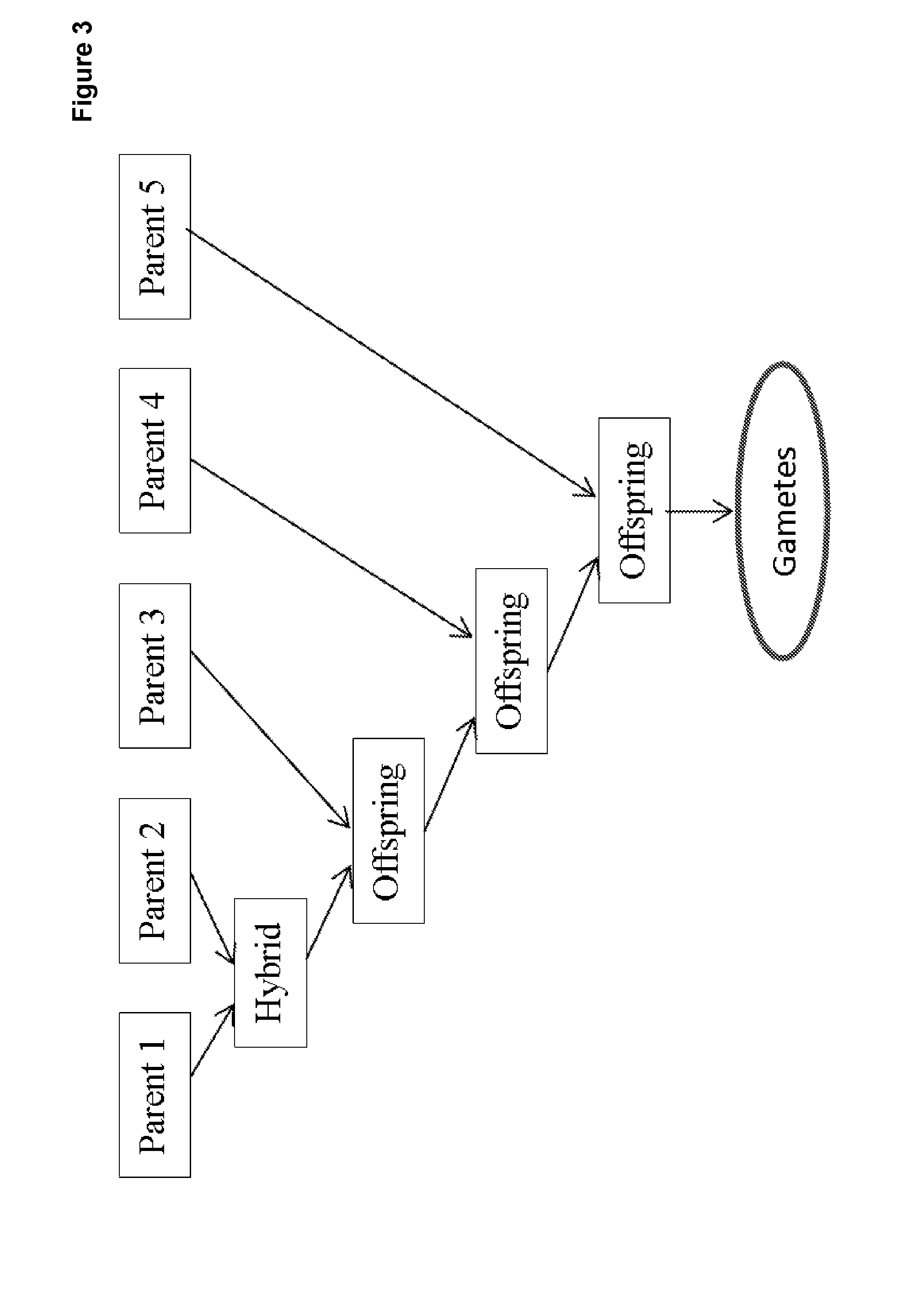
Patents
Literature
440 results about "Phenotypic trait" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A phenotypic trait, simply trait, or character state is a distinct variant of a phenotypic characteristic of an organism; it may be either inherited or determined environmentally, but typically occurs as a combination of the two. For example, eye color is a character of an organism, while blue, brown and hazel are traits.
High threonine producing lines of Nicotiana tobacum and methods of producing
InactiveUS7173170B2Improve the level ofImproved taste and aromaMutant preparationFermentationNicotiana tabacumThreonine
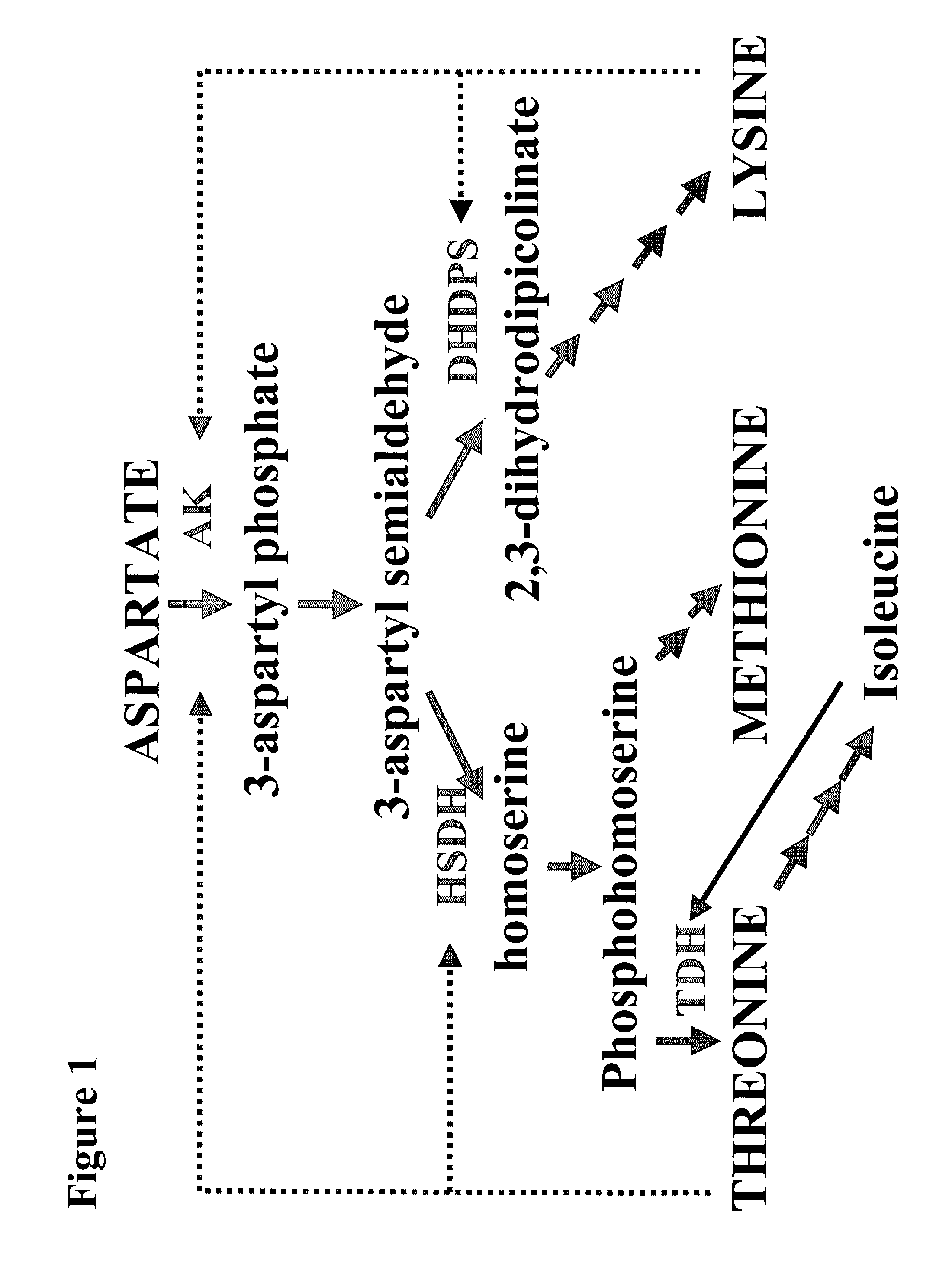
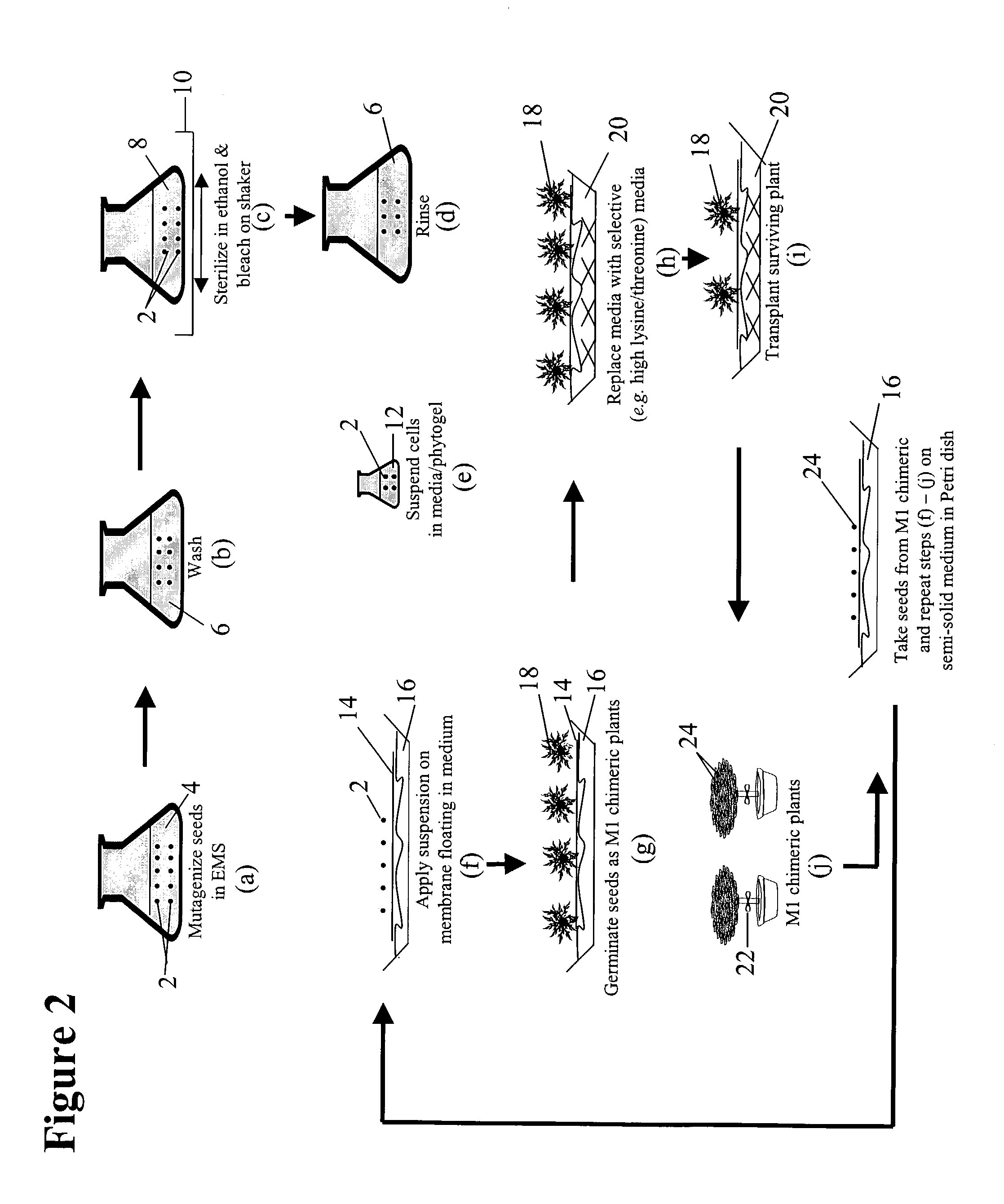
The present invention provides a method for producing plants with a desired phenotypic trait which comprises subjecting plants to mutagenesis, screening chimeric progeny for plants having the desired phenotypic trait, and propagating the survivors. In an embodiment, the phenotypic trait comprises an altered amino acid content. Preferably, the technique is used to generate Nicotiana tobacum plant lines having an increase in at least one amino acid. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides improved Nicotiana tobacum plant lines producing at least 1.35 nmole of threonine per milligram of dry plant weight. These plants are useful for improving the flavor and aroma of the tobacco.
