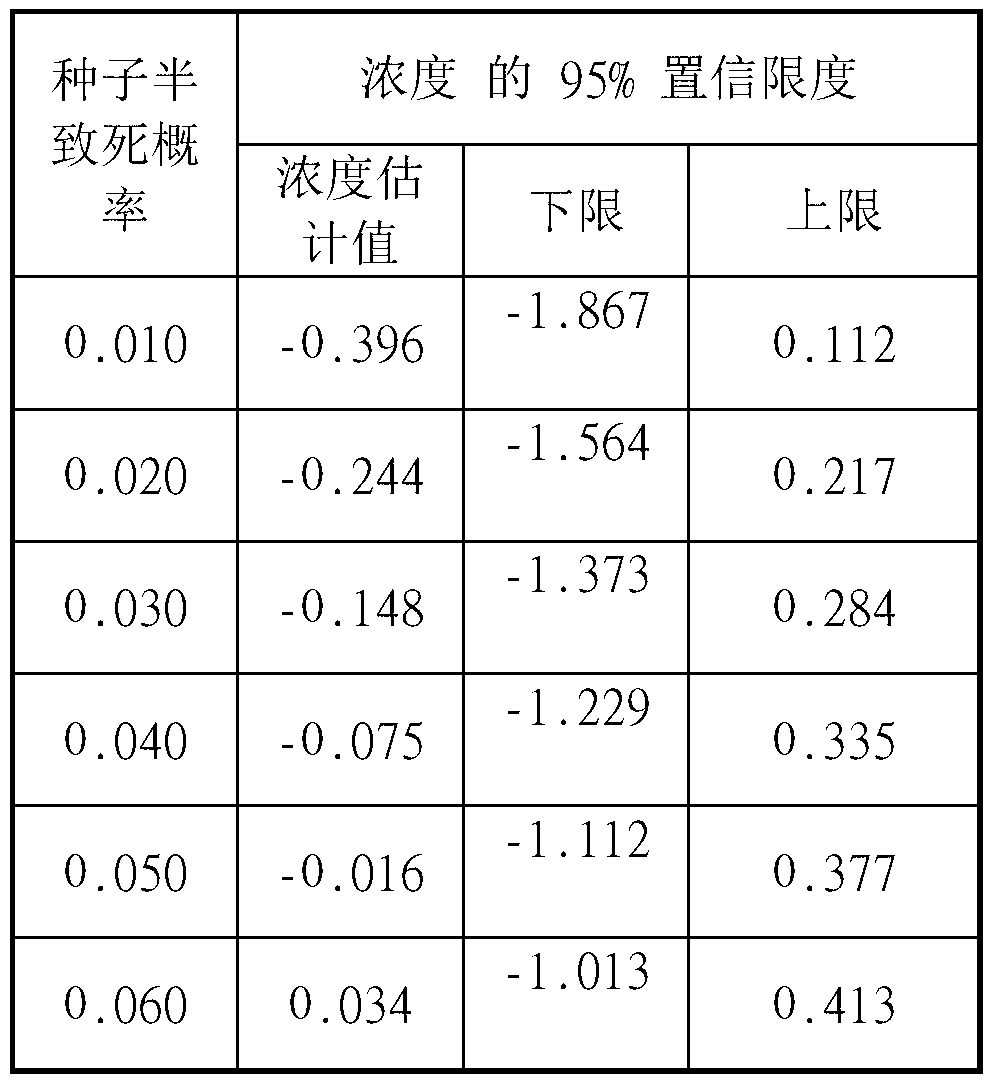
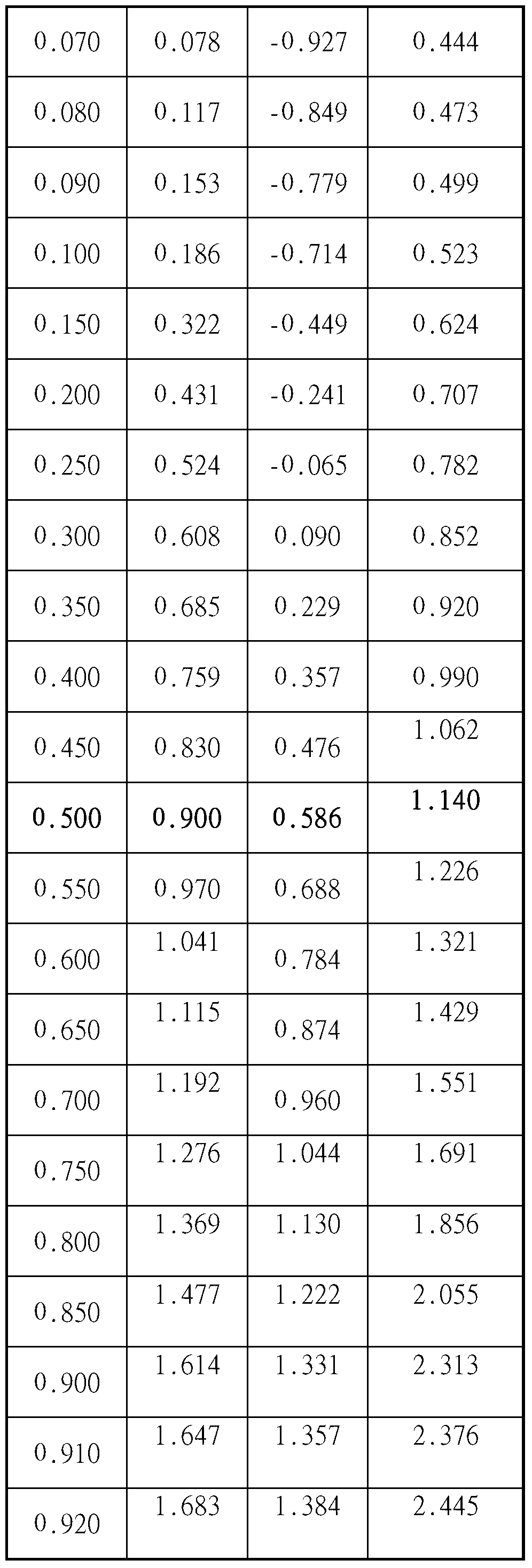
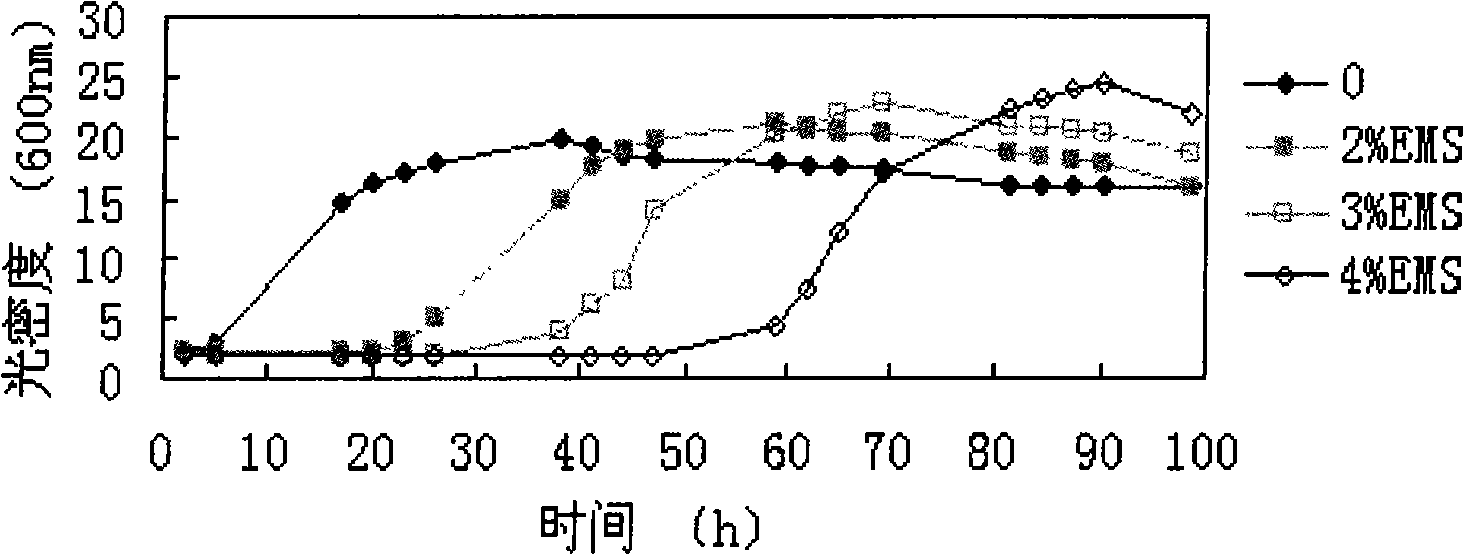
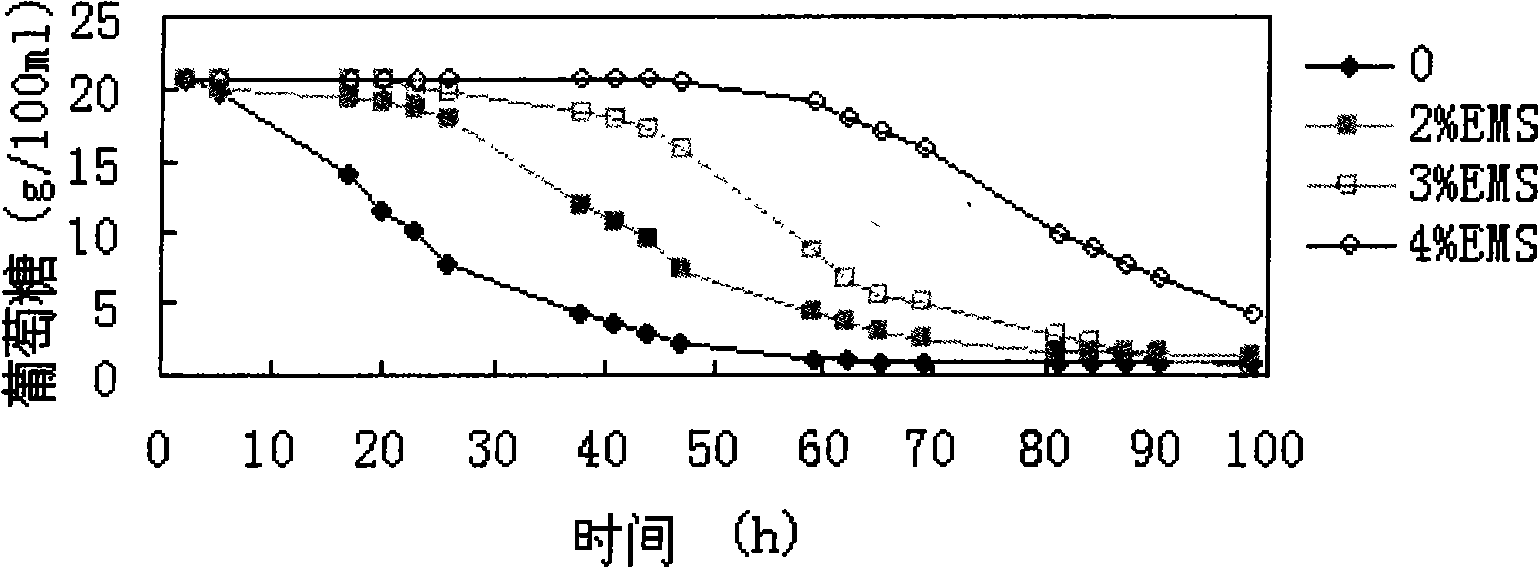
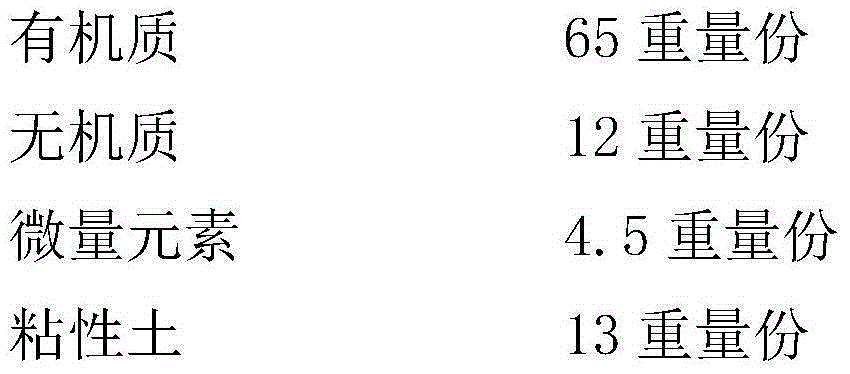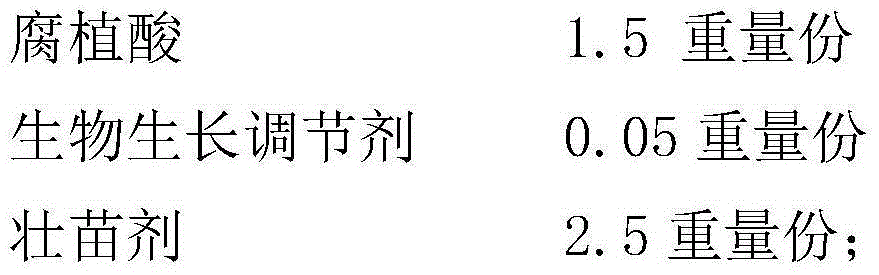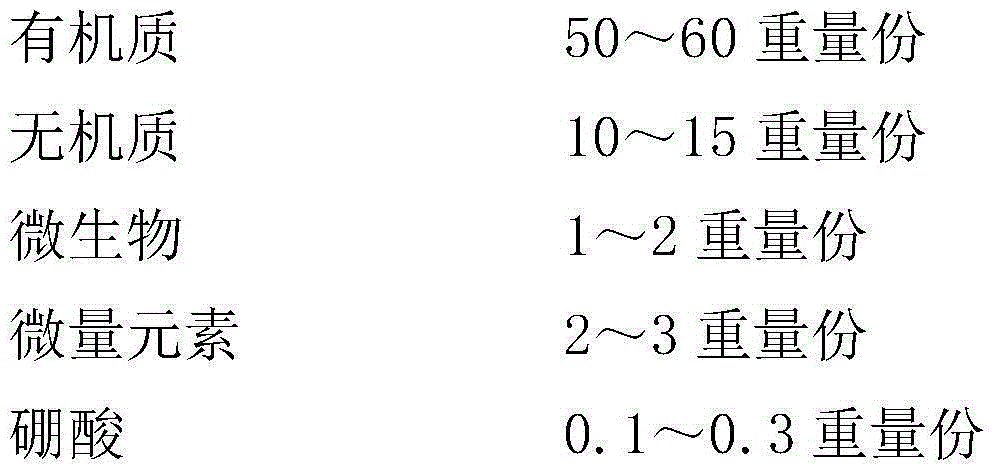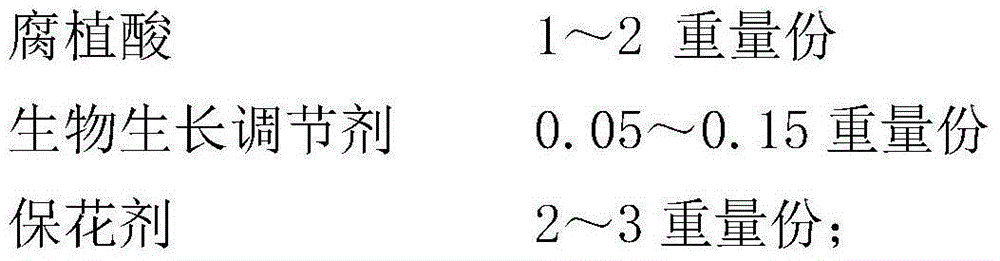Patents
Literature
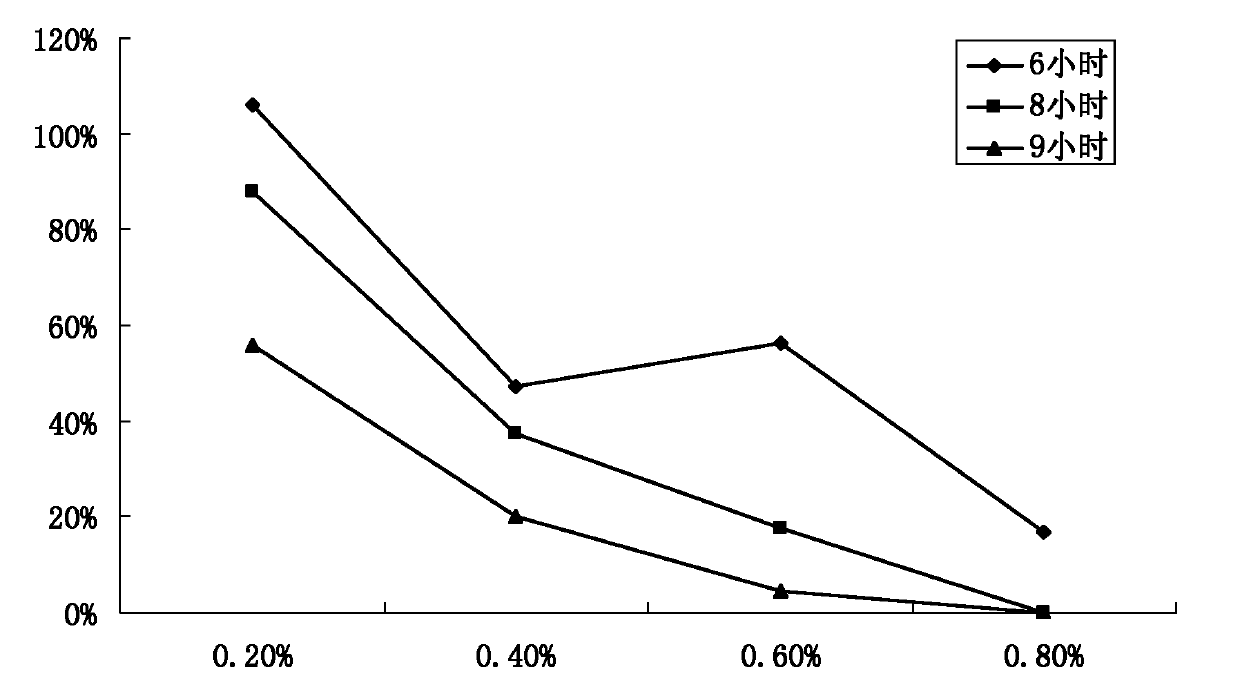
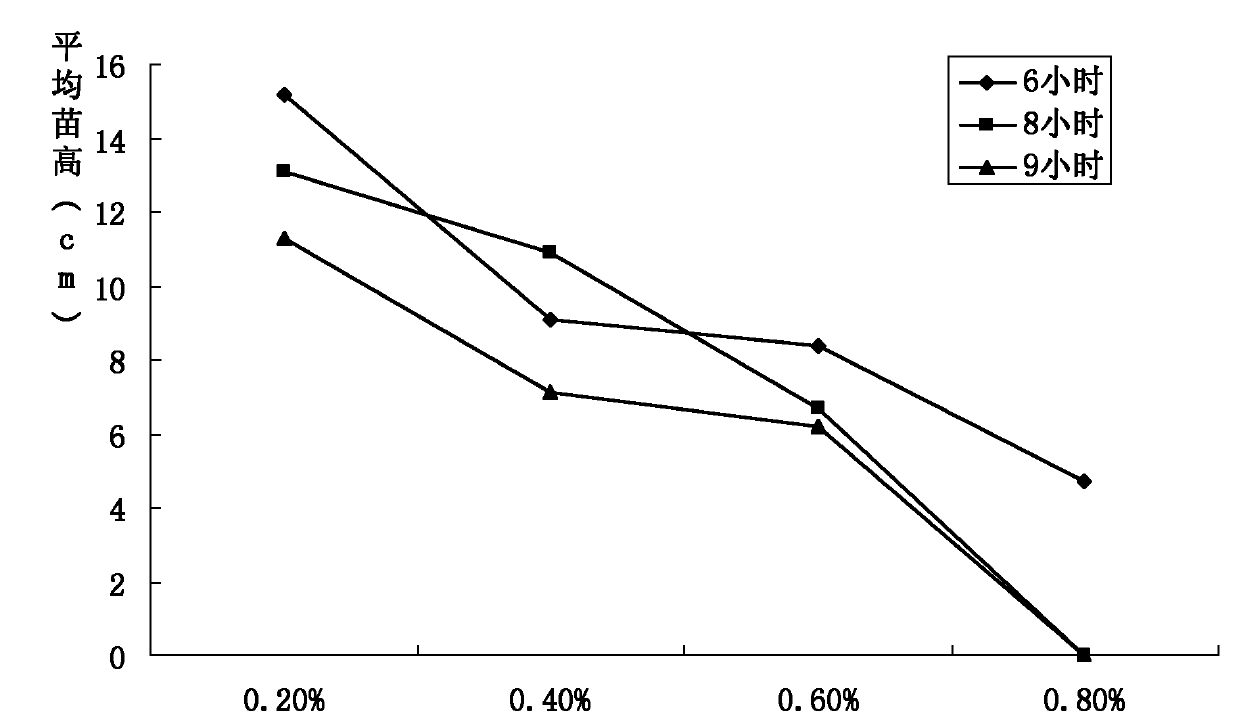
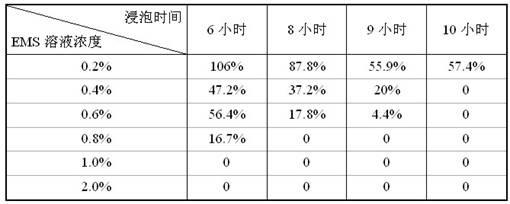
60 results about "Ethylmethane Sulfonate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Herbicide-resistant rape directive breeding method based on acetolactate synthase (ALS) target esterase
InactiveCN103070068AImprove breeding efficiencyReduce chanceSeed and root treatmentPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyEthylmethane Sulfonate
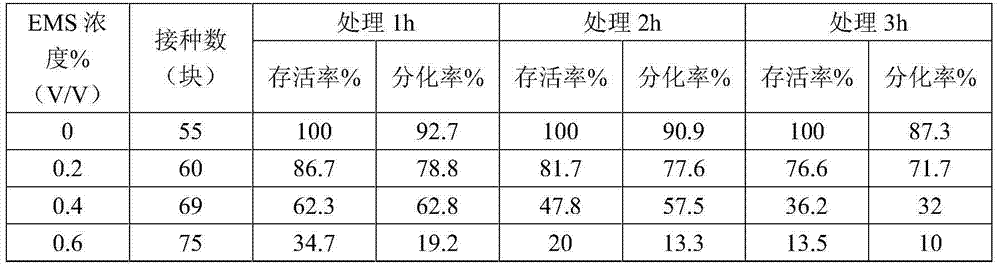
The invention provides a herbicide-resistant rape directive breeding method based on acetolactate synthase (ALS) target esterase, which belongs to a plant trait breeding method. The method comprises the following steps of selecting materials needed by production of rape or breeding of the rape, processing seeds with ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS), mutagenizing the seeds to be isolated and propagated to a M2 generation, and directionally screening herbicide-resistant mutant characters in a large group under the selection pressure of the herbicide adopting the ALS as the target esterase. In order to increase the probability for acquiring the mutant characters, the directive screening can be continuously conducted in multiple years, or conducted in multiple places in the same year or conducted in multiple places in multiple years until the needed mutant material is screened out.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Seed breeding method of moso bamboo by physical and chemical composite mutagenesis
InactiveCN102696478AHigh mutation rateVariations in traitsPlant genotype modificationEthylmethane SulfonateWarm water
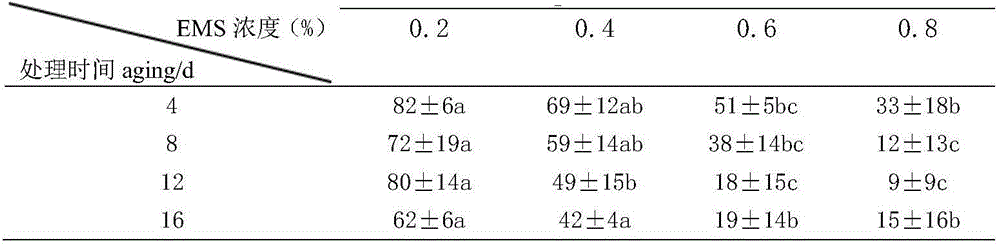
