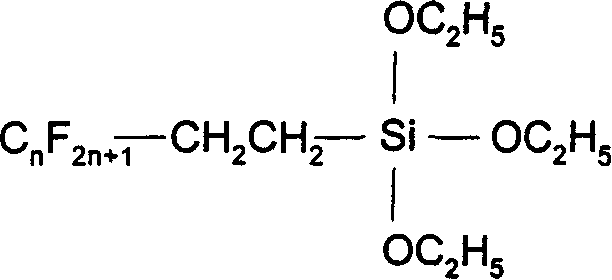
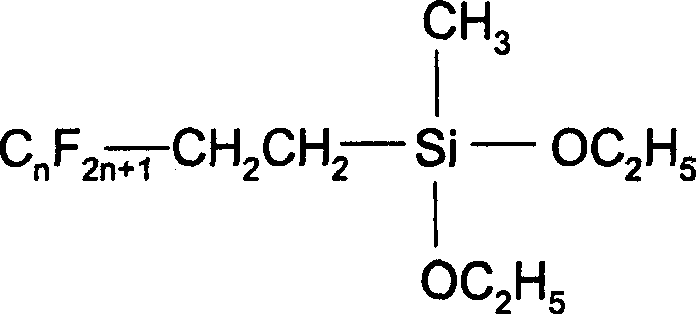
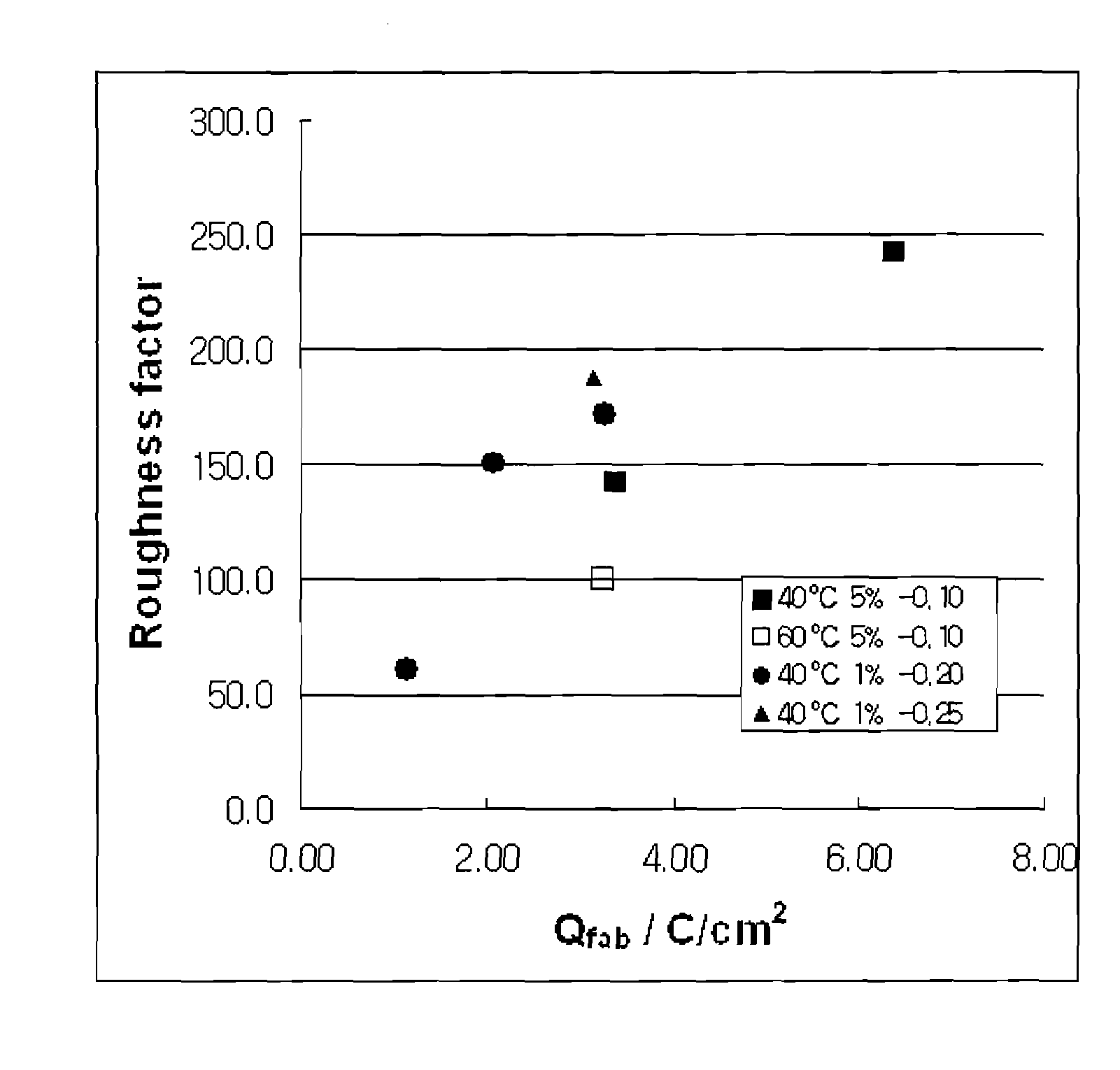
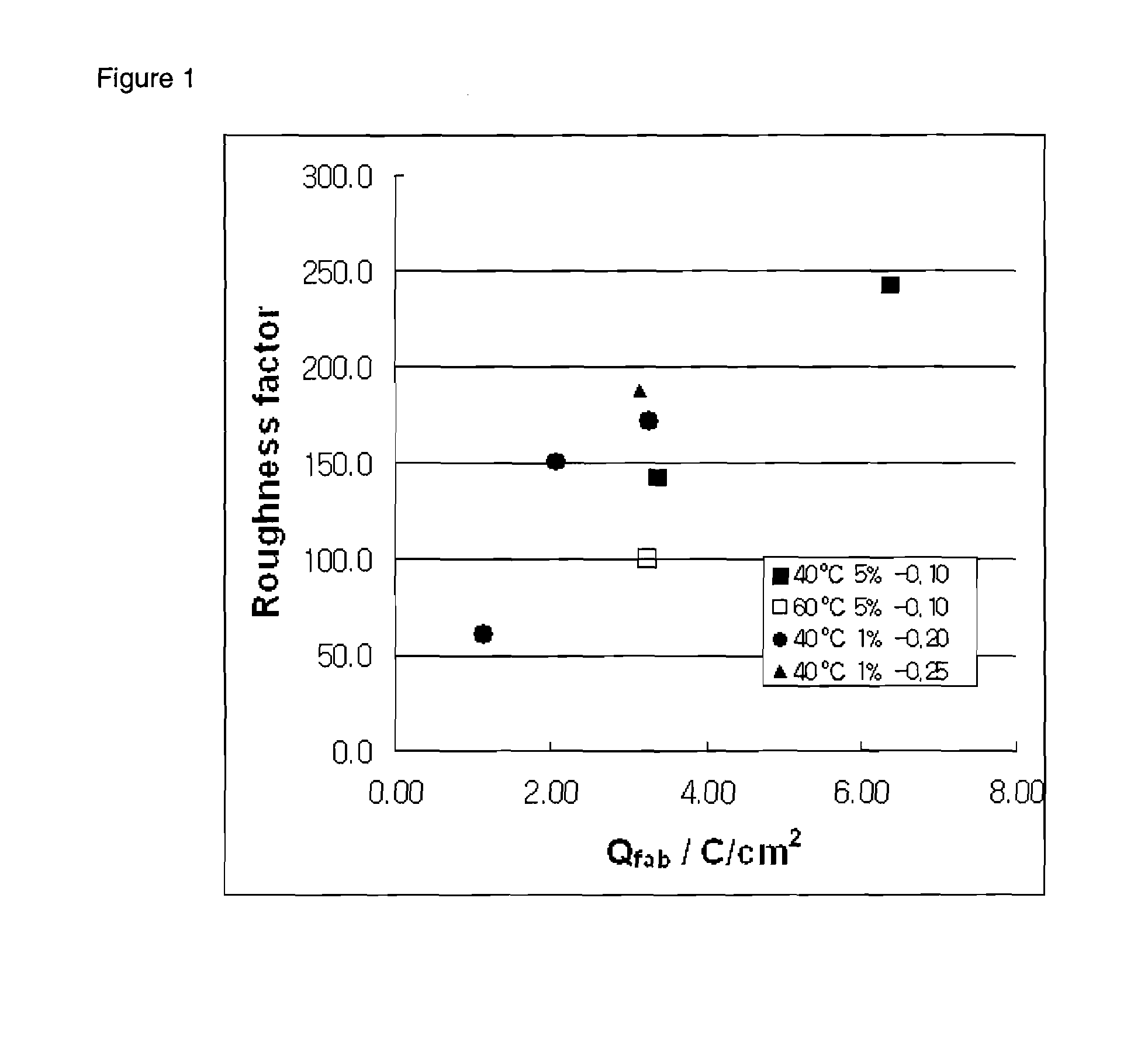
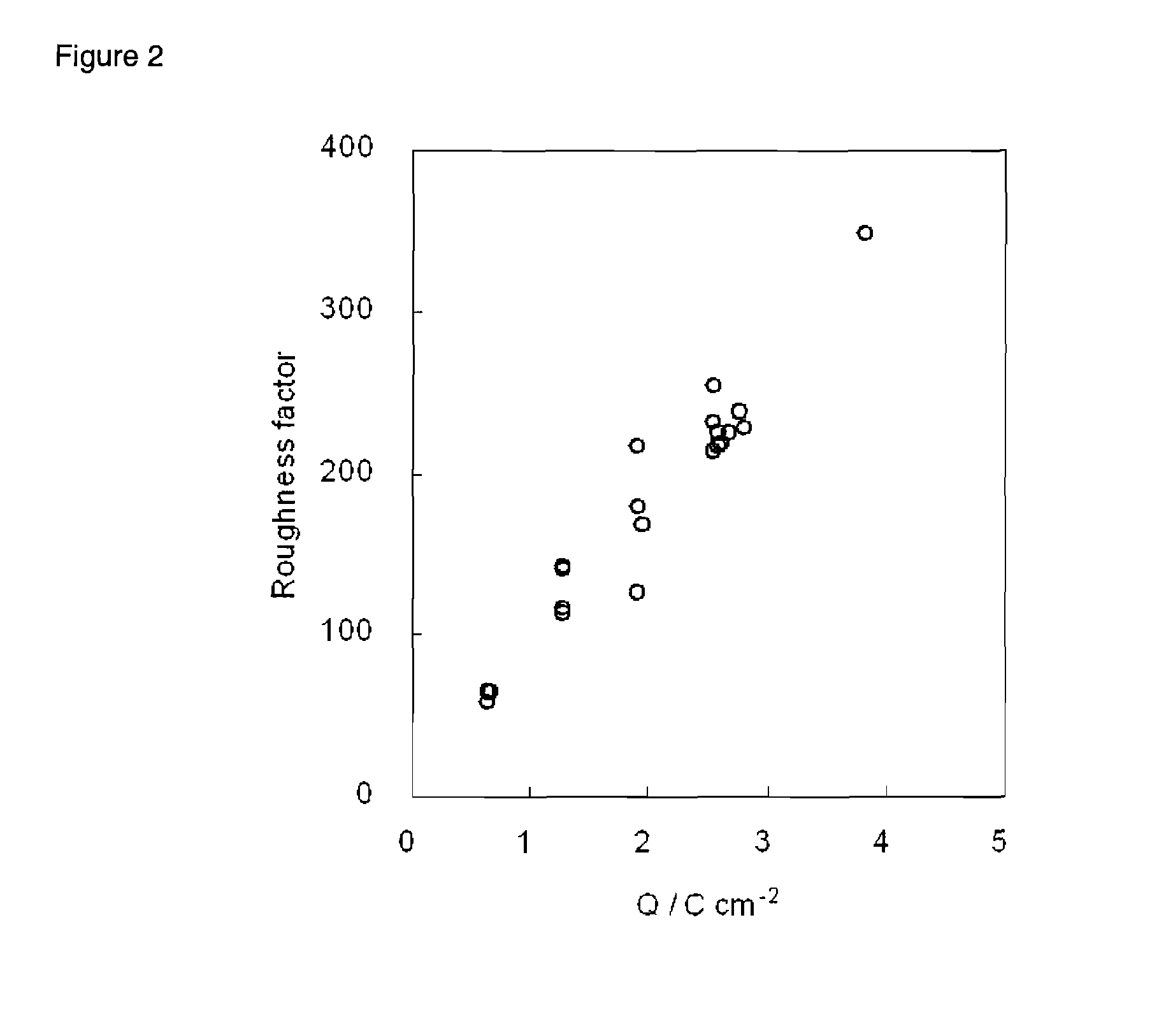
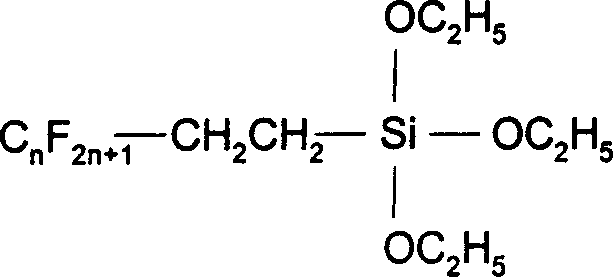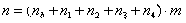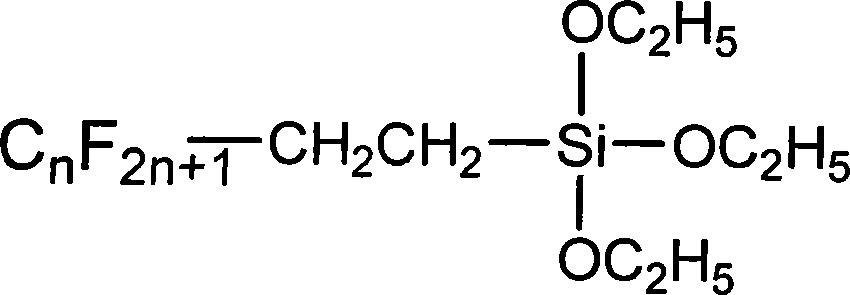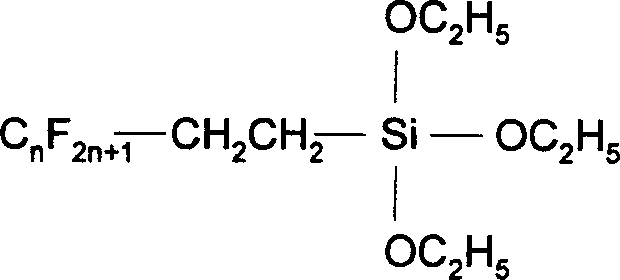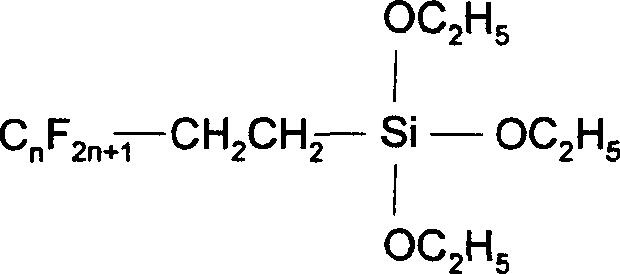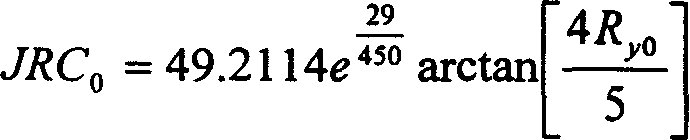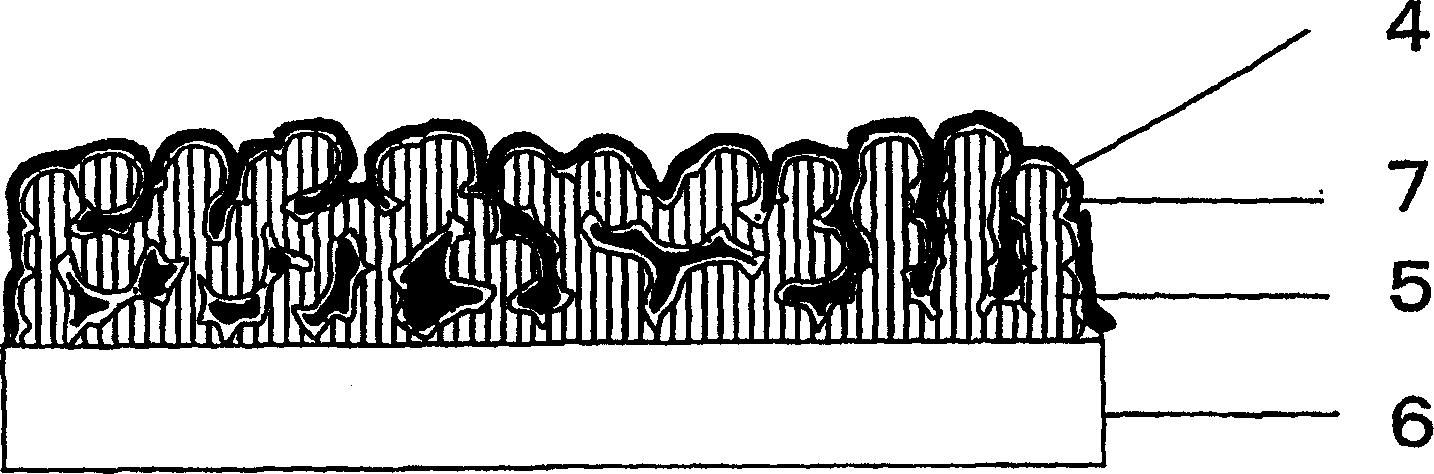Patents
Literature
59 results about "Roughness factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
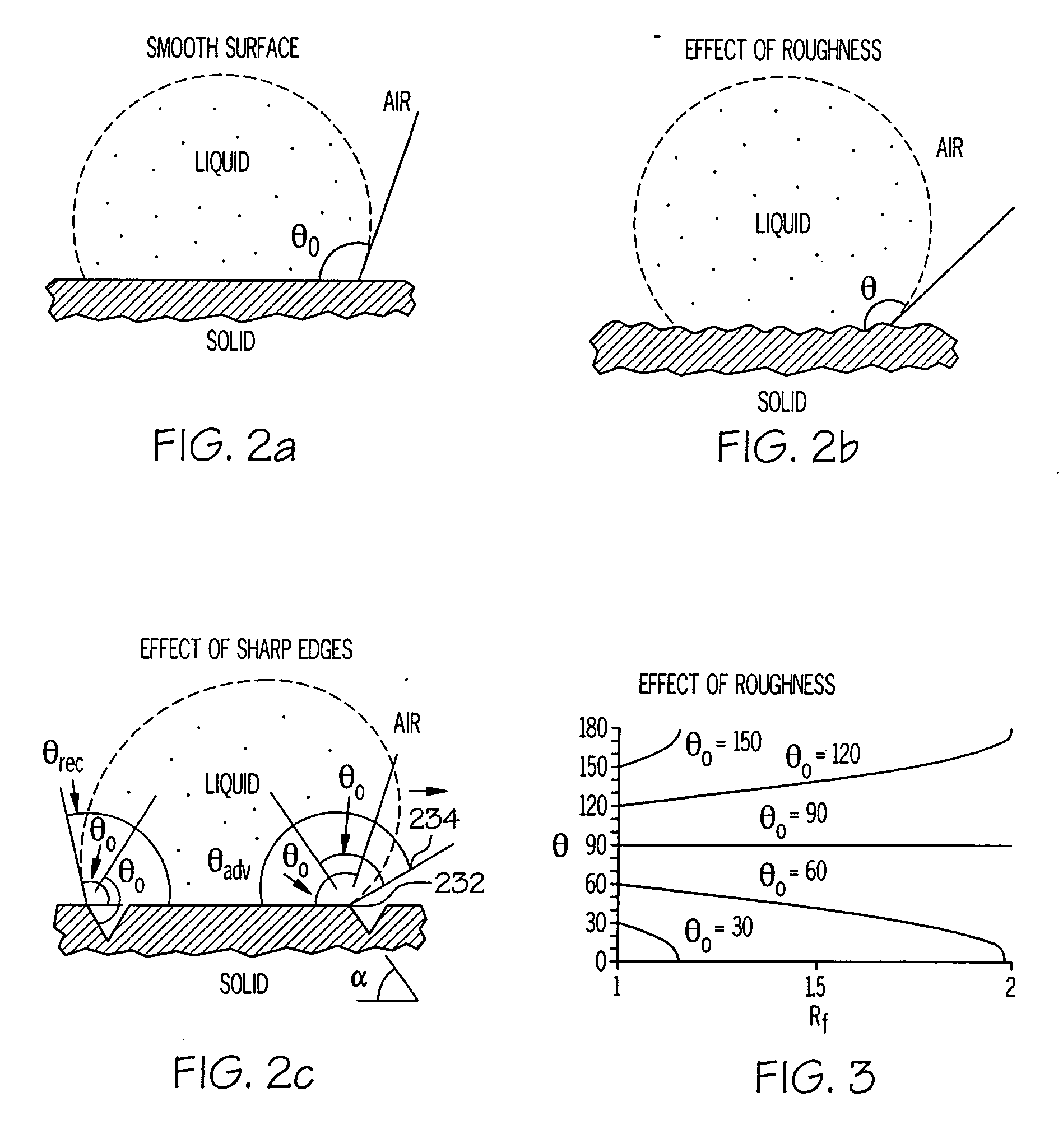
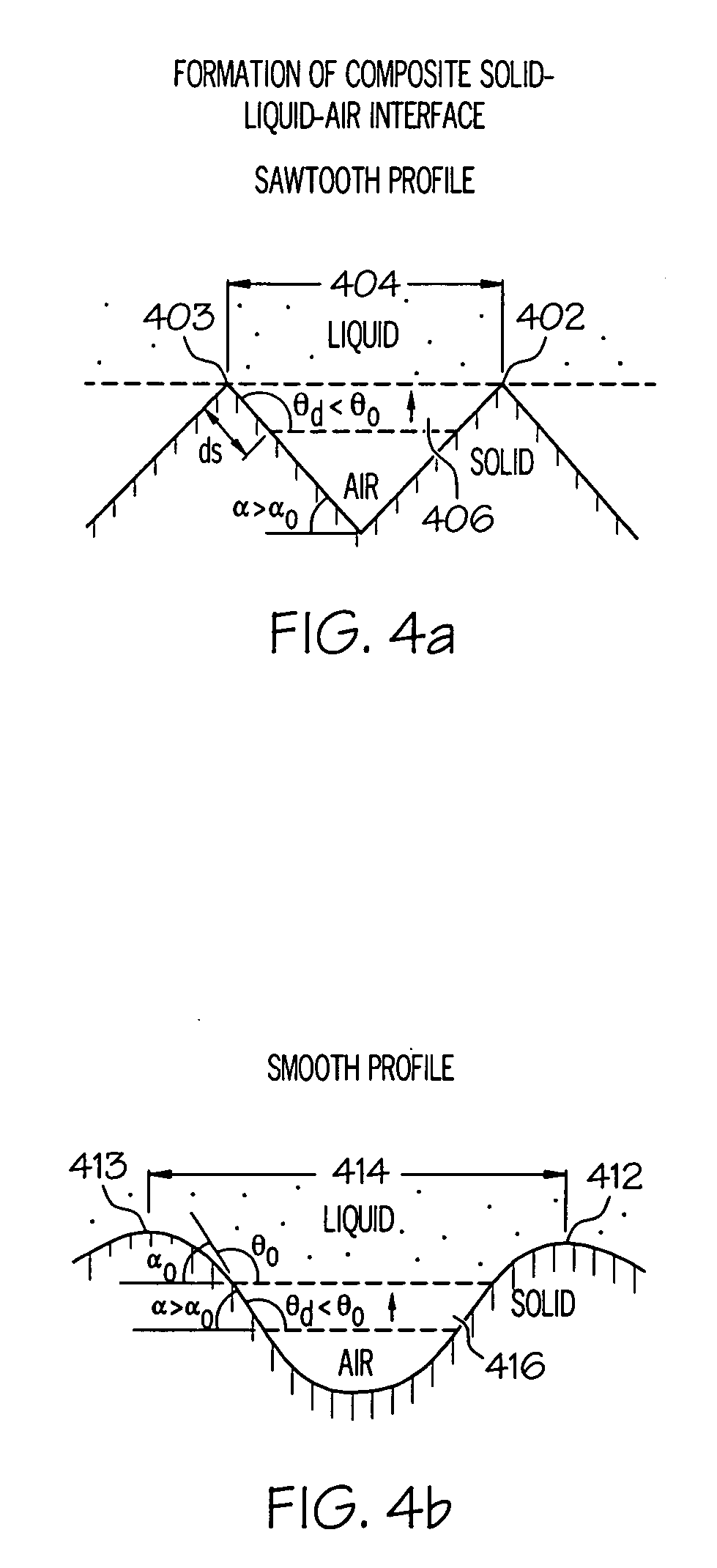
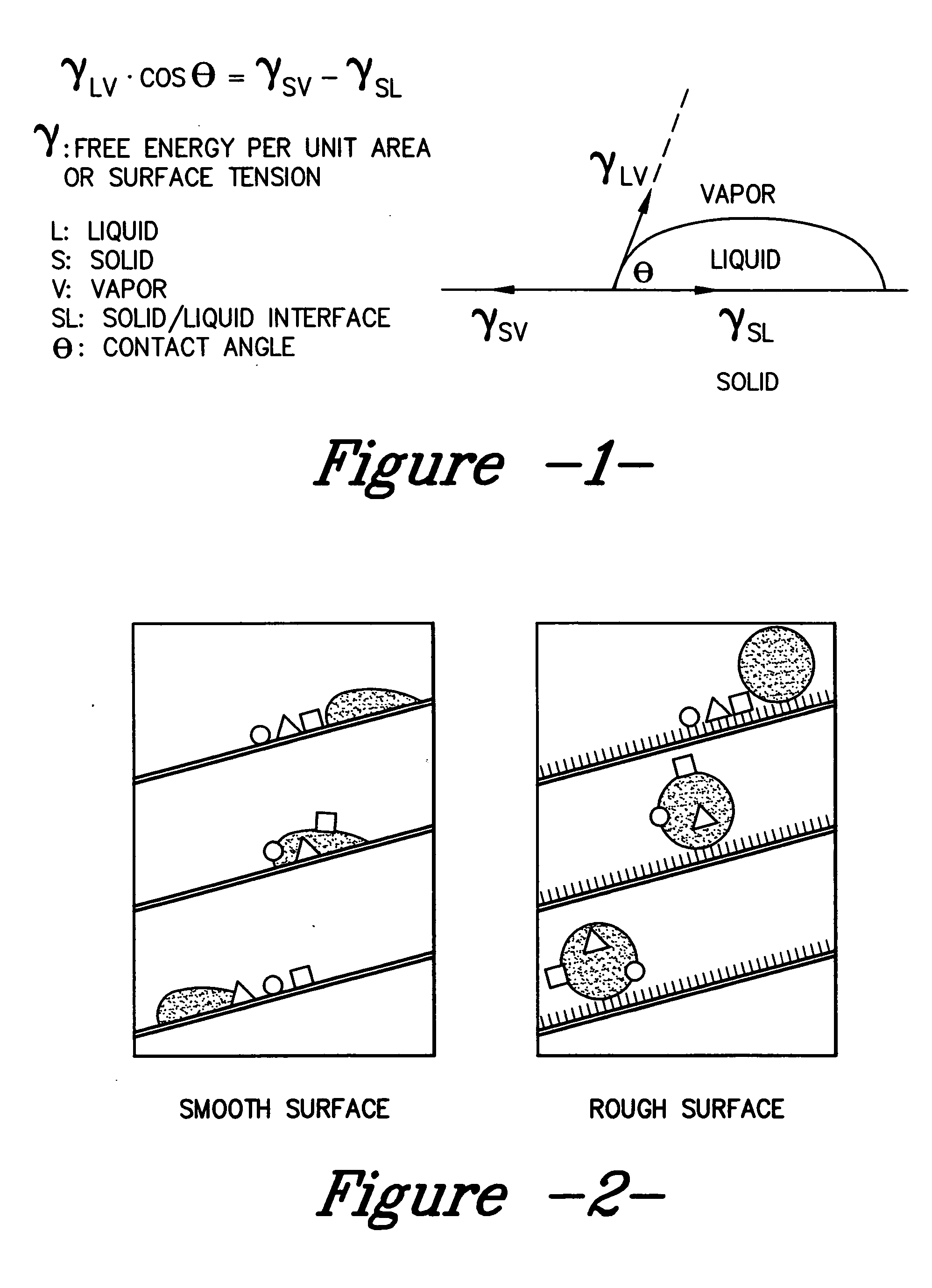
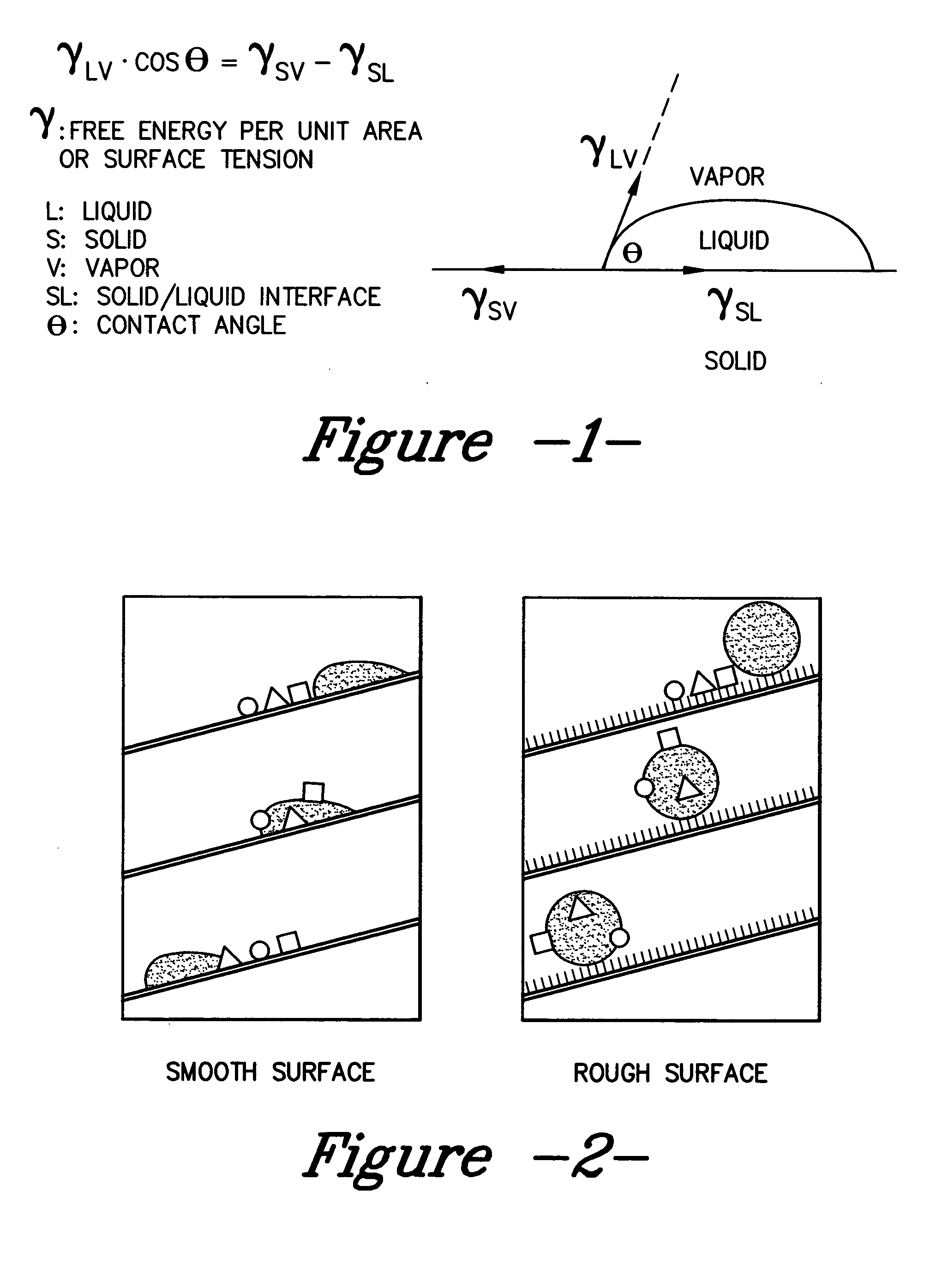
Roughness factor. A correction factor used in fluid-flow calculations to allow for flow resistance caused by the roughness of the surface over which the fluid must flow.
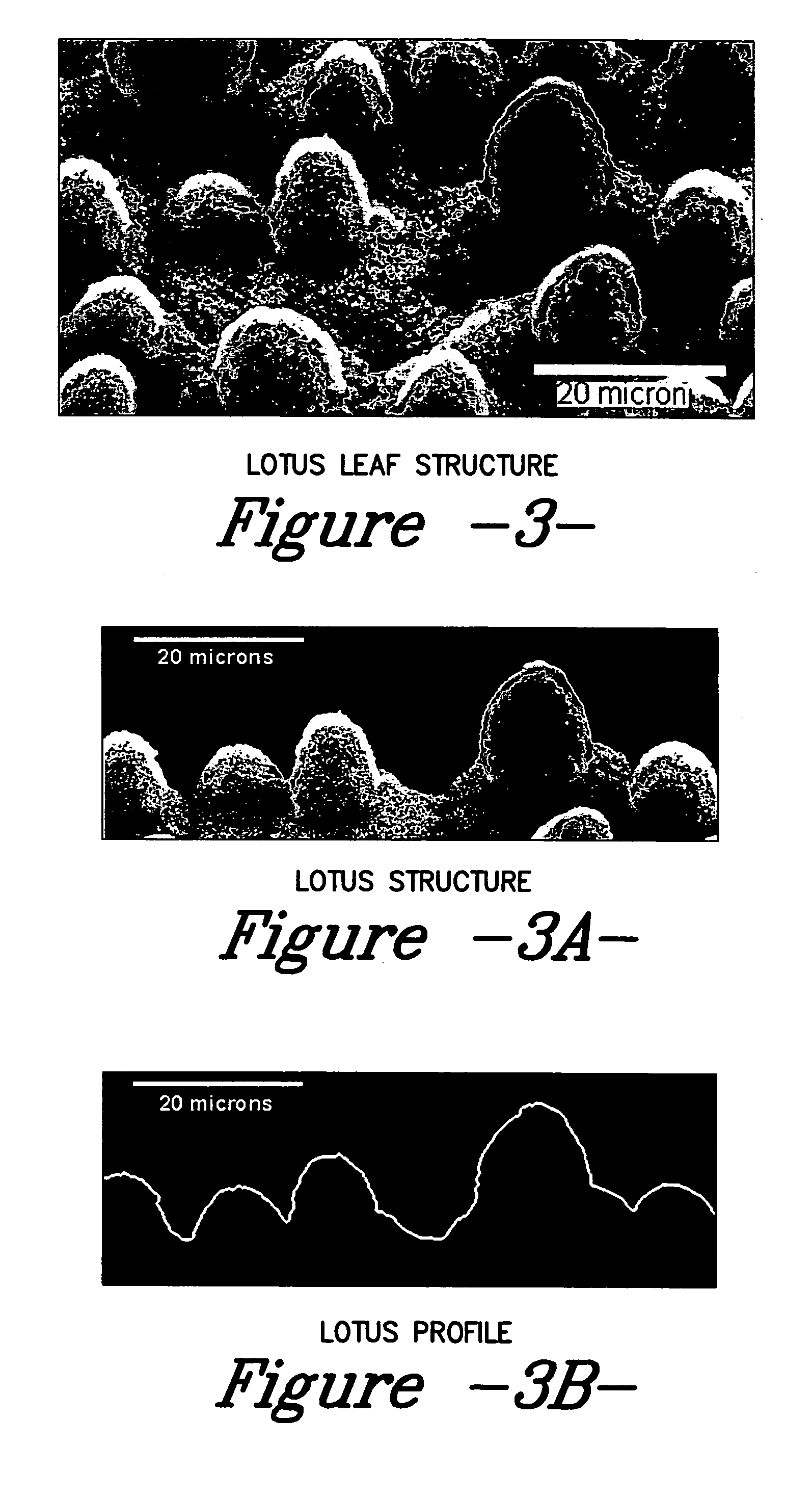
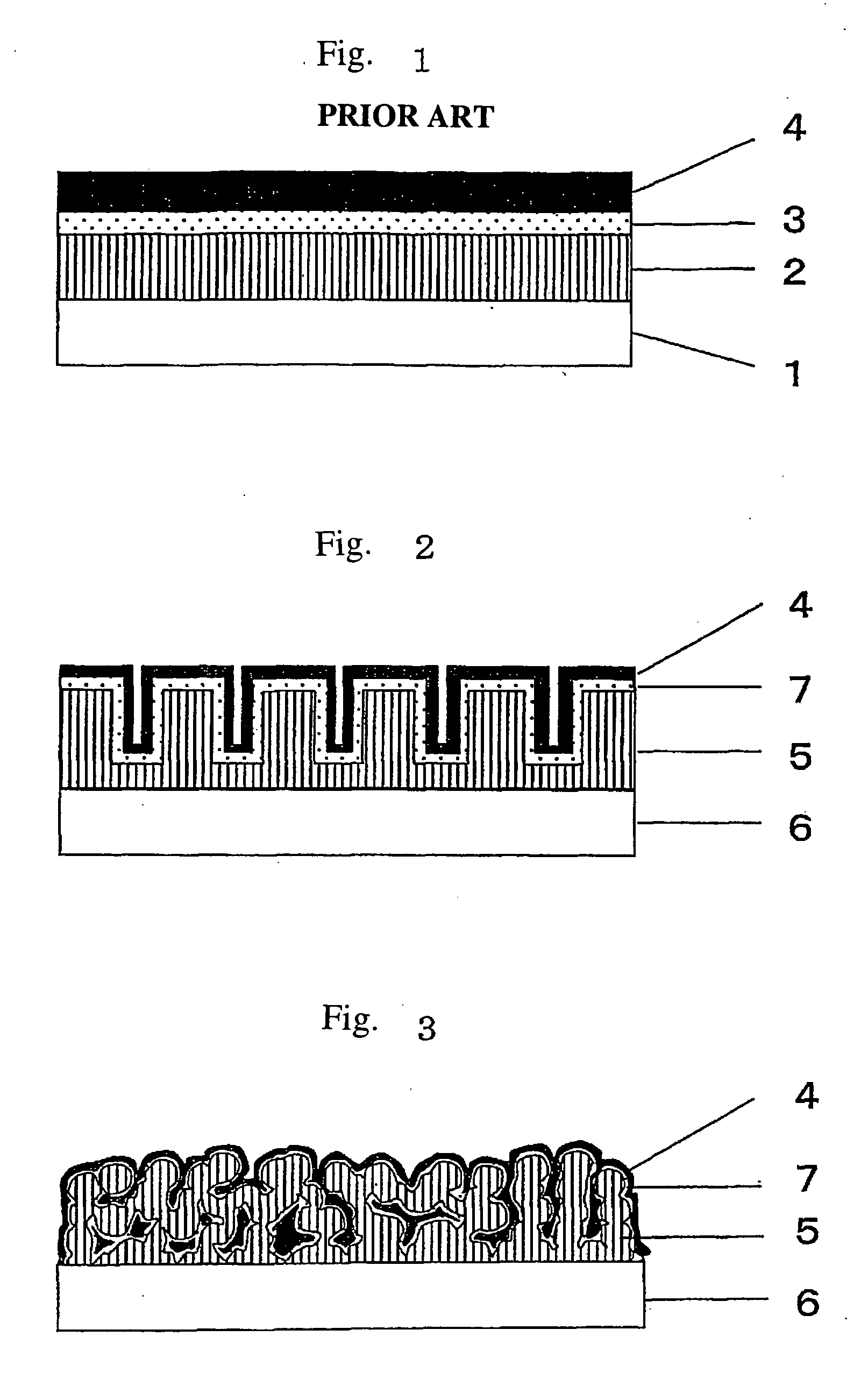
Surface topography for non-toxic bioadhesion control
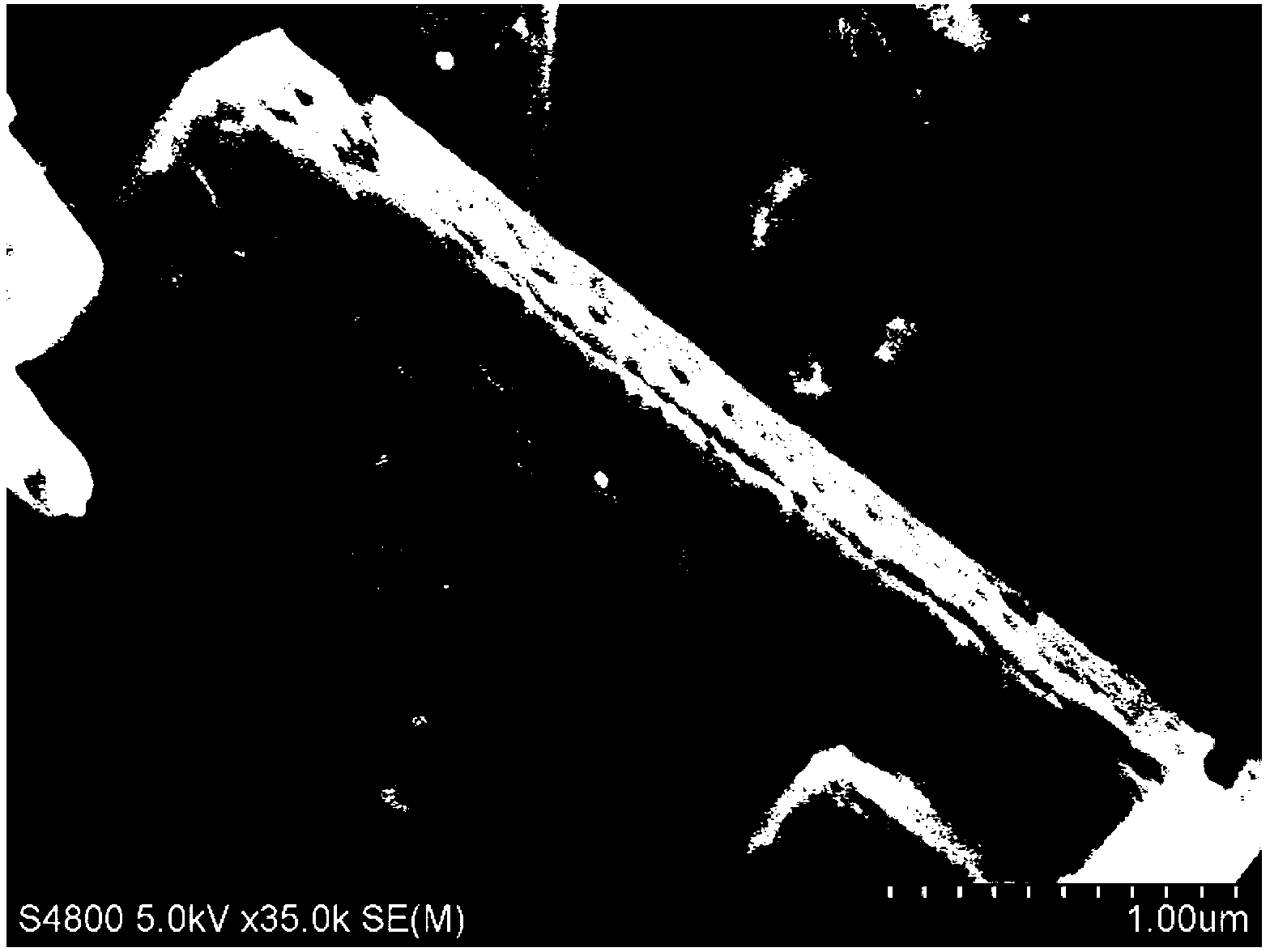
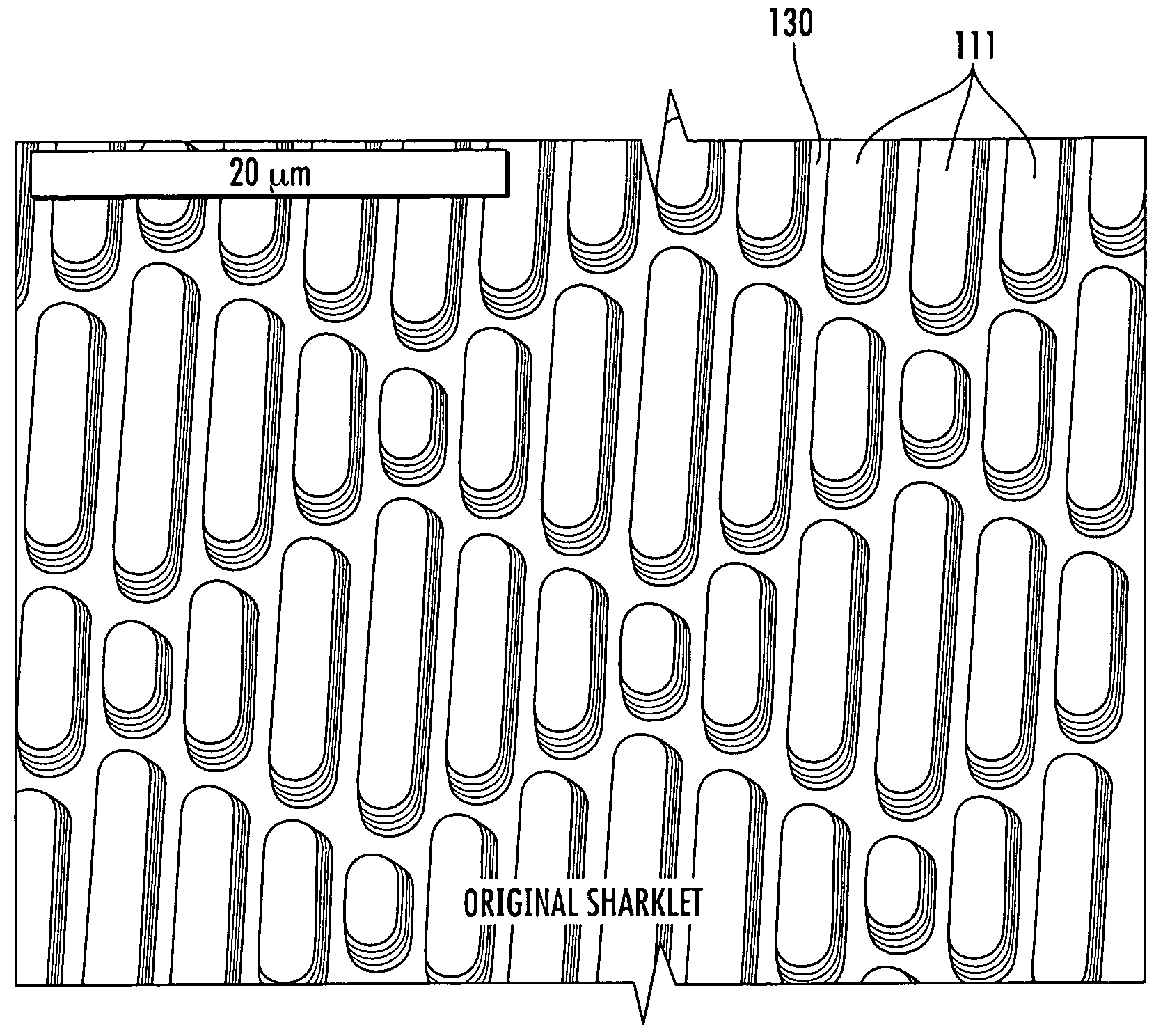
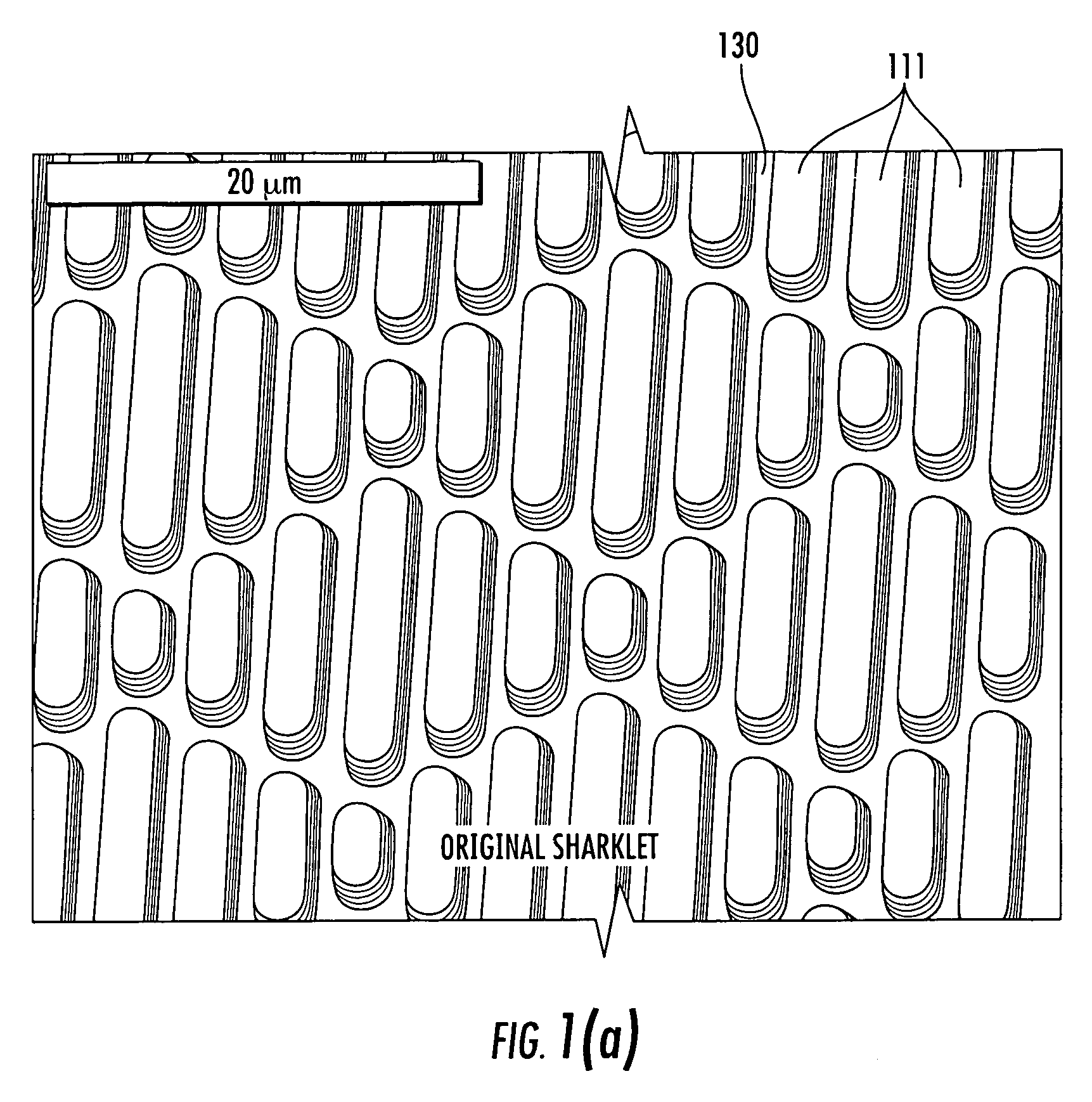
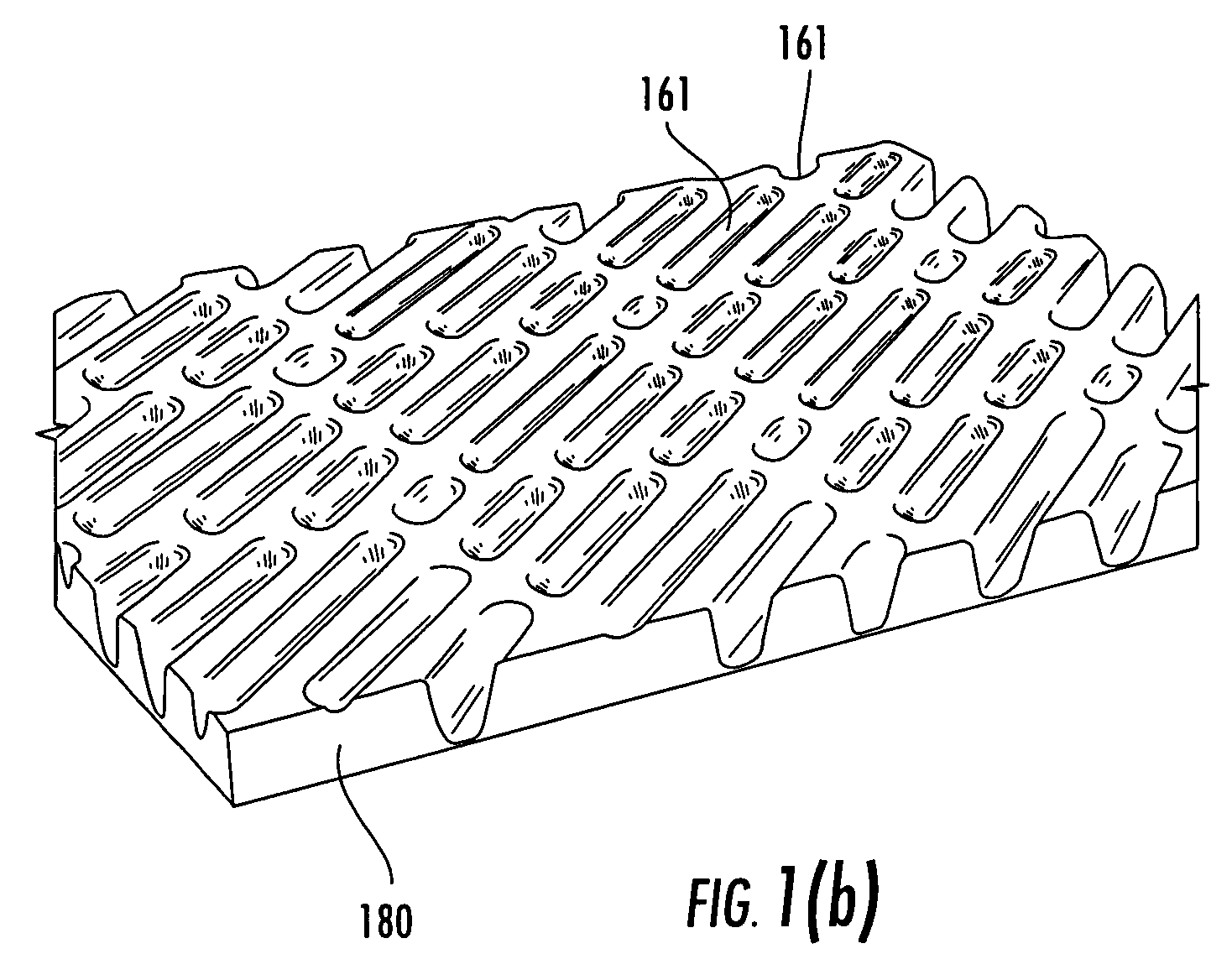
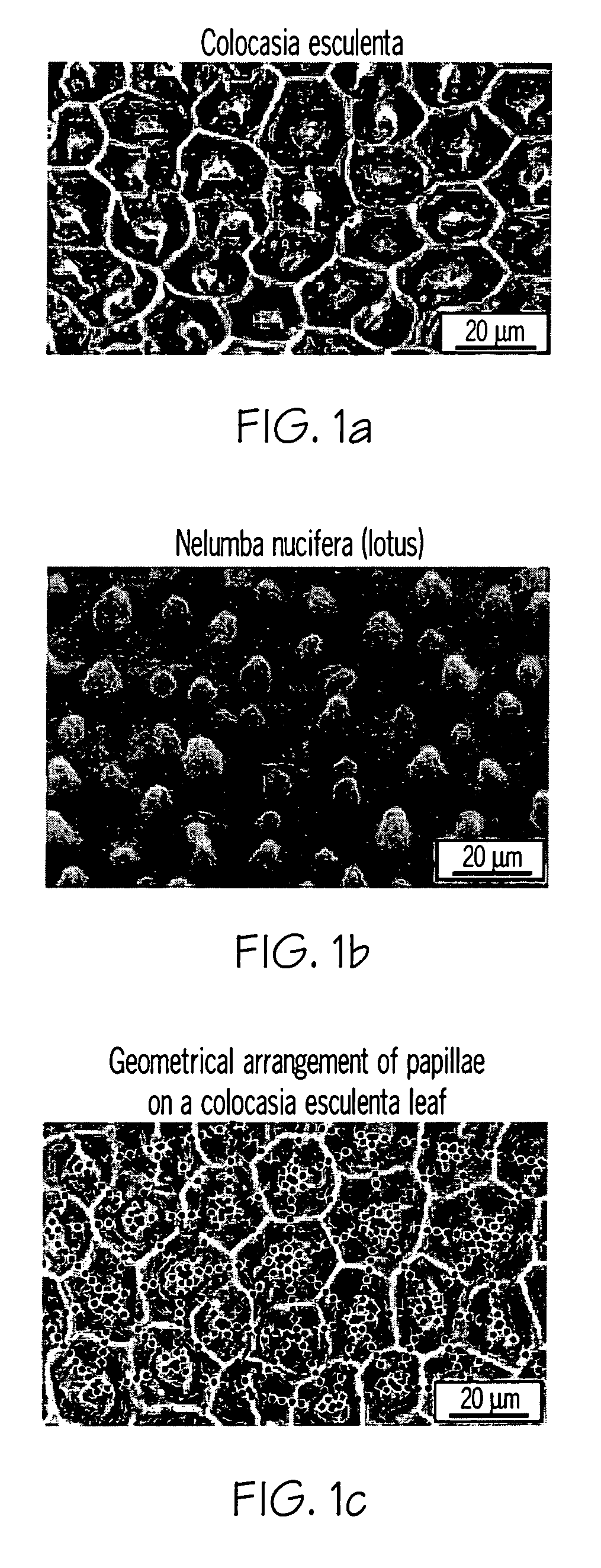
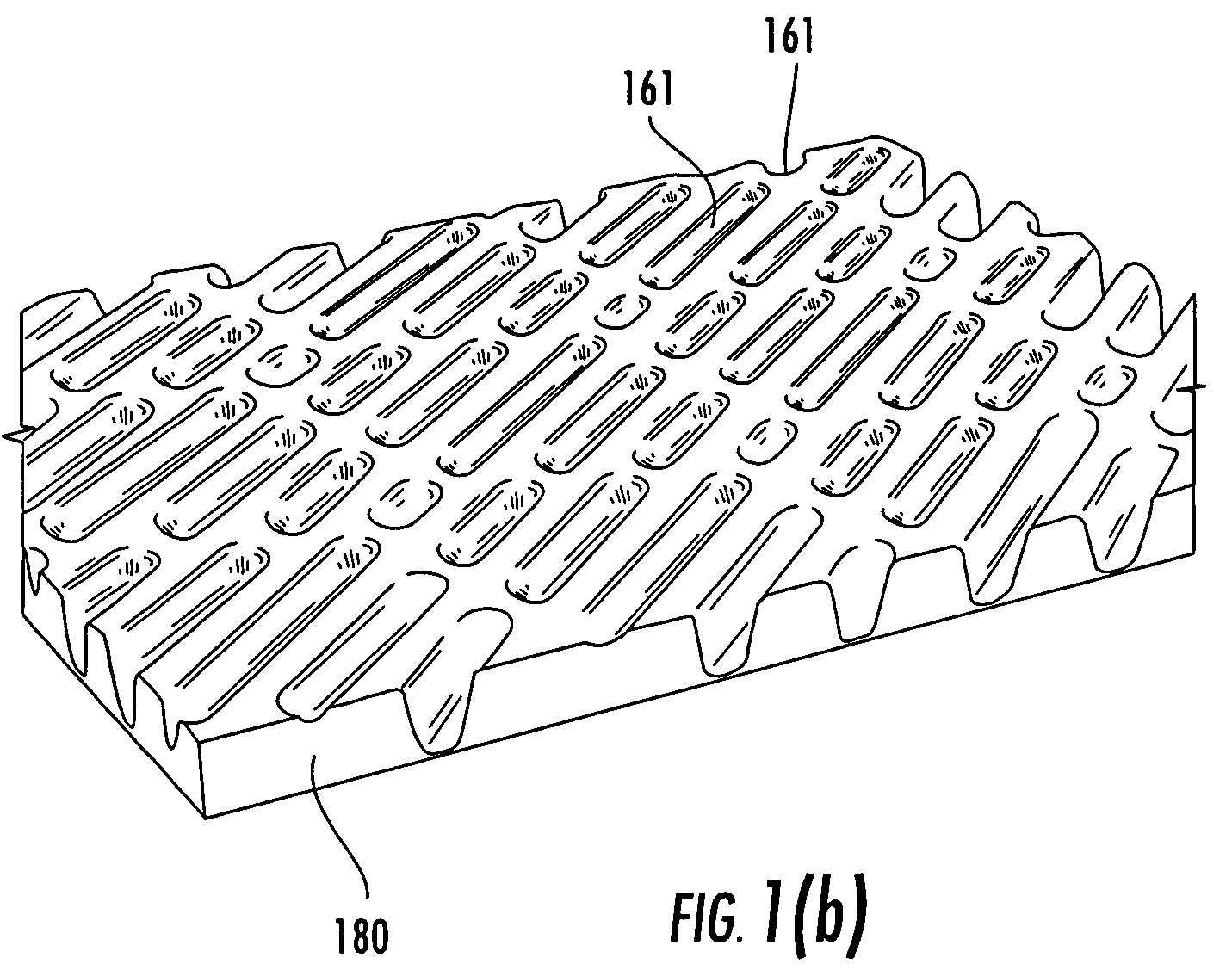
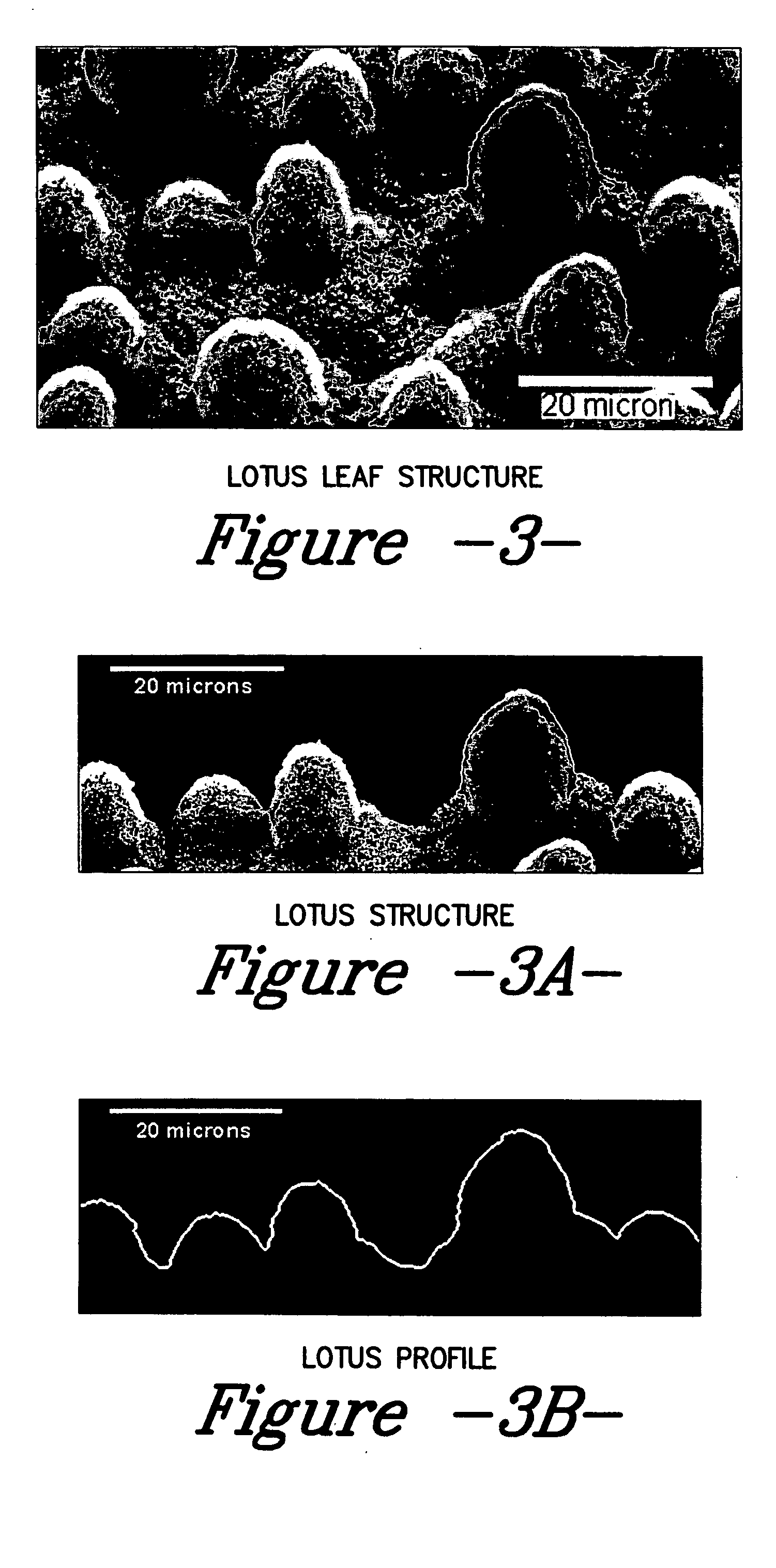
A coated surface for resisting or enhancing bioadhesion includes at least one patterned polymer including coating layer having a plurality of features attached to or projected into a base surface. The features each have at least one microscale (<1 mm) dimension and have at least one neighboring feature having a substantially different geometry. The patterned coating layer preferably provides an average roughness factor (R) of from 4 to 50. The coating layer resists or enhances bioadhesion as compared to the base surface.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Hydrophobic surface with geometric roughness pattern
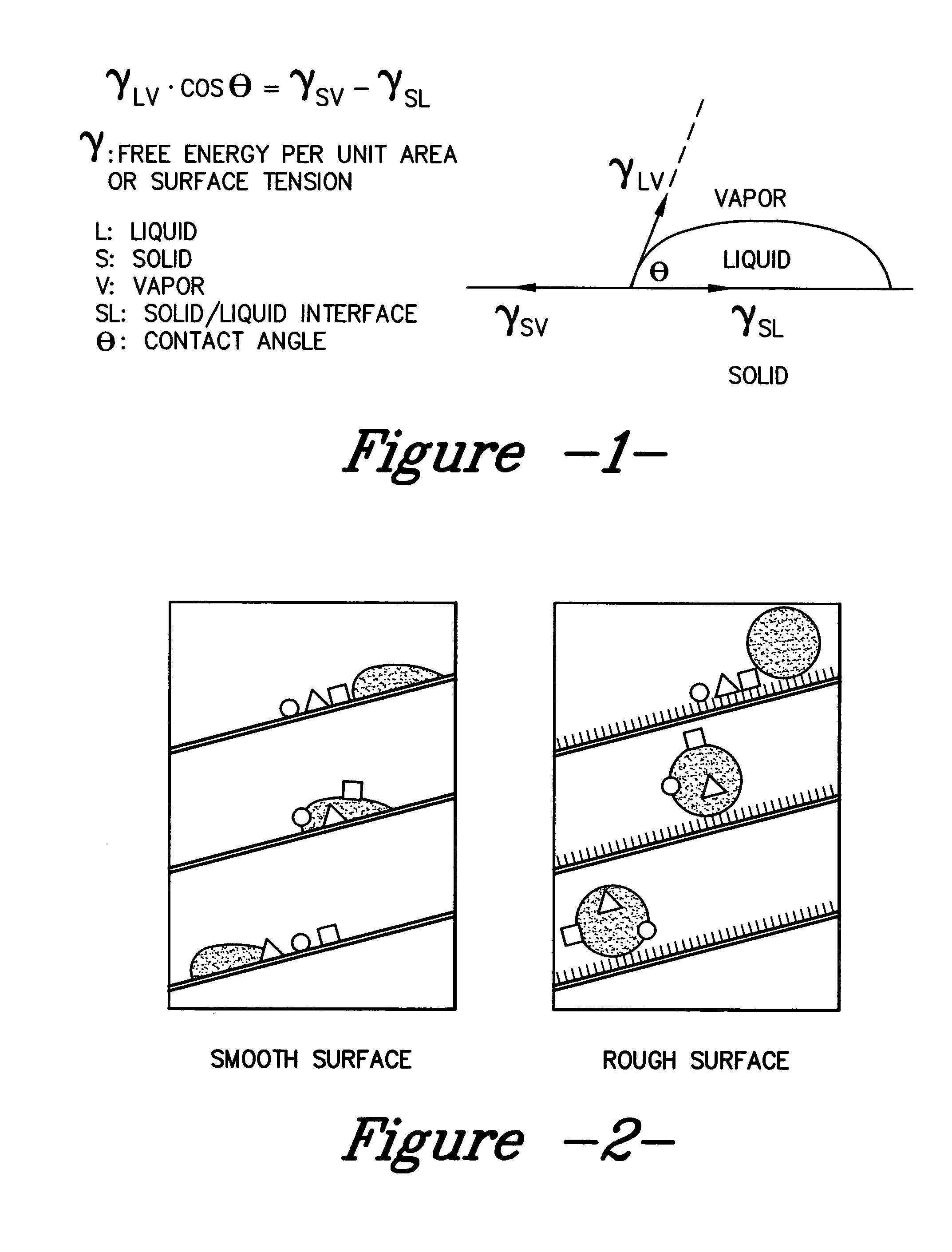
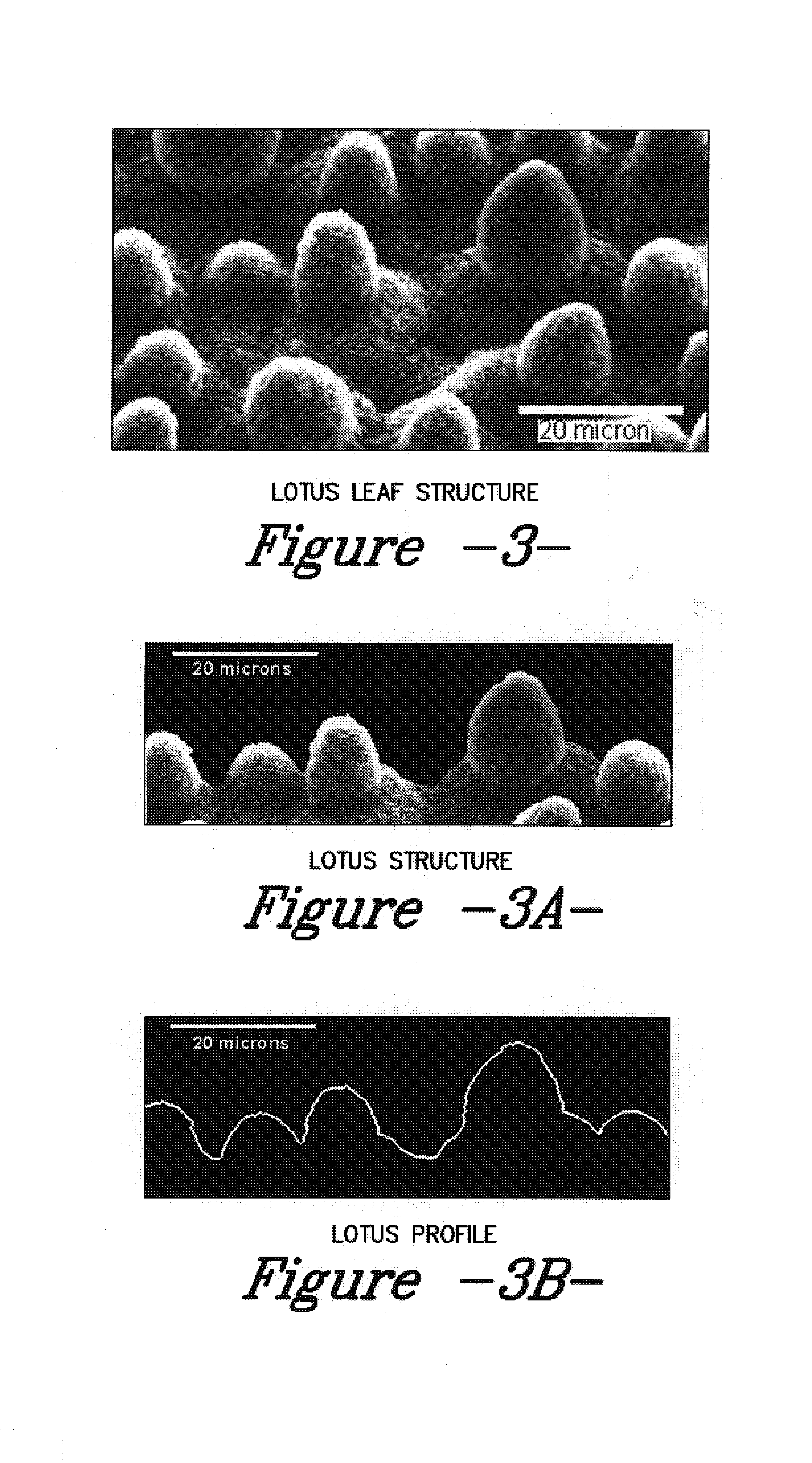
A hydrophobic surface comprising a substrate and a roughened surface structure oriented on the substrate material is provided. The substrate comprises a surface, which is at least partially hydrophobic with a contact angle to liquid of 90° or greater. The roughened surface structure comprises a plurality of asperities arranged in a geometric pattern according to a roughness factor, wherein the roughness factor is characterized by a packing parameter p that equals the fraction of the surface area of the substrate covered by the asperities. The p parameter has a value from between about 0.5 to about 1.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Surface topography for non-toxic bioadhesion control
ActiveUS20060219143A1Resisting and enhancing bioadhesionDifferent geometryPhotosensitive materialsPumpsCoated surfaceTopography
A coated surface for resisting or enhancing bioadhesion includes at least one patterned polymer including coating layer having a plurality of features attached to or projected into a base surface. The features each have at least one microscale (<1 mm) dimension and have at least one neighboring feature having a substantially different geometry. The patterned coating layer preferably provides an average roughness factor (R) of from 4 to 50. The coating layer resists or enhances bioadhesion as compared to the base surface.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Treated textile substrate and method for making a textile substrate
