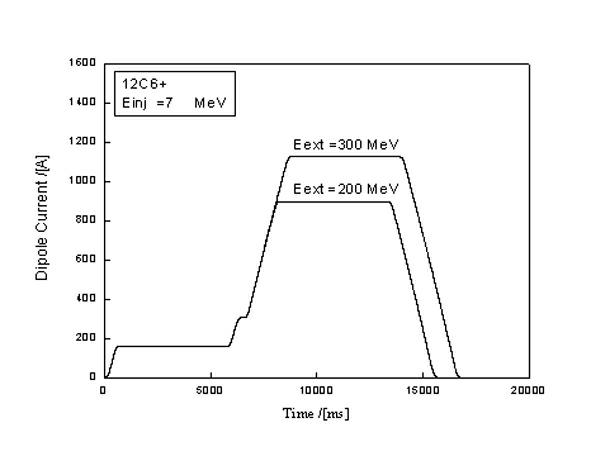
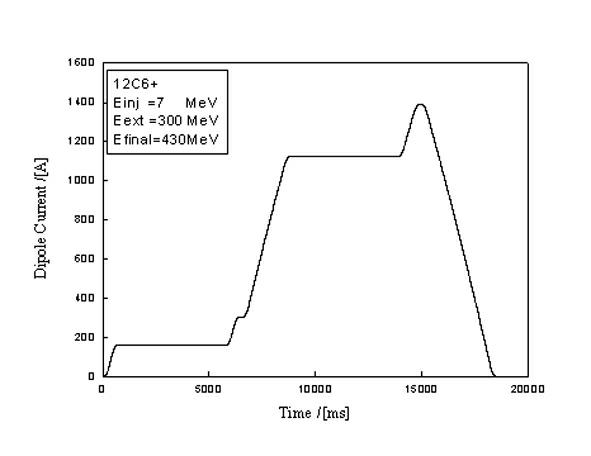
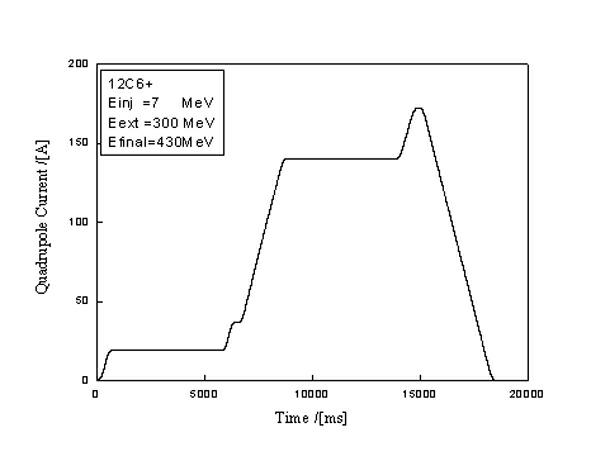
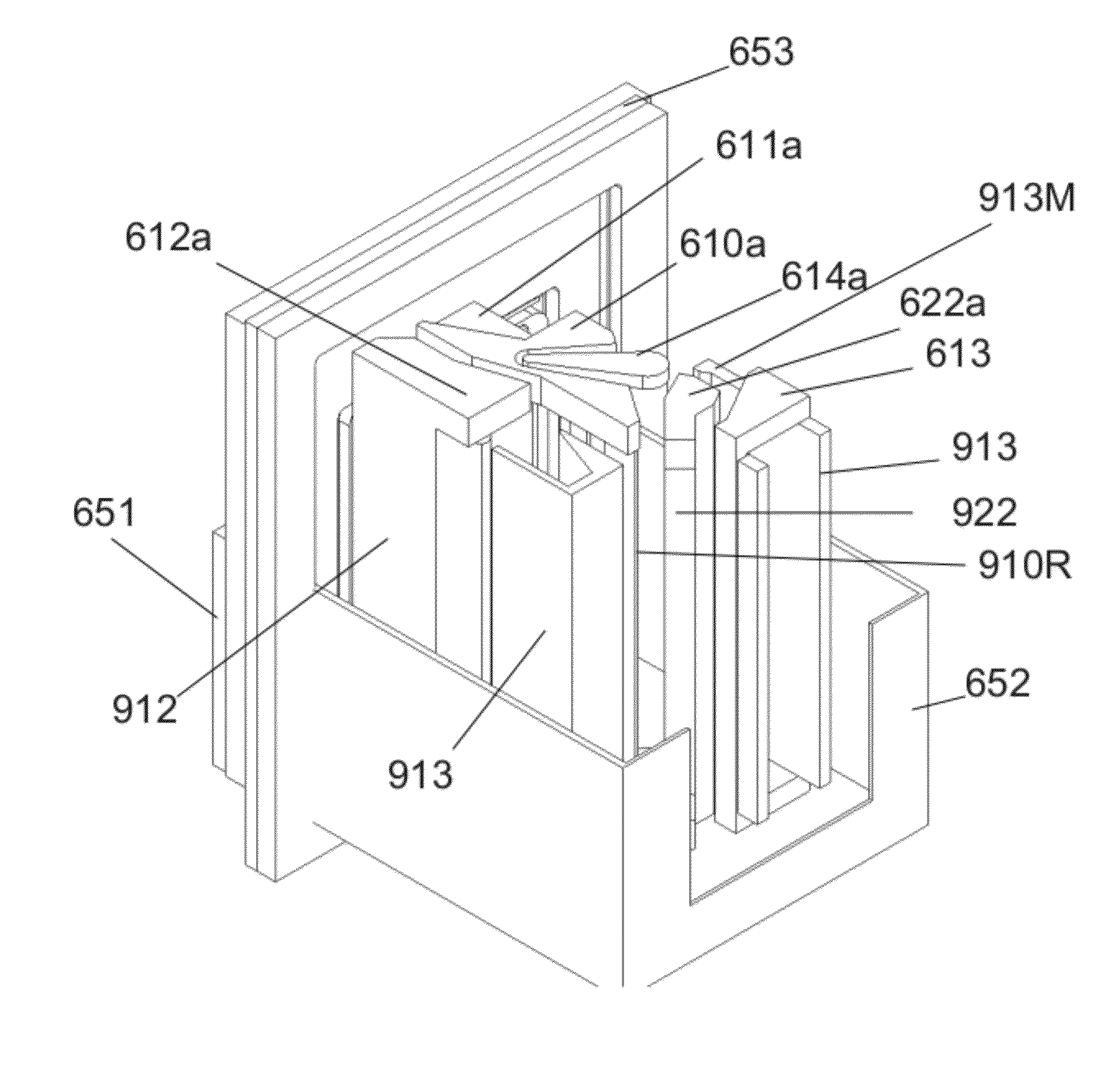
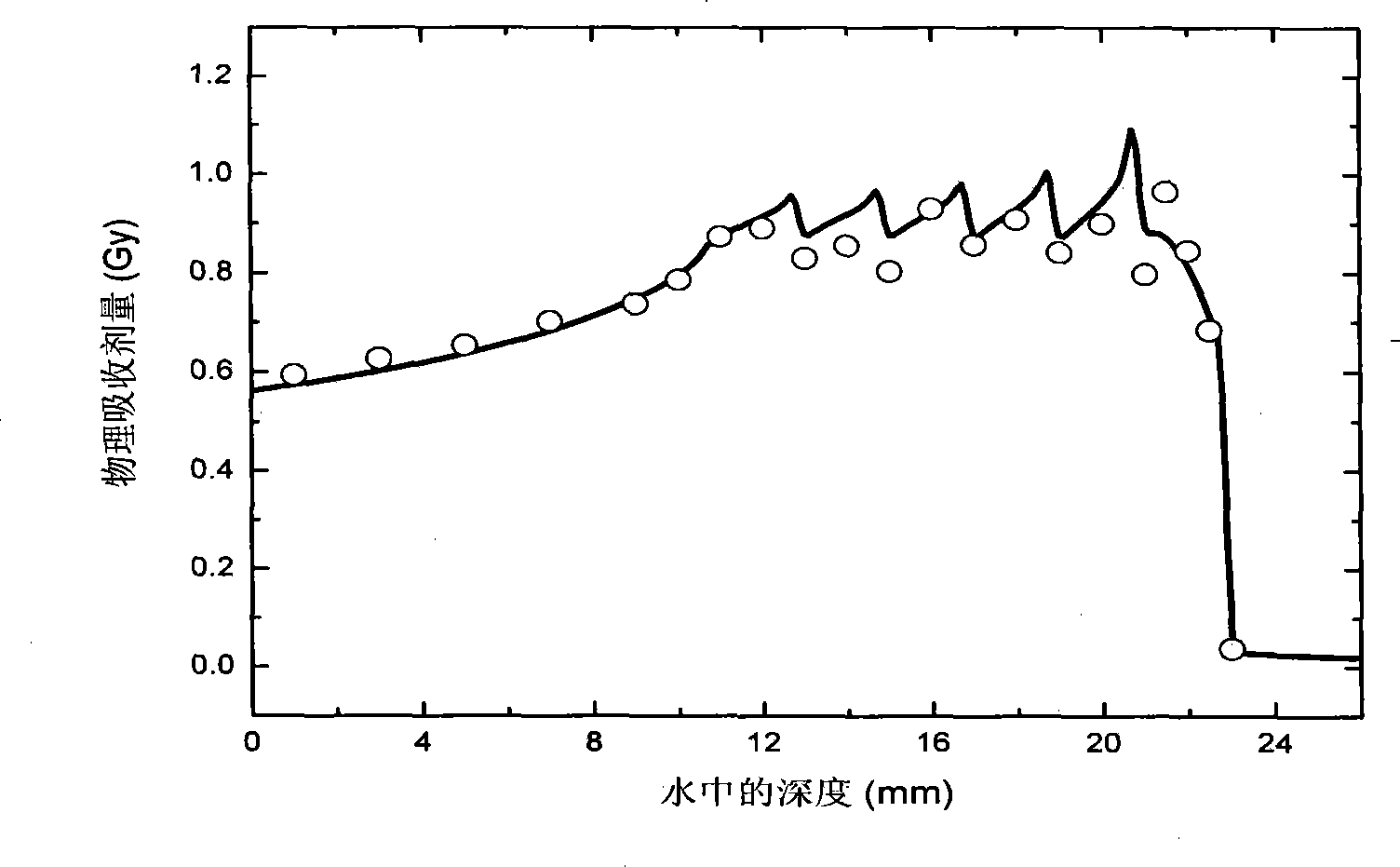
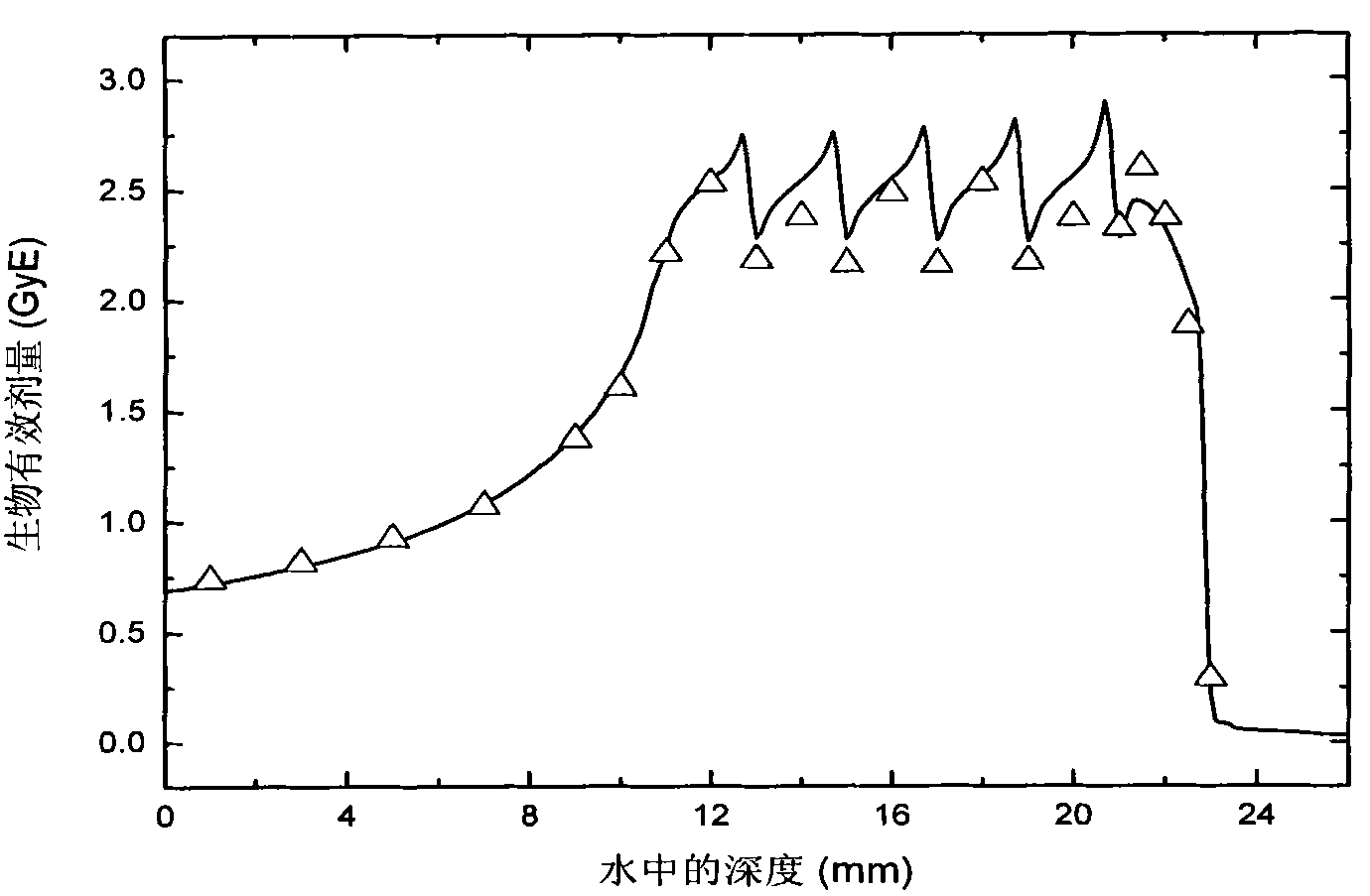
Patents
Literature
84 results about "Heavy ion beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
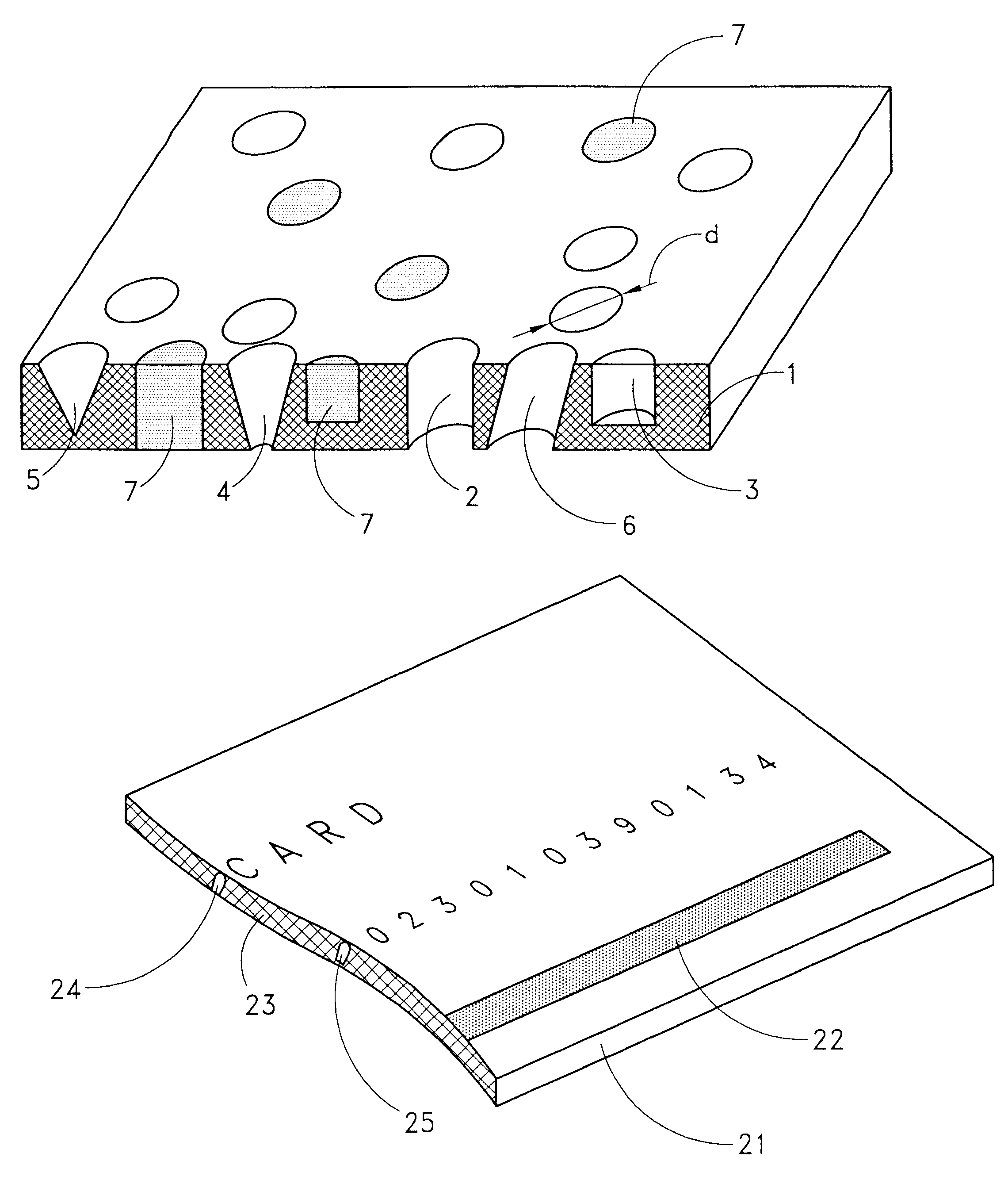
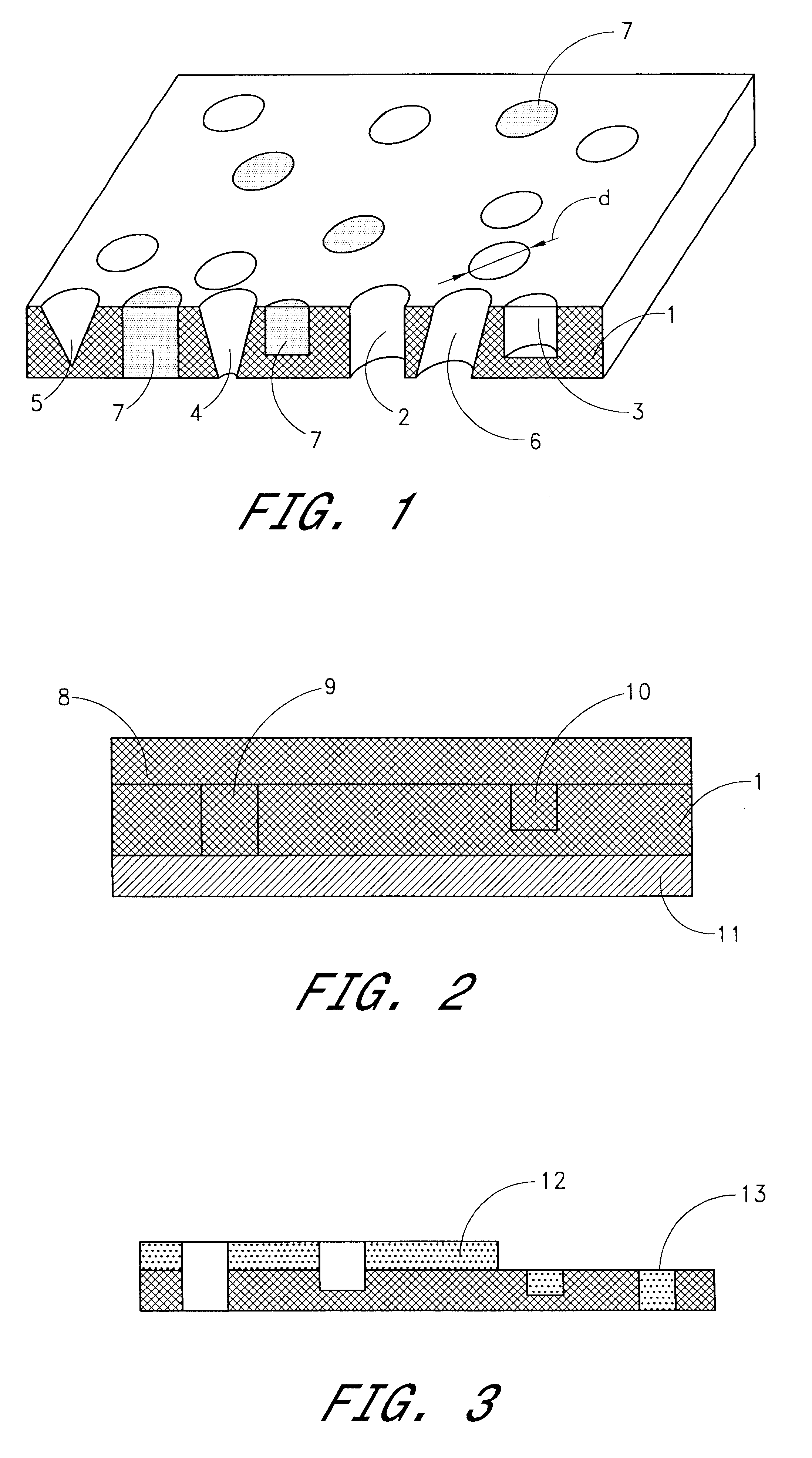
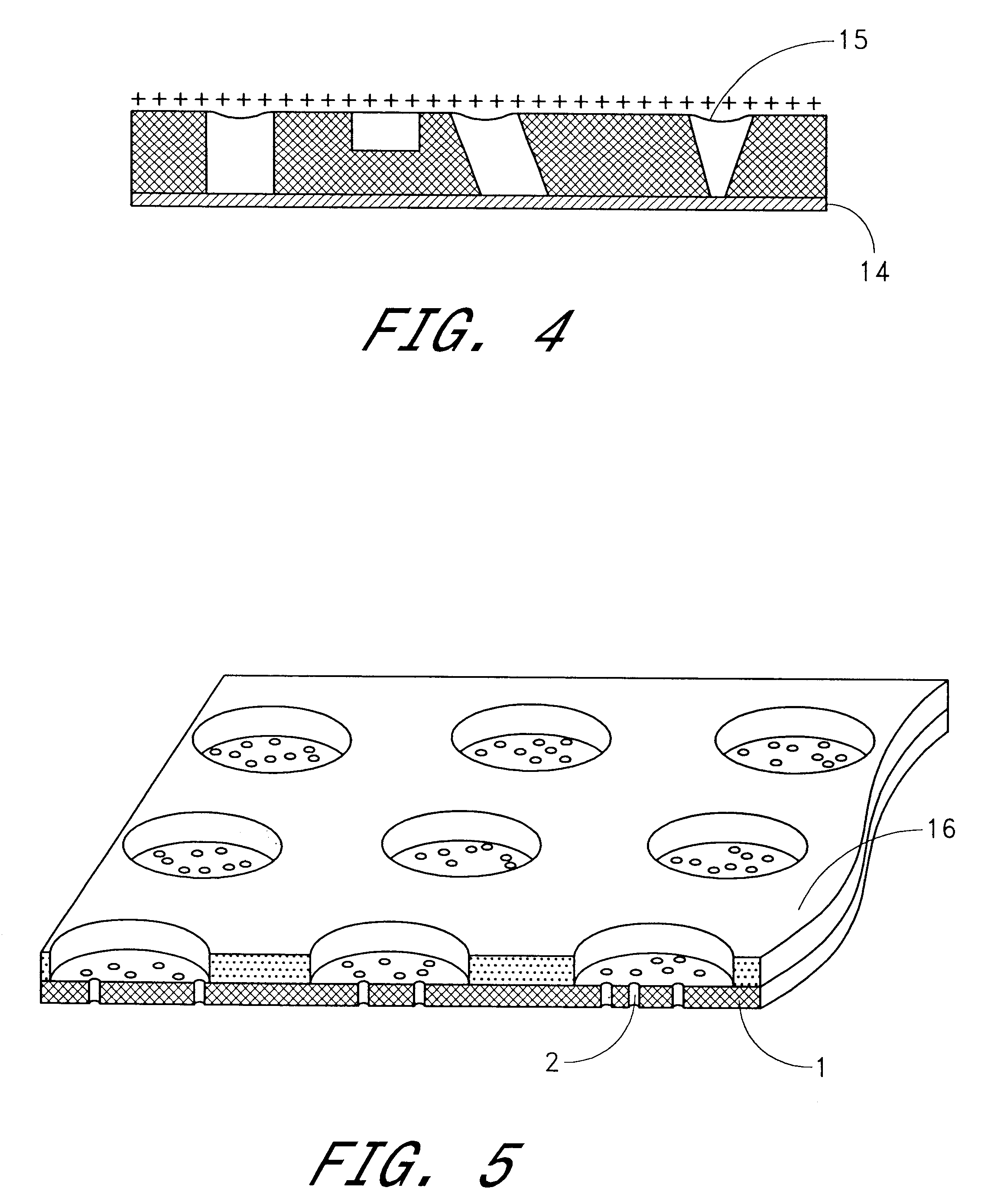
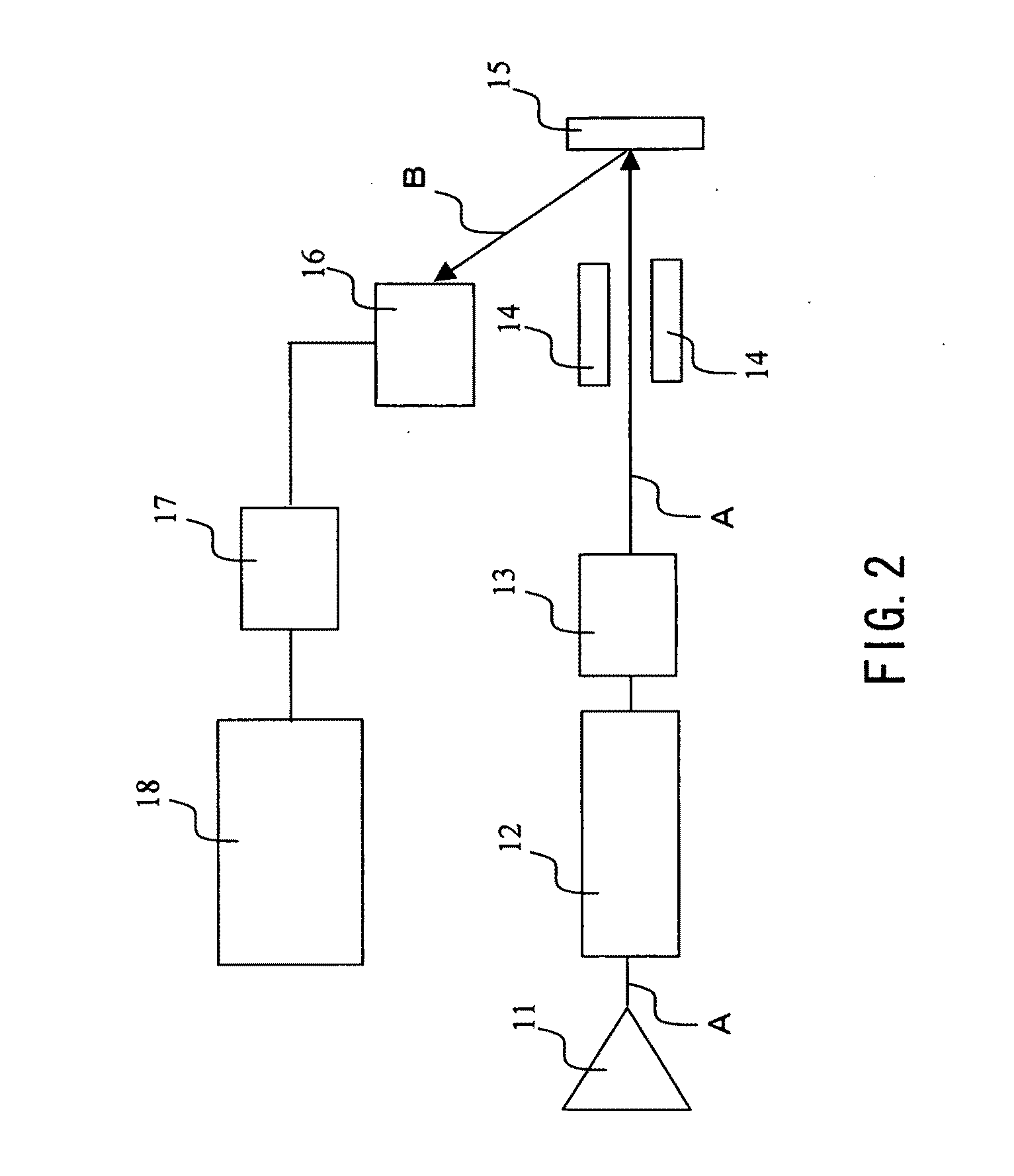
Tape data carrier, method and device for manufacturing the same
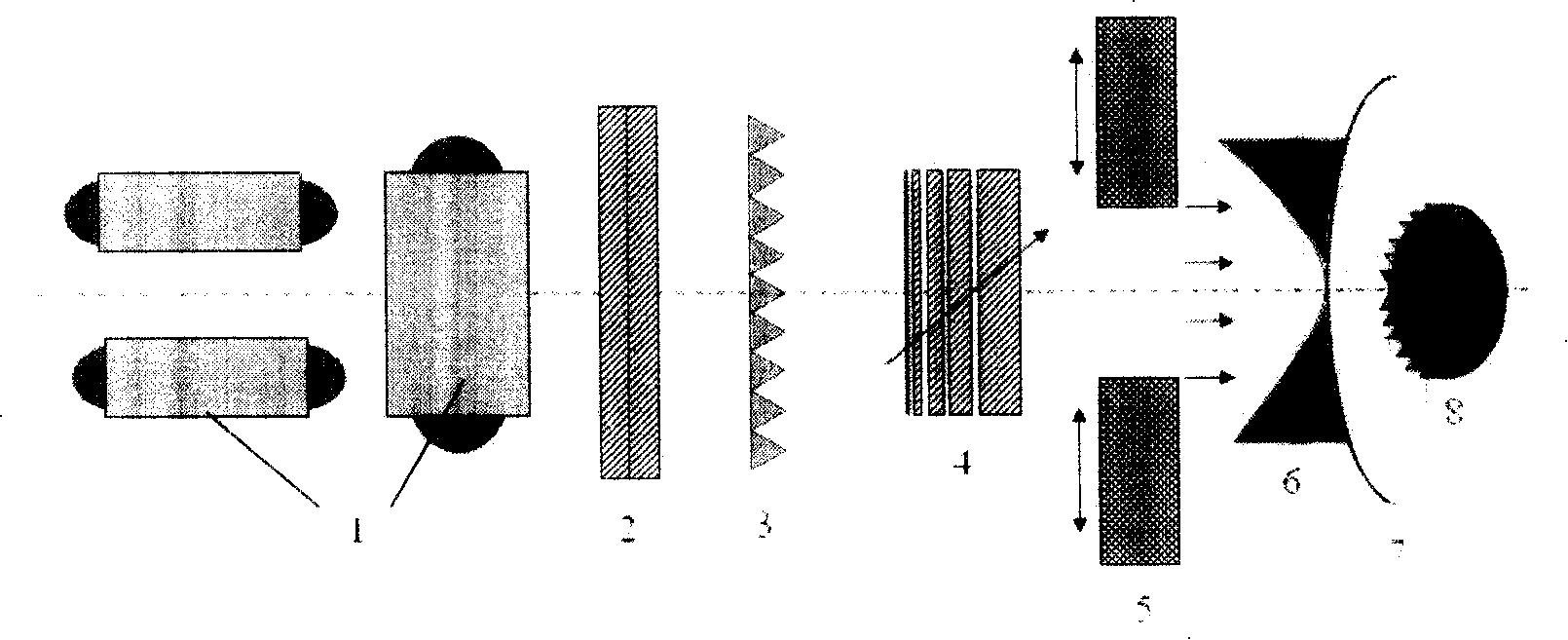
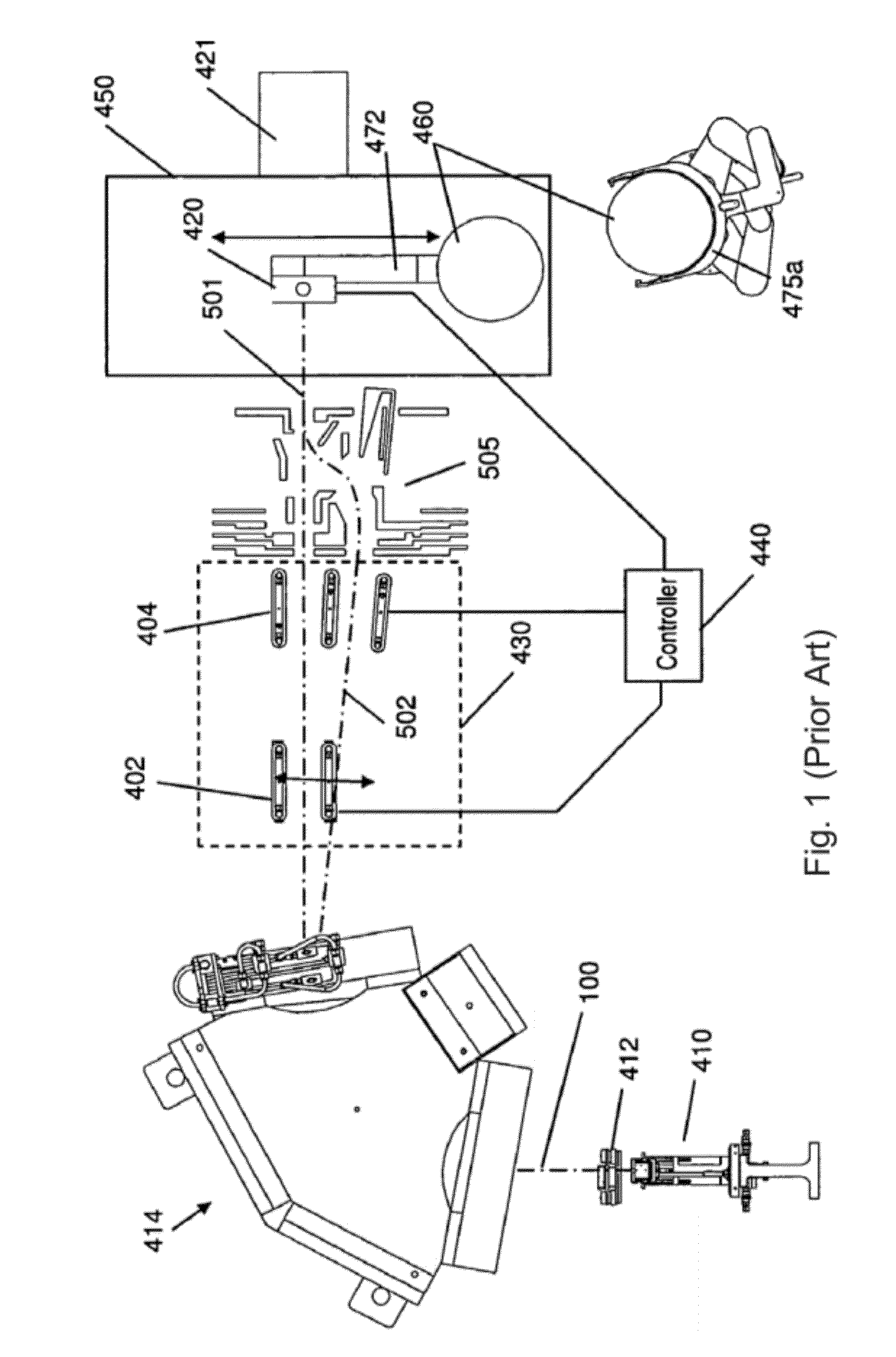
A tape data carrier for protecting articles and documents from counterfeiting and copying is formed by a polymer structure including at least one polymer layer of which at least one layer has at least one of through-perforations and pits. These through-perforations and pits are preferably between 0.001 mum and 20 mum in size and can be filled with different materials. The data carriers can carry concealed and visible macro-and micro- images created by heavy-ion bombardment of the polymer film, subsequent exposure of the bombarded film to ultraviolet radiation, and etching of the polymer film in a solvent. A device for manufacturing a data carrier of this type includes the following elements configured in series: a heavy ion source; a heavy ion beam-formation system; an ion guide; a three-dimensional amplitude modulation unit; and a target which is destined to become the data carrier. The three-dimensional amplitude modulation unit is designed to hold a matrix of wafers and is connected to a drive for rotating and translating the wafers. The drive is connected via a control unit to the three-dimensional amplitude modulation unit for positioning the target.
