Method for selecting statistically validated candidate genes
一种基因型、辅因子的技术,应用在分子遗传学领域,能够解决研究人员引入歧途、没有鉴定出基因等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
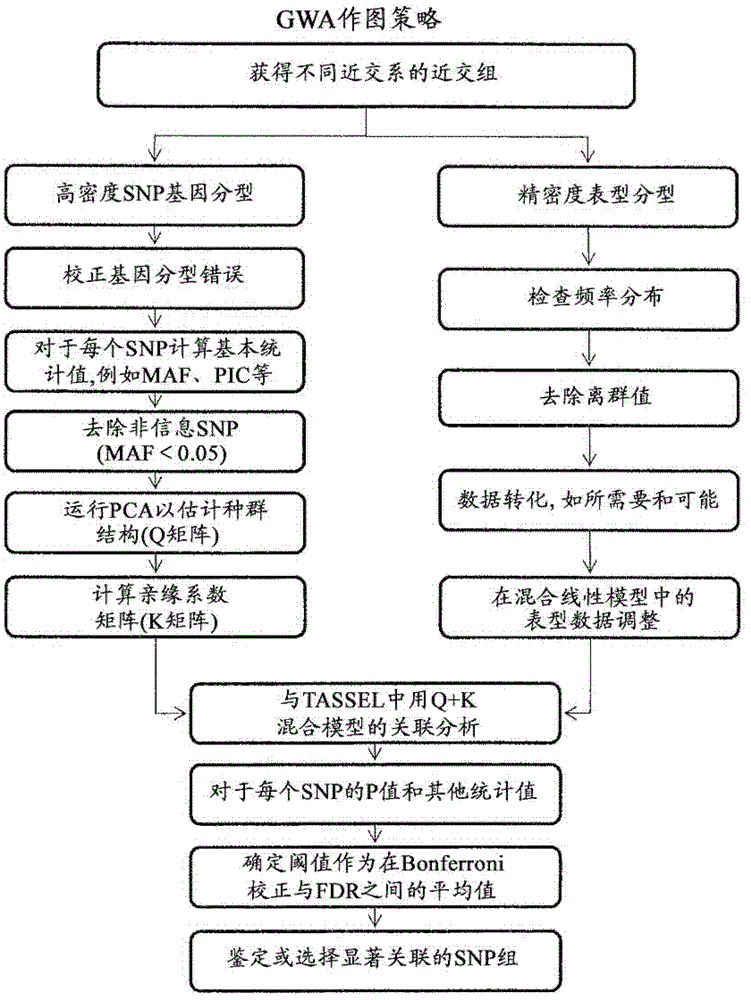
[0152] Example 1. QTL detection in nested populations
[0153] NAM was performed using SMR and MMR in combination with the permutation method described below to determine the LOD threshold for NAM.
[0154] Single Marker Regression (SMR):
[0155] The linear model used to describe the relationship between trait values and marker genotypes is:
[0156] the y ij =μ+x ij a+g i u i +e ij (Model 1)
[0157] where y ij is the phenotype value of individual j in subpopulation i; μ is the overall mean; a is the additive effect of QTL; g i is the indicator variable of subpopulation i; u i is the effect of subpopulation i; e ij is the residual; and where x if individual j carries an allele from a common parent ij is defined as 1, and if individual j carries alleles from other parents when x ij is defined as -1.
[0158] This definition is based on the fact that there are only two different alleles for each marker. To take advantage of the simplicity of regression, t...
