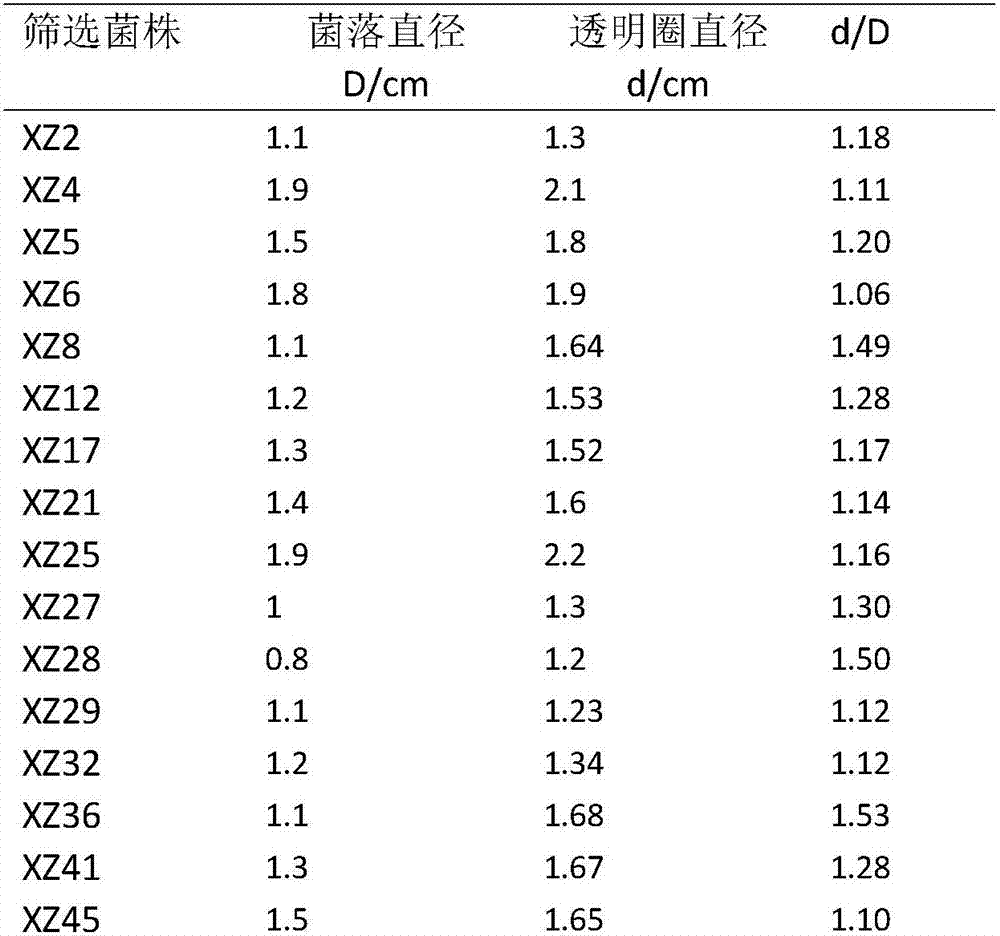
Patents
Literature
49results about How to "Improve mutagenesis efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Site-directed modification method for DNA viral genome
ActiveCN103397018ARealize fixed-point transformationQuick insertRecombinant DNA-technologyFermentationFreeze thawingRecombinant virus
The invention provides a site-directed modification method for DNA viral genome, and the problems in the prior art are solved that induction of site-directed mutagenesis of DNA viral genome is difficult, the operation of inserting an exogenous fragment is complex, and recombination rate is lower. The site-directed modification method comprises: transfecting cells by a plasmid carrying a nuclease system, infecting by a virus, after the cells show pathological changes, collecting the cells with pathological changes, performing freeze-thaw or ultrasonic processing, and centrifuging, separating the liquid supernatant to obtain a progeny virus. The site-directed modification method is capable of realizing applications to screening of virus attenuated vaccine strains, construction of viral genetic carriers and an oncolytic virus, research on virus function sequences, and the like; during modification of the viral genome, the method helps to improve mutagenesis efficiency, accurately control DNA virus for genome site-directed mutagenesis and specific gene knockout, simplify operation steps of inserting the DNA virus carrier by an exogenous gene, and improve efficiency that the exogenous gene is integrated to the viral genome, so that the work of screening high-flux recombination viruses is convenient to conduct.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Microbe mutagenizing atmospheric cold plasma method
InactiveCN1888063AImprove mutagenesis efficiencyShorten mutagenesis timeElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentElectrical/wave energy enzyme treatmentMicroorganismAtmospheric cold plasma
The atmospheric cold plasma microbe mutagenesis method belongs to the field of microbe mutagenesis technology, and features the cold plasma mutagenesis of microbe strain to denature. The microbe strain may be pronucleus microbe or eukaryotic microbe; the atmospheric cold plasma may have discharging medium of air, nitrogen or helium with discharge period of 10 s to 10 min, applied voltage of 1-100 kV and frequency of 0-15 MHz; and mutagenesed microbe may be in suspension or plate. Compared with other physical and chemical mutagenesis method, the present invention has the advantages of simple apparatus, low cost, operation safety and high mutagenesis effect, and may be applied widely in industrial microbe breeding.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for breeding microorganisms by plasma-induced mutation
InactiveCN101624591ARich varietySimplified typesMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesPlasma jetActive particles
The invention discloses a method for breeding microorganisms by plasma-induced mutation, which radiates microorganisms to be induced to mutate with a plasma jet flow that uses neutral active particles as acting particles to obtain mutated microorganisms. The method in which the neutral active particles in the plasma jet flow play a main induction role has the advantages of: ensuring the high activity of forward mutant strains and the high capability and genetic stability of produced target products, reducing mutagenesis period and improving mutagenesis efficiency, inducing a great variety of microorganisms such as prokaryotic microorganisms, eukaryotic microorganisms and archaebacteria in form of microbial community, bacterial suspension or spore suspension, simplifying experimental operation by avoiding culturing the processed microorganisms in the dark, having the characteristics of simple, safe and pollution-free whole operation, low equipment and experiment cost and the like and having great potential role in the field of industrial microorganism induced mutation breeding.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
In-vitro sodium azide (NaN3) mutation breeding technology of dendranthema morifolium
InactiveCN103039369AEasy to operateHigh mutation frequencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsInduced mutationShoot apex
The invention relates to a chemical mutation breeding technology in the field of biotechnologies, and particularly relates to an in-vitro sodium azide (NaN3) mutation breeding technology of dendranthema morifolium. The in-vitro NaN3 mutation breeding technology comprises the following steps of: performing culture in vitro on an immature stem, a stem tip or a leaf of the dendranthema morifolium to form an aseptic seedling; processing the stem tip and a stem segment of the aseptic seedling, which are taken as explants, by sodium azide (NaN3) in a breeding process to carry out induced mutation; rooting and transplanting a test-tube plantlet; and finally breeding excellent mutant in a field at a flowering phase. The in-vitro sodium azide (NaN3) mutation breeding technology can effectively overcome the obstacle of breed improvement of a clonal plant and the constraints of low bud-variation frequency and small mutational range under natural conditions, can be used for obtaining the excellent mutant within a short period of time, ensures high induced mutation efficiency, and has an important value to the genetic improvement of asexual propagation of the dendranthema morifolium with medicinal and ornamental values.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
Production technology for fermentatively producing sodium hyaluronate by utilizing bacterium
InactiveCN103173507ATo satisfy the market's needsImprove mutagenesis efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationStreptococcus zooepidemicusHydrogen
The invention relates to a production technology for fermentatively producing sodium hyaluronate by utilizing bacterium. The production technology comprises the following steps of: using streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus (Streptococcus Zooepidemicus) as an original strain; mutagenizing by virtue of nitrosoguanidine, and also mutagenizing by virtue of a protoplast in the presence of ultraviolet rays; introducing a special culture medium; carrying out submerged fermentation to produce high-output hyaluronic acid; and then carrying out a relative separation and purification technology to obtain a high-purity sodium hyaluronate product. According to the production technology for fermentatively producing the sodium hyaluronate by utilizing the bacterium, under the culture conditions that the culture temperature is 32 to 38 DEG C, the pH (Potential Of Hydrogen) of fermentation liquor is maintained within the range of 5.0 to 9.0, and a fermentation tank is at speed of stirring of 150 to 600rev / min, the output of the hyaluronic acid is greatly increased; and the production technology is suitable for being applied to industrial production.