The invention discloses a seed breeding method of moso bamboo by physical and chemical composite mutagenesis. The seed breeding method comprises the following five steps of: (1) collection of the moso bamboo seeds, wherein the purity of the seeds is more than or equal to 90%, the thousand seed weight is more than or equal to 28g, the moisture content is 10%-14%, and after being sealed, the seeds are stored for later use at the temperature of 4 DEG C; (2) irradiation ray selection of caesium Gamma rays with the atomic weight being 137 as an irradiation source, and selection of two types of mutagen treating liquid; (3) preparation of the two types of mutagen treating liquid; (4) physical and chemical composite mutagenesis treatment, wherein the radiation dose rate is 1Gy / min, the radiation dose is 30Gy, the seeds are soaked for tens of hours with warm water, after water-absorbing paper absorbs the surface water of the seeds completely, the seeds are soaked and mutagenized for eight hours by using a sodium azide solution (NaN3) or ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) solution with the concentration of 0.04mmol / L, and after being taken, the seeds are cleaned repeatedly for 2 hours by using clean water to obtain the moso bamboo seeds treated by composite mutagenesis; and (5) germination test of the seeds, verification of mutagenic effect and determination of mutagenesis dose. The seed breeding method disclosed by the method has the advantages that the mutants in mutagenesis are more in quantity, the character mutation is diversified, and the selection range of excellent characters needed in seed breeding is large.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Mutation breeding method for cunninghamia lanceolata
InactiveCN104542265AIncrease mutation rateHigh mutant seedling emergence ratePlant genotype modificationEthylmethane SulfonateMutation breeding
