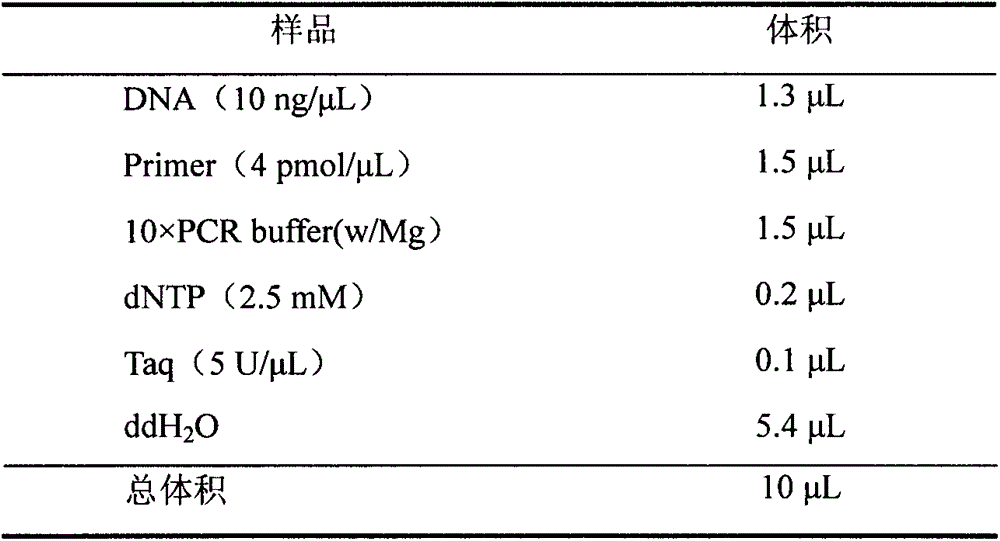
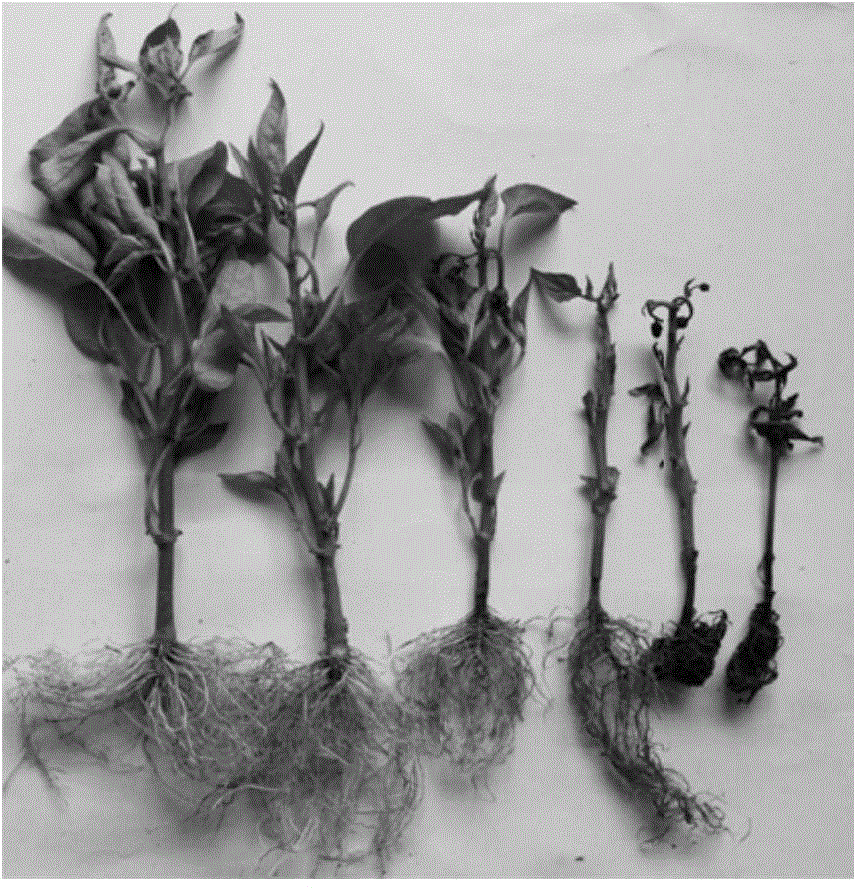Patents
Literature
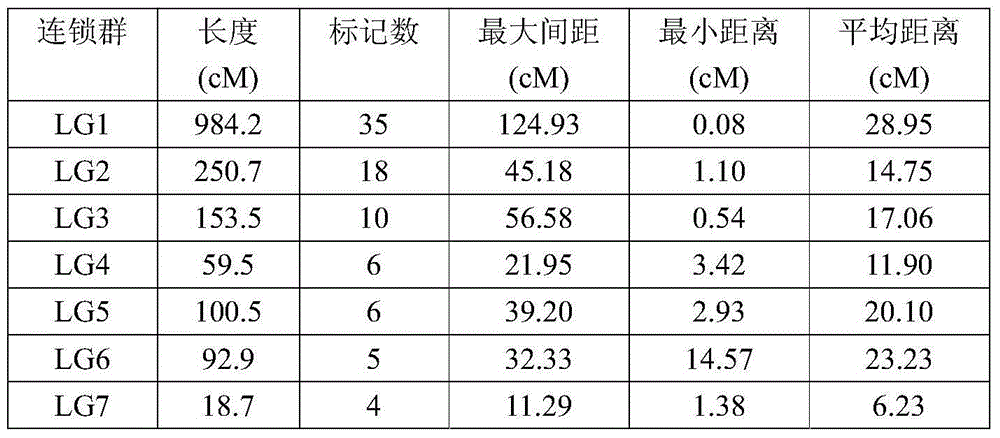
50 results about "F2 population" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for obtaining capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene and molecular marker, and application
InactiveCN104560973AAccurate identificationLarge amount of data informationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyData information
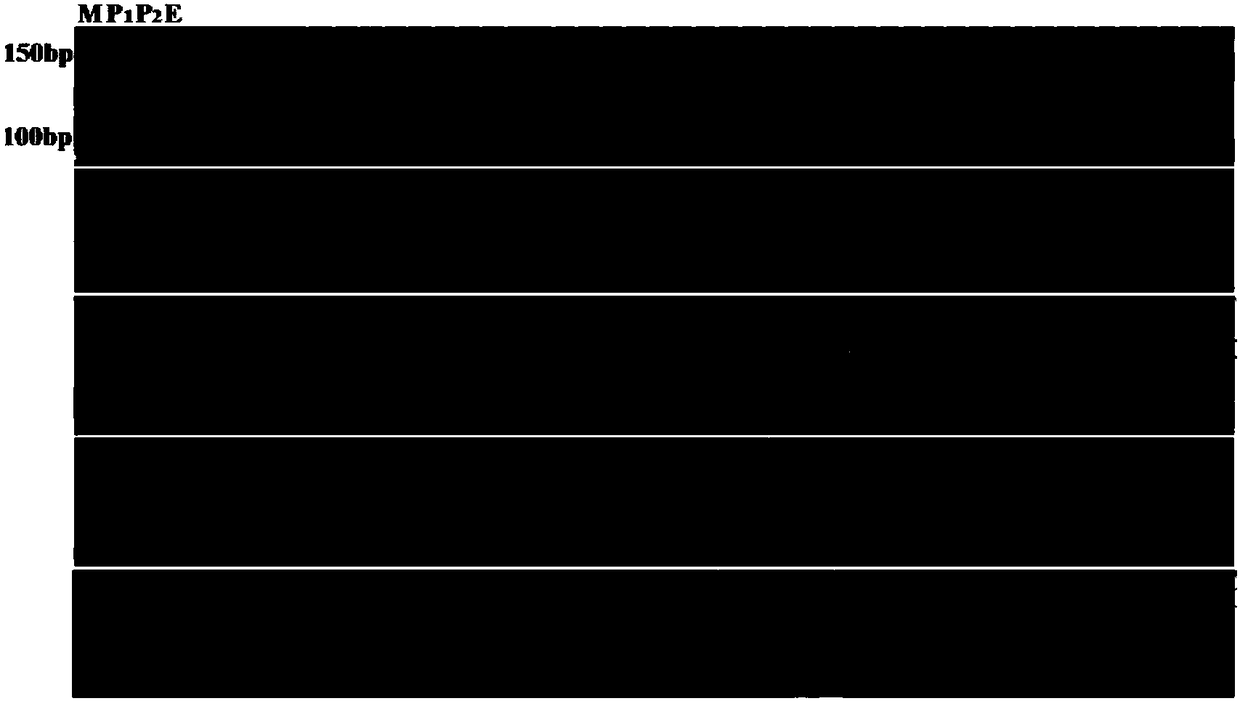
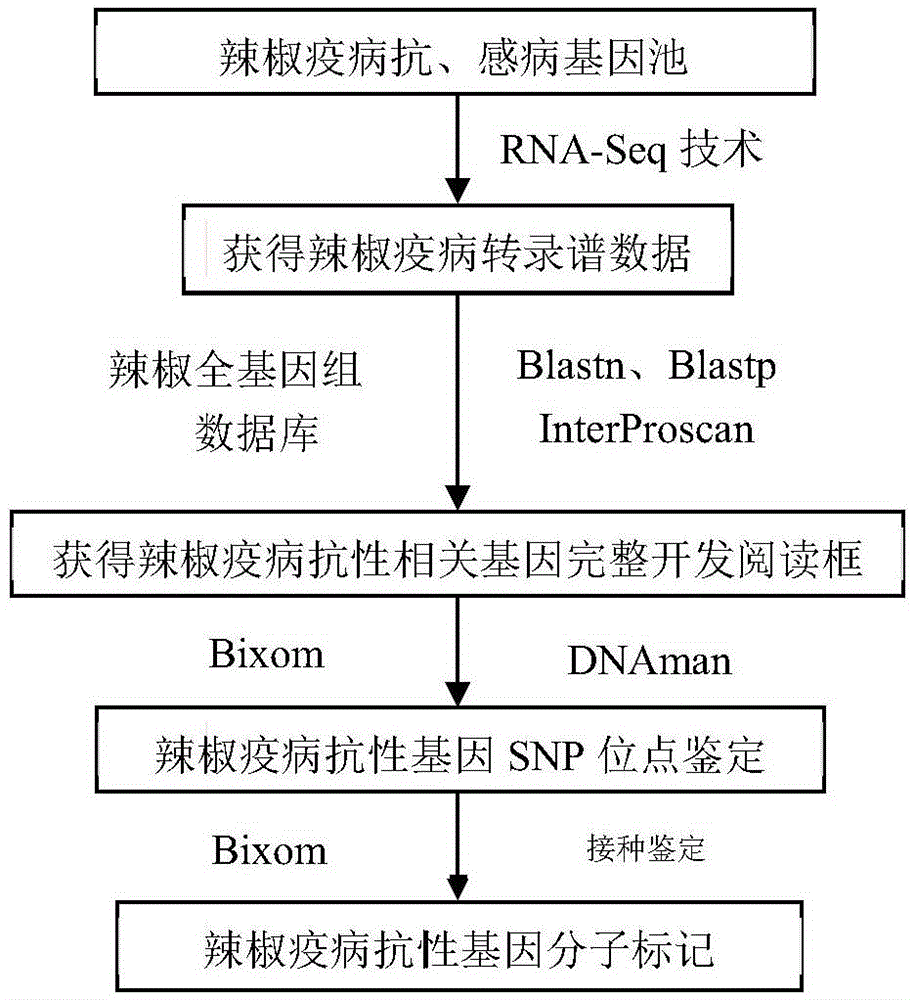
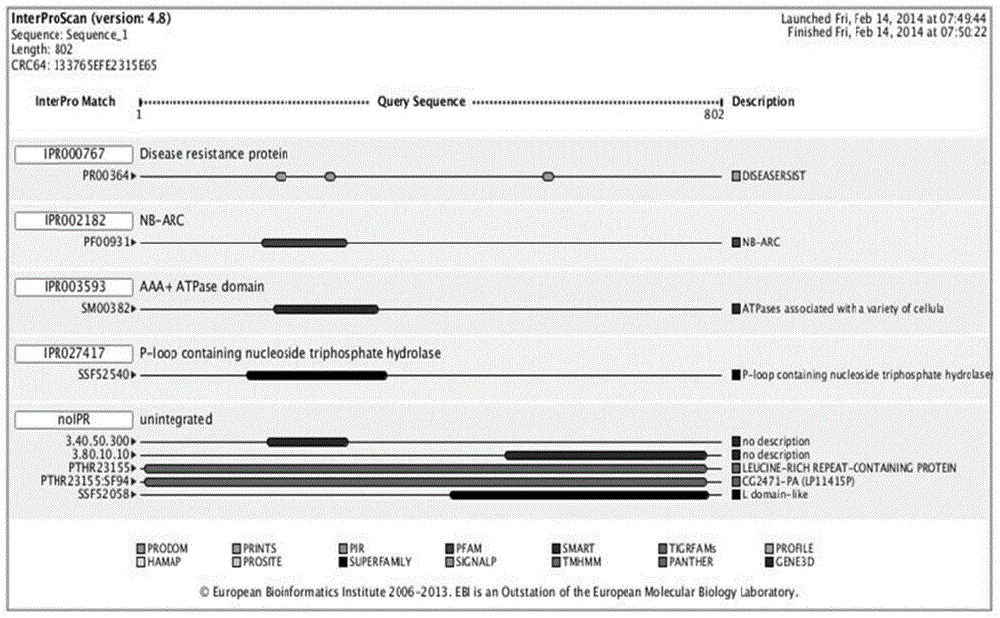
The invention relates to a method for obtaining a capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene and a molecular marker, and application. The method is used for obtaining the capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene by utilizing capsicum phytophthora transcriptome and whole-genome sequencing data information, differentially-expressed gene identification, bioinformatics analysis, molecular marker development and phytophthora inoculation identification and belongs to the technical field of capsicum biology. The method comprises the following steps: sequencing a phytophthora resistant and susceptible gene pool transcriptome obtained after phytophthora inoculation of an F2 population constructed by capsicum highly-resistant and highly-susceptible phytophthora materials, performing expression analysis and functional annotation on differential genes, extracting DNAs (Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) of a capsicum phytophthora highly-resistant and highly-susceptible phytophthora material genome, performing primer design and PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification, performing sequence difference analysis and SNP site identification, performing SNP specific primer design and validity verification, and performing other steps to efficiently obtain the capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene and the molecular marker. According to the method, the capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene can be accurately identified, and the effective molecular marker can be developed.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
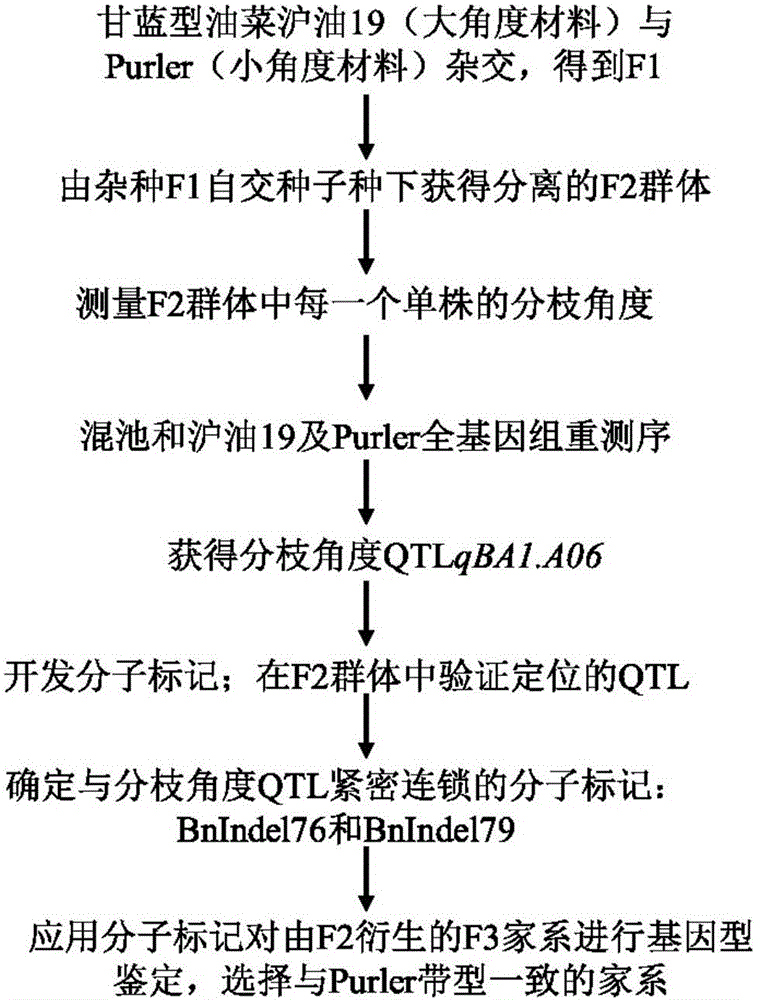
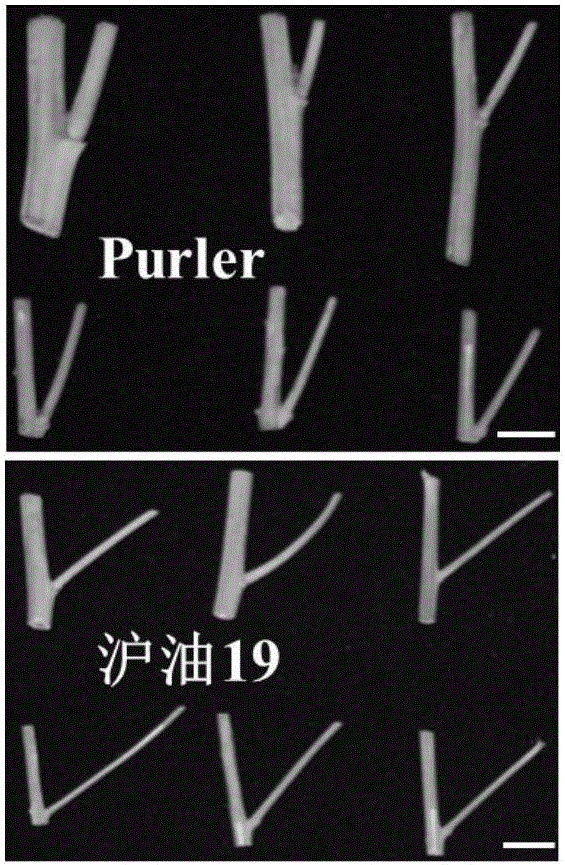
Molecular marker in close linkage with rape crotch angle character QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) and application
ActiveCN105969852ANot affectedAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceF2 population
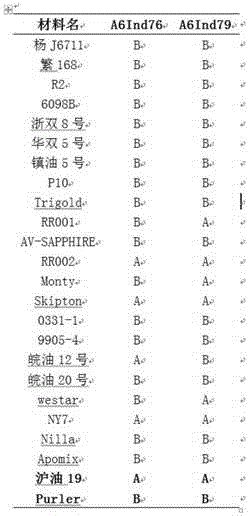
The invention discloses a molecular marker in close linkage with rape crotch angle character QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) and application. The molecular marker is characterized by carrying out hybridization by taking cabbage type rape variety Shanghai oil 19 as a female parent and Purler as a male parent, establishing F2 segregation population through selfing of hybrid F1, and analyzing, thus obtaining a crotch angle locus qBA1.A06; designing a primer by utilizing an Indel marker at the boundary of the crotch angle locus qBA1.A06 so as to detect the parents and the F2 population, thus obtaining a molecular marker BAIndel76 and a molecular marker BAIdenl79 which are in close linkage with the crotch angle character QTL; identifying a rape gene type formed after hybridization of the two parents by utilizing a marker primer, and carrying out auxiliary selection by utilizing the marker, thus greatly increasing the selection efficiency. According to the molecular marker disclosed by the invention, a novel genetic marker is provided for molecular breeding of the rape plant type, and useful information is also provided for accurate positioning on the crotch angle character QTL of the cabbage type rape and map-based cloning on related genes.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
