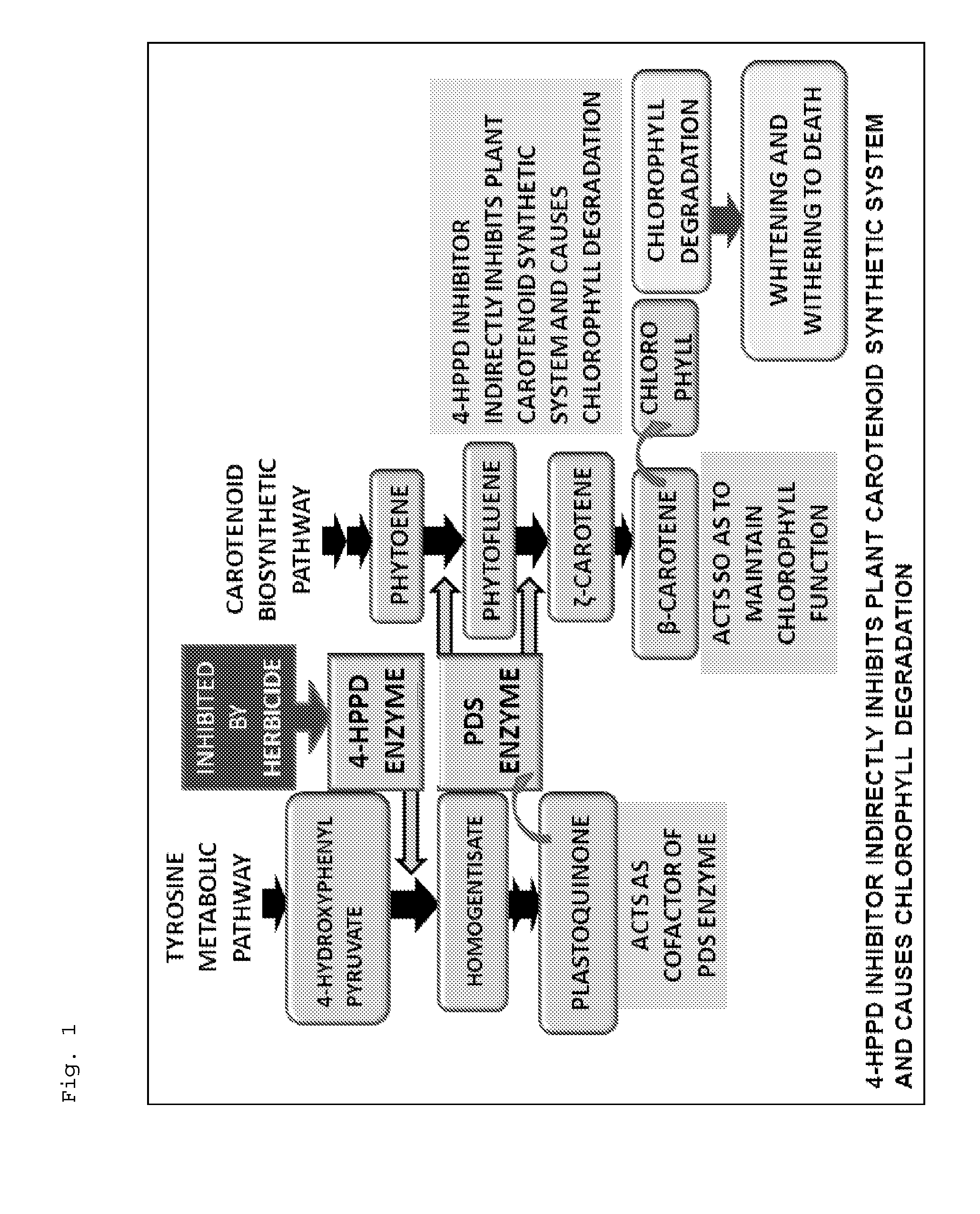
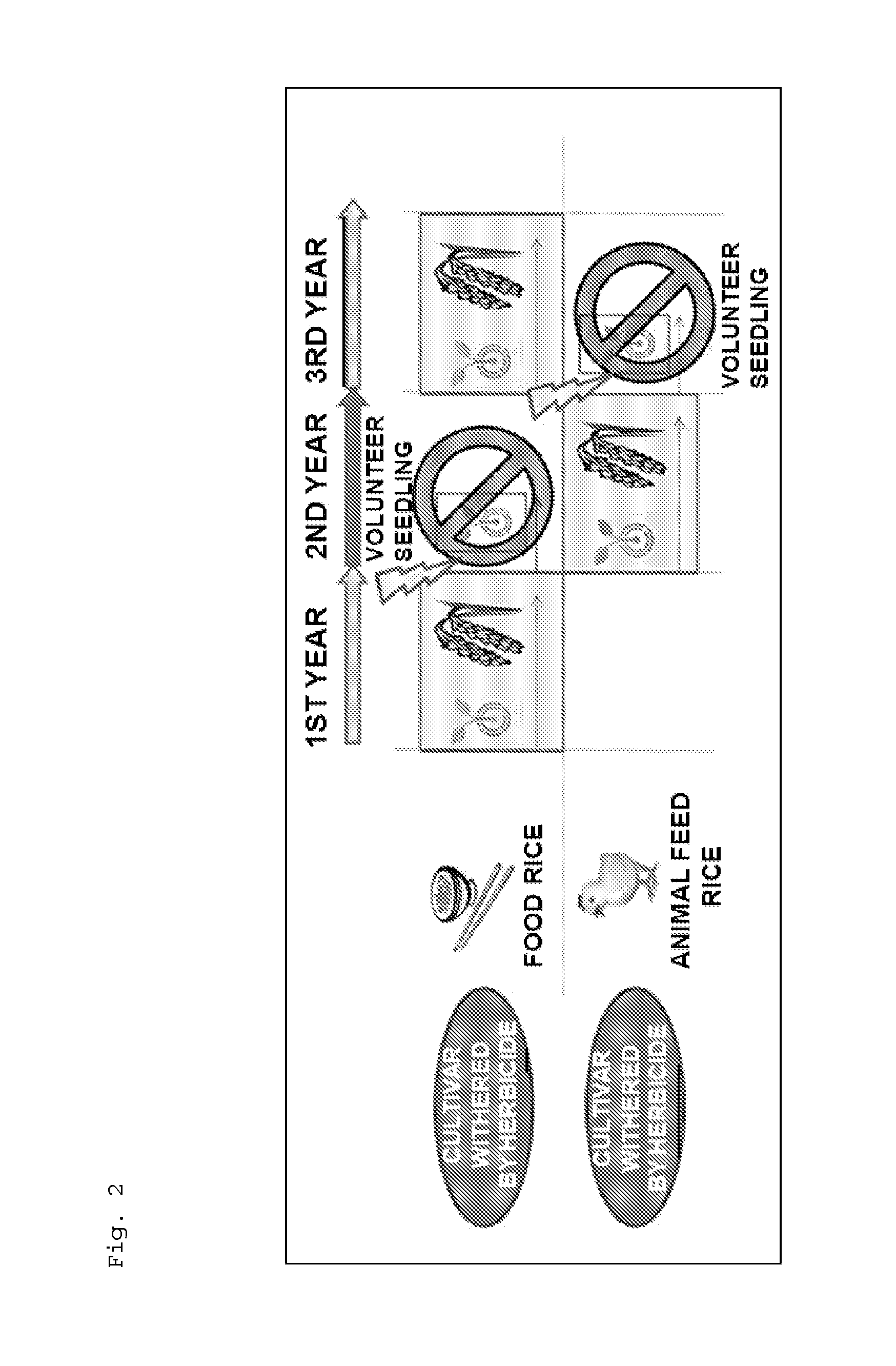
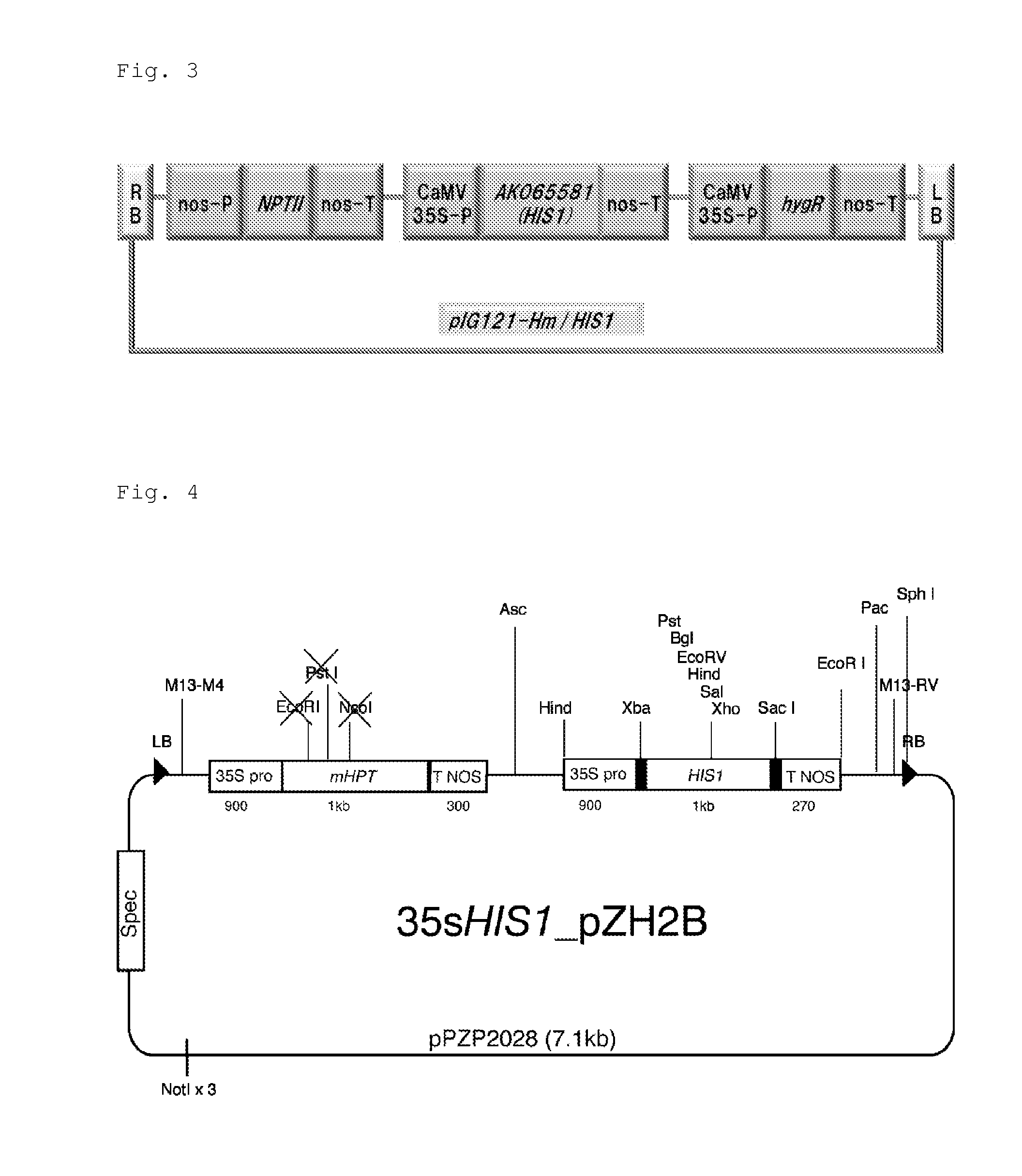
By a QTL analysis and so forth using 4-HPPD inhibitor-susceptible rice and 4-HPPD inhibitor-resistant rice, a hypothetical gene (HIS1 gene) of an iron / ascorbate-dependent oxidoreductase gene located on a short arm of chromosome 2 of rice has been identified as a 4-HPPD inhibitor-resistance gene. Further, it has also been revealed that a homologous gene (HSL1 gene) of the HIS1 gene is located on chromosome 6 of rice. Furthermore, it has been found out that utilizations of these genes make it possible to efficiently produce a plant having increased resistance or susceptibility to a 4-HPPD inhibitor and to efficiently determine whether a plant has resistance or susceptibility to a 4-HPPD inhibitor.