Owner:REYNOLDS TECH
Plant breeding method
InactiveUS20050144664A1Other foreign material introduction processesAgricultureNumeral systemPlant variety
Methods for using genetic marker genotype (e.g., gene sequence diversity information) to improve the process of developing plant varieties (e.g., single cross hybrids) with improved phenotypic performance are provided. Methods for predicting the value of a phenotypic trait in a plant are provided. The methods use genotypic, phenotypic, and optionally family relationship information for a first plant population to identify an association between at least one genetic marker and the phenotypic trait, and then use the association to predict the value of the phenotypic trait in one or more members of a second, target population of known marker genotype. Methods for identifying new allelic variants affecting the trait are also provided. Plants selected, provided, or produced by any of the methods herein, transgenic plants created by any of the methods herein, and digital systems for performing the methods herein are also provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Functional arrays for high throughput characterization of gene expression regulatory elements
InactiveUS20070161031A1Good curative effectEliminate side effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomicsHuman DNA sequencing
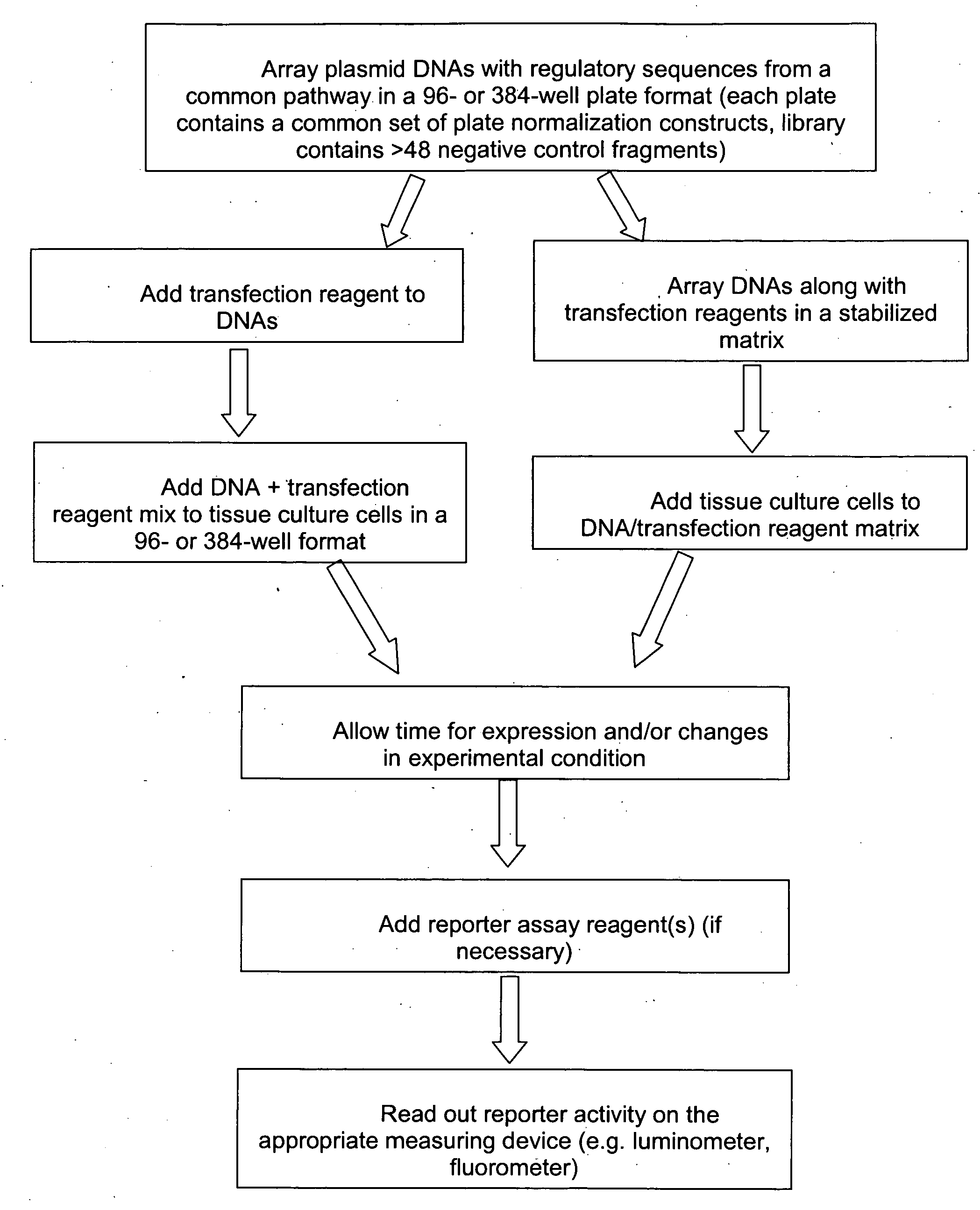
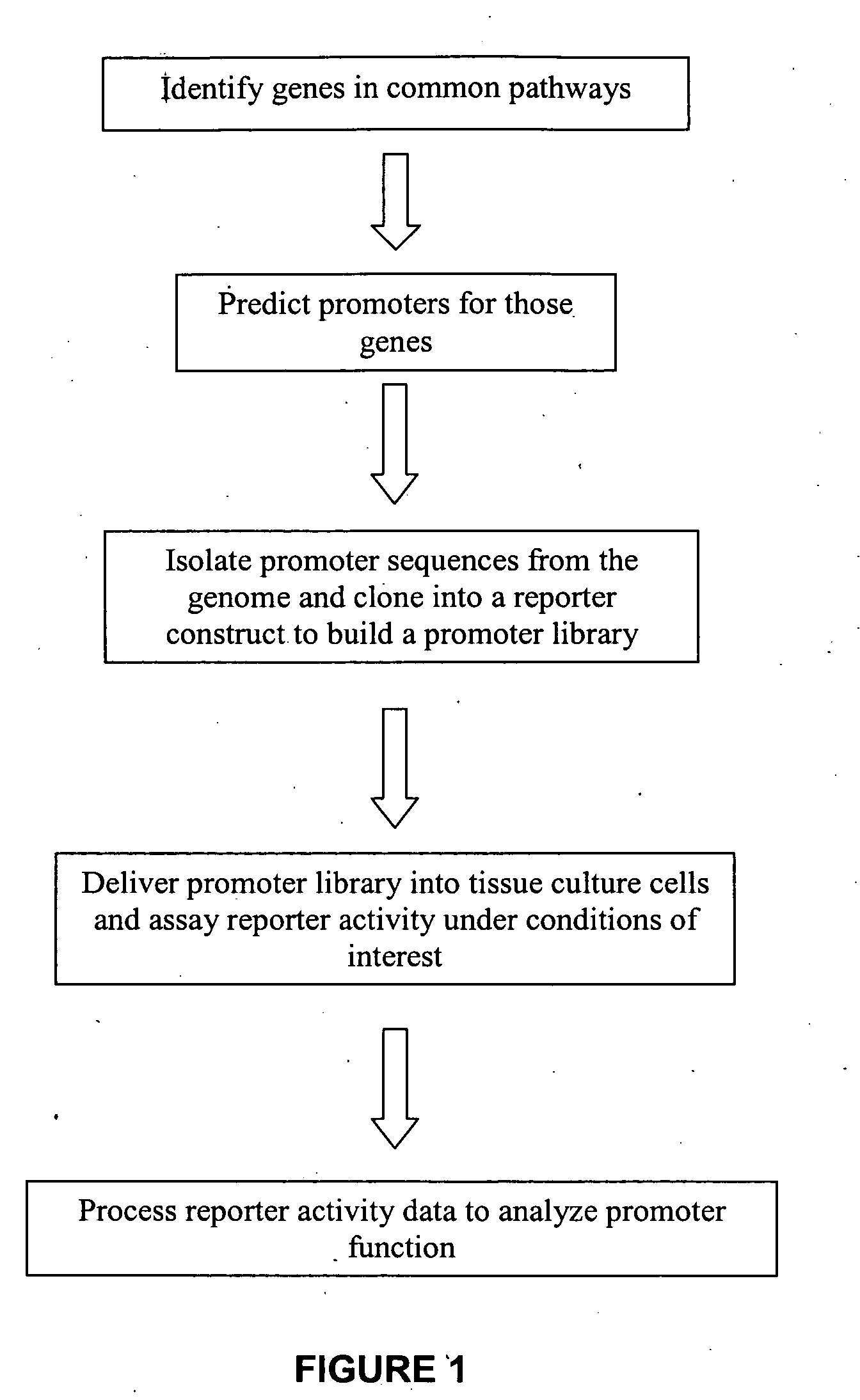
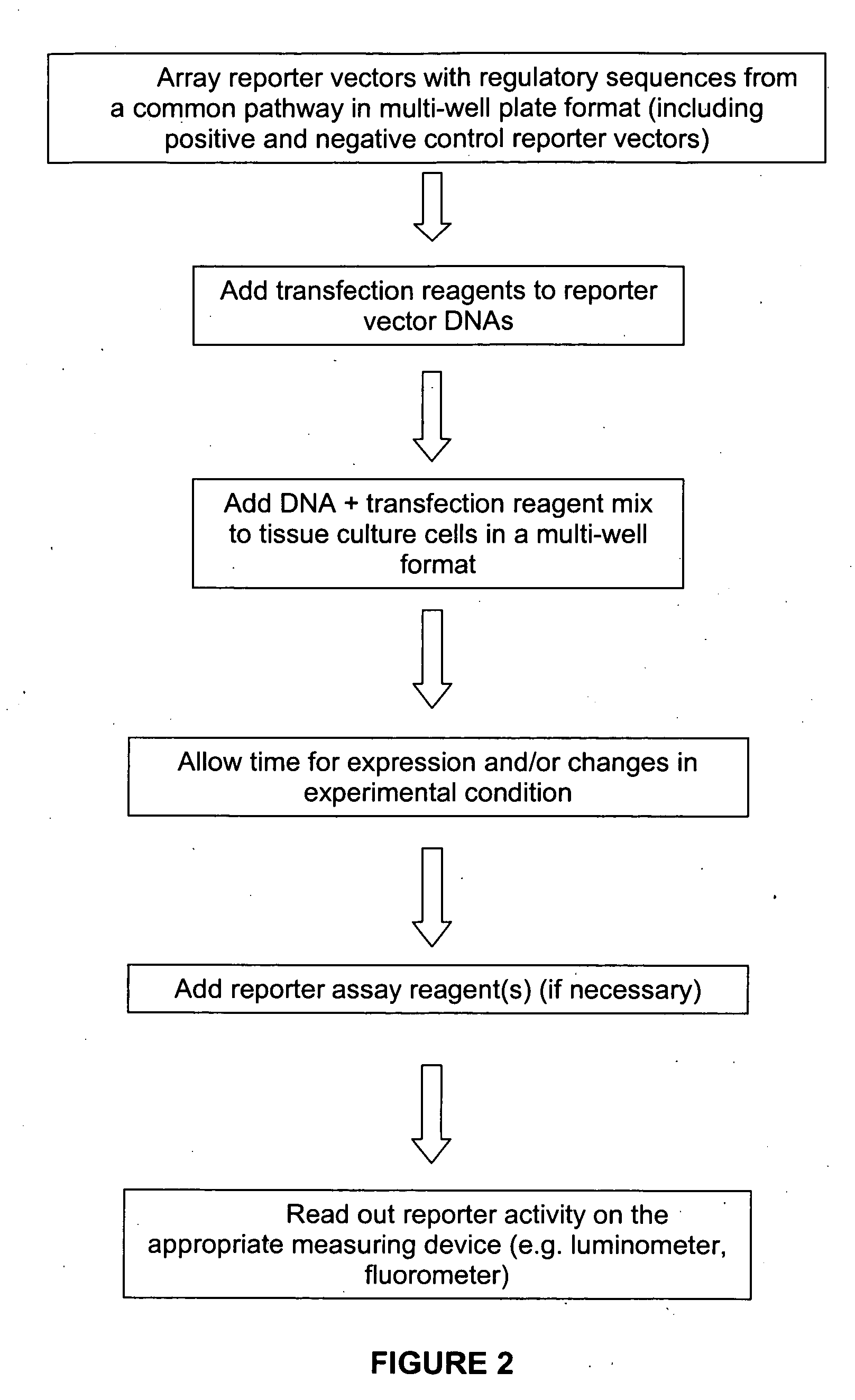
The present invention provides compositions, kits, assemblies, libraries, arrays, and high throughput methods for large scale structural and functional characterization of gene expression regulatory elements in a genome of an organism, especially in a human genome. In one aspect of the invention, an array of expression constructs is provided, each of the expression constructs comprising: a nucleic acid segment operably linked with a reporter sequence in an expression vector such that expression of the reporter sequence is under the transcriptional control of the nucleic acid segment, the nucleic acid segment varying in the library and having a diversity of at least 50. The nucleic acid segments can be a large library of gene expression regulatory elements such as transcriptional promoters. The present invention can have a wide variety of applications such as in personalized medicine, pharmacogenomics, and correlation of polymorphisms with phenotypic traits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Transcriptional regulatory elements of biological pathways tools, and methods
InactiveUS20090018031A1Determine effectNucleotide librariesLibrary screeningHuman DNA sequencingRegulation of gene expression
The present invention provides compositions, kits, assemblies, libraries, arrays, and high throughput methods for large scale structural and functional characterization of gene expression regulatory elements in a genome of an organism, especially in a human genome, that are part of a common pathway. In one aspect of the invention, an array of expression constructs is provided, each of the expression constructs comprising: a nucleic acid segment operably linked with a reporter sequence in an expression vector such that expression of the reporter sequence is under the transcriptional control of the nucleic acid segment. The present invention can have a wide variety of applications such as in personalized medicine, pharmacogenomics, and correlation of polymorphisms with phenotypic traits.
