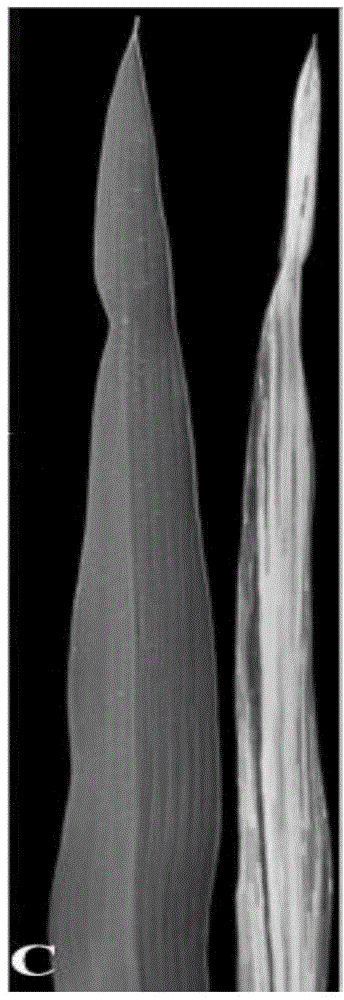
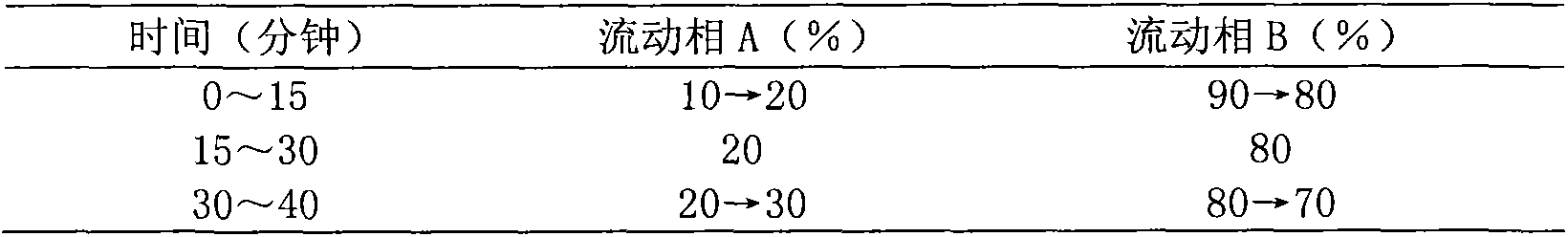
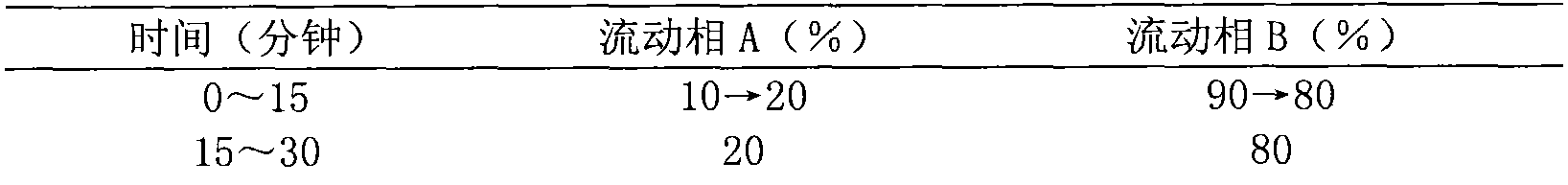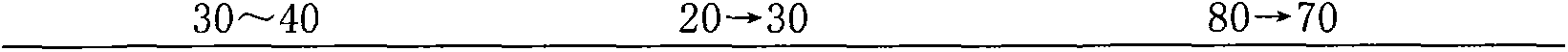Patents
Literature
122results about How to "Excellent agronomic traits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
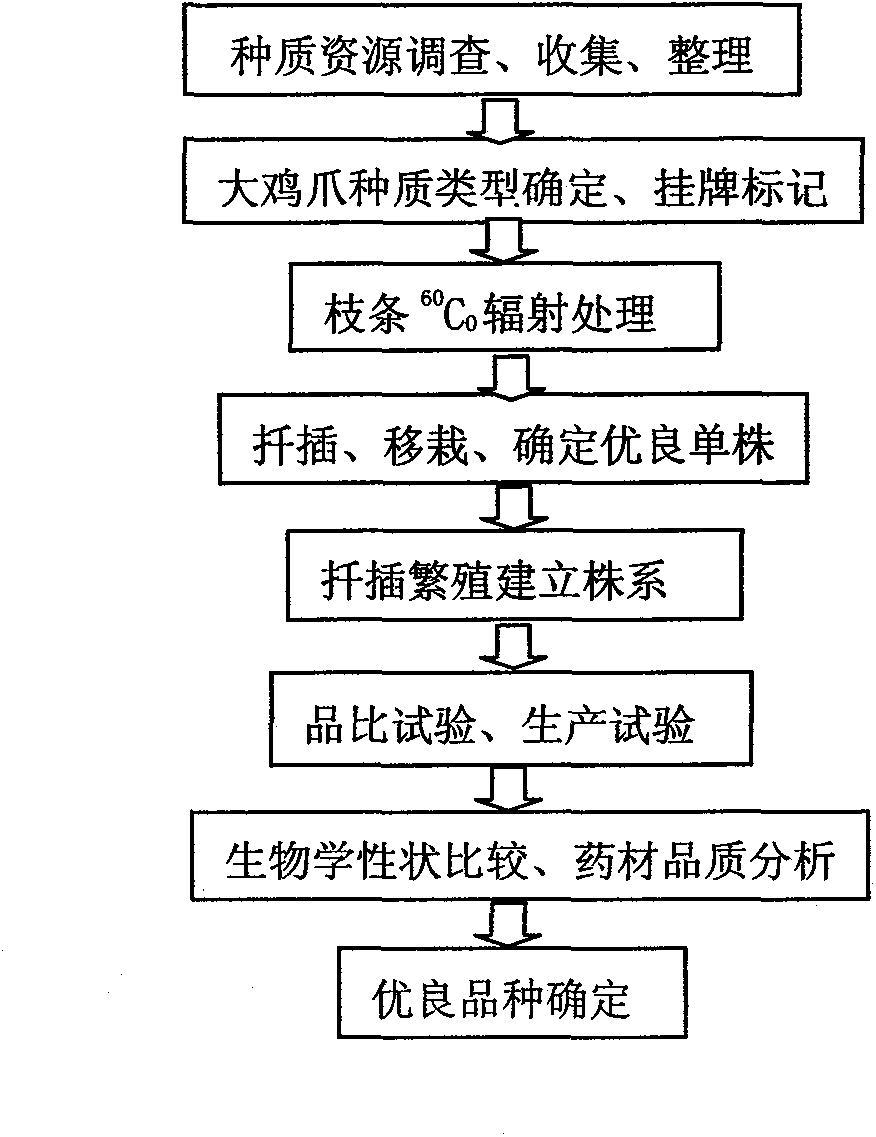
Method for cultivating spring corn in hilly region
The invention discloses a method for cultivating spring corn in hilly region wherein breeds, seeding date, density, mulch film blanketing and mulch film nursery sock grow transplanting, fertilizer application are considered for increasing maize production, experimental investigation and demonstration application are conducted to spread the fine breeds suitable for the Wuling Mountains which have the advantages of late ripening, medium late ripening, big ear, medium-sized to large ear.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for culturing potatoes in mountainous district
InactiveCN102487684ASlow plant growthPrevent growth advantageHorticultureInorganic fertilizerCell budding
The invention discloses a method for culturing potatoes in a mountainous district. The method comprises the following steps of: A, variety selection: selecting a variety with excellent stress resistance and yielding ability and detoxified seed potatoes according to the ecology, climate, height above sea level and regional division of labor of the mountainous district; B, seeding and rational close planting: seeding in time so as to ensure that no late frost is met during emergence of seedlings, wherein the early variety is dense within a reasonable density range, the interplanting density is 2,500-3,600 plants per Mu, and the pure planting density is 4,000-4,800 plants per Mu; C, fertilization: (1) combining an organic fertilizer and an inorganic fertilizer, and (2) carrying out nutritional regulation on leaves, spraying a 45-60PPM (Parts Per ,Million) paclobutrazol solution on leaves during a squaring stage, spraying a 0.25%-0.35% monopotassium phosphate solution on leaves during a full-bloom stage, and removing flower buds during the squaring stage, thus improving the potato yield; and D, integrated control of pest and disease damage: carrying out integrated control according to the occurrence condition of pest and disease damage during the growing period. The method disclosed by the invention is easy to practice and simple and convenient to operate, adopts the excellent potato variety and the detoxified seed potatoes, is timely in seeding, rational in close planting and scientific in fertilization, and can be used for improving the yield and quality of the potatoes.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
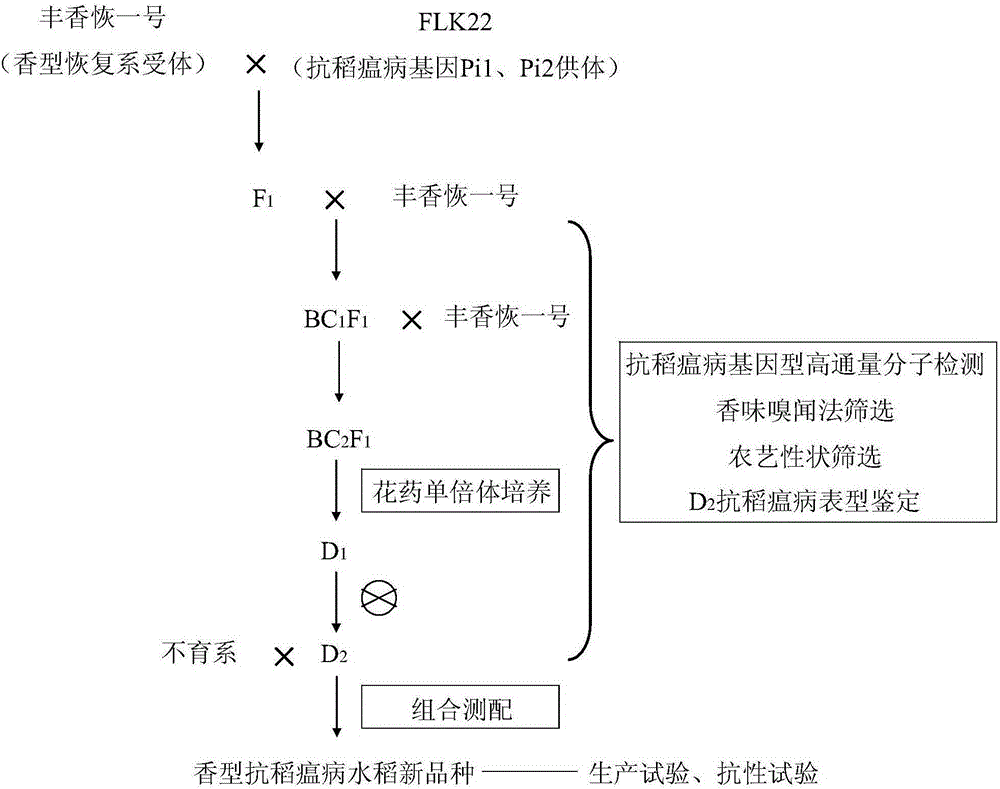
Method for efficient selective breeding of new odor type rice blast resisting rice variety
InactiveCN105210859AExcellent agronomic traitsStable fragrance artificial nose sniffingPlant genotype modificationMarker-assisted selectionHorticulture
The invention discloses a method for efficient selective breeding of a new odor type rice blast resisting rice variety. The method is characterized in that eurytopic and high-quality odor type rice restorer fengxianghui No. 1 is taken as a receptor parent, a rice blast resisting rice material containing rice blast resisting genes is taken as a donor parent, the conventional breeding technique is adopted, the high-throughput molecular marker-assisted selection technique, the rice anther in vitro culture technique and the human nose fragrance smelling and resistance field identification means are comprehensively utilized, a resistant improved odor type rice fengxianghui No. 1 restorer with stable fragrance, high rice blast resistance and excellent agronomic trait is prepared, and the odor type rice blast resisting rice variety is obtained through efficient selective breeding by means of combination and measuring matching of the resistant improved odor type rice fengxianghui No. 1 restorer and a sterile line. The method is efficient, quick and low in cost. Meanwhile, the traditional breeding technique and the modern molecular biological technique are effectively combined, the popularization and application values of the variety obtained through selective breeding are high, and the method can meet the requirement of enterprises for commercial breeding.