Owner:宁波林叶生物科技有限公司
Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain and mutation induction method and application thereof
InactiveCN107201315ASimple screening methodFast screening methodFungiMutant preparationAcid-fastBiotechnology
The invention discloses a Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain and a mutation induction method and application thereof. The mutation induction method includes: Paecilomyces thermophila screened from high-temperature-fermented compost and used for producing high-temperature-resistant and acid-resistant glucose oxidase is used as the original strain, protoplast ultraviolet and ethyl methane sulfonate compound mutation induction is performed, and the screened strain is subjected to budding spore diethyl sulfate-microwave compound mutation induction to obtain the Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain. The Paecilomyces thermophila mutant strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on January 11th, 2016, and the preservation number of the mutant strain is CGMCC No. 13182. Compared with a conventional mutation induction method, the mutation induction method has the advantages that the method is high in efficiency and simple in fast in screening, the productivity of the mutant strain is high, the yield of the mutant stain is 277.65% of that of the Paecilomyces thermophila original strain, fermentation liquor enzyme activity reaches 185U / ml, production cost is lowered, and the glucose oxidase produced by the mutant strain is good in high-temperature resistance and acid resistance and can be used as feed enzyme applied to feed industry.
Owner:XUZHOU UNIV OF TECH
Method and device for mutagenizing biomaterial
InactiveCN103911363AImprove mutagenesis efficiencyIncreased ratio of mutant coloniesMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesMutagenic ProcessBiology
The invention discloses a method and a device for mutagenizing a biomaterial and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps of 1, coating a solid medium with cells to be treated, and 2, mutagenizing the coating cells which comprise microbial cells and suspension cells of animals and plants. The method can substantially improve mutagenesis efficiency and screening efficiency and is conducive to mutagenesis breeding adopting automatic high-flux experimental equipment.
Owner:WUXI TMAXTREE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Cordyceps militaris strain screening and mutagenesis method capable of producing heat-resistant proteinase and cordycepin at high yield
The invention belongs to the field of microbial fungi, and relates to a Cordyceps militaris strain capable of producing heat-resistant proteinase and cordycepin at high yield and application thereof. The strain is prepared by the following steps: selecting a Cordyceps militaris wild-type strain newly separated from the natural world as the initial strain, carrying out composite mutagenization under the actions of Cordyceps militaris protoplast nitrosoguanidine and ultraviolet light, separating and screening to obtain the strain. The strain was collected by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 11th, 2016; the collection number is CGMCC No.13179; the strain is named HYCM12; and the classification designation is Cordyceps militaris. After the strain is subjected to deep liquid ventilation fermentation, the cordycepin content reaches 2.89 g / L, and the heat-resistant proteinase activity reaches 5326U / ml. Meanwhile, the method is simple to operate and easy to implement, has the advantages of short period, abundant and accessible raw material sources, low cost, no environmental pollution, low equipment and reagent price and the like, and is convenient for large-scale production.
Owner:XUZHOU HONGYU AGRI TECH