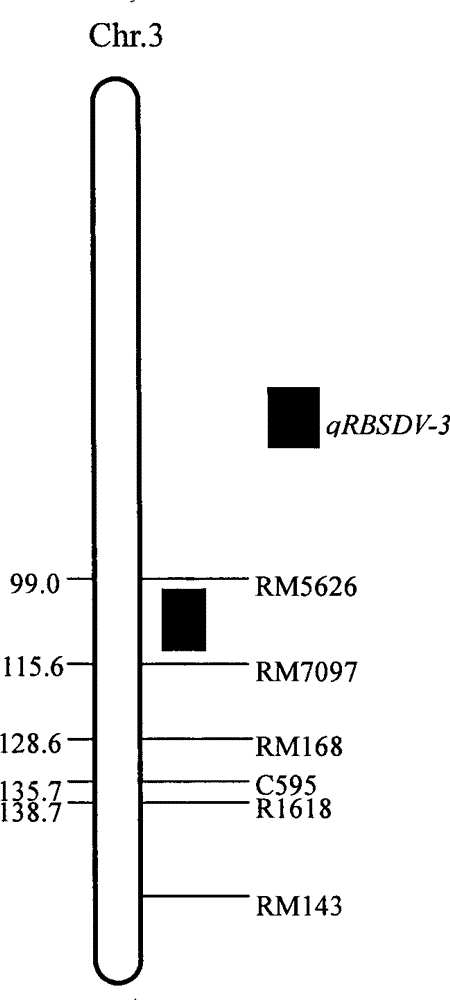
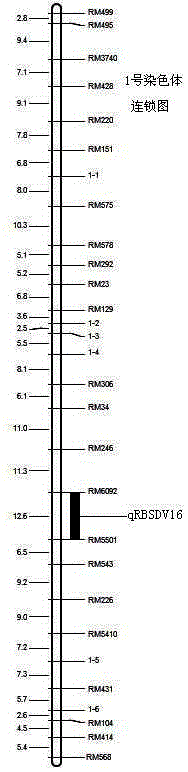
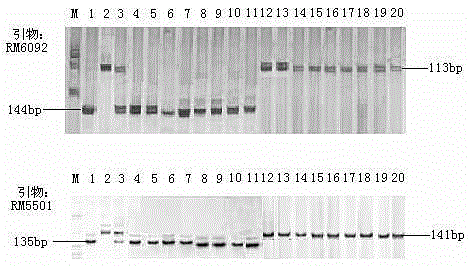
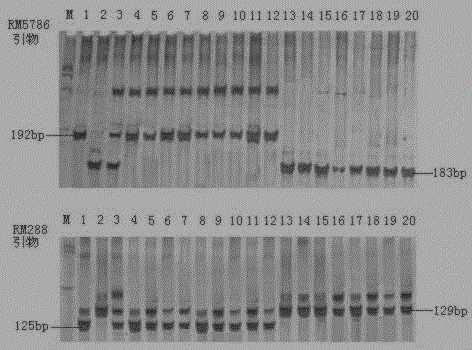
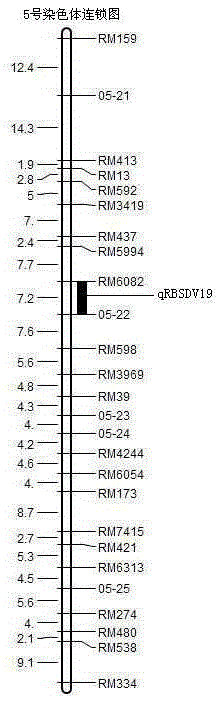
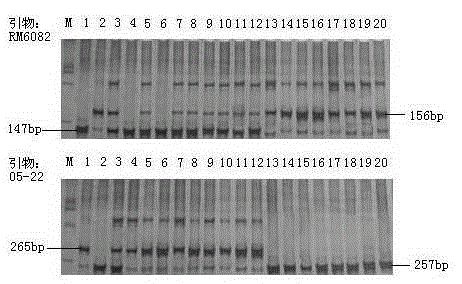
SSR (simple sequence repeat) markers on No.3 chromosome, closely linked to RBSDV (rice black-streaked dwarf virus) resistant QTL (quantitative trait locus) and application thereof
ActiveCN103555718ASpeed up the breeding processOvercome stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseRice plants
The invention discloses molecular markers closely linked to an RBSDV (rice black-streaked dwarf virus) major QTL (quantitative trait locus). The essence of the invention is that according to the linkage and segregation rules, the F2 population of the hybrid generation of Tetep and RBSDV susceptible varieties is taken as the mapping population and the SSR (simple sequence repeat) markers RM5626 and RM7097 on the No.3 chromosome, which are closely linked to the RBSDV resistant major QTL are obtained through analysis of linkage between the results of evaluation of disease resistance and the SSR marker data. Whether a plant has resistance to RBSDV can be judged by detecting the SSR marker banding pattern of the single rice plant of the hybrid combination generation of Tetep and derived varieties (lines) thereof and the RBSDV susceptible varieties. After the SSR markers are applied to assistant selection breeding of the RBSDV resistant varieties of Tetep and derived varieties (lines) thereof / RBSDV susceptible varieties, the defects of poor stability and repeatability of RBSDV resistance evaluation, time and labor waste, high technical threshold and the like in conventional breeding can be overcome and the results can conduce to simplifying the selection method and improving the breeding efficiency and then accelerating the breeding process of RBSDV resistant varieties.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Molecular marker linked to green retardation gene of pepper and application thereof
ActiveCN109207622ASolve the problem of long conventional breeding cycle and easy to be affected by the environmentSolve problems that are vulnerable to environmental influencesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceF2 population
The present invention discloses a molecular marker linked to green retardation gene of hot pepper and its application. Two highly homozygous materials are used to construct the F2 population. The chromosomal regions closely linked to the brown (green-stagnant) gene of pepper fruits are obtained by BSR population mapping, and the candidate genes are identified by molecular markers in the candidateregion. A KASP molecular marker is designed according to the single base mutation of candidate gene. The genotype identification of 90 individual plants in F2 population by using this marker showed that the coincidence rate is 100%. The results not only contribute to the color identification and assisted breeding of pepper fruits, but also provide a basis for map-based cloning of green retardationgene and molecular mechanism of green retardation, which is worth popularizing widely.
