Downy mildew resistance gene BrRLP48 on Chinese cabbage A04 chromosome and SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) marker linked to same
A technology for cabbage downy mildew and downy mildew resistance, applied in DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of long cycle of disease-resistant cabbage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
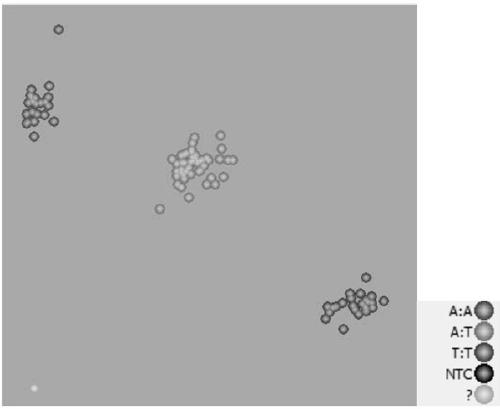
[0103] Example 1, the acquisition of SNP marker A04_5326733
[0104] 1. Test materials
[0105]F 1 The microspores of the population were obtained for chromosome doubling, and finally a doubled haploid population (DH, Doubled Haploid population) was obtained, and the DH population contained 80 individual plants.
[0106] F 1 Generation groups, the F 1 Each individual plant in the generation population is self-crossed, and F 2 group, F 2 The population contained 1056 individuals.
[0107] The DH population consisting of 80 strains and the F population consisting of 1056 strains were selected. 2 groups as targeting groups.
[0108] 2. Genotyping
[0109] Planting two parental materials in the greenhouse, the disease-resistant parent "MM" and the susceptible parent "Baiyang", F 1 generation group, F 2 Population and DH population plant material. The young leaves were taken, and the whole genome DNA was extracted according to Doyle and Dickson (1987) with a slightly mod...
Embodiment 2
[0126] Example 2, Application of A04_5326733 locus in identification of cabbage downy mildew resistance
[0127] 1. Test materials
[0128] With the F that is made up of 1056 strains in embodiment 1 2 The population, the disease-resistant inbred line "MM", and the susceptible inbred line "Baiyang" were used as test materials.
[0129] 2. Identification of downy mildew resistance
[0130] The downy mildew resistance of the tested materials was identified. The specific steps are as follows: plant the test material in the greenhouse, and inoculate downy mildew on the 16th day of planting when most of the two true leaves of the plants are fully unfolded and new true leaves are exposed (that is, the two-leaf one-core stage). Each mL will contain 1 x 10 4 or 1×10 5 The suspension of downy mildew pathogenic spores is evenly sprayed on the back of the leaves by spraying. Place the inoculated plants in a dark, 100% humidity environment at 18-20°C for 24 hours. Subsequently, move...
Embodiment 3
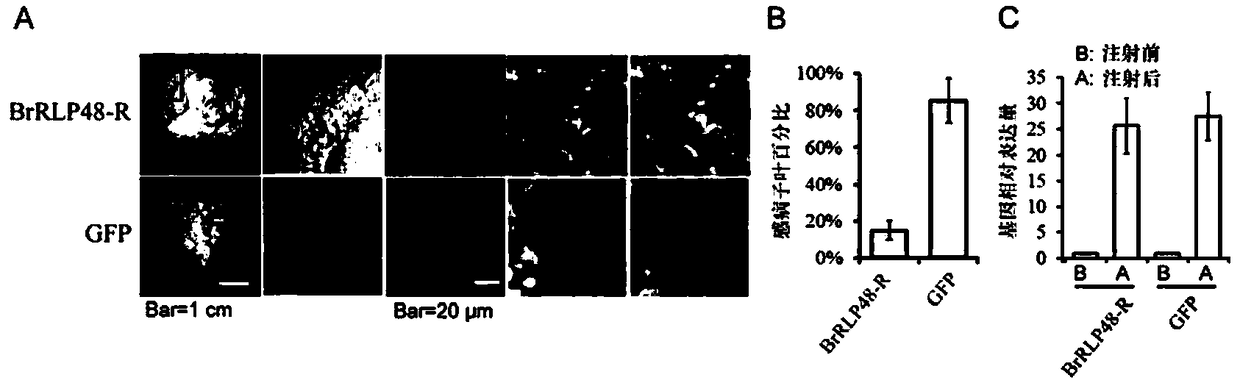
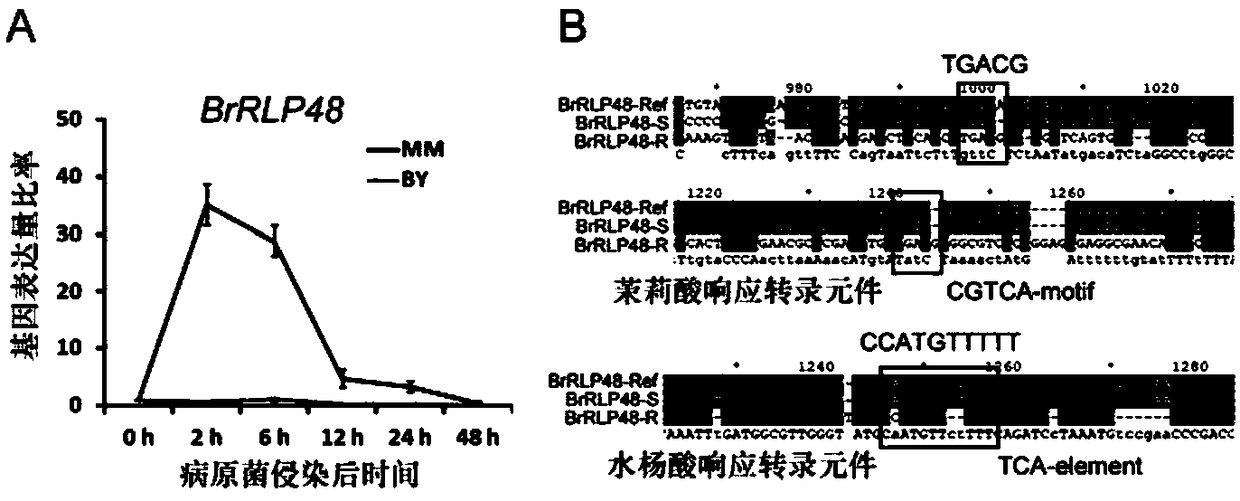
[0165] Example 3, disease resistance gene BrRLP48 and its functional analysis
[0166] 1. Transient expression experiment of disease resistance gene BrRLP48
[0167] There are 16 functionally annotated genes in the 160kb Bra-DM04 interval. According to the annotations, there are four possible candidate genes for disease resistance. The proteins encoded by these candidate genes all contain Leucine-rich repeat (LRR, Leucine-rich repeat) domains , because the marker A04_5326733 is inside the disease resistance candidate gene BrRLP48, which encodes a transmembrane protein containing 7 LRR (leucine-rich repeat) domains, and belongs to the receptor-like protein (RLP, receptor-like protein) family. Therefore, the BrRLP48 candidate gene was applied to the transient expression experiment of cotyledons of Chinese cabbage to verify its disease resistance function. The BrRLP48 candidate gene sequence is shown in sequence 6, the CDS sequence is shown in sequence 7, and the amino acid sequ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com