Owner:BELOUSOV BORIS ILICH +3
Monitoring system and monitoring method for SRAM type FPGA (field-programmable gate array) single particle functional interruption
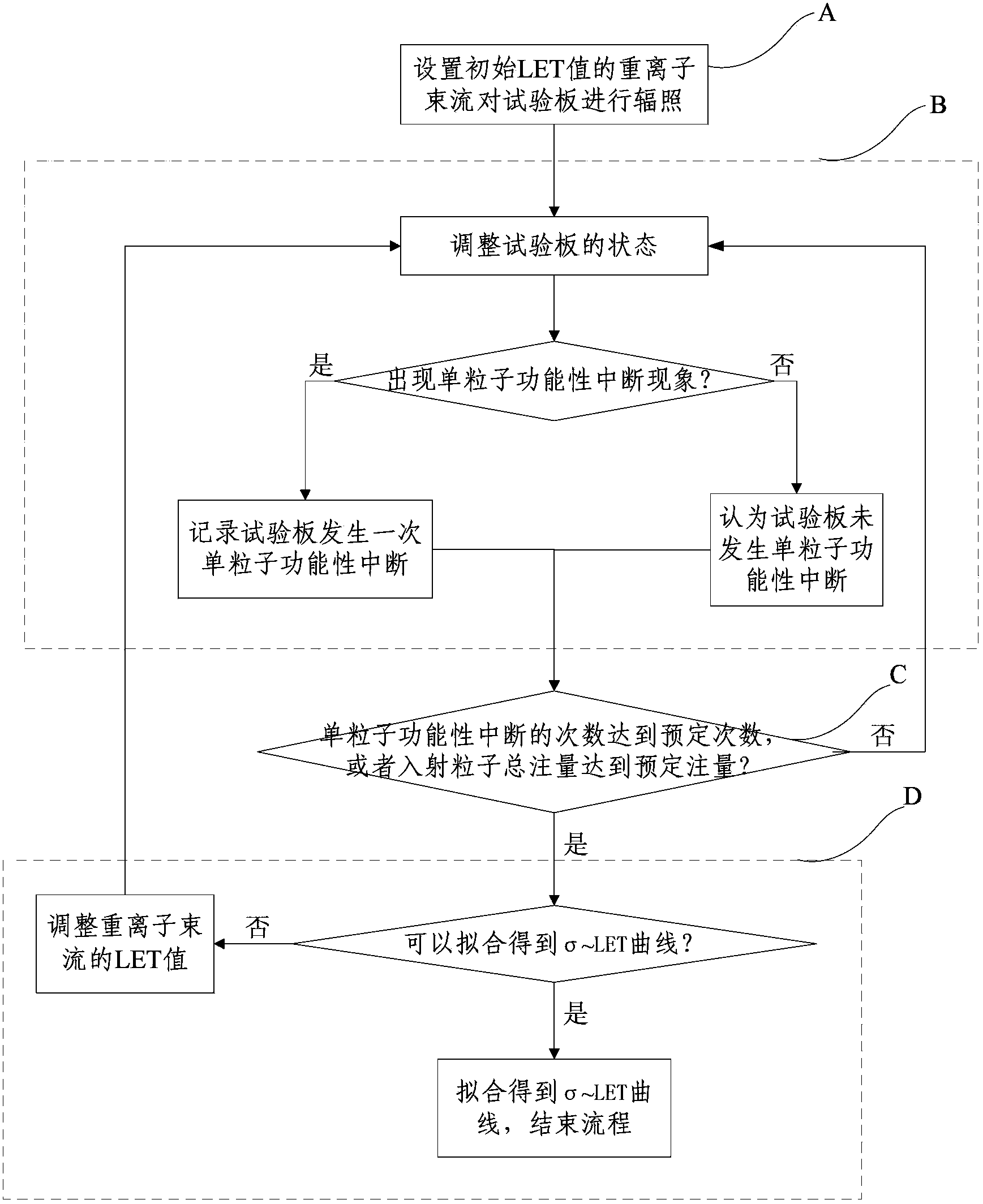
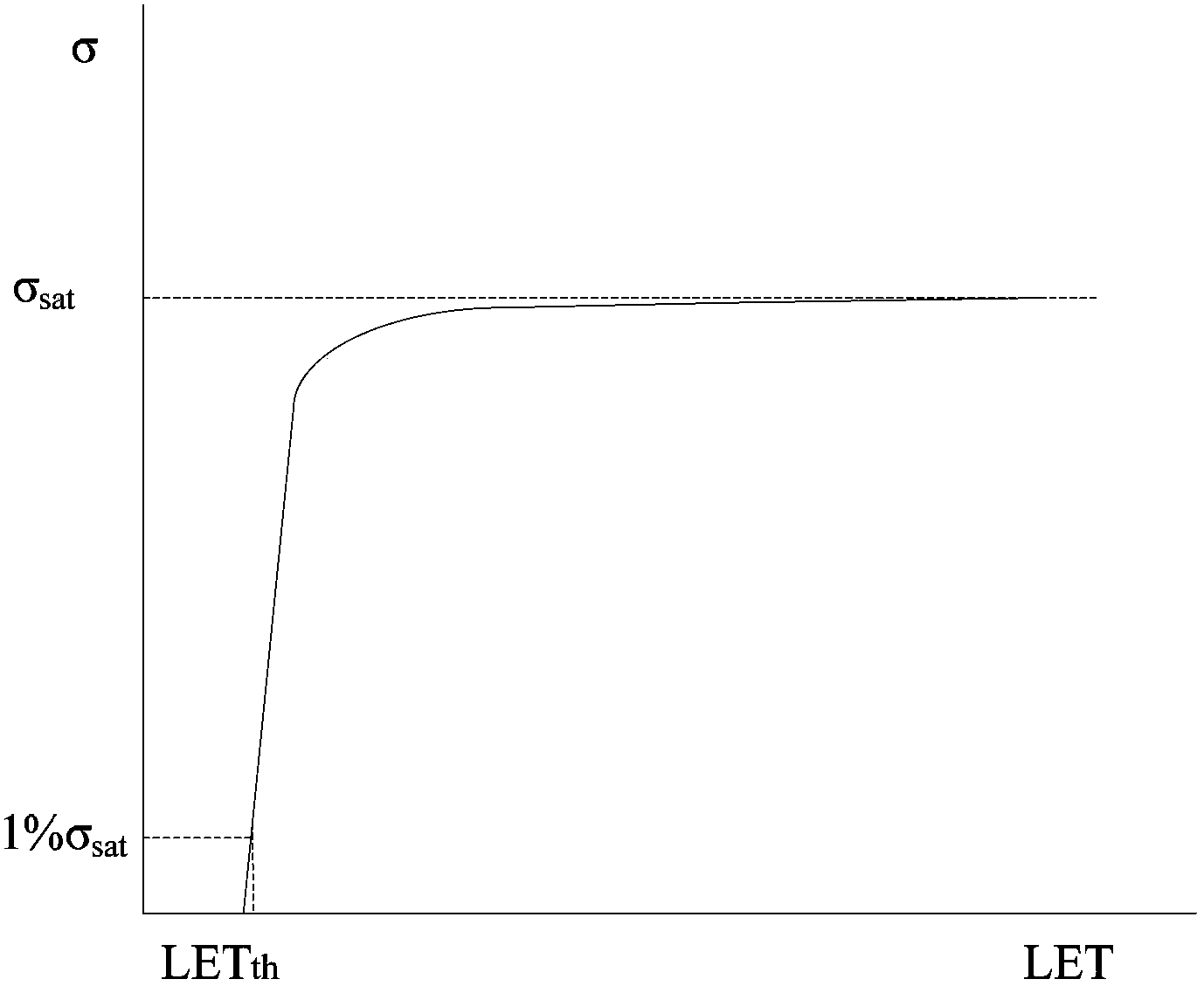
The invention discloses a monitoring system and a monitoring method for SRAM type FPGA single particle functional interruption, and relates to the field of a single particle. The method comprises the steps of: A, setting a heavy ion beam flow with an initial LET value to irradiate a test board; B, judging whether a single particle functional interruption phenomenon happens to the test board, if so, recording that the single particle functional interruption phenomenon happens one time to the test board, and if not, considering that the single particle functional interruption phenomenon does not happen to the test board; C, judging whether the test board satisfies the following condition that the number of the single particle functional interruption phenomenon reaches a predetermined number or the total injection quantity of incident particles reaches a predetermined quantity, if so, performing a step D, and if not, performing the step B; D, judging whether a [sigma]-LET curve can be obtained by means of fitting, if so, obtaining the [sigma]-LET curve by means of fitting, and if not, adjusting the LET value of the heavy ion beam flow and performing the step B. The system and the method provided by the invention are capable of predicting the SEFI rate of an FPGA in various kinds of space environments.