Owner:HEFEI FENGLE SEED
Breeding method for multifunctional rice variety
ActiveCN103891604AIncreased Resistant Starch ContentHigh in Vitamin APlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention particularly relates to a breeding method for a multifunctional rice variety, belonging to the technical field of special rice breeding. The method comprises the following steps: selecting four rice varieties with high resistant starch content, low water-soluble protein content, high cellulose content and high vitamin A content as materials, and performing hybrid and multi-cross polymerization; measuring and screening the agronomic trait, yield trait, resistant starch content, water-soluble protein content, cellulose content, vitamin A content and the like of a segregative generation to breed the multifunctional rice variety with excellent agronomic trait and yield trait, high resistant starch content, high cellulose content, high vitamin A content and low water-soluble protein content. Rice produced by using the variety has the health functions of reducing blood sugar and blood fat and losing weight, is suitable for taking by patients with kidney diseases and diabetes, and has a very good nutritional health function on the type of patients.
Owner:FUJIAN KINGSANTO DEV CO LTD
Breeding method for new cabbage type rape line
InactiveCN106134982AEasy to viewReduce erucic acid contentPlant genotype modificationSocial benefitsAgricultural science
The invention discloses a breeding method for a new cabbage type rape line, and belongs to the field of a plant new variety breeding method. According to the breeding method disclosed by the invention, a cabbage type rape line is synthesized by interspecific hybridization of cabbages and Chinese cabbages, and the synthesized cabbage type rape line is subjected to quality genetic improvement of economical characters, erucic acid and glucosinolate so as to breed one new ornamental rape line with a bran-new petal color and a bran-new stalk color; the new cabbage type rape line meets both requirements for ornamental value and oil use, and brings greater economic benefits and social benefits for rape production and the tour and sightseeing industry.
Owner:INST OF IND CROPS HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing corn type II embryogenic calli
InactiveCN102217533APromote regenerationExcellent agronomic traitsPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsF1 generationTransgenic technology
The invention discloses a method for preparing corn type II embryogenic calli. With the method, a corn inbred line which can produce type II embryogenic calli can be prepared. the method comprises the flowing steps: carrying out selfing among an initial corn inbred line to obtain seeds of an F1 generation; carrying out embryogenic callus induction upon embryos of the F1 generation seeds, such that embryogenic calli are obtained; collecting type II embryogenic calli; carrying out regenerating and cultivating upon the type II embryogenic calli until corn plants are obtained. The obtained corn plants form a target corn inbred line. With type II callus phenotype, the corn material provided by the present invention is easy to regenerate, and the regenerated plants have excellent agronomic properties. According to the present invention, a novel material for present transgenic acceptors is provided, a limitation that presently only non-inbred line Hill are utilized is solved, and the period for cultivating new species of corn by using transgenic technologies is shortened.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Breeding method for black and white sweet glutinous hybrid maize