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Preparation method of nano self-cleaning leather or product
InactiveCN101250597AWith self-cleaning functionImprove hydrophobicityLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsOil freeSpray coating
A preparation process of nano self-clearing leather or product comprises firstly mixing organic fluoro-resin, nano solid particles, silane coupling agent, triethanolamine and propylene glycol with water to obtain organic fluorine finishing agent, then conducting spray coating, brush painting or roller painting to leather or products with organic fluorine finishing agent under the constant temperature, preliminarily drying for 5-30 min under 30-50 DEG C, and finally completely drying leather and products under 50-95 DEG C. The process endows high roughness factors to leather and products through the compounding of organic fluorine finishing agent and nano solid particles which are used in the traditional leather production, thereby further increasing hydrophobic and oleophobic properties, and making leather have self-clearing function since leather is water free and oil free. Leather and products which are treated are led to have the super hydrophobic and oleophobic properties, and be water free and oil free, thereby realizing the purpose of self-clearing, not only increasing service life, but also having significant benefits in environmental-friendly and energy-saving aspects.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Production of feather dress fabric with self-cleaning function
InactiveCN1854384AHas superhydrophobic and oleophobic propertiesAchieve the purpose of self-cleaningPhysical treatmentFiberEngineering
A self-clean cloth with nanometer technology for feather garment and its preparing method which includes the following steps: construct concave convex nanophase structure on chemical fiber surface to increase microcosmic specific area by physical and chemical modification, graft active group on fiber surface, increase more nanophase solid grain to endow the cloth with high roughness factor so that hydrophobic and oleophobic capability of cloth was enhanced.
Owner:ZHONGKE BOSIDENG NANOMETER CLOTHING ORNAMENT SUZHOU
Treated textile substrate and method for making a textile substrate
InactiveUS20050186873A1Synthetic resin layered productsLiquid repellent fibresFiberChemical treatment
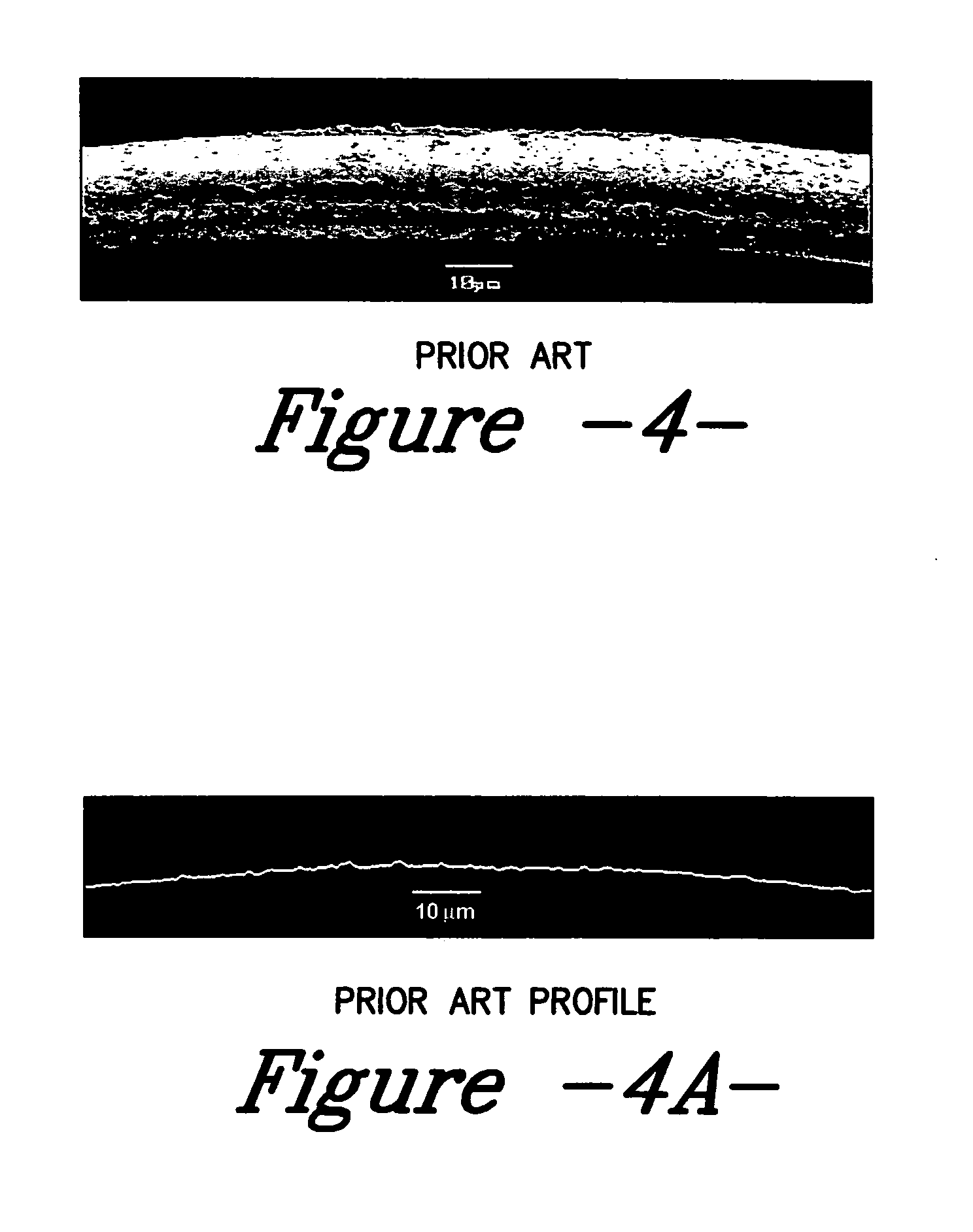
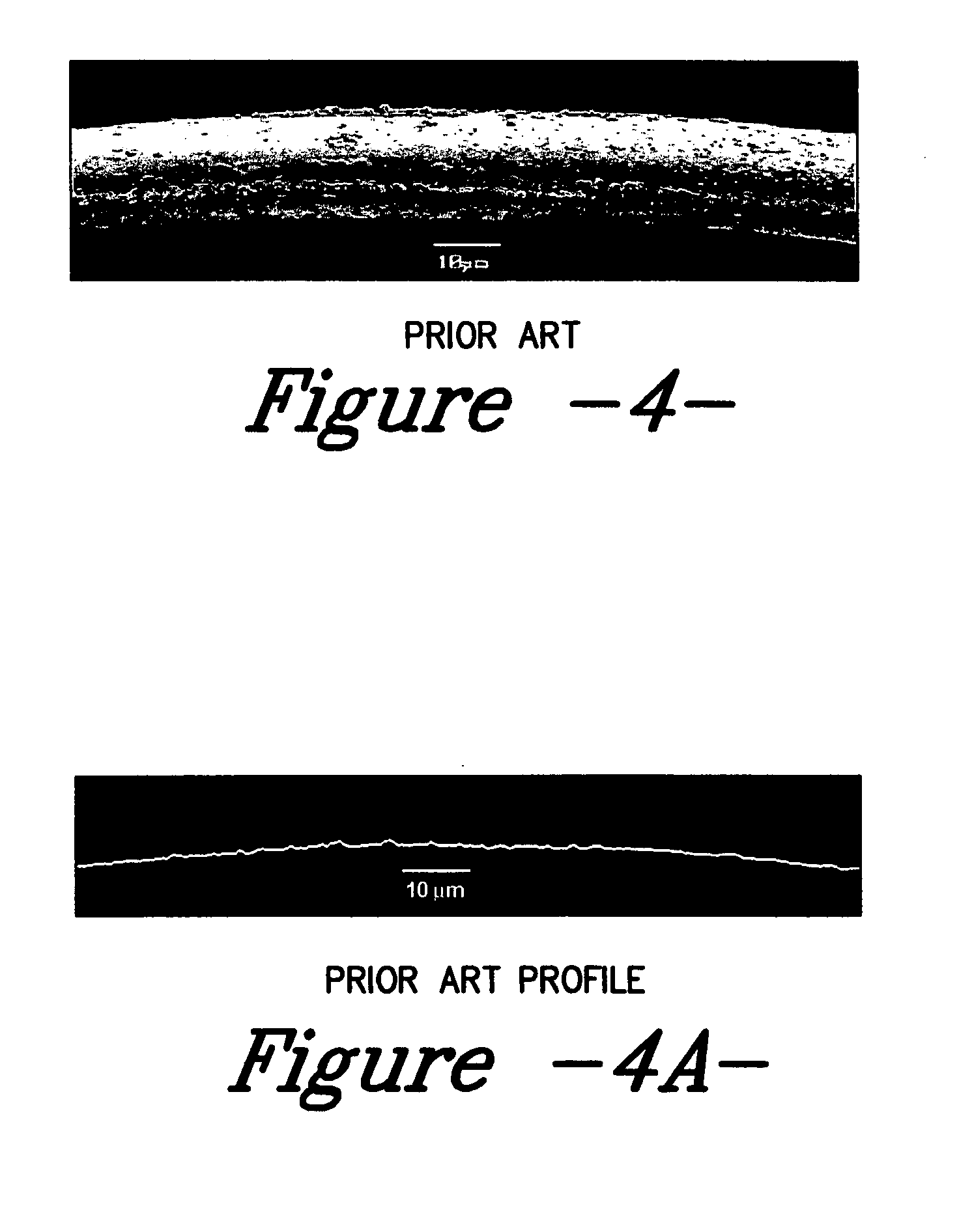
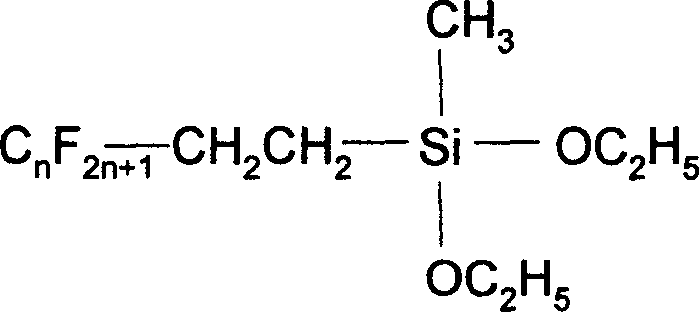
Compositions and methods for treating textile substrates to obtain superior liquid repellent properties are disclosed. Durable microscopic surface structures imparted to the fibrous substrate allow liquids to bead up and roll off of its surface. Mechanical abrasion or sanding techniques may be used to create the microscopic surface structures on the surface of a fibrous textile substrate, without substantially breaking fibers, followed by a chemical treatment using, for example, fluorocarbon-containing repellent compositions. Particles may be employed in combination with repellent compositions to achieve superior repellent properties. A property of the roughened surface fibers, the Roughness Factor, is used to characterize the microscopic surface structures on the treated textile surface. Treated textile substrates are disclosed which achieve superior water and oil repellency, even after multiple abrasion or laundering cycles.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Back-silting simulation method for basin channel of force tide firth artificial island operating area