Owner:SWITCHGEAR GENOMICS
Genetic trait breeding method
InactiveUS6946586B1Improve traitsStable introduction of DNAFermentationGenetic traitsPhenotypic trait
A method for screening for a trait associated with the altered expression of a gene of interest in plants is provided. The method is a combinatorial approach which uses traditional plant breeding techniques for modifying the patterns of expression of a gene of interest. Kits for use in the method and transgenic plants generated by the method are also provided.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Identification of seeds or plants using phenotypic markers
InactiveUS6865556B2Facilitates and enables trait identificationFacilitates and enables and fee collectionComputer security arrangementsElectric/magnetic computingPhenotypic traitCultivar
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
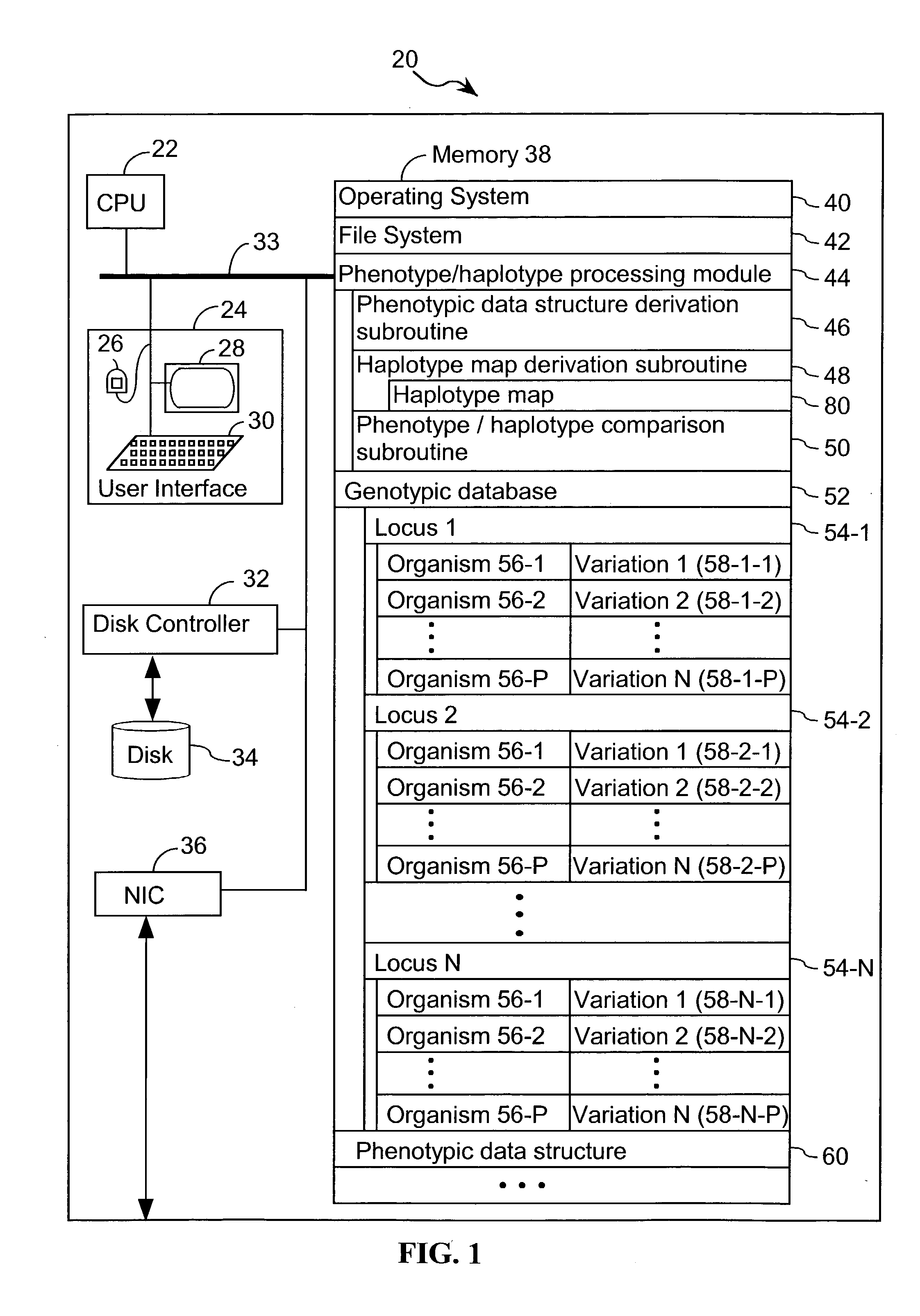
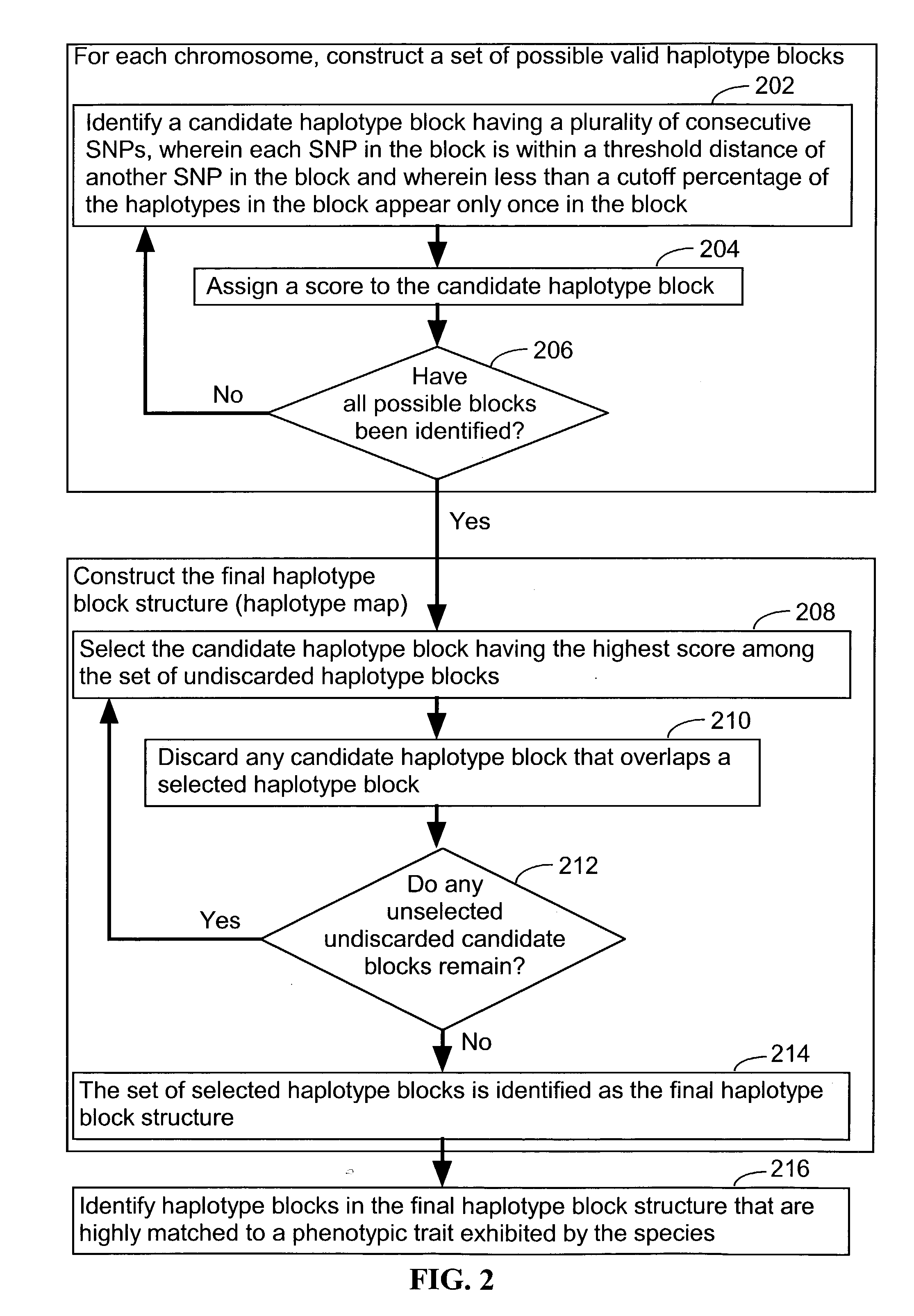
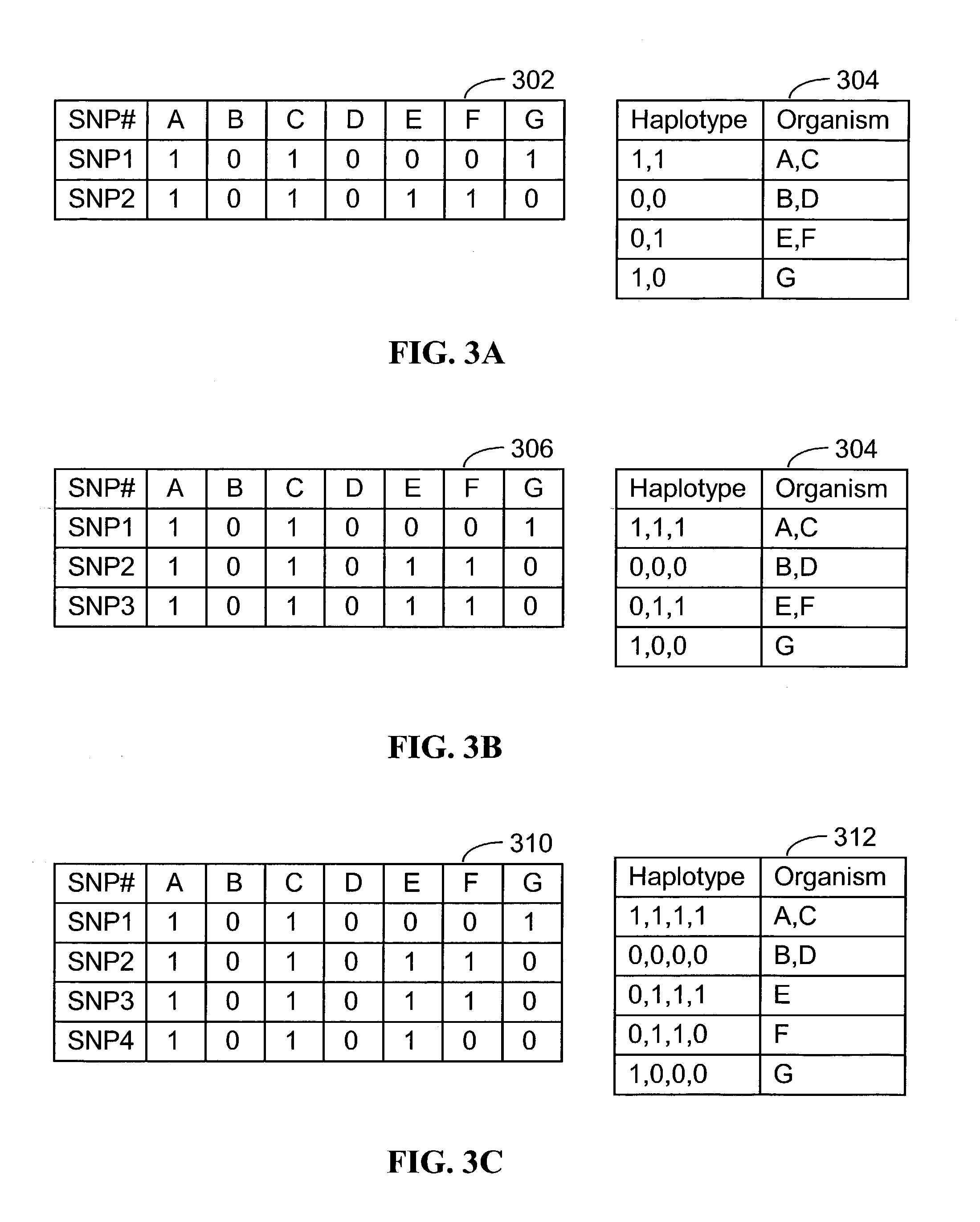
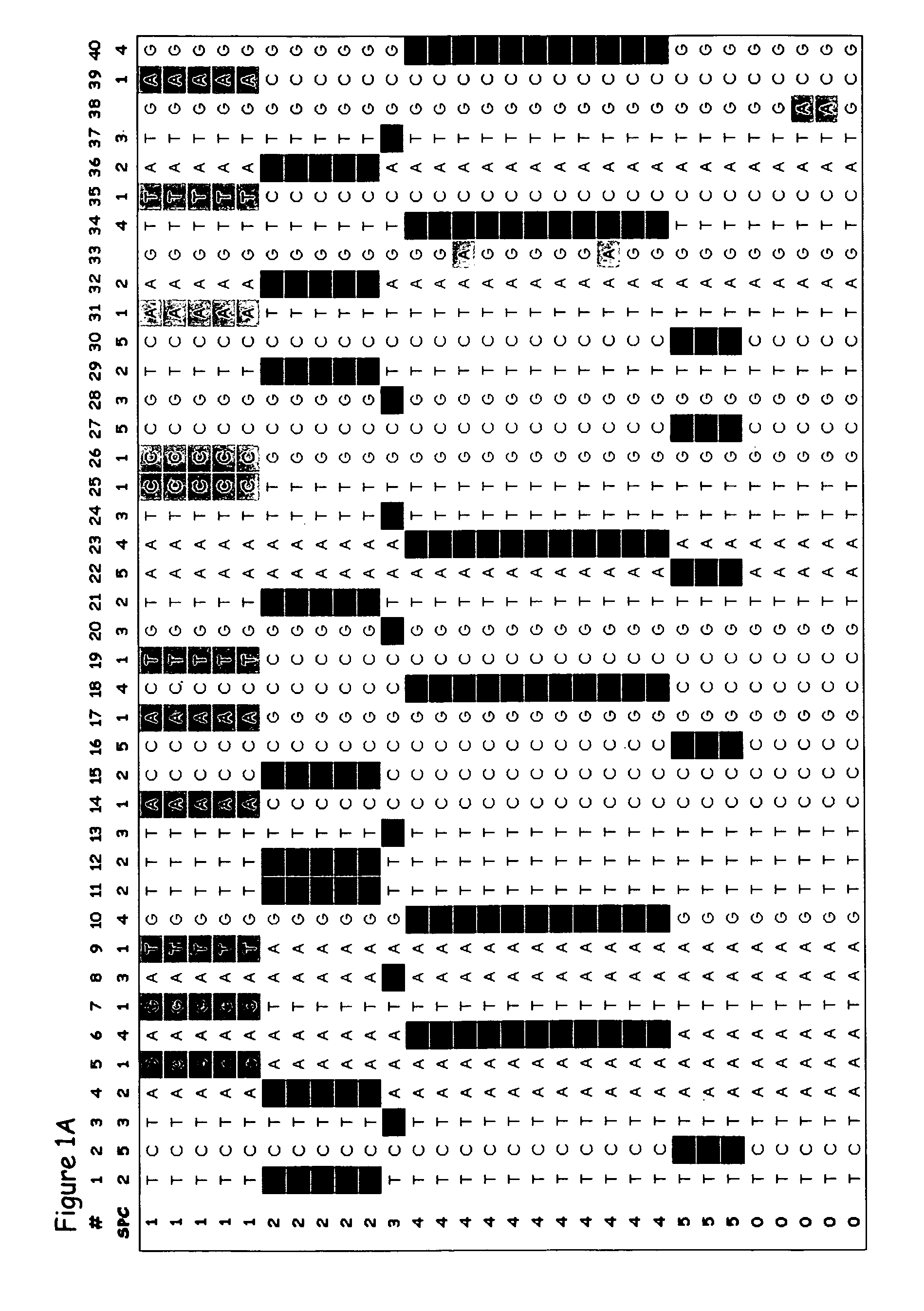
Systems and methods for predicting specific genetic loci that affect phenotypic traits
A database of genetic variations is analyzed to produce a haplotype map of the genome for strains of a single species. A computational method is used to rapidly map complex phenotypes onto the haplotype blocks within the haplotype map. The specific genetic locus regulating three different biologically important phenotypic traits in mice is identified using these systems and methods.