InactiveCN102986524AGood waxyIncrease sweetnessPlant genotype modificationWaxy cornAgricultural science
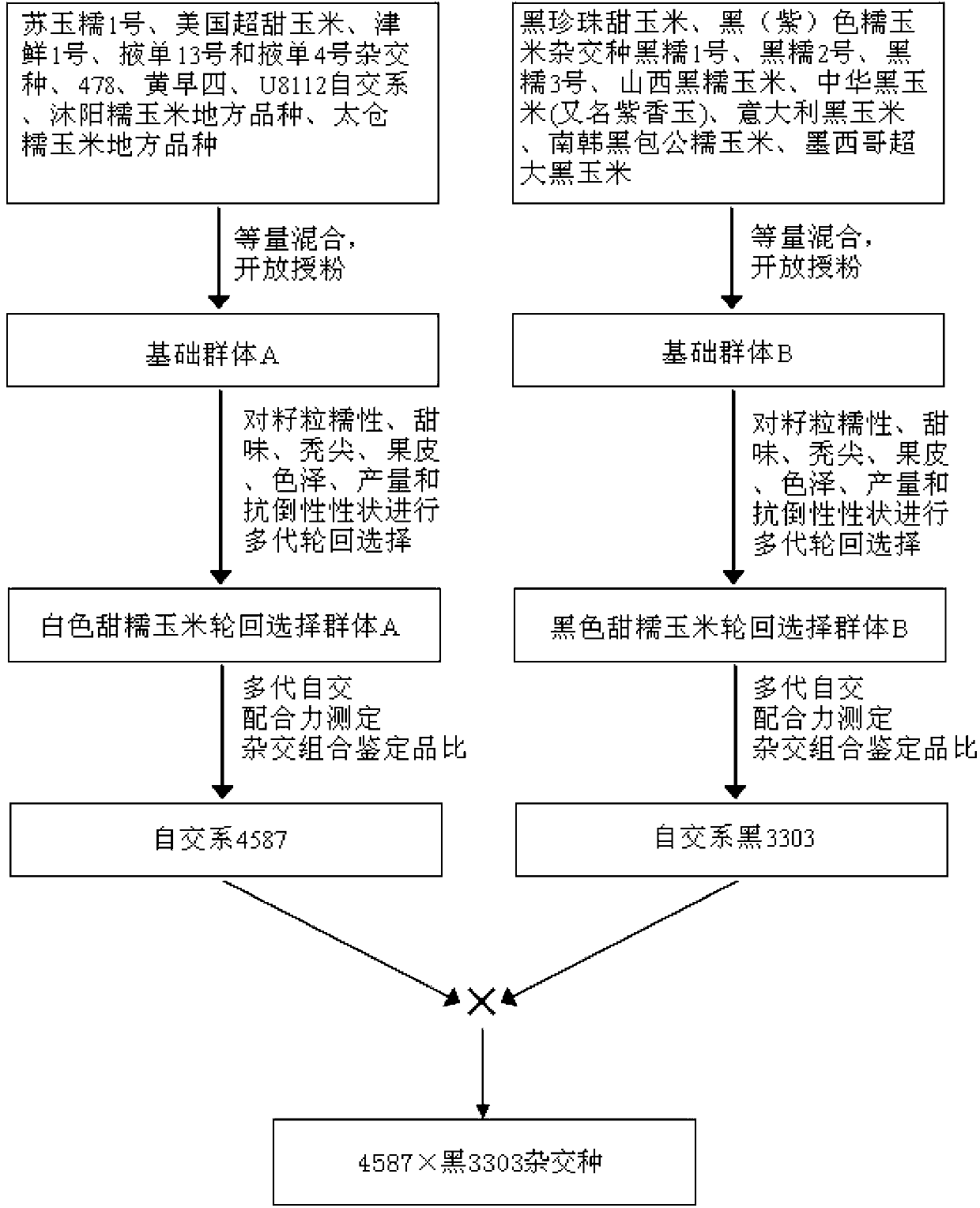
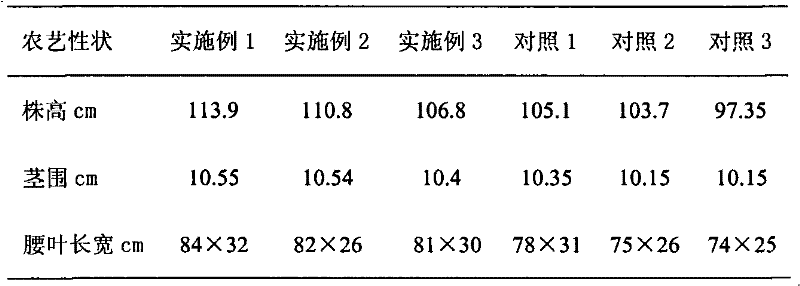
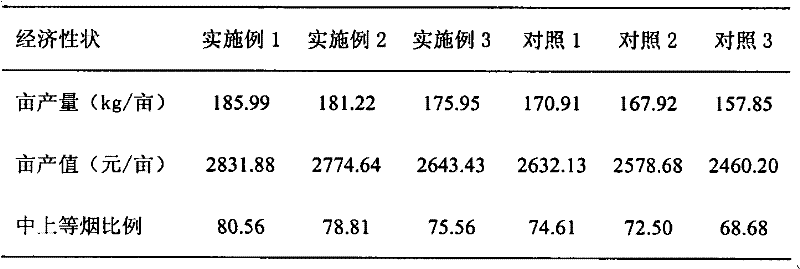
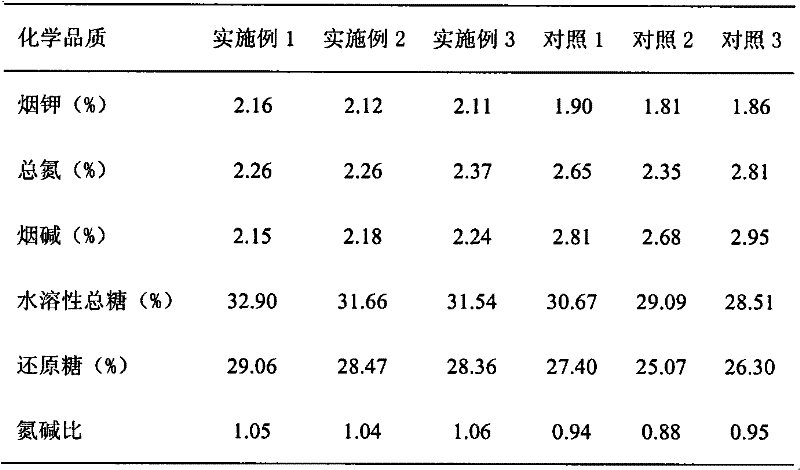
The invention discloses a breeding method for black and white sweet glutinous hybrid maize. The breeding method for black and white sweet glutinous hybrid maize comprises the steps of selecting ultra-sweet maize, glutinous maize, a common high yield multi-resistance maize-inbred line and the like from different regions to be equivalently mixed, openly pollinating the maize, establishing a basic group A, selecting black glutinous maize germplasm from different regions to be equivalently mixed, openly pollinating the maize, and establishing a basic group B; then carrying out recurrent selection to the properties of seeds of the maize to respectively form a white sweet glutinous maize recurrent selection group A and a black sweet glutinous maize recurrent selection group B, obtaining a serious inbred line through multi-generation inbreeding, and screening a white sweet glutinous maize inbred line 4587 and a black sweet glutinous maize inbred line 3303 through combination ability measurement and cross combination quality identification to obtain 4587 X black 3303 hybrid. The breeding method can ensure both the glutinous and sweet genes of a parent inbred line and the hybrid of the parent inbred line, and also ensure the appearance quality, the favorable edible quality, the stability and the consistency of the hybrid. Moreover, the seeds of the maize are black and white.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium compound fertilizer for tobacco 97 and application method for fertilizer
InactiveCN102584387APromote growthStrong disease resistanceFertilizer mixturesPotassium nitrateDiammonium phosphate
The invention discloses a nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium compound fertilizer for a tobacco 97. The compound fertilizer comprises the following single fertilizers in percentage by weight: 13 percent of ammonium nitrate, 38 percent of diammonium phosphate and 49 percent of potassium sulfate. Every 40 to 50 kilograms of the compound fertilizer contain 10 kg / 667m<2> of potassium nitrate and 15 kg / 667m<2>. After the compound fertilizer is used, the whole tobacco plant grows well and has high disease resistance, in particular high pectobacterium atrosepticum resistance; respective agronomic trait values are high; and the length and the width of the waist are increased by 7.69-9.45 percent and 2 to 3.22 percent respectively.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
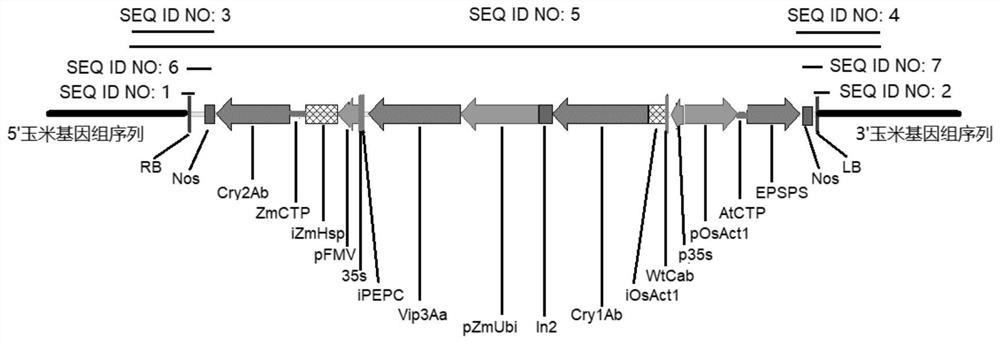
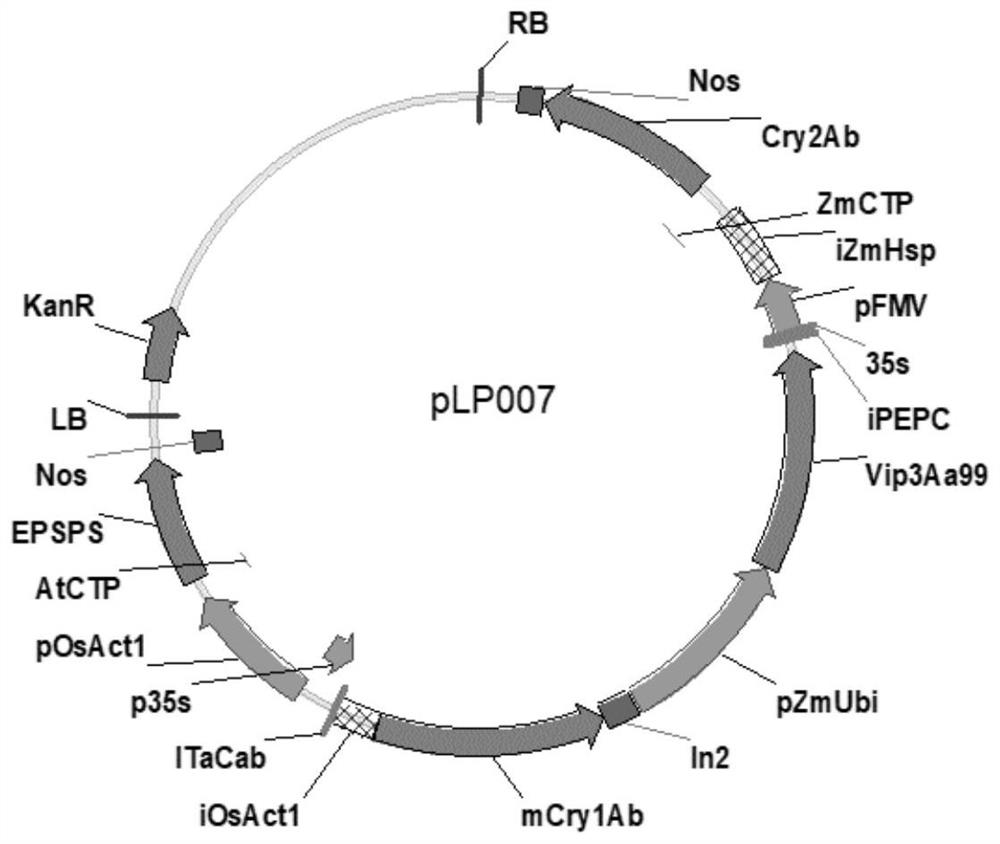
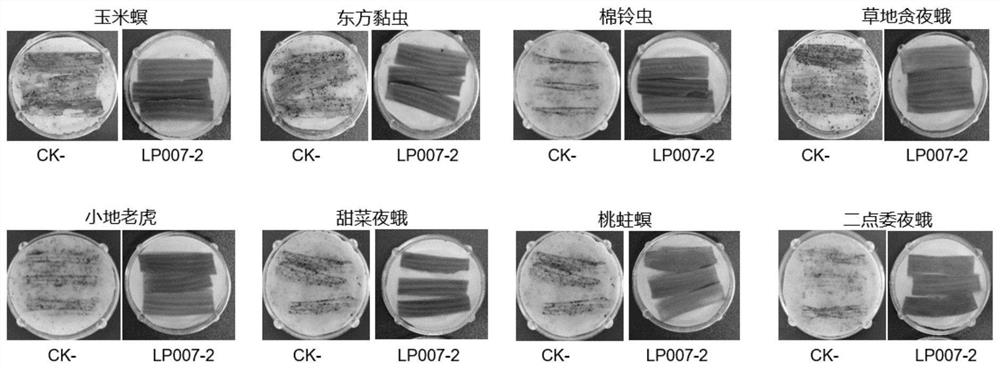
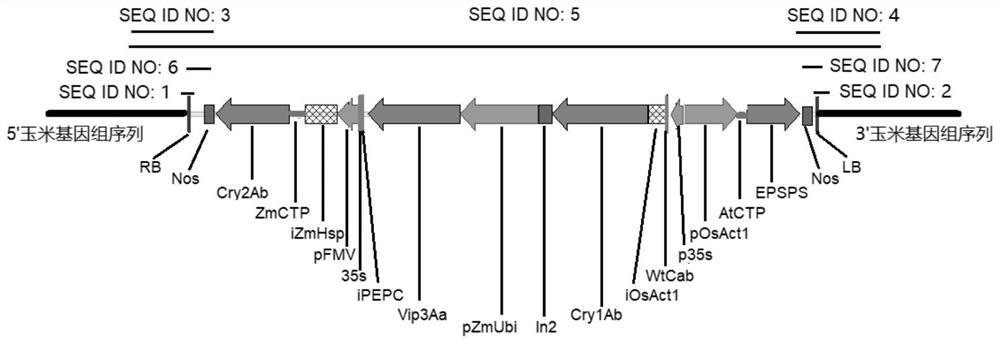
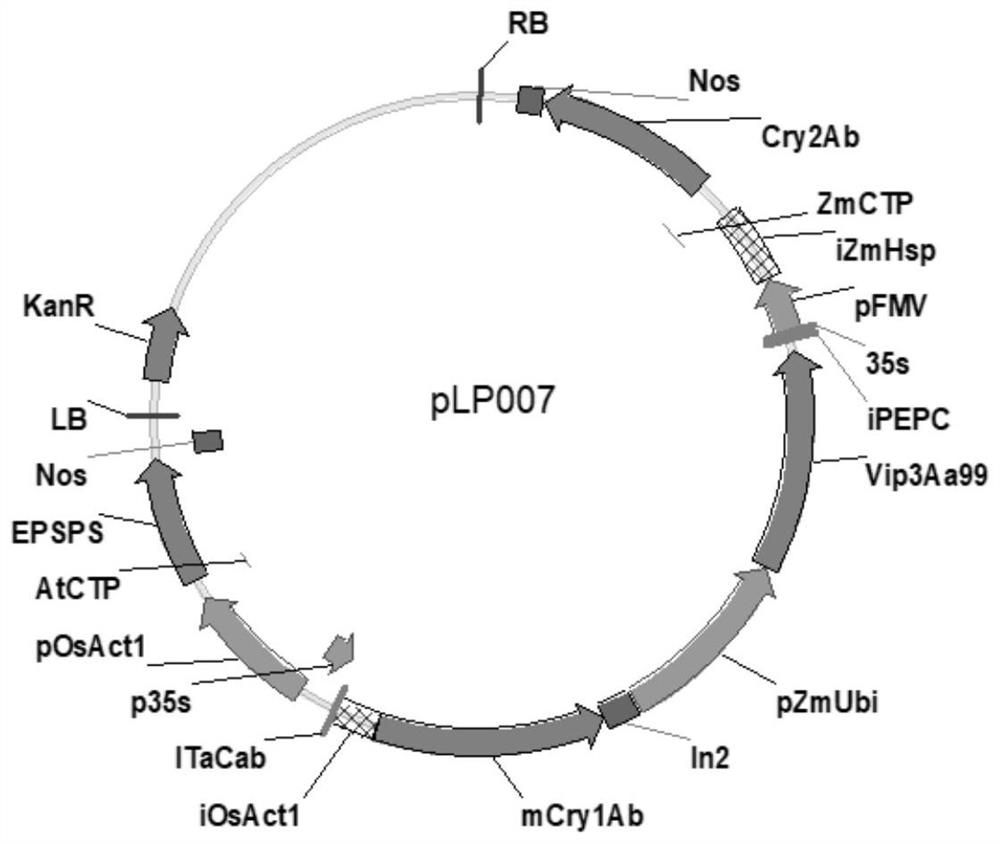
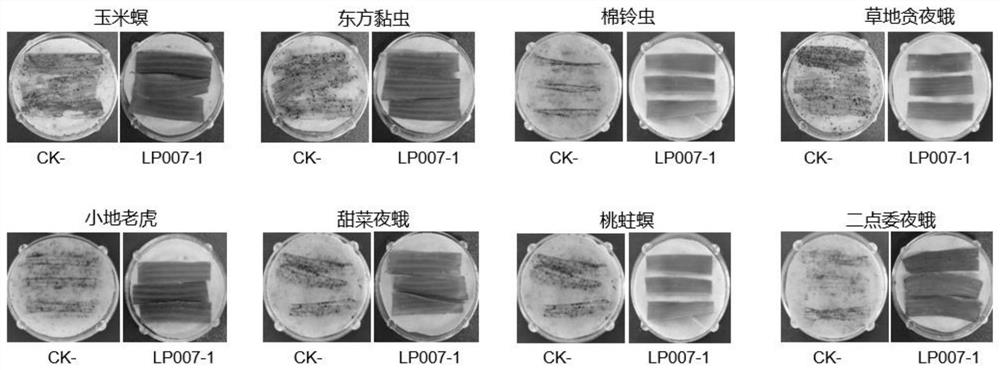
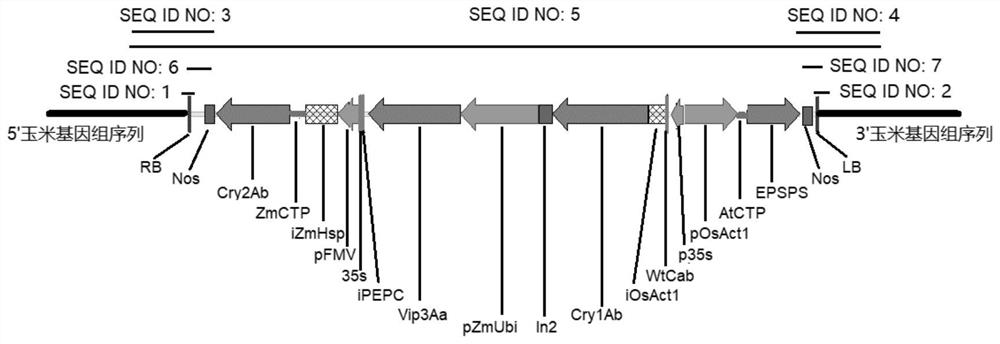
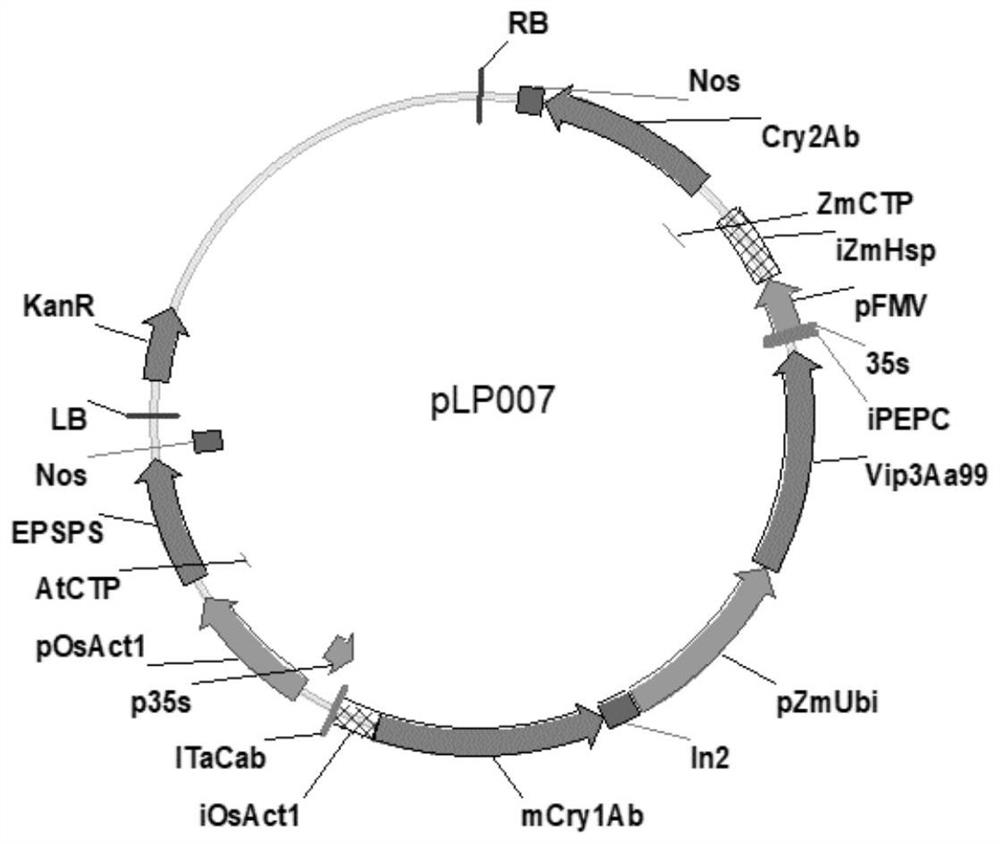
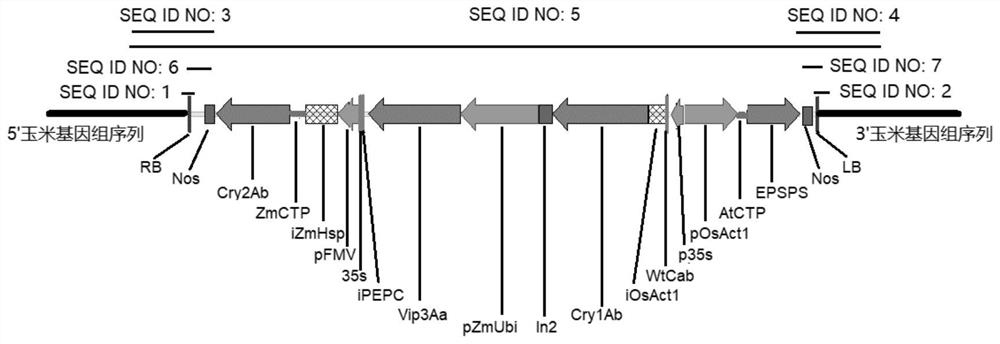
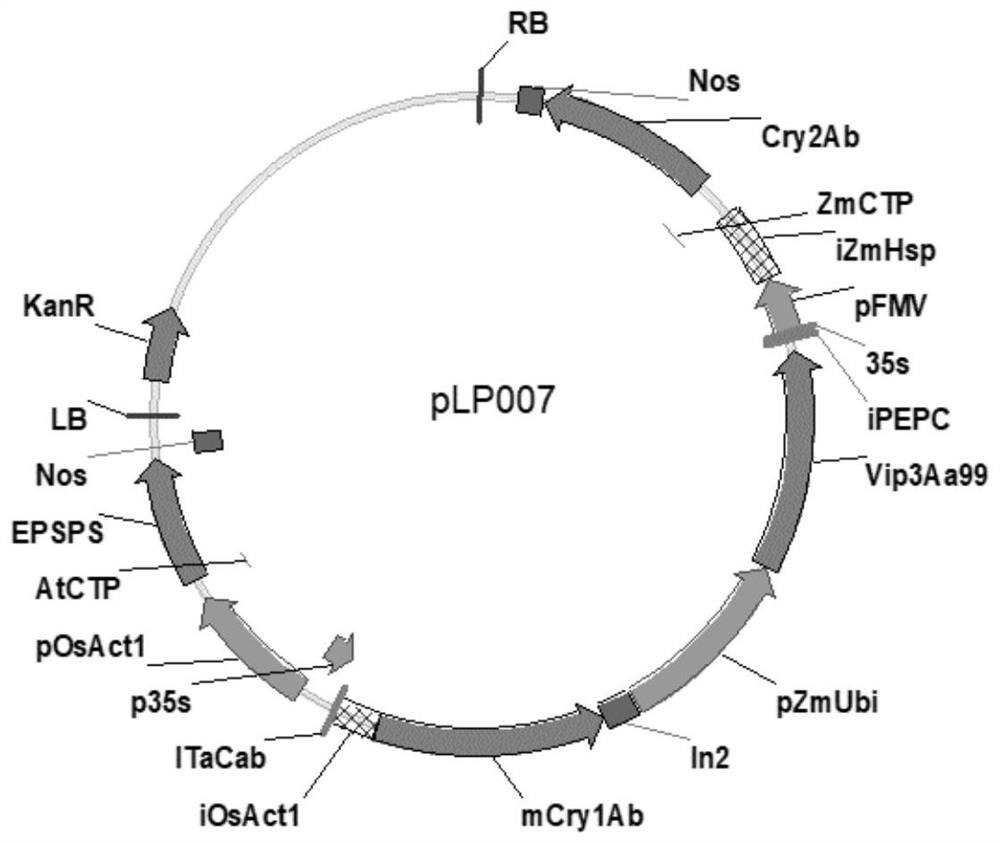
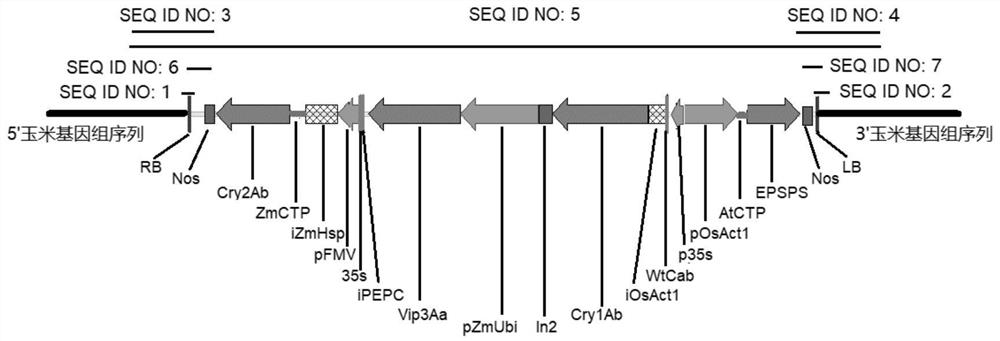
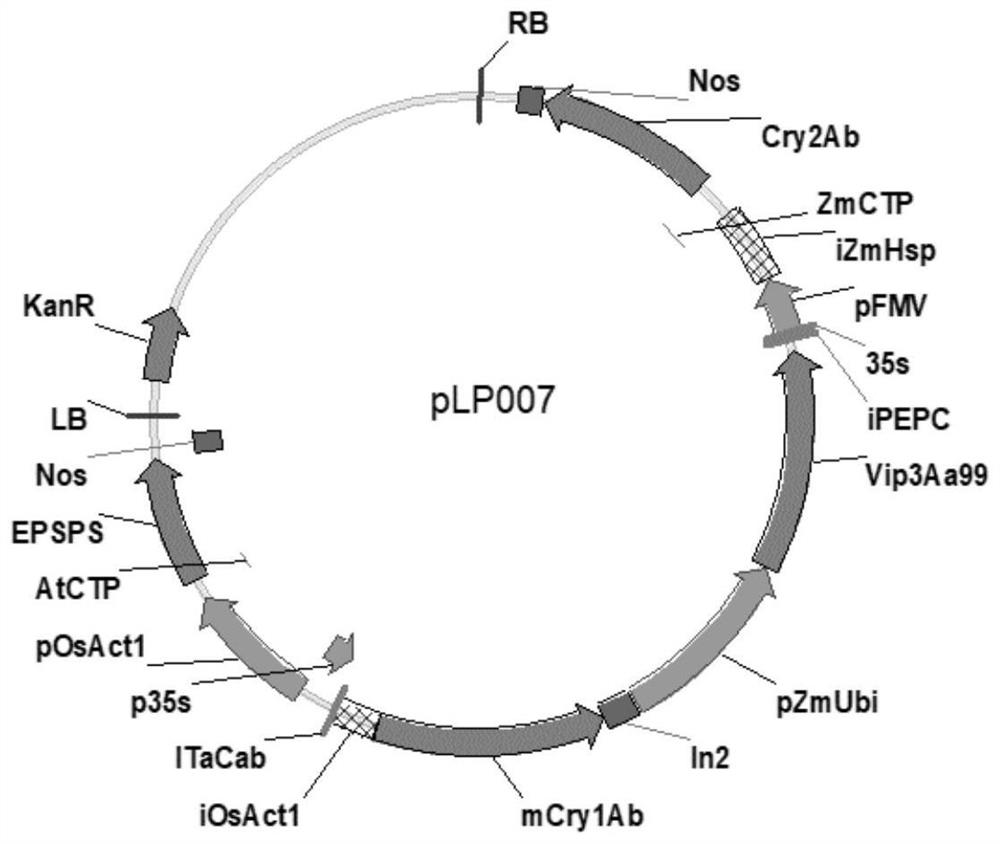
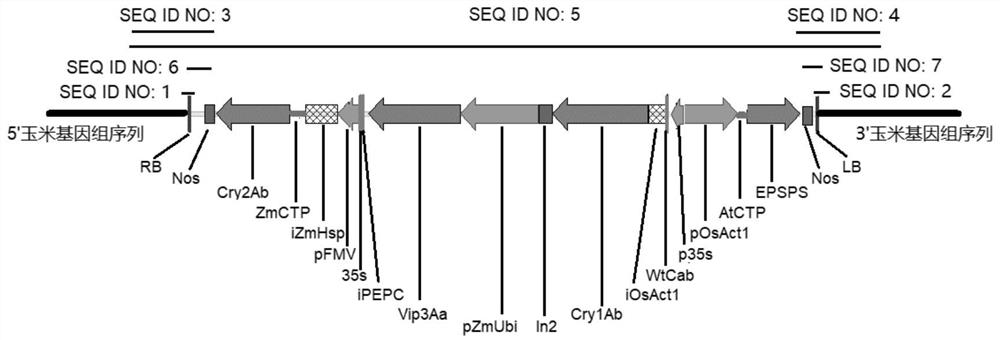
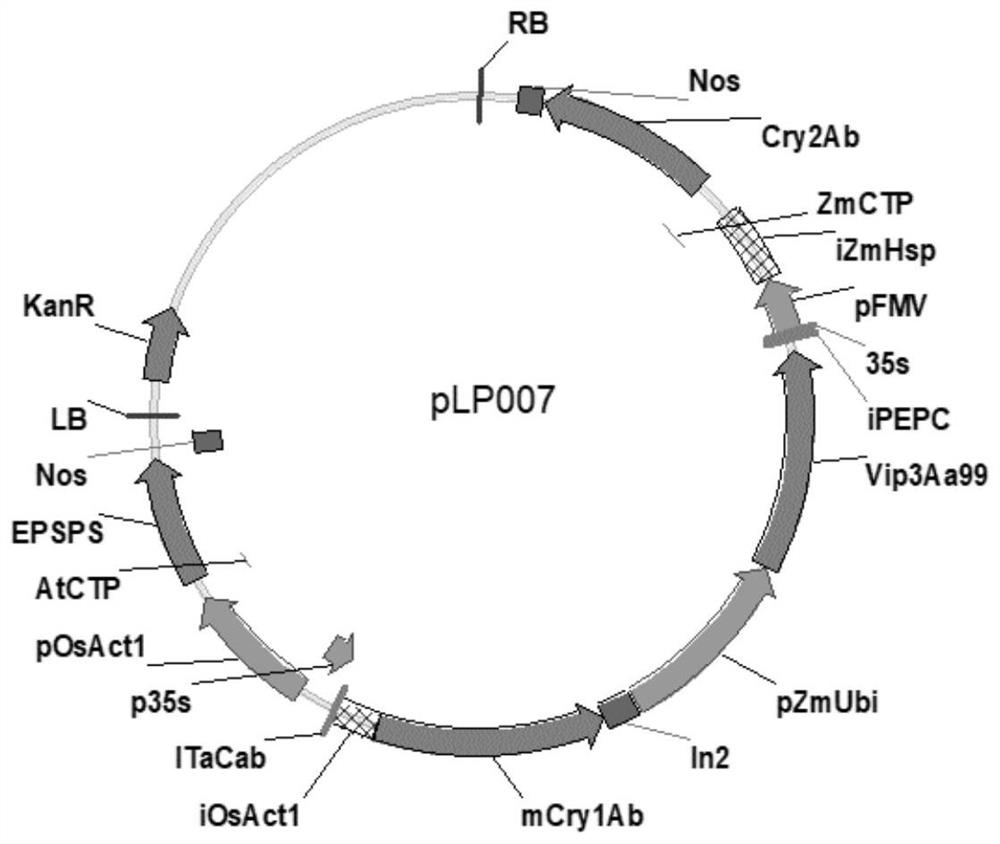
Transgenic maize event LP007-2 and detection method thereof
