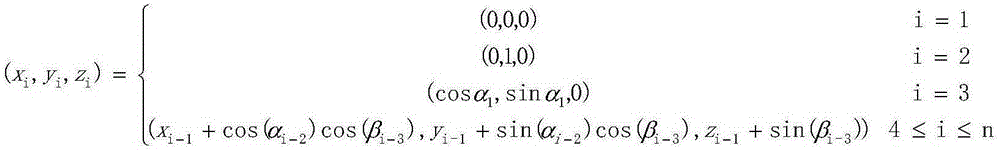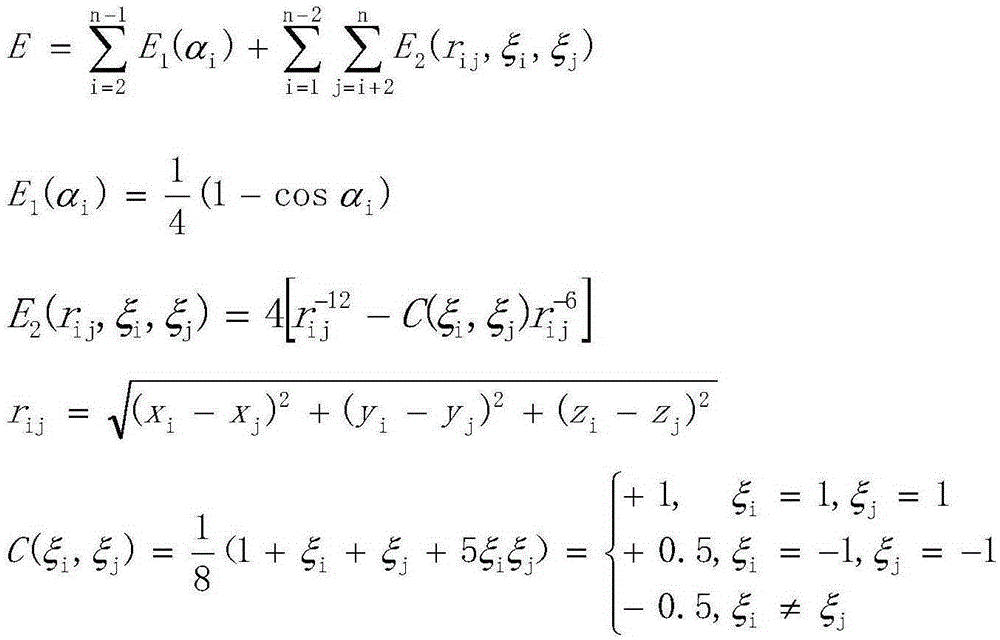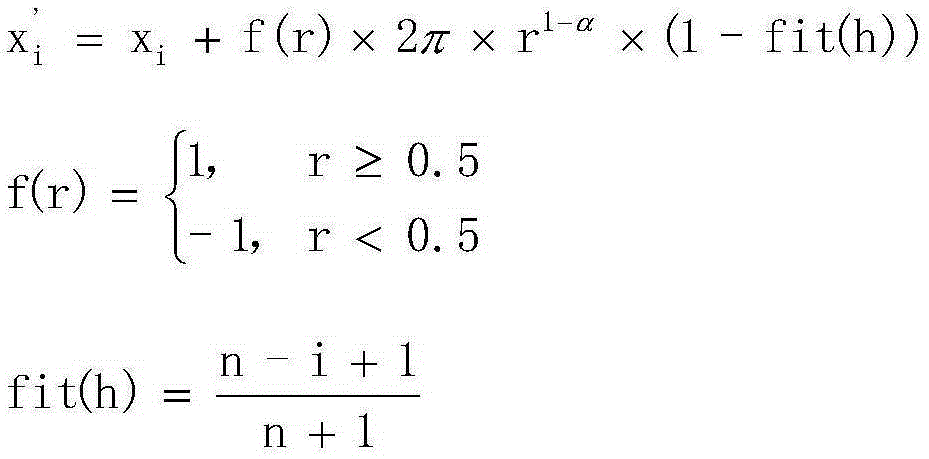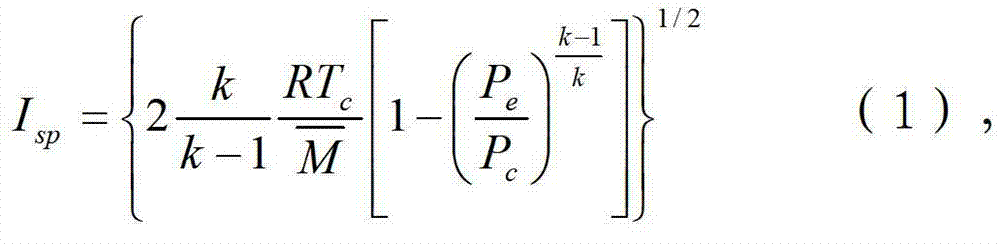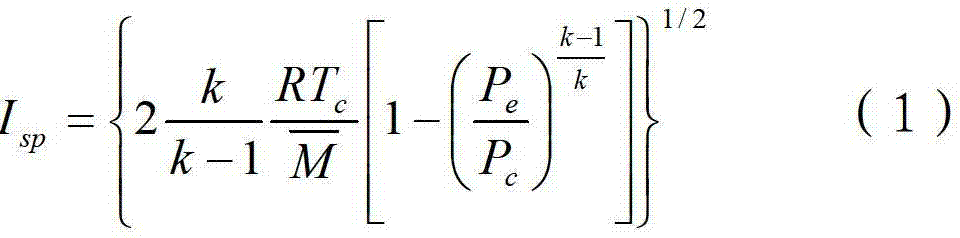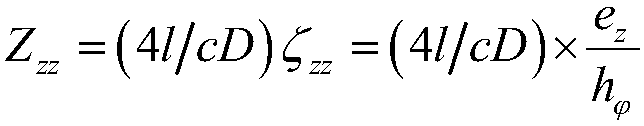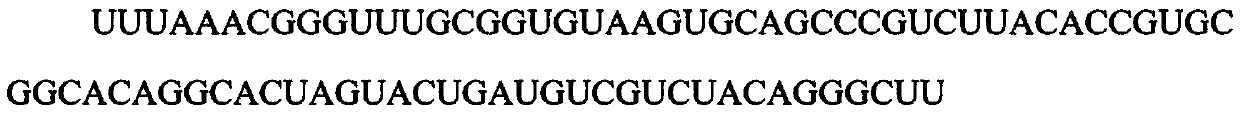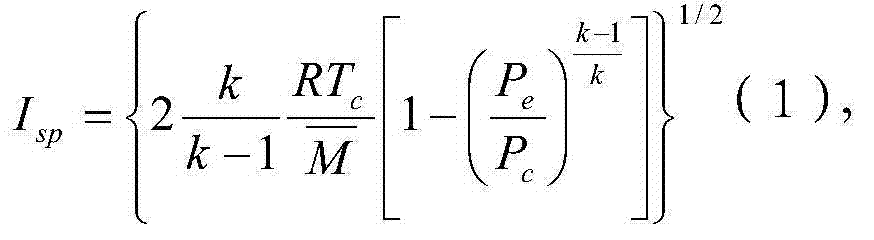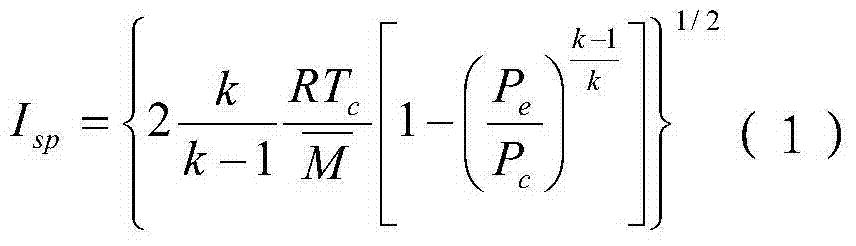Patents
Literature
30 results about "Minimum free energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The minimum free energy structure of a sequence is the secondary structure that is calculated to have the lowest value of free energy. It is synonymous with natural-mode structure, but it is not necessarily the structure that forms in nature. The lower the free energy, the more likely, in theory, the structure will form. Page.
Latex Adhesives Derived From Ionic Strength Induced Soy Protein Complexes
InactiveUS20080287635A1Easy to operateHigh strengthPeptide preparation methodsFiberProtein molecules
Macro hydrophobic clusters and complexes of soybean globular proteins were observed using TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope). Upon unfolding, hydrophobic groups of the proteins became exposed toward the surface of the protein and actively interacted with other hydrophobic groups of other protein molecules, thereby forming hydrophobic bonding. The hydrophobic bonding resulted in hydrophobic protein clusters, the formation of which was affected by the degree of protein unfolding, protein structure, and hydrophobic components. Such hydrophobic clusters followed the global minimum free energy theory and formed spherical like structures with diameters ranging from 100 nm to 3000 nm. Such an understanding lends applicability to many uses in adhesives, molding composites, surfactants for oil-water systems, bio-based interior construction paints and paper coatings, fiber production, and metal powder molding applications.
Owner:SUN XIUZHUI +2
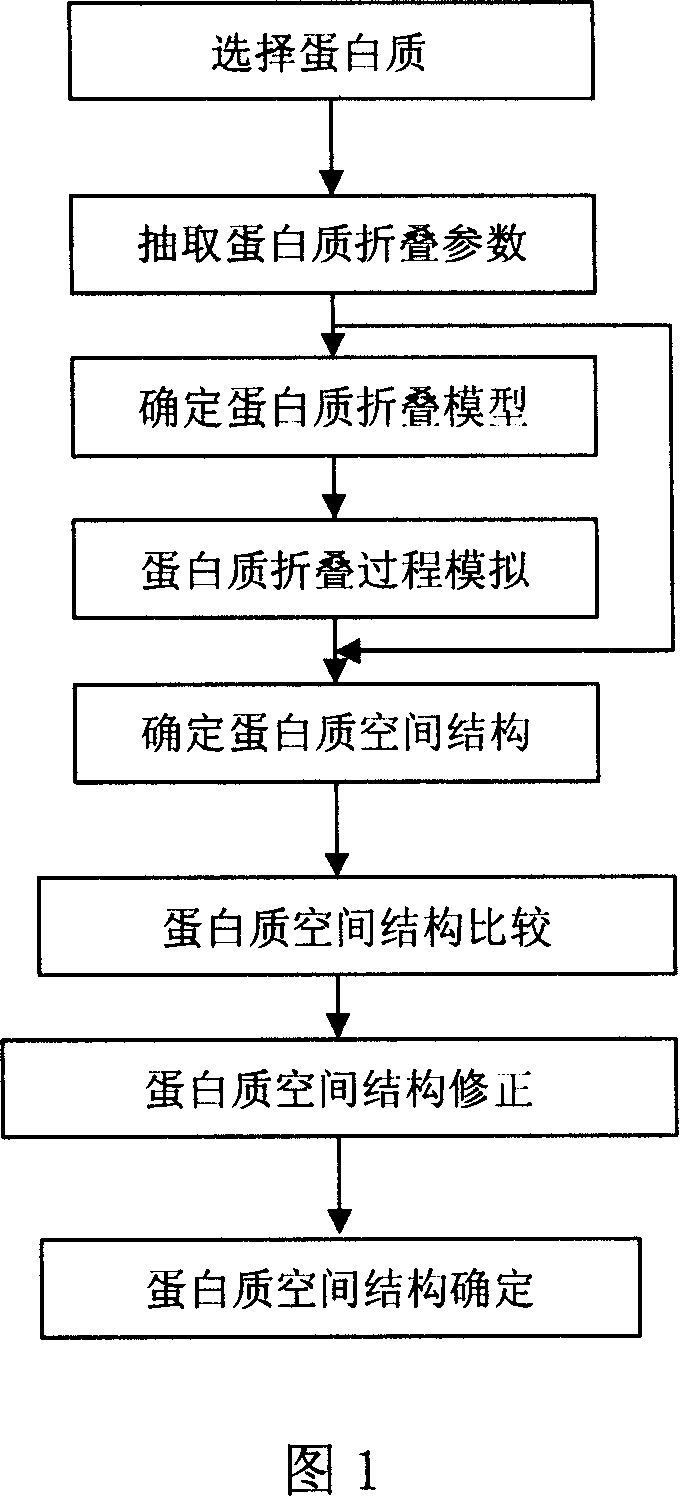
Computer simulation method for protein folding procedure based on synthesis algorithm
The invention discloses a computer simulating method based on protein folding course of synthetic algorism, which comprises the following steps: selecting non-lattice protein model; affirming energy function; searching three-dimensional structure of protein with minimum free energy; simulating the folding course; analyzing data; modifying. The invention combines the prediction of knowledge and the prediction of simulation, which improves the precision and calculating speed greatly without large amount of specific details in the folding course.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Semiconductor device with layered interconnect structure
