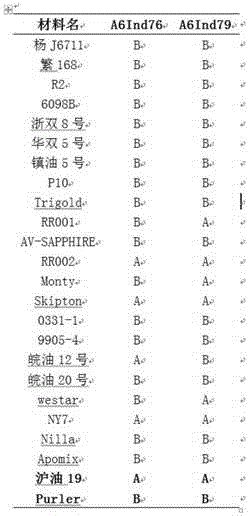
Molecular marker in close linkage with rape crotch angle character QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) and application
A branching angle and molecular marker technology, applied in the field of molecular biology and genetic breeding, can solve problems such as heavy workload, long process cycle, and constraints on the progress of QTL positioning, and achieve accurate and rapid screening, saving production costs, and convenient detection methods quick effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Construction and trait determination of rapeseed branching angle segregation population:
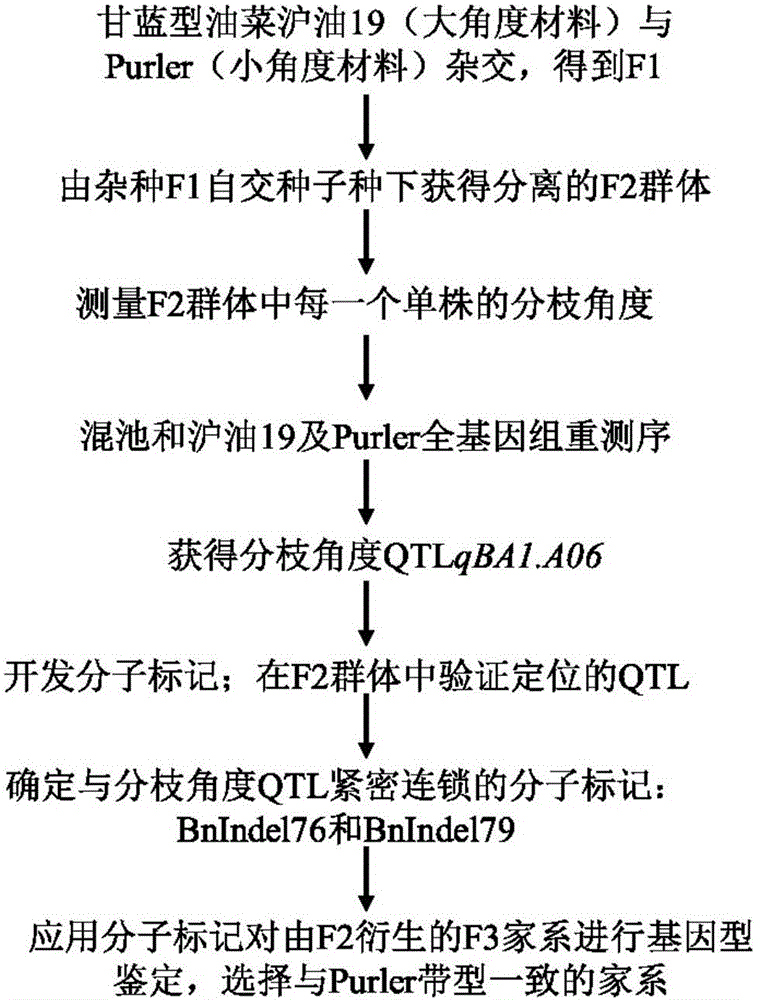
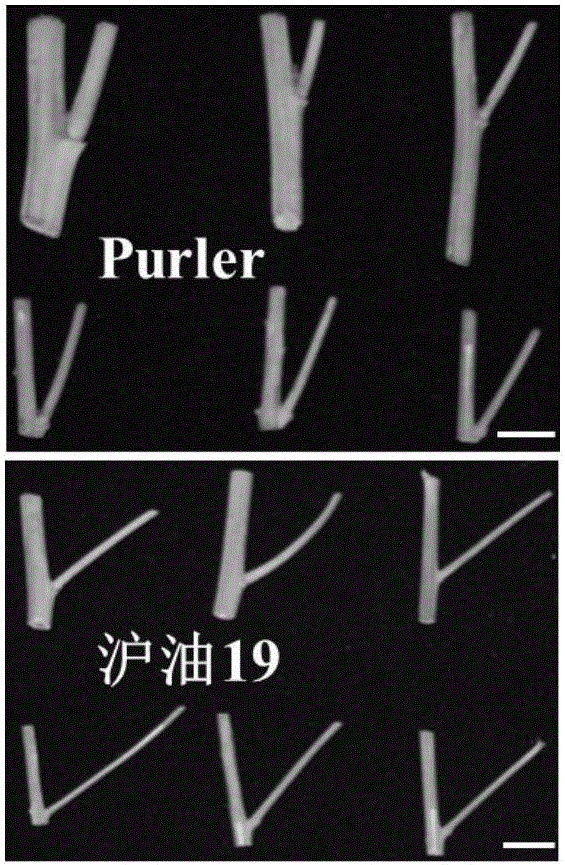
[0036] In this example, the F2 segregation population was constructed by crossing the large-branch angle material Huyou 19 and the small-branch angle material Purler. At the maturity stage of rapeseed, 277 lines and two parents were randomly selected from the F2 population to measure the branch angle. For the specific sampling and measurement methods, see the method of Wang Wenxiang et al. (2015).
Embodiment 2
[0038] Extraction of total DNA from leaves of parents and F2 populations:
[0039] Utilize CTAB method to extract total DNA from leaves, the specific steps are as follows:
[0040] (1) Take 0.5 grams of fresh leaves and put them into a 2 ml centrifuge tube, add 200 microliters of 2 times CTAB extract, then add steel balls and place them on an automatic grinder for grinding. After grinding, add 500 microliters to the centrifuge tube Put 2 times the CTAB extract in a constant temperature water bath at 65°C for 30 minutes, during which time mix 2-3 times;
[0041] (2) Add an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1, V / V), invert gently to make it fully mixed, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 10 minutes, gently draw 400 microliters of supernatant and transfer to another 1.5ml centrifuge tube;
[0042] (3) Add 1 / 10 volume (40 microliters) of sodium acetate to the supernatant, then add 2 times the volume of -20°C pre-cooled absolute ethanol, freeze at -20°C for half an hour to a...
Embodiment 3
[0045] QTL identification of branching angle in Brassica napus:
[0046] (1) In the F2 population, 30 copies of DNA from individual plants with extremely large branching angles were selected and mixed to form a large-angle pool, and 30 copies of DNA from plants with extremely small branching angles were mixed to form a small-angle pool. The HiSeq 2500 performs whole genome sequencing on two mixed pools and two parents, each pool constructs a 350bp library, the sequencing depth of the two DNA pools is 40×, and the sequencing depth of the two parents is 16×;
[0047] (2) Align the sequences obtained from the small-angle pool and the large-angle pool with the Brassica napus Darmor genome using BWA software, and then use SAMtools software (Li&Durbin, 2009) for SNP analysis, referring to SNP- in Takagi et al. (2013) The index calculation method calculates the SNP-index of all SNPs detected in the small-angle pool and the large-angle pool, and the difference between the subtractions...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com