ActiveCN112831584AImprove toleranceProtection from economic lossMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationOrder LepidopteraNucleic acid sequence
The present invention provides a nucleic acid sequence comprising one or more selected from the group consisting of sequences SEQ ID NO: 1-7 and complementary sequences thereof, said nucleic acid sequence being derived from a plant, seed or cell comprising the corn event LP007-2, a representative sample of the seed comprising said event having been preserved with preservation number CCTCC NO: P202015. The transgenic maize event LP007-2 of the invention is resistant to ingestion impairment of lepidoptera pests and tolerant to phytotoxic effects of agricultural herbicides containing glyphosate. The corn plant with double traits has the following advantages: economic loss caused by lepidoptera pests is avoided; an agricultural herbicide containing glyphosate can be applied to corn crops; the corn yield is not reduced; and the breeding efficiency is enhanced, and the molecular marker can be used for tracking transgenic insertion fragments in a breeding population and a progeny thereof. Meanwhile, the detection method provided by the invention can be used for rapidly, accurately and stably identifying the existence of the plant material derived from the transgenic maize event LP007-2.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Transgenic maize event LP007-1 and detection method thereof
PendingCN112852801AImprove toleranceReduce mortalityMicrobiological testing/measurementCereal cultivationTransgenesisGlyphosate
The present invention provides a nucleic acid sequence comprising one or more selected from the group consisting of sequences SEQ ID NO: 1-7 and complementary sequences thereof, said nucleic acid sequence being derived from a plant, seed or cell comprising the corn event LP007-1, a representative sample of the seed comprising said event having been preserved with preservation number CCTCC NO: P202014. The transgenic maize event LP007-1 of the invention is resistant to ingestion impairment of lepidoptera pests and tolerant to phytotoxic effects of agricultural herbicides containing glyphosate. The corn plant with double characters has the following advantages: economic loss caused by lepidoptera pests is avoided; an agricultural herbicide containing glyphosate can be applied to corn crops; the corn yield is not reduced; and the breeding efficiency is enhanced, and the molecular marker can be used for tracking transgenic insertion fragments in a breeding population and a progeny thereof. Meanwhile, the detection method provided by the invention can be used for rapidly, accurately and stably identifying the existence of the plant material derived from the transgenic maize event LP007-1.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Screening method of salt enduring species of tomato
InactiveCN1433680AStable agronomic traitsAvoid interference with physiological adaptationsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSalt resistanceScreening method
The method for screening tomato salt-enduring character is characterized by that it utilizes the rooting condition of NaCl forced tomato bud, multiplication condition of cotyledonary callus, growth vigor of seedling, rooting condition of collateral cutting of plant-forming stage and vigor of germination of next generation seed to comprehensively judge the sanility tolerance of tomato plant, at the same time accelerate the salt-tolerant breeding process of tomato. Said invention is simple and convenient, easy to learn, the screening process of the whole system is made under the controlled condition, so that it screening result is more reliable.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Breeding method of hybrid rice two-line sterile line with leaves carrying white midribs
