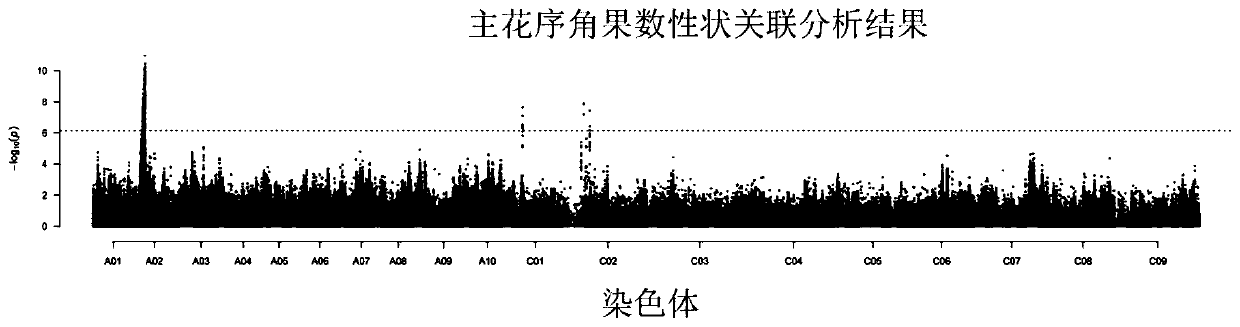
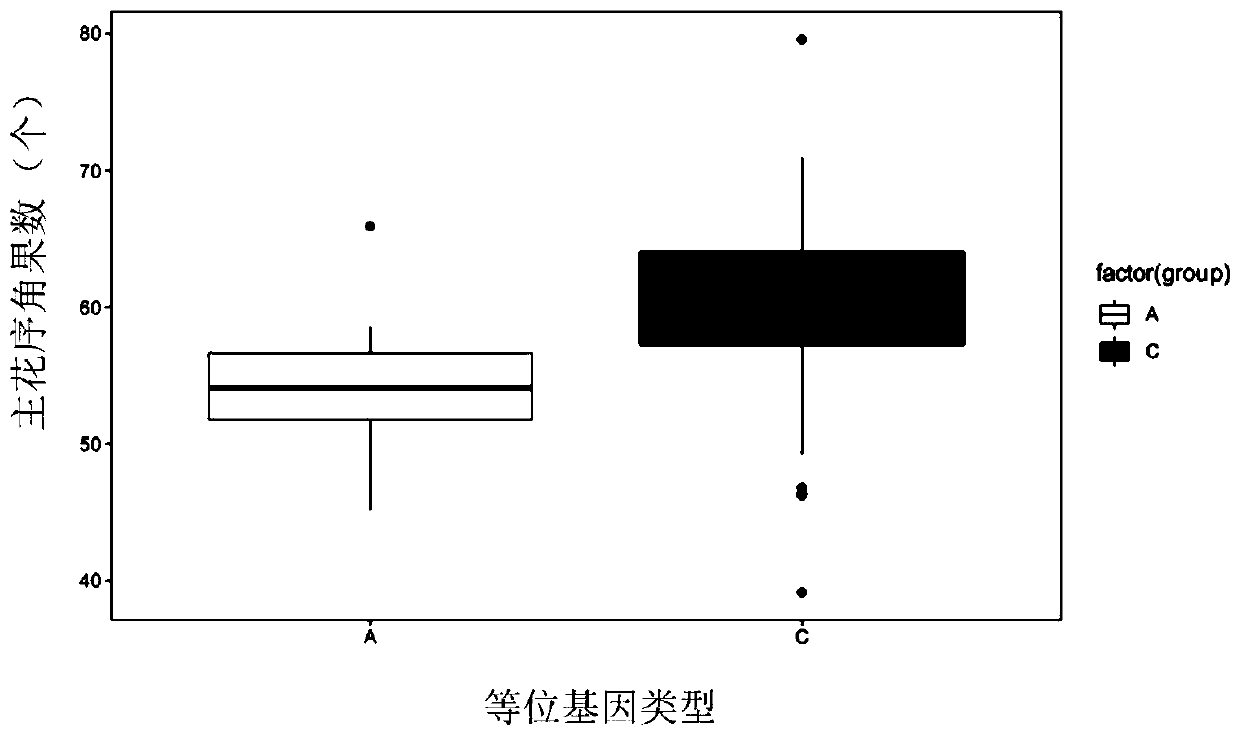
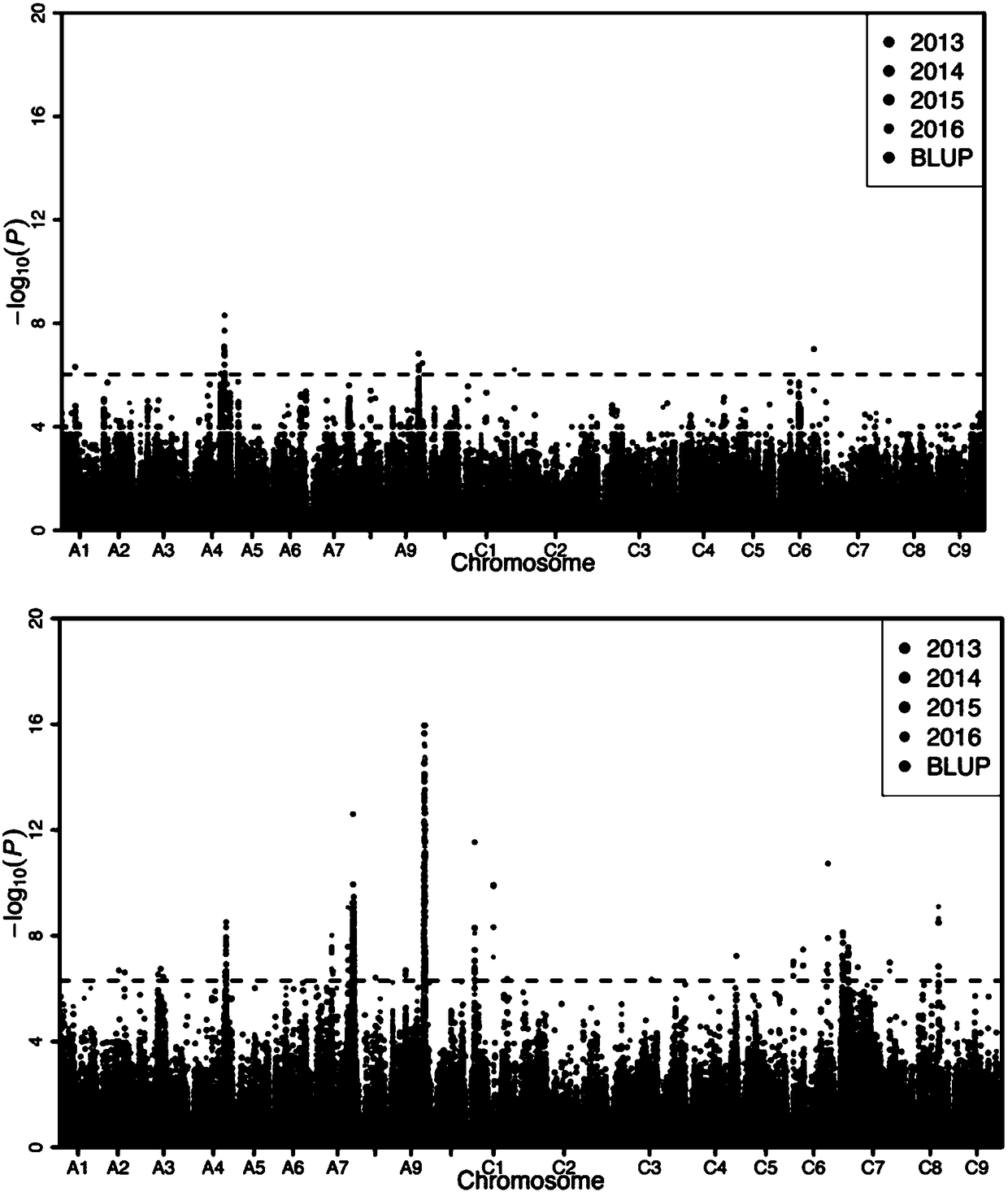
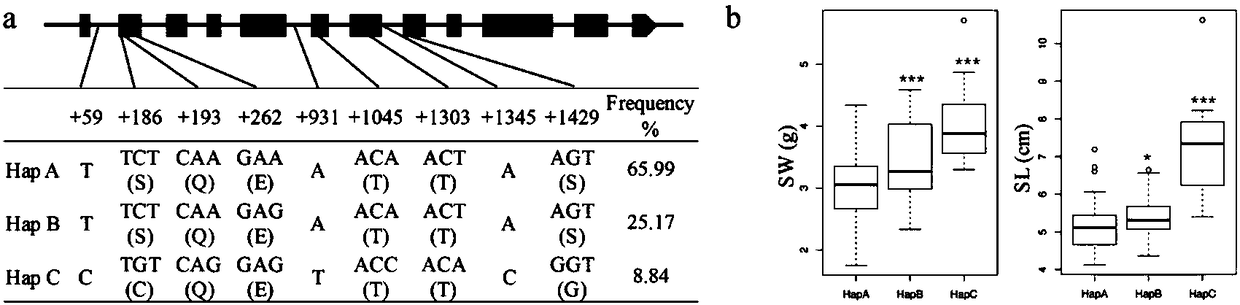
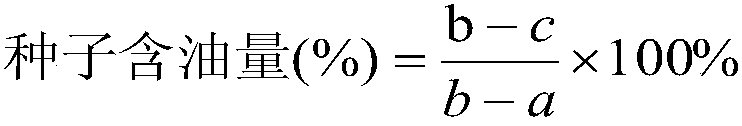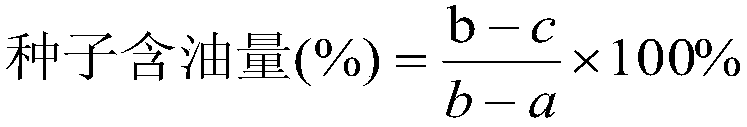Patents
Literature
104 results about "Silique" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A silique or siliqua (plural siliques or siliquae) is a type of fruit (seed capsule) having two fused carpels with the length being more than three times the width. When the length is less than three times the width of the dried fruit it is referred to as a silicle. The outer walls of the ovary (the valves) usually separate when ripe, then being named dehiscent, and leaving a persistent partition (the replum). Siliques are present in many members of the mustard family, Brassicaceae, but some species have silicles instead. Some species closely related to plants with true siliques have fruits with a similar structure that do not open when ripe; these are usually called indehiscent siliques (compare dehiscence).
