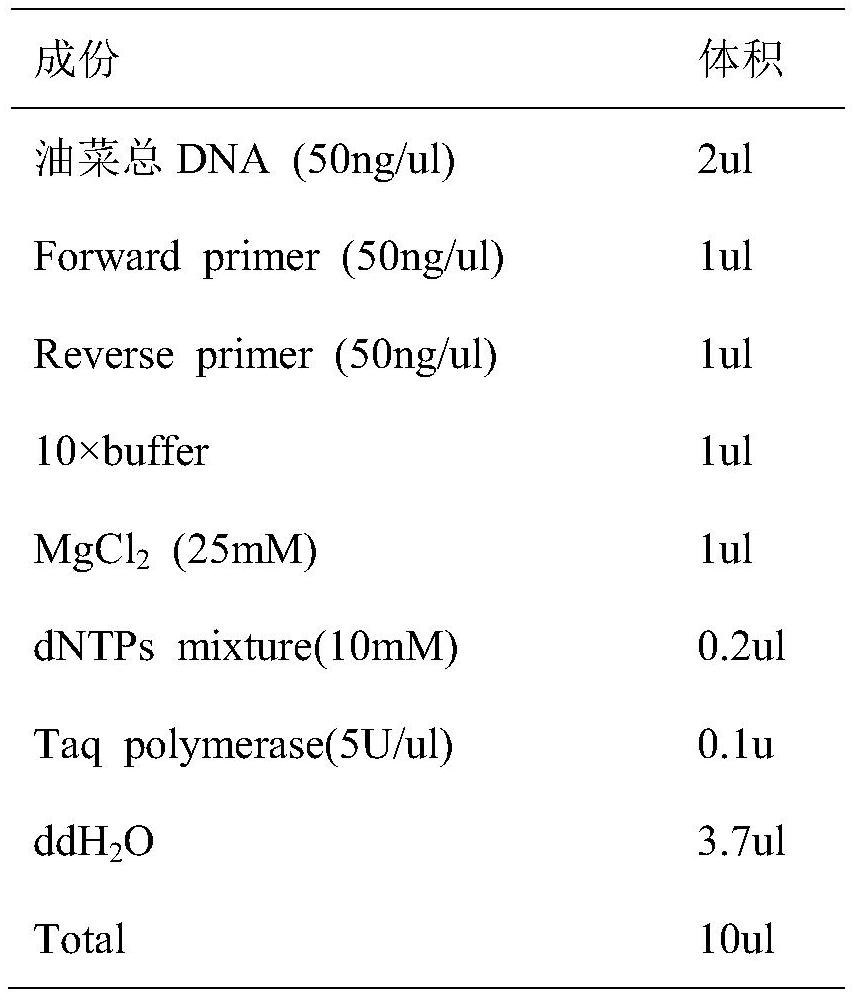
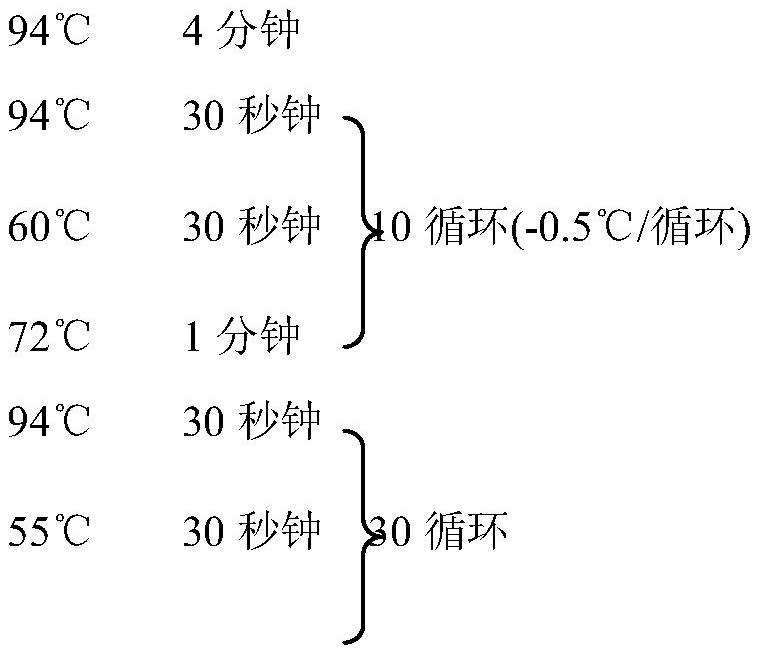
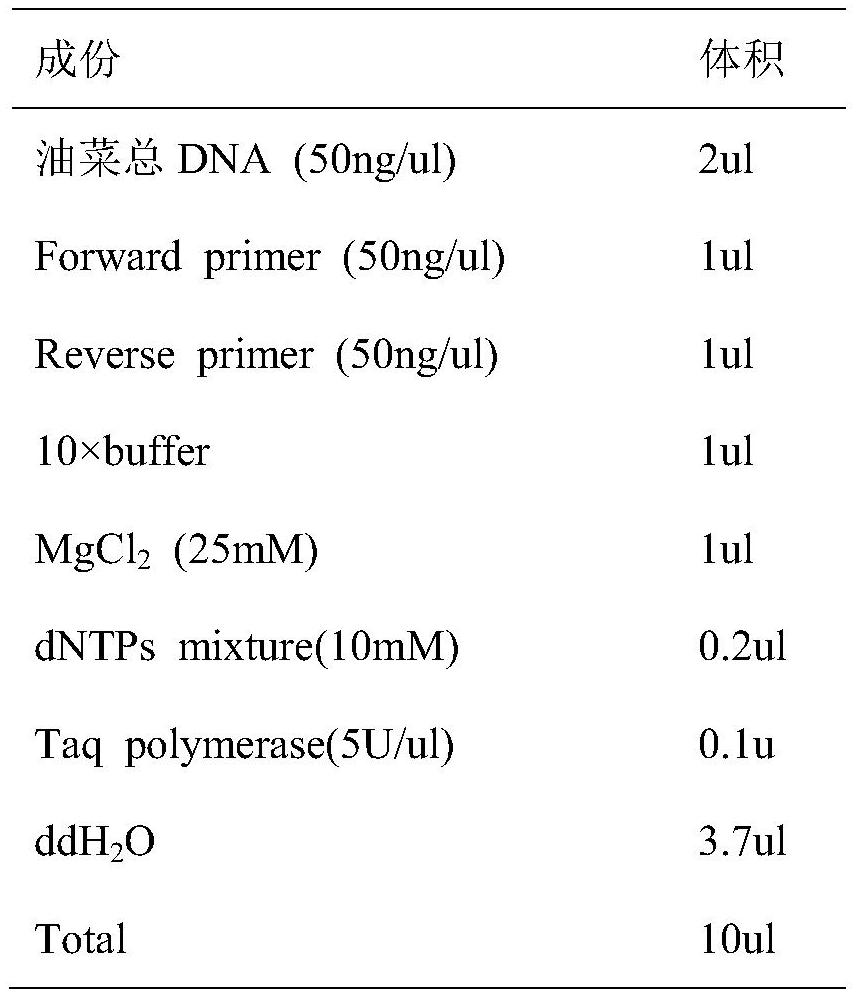
Patents
Literature
51results about How to "Selection inefficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
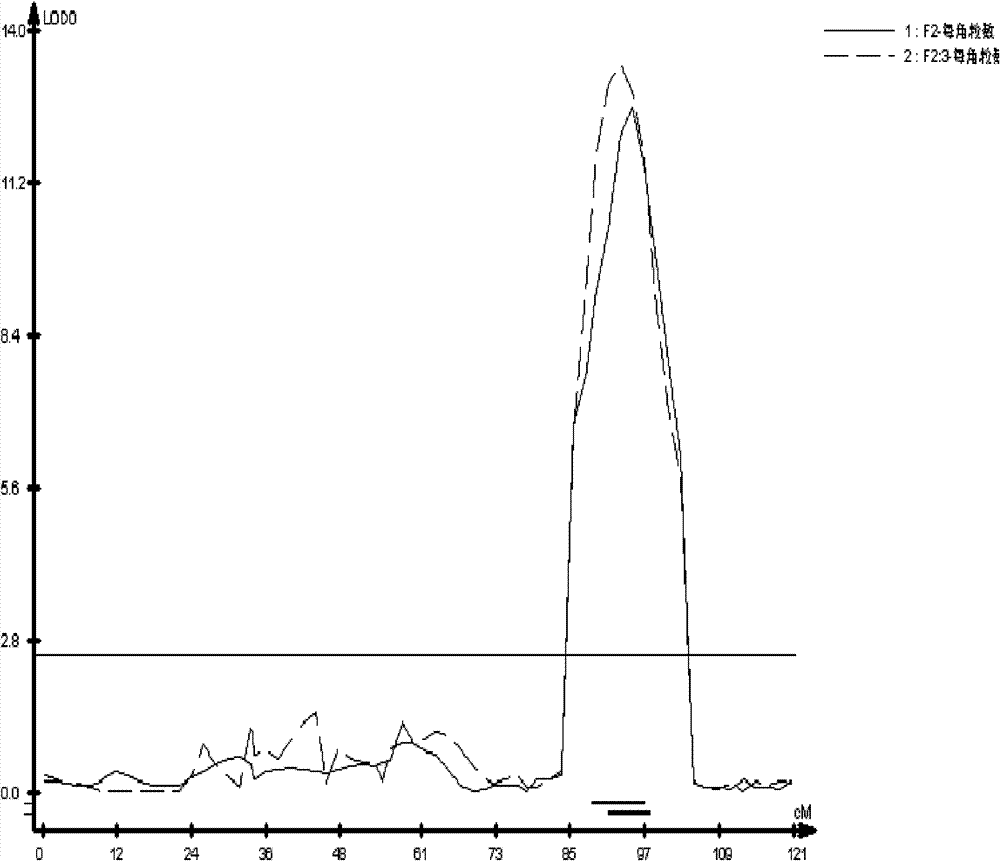
Molecular marker in close linkage with rape crotch angle character QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) and application
ActiveCN105969852ANot affectedAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceF2 population
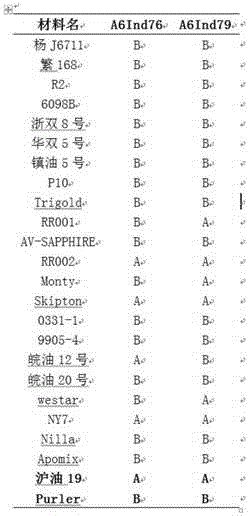
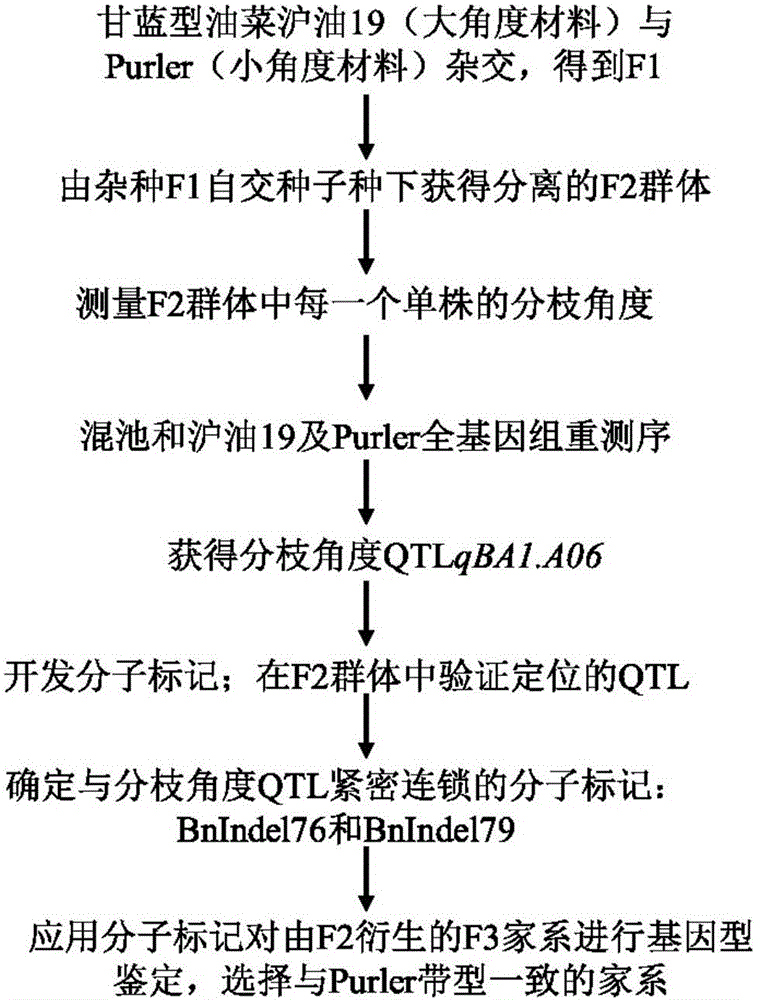
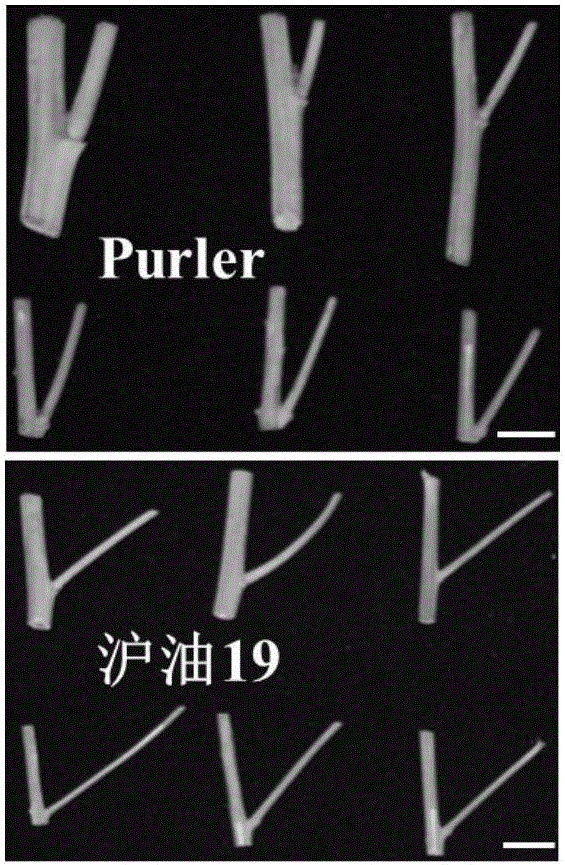
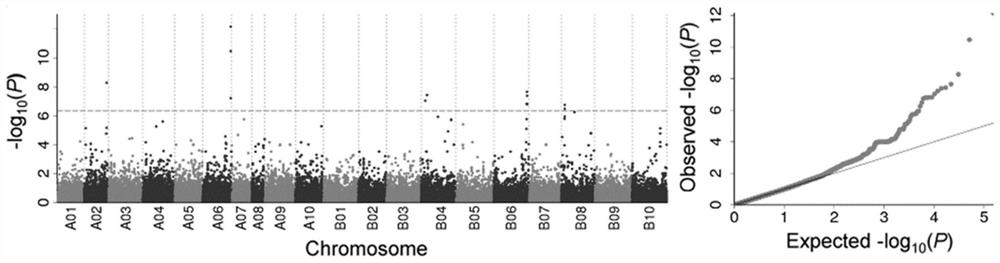
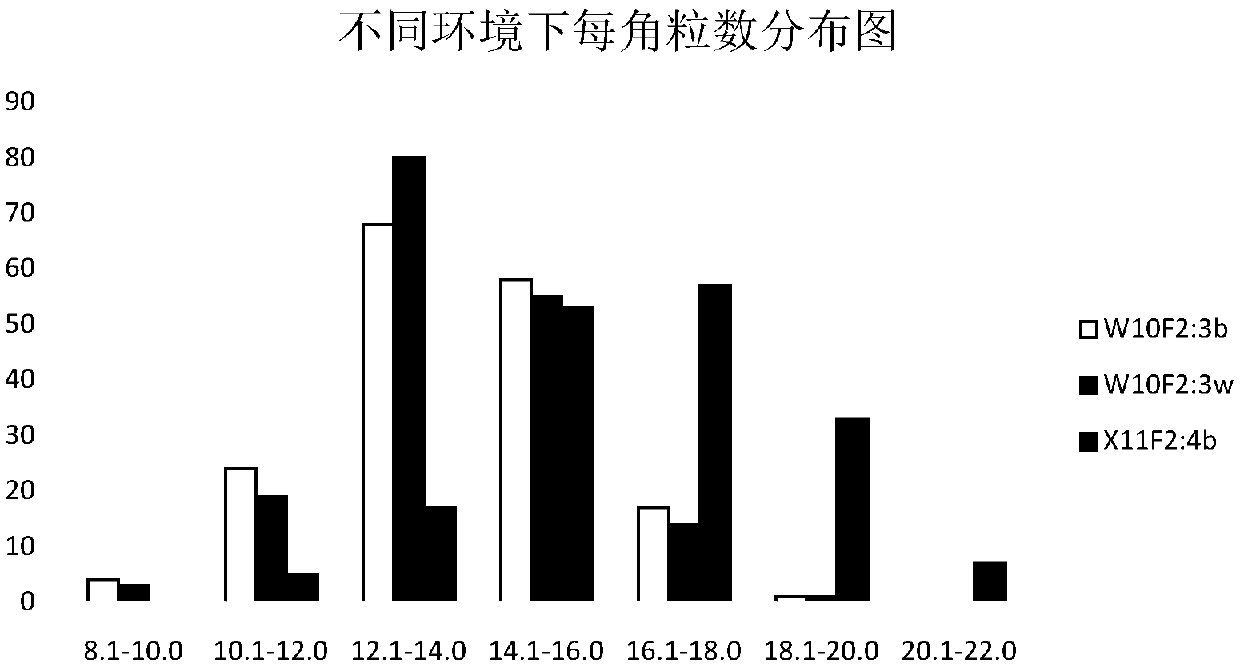
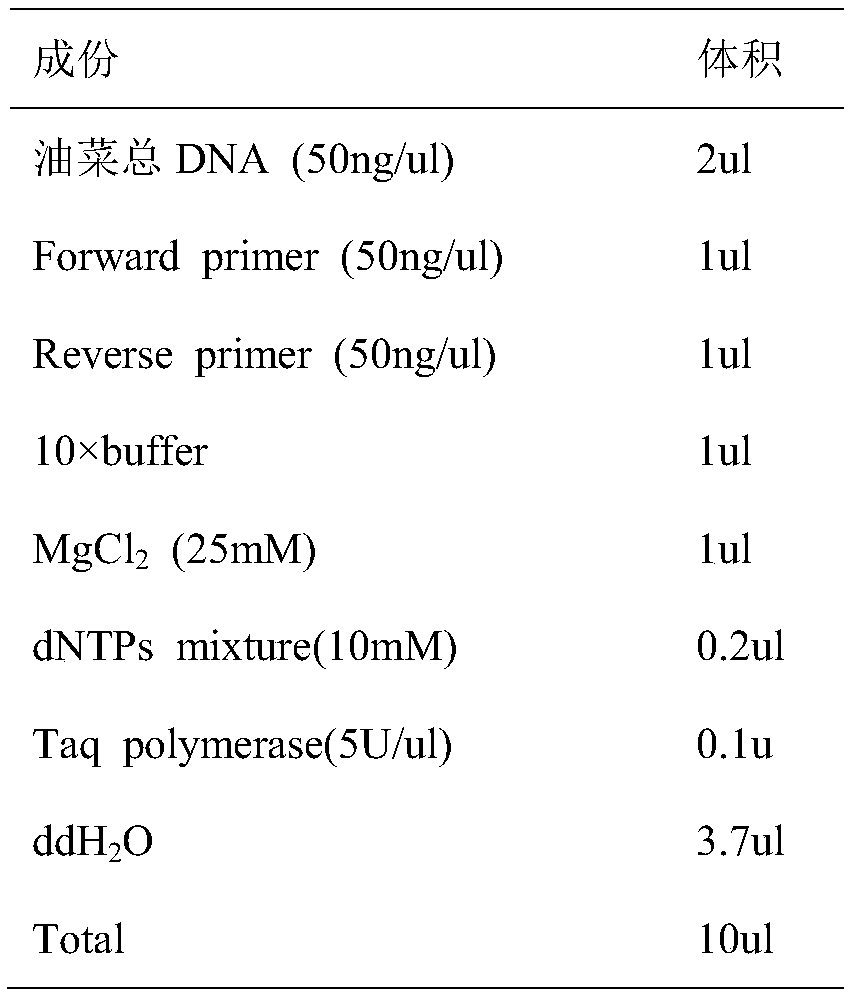
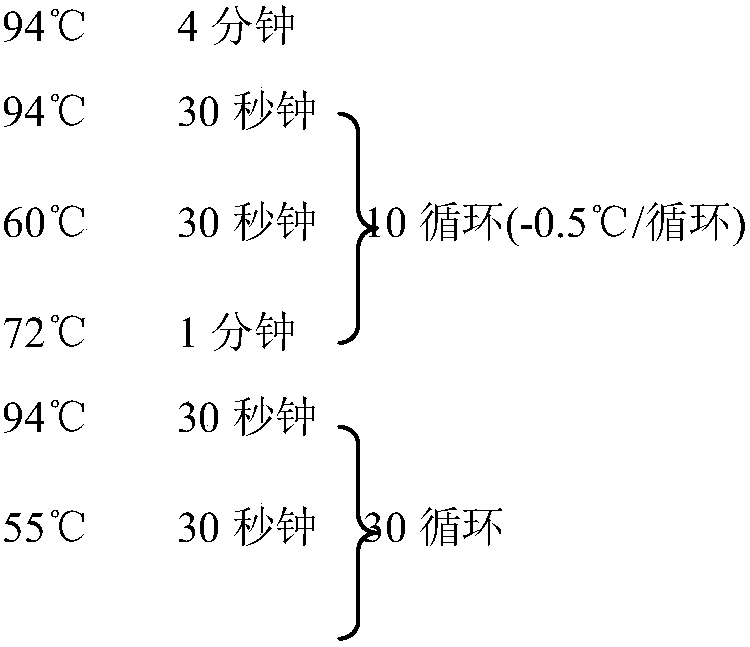
The invention discloses a molecular marker in close linkage with rape crotch angle character QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) and application. The molecular marker is characterized by carrying out hybridization by taking cabbage type rape variety Shanghai oil 19 as a female parent and Purler as a male parent, establishing F2 segregation population through selfing of hybrid F1, and analyzing, thus obtaining a crotch angle locus qBA1.A06; designing a primer by utilizing an Indel marker at the boundary of the crotch angle locus qBA1.A06 so as to detect the parents and the F2 population, thus obtaining a molecular marker BAIndel76 and a molecular marker BAIdenl79 which are in close linkage with the crotch angle character QTL; identifying a rape gene type formed after hybridization of the two parents by utilizing a marker primer, and carrying out auxiliary selection by utilizing the marker, thus greatly increasing the selection efficiency. According to the molecular marker disclosed by the invention, a novel genetic marker is provided for molecular breeding of the rape plant type, and useful information is also provided for accurate positioning on the crotch angle character QTL of the cabbage type rape and map-based cloning on related genes.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
SNP molecular marker related to pod and seed size on peanut A06 chromosome and application thereof
ActiveCN112094937ASpeed up the breeding processPrecise screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsBiotechnologyNucleotide
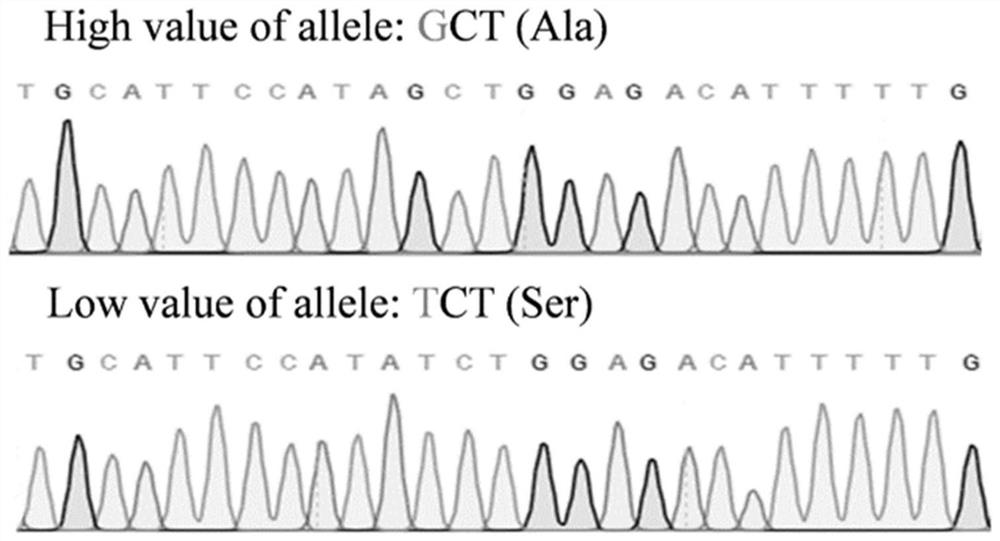
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular markers, and particularly relates to an SNP molecular marker related to pod and seed size on a peanut A06 chromosome and application thereof.The SNP molecular marker related to the pod and seed size on the peanut A06 chromosome is A06-107901527, and contains a nucleotide sequence with G / T polymorphism at the 12 site of the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. In the SNP molecular marker A06-107901527, the genotype of the site with the polymorphism is GG, the character value corresponding to the peanut pod and seed size is high, the genotype is TT, and the character value corresponding to the peanut pod and seed size is low. The SNP molecular marker is used for identifying the character phenotype of the peanut pod and seed size, theproduction cost can be greatly saved, and the selection efficiency can be improved.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rapeseed pod number major QTL molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN104805080AImprove selection efficiencySpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMarker-assisted selection