Owner:BEIJING SHENGTAOPING TEST ENG TECH RES INST
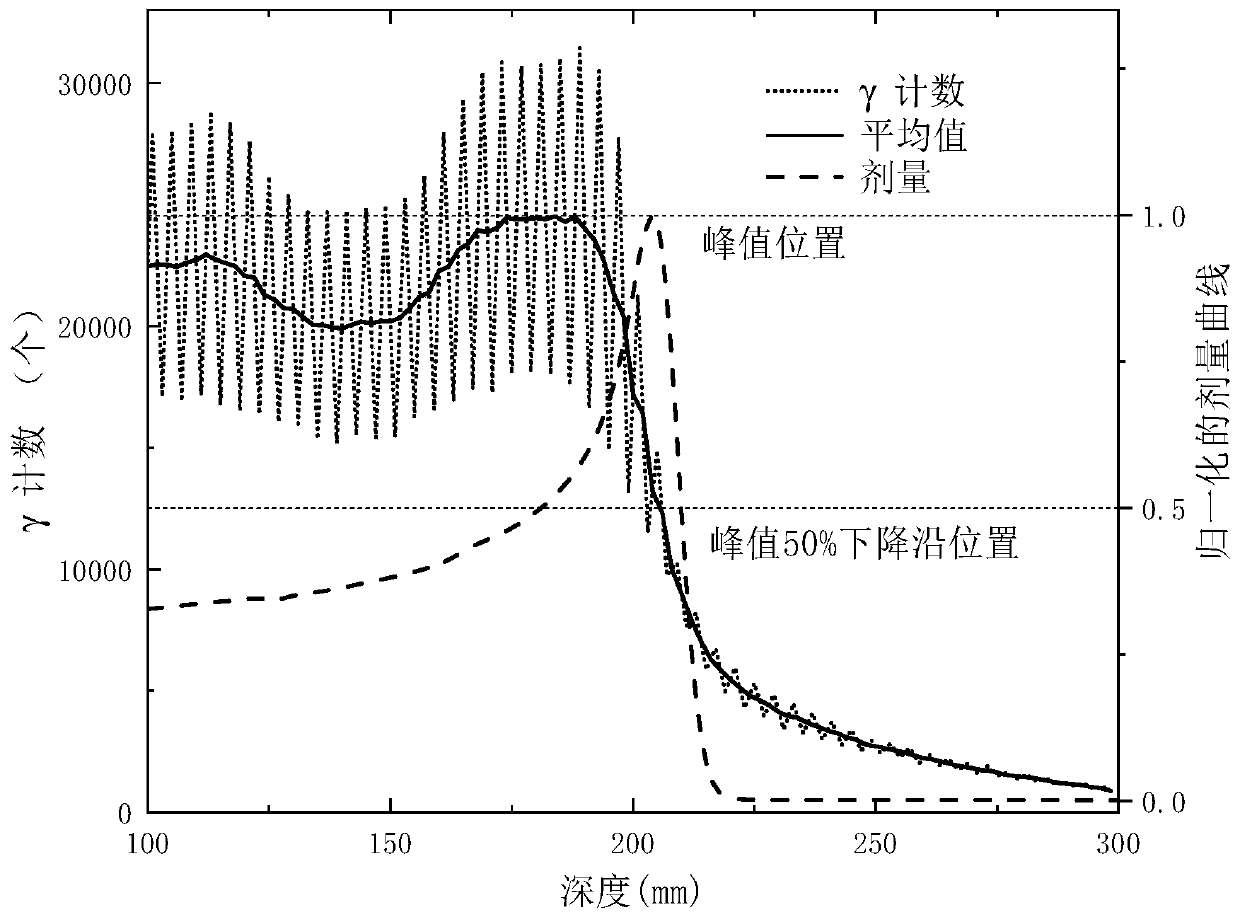
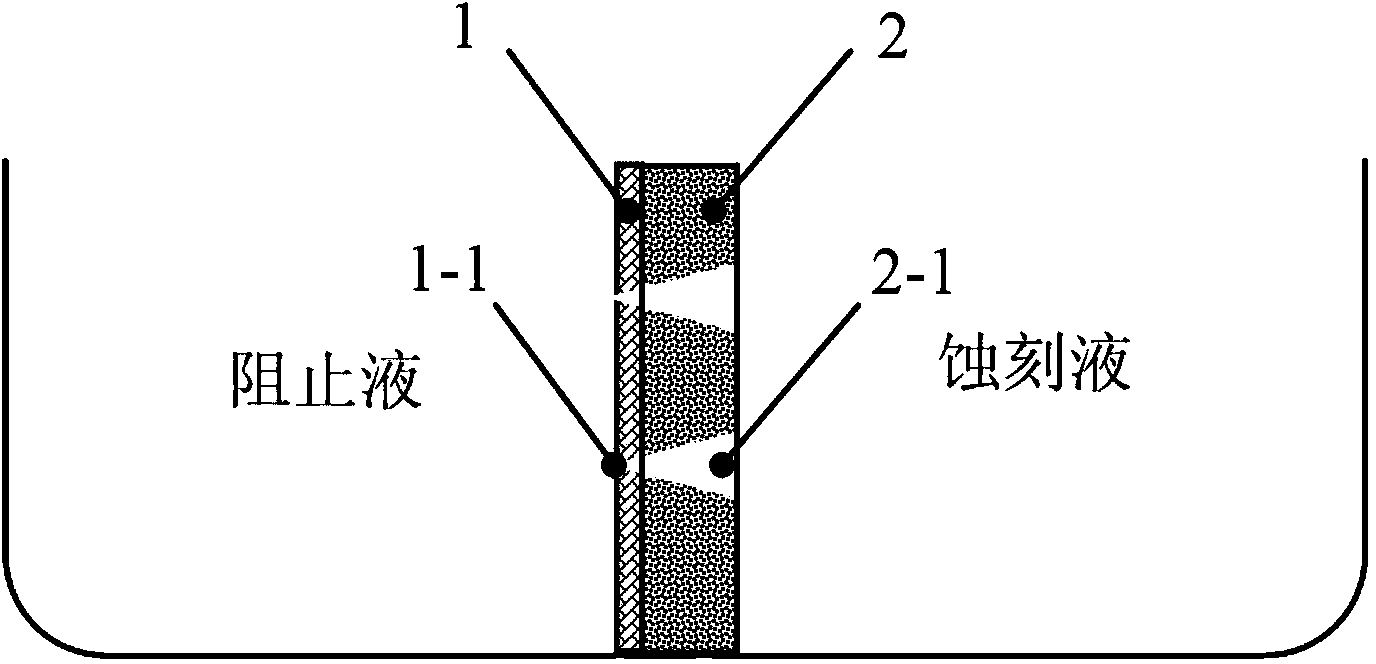
Heavy ion beam current transverse dosage distribution measuring detector and two-dimensional imaging method thereof
ActiveCN101900826ARealize two-dimensional displayX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentElectricityDose profile
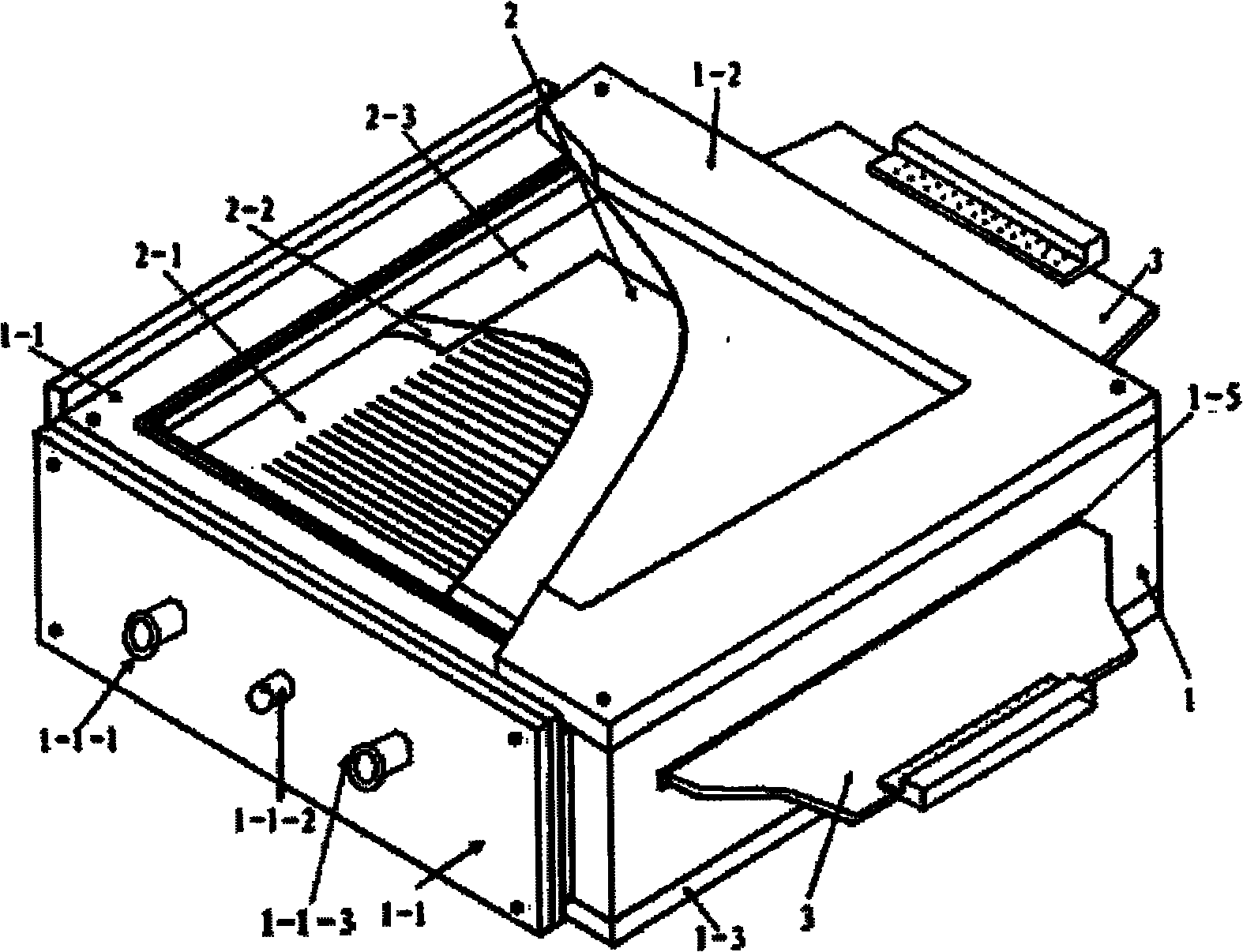
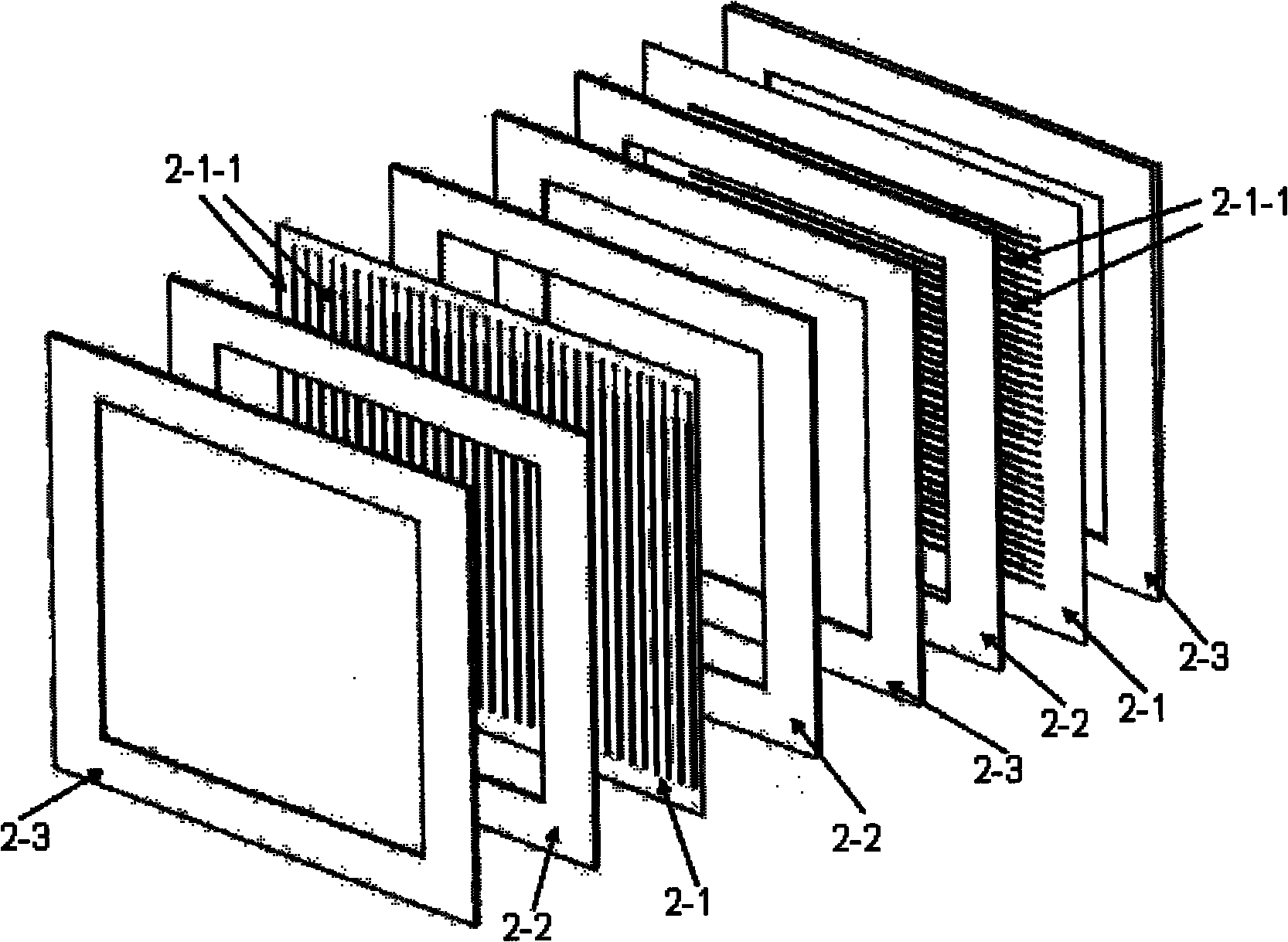
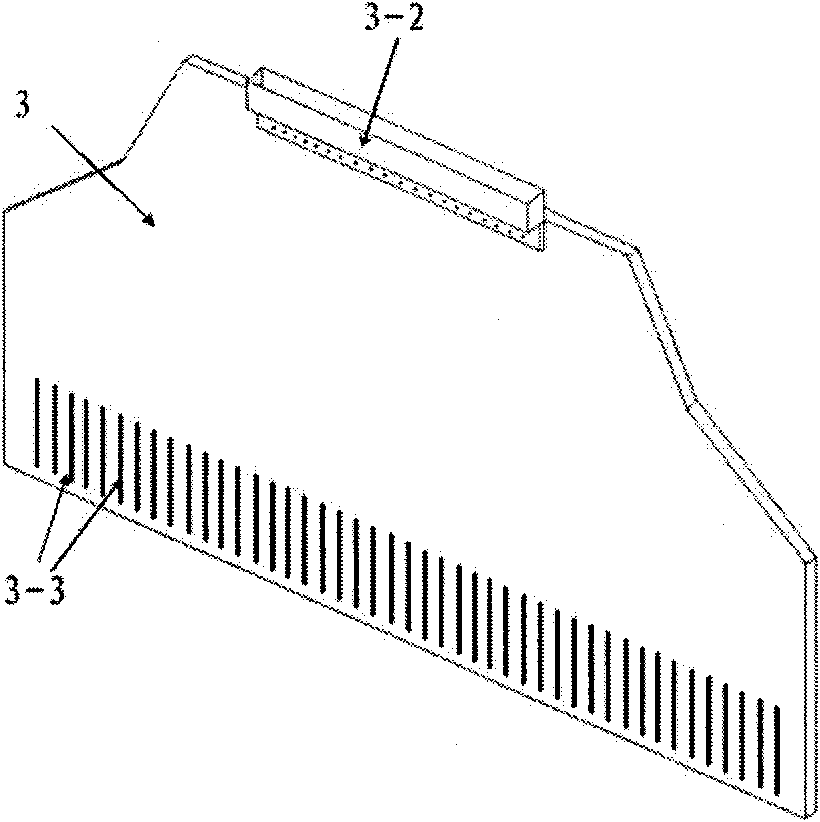
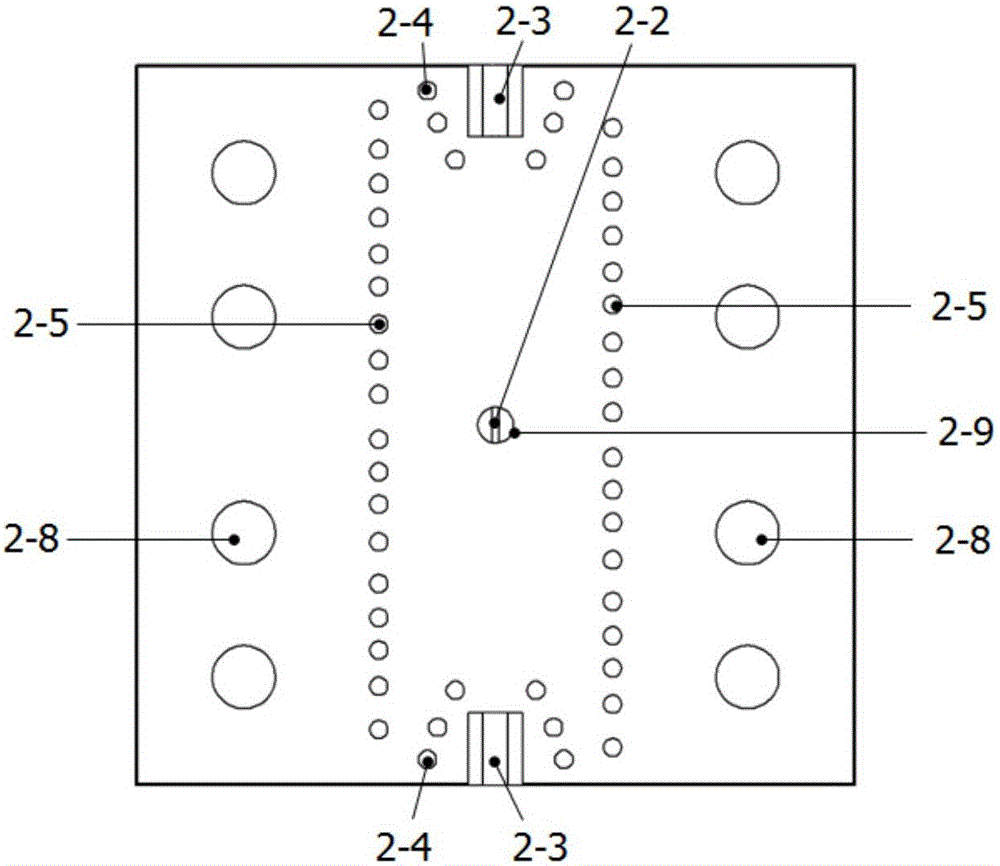
The invention relates to the field of heavy ion beam (comprising proton beam) tumor treatment technology, in particular to a heavy ion beam current transverse dosage distribution measuring detector and a two-dimensional imaging method thereof. The detector is mainly characterized by comprising a gas sealing cavity (1) in which an ionization chamber inner core (2) is arranged and a multi-path signal transfer board (3) electrically connected with the ionization chamber inner core (2); the gas sealing cavity (1) consists of a main body framework (1-1), an entrance window (1-2) and an exit window (1-3); the ionization chamber inner core (2) consists of two groups of ionization chamber units, and each ionization chamber unit consists of a signal pole (2-1), an insulating cushion board (2-2) and a high-voltage pole (2-3); and one end of the multi-path signal transfer board (3) is provided with a contact end (3-3) which is inserted into a sealing port (1-5) of the gas sealing cavity (1) and connected with the signal pole (2-1) of the ionization chamber inner core (2), while the other end is provided with a multi-core connector (3-2) which is a signal output port of a beam current profile monitoring detector.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Chemical synthesis technique of quinoxaline
InactiveCN101182313AShorten the development cycleLow costOrganic chemistryChemical synthesisQuinoxaline
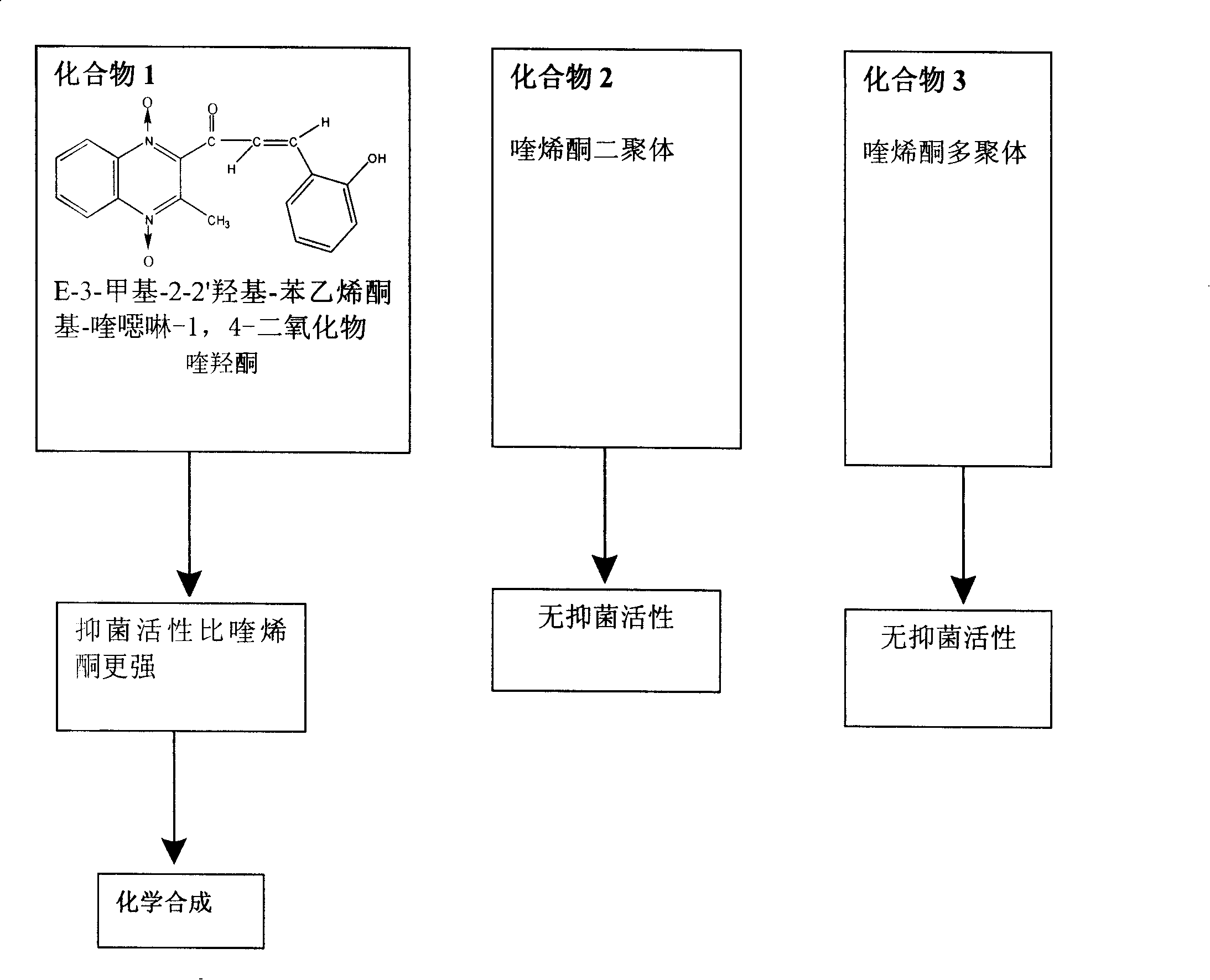
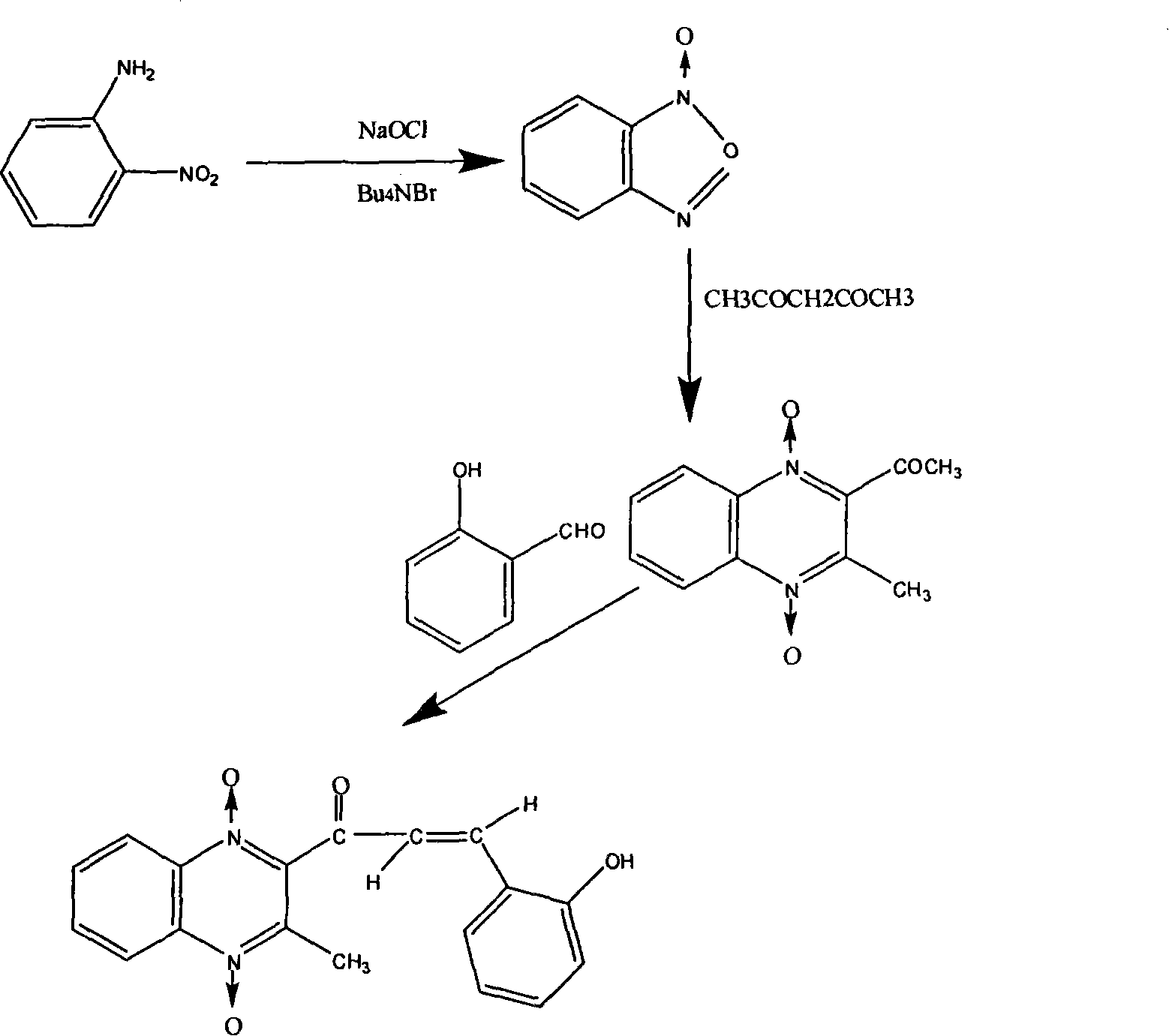
The present invention is a chemical synthesis process of quinolone, which relates to the field of veterinary drug feed additives. The existing synthesis technology is to select from various quinoxaline compound substituted derivatives, but these compounds have relatively large toxic and side effects, and simply change The side chain can no longer meet the needs. The present invention uses heavy ion beams to modify the structure of quinoxaline to produce new compound molecules. Through pharmacodynamic research, the standard sample is separated for chemical synthesis. The present invention designs three synthetic routes. Corresponding to the three chemical synthesis processes, the new compound was identified by spectrum, and it was determined to be quinolone. After further growth-promoting and toxicity tests, it showed obvious improvement and improvement compared with the lead compound quinolone. The invention has the beneficial effects of greatly shortening the development cycle and greatly saving the development cost, and shows that quinolone is a very vital veterinary drug feed additive.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Method and device for implanting heavy ion beams into synchrotron
ActiveCN101631419ASimple process requirementsSolution to short lifeMagnetic resonance acceleratorsMass numberHeavy ion beam
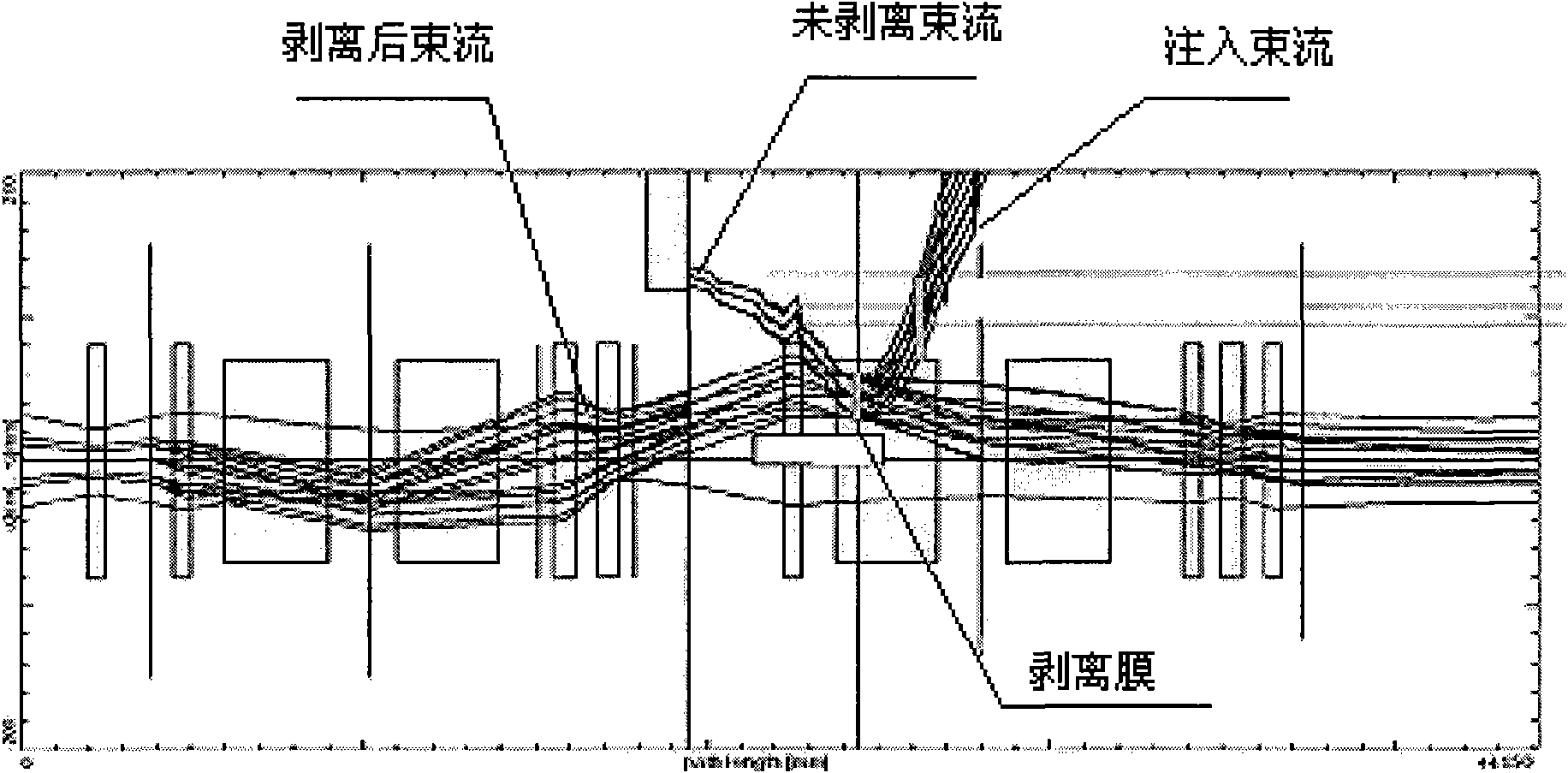
The invention mainly relates to a method and a device for implanting non-full stripping heavy ion beams which are provided by a cyclotron and have mass numbers less than or equal to 40 into a synchrotron. The method comprises the following steps: 1. accelerating the heavy ion beams which are not fully stripped and have mass numbers less than or equal to 40 until the energy is 5.0-10.0MeV / u and the intensity of the heavy ion beams is 2.0-6.0mu A; 2. deflecting the heavy ion beams with mass numbers less than or equal to 40 in the step 1 to a stripping foil and embossing the central track of the synchrotron to the position of the stripping foil in the position of an implanting point; 3. reducing the embossment of the central track in the step 2, implanting the stripped heavy ion beams to fill in the space of the synchrotron and enabling the heavy ion beams to carry out cyclotron in the synchrotron. The invention also provides the device for implanting the heavy ion beams into the synchrotron. The device has the advantages of simple device, convenient operation and high implantation efficiency and can realize multiple choices of the charge states of the heavy ion beams by adjusting the thickness of the stripping foil.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