Owner:HUNAN VEGETABLE RES INST
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) molecular marker related to watermelon peel background color and application of SNP molecular marker
ActiveCN108192990AHigh precisionSpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationGermplasmF2 population
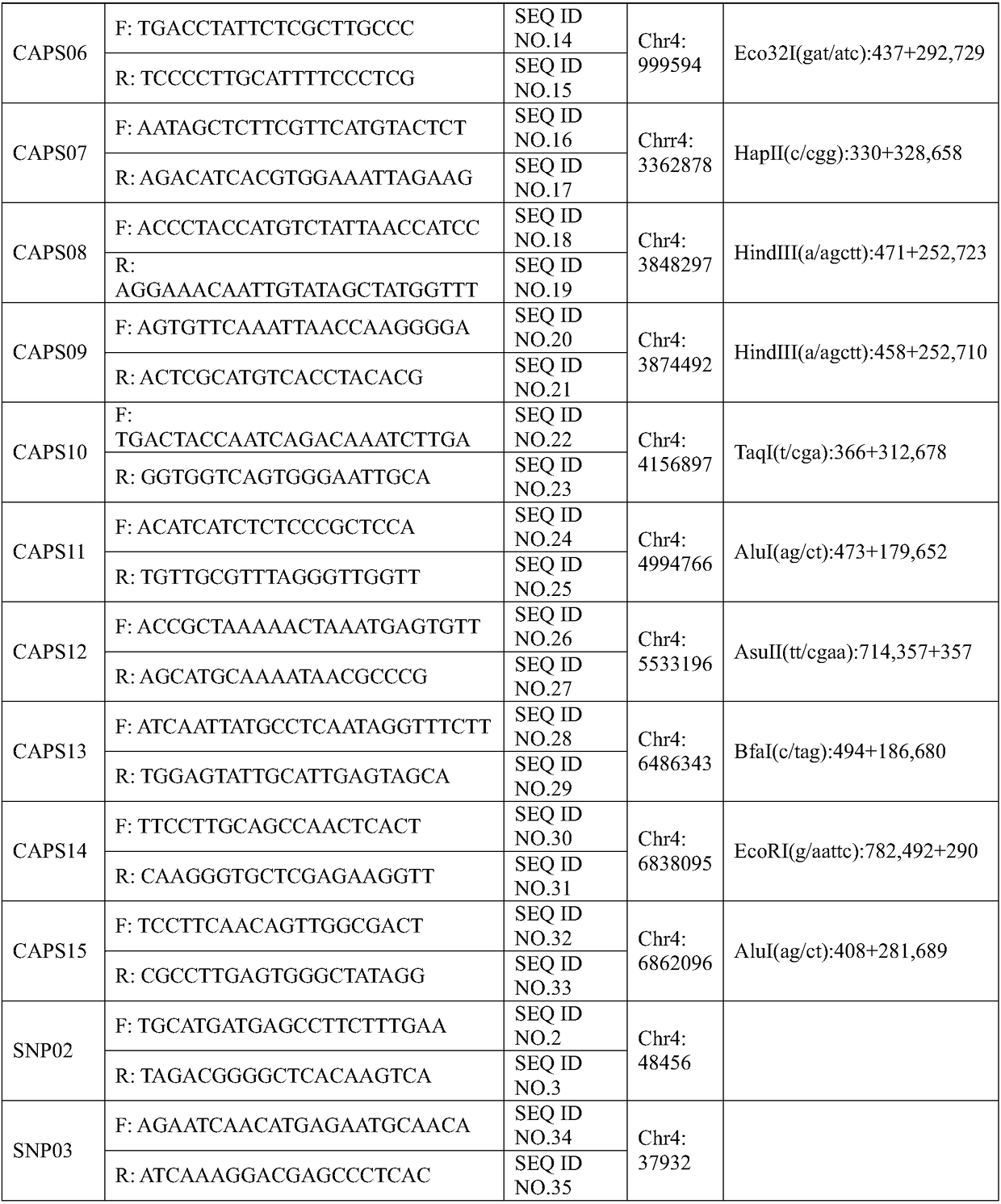
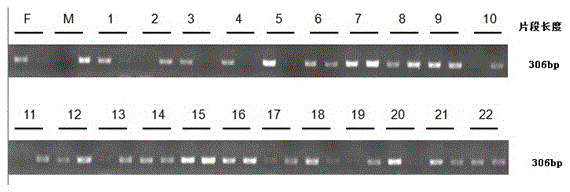
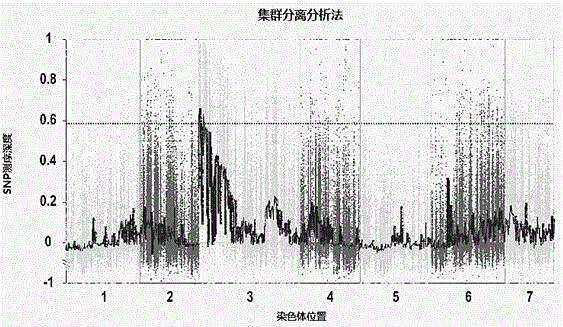
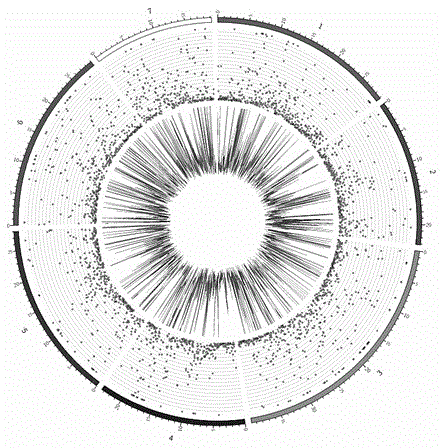
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) molecular marker related to watermelon peel background color and an application of the SNP molecular marker. An SNP site is located on the 48456th nucleotide of chromosome 4 of watermelon genome. The SNP molecular marker can be used for identifying the watermelon peel background color and has higher accuracy rate. The SNP molecular marker is utilized for identifying the watermelon peel background color of a hybrid F2 population, and a result indicates that the identification accuracy rate of the SNP molecular marker for the watermelon peel background color of hybrid population generations is 100%. The SNP molecular marker is utilized for identifying the peel background color of 20 parts of watermelon germplasm resources, and a result indicates that the identification accuracy rates of the SNP molecular marker for watermelons with yellow peel background color andwatermelons with green peel background color are both 100%. Therefore, the SNP molecular marker can rapidly and accurately identify the watermelon peel background color and can be applied to production on a large scale.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU FRUIT RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Cucumber male sterility gene related SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker and application
ActiveCN105420408APrecise positioningLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRe sequencingAgricultural science
The invention discloses a cucumber male sterility gene related SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marking method and application. The marking method comprises the steps of taking a YL-5 male sterile line as a female parent to hybridize with a distant related variety D37-1, so as to obtain a hybrid F1, performing selfing by the hybrid F1 to obtain an F2 population, and two phenotypes of male sterility and male fertility exist in an F2 segregation population, then utilizing a method of combination of re-sequencing and BSA, screening an SNP locus unrelated with the male sterility, and developing a male sterility gene related molecular marker. The marking method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of short period, low cost and high efficiency. Meanwhile, an important development approach is provided for molecular markers for molecular breeding, phyletic evolution and germplasm resource identification.
Owner:TIANJIN RES INST OF VEGETABLE
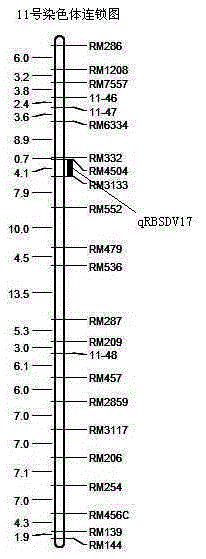
Rice variety Zhejiang 5 black-streaked dwarf virus resistant site qRBSDV17 and molecular marker method thereof
InactiveCN106834280AEliminate distractionsAccurate and reliable phenotyping methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRice black-streaked dwarf virusF2 population
The invention relates to a rice variety Zhejiang 5 black-streaked dwarf virus resistant site qRBSDV17 and a molecular marker method thereof. According to the rice variety IR24 black-streaked dwarf virus resistant site and the molecular marker method, the filial generation F2 population of a rice black-streaked dwarf virus resistant variety Zhejiang 5 and a susceptible variety Lianyungang 3 is adopted as a mapping population; the rice black-streaked dwarf virus resistance is identified by using a combined method of natural field identification and improved laodelphax striatellus antixenosis identification; linkage analysis is carried out on virus resistance identification results and SSR marker data to obtain two SSR markers, closely linked to rice black-streaked dwarf virus resistance major QTL, on the chromosome 1; the resistance of a plant to the rice black-streaked dwarf virus can be predicated by detecting banding pattern data of the primer markers on the chromosome 1. Therefore, the selecting efficiency of black-streaked dwarf virus resistant rice is greatly enhanced and the rice breeding progress is accelerated.
Owner:WUXI NANLIGONG TECH DEV
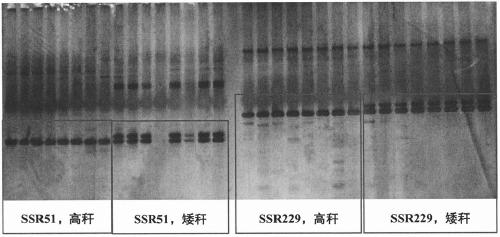
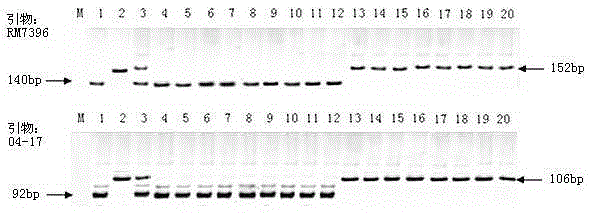
InDel6 and SSR229 markers closely linked to height of maize plant and application of InDel6 and SSR229 markers
ActiveCN109337998AImprove efficiencyEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerNucleotide
The invention discloses InDel6 and SSR229 markers closely linked to the height of a maize plant and application of the InDel6 and SSR229 markers. Labeled nucleotide sequences are: a forward primer 5'-TGTGGACGTGACACGCTT-3' and a reverse primer 5'-TCAGCCTTCGTCCACAGAC-3' of InDel6, and a forward primer 5'-GGGTCTTTCGCTGAATAACACT-3' and a reverse primer 5'-CAACCCTCACTACTAAAGCCGA-3' of SSR229. The invention also discloses the application of the markers in the high molecular marker-assisted selection breeding of corn plants. A specific method comprises the steps as follows: (1) performing genotype identification on BC and F2 population strains by molecular markers; (2) classifying high stalks and dwarf stalks according to results of the genotype identification in the step (1), and performing verification on genotype identification by combining phenotypic results. The molecular markers provided the invention are stable in performance, simple to detect, clear in electrophoresis bands and low inexperimental cost, have no need for enzymatic cleavage, improve the efficiency of maize plant type improvement, and accelerate the process of ideal plant type breeding of corn.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
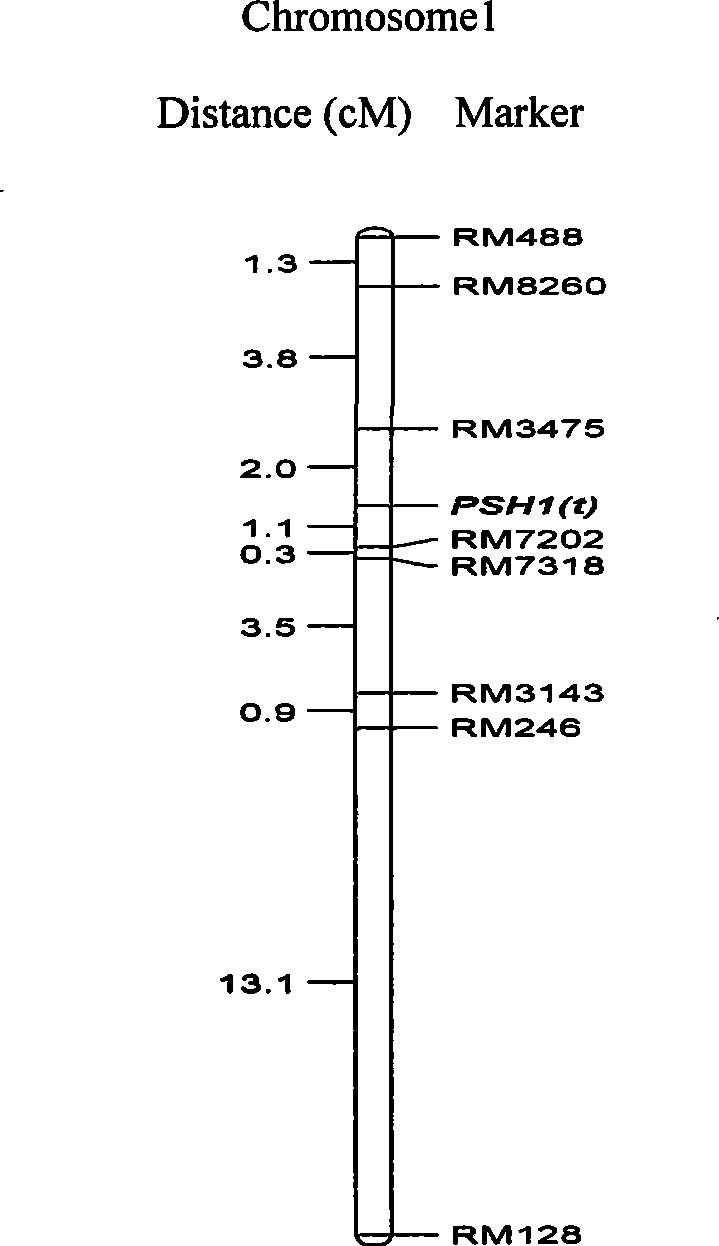
Numerator mark concatenated with rice purple pericladium gene PSH1 (t), acquiring method and application thereof
InactiveCN101368181ANot affectedMark stableMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationF2 populationMolecular genetics
The invention discloses a molecular marker of rice purple leaf sheath gene PSH1(t) linkage, and an acquired method and an application thereof, which belong to the field of molecular genetics. The rice non purple leaf sheath variety fragrant japonica 9407 and the purple leaf sheath variety R151 and the F2 which is obtained by hybridization are extracted with isolated population individual DNA. The two parents receives the PCR product polymorphism screening by utilizing 360 pairs of SSR molecular markers, then the screening of the molecular markers of purple leaf sheath gene linkage is carried out sequentially to a F2 mixing pool with purple leaf sheath DNA, a F2 mixing pool without purple leaf sheath DNA and each of the individuals of a F2 population, and the molecular genetic map of the purple leaf sheath gene PSH1(t) is constructed on the first chromosome. The selection efficiency of purple leaf sheath rice is greatly improved through the molecular markers of the major genes of purple leaf sheaths to test whether purple leaf sheath variety R151 and derived varieties (lines) thereof contain the genes of the purple leaf sheaths. The invention is specialized in the screening of the rice purple leaf sheath genes, and is used for the study of cloning the purple leaf sheath gene PSH1 (t).
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
SSR markers, closely linked to rice black-streaked dwarf disease resistance QTL, on chromosome 4 and application of SSR marker
InactiveCN106834281AResistance predictionImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention relates to SSR markers, closely linked to rice black-streaked dwarf disease resistance QTL, on a chromosome 4 and application of the SSR markers. According to the SSR markers, closely linked to rice black-streaked dwarf disease resistance QTL, on the chromosome 4, a filial generation F2 population of rice black-streaked dwarf disease resistant variety Zhejing 5 and susceptible variety Lianyuangang 3 is used as a mapping population; the rice black-streaked dwarf disease resistance is identified by using a combined method of natural field identification and improved laodelphax striatellus antixenosis identification; linkage analysis is carried out on disease resistance identification results and SSR marker data to obtain the two SSR markers, closely linked to rice black-streaked dwarf disease resistance major QTL, on the chromosome 4; and the resistance of a plant to the rice black-streaked dwarf disease can be predicated by detecting banding pattern data of the primer markers on the chromosome 4. Therefore, the selecting efficiency of black-streaked dwarf disease resistant rices is greatly enhanced and the breeding progress is accelerated.
