SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker related to bitter character of cucumber and application of SNP marker
A technology of cucumber and bitter taste, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and molecular biology, can solve problems such as difficult to ensure accurate results, unscientific, and inoperable, achieve accurate and reliable results, eliminate human factors, and speed up the breeding process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Acquisition of SNP markers related to cucumber bitterness traits
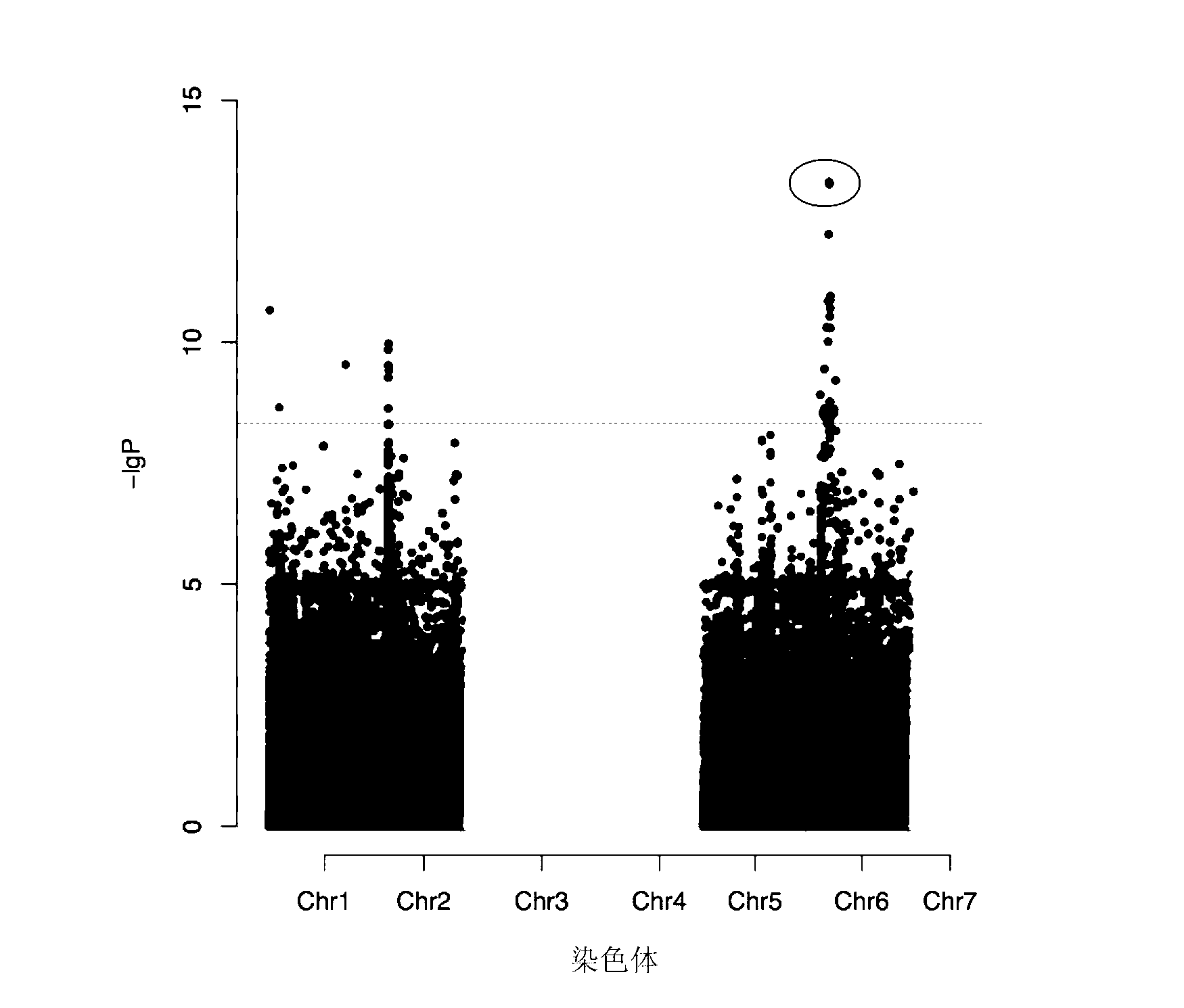
[0036] More than 3,000 cucumber resources were collected from all over the world, and 114 of them were selected as cucumber core germplasm resources, which represented 80% of the genetic diversity. Each resource was resequenced to generate a data volume of about 5G, covering an average of 10x cucumber genome. At the same time, these 114 germplasm resources were also identified for bitter taste phenotype. Using the method described in Yu J (Yu J, et al. (2005). Nature genetics 38(2):203-208) and Zhang Z (Zhang Z, et al. (2010). Nature genetics 42(4):355-360) , according to the Mixed Liner model, using TASSEL software for GWAS analysis, found a SNP site associated with the bitter phenotype from 1 million SNPs ( figure 1 ). The SNP site is located at the 1178th bp of the gene encoding the Csa6G088690 protein, G (leaves are bitter) is mutated to A (leaves are not bitter), and this mutation cause...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Correlation Analysis and Detection Application of Cucumber Different Genotypes and Bitterness Traits
[0047] Using cucumber 9930 (BiBi) with bitter leaves and cucumber 9110GT (bibi) with non-bitter leaves as parents, a F2 population consisting of 1800 individuals was constructed. According to the method for embodiment 2, 1800 F2 cucumber populations have been carried out PCR-dCAPS identification, PCR amplified sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the analysis result of amplified sequence 26bp site is as table 1 and figure 2 shown.
[0048] Table 1 Segregation of SNP loci in 1800 F2 cucumber populations
[0049]
[0050] It can be seen from Table 1 that the ratio of bitter cucumbers to non-bitter cucumbers is about 3, and bitterness is dominant relative to non-bitterness. F2 offspring meet the segregation expectation of 3:1, indicating that the SNP is linked to cucumber bitterness traits.
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3 Acquisition of Cucumber Csa6G088690 Gene
[0052] Firstly, a cucumber cDNA library was prepared, and then PCR amplification was performed using the forward primer 5'-AGATTAAAAGTGGGAAAAG-3' and the reverse primer 5'-CAGTTTTGAGCTACCC-3'.
[0053] The PCR reaction system is calculated as 20μl: 1μl of 10-20ng / μl template, 1μl of 10pmol / μl forward and reverse primers, 0.4μl of 10mmol / L dNTP mix, 1μl of 0.5U / μL high-fidelity Taq DNA polymerase, 10× 2 μl of PCR reaction buffer, the balance is water.
[0054] The PCR reaction conditions were: 94°C for 5 minutes; 35 cycles of 94°C for 20 seconds, 55°C for 20 seconds, 72°C for 2 minutes and 30 seconds; 72°C for 10 minutes.
[0055] The amplified fragment with a size of 2358bp (SEQ ID No.2) was connected to the T-vector (TAKARA), and no mutation was confirmed by sequencing.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com