ActiveCN104054570AImprove CMS and hybrid purityExcellent agronomic traitsPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceSingle plant
The invention discloses a breeding method of a hybrid rice two-line sterile line with leaves carrying white midribs. The breeding method comprises the following steps: with Zhe midrib rice as a male parent and a rice variety of the two-line sterile line as a female parent, hybridizing to obtain F1-generation seeds; selfing the F1-generation seeds; performing back-crossing on fertile rice plants with excellent characters and white midribs, which are selected from an F2-generation plant, and the rice variety of the two-line sterile line to obtain BC1F1-generation seeds; performing back-crossing on an excellent fertile plant which is selected from the BC1F1-generation seeds, and the rice variety of the two-line sterile line to obtain BC2F1-generation seeds; repeating selfing and back-crossing, performing one-time selfing after continuous back-crossing for twice, and performing back-crossing for the last time; and selfing later generations obtained after the last-time back-crossing, selecting sterile single plants with leaves carrying white midribs and excellent characters from the selfed later generations, and developing breeding of a system to obtain the hybrid rice two-line sterile line. In the sterile line obtained by the invention, the marked characters are expressed in the midribs of the leaves only, without influencing the economical characters; hybrids can be simply rejected, and the purity can be identified.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Selective breeding method for black glutinous maize inbred line
ActiveCN102870668AFull of nutritionUnique tastePlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceHigh stress
The invention discloses a selective breeding method for a black glutinous maize inbred line, which includes the following steps: (1) Jinnuo No. 8 is chosen as female parent and Suyunuo No. 5 is chosen as male parent for hybridization, so that hybrid ears are obtained; (2) after the seeds of the hybrid ears are planted, Jinnuo No. 8 is used as the male parent for backcross, so that backcrossed ears are obtained; (3) after being planted, the seeds of the backcrossed ears are bagged to be inbred, ears with black cobs and seeds are chosen, each ear is separately threshed, the seeds of each ear are planted in a row, and thereby different ear rows are formed; all the individual plants in each ear row are bagged to be inbred, so that inbred ears are obtained, and the inbred ears in the different ear rows are separately harvested; (4) the ear rows in which both the cobs and seeds of all the inbred ears are black are chosen to be left, the seeds of the inbred ears are planted, and according to stress resistance and qualitative character, the excellent individual plants are chosen to be continuously inbred for three generations, so that the black glutinous maize inbred line is obtained. The black glutinous maize inbred line has the advantages of rich nutrition, unique taste, thin pericarp, high glutinousness, high stress resistance, wide applicability and excellent agronomic character.