Owner:WUXI NANLIGONG TECH DEV
Molecular marker technology for identifying red grains and white grains of wheat
InactiveCN101760556AMolecular marker rapidMolecular markers are validMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceF2 population
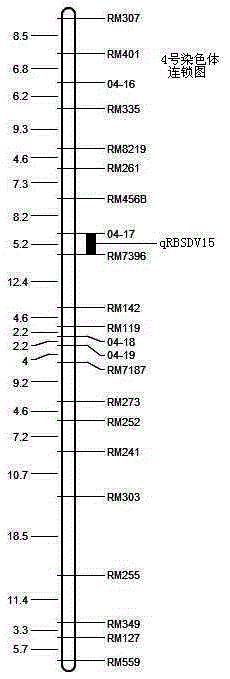
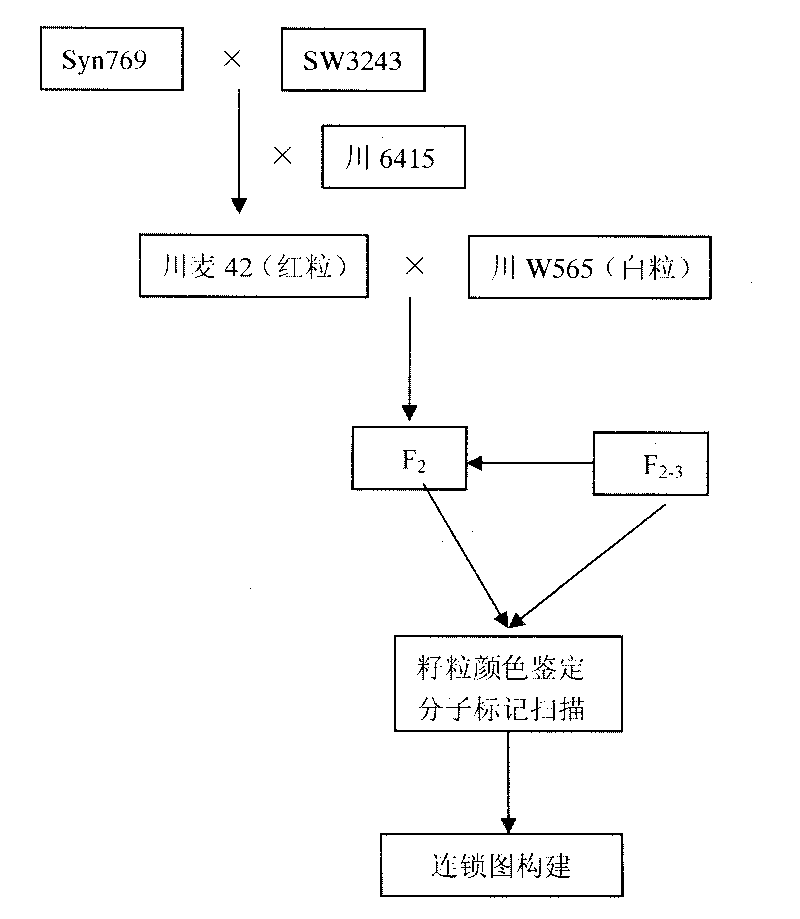
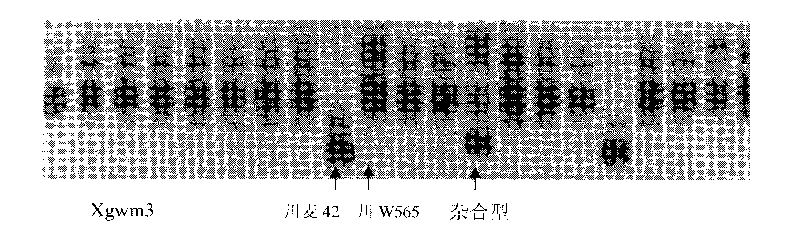
The invention discloses a molecular marker technology for identifying red grains and white grains of wheat, which comprises the following steps: utilizing synthetic hexapliod wheat derived varieties of red grain wheat Chuanmai 42 and Sichuan cultivated white grain wheat Chuan W565 for hybridization, constructing an F2 population for genetic analysis of red grain genes, and harvesting 1015 F2 plants for identifying grain color and carrying out the genetic analysis and the molecular marking of the red grain genes of Chuanmai 42, wherein 241 white grain single plants in the F2 population are selected, and an F2-3 family is constructed for verifying the F2 result. The molecular marker technology utilizes an SSR modular marker for carrying out mapping on the red grain genes carried in the synthetic hexapliod wheat derived variety-Chuanmai 42, thereby being fast, accurate and effective to select the white grain variety, eliminating the red grain variety and accelerating the breeding process of the white grain wheat.
Owner:CROP INST SICHUAN PROVINCE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rapid three-line sterile line breeding method for paddy rice
InactiveCN107466839AReduce workloadIncrease success ratePlant genotype modificationAgricultural sciencePollination
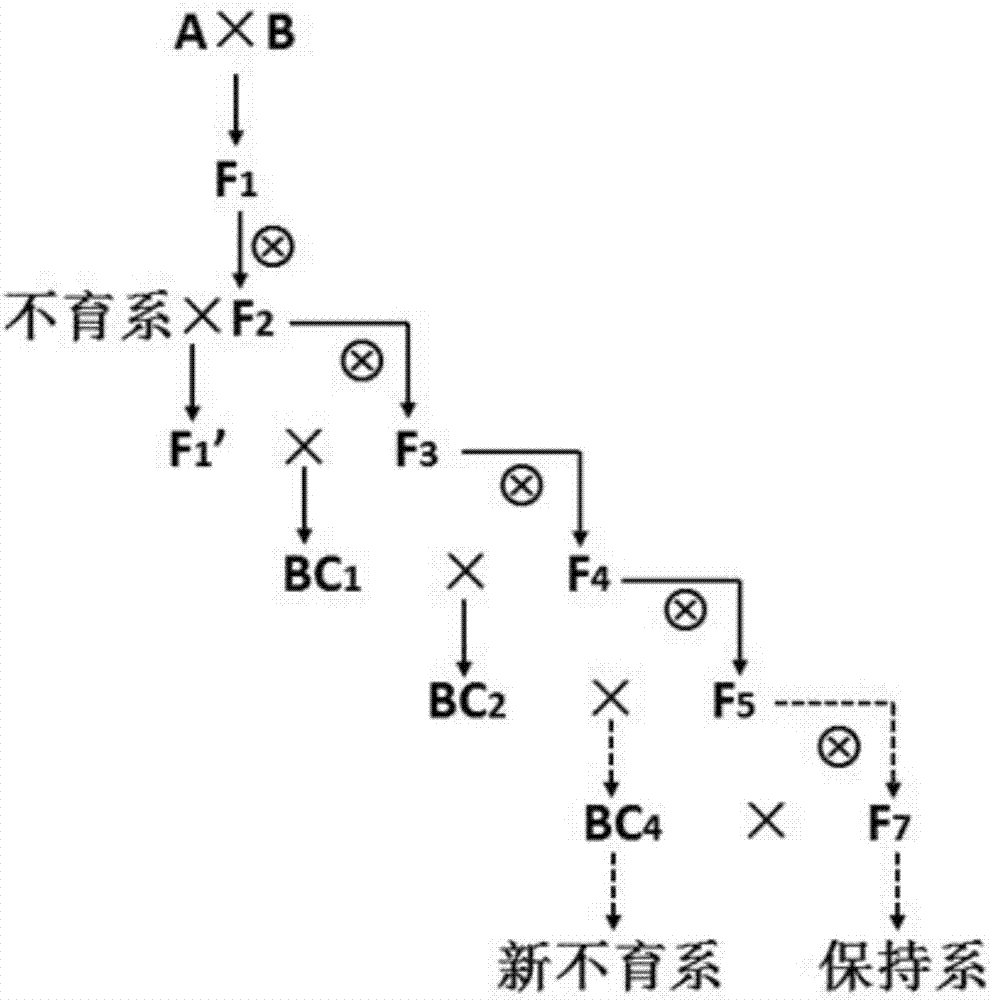
The invention discloses a rapid three-line sterile line breeding method for paddy rice, which includes the following steps: maintainer lines A and B, the excellent traits of which complement each other, are chosen to be hybridized, so that F1 is obtained, and F2 is then obtained by selfing; individual plants which are suitable for a breeding objective are chosen from the F2 population, the backcrossing of sterile cytoplasm is carried out, and a sterile line is rapidly stabilized. In segregative generations, the method adopts the combination of mixed pollination and individual plant selection, consequently, workload is greatly decreased, the sterile line is rapidly stabilized, and the breeding time is greatly shortened.
Owner:GUIZHOU CROP VARIETIES RESOURCE INST
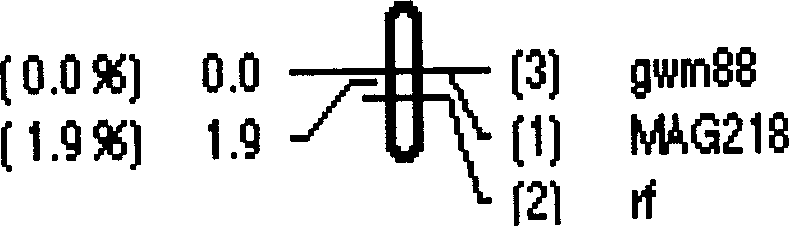
Wheat fertile activity recovery gene RF6 molecular mark and its obtaining method
InactiveCN1570103AQuick and accurate transferAvoid influenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceTriticeae
The invention relates to wheat fertility recovery gene Rf6 molecular tag and its obtaining method and belongs to crop breeding and production fields. F2 population arising from wheat T.um-bellulatum translocation line N2114 with susan is analysed in individual genotype and its fertility. Codominant SSR mark MAG218 and dominant mark gwm88 is obtained, which are closely linked to T cell cytoplasm sterility fertility recovery gene Rf6, and can determine the existence of Rf6 and forecast the wheat plant fertility, so can screening the Rf6 plant rapidly.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
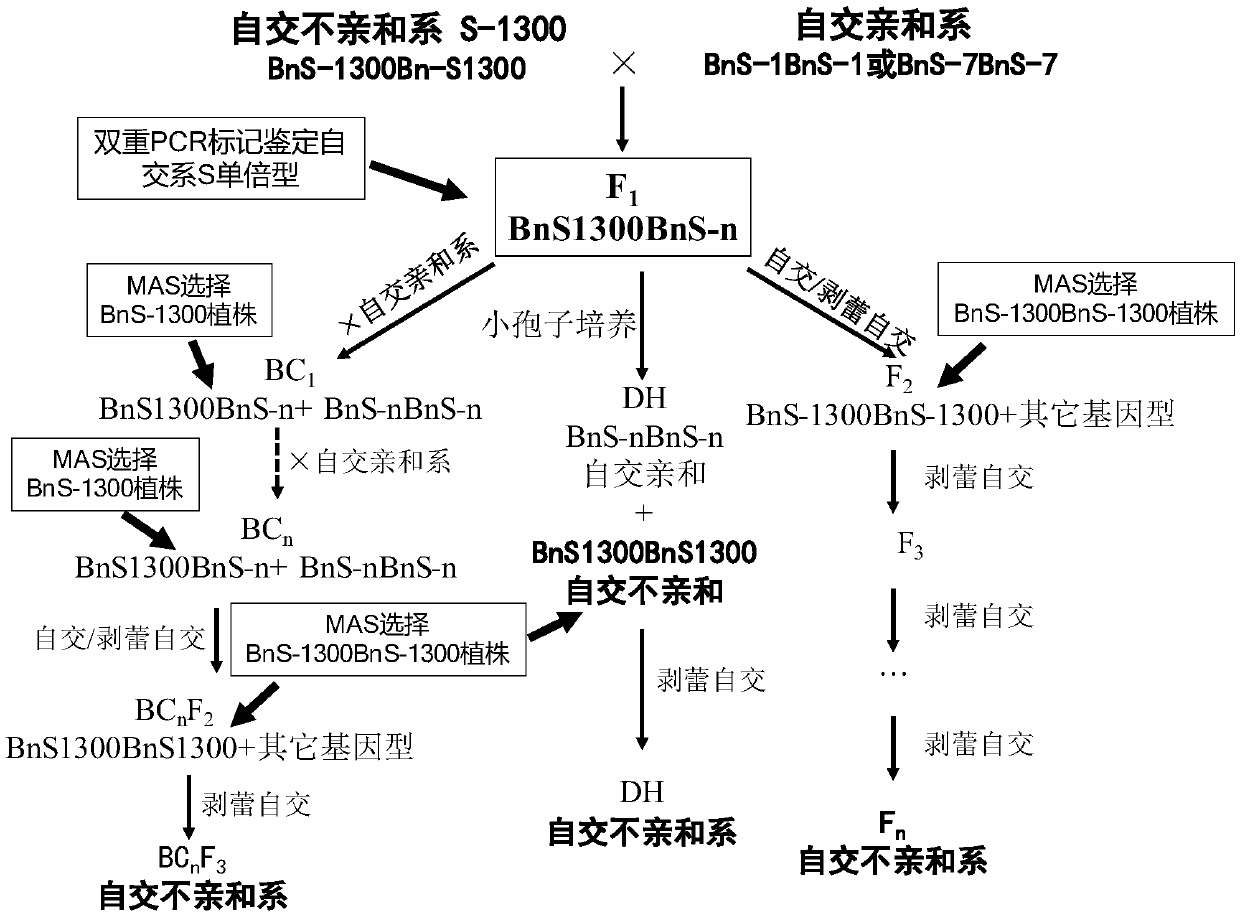
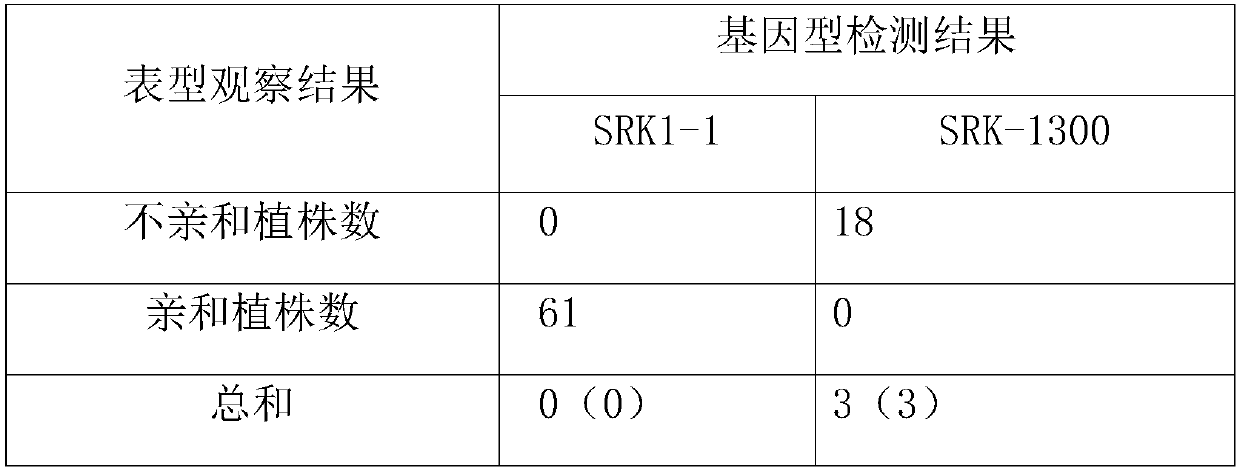
Method for breeding rape self-incompatible line assisted by S haplotype molecular markers
InactiveCN109566399AAvoid misjudgmentAccurate judgmentMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissue cultureAgricultural scienceBackcross population
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape molecular breeding, and discloses a method for breeding a rape self-incompatible line assisted by an S haplotype molecular marker, which comprisesthe following steps of: identifying an S haplotype of inbred line, double haploids of the self-incompatible line and inbred line, F2 populations of the self-incompatible line and inbred line, backcross populations of the self-incompatible line and inbred line and an S haplotype of the offspring by utilizing a molecular marker technology, the self-incompatible line of cabbage type rape is obtained,the method can overcome the defect of selection according to the self-incompatible phenotype in the rape breeding process, the breeding workload is greatly reduced, and the rapid cultivation of the self-incompatible line of the cabbage type rape is achieved, meanwhile, the S haplotype is detected by utilizing multiple PCR molecular markers, the error judgment on the result caused by the error ofthe experimental operation process is overcome, and the S haplotype of a plant can be accurately judged.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
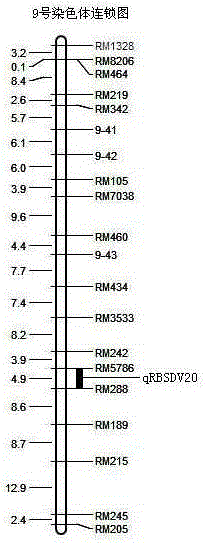
SSR markers in close linkage to rice black-streaked dwarf resistant QTL on chromosome 9 and application thereof
ActiveCN105349539AImprove selection efficiencyEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention relates to SSR markers in close linkage to rice black-streaked dwarf resistant QTL on a chromosome 9 and application thereof. According to the invention, a filial generation F2 population of a rice black-streaked dwarf resistant variety Guangfu japonica rice and a susceptible variety Yangnong japonica rice No.2 is used as a mapping population, rice black-streaked dwarf resistance identification is carried out through a method of combining field natural identification and improved laodelphax striatellus antixenosis identification, and a disease resistance identification result and SSR marker data are subjected to linkage analysis, so that two SSR markers in close linkage to rice black-streaked dwarf resistant main effect QTL on the chromosome 9 are obtained. Through detecting banding pattern data of the SSR markers on the chromosome 9, the resistance of plants to rice black-streaked dwarf can be predicted, the selection efficiency of rice black-streaked dwarf resistant rice is improved greatly and a breeding process is accelerated.