Method for producing mutant of hemerocallis middendorffii by in vitro mutagenesis of ethyl methane sulfonate
InactiveCN106973791AImprove seedling efficiencyImprove the level of breeding technologyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsLethal doseNormal growth
Owner:INST OF DRY LAND FARMING SHANXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for breeding high-yield ascomycin strain by performing femtosecond laser mutagenesis on streptomyces hygroscopicus ascomycota subspecies and culture medium preparation
InactiveCN102250872ANot suitable for damageShort pulse timeMutant preparationElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentStreptomyces hygroscopicusAscomycota
The invention discloses a method for breeding an high-yield ascomycin strain by performing femtosecond laser mutagenesis on streptomyces hygroscopicus ascomycota subspecies and a culture medium preparation method; the method comprises the following steps: at room temperature, mixing mature slant spores of the streptomyces hygroscopicus ascomycota subspecies (ATCC14891) and sterile water to obtain monospore suspension containing 106-107 spores per milliliter; irradiating the spore suspension for 1-10 min by using the titanium sapphire femtosecond laser with centre wavelength of 800 nm, pulse width of 150 fs and frequency of 76 MHz under a irradiation power of 10-30m W; properly diluting the spore suspension, coating on a solid panel to culture, then screening by using a shake flask to obtain a high-yield ascomycin mutation strain. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the used femtosecond laser mutagenesis method is feasible and safe to operate; the mutation effect is better than that of the traditional physical and chemical mutagenesis method, and the femtosecond laser mutagenesis method has great popularization value in breeding of microorganism pharmaceutical strains; by using the femtosecond laser irradiation to perform the mutagenesis, the high-yield ascomycin mutation strain can be bred. The positive mutation rate of the mutation strain is 5-30%, and fermenting unit is improved by 10-60% in comparison with that of an original strain.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for quickly obtaining autopolyploid of jujube tree in field
InactiveCN101773068AThe method is simple and fastImprove mutagenesis efficiencyPlant genotype modificationCambiumColchicine
The invention relates to a method for quickly obtaining the autopolyploid of the jujube tree in a field. The branch of the jujube tree is heavily cut back, callus induction is carried out on the cambium of the section, colchicine is then utilized to treat the callus, and the autopolyploid can be quickly obtained by means of the regeneration of the callus. A strong branch is selected and cut back, the cambium of the section is covered by absorbent cotton, medical solution containing 5.0mg / L of TDZ and 2.0mg / L of AgNO3 is rapidly dipped on the cambium of the section, and the cambium of the section is covered by three layers, i.e. plastic bag plus wet mug plus plastic bag; when the section becomes red brown, the cambium is cracked, and when transparent microcallus appears, 0.05 percent of colchicine (containing 0.1 percent of dimethyl sulfoxide) is used to treat the callus for 24 hours; when the callus of the section is sprouted, the covering is removed in time, and the ploidy of the chromosome of the sprout is tested. The technique is applied in the polyploid breeding practice on jujube trees, the method is simple and convenient, and the autopolyploid can be quickly obtained and applied in production.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV. +1
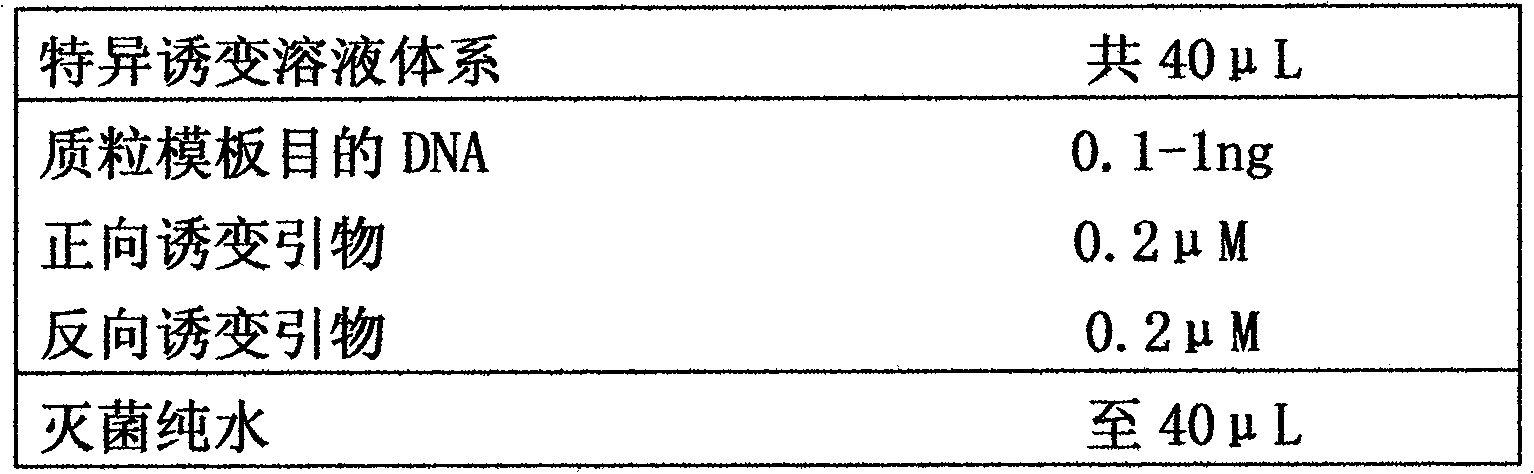
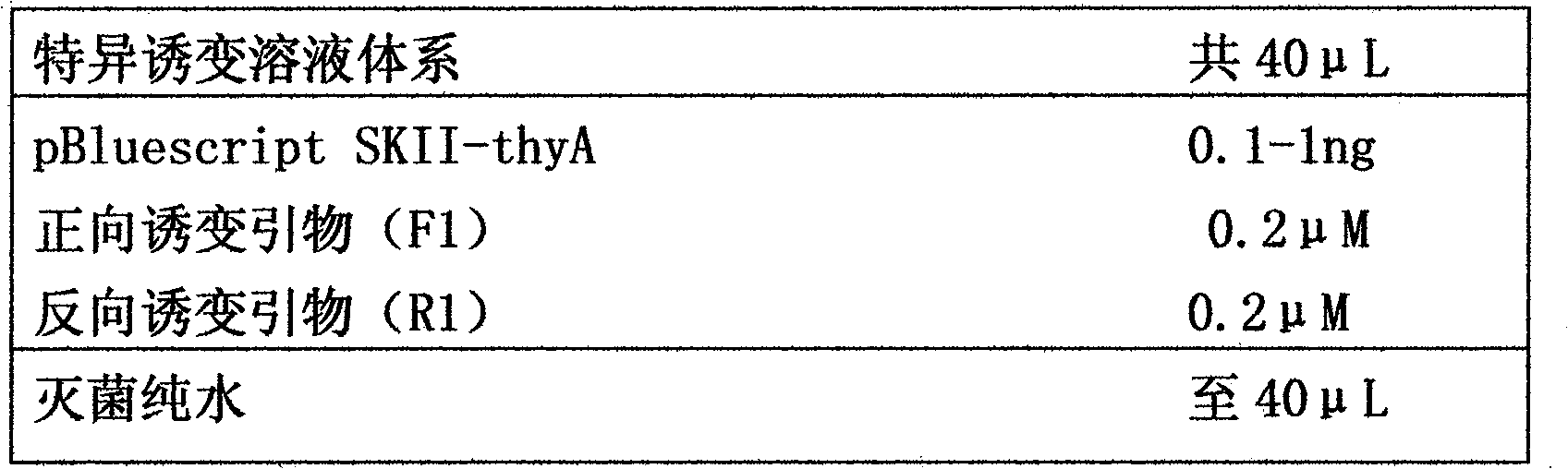
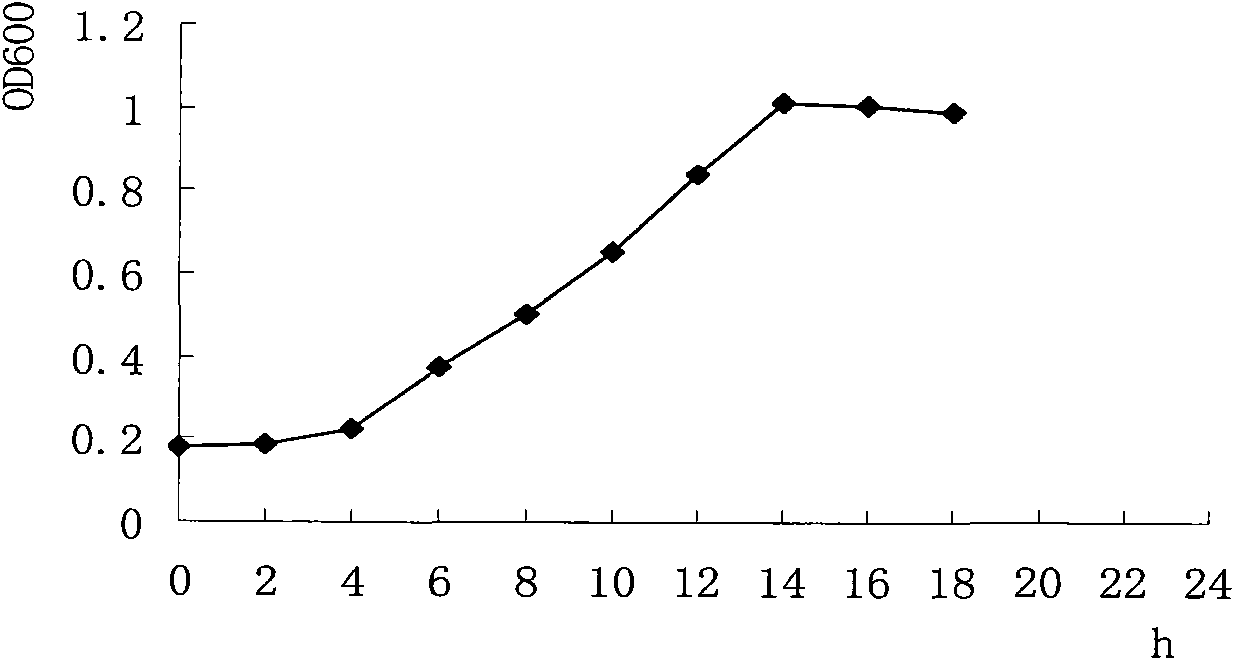
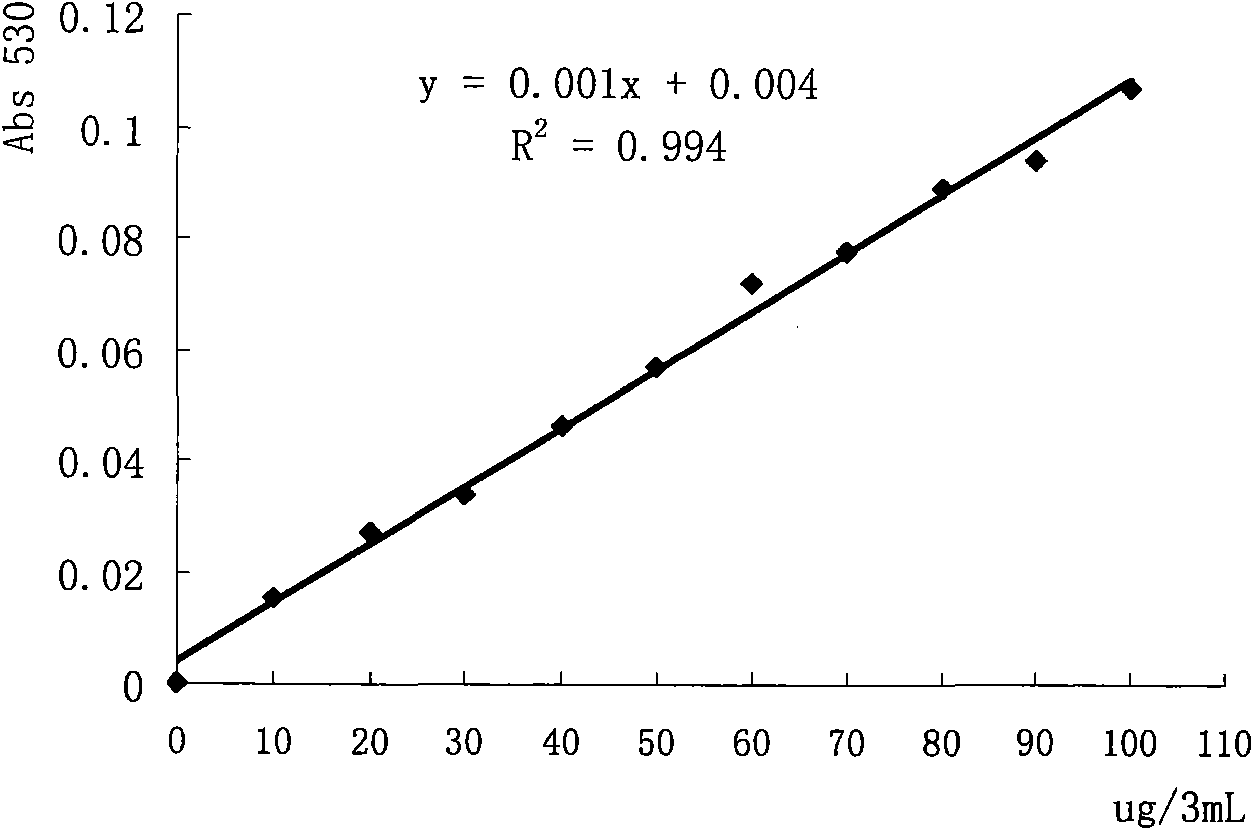