InactiveUS6989599B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMinimum free energyElectrical conductor
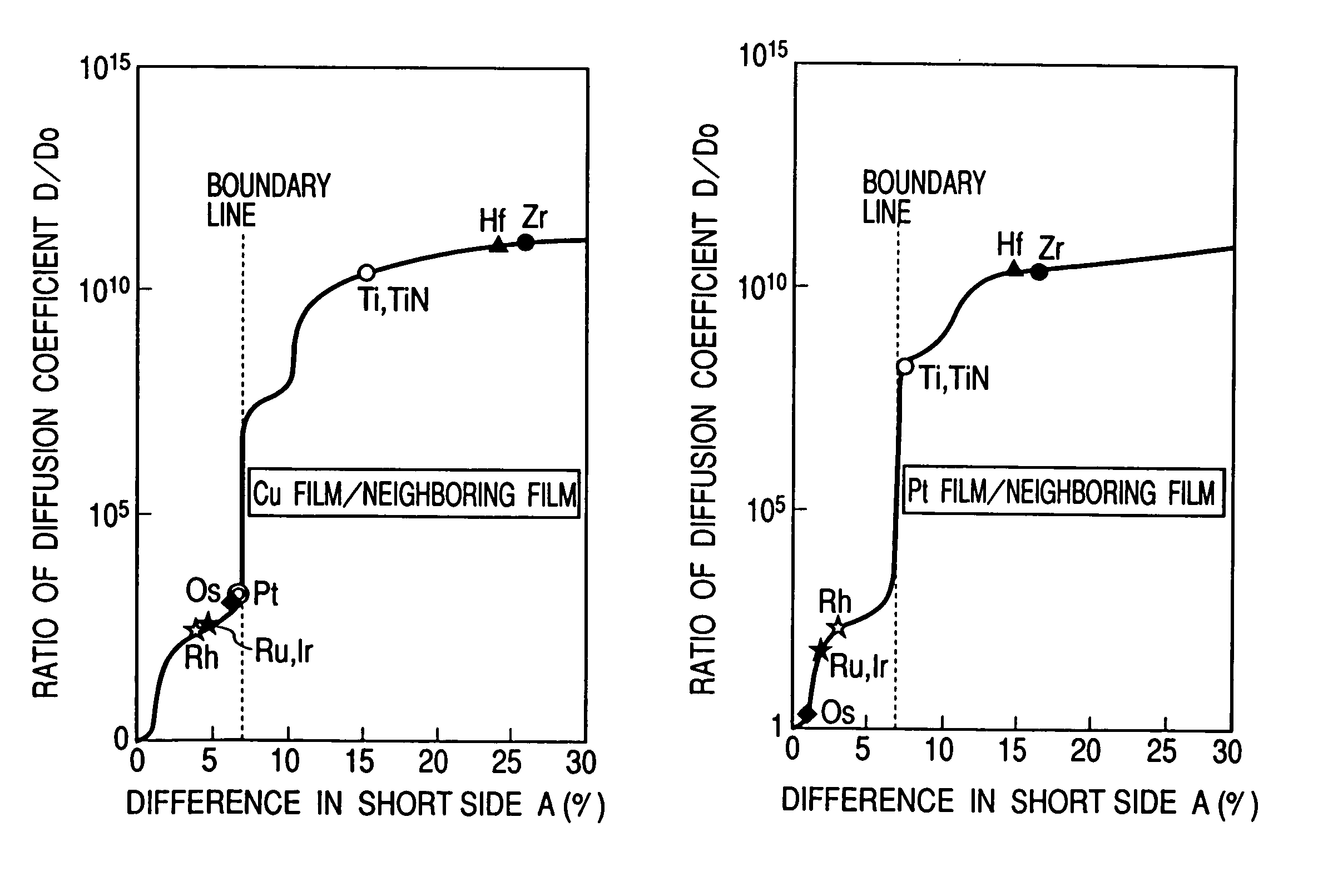
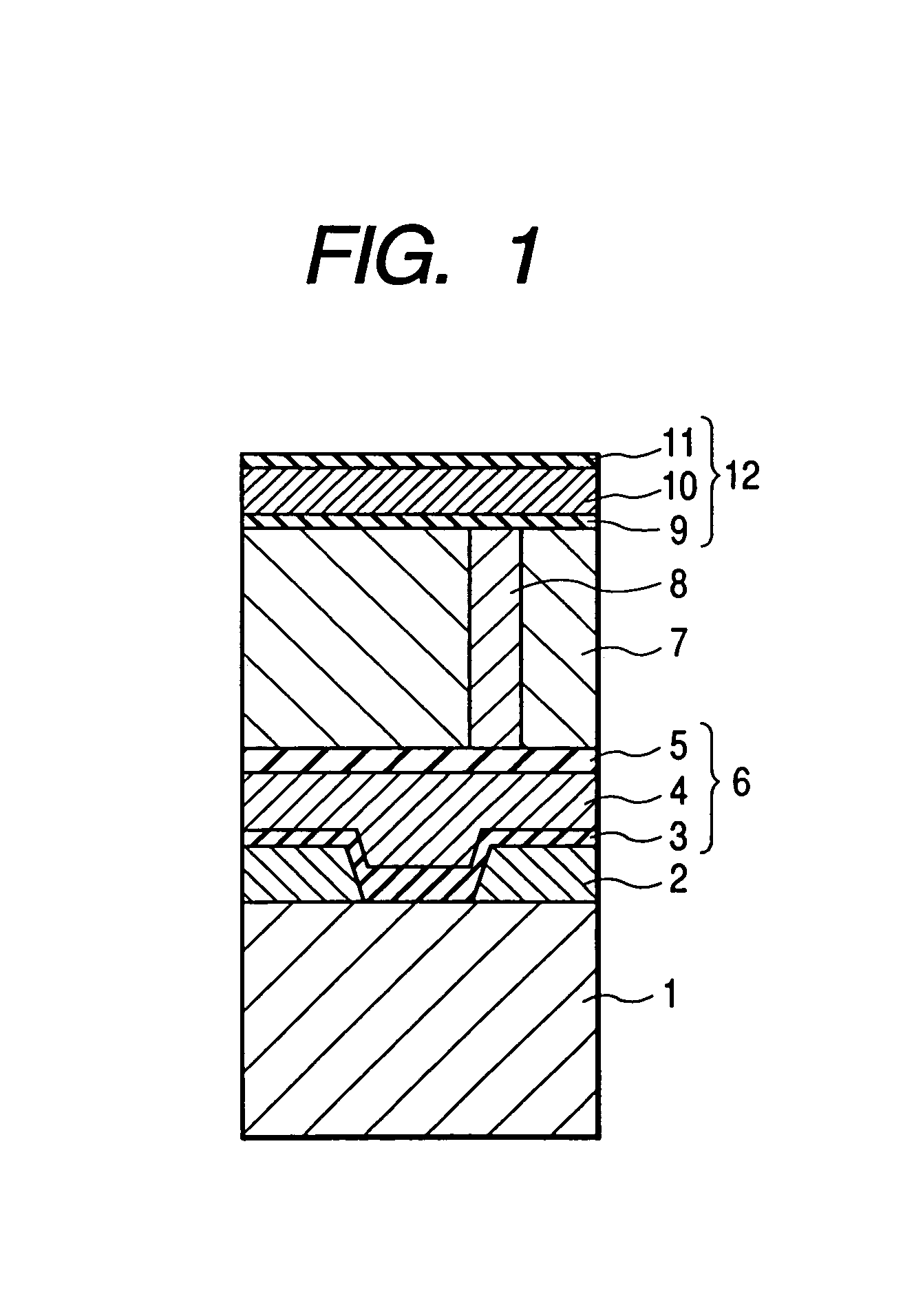
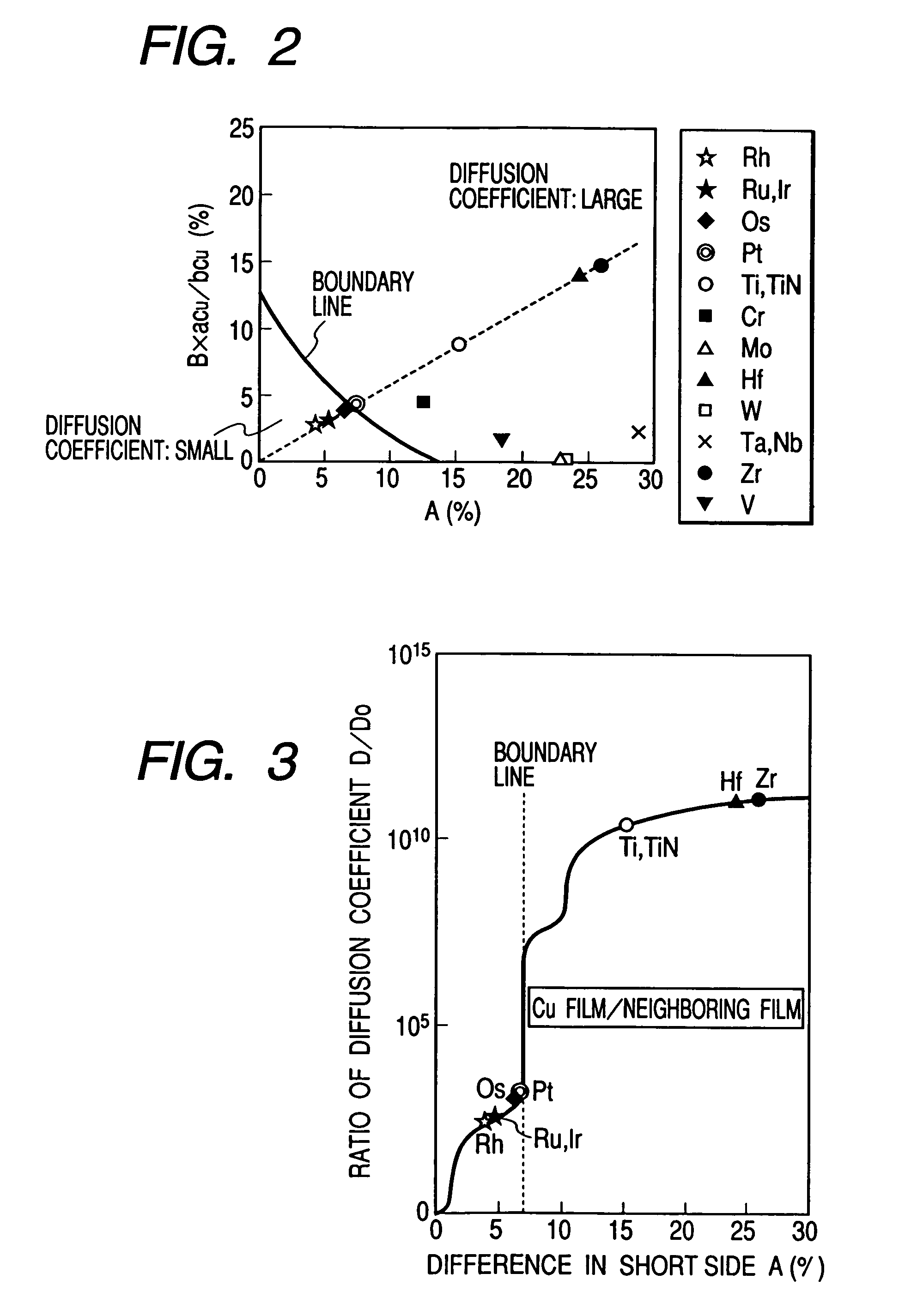
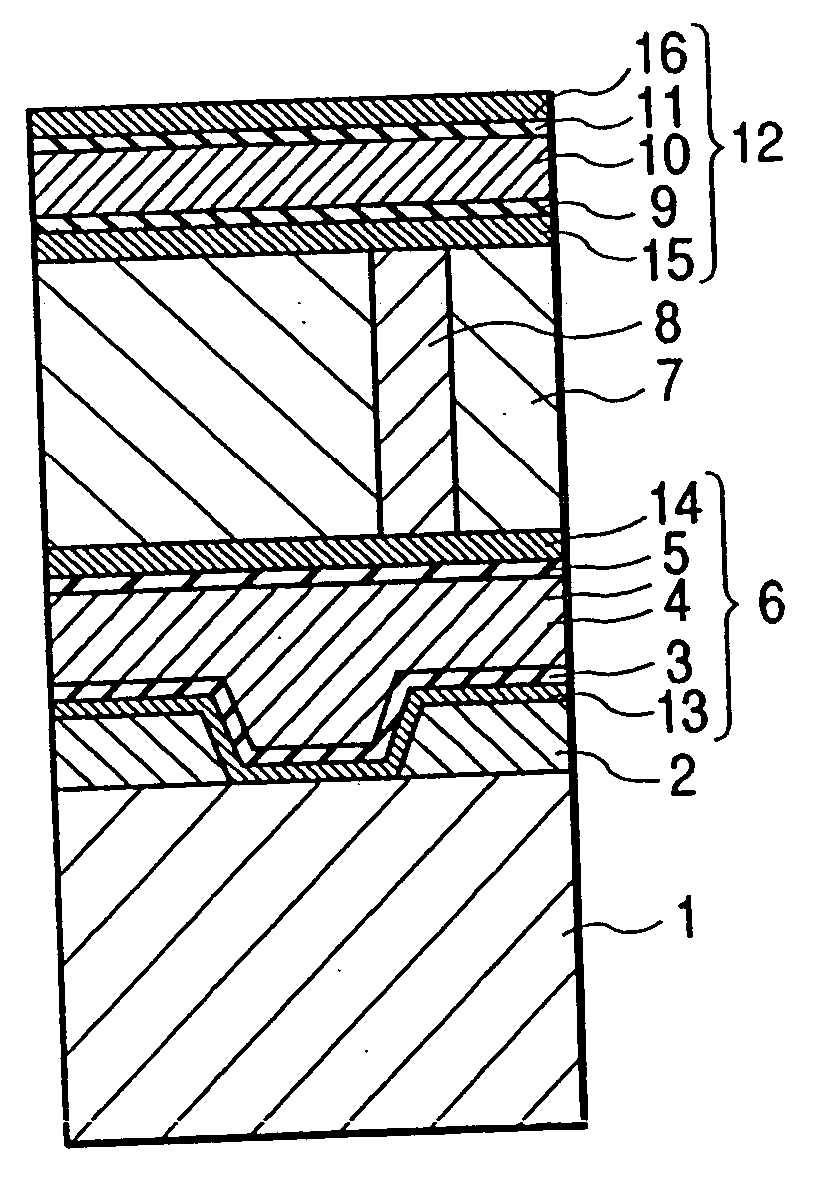
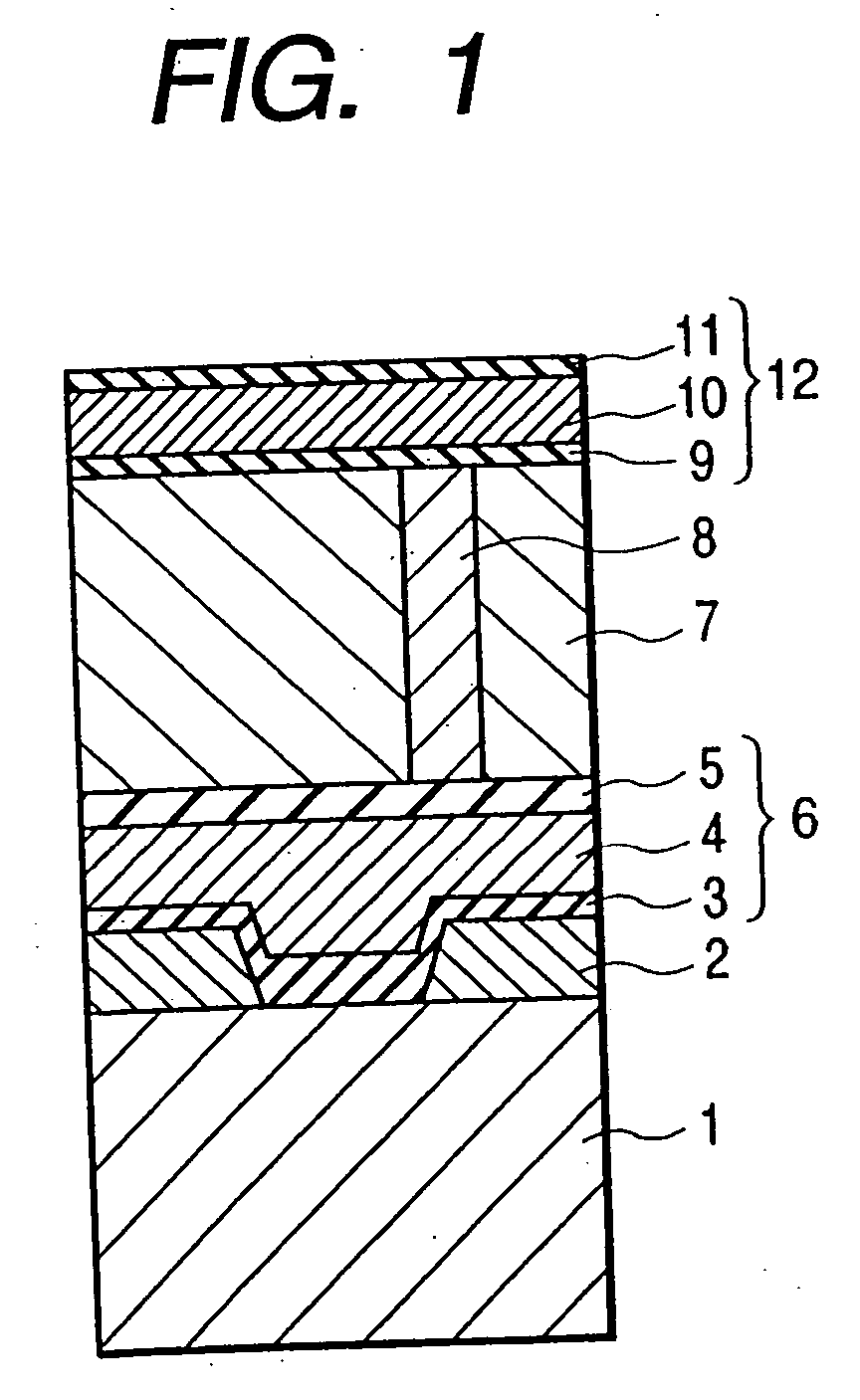
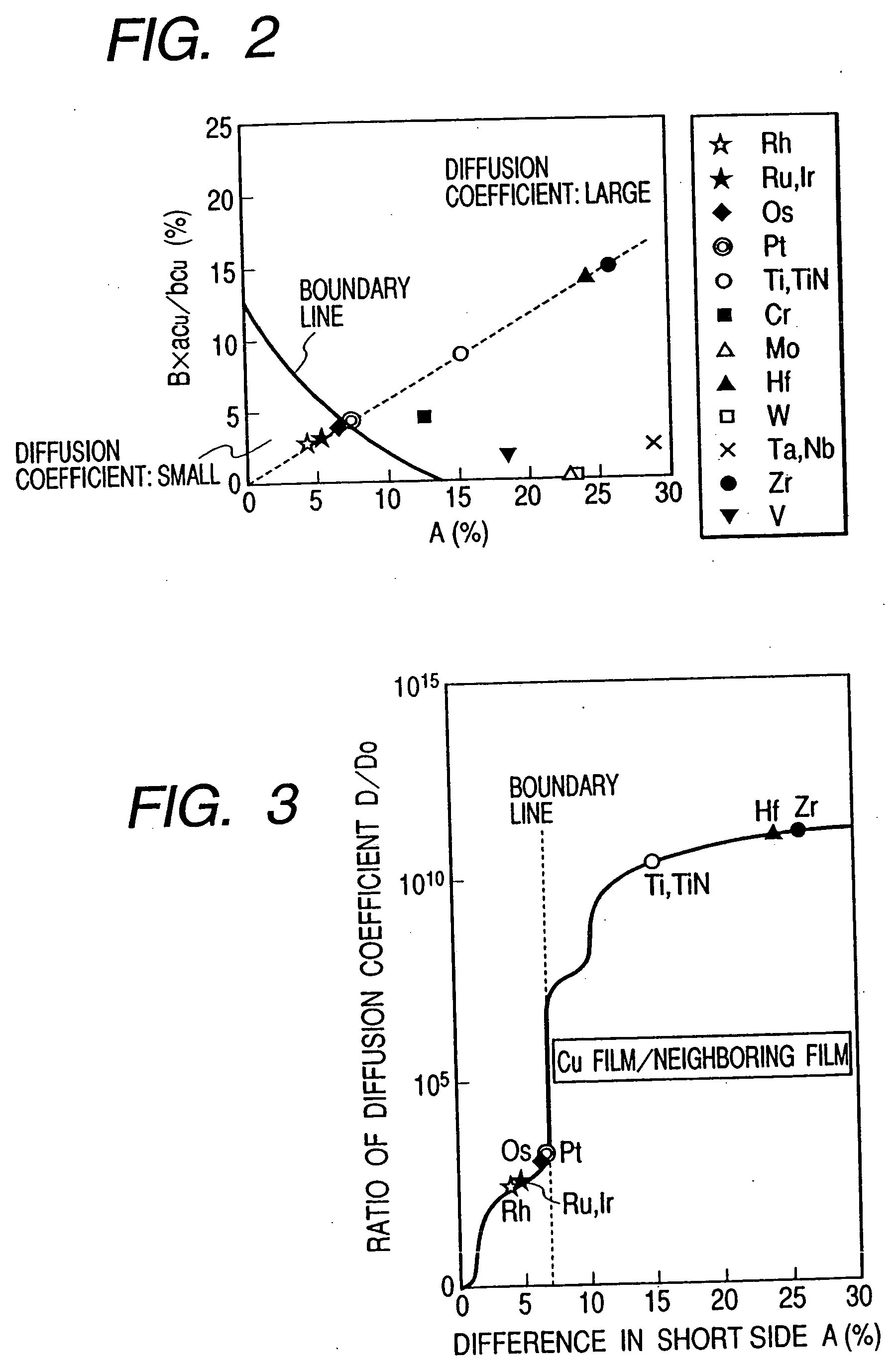
A reliable semiconductor device is provided with a layered interconnect structure that may develop no problem of voids and interconnect breakdowns, in which the layered interconnect structure includes a conductor film and a neighboring film so layered on a semiconductor substrate that the neighboring film is in contact with the conductor film. In the device, the materials for the conductor film and the neighboring film are so selected that the difference between the short side, ap, of the rectangular unit cells that constitute the plane with minimum free energy of the conductor film and the short side, an, of the rectangular unit cells that constitute the plane with minimum free energy of the neighboring film, {|ap−an| / ap}×100=A (%) and the difference between the long side, bp, of the rectangular unit cells that constitute the plane with minimum free energy of the conductor film and the long side, bn, of the rectangular unit cells that constitute the plane with minimum free energy of the neighboring film, {|bp−bn| / bp}×100=B (%) satisfy an inequality of {A+B×(ap / bp)}<13. In this way, the diffusion of the conductor film is retarded.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Protein structure prediction method based on improved niche genetic algorithm
InactiveCN105184112AIncrease diversityAvoid duplicate solutionsSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum free energyAlgorithm
The invention relates to the field of protein structure prediction and discloses a protein structure prediction method based on the improved niche genetic algorithm. According to the method, the niche genetic algorithm is introduced into protein structure prediction, and the genetic algorithm is improved to a certain extent in terms of selection and variation. Based on data obtained from experiments and results obtained through comparison with other methods, the method has the advantages that the corresponding minimum free energy value of protein can be searched more comprehensively, so that a more stable protein structure is obtained; operation time is shortened greatly, meaning that the method has high time efficiency.