Owner:NANJING INST OF VEGETABLE SCI
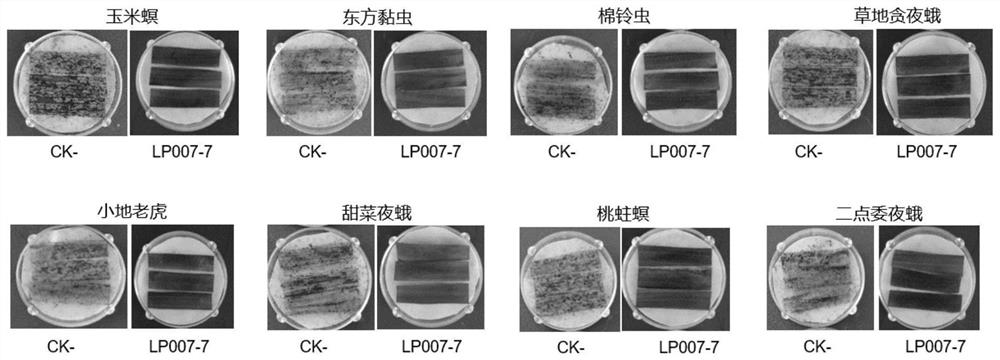
Transgenic maize event LP007-7 and detection method thereof
ActiveCN112852991AReduce mortalityLow victimization rateMicrobiological testing/measurementCereal cultivationOrder LepidopteraNucleic acid sequence
The present invention provides a nucleic acid sequence comprising one or more selected from the group consisting of sequences SEQ ID NO: 1-7 and complementary sequences thereof, said nucleic acid sequence being derived from a plant, seed or cell comprising the maize event LP007-7, a representative sample of the seed comprising said event having been preserved with preservation number CCTCC NO: P202020. The transgenic maize event LP007-7 of the invention is resistant to ingestion impairment of lepidoptera pests and tolerant to phytotoxic effects of agricultural herbicides containing glyphosate. The corn plant with double characters has the following advantages: economic loss caused by lepidoptera pests is avoided; an agricultural herbicide containing glyphosate can be applied to corn crops; the corn yield is not reduced; and the breeding efficiency is enhanced, and the molecular marker can be used for tracking transgenic insertion fragments in a breeding population and a progeny thereof. Meanwhile, the detection method provided by the invention can be used for rapidly, accurately and stably identifying the existence of the plant material derived from the transgenic maize event LP007-7.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Dominant dwarf rice related protein, encoding gene thereof and application
ActiveCN101747420AIncrease productionGood plant height traitsMicroorganismsPlant peptidesBiotechnologyProtein
The invention discloses dominant dwarf rice related protein, an encoding gene thereof and application. The protein is the following a) or b) protein: a) the protein which comprises an amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence list; b) the protein which comprises the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 1 in the sequence list, is through the replacement and / or the missing and / or the adding of one or more amino acid residues, is related to the character of a dwarf plant, and is derived from a). A mutant gene Slrl-d4 provided by the invention is mutated from a single base of a TVHYNP motif on the N terminal of a gene SLRl (SLENDERRICEl). The mutant gene is a dominant gene, can lead a rice plant to produce the character of the dwarf plant, so as to facilitate the improvement of the rice yield; the height of an F1 generation plant obtained by the hybrid of the mutant containing the gene and a normal wild-type indica rice 3037 is between that of the mutant parent and the wild parent, and the F1 generation plant shows good plant height and does not have other bad character. Therefore, the mutant gene is a novel dwarf plant resource with excellent economical character, and will display a significant role in the breeding of the plant, in particular the rice.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for rejuvenating and detoxifying edible fungal strain by using protoplast regeneration technology
The invention relates to the domain of cell engineering, in particular to a method for rejuvenating and detoxifying an edible fungal strain by using protoplast regeneration technology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting parents, preparing protoplast, regenerating the protoplast, and establishing an evaluation standard for rejuvenating and detoxifying the edible fungal strain. The step of preparing the protoplast comprises the step of selecting steady infiltration agent solute, steady infiltration agent concentration, degrading enzyme, enzymolysis time and enzymolysis temperature; and the step of regenerating the protoplast comprises the step of selecting a pre-culture medium and a culture method. The method has the advantages that the effects of removing viable bacteria in the edible fungal and inhibiting factor accumulation are achieved by obtaining the protoplast so as to fulfill the purposes of rejuvenating and detoxifying the edible fungal and recover good properties of the edible fungal. For example, the comprehensive properties of oyster mushroom 89 and pleurotus ferulae 10 are remarkably superior to those of a contrast variety in the aspects of yield, adaptability, commercial property, impure fungal resistance and the like, and the remarkable economic benefit is produced.
Owner:TANGSHAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for recurrently and selectively breeding non-glutinous rice by using recessive cytoblast sterile material
ActiveCN101773067ARich genetic baseBreak the chainMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceMarker-assisted selection
The invention discloses a method for recurrently and selectively breeding non-glutinous rice by using a recessive cytoblast sterile material, which mainly comprises the following steps: hybridizing a sterile strain with recessive cytoblast sterile gene ms-np serving as a female parent and 20 to 30 rice materials serving as male parents, and backcrossing one generation; then, selecting seeds on excellent sterile strains in the later generations, and equivalently mixing the seeds to form a first recurrent selective population; and repeating the recurrent selection process, selecting the excellent fertile strains to a pedigree method at any time, combining molecular marker-assisted selection, and breeding a new variety. The method has the advantages that: recessive cytoblast sterility is used for performing a large amount of hybridization so as to enrich the hereditary basis of the breeding material; new rice materials can be added at any time so as to continually improve the population; moreover, the method avoids manual castration and pollination so as to save a large amount of manpower; and by utilizing a DNA molecular marker for assisting in selection, the method shortens the breeding progress and time, and reduces the breeding cost.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Ultraviolet mutation breeding and acclimatization method of salt-resisting domestic fungus
InactiveCN102487821AOpen up a new way of mutation breedingEasy to operateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureDry weightUltraviolet
The invention discloses an ultraviolet mutation breeding and acclimatization method of a salt-resisting domestic fungus. According to the invention, initial domestic fungus strains are activated and are subject to mycelium ultraviolet mutation; salt-resisting stains are subject to primary screening, acclimatization and secondary screening by using salt-containing selective culture media, such that the salt-resisting stain is obtained. The method is suitable to be used in salt-resisting stain breeding and acclimatization of domestic fungus varieties such as cap fungus, shiitake fungus and Jew's ear. The method is advantaged in that: the high-salt-resisting mutation strain is obtained with the mycelium ultraviolet mutation and acclimatization method, such that a novel approach of salt-resisting cap fungus breeding is developed. The operation processes are simple, a small amount of equipment is required, the cost is low, such that the domestic fungus breeding method is easy to popularize. A mutation period is short, a forward mutation rate is improved, and an effect is substantial. The obtained strain has a salt-resisting capacity of 2%, stable hereditary characters, and excellent agronomic characters. When the method is used in the productions in saline alkali lands, the quality of cap fungus fruiting bodies is improved; and a fresh-to-dry weight ratio and a storing tolerance are improved by more than 50%. Therefore, the quality of cap fungus is effectively improved, the production cost is reduced, and the economic benefits are substantially improved.