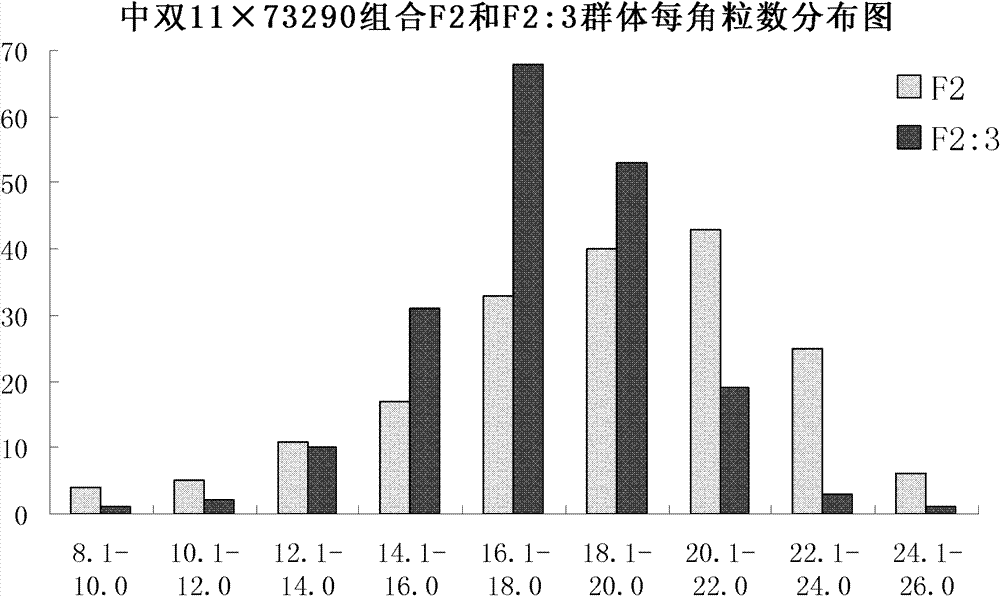
The invention discloses a rapeseed pod number major QTL molecular marker and its application. The marker can be used for marker-assisted selection in pod number character improvement and fine mapping and map-based cloning of QTL site. Primers of the molecular marker are CNU400F:5'-CGAGTTTTTGTGTGTACGTATAGTAAT-3' and CNU400R:5'-CCAAAGTGCGTAAAGGAAGG-3'. Rapeseed Zhongshuang 11 and 73290F3 generation are selected by the use of the marker, and silique number of the screened F3 single plant is higher than that of Zhongshuang 11 by 92.3%. Thus, the marker is utilized for assistant selection so as to greatly enhance selection efficiency of high yield breeding.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Soybean lodging-resistant major gene locus and application
InactiveCN103088148ANot affectedSelection inefficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular marker
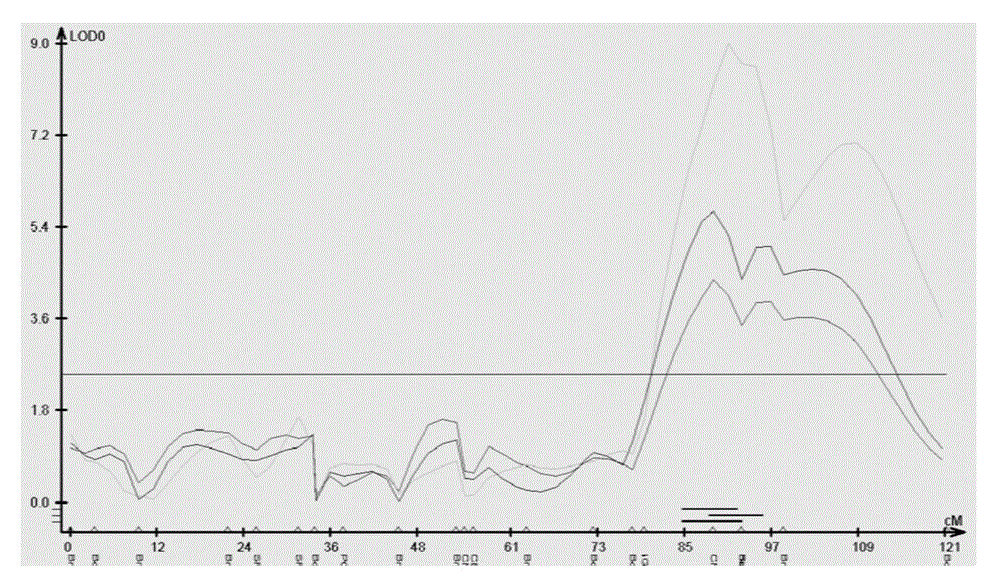
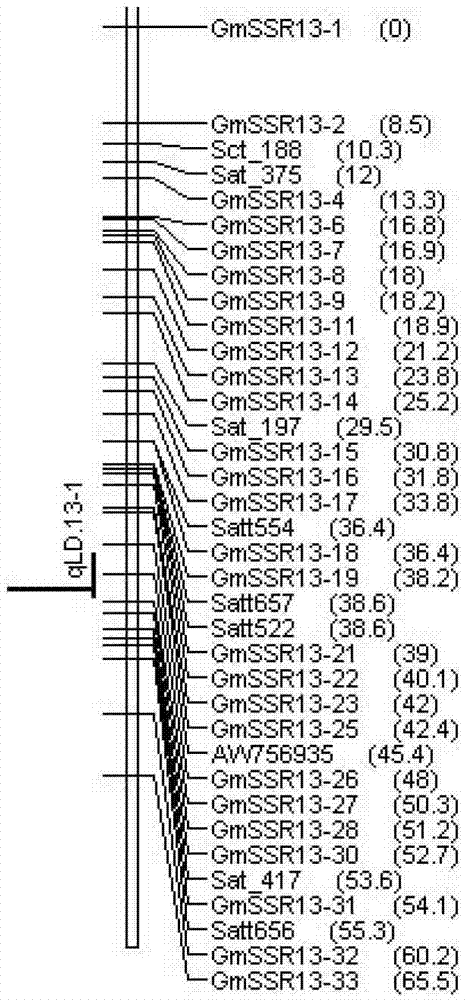
The invention discloses a soybean lodging-resistant major gene locus and an application, and provides the soybean lodging-resistant major gene locus and the application thereof in molecular marker-assisted selection breeding. The soybean lodging-resistant major gene locus is qLD.13-1 and the contribution rate is 37.6%. A molecular marker which is tightly interlocked with the soybean lodging-resistant major gene locus is GmSSR13-27. The tightly-interlocked molecular marker is used for detecting whether a breeding group family contains the major gene locus or not and the lodging resistance can be predicated; and the selection efficiency of soybean lodging-resistant breeding is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Seed number per pod character major gene site of rape and application thereof
InactiveCN102226189AThe detection method is convenient and fastPrecise screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationField experimentGenotype Analysis
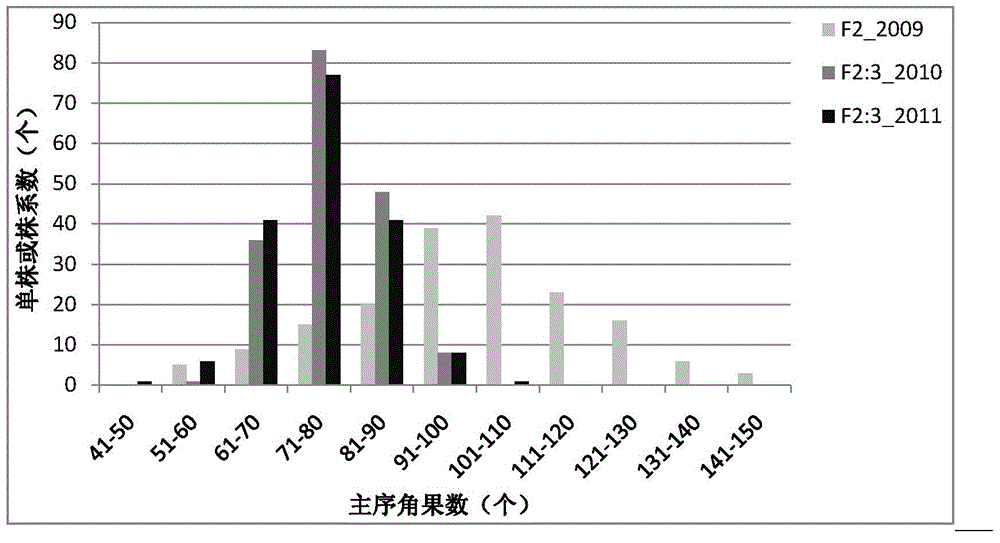
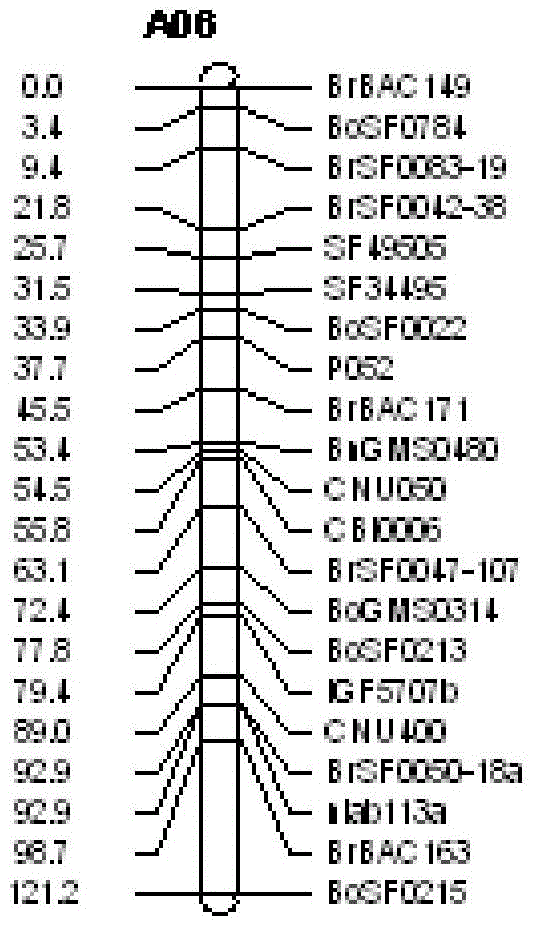
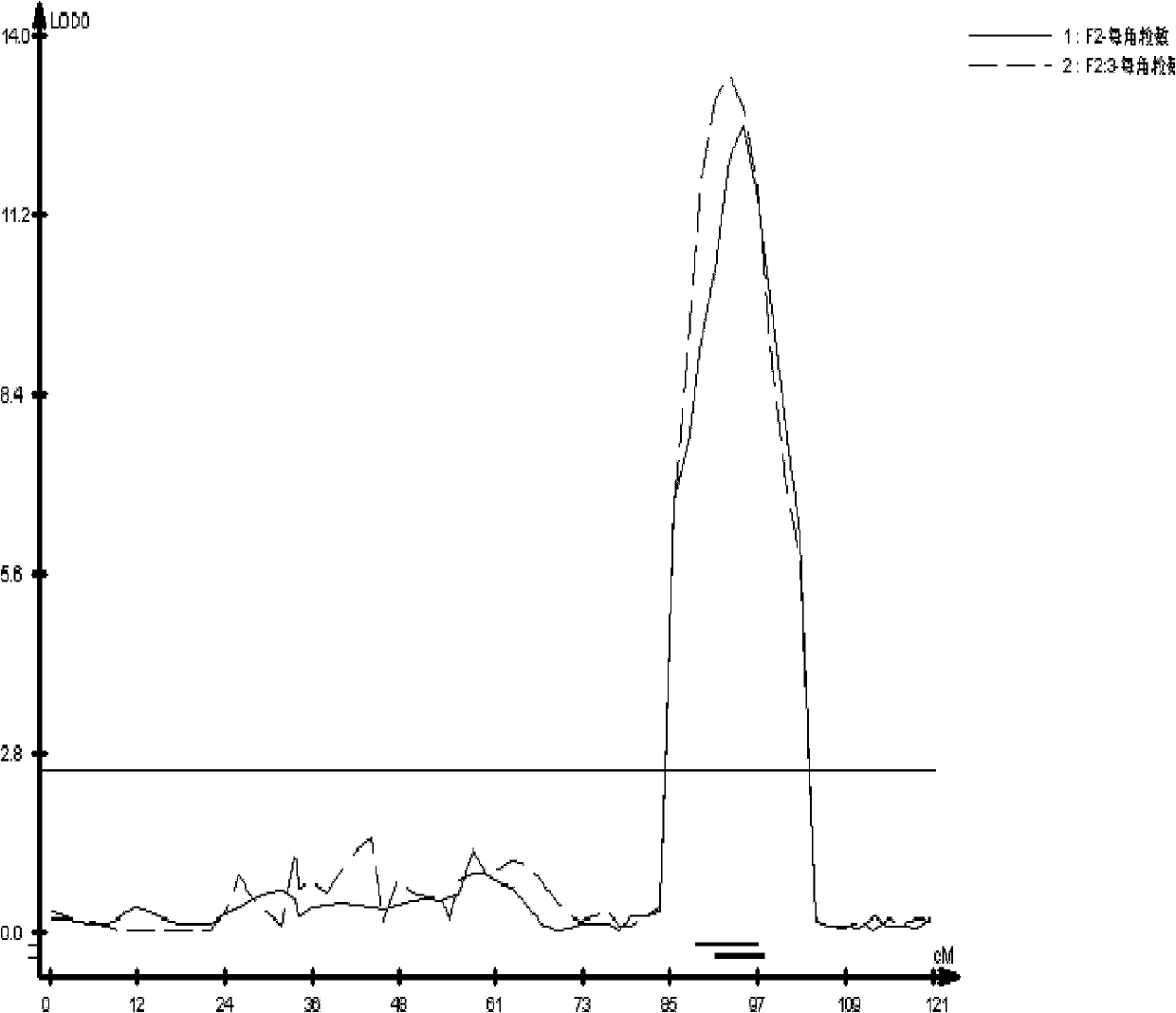
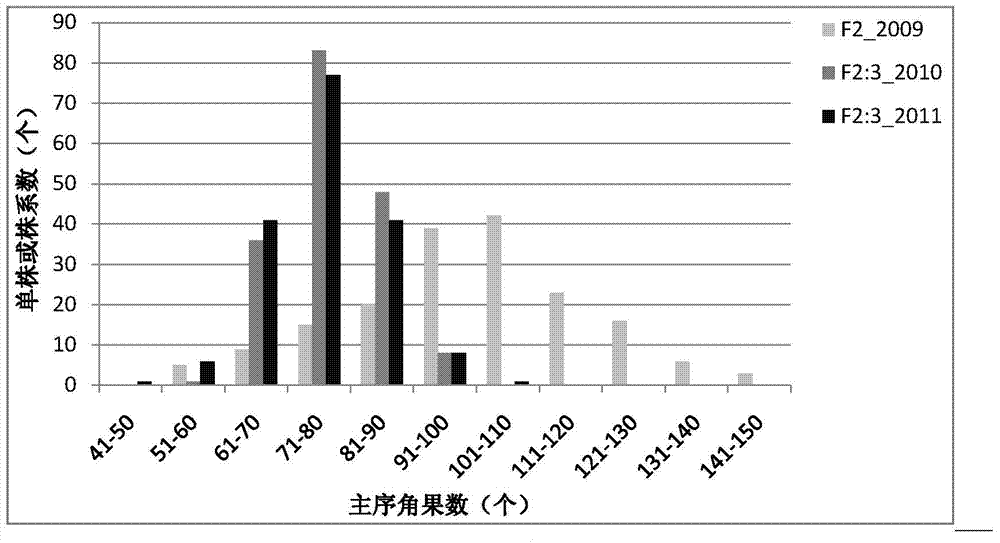
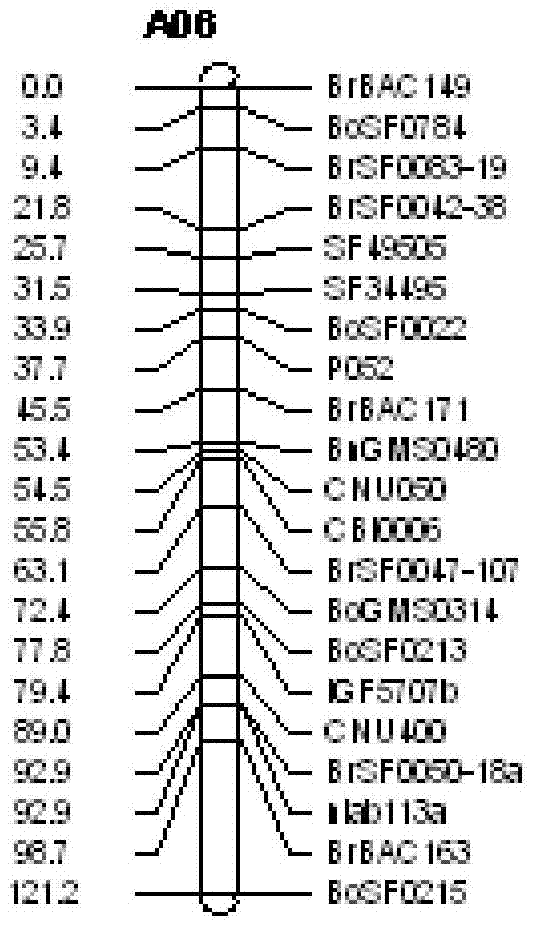
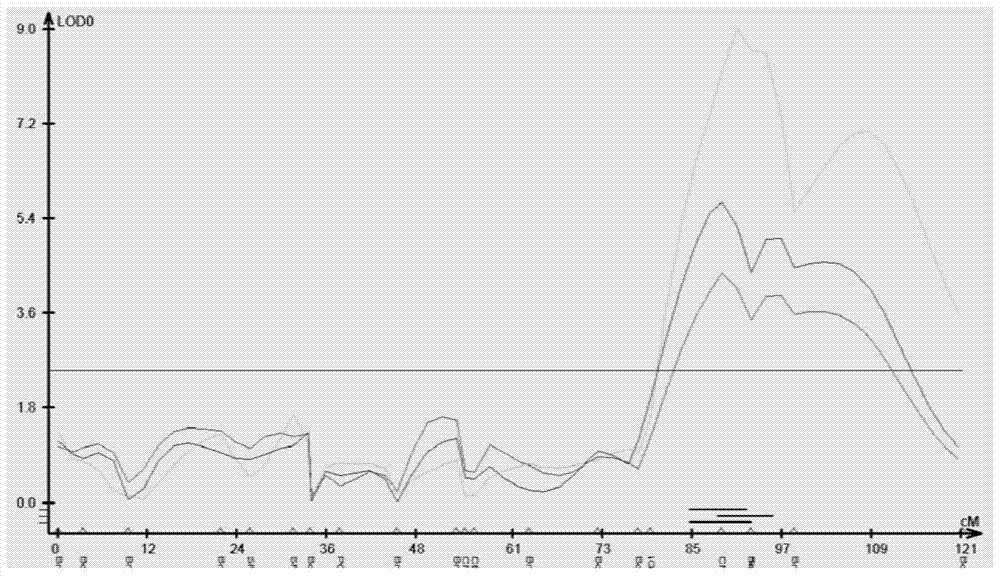
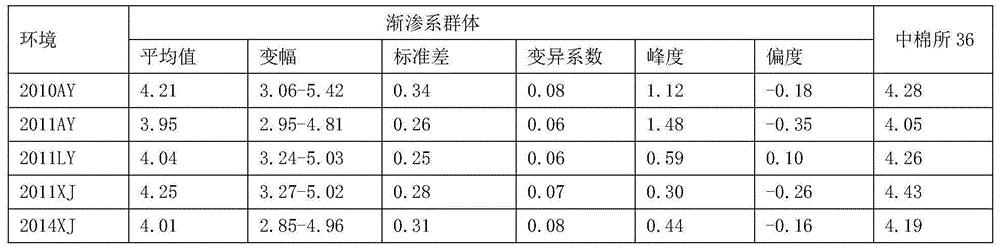
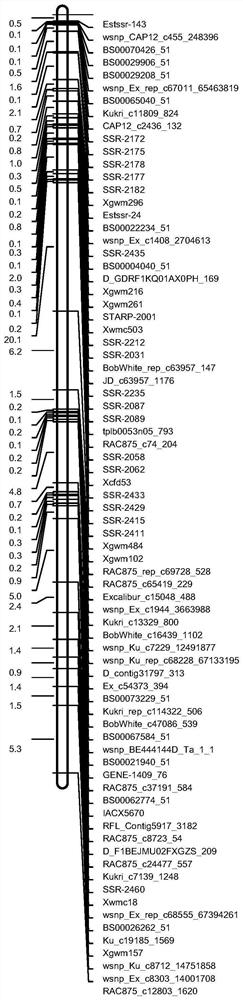
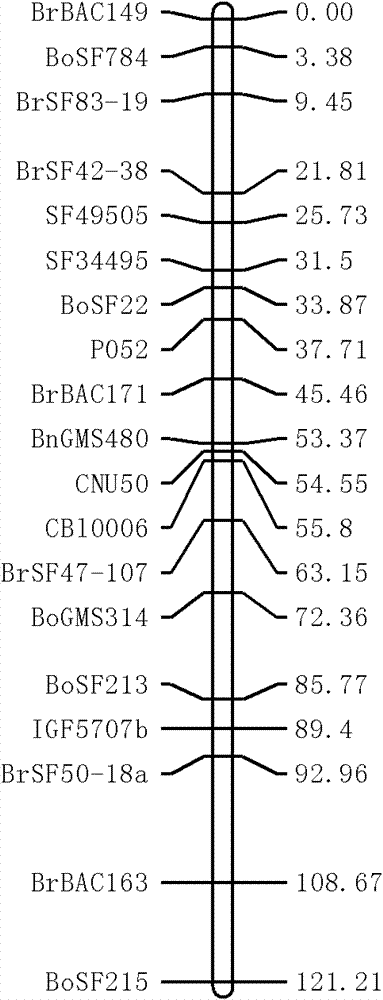
The invention discloses a seed number per pod character major gene site of rape and application thereof. The process comprises the following steps: (1) hybridizing by Brassica napus variety with obvious difference on each seed number per pod character; (2) carrying out polymorphism screening for parent DNA by public and developed SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) and SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) primers, and building a genetic linkage map by molecular mark gene type analysis to an F2-generation segregation population; (3) obtaining the phenotype data of each seed number per pod character by field experiments and variety research to F2 and F2:3 segregation population; and (4) combining the gene type and the phenotype data of the segregation population to carry out QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) detection. The major gene site qQN.A6 and the molecular marker BrSF50-18 for controlling seed number per pod of rape on an A6 linkage group are obtained. The F3 generation derived from two parents is analyzed by the marker, and an individual plant with the marker is kept. A variety research result shows that the ratio of the seed number per pod is 83.4% higher than the F3 individual plate of F2:F3 family mean value, and thus, the marker is used for assisted selection to greatly improve the selection efficiency of high-yield breeding.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Wheat anti-gibberellic in-vitro directional selection breeding method