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
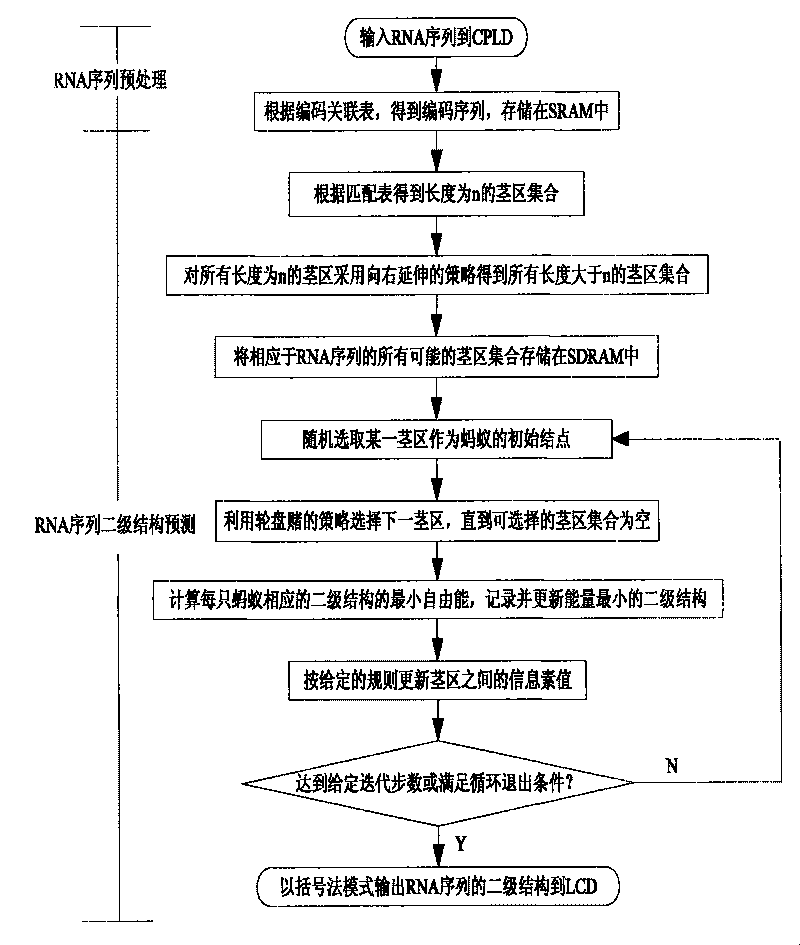
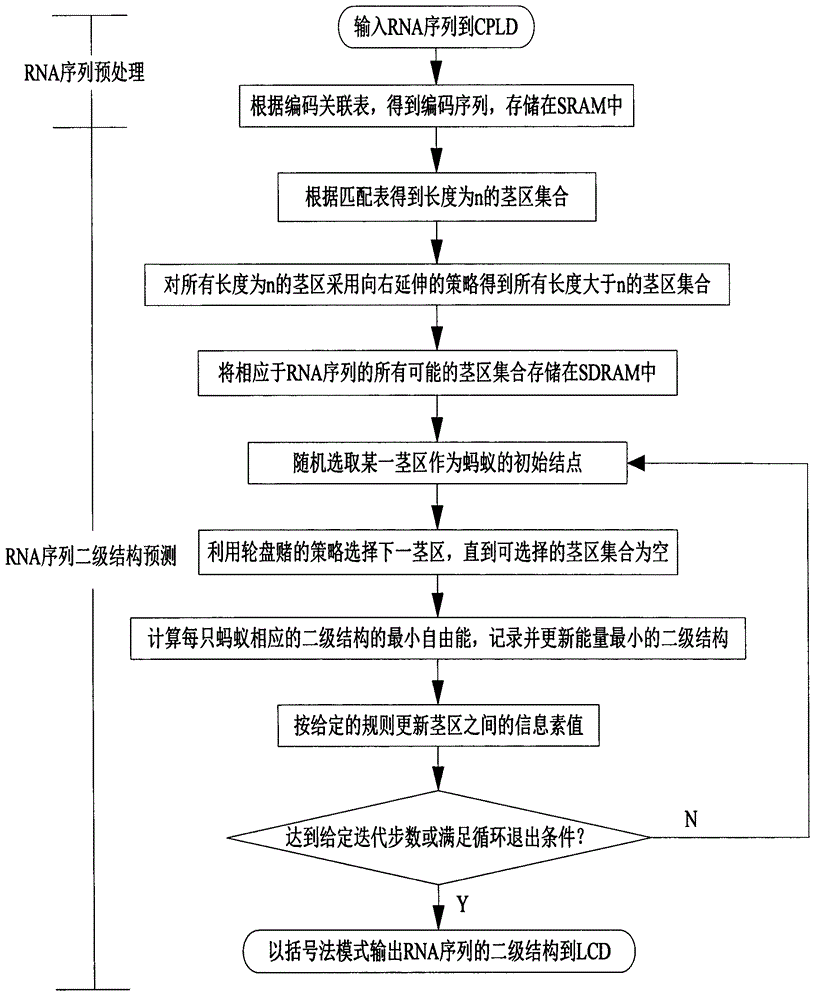
RNA sequence secondary structure prediction method based on base fragment coding and ant colony optimization
InactiveCN101717822AAccurate predictionIntuitive and accurate structural expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum free energyTrue positive rate
The invention relates to a RNA sequence secondary structure prediction method based on base fragment coding and ant colony optimization, belonging to the field of bioinformatics research. The RNA sequence secondary structure prediction method comprises the steps of: recoding an RNA sequence, and obtaining a corresponding coding sequence according to corresponding values in a coding table and a coding association list; eliminating a redundancy stem region by a strategy of extending rightwards according to an exact matching table and a partial matching table to obtain all possible useable stem region sets; giving two-dimensional heuristic information in the ant colony optimization, selection rule of an initial stem region and the next stem region and updating strategy of pheromones to construct compatible subsets of all possible stem region sets; and finally obtaining a secondary structure with minimum free energy. The invention can rapidly, accurately and effectively predict the secondary structure without including a pseudojnot RNA sequence, can output the obtained result in a bracket mode way, and is superior to the main prediction technology at present in the aspects of sensitivity and specificity of the prediction of the RNA sequence second structure.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
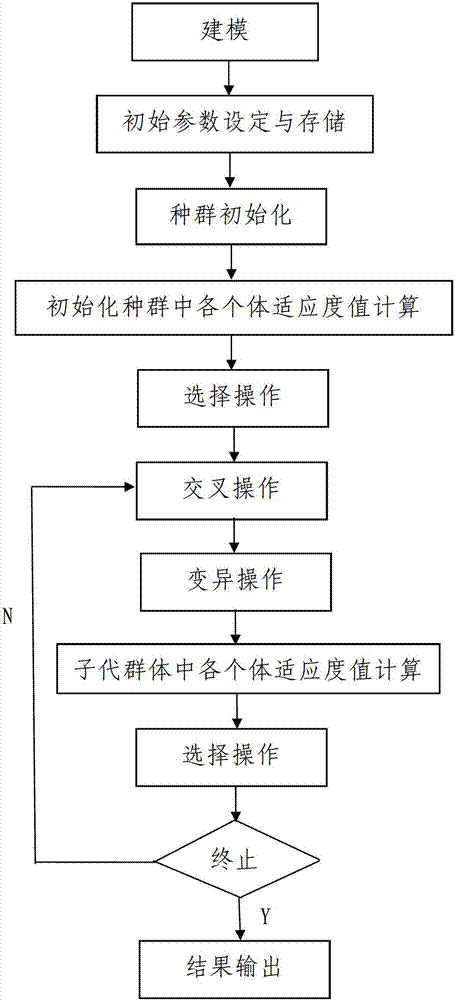
Solid propellant formulation optimization design method based on genetic algorithm
ActiveCN103198356AThe method steps are simpleReasonable designGenetic modelsPressure gas generationMinimum free energyGenetic algorithm
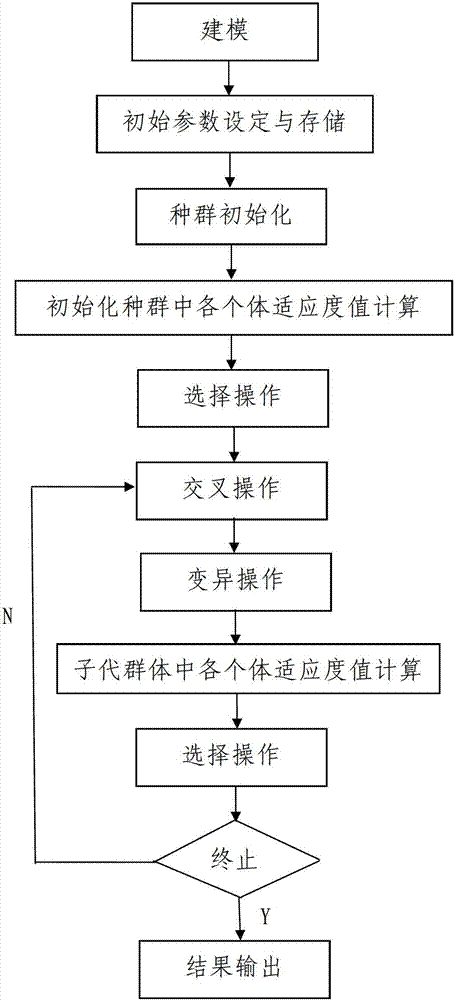
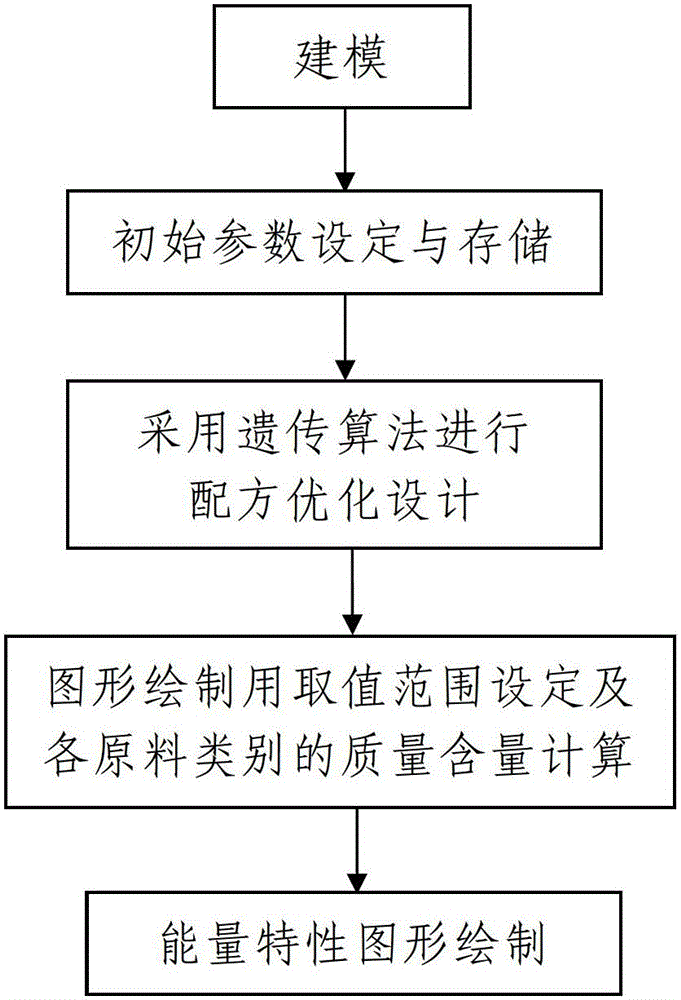
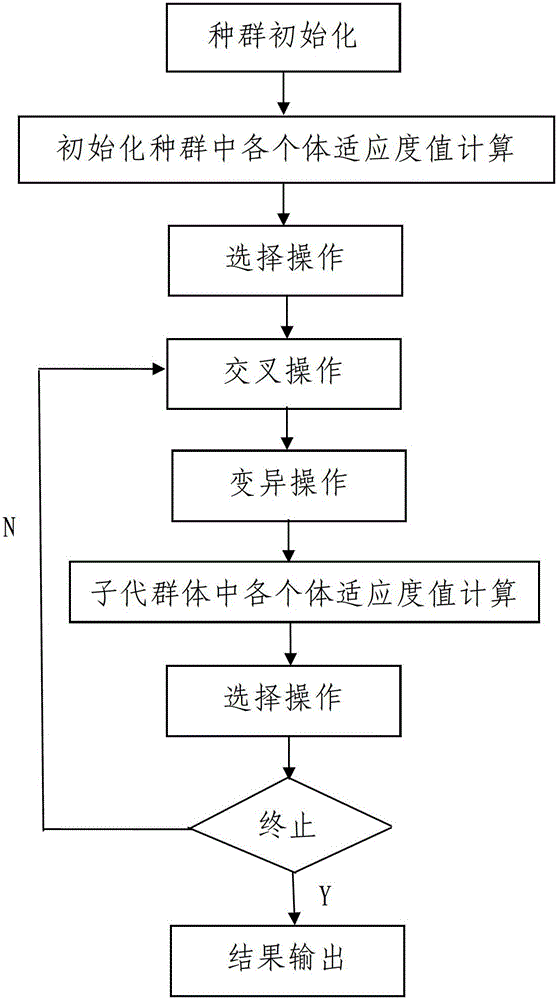
The invention discloses a solid propellant formulation energy optimization design method based on a genetic algorithm. The method comprises a first step of modeling, and building an energy characteristic calculation model of solid propellant according to a minimum free energy principle; a second step of setting and storing initial parameters, inputting component species used by the solid propellant, and a chemical formula and a quality proportion range of each component, and inputting species of combustion products produced by the solid propellant after being combusted, and chemical formulas and relative molecular mass of all the combustion products or selecting all the combustion products in a combustion product data base; and a third step of calling a genetic algorithm module by a data processor, and conducting optimization design to quality proportion of the designed solid propellant. The solid propellant formulation energy optimization design method based on the genetic algorithm is simple in steps, reasonable in design, convenient to achieve, good in using effect, capable of fast obtaining an optimum proportion of highest specific impulse of the solid propellant and effectively overcoming the defects, existing in an existing solid propellant compound design process, of being high in energy characteristic test cost, long in period, large in test dose, and the like.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Liquid drop contact angle solving method under given surface second-level nano-micro structure
ActiveCN105912502ACalculation simplificationSimplified free energyDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsMicro structureMeasuring instrument
The invention discloses a liquid drop contact angle calculation method under a given surface second-level nano-micro structure. The calculation method comprises the following steps: adopting a nano-micro geometric measuring instrument to measure the structure size of the given second-level nano-micro structure to obtain the side length, the space and the height of the nano-micro structure; adopting general assumptions in Young equation, Wenzel equation and CB equation deduction, and calculating a roughness factor and an area fraction under micrometer and nanometer size under the assumptions; according to different infiltration states under a micrometer structure and a nanometer structure, dividing the infiltration states of the second-level nano-micro structure into four situations, and inducing and simplifying the system free energy calculated modes of four given surface second-level nano-micro structures; and in virtue of a C++program compiling module in Visual Studio2012 software, applying a Soushan method to calculate the system free energy under different infiltration states, finding interface minimum free energy under a stable state, and obtaining a contact angle corresponding to the interface minimum free energy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
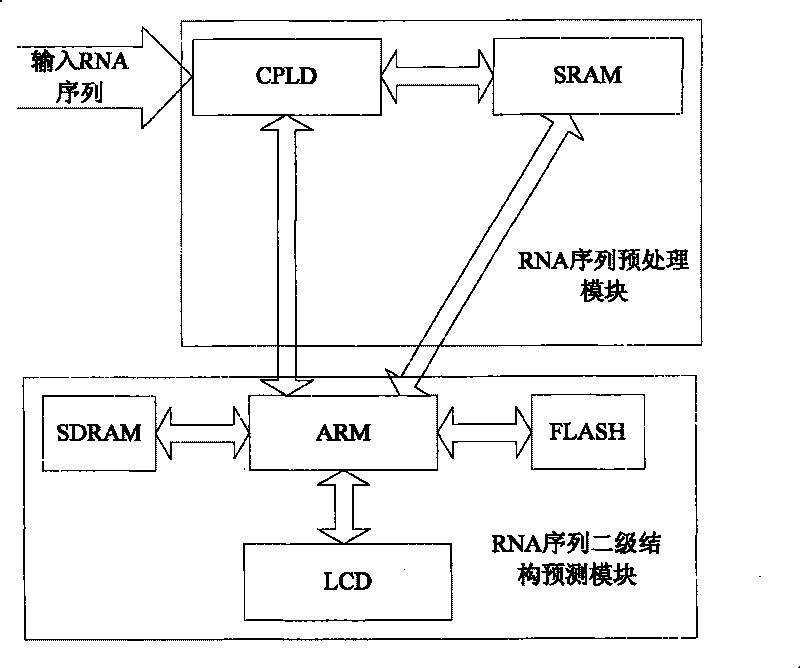
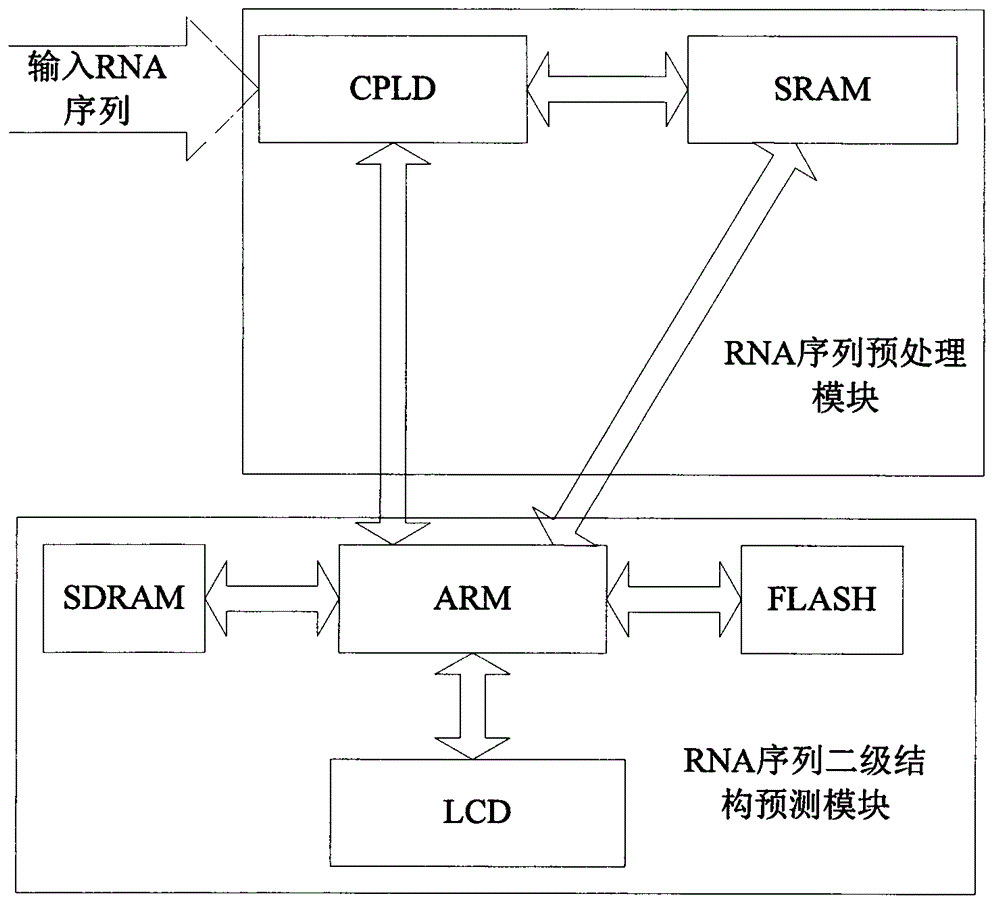
Method for predicting secondary structure of ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequence based on complex programmable logic device (CPLD) base fragment encoding and ant colony algorithm