Owner:NAT AGRI & FOOD RES ORG +1
SSR primer group of taro and application thereof
ActiveCN111455085AHigh polymorphic percentageVerify that the amplification effect is goodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme digestionGenetic diversity
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular markers, especially to a primer group of a taro and application thereof. According to the invention, the taro is used as a material, and the DNA of the taro is extracted and subjected to enzyme digestion, sequencing and analysis to obtain corresponding SSR primers, so more effective SSR markers can be provided for application research of genetic diversity and genetic relationship of the taro; analysis shows that the primers have the characteristic of high polymorphic percentage, and amplification effect is better when the primers are used for verification; selection of the primer group provides a valuable genetic tool for research, such as QTL analysis, genetic relationship identification, genetic diversity research and heterosis prediction, of the taro in genetic breeding, and a reference basis can be provided for reasonable selection and matching of breeding parents of the taro and innovative utilization of taro germplasm through research on the genetic relationship between pedigree parents.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Gene mapping multi-inspection method
ActiveCN104573409AIncrease profitShort cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsGene mappingQtl analysis
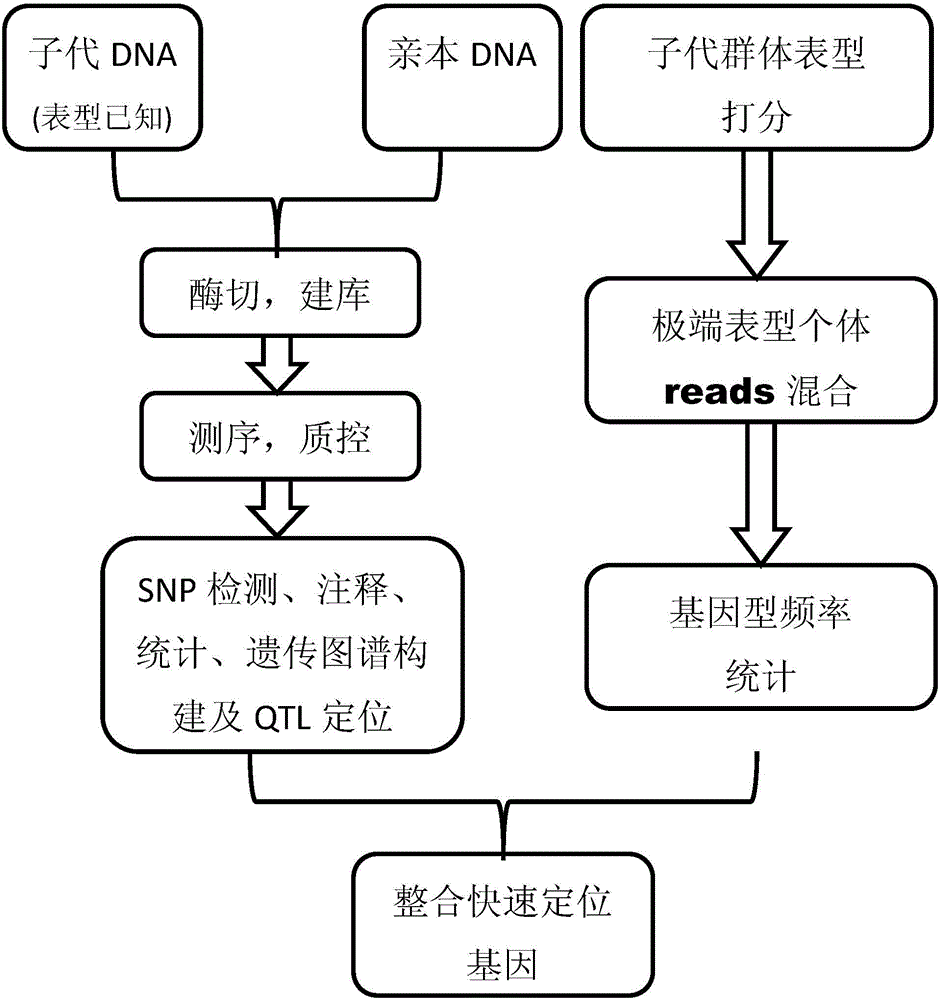
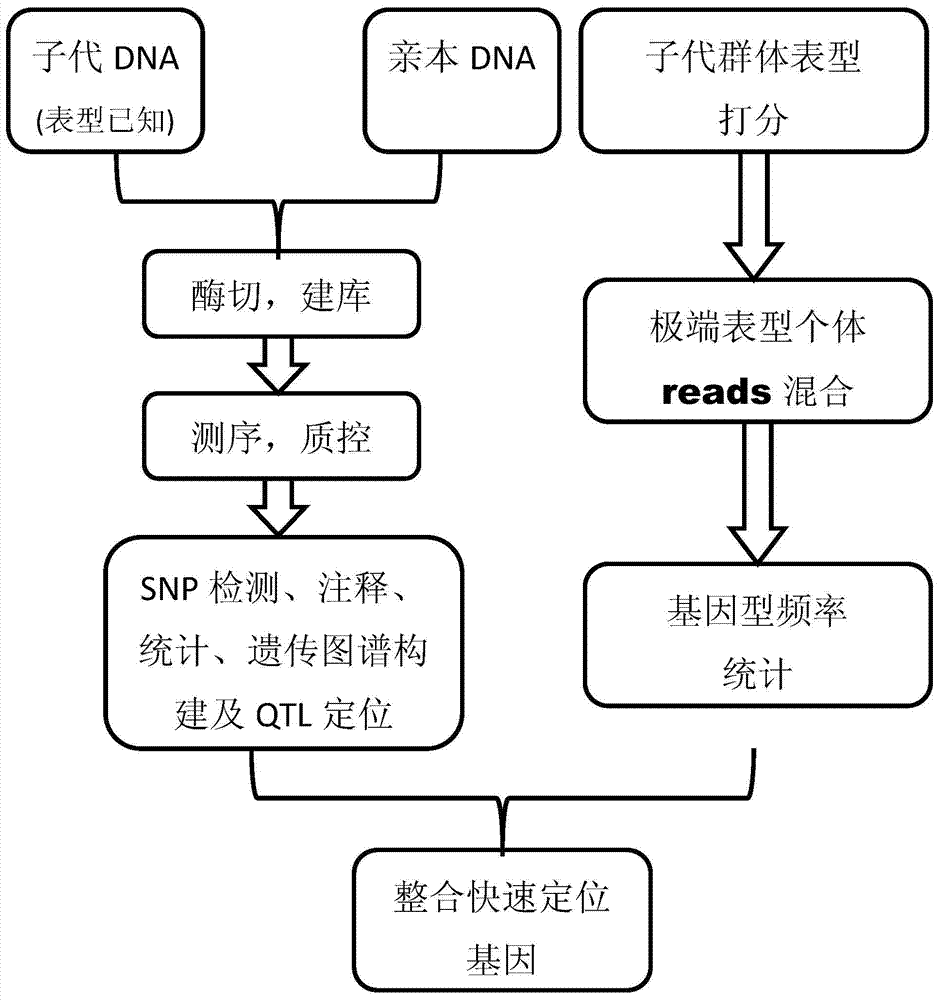
The invention discloses a gene mapping multi-inspection method. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of 1, sequencing a parent DNA sample and a filial generation DNA sample to obtain a high-precision short segment sequence; 2,comparing the obtained high-precision short segment sequence with a reference sequence, or mutually clustering to obtain accurate SNP information; 3, converting the SNP information into group SNP, further converting into a standard molecular standard format, creating a genetic map, and performing QTL analysis on the basis of the genetic map to obtain QTL seat information; 4, identifying the phenotype information of filial generation DNA sample, accurately counting the phenotype value distribution, grouping the phenotype values according to gradient, respectively blending the high-precision short segment sequences of the filial generation DNA sample, corresponding to the extreme phenotype values, analyzing the genotype frequency distribution, and performing chi-square test and rank sum test to find out related obvious areas; 5, integrating the QTL seat information and the accurate gene mapping information obtained in step 4.