Owner:SUQIAN CHOOSAN SEED IND
Guangfu japonica rice black-streaked dwarf locus and molecular marking method
ActiveCN105349677AResistance predictionImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceF2 population
The invention relates to a Guangfu japonica rice black-streaked dwarf locus and molecular marking method. According to the invention, a filial generation F2 population of a rice black-streaked dwarf resistant variety Guangfu japonica rice and a susceptible variety Yangnong japonica rice No.2 is used as a mapping population, rice black-streaked dwarf resistance identification is carried out through a method of combining field natural identification and improved laodelphax striatellus antixenosis identification, and a disease resistance identification result and SSR marker data are subjected to linkage analysis, so that two SSR markers in close linkage to rice black-streaked dwarf resistant main effect QTL on a chromosome 5 are obtained. Through detecting banding pattern data of the SSR markers on the chromosome 5, the resistance of plants to rice black-streaked dwarf can be predicted, the selection efficiency of rice black-streaked dwarf resistant rice is improved greatly and a breeding process is accelerated.
Owner:HENAN BAIYU PLANT IMMUNE TECH CO LTD
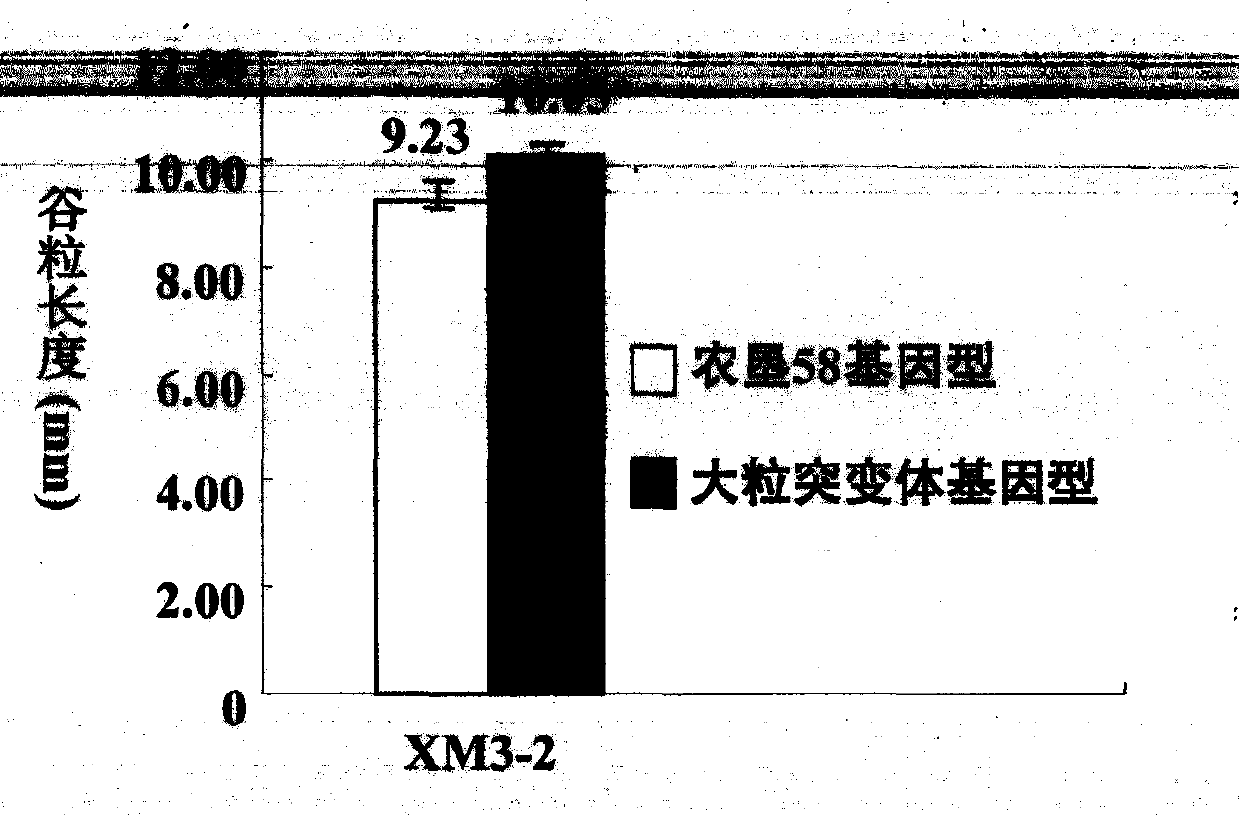
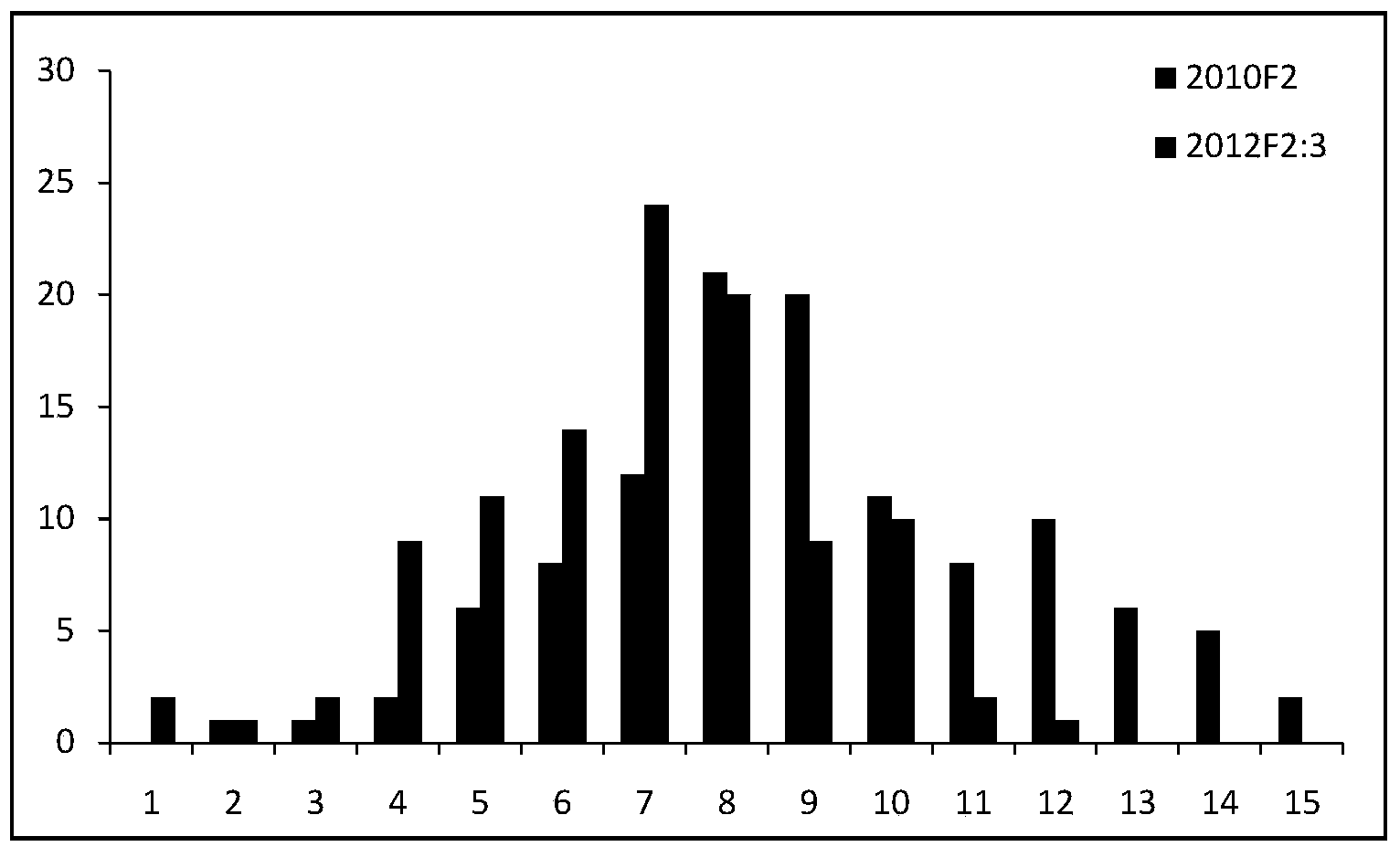
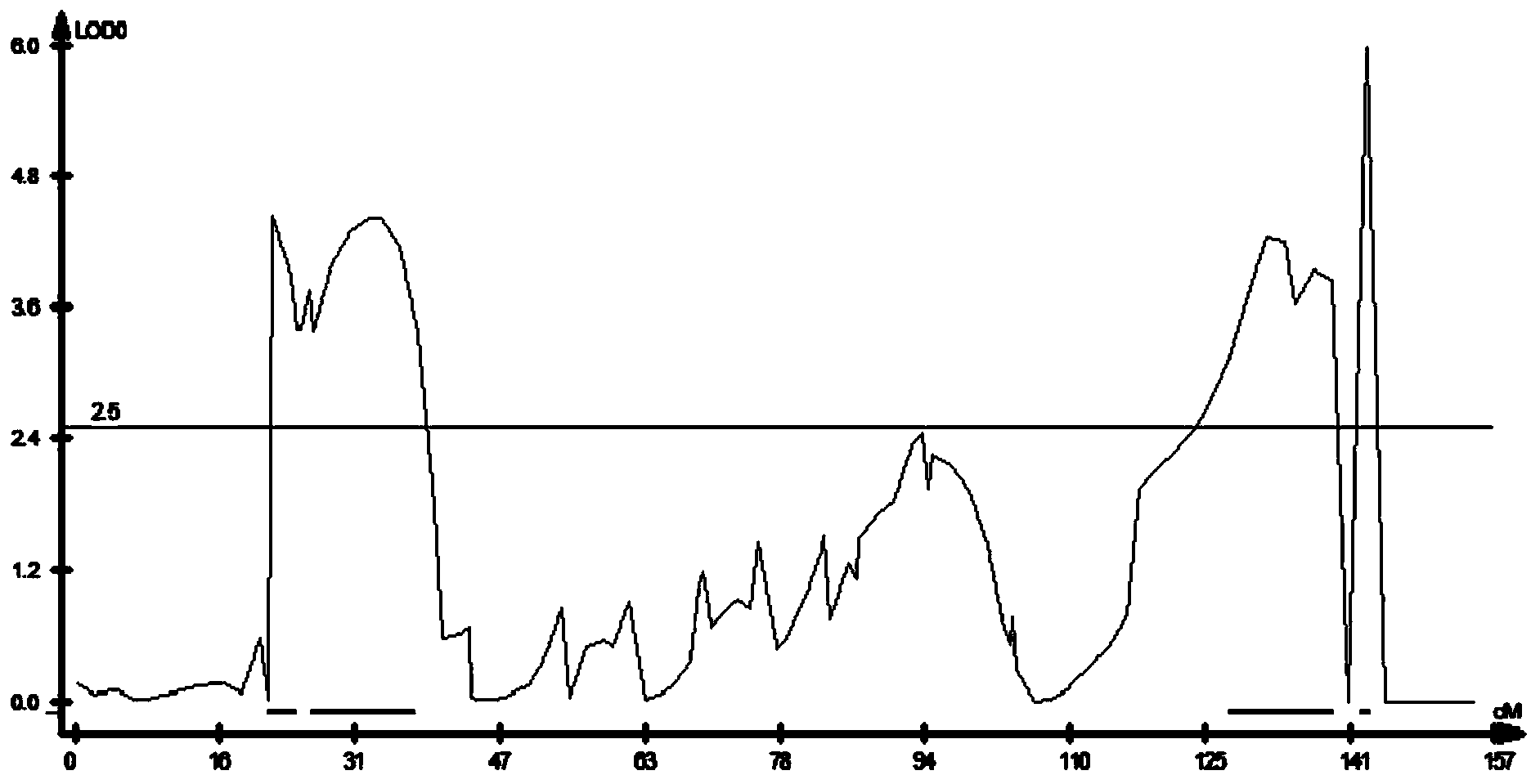
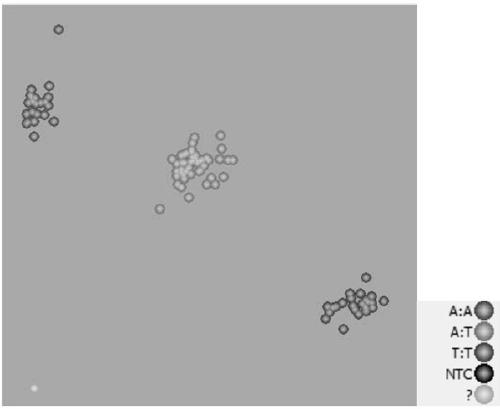
New space-mutated rice grain length gene qGS3a and molecular marker method thereof
InactiveCN103468715AGood appearanceGood yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringAgricultural scienceMarker analysis
The invention relates to a new gene qGS3a for simultaneously increasing rice grain length and grain weight and a molecular marker method thereof, belonging to the fields of rice high-yield good-quality breeding and molecular genetics. The invention is characterized in that single marker analysis is performed according to the linkage segregation law by using F2 population of large-grain mutant and original parent Nongken 58 and derivative F3 family to locate the new grain length gene qGS3a on the 3rd chromosome, thereby obtaining PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification-based practical and economical marker XM3-2 which is closely linked with the new qGS3a. The new gene qGS3a is used for auxiliary selective breeding and polymerization breeding of appearance quality and yield of rice, can effectively overcome the defects in spontaneous mutant genes, can perform genotype selection on the low-generation breeding population in the seedling stage to obtain the breeding material with better appearance quality and yield components, omits the grain identification process in the adult-plant stage, enhances the breeding efficiency and accelerates the breeding process.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Oil content character main gene locus of rape 6F313 and applications thereof
ActiveCN103667484ASpeed up the breeding processEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceF2 population
The invention discloses an oil content character main gene locus of rape 6F313 and applications thereof. The method to find the locus comprises the following steps: (1) hybridizing a combination of rape 6F313 with a high oil content (50%) and rape Y817 with a low oil content (35%) so as to obtain F2 generation population with separated oil content character and a F2:3 family; (2) establishing a linkage map of F2 generation segregation population by utilizing the SNP chip of rape 60K, then obtaining the molecular label tightly linked with the oil content character and the main gene locus according to the oil content data of the F2 population and the F2:3 family. The invention discloses a main gene locus 6F313A10OC which locates on the A10 chromosome and controls the high oil content character of rape 6F313, and discloses two molecular labels 6F313A10OC-1 and 6F313A10OC-2 which are tightly linked with the main gene locus at the same time. The tightly linked molecular labels can detect whether rape 61616 or derivated species (line) contains a main gene QTL locus or not, thus can predict the oil content, so the breeding efficiency of high oil content rape is greatly improved.