The invention discloses a mutation breeding method for cunninghamia lanceolata. The method comprises the following steps: especially adopting ripen seeds of a cunninghamia lanceolata seed garden; carrying out low-temperature overwintering treatment, carrying out constant-temperature seed soaking stimulation on a gibberellin solution with specific concentration, immediately putting the gibberellin solution subjected to constant-temperature seed soaking stimulation into clear water, carrying out variable-temperature soaking for 3 days, and carrying out sprout promoting treatment; respectively carrying out colchicine mutation treatment, ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) mutation treatment and sodium azide (NaN3) mutation treatment; and finally seeding and germinating the cunninghamia lanceolata seeds which are subjected to mutation treatment, so as to obtain a large group of cunninghamia lanceolata mutation seedlings. The cunninghamia lanceolata mutation seedlings obtained by the mutation method have the characteristics of obvious phenotypic characteristic variation, large population growth characteristic variation range and the like; a great number of mutated cunninghamia lanceolata materials can be formed within a short period of time by the method disclosed by the invention; and a foundation is laid for breeding of a new variety of cunninghamia lanceolata.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Efficient induction medium formula of sorghum anther
InactiveCN104686371AImprove recovery rateImprove cultivation efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsEthylmethane SulfonateSucrose
The invention provides an efficient induction medium of sorghum anther. The formula of the medium is composed of a certain content of KNO3, NH4NO3, KH2PO4, CaC12 2H2O, MgSO4, Na2-EDTA, FeSO4 7H2O, MnSO4 H2O, ZnSO4 7H2O, H3BO3, KI, CuSO4 5H2O, CoC1 6H2O, NaMoO4 2H2O, ethylmethane sulfonate, glycine, inositol, vitamin B1, vitamin B6, nicotinic acid, D-arabinose base-2-deoxidation hexose, cane sugar, Phytagel, 2,4-D, kinetin, compound phthalein nucleic acid, plant sulfuration kinetin PSK-alpha, insulin and protein hydrolysate. The medium has the advantages of being capable of remarkably improving the callus rate of the sorghum anther and substantially improving the cultivation efficiency of the sorghum anther.