InactiveCN102880811AAccurate predictionIntuitive and accurate structural expressionSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum free energyProgrammable logic device
The invention discloses a method for predicting a secondary structure of a ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequence based on complex programmable logic device (CPLD) base fragment encoding and ant colony algorithm and belongs to the field of bioinformatics research. The method comprises the following steps: recoding the RNA sequence according to an association table by using the CPLD; obtaining a corresponding encoding sequence according to corresponding value in an encoding table and an encoded association table, removing a redundancy stem area through a right extension strategy through a complete matching table and an incomplete matching table, and obtaining all possible stem area sets; giving two-dimensional heuristic information and a selection rule of an initial stem area and the next stem area in the ant colony algorithm, and constructing a compatible subset of all the possible stem area sets through an information element update strategy; and finally, obtaining the secondary structure with the minimum free energy. The method can rapidly, accurately and effectively predict the secondary structure of the RNA sequence which does not contain false knots and output the obtained result in a bracketing mode, has sensitivity and specificity in the aspect of judging two parameters for predicting the advantages and weakness of the secondary structure of the RNA sequence, and is superior to the conventional mainstream prediction technology.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for determining detonation parameters of liquid explosive
The invention relates to detonation parameters of liquid explosive and provides a method for calculating CJ detonation pressure, detonation speed, detonation temperature and specific volume of the liquid explosive through a thermodynamic function of compounds and a minimal free energy method, and the invention belongs to the technical field of energetic materials. A VLW program is created on the basis of a BKW program and is used for calculating such function relations of the liquid explosive as CJ detonation pressure, detonation speed, detonation temperature, specific volume and the like through the thermodynamic function of compounds by utilizing the minimal free energy method.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Compositions and Methods for Protein Production
ActiveUS20130084641A1Increase productionReduce productionLibrary screeningFermentationMinimum free energyFree energies
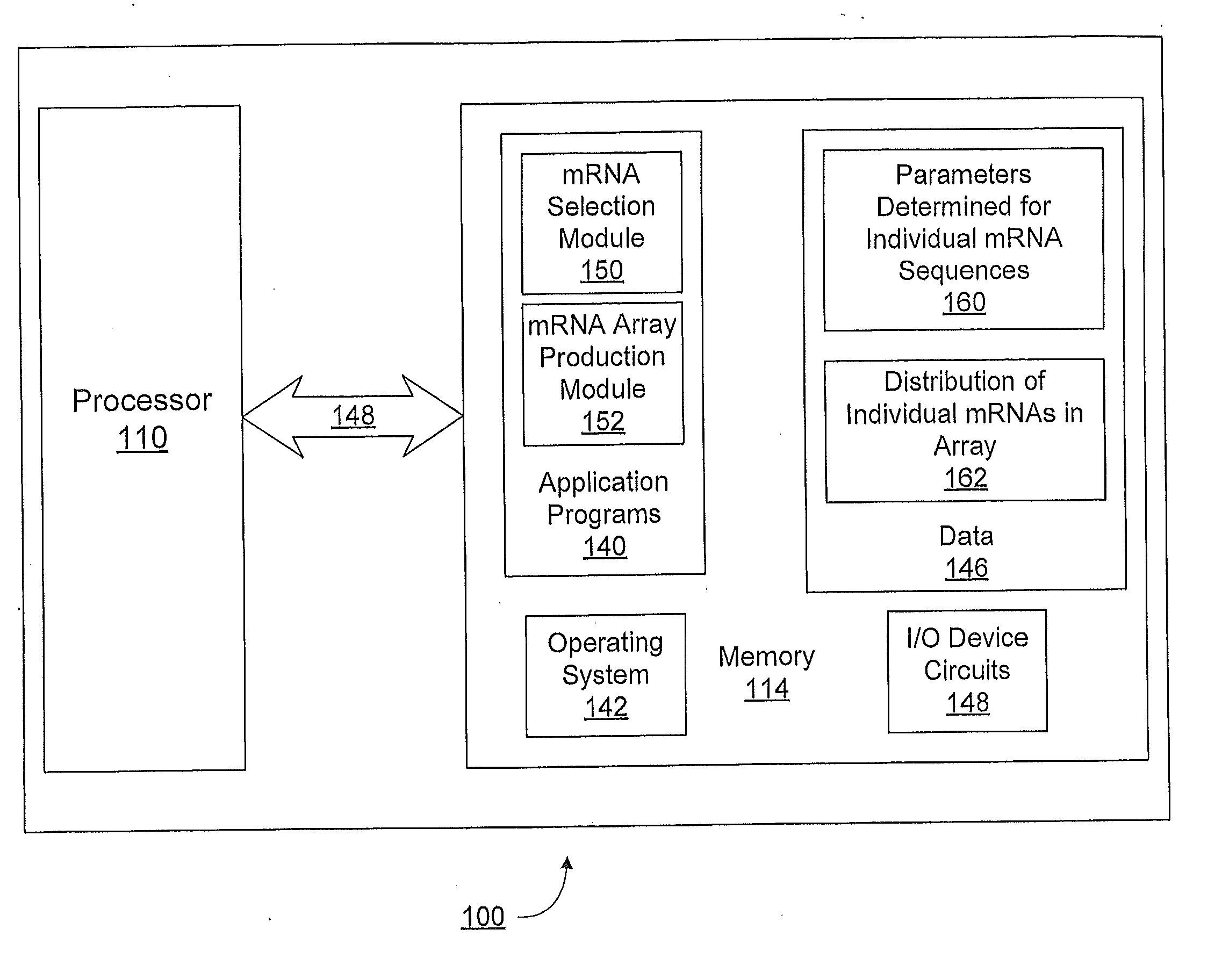
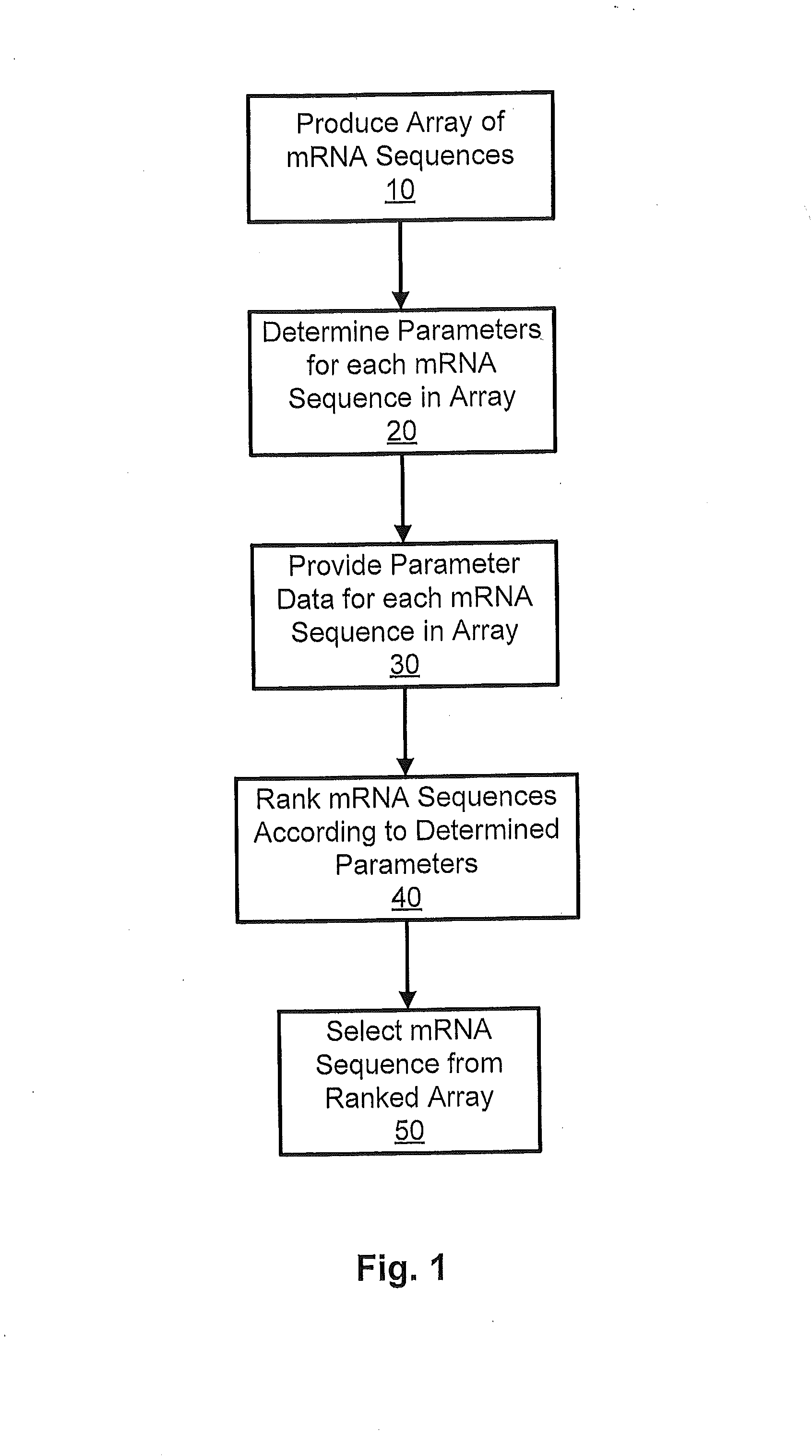
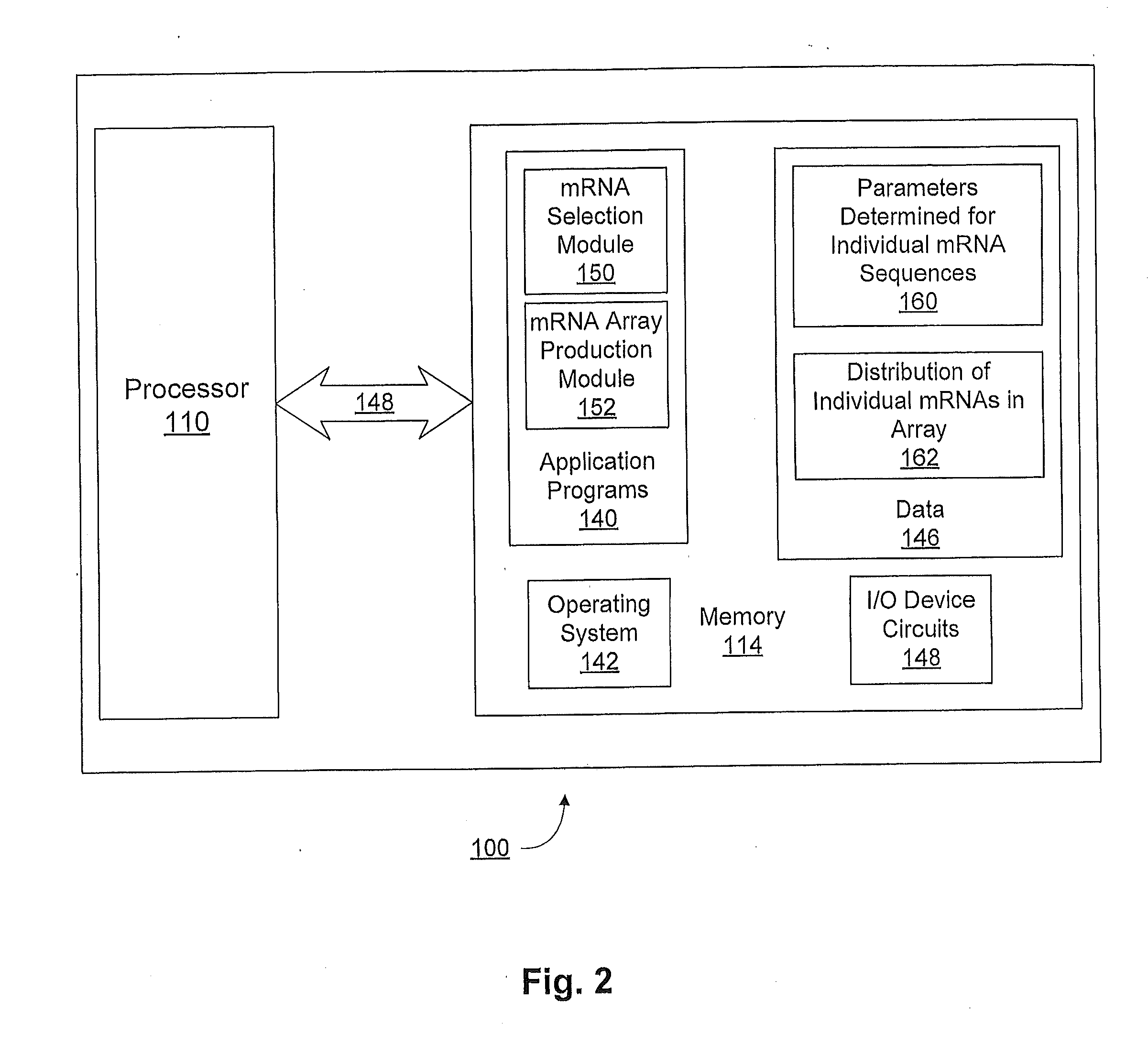
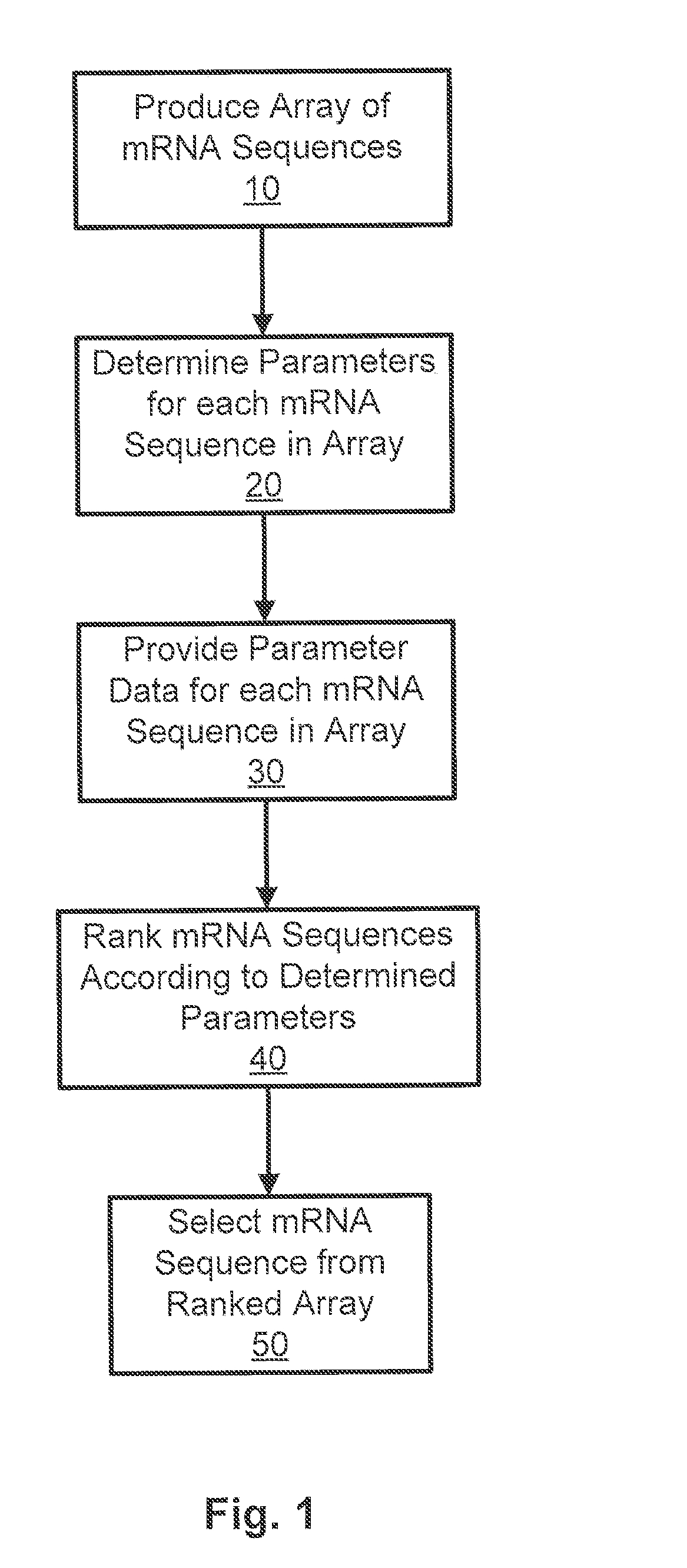
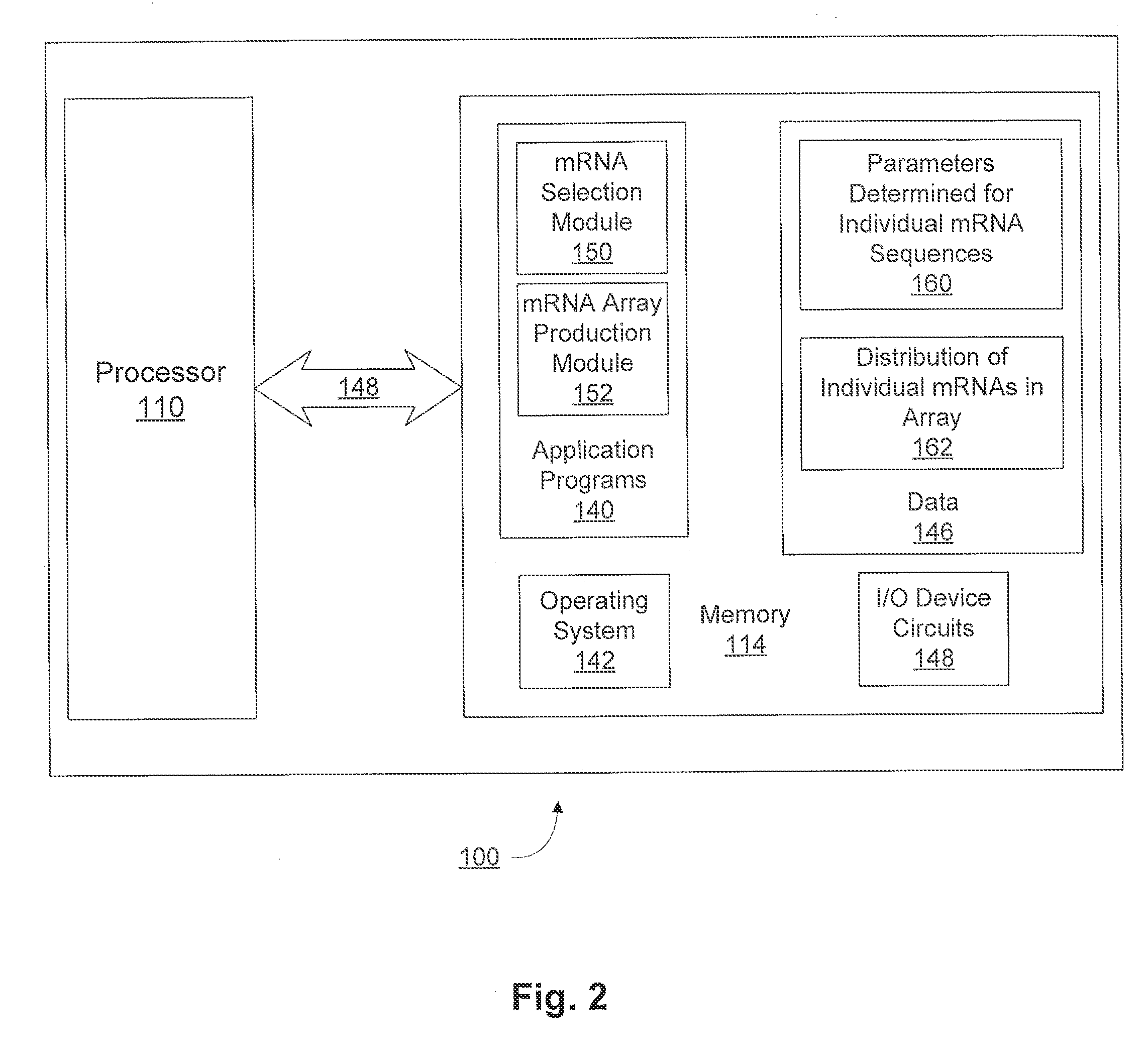
The present invention provides a method of selecting a mRNA for production of a polypeptide of interest comprising: a) producing an array of individual mRNA sequences comprising different nucleotide sequences encoding the polypeptide of interest; b) determining one or more or two or more of the following parameters for each individual mRNA sequence of (a): (i) minimum free energy (MFE) RNA secondary structure; (ii) ensemble free energy (EFE); (iii) frequency of the minimum free energy (FMFE) RNA secondary structure in a thermodynamic ensemble; and (iv) ensemble diversity (ED); c) ranking the individual mRNA sequences of the array according the parameters determined in step (b); and d) selecting a mRNA sequence from the ranked array of step (c), wherein the selected mRNA produces the polypeptide of interest. The present invention further provides a method of selecting a mRNA for enhanced and reduced production of a polypeptide of interest.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Oligonucleotide chain probe participating in polymerization extension and nucleic acid amplification kit thereof
PendingCN109988758AImprove amplification reaction efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMinimum free energyFluorescent quenching
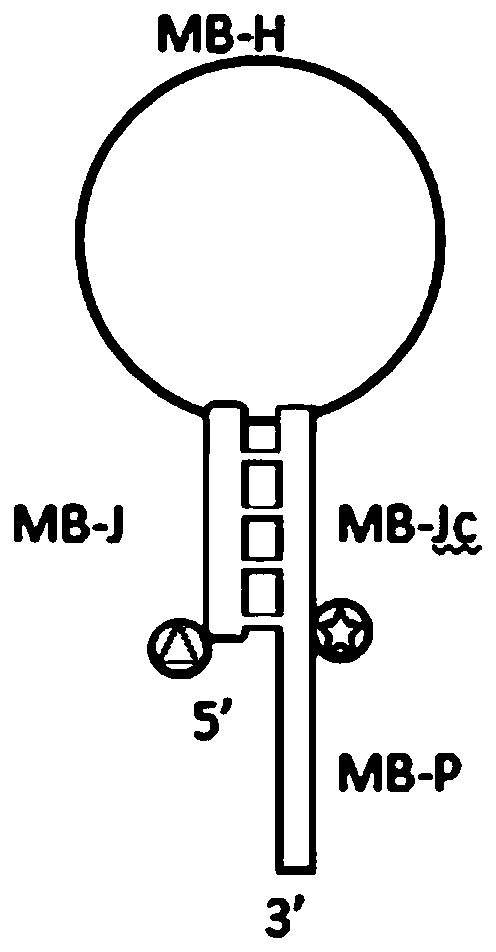
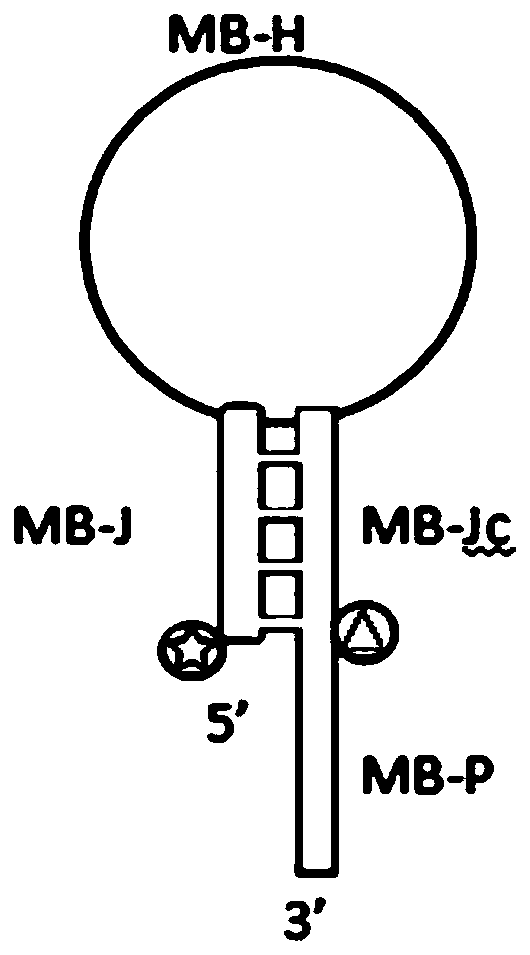
The invention discloses an oligonucleotide chain probe participating in polymerization extension. A minimum free energy structure of the oligonucleotide chain probe is of a stem-loop structure, and the sequence of the oligonucleotide chain probe sequentially comprises the following four sections from the 5'end to the 3'end: a stem structure sequence MB-J, a loop sequence MB-H, a stem structure complementary sequence MB-Jc and a single-chain tail sequence MB-P, wherein a fluorescent quenching group and a fluorescent group are respectively connected to the 5'end of the MB-J and an intermediate base of the MB-Jc chain, and two connection positions are adjacent in the stem-loop structure; and the MB-H and MB-P are all or partially complementary to a target sequence; and the 3'end of the MB-P is complementary to the target sequence and can be extended and polymerized. The oligonucleotide chain probe participating in the polymerization extension has the functions of primers and molecular beacons. The invention further discloses a constant-temperature nucleic acid amplification kit, which comprises the oligonucleotide chain probe participating in the polymerization extension.