Fast high-flux gene site-directed mutagenesis method
ActiveCN101139586BSimple and fast operationShort experiment cycleBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologySequence analysisDpnI restriction endonuclease
Owner:桂林精成生物科技有限公司
Cultivation method of stress-resistant broccoli new variety
InactiveCN110663551ARich germplasm resourcesReduce usagePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention discloses a cultivation method of a stress-resistant broccoli new variety. The method includes: building callus regeneration systems of different sources; building a broccoli loose embryonic callus induction system; screening an appropriate mutagenesis method; building an efficient regeneration system, and acquiring a regeneration culture medium; acquiring a callus growth culture medium with screening pressure; screening resistant calluses; inducing regenerated buds to obtain regenerated seedlings; further breeding individual plants survived under the screening pressure, and transplanting to a natural environment to perform further selective culture to obtain ideal stress-resistant mutants so as to obtain the stress-resistant broccoli new variety. The method has the advantages a foundation is laid for the cultivation of high-quality vegetable varieties with disease resistance, drought resistance, cold resistance and the like during production, chemical fertilizer use reduction and ecological system restoration are promoted, a new approach is provided for vegetable stress-resistant breeding, vegetable seed resources are enriched, and a foundation is laid for safety vegetable production.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
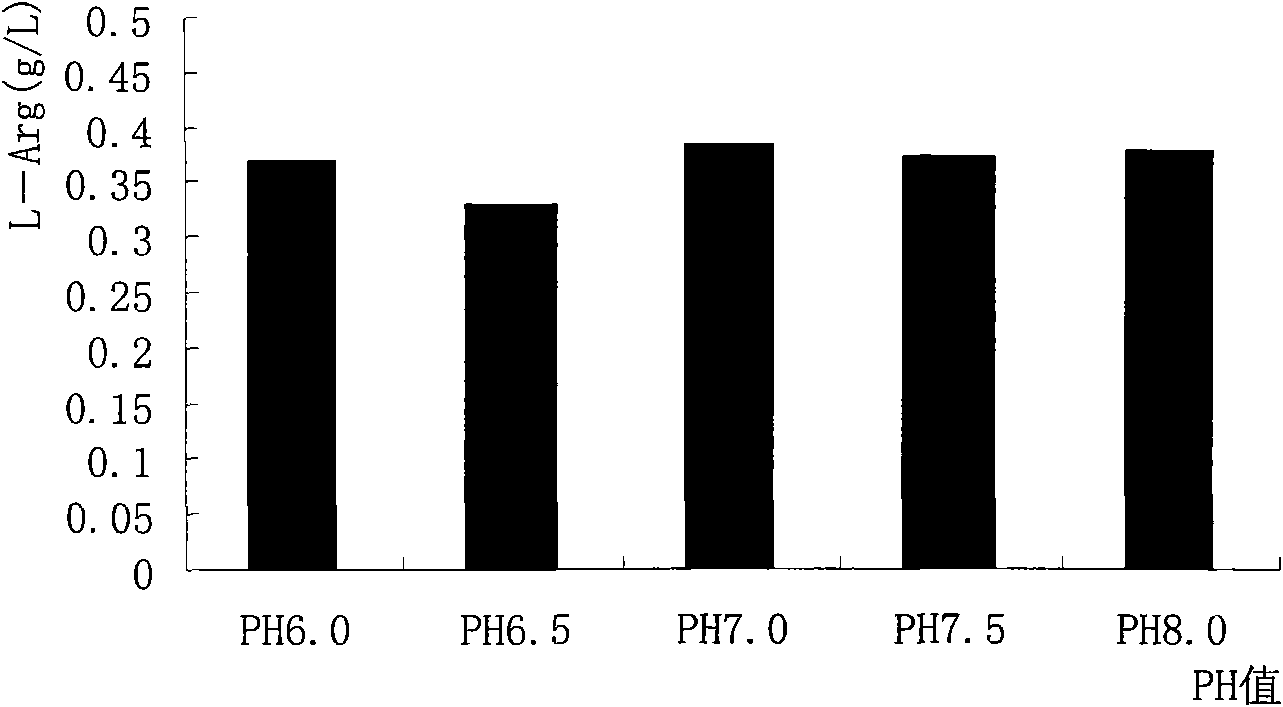
L-arginine producing strain corynebacterium glutamicum and preparation method and application
ActiveCN101928682AImprove mutagenesis efficiencyAcidogenic stabilityBacteriaMutant preparationChemistryMutagenic Process
The invention discloses L-arginine producing strain corynebacterium glutamicum ZD2009, CCTCC NO:M209260 and a preparation method and application. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: A, performing ultraviolet mutagenesis, namely culturing the corynebacterium glutamicum, centrifuging, removing supernatant, washing, and scattering the strain by using glass beads to obtain cell suspension; B, performing 1-methyl-3-nitro-1-nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis, namely culturing the corynebacterium glutamicum, centrifuging, removing the supernatant, washing, scattering the strain by using the glass beads, washing with phosphate buffer after washing, adding 1-methyl-3-nitro-1-nitrosoguanidine for mutagenesis, washing with the phosphate buffer to remove the 1-methyl-3-nitro-1-nitrosoguanidine and stopping the mutagenesis; C, determining shake flask fermentation conditions; D, determining a fermentation medium and inoculation amount; E, determining pH value; and F, determining liquid loading amount. The acid producing amount of the L-arginine producing strain corynebacterium glutamicum reaches 44g / L; and the strain produces the acid stably, has high genetic stability, reduces production cost and improves efficiency.
Owner:HUNAN NEW WELLFUL CO LTD
Sodium azide mutagenizing method for juvenile citrus internodal stem segments
ActiveCN108307915AFacilitate progress in creating variantsPromote progressBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSodium azideBud