Owner:HANGZHOU HEYI GENE TECH
Molecular markers and QTL sites of free proline content of strong winter Brassia campestris L.
ActiveCN105018595AImprove screening efficiencyReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassiaQtl analysis
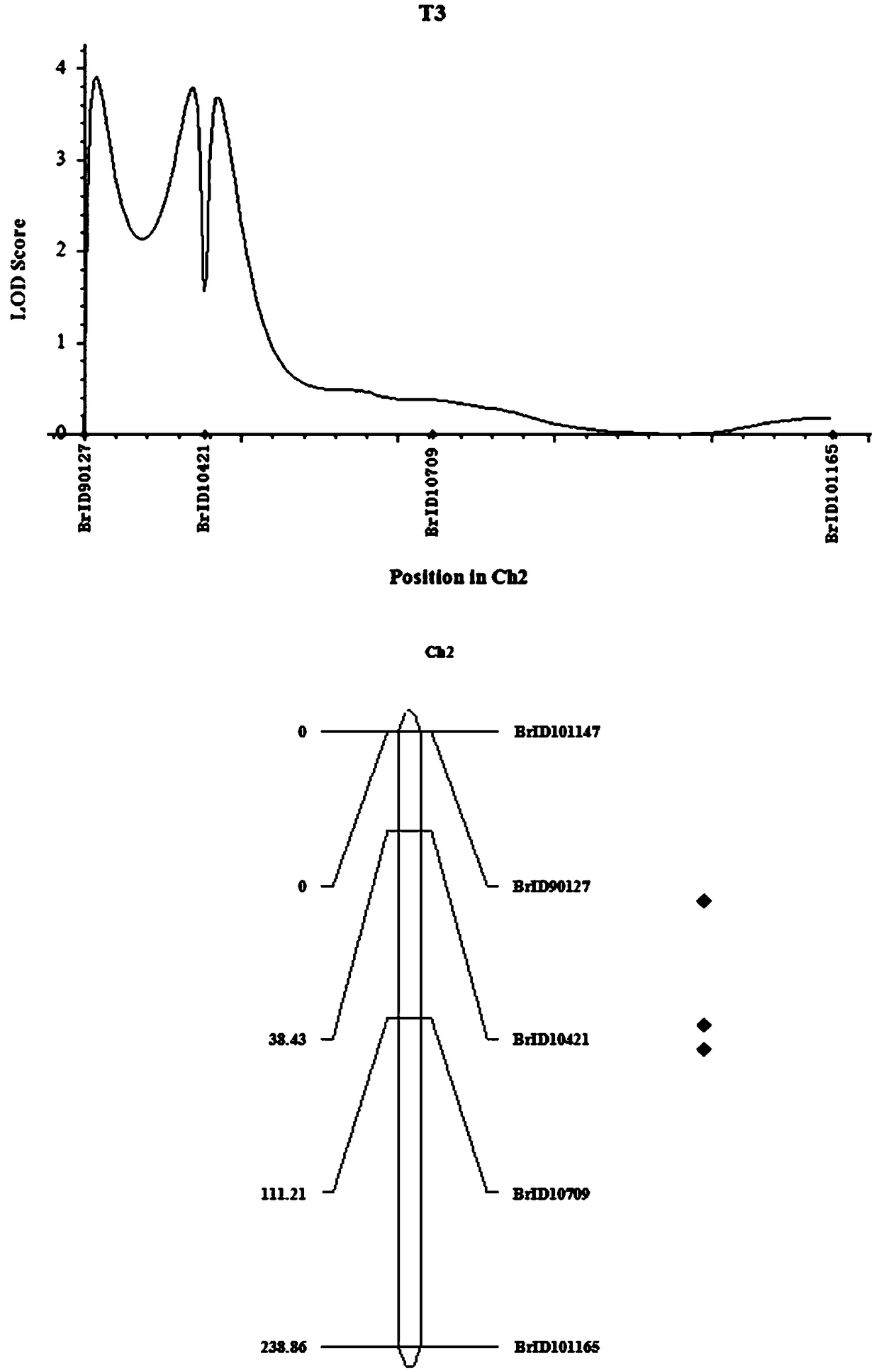
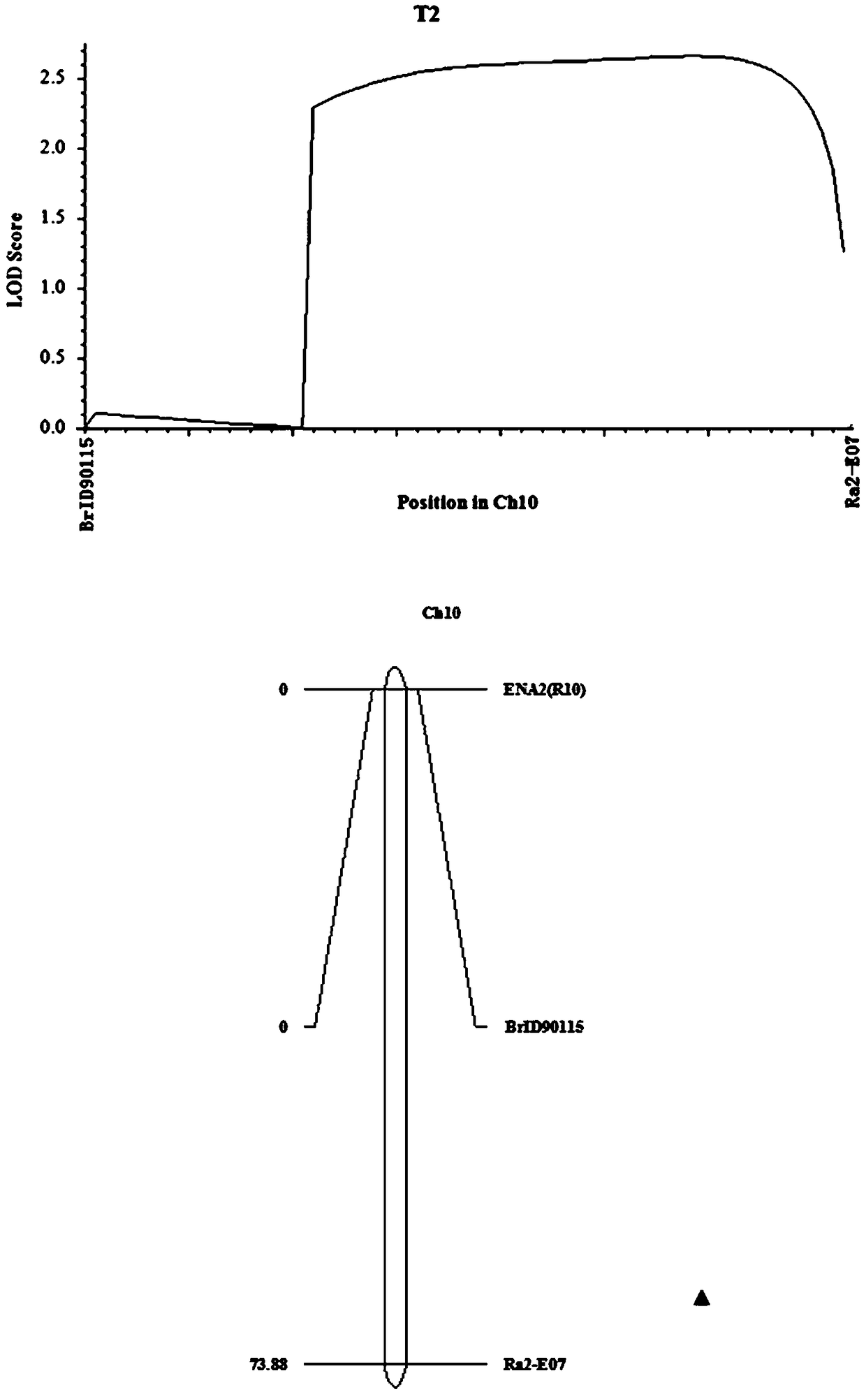
The invention discloses molecular markers and QTL sites of free proline content of strong winter Brassia campestris L. Screening comprises the following steps: (1) constructing an F2-generation segregation population through hybridization of parents obtained through multi-generation bagged self-crossing, i.e., strong winter superstrong-cold-resistance winter rape Longyou No. 7 and strong-cold-resistance winter rape Longyou No. 9; (2) extracting leaf DNAs of the two parents and the F2-generation segregation population by using a CTAB method; (3) carrying out polymorphism primer screening on the DNAs of the two parents by using SSR and InDel primer pairs; (4) constructing a genetic linkage map according to obtained genotype data of the F2-generation segregation population and carrying out QTL analysis; and (5) naming the obtained three QTL sites of the free proline content of strong winter Brassia campestris L. as Qfre.gsau-2A, Qfre.gsau-3A and Qfre.gsau-6A, respectively, and acquiring the six molecular marks linked with the free proline content of strong winter Brassia campestris L., i.e., BrID10709, BrID101165, BrID90131, BrID10157, BrID10397 and 8C0419-1.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker for regulating main effect QTL (quantitative trait loci) of hundred-grain weight of corn and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN104673924AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceQtl analysis
The invention discloses a molecular marker for regulating main effect QTL (quantitative trait loci) of hundred-grain weight of corn and application of the molecular marker. By taking general DNA of corn as a template, PCR amplification is carried out on SSR primers Sym035 and Sym119 to obtain DNA fragments which are 165 bp and 147 bp long through gel electrophoresis; a QTL for regulating hundred-grain weight of corn exists between the SSR molecular markers Sym035 and Sym119 on a Bin5.06 region on the fifth chromosome. By using similar F2: 3 colony, QTL analysis on grain length, grain width and grain thickness show that a QTL for grain width is positioned between the molecular markers Sym024 and Sym128, and the genetic distance is 13.1cM. Correlation coefficients between hundred-grain weight and grain length, grain width and grain thickness in a segregation population are respectively 0.532, 0.726 and 0.187. Reduction of hundred-grain weight of single segment substitution lines SSSL-Z22 is mainly induced by reduction of grain width.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
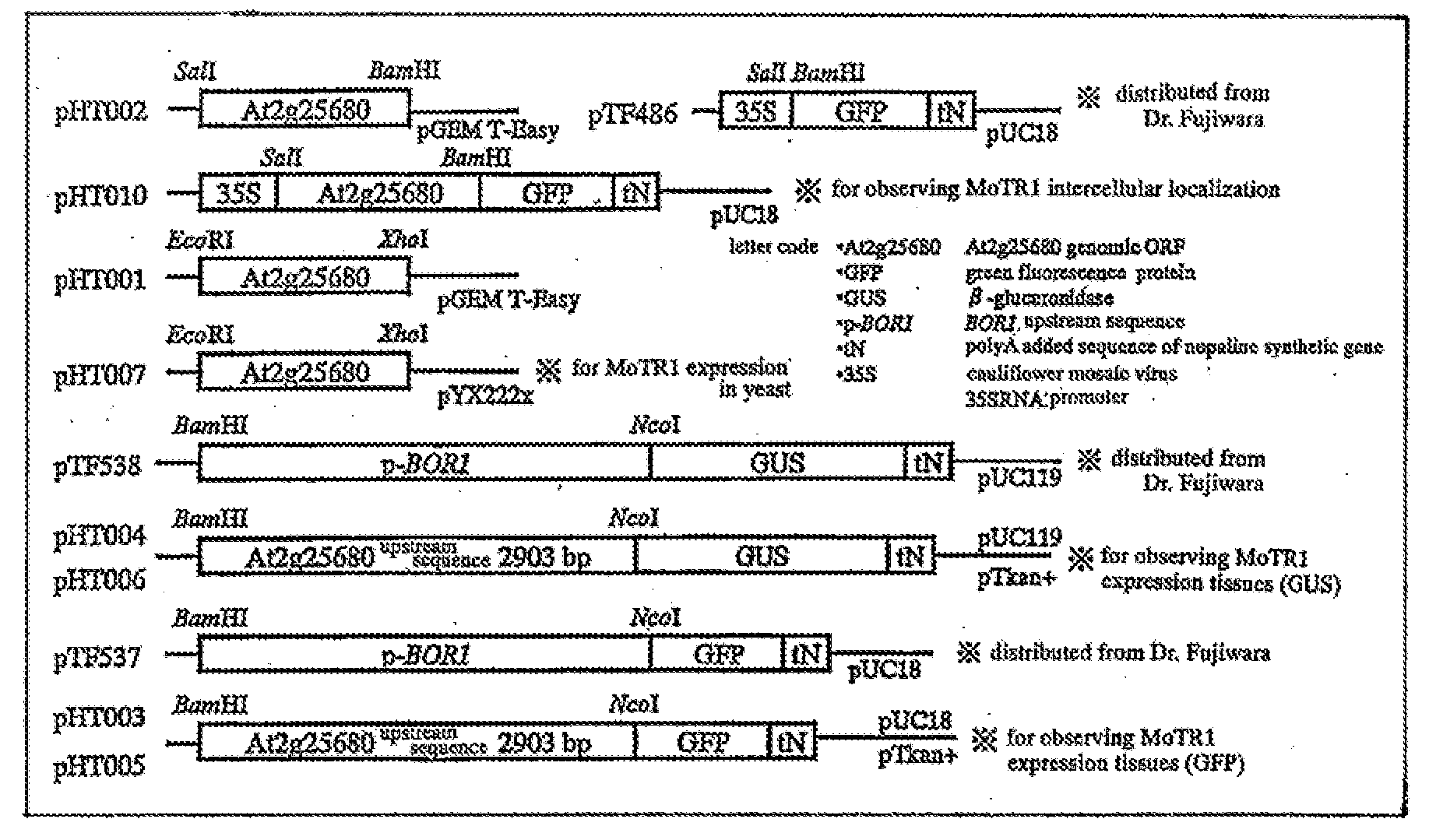
Molybdenum Transporter and Gene Thereof