InactiveCN104969856ASelection inefficiencySmall chance of selectionPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceDirectional selection
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop disease-resistance genetic breeding, and provides a wheat anti-gibberellic in-vitro directional selection breeding method, which comprises: (1) Fusarium graminearum strain separation and culture; (2) crude toxin obtaining; (3) hybridization F1 generation seed obtaining; (4) resistant microspore arrhenokaryon development; (5) resistant callus differentiation; (6) haploid seedling obtaining; (7) anti-gibberellic strain obtaining; and (8) anti-gibberellic characteristic identification on the doubled haploid individual so as to screen the stable anti-gibberellic strain line. According to the present invention, the toxin is used to stress the wide microspore genotype variation and massive microspore cell populations due to gene recombination in the F1 generation anther tissue, the sensitivity difference of the resistant genotype microspore and the non-resistant genotype microspore on toxin is used to screen the resistant genotype, the selection characteristic is directional, the selected groups are large, and the selection efficiency is high.
Owner:平顶山市平丰种业有限责任公司
Molecular marker of pot shattering resistance trait major gene locus of rapes and application
ActiveCN102747080AImprove accuracySelection inefficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceField experiment
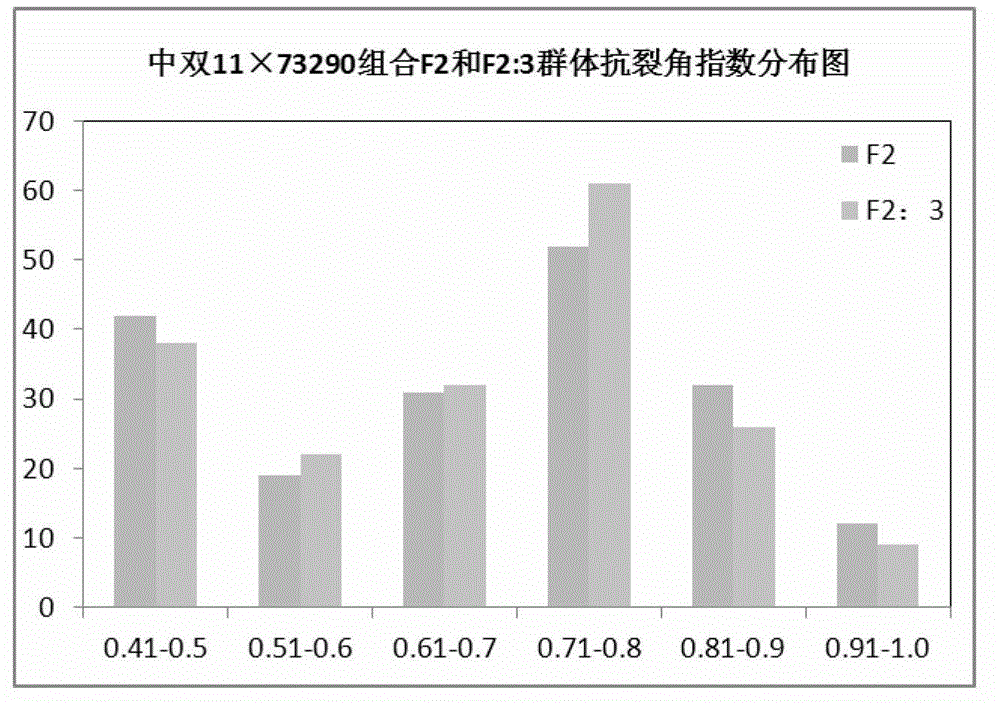
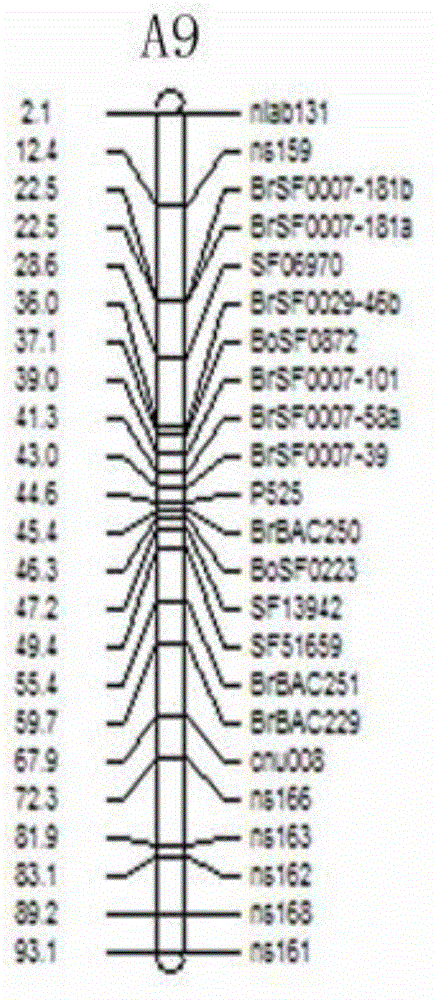
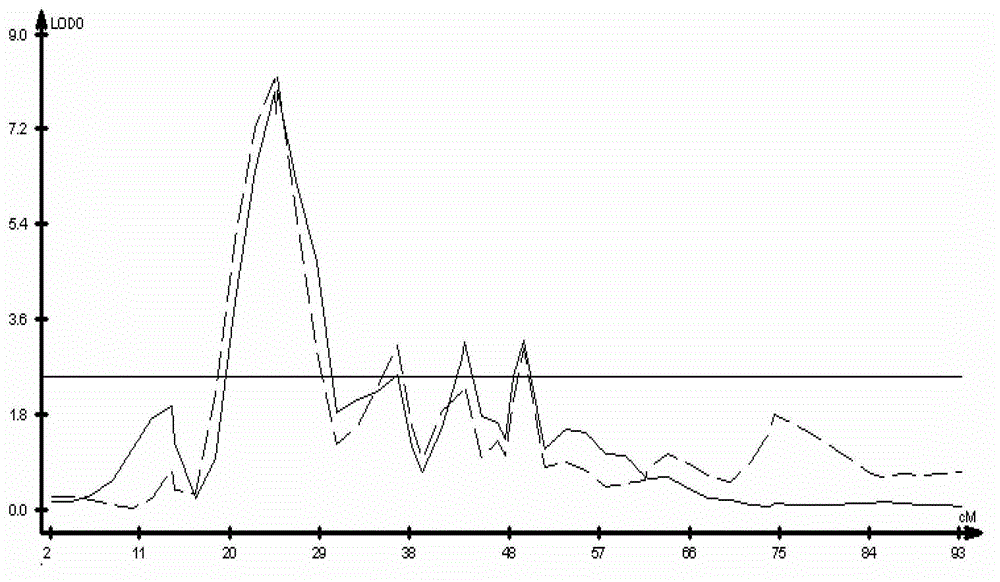
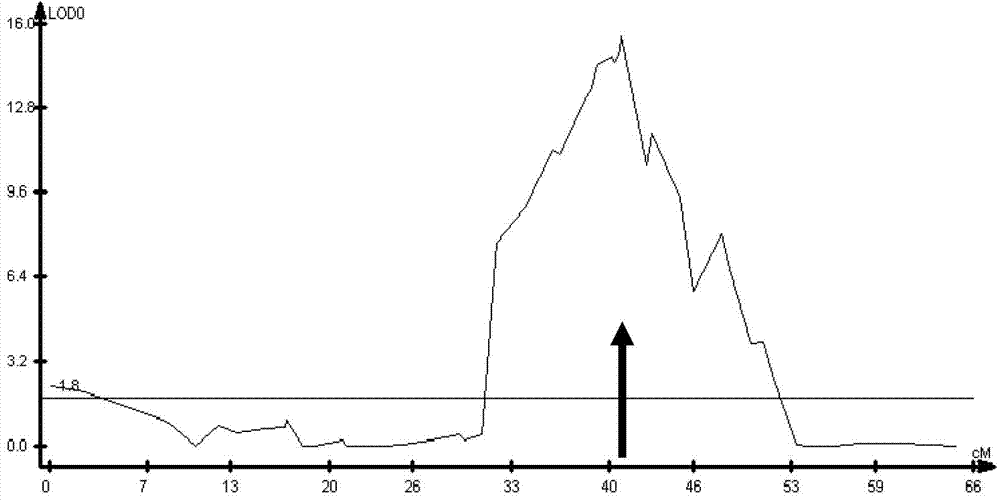
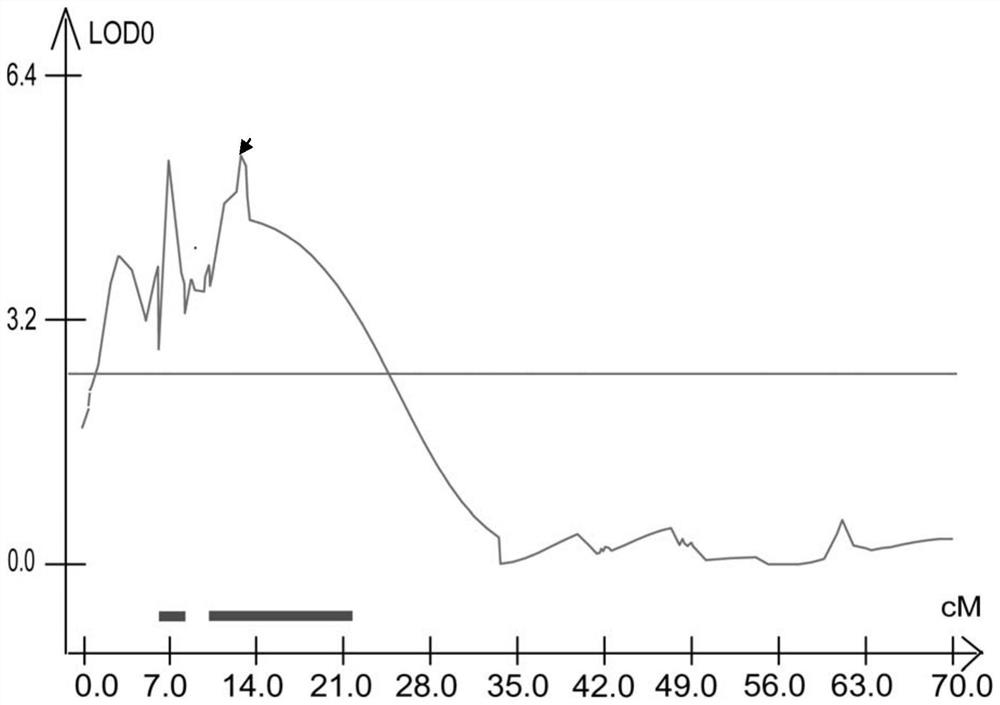
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a pot shattering resistance trait major gene locus of rapes and an application. The steps are as follows: 1) hybridizing double 11 variety and 73290 variety (which have obvious differences in the pot shattering resistance traits) in a cabbage type rape varieties, and carrying out selfing on progenies to obtain F2 and F2:3 segregation populations with the segregated pod shattering resistance traits; 2) carrying out polymorphic screening on parent DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) by utilizing an SSR (simple sequence repeat) primer, and establishing a genetic linkage map by carrying out SSR molecular marker genotyping on the F2 progeny segregation populations; 3) carrying out field experiments and plant inquisition on the F2 and F2:3 segregation populations so as to obtain phenotype data of the pod shattering resistance traits; and 4) carrying out QTL (quantitative trait locus) detection by combining with the developed high-density molecular marker genetic linkage map and genotype and the phenotype data of the segregation populations, utilizing QTL Cart2.5 software to obtain the major gene locus Psr.A9 for controlling the pod shattering resistance of the rapes on a cabbage type rape A9 linkage group and also obtain the molecular marker BrSF0007-39 closely linked with the major gene locus. The selection efficiency of breeding with the pod shattering resistance can be greatly improved by utilizing the marker for assistant selection.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Simple screening method for wheat gene producing unreduced gamete