Owner:SANDHILL BIO CORP +1
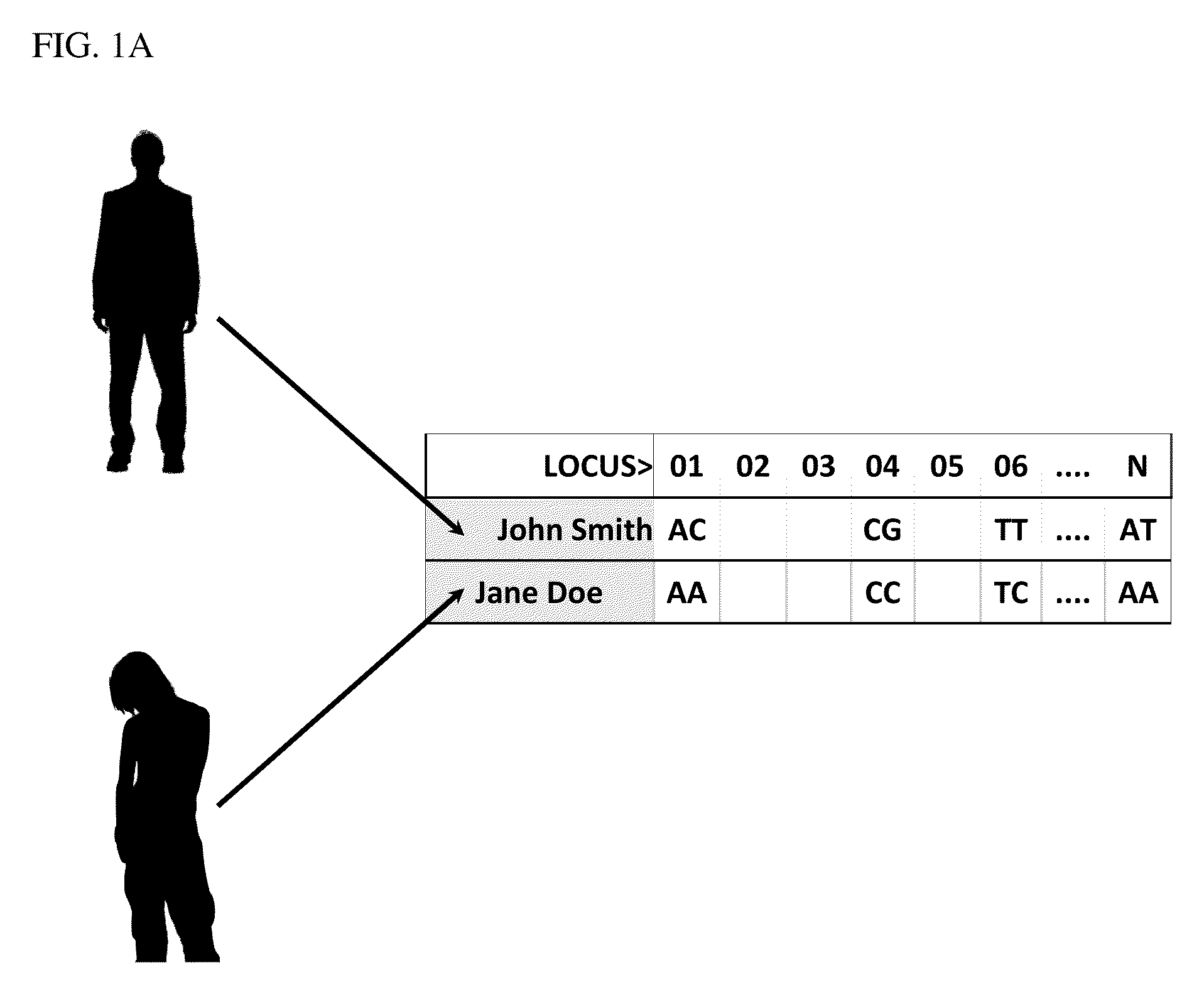
Genetic diagnosis using multiple sequence variant analysis
The present invention is in the field of nucleic acid-based genetic analysis. More particularly, it discloses novel insights into the overall structure of genetic variation in all living species. The structure can be revealed with the use of any data set of genetic variants from a particular locus. The invention is useful to define the subset of variations that are most suited as genetic markers to search for correlations with certain phenotypic traits. Additionally, the insights are useful for the development of algorithms and computer programs that convert genotype data into the constituent haplotypes that are laborious and costly to derive in an experimental way. The invention is useful in areas such as (i) genome-wide association studies, (ii) clinical in vitro diagnosis, (iii) plant and animal breeding, (iv) the identification of micro-organisms.
Owner:METHEXIS GENOMICS
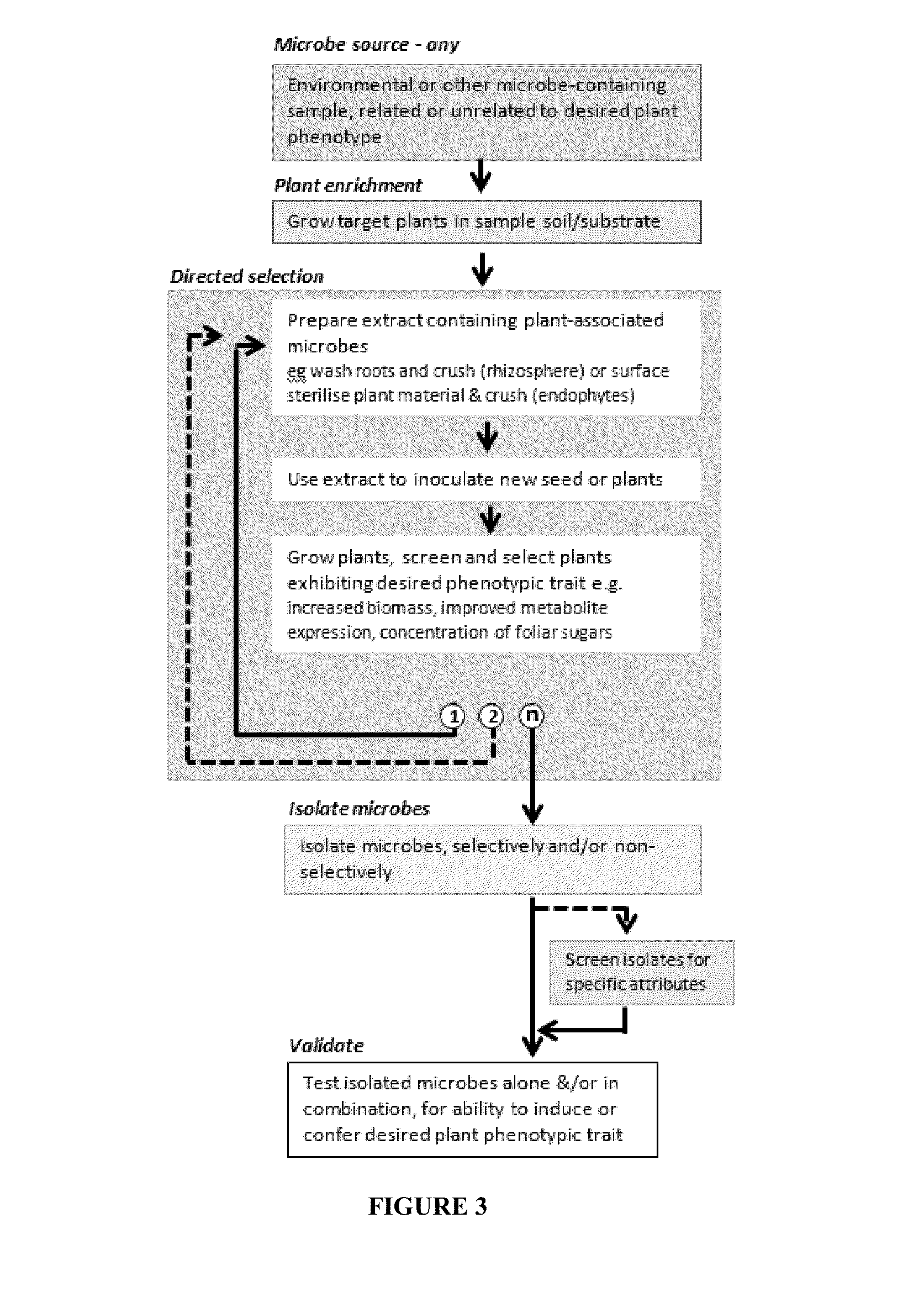
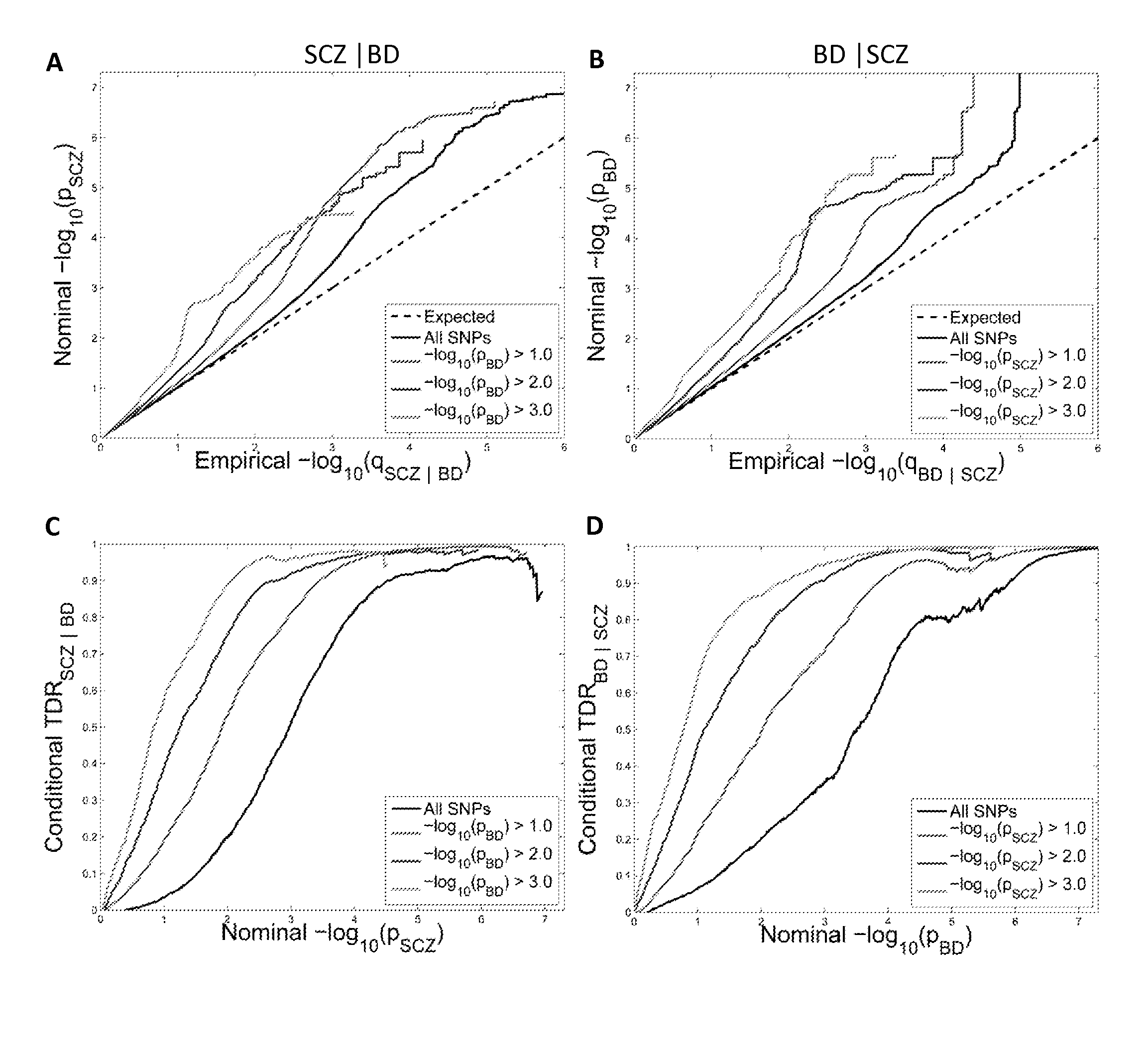
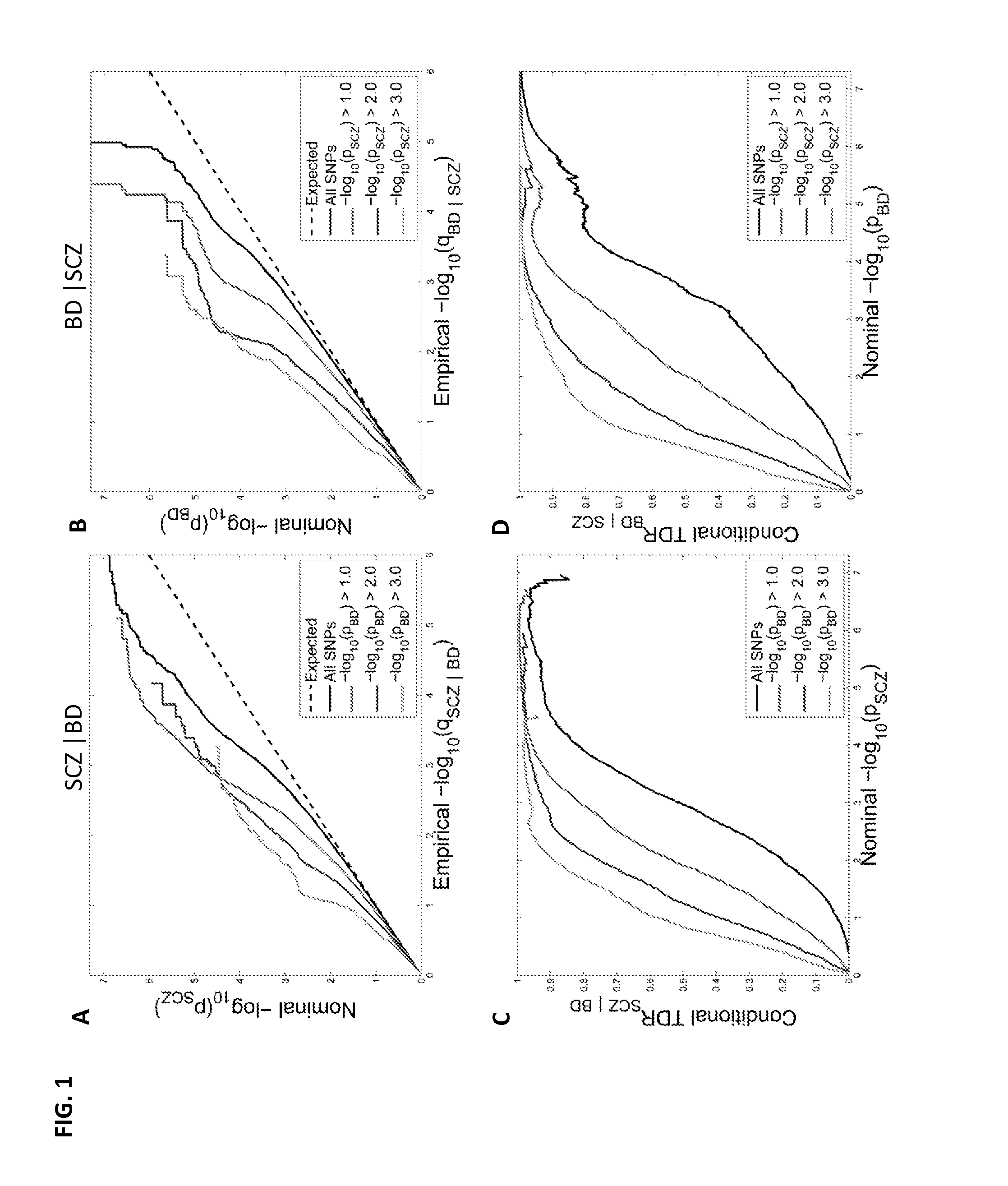
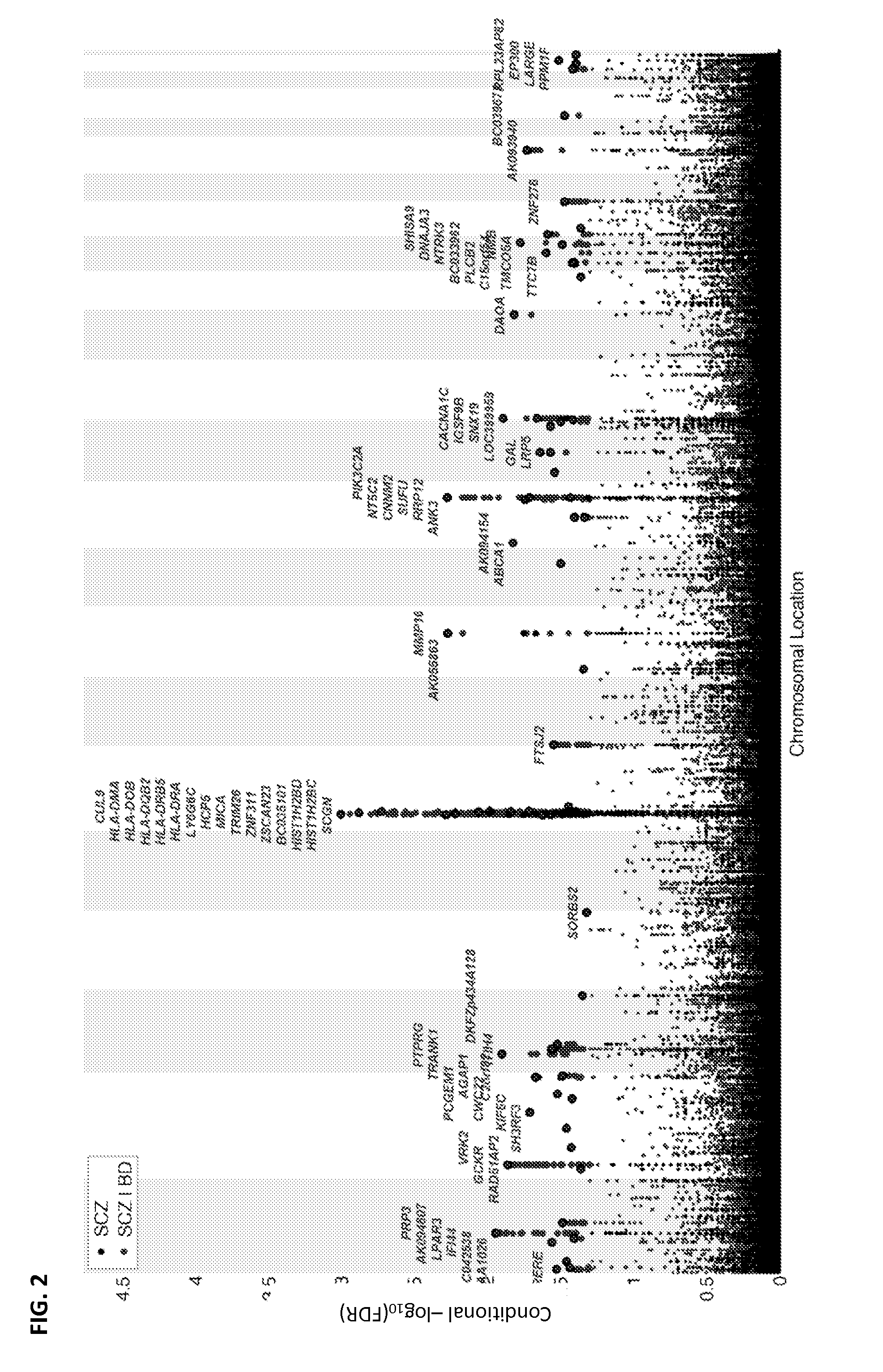
Accelerated directed evolution of microbial consortia for the development of desirable plant phenotypic traits
ActiveUS20150080261A1Efficient and fast and broadly applicableBiocideBacteriaPhenotypic traitPlant phenotyping
Owner:BIOCONSORTIA
Systems and methods for identifying polymorphisms
InactiveUS20150356243A1Convenient treatmentGood estimateHealth-index calculationProteomicsDiseasePhenotypic trait
Owner:MULTIMODAL IMAGING SERVICES CORP +1
Rooted plant assay system
ActiveUS20080153102A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPhenotypic trait
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Maize inbred line resistant to MRDV bred by using molecule making
InactiveCN101138313AGuaranteed availabilityVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationDiseasePhenotypic trait