Method for mechanically harvesting winter rape efficiently with low power consumption
InactiveCN102124898AIncrease harvest yieldAvoid pollutionSeed and root treatmentCrop conditionersDiseaseLoss rate
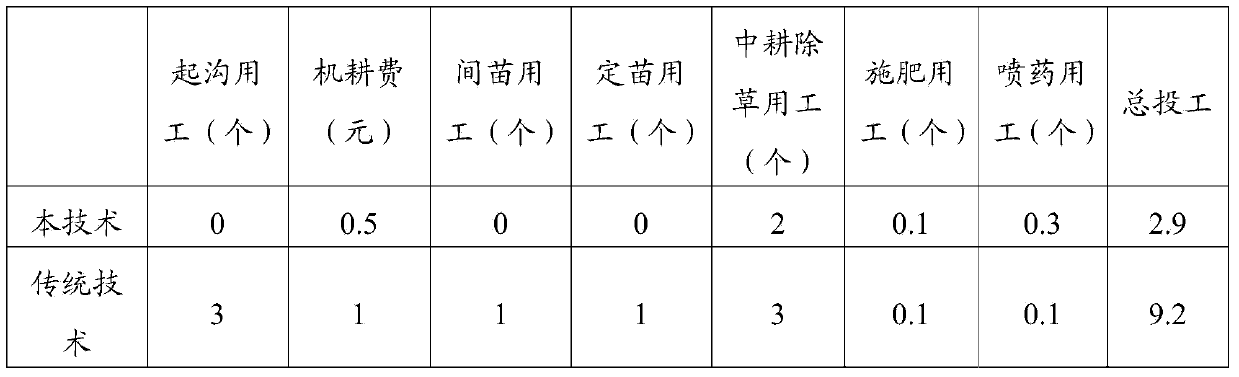
The invention discloses a method for mechanically harvesting winter rape efficiently with low power consumption. The method comprises the following steps of: A, constructing a rape group suitable for mechanical harvest: selecting the variety suitable for mechanical production, performing mechanical precise-quantity direct seeding when the soil water content is 30 to 40 percent, and constructing an ideal group and a plant type by fertilizer and water application and disease inset pest and weed control; B, adjusting a mature period: spraying a ripener two to three days before the harvest of rape seed ripening stage in the regions of contradictory seasons; C, harvesting at right time: observing and measuring the morphological physiological index of the plant before the harvest of the rape, wherein more than 95 percent of siliques, namely yellow loquat fruits in the cropland are suitable for mechanical harvest; D, mechanically harvesting and measuring loss rate: harvesting by a special rape harvesting mechanism in a combining way in the period suitable for harvest; E, smashing and returning rape straw to the cropland: flooding the straw in water immediately after the harvest of rape, decaying and returning to the cropland. The method is easy and convenient to operate, improves a one-time efficient branch height, reduces the branch number, reduces the thickness of the pod layer, solves the problems of high harvest loss rate, and improves the yield.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for assist-breeding low erucic acid, low sulfuric glucoside cabbage type rape self-incompatible line with microspore cultivation and SSR making
InactiveCN101248753AShort termSave human effortVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationSporeInflorescence
The invention belongs to the technology field of the cole breeding, in particular to the method of the seed selection of the Brassica napus self incompatible line with low erucidic acid and sulfuric glucoside utilizing microspore culture and SSR marker assistance. The method is characterized in selecting the Brassica napus self incompatible line S-1300 as the female parent and maintenance line 04P63 External-52 as the male parent, crossbreeding and obtaining F1, microspore culture F1 and obtaining double haploid (DH) self incompatible line; further screening and obtaining the DH material of the Brassica napus self incompatible line with low erucidic acid and sulfuric glucoside; analyzing the variation of the self incompatible double haploid (DH) line by using the SSR markers, studying six major traits of the self incompatible double haploid (DH) line including the plant height, the first branch number, the first branch silique number, main inflorescence length, main inflorescence silique number and yield per plant; screening the double-low Brassica napus self incompatible double haploid (DH) line superior to the S-1300 in production, related trait and general combining ability. The seed selection provides an easy, rapid and effective method of the double-low Brassica napus inbred incompatible double haploid (DH) line.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Seed breeding method of naturally-capped dwarf compact cabbage-type rape
InactiveCN105123510AImprove efficiencyExcellent homozygous germplasmPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeF1 generation
The invention discloses a seed breeding method of a cabbage-type rape, wherein the seed breeding method is suitable for mechanical harvest and the cabbage-type rape is naturally capped in main inflorescence, is limited in siliques and is dwarf and compact in character. The seed breeding method includes following steps: (1) with the cabbage-type dwarf rapes 3H004 and compact-plant rapes 7399-8 as parents to performing hybridization to obtain an F1-generation; (2) in an early blooming period, selecting the buds being 3.0-4.0 mm in length on the main inflorescence and upper branched inflorescences of the F1 plant, perforning mutagenesis with EMS (ethyl methylsulfonate) and then performing colchicines doubling and microspore induction culture to obtain a DH separated population; (3) with plant height, branch characters, main inflorescence length, total silique number, growth period and oil-containing quantity and the like main characters, performing multi-year and multi-point in-field phenotype character identification to the DH separated population; and (4) selecting the variation materials which is naturally capped in main inflorescence, is limited in siliques, is lower than the upper branched inflorescences in height, is concentrated in blossom period and silique layers, and is dwarf and compact. The method can be used for obtaining the rape which is naturally capped in main inflorescence, is limited in siliques and is dwarf and compact in character. The method, when being popularized, can reduce planting cost of rapes and achieves excellent economical benefit.
Owner:陕西省杂交油菜研究中心
Breeding design and identification method for short-haulm compact type cole suitable for mechanized harvest
InactiveCN101292626AQuickly and effectively design breeding technology systemReduce planting costsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationStem lengthMolecular identification
The invention pertains to the field of rape breeding and discloses a method for seed selection and identification of a novel dwarf compact type rape adapting to high-density planting and mechanized harvesting. The rape of Variety 5148-2 with apreservation number of CCTCC-P200601 that is bred by Huazhong Agricultural University and yellow-seed rape of DH series YN90-1016 that is synthesized artificially in Canada are taken as seed-parents and crossbred to obtain F1. In inflorescence, the main anthotaxy of an F1 plant and the flower buds with a size ranging from 2.8mm to 3.8mm at the upper branches of the P1 plant are selected, and then chromosome doubling with colchicine and microspore culture are carried out successively to obtain the segregation populations of double haploid. Filed phenotypic characteristic identification are applied for years in various spots to the segregation populations; variant rape materials with five major traits, namely, stem length, branch trait, length of anthotaxy, quantity of silique and growth period differing from those of the common rape and dwarf, compact plant, smallish and acervate branches and main anthotaxy, concentrative florescence and compact pod bearing layers phenotypes are selected to obtain the novel dwarf compact type rape adapting to mechanized harvesting. The invention also discloses a method for molecular identification.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
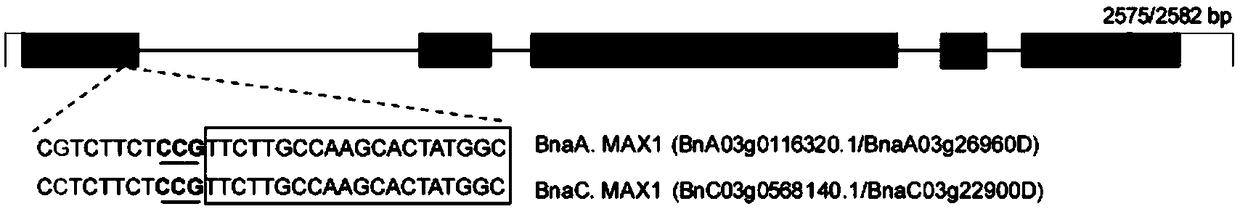
Method and application of knocking out BnMAX1 gene in Brassica napus by CRISPR-Cas9 system
ActiveCN109266646ASimplify build stepsSpeed up the research processPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionBrassicaHypocotyl
The invention discloses a method and application of knocking out a BnMAX1 gene in Brassica napus by a CRISPR-Cas9 system, two sgRNAs of specifically targeting Brassica napus BnMAX1 gene are designed and synthesized into oligo dimer, are connected with Cas9 vector, and introduced into hypocotyl callus of Brassica napus by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation to regerated into shoots. Cas9 nuclease was guided by sgRNA to cleave target sequence. Each sgRNA could pass through CRISPR-Cas9 system mediates the cleavage of BnMAX1 gene in A and C genomes, and achieves the goal of gene knockout. Phenotypic identification showed that homozygous mutant lines increased the number of branches and pods per plant, decreased plant height and increased yield.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rapeseed pod number major QTL molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN104805080AImprove selection efficiencySpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMarker-assisted selection
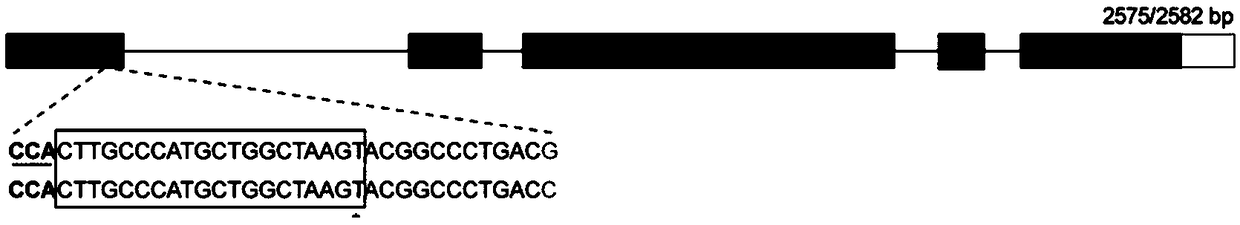
The invention discloses a rapeseed pod number major QTL molecular marker and its application. The marker can be used for marker-assisted selection in pod number character improvement and fine mapping and map-based cloning of QTL site. Primers of the molecular marker are CNU400F:5'-CGAGTTTTTGTGTGTACGTATAGTAAT-3' and CNU400R:5'-CCAAAGTGCGTAAAGGAAGG-3'. Rapeseed Zhongshuang 11 and 73290F3 generation are selected by the use of the marker, and silique number of the screened F3 single plant is higher than that of Zhongshuang 11 by 92.3%. Thus, the marker is utilized for assistant selection so as to greatly enhance selection efficiency of high yield breeding.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Breeding method of rape with high-density siliques on main inflorescence and application
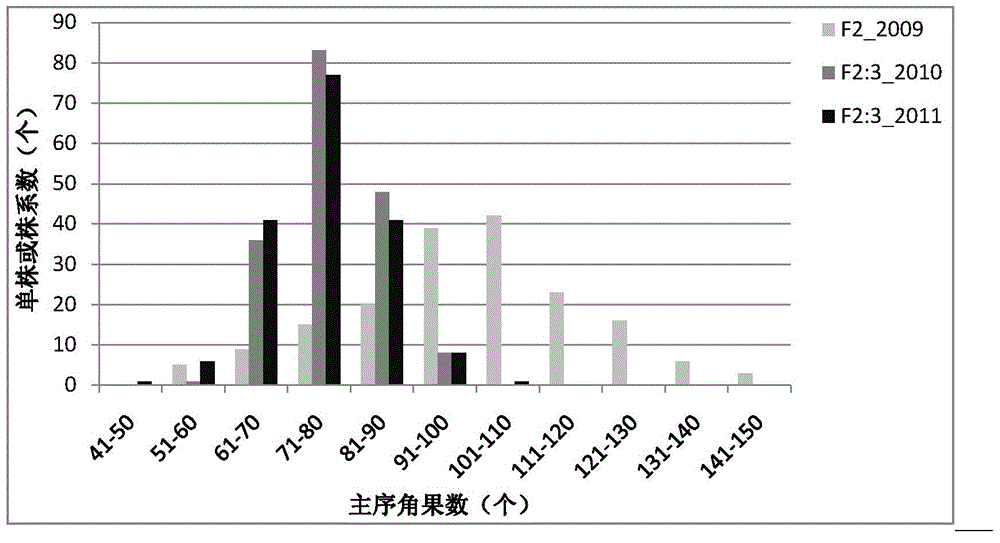
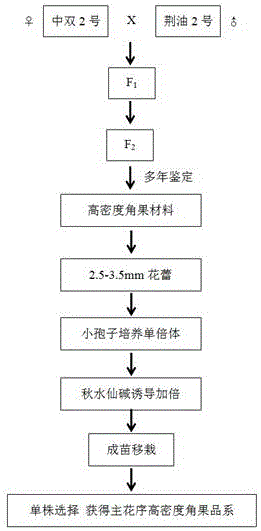
The invention discloses a breeding method of rape with high-density siliques on a main inflorescence and application. The breeding method comprises the following steps: adopting double-2 in the variety of cabbage type rape and nepeta oil-2 in the variety of cabbage type rape as parents for hybridization to obtain F1, and conducting bagged selfing propagation to obtain a segregated population; selecting single plants in the segregated population to conduct identification on phenotypic characteristics in the field continuously for 4 years, selecting single plants with high-density siliques on the main inflorescence (number of effective siliques on the main influorescence / main-inflorescence length being greater than 2 pieces / cm); in a flowering period, selecting flower buds 2.5-3.5mm in length on the main inflorescence, using colchicine to double chromosomes, using microspores for culture to obtain a double-haploid population, and selecting single plants to breed into strain with high-density siliques on the main inflorescence and stable characters; using the strain and double 11 in the variety of cabbage type rape (the density of siliques on the main inflorescence is about 1.7 pieces / cm) to conduct hybridization, utilizing F2:3 populations to conduct genetic segregation analysis and finding that the characters of the high-density siliques are controlled by 2 pairs of additive-dominant-epistatic main genes. The breeding method and the application disclosed by the invention have the advantages that the variety of rape with high-density siliques on the main inflorescence can be bred by utilizing hybridization of the high-density silique materials on the main inflorscence and common rape, and the yield per unit of the rape can be greatly increased.