example 2
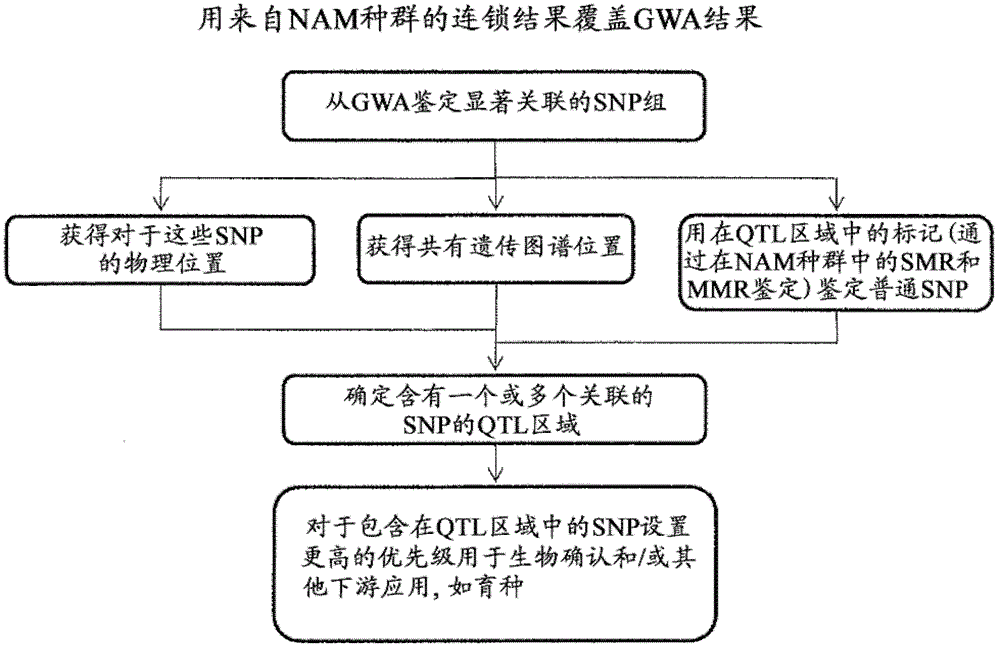
[0172] Example 2. Method for selecting lead candidates for further validation after genome-wide joint mapping Law
[0173] With the advent of omics, the identification of key candidate genes (those that function in phenotypes or complex biological processes) among the thousands of genes in the genome has paradoxically become one of the major hurdles. Indeed, contrary to some early concerns (that the lack of sufficient comprehensive data will remain a limiting factor), it is the exact opposite that scientists are now challenged by the deluge of information. This has translated into the need for sophisticated tools to mine, integrate, and prioritize vast amounts of information. The present invention will help to prioritize candidate leads identified through genome-wide joint mapping (for example using sequences from Solexa technology) for further validation and implementation in marker assisted breeding.
[0174] QTL mapping for traits of interest was performed using nested...
example 3
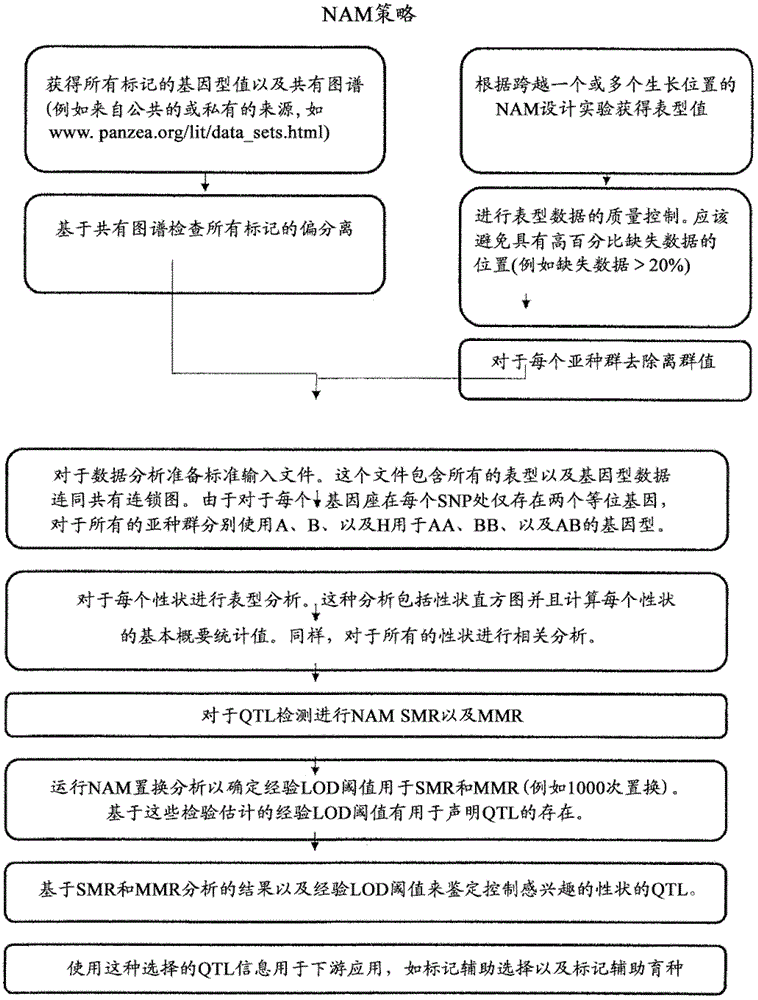
[0176] Example 3. QTL detection using NAM SMR and MMR
[0177] Experimental design and preparation of phenotypic and genotypic data
[0178] These NAM RIL lines were grown across five locations over a two-year period. Traits of interest, including primarily starch and protein in the corn ethanol project, were assessed across the locations and years. The phenotypic data from each location was unbalanced. These unbalanced data structures suggest that it is necessary to obtain corresponding genotype data for these lines. To do so, genotype data (www.panzea.org / lit / data sets.html) were downloaded for all these markers and genotype information was extracted for the NAM lines evaluated. Also, to perform SMR and MMR, consensus linkage maps were found from the same website and downloaded for further use.
[0179] Methods of Data Analysis
[0180] QTLs responsible for starch and protein in maize were detected using NAM SMRs as well as MMRs. Details of these methods are describe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com