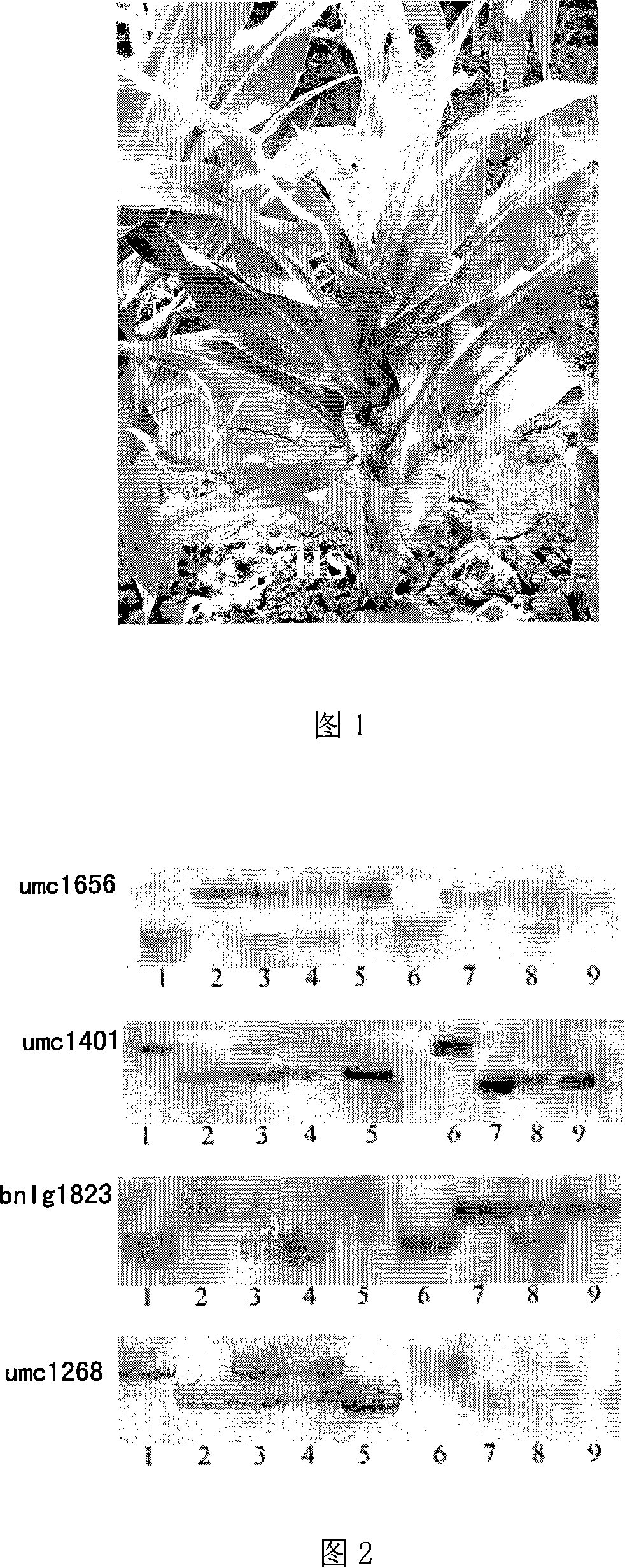
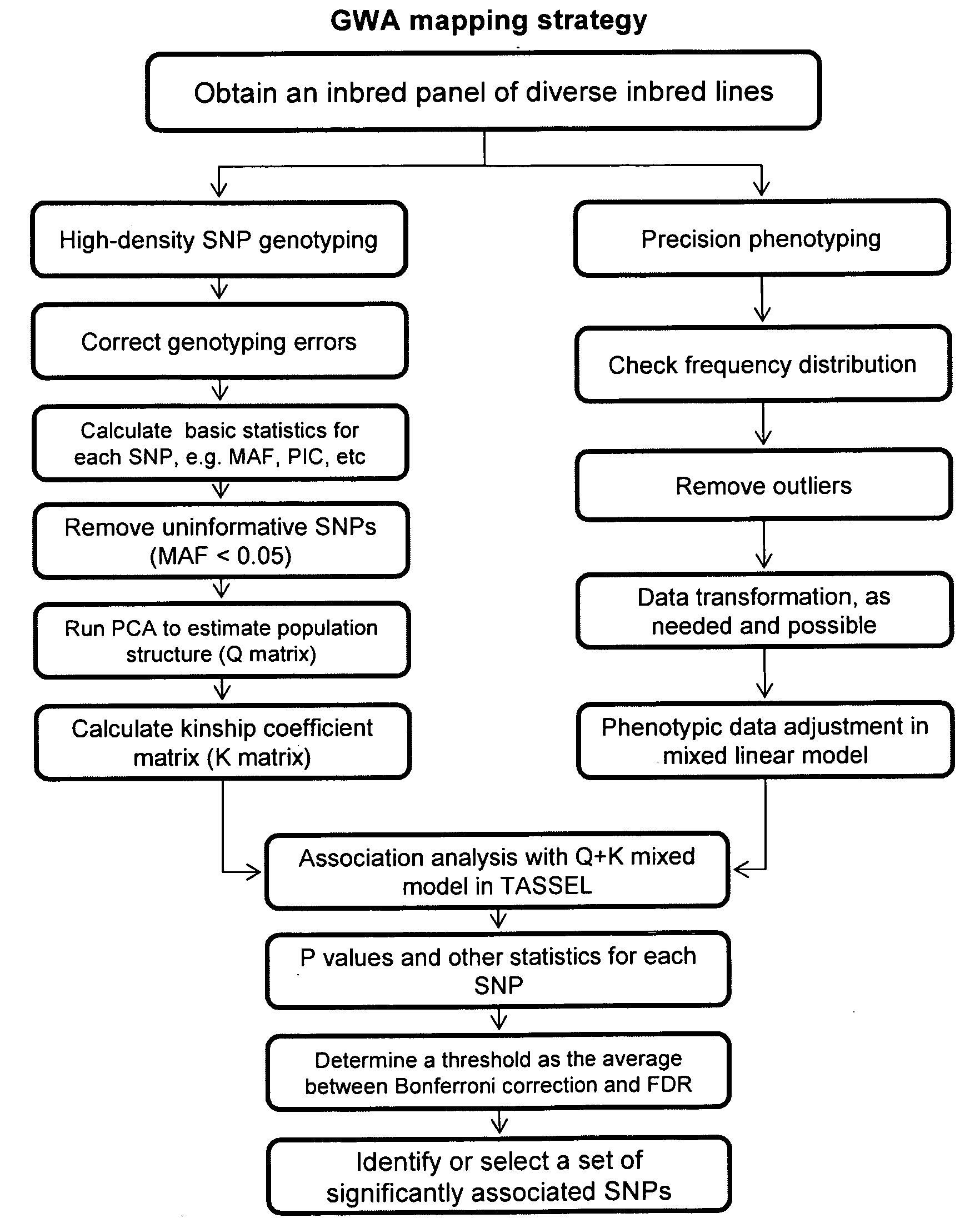
The present invention discloses a corn inbred method for selecting the anti-rough dwarf disease corns which utilizes the molecule marking at the rough dwarf disease resistance points of corns, i.e. the molecule marks on the three points from the inbred rough dwarf disease resistant corns are applied for rough dwarf disease resistant corns breeding and gene pyramiding breeding. The rough dwarf disease resistant and rough dwarf disease sensing corns are taken as the materials for building and separating the groups; the closely linked molecule marks of umc1656, bnlg2191, umc1401, umc1666, bnlg1823 and umc1268 of three rough dwarf disease resistant gene points are used for auxiliary choice; plants with three or two disease resistant gene points are taken as the chosen material for backcrossing and inbreeding; with the comprehensive choice and homozygosis, the high-quality inbred corns of the high property of rough dwarf disease resistance are obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Seed selection method of peanut in population and variety
The invention relates to agricultural breeding field, in particular to a peanut population variety selection method. Peanut population is obtained by female parent group hybridization with male parent group, in which female parent group is obtained through peanut parent hybridization of different aim character, male parents is chosen from homozygous strain or variety, or segregating generation of heterozygote, and F1 generation hybridize, individual plant with segregation character is produced, or after each individual plant selfing. The method includes five steps of hybridization, selfing, determination, classification and population improvement. The population variety has characters of coherence, stability, specificity, high adaptability, disease resistance and high yield.