Owner:贵州省油菜研究所
High-bud-ratio storage method for rape seeds
InactiveCN104641815AKill completelyPrevent regenerationAgriculture tools and machinesSeed and root treatmentAgricultural scienceProper time
The invention discloses a high-bud-ratio storage method for rape seeds. The high-bud-ratio storage method for the rape seeds comprises the following steps: 1) harvesting in proper time, and harvesting the rape seeds until 70-80% of siliques are yellow; 2) drying in time, insolating the seeds for 16-30 hours after the rape seeds are threshed, and permitting the rape seeds to enter a depot by airing and cooling the rape seeds after the rape seeds are dried in the sun; 3) removing sediment impurities, carrying out winnowing one time before the rape seeds enter the depot to remove garbage impurities and bacteria; 4) controlling moisture, and controlling storage moisture to be within 9-10%; 5) before depot entry, carrying out traditional Chinese medicine smudging sterilization and disinfection on a grain depot; 6) utilizing cooling equipment to control temperature in the grain depot to be 5-8DEG C, causing the seeds to enter a bag, putting the seed bags onto a wooden support in the grain depot, and forming a gap between bags, wherein each bag weighs 20-30kg; 7) carrying out ventilation and aeration one time by ventilation equipment in every 15-20 days, controlling the temperature to be 5-8DEGC, and controlling the moisture to be 50-70%; 8) carrying out processing and selling after a larval period ends.
Owner:CHAOHU XINYU BREEDING FARMER PROFESSIONAL COOP
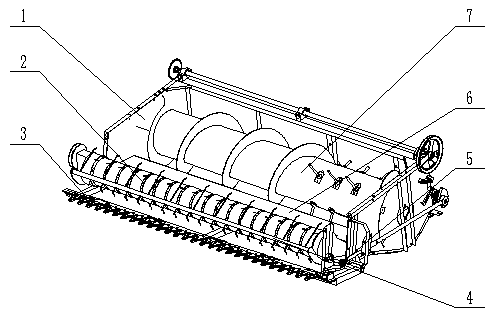
Device for strip-like laying and spring-tooth picking and conveying of oilseed rapes
A device for strip-like laying and spring-tooth picking and conveying of oilseed rapes is sequentially provided with a cutting knife assembly, a conveying belt, an auger assembly and a header rack assembly in the conveying direction from front to back, wherein a spring-tooth pickup device assembly is installed at the position, above the conveying belt for a distance, two ends of the spring-tooth pickup device assembly are movably are installed on the inner side of the header rack assembly, a driving system for driving the cutting knife assembly, the auger assembly, the conveying belt and the spring-tooth pickup device assembly is arranged on the header rack assembly, and a floating winding prevention device is arranged above the spring-tooth pickup device assembly. It can be ensured that the device has lower blockage probability in the oilseed rape conveying process, it also can be ensured that oilseed rapes are smoothly picked up, and reduction of silique pod loss before oilseed rapethreshing is facilitated.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Cultivation method for interplanting mustard type spring rape and flax
The invention relates to a cultivation method for interplanting mustard type spring rape and flax. The cultivation method comprises the following steps of a1, selecting a cultivation variety; a2, preparing before sowing; a3, sowing; a4, thinning and establishing; a5, fertilizing; a6, intertilling to loosen the soil; a7, preventing damage by disease and insect; a8, harvesting in good time; a9, performing multiple sowing of Chinese cabbage; after the rape is harvested in the first ten-day period of August, Chinese cabbage seedlings are transplanted between ridges, and about 10,000kg of Chinese cabbage can be harvested per mu. According to the cultivation method, the two crops are large in there-dimensional space interval and are breathable, the humidity of field after rainfall is difficultly increased, downy mildew and powdery mildew of the rape difficultly occur, and the occurrence quantity of aphids is small; in addition, because the air permeability in the field is good, rape plants are sturdy and tall, pods seed vigorously, and high yield is promoted.
Owner:HIGH LATITUDE CROPS INST TO SHANXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Cultivating method for high-oleic acid rapeseed variety
InactiveCN105613258AReduce workloadImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBrassicaSpore
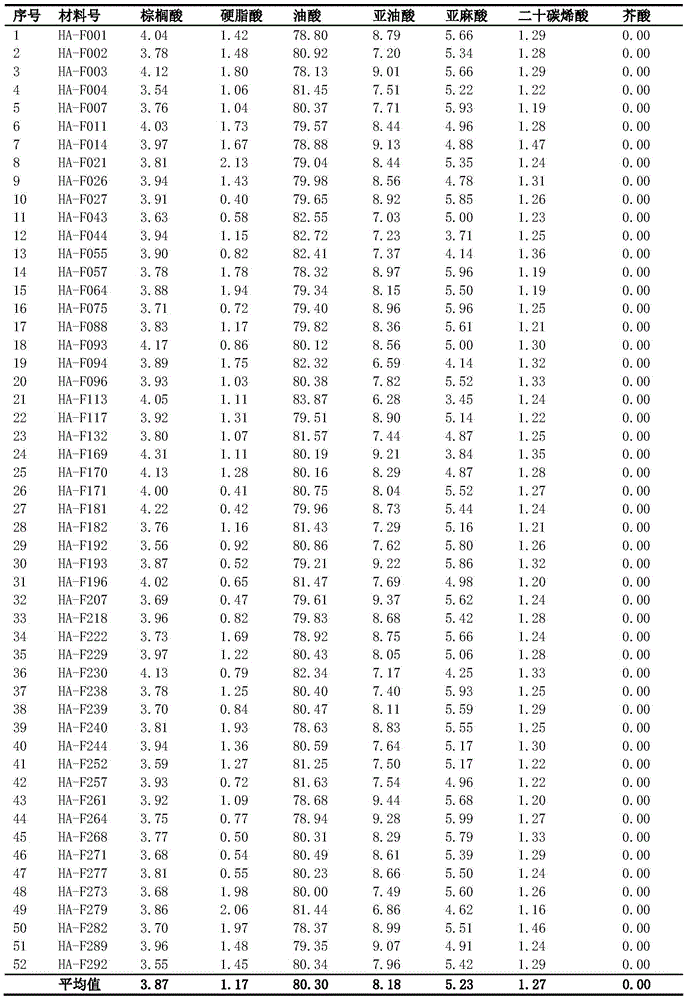
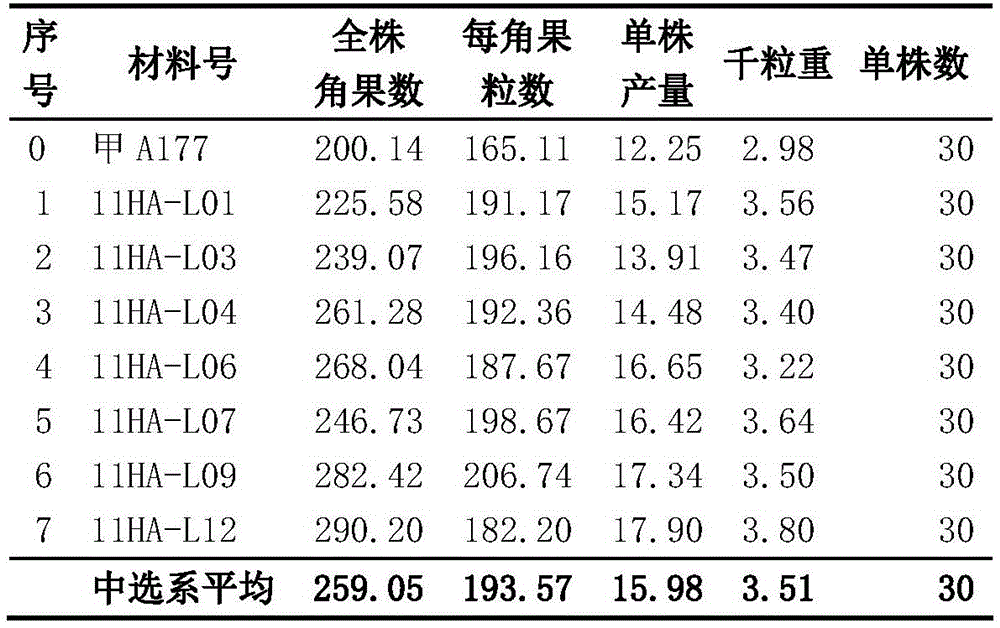
The invention belongs to the field of rapeseed breeding, and particularly relates to a cultivating method for a high-oleic acid rapeseed variety. The cultivating method is characterized by comprising the following steps: performing hybridization by taking first Brassica napus L. A177 with the oleic acid content of 65 percent or below as a female parent and taking first high-oleic acid Brassica napus L. H003 which has the preservation number of CCTCC NO:P201604 and has the oleic acid content of at least 78 percent as a male parent, and obtaining F1 through artificial emasculation; planting the F1, obtaining a separated DH line through microspores culture; performing high-oleic acid molecular marker identification on strain seedling stage of a DH line group, and determining the genotype of each strain; measuring the content of oleic acid of each single plant by utilizing a gas chromatograph, and determining the content of the oleic acid of the each primarily selected line; selecting the parent strains of which the characters, such as the whole plant pod number, the seed number per pod, the thousand seed weight and the yield per plant, are superior to the parent strain with the oleic acid content lower than 69 percent from the DH strain with the oleic acid content of greater than 75 percent to obtain the high-oleic acid rapeseed selected line and variety of which the oleic acid is greater than 78 percent.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