ActiveCN108256137ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityMathematical model
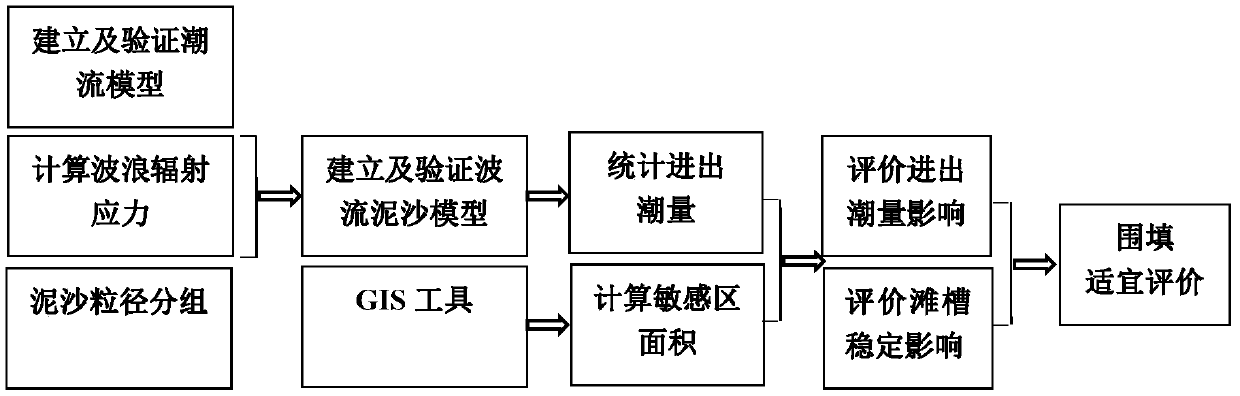
The invention discloses a method for simulating back-silting of a basin channel of a force tide firth artificial island operating area. The method comprises the steps of establishing a water flow mathematical model by use of a water flow sediment mutual feedback calculation mode and variable roughness factors changing with geomorphology and tide levels; calculating representative wave radiation stresses at different tide levels; optimizing an artificial island plane modality; performing wave, tide and runoff and sediment discharge coupling fitting; and finally, counting aback-silting amount. According to the method, in a wave current sediment mathematical model construction process, the requirement of basin channel back silting simulation of force tide firth artificial island operating areas with different geomorphologic shapes can be adapted and satisfied for the unique dynamic geomorphology characteristics of irregular coastlines of a semi-closed force tide firth offshore artificialisland, large tidal volume of inflow and outflow of force tides, wide tidal flat and complex geomorphology, strong tidal current under the action of rotary current, high influence of waves and combined action of sediment movements affected by wave currents in consideration of the variable roughness factors changing with the geomorphology and the tide levels.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST +1
Preparation method of one-dimensional metal titanate nanorods
InactiveCN103011264AImproved pore size distributionLarge roughness factorMaterial nanotechnologyTitanium compoundsNanoparticleEthylene glycol
A preparation method of one-dimensional metal titanate nanorods relates to a preparation method of titanate nanorods, and mainly solves the problems that a titanate photocatalyst material prepared in the prior art has a relatively small specific surface area, a relatively low roughness factor and non-uniform size and shape. The preparation method of one-dimensional metal titanate nanorods comprises the following specific steps: 1, preparing a metal salt ethylene glycol solution; 2, adding a titanium source; 3, centrifuging and eluting; 4, drying; and 5, roasting to obtain the one-dimensional metal titanate nanorods. The preparation method has the advantages as follows: 1, the specific surface area of the prepared one-dimensional metal titanate nanorod photocatalyst is 2-43 times of the surface area of the titanate nanoparticle photocatalyst material prepared in the prior art; and 2, the prepared one-dimensional metal titanate nanorod photocatalyst has an apparent pore size distribution and a relatively large roughness factor. The preparation method is mainly applied to preparation of the one-dimensional titanate nanorods.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20060137737A1Low costLarge roughness factorFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesAll solid statePhotoelectric conversion