Owner:RICE RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Method for selecting statistically validated candidate genes
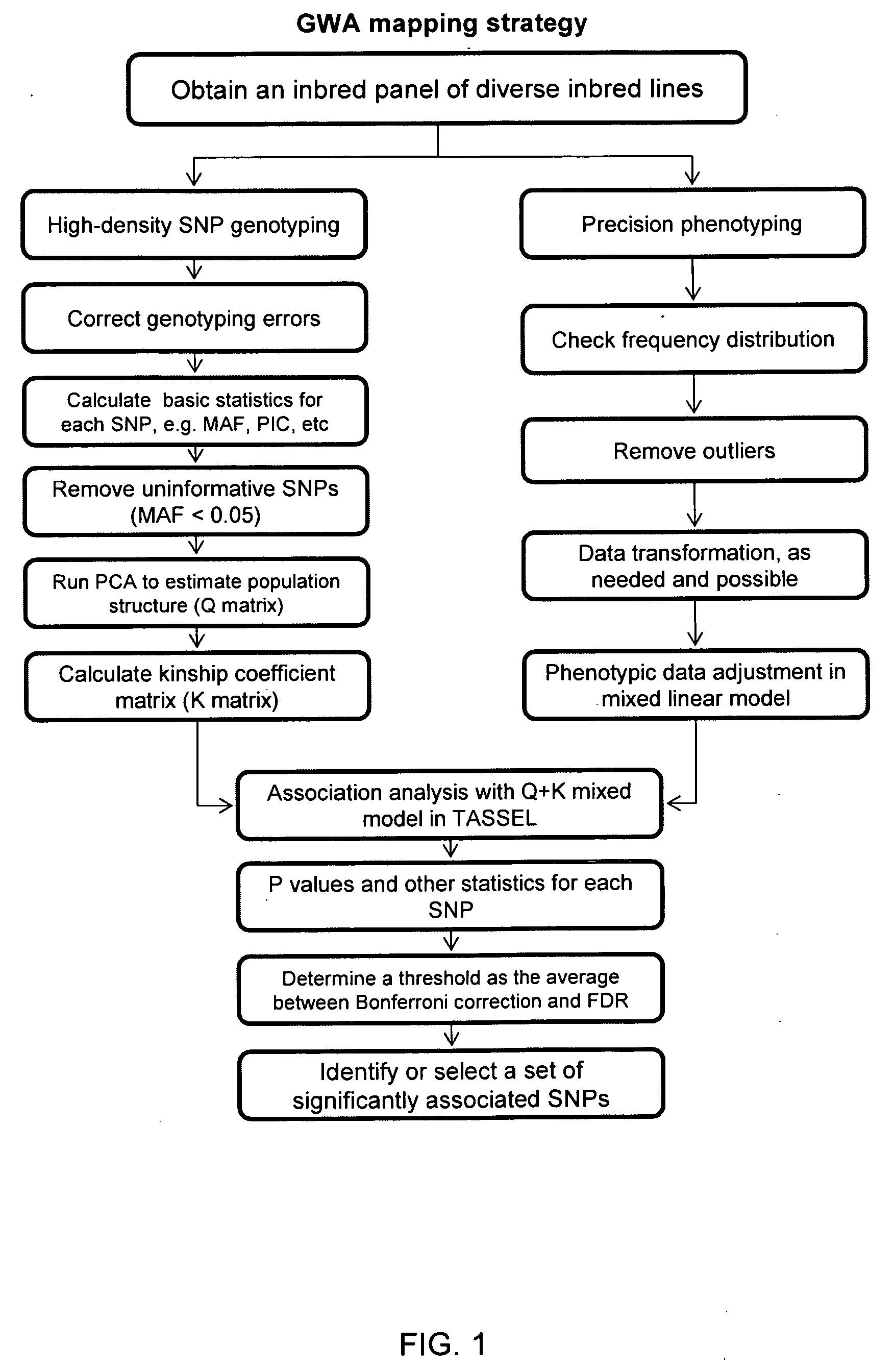
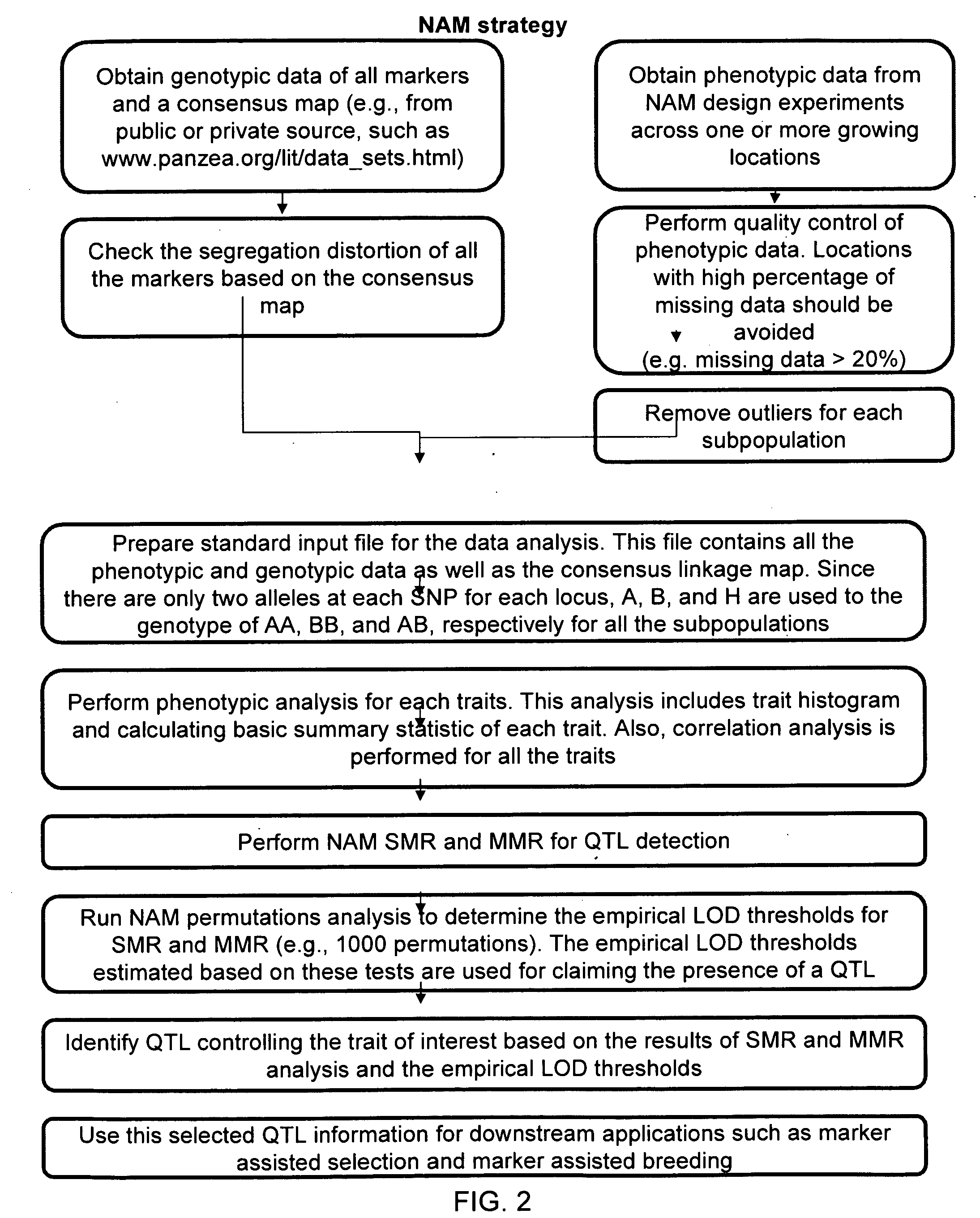
Provided herein are methods for evaluating associations between candidate genes and a trait of interest in a population. The methods include a combination of genome-wide association analysis and one or more of nested association mapping (NAM), expression QTL analysis (eQTL), and allele epistastic analysis (AEA). Markers are selected or prioritized if they are shown to be positively-correlated with a trait of interest using GWA and a combination of one or both of NAM and eQTL. Also provided are models for evaluating the association between a candidate marker and a trait in a nested population of organisms. These methods include single marker regression and multiple marker regression models. Markers identified using the methods of the invention can be used in marker assisted breeding and selection, as genetic markers for constructing linkage maps, for gene discovery, for identifying genes contributing to a trait of interest, and for generating transgenic organisms having a desired trait.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Wheat-rye T2BL.1RS translocation line germplasm breeding method
InactiveCN101263782AExcellent yield traitsPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsDiseaseHigh resistance
The invention provides a breeding method for the germ plasm of a new translocation line wheat-rye T2BL.1RS, which is characterized in that, distant hybridization is performed by taking common wheat variety Xiaoyan 6 as female parent and relative plant rye variety German White as male parent; seeds are acquired after immature embryo salvation culture, colchicine half root soaking method and chromosome doubling; backcross seeds are acquired after disease resistance identification, cytological identification and backcrossing utilizing the original parent Xiaoyan 6 as male parent; then after disease resistance identification and cytological identification, individual plants with excellent comprehensive characters are selected in direction for self crossing, and after continuous self cross selective breeding for six generations, the finally acquired individual plant is confirmed to be wheat-rye T2BL.1RS translocation line after identified by continuous total genome in situ hybridization and three-probe multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization. The breeding method for the germ plasm of a new translocation line wheat-rye T2BL.1RS has the advantages that, the wheat-rye T2BL.1RS translocation line has high resistance to stripe rust, current prevalent fungus strain, powdery mildew and other important virus strains; the invention has excellent high yield character; the method lays an excellent germplasm base for the cultivation of breakthrough new wheat variety with disease resistance and high yield.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker related to bitter character of cucumber and application of SNP marker
ActiveCN103013966ASpeed up the breeding processEasy to identifyFungiBacteriaPhenotypic traitBitter taste
The invention provides an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker related to the bitter character of cucumber and application of the SNP marker. The SNP marker is located at the NO.1178bp of the gene sequence for coding the Csa6G088690 protein of cucumber; cucumber with basic groups G at the NO.1178bp is bitter; and cucumber with basic groups A at the NO.1178bp is not bitter. According to the invention, a genome wide association study (GWAS) method is adopted to screen out the SNP marker related to the bitter taste character of cucumber, a derived cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences (dCAPS) method is adopted to detect the gene types of cucumber to be detected, and bitter or non-bitter cucumber variety breeding is carried out according to the gene types, so as to speed up the breeding process of non-bitter cucumber. The SNP marker is more accurate and reliable in result than the traditional method of subjectively judging whether cucumber is bitter or not, is simpler and more convenient than HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) for identifying bitter substances, and can be used for large-scale screening of breeding materials. Besides, the invention discovers the committed step for the Csa6G088690 protein of cucumber to control the synthesis pathway of bitter of cucumber for the first time.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for breeding new golden-shell crassostrea gigas strain
ActiveCN103858803AAccelerate the cultivation processIncrease incomeClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOysterPhenotypic trait
The invention discloses a method for breeding a new golden-shell crassostrea gigas strain. The method is characterized by including the operating steps of (1) breeding the first generation: selecting wild parent crassostrea gigas with golden left shells, and creating a plurality of families without genetic relationships; (2) breeding the second generation: selecting the families with the obvious golden-shell characters from the created first-generation families, and screening out the crassostrea gigas with the golden left shells and the golden right shells to carry out inner-family inbreeding; (3) breeding the third generation: carrying out inter-family hybridization on the families, with the left shells and the right shells being in the golden characters, obtained from the created second-generation families; (4) breeding the fourth generation: carrying out stability verification on the families with the left shells and the right shells being in the golden characters. According to the method, the breeding process of the new crassostrea gigas shell-color strain is accelerated, and new products of bred shellfishes are increased; the product additional value is increased through the color characters, the breeding yield is improved through the growth characters, incomes of breeding enterprises and farmers are increased, and the market prospects are broad.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Plant breeding method
Methods for using genetic marker genotype (e.g., gene sequence diversity information) to improve the process of developing plant varieties (e.g., single cross hybrids) with improved phenotypic performance are provided. Methods for predicting the value of a phenotypic trait in a plant are provided. The methods use genotypic, phenotypic, and optionally family relationship information for a first plant population to identify an association between at least one genetic marker and the phenotypic trait, and then use the association to predict the value of the phenotypic trait in one or more members of a second, target population of known marker genotype. Methods for identifying new allelic variants affecting the trait are also provided. Plants selected, provided, or produced by any of the methods herein, transgenic plants created by any of the methods herein, and digital systems for performing the methods herein are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Directed strategies for improving phenotypic traits
ActiveUS20160132635A1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsPhenotypic traitAgronomy