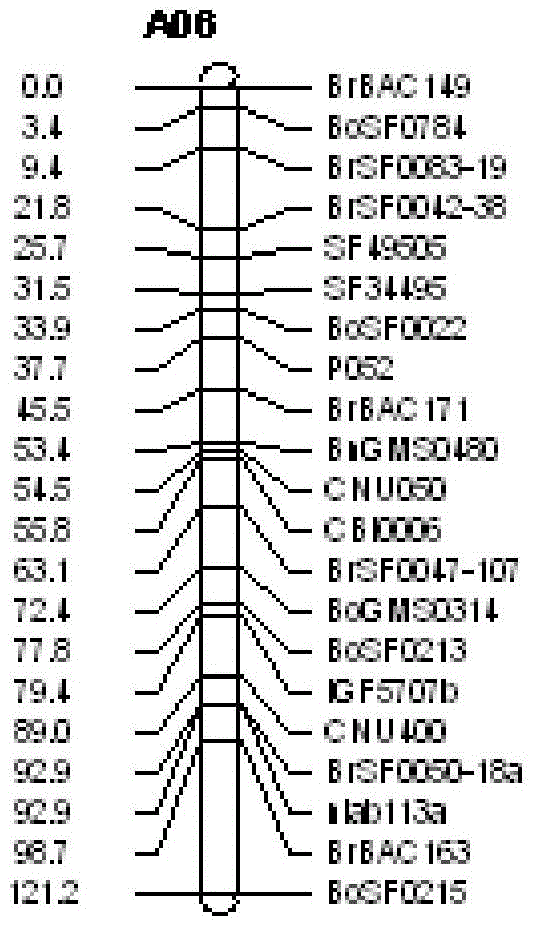
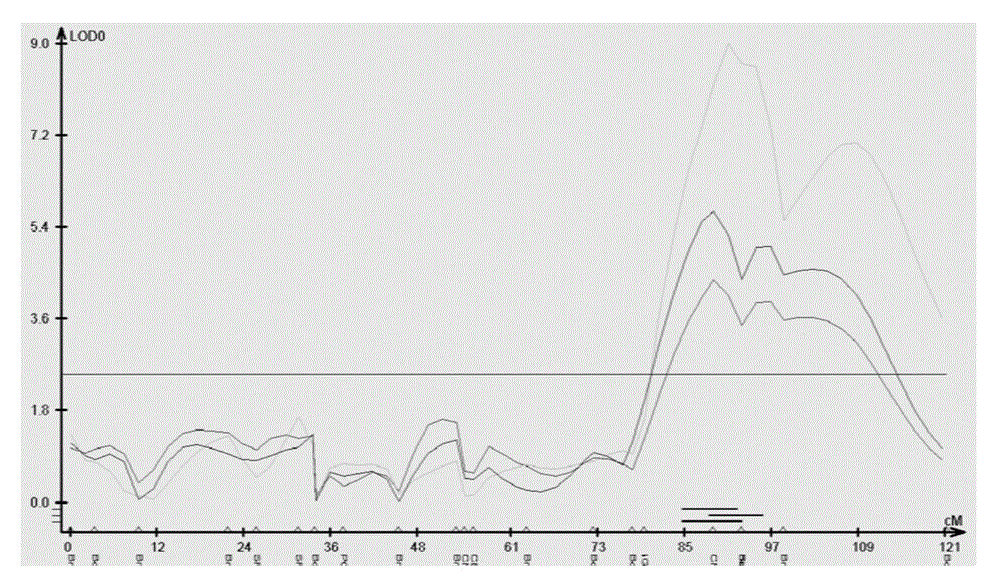
Main effect QTL site of the main inflorescence pod number character of Brassica napus, development of SNP molecular markers and application thereof
ActiveCN110358854AHigh contribution rateAccelerate the process of high-yield breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassicaAgricultural science
The invention provides a main effect QTL site of the main inflorescence pod number character of Brassica napus. The main effect QTL site is located between bases 5808417 and 7114866 in the A02 chromosome of Brassica napus. Preferably, the contribution rate of the main effect QTL site to the main inflorescence pod number of Brassica napus is 10.6%. The site is closely linked to the first SNP molecular marker. The first SNP molecular marker is located at base 5580417, which is C or T. This mutation leads to polymorphism. The site is closely linked to the second SNP molecular marker. The second SNP molecular marker is located at base 7113686, which is A or C. This mutation leads to polymorphism. The site is closely linked to the peak SNP molecular marker. The peak SNP molecular marker is located at base 6926697, which is A or C. This mutation leads to polymorphism. The invention also provides development of related SNP molecular markers and application thereof. The main effect QTL site ofthe main inflorescence pod number character of the Brassica napus provided by the invention has a high contribution rate to the main inflorescence pod number character of the Brassica napus, plays akey role in the regulation of the main inflorescence pod number of the Brassica napus. It can be used for map-based cloning and molecular marker-assisted selection, and is suitable for large-scale promotion and application.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker and application closely related to grain weight and silique length of oilseed rape
ActiveCN108300801AImprove breeding efficiencyShorten the breeding periodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGrain weightNucleotide sequencing
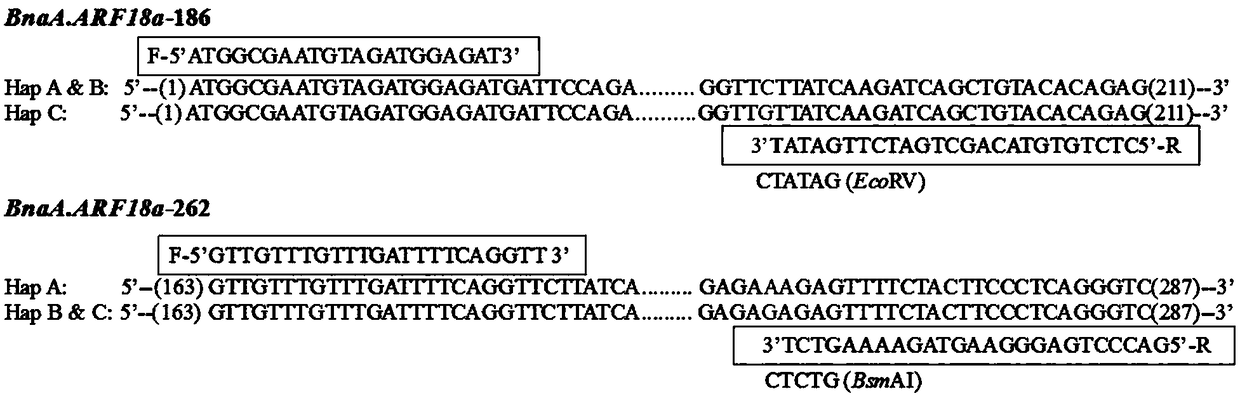
The invention relates to the field of oilseed rape breeding and molecular biology, in particular to a molecular marker and application closely related to the grain weight and silique length of oilseedrape. The molecular marker closely related to the grain weight and silique length of the oilseed rape is characterized by the molecular marker to the molecular marker of gene BnaA.ARF18a, and a nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The molecular marker solves the problem that the grain weight and the silique length in a conventional breeding method can be only identified later, so that thebreeding period is long, the breeding is easily affected by the environment, and the selection efficiency is low, the efficiency of the oilseed rape breeding is improved, the grain weight and siliquelength of different breeds of oilseed rape single plants can be quickly and reliably identified in the seedling stage of the oilseed rape, the breeding efficiency of the oilseed rape is improved, andthe breeding cycle of the oilseed rape is greatly shortened.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
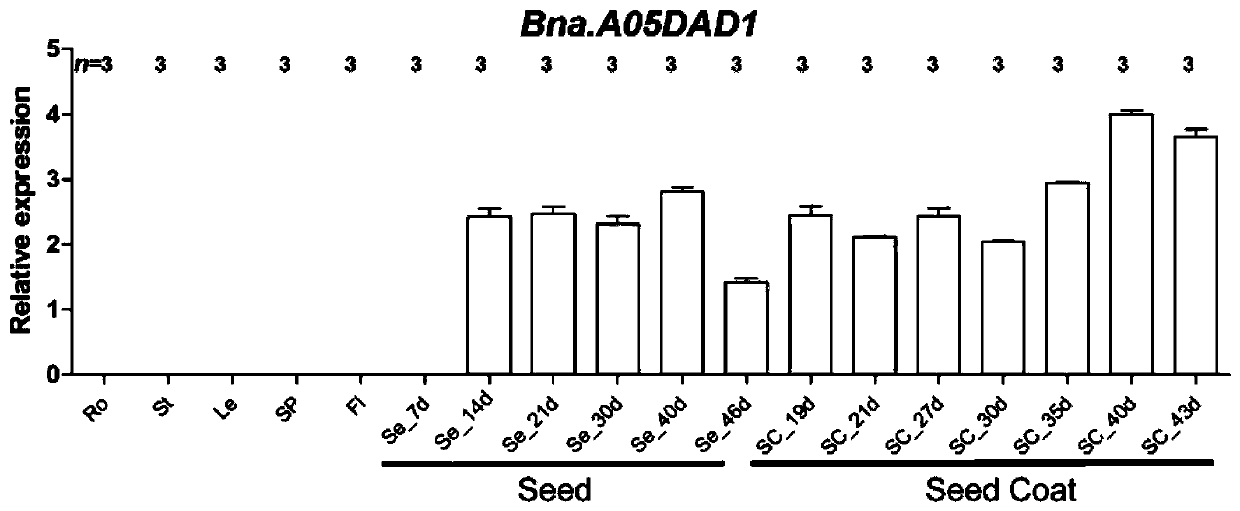
Application of brassica napus Bna.A05DAD1 gene and method
ActiveCN111518814AIncrease productionIncrease the lengthPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyBrassica
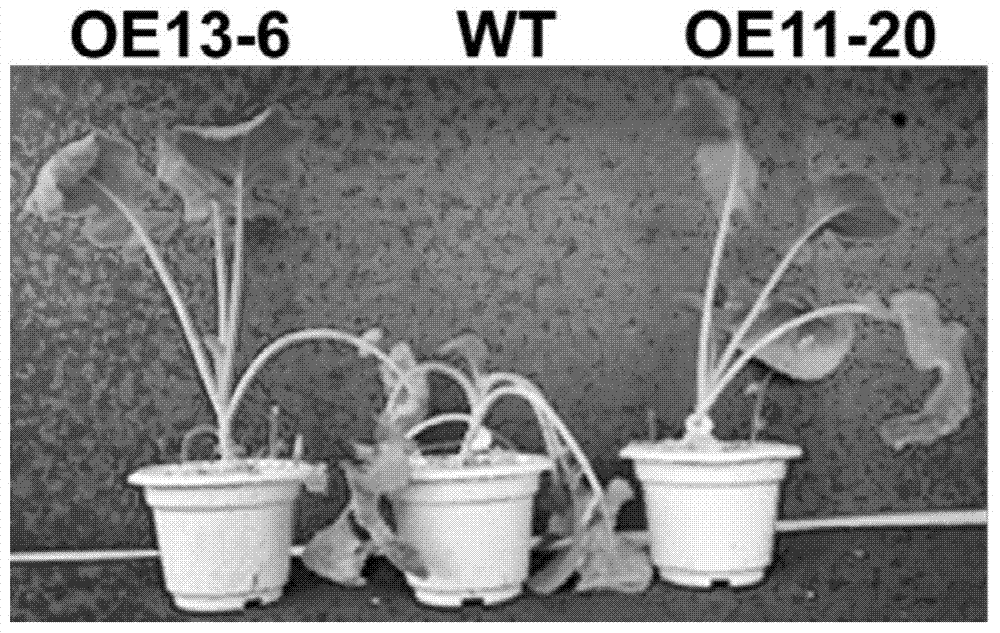
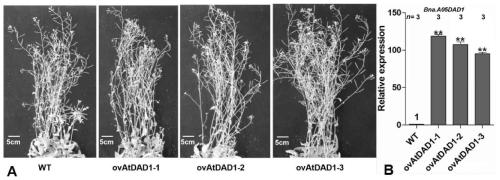
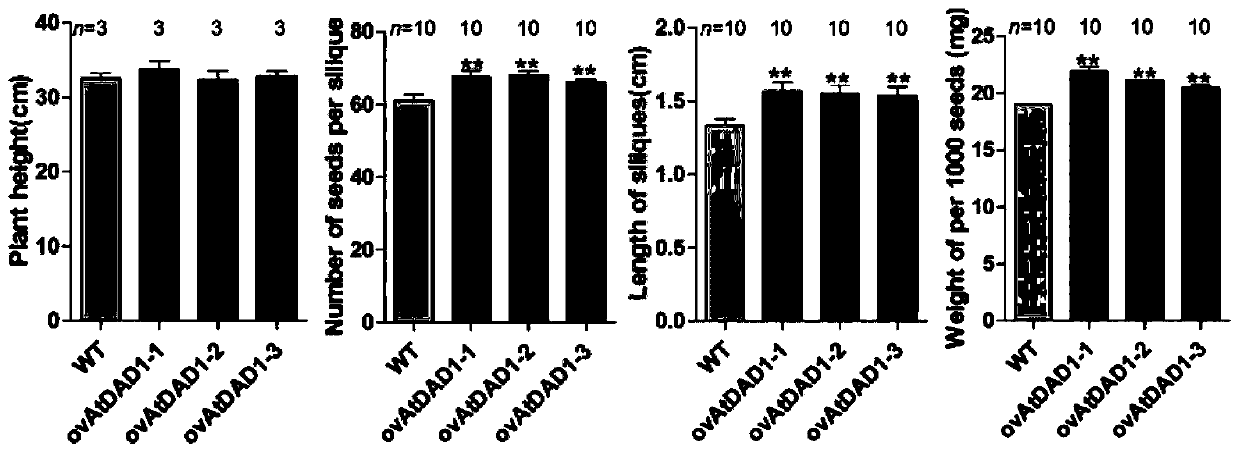
The invention discloses an application of a brassica napus DAD1 gene and a method. By using a cloned full-length coding sequence of the brassica napus DAD1 gene, an overexpression vector driven by a 35S promoter is successfully constructed. Arabidopsis thaliana and brassica napus are respectively subjected to genetic transformation by an agrobacterium infection method, T3-generation positive transgenic plants are obtained, and agronomic trait investigation of the transgenic plants shows that: overexpression of the brassica napus Bna.A05DAD1 can significantly increase the silique length, the number of seeds per silique and the thousand seed weight of seeds, and the brassica napus Bna.A05DAD1 has important significance in increasing the yield of brassica napus.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Simple method for artificially synthesizing cabbage type rape
The invention discloses a simple method for artificially synthesizing a cabbage type rape. The simple method comprises the following steps of: when wild cabbage and Chinese cabbage are hybridized, carrying out fertilization on the stigma of a female parent; after 16-144 hours, directly spraying a colchicine aqueous solution with percent concentration of 0.05%-0.15% on young ovary; and after the ovary grows to naturally-matured silique, harvesting full seeds, i.e., obtaining artificially-synthesized wild cabbage type rape seeds. Therefore, a new means with convenience, fastness and high efficiency is provided for obtaining the new germplasm of the cabbage type rape.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +2
Maca plantation method