The present invention provide an all solid-state photoelectric conversion device which comprises a semiconductor, an electrically conductive substrate arranged on one surface of the semiconductor and forming an ohmic junction therewith, an electrically conductive film arranged on the other surface and forming a Schottky junction with the semiconductor, and a sensitizing dye layer arranged on the electrically conductive film, the roughness factor of the surface of the semiconductor forming a Schottky junction being 5 or greater. The photoelectric conversion device has a large effective surface area and a high durability and can be manufactured at a low cost.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP
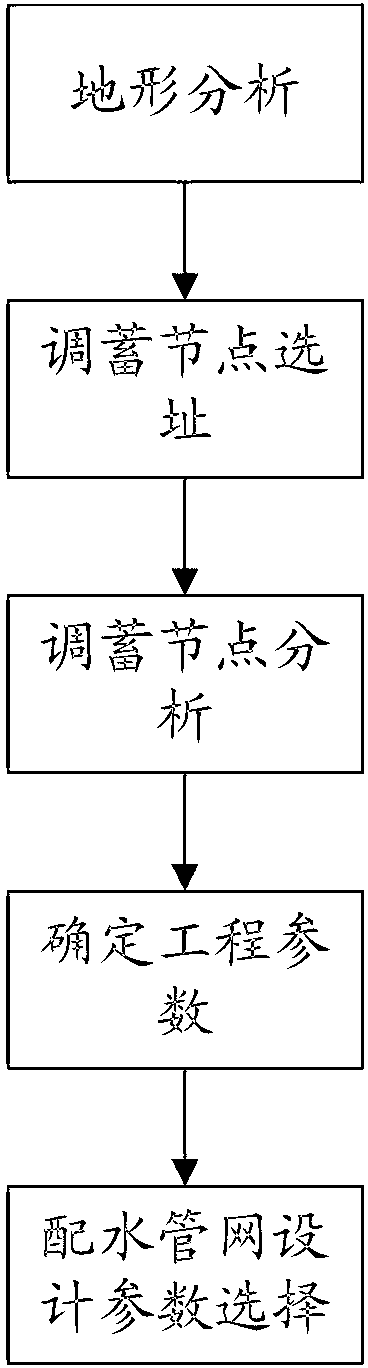
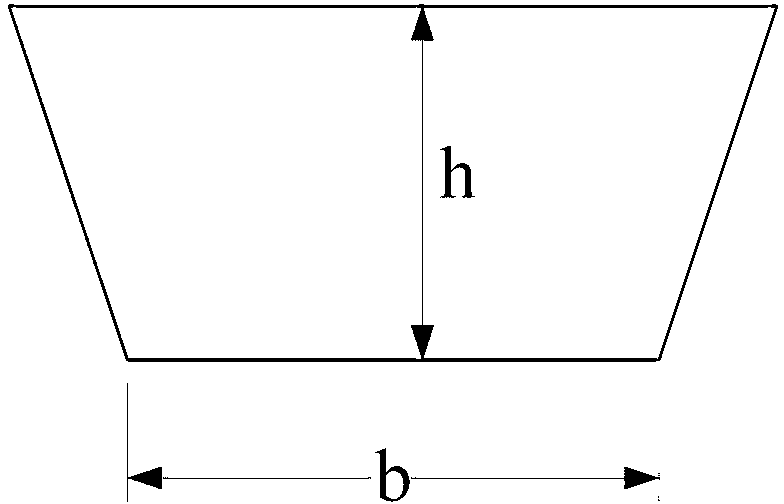
Design method of water conveyance system
ActiveCN103324814ARealize regularizationSolve social problemsSpecial data processing applicationsWater useEngineering
The invention relates to a design method of a water conveyance system. The steps comprise terrain analysis, regulation and storage node site selection, regulation and storage node analysis, engineering parameter confirmation, and water distribution network design parameter selection. The terrain analysis and the regulation and storage node analysis are adopted, the safety and social factors of a regulation and storage node are fully considered, and the design technology problem and related social and environment protection problems of the tail end of a water transfer project are solved to the maximum degree. Meanwhile, a supply and demand balance model is established for solving the contradiction among water transfer, water supply and water use, a roughness factor and the design elements of a water supply network are fully considered, and the regularization process of water transfer project design is achieved.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Fabrication of mesoporous metal electrodes in non-liquid-crystalline phase and its application
ActiveUS8343690B2High roughness factorEasy constructionCell electrodesSurface reaction electrolytic coatingLiquid crystallineElectrochemistry
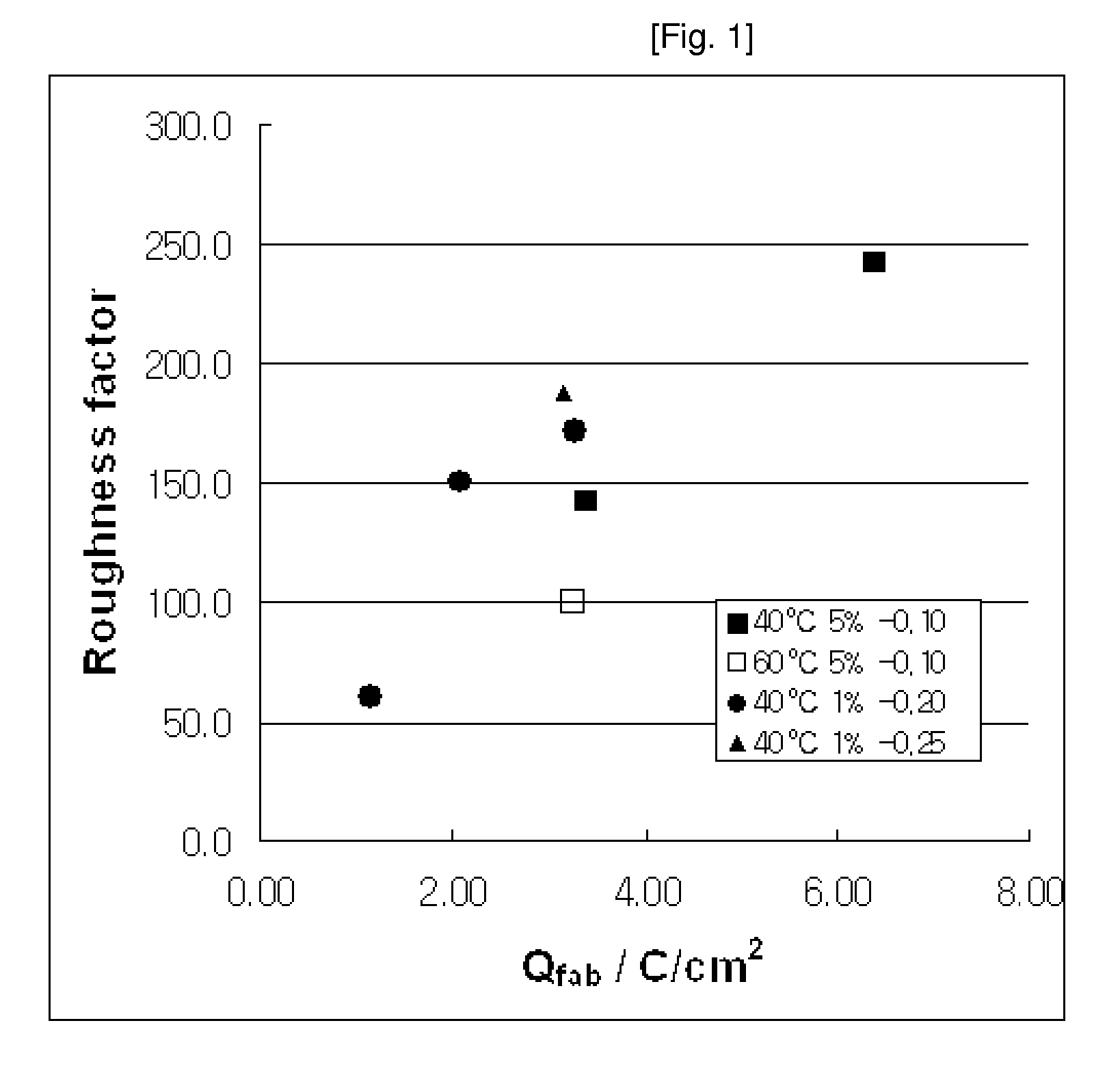
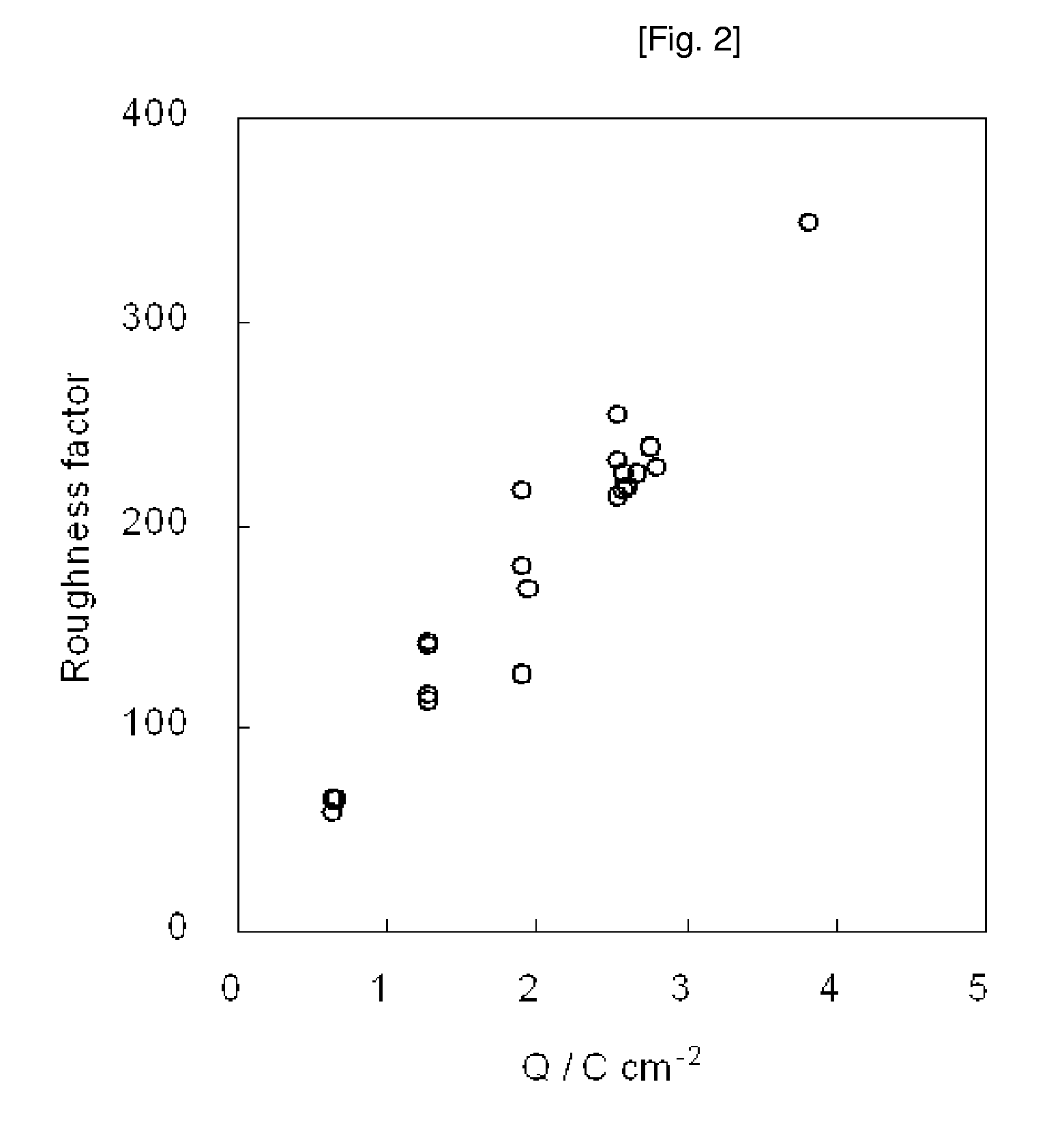
A method for the fabrication of a mesoporous metal electrode in a non-liquid crystalline phase was tested. Specifically, there was tested the efficacy of the method for the fabrication of a mesoporous metal electrode which comprises forming the mesoporous metal electrode on a substrate by chemical or electrochemical reduction of a mixture comprising a solvent, a structure-directing agent, and a source of a metal, characterized in that the mixture is maintained in a non-liquid crystal phase. Furthermore, the usefulness of the mesoporous metal electrode thus prepared from the non-liquid crystalline phase was also tested. The mesoporous metal electrode prepared from the non-liquid crystalline phase had a large surface area, and a roughness factor thereof was controlled by charges passed during electroplating. The method made it possible to fabricate the mesoporous metal electrode in the non-liquid crystalline phase, even more flexible than a liquid crystalline phase. The mesoporous metal electrode prepared by the method had randomly distributed mesopores on the surface thereof and retained a large roughness factor. The method was found to be a good alternative to the conventional fabrication of porous platinum films in the liquid crystalline phase. Furthermore, the method was found to be suitably applicable to automatic processes, because the mesoporous metal electrode was prepared in the highly flexible non-liquid crystalline phase. Recovery and recycling of raw materials were also improved. The mesoporous metal electrode prepared by the method can be suitably used for the detection of glucose and proton, and as a cathode or an anode of fuel cells.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Preparation method of self-cleaning leather or product containing nano functional material