The present invention provides a method for improving at least one phenotypic trait of interest in subsequent generation(s) of a population of individuals, preferably crop plants or cattle. Particularly, the method identifies the combination of at least three individuals that gives, upon subsequent intercrossing, the highest estimated probability of improving the at least one phenotypic trait of interest in the subsequent generation(s). Also provided is a computer-readable medium comprising instructions for performing the method.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Method for breeding blue crab families
ActiveCN103250666AIncrease specificationImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMatingGenetic diversity
A method for breeding blue crab families comprises the following steps: S1, collecting blue crabs bred in different populations of China to construct base groups, and conducting genetic diversity comprehensive evaluation, S2, respectively selecting parent crabs from the different populations, establishing the families according to the complete diallel cross mode to grow larvae and breed in a standardizing mode, and calculating hybrid heterosis rates, S3, utilizing the crabs with outstanding hybrid heterosis to mate and combine, constructing the families through indoor artificial directional mating to grow the larvae and breed in the standardizing mode, and twice screening stocking families, S3, over-wintering mated female crabs of parent groups bred indoors of the stocking families, S4, selecting the parent crabs with high egg-laying rates from each family in following spring to grow the larvae and breed in the standardizing mode, and utilizing the breeding method to continue to screen the families. By means of the method for breeding the blue crab families, the growth rate and the survival rate of the blue crabs are used as indexes, blue crab families breeding is conducted, family economic characters are comprehensively evaluated, according to breeding results, blue crab norms are improved in the harvesting process, the breeding survival rate is improved, so that breeding benefits are greatly increased, and deviation caused by single character breeding is avoided.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Molecular genetic maker for egg quality of laying hen and application of molecular genetic marker
InactiveCN106701919AHigh precisionEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMarker-assisted selectionNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of laying hen molecular genetic marker assisted selecting, and particularly relates to a molecular genetic marker for egg quality of a laying hen and application of the molecular genetic marker. The molecular genetic marker is a partial sequence of genes VLDLR and CTSD of the laying hen, and a VLDLR nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and VLDLR nucleotide sequences are as shown in SEQ ID No.2-4. The molecular making method is utilized for selecting egg quality characters, so that a molecular marking method which is more effective, simpler and more convenient to implement is provided for marker assisted selecting in chicken breeding work; meanwhile, the molecular genetic marker can overcome the defects that the normal egg quality character selecting method is great in workload, is easily affected by the environment, is long in breeding period and the like, and provides an effective molecular marker breeding means for egg quality character improving, so that genetic progress of chicken is quickened.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Acipenser dabryanus microsatellite marker as well as screening method and application of acipenser dabryanus microsatellite molecular marker
InactiveCN106434949APromote rapid developmentCutting costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideGenetic diversity
The invention belongs to the field of microsatellite molecular markers and particularly relates to an acipenser dabryanus microsatellite marker as well as a screening method and application of the microsatellite molecular marker, wherein the acipenser dabryanus microsatellite marker has the nucleotide sequence of any one or more of SEQ ID No.1-8. In the invention, the development of microsatellite molecular markers using the high-throughput sequencing technology is faster and costs less than a traditional method; and moreover, the functional traits of corresponding EST sequence can be found while the microsatellite sites are obtained, and the gene relevance is relatively strong. In the invention, through the developed microsatellite sites, basic data is provided for the genetic diversity of acipenser dabryanus, and the study fields such as genetic diversity analysis, genetic map establishment, gene location, variety identification, germplasm conservation, quantitative character gene analysis and parent-child relationship identification can be carried out. According to actual needs, any one or more markers disclosed by the invention can be adopted, or any one or more pairs of specific primers corresponding to related markers can be analyzed and studied.
Owner:FISHERIES INST SICHUAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Establishment method of goat resource population
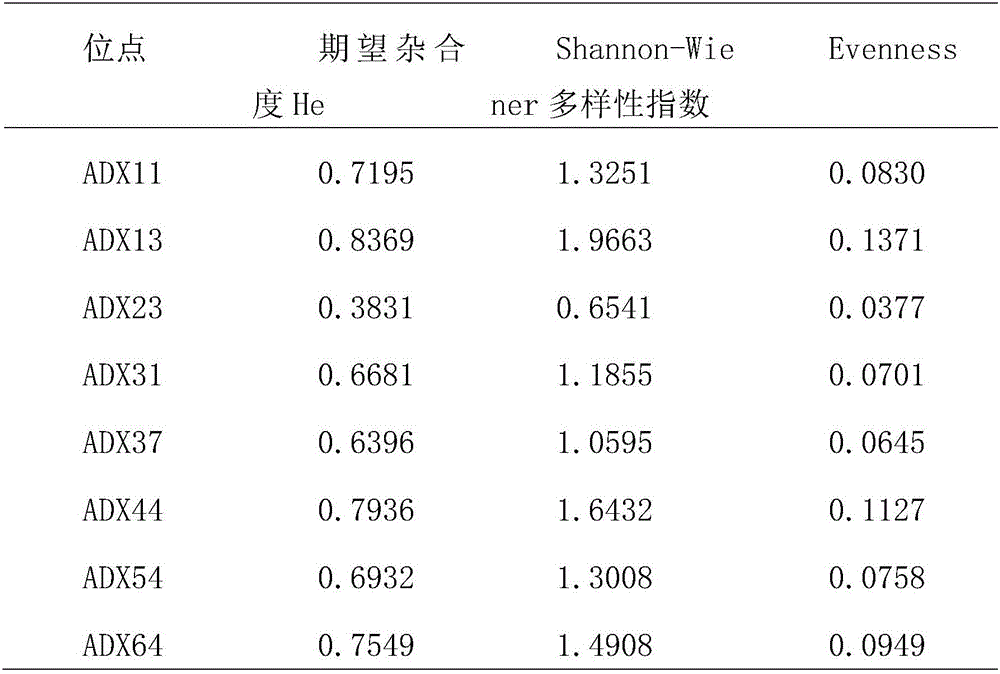
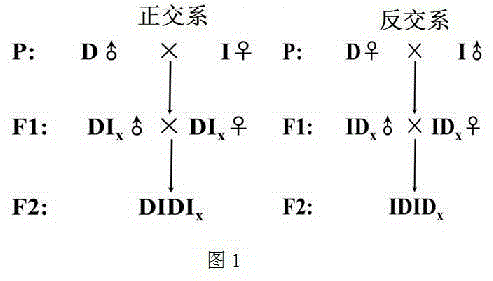
InactiveCN105123621AImprove economyImprove international competitivenessAnimal husbandryNational levelReciprocal cross
The invention belongs to the field of establishment of a population genetic resource bank, and provides a scientific establishment method of a goat resource population bank, and provides a goat reference family system establishment case, and relates to two national-level genetic resource varieties, namely, a Dazu black goat and an Inner Mongolia Cashmere goat (Alxa type). According to the resource population establishment method, forward cross and reciprocal cross of Dazu black goat and Inner Mongolia Cashmere goat (Alxa type) are utilized, random mating of genetic relationship is avoided for F1, so that Mendel genetic characters are separated, a goat economic character QTL or a functional gene is located by virtue of a genome means, and a relatively-precise genetic mark is provided for the goat breeding. The genetic resource bank comprises goat population, a genealogy inforamtion database, a phenotypic character database, a DNA sample library, an RNA sample library and a genetic variation information database.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Selective breeding method for high-nutrition rice varieties
The invention discloses a selective breeding method for high-nutrition rice varieties, which belongs to the technical field of special rice seed breeding. The selective breeding method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: selecting high-yield, high-quality and disease-resistant rice varieties as recurrent parents; hybridizing the recurrent parents with iron-rich rice variety IR164, high-sugar rice variety Bai Tian No.1, high-lysine rice variety Milyang 164 and high-cellulose rice variety water source 464 respectively; performing backcross and convergent cross for times; and breeding the high-nutrition rice varieties having economical characters and yield characters which are similar to the economical characters and yield characters of the recurrent parents, and rich in the nutritional ingredients of iron, sugar, lysine, cellulose and the like by selecting the economical characters, yield characters, iron content, sugar content, lysine content, cellulose content and the like of separating generations.
