Plant induced mutation breeding method for enhancing mutation frequency and mutation spectrum
A technology of mutation breeding and mutation frequency, which is applied in the fields of botany equipment and methods, plant products, mutant preparation, etc., can solve the problems that have not been reported, and achieve the goal of accelerating the breeding program, increasing the mutation frequency, and shortening the breeding cycle Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
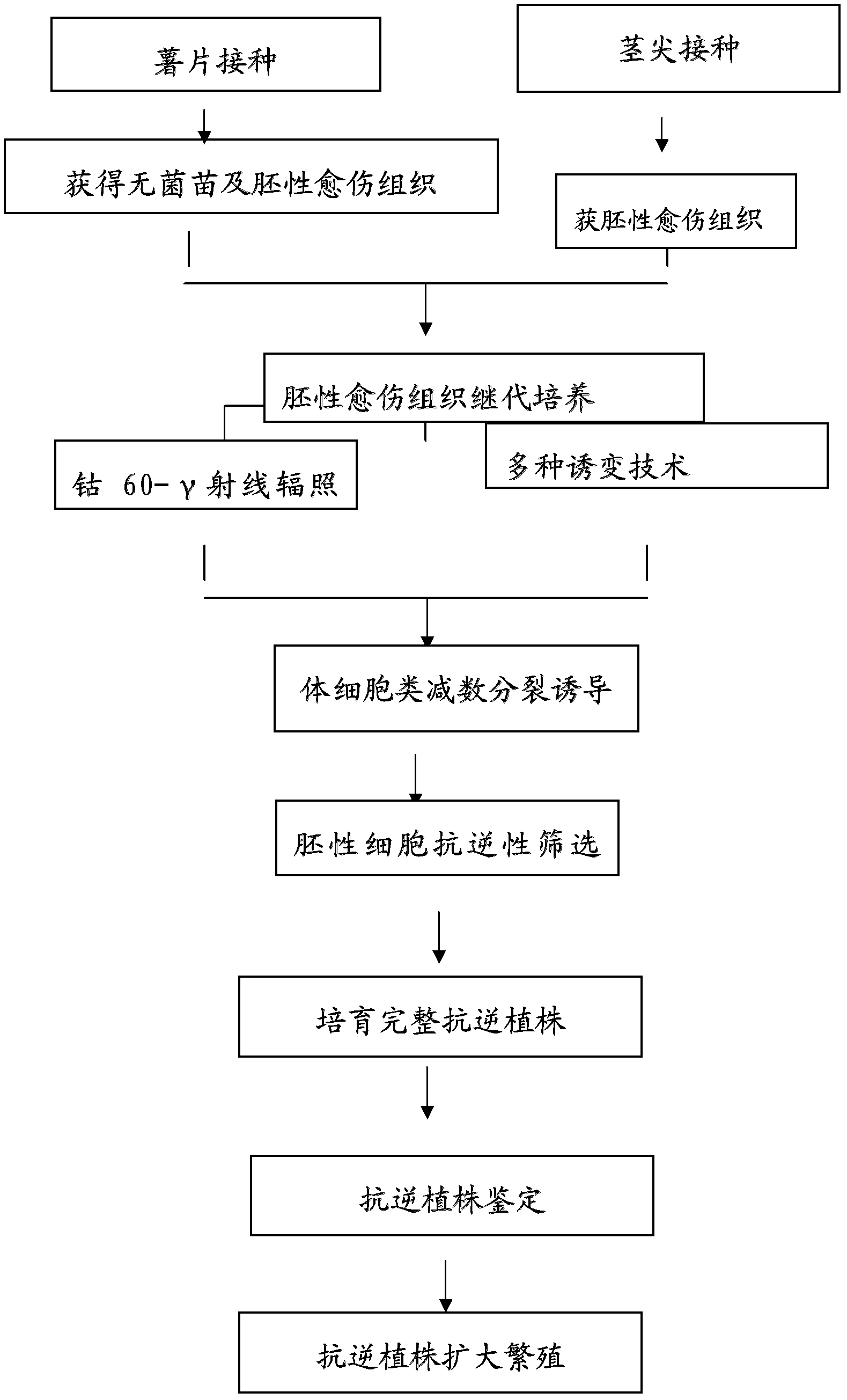
[0040] Example 1: A large number of sweet potato embryogenic cell clusters occur
[0041] 1.1. Materials and methods
[0042] 1.1.1. Induction materials for sweet potato sterile seedlings:
[0043] MS medium, Murashige T and Skoog F A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. (1962) Physiol Plant 15(3): 473-497.