Owner:吕娜
Method for mutagenizing barbadosnut seeds by ethylmethane sulfonate
InactiveCN103340150AAvoid the effects of large variations in germination rateShorten the timePlant genotype modificationRadicleEthylmethane Sulfonate
The invention discloses a method for mutagenizing barbadosnut seeds by ethylmethane sulfonate. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: first, performing pre-bud forcing treatment at 30 DEG C on the barbadosnut seeds, selecting the seeds which are broken and exposed with unexpanded radicles after 3-7 days and soaking the seeds in a 0.9% EMS (Ethylmethane Sulfonate) liquor and soaking for 7 hours; forcing buds of the treated seeds at 28 DEG C and culturing for 3-4 days; and sowing mutagenized survival seeds in a soft peat soil substrate with radicles facing downward, and earthing by 1cm to breed. According to the method, the defects in the prior art are overcome, the mutagenizing concentration and time of EMS are reduced and the mutagenizing efficiency of the barbadosnut seeds by ethylmethane sulfonate is improved so as to facilitate selection by mutation of barbadosnut and promote industrialized development of the barbadosnut.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for creating distiller's yeast ethanol high yield bacterial strain
InactiveCN101323837AIncrease productionLow residual sugarFungiMutant preparationEthylmethane SulfonateSpore
The invention discloses a method for constructing the ethanol high-yield strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which comprises the following steps: (1) ethylmethane sulfonate is utilized to carry out random mutagenesis to the amphiploid strains of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae to cause the final concentration of the volume of the ethylmethane sulfonate in the bacteria liquid to be processed to be 2 to 4 percent and the concentration of the amphiploid strains of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae to be 2 multiplied by 10<6> to 6 multiplied by 10<6> cell / ml; (2) 3 to 5 rounds of the sexual recombination of high efficient sporulation, spore purification and full integration cause genome recombination between strains in a library to construct the ethanol high-yield strains of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The ethanol output of the recombinant strains constructed by the method of the invention is increased by 8.88 percent compared with that of contrast strains, residual sugar is reduced by 64.37 percent, the fermentation cycle is shortened by 10 hours and ethanol and high osmotic resistance are 5.10 times of that of the contrast strains, thus providing excellent strains for the industrial production of fuel ethanol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for screening dandelion salt-tolerance mutants
ActiveCN104719162ANormal growthAccelerate the process of breeding for salt toleranceHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEthylmethane SulfonateAlkali soil
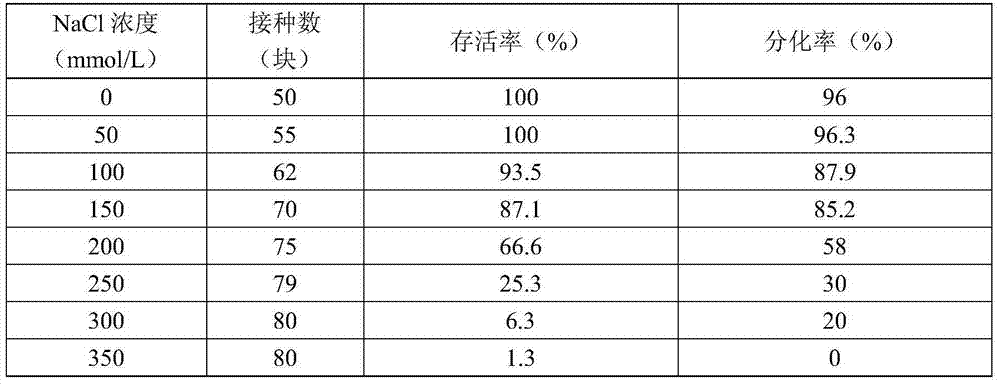
The invention discloses a method for screening dandelion salt-tolerance mutants. The method comprises the steps that full seeds are selected and cultured; aseptic seedlings are acquired and cut into slices; the slices are subjected to callus induction; embryonic calluses are obtained, sequentially inoculated to a liquid differential medium containing EMS (Ethylmethane Sulfonate) and a solid differential medium containing NaCl, and screened; salt-tolerance test-tube seedlings are obtained; acclimatization and transplant are performed to make the salt-tolerance test-tube seedlings survive; then the salt-tolerance test-tube seedlings are transplanted a greenhouse; and salt-tolerance dandelion plants are obtained with the combination of coastal original saline alkali soil potting saline-alkaline tolerance identification method. The method for screening the dandelion salt-tolerance mutants is simple to operate, good in effect, high in efficiency, and very wide in application prospect, and accelerates a dandelion salt-tolerance breeding course.
Owner:COASTAL AGRI RES INST HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Method for induction mutating woody plant by using ethylmethane sulfonate
InactiveCN1961648AHigh mutagenesis rateReduce volumePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsEthylmethane SulfonateWoody plant
The invention relates to a method for using methanesulfonic acid carbethoxy to induce woody plant, especially using callus blast cell to induce the methanesulfonic acid carbethoxy to obtain woody plant variable kind, wherein it comprises selecting explant, processing, differentially cultivating, inducing and selecting; said explant is woody plant seed, to be cut into 1-2mm stem sections to be planted into culture medium, via differential cultivation, to induce the methanesulfonic acid carbethoxy of callus blast cell. The invention can obtain variable kind in the full expression of plant cell, with high yield. And the processed element is single cell, with small volume and high number, to reduce the cost.
Owner:上海光兆植物速生技术有限公司
Method for obtaining excellent clone through fiber bamboo subterraneous stem in-situ multiple mutagenesis
ActiveCN110574681ADirected genetic improvementEasy to operatePlant genotype modificationEthylmethane SulfonateFiber
The invention discloses a method for obtaining an excellent clone through fiber bamboo subterraneous stem in-situ multiple mutagenesis. The method comprises the steps that a subterraneous stem of fiber bamboo is selected; an internal irradiation mutagenic agent is selected to be prepared into mutagenic agent solutions separately; a chemical mutagenic agent ethylmethane sulfonate is selected to beprepared into mutagenic agent solutions separately; a stainless steel continuous syringe is used for filling different segments of the selected subterraneous stem of the fiber bamboo with the internalirradiation mutagenic agent of different concentrations, and injection ports are sealed by non-sticking adhesive tapes; after 30-40 days, the stainless steel continuous syringe is used for filling the different segments of the selected subterraneous stem of the fiber bamboo with the chemical mutagenic agent solution, and the injection ports are sealed by non-sticking adhesive tapes; after earthing is performed for 60-90 days, different mutagenic buds on the segments, subjected to multiple treatment of the internal irradiation mutagenesis and mechanical mutagenesis, of the subterraneous stem are germinated into bamboo, and through screening and underground root dividing propagation, the clonal new germplasm or new species of the fiber bamboo with excellent traits.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for creating sesame mutants with EMS mutagenic agent
ActiveCN106258932AImprove mutagenesis efficiencyHigh mutation rateSeed and root treatmentPlant cultivationEthylmethane SulfonateSesamum orientale
The invention belongs to the technical field of sesame breeding, and particularly relates to a method for efficiently creating sesame mutants with an ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) mutagenic agent on a large scale. The method includes the steps that sesame seeds are treated with the EMS mutagenic agent, the seeds are planted, seedlings are transplanted, and the mutants are obtained. According to the method, by optimizing EMS treatment conditions, the mutation efficiency is significantly improved; meanwhile, by carrying out material planting and character observation with single plants and single strains as the unit, the mutant character survey efficiency and accuracy can be significantly improved. The method further has the advantages that the method can be applied to sesame mutant library establishment and directly applied to new variety breeding, various types of mutants can be obtained, and genetic backgrounds are clear and consistent and bring convenience to gene cloning. In general, the method can overcome the technical bottlenecks of good germplasm deficiency, low germplasm creating efficiency and the like in sesame breeding to some extent, and a material foundation can be laid for breeding of good new verities.