The invention discloses a sodium azide mutagenizing method for juvenile citrus internodal stem segments, comprising: I, taking citrus young plantlets more than 1 mm in stem thickness and 5-10 cm in plantlet height, cutting to obtain internodal stem segments, soaking the internodal stem segments in a mutagenizing liquid, mutagenizing in darkness for 1-3 h, wherein the mutagenizing liquid includes sodium azide having a concentration of 0.5-2 mmol / L; II, subjecting the mutagenized internodal stem segments to tissue culture until sectional wounds of the internodal stem segments grow regenerated buds; III, using an SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) molecular markup method to detect the regenerated buds that vary, and subjecting the varied regenerated buds to rooting culture to obtain complete citrus variant plants. It is clarified that sodium azide-mutagenized juvenile citrus internodal stem segments may produce stable variant plants. The method of the invention has mutagenizing efficiency of greater than 10% and has significant mutagenizing effect and good operating convenience.
Owner:HUNAN INST OF GARDENING
Method for high-flux directed mutagenesis of glyphosate resistance of sugarcane through plasma
PendingCN107646676AMutagenesis convenienceEasy to operatePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsHigh concentrationGlyphosate
The invention discloses a method for high-flux directed mutagenesis of the glyphosate resistance of sugarcane through plasma. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out irradiation mutagenesis treatment on embryonic calluses of the sugarcane under aseptic conditions by a plasma instrument under a mutagenesis power being 140-200 W and a discharging spacing being 35-45 mm for 110-140 s under the protection of nitrogen; and carrying out buffering culture, medium-high-concentration glyphosate stress screening and differentiation seedling formation on the processed calluses, and carrying out bottled seedling glyphosate stress screening and potted seedling glyphosate foliar application stress screening. The method has the advantages of safety in operation, simplicity, easiness in implementation, large throughout, less pollution, and realization of high screening efficiency, reduction of the subsequent screening workload and visual determination of the resistance of mutant strainsdue to the implementation of oriented stress screening.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL BIOENGINEERING INST (GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST)
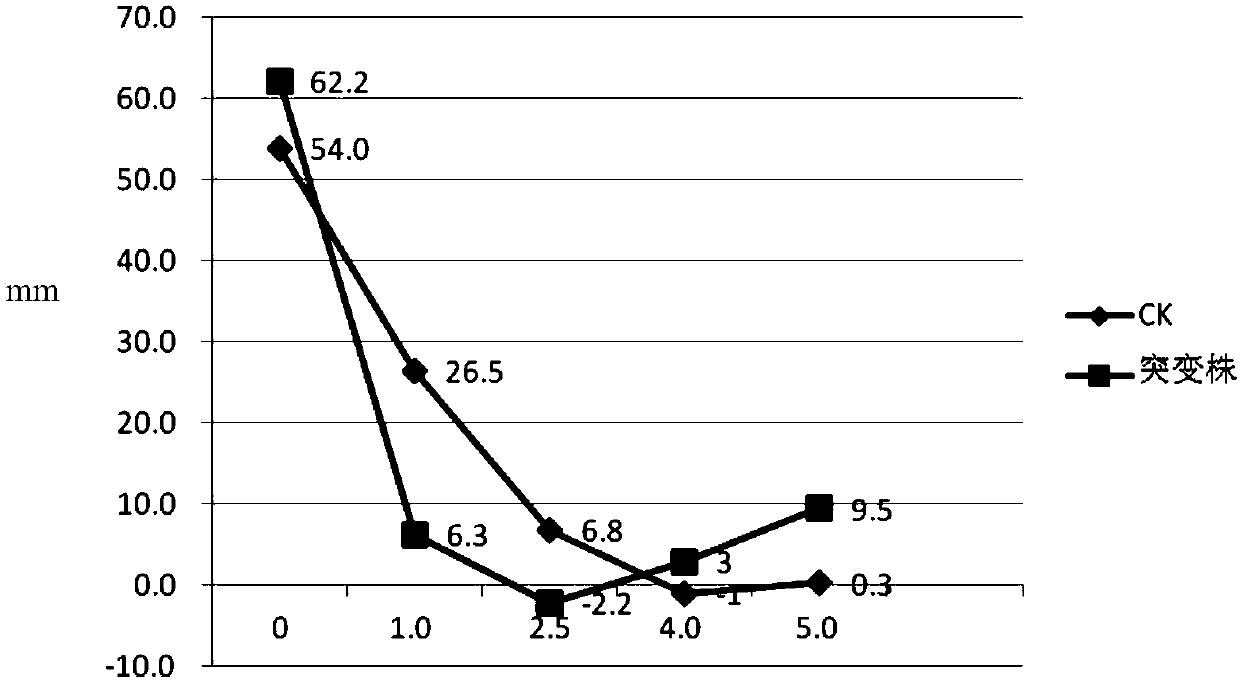
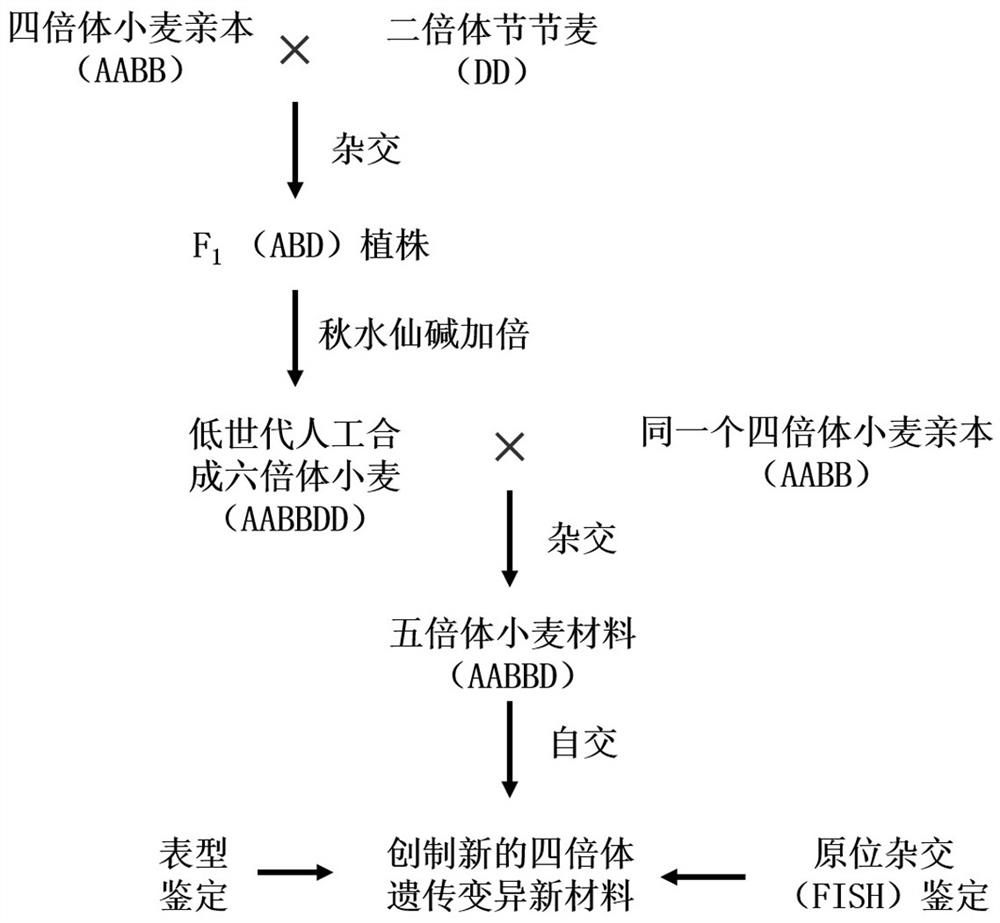
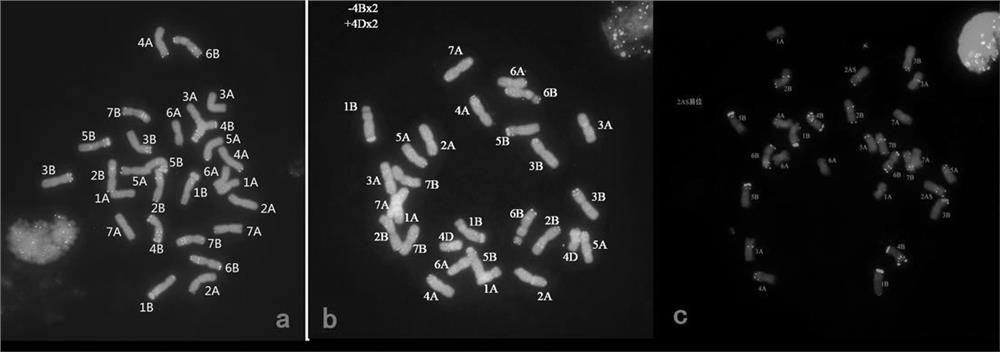
Method for widening tetraploid wheat genetic variation
PendingCN112806257ANo risk of contaminationVariation types are richPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for widening tetraploid wheat genetic variation. The method comprises the following steps that parent tetraploid wheat AABB is utilized to hybridize with diploid aegilops tauschii DD, in-vitro culture is carried out on a hybrid young embryo ABD to obtain an ABD plant seedling, then chromosome doubling treatment is carried out to obtain low-generation artificially synthesized hexaploid wheat AABBDD, the low-generation artificially synthesized hexaploid wheat AABBDD is backcrossed with the same parent tetraploid wheat AABB to obtain a pentaploid wheat material AABBD, the pentaploid wheat material is used for selfing, chromosome behaviors such as chromosome exchange, translocation, inversion, deletion and insertion are generated through chromosome recombination in the selfing process, rich variation types are generated in genetic offspring, and a new tetraploid wheat material composed of different chromosomes is formed. According to the method, the chromosome of the tetraploid wheat can be induced to generate new structural variation in a relatively short time, and the method is high in beneficial mutation efficiency, rich in mutation type, environment-friendly, safe and low in cost.
Owner:CROP INST SICHUAN PROVINCE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method of utilizing sodium azide to induce bud mutation of poinsettia