InactiveUS20080216199A1Effective fertilizing methodEffective breeding strategyFungiImmunoglobulinsCation PumpQtl analysis
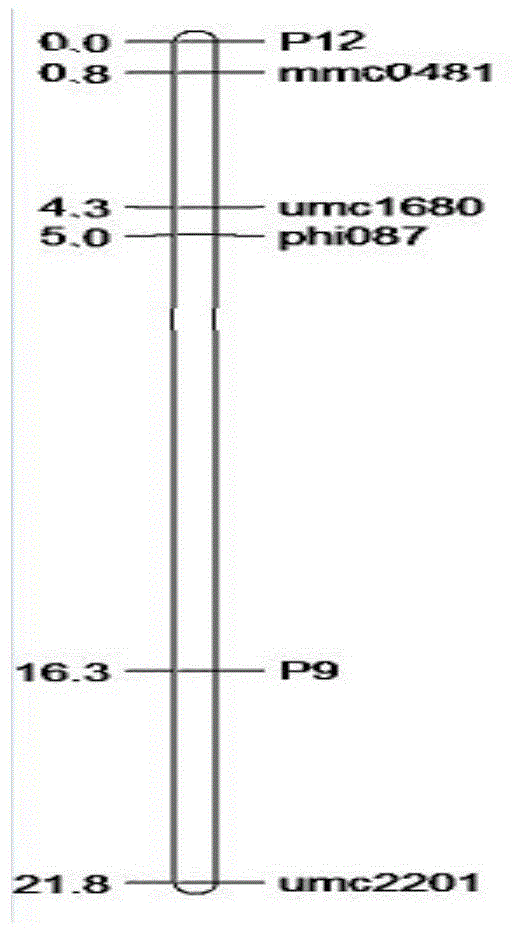
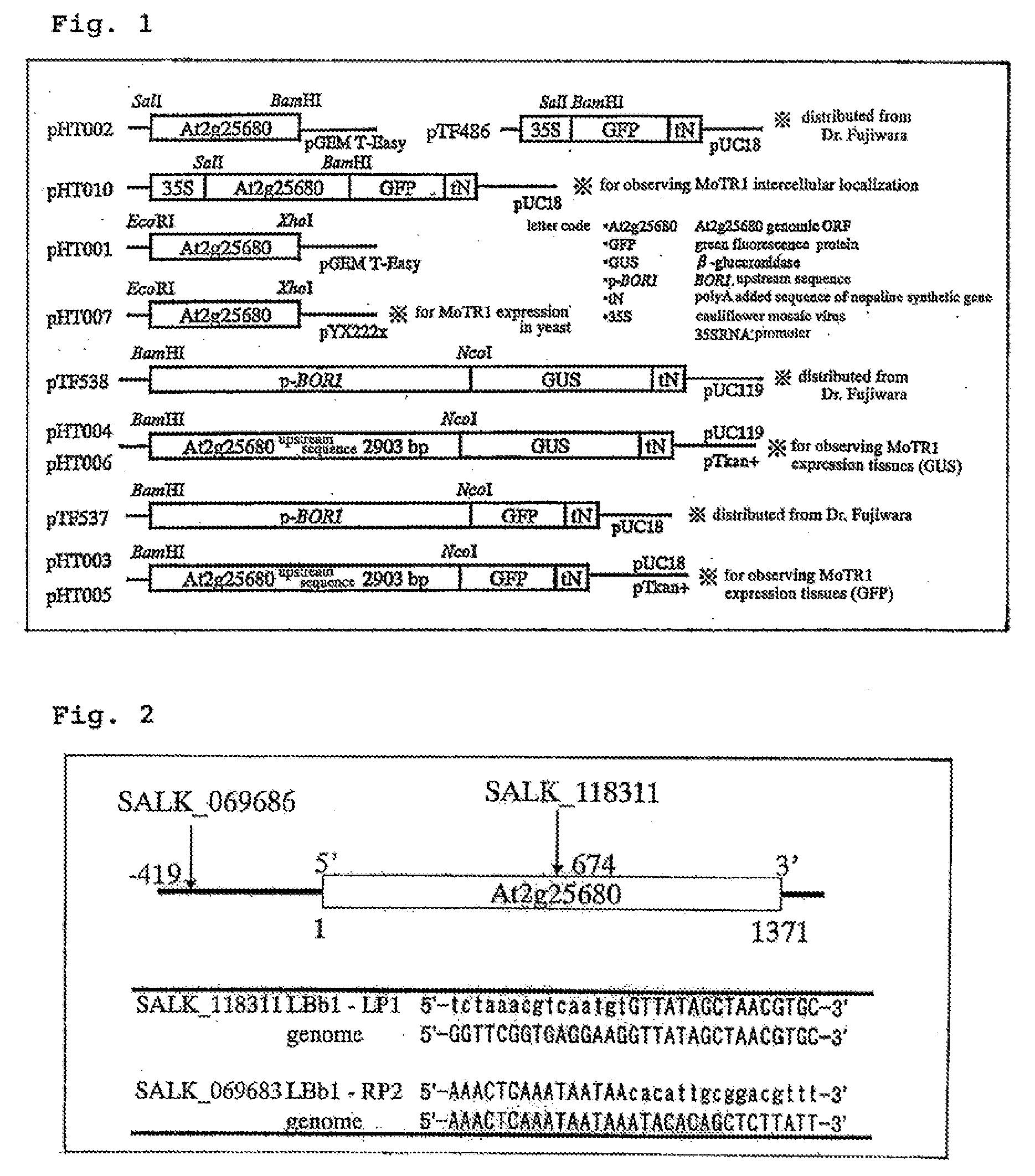
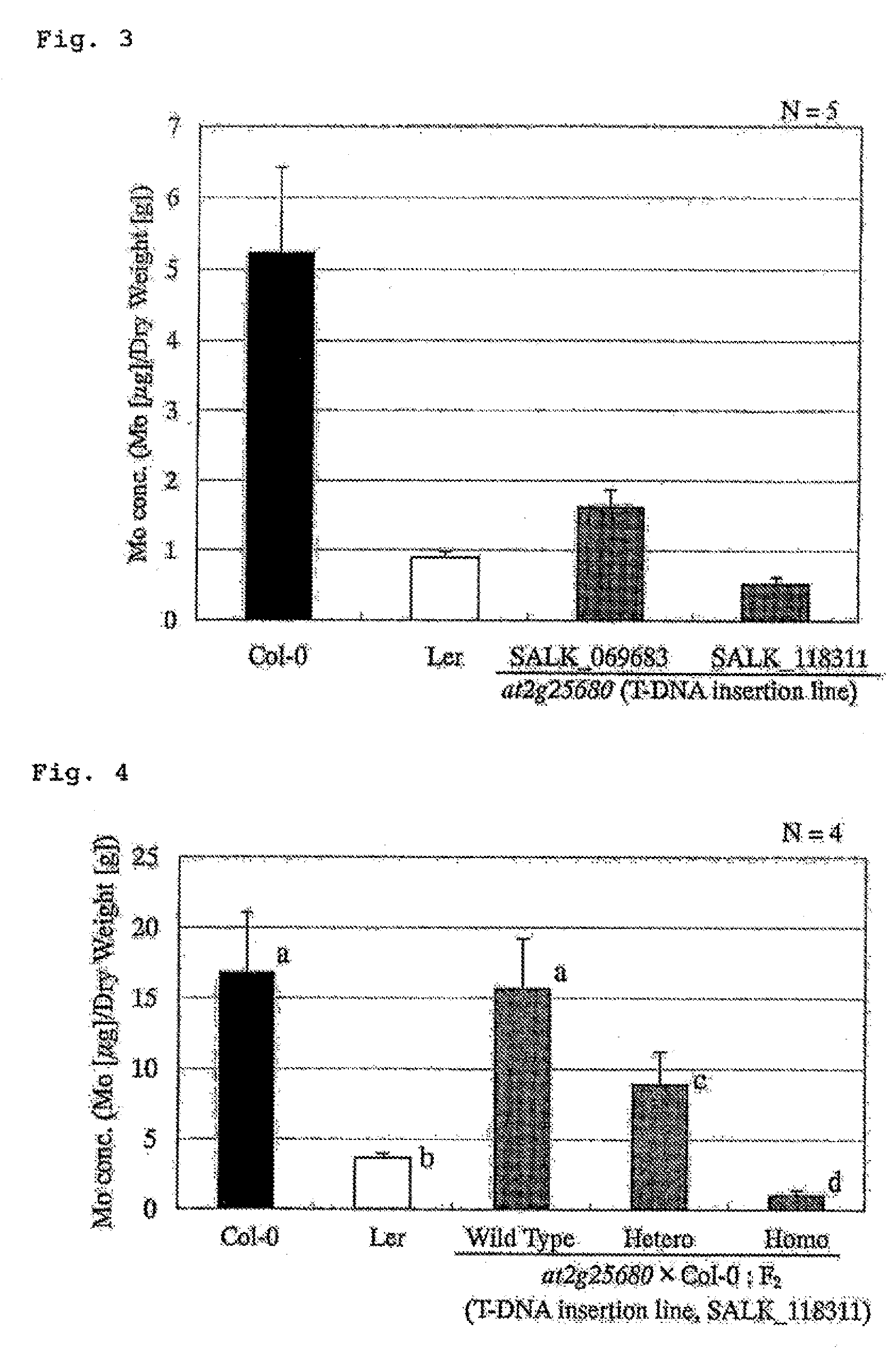
It is to provide a novel molybdenum ion transporter MoTR1 gene responsible for molybdenum transport for the first time in plants, enabling to promote effectively molybdenum absorption from the environment or molybdenum transport in vivo. By QTL analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana accessions Col-0 and Ler, it was found that QTL which dominates Mo concentration in leaves was present on the chromosome No: 2. In the present invention, the region in which the causal gene is present was limited to 172 kb, by a genetic analysis. In the region, the gene At2g25680 having a domain common to sulfate ion transporter, while its function is not revealed was present. Thus, knockout strains of 2 separate lines in which a foreign gene fragment (T-DNA) was introduced at At2g25680 were obtained, Mo concentration in leaves was measured, and MoTR1 gene was identified.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method for selecting statistically validated candidate genes
ActiveUS8170805B2Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesQtl analysisCandidate Gene Association Study
Provided herein are methods for evaluating associations between candidate genes and a trait of interest in a population. The methods include a combination of genome-wide association analysis and one or more of nested association mapping (NAM), expression QTL analysis (eQTL), and allele epistastic analysis (AEA). Markers are selected or prioritized if they are shown to be positively-correlated with a trait of interest using GWA and a combination of one or both of NAM and eQTL. Also provided are models for evaluating the association between a candidate marker and a trait in a nested population of organisms. These methods include single marker regression and multiple marker regression models. Markers identified using the methods of the invention can be used in marker assisted breeding and selection, as genetic markers for constructing linkage maps, for gene discovery, for identifying genes contributing to a trait of interest, and for generating transgenic organisms having a desired trait.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) linked molecular marker for controlling corn female parent haploidy production and application thereof
ActiveCN106191263APromote engineering applicationReduce blindnessMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceQtl analysis
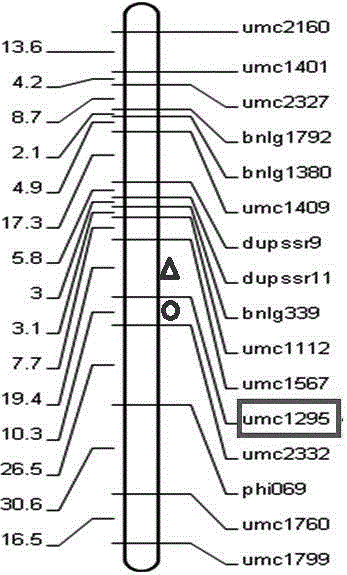