Owner:武汉中油种业科技有限公司
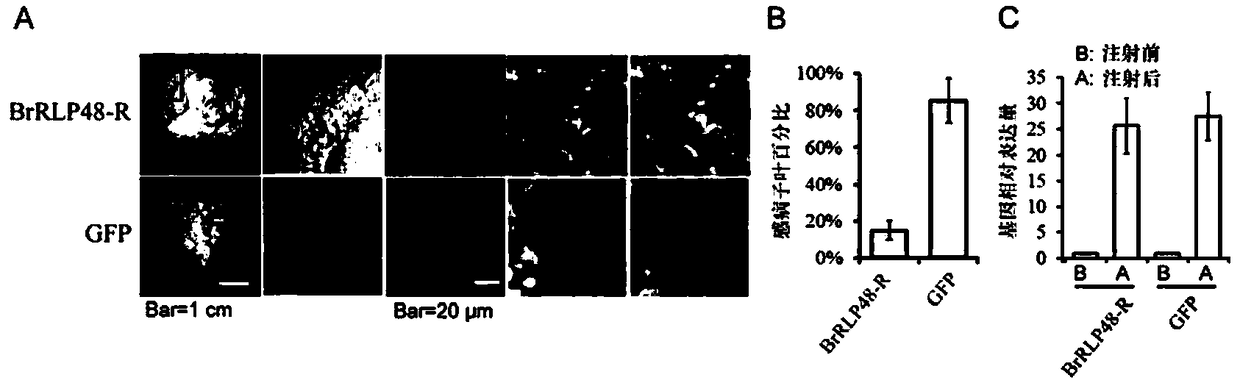
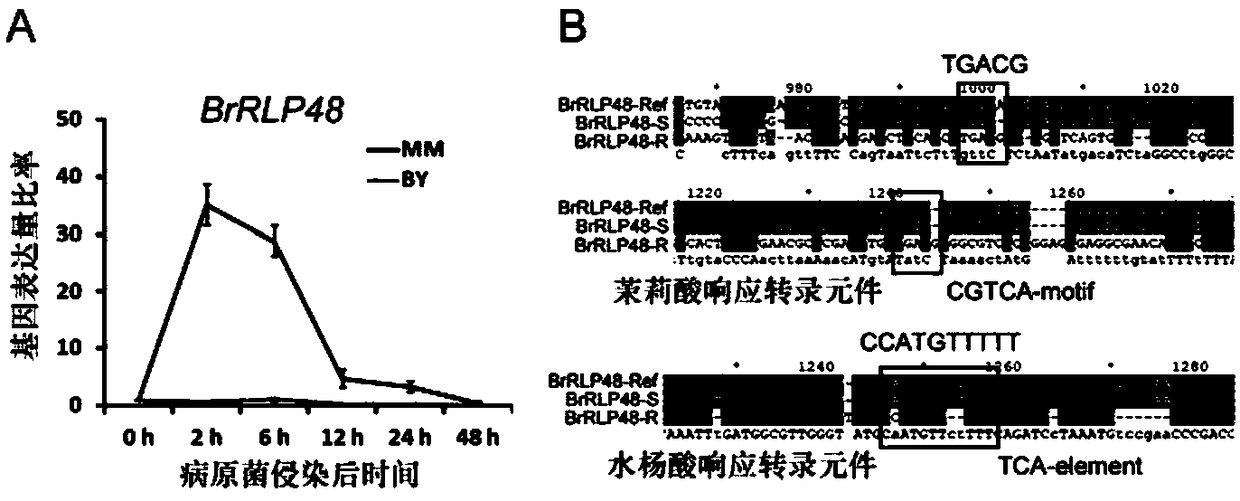
Downy mildew resistance gene BrRLP48 on Chinese cabbage A04 chromosome and SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) marker linked to same
ActiveCN109136401ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceF2 population
The invention discloses downy mildew resistance gene BrRLP48 on Chinese cabbage A04 chromosome and an SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) marker linked to the same. DH and F2 populations of Chinese cabbage disease-resistant inbred line MM and susceptible inbred line Bai Yang are used herein to successfully locate QTL (quantitative trait locus) Br-DM04 related to Chinese cabbage downy mildew resistance on Chinese cabbage No. 4 chromosome; 22.3% of phenotypic variations can be interpreted, the downy mildew resistance gene and the SNP molecular marker A04_5326733 linked thereto can be located. The molecular marker A04_5326733 based on KASP (competitive allele-specific PCR) technique is applicable to identification and molecular breeding of Chinese cabbage downy mildew resistant breeds.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Primer group for construction of mustard SSR genetic map and construction method of genetic map
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a primer group for the construction of a mustard SSR genetic map and a construction method of the genetic map. The primer group is an EST-SSR primer based on information development of hot pickled mustard tuber transcriptome sequence, and contains 112 pairs of polymorphic primers. A stem-inflated the ''Zhejiang Tong No.1'' multiple-year inbred line as a female parent and a stem-non-inflated ''Qiuai large-leaf yellow potherb mustard'' multiple-year inbred line tiller mustard as a male parent are subjected to hybridization to obtain F1 progeny; and F1 inbreeding is conducted to obtain a F2 mapping population. 112 pairs of polymorphic primers are used for the construction of the mustard genetic map through two parents and 200 F2 populations. The invention constructs the very first SSR genetic map of a mustard vegetable germplasm peculiar to our country and provides basis for further QTL mapping and marker-assisted breeding.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
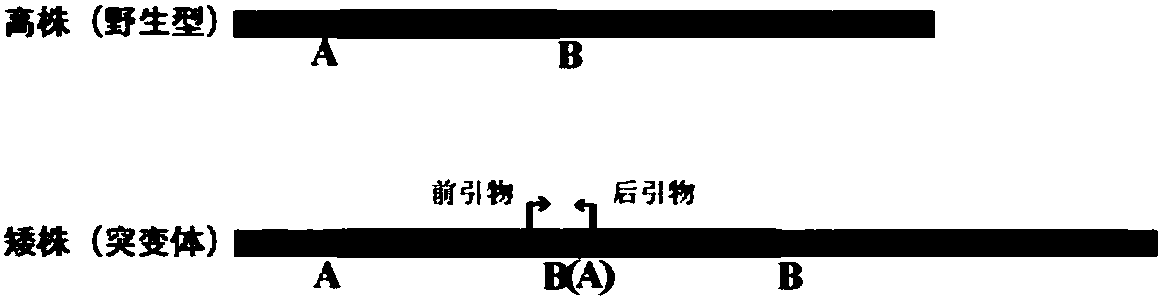
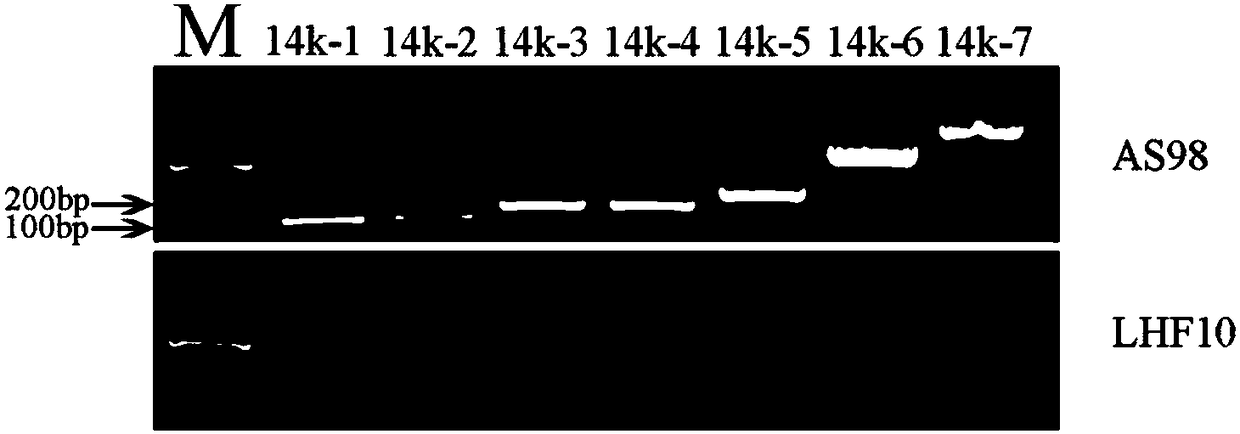
Molecular marker closely linked to dwarfing traits of upland cotton AS98 and application
ActiveCN108531644AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and discloses a molecular marker closely linked to dwarfing traits of upland cotton AS98 and application. The molecular marker is located on a D12 chromosome, a specific primer pair using the molecular marker can amplify 120 bp. products, a forward primer sequence of the specific primer pair is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and a reverse primer sequence of the specific primer pair is shown as SEQ ID No.2. A pair of primers for identifying mutants and wild types of the upland cotton dwarfing material AS98 are found out. 90% or more of phenotypic variations can be explained in an F2 population constructed by the upland cotton AS98 and a wild type LHF10. The molecular marker can be used for molecular marker-assisted selection and map cloning ofupland cotton AS98 dwarfing varieties, and a certain theoretical basis is provided for revealing cotton dwarfing mechanism and cultivating new dwarfing varieties.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
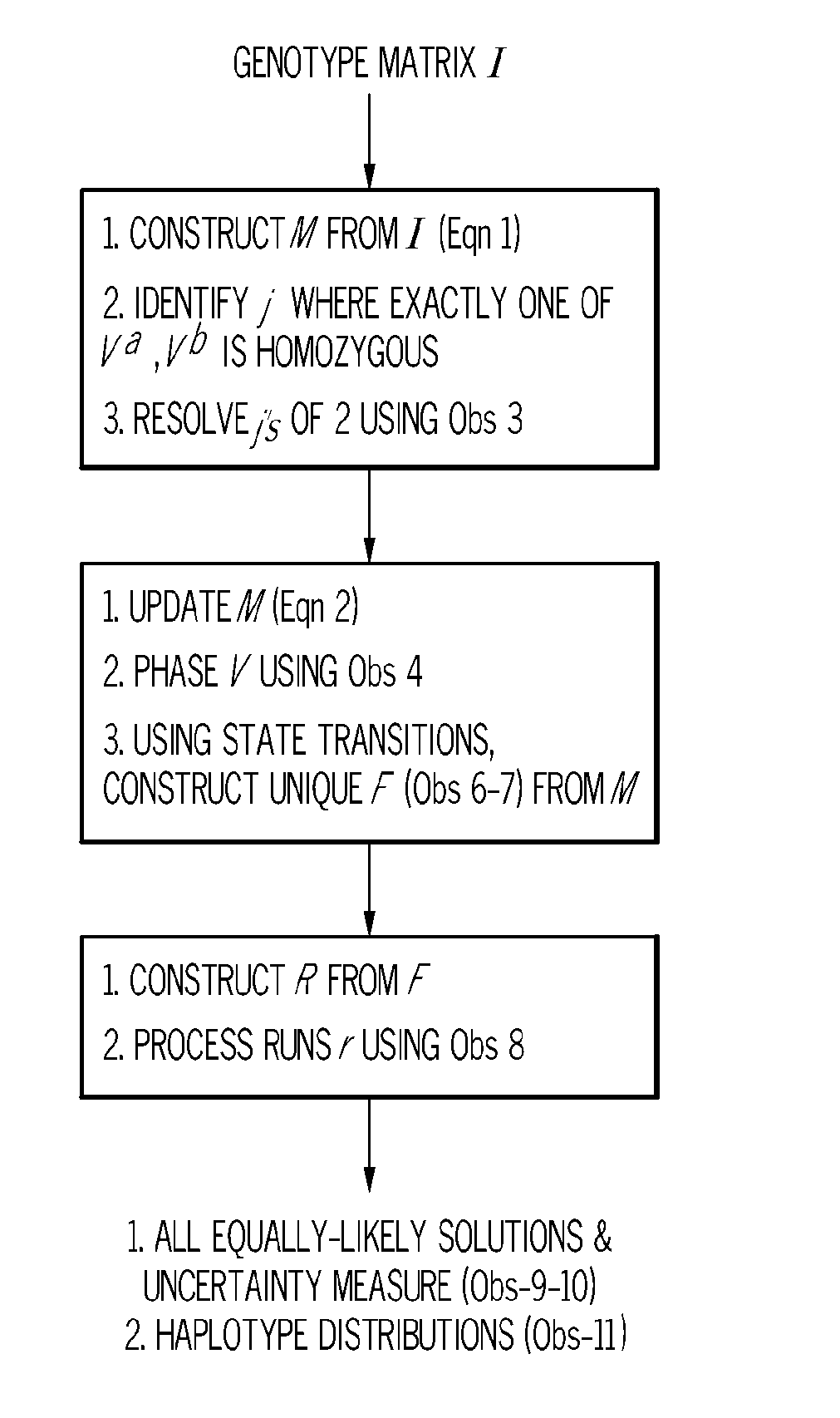
Exact haplotype reconstriction of f2 populations
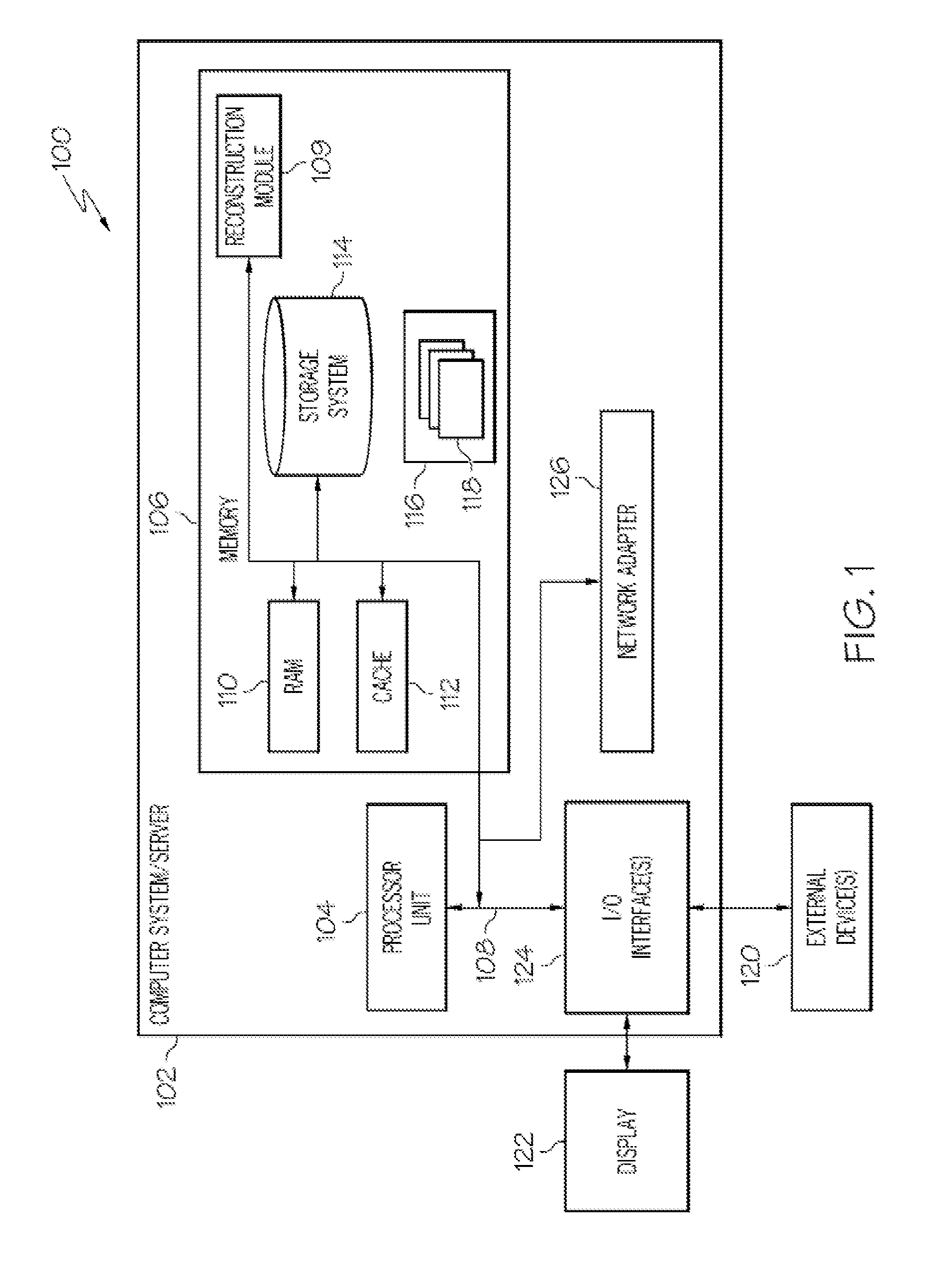
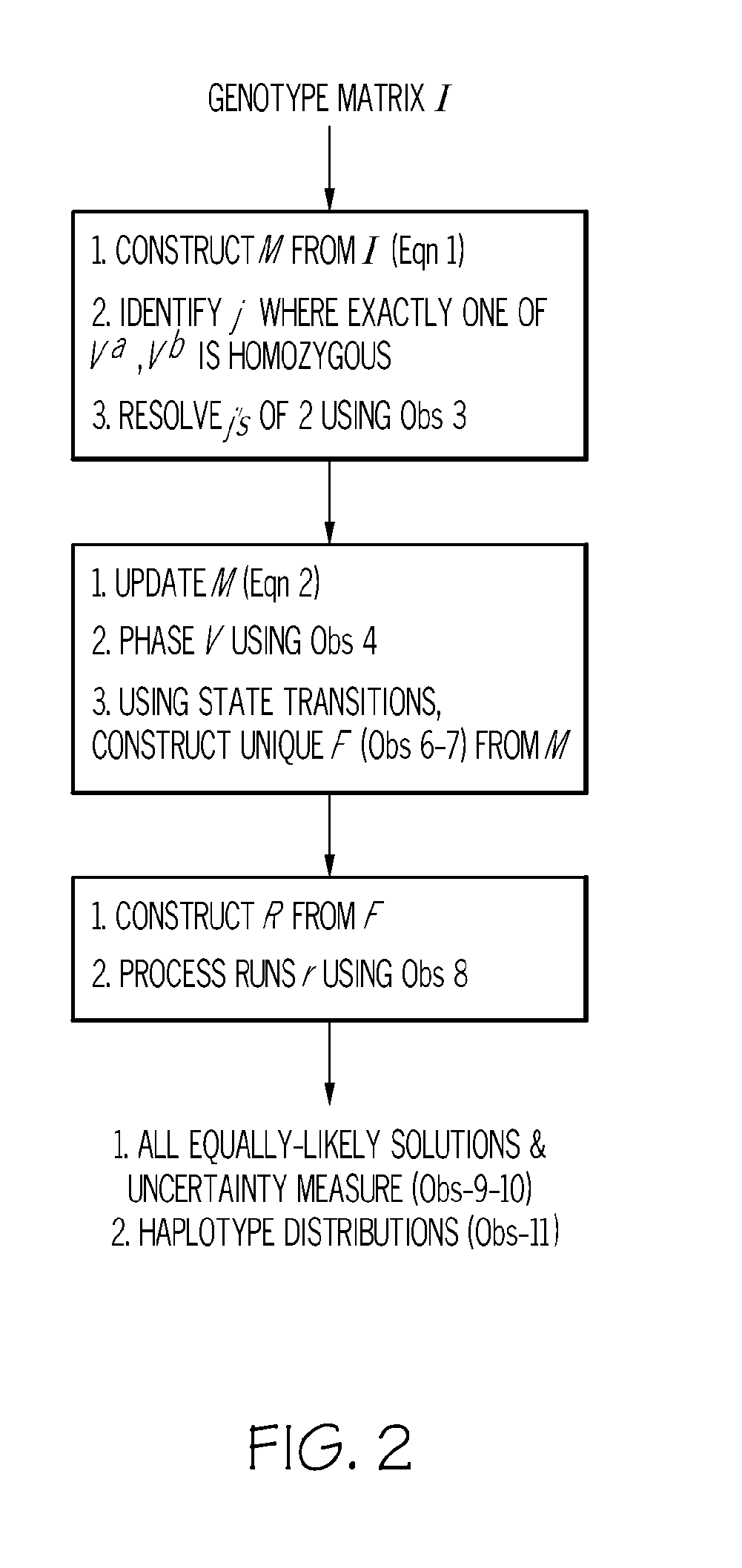
A system for reconstructing haplotypes from genotype data includes a memory, a processor, and a reconstruction module. The reconstruction module is configured to access a set of progeny genotype data including n progenies encoded with m genetic markers. A first set of parent haplotypes associated with a first parent of the n progenies and a second set of parent haplotypes associated with a second parent of the n progenies are identified based on at least the set of progeny genotype data. An agglomerate data structure including a collection of sets of haplotype sequences characterizing the n progenies is constructed based on the set of progeny genotype data and the first and second sets of parent haplotypes. Each set of haplotype sequences includes a number of crossovers equal to a total minimum number of observable crossovers in the n progenies.