Owner:QUICKING BIOTECH +1
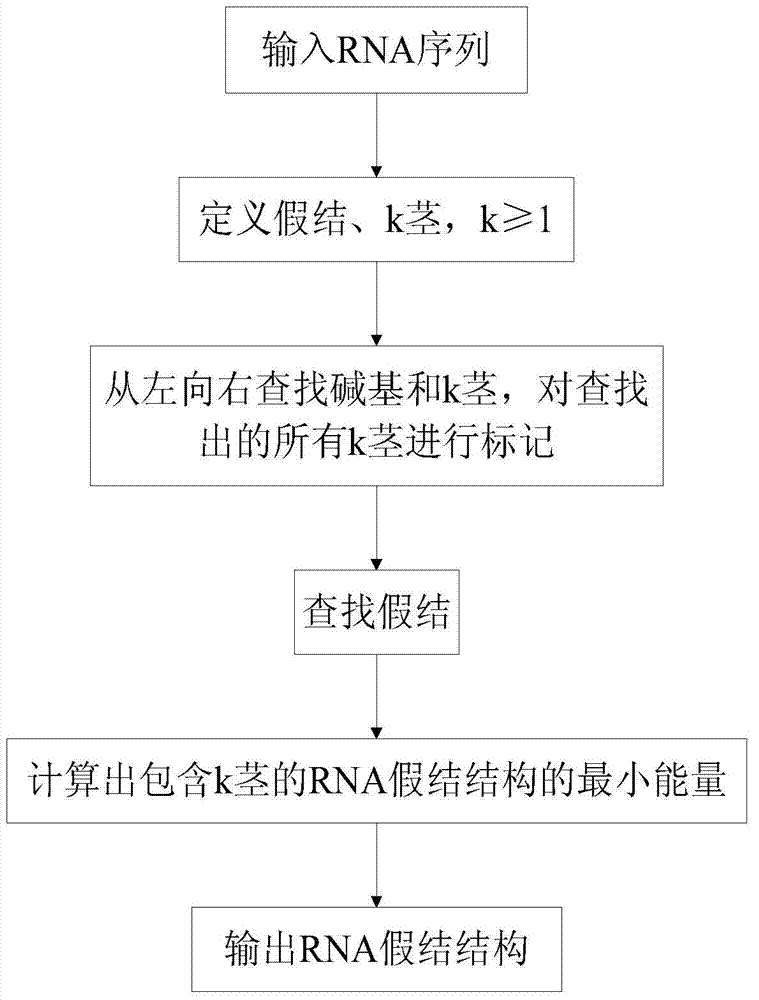
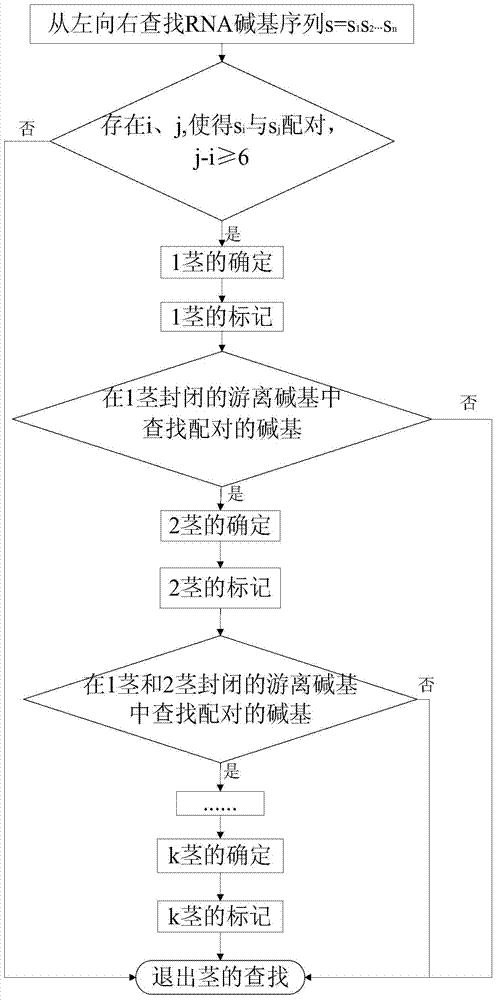
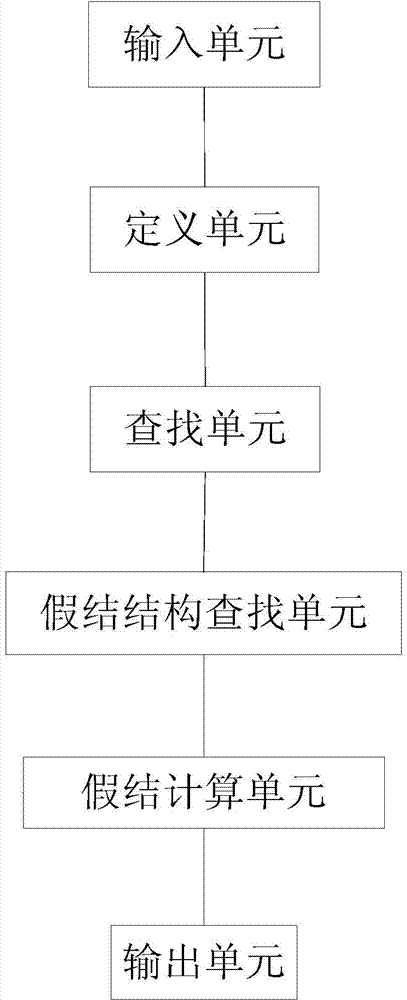
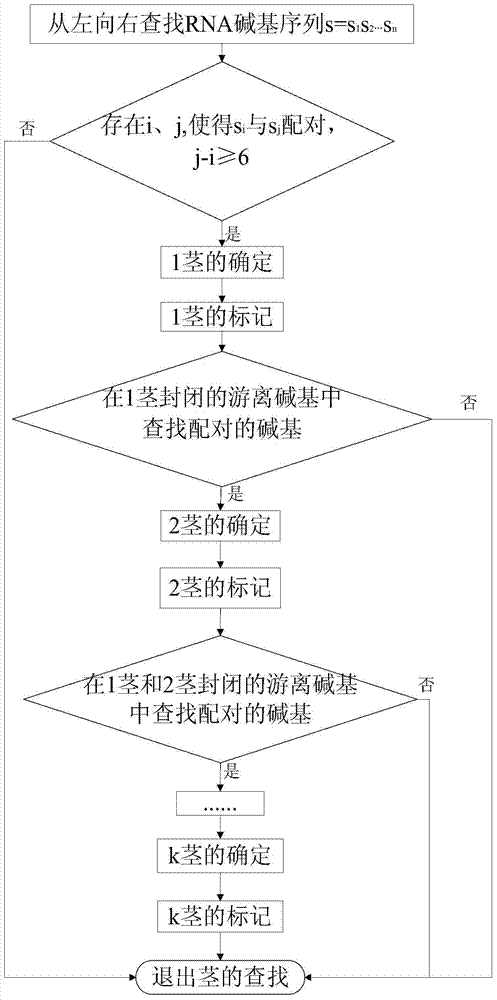
Prediction method and device for RNA false knot structure based on k stems
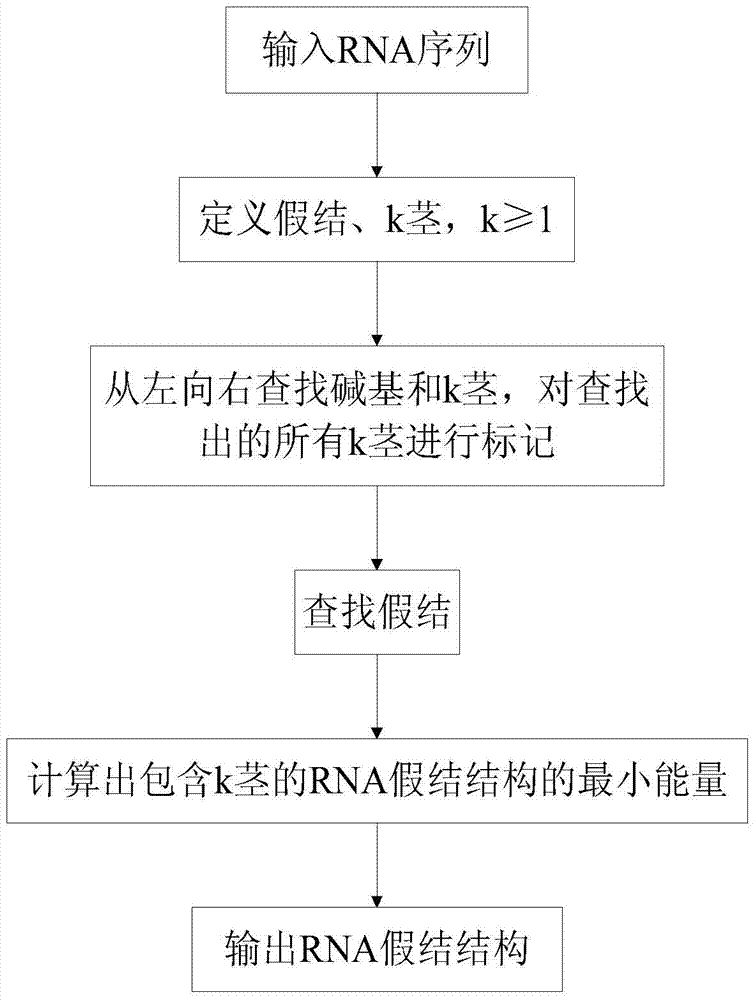
InactiveCN104298894AReduce time complexityReduce space complexitySpecial data processing applicationsMinimum free energyPredictive methods
The invention provides a prediction method and device for an RNA false knot structure based on k stems. The prediction method comprises the following steps that a section of RNA base sequence is input, and false knots and k (k is larger than or equal to one) stems are defined; RNA bases and k stems are searched for from left to right, and all the found k stems are subjected to determined marking; the false knots are searched for according to the characteristic that the k stems intersect to form the false knots, and the minimum free energy of the RNA false knot structure including the k stems is calculated; the RNA false knot structure is output. According to the prediction method, the searching speed is high, the accuracy is high, and the sensibility, specificity and the like are better than that of other related algorithms such as a PKNOTS algorithm. The prediction method is more effective on the aspect of plane false knot prediction than the PKNOTS algorithm.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV +1
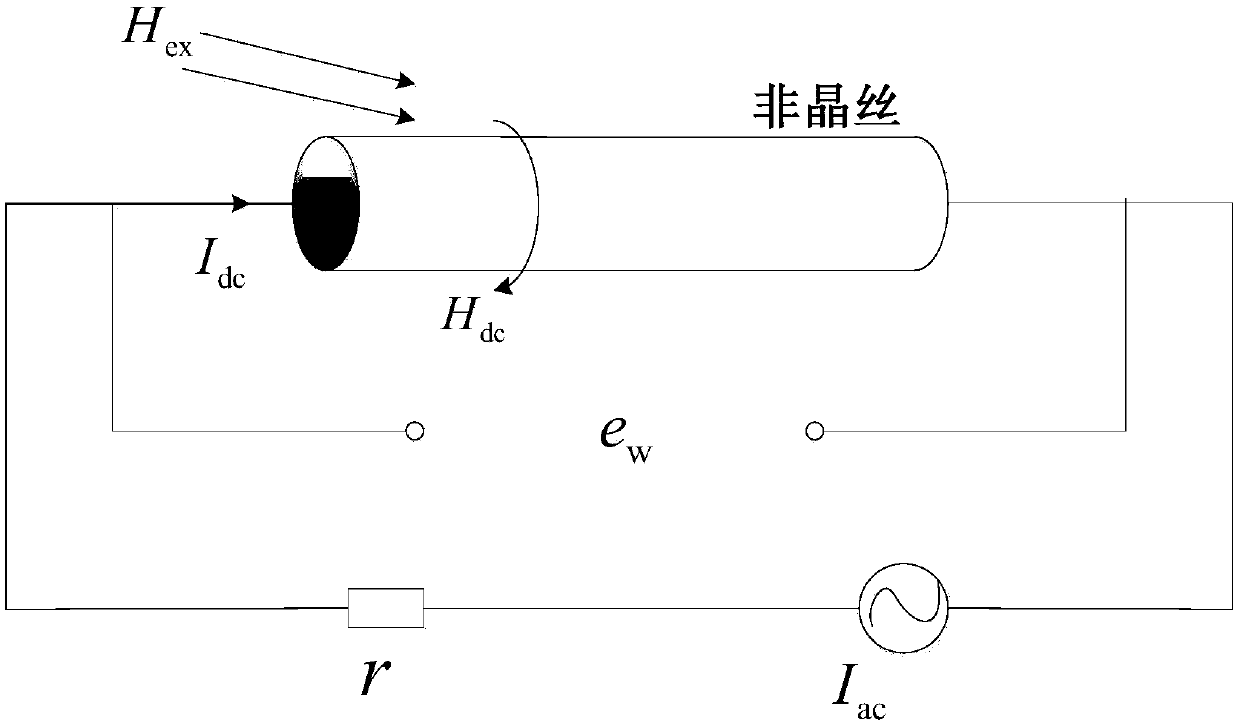
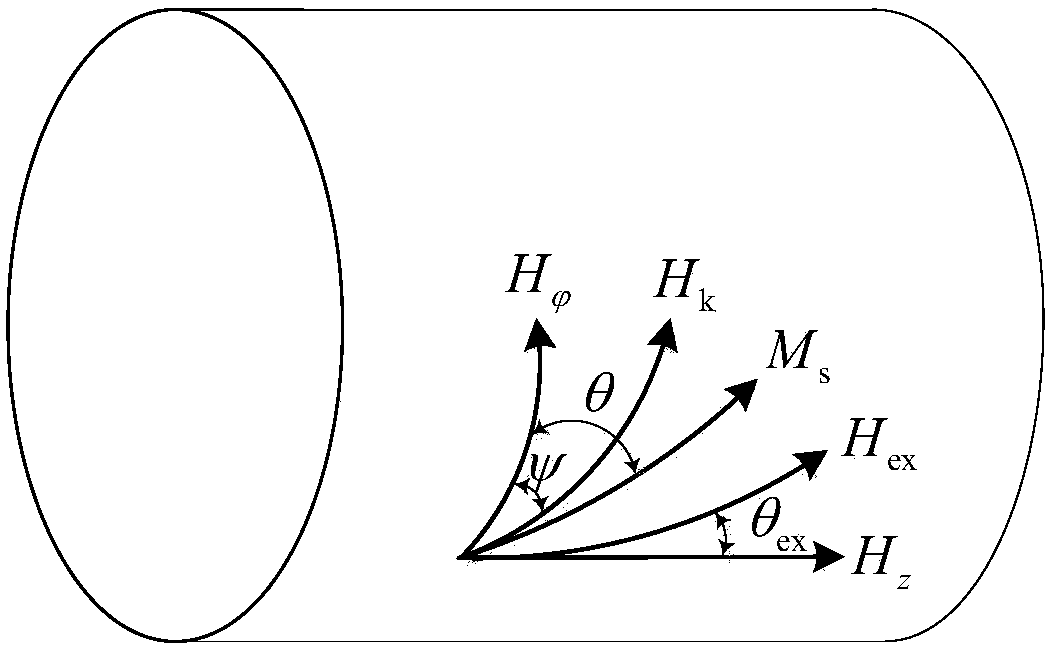
Giant magneto-impedance modeling method of amorphous wire under effect of non-axial magnetic field
ActiveCN107748813AImprove working environmentHigh sensitivityPermeability measurementsDesign optimisation/simulationHigh frequency approximationMagnetization
The invention provides a giant magneto-impedance modeling method of amorphous wire under the effect of a non-axial magnetic field. At first, by means of the LLG equation, a magnetization vector rotation equation is constrained and an expression of total energy inside amorphous wire is built; then, according to the principle of minimum free energy of system, a magnetization vector motion equation is built; amorphous wire magnetic conductivity tensor under the effect of a non-axial magnetic field is obtained through solving the motion equation; an electromagnetic field equation of the circumferential and axial magnetic field parameters of amorphous wire are established by using the intrinsic relationship between magnetic field strength and magnetic induction strength and Maxwell equation; finally, for the application conditions of high frequency and low frequency, the solution of the amorphous wire electromagnetic field equation is simplified; a general expression of amorphous wire giantmagneto-impedance by means of a high frequency and low frequency approximation. The giant magneto-impedance modeling of amorphous wire under effect of non-axial magnetic field can be accurately builtand the method for calculating giant magneto-impedance is given.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Pseudoknot-carrying nucleic acid structure prediction method based on multi-target genetic algorithm
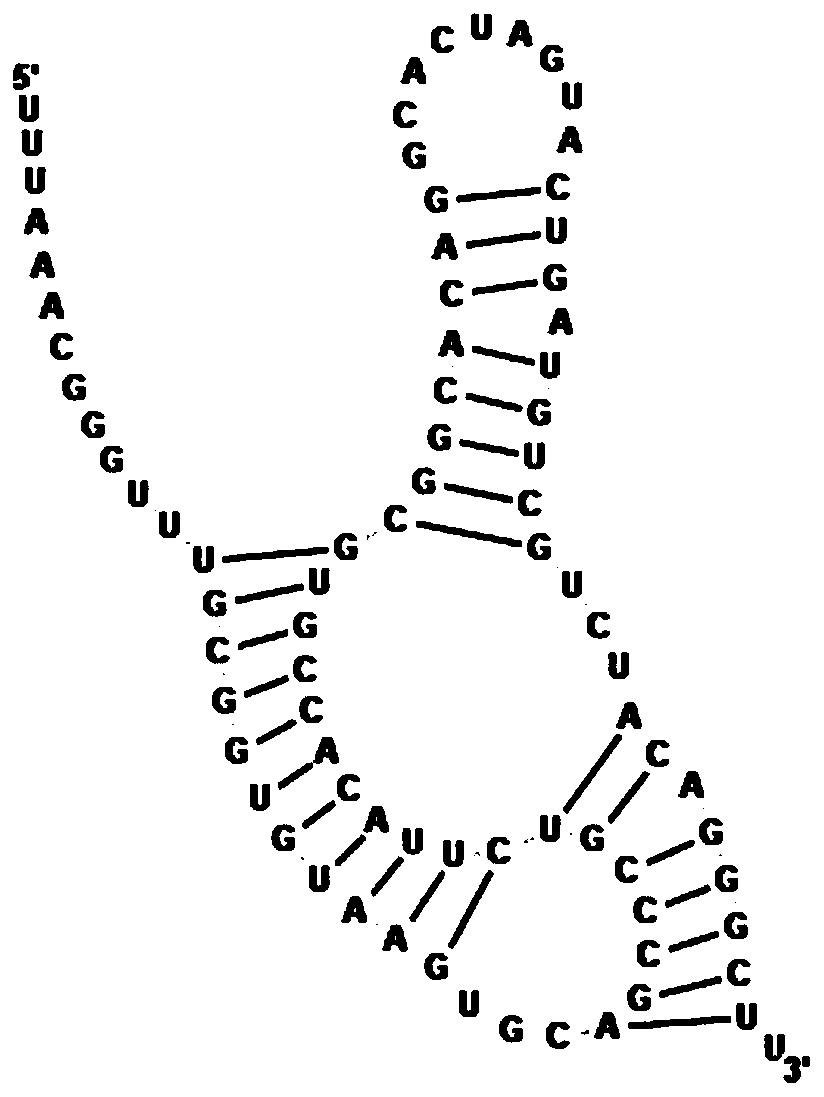
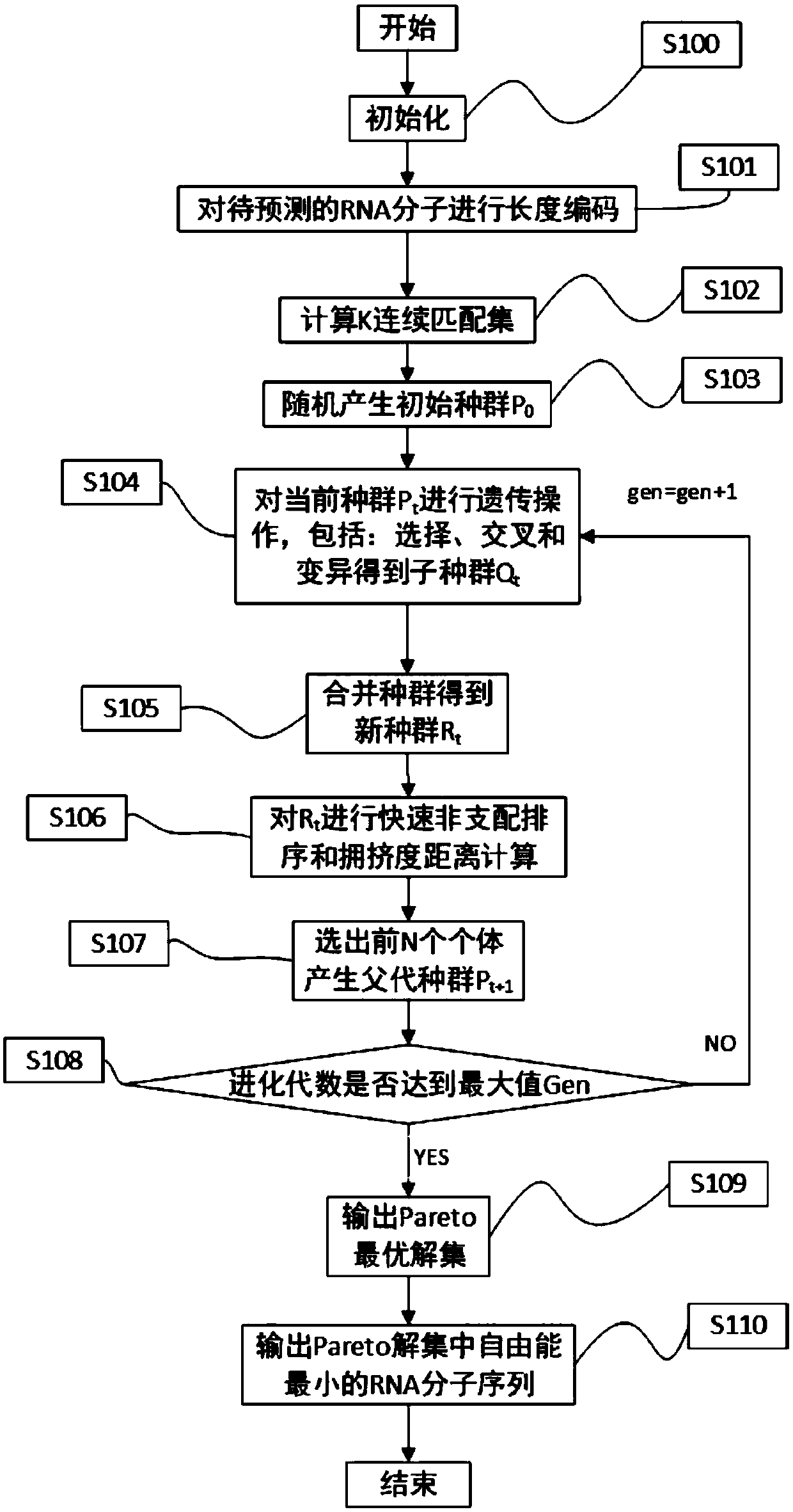
The invention relates to a pseudoknot-carrying nucleic acid structure prediction method based on a multi-target genetic algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: determining a K continuousmatching set according to a minimum stem zone number and a minimum base number in cycles, generating an initial population, carrying out selection, crossover and variation on an RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)molecular sequence by using a multi-target genetic algorithm, carrying out nondominant sequencing and crowding distance sequencing so as to obtain an optimal solution set with a Pareto molecular structure, and finally selecting an RNA molecular structure with the minimum free energy from the optimal solution set as a final prediction result. By adopting the method, the time complexity and the space complexity are degraded, and the pseudoknot-carrying RNA molecular structure prediction accuracy is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Using Helmholtz Minimum Free Energy Slopes to Define Glial Cells that Diagnose Brain Disorder
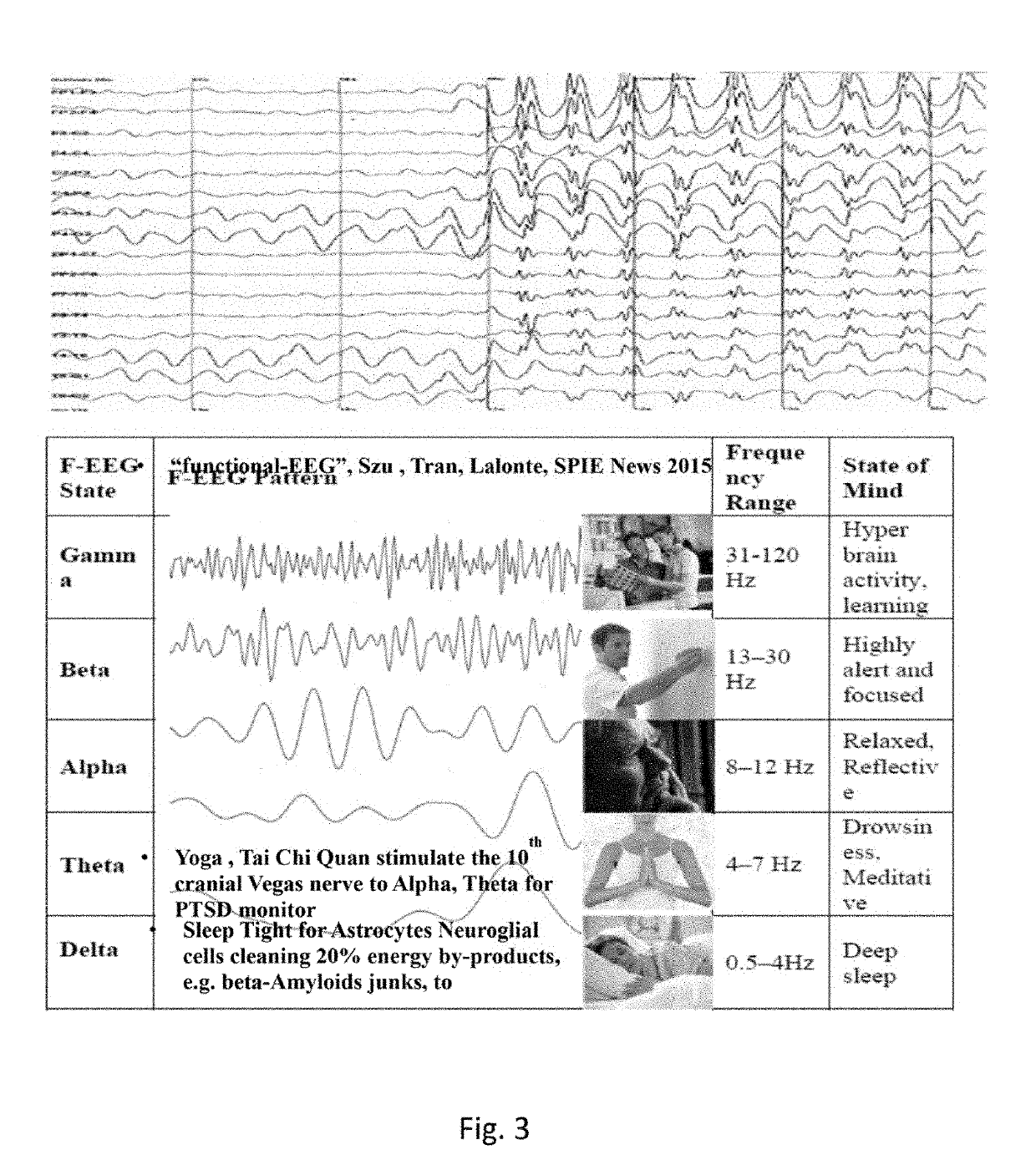
InactiveUS20190125272A1Minimal energyAttracting forceImage enhancementMedical imagingMinimum free energySchizophrenia
A method of diagnosing a disorder includes obtaining a medical image of a subject. A Helmholtz Minimum Free Energy is computed from the medical image. A negative slope of the Helmholtz Minimum Free Energy is determined, from which a glial force is computed. The existence of a disorder in the subject is diagnosed if a value of the glial force is within a predetermined range. The disorder can be, for example, a brain disorder, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and / or schizophrenia. Other examples of disorders are epilepsy and rheumatoid arthritis. The subject can be, for example, a human subject.
Owner:SZU HAROLD
Compositions and methods for protein production
ActiveUS20150152408A1Increase productionReduce productionLibrary screeningDNA preparationMinimum free energyFree energies
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
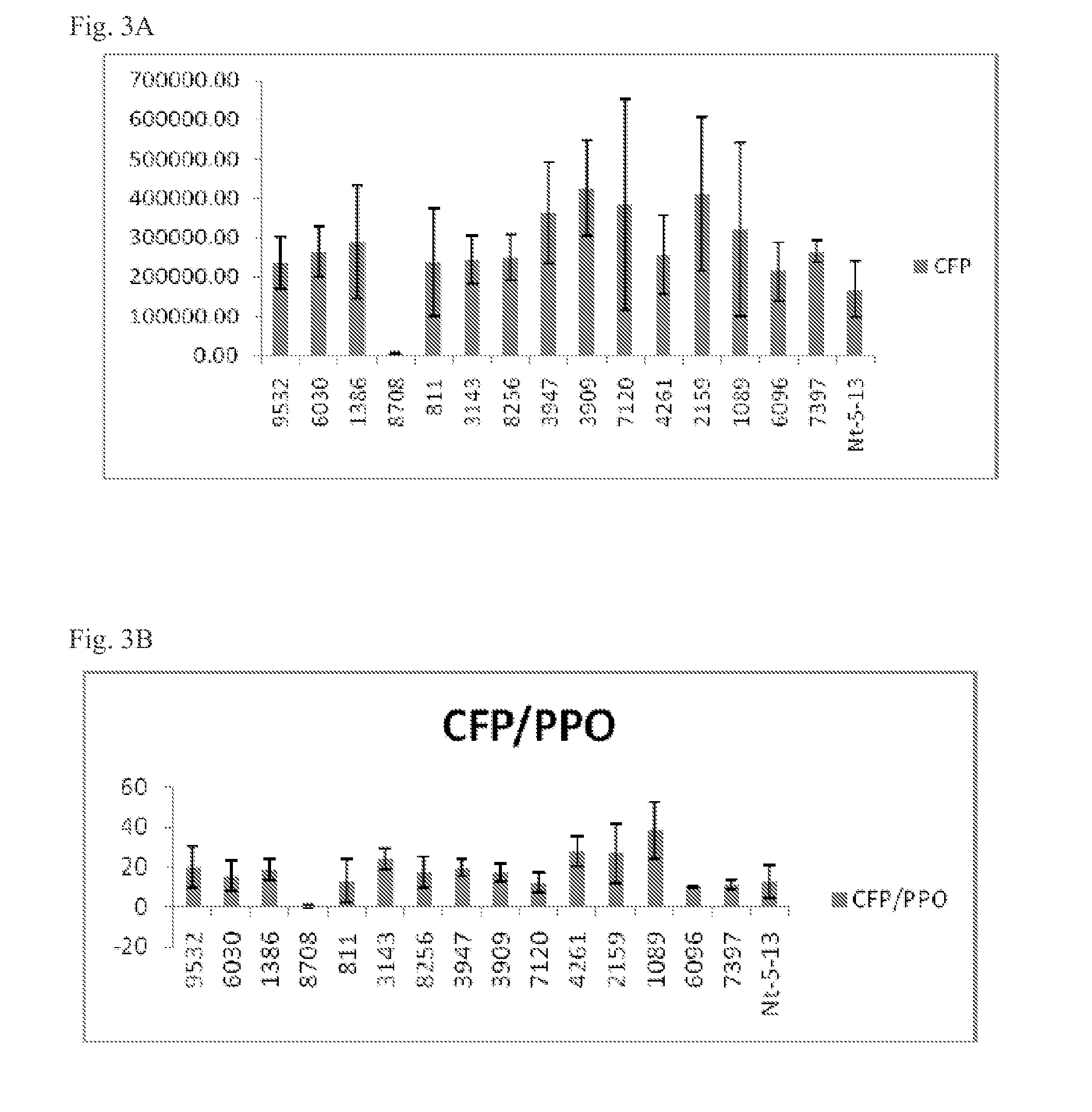
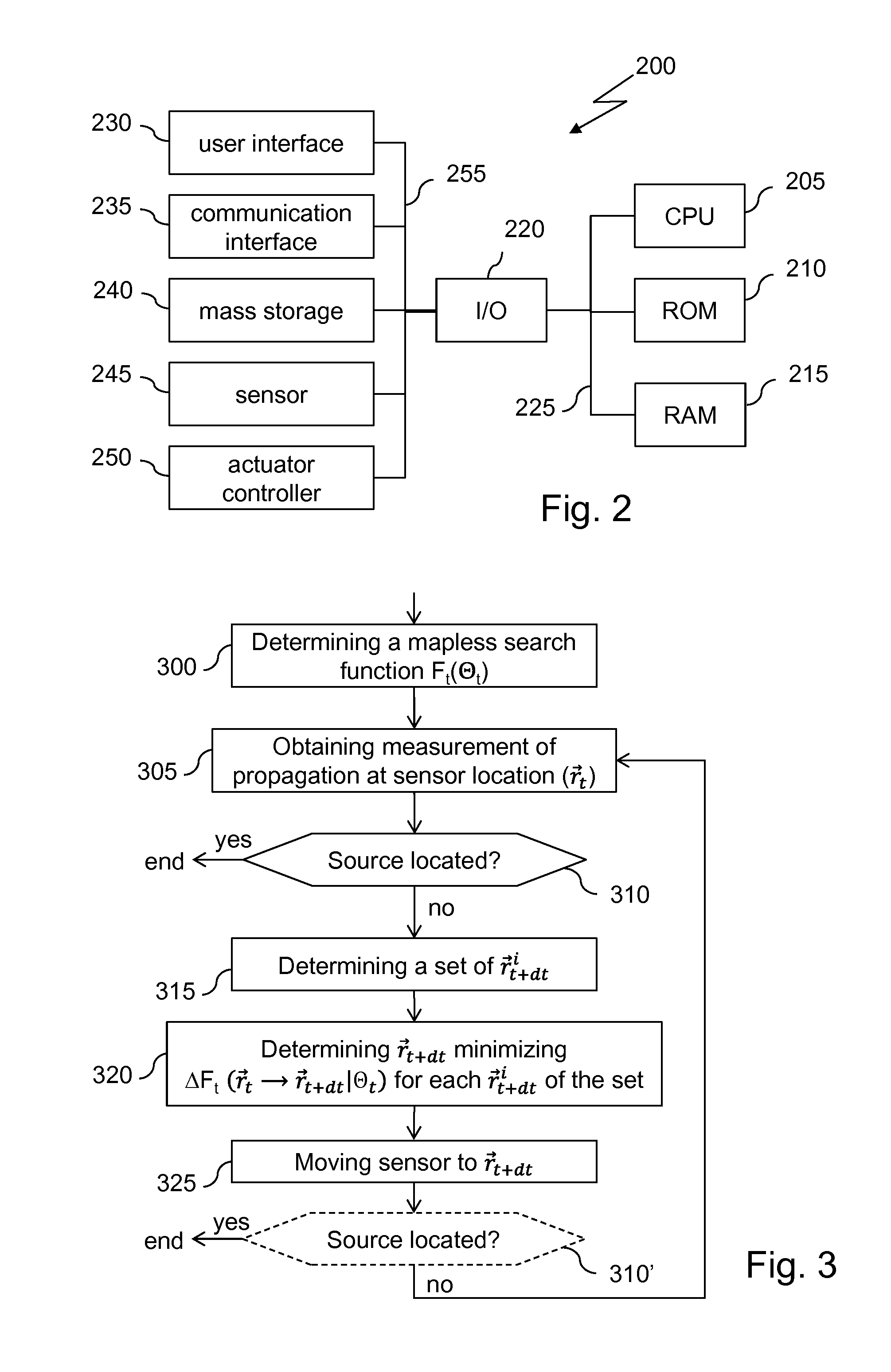
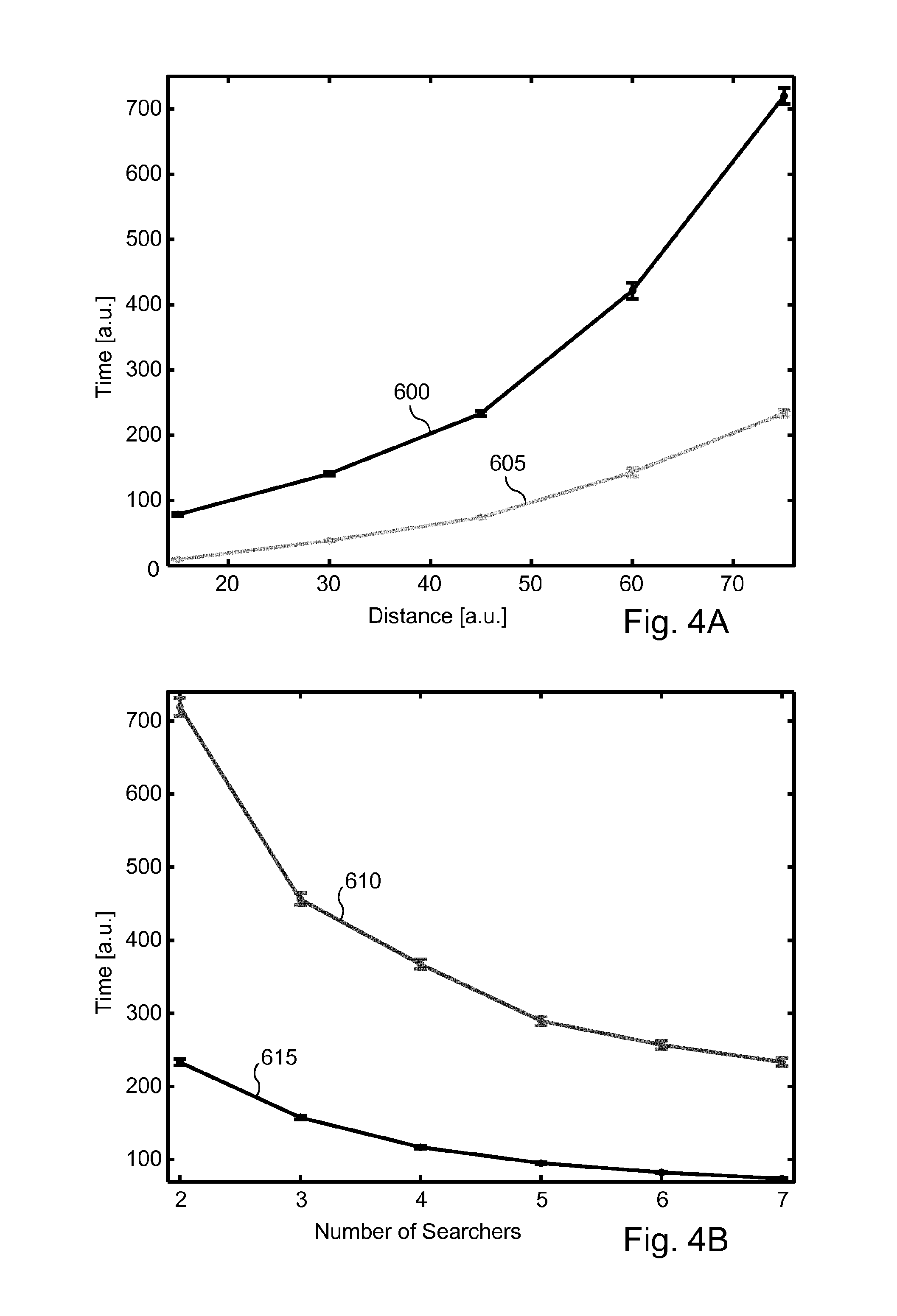
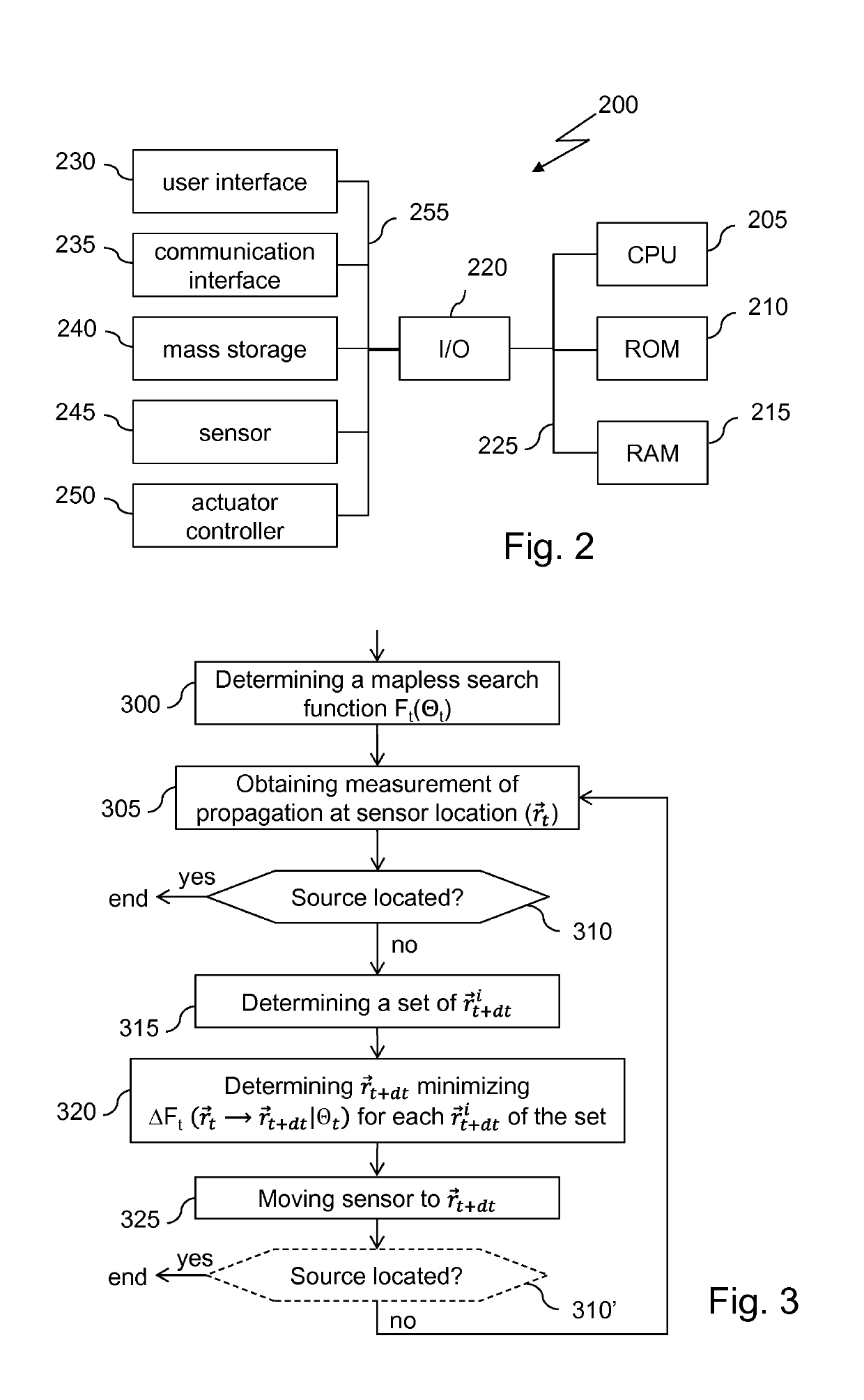
Method, device, and computer program for locating an emitting source of which measurements of emission propagation at locations different from that of the emitting source can be obtained from those locations, lacking space perception
InactiveUS20150377849A1Computer controlSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum free energyFree energies