ActiveCN100998312AIncrease vitalitySimplify workHorticulture methodsPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyAegilops variabilis
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Soybean mosaic virus major gene locus and application thereof
InactiveCN103114145AEasy to useSelection inefficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSoybean mosaic virusVirology
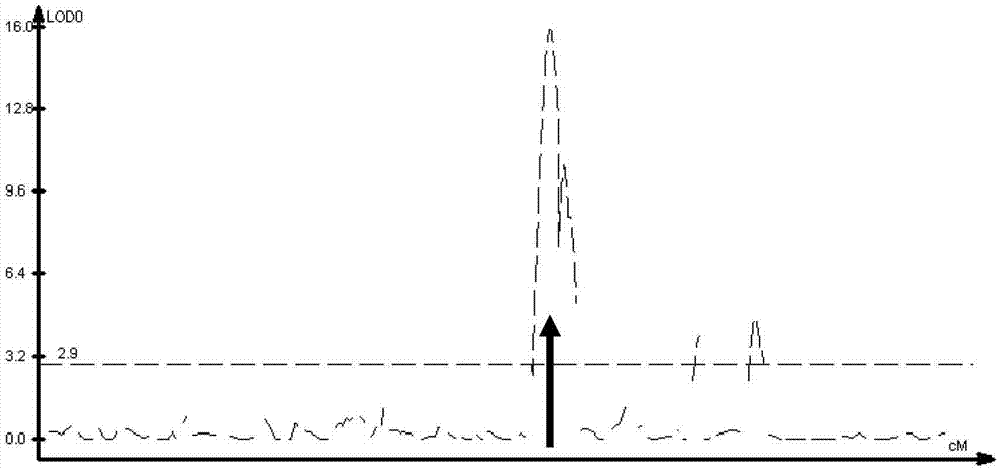
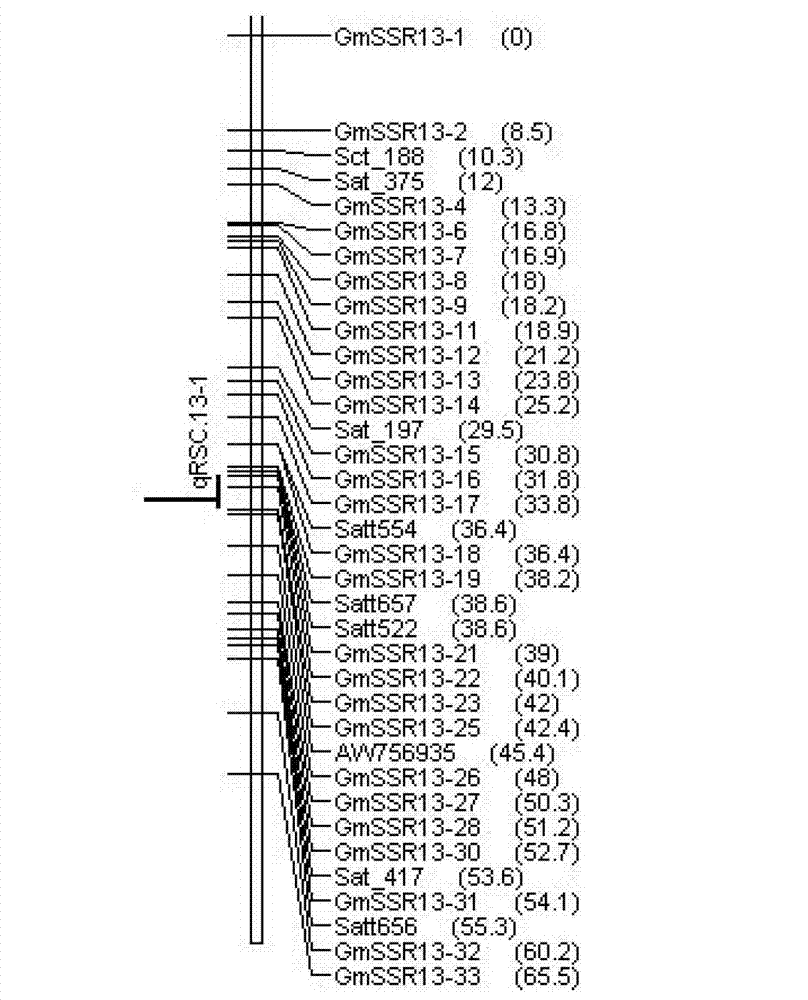
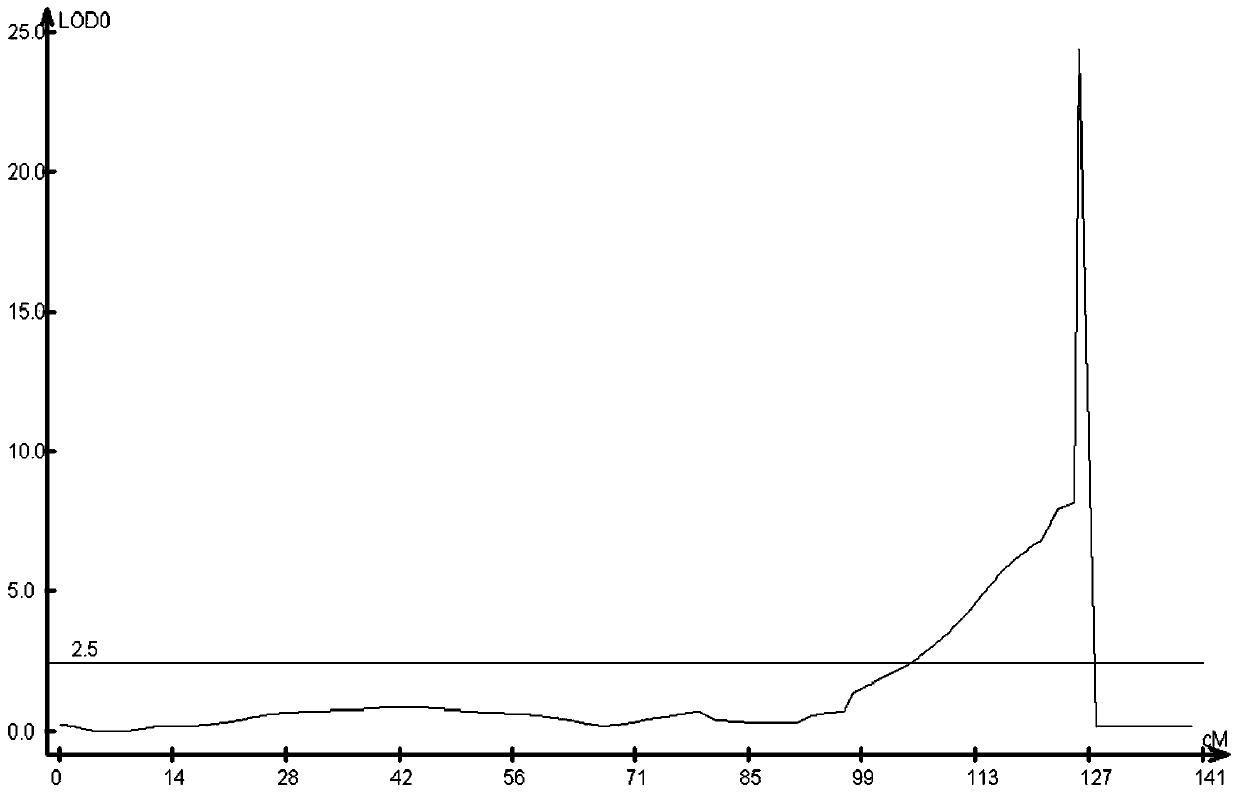
The invention discloses a soybean mosaic virus major gene locus and application thereof, and in particular relates to the soybean mosaic virus major gene locus and the application of the soybean mosaic virus major gene locus in molecule marker assistant selective breeding. The soybean mosaic virus major gene locus is qRSC.13-1 with a contribution rate of 32.4%; the molecule which is tightly interlocked with the mosaic virus major gene locus is marked as GmSSR13-23. The tightly interlocked molecule marker is utilized to detect whether the breeding population system contains the major gene locus or not, so that the mosaic virus performance can be predicated, and the selection rate of the soybean mosaic virus breeding is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Soybean anti-rust gene locus and application thereof
ActiveCN104164501AEasy to useThe detection method is convenient and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular marker
The invention discloses a soybean anti-rust gene locus and application thereof, particularly a soybean anti-rust gene locus and application thereof in molecular marker assisted selective breeding. The anti-rust gene locus is rpp.18-1, and the molecular marker closely linked with the anti-rust gene locus is GmSSR18-21. The soybean rust resistance can be predicted by judging whether the closely linked molecular marker detection breeding material contains the major gene locus, thereby greatly enhancing the selection efficiency for soybean anti-rust breeding.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Linkage molecular markers of maize rough dwarf disease resistance main-effect QTL and application of linkage molecular markers
ActiveCN110628941ASelection inefficiencyReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular breedingChromatophore
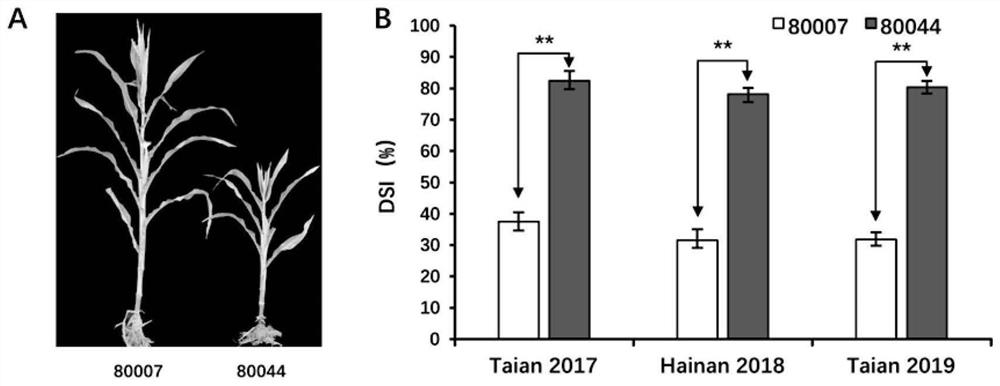
The invention relates to the technical field of maize molecular breeding and biology, in particular to a maize rough dwarf disease resistance main-effect QTL, molecular markers closely linked with themain-effect QTL and application of the molecular markers. The main-effect QTL for controlling maize rough dwarf disease resistance is positioned on a maize chromosome 2 for the first time. In a conventional breeding method, identification of the maize rough dwarf disease resistance needs to wait for maize pollinating, the time and labor are wasted, and selection accuracy is poor; and infected single plants can be eliminated in a seedling stage by detecting the main-effect QTL of maize rough dwarf disease resistance, the production cost is saved, and the selection efficiency is greatly improved. The main-effect QTL of maize rough dwarf disease resistance is clear in position and high in contribution rate, the rough dwarf disease resistance character of a maize inbred line material can be remarkably improved, and a detection method is convenient and rapid and is not affected by the environment. The resistance to rough dwarf disease can be predicted by detecting the molecular markers closely linked with rough dwarf disease resistance, so that a rough dwarf disease resistance material is accurately and quickly screened.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker for breeding bright-peel tomato varieties and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN111621588AReduce planting sizeShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationGeneticsFruit development