The invention discloses a QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) linked molecular marker for controlling corn female parent haploidy production. The molecular marker comprises a primer umc1295, wherein the sequence of the primer umc1295 is SEQ ID NO: F1:5'-GTCGATCTTCCTCCCCATCA-3'; SEQ ID NO: R1: 5'-CGTTTCTATCTATGGAGGAGTGCG-3'. Through SSR molecular marker and QTL analysis, a QTL locus for controlling the corn female parent haploidy production exists on a seventh chromosome, is linked with the molecular marker umc1295, and is located on 7.04bin of the seventh chromosome. The analysis result indicates that whether the marker exists or not directly relates to the haploidy production capacity of plants, and the marker can be used for forecasting female parent haploidy production frequency. Compared with the prior art, through the detection of the molecular marker, the haploidy production capacity of corn female parent can be forecasted in an early stage, so that the blindness of induction is reduced, the induction efficiency is improved, and the engineering application of a haploidy breeding technique is accelerated.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Genetic markers linked to fusarium head blight-resistance factor and utilization thereof
InactiveUS20070162997A1Easy to judgeImprove isolationMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesQtl analysisResistance Factors
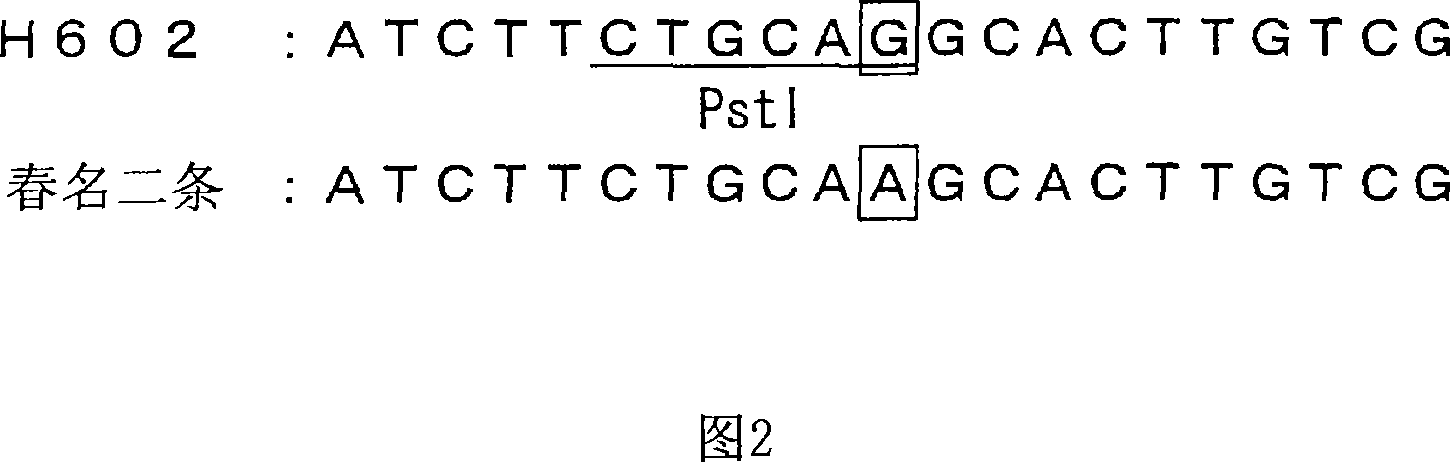
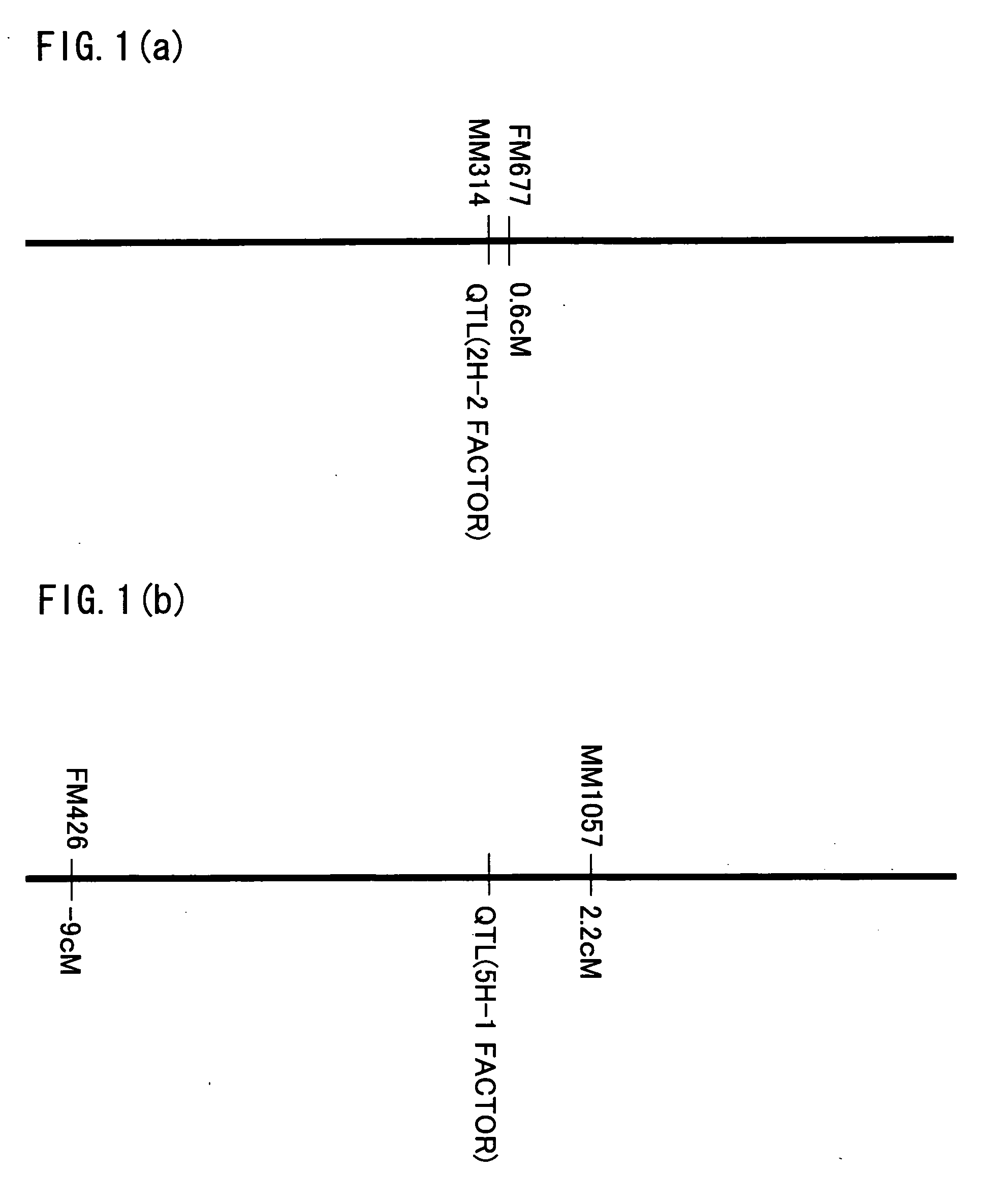
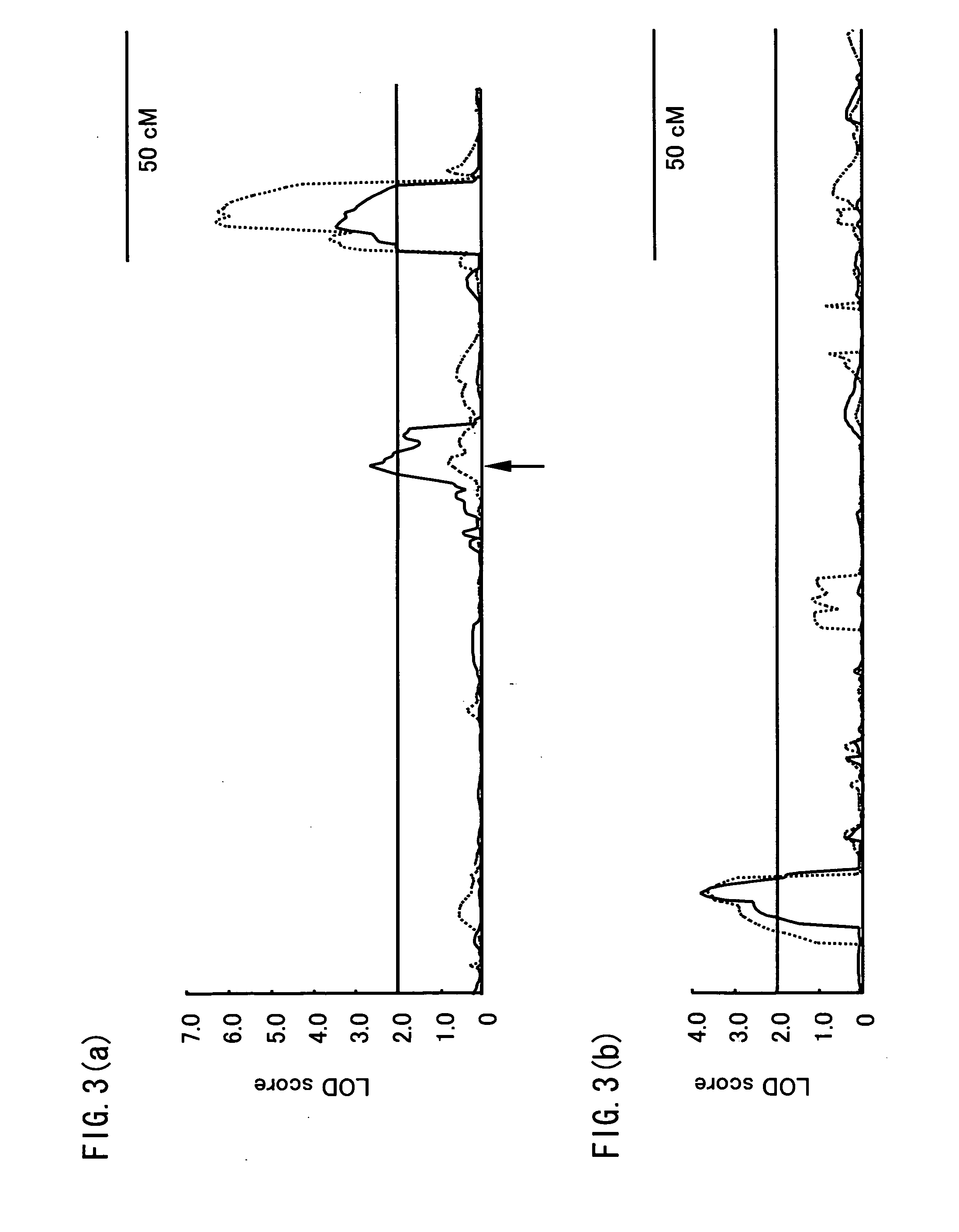
QTL analysis on the resistance to Fusarium head blight is performed by using an RI line (RHI population) grown by crossing Russia 6 (two-row, resistant) with H.E.S.4 (six-row, susceptible), an RI line (RI2 population) grown by crossing Harbin 2-row (resistant) with Turkey 6 (susceptible), and a DH line (DHHS population) grown by crossing Haruna Nijo (resistance) with H602 (susceptible). As a result, QTLs are detected on the 2H, 4H and 5H chromosomes in the RHI population, on the 2H, 4H and 6H chromosomes in the RI2 population and on the 2H, 4H and 5H chromosomes in the DHHS population. Furthermore, genetic markers linked to these QTLs (MM314, FM677, FM426, MM1057, MMtgaEatc128, FMgcgEatc 530, FXLRRfor_XLRRrev119, FMacgEcgt288, HVM67, FMataEagc408, HVM11, Bmag125, k04002, k05042, k03289, HvLOX and k00835) are found out.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
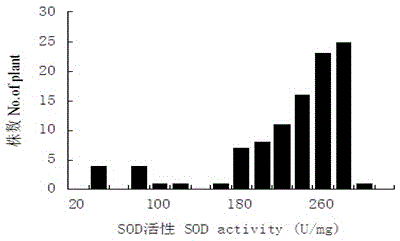
Strong-winter winter rape (Brassica campestris) SOD enzyme molecular marker and QTL locus
ActiveCN105039508AImprove screening efficiencyReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassicaGenetics
The invention discloses a strong-winter winter rape (Brassica campestris) SOD enzyme molecular marker and a QTL locus. A screening process includes following steps: (1) performing hybridization between a multi-generation bagged-selfing parent strong-winter super-cold-winder-resistant rape 'Longyou #7' and strong-cold-winder-resistant rape 'Longyou #9' to construct an F2-generation segregation population; (2) extracting leaf DNA of the two parents and the F2-generation segregation population through the CTAB method; (3) performing polymorphic primer screening to the two parent DNA through SSR and InDel primers; (4) obtaining genotype data through the F2-generation segregation population to construct a genetic linkage map and carry out QTL analysis; and (5) obtaining two QTL loca of SOD enzyme of the strong-winter winter rape (Brassica campestris), which are respectively named Qsod.gsau-6A and Qsod.gsau-7A. Four molecular markers, which are linked with the QTL loca of the SOD enzyme of the strong-winter winter rape (Brassica campestris), are respectively named Ra1-F06, Ra2-D04, 8C0108 and Ol12E03.