A method and device for locating an emitting source of which measurements of emission propagation at locations different from that of the emitting source can be obtained from those locations, lacking space perception, using a sensor mobile along a self-generated path. After having obtained an emission propagation measurement from the mobile sensor at the mobile sensor location, a free energy variation for moving the sensor from its current location to each of plural possible next locations of the mobile sensor is computed, the free energy being computed as a function of a standardized projected probability field of the location of the diffusing source based on previous emission propagation measurements obtained along the self-generated path. A minimum free energy variation value amongst the computed free energy variations is determined and the location associated with the determined minimum free energy variation is identified as being the next location of the sensor.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Ployglutamine pathogenesis analyzing method
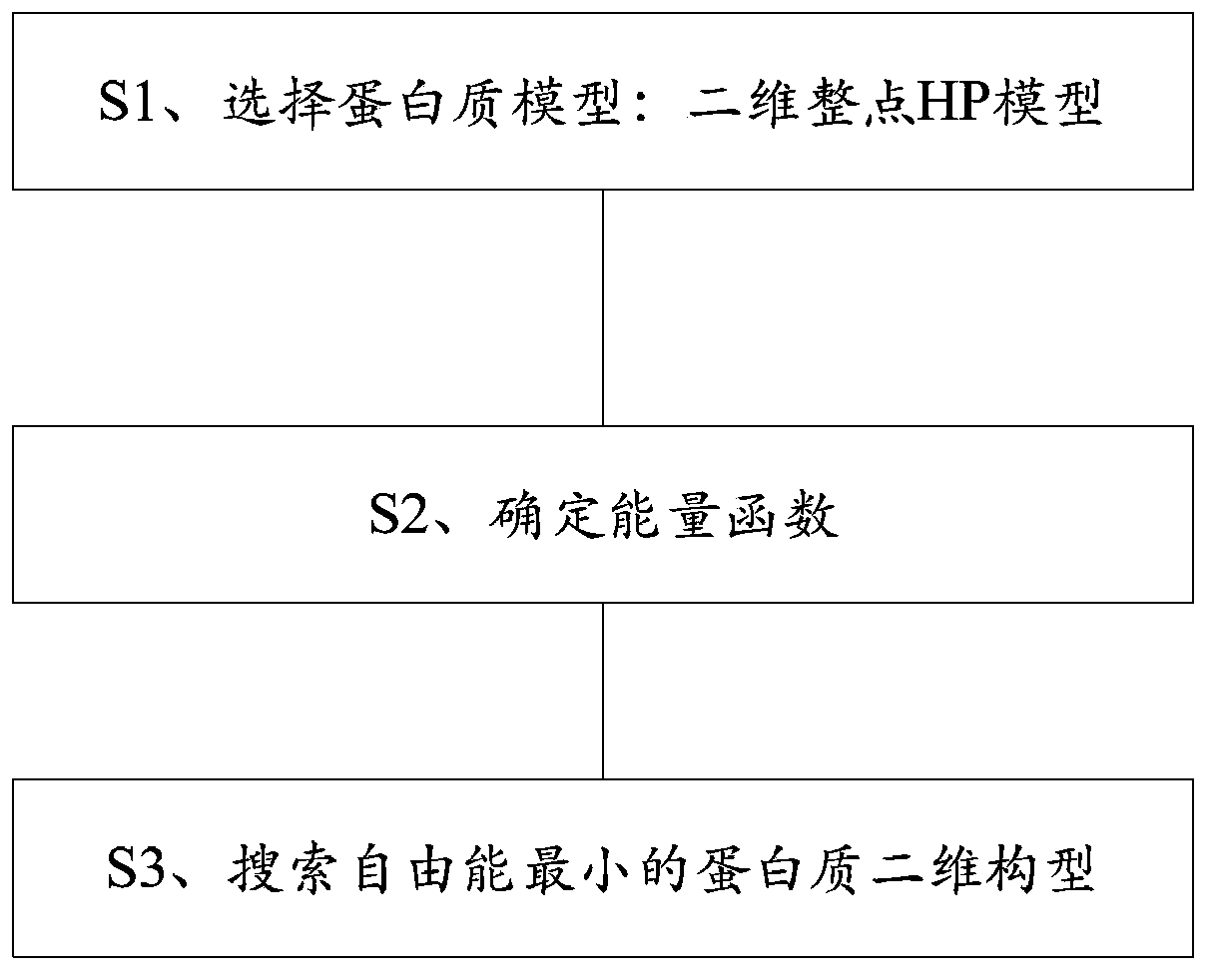
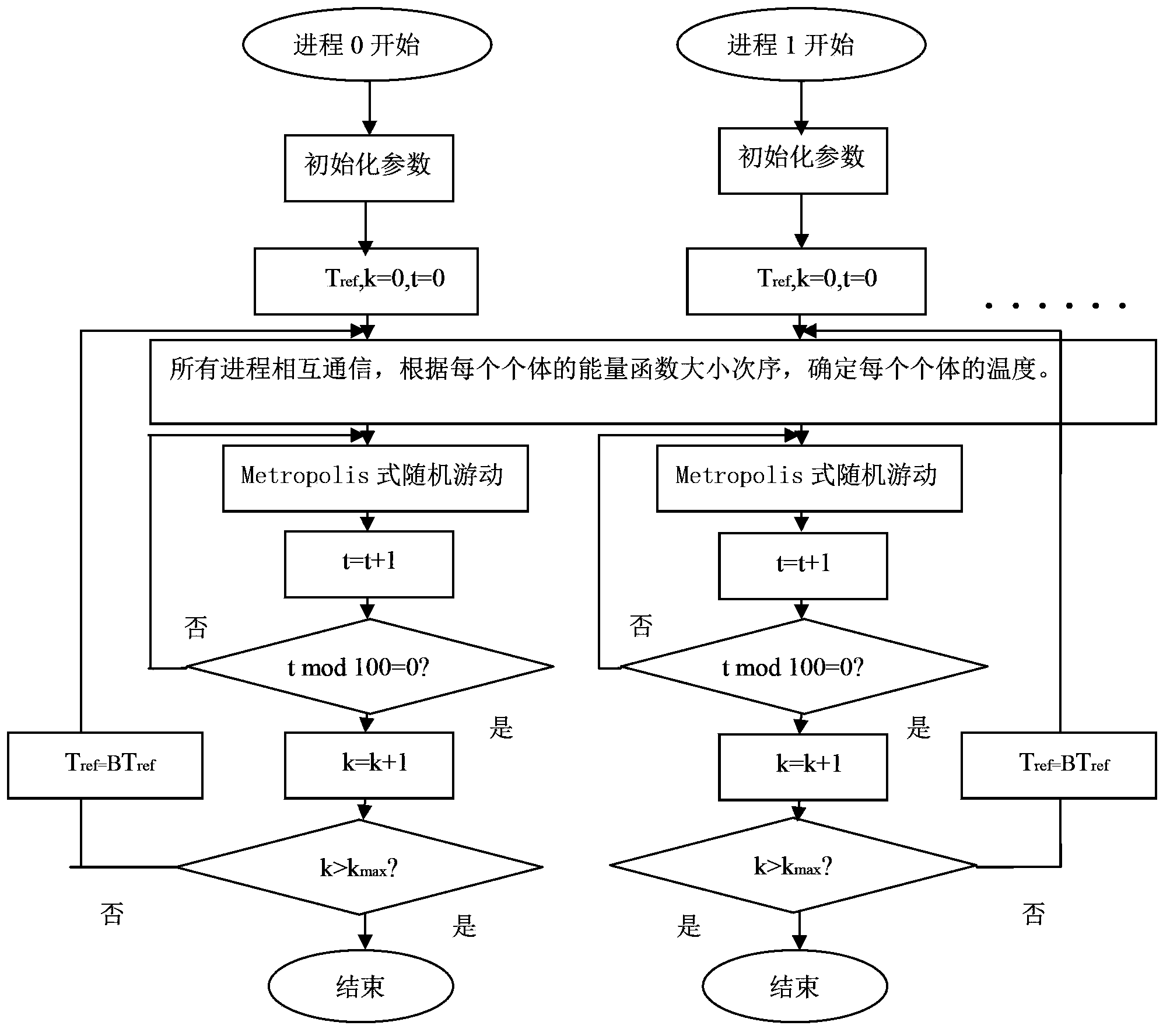
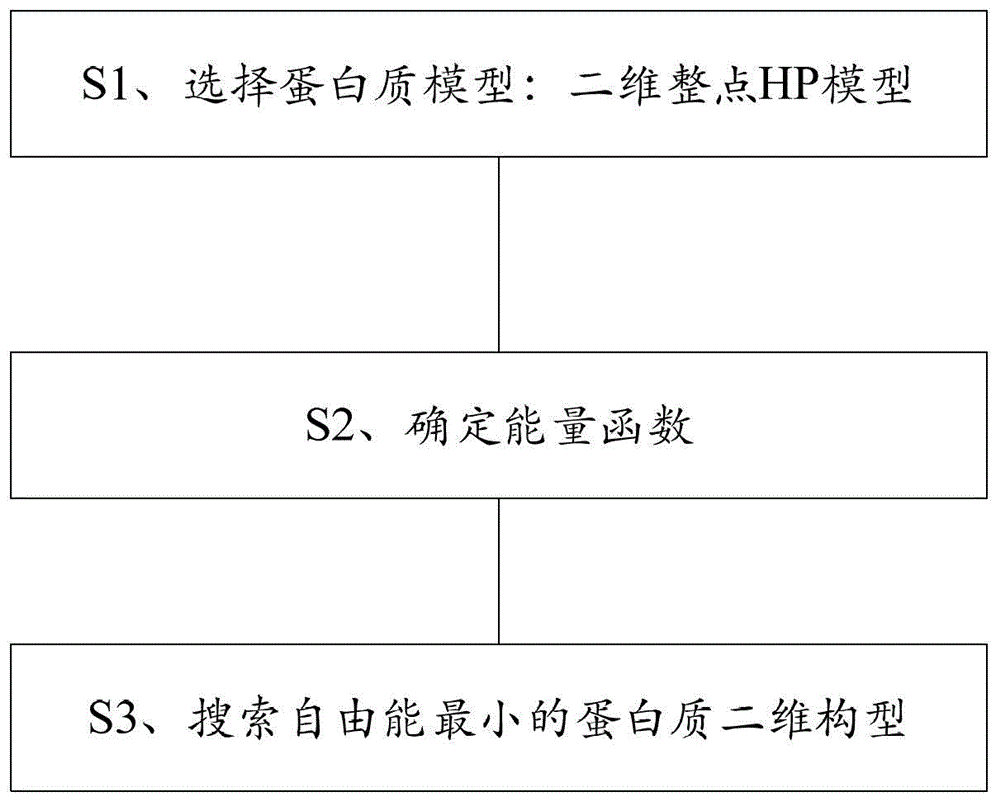
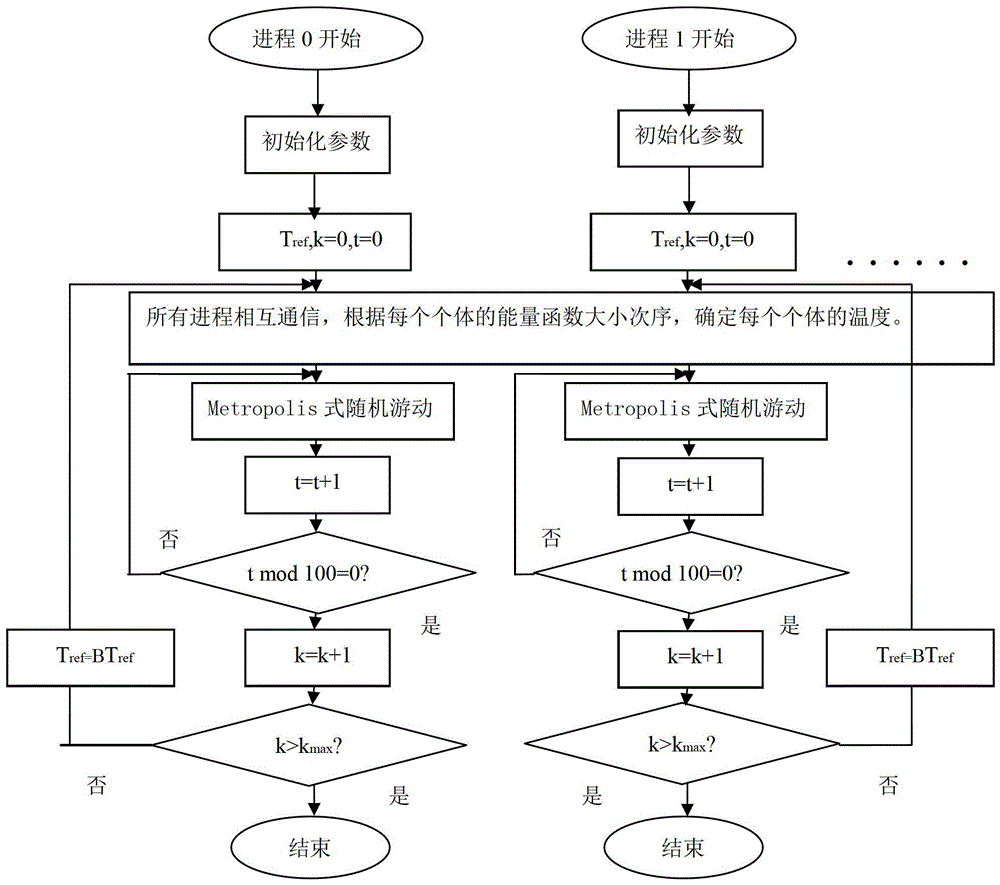
ActiveCN103902847AIndividual changes are goodFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum free energyParallel algorithm
The invention relates to a ployglutamine pathogenesis analyzing method which includes the following steps of S1, selecting a protein model which is a two-dimensional integral HP model; S2, determining an energy function; S3, searching for a protein two-dimensional structure with the minimum free energy, namely, searching for a two-dimensional structure corresponding to protein with the minimum energy by the adoption of MPI parallel algorithm of a peer-to-peer mode. Compared with the prior art, individual temperatures of the structure are determined through the sequence of individuals in a polyglutamine protein structure group, higher temperature is distributed to the inferior individuals so that the inferior individuals are more likely to change into the superior individuals, and meanwhile, by means of cooling factors, convergence speed is increased in a parallel mode.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method, device, and computer program for locating an emitting source of which measurements of emission propagation at locations different from that of the emitting source can be obtained from those locations, lacking space perception
A method and device for locating an emitting source of which measurements of emission propagation at locations different from that of the emitting source can be obtained from those locations, lacking space perception, using a sensor mobile along a self-generated path. After having obtained an emission propagation measurement from the mobile sensor at the mobile sensor location, a free energy variation for moving the sensor from its current location to each of plural possible next locations of the mobile sensor is computed, the free energy being computed as a function of a standardized projected probability field of the location of the diffusing source based on previous emission propagation measurements obtained along the self-generated path. A minimum free energy variation value amongst the computed free energy variations is determined and the location associated with the determined minimum free energy variation is identified as being the next location of the sensor.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Method for designing high-sensitivity and high-specificity mismatch nucleic acid sequences
InactiveCN109136331AQuick fixImprove Amplification SensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMinimum free energyNucleic acid sequencing
The invention discloses a method for designing high-sensitivity and high-specificity mismatch nucleic acid sequences. The method includes computing delta MFE (minimum free energy) values of mismatch sequences, target sequences and homologous interference sequences to determine candidate mismatch nucleic acid sequences. The method has the advantages that the shortcoming of dependence on experienceof mismatch nucleic acid sequence designs can be overcome by the aid of the method, mismatch nucleic acid sequences can be reduced to a great extent, particularly, workload for designing mismatch primers can be relieved to a great extent, a few candidate nucleic acid sequences can be quickly obtained from large quantities of mismatch nucleic acid sequences, and the method is favorable for determining the optimal nucleic acid sequences from the few candidate nucleic acid sequences; the high-sensitivity and high-specificity mismatch nucleic acid sequences still can keep high affinity with the target sequences with low concentration on the basis of mismatch primers designed by the aid of the method, and is poor in affinity with the homologous interference sequences, accordingly, the amplification sensitivity of the target sequences can be effectively improved, and the method can be effectively used for highly homologous nucleic acid sequences and can be particularly effectively used for miRNA [micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid)] amplification.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
System and method of binding energy for polymer molecule
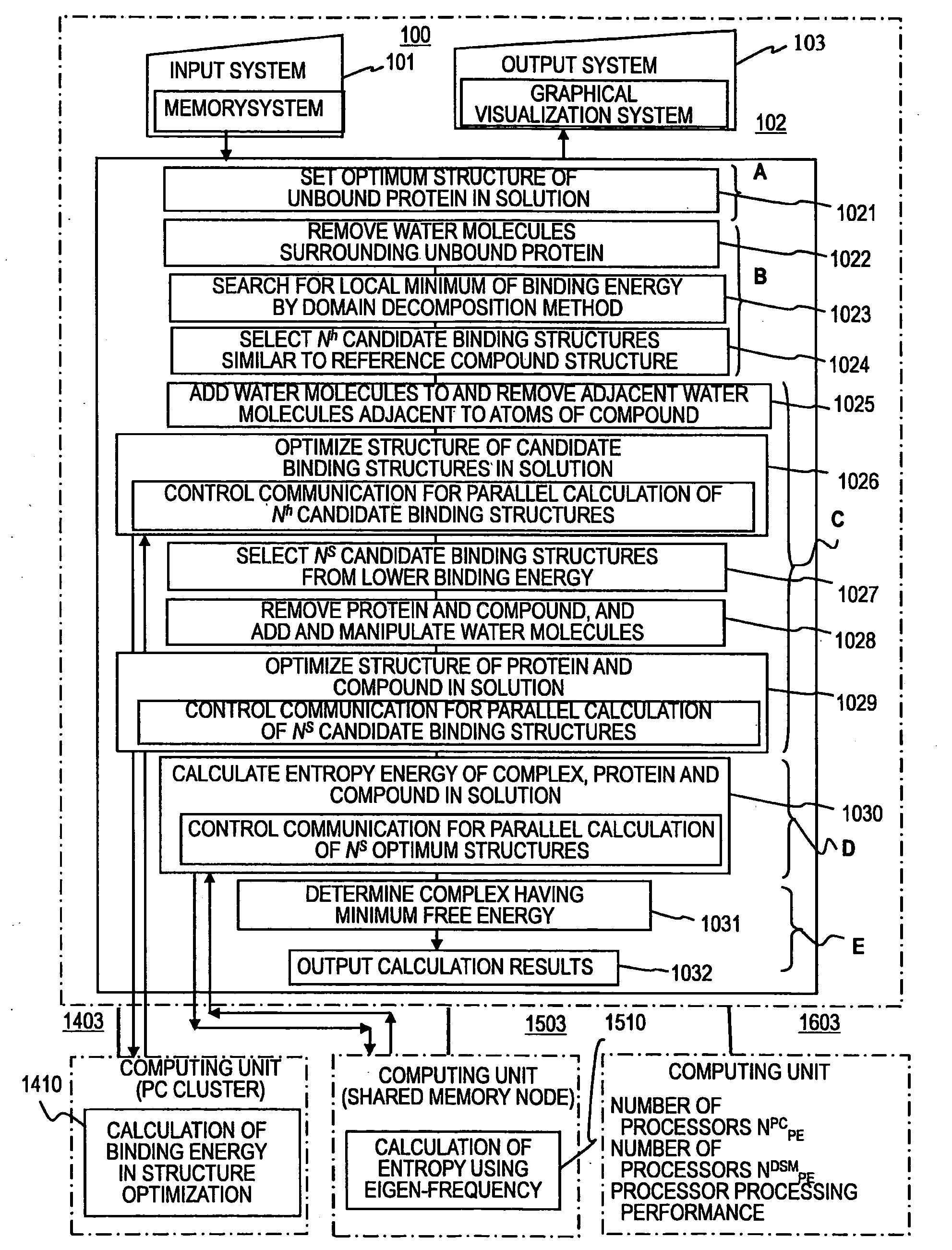
InactiveUS20090037151A1Mining valueReduce the amount requiredAnalogue computers for chemical processesForecastingBinding energyMinimum free energy
Provided is a design method of binding energy for polymer molecule, including: receiving a reference binding structure of a complex including a protein in a hydration state and a compound; setting an optimum structure of an unbound protein in a solution; searching for a local minimum value in a binding energy in a search region after removing the water molecules from the protein, and selecting Nh candidate binding structures; adding the removed water molecules, carrying out structure optimization for the compound, protein, and complex in the solution, and selecting NS candidate binding structures; calculating entropy in the solution for the candidate binding structures for which the structure optimization for the protein and the compound in the solution has been carried out for the selected candidate binding structures; and determining a complex structure having a minimum free energy, which is a sum of the binding energy and an entropy energy.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
A Calculation Method of Droplet Contact Angle Under Given Surface Secondary Micro-Nano Structure
ActiveCN105912502BDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsMicro nanoMicro structure