Owner:天津市林业果树研究所
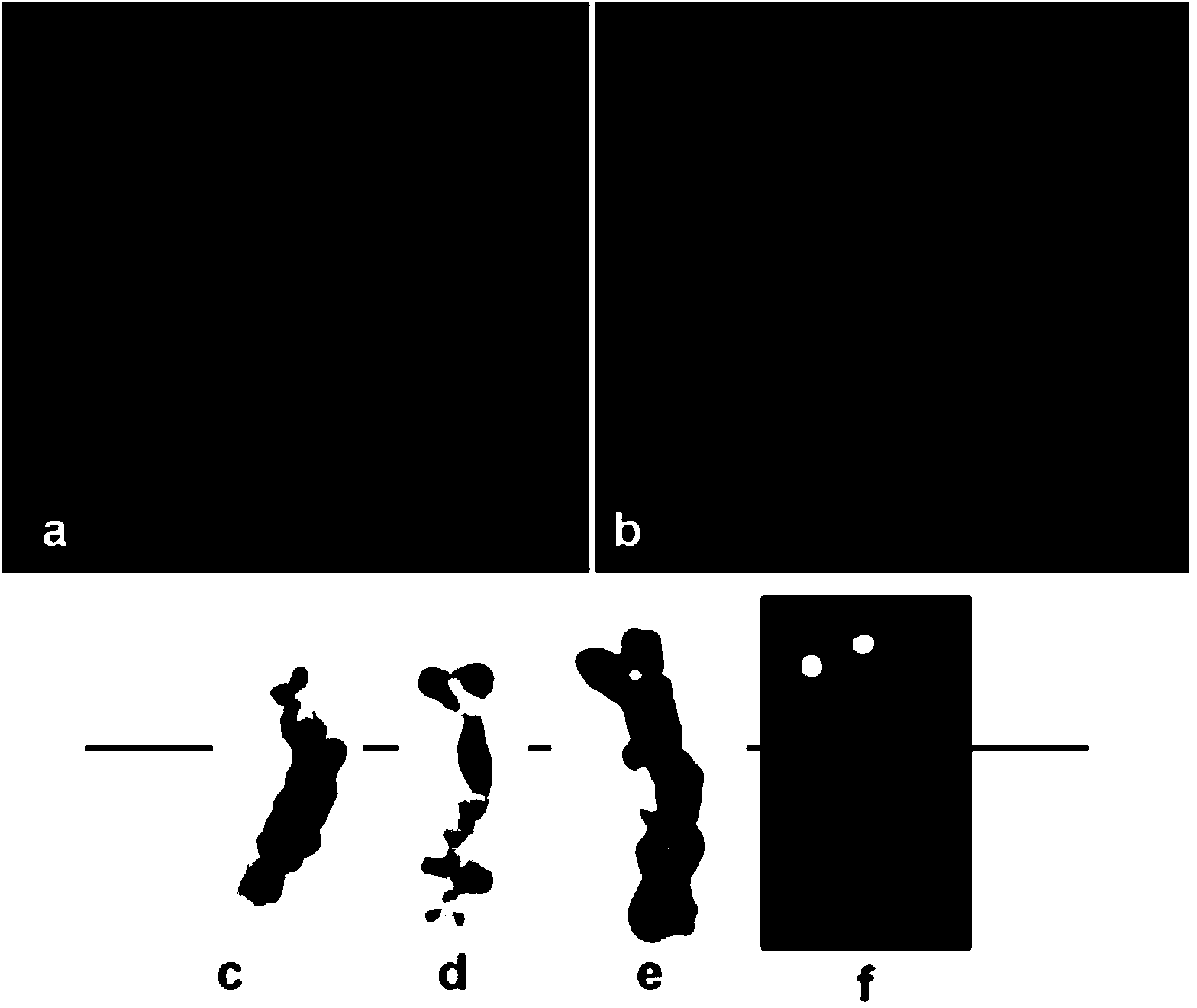
Method for seed selection of excellent honeysuckle flower Lonicera japonica Thunb II variety
InactiveCN103229716AMaintain genetic stabilityIncrease productionPlant genotype modificationHorticultureMedicinal herbsChlorogenic acid
The invention relates to a method for seed selection of an excellent honeysuckle flower Lonicera japonica Thunb II variety and is suitable for seed selection of a novel honeysuckle flower variety. The method comprises the following steps of collecting branches of a large chicken feet-type farm-variety plant in the main honeysuckle flower producing area in the Pingyi county of the Shandong province, carrying out irradiation mutagenesis by 15 to 25Gy of <60>Co-gamma rays, carrying out cottage and transplant, carrying out single-plant seed selection of variant individuals, carrying out cottage and transplant to obtain a plant system, and carrying out variety comparison and production test. The novel Lonicera japonica Thunb II plant has a short, thick and straight limb, a large amount of branches, long circle-shaped leaves, sparse and short pubescence at leaf veins and leaf edges, internode length of 2.5 to 7cm, average flower bud length of 4.16cm, a large amount of flowers, a long bud period, compact pier piles, concentrated buds, chicken feet-shaped flowers and an early flowering phase, can be picked easily, and is suitable for close planting. Compared with the original large chicken feet-type farm-variety, the honeysuckle flower Lonicera japonica Thunb II obtained by the method has a honeysuckle flower medicinal material yield improved by 20.2%, chlorogenic acid content improved by 17.95% and galuteolin content improved by 15.20%.
Owner:张龙霏 +2
Rice final height-related protein, coding gene thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN101619094AExcellent agronomic traitsHas a high leaf width traitFungiBacteriaFinal heightAgricultural science
The invention discloses a rice final height-related protein, a coding gene thereof and application thereof. The protein is an a) protein or b) protein, wherein the a) protein is formed by an amino acid sequence expressed as the No.2 sequence in a sequence list; and the b) protein is formed by substituting and / or reducing and / or adding one or more amino acids to the amino acid sequence expressed as the No.2 sequence in sequence list, related to the final height of rice and derived from the a) protein. The coding gene of the protein particularly is a 1) gene, 2) gene or 3) gene: the 1) gene is a DNA molecule having a amino acid sequence expressed as the No.1 sequence in the sequence list; under strict conditions, the 2) gene can be crossed with the DNA sequence defined by the No.1 sequence in the sequence list and code the DNA molecule of the rice final height-related protein; and the 3) gene has over 90 percent homology with the 1) gene, and can code the DNA molecule of the rice final height-related protein. The rice final height-related protein and the coding gene thereof have important application values in molecular breeding work.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Breeding method of pepper
InactiveCN104813917AStrong low light abilityExcellent agronomic traitsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue culturePolyethylene glycolPollination
The invention discloses a breeding method of pepper. According to the method, artificial pollination is performed after artificial emasculation of the pepper, a first-filial generation is obtained firstly and then three generations are back-crossed, and then the breeding of the pepper is quickened through a tissue culture technology; a drought-resistant strain is induced through stress treatment of polyethylene glycol. The obtained pepper new product has good stress resistance, can resist the diseases such as diseases, virus diseases and anthracnose of the pepper, is low-temperature-resistant, has high weak light capacity, and organically combines the advantages of different pepper resources. The method has the advantages of superior agronomic characters, good plant growth, increased plant height, difficulty in lodging and high yield.
Owner:CHANGZHOU KEHONG ELECTRONICS DEVICES
Breeding and identifying method of soft and powdery mildew resistant triticum aestivum-Dasypyrum villosum translocation line
ActiveCN104365471AValid identificationExcellent agronomic traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceTriticeae
The invention discloses a breeding and identifying method of a soft and powdery mildew resistant triticum aestivum-Dasypyrum villosum translocation line. The method comprises the steps of hybridizing and backcrossing a triticum aestivum-Dasypyrum villosum 5V alien addition line DA5V and a Chinese spring ph1b1b mutant, identifying individual plants relevant to 5VS and ph1b1bph1b1b from BC1F1 by use of a molecular marker, identifying individual selfed seeds by use of GISH (genomic in situ hybridization) technology, and analyzing individual plants containing translocated chromosomes by use of C-zoning, GISH and molecular markers to prove that the translocated chromosome is T5VS.5AL. A PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer is designed by use of an EST (Expressed Sequence Tag) located on the homologous chromosome group of the fifth part of triticum, a co-dominant marker capable of identifying the translocated chromosome specially can be screened, and homozygosis and heterozygosis translocations can be distinguished. The breeding utilization value of the translocation line can be disclosed through agronomic traits, kernel hardness analysis and powdery mildew resistance identification.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
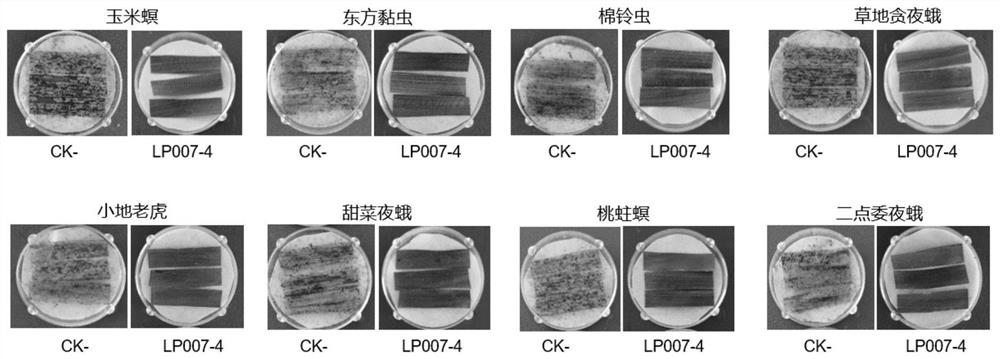
Transgenic maize event LP007-4 and detection method thereof
ActiveCN112831585AImprove toleranceProtection from economic lossMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationOrder LepidopteraNucleic acid sequence
The present invention provides a nucleic acid sequence comprising one or more selected from the group consisting of sequences SEQ ID NO: 1-7 and complementary sequences thereof, said nucleic acid sequence being derived from a plant, seed or cell comprising the corn event LP007-4, a representative sample of the seed comprising said event having been preserved with preservation number CCTCC NO: P202017. The transgenic maize event LP007-4 of the invention is resistant to ingestion impairment of lepidoptera pests and tolerant to phytotoxic effects of agricultural herbicides containing glyphosate. The corn plant with double characters has the following advantages: economic loss caused by lepidoptera pests is avoided; an agricultural herbicide containing glyphosate can be applied to corn crops; the corn yield is not reduced; and the breeding efficiency is enhanced, and the molecular marker can be used for tracking transgenic insertion fragments in a breeding population and a progeny thereof. Meanwhile, the detection method provided by the invention can be used for rapidly, accurately and stably identifying the existence of the plant material derived from the transgenic maize event LP007-4.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Breeding method for improved variety of Lonicera japonica Thunb No.1
InactiveCN103229642AHigh production performance is obviousMaintain genetic stabilityHorticultureFlowering seasonChlorogenic acid
The invention relates to a breeding method for an improved variety of Lonicera japonica Thunb No.1, and is applicable to breeding of new variety of Lonicera japonica Thunb. Farmyard germplasm type Lonicera japonica Thunb branches from main producing area of pingyi county, ShanDong province, are collected; 15-25 Gy60Co-Gamma is taken for radiation induced mutation, and then cuttage and transplant are carried out; seed selection, cottage and transplant for variation individual plant are performed so as to form a strain; the Lonicera japonica Thunb No.1 obtained through variety comparison and production testing has thick and upright branches, oblong, linear oblong and oblong-ovate leaves, has dark green and thick leaves, and has more blossom buds; and flower buds are 4.5 cm in length, bracts are oval and oblong-ovate, the flower season comes earlier, saline-alkaline tolerance and barren resistance and strong adaptability are achieved, and plant diseases and insect pests are less. Compared with common Lonicera japonica Thunb, the Lonicera japonica Thunb No.1 has the advantages that the flower season starts two to three days earlier, the flower bud yield is improved by 16.20 percent, the content of galuteolin of flower bud is 0.106 percent, and the content of chlorogenic acid accounts for 1.75 percent, which is higher than the quality standard of Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (2010).