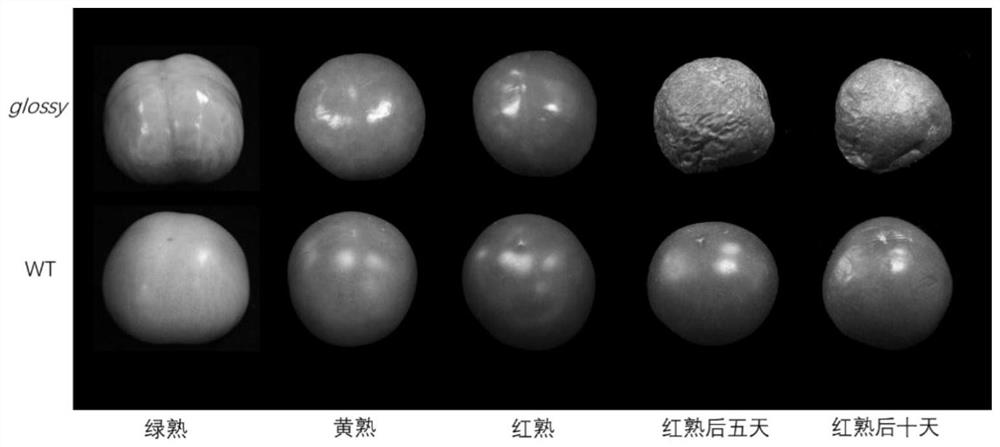
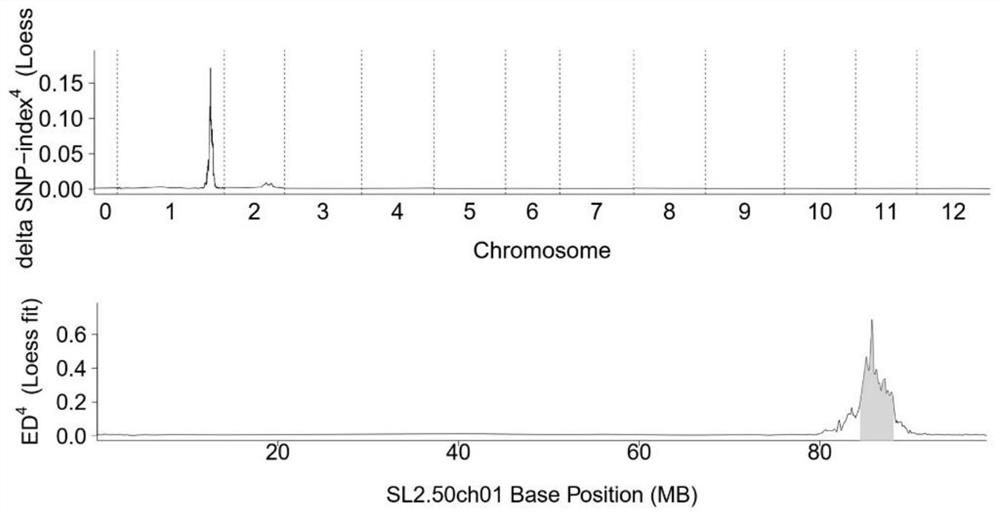
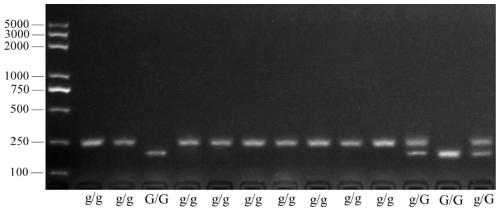
The invention relates to the field of tomato molecular marker breeding, in particular to a molecular marker for breeding bright-peel tomato varieties and an application of the molecular marker. Tomatospontaneous mutant glossy and wild tomato LA1375 are used to construct an F2 segregation population, the glossy gene is located within 600 kb of chromosome 1 by BSR positioning strategy and linkage analysis, and the molecular marker GLS closely linked with the glossy gene is obtained. Tomato varieties are bred by the molecular marker and a prime of the molecular marker, resources are provided fordevelopment of special tomato varieties, and a foundation is laid for fruit development biology research.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker and application of a main effect qtl of rapeseed silique number
ActiveCN104805080BNot affectedAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMarker-assisted selection
The invention discloses a rapeseed pod number major QTL molecular marker and its application. The marker can be used for marker-assisted selection in pod number character improvement and fine mapping and map-based cloning of QTL site. Primers of the molecular marker are CNU400F:5'-CGAGTTTTTGTGTGTACGTATAGTAAT-3' and CNU400R:5'-CCAAAGTGCGTAAAGGAAGG-3'. Rapeseed Zhongshuang 11 and 73290F3 generation are selected by the use of the marker, and silique number of the screened F3 single plant is higher than that of Zhongshuang 11 by 92.3%. Thus, the marker is utilized for assistant selection so as to greatly enhance selection efficiency of high yield breeding.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
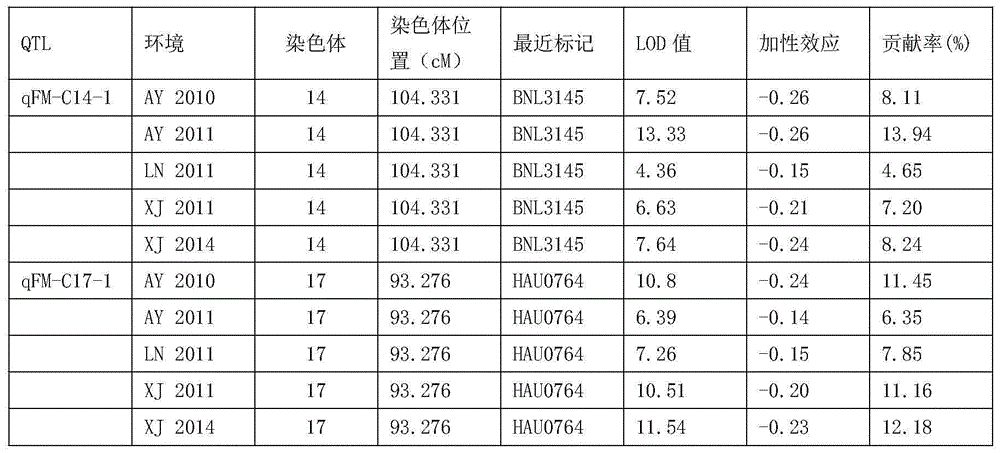
Gossypium-barbadense-Hai-1-derived molecular markers related to fiber Micronaire value and application thereof
ActiveCN105177175ADecreased fiber micronaireHelps to filterMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFiberAgricultural science
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular breeding, particularly Gossypium-barbadense-Hai-1-derived molecular markers related to fiber Micronaire value and application thereof. The molecular markers are BNL3145330 and HAU0764220. The molecular markers are beneficial to overcoming the defects in the fiber quality identification in the existing breeding technique, and can enhance the fiber Micronaire value selection efficiency and accelerate the culturing progress of high-quality new species.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
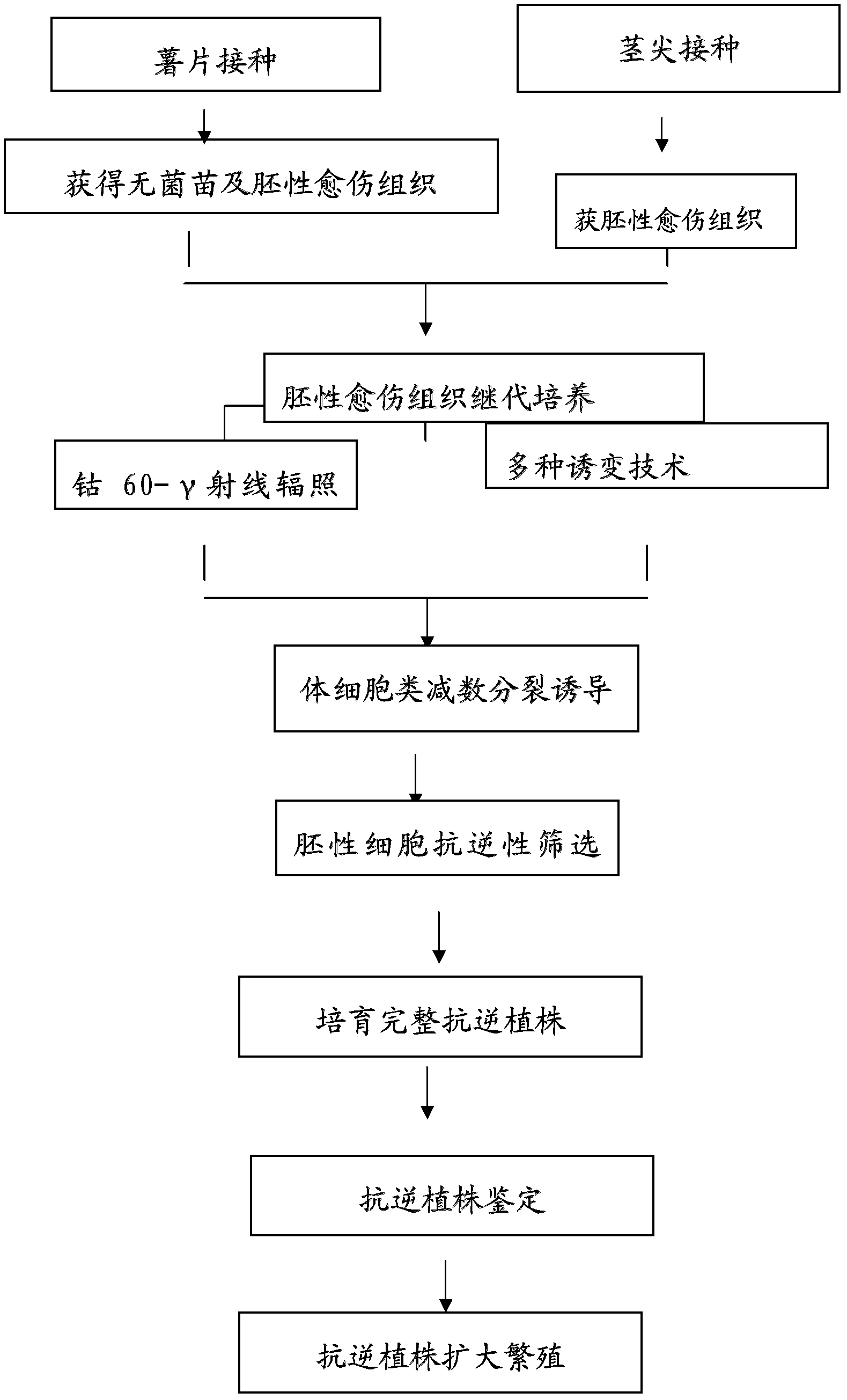
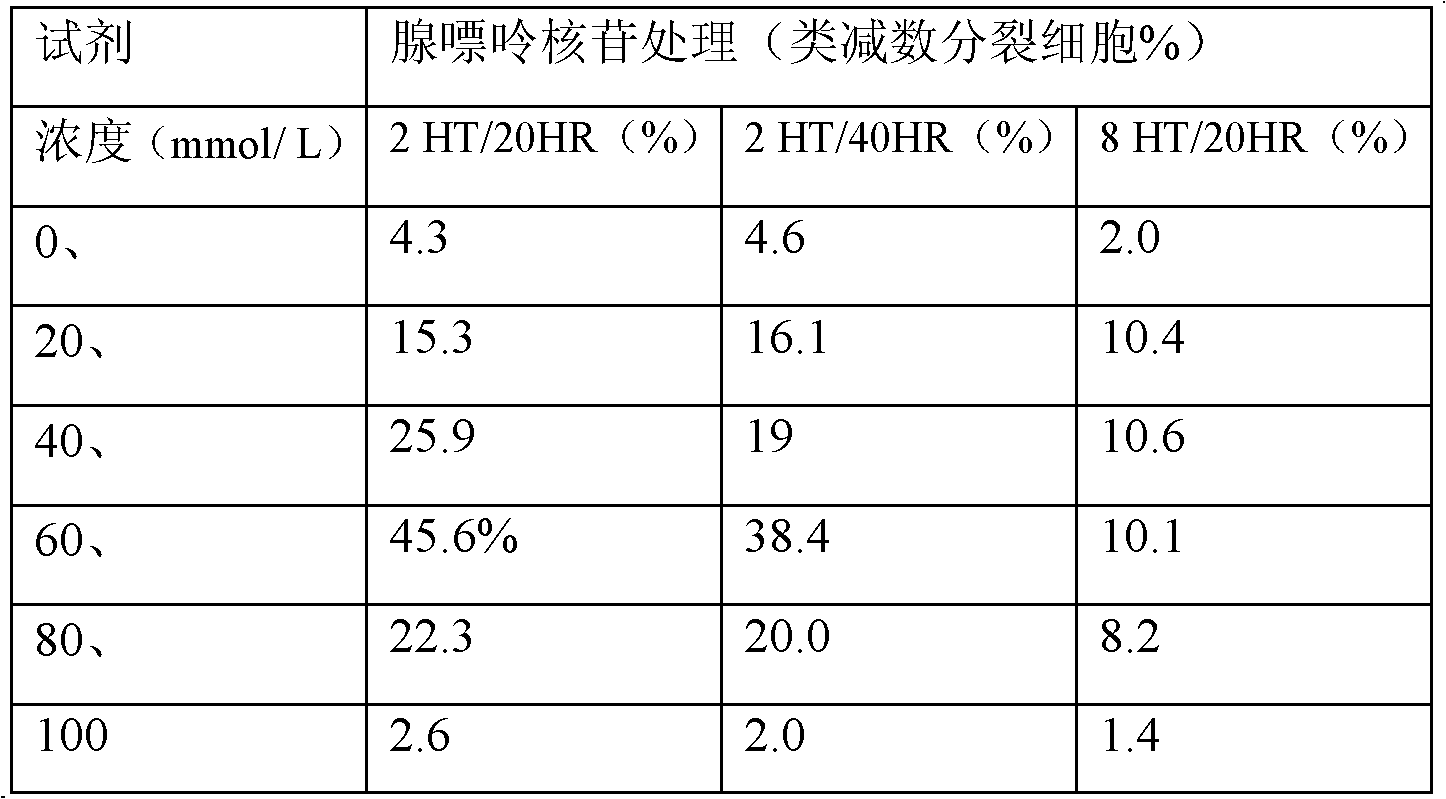
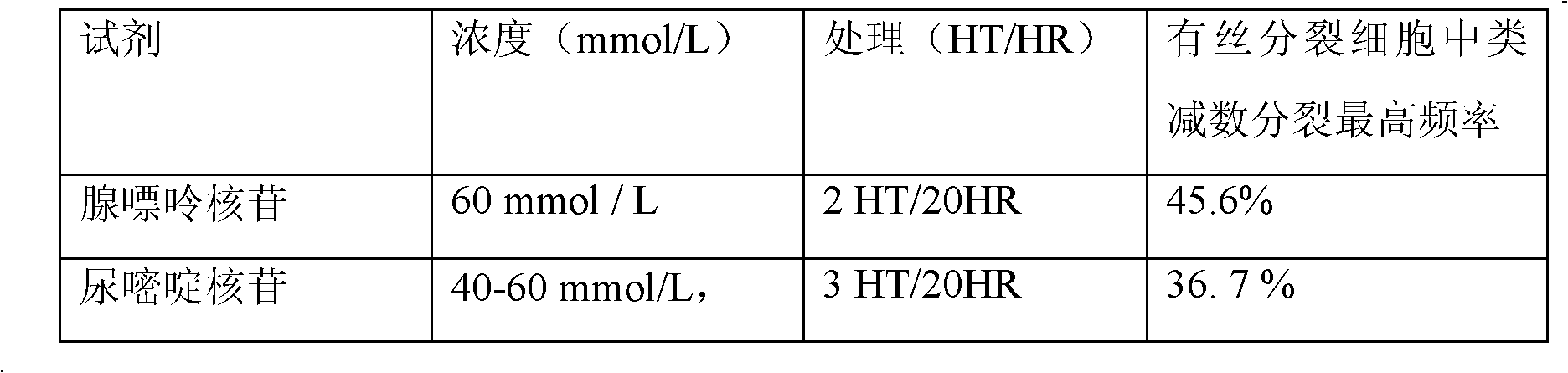
Plant induced mutation breeding method for enhancing mutation frequency and mutation spectrum
ActiveCN102250873BHigh mutation efficiencyAccelerated Breeding ProgramMutant preparationAngiosperms/flowering plantsInduced mutationAction spectrum