InactiveCN101250596AWith self-cleaning functionSimple processLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsFiberSpray coating
A preparation process of self-clearing leather or products comprises nano functional material, which comprises mixing nano inorganic solid particles and alcohol solution of fluorine-containing alkyl triethoxy silane compound to prepare mixing solution, then impregnating through the impregnation method or conducting spray coating through the spraying process, and then drying. Since fluorine-containing alkyl triethoxy silane compound is used, therefore the process has high bonding strength to leather fiber, has excellent water repellency and oil repellency without high temperature cross-linking, has simple processing technique to face fabric, and can save energy. Leather is endowed with higher roughness factors through adopting the compounding of nano solid particles, thereby further increasing hydrophobic and oleophobic properties, and making leather have self-clearing function since leather is water free and oil free.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
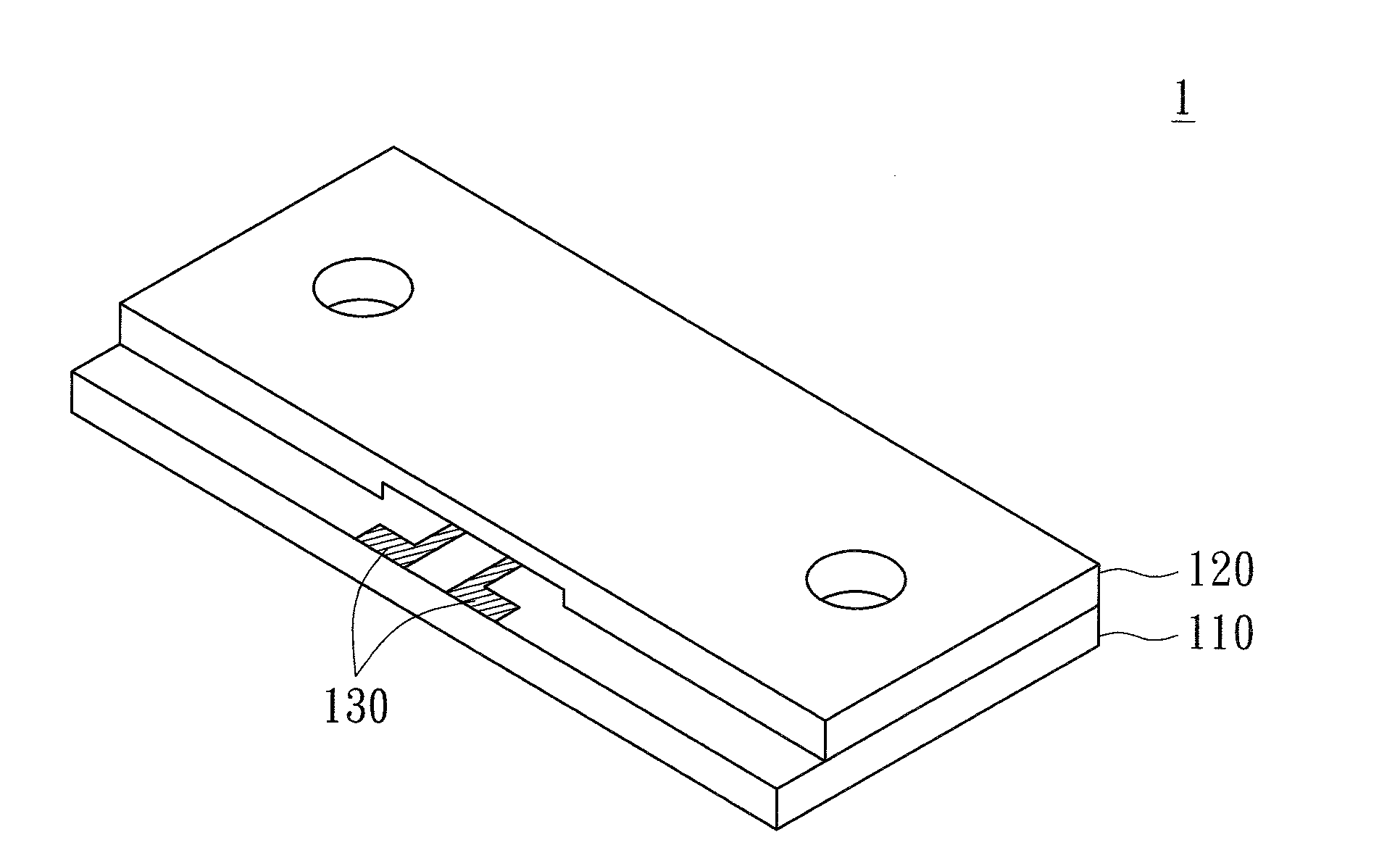
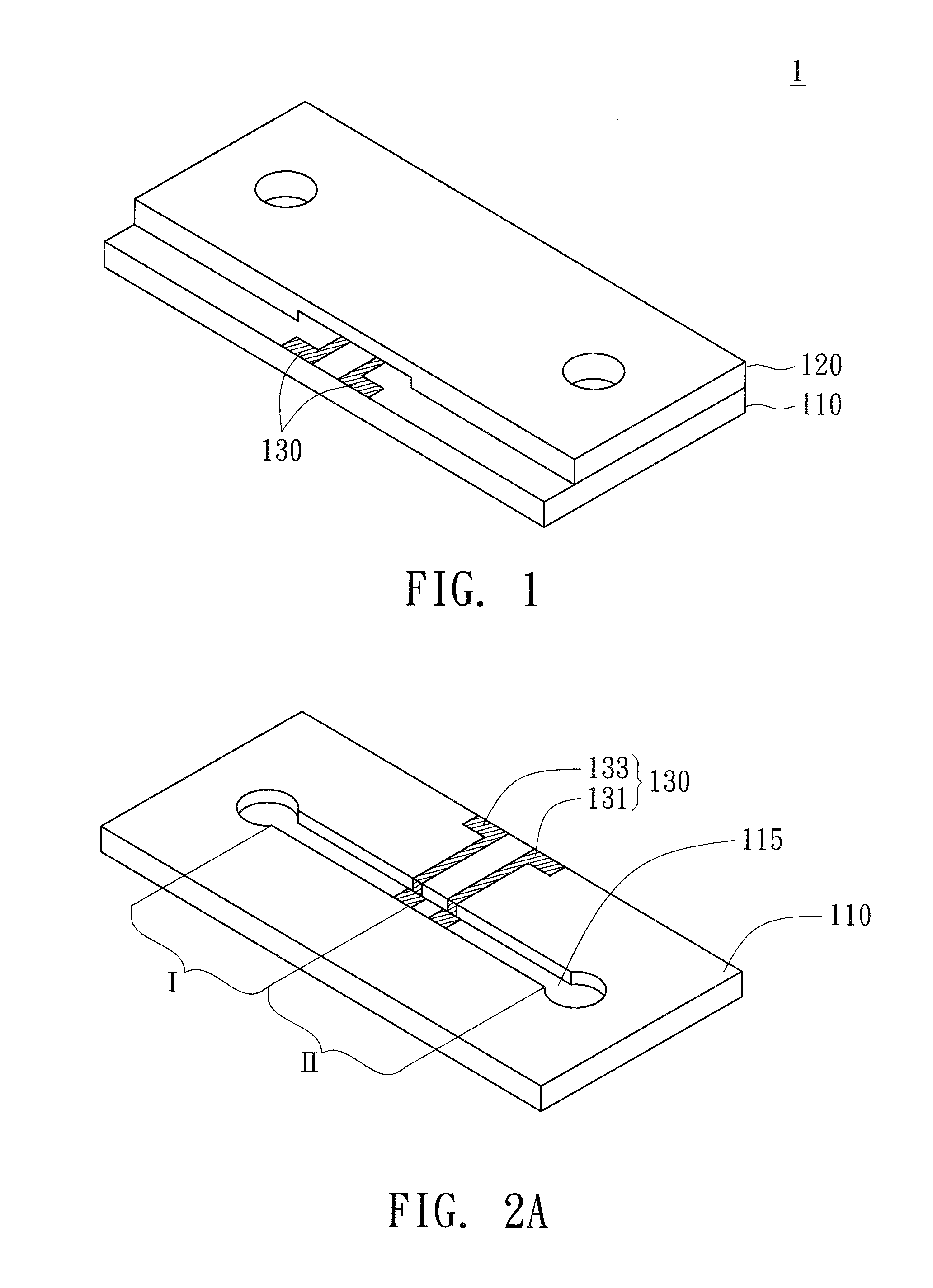
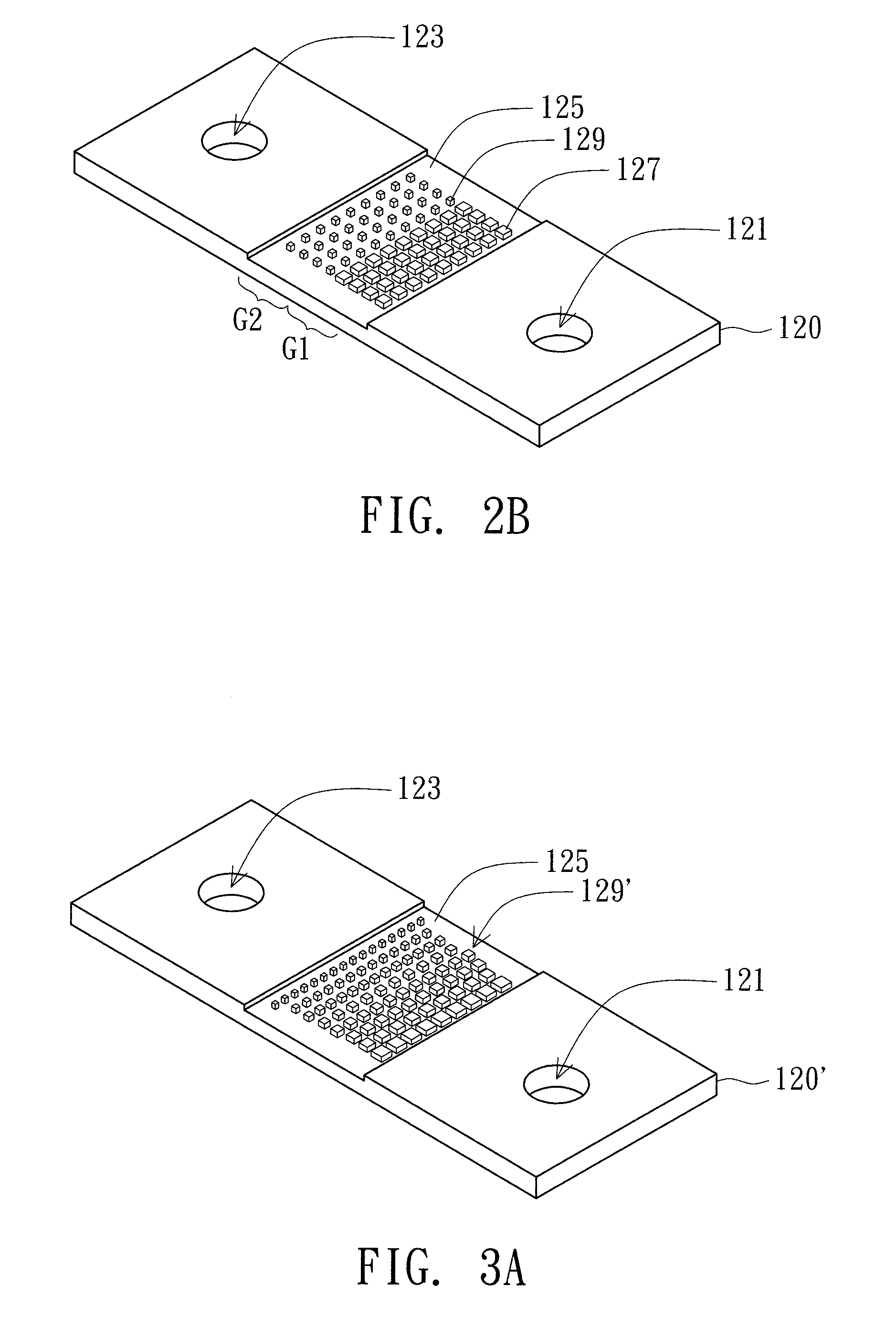
Bubble micro-pump and two-way fluid-driving device, particle-sorting device, fluid-mixing device, ring-shaped fluid-mixing device and compound-type fluid-mixing device using the same
A bubble micro-pump includes a first component, a second component and a bubble-generating unit. The first component includes a flow path having a first area and a second area. The second component above the first component has a first roughness surface and a second roughness surface. The first roughness surface opposite the first area has a first roughness factor, and the second roughness surface opposite the second area has a second roughness factor smaller than the first roughness factor. The bubble-generating unit on the first component generates bubble in the first area and the second area when a fluid fills the vacancy between the first component and the second component. Due to the difference in roughness factor, the backfilling velocity of the fluid in the first area is faster than that in the second area when the bubble starts to vanish, such that the fluid is driven to flow.
Owner:QISDA CORP
Treated textile substrate and method for making a textile substrate
ActiveUS20050186872A1Increased durabilityPattern makingSynthetic resin layered productsChemical treatmentFiber
Compositions and methods for treating textile substrates to obtain superior liquid repellent properties are disclosed. Durable microscopic surface structures imparted to the fibrous substrate allow liquids to bead up and roll off of its surface. Mechanical abrasion or sanding techniques may be used to create the microscopic surface structures on the surface of a fibrous textile substrate, without substantially breaking fibers, followed by a chemical treatment using, for example, fluorocarbon-containing repellent compositions. Particles may be employed in combination with repellent compositions to achieve superior repellent properties. A property of the roughened surface fibers, the Roughness Factor, is used to characterize the microscopic surface structures on the treated textile surface. Treated textile substrates are disclosed which achieve superior water and oil repellency, even after multiple abrasion or laundering cycles.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Method and device for simulating variable roughness factor ice cover in ice water dynamic test