Owner:HENAN SESAME RES CENT HENAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Wheat mutation breeding method
InactiveCN103299900AIncrease frequency of chemical mutagenesisLittle physical damagePlant genotype modificationEthylmethane SulfonateChemical mutagens
The invention provides a wheat mutation breeding method and aims to improve the chemical mutagenesis efficiency, generate a relative high point mutation frequency and have relative little chromosomal aberration. The wheat mutation breeding method disclosed by the invention adopts a 0.5% EMS (Ethylmethane Sulfonate)-phosphoric acid buffering solution to treat wheat pollen to induce andro gametes to have variation so as to obtain variant seeds; the 0.5% EMS-phosphoric acid buffering solution takes a phosphoric acid buffering solution as a solvent and a chemical mutagen ethylmethane sulfonate EMS is diluted to the volume ratio concentration of 0.5%; the mol concentration of the phosphoric acid buffering solution is 1 / 15mol / L; the dosage of the 0.5% EMS-phosphoric acid buffering solution is 25-50 microliters on each floret; and the wheat pollen is pollen which is about to be ripe or pollen grains which are primarily ripe.
Owner:WHEAT RES INST OF AGRI SCI
Method for constructing pepper mutant library from ethylmethane sulfonate
PendingCN108617502AImprove anti-aphid performanceHigh yieldPlant genotype modificationGenomicsEthylmethane Sulfonate
The invention discloses a method for constructing a pepper mutant library from ethylmethane sulfonate. The method is characterized in that a Zunla 1 is used as a mutagenesis object; on the premise ofpointing out the influence of treating fluid dose and excluding space of each seed on germination percentage, semi-lethal dose is determined by comparing the germination percentage of pepper seeds with EMS treating fluid with different concentrations at different mutagenesis time; the pepper seeds are treated by mutagenesis of the semi-lethal dose; mutation frequency and mutation types of M2 generation are investigated, a mutant capable of stably inheriting of M4 generation is identified and a mutant library is constructed; the mutation types of leaves, stems, fruits, growth period, flower organs, fertility and the like are obtained and create abundant materials for functional genomics reach of pepper; and meanwhile, partial beneficial mutation can be directly applied to breeding practice.
Owner:GUIZHOU SERICULTURE RES INST GUIZHOU PEPPER RES INST
Culture medium for anti-glufosinate-ammonium alfalfa plants and soil screening method
InactiveCN104186308AEasy and fastHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEthylmethane SulfonateGermplasm
The invention mainly relates to a screening method of anti-glufosinate-ammonium alfalfa plants, in particular to an anti-glufosinate-ammonium germplasm screening method. A screening method for a culture medium for anti-glufosinate-ammonium alfalfa plants is mainly characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) germinating seeds by the MS (Murashige and Skoog) culture medium; (2) screening the dose; (3) inducing alfalfa seeds through ethylmethane sulfonate median lethal dose; (4) screening the anti-glufosinate-ammonium alfalfa plants; and (5) screening resistant plants again. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of being simple and easy to implement, taking effect quickly, and being capable of obtaining the herbicide resistant alfalfa individual plant in a short term. The method adopts a mutation measure, utilizes a chemical mutagen EMS (ethylmethane sulfonate) to induce the alfalfa seeds to cause point mutation, can screen the herbicide resistant alfalfa individual plant by the culture medium and the soil screening method, can provide a new germplasm resource for conventional breeding and can provide a reference for breeding of herbicide resistant agents of other plants.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Breeding method of rice variety with stripe vein marked characters
The invention relates to a breeding method of a rice variety with stripe vein marked characters, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out physicochemical mutation treatment by utilizing ion beams or gamma rays and ethylmethane sulfonate, inducing color variation of rice vein stripes, and screening rice vein mutants; selecting the mutant marked with vein stripes on blades for individually planting until the mutant is stably expressed; hybridizing and backcrossing the stripe vein mutation material with the conventional rice, analyzing the genetic rules of the character, hybridizing and backcrossing the stripe vein mutation material with the conventional rice and the parents of the hybrid rice, identifying the fertility, carrying out test-crossing and mating tests, and selecting two nuclear sterile lines marked with recessive stripe veins, a restoring line, three maintenance lines and a conventional rice material; and matching the two bred nuclear sterile lines, the bred restoring line and the bred maintenance lines, and verifying the validity to acquire hybrid rice parents, hybrid rice combination and conventional rice varieties marked with veins. The invention realizes the purposes of quickly, simply, conveniently, visually and accurately identifying the characteristics and the individualities of rice varieties and quickly and accurately identifying the purity of varieties in the seedling stage, and the invention increases new gene types of rice.
Owner:WIN ALL HI TECH SEED CO LTD
Creation method of switchgrass mutants
InactiveCN104137773AThe mutagenesis process is simple and easyShort experiment cycleHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEthylmethane SulfonateBiotechnology research
The invention discloses a creation method of switchgrass mutants. The creation method comprises the following steps: after a lots of switchgrass multiple shoots are cultured in a tissue culture manner, stripping out individual multiple shoots, cutting off the upper sheaths after acclimatization under natural conditions, performing soaking treatment on the parts 1.5-2cm above the left base parts by use of a solution of ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) for 3 hours, and after the completion of the soaking treatment, transplanting the multiple shoots of which the sheaths are cut off into a culture medium for culture, and after complete rooting, transplanting to a greenhouse or land, and screening out the mutants according to the phenotypes of the switchgrass. The method is capable of realizing large-scale processing of the mutational original acceptor material and thus increasing the basic number of the variants, and meanwhile, a near-isogenic line material only different from the original acceptor material in target traits can be obtained; and in addition, the mutagenesis process is simple and feasible, the processing cost is relatively low, and the breeding period can be effectively shortened; in short, the method is suitable for creating new materials for the modern biotechnology research of the switchgrass.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Dendrocalamus farinosus breeding method through in-vitro induced mutation by using ethylmethane sulfonate
ActiveCN108522281AEnhanced Mutation BreedingEasy to industrializeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEthylmethane SulfonateInduced mutation
The invention discloses a Dendrocalamus farinosus breeding method through in-vitro induced mutation by using ethylmethane sulfonate. The invention provides a method for obtaining mutant plants of Dendrocalamus farinosus. The method comprises the following step: carrying out induced mutation on calli derived from the Dendrocalamus farinosus by using ethylmethane sulfonate. The method for obtainingthe mutant plants of the Dendrocalamus farinosus further comprises the following step: culturing the induced-mutated calli to obtain regenerated plants. The method for obtaining the mutant plants of the Dendrocalamus farinosus further comprises the following step: screening the mutant plants from the regenerated plants. According to the method provided by the invention, an induced mutation technology and in-vitro culture are combined, and the calli of the Dendrocalamus farinosus are subjected to in-vitro induced mutation by using ethylmethane sulfonate, so that a large quantity of homogeneousinduced-mutated colony can be obtained. According to the method, the mutation frequency and breeding efficiency are increased extremely, the improvement on induced mutation breeding of the Dendrocalamus farinosus is facilitated, the industrialized development of the Dendrocalamus farinosus is promoted, and the method has a great application and popularization value.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chinese pumpkin mutant induction method
PendingCN110876336AEfficient constructionPlant genotype modificationEthylmethane SulfonatePumpkin seed
The invention provides a Chinese pumpkin mutant induction method, including the steps of (1), soaking plump and uniform pumpkin seeds in water and carrying out germination accelerating treatment, andthen soaking the seeds in an ethylmethane sulfonate solution with volume concentration being 1.6-1.8% for 12 hours; (2), cleaning the seeds treated in the step (1) with clean water, spreading the cleaned seeds in culture vessels of which the internals are covered with wet filter paper, accelerating germination in an incubator, and sowing seeds, growing seedlings and planting in field sequentially;(3), pinching when plants grow 5 leaves and 1 bud tip, pruning and remaining two vines each plant, and marking the plants as the M1 generation; (4), observing characters of plants in the M1 generation, and performing same-vine selfing to reserve seeds to obtain selfined pumpkin seeds, marking the seeds as the M2 generation; observing characters of plants in the M2 generation, and screening to obtain the mutants. By the Chinese pumpkin mutant induction method for induction of pumpkin, the seed germination rate is 59%, the total phenotypic mutation frequency of the plants in the M2 generation is up to 11.2%, and thus, a Chinese pumpkin mutant library can be constructed effectively.