Owner:张永清 +2
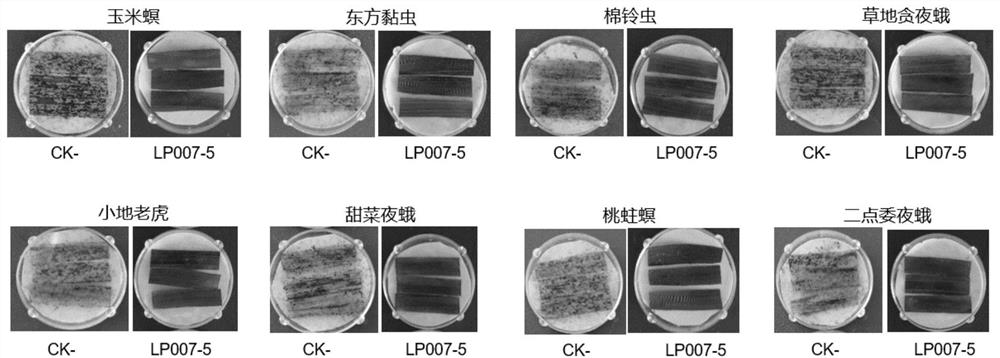
Transgenic Zea mays L. event LP007-5 and detection method thereof
ActiveCN113151534AImprove toleranceProtection from economic lossMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationOrder LepidopteraNucleic acid sequence
The invention provides a nucleic acid sequence. The nucleic acid sequence comprises one or more of sequences SEQ ID NO: 1-7 and complementary sequences thereof, the nucleic acid sequence is derived from a plant, seed or cell comprising a Zea mays L. event LP007-5, and a representative sample of the seed comprising the event is preserved with the preservation number CCTCC NO: P202018. The transgenic Zea mays L. event LP007-5 is resistant to an ingestion impairment of a lepidoptera pest and tolerant to a phytotoxic effect of an agricultural herbicide containing glyphosate. A Zea mays L. plant with double characters has the following advantages that economic loss caused by the lepidoptera pest is avoided; the agricultural herbicide containing the glyphosate can be applied to a Zea mays L. crop; the Zea mays L. yield is not reduced; and the breeding efficiency is improved, and a molecular marker can be used for tracking a transgenic insertion fragment in a breeding population and a progeny thereof. Meanwhile, a detection method can be used for rapidly, accurately and stably identifying the existence of a plant material derived from the transgenic Zea mays L. event LP007-5.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Simplified seed production method of small-grain hybrid rice and small-grain hybrid
ActiveCN110959524ASimple and fast operationImprove efficiencyPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyHybrid seed
The invention discloses a simplified seed production method of small-grain hybrid rice and a small-grain hybrid seed. The simplified seed production method comprises the following steps: 1) cultivating strong seedlings by using Bing 4114 as a male parent; 2) directly sowing the small-grain sterile line Zhuo 201S serving as a female parent in a field, and throwing the male parent subjected to seedling strengthening in the step 1) into the field with the female parent; and 3) after maturity, harvesting the male parent and the female parent in a mixed manner, and screening and separating to obtain the small-grain hybrids. According to the simplified seed production method of the small-grain hybrid rice, disclosed by the invention, the Bing 4114 with high combining ability, strong disease resistance and homozygous genotype is selected as the male parent, and the small-grain sterile line Zhuo 201S with high stigma exsertion rate, good outcrossing characteristic and excellent agronomic traits is selected as the female parent for mixed sowing hybrid seed production; the high-yield, high-quality and disease-resistant rice small-grain hybrid seeds are obtained, male parents and female parents of the small-grain hybrid seeds are subjected to mixed sowing and mixed harvesting, male parent and female parent seed separation is achieved in combination with screening and separation, and therefore simplified seed production of the small-grain hybrid seeds is achieved.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for preparing novel downy-mildew-resistant common head cabbage germplasm through protoplast asymmetric fusion
InactiveCN102181424AImprove economyExcellent agronomic traitsGenetic engineeringFermentationHigh resistanceResistant genes
The invention discloses a method for creating a novel downy-mildew-resistant common head cabbage germplasm through a protoplast asymmetric fusion technology, solves the problems that a common head cabbage variety which has high resistance against downy mildew of cruciferae and is even immune is substantially not available in production at present and overcomes the defects of incompatible distant hybridization, large difficulty and high investment of a genetic engineering technology and the like. The method for preparing the novel downy-mildew-resistant common head cabbage germplasm through the protoplast asymmetric fusion is characterized in that: a brussels sprout carrying downy-mildew-resistant gene is used as a donor; protoplast of the donor is treated through UV (Ultraviolet) ray; the common head cabbage which is sensitive to the downy mildew and has other superior economical and agronomic characters is used as a receptor; and the novel downy-mildew-resistant common head cabbage germplasm is created through a protoplast asymmetric fusion method. In the method, the downy-mildew-resistant gene of the brussels sprout is transferred into a common head cabbage, so that a system for quickly breeding the novel disease-resistant germplasm is established by using a protoplast fusion technology, and a modern cabbage germplasm resource innovation and disease-resistant breeding high-efficiency technical platform is established.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Breeding method of early-maturity middle japonica rice variety
ActiveCN107251834AExcellent agronomic traitsCompact plantPlant genotype modificationPhenotypic traitJaponica rice
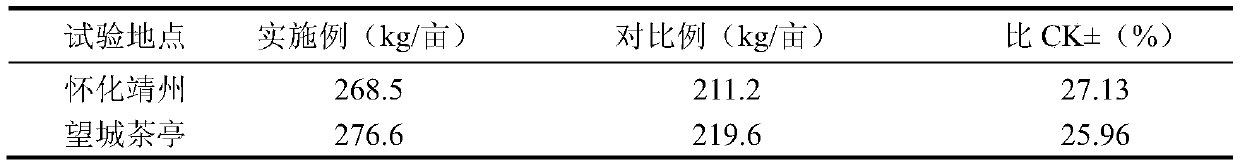
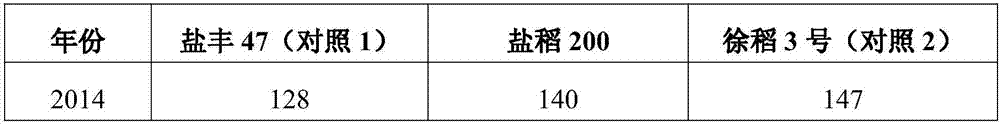
The invention relates to a breeding method of an early-maturity middle japonica rice variety, and belongs to the technical field of plant breeding. The breeding method comprises: using Yanfeng 47 as a female parent and Xudao No.3 as a male parent to perform artificial hybridization matching in Yancheng of Jiangsu province to obtain F0 seeds, planting the seeds in Sanya of Hainan province in winter of the same year, and performing mixed harvesting of F1 seeds at maturity; performing mixed line planting of generations F2 to F5 in Dandong of Liaoning province, Yancheng of Jiangsu province, Dandong of Liaoning province, and Yancheng of Jiangsu province respectively, planting two parents at the same time for each generation as control, and performing mixed harvesting of seeds at maturity, wherein the maturity period of selected individual plants was between that of the two parents, and other characters are similar to that of conventional breeding; planting a strain identification nursery of the generation F6 in Yancheng, and breeding the generation F7 into a new early-maturity middle japonica rice variety 'Yandao 200', which matures 7-8 days earlier than Xudao No.3 in Jiangsu. The yield, resistance, quality and other indexes of the early-maturity middle japonica rice variety conform to the standard of rice variety approval above the provincial level.
Owner:JIANGSU COASTAL AREA AGRI SCI RES INST
Select breeding method of early-maturing high-nutritious red-peel red-fruit-pulp colorized potato
InactiveCN107114231ARich varietyExpand the planting areaPlant genotype modificationOxidation resistantSolanum tuberosum
The invention discloses a select breeding method of an early-maturing high-nutritious red-peel red-fruit-pulp colorized potato. The method comprises the following steps: selecting high-quality early-maturing high-yield broad-application potato varieties to cross-fertilize with oxidation-resistant potato varieties highly containing anthocyanin, polyphenol and the like through sexual hybridization, after single-plant system selection and many years field evaluation of asexual generation, conducting stem peel and fruit pulp color screening on early separate separation, conducting screening of agronomic trait, yield trait, mature period and the like on advanced lines, and breeding red-peel red-fruit-pulp early-maturing new potato varieties being excellent in agronomic traits, rich in antioxidant active substances and capable of maturing in 65 days. The potato has high quality, fragrant taste after steaming, delicate taste, dry matter content of 19.3%, starch content of 13.6%, high anthocyanin content, and polyphenol and antioxidant activity reaching to 800 to 1100mg / kg. The potato cultivated in the invention enriches the varieties of colorized potatoes and expands the planting area of colorized potatoes.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
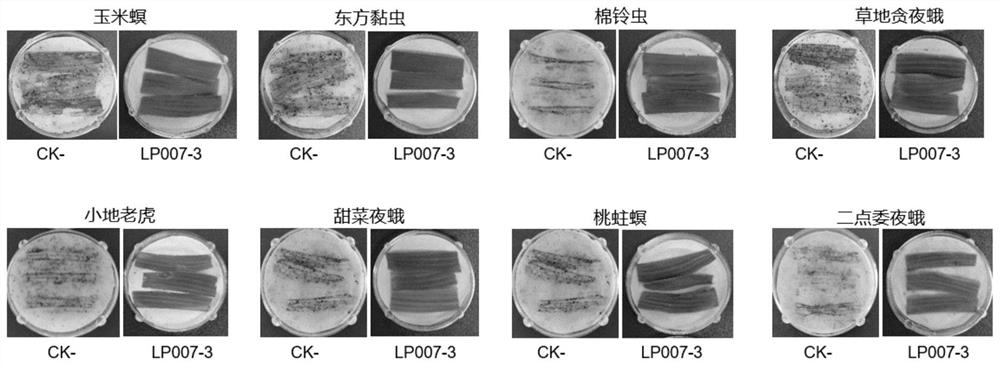
Transgenic maize event LP007-3 and detection method thereof
ActiveCN112877454AImprove toleranceNo reduction in productionMicrobiological testing/measurementCereal cultivationOrder LepidopteraNucleic acid sequence
The present invention provides a nucleic acid sequence comprising one or more selected from the group consisting of sequences SEQ ID NO: 1-7 and complementary sequences thereof, the nucleic acid sequence is derived from a plant, seed or cell comprising the corn event LP007-3, and a representative sample of the seed comprising said event is preserved with preservation number CCTCC NO: P202016. The transgenic maize event LP007-3 of the invention is resistant to ingestion impairment of lepidoptera pests and tolerant to phytotoxic effects of agricultural herbicides containing glyphosate. The corn plant with double characters has the following advantages: economic loss caused by lepidoptera pests is avoided; an agricultural herbicide containing glyphosate can be applied to corn crops; the corn yield is not reduced; and the breeding efficiency is enhanced, and the molecular marker can be used for tracking transgenic insertion fragments in a breeding population and a progeny thereof. Meanwhile, the detection method provided by the invention can be used for rapidly, accurately and stably identifying the existence of the plant material derived from the transgenic maize event LP007-3.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com