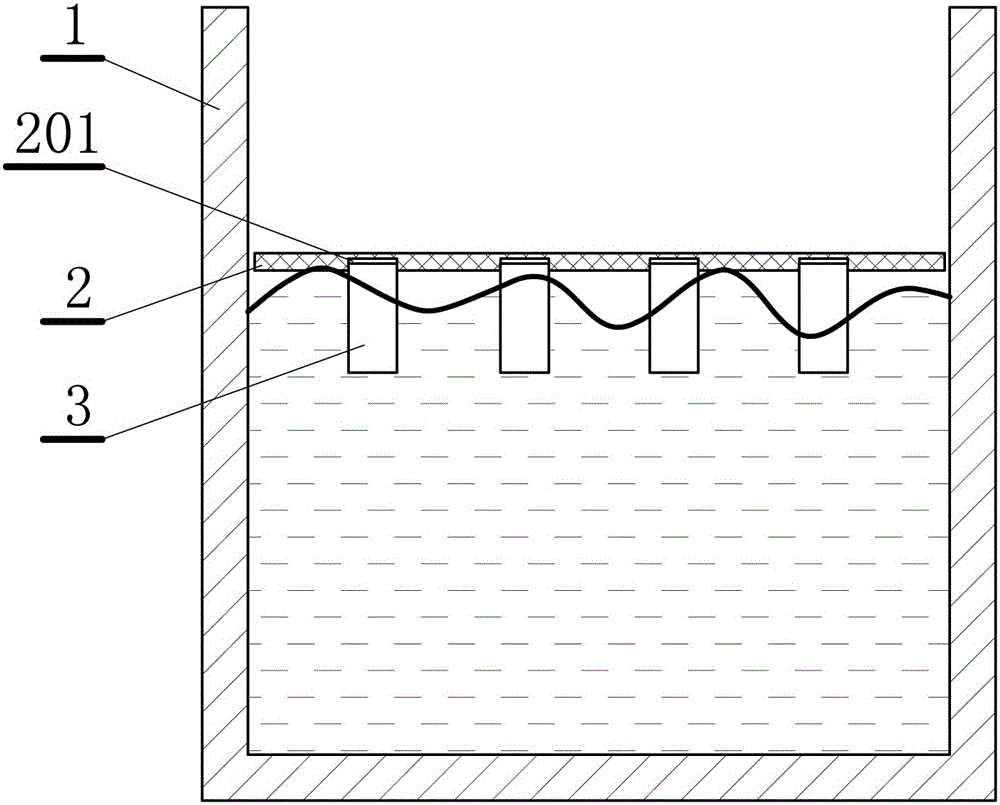
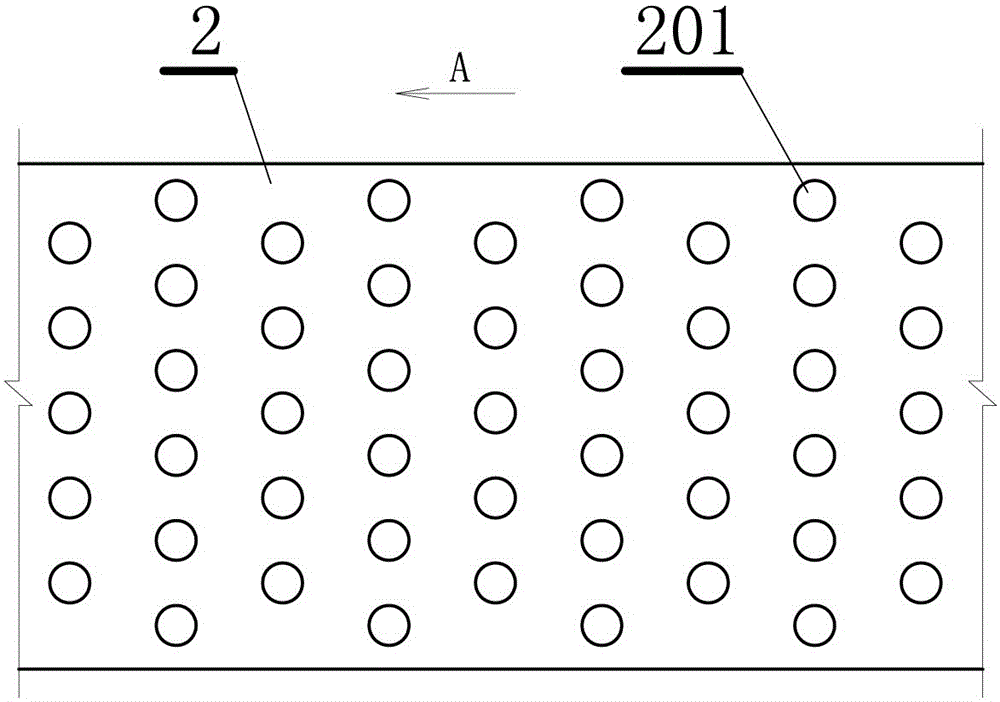
The invention relates to a method and device for simulating a variable roughness factor ice cover in an ice water dynamic test. The device comprises a simulated ice cover plate which is matched with a simulated river course is width, the simulated ice cover plate is made of polyethylene boards, multiple fixing holes are formed in the simulated ice cover plate uniformly, rough blocks for simulating the roughness factor are fixed in the fixing holes correspondingly according to test requirements, and the rough blocks are made of polyethylene bars. According to the method and device, the ubiquitous material, namely the polyethylene, serves as the material for simulating the ice cover, the ice cover plane is simulated by boards, the long-strip-shaped polyethylene materials are erected on the board for simulating the rough surface of the ice cover, and simulated ice covers of different roughness factors are formed. Due to the fact that the long-strip-shaped materials which are different in length and density can be replaced in various simple ways, the ice covers of different roughness factors can be simulated, the test can be accelerated, and the test cost can be reduced greatly.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Measuring and calculating method for length of deep pool segment of step-deep pool type debris flow drainage canal
ActiveCN105178255ABalanced excretion without flushing or siltingAvoid direct impactArtificial water canalsDrainage canalDebris flow
The invention discloses a measuring and calculating method for the length of a deep pool segment of a step-deep pool type debris flow drainage canal. According to the measuring and calculating method, firstly, the unit weight of a debris flow body, the designed longitudinal slope of the drainage canal, the casting angle of debris flow, the designed suspension height of a step segment, the designed width of the drainage canal and the designed peak flow of the drainage canal are determined; then the roughness factor of the drainage canal, the permissible velocity and the overflowing mud depth of the debris flow are determined; afterwards, the average velocity of a debris flow cross section is determined, and the permissible velocity is compared with the average velocity of the debris flow cross section; and finally, the length of the deep pool segment of the step-deep pool type debris flow drainage canal is determined through a measuring and calculating formula of the deep pool segment. Proceeding from the complete movement process of fluid in the canal, the method is based on strict theoretical derivation, and the influence of the properties of the debris flow on the casting range is considered in combination with experiments, so that the length of the deep pool segment of the step-deep pool type debris flow drainage canal is determined reasonably, and a basis is provided for the design of the step-deep pool type drainage canal; the precision of a calculated result is high; the method is adapted to the actual requirement of engineering.