The invention relates to a plant induced mutation breeding method for enhancing mutation frequency and mutation spectrum, belonging to the field of induced mutation breeding. The method comprises the following steps: (1) induced mutation: carrying out induced mutation on embryonic cells, and carrying out secondary amplification culture; (2) meiosis-like induction: carrying out meiosis-like induction on the cells subjected to induced mutation and secondary amplification culture; and (3) naturally doubling to obtain the mutant homozygote cells, and screening the mutant homozygote by combining the breeding objective and mutant characters. The invention can be used for screening a great deal of materials in vitro within a short time to obtain a unicell-derived homozygote stress-tolerant mutant, thereby obviously shortening the breeding period and greatly enhancing the selection efficiency.
Owner:石春鸿 +1
Molecular marker tightly linked to kiwi fruit total acid content trait QTL locus and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN106978500AThe detection method is convenient and fastNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerAgricultural science
The invention discloses a molecular marker tightly linked to a kiwi fruit total acid content trait QTL locus and application of the molecular marker. As for a primer designed according to the molecular marker, a forward primer TA-F is 5'-GTAAATGCATGGTAAAGAGGTCC-3', and a reverse primer TA-R is 5'-AGGAGAAAGGGAAAATAAAACGC-3'. As for the molecular marker, a major QTL locus for controlling total acid in a kiwi fruit is located for the first time, 21.75 percent phenotype variance can be explained, and the total acid content of the kiwi fruit can be forecasted by detecting the molecular marker relevant to the total acid content, so that superior individual plants with higher total acid content are accurately and rapidly screened.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
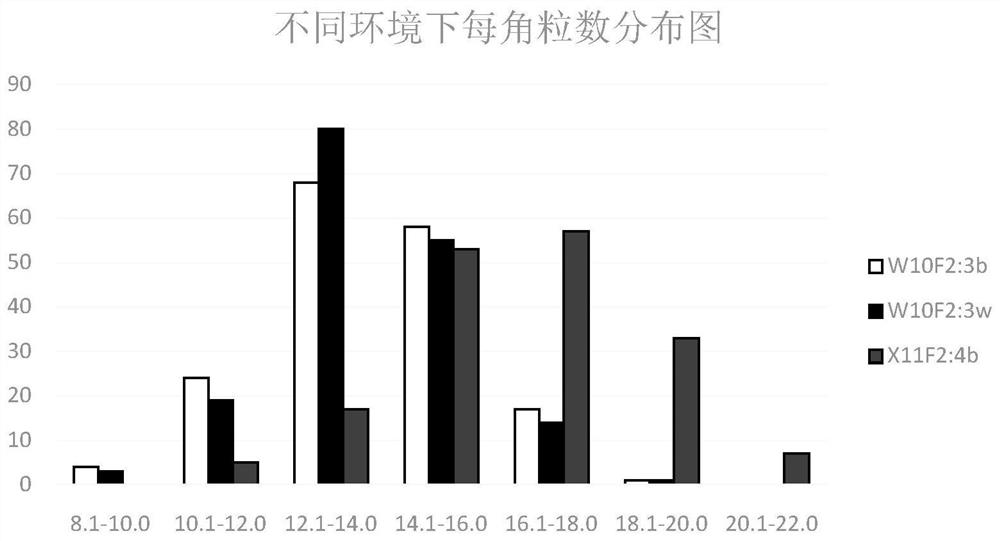
Molecular marker primers of major gene loci of NSS (Number of Seeds per Silique) trait of rape and application of molecular marker primers
ActiveCN109680093AClear detection methodThe detection method is convenient and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationQuantitative trait locusField experiment
The invention belongs to the technical fields of molecular biology and genetic breeding and particularly discloses molecular marker primers of major gene loci of an NSS (Number of Seeds per Silique) trait of rape and application of the molecular marker primers. Phenotype data of the NSS trait are obtained through subjecting F2 and F2 :3 family separated colonies of Zhongshuang 11# and 73290 to field experiment and seed examination; QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) detection is carried out with reference to genotypes and genetic maps of an F2 separated colony. The major gene loci, i.e., qSN.A7 and a molecular marker Ni201 for controlling NSS of the rape on an A7 linkage group are obtained. Through subjecting F3 derived from two parent plants to genotype analysis by the marker, a result indicates that an NSS mean of selected single plants carrying over favorable genes exceeds that of single plants carrying over unfavorable genes; proven by seed examination results, a mean of NSS of singleplants carrying over favorable markers is higher than that of single plant colonies carrying over the unfavorable genes by 88.0%; therefore, the efficiency of selection of high-yield seed breeding canbe increased greatly through carrying out auxiliary selection by using the marker.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Linked Molecular Markers and Applications of Major QTLs for Resistance to Rough Dwarf Disease in Maize