The invention relates to a maca plantation method, and belongs to the technical field of agriculture plantation. A seedling growing process includes nutrient soil preparation, seed processing, sowing and seedbed managing, field management includes soil working, colonization, fertilizing water management and insect pest control, and final seed reservation includes selecting macas which are in accordance with the characteristics of the type, have tidy shape, glorious surface, less fibrous root, short and rough root tips, and are disease-free as seed plants. The seed plants are transplanted to a cleaned seed field, wherein the plant spacing is 10-20cm, and the line spacing is 30 cm. When the maca is planted, the soil is compacted. After colonization, sufficient root setting water is poured. Aphid is controlled during a flowering phase. When yellowish-brown initially appears on silique, the plants are pulled out timely and placed in a large dustpan. After the plants are exposed to the sun slightly, seeds are shaken off. The seeds are, after being aired, stored in ventilating bags in ventilating, cool and dry places. The method solves the problem the prior art is long in production period, high in investment cost and low in effective component content in maca.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of PLD alpha1 gene in aspects of increasing crop drought resistance and seed production
InactiveCN103773784AImprove water retentionImprove drought resistanceGenetic engineeringFermentationStomaArid
The invention belongs to the fields of plant molecular breeding and biotechnology and discloses application of a PLD alpha1 gene in aspects of increasing crop drought resistance and seed production. The nucleotide sequence of the PLD alpha1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, or the similarity of the nucleotide sequence of the PLD alpha1 gene is more than or equal to 70% compared with the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also discloses a method for increasing rape drought resistance and rape seed production. Experiments show that rape with stoma-specific overexpressed AtPLDalpha1 can effectively regulate stomas of plants to be closed under drought stress, so that moisture transpiration of leaves is reduced, and the water retaining capacity and the drought resistance of the plants are improved; the genetically modified rape plant has the characteristics that the flowering phase is postponed, vegetative growth is vigorous, the silique quantity is high, and the main inflorescence and the plant height of the rape are remarkably higher than those of the wild type rape when being suffered from an arid season in an early phase or an intermediate phase under a natural growth condition in the fields.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
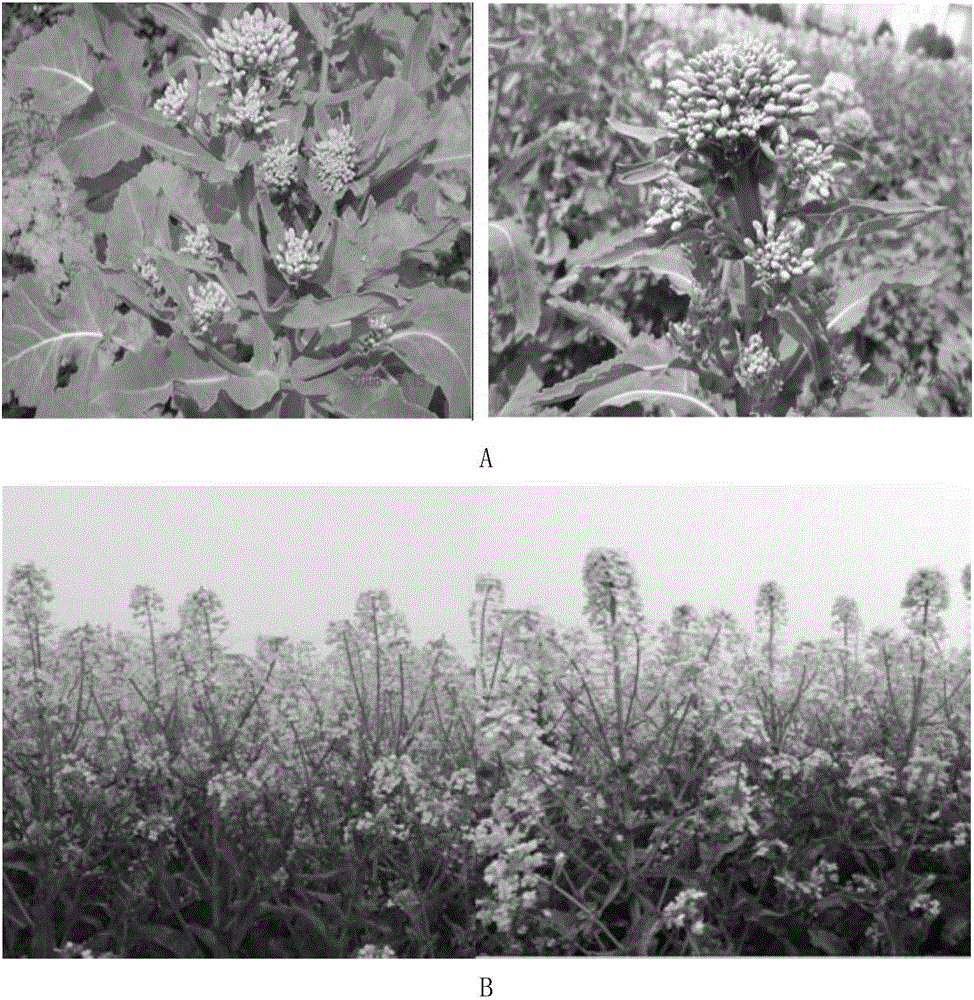
Breeding method for multi-pod main inflorescence brassica oleracea type hybrid rape combination
ActiveCN105766626AIncrease the number of siliques in the main inflorescenceAchieving the goal of saving cost and increasing efficiencyPlant genotype modificationAnimal scienceZoology
The invention discloses a breeding method for a multi-pod main inflorescence brassica oleracea type hybrid rape combination. The breeding method comprises the following steps: (1) breeding of a multi-pod main inflorescence maintainer line and a sterile line: A) performing hybridization by taking a multi-pod main inflorescence rape CGMCC NO.12262 as a male parent and taking an ordinary maintainer line as a female parent, B) performing back-crossing by taking F1 as a non-recurrent parent and taking an ordinary maintainer line as a recurrent parent, and performing continuous back crossing to obtain the multi-pod main inflorescence maintainer line by taking a back-crossing offspring as a non-recurrent parent, and C) performing hybridization by taking an ordinary cytoplasm male sterile plant as a female parent and taking the multi-pod main inflorescence maintainer line as a male parent, and performing continuous back-crossing to obtain the multi-pod main inflorescence sterile line; (2) breeding of a multi-pod main inflorescence hybrid rape combination: performing hybridization on the multi-pod main inflorescence sterile line and an ordinary cytoplasm male sterile restorer line to breed the multi-pod main inflorescence hybrid rape combination. According to the method, the main inflorescence pod number of the hybrid rape combination can be remarkably increased, and new rape varieties suitable for light, simple and high-density planting can be screened more easily.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Oilseed rape crop sesame cultivation method
The invention relates to the technical field of agriculture planting, and discloses an oilseed rape crop sesame cultivation method. According to the oilseed rape stubble sesame cultivation method, after previous crops of oilseed rape are harvested, the field layout of original ridge surfaces and three furrows is kept, straws of the oilseed rape are cleaned out, threshed siliques of the oilseed rape are evenly broadcasted in the field, then surface soil is straightly harrowed along the ridge surfaces, the surface soil is straightly harrowed again along the ridge surfaces to cover seeds of sesame after the seeds of the sesame are broadcasted, weed sealing is conducted after completing, and field management is conducted until harvest. Intertillage is conducted when the sesame has 4-5 leaves, the broadcasting shipping tube technique is executed, planting is conducted in a wide and narrow row spacing mode, a narrow row ranges from 20 cm to 30 cm, a wide row ranges from 50 cm to 6o cm, and row spacing ranges from 15 cm to 20 cm. According to the oilseed rape crop sesame cultivation method, the sesame is planted on the crops of the oilseed rape, the siliques of the oilseed rape return to the field, the cropping system is optimized, planting diversity is prompted, the original three furrows of the field of the oilseed rape are repeatedly used, labor is saved, and the yield of the sesame is increased finally.