The invention discloses a liquid drop contact angle calculation method under a given surface second-level nano-micro structure. The calculation method comprises the following steps: adopting a nano-micro geometric measuring instrument to measure the structure size of the given second-level nano-micro structure to obtain the side length, the space and the height of the nano-micro structure; adopting general assumptions in Young equation, Wenzel equation and CB equation deduction, and calculating a roughness factor and an area fraction under micrometer and nanometer size under the assumptions; according to different infiltration states under a micrometer structure and a nanometer structure, dividing the infiltration states of the second-level nano-micro structure into four situations, and inducing and simplifying the system free energy calculated modes of four given surface second-level nano-micro structures; and in virtue of a C++program compiling module in Visual Studio2012 software, applying a Soushan method to calculate the system free energy under different infiltration states, finding interface minimum free energy under a stable state, and obtaining a contact angle corresponding to the interface minimum free energy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A Method for Obtaining Droplet Contact Angle on Regular Second-Order Structured Surface
ActiveCN106570300BImprove accuracyStable wet stateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum free energyFree energies
The invention discloses an acquiring method for a regular second-order structure surface liquid drop contact angle. The method comprises steps of deduction of a fundamental assumption of any three-dimensional structural model thermodynamic analysis and a system relative free energy function, sweeping from the top to the bottom end of a second-order structure to elicit relative free energy function of a system under different segments according to differences of an infiltration model and infiltration depth of a liquid drop along a depth direction of the second-order structure, programming a second-order structure volume geometric constraint condition and the relative free energy function via Matlab software, seeking relative free energy of the system under different infiltration models and infiltration depths in a segmental way, and determining a system minimum free energy and a stable wetting state to achieve a relative balance contact angle. The acquiring method solves deficiencies of redundant test measuring process of solid surface contact angle and great result error in the practical application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for calculating shape of PW-Cassie condensate droplet on super-hydrophobic surface
PendingCN113109211ASolve the calculation problem of contour shapeGuidance Design EfficientSurface tension analysisSuperhydrophobeMinimum free energy
A method for calculating the shape of a PW-Cassie condensate droplet on a super-hydrophobic surface comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a calculation hypothesis; (2) establishing an isolated droplet system; (3) calculating the free energy of the isolated droplet system; (4) optimizing the free energy of the surface of the condensate droplet; (5) writing a program by utilizing a nonlinear optimization function fmincon in MATLAB software, and searching variables ui and vi (i = 1, 2,..., N + 1) to enable the free energy of the system to be minimum under the constraint; and recording the coordinates of the discrete point pi (ui, vi) corresponding to the minimum free energy, and fitting the discrete point pi (ui, vi) to obtain a profile curve. According to the method, the problem of calculation of the contour form of the PW-Cassie condensate droplets partially infiltrated on the super-hydrophobic surface is solved, the coincidence degree with experimental observation is better, and the method has extremely important guiding significance for theoretical research on heat transfer of the PW-Cassie condensate droplets on the super-hydrophobic surface and is expected to guide design of an efficient condensation heat transfer surface.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
RNA tertiary structure prediction method based on parallel and Monte Carlo strategies
ActiveCN114121146AEfficient structure predictionAvoid enumerating all conformations at onceSystems biologyInstrumentsComputational scienceMinimum free energy
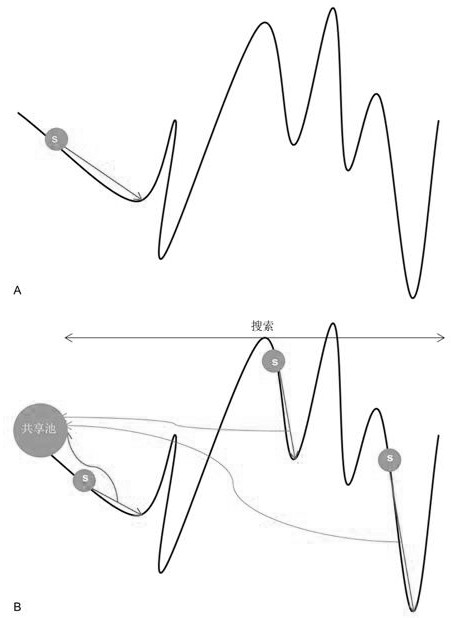
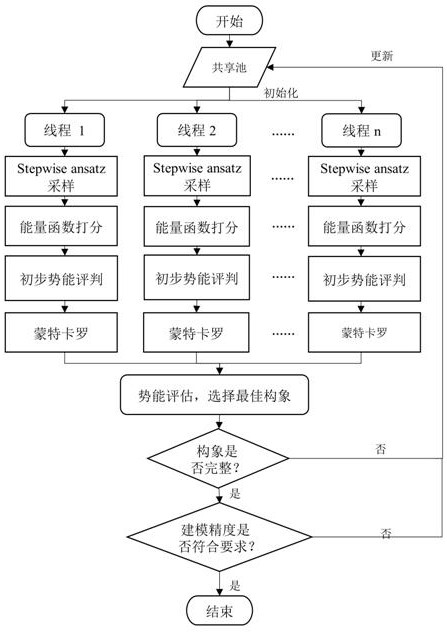
The invention discloses an RNA tertiary structure prediction method based on parallel and Monte Carlo strategies, and belongs to the field of structure prediction. The method comprises the following steps: performing conformation space sampling by using a parallel mechanism; scoring is carried out according to the latest updated energy function; performing reasonability judgment on the conformation based on Monte Carlo operation of Stepwise annatz through two rounds of potential energy judgment; and finally, judging structural integrity and modeling precision, and processing a result until a stable high-precision and high-integrity RNA tertiary structure is obtained. According to the RNA tertiary structure prediction method provided by the invention, the high-precision and high-integrity RNA tertiary structure can be obtained. The RNA three-level structure prediction method based on parallel and Monte Carlo strategies is high in flexibility, the Monte Carlo times can be specified, and the modeling precision and the modeling time cost can be measured by a user; according to the method, the problem that RNA motif modeling is incomplete in the prior art is solved; according to the method, the breadth and depth of conformation sampling are increased, the influence of pseudo minimum free energy is reduced, and the modeling precision is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
A Genetic Algorithm Based Optimal Design Method for Solid Propellant Formula