[0044] Reagent:
[0045] 2,4-D: (2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) Beijing Puboxin Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0046] BA: (6-benzyl adenine) Beijing Jyuzhou Tongye Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0047] 1AA: (Indoleacetic acid) Beijing Jiuzhou Tongye Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0048] NOA: (Naphthyloxyacetic acid) Beijing Jiuzhou Tongye Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0049] NAA (α-naphthaleneacetic acid) Beijing Jiuzhou Tongye Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0050] KT, (Kinetin) Beijing Jiuzhou Tongye Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0051] Paclobutrazol: Beijing Jiuzhou Tongye Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0052] GA3 (Gibberellin) Beijing Jiuzhou Tongye Biot...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Example 2: 60 Co-γ-ray Irradiation Treatment of Sweet Potato Stem and Embryogenic Cells
[0071] 2.1. Materials and methods
[0072] 2.1.1. Preparation of irradiation treatment material: use the sweet potato embryogenic cell line established by the present invention as material, select well-developed, and be in vigorous division state (callus granular, dense, bright yellow in color and luster, young and tender in texture) The callus was transferred to fresh subculture medium (MS+2, 4-D 0.05-0.2mg / L+6-BA 0.5-1mg / L+KT0.5-1mg / L+NOA0. 5-1mg / L+IAA0.5-1mg / L+TDZ0.5mg / L). Irradiation was carried out 10-15 days after transfer to the subculture medium.