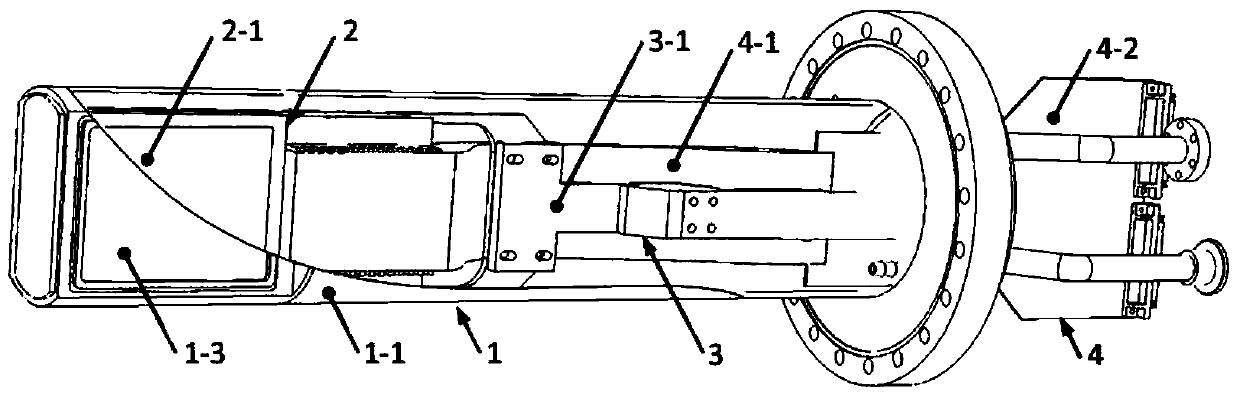
Position sensitive detector for higher energy heavy ion beam diagnosis
The invention relates to the field of radioactive nuclear beam physics, heavy ion beam cancer treatment, heavy ion irradiation materials and heavy ion irradiation breeding. A position sensitive detector for higher energy heavy ion beam diagnosis is mainly characterized in that a beam probe is arranged in an air seal cavity, and the beam probe is fixedly connected to a fixing support of a port sealing flange assembly. The air seal cavity comprises an incidence window arranged on one side of an air box and an exitance window arranged on the other side of the air box. The beam probe is composed of two beam measuring units. Each beam measuring unit is composed of a high voltage pole, an insulating cushion plate and a signal pole which are sequentially arranged. The port sealing flange assembly is composed of the fixing support and a port sealing flange. A multichannel signal leading out pin board comprises a multichannel signal leading out board and a multichannel signal pin board. A contact end is arranged at one end of the multichannel signal pin board, inserted into a sealing opening of a sealing flange, and is connected with the signal output end of the multichannel signal leading out board. A multi-core connector is arranged at the other end of the multichannel signal pin board and serves as a signal output end opening of the beam position sensitive device. The signal input end of the multichannel signal leading out board is connected with the signal poles of the beam probe.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
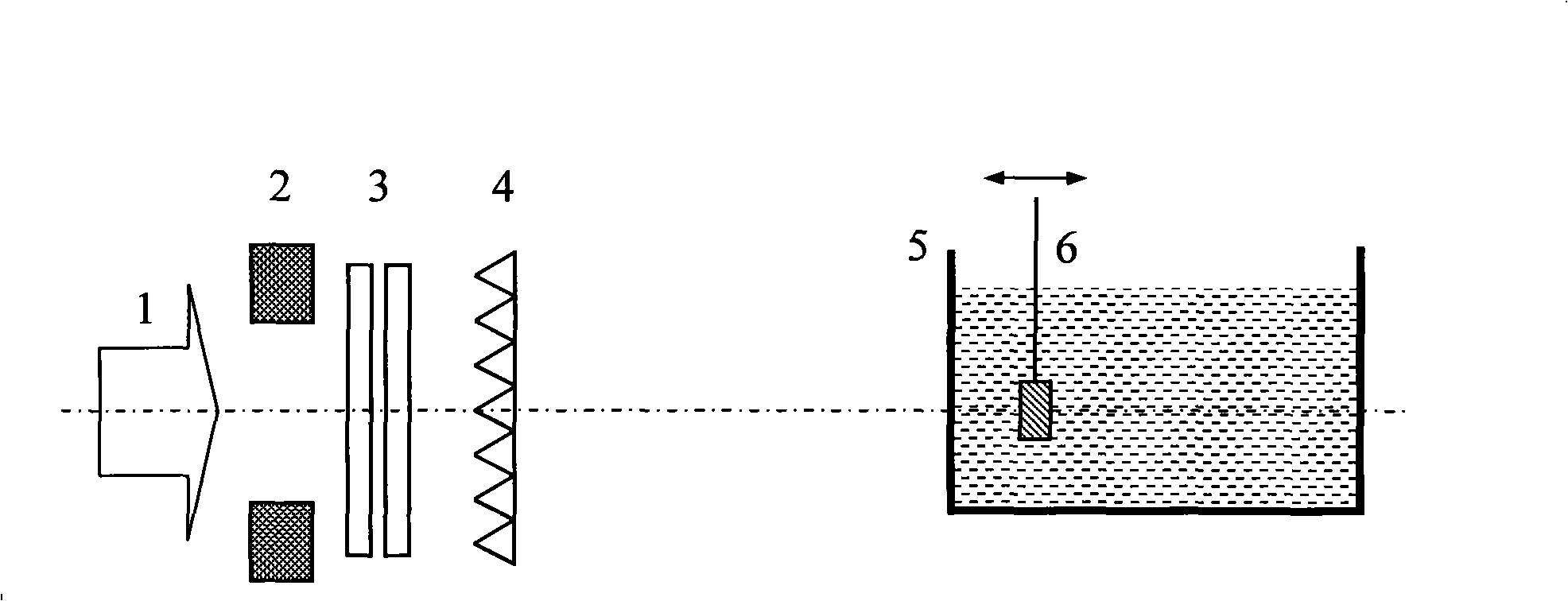
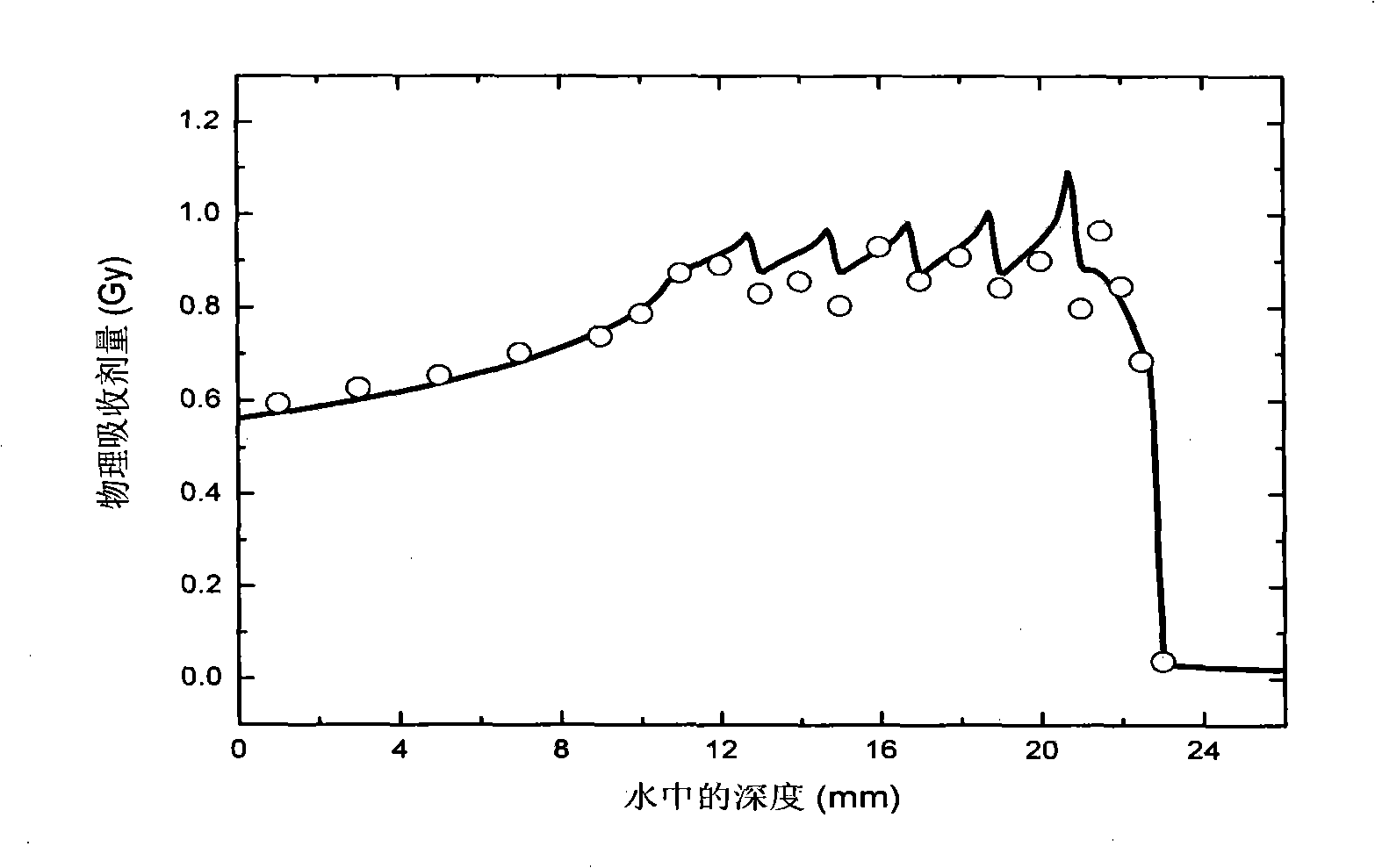
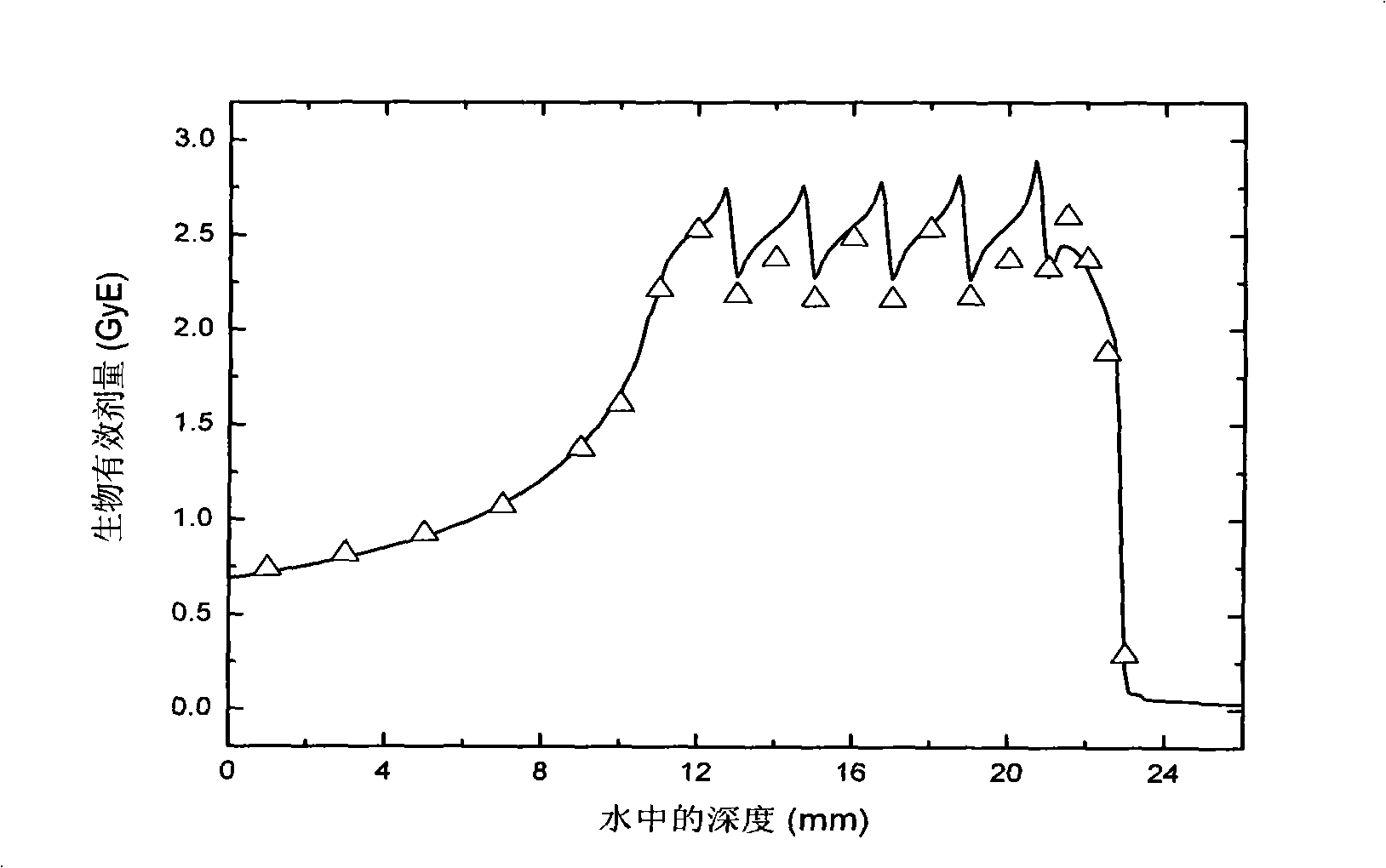
Dose monitoring detector calibration device and method in heavy ion beam treating carcinoma
ActiveCN101285887A3D Conformal Radiation Therapy ControlImprove treatment efficiencyDosimetersBragg peakTumor target
The invention relates to a device and a method for demarcating and calibrating a dose monitoring detector in heavy ion beam cancer treatment. The structure of the device is characterized in that a collimator, the dose monitoring detector, a mini ridge-shaped filter, a water tank and a standard ionization chamber are arranged on a beam flux axis in sequence. The standard ionization chamber is arranged inside the water tank. The depth position of an irradiation beam mini spread-out Bragg peak in water is obtained by measuring absorbed dose of the standard ionization chamber at different depth in aqueous medium. At the depth position, the dose monitoring detector is demarcated and calibrated by the standard ionization chamber so as to obtain demarcating and calibrating factors of the measurement of the dose monitoring detector for the mini spread-out Bragg peak cancer treatment beam with a Gauss arrangement. With the demarcating and calibrating factors, the entire process of three-dimensional conformal irradiation therapy with uniform physical absorption dose or uniform biological effective dose in a tumor target volume can be conveniently controlled, the requirements of the treatment of different clinical cases in practical clinical treatment are satisfied, and the treatment efficiency of a treatment device is improved.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
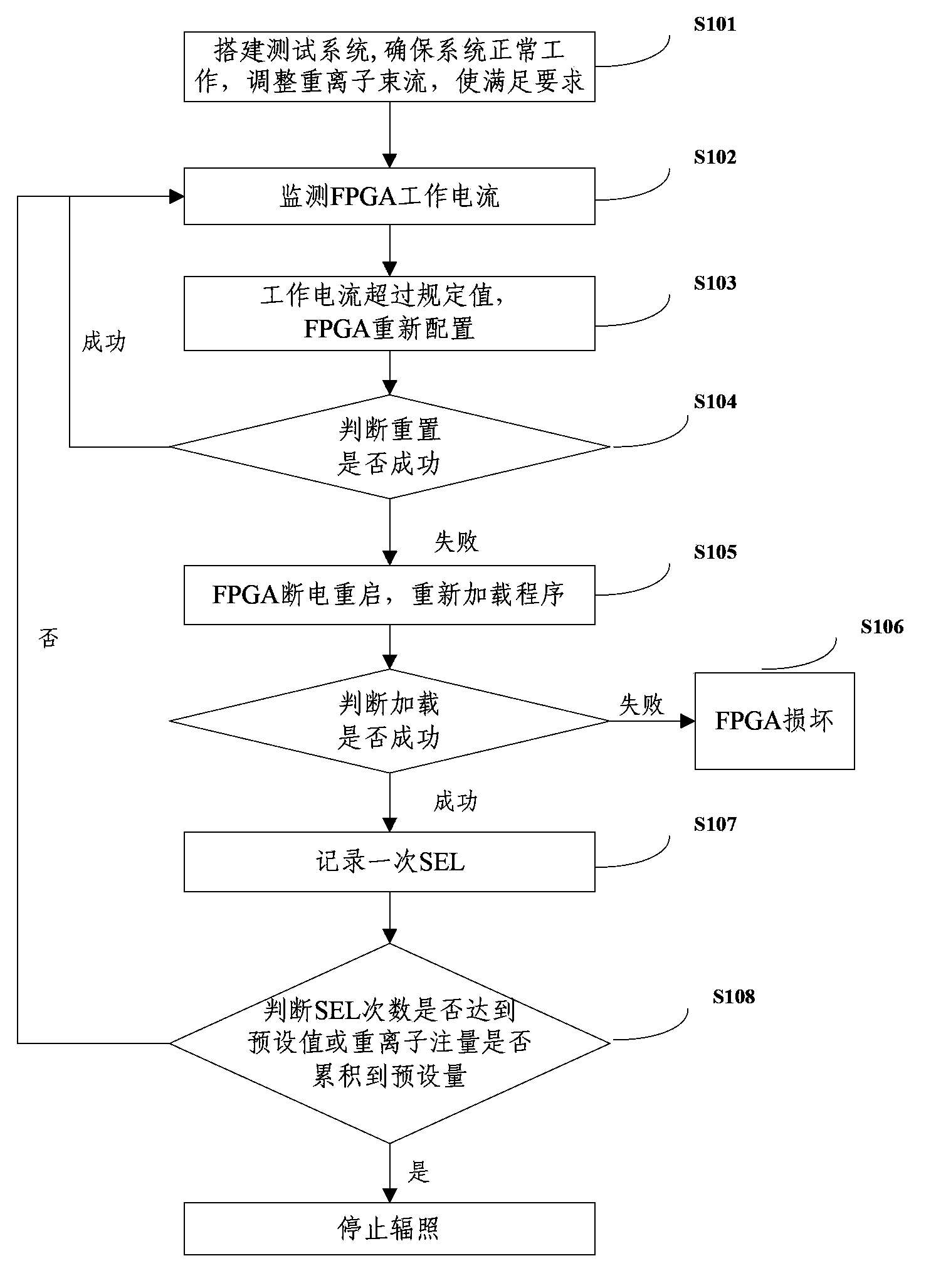
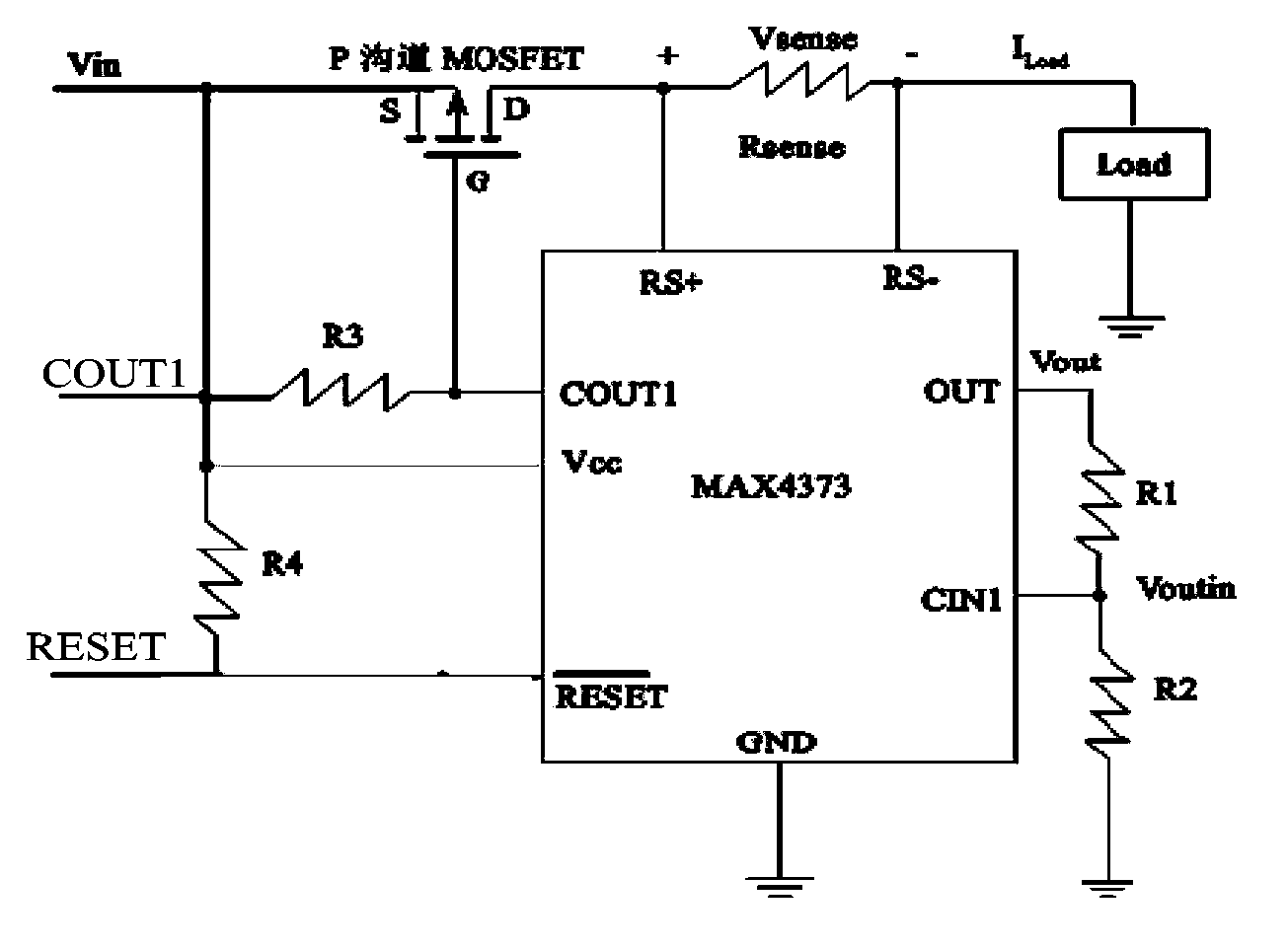
Single particle latch monitoring method and apparatus of FPGA
ActiveCN103777135AReal-time monitoring of working currentEasy to judgeDigital circuit testingCurrent/voltage measurementHeavy ion beamMonitoring methods
The invention discloses a single particle latch monitoring method and apparatus of an FPGA. The method specifically comprises the following steps: using a heavy ion beam flow to irradiate the FPGA, monitoring the working current of the FPGA, and when the working current exceeds a specified value, performing reconfiguration on the FPGA; if the reconfiguration fails, performing power-off restarting on the FPGA, and reloading a program; and if program reloading succeeds, recording a single particle latch for once. By using the method provided by the invention, the working current of a device can be monitored in real time, the determination of an FPGA single partial latch is facilitated, at the same time, since a programmable power supply controlled by a computer is employed, a tested device can be protected.