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
A kind of Taro ssr primer set and its application
ActiveCN111455085BHigh polymorphic percentageVerify that the amplification effect is goodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme digestionGenetic diversity
The present invention relates to the technical field of molecular markers, in particular to a taro SSR primer set and its application. The present invention uses taro as a material, extracts taro DNA, performs enzymatic digestion, sequencing, and analysis to obtain corresponding SSR primers, which can be used for the heredity of taro The applied research on diversity and genetic relationship provides more effective SSR markers. After analysis, this primer has the characteristics of high polymorphic percentage, and the effect of using this primer to verify and amplify is better; the choice of this primer set is Taro in genetic breeding It provides valuable genetic tools for research such as QTL analysis, phylogenetic relationship identification, genetic diversity research and heterosis prediction, and through the study of the genetic relationship between pedigree parents, it can be used for the rational selection of breeding parents of taro and the innovation of taro germplasm. Use to provide reference.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
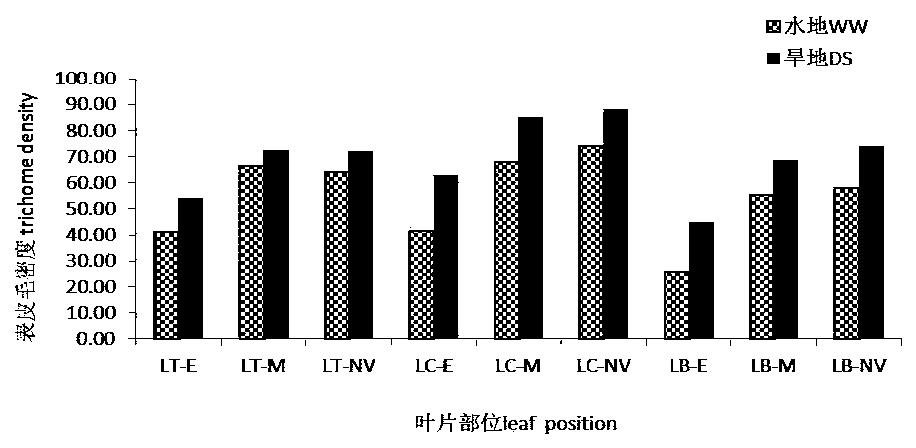
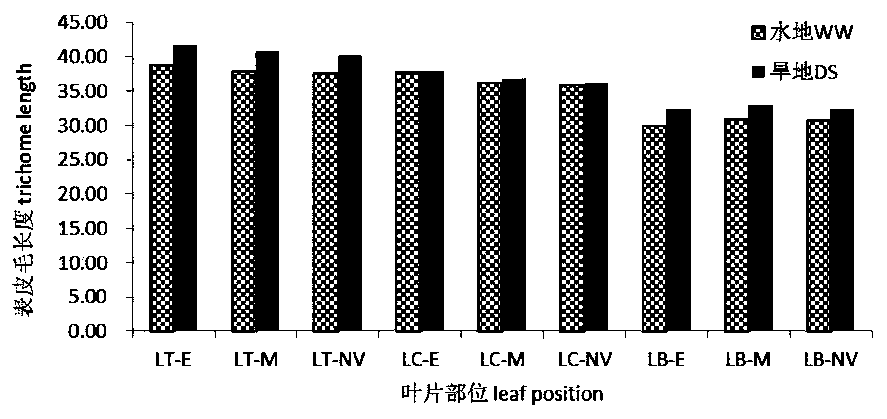
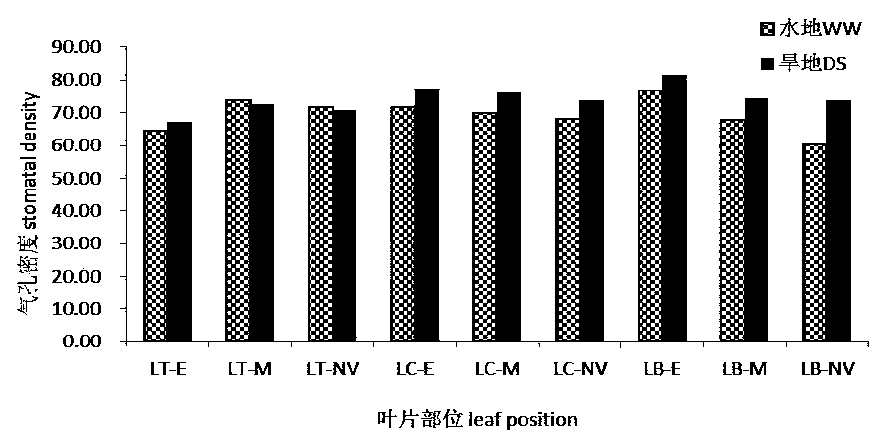
QTL sites controlling relevant characters of epidermal hair and stomata of wheat and analysis method
ActiveCN110791587AAccurate method for measuring phenotypic dataEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStomaGenetics
The invention discloses a group of QTL (quantitative trait locus) sites controlling relevant characters of epidermal hair and stomata of wheat and an analysis method and belongs to the field of molecular biology. The QTL sites comprise Qtd-2A-1, Qtd-2B-1, Qtd-7D-1, Qtl-7D-1, Qtl-7D-2, Qsl-6A-1, Qsl-5A-2 and Qsl-4A. The QTL analysis method comprises the steps of: (1) constructing a wheat DH population, (2) collecting phenotype data of the relevant characters of the epidermal hair and the stomata of the wheat under normal irrigation and drought stress conditions, and (3) performing QTL analysisusing a genetic linkage map according to the phenotype data. The QTL sites and the analysis method have the benefits that the influence of the drought stress condition on the relevant characters of the epidermal hair and the stomata is researched; at the same time, QTL analysis is performed on the relevant characters of the epidermal hair and the stomata in different positions of leaves under thetwo moisture conditions; and the stable expression QTL sites in different environments are explored.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Molecular Marker and QTL Mapping of Cat Enzyme in Strong Winter Brassica napus
