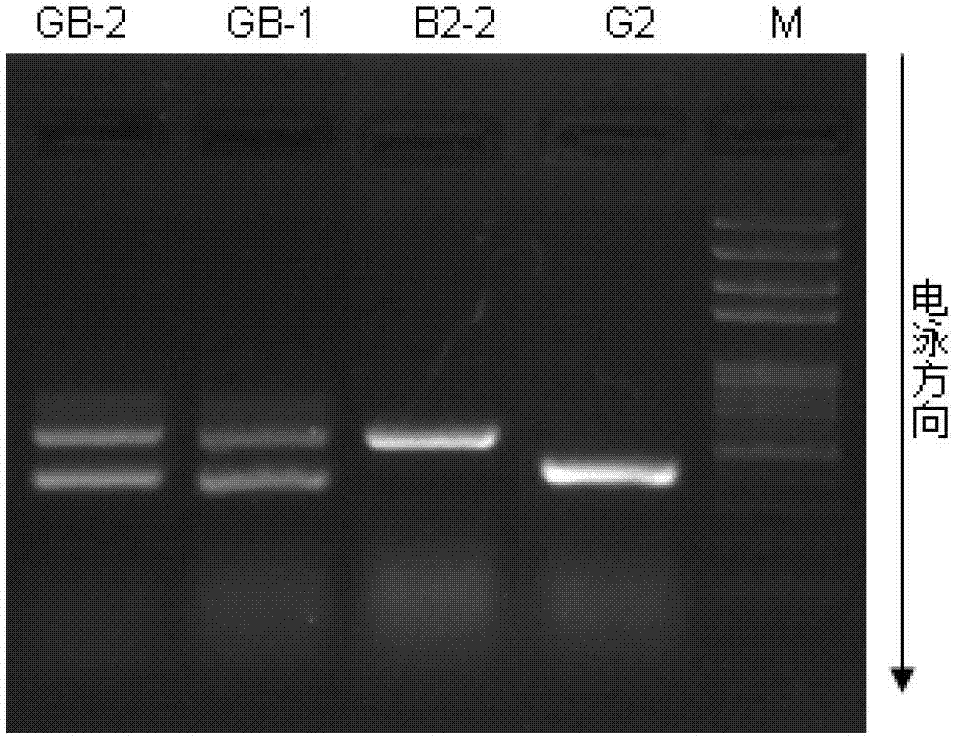
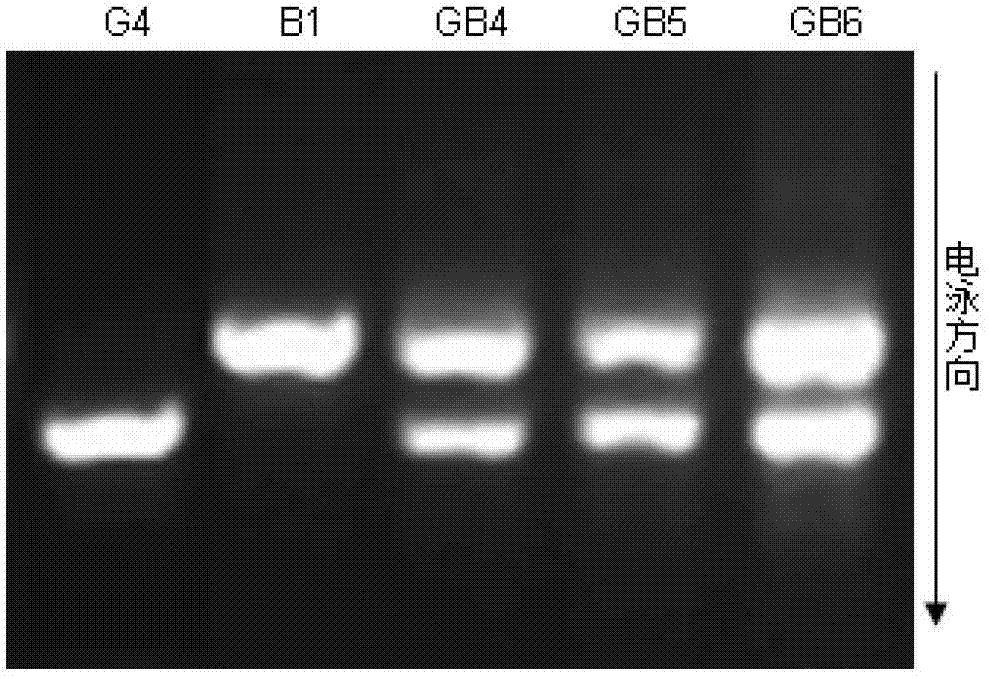
Simple method for artificially synthesizing cabbage type rape
A technology of Brassica napus and a simple method, which is applied in the field of artificial synthesis of Brassica napus, can solve the problems of hybridization incompatibility between cabbage and Chinese cabbage species, such as workload, low efficiency, and long time consumption, so as to overcome incompatibility and The effect of heavy workload, high efficiency and small workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Example 1: Brassica napus artificially synthesized by cabbage G3 strain and Chinese cabbage B1 strain
[0016] 1. Material planting: On October 10, 2010, the cabbage G3 strain and the Chinese cabbage B1 strain were planted in the rape test field. On March 10, 2011, the cabbage B1 entered the flowering period, and on March 23, the cabbage G3 entered the flowering period.
[0017] 2. Hybridization: The early flowering cabbage B1 is used as the male parent, and the relatively late flowering cabbage G3 is used as the female parent. Between 9 and 10 in the morning, on the inflorescence of cabbage G3, select 11 flower buds whose petals are about to unfold but have not yet opened, and remove all other flower buds that have opened and have not opened; then completely remove the stamens of the 11 flowers, and remove the The pollen of B1 was pollinated on the stigma of cabbage G3, and bagged with a sulfuric acid paper bag to prevent pollen from other sources from falling on the s...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Example 2: Artificially synthesizing Brassica napus using Brassica oleracea G2 strain and Chinese cabbage B2-2 strain