Owner:BEIJING SHENGTAOPING TEST ENG TECH RES INST
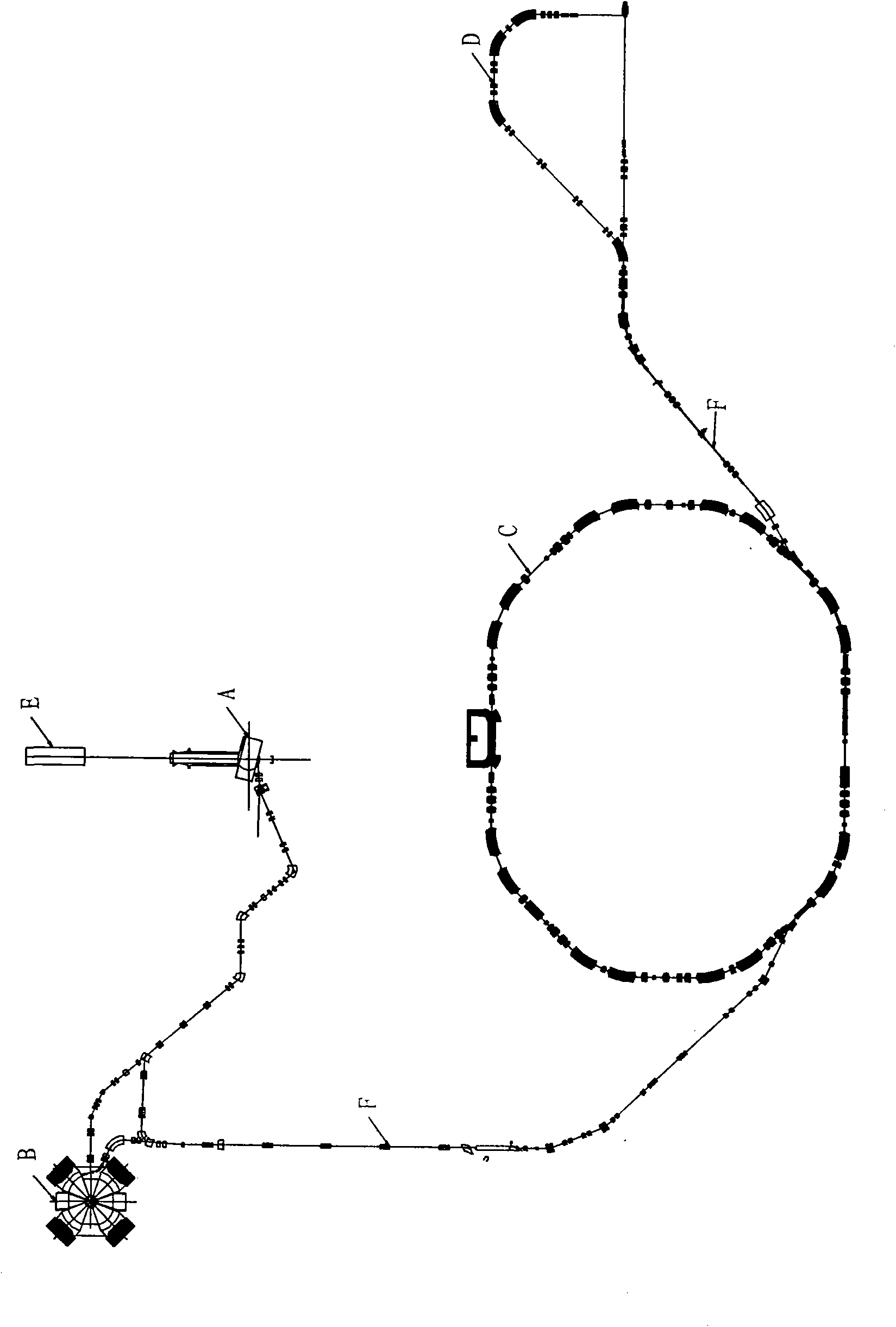
Accelerator used for cancer therapy with protons-heavy ion beams
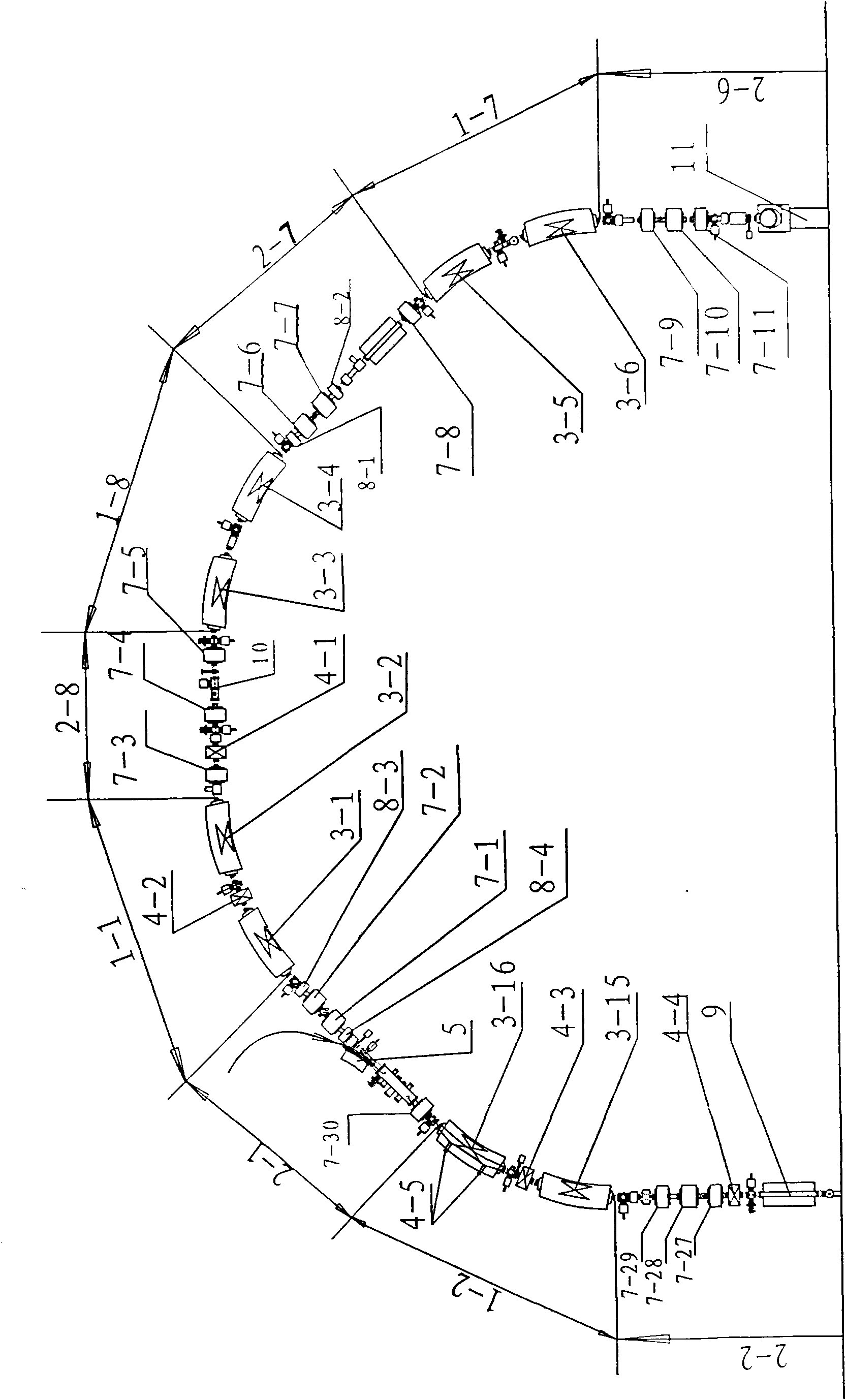
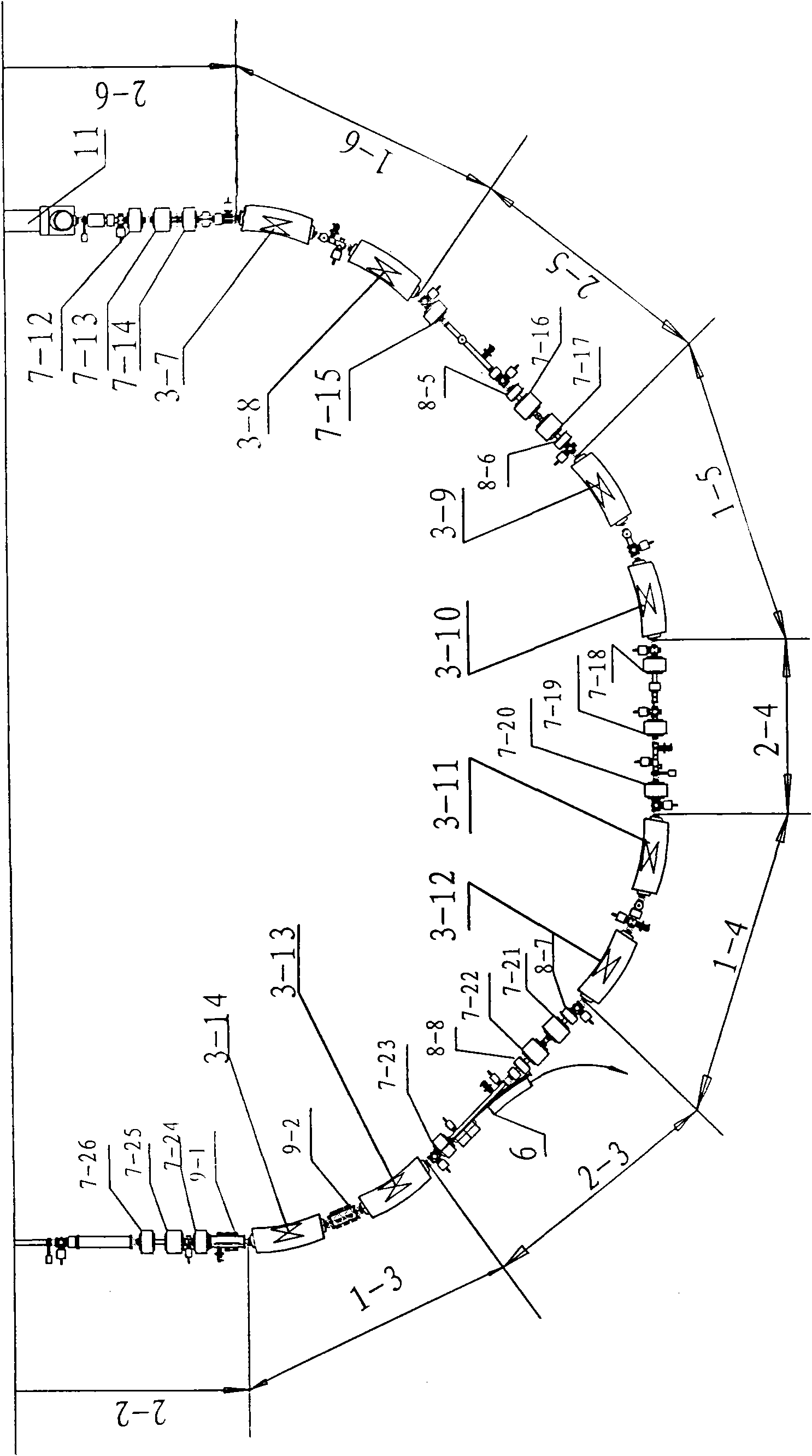
ActiveCN101631420AFulfillment requirementsTo achieve the requirements of the beam current parametersMagnetic resonance acceleratorsRadiation therapyMass numberSynchrotron
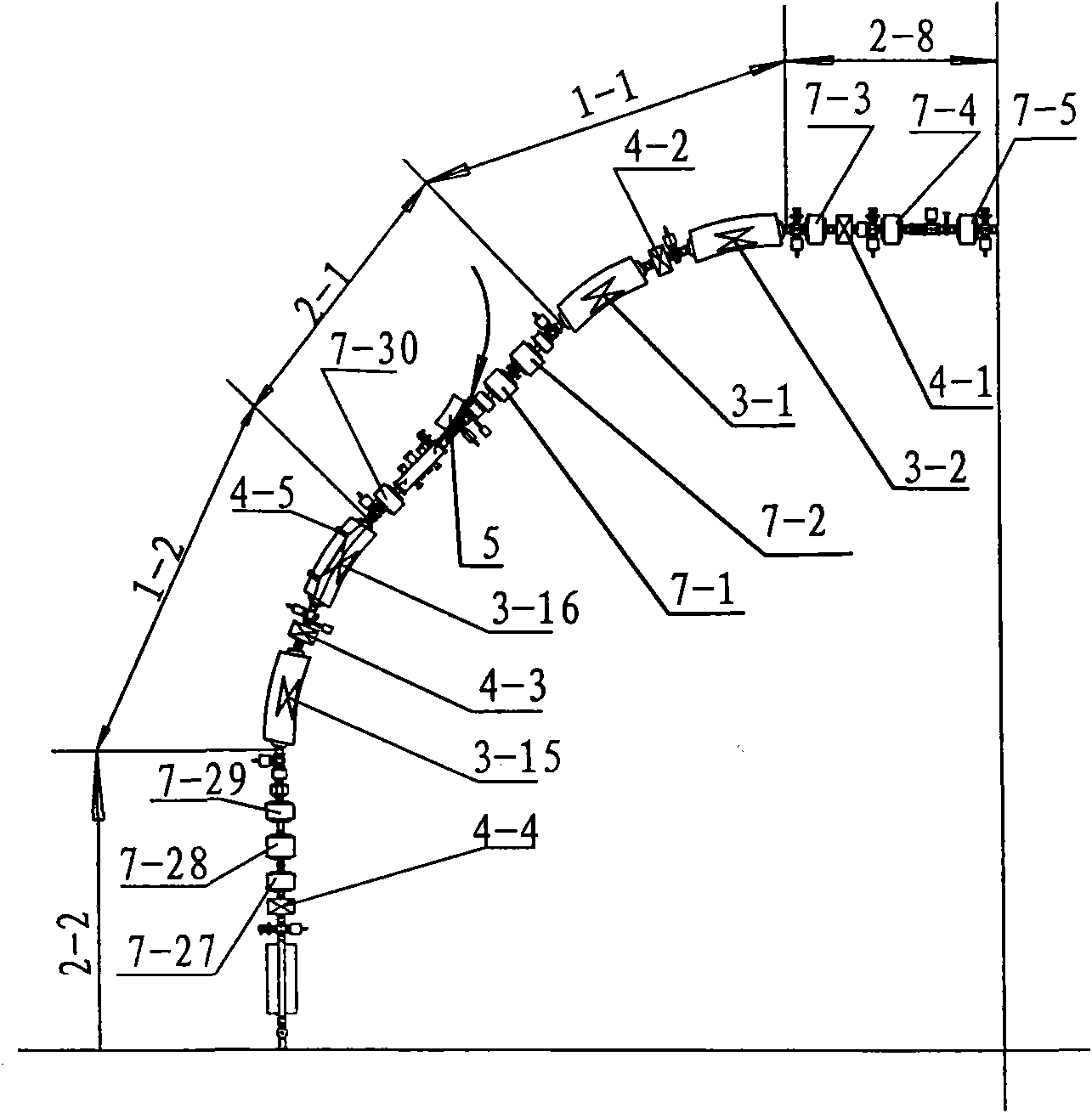
The invention relates to an accelerator which combines a cyclotron and a synchrotron and is used for cancer therapy with protons-heavy ion beams, comprising an ion source E and the synchrotron C. The accelerator is characterized in that the synchrotron C comprises a septum magnet implanting device (5), a septum magnet extracting device (6), a radio-frequency accelerating device (9), eight bending sections of the synchrotron (1-1 to 1-8) and eight straight sections of the synchrotron (2-1 to 2-8), which are connected by an ion beam transmission line F; the ion beam implantation end of the synchrotron C is provided with a sector focusing cyclotron A or / and a separated sector focusing cyclotron B. By adopting the method of combining the cyclotron and the synchrotron, a set of accelerator devices required by cancer therapy with protons and heavy ion beams is set up to realize the requirements of clinical therapy on beam parameters; the mass numbers of the protons and the heavy ions are less than or equal to 40; the protons and heavy ion beams have wide energy range from 10MeV / u to 400MeV / u and high flux (the ion number provided by each pulse is up to 10<7-10> magnitude).
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
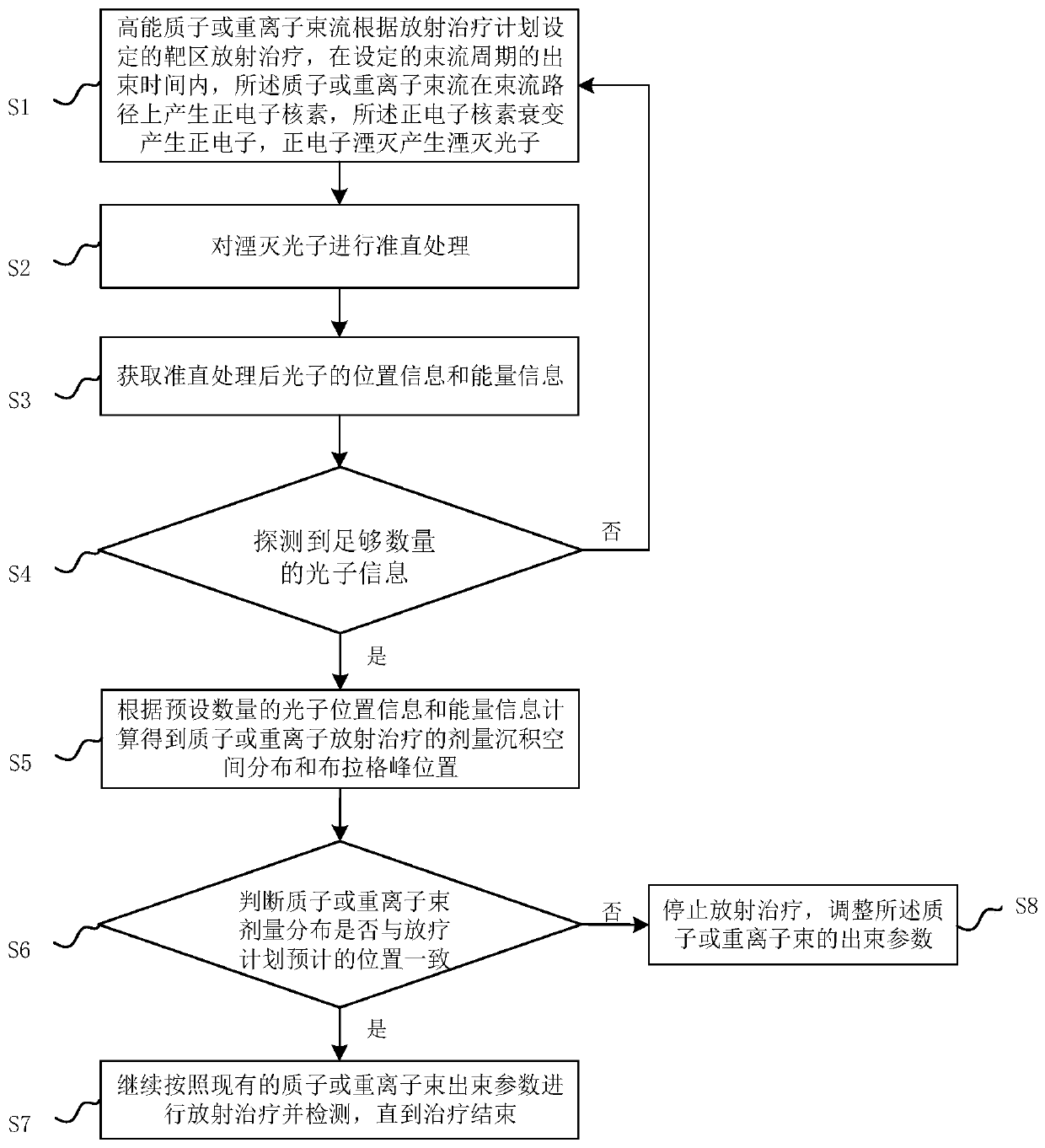
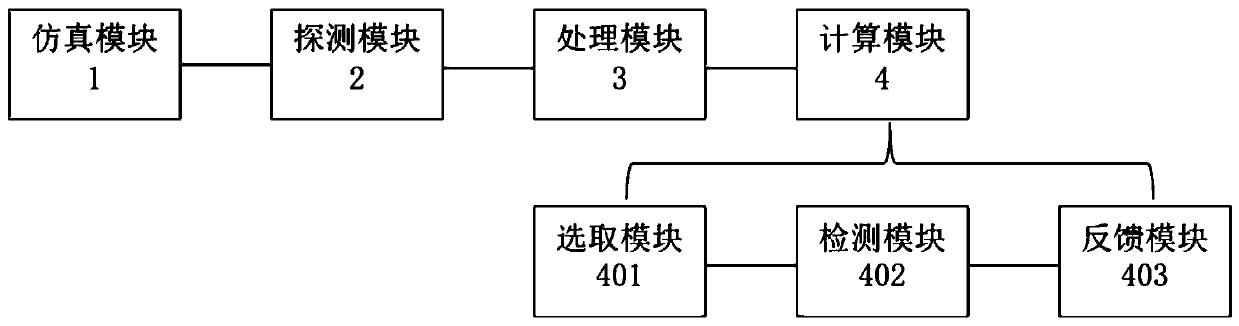
Method and system for real-time monitoring proton or heavy ion radiotherapy doses
InactiveCN110270014AHigh precisionImprove detection efficiencyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyHeavy particleHeavy Ion Radiotherapy
The invention relates to a method and a system for real-time monitoring proton or heavy ion radiotherapy heavy particle radiotherapy doses. The monitoring method utilizes distribution information of positron radionuclide produced during the high-energy proton or heavy ion radiotherapy, and measures position and energy information of annihilation photons in the intermittent time of beams according to beam cycles of protons or heavy ions to obtain dose deposition spatial distributions in the proton or heavy ion radiotherapy, thereby realizing the monitoring of dose distributions of proton or heavy ion beams. Compared with the traditional instantaneous gamma measurement method, the method has a higher detection efficiency, and the method effectively reduces statistical noise, and improves accuracy of the dose deposition of the proton or heavy ion radiotherapy; compared with the traditional positron emission tomography method, the method can realize a faster one-dimensional distribution of dose along the beam direction by carrying out a collimation treatment on the annihilation photons along the beam direction and then detecting the position and energy information of the photons, thus the method is conducive to improving monitoring efficiency.
Owner:彭浩
Three-dimensional conformal Irradiation unit of heavy ion beam on tumour target area
ActiveCN101199425AHigh degree of conformityImprove therapeutic efficacyRadiation diagnosticsBragg peakDisease
The invention relates to a device used in 3-D conformal radiotherapy to gross tumor volume with heavy ion beams, comprising a magnet scanning system, a beam monitor system, a mini-ridge filter, a range shifter, a multi-leaf collimator and a patient body surface compensator, which are sequentially arranged on the body surface of the patient. The centers of the components and the center of the gross tumor volume are located at the beam axis. The invention overcomes the defects that the conformality is low and the scatterer impairs beam quality in current 2-D conformal radiotherapy by heavy ion beams based on a passive beam flow distribution system, and adopts 3-D conformal irradiation without the scatterer needed in current 2-D conformal radiotherapy, thus improving conformality in the therapy to the gross tumor volume with heavy ion beams. The invention can protect the health organs around the gross tumor volume to the largest extent and reduce incidence of disease at the normal organs without reducing the rate of using large quantity of Bragg peak to efficiently kill the cells in the gross tumor volume, thus improving curative effect of the heavy ion beams.
