Breeding method for multi-pod main inflorescence brassica oleracea type hybrid rape combination
A technique for multi-cornered main inflorescences of Brassica napus, which is applied in the fields of botany equipment and methods, applications, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problems of rising labor costs, declining rapeseed planting area, low degree of mechanization, etc., to increase the angle of main inflorescences The effect of fruit number
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1, Breeding "Main Inflorescence Polygonal" Brassica napus Maintainer Line
[0054] 1. Discovery and breeding of "multi-horned main inflorescence" Brassica napus strain
[0055] In 2004, a mutant single plant with abnormally many horns in the main inflorescence was found in the breeding materials. After selfing and directional selection for many years, a new line 12R1402 with stable "multi-cornered main inflorescence" was bred from the offspring of the mutant strain. The maximum number of effective siliques in the main inflorescence of the strain is 300, with an average of about 180. A new strain 12R1402 with stable characteristics of "polygonal main inflorescence" was bred, and it was preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Committee for Microbial Culture Collection (CGMCC for short, address: Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing) on April 8, 2016 No. 1 Courtyard No. 3, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Zip Code 10...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Example 2, Breeding "Main Inflorescence Polygonal" Cytoplasmic Male Sterile Line
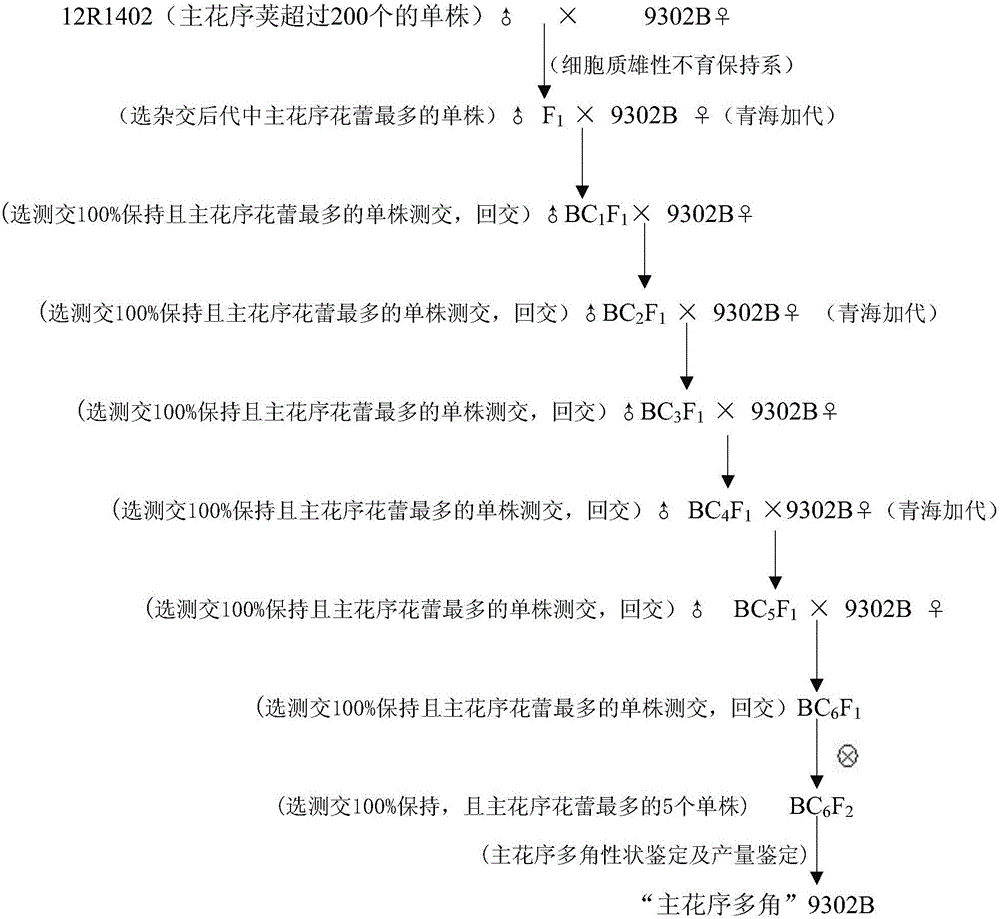
[0109] 1. Based on the continuous backcrossing of the Qinyou 7 sterile line and the maintainer line "Main Inflorescence Duojiao" 202B, the "Main Inflorescence Duojiao" cytoplasmic male sterile line 202A was selected
[0110] Since 2009, according to image 3 For hybridization and backcrossing:
[0111] 1) hybridization
[0112] In March 2009, 10 sterile plants of Brassica napus Qinyou No. 7 (National Inspection Oil 2004014) were used as female parents, and 10 "Main Inflorescence Polygonal" 202B bred in Example 1 were used as male parents, and crossed to obtain 10 F 1 ; The male parent takes the powder plant and bags it for self-breeding.
[0113] 2) 1st backcross
[0114] In July 2009, from 10 hybrid progeny F 1 Select the single plant with the most flower buds in the main inflorescence (the number of flower buds in the main inflorescence is about twice that of Huyou 17), and record...
Embodiment 3
[0160] Embodiment 3, main inflorescence multi-corner hybrid combination breeding
[0161] 1. Breeding hybrid rape combination with multi-corner main inflorescence based on "multi-corner main inflorescence" 202A
[0162] 1. Breeding
[0163] In 2012 according to Figure 5 Perform combined screening:
[0164] In March 2012, using the 50 cytoplasmic male sterile line "Main Inflorescence Polygonal" 202A selected in Example 2 as the female parent, the Brassica napus restorer lines 7P76, 7P71 and 7P83 (7P76, 7P71 and 7P83 was 100% recovered by test crossing the fully fertile lines isolated from Qinyou 8 (Guo Shenyou 2004015), Huayouza 8 (Guo Shenyou 2004007), and Zhongyouza 8 (Guo Shenyou 2004004) The strains obtained through systematic breeding) were crossed with the male parent, and 3 hybrid combinations F 1 seed.
[0165] In October 2012, 3 hybrid combinations of 100 plants were planted; in May 2013, the hybrid combination F was identified 1 , more than 90% of the main infl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com