Owner:INST OF MOUNTAIN HAZARDS & ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for obtaining drain basin unit lines by utilizing complete two-dimensional shallow water equation sets
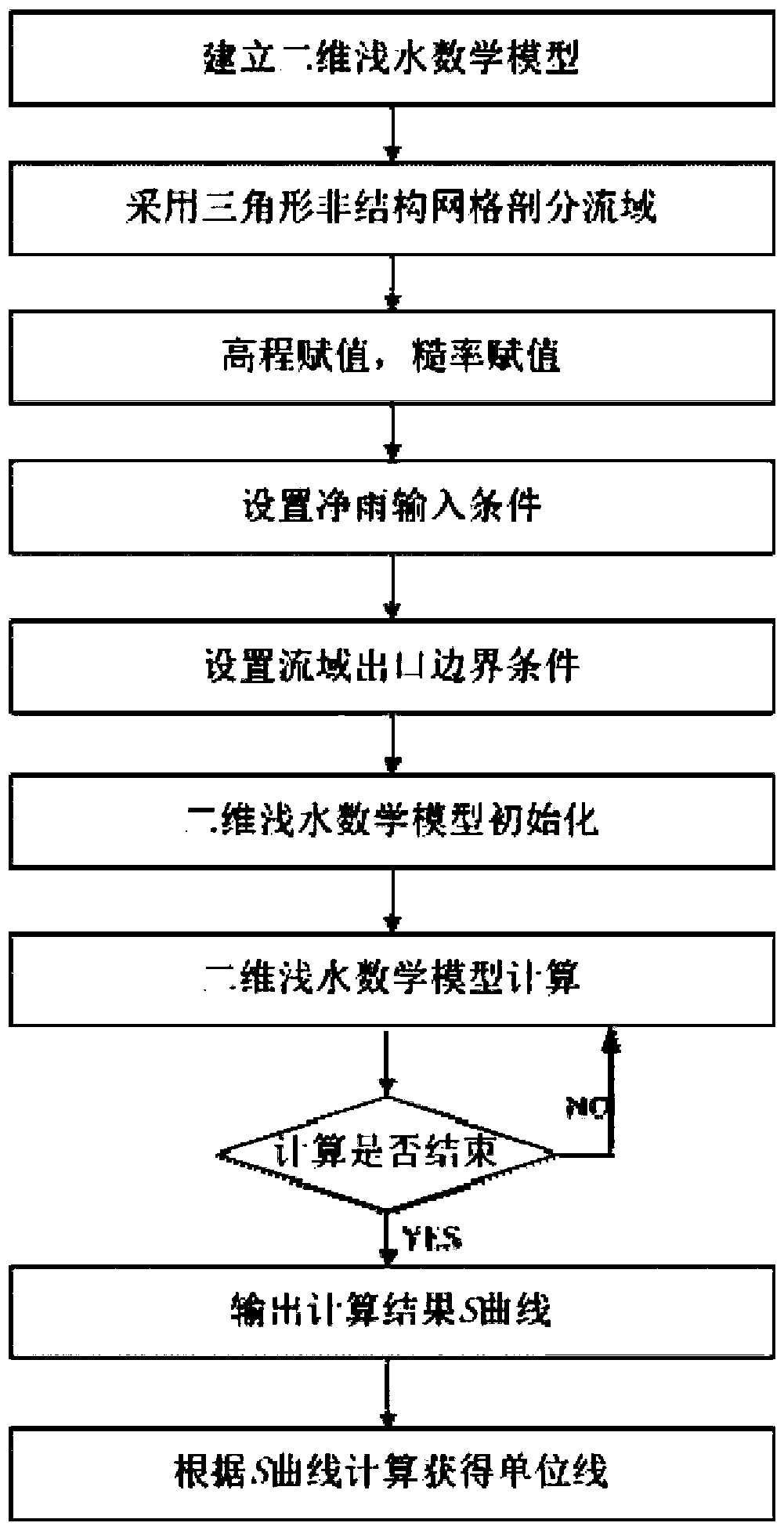
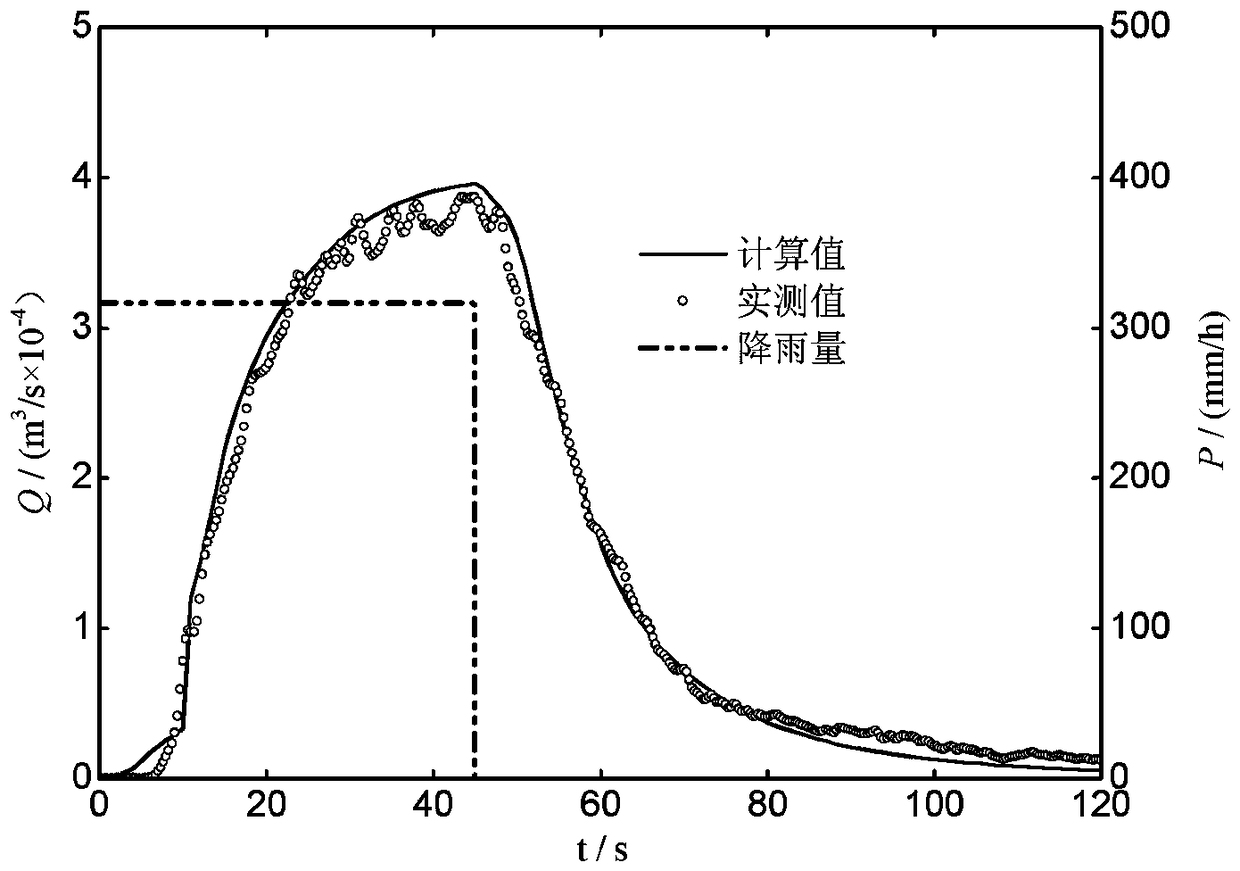
ActiveCN108446502ASimulation is accurateOvercoming the problem of requiring a large amount of rainfall runoff dataClimate change adaptationDesign optimisation/simulationFree fallingWater model
The invention discloses a method for obtaining drain basin unit lines by utilizing complete two-dimensional shallow water equation sets. According to the method, a hydrological problem is solved by utilizing a hydrodynamic way. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly discretizing a two-dimensional shallow water equation set to establish a high-resolution two-dimensional shallow watermathematic model, so as to ensure that the two-dimensional shallow water model is capable of correctly simulating slope runoff processes; carrying out elevation assignment and roughness factor assignment by adoption of a triangular unstructured grid division calculation area; in order to avoid the problem of non-conservative drainage basin outlet water yield caused by drainage basin depression impounding, setting continuous time interval net rainfall processes as model input conditions; setting a drainage basin outlet as a free falling outflow condition; carrying out two-dimensional shallow water mathematic model calculation after setting a drainage basin initial state; after the calculation is ended, enabling a flow process at the drainage basin outlet as an S curve of the drainage basin;and obtaining a time interval unit line of the drainage basin by utilizing a conversion formula. The method is capable of covering the shortages of existing hydrological methods, and providing a newway for flood confluence analysis and calculation of regions without hydrological data.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Method for preparing cuprous oxide (Cu2O) with hierarchical flower-like structure
InactiveCN102502771AHigh crystallinityImprove stabilityNanotechnologyCopper oxides/halidesFlower likeCrystallinity
The invention discloses a method for preparing cuprous oxide (Cu2O) with a hierarchical flower-like structure, relates to a method for preparing nanometer Cu2O, and aims to solve the problem that a Cu2O nanometer material prepared by the prior art has a relatively small specific surface area and a relatively low roughness factor. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a copper salt solution; secondly, adding a nonionic surfactant for activating; thirdly, adding a reducing agent solution for reducing; and finally, separating, washing and drying in turn to obtain the Cu2O with the hierarchical flower-like structure. The method has the advantages that: 1, the Cu2O with the hierarchical flower-like structure is prepared; 2, compared with the conventional Cu2O nanometer material, the Cu2O has a larger specific surface area and obvious pore size distribution; 3, the Cu2O has high crystallinity and stability; and 4, the Cu2O can be used for degrading toxic and harmful pollutants in water under the catalysis of visible light. The method is mainly used for preparing the Cu2O with the hierarchical flower-like structure.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Fabrication Of Mesoporous Metal Electrodes In Non-Liquid-Crystalline Phase And Its Application
ActiveUS20080096089A1High roughness factorEasy constructionCell electrodesSurface reaction electrolytic coatingLiquid crystallineElectrochemistry
A method for the fabrication of a mesoporous metal electrode in a non-liquid crystalline phase was tested. Specifically, there was tested the efficacy of the method for the fabrication of a mesoporous metal electrode which comprises forming the mesoporous metal electrode on a substrate by chemical or electrochemical reduction of a mixture comprising a solvent, a structure-directing agent, and a source of a metal, characterized in that the mixture is maintained in a non-liquid crystal phase. Furthermore, the usefulness of the mesoporous metal electrode thus prepared from the non-liquid crystalline phase was also tested. The mesoporous metal electrode prepared from the non-liquid crystalline phase had a large surface area, and a roughness factor thereof was controlled by charges passed during electroplating. The method made it possible to fabricate the mesoporous metal electrode in the non-liquid crystalline phase, even more flexible than a liquid crystalline phase. The mesoporous metal electrode prepared by the method had randomly distributed mesopores on the surface thereof and retained a large roughness factor. The method was found to be a good alternative to the conventional fabrication of porous platinum films in the liquid crystalline phase. Furthermore, the method was found to be suitably applicable to automatic processes, because the mesoporous metal electrode was prepared in the highly flexible non-liquid crystalline phase. Recovery and recycling of raw materials were also improved. The mesoporous metal electrode prepared by the method can be suitably used for the detection of glucose and proton, and as a cathode or an anode of fuel cells.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Preparation method of feather dress fabric or slopwork productions with nanometer self-cleaning function
InactiveCN100334291CHas superhydrophobic and oleophobic propertiesAchieve the purpose of self-cleaningPhysical treatmentFiberSolid particle
Owner:ZHONGKE BOSIDENG NANOMETER CLOTHING ORNAMENT SUZHOU
Method for taking values of mechanical and hydraulic properties of rock mass structural plane
InactiveCN1654954AThe result is objectiveStable reliabilityEarth material testingMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsProperty valueSample length
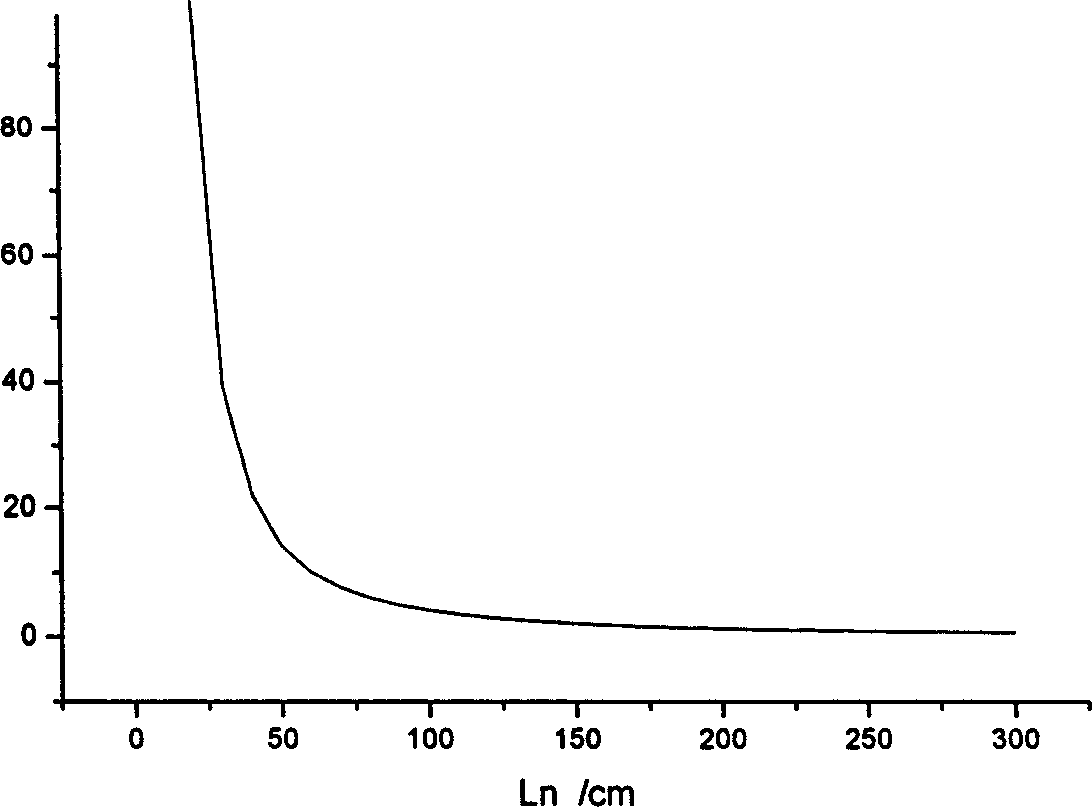
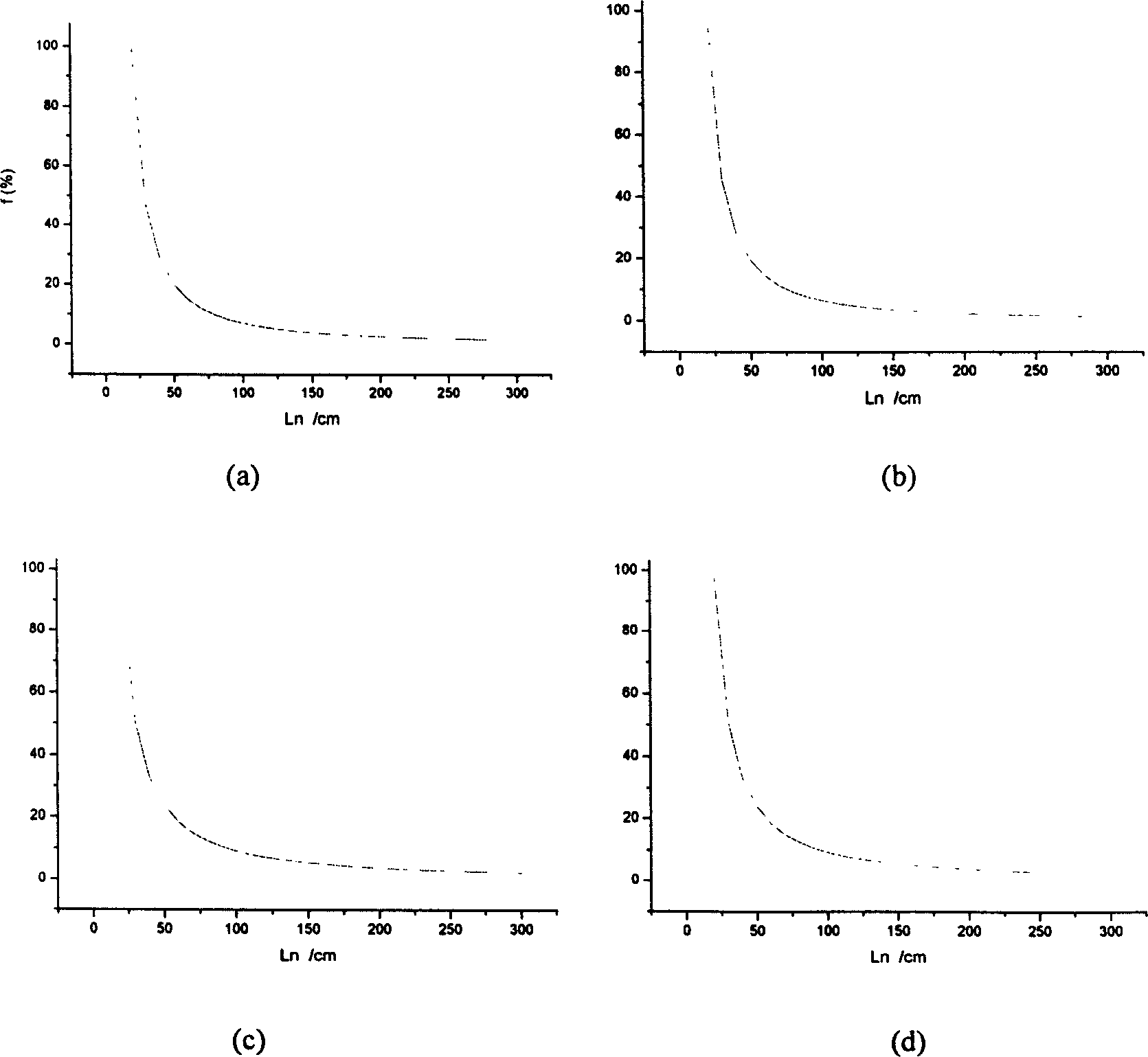
This invention relates to a large rock structure face mechanics and hydraulics property value fetch method including the following steps: uniformly arranging two test section of 10cm and 30cm demanded by statistics corresponding to the required measurement directions on a small size rock and plotting profile curves of the above mentioned section, measuring the fluctuation amplitudes of the profile curves, computing the factor value of each section roughness to compute the desired values based on the roughness factor E(JRCo), E(JRC30), obtaining D30 of JRC diameter effect to be substituted into a related JRC effect rate formula to get the Ln-f relationship map, when f=50%, the related sample length on Ln-f curve -the roughness efficiency is Ln taken as the substitution formula of rock structure face mechanics and hydraulics property value fetch.
Owner:杜时贵
Photoelectric conversion device
InactiveCN1856883AElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureAll solid statePhotoelectric conversion
The present invention provide an all solid-state photoelectric conversion device which comprises a semiconductor, an electrically conductive substrate arranged on one surface of the semiconductor and forming an ohmic junction therewith, an electrically conductive film arranged on the other surrface and forming a Schottky junction with the semiconductor, and a sensitizing dye layer arranged on the electrically conductive film, the roughness factor of the surface of the semiconductor forming a Schottky junction being 5 or greater. The photoelectric conversion device has a large effective surface area and a high durability and can be manufactured at a low cost.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CO LTD
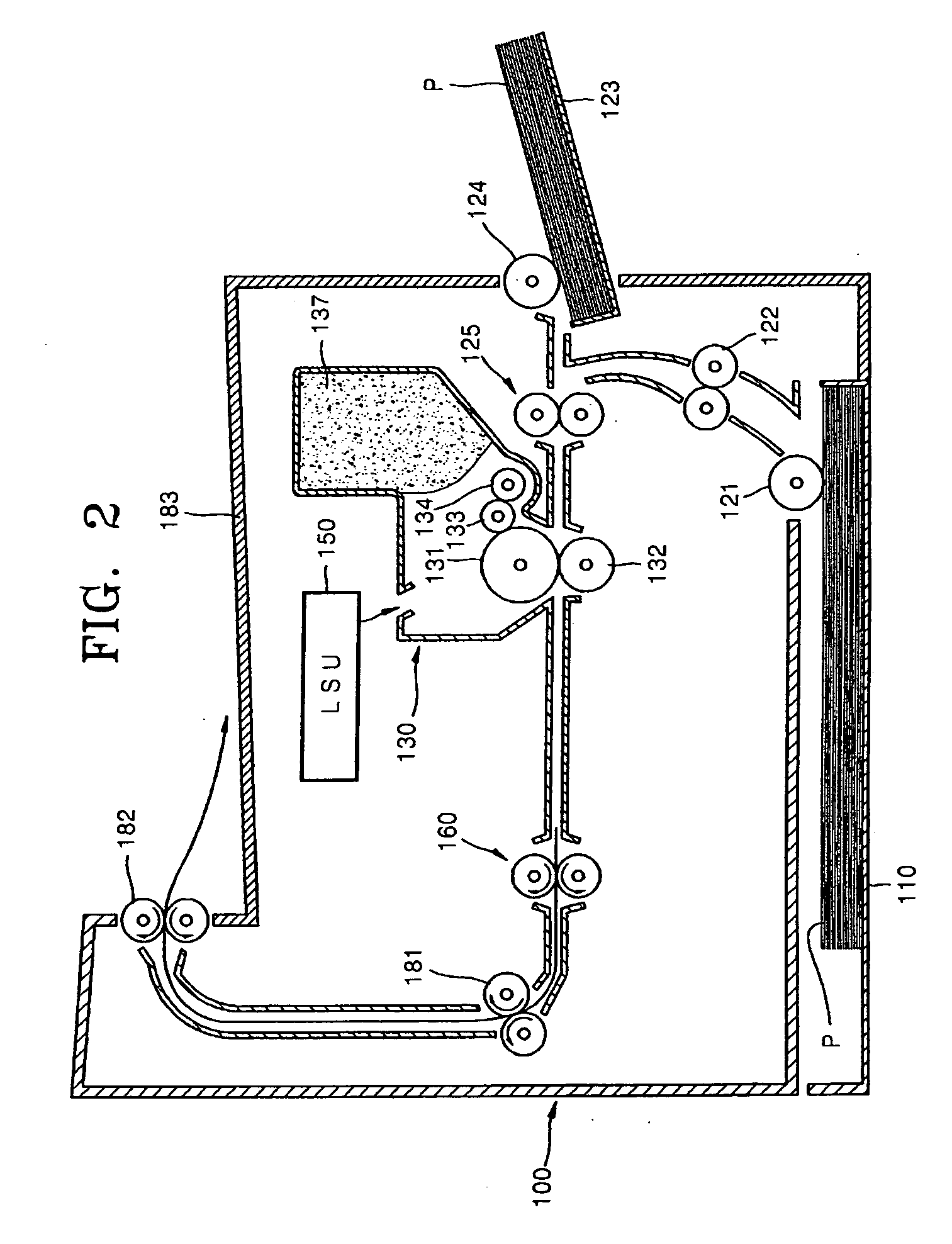
Fuser roller, fusing unit, image-forming apparatus, and method thereof
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Liquid drop contact angle solving method under given surface second-level nano-micro structure
ActiveCN105912502ACalculation simplificationSimplified free energyDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsMicro structureMeasuring instrument