Owner:国科离子医疗科技有限公司
Operation method for eliminating hysteresis effect influence of synchronous accelerator
InactiveCN102548182AEasy to operateGuaranteed uptimeMagnetic resonance acceleratorsHysteresisPower controller
The invention relates to an operation method for eliminating a hysteresis effect influence of a synchronous accelerator. The operation method is used for solving the problem that the position and intensity of heavy ion beams in the synchronous accelerator under different energy conditions are inconsistent because a magnet has a hysteresis effect. The operation method of an accelerator in a magnetic field major cycle mode mainly comprises the following steps of: 1, determining the maximal energy value of a beam of the synchronous accelerator required for a tumor cell therapy; 2, calculating a power operation curve of a dipolar magnet, a quadrupole magnet and a sectupole magnet for controlling a beam track by using magnetism measuring parameters; 3, uploading an operation curve data packet of the magnets to a remote database connected with a power supply controller; 4, analyzing the data packet by the remote database and issuing data to corresponding control front-ends; and 5, trigging data by using a trigger to output the data to the power source of the related power supply and control the track of the heavy ion beam.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
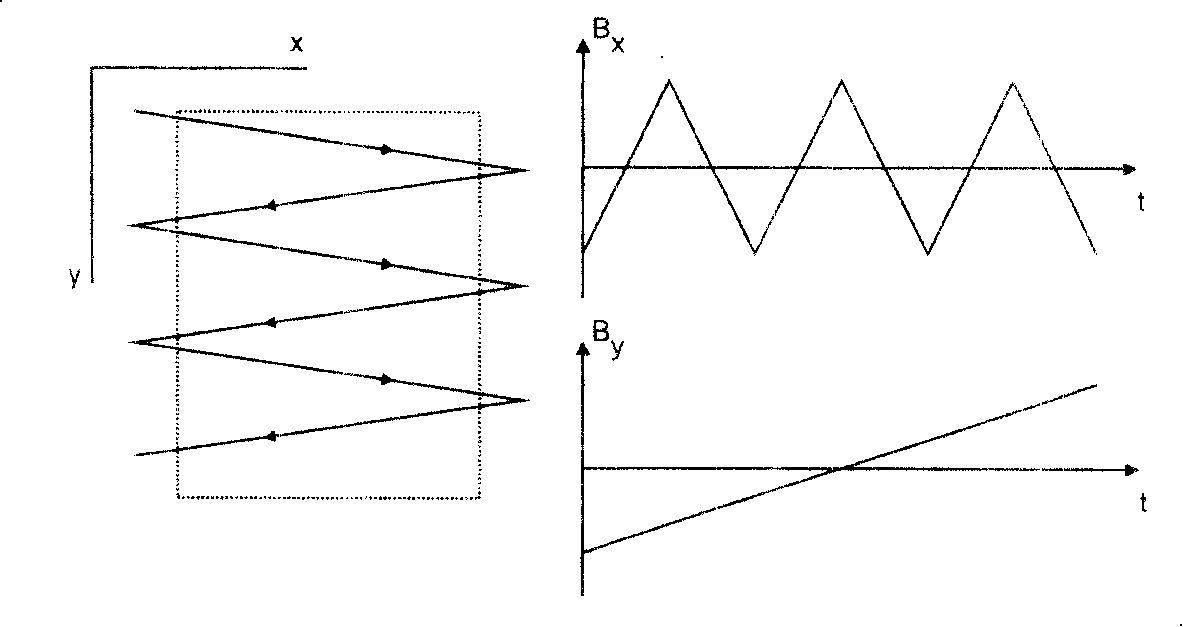
Deceleration apparatus for ribbon and spot beams
ActiveUS20120097861A1Improve consistencyMinimizing non-uniformityThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersIon beamLight beam
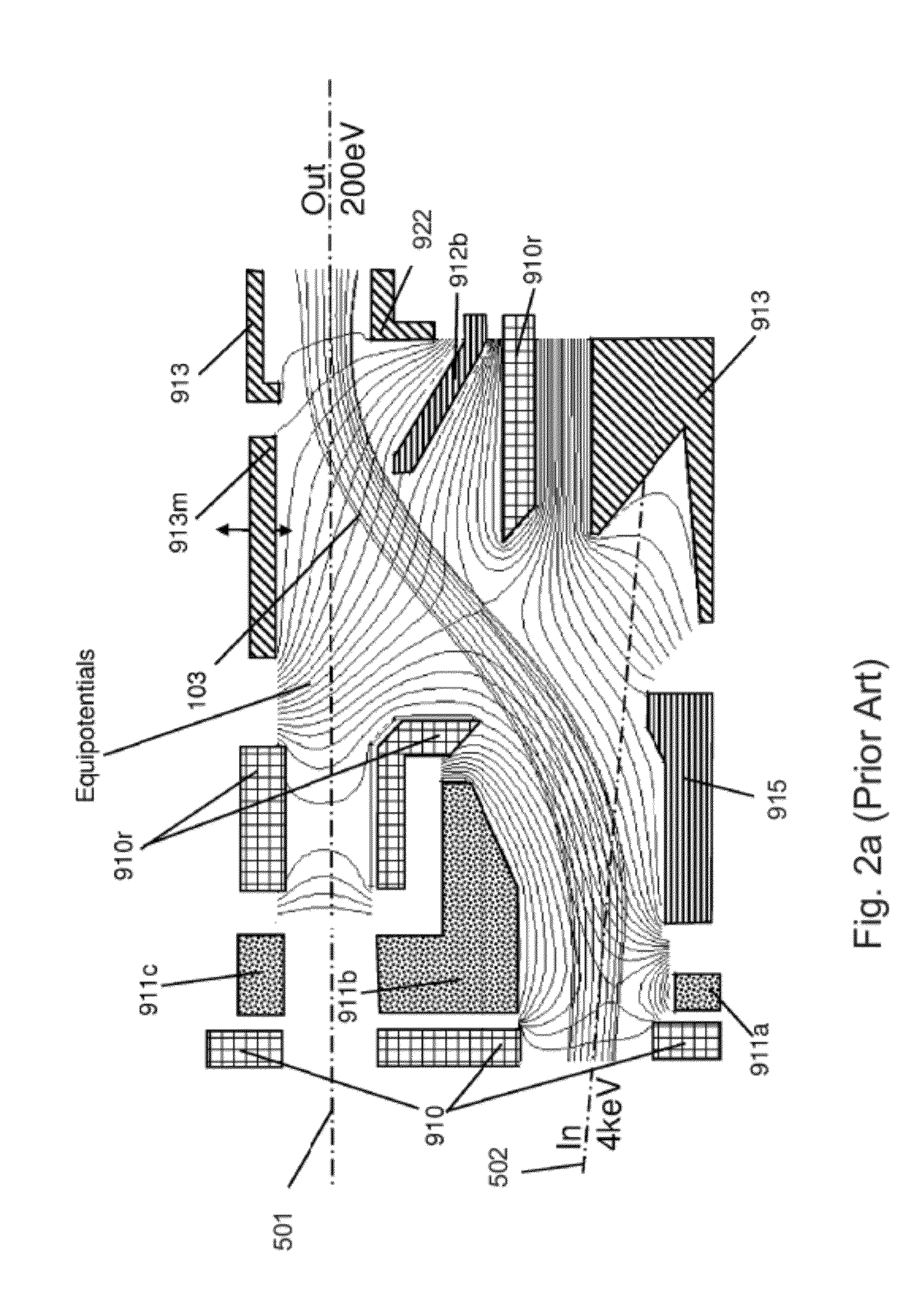
A deceleration apparatus capable of decelerating a short spot beam or a tall. ribbon beam is disclosed. In either case, effects tending to degrade the shape of the beam profile are controlled. Caps to shield the ion beam from external potentials are provided. Electrodes whose position and potentials are adjustable are provided, on opposite sides of the beam, to ensure that the shape of the decelerating and deflecting electric fields does not significantly deviate from the optimum shape, even in the presence of the significant space-charge of high current low-energy beams of heavy ions.
Owner:ADVANCED ION BEAM TECHNOLOGY INC
Second ion mass spectrometry method and imaging method
InactiveUS20100155591A1Avoid damageImprove ionization efficiencyIon sources/gunsIsotope separationCompound (substance)Heavy ion beam
The provision of a new method for analyzing organic molecules such as protein and endocrine disrupting chemicals with excellent sensitivity. A secondary ion mass spectrometry method using a heavy ion beam as a primary ion beam enables the detection of, for example, an organism-related material at the sub-amol level with high sensitivity. As a result, favorable imaging of an organism-related sample can be performed.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
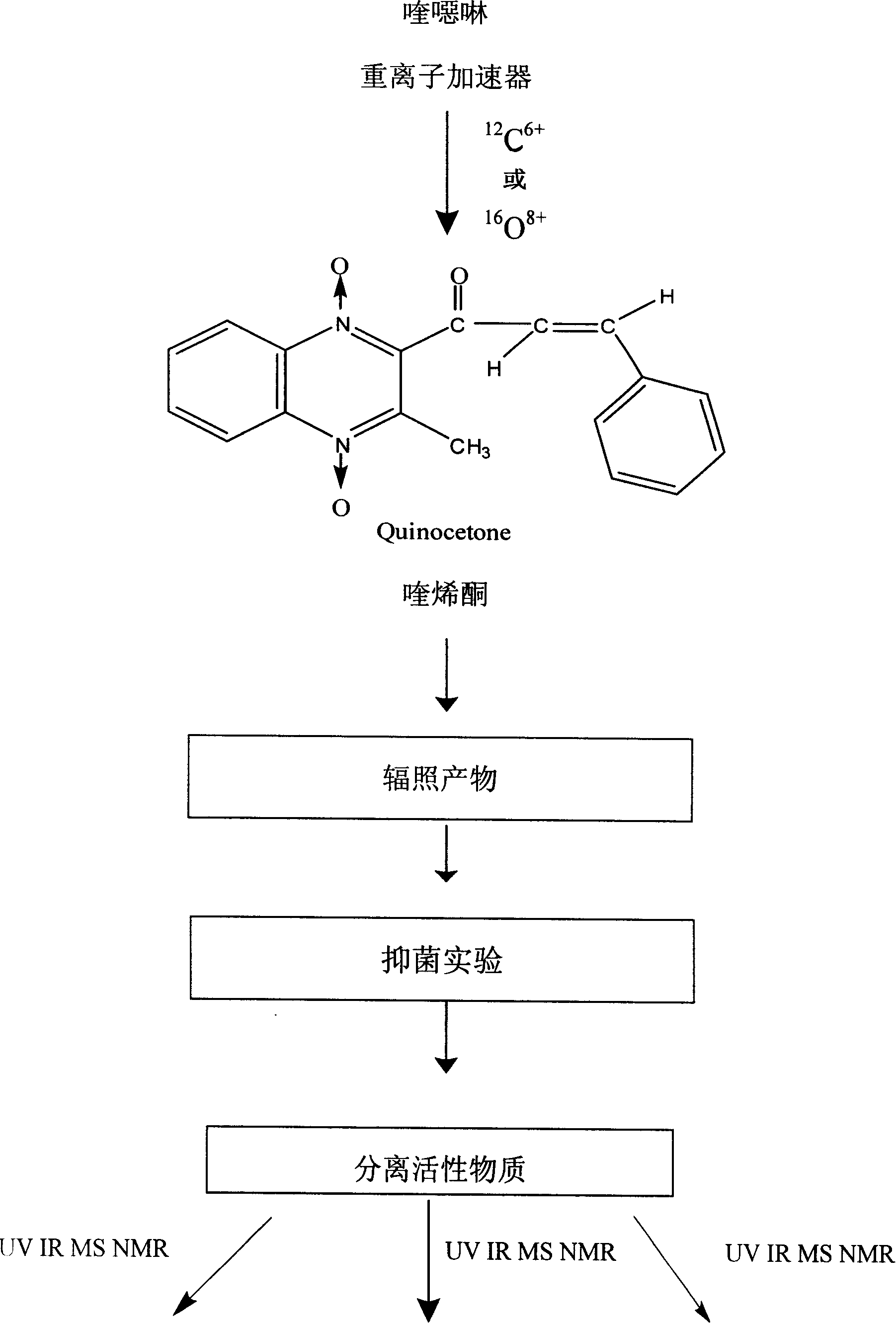
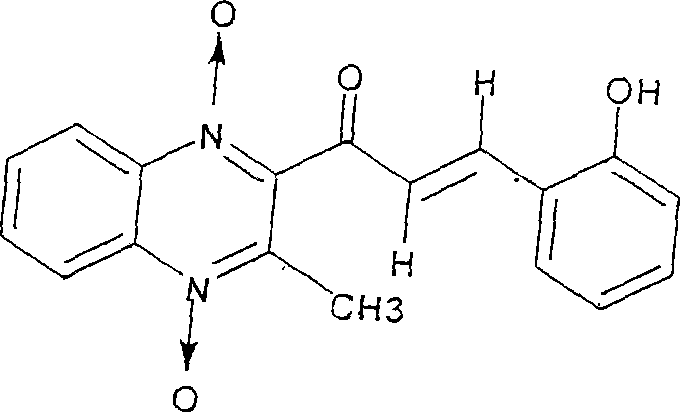
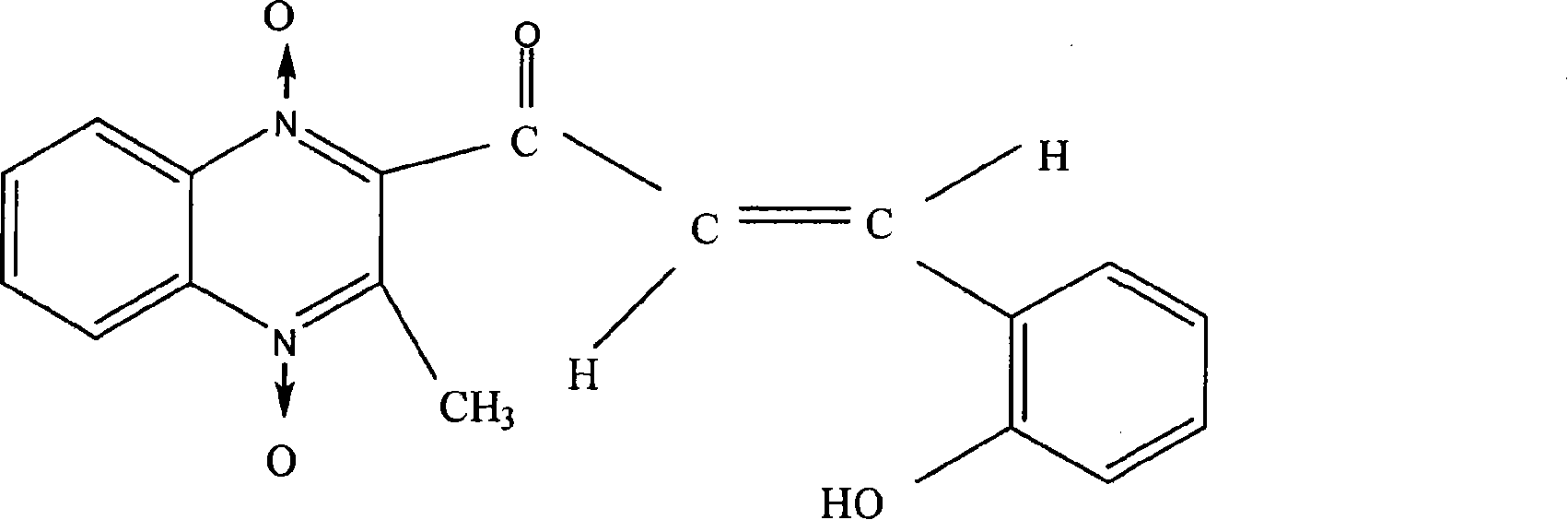
Quinoxaline acquired by heavy ion beam irradiation effect
InactiveCN101081836AImprove antibacterial propertiesSimple methodOrganic chemistryQuinoxalineChemical synthesis
The present invention is heavy ion beam irradiation effect to obtain quinhydroxy ketone, and relates to heavy ion beam irradiation technology. Heavy ion beam irradiation process for developing new medicine is superior to available chemical synthesis process, which has long developing period, high cost and high manpower consumption, and can obtain new matter in short period and separate out lead compound with obvious medicine effect. The heavy ion beam irradiation process of obtaining quinhydroxy ketone is to irradiate quinalkenyl ketone with 16O8+ and 12C6+ heavy ions in the initial energy of 75 MeV / micron, and energy depositions of 1.585x10<2> Gy-1.585x10<12>Gy and 1.656x10 Gy-1.656x10<9>Gy. The irradiation product quinhydroxy ketone has strengthened antibacterial activity and lowered toxicity, and the present invention provides one effective way for developing new medicines.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
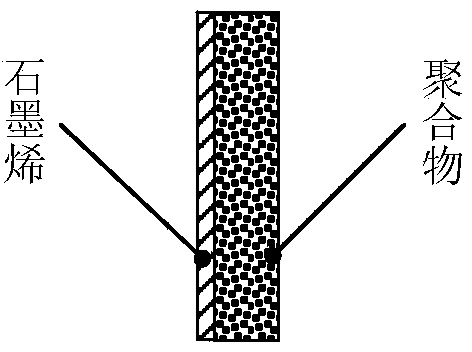
Porous graphene composite material supported by micropore and preparation method of material
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
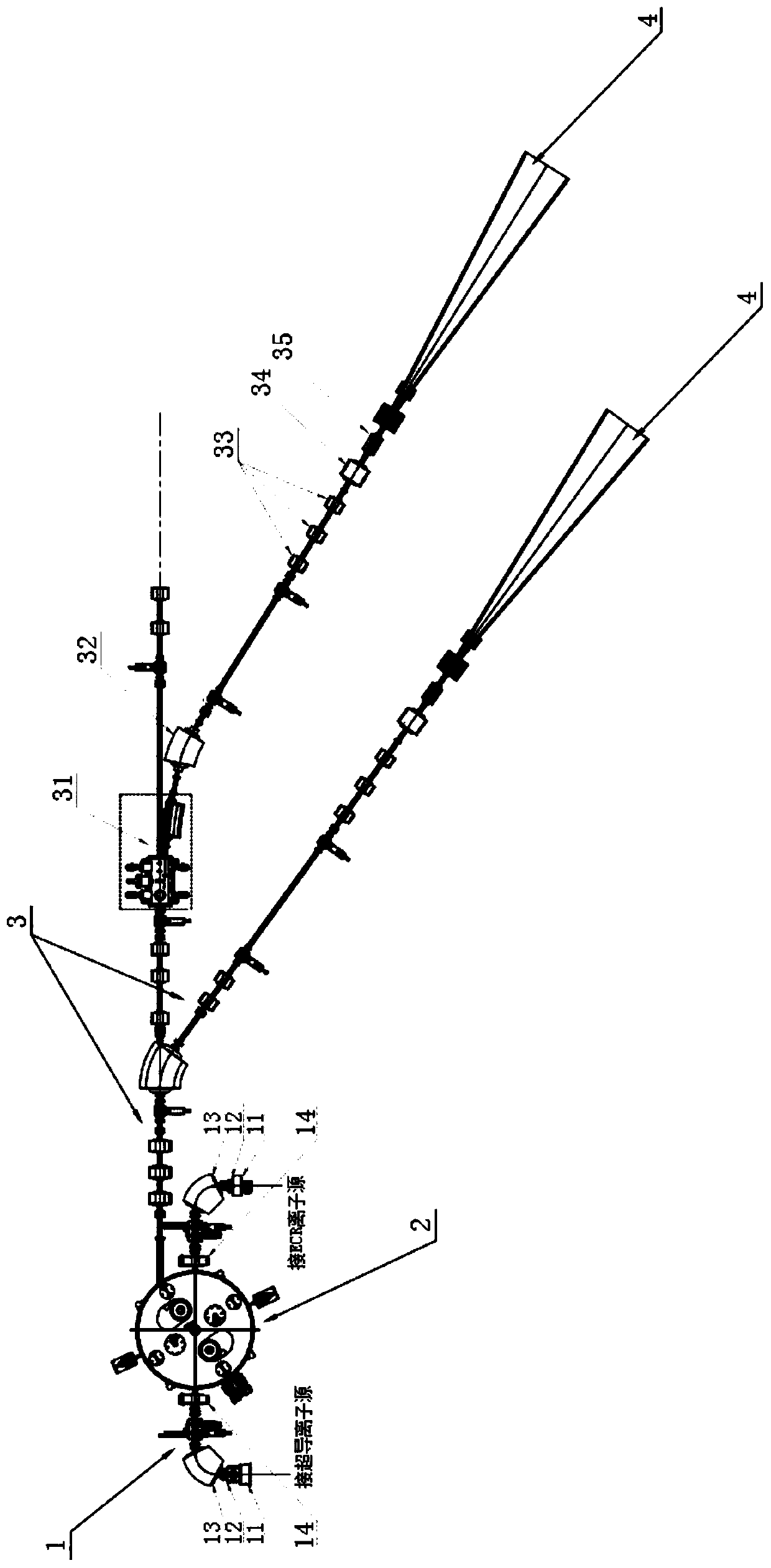
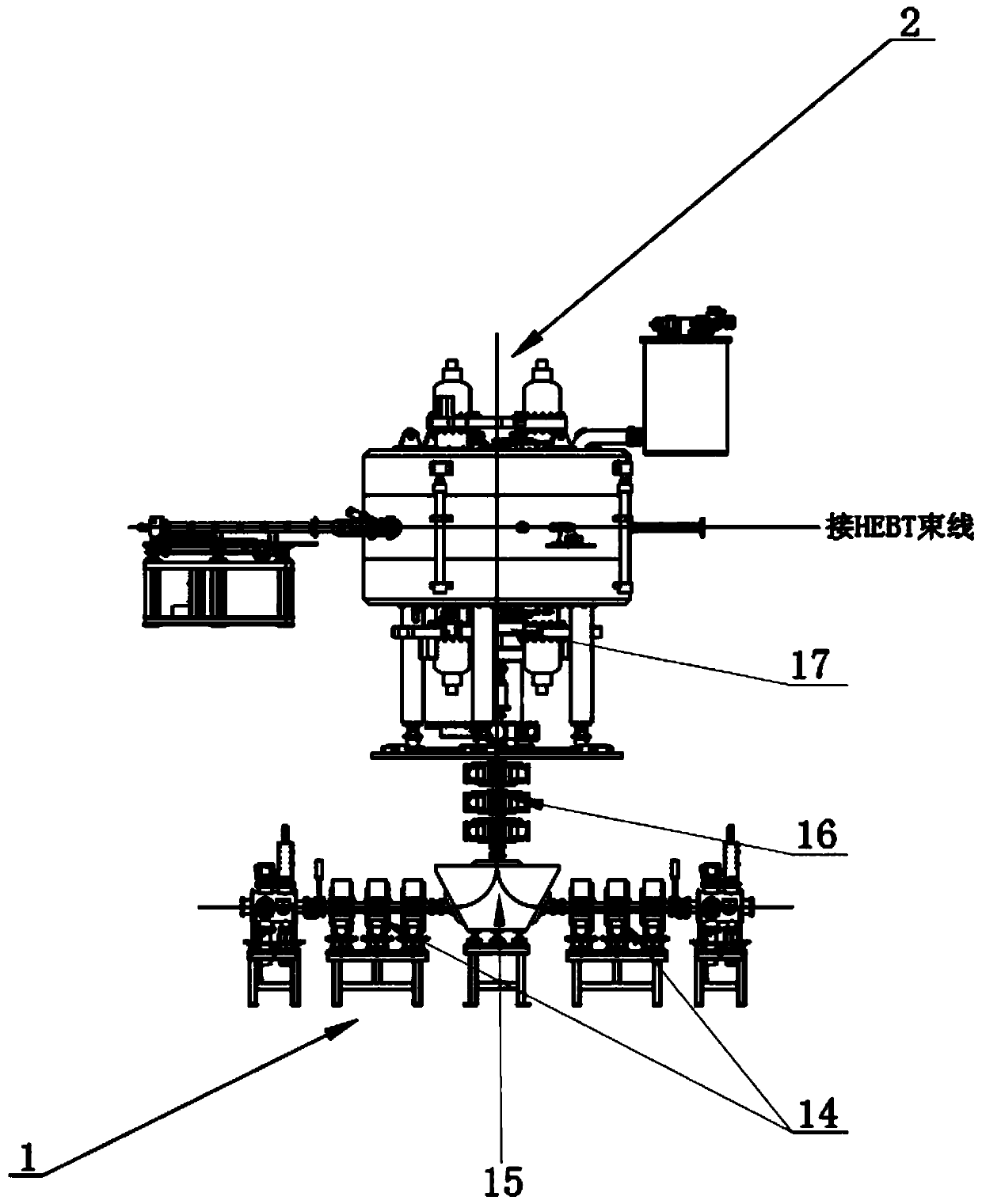
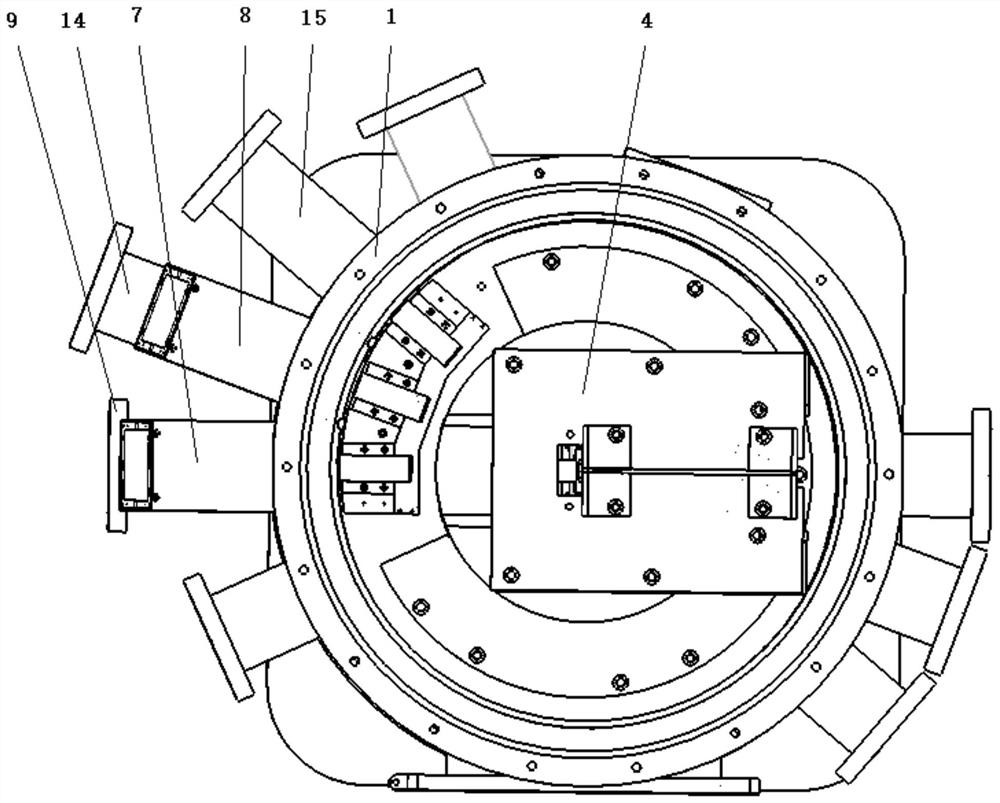
Heavy ion production device for industrial production of nuclear track membrane
ActiveCN111292866AReduce volumeReduce weightAcceleratorsIrradiation devicesParticle acceleratorNuclear engineering
The invention relates to a heavy ion production device for industrial production of nuclear track membrane. The heavy ion production device comprises an ion source, an LEBT beam line, a particle accelerator, an HEBT beam line and a membrane irradiation terminal; the ion source is used for generating a heavy ion beam in a high charge state and carrying out primary acceleration on the heavy ion beam; the LEBT beam line is used for analyzing the heavy ion beam and transmitting the heavy ion beam to the particle accelerator in a matching manner; the particle accelerator performs main accelerationon the heavy ion beam and then injects the heavy ion beam into the HEBT beam line; the HEBT beam line splits the injected heavy ion beam into a plurality of heavy ion beams and then transmits the heavy ion beams to a plurality of membrane irradiation terminals, and the membrane irradiation terminals lead out the heavy ion beams and irradiate a thin membrane placed in the atmospheric environment. Due to the fact that the thin membrane can be placed in the atmospheric environment to be irradiated, the thin membrane is convenient and rapid to replace, the thin membrane replacing time is greatly shortened, multiple terminals can irradiate the thin membrane at the same time, the irradiation efficiency of the thin membrane is greatly improved, and thus the production efficiency of the nuclear track membrane is improved.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
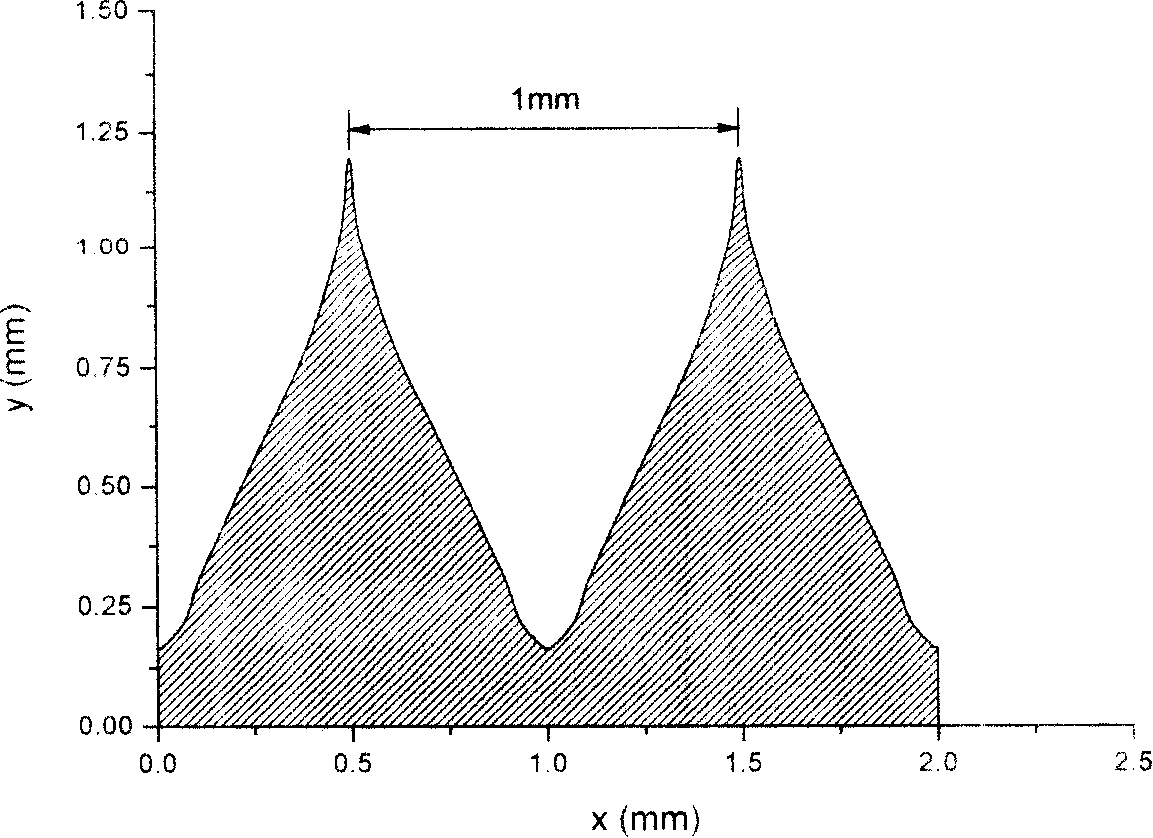
Manufacturing method of pinhole collimator
ActiveCN103347362AImprove straightnessImprove qualityAcceleratorsMicrobeam irradiationHeavy ion beam
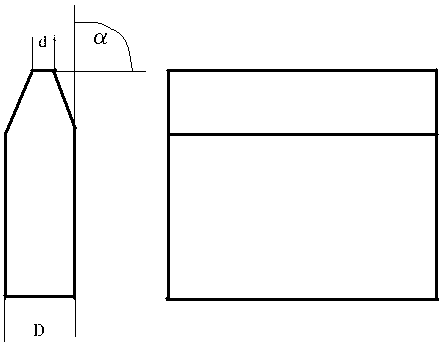
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of a collimator. The problems that the shape of a pinhole of an existing pinhole collimator is not ideal, so that low-energy scattering of heavy ion microbeams is serious, heavy ion beam spots are large, and the application needs can not be met are solved. The manufacturing method of the pinhole collimator includes the following steps: 1) blade grinding, the top ends of cutting edges of blades are ground to be smooth and clean by using precision abrasive paper; 2) slit structure splicing, the cutting edges of the two blades are oppositely fixed on a bottom liner, and a slit is reserved between the cutting edges; 3) assembling, two slit structures are fixed together in an overlaying mode to form the pinhole of the pinhole collimator. The top ends of the cutting edges of the blades of the pinhole collimator manufactured according to the manufacturing method are good in straightness, the width of the spliced slit can be smaller than 1 micron, low-energy scattering ingredients of the heavy ion microbeams can be better lowered, the generated heavy ion beam spots are good in quality, and the application in heavy ion microbeam irradiation equipment is well achieved.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Proton heavy ion-beam-flow vertical beam bunch shape measurement detector
ActiveCN106501840AHigh bandwidthImprove anti-interference abilityX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentBand shapeOptoelectronics