InactiveCN107912297APromote research and developmentShorten the breeding periodPlant genotype modificationAxillary budGreenhouse
The invention discloses a method of utilizing sodium azide to induce bud mutation of poinsettia. The method includes treatment steps: using a scalpel to pinch poinsettia, reserving an internode on anaxillary bud of 2-5cm during pinching, using a liquid transfer gun to extract 100-500ml of NaN3 solution, injecting into the internode, and wrapping a notch; putting treated poinsettia in a greenhousefor culture, watering, fertilizing, and waiting for a new bud to grow out after 1 month, wherein concentration of the NaN3 solution is 0.02-0.08%. The method specifies conditions like concentration and treatment methods for effectively inducing bud mutation of poinsettia, is simple and convenient in research and development and can be effectively applied in bud mutation breeding of poinsettia, and the problem that poinsettia is small in natural mutation rate and the problem that resource innovation of poinsettia cannot be performed actively on a large-scale are solved.
Owner:东莞市粮作花卉研究所
Method for establishing mutant strain by utilizing plasma induced lucid ganoderma protoplast
The invention discloses a method for establishing a mutant strain by utilizing a plasma induced lucid ganoderma protoplast. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a lucid ganoderma protoplast is established, wherein a liquid lucid ganoderma culture mycelium is prepared, a mycelium homogenate is prepared, a cell wall resolvase solution is prepared and cell walls are dissolved, the protoplast is separated and collected, and the protoplast concentration is corrected and saved; 2, protoplast mutation is induced by low-temperature plasma, wherein preparation is performed before protoplast mutation, a plasma mutagenesis device is ventilated for balance, a reaction system is electrified for protoplast mutation, a flat protoplast plate is evenly coated and standing regeneration and culture are performed, a mutant strain is selected, the colonial morphology and growing rate are observed and recorded, and hypha morphology is observed under a light microscope, active substances and stability of the mutant strain are detected, and the strain is saved. The method has the advantages of stably and efficiently utilizing plasma to induce the lucid ganoderma protoplast so as to establish the mutant strain.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
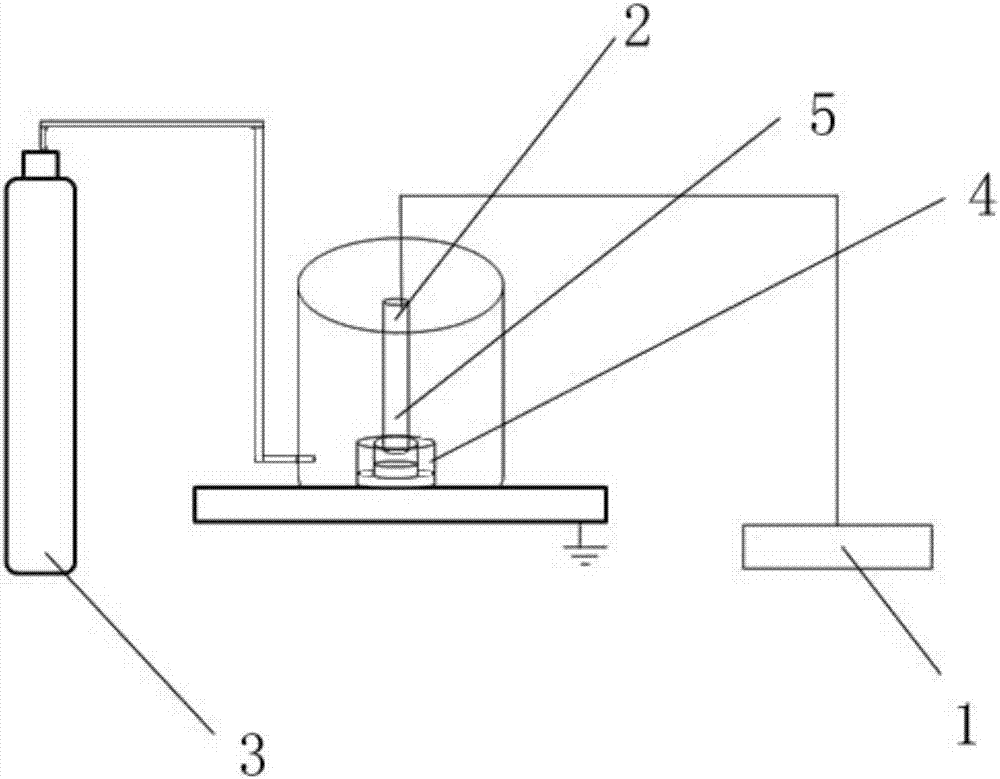
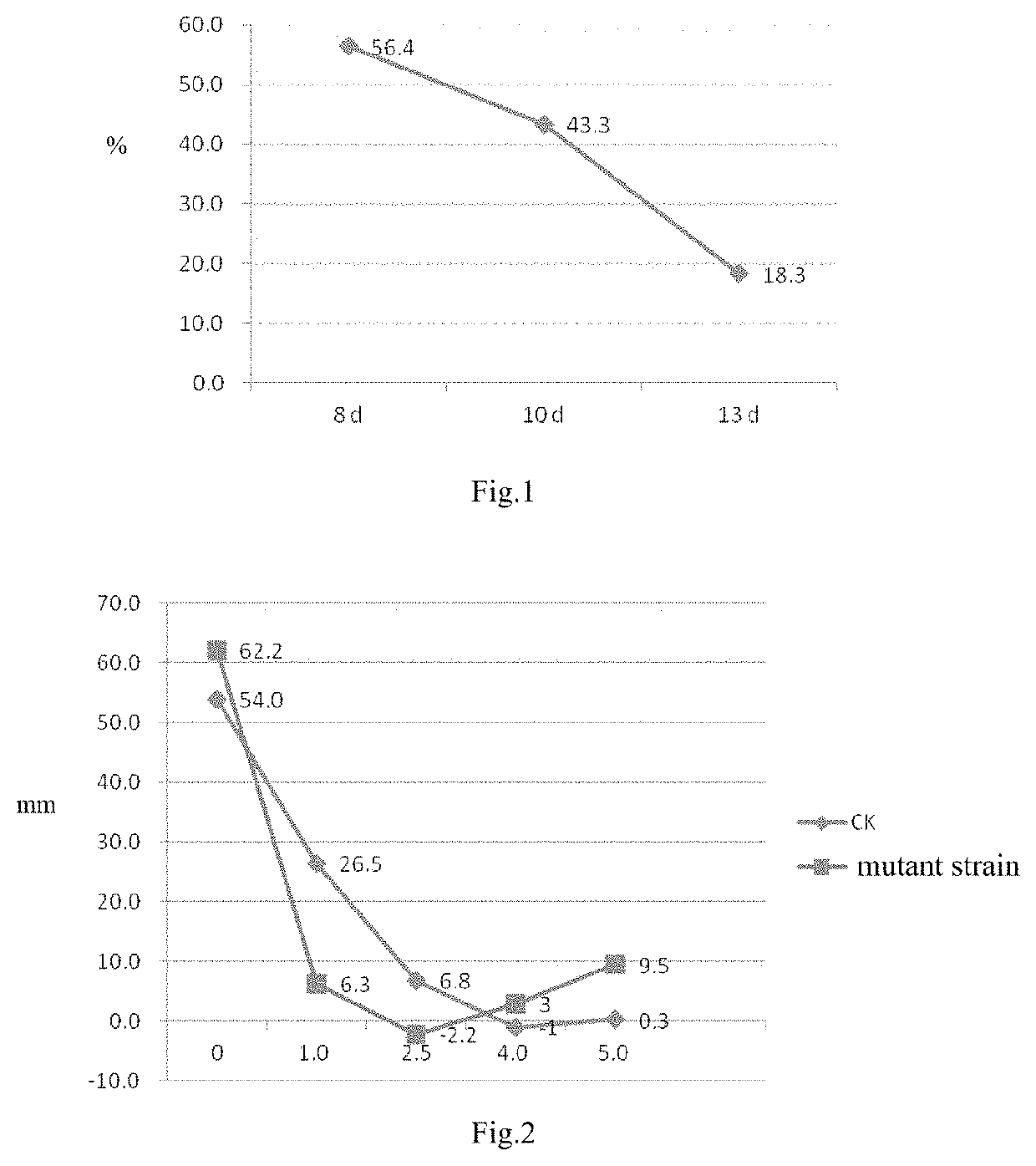
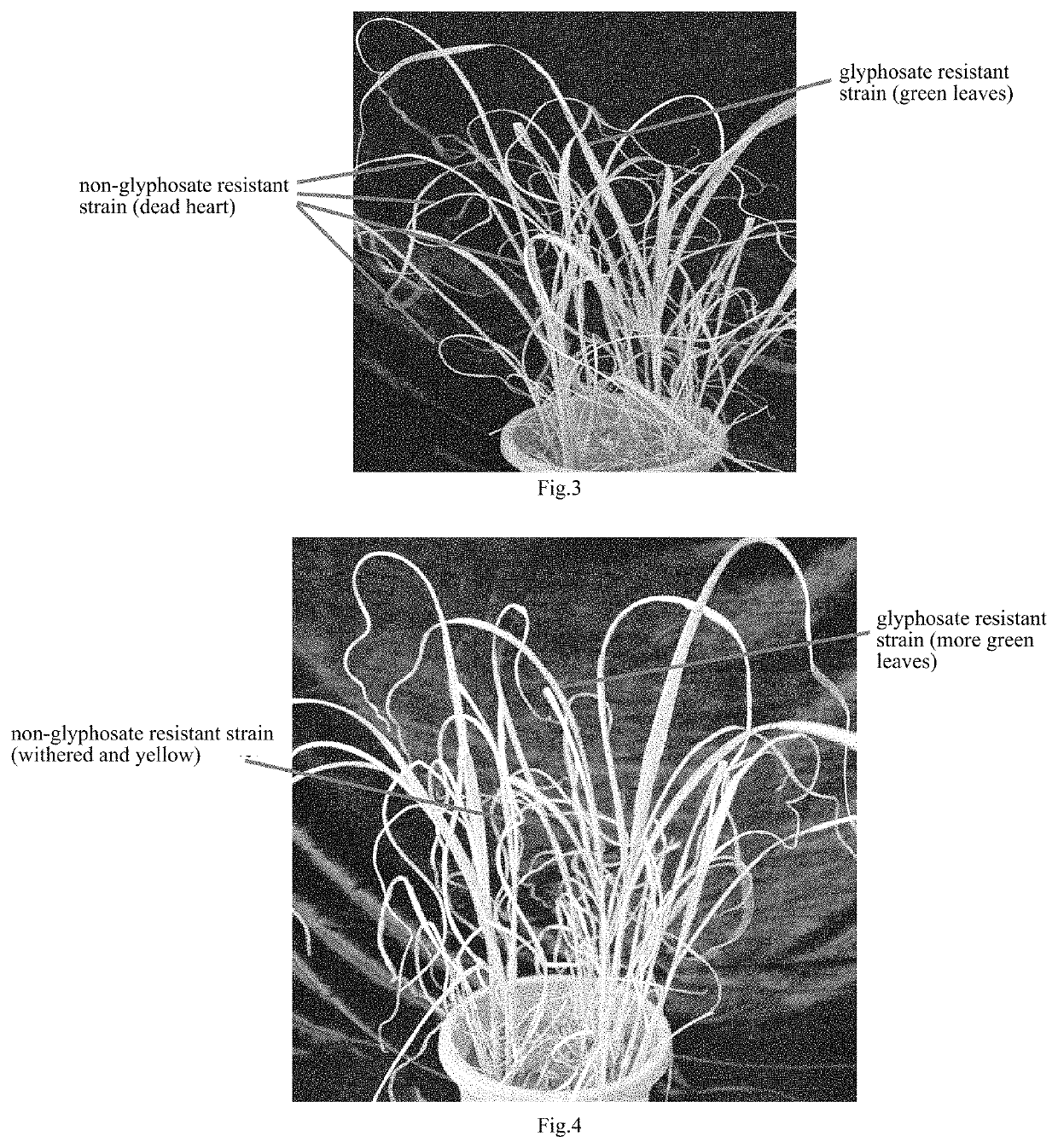
Method for conducting high-throughput and directed mutagenesis for sugarcane resistance to glyphosate by plasma
ActiveUS20210345571A1Easy to operateReduce pollutionPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGlyphosateSugar cane
The present invention relates to a method for conducting high-throughput and directed mutagenesis for sugarcane resistance to glyphosate by plasma. The method is as follows: sugarcane embryonic calli are irradiated by a plasma instrument under a sterile condition for mutagenesis, wherein the mutagenesis power is 140˜200 W, the discharging distance is 35˜45 mm, the mutagenesis time is 110˜140 s and the protective gas is nitrogen; buffering culture, moderate / high concentration of glyphosate stress screening, differentiation into seedlings, glyphosate stress screening of bottle seedlings and stress screening via spraying glyphosate on the leave surfaces of potted plants are conducted for the treated calli. The present invention has the advantages of safe operation, simplicity, practicability, high handling capacity, low contamination, and due to implementation of directed stress screening, high screening efficiency, decreased subsequent screening workload and visual identification of resistant mutant strains.