Owner:HUNAN VEGETABLE RES INST
Acid solution system capable of relieving damage of mud to low-permeability reservoir
InactiveCN104059624ASlow reaction speedSlow responseDrilling compositionEthylmethane SulfonateClay minerals
The invention discloses an acid solution system capable of relieving damage of mud to a low-permeability reservoir, which is composed of the following components in percentage by weight: 5-10% of methyl sulfonic acid derivative, 2-5% of isoascorbic acid, 0.5-1% of nonionic surfactant, 0.1-0.5% of corrosion inhibitor, 3-5% of hydrofluoric acid, 3-10% of low-polymer alcohol and the balance of water. The methyl sulfonic acid derivative is aminomethane sulfonate, ethyl methanesulfonate, methyl methanesulfonate, methanesulfonic acid or mixture thereof; the nonionic surfactant is fatty alcohol polyethenoxy ether; the corrosion inhibitor is imidazoline quaternary ammonium salt; and the low-polymer alcohol is methanol, ethanol, isopropanol or mixture thereof. The system can effectively relieve damage of clay minerals in drilling mud to the reservoir, and can restore the permeability of the reservoir, so that oil gas can flow into the shaft from the stratum; and thus, the system has important practical meanings.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Method for efficiently producing jatropha M_2 seeds processed by EMS (methanesulfonic acid ethyl ester)
InactiveCN102017891AHigh frequency of morphological mutationsEfficient productionSeed and root treatmentPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyEthylmethane Sulfonate
The invention relates to a method for efficiently producing jatropha M_2 seeds processed by EMS (methanesulfonic acid ethyl ester), which comprises the following steps: a preprocessing step: collecting jatropha seeds, and preprocessing the jatropha seeds; a mutagenizing step: mutagenizing the jatropha seeds for an appropriate time by using an EMS solution (with appropriate concentration), and in the process of chemical mutagenizing, simultaneously mixing the seeds with the solution so as to ensure that the EMS solution is uniform in concentration and the jatropha seeds can be fully contacted with the EMS solution; a seedling raising and transplanting step: carrying out seedling raising and timely transplanting on the jatropha M_1 seeds subjected to mutagenizing so as to cultivate jatropha M_1 plants; and a self-pollination step: after the cultivated jatropha M_1 plants reach the flowering stage, carrying out self-pollination on the jatropha M_1 plants, after the fruits of the jatropha M_1 plants get ripe, obtaining the jatropha M_2 seeds. The method in the invention has the advantages that an ethylmethane sulfonate is used as a mutagen for mutagenizing the jatropha seeds, the preprocessing step and the mixing and self-pollination are adopted in the process of mutagenizing, the jatropha M_2 seeds processed by EMS can rapidly be obtained.
Owner:嘉汉林业(广州)有限公司
Special fertilizer for mat grass planting
InactiveCN105061020AIncrease sweetnessReduce acidityFertilizer mixturesEthylmethane SulfonateChange color
The invention discloses a special fertilizer for mat grass mat planting, and relates to the technical field of fertilizers. The special fertilizer is characterized by comprising the following components in parts by weight: 60-70 parts of organic matters, 10-13 parts of inorganic substances, 4-5 parts of trace elements, 10-15 parts of clay soil, 1-2 parts of humic acid, 0.03-0.08 part of a biological growth regulator and 2-3 parts of a seedling promoter; and the seedling promoter comprises the following components in parts by weight: 2-3 parts of ethylmethane sulfonate, 1-3 parts of brassinolide, 1-3 parts of compound sodium nitrophenolate and 0.3-0.4 part of a rear-earth element. The special fertilizer is comprehensive in nutrient, high in fertilizer supply capacity, strong in mat grass stress resistance, resistant to lodging and breaking, deep in grass color, not liable to change color and high in yield.
Owner:安徽省寿县板桥草制工艺品有限公司
Method for mutagenizing flax seeds and screening salt-tolerance mutants
InactiveCN105638454AImprove use valueProcess conditions are easy to controlPlant genotype modificationEthylmethane SulfonateRoom temperature
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Method for cultivating non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore plants
InactiveCN110547193AEmbryo effectExtended production timePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsEthylmethane SulfonateEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for cultivating non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore plants. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting flower buds; (2) cultivating microspore derivedembryos, wherein the flower buds are sterilized and washed and rinsed with a 1 / 2NLN-13 culture medium; the rinsed flower buds are added into the 1 / 2NLN-13 culture medium and fully ground, filtered andcentrifuged, a yellow-green precipitate is diluted with a NLN-13 culture medium and split-charged into a culture dish after treatment with ethylmethane sulfonate, activated carbon is added into the culture dish to enable the concentration of the activated carbon to be 1 mg / mL, heat shock treatment is carried out, and then dark culture is carried out for 14 days to form embryoid bodies; (3) germinating mature embryos into plants, wherein the embryoid bodies undergo shaking culture, the mature embryos becoming green are transferred to an improved solid 1 / 2MS culture medium for 40 days, and thenacclimatization and transplanting are directly carried out. According to the method, under the condition that the embryo yield can be guaranteed, the operation steps are simplified, the operation time is greatly shortened, and the plant production efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Flowering phase special fertilizer for kiwifruit planting
InactiveCN105085033AImprove water retentionAdd flavorFertilizer mixturesEthylmethane SulfonateRare-earth element
The invention relates to the technical field of fertilizer, in particular to flowering phase special fertilizer for kiwifruit planting. The flowering phase special fertilizer is characterized by comprising, by weight, 50-60 parts of organic matter, 10-15 parts of inorganic matter, 1-2 parts of microorganisms, 2-3 parts of microelement, 0.1-0.3 parts of boric acid, 1-2 parts of humic acid, 0.05-0.15 part of biological growth regulator and 2-3 parts of flower retention agents. The flower retention agent comprises, by weight, 2-3 parts of ethylmethane sulfonate, 0.1-0.2 part of abscisic acid inhibitor, 1-3 parts of brassinolide and 0.3-0.4 part of rare earth element. The microorganisms comprise thermophilic sporotrichumsp, dinitrogenase, phosphate-solubilizing enzymes and potassium-solubilizing enzymes by the ratio of 0.5:0.6:1:1.2. The flowering phase special fertilizer is comprehensively nutritional, high in fertilizer supplying capacity, capable of improving the soil quality and small in environmental pollution, and kiwifruit is high in stress resistance and yield.
Owner:ANHUI RUNSHENG AGRI DEV CO LTD
Method for cultivating clivia
InactiveCN108156882AGood regulationImprove seedling growth rateBiocidePlant growth regulatorsEthylmethane SulfonateClivia miniata
The invention discloses a method for cultivating clivia. The method comprises the following steps: (1) seed soaking treatment: first, soaking clivia seeds with an ethylmethane sulfonate solution, thenrinsing the seeds clean, soaking the seeds with an acetic acid solution, and finally soaking the seeds with warm boiled water; (2) seed pregermination treatment: putting the seeds into a pregermination box for pregermination; (3) seed sowing: filling a special cultivation substrate for clivia into the bottom of a planting basin, and uniformly mixing the clivia seeds and a seed dressing agent, andsowing the mixture in the special cultivation substrate for clivia; (4) growth period management; and (5) flowering period management: dropwise applying an auxin composition to two axils of clivia going to be flower and extract arrows, usually for 1 to 2 times, with an interval of 10 days between the two times. The method for cultivating clivia has the functions of realizing dwarf plants, strongseedlings, developed root systems, no overgrowth phenomenon in summer, and good stress resistance, inducing clivia to blossom in advance, and promoting the rapid growth of flower arrows.