The invention relates to the accelerator beam flow diagnosis, beam flow measurement, and vertical beam bunch shape measurement field and especially relates to a proton heavy ion-beam-flow vertical beam bunch shape measurement detector. The detector comprises a detector main body and a microwave band shape line structure arranged on the detector main body. The detector main body comprises a flange. A tantalum copper composite board is connected to the flange through a support frame. A water cooling pipe is arranged between the flange and the tantalum copper composite board. The microwave band shape line structure is arranged on an inner side of the tantalum copper composite board. The microwave band shape line structure is fixed to a microwave band shape line bottom plate. Adaptors are arranged above and below the microwave band shape line structure respectively. The microwave band shape line structure comprises a medium substrate. Upper layer ground and lower layer ground are arranged above and below the medium substrate respectively. The medium substrate is provided with a positioning hole, a first metallization through hole and a second metallization through hole. A band shape line conduction band and a microstrip line conduction band are arranged on the medium substrate. The structure is compact, processing and operation control are easy to achieve, time resolution is high and anti-interference performance is high.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Bragg curve detector for quick measurement in heavy-ion cancer therapy and using method thereof
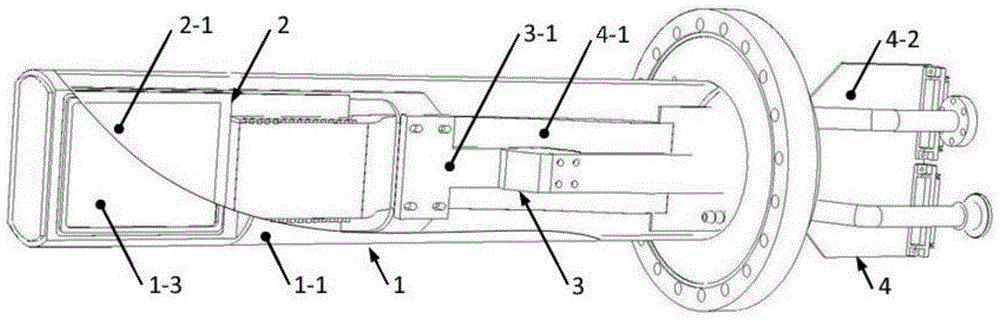
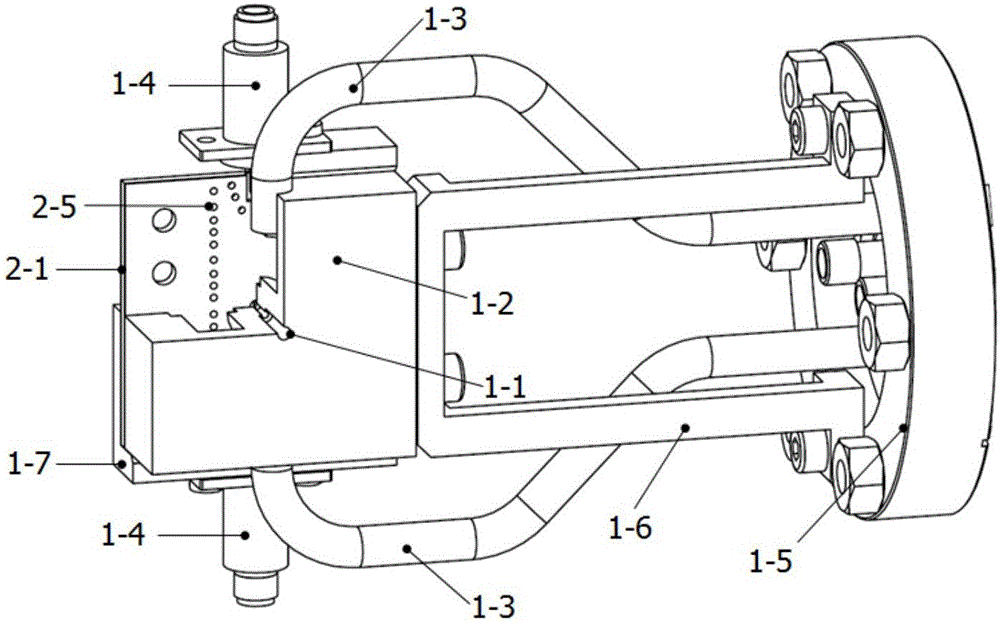
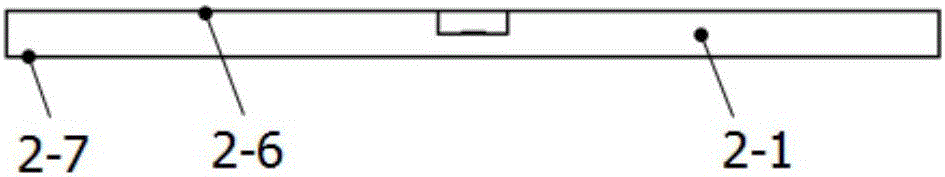
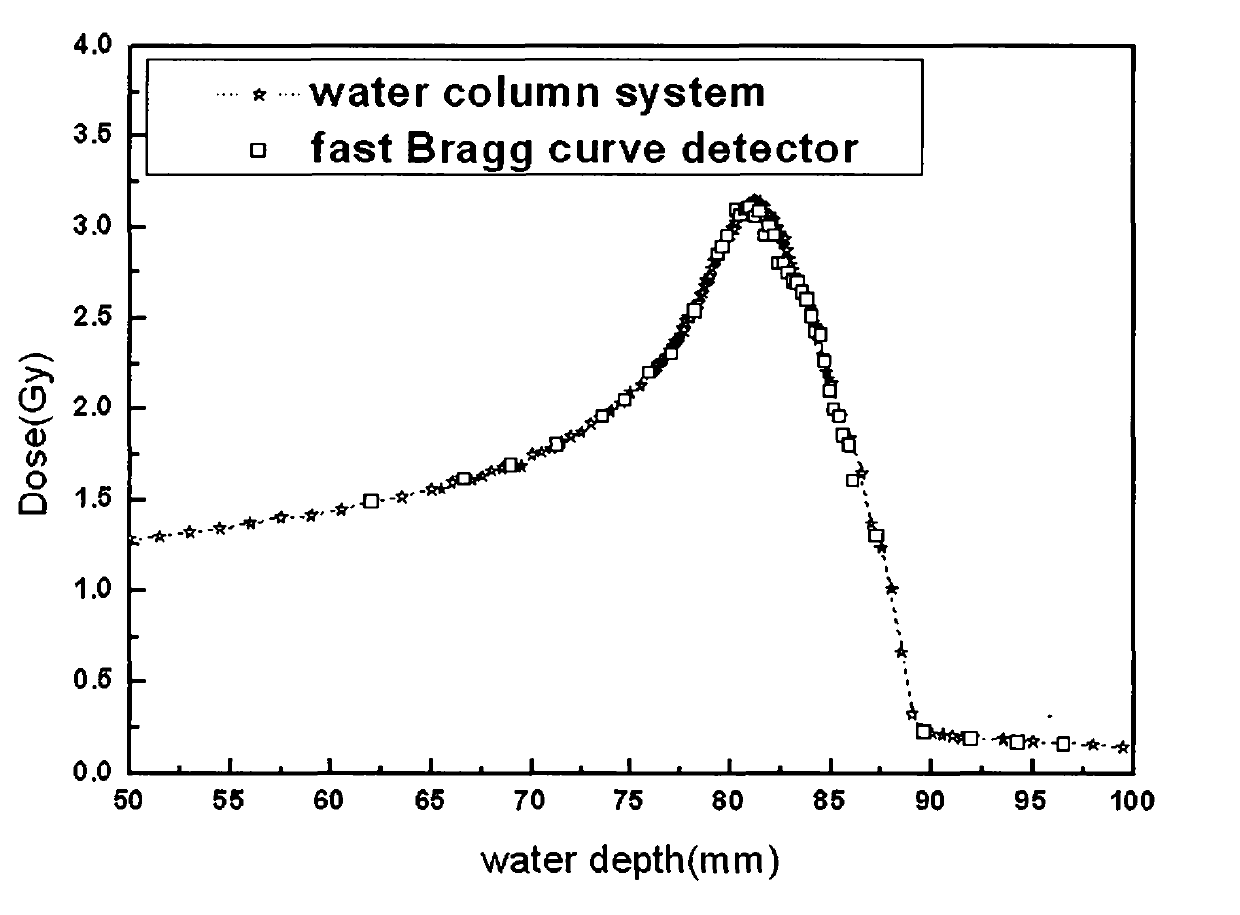
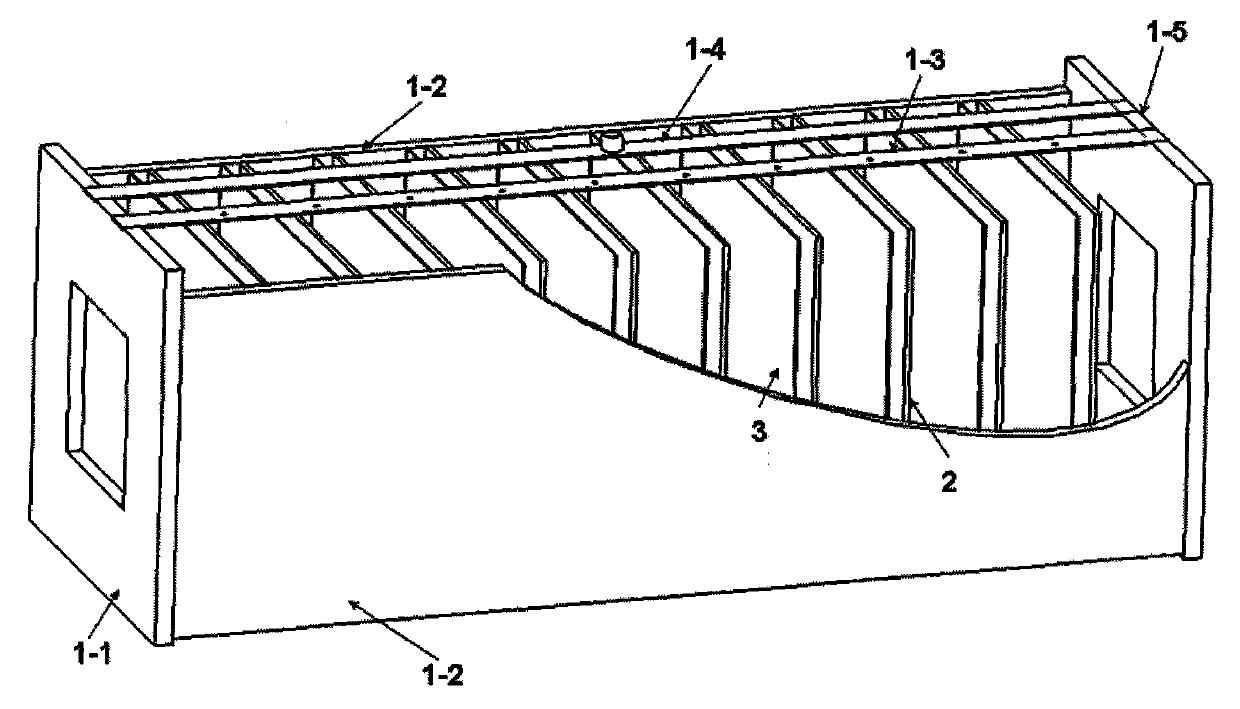
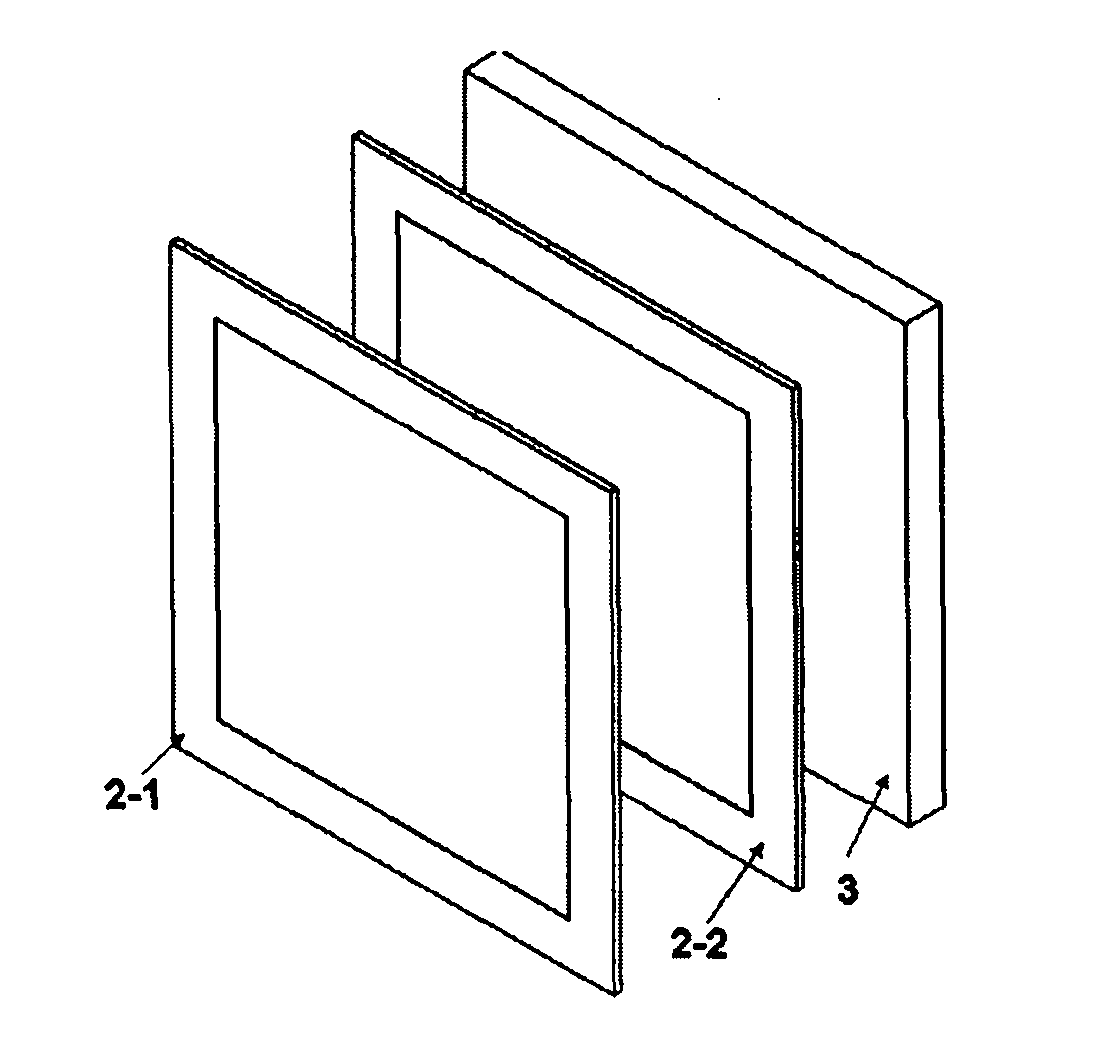
The invention relates to the field of technology of heavy-ion beam cancer therapy, in particular to a Bragg curve detector and a using method thereof. A Bragg curve detector for quick measurement in heavy-ion cancer therapy comprises an outer frame (1) and a plurality of unit ionization chambers (2), and is mainly characterized in that: water equivalent bodies (3) with different thicknesses are arranged in front of the unit ionization chambers (2); an incidence window (1-1) and an emergence window (1-5) are arranged at front and rear ends of the outer frame (1); a supporting plate (1-2) with a groove, a signal lead-out plate (1-3) and a high-voltage input plate (1-4) are arranged between the incidence window (1-1) and the emergence window (1-5); each unit ionization chamber (2) comprises a signal pole (2-1) which is connected with the signal lead-out plate (1-3) and a high-voltage plate (2-2) which is connected with the high-voltage input plate (1-4); and the unit ionization chambers (2) and the water equivalent bodies (3) in front are arranged inside the supporting plate (1-2) with the groove. The detector can realize Bragg curve measurement on incident particles in ms-order time.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
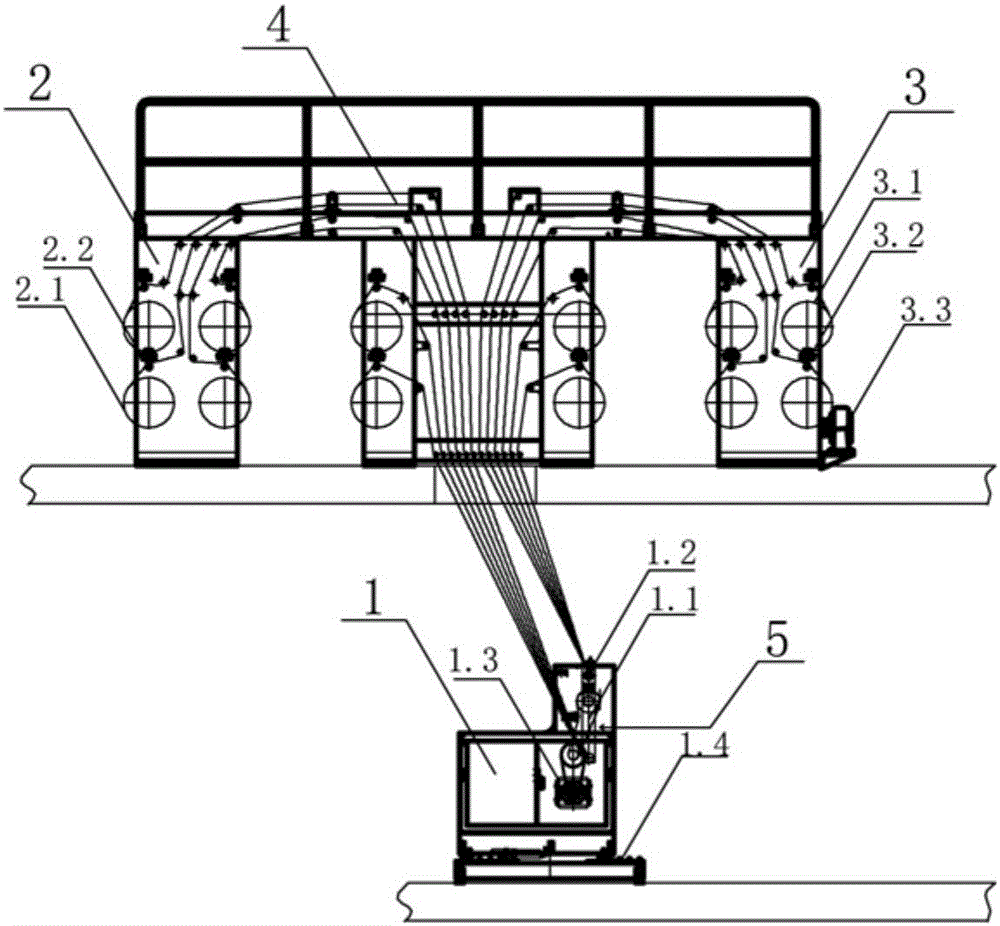
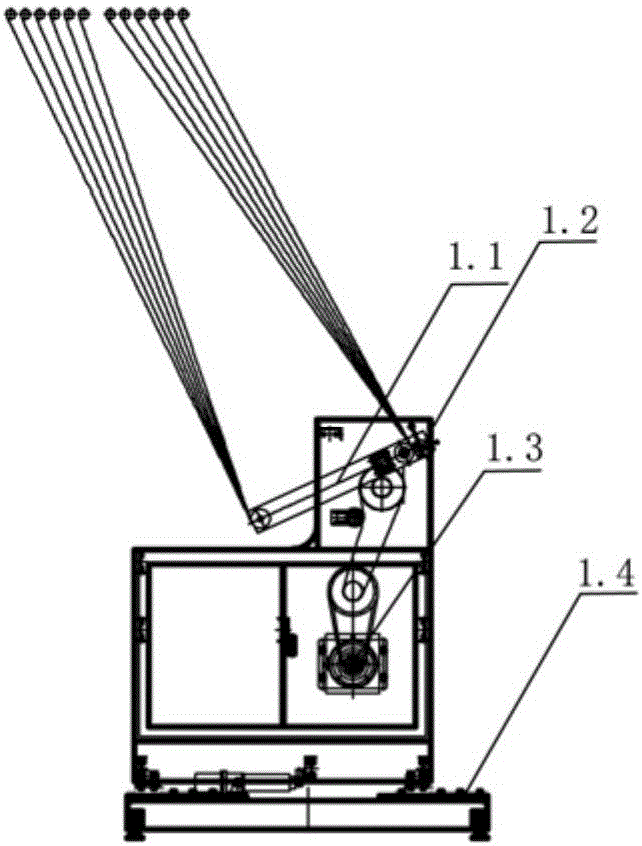
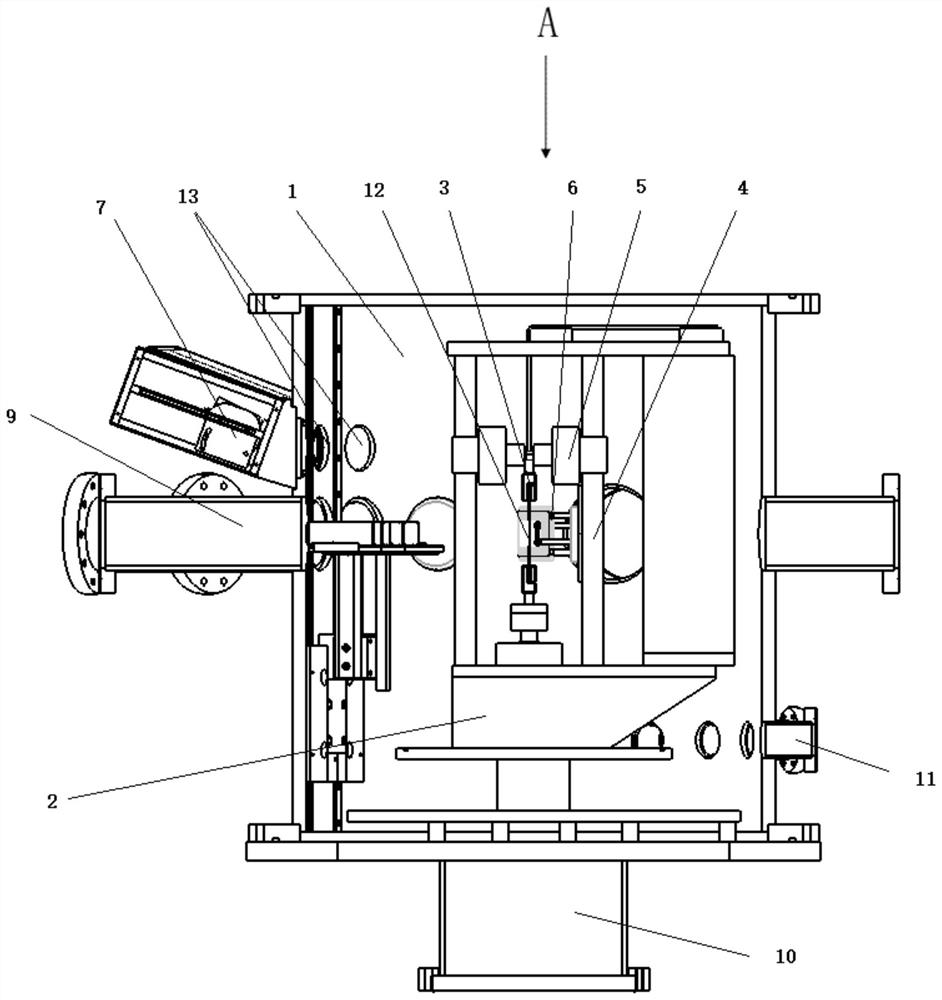
Nucleopore membrane atmosphere irradiation transmission device
ActiveCN106178967ADoes not affect rangeImprove stabilitySemi-permeable membranesHigh energyHeavy ion beam
The invention relates to a nucleopore membrane atmosphere irradiation transmission device. The device is mainly used for nucleopore membrane irradiation processing and nucleopore membrane preparation. The nucleopore membrane atmosphere irradiation transmission device is characterized by comprising a traction mechanism and an unwinding mechanism and a rolling mechanism; a draft arm irradiated by heavy ion beams is arranged on the traction mechanism; a heavy ion beam irradiation area is arranged on the traction mechanism, a heavy ion beam irradiation angle adjusting mechanism is arranged on the draft arm; a servo motor of a membrane material walking tractive force is arranged below the traction mechanism; a guide rail is arranged at the bottom of the traction mechanism, the traction mechanism moves on the guide rail back and forth, so that distance between a membrane material and a heavy ion beam flow vacuum window is changed; several unreeling shafts are arranged on the unwinding mechanism, an unreeling pressure roller is arranged on the unreeling shafts, several reeling shafts are arranged on the rolling mechanism, a rolling pressure roller is arranged on the reeling shaft, and the servo motor is arranged on the rolling mechanism. The device is used for irradiation production of a high-energy heavy ion beam irradiation accelerator, under irradiation in atmosphere, multilayer can be irradiated at one time; and the device can change air layer distance and irradiation angle in a flexible mode.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Position Sensitive Detectors for Higher Energy Heavy Ion Beam Diagnostics
The invention relates to the fields of radioactive nuclear beam physics, heavy ion beam therapy of tumors, heavy ion irradiation materials and heavy ion irradiation breeding. A position-sensitive detector for high-energy heavy ion beam diagnosis, its main feature is that a beam probe is provided in a gas-sealed cavity, and the beam probe is fixedly connected to the fixed bracket of the port sealing flange assembly; The gas-tight chamber includes an incident window on one side of the gas box, and an exit window on the other side; the beam probe consists of two sets of beam measurement units, and each set of beam measurement units consists of a high-voltage pole, an insulating backing plate The port sealing flange assembly is composed of a fixed bracket and a port sealing flange; the multi-channel signal lead-out adapter board includes a multi-channel signal lead-out board and a multi-channel signal adapter board; the multi-channel signal adapter board One end is provided with a contact end inserted into the sealing port of the sealing flange to connect with the signal output end of the multi-channel signal lead-out board, and the other end is provided with a multi-core connector which is the signal output port of the beamline position sensitive detector, and the multi-channel signal lead-out board The signal input end of the sensor is connected to the signal pole of the beam probe.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for irradiation-mutating japonica rice in Northeast China through heavy-ion beam C
InactiveCN106613926AShortened steady speedHigh mutation ratePlant genotype modificationRice cultivationHeavy ion beamJaponica rice
The invention relates to a method for irradiation-mutating japonica rice in Northeast China through aheavy-ion beam C, in particular to a breeding method of japonica rice. The method for irradiation-mutating the japonica rice in Northeast China through the heavy-ion beam C provided by the invention aims to solve the problem of low mutation rate and beneficial mutation rate of an existing heavy-ion beam irradiation method. The method comprises the steps of (1) selecting japonica rice varieties in Northeast China as irradiation materials; (2) adopting a heavy-ion accelerator as an instrument, and using the heavy-ion beam C for irradiating germ surfaces of the japonica rice in Northeast China; (3) irradiating current M0 seeds, then normally sowing, transplanting survived rice seedling individual plants, mixed harvesting, threshing and storing all seed grains on M1; (4) in the spring of next year, planting M1 individual plants to obtain M2 generation, and appearing mutated plants; (5) in the winter of the year, adding-generation planting variant plants harvested from the M2-generation individual plants to obtain M3 generation in Sanya, Hainan; (6) in the spring of next year, planting the individual plants harvested from M3 to obtain M4 generation, monitoring yield, testing seeds, and selecting materials with the roughness factor being not less than 77 percent, the head rice rate being not less than 62 percent, the amylose being ranged from 15 to 20 percent, and the chalkiness percentage being below 20 percent. The method provided by the invention is used for breeding the japonica rice in Northeast China.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Dose monitoring detector calibration device and method in heavy ion beam treating carcinoma
ActiveCN101285887BImprove treatment efficiencyConvenient control of physically absorbed doseDosimetersTumor targetParanasal Sinus Carcinoma
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Heavy ion beam irradiation breeding method of artemisia carvifolia
ActiveCN108668889AImprove the status quo of a single genetic structureIncrease frequencyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationDiseaseArtemisia carvifolia