[0021] Planting of materials: On October 10, 2011, the cabbage G2 strain and the Chinese cabbage B2-2 strain were planted in the rape test field. On March 10, 2012, the Chinese cabbage B2-2 entered the flowering period, and on March 23, the G2 entered the flowering period.
[0022] Hybridization: The early flowering cabbage B2-2 was used as the male parent, and the relatively late flowering cabbage G2 was used as the female parent. Between 9 and 10 in the morning, on the inflorescence of cabbage G2, select 18 flower buds whose petals are about to unfold but have not yet opened, and remove all other flower buds that have opened and have not opened; then completely remove the stamens of the 18 flowers, and remove the The pollen of B2-2 was pollinated on the stigma of cabbage G2, and bagged with a sulfuric acid paper bag to prevent pollen from other sourc...
Embodiment 3
[0025] Example 3: Brassica napus artificially synthesized by cabbage G4 strain and Chinese cabbage B1 strain
[0026] Material planting: On October 10, 2011, the cabbage G4 strain and the Chinese cabbage B1 strain were planted in the rape test field. On March 10, 2012, the Chinese cabbage B1 entered the flowering period, and on March 23, the G4 entered the flowering period.
[0027] Hybridization: The early flowering cabbage B1 was used as the male parent, and the relatively late flowering cabbage G4 was used as the female parent. Between 9 and 10 in the morning, on the inflorescence of cabbage G4, select 23 flower buds whose petals are about to unfold but have not yet opened, and remove all other flower buds that have opened and have not opened; then completely remove the stamens of the 23 flowers, and remove the The pollen of B1 was pollinated on the stigma of cabbage G4, and bagged with a sulfuric acid paper bag to prevent pollen from other sources from falling on the stigm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com