Owner:HEFEI SHENWO HORTICULTURE CO LTD
Method of screening mutants being insensitive to strigolactone
InactiveCN106718854AOriginalityPracticalPlant genotype modificationEthylmethane SulfonateStrigolactone
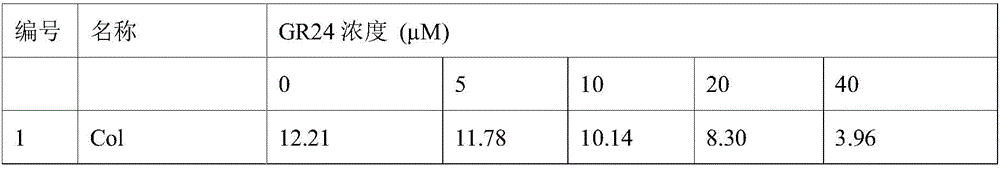
The invention discloses to a method of screening mutants being insensitive to strigolactone. The method includes the steps of: 1) processing of wile-type arabidopsis thaliana seeds: A) weighing seeds and washing the seeds in distilled water; B) adding ethylmethane sulfonate and uniformly mixing the components in a fume cupboard; C) pouring processed ethylmethane sulfonate in NaOH and cleaning the seeds; D) placing the cleaned seeds in an agar solution and moving the seeds into soil by means of a pipette gun for growth; 2) screening of the mutants being insensitive to strigolactone: A) when the seeds are matured, harvesting the seeds and placing the seeds in a centrifugal tube, and disinfecting the seeds with a bleaching agent solution and placing the seeds in a refrigerator; B) sowing the seeds on an AT culture medium containing the strigolactone by means of the pipette gun; C) irradiating the culture dish, and placing the culture dish in a dark place so that the seeds are germinated; and D) selecting a long-root-system arabidopsis thaliana mutant single plant and transplanting the single plant in soil. The method has simple operations and short screening period, and can quickly and high-effectively screen the arabidopsis thaliana mutants being insensitive to the strigolactone.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
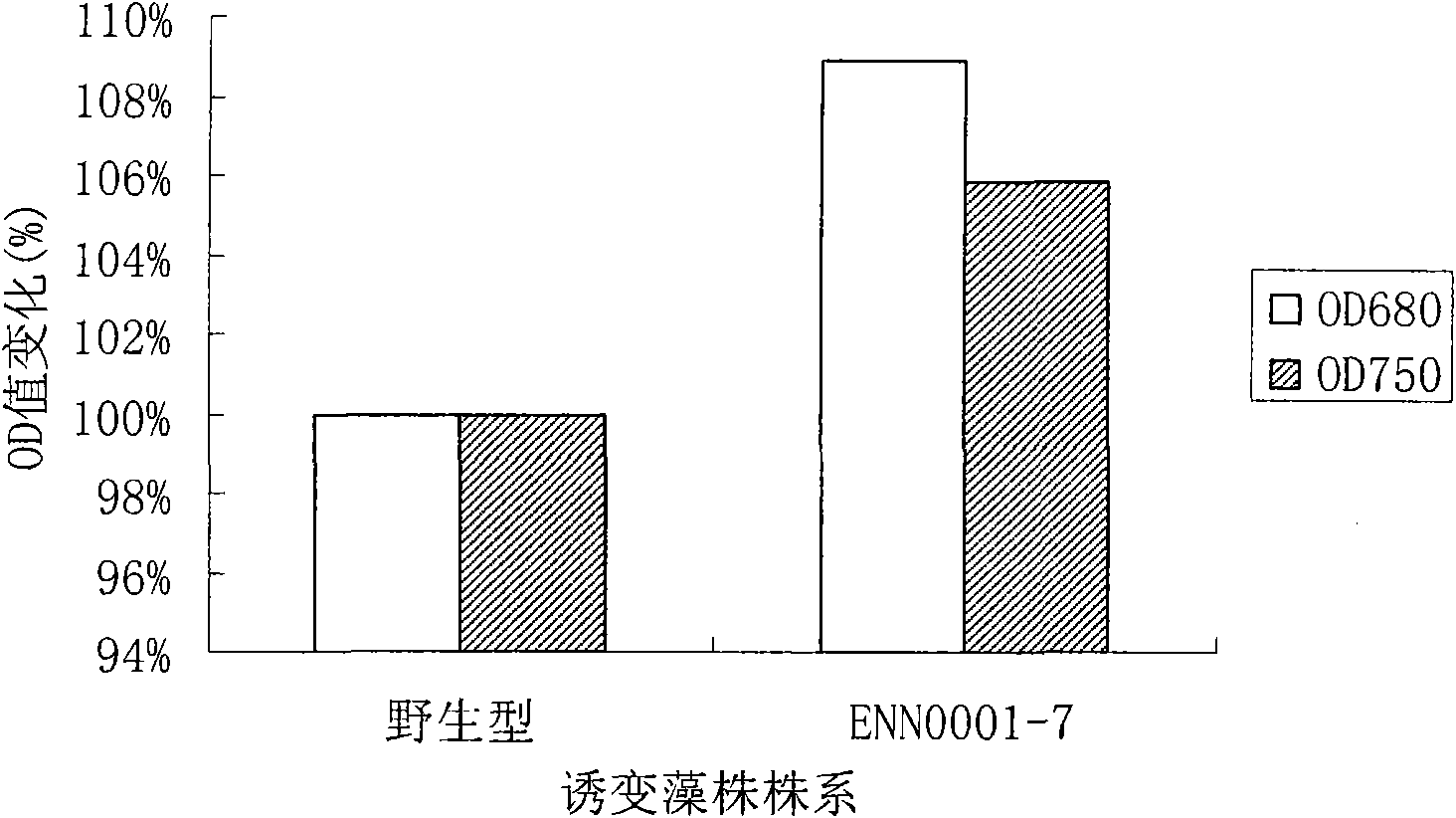
High-growth-rate Dunaliella tertiolecta obtained through ethylmethane sulfonate mutation breeding
ActiveCN101597569BFast and easy growthUnicellular algaeMutant preparationGerm plasmEthylmethane Sulfonate
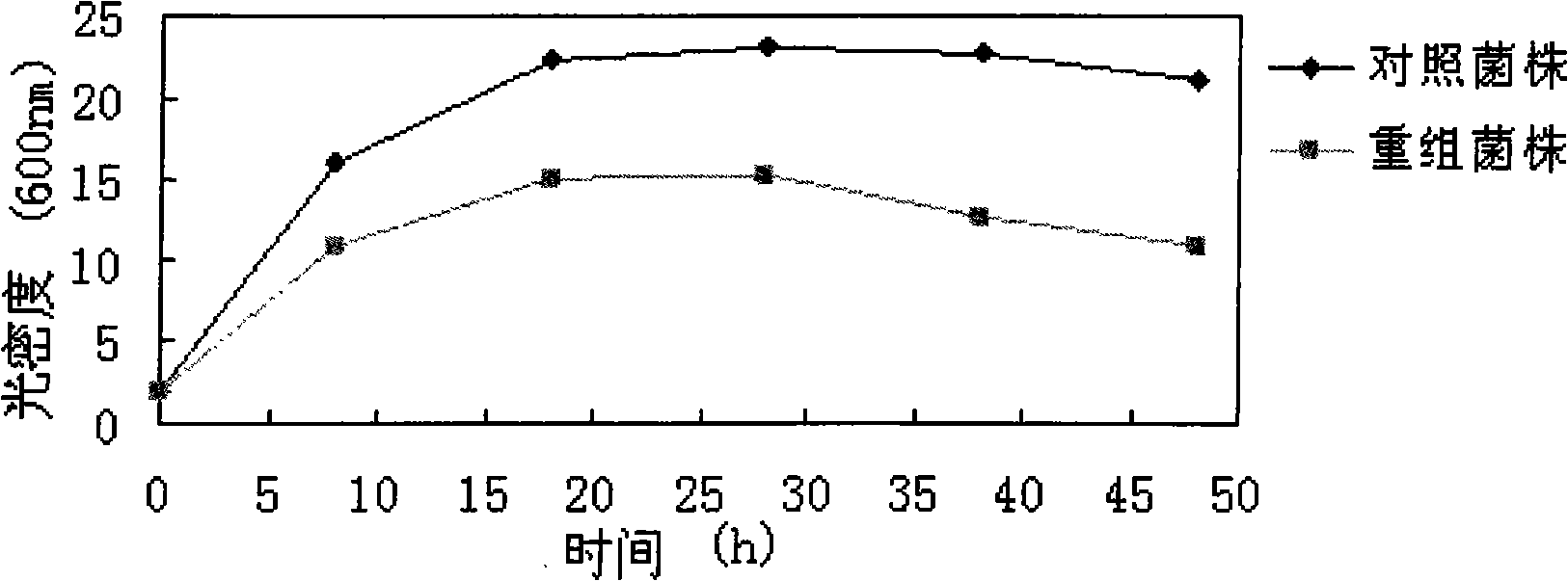
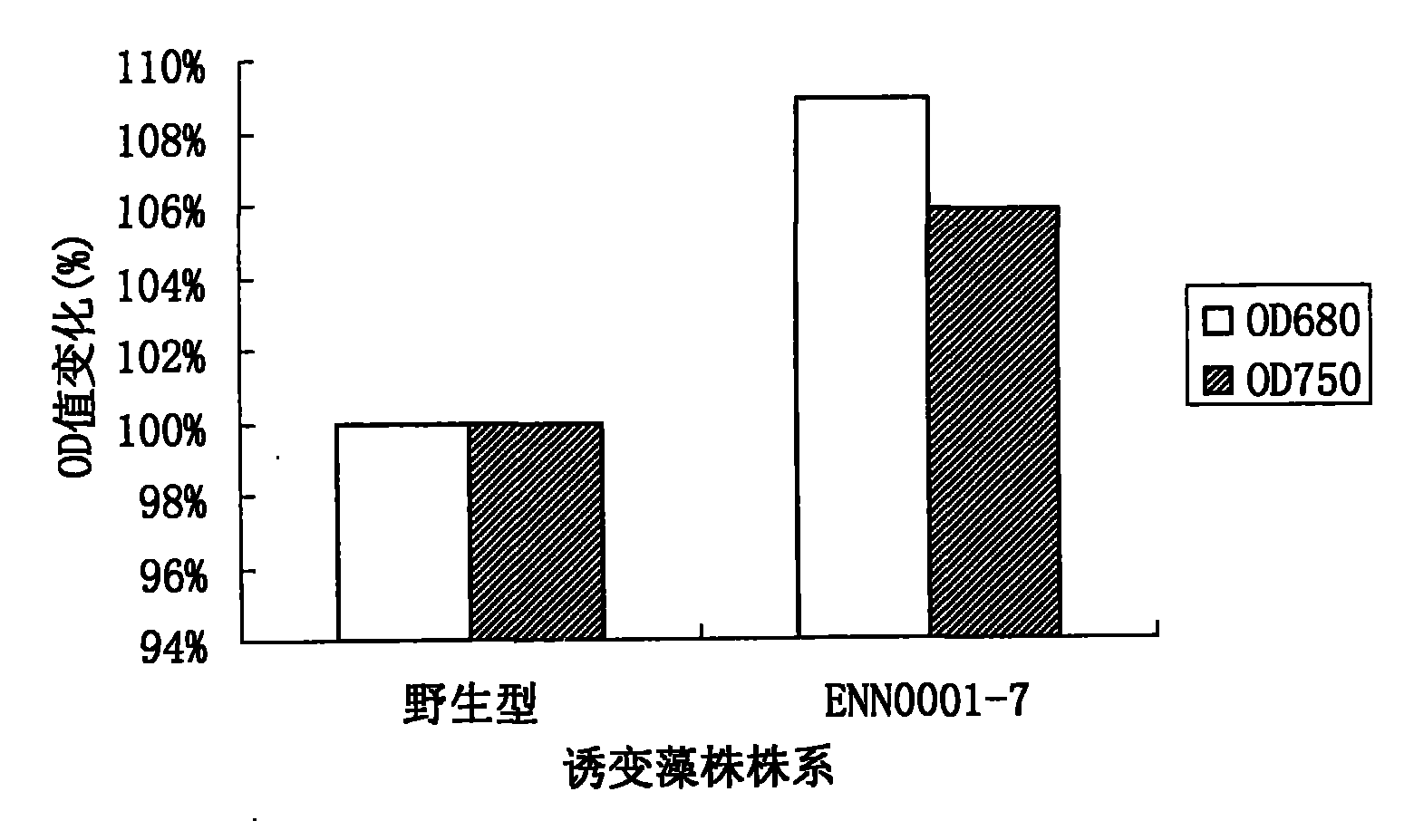
The invention relates to a method adopting ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) to perform chemomorphosis on Dunaliella tertiolecta, which performs screening by using the growth rate of microalgae as an index under a normal culture condition to finally obtain a mutagenic strain ENN0001-7 with higher growth rate compared with a wild strain. Compared with the wild strain, the chlorophyll content (OD680) ofthe mutagenic strain obtained by the method is increased by 8.9 percent, and the biomass (OD750) is increased by 5.9 percent. The strain with stable and high growth rate obtained by the method provides a valuable germ plasm resource for mass production.