The invention relates to a heavy ion beam irradiation breeding method of artemisia carvifolia. The method comprises the following steps: (1), planting high quality seeds from Yongzhou of Human in fields of Yuzhou of Henan, and screening and reserving seeds according to yield, disease resistance, cold resistance and artemisinin content; (2), performing irradiation induced mutation on artemisia carvifolia seeds obtained in the first step through heavy ion beam, so as to obtain irradiated seeds; meanwhile taking nonirradiated artemisia carvifolia seeds obtained in the first step as a comparison;(3), plating the irradiated seeds to the fields, so as to form a first-generation group; meanwhile taking the nonirradiated artemisia carvifolia seeds as a comparison to select variant individual plants, and determining an optimal irradiation dosage; (4), selecting beneficial mutation types, and screening excellent variant strains; (5), performing identification test on the yield, quality and resistance of the excellent variant strains, observing and detecting hereditary stability an SRAP molecular marker, performing provincial region production testing and quality detection on stable strains,then performing variety technical evaluation, and declaring new varieties. The method effectively improves the breeding efficiency.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Irradiation on-line internal friction in-situ measurement device
PendingCN113030128AIntuitive access to changes in mechanical propertiesExcellent radiation resistance materialMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial thermal analysisPhysical chemistryHeavy ion beam
The invention belongs to the technical field of irradiation measurement, and particularly relates to an irradiation on-line internal friction in-situ measurement device. The device comprises a sealed vacuum chamber (1) provided with a heavy ion beam pipeline (9), the interior of the vacuum chamber (1) is used for arranging an irradiation sample (12) and can heat the irradiation sample (12), an accelerated heavy ion beam can irradiate the interior of the irradiation sample (12) through the heavy ion beam pipeline (9), and the device further comprises a displacement detector (7) used for measuring the displacement change of the irradiation sample (12). The device realizes on-line in-situ measurement of the mechanical property of the material in a heavy ion irradiation experiment in a high-temperature environment, can visually obtain the change of the mechanical property of the material by measuring an internal friction spectrum in the irradiation process, and obtains the type, concentration and dynamic diffusion process of irradiation defects generated in the material irradiation process, and information of irradiation embrittlement, defect evolution and the like of the material under irradiation conditions such as temperature, irradiation dose and the like is obtained.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Porous graphene composite material with microporous support and preparation method thereof
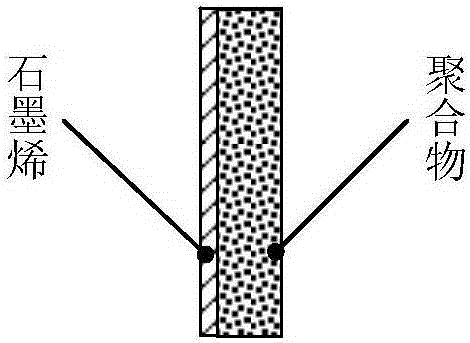
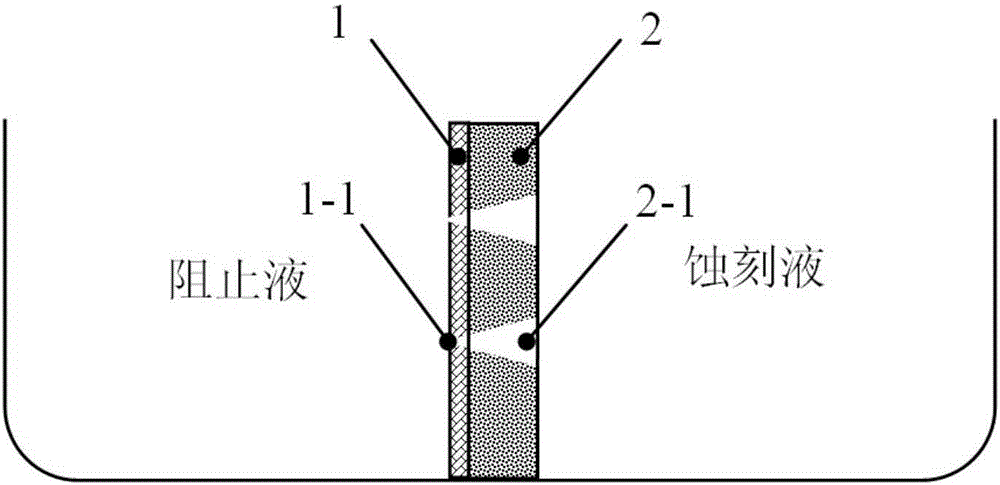
The invention discloses a method for preparing graphene nanoholes supported by micropores, and belongs to the fields of heavy ion beam application and film processing. A porous graphene composite material with microporous support includes a single-layer graphene on a polymeric film, and nano-scale holes on the graphene coincide with and communicate with tapered holes on the polymeric film. The invention adopts high-energy heavy ions to irradiate the graphene / polymer film composite structure, utilizes the radiation damage effect of heavy ions to form holes with a diameter of several nanometers on the graphene, and simultaneously produces columnar damage regions in the polymer film. Then, the irradiated area of the polymer is etched by chemical etching to form tapered nanopores. Since the positions of the graphene holes and the tapered holes on the polymer coincide and communicate, graphene with microporous supports can be obtained. Nanopores, making graphene nanopores have broad application prospects in ion rectification, ion filtration and screening, and biomolecular detection.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for mutagenizing soybeans through heavy ion beam C irradiation
InactiveCN111742841AShortened steady speedHigh mutation ratePlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyHeavy ion beam
The invention discloses a method for mutagenizing soybeans through heavy ion beam C irradiation, relates to a soybean breeding method, and aims to solve the technical problems of low mutation rate andfavorable mutation rate of an existing heavy ion beam irradiation method. The method comprises the following steps of 1, irradiating soybean seed hilum by adopting heavy ion beam carbon ions to obtain current-generation M0 seeds; 2, irradiating the current-generation M0 seeds by adopting the heavy ion beam carbon ions, and performing sowing to obtain a generation M1; 3, in spring of the second year, planting all M1-generation single plants in plant rows, harvesting, numbering and storing all variant single plants, and performing seed testing indoors; 4, in winter of the same year, performingharvesting, numbering and seed testing on strain single plants which are continuously separated from a generation M3; and 5, in spring of the third year, planting the single plants harvested from theM3 to obtain a generation M4, and selecting out a strain with excellent characters and stable inheritance to complete the process. According to the method, the mutation rate can be increased, offspring mutation materials are rich, multiple beneficial types are achieved, and excellent mutation characters such as high protein, lodging resistance, high yield and large grains can be screened out.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
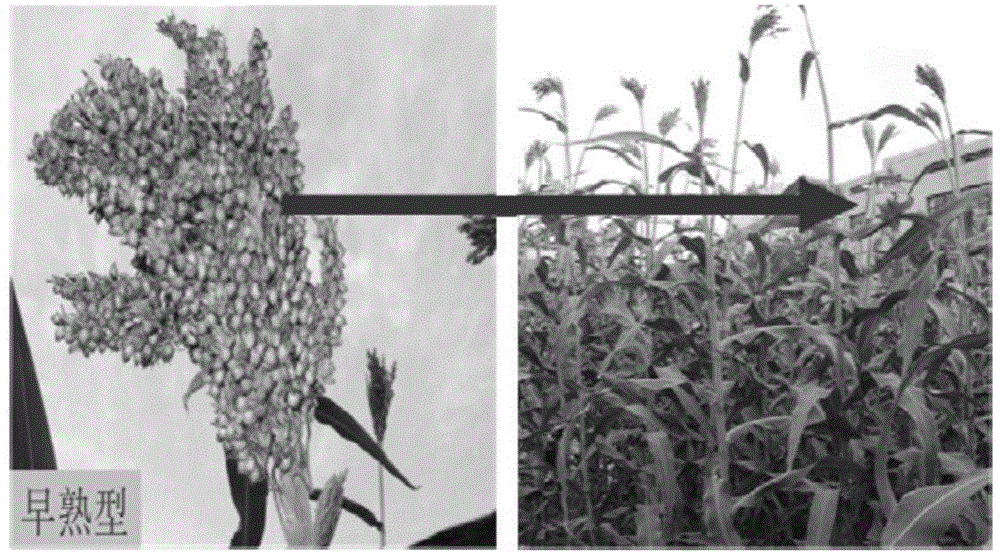
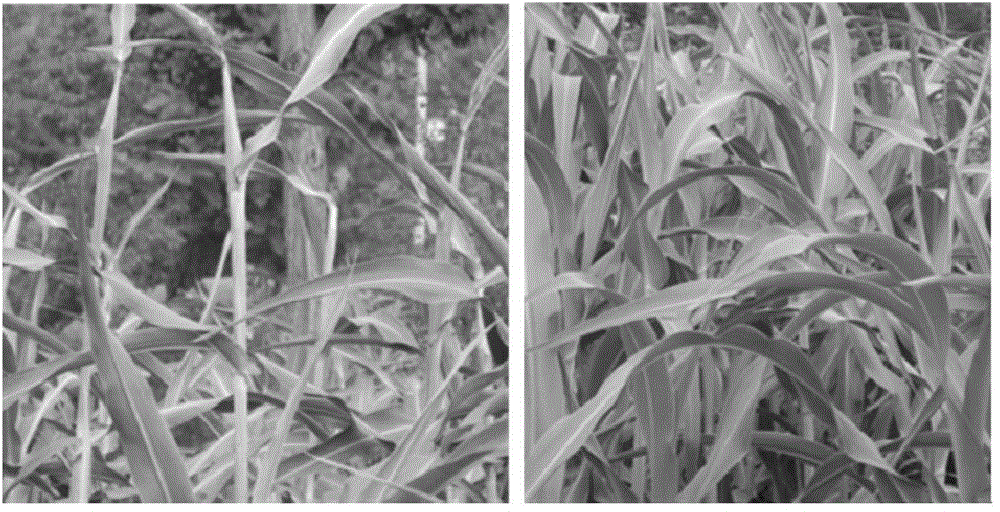
Sweet sorghum breeding method
InactiveCN104782480AExcellent agronomic traitsImprove economyPlant genotype modificationRadiation DosagesDose rate
The invention belongs to the technical field of agriculture, relates to a sweet sorghum breeding method, in particular to a method for breeding sweet sorghum by using a heavy ionmutation breedingtechnique. The sweet sorghum breeding method is mainly characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) performing heavy ion beam radiation, namely, providing carbon, oxygen or argon heavy ion beams by using a heavy ion accelerator, and performing radiation treatment on sweet sorghum seeds at a vertical radiation terminal for 4-6 minutes under the conditions that the energy is 80-100MeV / mu, the radiation dosage is 80-120Gy and the dosage rate is 20-30Gy / minute; (2) performing mutant screening; (3) performing mutant detection; (4) performing hybridized combination optimization. Due to the adoption of the breeding method provided by the invention, after heavy ion radiation, mutant planting resources which are good in precocity property, high in sweet, high in yield and resistant to adversity can be obtained, after being planted for M3-M4 generations, the mutants can be stabilized, and the efficiency of mutant screening, mutant detection and hybridized combination blending is increased by more than 10% when being compared with that of a single crossbreeding method.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
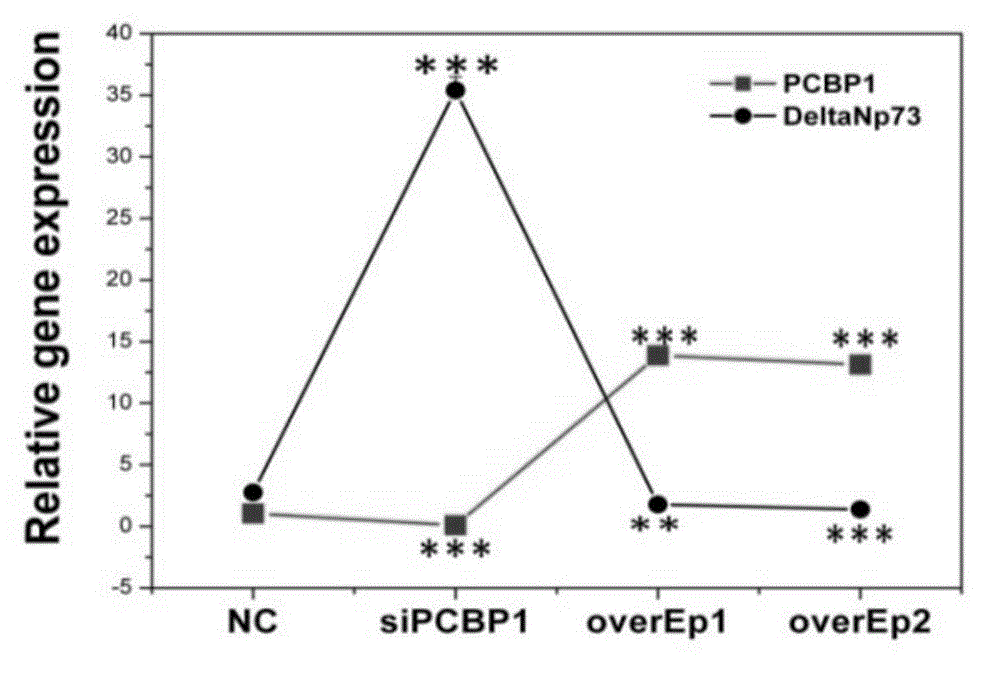
Application of PCBP1 gene in preparing radiotherapy sensitivity enhancing kit
InactiveCN104338150ASignificant radiosensitization synergistic effectPrevent proliferationGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCyclin D1Lymphatic Spread
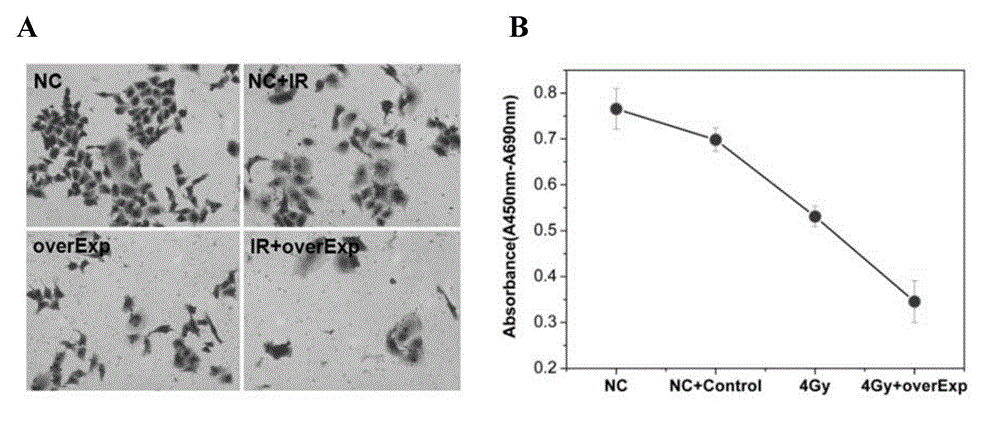
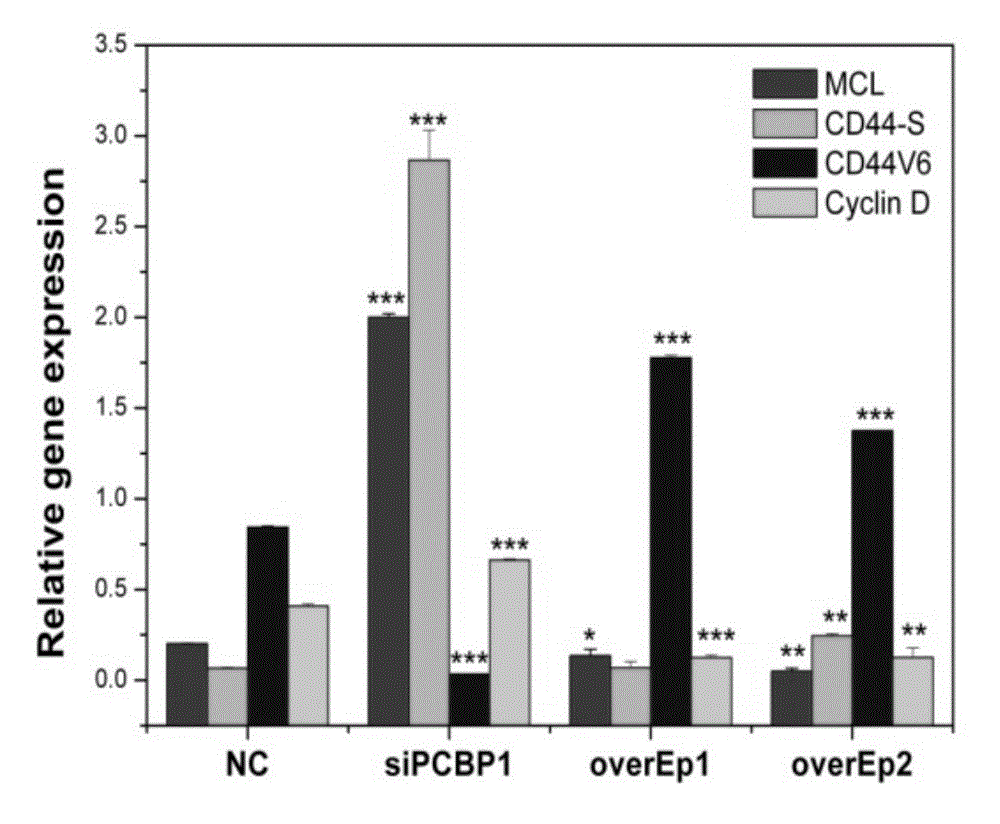
The invention discloses application of a PCBP1 gene in preparing a radiotherapy sensitivity enhancing kit, and in particular relates to application of the PCBP1 gene in preparing a sensitivity enhancing kit for tumor radiotherapy utilizing ionizing radiation including heavy ion rays. The nucleotide sequence of the PCBP1 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and the PCBP1 gene is established in eukaryotic expression plasmid. Together with heavy ion beams, the PCBP1 gene regulates and controls expression of the CD44v6 gene related to tumor metastasis and invasion, inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of HeLa tumor cells, remarkably down-regulates the cell cycle regulatory protein Cyclin D1, prompts cells to generate G0 / G1 retardation, enhances the radiotherapy sensitivity of HeLa cells, up-regulates pro-apoptotic protein Tap73 and expression of the mitochondria apoptosis pathway MCL, down-regulates the apoptosis inhibition DelNp73 protein, and induces apoptosis of many HeLa cells.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com