ActiveCN104988212BImprove screening efficiencyReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassicaQtl analysis
The invention discloses strong winterness brassica campestris L. CAT enzyme molecule markers and QTL loci. The screening steps are that (1), multi-generation bagging selfing parent strong winterness superstrong cold resistant winter rape 'the 7th Longyou' and strong cold resistant winter rape 'the 9th Longyou' are utilized for hybridization to construct a generation F2 segregation population; (2), a CTAB method is utilized for extracting leaf DNA of the generation F2 segregation population and the two parents; (3), SSR and InDel primers are utilized for performing polymorphism primer selection on the DNA of the two parents; (4), genetype data are obtained through the generation F2 segretation population to construct a genetic linkage map and QTL analysis; and (5), three strong winterness brassica campestris L. CAT enzyme QTL loci are obtained and named as Qcat.gsau-2A-1, Qcat.gsau-2A-2 and Qcat.gsau-2A-3 respectively; and three molecule markers linked with the strong winterness brassica campestris L. CAT enzyme QTL loci are BrID90127,BrID10421 and BrID10709.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Multiple testing methods for gene mapping
ActiveCN104573409BIncrease profitShort cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsGene mappingSequence analysis
The invention discloses a multiple detection method for gene positioning, which is characterized in that it comprises: step 1: sequence the DNA samples of parents and offspring to obtain high-precision short fragment sequences; step 2: sequence the obtained high-precision DNA samples The short fragment sequence is compared with the reference sequence or clustered with each other to obtain accurate SNP information; Step 3: convert the SNP information into a population SNP, and further convert it into a standard molecular standard format to construct a genetic map, and on the basis of the genetic map Step 4: Identify the phenotypic information of the progeny DNA samples, and accurately count the distribution of phenotypic values, group the phenotypic values according to gradients, and group the extreme phenotypic values corresponding to the offspring The high-precision short fragment sequences of the first-generation DNA samples are mixed separately, the genotype frequency distribution is analyzed, and the relevant significant regions are found through the chi-square test and the rank sum test; Step 5: Integrate the QTL locus information and Step 4 to obtain accurate gene positioning information.