ActiveCN110628941BImprove roughness resistance traitsNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention relates to the technical field of maize molecular breeding and biology, in particular to a maize rough dwarf disease resistance main-effect QTL, molecular markers closely linked with themain-effect QTL and application of the molecular markers. The main-effect QTL for controlling maize rough dwarf disease resistance is positioned on a maize chromosome 2 for the first time. In a conventional breeding method, identification of the maize rough dwarf disease resistance needs to wait for maize pollinating, the time and labor are wasted, and selection accuracy is poor; and infected single plants can be eliminated in a seedling stage by detecting the main-effect QTL of maize rough dwarf disease resistance, the production cost is saved, and the selection efficiency is greatly improved. The main-effect QTL of maize rough dwarf disease resistance is clear in position and high in contribution rate, the rough dwarf disease resistance character of a maize inbred line material can be remarkably improved, and a detection method is convenient and rapid and is not affected by the environment. The resistance to rough dwarf disease can be predicted by detecting the molecular markers closely linked with rough dwarf disease resistance, so that a rough dwarf disease resistance material is accurately and quickly screened.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Hyperspectral Band Selection Method Based on Normalized Multidimensional Mutual Information and Clonal Selection
ActiveCN107527061BTo achieve the purpose of band selectionThe band fully reflects theCharacter and pattern recognitionClonal selectionAlgorithm
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Molecular marker of pot shattering resistance trait major gene locus of rapes and application
ActiveCN102747080BImprove accuracySelection inefficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceField experiment
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a pot shattering resistance trait major gene locus of rapes and an application. The steps are as follows: 1) hybridizing double 11 variety and 73290 variety (which have obvious differences in the pot shattering resistance traits) in a cabbage type rape varieties, and carrying out selfing on progenies to obtain F2 and F2:3 segregation populations with the segregated pod shattering resistance traits; 2) carrying out polymorphic screening on parent DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) by utilizing an SSR (simple sequence repeat) primer, and establishing a genetic linkage map by carrying out SSR molecular marker genotyping on the F2 progeny segregation populations; 3) carrying out field experiments and plant inquisition on the F2 and F2:3 segregation populations so as to obtain phenotype data of the pod shattering resistance traits; and 4) carrying out QTL (quantitative trait locus) detection by combining with the developed high-density molecular marker genetic linkage map and genotype and the phenotype data of the segregation populations, utilizing QTL Cart2.5 software to obtain the major gene locus Psr.A9 for controlling the pod shattering resistance of the rapes on a cabbage type rape A9 linkage group and also obtain the molecular marker BrSF0007-39 closely linked with the major gene locus. The selection efficiency of breeding with the pod shattering resistance can be greatly improved by utilizing the marker for assistant selection.