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
Greenhouse kaffir lily cultivation method
InactiveCN107197764AImprove water absorption and retention capacityQuality assuranceSeed and root treatmentFertilising methodsEthylmethane SulfonateGreenhouse
The invention discloses a greenhouse kaffir lily cultivation method. According to the method, the temperature, humidity, lighting, watering and fertilization and other aspects in a greenhouse are strictly controlled at stages of kaffir lily nutrition medium preparation, seed preprocessing, tissue-culture cultivation, root rearing and flower growing, kaffir lily seeds are preprocessed by using an ethylmethane sulfonate solution, so that kaffir lily plants grow healthier and stronger, a cultivation period is short, the survival rate is high, and the strong seedling rate is high.
Owner:HEFEI SHENWO HORTICULTURE CO LTD
Breeding method of double main stem semi-dwarf brassica napus
PendingCN111887148AImprove lodging resistanceIncrease productionPlant genotype modificationEthylmethane SulfonateBrassica
The invention belongs to the technical field of rapeseed breeding, and discloses a breeding method of double main stem semi-dwarf brassica napus. The breeding method includes using ethylmethane sulfonate to mutagenize seeds of the inbred line of brassica napus, selecting double main stem tall plants to perform selfing, and selecting double main stem semi-dwarf plants to perform selfing; cultivating haploid plants, and performing doubling treatment to obtain the population of double main stem semi-dwarf brassica napus; and performing field identification, and obtaining the double main stem semi-dwarf brassica napus. The provided double main stem semi-dwarf brassica napus has the traits of double main stalks and semi-dwarf stems, so that lodging problems can be solved, the yield and qualityof the brassica napus can be enhanced, mechanized harvesting can be realized, and the overall efficiency of the brassica napus can be increased; EMS mutation is performed on the brassica napus, so that natural mutation rate of organisms can be increased; the method is simple and easy to operate and strong in specificity; and certain bases on DNA can be located through mutation, so that progenies can be easily and stably obtained through inheritance.
Owner:贵州省油菜研究所
Method for culturing new variety of smilax riparia with tissue mutation of flower stalks
ActiveCN111296293ANot deformedDominant mutation highPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyEthylmethane Sulfonate
The invention belongs to the technical field of planting reproduction and in particular relates to a method for culturing a new variety of smilax riparia with tissue mutation of flower stalks. According to the method for culturing the new variety of smilax riparia with tissue mutation of the flower stalks, smilax riparia flower stalks are adopted as a material which is soaked into ethylmethane sulfonate of an appropriate concentration for a certain time, and furthermore, by using a plant tissue culture technology, and methods of flower stalk tissue adventitious bud induction, adventitious budrooting and rejuvenation, and the like, a novel artificial cultivated variety of smilax riparia which has the characteristics of being good in single plant independence, high in single plant genetic information purity, clear in single plant source, and the like, can be obtained. The variety is stable in genetic property and can be cultivated as a strain to construct a smilax riparia mutant library.
Owner:通化天妍生物技术有限公司 +1
High-growth-rate Dunaliella tertiolecta obtained through ethylmethane sulfonate mutation breeding
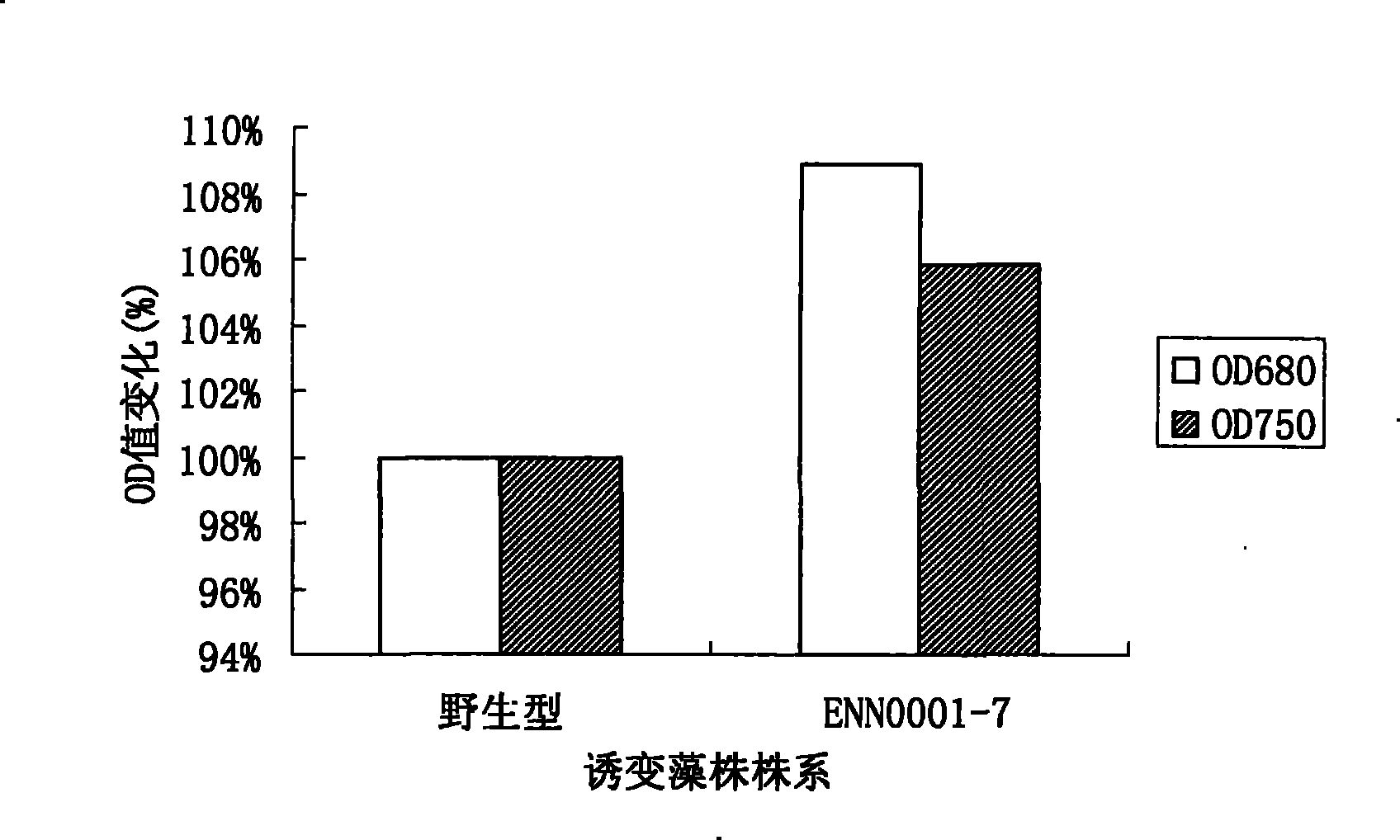
ActiveCN101597569AFast growthFast and easy growthUnicellular algaeMutant preparationEthylmethane SulfonateGerm plasm
The invention relates to a method adopting ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) to perform chemomorphosis on Dunaliella tertiolecta, which performs screening by using the growth rate of microalgae as an index under a normal culture condition to finally obtain a mutagenic strain ENN0001-7 with higher growth rate compared with a wild strain. Compared with the wild strain, the chlorophyll content (OD680) of the mutagenic strain obtained by the method is increased by 8.9 percent, and the biomass (OD750) is increased by 5.9 percent. The strain with stable and high growth rate obtained by the method provides a valuable germ plasm resource for mass production.
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com