Owner:DINGLUO FENGZHI CHANGSHUN TECH CO LTD
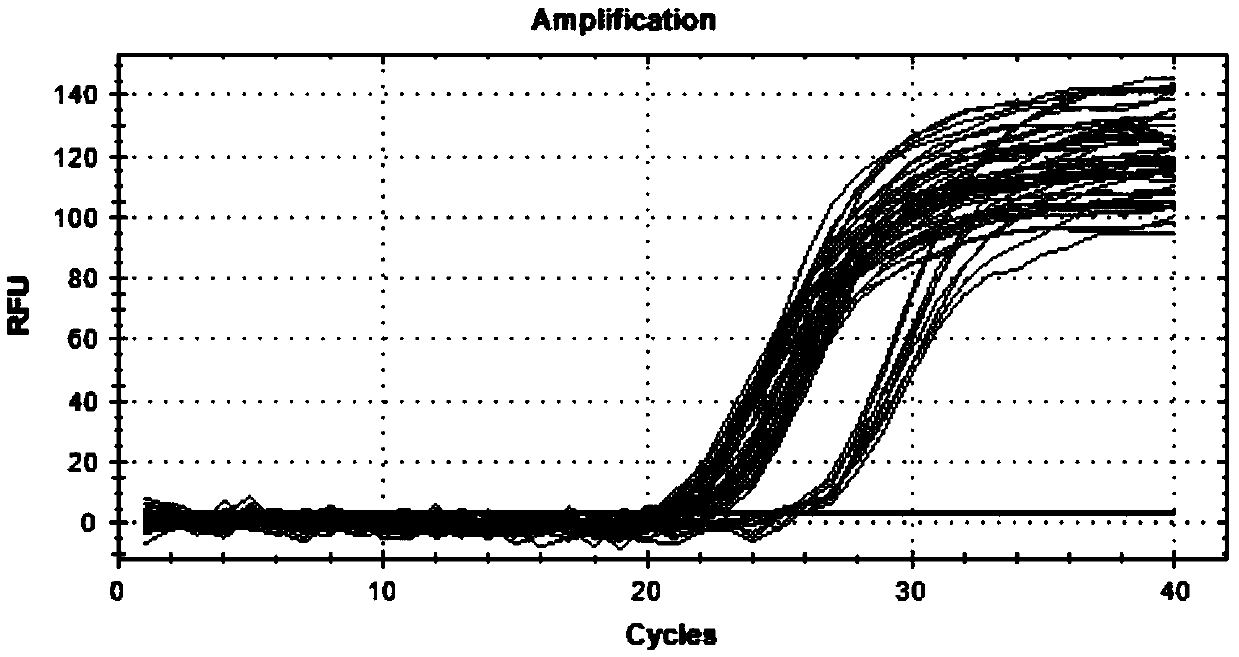
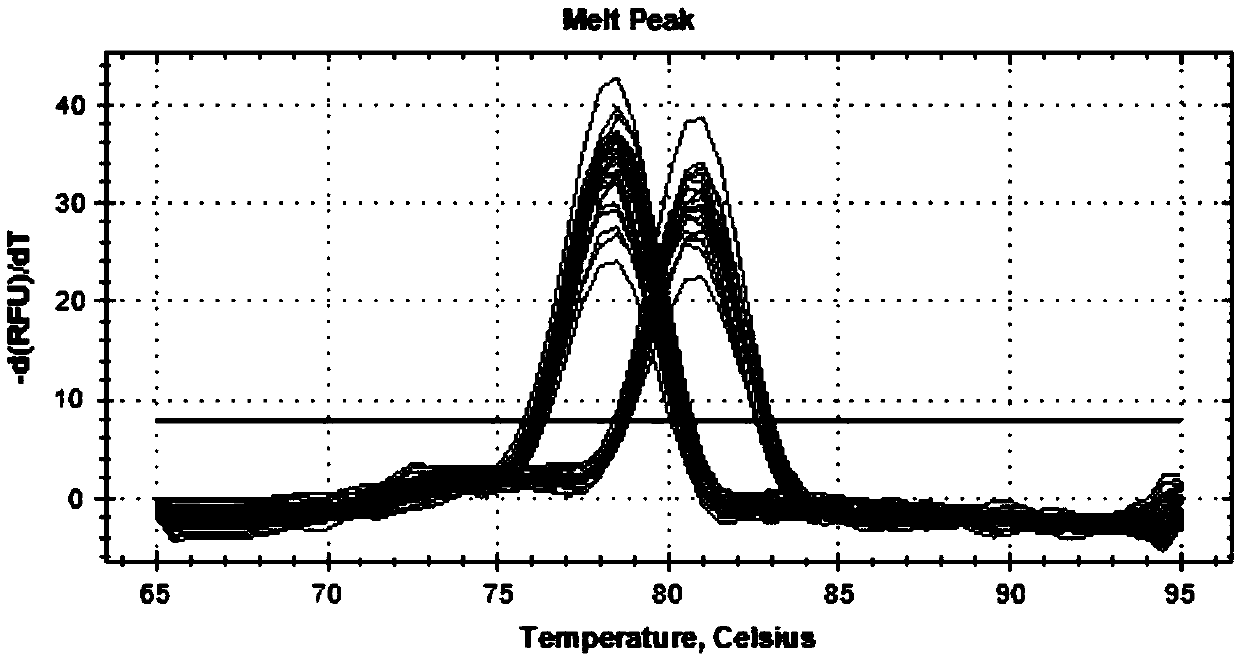
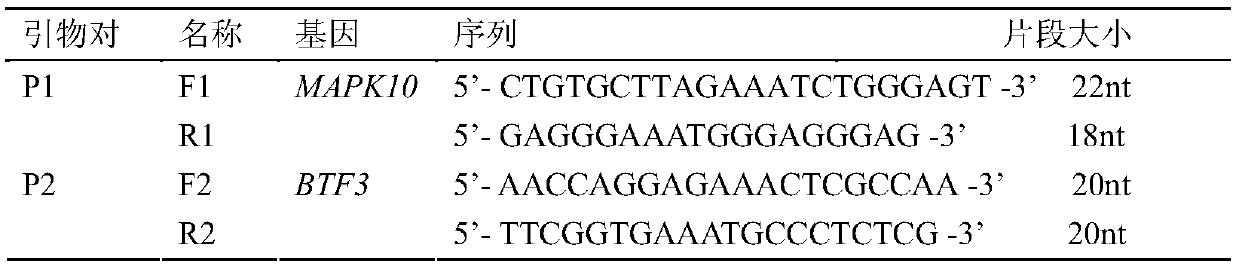
Method for detecting CNV (copy number variation) mark of MAPK10 gene of Nanyang cattle and application thereof
ActiveCN105506111AExcellent genetic resourcesFacilitates marker-assisted selectionMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesMarker-assisted selection
The invention discloses a method for detecting a CNV (copy number variation) mark of a MAPK10 gene of Nanyang cattle and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: respectively amplifying the CNV region and reference gene BTF3 of the MAPK10 gene of Nanyang cattle through a real-time fluorescence quantification PCR method by taking blood genome DNA of Nanyang cattle as a template; dividing the result into insert type, deficient type and normal type according to log22-delta delta Ct; and identifying CNV of the MAPK10 gene of Nanyang cattle. Analysis correlated to Nanyang cattle production data indicates that the growth and development of Nanyang cattle is remarkably influenced by different copy numbers of MAPK10, wherein the birth weight, 18-month-aged body height and 24-month-aged body weight and daily gain of a normal type individual body are remarkably higher than those of the insert type and deficient individual bodies. The CNV mark closely related to the production traits of Nanyang cattle is detected on DNA level, and can be used as an important candidate molecular mark for marker assisted selection of the growth traits of Nanyang cattle of China.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for cultivating corn allopolyploid by using unreduced gamete characteristic of tripsacum dactyloides
ActiveCN103609428AOvercoming reproductive barriersImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationHeterologousBridge material
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a corn allopolyploid by using an unreduced gamete characteristic of tripsacum dactyloides, belonging to the field of corn distance hybridization. The method comprises the steps of: hybridizing an MTF-1 (metal-responsive transcription factor) as a female parent with corn or tetraploid perennation corn as a male parent, and then selecting a filial generation plant which is capable of overwintering, namely a new corn allopolyploid, wherein the tiller number of the filial generation plant is more than 15 and the chromosome number of the filial generation plant is a sum of the chromosome number of a female parent and the chromosome number of the male parent. According to the method provided by the invention, the dysgenesis of corn affinis species is overcome and a good inheritance basis is provided for breeding ground-breaking corn species by using the bred corn allopolyploid as a bridge material transfer character. In addition, the method provided by the invention provides a model to breed allopolyploids of other species. The corn allopolyploid bred by the method provided by the invention is perennial, adopts vegetative propagation, and provides a material to corn allopolyploid origin and evolution research and allopolyploid breeding. The method provided by the invention is simple, is short in time, high in efficiency and small in workload.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for producing seeds of new Nero-Aurea tilapia
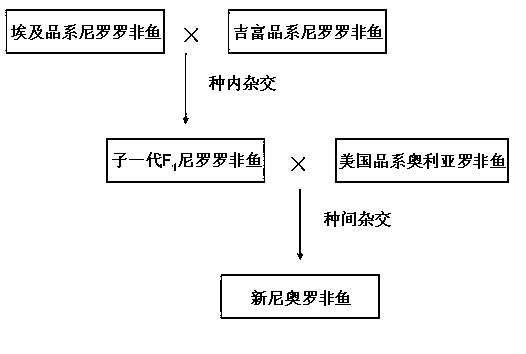
InactiveCN102696520AFast growthIncrease male rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPhenotypic traitInterspecific hybridization
The invention discloses a method for producing seeds of new Nero-Aurea tilapia. The method comprises the following steps: (a) carrying out intraspecific hybridization by taking a female of an Egypt strain in Nile tilapia as a female parent and a male of a Gift strain in the Nile tilapia as a male parent to obtain first filial generation F1 of Nile tilapia; and (b) carrying out interspecific hybridization propagation by taking the female in first filial generation F1 of the Nile tilapia as the female parent and the male of American strain of oreochromis aurea as the male parent to obtain hybrid generation, namely the new Nero-Aurea tilapia. With the adoption of the method provided by the invention, a seed producing technique combining intraspecific hybridization with interspecific hybridization is utilized, excellent characters are combined, and the growth speed and the male rate of the tilapia are improved, thereby the cultural output and benefits of the tilapia are improved.
Owner:GUANGXI INST OF FISHERIES
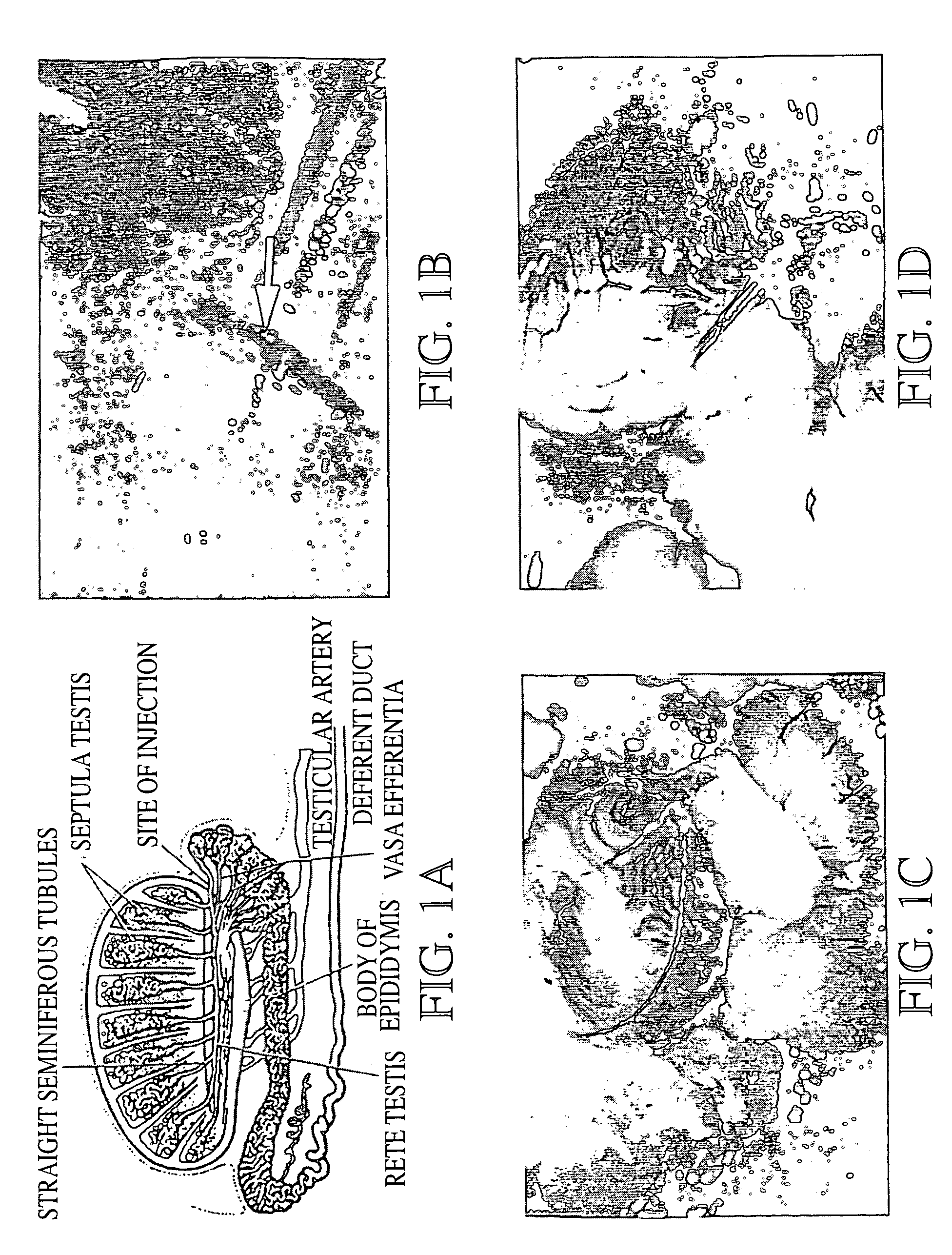
Genetic modification of male germ cells for generation of transgenic species and genetic therapies
InactiveUS7294755B1Facilitate in vitro transfectionGood chanceGenetically modified cellsGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryNucleotide
Disclosed is an in vivo method of incorporating exogenous genetic material into the genome of a vertebrate, which involves administering to a male vertebrate's testis a gene delivery mixture comprising a viral vector, such as a retroviral vector, to deliver a polynucleotide encoding a desired trait or product. Also disclosed is an in vitro method of incorporating exogenous genetic material into the genome of a vertebrate, in which germ cells are obtained from a donor male vertebrate and are genetically modified in vitro, before being transferred to a recipient male vertebrate. After the transfer, the male vertebrate bearing the genetically modified germ cells is bred with a female vertebrate such that a transgenic progeny is produced that carries the polynucleotide in its genome. Also disclosed are non-human transgenic vertebrates produced in accordance with the method, including transgenic progeny. A transgenic cell derived from the transgenic vertebrate is also disclosed, being a germ cell, such as a spermatozoan or ovum, a precursor cell of either of these, or a somatic cell. A method of producing a non-human transgenic vertebrate animal line comprising native germ cells carrying in their genome at least one xenogeneic polynucleotide is disclosed, as is vertebrate semen containing the transgenic male germ cells useful in practicing the method.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD +1
Rooted plant assay system
ActiveUS8076142B2Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPhenotypic trait
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Method and system for generating a virtual progeny genome
Owner:ANCESTRY COM DNA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com