Owner:信阳市农业科学院
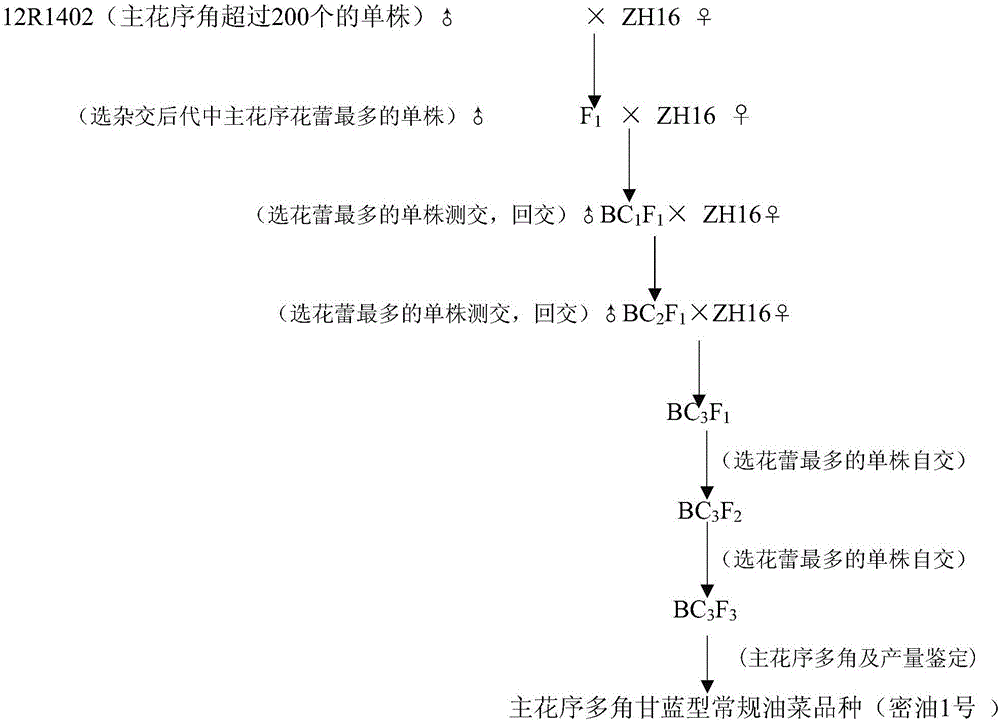
Breeding method of main-inflorescence multi-silique brassica napus type conventional rape variety
The invention discloses a breeding method of a main-inflorescence multi-silique brassica napus type conventional rape variety. The breeding method comprises the following steps: (A) carrying out hybridization by taking main-inflorescence multi-silique brassica napus type rape CGMCC NO.12262 as a male parent and brassica napus type rape strain as a female parent, thus obtaining hybrid progeny F1; (B) carrying out backcrossing by taking the hybrid progeny F1 as a non-recurrent parent and the brassica napus type rape strain as a recurrent parent, thus obtaining backcross progeny; (C) carrying out backcrossing by taking the backcross progeny as a non-recurrent parent and the brassica napus type rape strain as a recurrent parent, thus obtaining backcross progeny; (D) carrying out self-cross on the backcross progeny, thus obtaining the main-inflorescence multi-silique brassica napus type conventional rape variety. Conventional rape varieties having the character of having multiple siliques on the main inflorescence can be bred by utilizing the breeding method disclosed by the invention, and the conventional rape varieties can be used as rape varieties which are suitable for simplified and high-density planting.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for identifying hybrid seeds of winter cole-wort and mustard type winter rape
InactiveCN104611404AThose with deep staining have strong activityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementSiliqueRefrigerated temperature
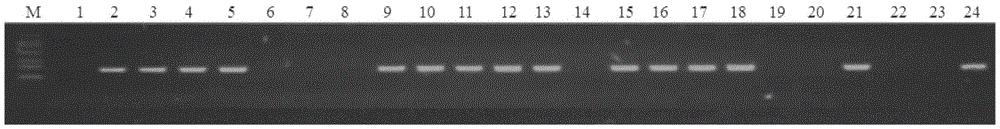
The invention relates to a method for identifying hybrid seeds of winter cole-wort and mustard type winter rape. With the adoption of the method, the condition that the hybrid seeds of winter cole-wort and mustard type winter rape are real hybrid seeds is identified. The method for identifying the hybrid seeds of winter cole-wort and mustard type winter rape is characterized by comprising steps as follows: (1), sampling; (2), weighing 0.2-0.3 g of flower buds, flowers and silique respectively, performing homogenizing by adopting a phosphate buffer having the pH of 7.8 and containing 2 mmol of ASA (acrylonitrile styrene acrylate) and 5 mmol of EDTA-Na2 (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid-Na2) under ice-bath respectively, performing centrifugation for 10 min at 12,000 r / min, and taking a liquid supernatant and storing the liquid supernatant in a refrigerator at the temperature of subzero 20 DEG C for standby. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is adopted, concentrations of separation gel and spacer gel are 7% and 4% respectively, and pH values are 8.8 and 6.8 respectively; an electrode buffer adopts a Tris-glycine system, the pH value is 8.3, and the loading quantity of samples is 30 mu L; when electrophoresis starts, steady voltage is 100 V, the voltage is regulated to be 200 V after the samples pass the concentrated gel, and the electrophoresis time is about 5 h; after electrophoresis is finished, the samples are placed in a dyeing liquid benzidine solution for dyeing until a clear blue stripe can be observed, and the samples are photographed for storage after washed by flowing water; a migration rate Rf value is quotient obtained by dividing the migration distance from an original point to the stripe by the distance from the original point to an indicator.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
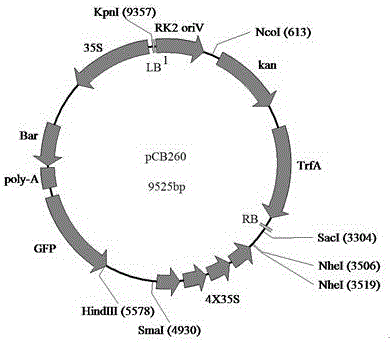
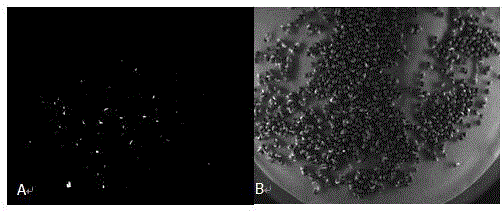
Method for obtaining brassica napus material suitable for high-density planting and mechanized harvesting
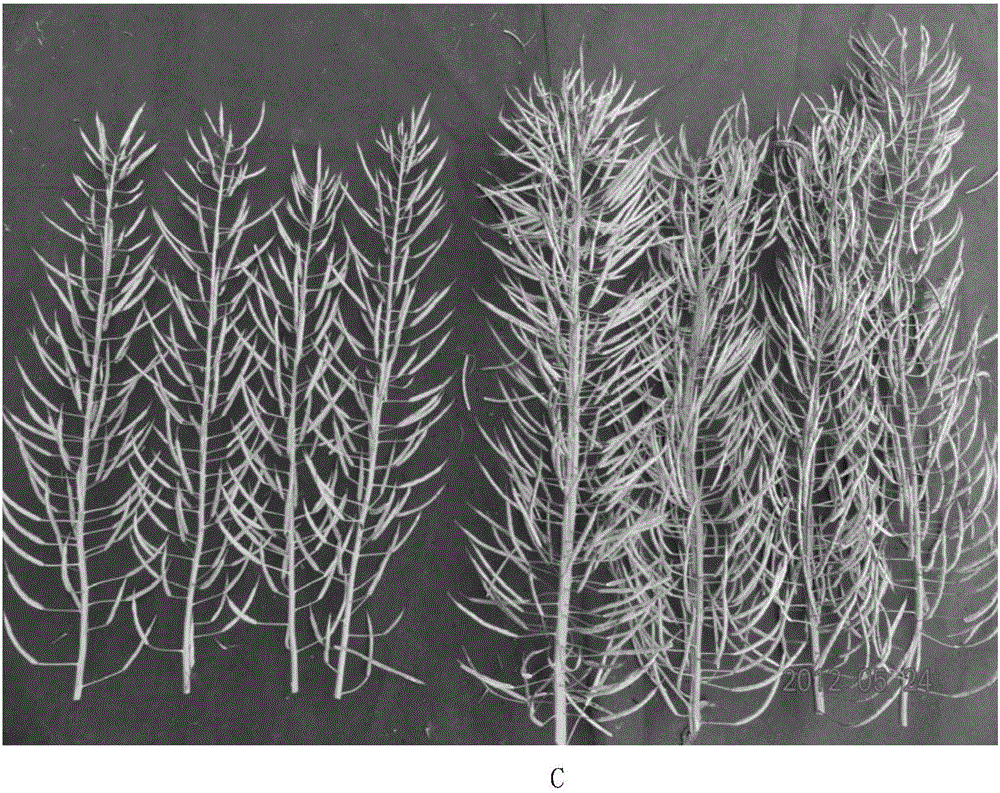
InactiveCN106834340AHigh speedLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionPlanting seedPlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to a method for obtaining a brassica napus material suitable for high-density planting and mechanized harvesting, belonging to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and biology. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: transforming an activation tagging vector pCB260 into brassica napus by adopting an agrobacterium flower soaking method; screening transformed plant seeds by utilizing a green fluorescent protein (GFP); screening brassica napus transformation plants by using herbicide phosphinothricin; and finally, identifying the transformed plants by using a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method. Phenotypic analysis of the transformed plants discovers that subramose brassica napus mutants are obtained and recorded as sfz. The plant accords with Mendel's law in F2-generation growth, the leaf surface at the seedling stage is bright, a few branches can grow at the maturation stage, the effective branch height is increased, and the siliques are centralized on the top of the plant. The brassica napus mutant obtained by transforming the brassica napus by utilizing the activation tagging vector pCB260 provides a novel material for large-scale mechanized production study and has important application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Propagation method for radish parent material
InactiveCN110235778AHigh purityImprove pollination rateRoot crop cultivationPlant genotype modificationDiseased plantPollen