Owner:HANGZHOU HEYI GENE TECH
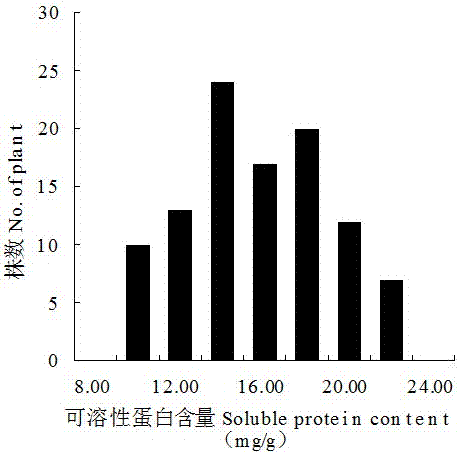
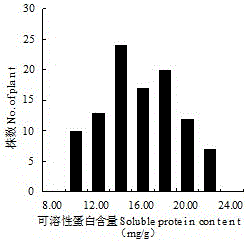
Molecular markers and qtl localization of soluble protein content in strong winter Chinese cabbage
ActiveCN104988138BImprove screening efficiencyReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassicaF2 population
The present invention discloses molecular markers and QTL sites of soluble protein content in Chinese cabbage-type winter rapeseed with strong winter nature, and the screening steps include: (1) parent strong winter nature super strong cold winter rapeseed 'Longyou 7' which is self-crossed by bagging for multiple generations '' and rapeseed 'Longyou 9' with strong cold winter resistance to construct F2 segregation population; (2) CTAB method was used to extract leaf DNA of two parents and F2 generation segregation population; (3) SSR and InDel primers were used to analyze the DNA Screening of polymorphic primers; (4) Construction of genetic linkage map and QTL analysis of genotype data obtained from F2 segregation population; (5) Two QTL loci for soluble protein content in Chinese cabbage-type winter rape were obtained, named Qsol.gsau‑8A; 2 Molecular Markers BrID10839 and Ra2‑E12 Linked to QTL Loci for Soluble Protein Content in Hardy Winter Brassica napus.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Corn ear weight main effect qtl, its acquisition method and application
The invention provides a maize single panicle weight main effect QTL, as well as an acquisition method and application thereof. The QTL comprises qEW-1, qEW-2, qEW-3, qEW-4 and qEW-5. The method comprises the following steps: configuring cross combination by taking a high-yield early-maturity maize inbred line SG5 as a female parent and a maize inbred line SG7 with relatively poor yield trait as a male parent, and constructing an F2 genetic group of the cross combination; performing GBS sequencing-basing typing on the F2 genetic group, and performing genotyping by combining differential SNP validated based on SG5 and SG7 parents; investigating the yield trait of single F2 panicle, performing QTL analysis on the F2 single panicle yield trait by utilizing a winQTLcart2.5 software composite interval mapping method, and analyzing the chromosome region of the main effect QTL and the genetic effect. According to the method, a theoretic base is provided to excavating and controlling the maize single panicle weight main effect QTL and linked marker, a molecular marker closely linked with the target QTL is acquired, and foundation is laid to maize single panicle yield trait QTL candidate gene prediction, cloning and molecular mark assisted breeding.
Owner:LIUPANSHUI NORMAL UNIV
Strong winterness brassia campestris L. soluble protein content molecular markers and QTL location
ActiveCN104988138AImprove screening efficiencyReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassiaQtl analysis
The invention discloses strong winterness brassia campestris L. soluble protein content molecule markers and QTL loci. The screening steps are that (1), multi-generation bagging selfing parent strong winterness superstrong cold resistant winter rape 'the 7th Longyou' and strong cold resistant winter rape 'the 9th Longyou' are utilized for hybridization to construct a generation F2 segregation population; (2), a CTAB method is utilized for extracting leaf DNA of the generation F2 segregation population and the two parents; (3), SSR and InDel primers are utilized for performing polymorphism primer selection on the DNA of the two parents; (4), genetype data are obtained through the generation F2 segretation population to construct a genetic linkage map and QTL analysis; and (5), two strong winterness brassia campestris L. soluble protein content QTL loci are obtained and named as Qsol.gsau-8A; and two molecule markers linked with the strong winterness brassia campestris L. soluble protein content QTL loci are BrID10839 and Ra2-E12.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Method for selecting statistically validated candidate genes
Provided herein are methods for evaluating associations between candidate genes and a trait of interest in a population. The methods include a combination of genome-wide association analysis and one or more of nested association mapping (NAM), expression QTL analysis (eQTL), and allele epistastic analysis (AEA). Markers are selected or prioritized if they are shown to be positively-correlated with a trait of interest using GWA and a combination of one or both of NAM and eQTL. Also provided are models for evaluating the association between a candidate marker and a trait in a nested population of organisms. These methods include single marker regression and multiple marker regression models. Markers identified using the methods of the invention can be used in marker assisted breeding and selection, as genetic markers for constructing linkage maps, for gene discovery, for identifying genes contributing to a trait of interest, and for generating transgenic organisms having a desired trait.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Molecular marker of QTL (quantitative trait loci) loci in flowering period of maize chromosome 9 and application of molecular marker of QTL loci in flowering period of maize chromosome 9
ActiveCN108977569APleiotropicNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomicsAgricultural science
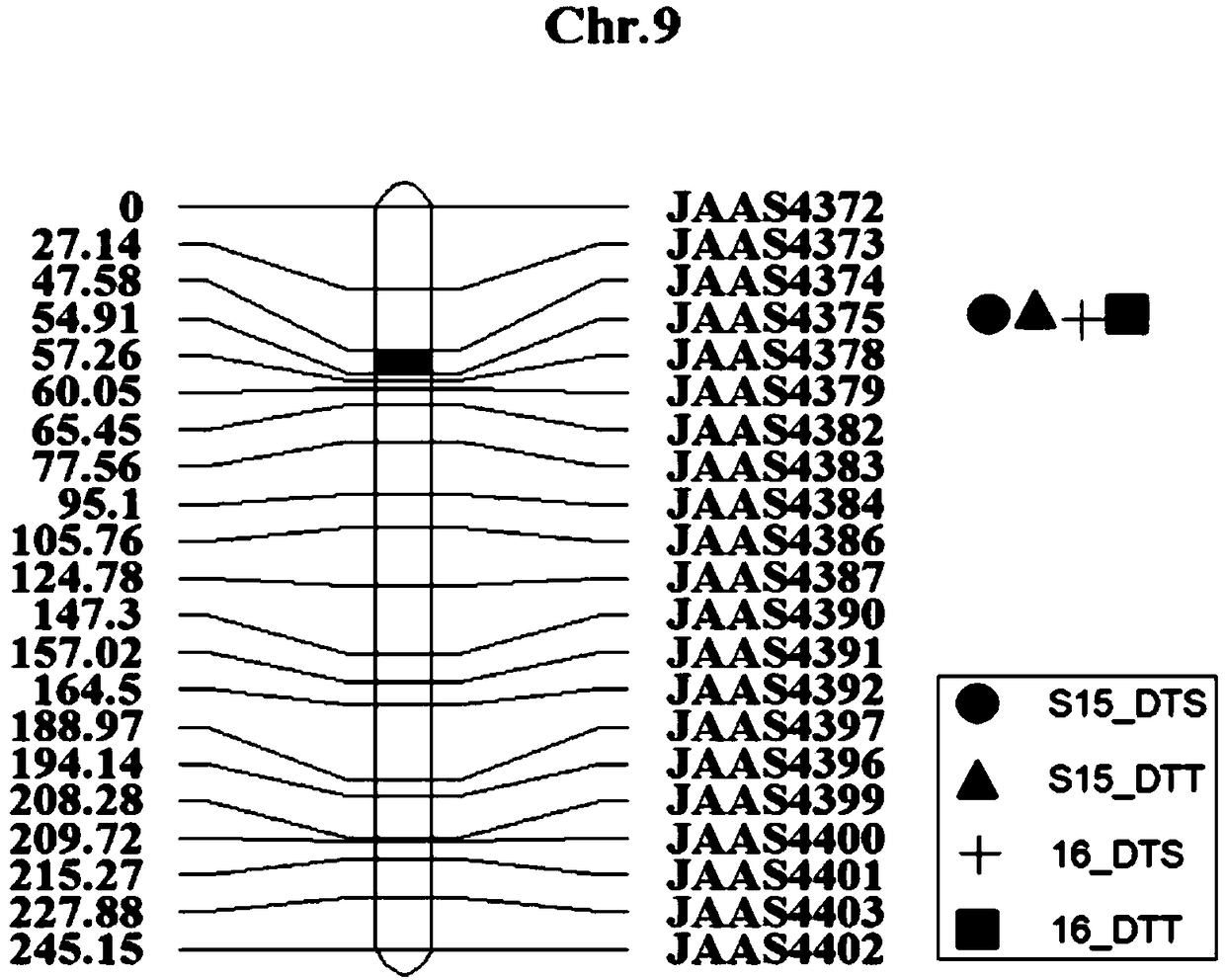
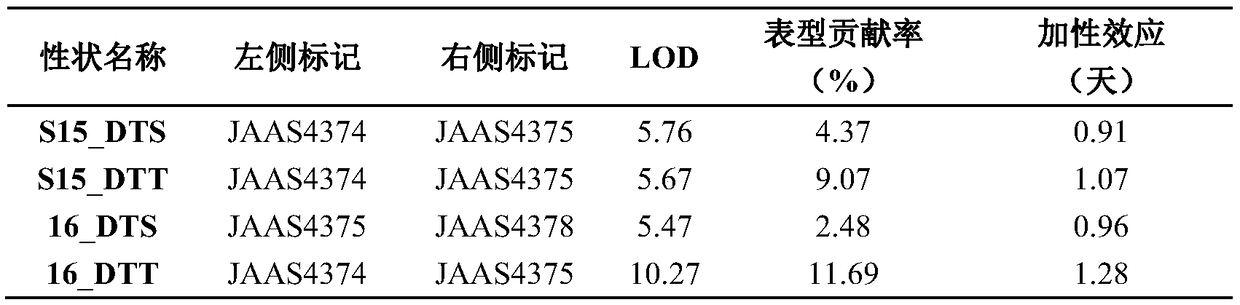
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and discloses a molecular marker of QTL (quantitative trait loci) loci in a flowering period of a maize chromosome 9 and application of the QTLloci in the flowering period of the maize chromosome 9. The molecular marker comprises SEQ ID NO. 1 to 4. A BC1RIL population is used as a material to identify a QTL locus of the maize flowering period between InDel markers JAAS4374 and JAAS4375 on a maize chromosome 9 by genomics analysis, molecular marker development, phenotypic identification, QTL analysis and a series of processes. The locuscan explain 10.4% of phenotypic variation in a silking period, and can explain 3.4% of phenotypic variation in a pollinating period at the same time, and the locus is a stably expressed locus which controls the flowering period of maize and has pleiotropy. The analysis shows that the marker can be used for prediction and selection of the flowering period of maize.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com