Owner:IBM CORP
Molecule mark for assisting root-knot nematodes N resistant gene selection
The invention provides a molecular mark assisting selection of a root-knot nematode resistant N gene. The invention adopts a F2 population which containing the 'N' gene and is composed of inbred line Carolina Wonder and susceptible inbred line solanaceous phylum and artificial inoculated root-knob nematode, together with the BSA and AFLP technologies, to develop molecular marks and obtain a molecular mark E39 / M41-527.The primers augmenting the E39 / M41-527 are represented in the sequence table SEQ ID NO.1, and NO.2. According the analysis of AFLP, the molecular mark E39 / M41-527 shows polymorphism in a resistant-susceptible pool; and by the analysis of a Joinmap3.0 mapping software, the genetic distance of the N gene is 6.258 cm. The invention provides a foundation for selection of root-knot nematode resistant N gene in peppers.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rice variety IR24 black-streaked dwarf virus resistant site and molecular marker method thereof
InactiveCN106834424AImprove selection efficiencyEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementRice black-streaked dwarf virusCombined method
The invention relates to a rice variety IR24 black-streaked dwarf virus resistant site and a molecular marker method thereof. According to the rice variety IR24 black-streaked dwarf virus resistant site and the molecular marker method, the filial generation F2 population of a rice black-streaked dwarf virus resistant variety IR24 and a susceptible variety is adopted as a mapping population; the rice black-streaked dwarf virus resistance is identified by using a combined method of natural field identification and improved laodelphax striatellus antixenosis identification; linkage analysis is carried out on virus resistance identification results and SSR marker data to obtain a SSR marker, closely linked to rice black-streaked dwarf virus resistance major QTL, on the chromosome 8; the resistance of a plant to the rice black-streaked dwarf virus can be predicated by detecting banding pattern data of the primer marker on the chromosome 8. Therefore, the selecting efficiency of black-streaked dwarf virus resistant rice is greatly enhanced and the rice breeding progress is accelerated.
Owner:YIELEAD RICE IND
Rice variety Zhejiang 5 black-streaked dwarf virus resistant site qRBSDV17 and molecular marker method thereof
InactiveCN106834425AEliminate distractionsAccurate and reliable phenotyping methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementRice black-streaked dwarf virusCombined method
The invention relates to a rice variety Zhejiang 5 black-streaked dwarf virus resistant site qRBSDV17 and a molecular marker method thereof. According to the rice variety IR24 black-streaked dwarf virus resistant site and the molecular marker method, the filial generation F2 population of a rice black-streaked dwarf virus resistant variety Zhejiang 5 and a susceptible variety Lianyungang 3 is adopted as a mapping population; the rice black-streaked dwarf virus resistance is identified by using a combined method of natural field identification and improved laodelphax striatellus antixenosis identification; linkage analysis is carried out on virus resistance identification results and SSR marker data to obtain two SSR markers, closely linked to rice black-streaked dwarf virus resistance major QTL, on the chromosome 11; the resistance of a plant to the rice black-streaked dwarf virus can be predicated by detecting banding pattern data of the primer markers on the chromosome 11. Therefore, the selecting efficiency of black-streaked dwarf virus resistant rice is greatly enhanced and the rice breeding progress is accelerated.