The invention discloses a propagation method for a radish parent material. The method comprises the steps of radish stock tree planting, wherein concentrated planting is performed on each selfing line stock tree, and distinguishing is performed; 2, net house building, wherein bamboo poles are selected as stand columns and transverse rods of a net house, strips of cloth are adopted for binding and fixing, according to the number of radish selfing material trees, the size of the net house is determined, the net house is covered with a net cover, the lower portion is closed by soil, and osmia is prevented from flying out; 3, osmia release, wherein before osmia is released, a honeycomb and a mud disc need to be prepared inside each net house, and the honeycomb is suspended at the southeast corner of the upper portion of each net house. The released osmia can be released according to the ratio of radish plants to osmia being 1:5; 4, flowering phase plant and osmia management, wherein weak and diseased plants and special-shaped plants are removed from radish plants surviving after planting, before a full-bloom stage, plants are bound one time, the plants are surrounded by fish nets at the periphery, the distance between the fish nets and the external net houses is controlled to be about 40 cm, and the phenomenon that branches stretch to the edges of the net houses, and external pollen is received, so that hybrids are caused; 5, osmia recycling and storing; 6, seed harvesting, wherein the radish flowering phase is 30-40 d generally, after pollination is completed, non-podding flower ends are sheared off on sunny days in time, after the net cover and the bamboo poles are removed, pesticide is sprayed to radish plants, and insect diseases are prevented. Harvesting is performed when silique is yellowed, and after airing is performed for about 3 d, threshing is performed.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
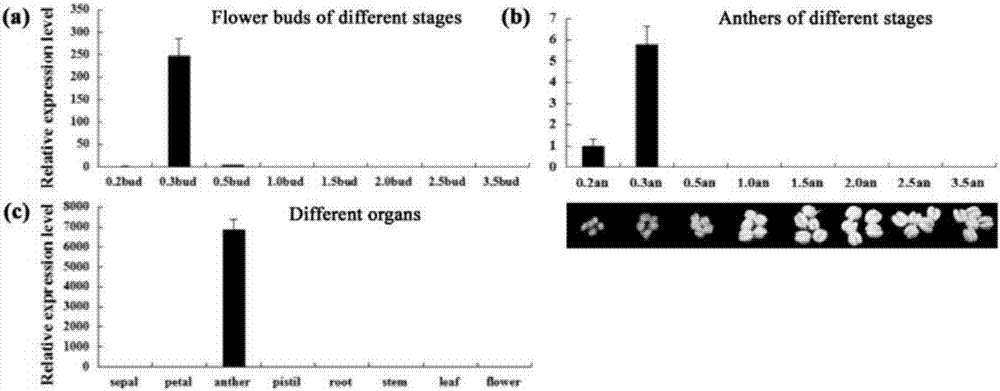
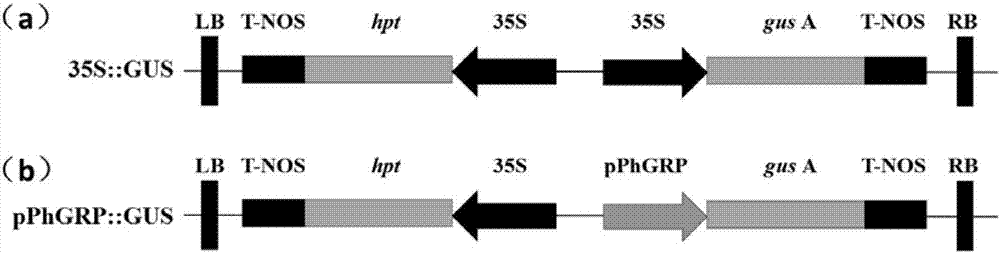
Identification method and application of petunia anther early specific expression promoter pPhGRP
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering and relates to an identification method and application of a petunia anther development early specific expression promoter pPhGRP. The separated promoter has a nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO: 1. A result of a quantitative PCR test on a promoter-driven petunia endogenous gene shows that the promoter-driven gene only is specifically expressed in the anther development early stage and is not expressed in other stages or in other tissues. The biological function verification and GUS staining detection results show that the promoter pPhGRP-driven reporter gene is not expressed in root, leaves and silique of arabidopsis thaliana and only is specifically expressed in the anther. The promoter pPhGRP-driven toxin gene Barnase only is specifically expressed in the petunia anther and is not expressed in other stages or in other tissues so that the male sterile line having other normally developed organs is obtained. The promoter can be used for male sterility genetic engineering, anther development regulation and control, and heterosis utilization.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Rape seed husk color regulation and control method
The invention relates to a rape seed husk color regulation and control method, which comprises the step of spraying fully and evenly mixed solution to rape siliques at dusk on a cloudy day or a sunny day prior to 8 days to 15 days before rape harvesting, wherein the solution contains 60-80mg / L abscisic acid and 0.5-0.8g / L Tween 40. By adopting the method, the synthesized seed husk pigment can be reduced, the content of the seed husk pigment is reduced, the seed husk transparency is increased, the formation of yellow rape seeds is facilitated and the quality of rape is improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of oilseed rape alpha-6 microtubulin gene in increasing yield of oilseed rape
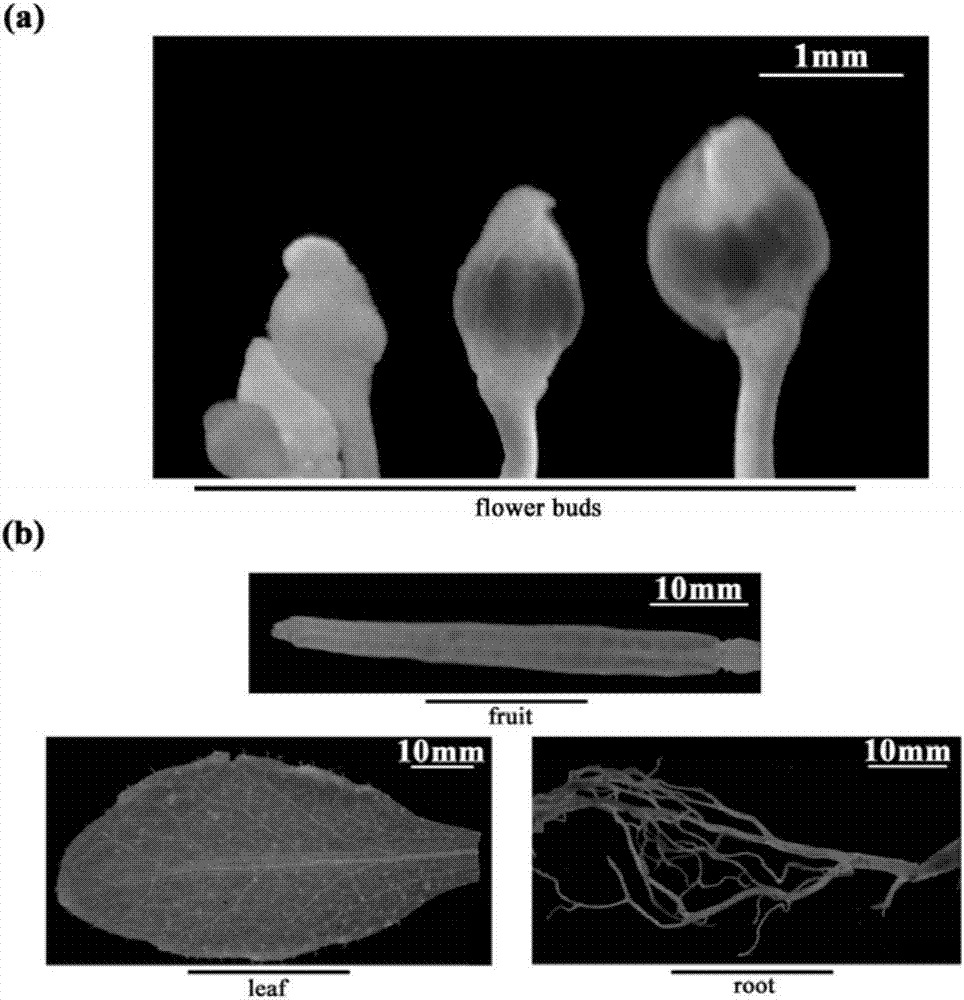
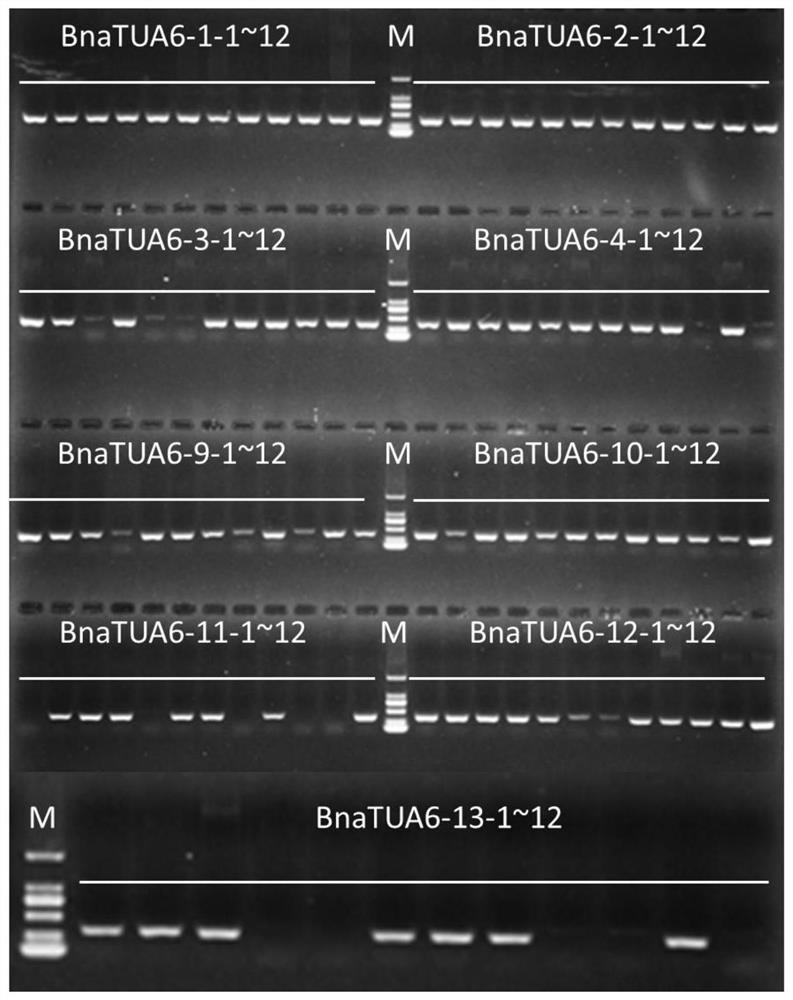
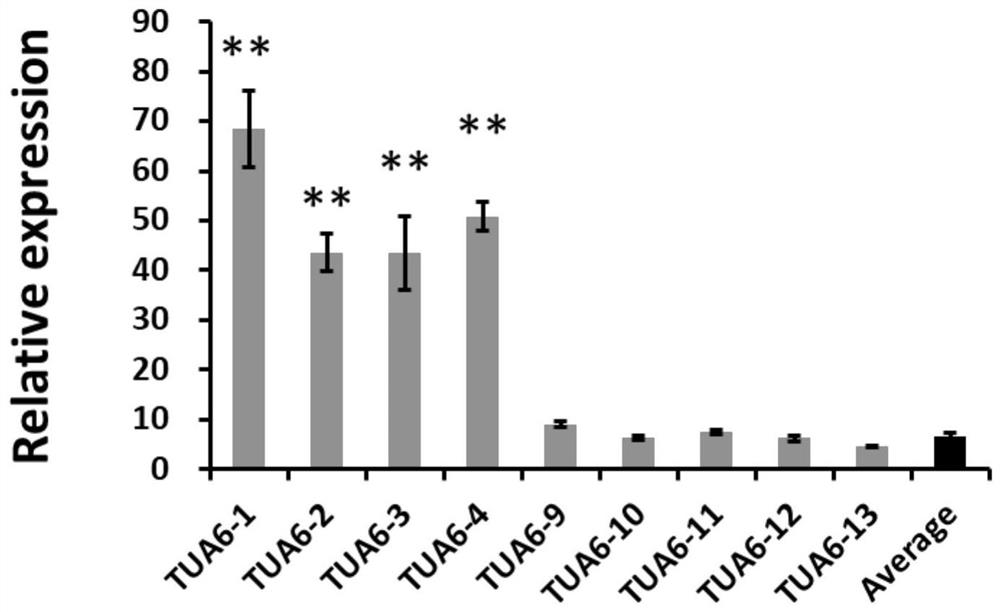
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to application of an oilseed rape alpha-6 tubulin gene in increasing the yield of oilseed rape. The nucleotide sequence of the oilseed rape BnaTUA6 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and the encoding protein of the oilseed rape BnaTUA6 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. By conducting overexpression on the gene in arabidopsis thaliana, it is found that the grain weight and seed size of a transgenic line are remarkably increased, the number of grains per silique is not remarkably changed, and a guarantee is provided for increasing the final yield. Therefore, the oilseed rape alpha-6 tubulin gene has a good application prospect in high-yield breeding of crops such as oilseed rape.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
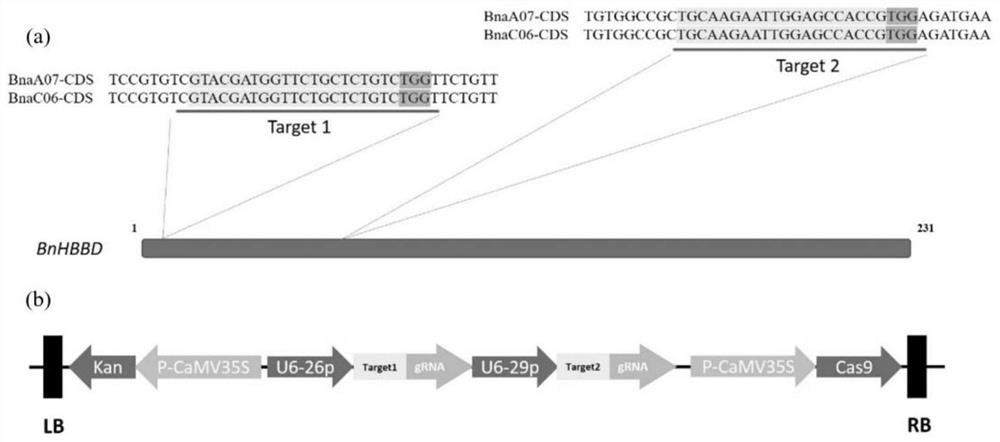
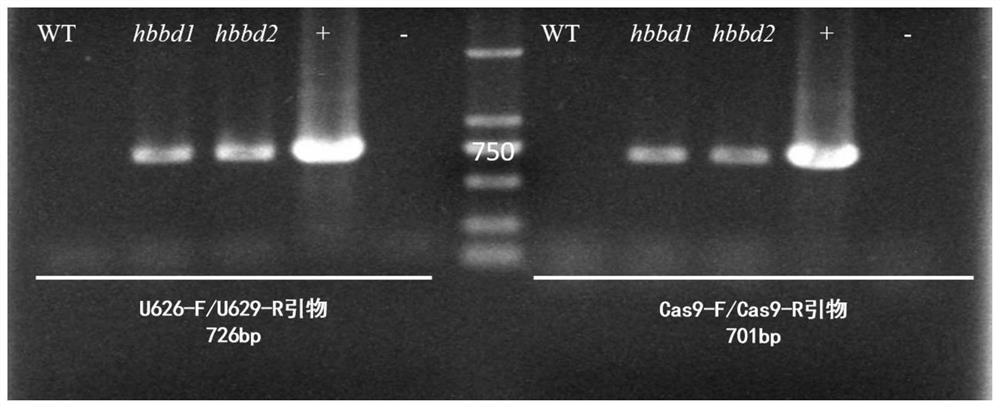
Brassica napus BnHBBD gene site-specific mutagenesis method and application