[0073] 2.1.2. Irradiation treatment method: Send the embryogenic callus cultured in vitro to the Institute of Atomic Energy, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences 60 Co-γ-ray irradiation treatment, the radiation dose is 10, 20, 30, 40, 60Gy, and 4 bottles of callus are used for each treatment. After irradiation, the embry...
Embodiment 3
[0079] Example 3: Induction of meiosis in sweet potato embryogenic cells
[0080] 3.1 Materials and methods:
[0081] 3.1.1. Materials:
[0082] One of the test materials used in the present invention is golden leaf potato. Golden leaf potato is an annual ground cover newly developed in recent years. Because of its golden and translucent color, it is very eye-catching, especially in summer, and it can play a very important role in flowers. Good foil.
[0083] After the dedifferentiation treatment described in Example 1 and the irradiation mutagenesis treatment described in Example 2, the embryogenic cells of Auranthus chinensis were obtained for the meiosis-like induction experiment in this implementation.
[0084] 3.1.2. Method
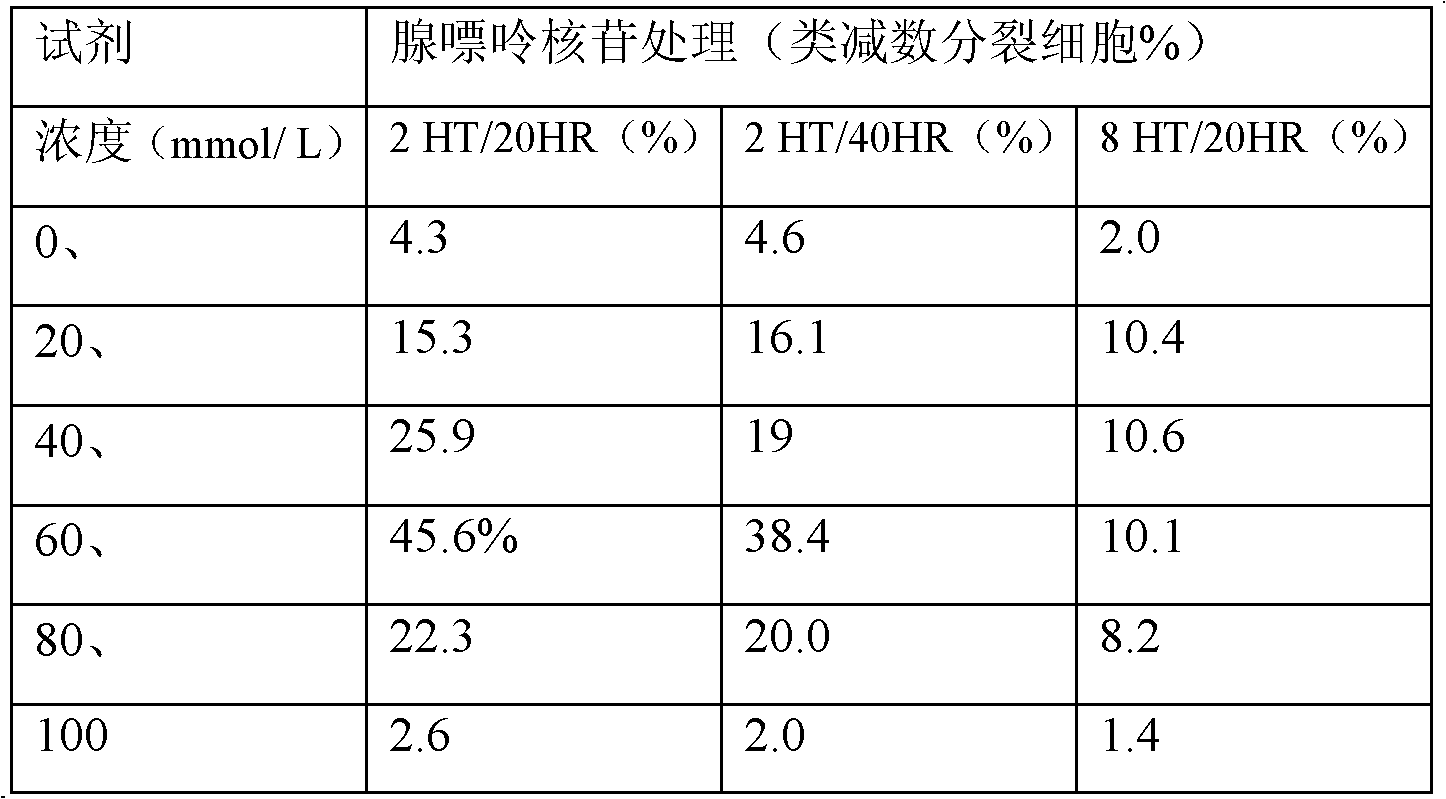
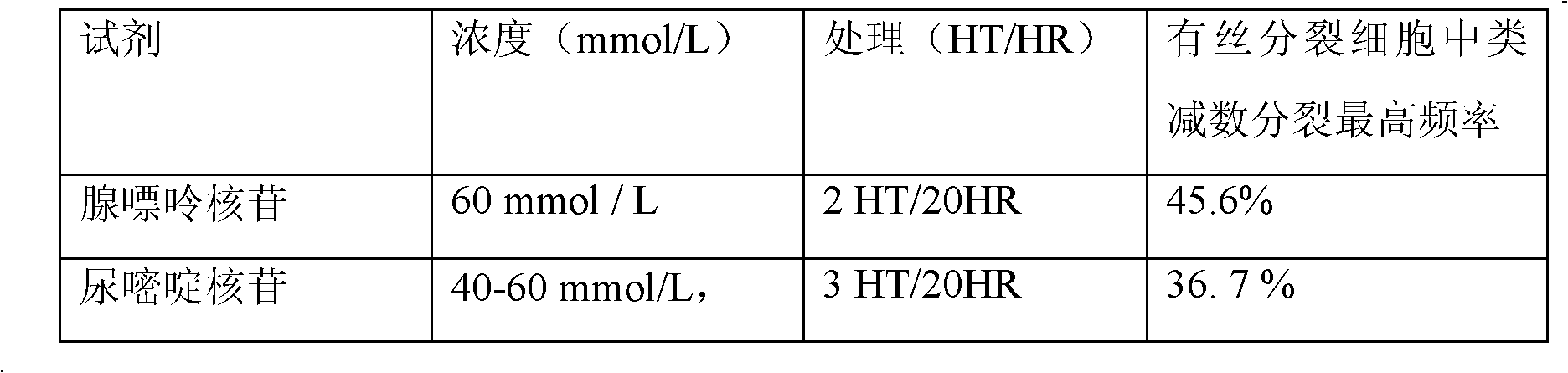
[0085] Optimal conditions for mitotic index under treatment with purine nucleosides
[0086] Taking sweet potato embryogenic cells without drug treatment as a control, observe the mitotic index (the percentage of dividing cells in 100 cells) and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com