The invention discloses a liquid drop contact angle calculation method under a given surface second-level nano-micro structure. The calculation method comprises the following steps: adopting a nano-micro geometric measuring instrument to measure the structure size of the given second-level nano-micro structure to obtain the side length, the space and the height of the nano-micro structure; adopting general assumptions in Young equation, Wenzel equation and CB equation deduction, and calculating a roughness factor and an area fraction under micrometer and nanometer size under the assumptions; according to different infiltration states under a micrometer structure and a nanometer structure, dividing the infiltration states of the second-level nano-micro structure into four situations, and inducing and simplifying the system free energy calculated modes of four given surface second-level nano-micro structures; and in virtue of a C++program compiling module in Visual Studio2012 software, applying a Soushan method to calculate the system free energy under different infiltration states, finding interface minimum free energy under a stable state, and obtaining a contact angle corresponding to the interface minimum free energy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
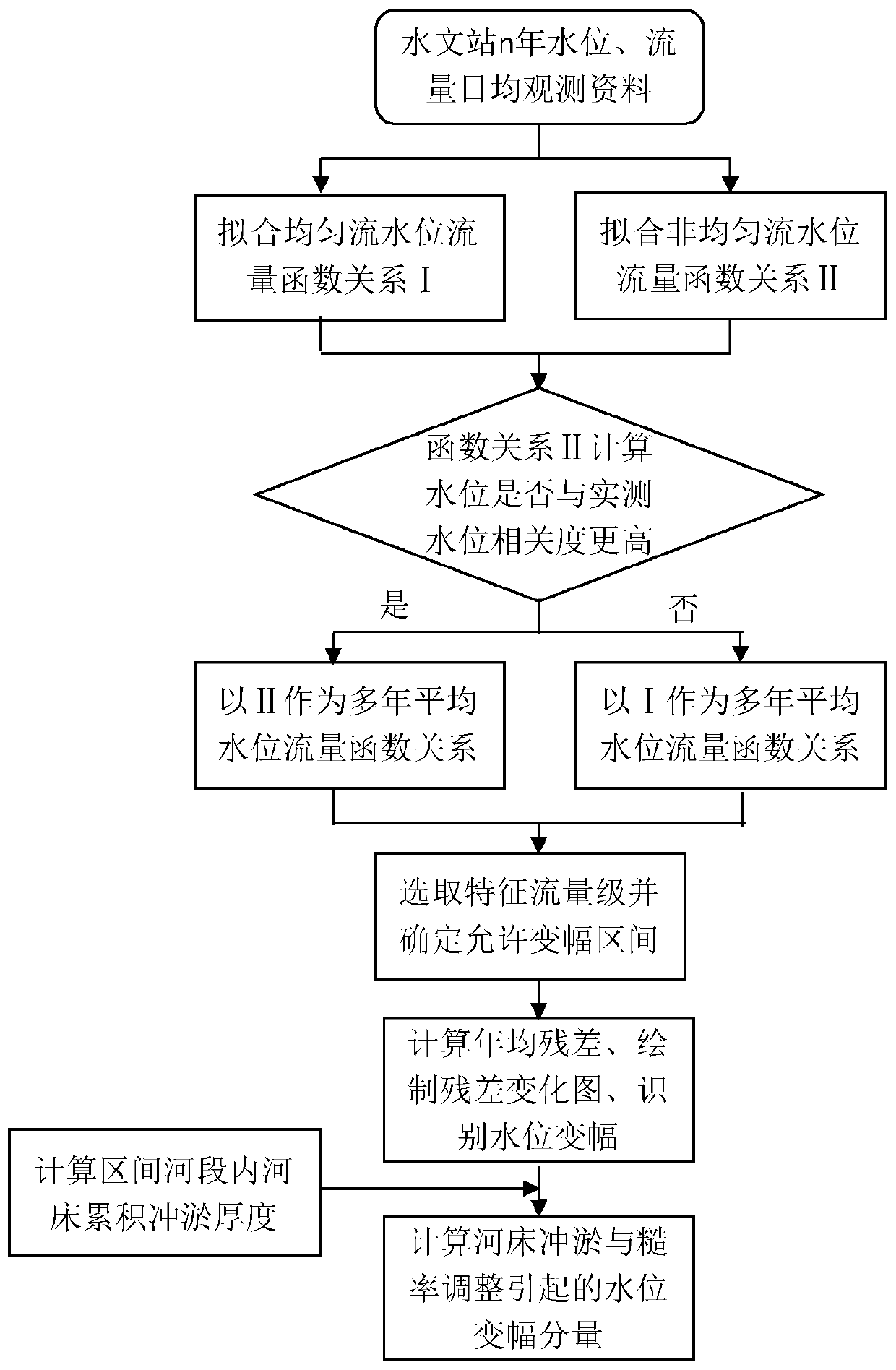
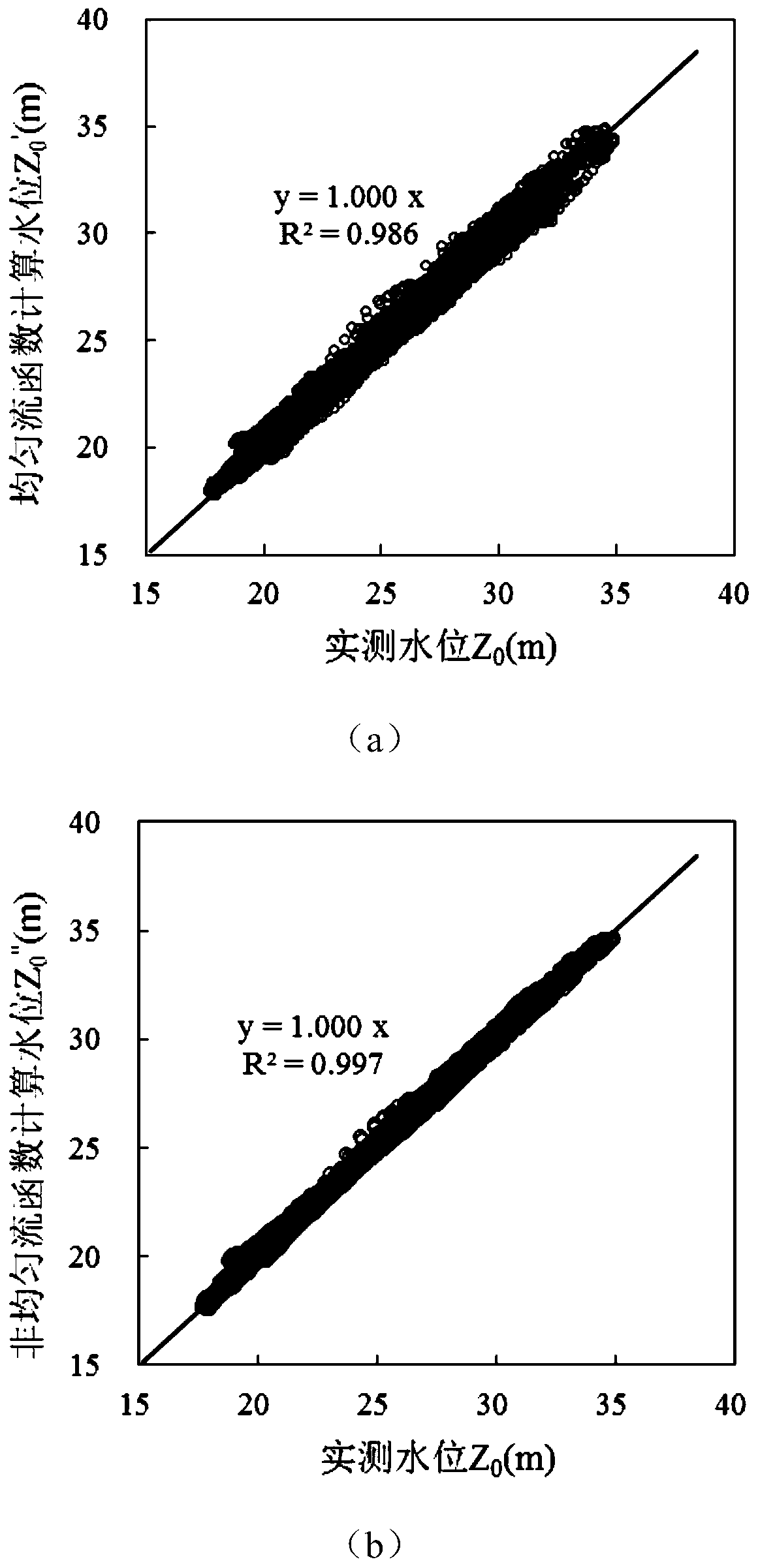
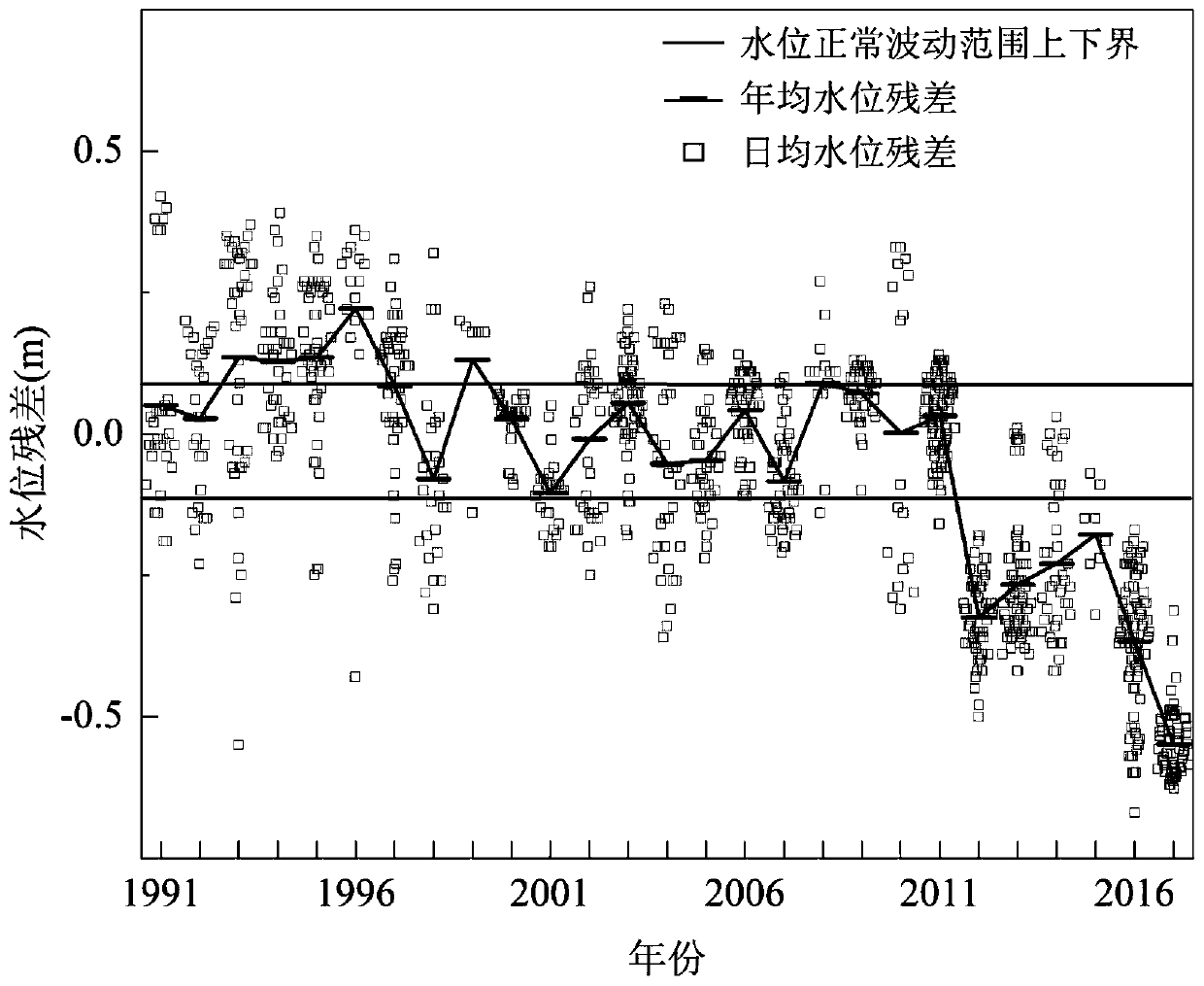
Method for identifying influence amplitude of riverway adjustment on water level by utilizing horizontal residual errors
ActiveCN110399587AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityComplex mathematical operationsTransverse axisRiver regulation
The invention provides a method for identifying the influence amplitude of river regulation on the water level by utilizing a leveling residual error, which comprises the following steps of: 1, eliminating the influence of backwater jacking, and determining a multi-year average water level-flow function relationship of a river section inlet; 2, calculating a water level residual error under the characteristic flow according to the actually measured flow water level value and the multi-year average water level-flow function relationship; 3, drawing a change graph of annual average water level residual error along with time under a specific flow level in the coordinate plane by taking the year as a transverse axis and the annual average residual error as a longitudinal axis, and identifyinginterannual characteristics of water level change under the specific flow level on the basis of the change graph, so as to obtain a water level accumulated amplitude [delta]Z from the Nth year to theMth year; 4, quantitatively analyzing the influence effect of riverbed erosion and deposition and roughness factors; and 5, repeatedly executing the steps 2-4 to obtain water level accumulated amplitude components [delta]Zb and [delta]Zr under each characteristic flow level caused by riverbed erosion and deposition and roughness adjustment, thereby determining the influence amplitude of riverway adjustment on the water level.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Preparing method of self-cleaning polyurethane synthetic leather with lotus effect
InactiveCN110485172AGood wear resistance and stabilityRaise the roughness factorTextiles and paperSolvent freeSolvent
The invention discloses a preparing method of self-cleaning polyurethane synthetic leather with a lotus effect. Polycarbon waterborne polyurethane surface-layer resin is taken as a carrier, closed-type aroma microcapsules and siloxane polymers with certain concentrations are dissolved and dispersed to form surface-layer pulp, and then the surface-layer pulp coats fluffy release paper of a lotus-leaf-simulation microstructure to prepare a wear-resistance controlled-release aroma dry-method surface layer with natural high-roughness factors; a low-pressure casting process is adopted, hydrolysis-resistance slow-resilience solvent-free polyurethane resin is adopted for preparing a foaming interlayer, and then microfiber base cloth fits the foaming interlayer to obtain the solvent-free polyurethane synthetic leather finished product. According to the prepared self-cleaning controlled-release aroma functional solvent-free polyurethane synthetic leather with the lotus effect, processes like dipping, rolling and spraying are not needed, the leather has a self-cleaning function, the process is efficient, environmentally friendly and clean, no DMF is left in the product, the leather is soft and smooth in hand feeling and generates a strong sense of genuine leather, the fragrance holding time of the leather is at least prolonged by 240 days compared with leather which is processed directlythrough essence, and the leather has the advantages of wear resistance, good hydrolysis resistance and other good physical properties.
Owner:ANHUI ANLI MATERIAL TECH
Fuser roller, fusing unit, image-forming apparatus, and method thereof
InactiveUS20080013994A1Promote contractionPrevent peelingElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
A fuser roller and a fusing unit including the fuser roller are to be used in an image-forming apparatus. The fuser roller includes a tubular fusing portion, an inner tube, and a heating portion. The inner tube is inserted into the fusing portion. The heating portion is installed to enclose an outer surface of the inner tube and press against an inner surface of the fusing portion, and to radiate heat. The fusing portion is surface treated to have a roughness factor of Ra 3-5μm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
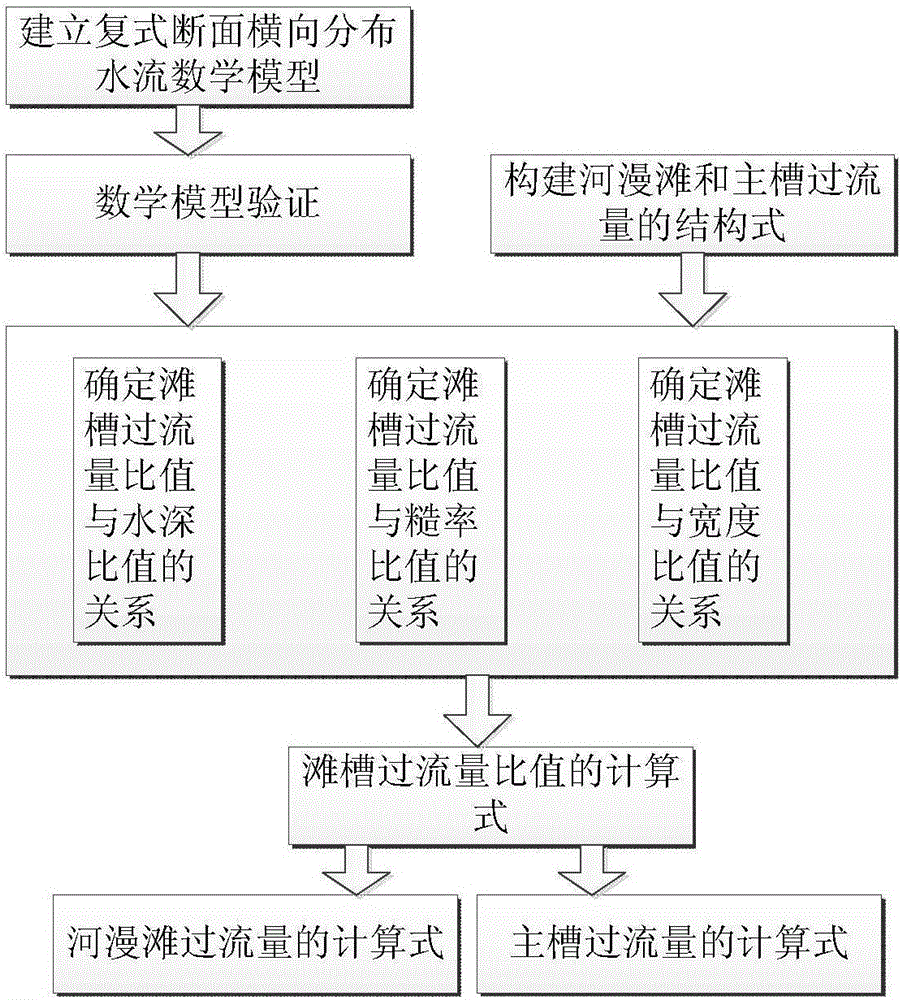
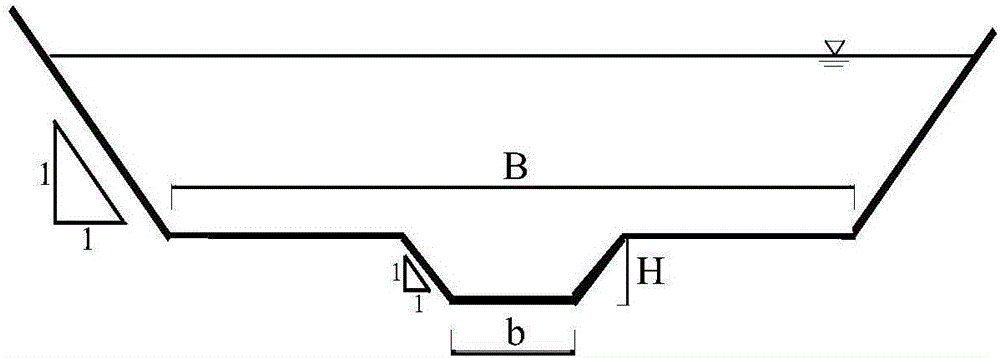
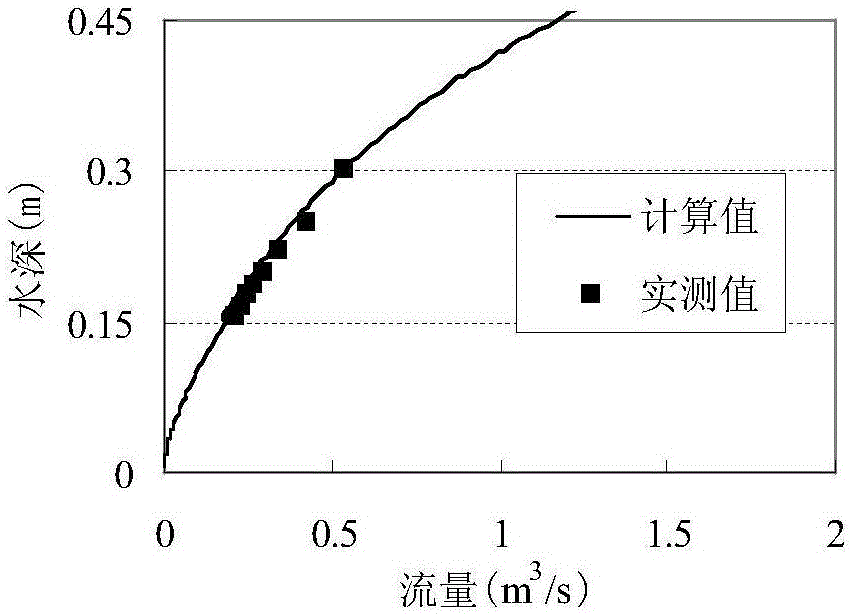
Overbank flow floodplain and channel excess flow computing method
InactiveCN106320255AGuarantee sustainable developmentEnsure stability and harmonyHydraulic engineering apparatusComplex mathematical operationsMathematical modelMain channel
The invention discloses an overbank flow floodplain and channel excess flow computing method. According to the method, a computing formula of floodplain and main channel excess flow is built, and the floodplain and channel excess flow ratio in the computing formula is closely related to the water depth ratio, the width ratio and the roughness factor ratio. In order to determine a mutual relation, a compound section transverse distribution flow mathematical model is adopted for computing the floodplain and channel excess flow under different conditions, the relational expression between the floodplain and channel excess flow ratio and the water depth ratio, the relational expression between the floodplain and channel excess flow ratio and the width ratio, and the relational expression between the floodplain and channel excess flow ratio and the roughness factor ratio are obtained through analysis, and finally the overbank flow floodplain and channel excess flow is comprehensively obtained through the computing method. According to the computing method, when fluvial cross section conditions are certain, the floodplain and channel excess flow can be rapidly obtained according to the forecast cross section flow, and a basis is provided for planning and utilization of floodplain and water resources.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for irradiation-mutating japonica rice in Northeast China through heavy-ion beam C
InactiveCN106613926AShortened steady speedHigh mutation ratePlant genotype modificationRice cultivationHeavy ion beamJaponica rice
The invention relates to a method for irradiation-mutating japonica rice in Northeast China through aheavy-ion beam C, in particular to a breeding method of japonica rice. The method for irradiation-mutating the japonica rice in Northeast China through the heavy-ion beam C provided by the invention aims to solve the problem of low mutation rate and beneficial mutation rate of an existing heavy-ion beam irradiation method. The method comprises the steps of (1) selecting japonica rice varieties in Northeast China as irradiation materials; (2) adopting a heavy-ion accelerator as an instrument, and using the heavy-ion beam C for irradiating germ surfaces of the japonica rice in Northeast China; (3) irradiating current M0 seeds, then normally sowing, transplanting survived rice seedling individual plants, mixed harvesting, threshing and storing all seed grains on M1; (4) in the spring of next year, planting M1 individual plants to obtain M2 generation, and appearing mutated plants; (5) in the winter of the year, adding-generation planting variant plants harvested from the M2-generation individual plants to obtain M3 generation in Sanya, Hainan; (6) in the spring of next year, planting the individual plants harvested from M3 to obtain M4 generation, monitoring yield, testing seeds, and selecting materials with the roughness factor being not less than 77 percent, the head rice rate being not less than 62 percent, the amylose being ranged from 15 to 20 percent, and the chalkiness percentage being below 20 percent. The method provided by the invention is used for breeding the japonica rice in Northeast China.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com