Owner:INST OF NANFAN & SEED IND GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Lucid ganoderma fungus with high glycopeptide composite yield, its mutagen breeding method and use
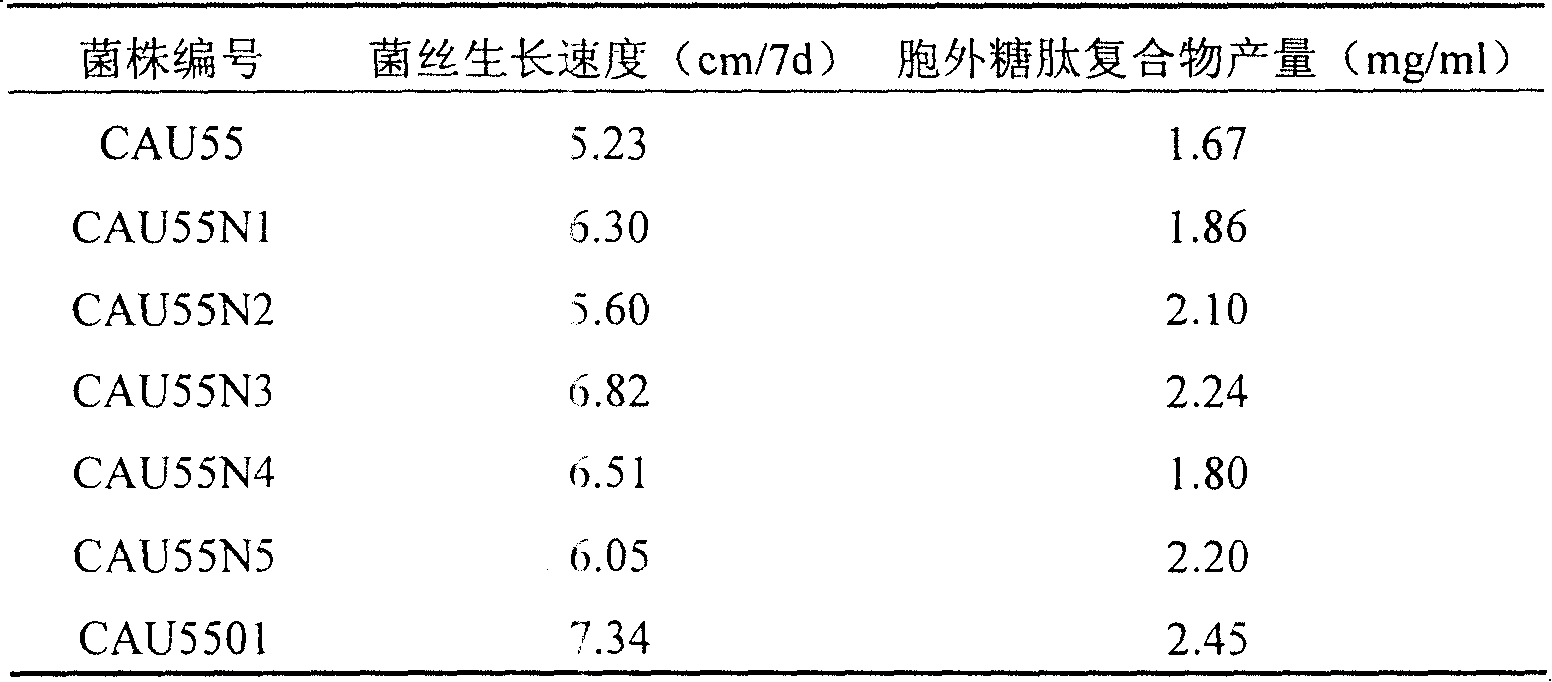
InactiveCN100387704CChange heredityGuaranteed stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesFiltrationBiotin
The invention involves a kind of Ganoderma Lucidum that can produce saccha-peptide complexes in high yield, the method of mutagenesis and selection, the purpose of it. The name of the fungi is Ganoderma Lucidum according to Systematic nomenclature, held by 2004-11-22 in , and the holding number is CGMCC No.1251. The first step of mutagenesis and selection is to culture the Ganoderma Lucidum CAU55 which is bought from as the initial strain and the holding number of which is CGMCC 5.533 in solid medium and fluid medium in turn and get the mycelia solution of the initial strain CAU55. The second step is to treat the mycelia solution with enzymolysis and filtration and get the protoplast deposit of the initial strain CAU55. The last step is to treat the protoplast with ultraviolet mutagenesis and regenerative cultivation, in the end getting the Ganoderma Lucidum CAU5501 that can produce saccha-peptide complexes in high yield. This kind of Ganoderma Lucidum is useful for preparing the feed additive of saccha-peptide complexes from liquid fermentation and some microbiological pharmaceutics like immunopotentiator and beneficial biotin.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for obtaining cotton mutants by using heavy ion beam mutagenesis
ActiveCN109984033AImprove seed vigorIncrease vitalityPlant genotype modificationHeavy ion beamSelfing
The invention discloses a method for obtaining cotton mutants by using heavy ion beam mutagenesis. The method comprises the steps of utilizing heavy ion beams to carry out mutagenesis, covering cottonseeds subjected to mutagenesis with films, and then sowing the seeds; transplanting mutagenized plants when two leaves and one sprout of each mutagenized plant grow out; carrying out flower sealing and selfing treatment on all plants of M1 generation; harvesting selfing bolls of single plants after the plants are mature; adopting plant lines for sowing; carrying out analysis and investigation onthe characteristics of plants of M2 generation in a growth period; screening out mutants different in phenotypic variation; harvesting the plants one by one, and continuing planting according to the plant lines until the mutants with stable phenotypic variation are obtained.
Owner:COTTON RES INST HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FOREST SCI
A plant material chemical mutagenesis treatment device
ActiveCN103535272BKeep aliveIncrease sensitivityPlant phenotype modificationPlant genotype modificationTemperature controlReaction temperature
The invention discloses a chemical mutagenesis processing device for plant material, wherein the chemical mutagenesis processing device for plant material comprises a frame (1), at least one mutagenesis processing chamber (5) and at least one continuous dosing chamber (4), wherein the at least one mutagenesis processing chamber (5) is used for placing plant material for mutagenesis, arranged on the frame (1) and provided with a medicine liquid inlet (15) and a discharge hole (19); the inside of the mutagenesis processing chamber (5) is provided with a temperature control heating device (16) which is used for heating the medicine liquid and detecting the temperature; at least one continuous dosing chamber (4) is used for holding the medicine liquid, arranged on the frame (1) to be corresponding to the mutagenesis processing chamber (5) and provided with the medicine liquid outlet (12); the height of the medicine liquid outlet (12) is greater than the height of the corresponding medicine liquid inlet (15); the medicine liquid outlet (12) is connected to the corresponding medicine liquid inlet (15) through the liquid inlet pipe (32); the liquid inlet pipe (32) is provided with a liquid inlet valve (31). Through the device, the best reaction temperature can be kept for the whole mutagenesis process; the activity of the mutagenic agent is guaranteed; the device is high in mutagenesis efficiency and good in effect.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
A treatment method for improving the rate of rice radiation-induced healing distortion
InactiveCN106718862BIncrease chance of mutagenesisReduce mortalityPlant genotype modificationCobalt-60Generation rate
The invention discloses a treatment method capable of increasing the rice healing aberration generation rate by irradiation mutagenesis. The treatment method includes the steps of (1), exposing rice seeds to high-dose cobalt-60 gamma-ray to radiation; (2), subjecting the rice seeds obtained after the step (1) to microwave irradiation; (3), exposing the rice seeds obtained after the step (2) to low-dose cobalt-60 gamma-ray to radiation; (4), subjecting the rice seeds obtained after the step (3) to microwave irradiation; (5), cultivating the rice seeds obtained after the step (4) and performing excellent character selection, superior single selection and excellent resource and variety identification. The treatment method treats the rice seeds by combining cobalt-60 gamma-ray irradiation with microwave irradiation, so that the restriction that variation types are generated through single mutagenesis is overcome, and mutagenesis efficiency is improved.