ActiveCN103198356BThe method steps are simpleReasonable designGenetic modelsPressure gas generationMinimum free energyGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses a solid propellant formulation energy optimization design method based on a genetic algorithm. The method comprises a first step of modeling, and building an energy characteristic calculation model of solid propellant according to a minimum free energy principle; a second step of setting and storing initial parameters, inputting component species used by the solid propellant, and a chemical formula and a quality proportion range of each component, and inputting species of combustion products produced by the solid propellant after being combusted, and chemical formulas and relative molecular mass of all the combustion products or selecting all the combustion products in a combustion product data base; and a third step of calling a genetic algorithm module by a data processor, and conducting optimization design to quality proportion of the designed solid propellant. The solid propellant formulation energy optimization design method based on the genetic algorithm is simple in steps, reasonable in design, convenient to achieve, good in using effect, capable of fast obtaining an optimum proportion of highest specific impulse of the solid propellant and effectively overcoming the defects, existing in an existing solid propellant compound design process, of being high in energy characteristic test cost, long in period, large in test dose, and the like.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Analysis method of pathogenic mechanism of polyglutamine
ActiveCN103902847BIndividual changes are goodFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum free energyParallel algorithm
The invention relates to a ployglutamine pathogenesis analyzing method which includes the following steps of S1, selecting a protein model which is a two-dimensional integral HP model; S2, determining an energy function; S3, searching for a protein two-dimensional structure with the minimum free energy, namely, searching for a two-dimensional structure corresponding to protein with the minimum energy by the adoption of MPI parallel algorithm of a peer-to-peer mode. Compared with the prior art, individual temperatures of the structure are determined through the sequence of individuals in a polyglutamine protein structure group, higher temperature is distributed to the inferior individuals so that the inferior individuals are more likely to change into the superior individuals, and meanwhile, by means of cooling factors, convergence speed is increased in a parallel mode.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor device and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20060183324A1Prevent the voids and breakdowns in copper (CuInhibited DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMinimum free energyElectrical conductor
Provided is a reliable semiconductor device with a layered interconnect structure that may develop no trouble of voids and interconnect breakdowns, in which the layered interconnect structure comprises a conductor film and a neighboring film as so layered on a semiconductor substrate that the neighboring film is contacted with the conductor film. In the device, the materials for the conductor film and the neighboring film are so selected that the difference between the short side, ap, of the rectangular unit cells that constitute the plane with minimum free energy of the conductor film and the short side, an, of the rectangular unit cells that constitute the plane with minimum free energy of the neighboring film, {|ap-an| / ap}x100=A (%) and the difference between the long side, bp, of the rectangular unit cells that constitute the plane with minimum free energy of the conductor film and the long side, bn, of the rectangular unit cells that constitute the plane with minimum free energy of the neighboring film, {|bp-bn| / bp}x100=B (%) satisfy an inequality of {A+Bx(ap / bp)}<13. In this, the diffusion of the conductor film is retarded.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Optimization Method of Solid Propellant Formula Based on Genetic Algorithm and Energy Characteristic Graph
ActiveCN103136430BThe method steps are simpleReasonable designGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsMinimum free energy
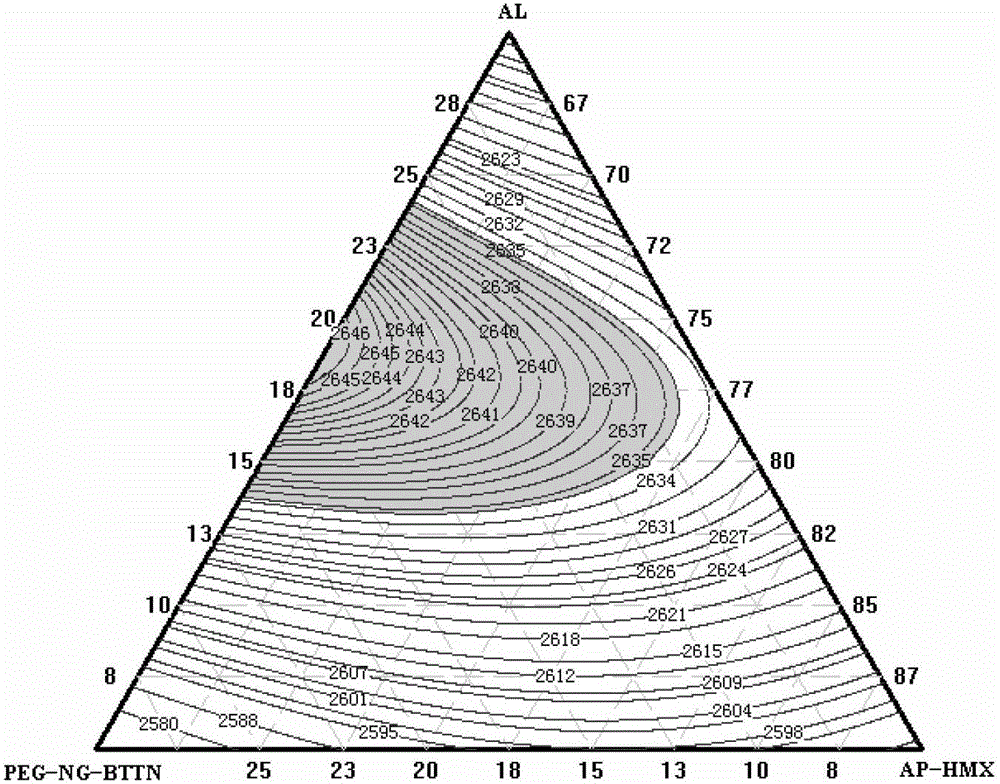
The invention discloses a solid propellant formula optimization method based on a genetic algorithm and an energy feature graph. The solid propellant formula optimization method based on the genetic algorithm and the energy feature graph includes a first step of modeling, namely, establishing four energy feature calculation models according to a minimum free energy principle; a second step of setting and storing initial parameters; a third step of utilizing the genetic algorithm to implement formula optimization design; a fourth step of setting a value range used for graphic plotting and calculating mass contents of various kinds of raw material; and a fifth step of drawing the energy feature graph. The drawing process includes the steps of energy feature parameter inputting, energy feature curvilinear equation fitting, energy feature graph drawing, and synchronous energy feature graph displaying. The method is simple in step, reasonable in design, convenient to achieve and good in use effect, combines the genetic algorithm and the energy feature graph to carry out the solid propellant formula optimization design, and overcomes the defects that the energy feature experimental cost is high, the period is long and the experimental quantity is large and the like in an existing solid propellant formula optimization design process.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Method and device for predicting ribonucleic acid pseudoknot structure based on k-stem
InactiveCN104298894BReduce time complexityReduce space complexitySpecial data processing applicationsMinimum free energyPresent method
The present invention provides a kind of prediction method and device of the ribonucleic acid (RNA) pseudoknot structure based on k stem, and prediction method comprises the following steps: input a section of ribonucleic acid base sequence; Define pseudoknot, k (k≥1) stem; From Search RNA bases and k stems from left to right, and mark all k stems found out; according to the characteristics of k stems crossing to form pseudoknots, find pseudoknots; calculate the minimum structure of ribonucleic acid pseudoknots containing k stems Free energy; pseudoknot structure for export of ribonucleic acid. The method involved in the present invention has fast search speed, high correct rate, sensitivity and specificity, and is superior to other related algorithms, such as PKNOTS algorithm. This method is more effective than the PKNOTS algorithm in the prediction of planar pseudoknots.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com