The invention provides a brassica napus BnHBBD gene site-specific mutagenesis method and application, and belongs to the technical field of plant gene editing and plant breeding. According to the invention, target spots Target1 and Target2 are designed and screened according to the BnHBBD gene in the brassica napus, sgRNA sequences are designed, then the two target spots are respectively connected with two same sgRNA sequences, a double-target-spot gene editing vector pKSE401-BnHBBD-CRISPR is constructed, the brassica napus is converted, site-directed mutagenesis of the BnHBBD gene of the brassica napus is realized, the exogenous gene carried by the vector is separated through selfing to obtain a new non-transgenic rape material which is long in flowering period, resistant to sclerotiniose and not easy to crack in silique. According to the invention, the gene editing technology is utilized to edit in the brassica napus, so that the obtaining period of new germplasm is greatly shortened, and innovative germplasm is provided for breeding of the brassica napus.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
High-temperature tolerance high-efficiency screening and identifying method in filling stage of rapeseeds
ActiveCN107581061AEasy to operateImprove accuracyPlant genotype modificationGrowth plantHeat resistance
The invention discloses a high-temperature tolerance high-efficiency screening and identifying method in filling stage of rapeseeds. The high-temperature tolerance high-efficiency screening and identifying method comprises the following steps of selecting the rape materials; planting the to-be-screened rape materials under the conventional condition; marking the flowers which flower at the same day, and obtaining a plurality of even number of siliques; mixing the siliques of each type of rape material, averagely separating into two groups, respectively inserting all siliques into a plant culture medium via silique stems, and respectively putting containers loaded with the siliques of each type of rape material into a plant growth box or a plant growth chamber for proper-temperature groupsand high-temperature groups; setting the culture environment of the siliques; measuring the related biology indexes of the high-temperature tolerance in the filling stage of each treated sample; screening the high temperature-resistant rape material. The high-temperature tolerance high-efficiency screening and identifying method has the advantages that the operability is strong, the accuracy is high, the repeatability is good, the identifying efficiency is high, the time is shortened, and the energy consumption is decreased; the wide application prospect is realized in the breeding of heat-resistant varieties, and predicting of ecological suitability of varieties, and the technical foundation is provided for the genetic improvement of the high-temperature tolerance in the filling stage ofthe rapeseeds.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Hemicellulase, and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN107022533AReduce functionReduce expressionHydrolasesGenetic engineeringAgricultural scienceSoil contamination
The invention discloses hemicellulase, and a coding gene and pplication thereof. The amino acid residue sequence of the hemicellulase is shown as (a) or (b): (a) an amino acid residue sequence shown as SEQ ID No:1; (b) an amino acid residue sequence which has the regulation and control effects on plant silique cracking and is obtained through the substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or several amino acid residues on the amino acid residue sequence shown as SEQ ID No:1. After the hemicellulase gene is mutated or subjected to suppression expression, the silique cracking time can be obviously delayed; meanwhile, the plant silique cracking rate is reduced, so that the seed yield reduction and the land pollution loss caused by relevant crop silique early cracking due to environment factors are reduced; further, the high yield of crop seeds is ensured; high practical application value is realized; the application prospects are wide.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
A05 chromosome major QTL locus of brassica napus major inflorescence silique density character, SNP molecular marker and application
ActiveCN111500756AHigh contribution rateSpeed up the process of density breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBrassica
The invention provides an A05 chromosome major QTL locus of a cabbage type rape major inflorescence pod density character. The A05 chromosome major QTL locus is located between a 20957390th basic group and a 21315610th basic group of an A05 chromosome of cabbage type rape. Preferably, the contribution rate to the brassica napus main inflorescence silique density character is 15.36%. The SNP molecular marker is closely linked with a first SNP molecular marker, is located at the 20957390th basic group and is A or G, and the mutation causes polymorphism. The SNP molecular marker is closely linkedwith a second SNP molecular marker, is located at the 21315610th basic group and is C or T, and the mutation causes polymorphism. The SNP molecular marker is closely linked with a peak SNP molecularmarker, is located at the 21171737th basic group and is C or T, and the mutation causes polymorphism. The invention further provides a related SNP molecular marker and application. The A05 chromosomemajor QTL locus is high in contribution rate to cabbage type rape main inflorescence pod density traits, plays a key role in adjustment and control of cabbage type rape main inflorescence pod density,can be used for map-based cloning and molecular marker-assisted selection, and is suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:贵州省油菜研究所
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com