Owner:湖南省核农学与航天育种研究所
Chemical mutagenesis processing device for plant material
ActiveCN103535272AKeep aliveIncrease sensitivityPlant phenotype modificationPlant genotype modificationTemperature controlCompound (substance)
The invention discloses a chemical mutagenesis processing device for plant material, wherein the chemical mutagenesis processing device for plant material comprises a frame (1), at least one mutagenesis processing chamber (5) and at least one continuous dosing chamber (4), wherein the at least one mutagenesis processing chamber (5) is used for placing plant material for mutagenesis, arranged on the frame (1) and provided with a medicine liquid inlet (15) and a discharge hole (19); the inside of the mutagenesis processing chamber (5) is provided with a temperature control heating device (16) which is used for heating the medicine liquid and detecting the temperature; at least one continuous dosing chamber (4) is used for holding the medicine liquid, arranged on the frame (1) to be corresponding to the mutagenesis processing chamber (5) and provided with the medicine liquid outlet (12); the height of the medicine liquid outlet (12) is greater than the height of the corresponding medicine liquid inlet (15); the medicine liquid outlet (12) is connected to the corresponding medicine liquid inlet (15) through the liquid inlet pipe (32); the liquid inlet pipe (32) is provided with a liquid inlet valve (31). Through the device, the best reaction temperature can be kept for the whole mutagenesis process; the activity of the mutagenic agent is guaranteed; the device is high in mutagenesis efficiency and good in effect.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
A kind of allopolyploid induction production method of hybrid pennisetum
InactiveCN107155875BSimple and fast operationEasy to obtainHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAnimal scienceColchicine
The invention relates to an allopolyploid induction growth method of hybridized Chinese pennisetum. The method comprises the following steps: immersion of allotriploid hybridized Chinese pennisetum F1 seeds in a mutagen containing colchicine and dimethylsulfoxide, initial culture, polyploid identification, proliferation culture, expanded production and transplanting. The method allows a large number of mutagenic seedlings to be obtained in a short time, greatly improves the culture efficiency and saves the production cost.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
A kind of method utilizing ems mutagenesis to create watermelon mutant
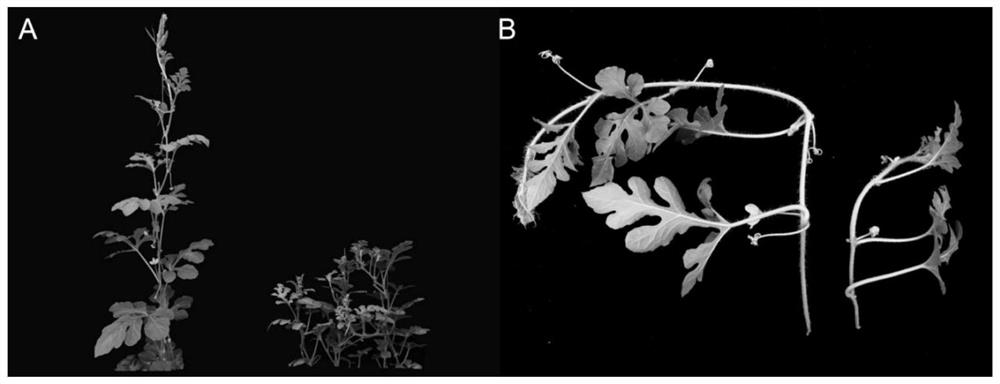
ActiveCN112640779BOvercome the disadvantages of damaging the female flowers of watermelonImprove mutagenesis efficiencyPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention belongs to the technical field of watermelon breeding, and in particular relates to a method for using EMS mutagenesis to create watermelon mutants. The method includes collecting fully open male flower anthers, fully stirring the anthers with EMS-paraffin oil solution to obtain EMS-treated pollen, dipping the pollen to pollinate the open female flowers on the same day, and spraying evenly the female flowers pollinated by EMS pollen with an appropriate concentration of gualin Ovary, harvesting and planting M0 generation seeds, and obtaining watermelon EMS mutant individuals with rich variation in M1 generation. Various mutants such as male sterility, dwarfing, tetraploid, and leaf deformity can be obtained through the present invention, which effectively solves the problems of narrow genetic background, less genetic variation, lack of excellent germplasm, etc. in watermelon functional gene research and variety breeding. The low efficiency of germplasm creation and other technical bottlenecks can be used to construct a watermelon mutant library, which is convenient for functional gene research, can greatly promote the mining and application of excellent watermelon genes, and provide material support for the breeding of excellent new varieties.
Owner:PEKING UNIV INST OF ADVANCED AGRI SCI +1
A kind of polyploid induction method of mat grass
InactiveCN106665343BStrong poisonous effectImprove stabilityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsHigh concentrationPre treatment
Owner:湖南新春农业生物高科技有限公司 +1
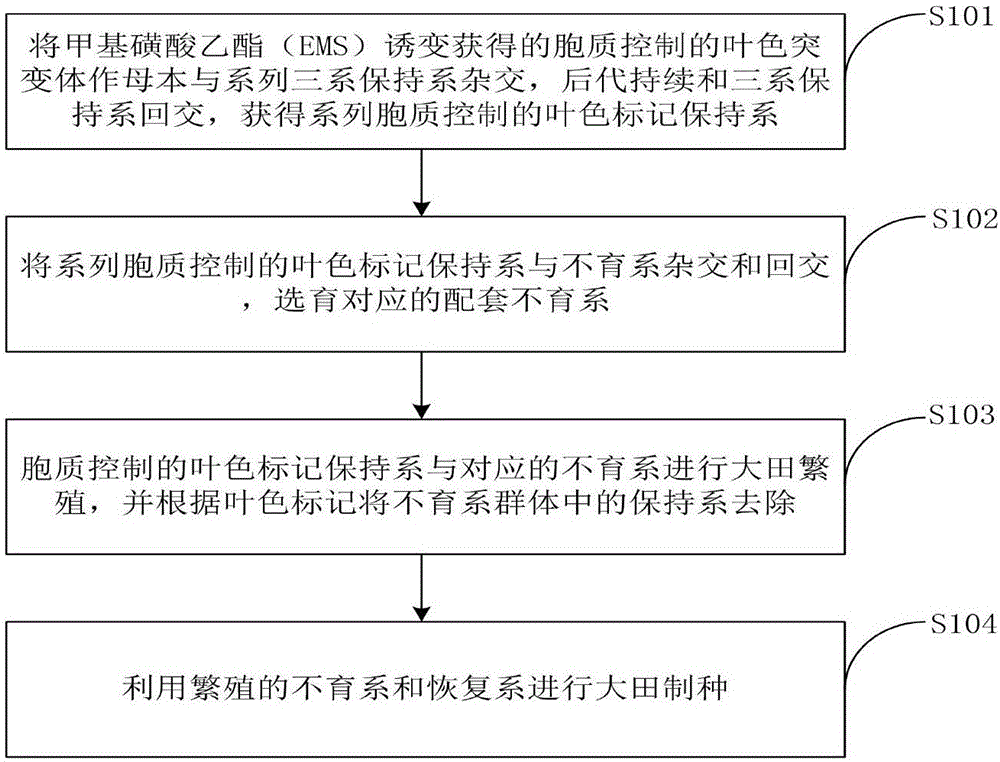
Method for improving purity of hybrid rice seeds through cytoplasm-controlled leaf color mutant
InactiveCN106234210AImprove mutagenesis efficiencyHigh purityPlant genotype modificationEthylmethane SulfonateColor marker
The invention discloses a method for improving the purity of hybrid rice seeds through a cytoplasm-controlled leaf color mutant. The method comprises the steps that the cytoplasm-controlled leaf color mutant obtained through ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) mutagenesis is taken as a female parent to cross with a three-line maintainer line, later generations continuously back-cross with the three-line maintainer line, and a serial cytoplasm-controlled leaf color marker maintainer line is obtained; the serial cytoplasm-controlled leaf color marker maintainer line crosses and back-crosses a sterile line, and a corresponding matched sterile line is bred; the cytoplasm-controlled leaf color marker maintainer line and the corresponding sterile line are subjected to large-field propagation, and the maintainer lines in the sterile line group are removed according to a leaf color marker; the propagated sterile systems and a restoring line are subjected to large-field seed production. According to the method, the sterile lines and the maintainer lines are easily separated by the cytoplasm gene-controlled leaf color mutant, the maintainer lines mixed in the sterile lines can be removed from the source of sterile line propagation, and then the purity of the hybrid rice seeds is effectively improved.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Sodium azide mutagenesis treatment method of juvenile internode stems of citrus
ActiveCN108307915BFacilitate progress in creating variantsPromote progressPlant growth regulatorsBiocideCitrus volkamerianaSodium azide
The invention discloses a sodium azide mutagenizing method for juvenile citrus internodal stem segments, comprising: I, taking citrus young plantlets more than 1 mm in stem thickness and 5-10 cm in plantlet height, cutting to obtain internodal stem segments, soaking the internodal stem segments in a mutagenizing liquid, mutagenizing in darkness for 1-3 h, wherein the mutagenizing liquid includes sodium azide having a concentration of 0.5-2 mmol / L; II, subjecting the mutagenized internodal stem segments to tissue culture until sectional wounds of the internodal stem segments grow regenerated buds; III, using an SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) molecular markup method to detect the regenerated buds that vary, and subjecting the varied regenerated buds to rooting culture to obtain complete citrus variant plants. It is clarified that sodium azide-mutagenized juvenile citrus internodal stem segments may produce stable variant plants. The method of the invention has mutagenizing efficiency of greater than 10% and has significant mutagenizing effect and good operating convenience.
Owner:HUNAN INST OF GARDENING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com