Owner:OIL CROPS RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Simple screening method for wheat gene producing unreduced gamete
ActiveCN100998312BIncrease vitalitySimplify workHorticulture methodsPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyAegilops variabilis
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
A Molecular Marker Tightly Linked to the Main Effect QTL of Wheat Plant Height Trait and Its Application
ActiveCN108913804BVulnerableNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGene type
The invention discloses a molecular marker closely linked with a major QTL of a wheat plant height character, and an application of the molecular marker. The invention provides a primer pair for detecting a to-be-detected wheat plant height, which is a primer pair used for amplifying target fragments; the target fragments are fragments including fragments obtained by amplification through a primer1 and a primer 2; the primer 1 is a single-stranded DNA molecule as shown in a sequence 1; and the primer 2 is a single-stranded DNA molecule shown in a sequence 2. An experiment proves that the primer pair SSR-2433 is used for carrying out assisted selection on wheat segregation populations. A result shows that a single plant with a gene type consistent with that of a high-straw parent Jing 411is obviously higher than a single plant with a gene type consistent with that of a dwarf parent, which indicates that the primer pair SSR-2433 is feasible and effective for molecular marker-assisted selection of wheat dwarf breeding.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A Molecular Marker Tightly Linked to the Qtl Locus of Kiwi Fruit Weight Traits and Its Application
ActiveCN106868201BPrecise screeningSelection inefficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceActinidia
The invention discloses a molecular marker closely linked with a weight trait QTL site of a kiwifruit fruit and application of the molecular marker. Primers designed according to the molecular marker are FW-F:5'-CCTGAAGGGTTGACTGGAAA-3' and FW-R:5'-CTTGCAGGCATGAGGAAAGC-3'. The molecular marker firstly locates a main-effect QTL site for controlling fruit weight in a kiwifruit, can explain phenotypic variance of 16.24%; and the molecular marker associated with the fruit weight trait is detected, so that the weight of the kiwifruit fruit can be predicated, and therefore, an excellent individual plant with relatively great fruit weight can be accurately and quickly screened out.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Seed number per pod character major gene site of rape and application thereof
InactiveCN102226189BThe detection method is convenient and fastPrecise screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenotype AnalysisField experiment
The invention discloses a seed number per pod character major gene site of rape and application thereof. The process comprises the following steps: (1) hybridizing by Brassica napus variety with obvious difference on each seed number per pod character; (2) carrying out polymorphism screening for parent DNA by public and developed SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) and SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) primers, and building a genetic linkage map by molecular mark gene type analysis to an F2-generation segregation population; (3) obtaining the phenotype data of each seed number per pod character by field experiments and variety research to F2 and F2:3 segregation population; and (4) combining the gene type and the phenotype data of the segregation population to carry out QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) detection. The major gene site qQN.A6 and the molecular marker BrSF50-18 for controlling seed number per pod of rape on an A6 linkage group are obtained. The F3 generation derived from two parents is analyzed by the marker, and an individual plant with the marker is kept. A variety research result shows that the ratio of the seed number per pod is 83.4% higher than the F3 individual plate of F2:F3 family mean value, and thus, the marker is used for assisted selection to greatly improve the selection efficiency of high-yield breeding.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
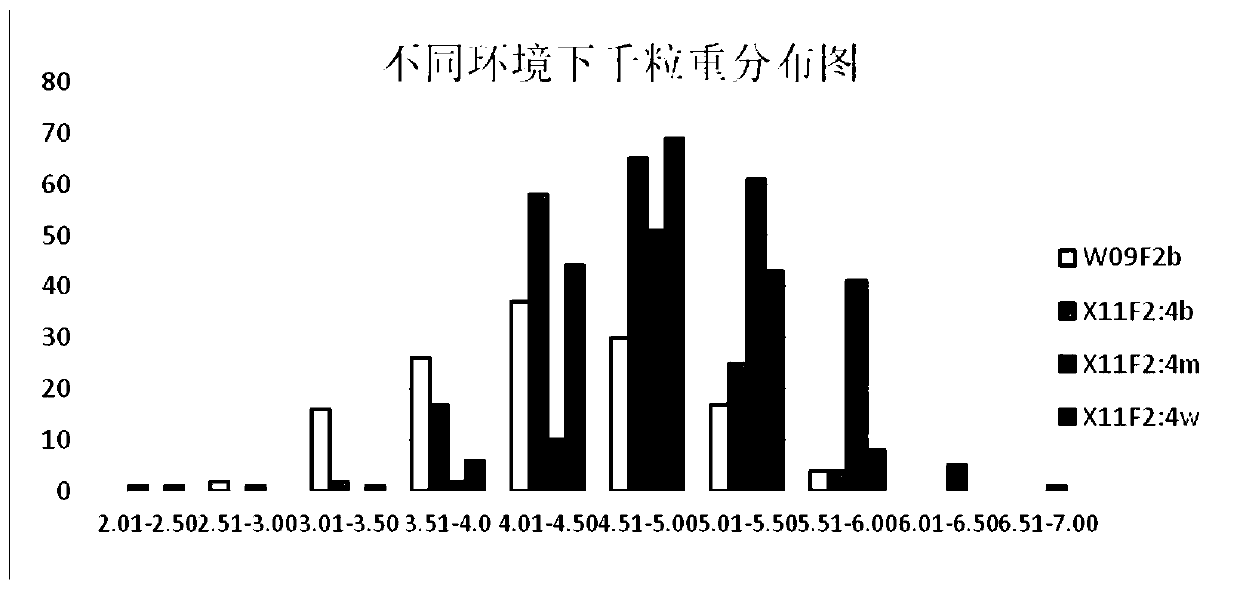
Molecular marker CNU288 primer of rape grain weight trait main effect gene locus and application
ActiveCN111118196AThe detection method is convenient and fastEasy to breedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenotype Analysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and genetic breeding, and particularly discloses a molecular marker CNU288 primer of a rape grain weight trait main effect gene locusand an application. The applicant obtains phenotype data of grain weight traits through performing field experiment and seed selection on F2 genealogy of Zhongshuang No. 11 and 73290; and through combination with genotypes and genetic atlas of F2 segregation populations, QTL detection is performed, and a main effect gene locus qSW.A3 and a molecular marker CNU288 for controlling rape grain weighton an A3 linkage group are obtained. The marker is used for performing genotype analysis on F3 generation derived from two parents, the thousand-grain weight average value (4.89g) of selected single plants carrying favorable genes exceeds the thousand-grain weight average value (4.51g) of single plants carrying unfavorable genes, and the seed selection result indicates that the proportion that thegrain weight of single plants carrying favorable markers is higher than the average value of the grain weight of single plant groups carrying unfavorable genes is as high as 82.9%, so that when the marker is used for performing auxiliary selection, the selection efficiency of high-yield breeding can be greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A Molecular Marker Primer and Application of the Main Effect Gene Locus of Rapeseed Seeds Per Corner Trait
ActiveCN109680093BClear detection methodThe detection method is convenient and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenotype Analysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and genetic breeding, and specifically discloses a molecular marker primer and application of a main effect gene locus of the number of seeds per corner of rapeseed, through the F2 and F2:3 families of Zhongshuang 11 and 73290 The segregation population was subjected to field experiments and breeding tests to obtain the phenotypic data of the trait of kernel number per corner; combined with the genotype and genetic map of the F2 segregation population, QTL detection was carried out. Obtained the main effect gene loci controlling the number of seeds per corner of rapeseed on the A7 linkage group qSN.A7 and the molecular marker Ni201. Through the genotype analysis of the F3 generation derived from the two parents by this marker, the average number of grains per corner of the selected single plant carrying the favorable gene exceeds the average value of the single plant carrying the unfavorable gene, and the test results show that the single plant carrying the favorable marker has a The proportion of grain number higher than the average value of individual plants carrying unfavorable genes was as high as 88.0%, so the use of this marker for assisted selection can greatly improve the selection efficiency of high-yield breeding.
Owner:OIL CROPS RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
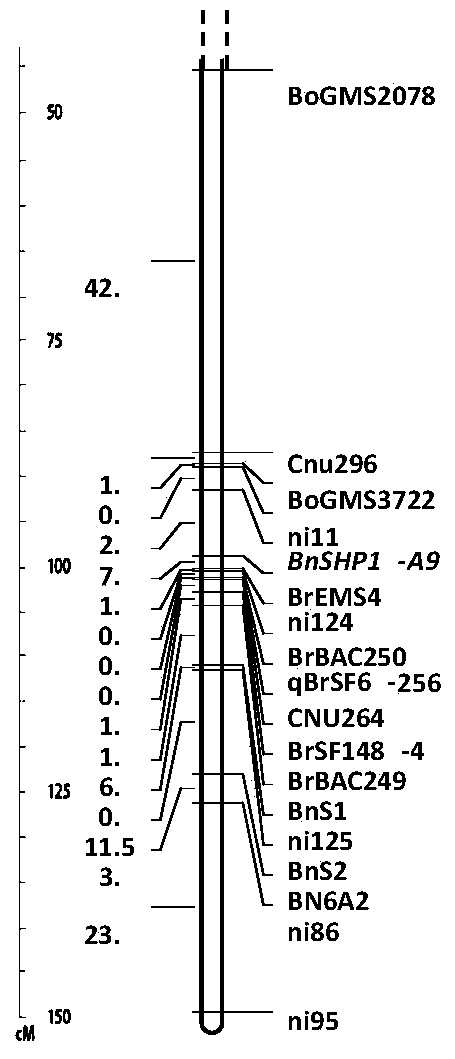
Molecular markers related to the main effect QTL of anti-cracking angle trait in rapeseed and its application
ActiveCN105821153BNot affectedPrecise screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceResistant strain
The invention discloses a molecular marker related to oilseed rape pod-shattering resistance quantitative trait loci (QTL) and application. The magnitude of phenotype interpretation variation reaches 38%. A corresponding sectional SSR molecular marker is developed. The SSR molecular marker related to oilseed rape pod-shattering is BnS1 and BnS2, and the primer sequence of BnS1F is AGCTAAGAGCTGAAGCACGG, the primer sequence of BnS1R is AGATGCTGAAATTCGTCTGTGA, the primer sequence of BnS2F is TCAACTTGACATGTTCACTAATAGTTT, and the primer sequence of BnS2R is CAATAGACACGGAAATGGGC. By means of the molecular marker, the efficiency of screening advanced-line backcrossing imported pod-shattering-resistant strains reaches 93.4%, and the molecular marker can be applied to oilseed rape genetic improvement; the method and the marker have wide application prospect in the field of oilseed rape pod-shattering resistance breeding.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
SNP molecular marker combination for detecting rice Wx gene and application of SNP molecular marker combination
ActiveCN113046349AImprove qualityEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyElectrophoreses
The invention discloses an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker combination for detecting a rice Wx gene, and the combination contains four molecular markers, namely Wx01, K_060585, K_060586 and K_060591; and wherein the polymorphism of the Wx01 is G / T, the polymorphism of the K_060585 is A / C, the polymorphism of the K_060586 is T / C, and the polymorphism of the K_060591 is C / A. By utilizing the molecular marker provided by the invention, the Wx gene can be efficiently detected, the molecular marker can be used for different haplotypes of the Wx gene and auxiliary selective breeding, the breeding efficiency can be improved, the breeding cost can be reduced, the breeding period can be shortened, targeted multi-gene polymerization can be carried out, the breeding efficiency can be improved, and huge social and economic benefits can be brought. The marker is used for genotyping by applying a KASP technology principle, enzyme digestion, electrophoresis, sequencing and the like are not needed, the operation is simple and convenient, and high-throughput rapid detection is facilitated.
Owner:HUAZHI RICE BIO TECH CO LTD
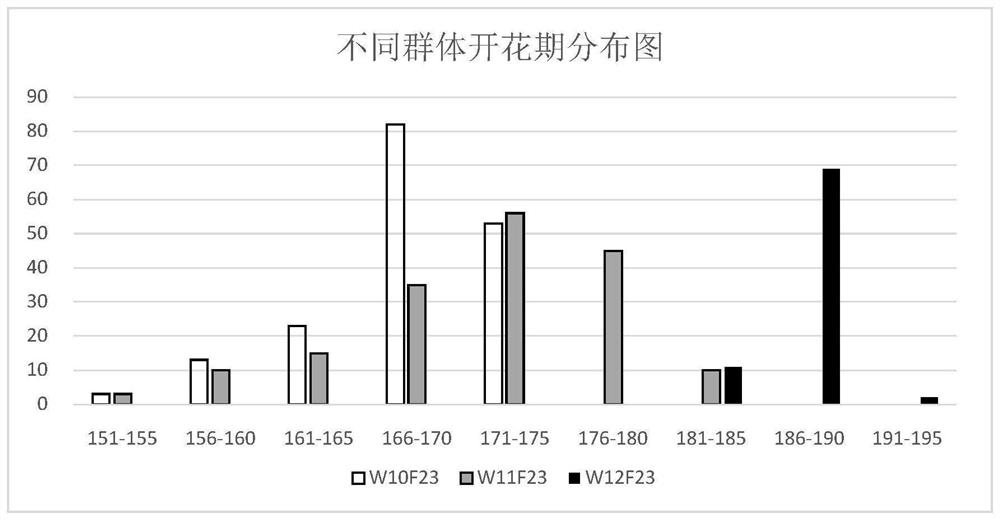
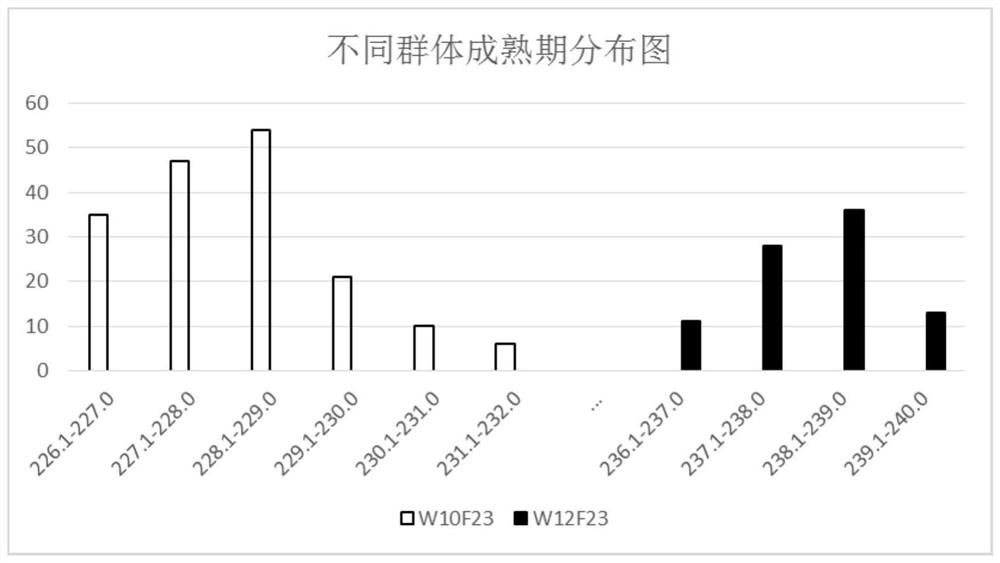
The Molecular Marker brsf0239 Primer and Its Application of the Major Qtl Locus in Flowering and Ripening Stages of Brassica napus
ActiveCN110004242BClear detection methodThe detection method is convenient and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBrassica
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and genetic breeding, and specifically discloses the molecular marker BrSF0239 primer of the main QTL locus in flowering stage and maturity stage of Brassica napus and its application. The phenotype data of flowering period traits were obtained by field experiment and trait investigation of F2:3 family segregation population; combined with the genotype and genetic map of F2 segregation population, QTL detection was carried out, and the joint control of flowering and maturity stages of rapeseed on A2 linkage group was obtained The main effect loci of the rapeseed flowering stage contribute 17.2%, the additive effect is 2.1, and the dominant effect is 0.9; the contribution rate to rape maturity stage is 9.4%, the additive effect is 0.6, and the dominant effect is 0.9. The effect is 0.4. By detecting molecular markers related to maturity traits, the length of maturity can be predicted, and early-maturing varieties can be accurately and quickly screened.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A Molecular Marker Tightly Linked to the Qtl Locus of the Transverse Diameter Trait of Kiwifruit Fruit and Its Application
ActiveCN107034278BThe detection method is convenient and fastSelection inefficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceActinidia
The invention discloses a molecular marker in close linkage with transverse-diameter QTL (quantitative trait loci) of kiwifruit fruits and application of the molecular marker. Primers designed according to the molecular marker are TD-F:5'-GATTGCCCCTTTGCTCTATGA-3' and TD-R:5'-CATGGTCTTGTGCCACCAAT-3. The molecular marker and the application have the advantages that the major effective QTL for controlling the transverse diameters of the fruits are positioned in kiwifruits for the first time, 14.61% of phenotypic variance can be explained, the molecular marker related to transverse-diameter traits of the fruits is detected, and accordingly the transverse diameters of the kiwifruit fruits can be predicted and further can be accurately and quickly screened.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com