Owner:WUXI NANLIGONG TECH DEV
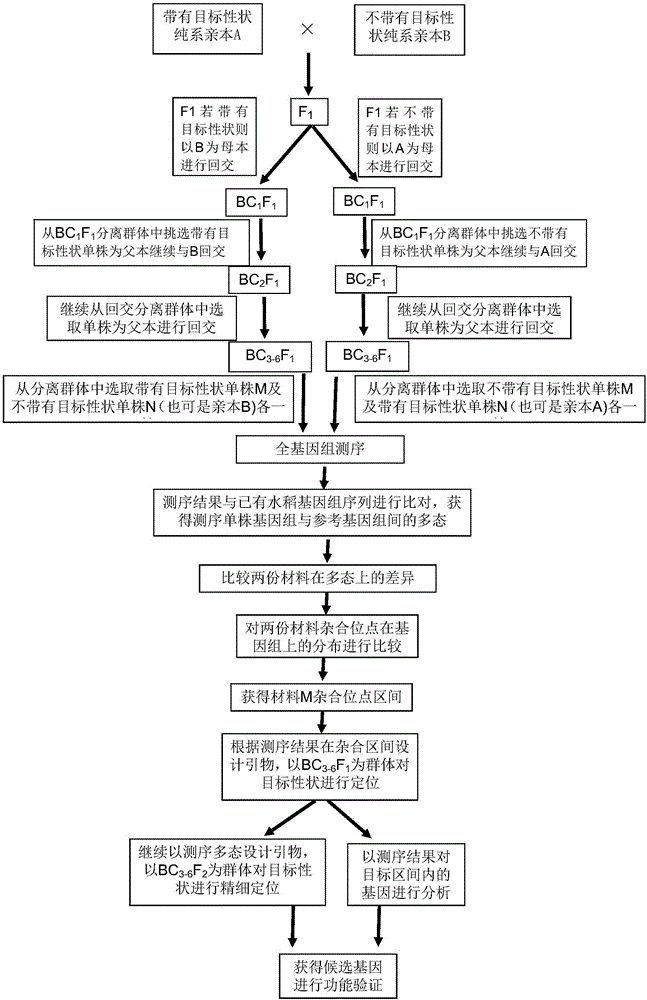
Method for separated identification and fine positioning of rice agronomic trait gene by whole genome sequencing
ActiveCN106480172APrecise positioningAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementRe sequencingBackcross population
The invention discloses a method for separated identification and fine positioning of a rice agronomic trait gene by whole genome sequencing; firstly, a 3-6 generation backcross population having separated target traits is obtained by backcross, two individual plants having the target trait with the biggest difference are selected for re-sequencing, heterozygous loci in sequencing results are compared and analyzed, and target trait candidate loci are screened; and then QTL separated identification and fine positioning are performed by using backcross F2 population linkage analysis. The method can quickly and accurately identify and finely position the rice QTLs, and lays a firm foundation for further cloning and functional analysis.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Method for preserving segregation population or distant hybirdization progeny of eggplant through stem microcuttage
The invention provides a method for preserving a segregation population or distant hybirdization progeny of an eggplant through stem microcuttage. The method comprises the following main steps: selecting a proper eggplant stem and carrying out sterilization; then carrying out cuttage on a bud mitogenetic medium, wherein buds successively grow out from leaf axil in 7 to 10 d; when the buds grow to 1 to 2 cm high, cutting the buds from positions near bases and sterilizing the cut buds; then transferring and inoculating the sterilized buds onto a subculture medium for culture; when the buds grow to 3 to 4 cm high, transferring the buds to a rooting medium for culture, wherein robust roots grow in 10 to 15 d and new eggplant seedlings are formed; and subjecting the new eggplant seedlings to domestication for a certain period of time and then planting the seedlings in a field, wherein the survival rate of the seedlings is 95 to 100%. If an F2 population is to be preserved for a long time, it only needs unintermittent transferring and inoculation onto the subculture medium once every 30 d. Compared with conventional cuttage and common tissue culture, the method provided by the invention has the following advantages: the method integrates the advantages of conventional cuttage and common tissue culture, i.e., short culture time, a small occupied land area, no invasion by insect diseases, easily controllable ambient conditions, convenience in management, and good stability and small possibility of variation due to generation of buds from stems. Thus, the method has critical application values in genetic and breeding research.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Indel molecular marker closely linked with capsicum annuum clustered inflorescence genes, primers and application
ActiveCN110592255AResolution cycleSolve efficiency problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceCandidate Gene Association Study
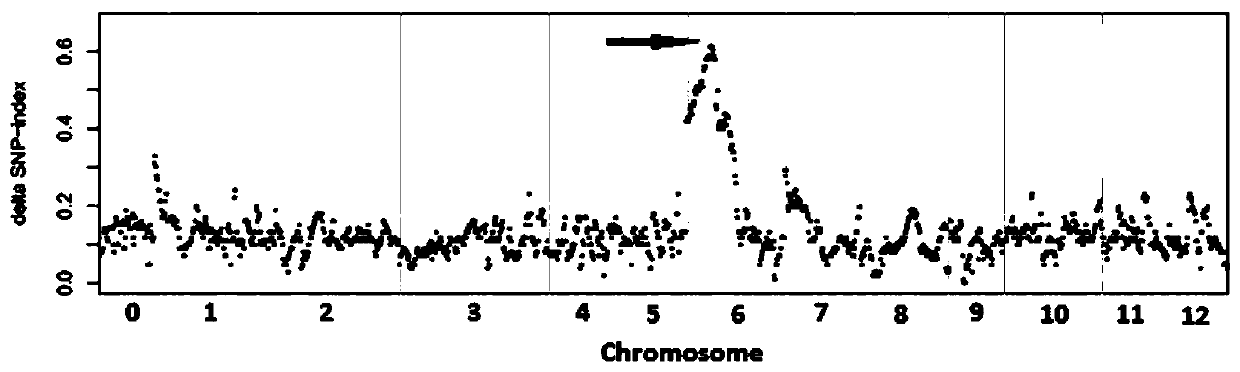
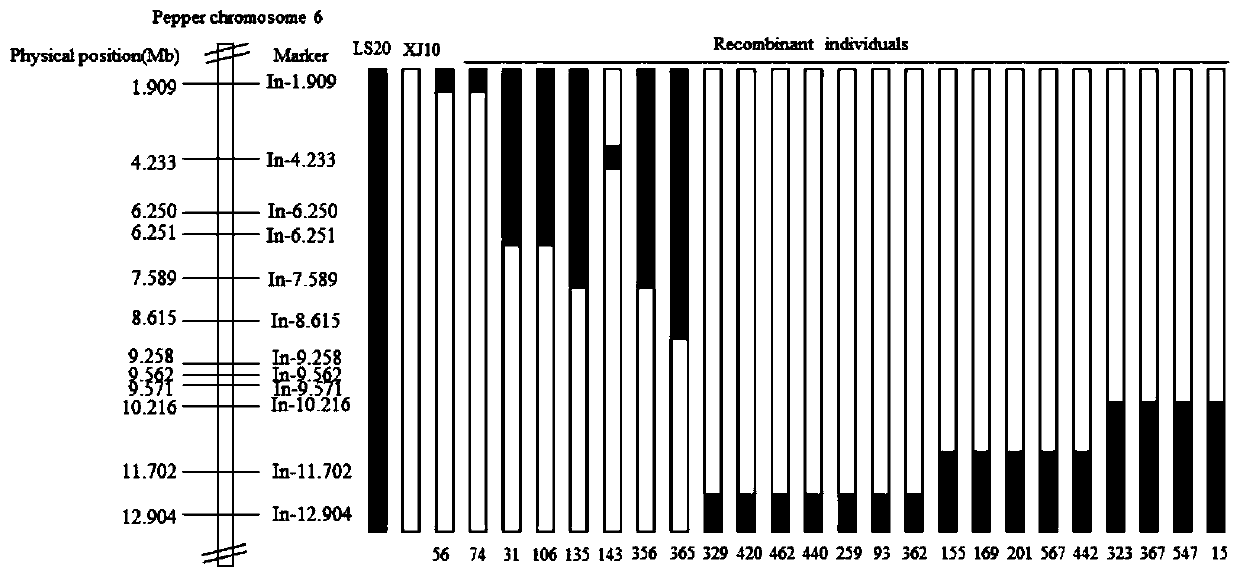
The invention discloses an Indel molecular marker closely linked with capsicum annuum clustered inflorescence genes, primers and application. An F2 population is constructed by utilizing two highly-homozygous inbred lines. A chromosome region closely linked with capsicum annuum clustered inflorescences is acquired by using a BSR and linkage positioning method, and an InDel marker is developed in acandidate interval for verification. Finally, InDel closely linked with the vicinity of a candidate gene is obtained, a molecular marker In-9258 is designed according to the InDel, genotype identification is conducted on 100 randomly-sampled single plants of the F2 population by using the marker, and the coincidence rate reaches 100%. The research result not only can be used for capsicum annuum inflorescence type identification and molecular assisted breeding, but also provides a basis for controlling map-based cloning of capsicum annuum clustered inflorescence genes and for analyzing the forming molecular mechanism of clustered inflorescences.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +1
Method for creating ornamental sunflower purple-flower novel variety with high selfing setting percentage
PendingCN109452163AImprove firmnessShort cycleAgriculturePlant genotype modificationPollinationF2 population
The invention discloses a method for creating ornamental sunflower purple-flower novel variety with high selfing setting percentage. The method adopts the scheme with the following steps of hybridizing the varieties with far genetic relationship, and segregating the hybrid F2 population to obtain a purple-flower sterile single plant; using the purple-flower single plant as a female parent, and selecting the parent with higher selfing setting percentage as a male parent to hybridize; after hybridizing, producing the fertile and sterile purple-flower single plants; using the purple-flower fertile single plant as the female parent, and using the previous male parent as a recurrent parent to backcross for multiple generations; after backcrossing for multiple generations, performing selfing, soas to obtain the purple-flower novel variety with genetic stability and high selfing setting percentage; during pollination in the hybridizing process each time, combining the artificial pollen brushing type and the bee pollination type. The method has the advantages that the purple-flower sunflower seed resource with high setting percentage can be effectively obtained; the innovation cycle of the material is short, and the required sunflower seed resource can be innovatively obtained after 5 to 6 generations; the technique is simple, and the operation is easy.
Owner:贵州省油料研究所
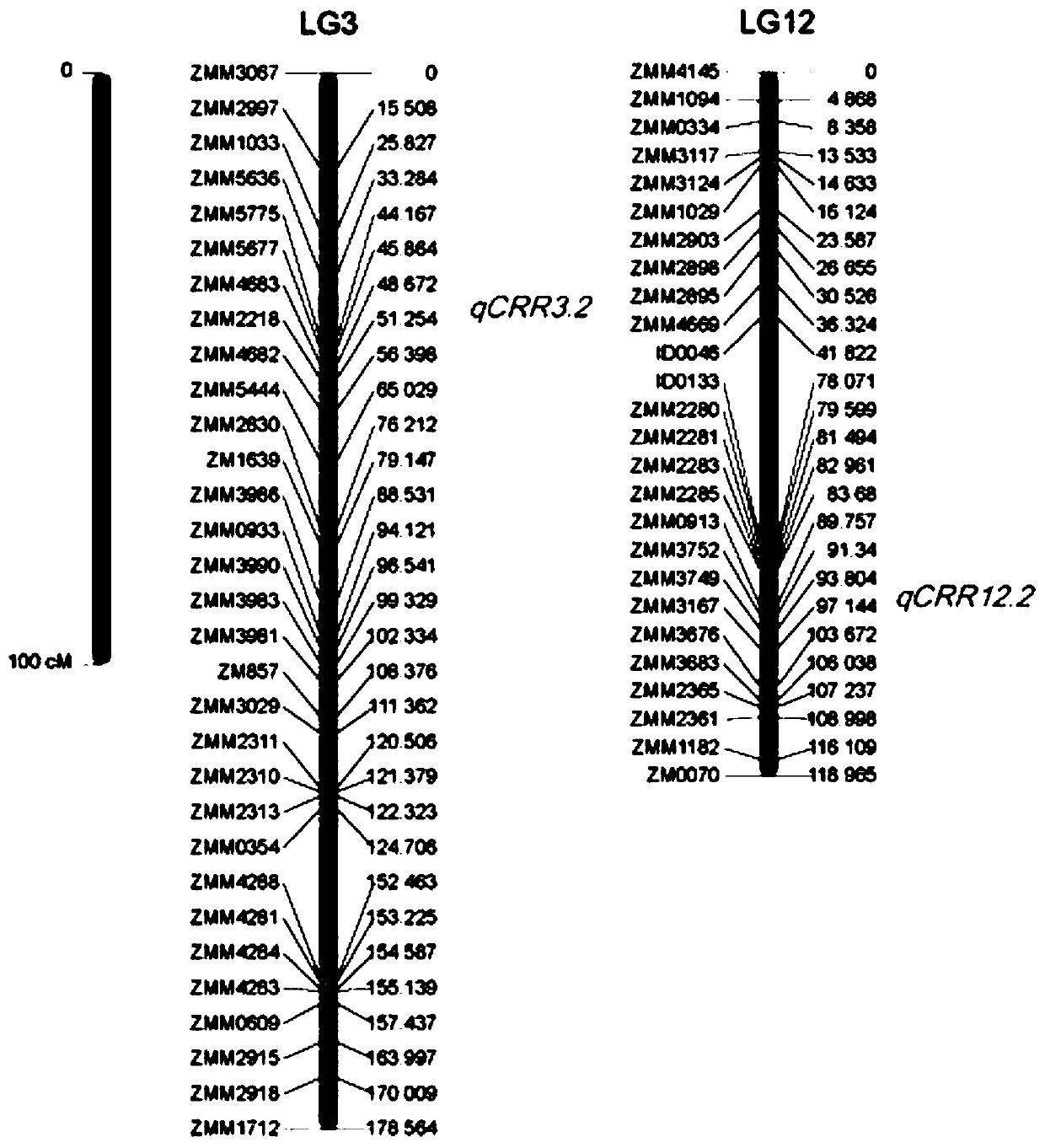
The ssr molecular marker closely linked to the main gene locus of sesame resistance to stem spot blight and its application
ActiveCN107058518BEasy to detectWith a clear purposeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSesamumAgricultural science
The invention provides an SSR (Simple Sequence Repeats) molecular marker closely linked to sesame stem rot resisting major genetic locus and applications thereof. Four SSR molecular markers closely linked to the sesame stem rot resisting major genetic locus are adopted and respectively named as ZMM0913, ZMM3752, ZMM5636 and ZMM5775; the primer sequences of the molecular markers respectively are: ZMM0913F:5'-CTCATGTGGAACGAGGCATA-3', ZMM0913R:5'-ATGGCCACCACCTAACATTC-3',ZMM3752F:5'-CAACGATGAGATGGCTTTGA-3',ZMM3752R:5'-TCTTGCACGCACAGTAGTCC-3',ZMM5636F:5'-CTGCTCATCACCTCTGGAAAG-3',ZMM5636R:5'-TGACCTATGATGTGATAACAGTTGG-3',ZMM5775F:5'-TTCACTTTGCTTTTGTTGCC-3', ZMM5775R:5'-GCCCATTCCATGAGTTTTTG-3'. Proved by F2 population verification, the four molecular markers: the ZZM0913, the ZZM3752, the ZZM5636 and the ZZM5775 are capable of increasing the efficiency of screening the stem rot resisting sesames, so that the molecular markers can be applied to the sesame stem rot resisting molecular marker-assisted selection breeding.
Owner:OIL CROPS RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com